⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-11 更新
Probable evidence for a transient mega-electron volt emission line in the GRB 221023A
Authors:Lu-Yao Jiang, Yun Wang, Yu-Jia Wei, Da-Ming Wei, Xiang Li, Hao-Ning He, Jia Ren, Zhao-Qiang Shen, Zhi-Ping Jin
Detection of spectral line in gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) is importance for studying GRB physics, as it provides insights into the composition and physical conditions of the GRB environment. However, progress in detecting X-ray or gamma-ray emission and absorption lines in GRB spectra has been relatively slow, only the narrow emission line feature of about 10 MeV found in GRB 221009A has exhibited a significance exceeding $5 \sigma$. Here, we report the probable evidence of a narrow emission feature at about 2.1 mega-electron volts (MeV) in the spectrum of GRB 221023A. The highest statistical significance of this feature is observed in the time interval between 8 and 30 seconds after Fermi Gamma-Ray Burst Monitor trigger, with the chance probability value $<2.56 \times 10^{-5}$ (after accounting for the look-elsewhere effect), corresponding to a Gaussian-equivalent significance $> 4.20 \sigma$. We interpret this feature as being generated through the de-excitation of excited electrons in the relativistic hydrogen-like high-atomic-number ions entrained in the GRB jet.
在伽马射线暴(GRBs)中检测光谱线对于研究GRB物理非常重要,因为它为GRB环境的组成和物理条件提供了见解。然而,在GRB光谱中检测X射线或伽马射线发射和吸收线的进展相对较慢,仅在GRB 221009A中发现的约10MeV的窄发射线特征才具有超过$5 \sigma$的显著性。在这里,我们报告了GRB 221023A光谱中大约2.1兆电子伏特(MeV)的窄发射特征的可能证据。此特征在费米伽马射线暴监视器触发后8至30秒的时间间隔内具有最高的统计显著性,机会概率值小于$2.56 \times 10^{-5}$(考虑了其他地方效应),对应于高斯等效显著性大于$ 4.20 \sigma$。我们将此特征解释为由GRB喷流中携带的高相对论性氢类高原子序数离子的激发态去激发所产生。
简化版翻译
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 5 figures, 3 tables. Publication in the Nature Communications
Summary
GRB 221023A光谱中可能检测到窄发射特征,其能量约为2.1兆电子伏特(MeV)。该特征在触发后8至30秒的时间间隔内观察到了最高统计显著性,并且几率极低。对其产生的可能解释是相对论性氢类高原子序数离子在GRB喷射中的激发电子的退激发所致。这一发现对于研究GRB物理具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- GRB 221023A光谱中可能发现了能量约为2.1MeV的窄发射特征。
- 这一特征在触发后的特定时间间隔(8至30秒)内显示出最高统计显著性。
- 特征的可能性证据超过了$4.20 \sigma$的显著性水平。
- 特征的产生可能与GRB喷射中的相对论性氢类高原子序数离子的激发电子退激发有关。
- 这一发现为研究GRB的物理环境提供了新线索,特别是关于GRB的组成和物理条件。
- 尽管进展缓慢,但检测GRB光谱中的X射线或伽马射线发射和吸收线仍然至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

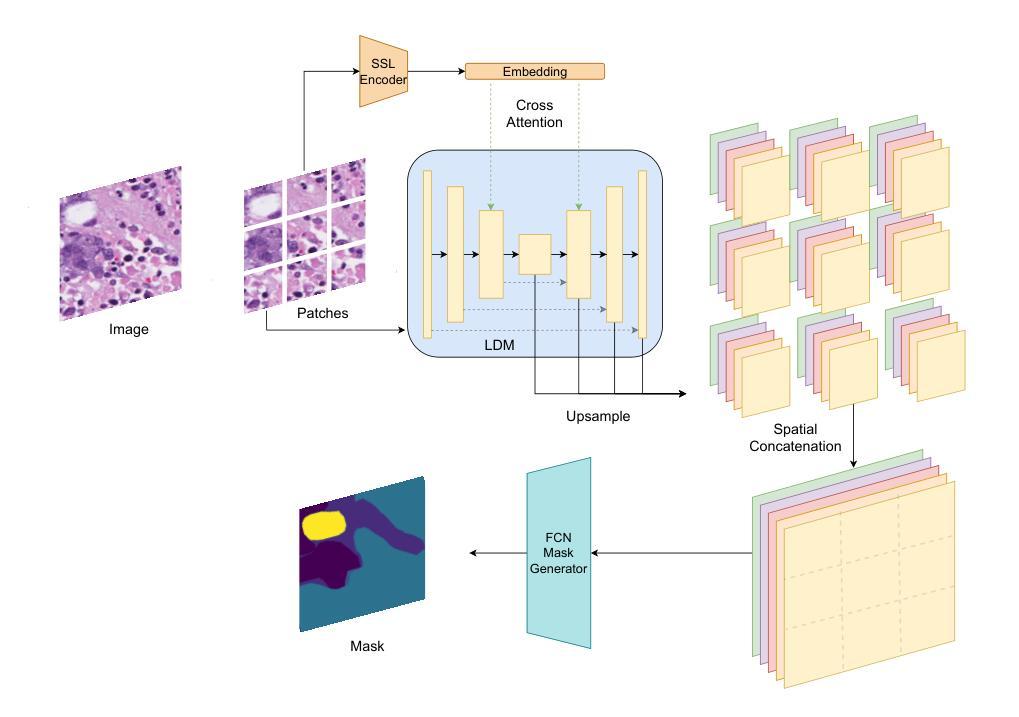
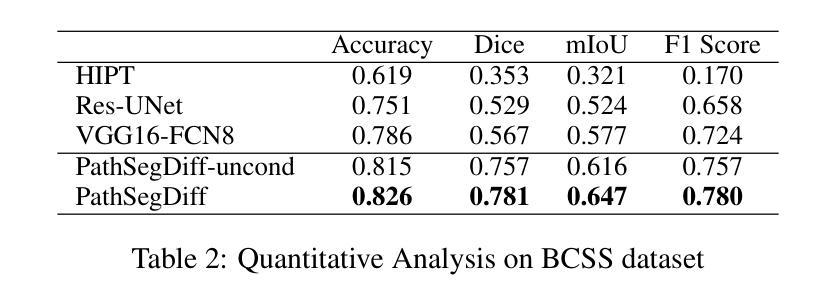
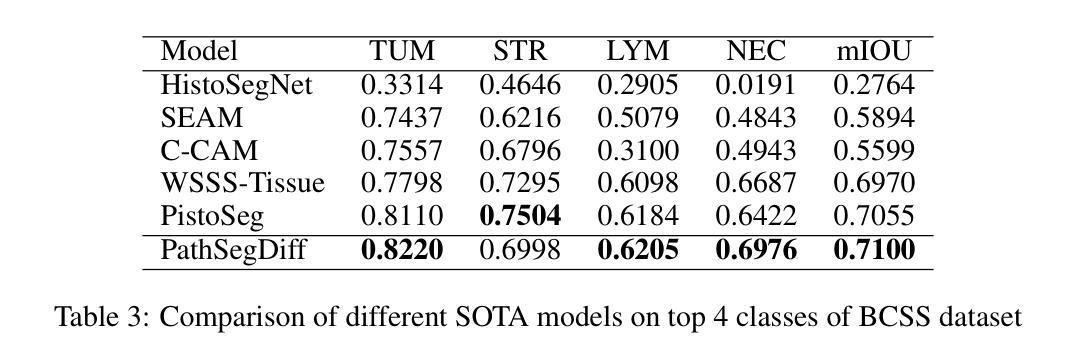
PathSegDiff: Pathology Segmentation using Diffusion model representations
Authors:Sachin Kumar Danisetty, Alexandros Graikos, Srikar Yellapragada, Dimitris Samaras
Image segmentation is crucial in many computational pathology pipelines, including accurate disease diagnosis, subtyping, outcome, and survivability prediction. The common approach for training a segmentation model relies on a pre-trained feature extractor and a dataset of paired image and mask annotations. These are used to train a lightweight prediction model that translates features into per-pixel classes. The choice of the feature extractor is central to the performance of the final segmentation model, and recent literature has focused on finding tasks to pre-train the feature extractor. In this paper, we propose PathSegDiff, a novel approach for histopathology image segmentation that leverages Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) as pre-trained featured extractors. Our method utilizes a pathology-specific LDM, guided by a self-supervised encoder, to extract rich semantic information from H&E stained histopathology images. We employ a simple, fully convolutional network to process the features extracted from the LDM and generate segmentation masks. Our experiments demonstrate significant improvements over traditional methods on the BCSS and GlaS datasets, highlighting the effectiveness of domain-specific diffusion pre-training in capturing intricate tissue structures and enhancing segmentation accuracy in histopathology images.
图像分割在计算病理学流程中非常重要,包括准确的疾病诊断、亚型分类、结果预测和生存预测。训练分割模型的常见方法依赖于预训练的特征提取器和配对图像和掩膜注释的数据集。这些被用来训练轻量级的预测模型,将特征转化为像素级分类。特征提取器的选择是最终分割模型性能的核心,最近的文献主要集中在寻找预训练特征提取器的任务。在本文中,我们提出了PathSegDiff,一种利用潜在扩散模型(LDMs)作为预训练特征提取器的新颖方法来进行组织病理学图像分割。我们的方法使用一个受自我监督编码器引导的疾病特异性LDM,从苏木精伊红染色的组织病理学图像中提取丰富的语义信息。我们采用简单的全卷积网络来处理从LDM中提取的特征并生成分割掩膜。我们的实验表明,与传统的方法相比,BCSS和GlaS数据集上的结果有了显著的改进,这突出了领域特定的扩散预训练在捕捉复杂的组织结构和提高组织病理学图像分割精度方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割在计算病理学流程中至关重要,包括准确疾病诊断、亚型分类、结果预测和生存预测。本文提出一种新型分割方法PathSegDiff,采用潜在扩散模型(LDMs)作为预训练特征提取器,通过自监督编码器引导,从H&E染色组织病理图像中提取丰富语义信息。实验结果在BCSS和GlaS数据集上显著优于传统方法,凸显领域特定扩散预训练在捕捉复杂组织结构和提高组织病理图像分割准确性方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割在计算病理学中有重要应用,涉及疾病诊断、亚型分类、结果预测和生存预测。
- 传统方法依赖预训练特征提取器和配对图像与掩膜注释数据集来训练预测模型。
- 特征提取器的选择对最终分割模型性能至关重要。
- 近期研究关注于寻找预训练特征提取器的任务。
- PathSegDiff是一种新型组织病理图像分割方法,利用潜在扩散模型(LDMs)作为预训练特征提取器。
- PathSegDiff通过自监督编码器引导,提高分割准确性,并在BCSS和GlaS数据集上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

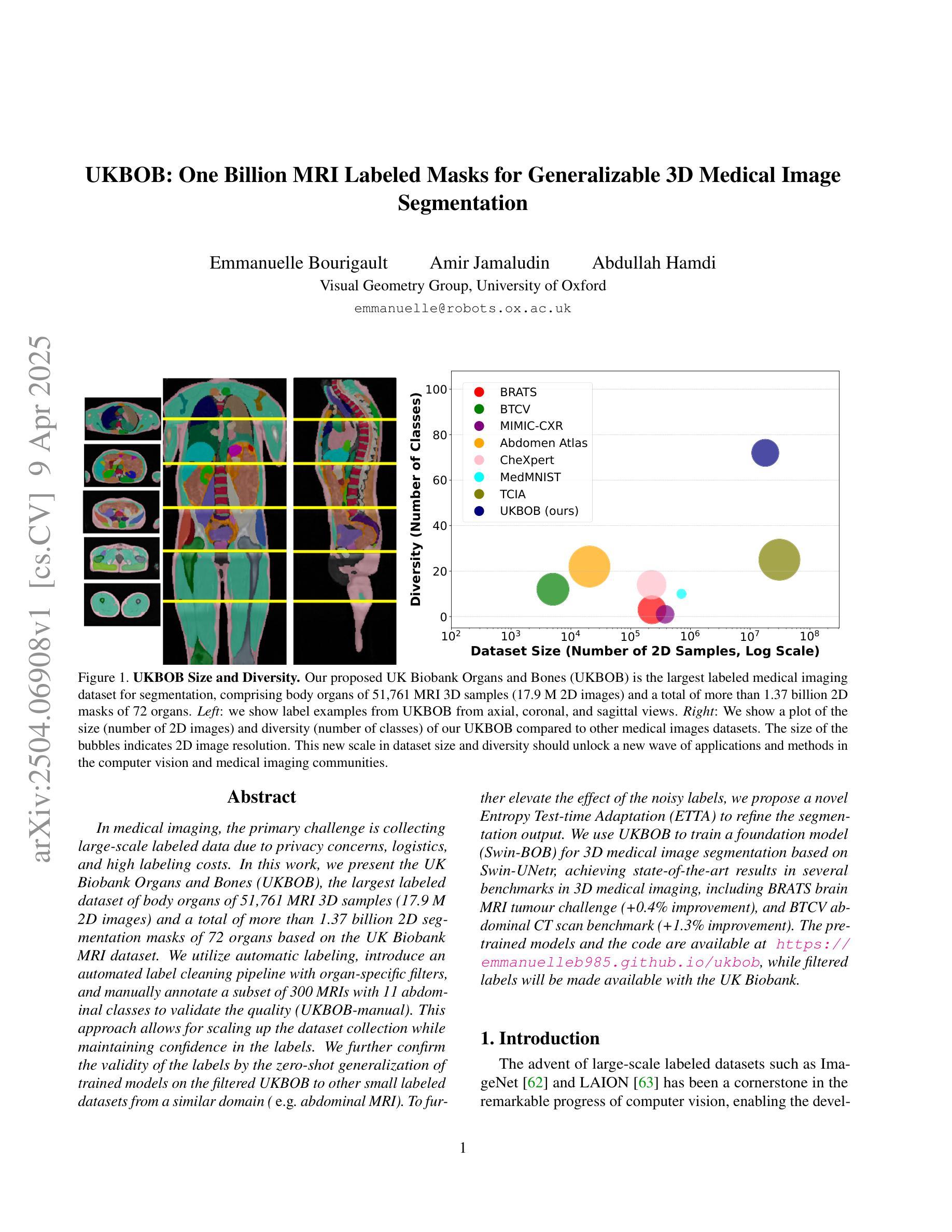
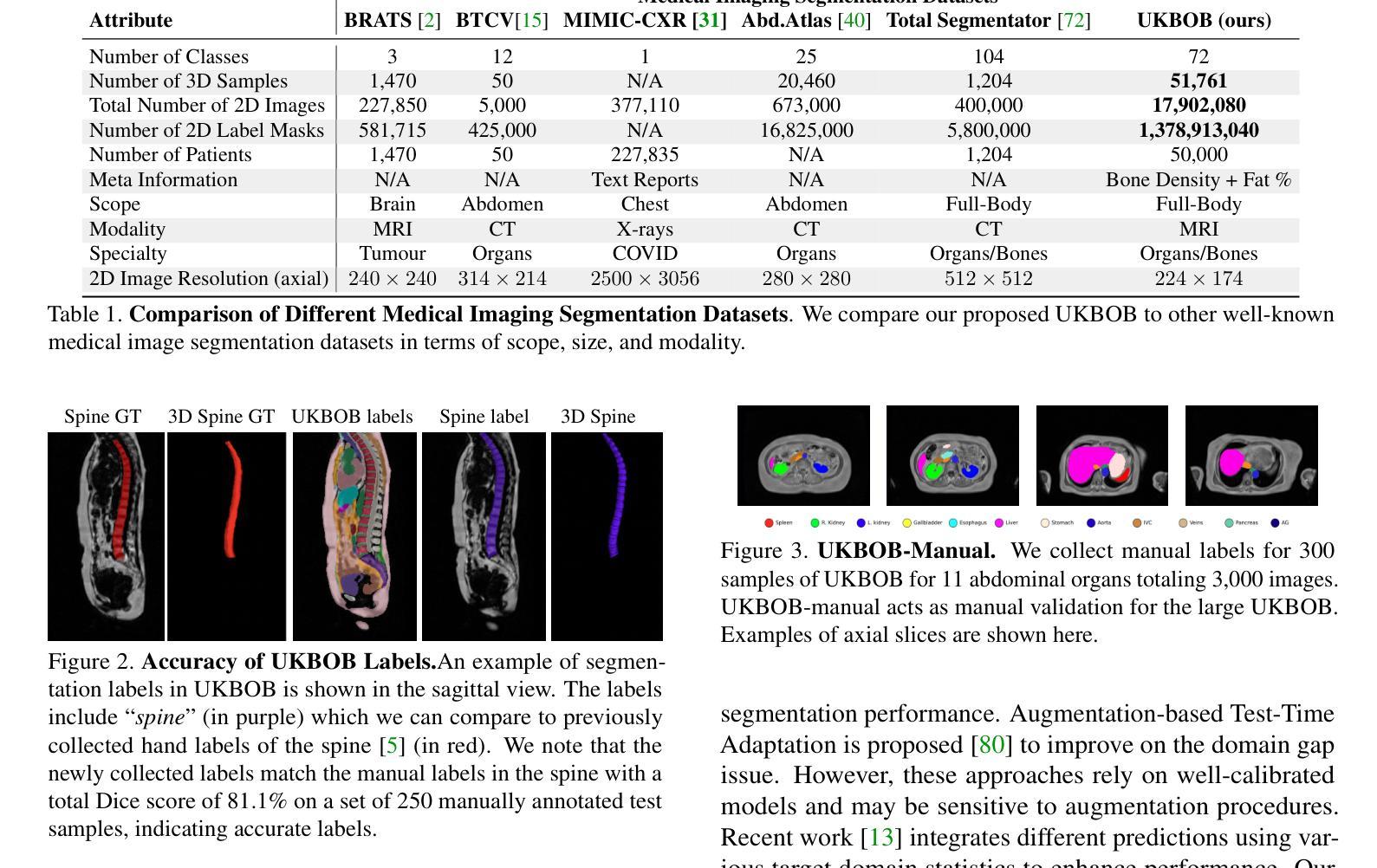
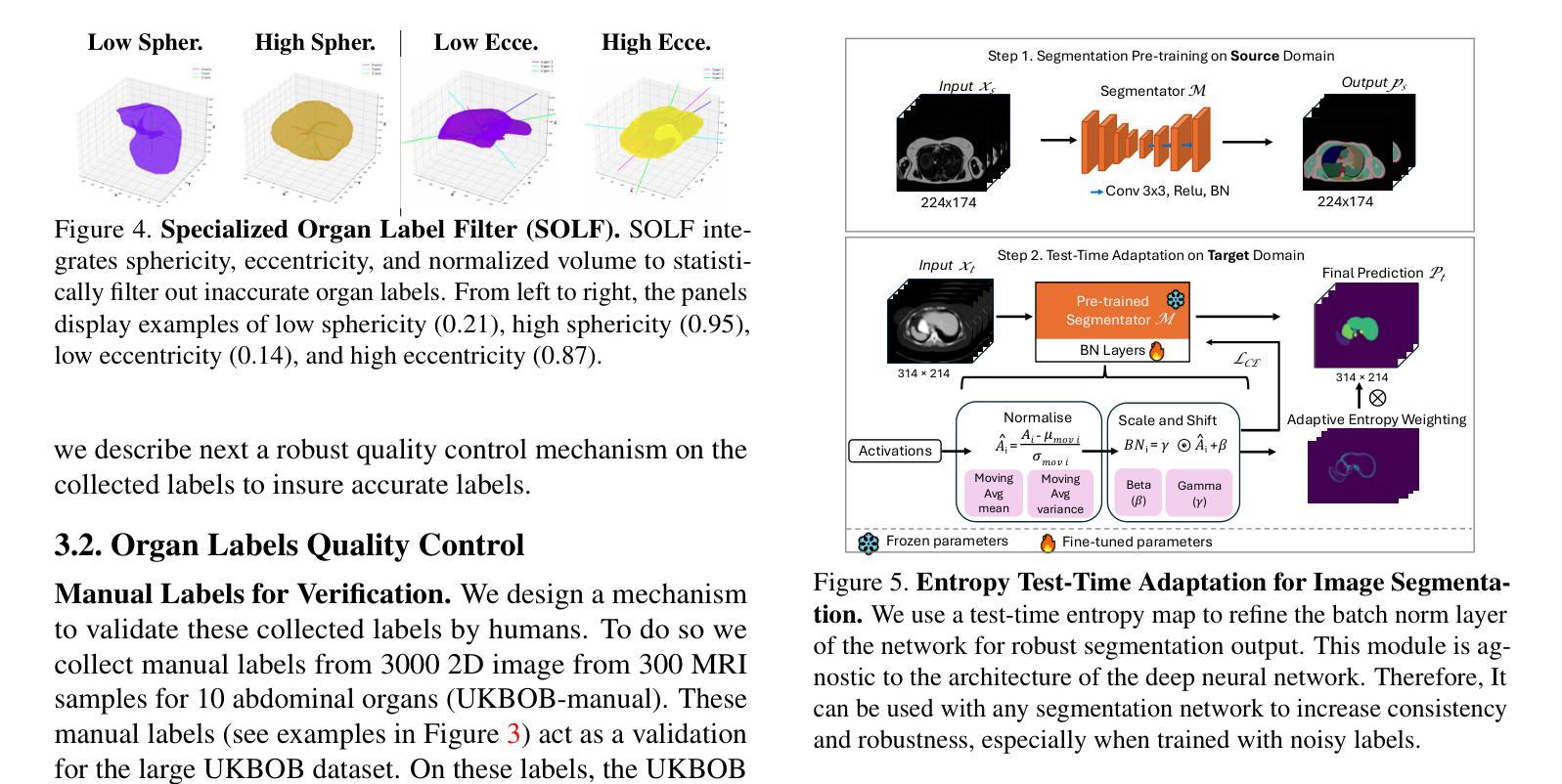
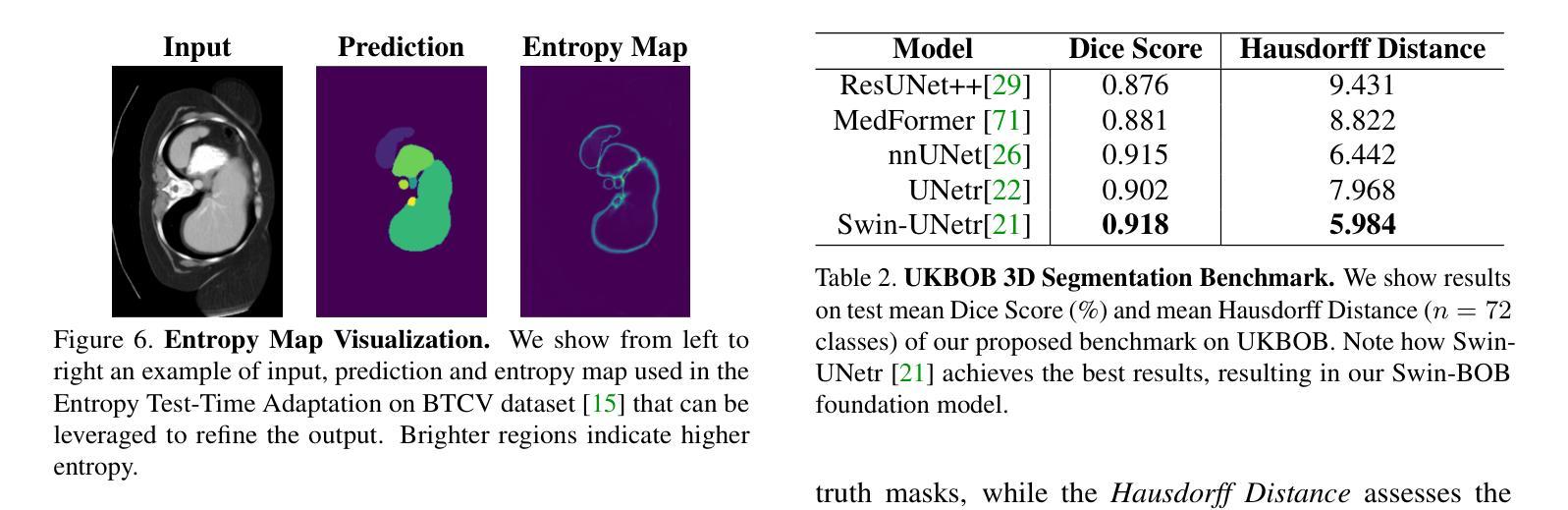
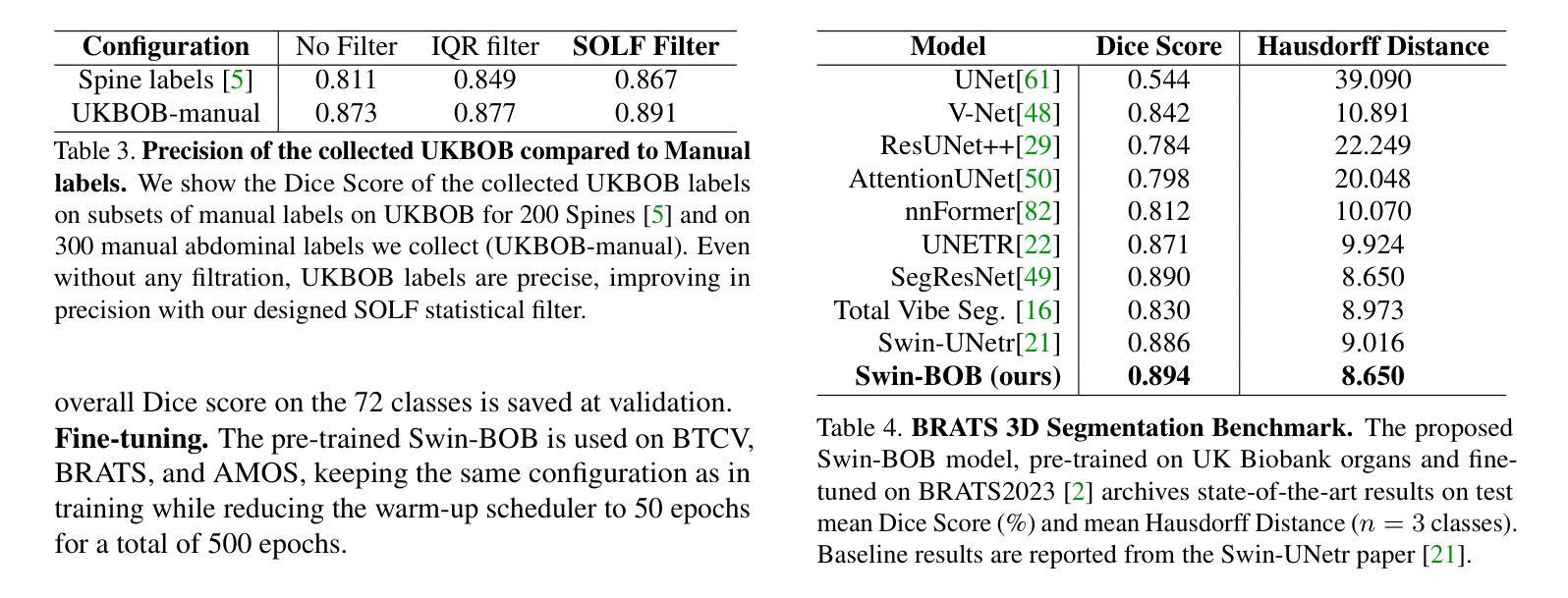
UKBOB: One Billion MRI Labeled Masks for Generalizable 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Emmanuelle Bourigault, Amir Jamaludin, Abdullah Hamdi
In medical imaging, the primary challenge is collecting large-scale labeled data due to privacy concerns, logistics, and high labeling costs. In this work, we present the UK Biobank Organs and Bones (UKBOB), the largest labeled dataset of body organs, comprising 51,761 MRI 3D samples (equivalent to 17.9 million 2D images) and more than 1.37 billion 2D segmentation masks of 72 organs, all based on the UK Biobank MRI dataset. We utilize automatic labeling, introduce an automated label cleaning pipeline with organ-specific filters, and manually annotate a subset of 300 MRIs with 11 abdominal classes to validate the quality (referred to as UKBOB-manual). This approach allows for scaling up the dataset collection while maintaining confidence in the labels. We further confirm the validity of the labels by demonstrating zero-shot generalization of trained models on the filtered UKBOB to other small labeled datasets from similar domains (e.g., abdominal MRI). To further mitigate the effect of noisy labels, we propose a novel method called Entropy Test-time Adaptation (ETTA) to refine the segmentation output. We use UKBOB to train a foundation model, Swin-BOB, for 3D medical image segmentation based on the Swin-UNetr architecture, achieving state-of-the-art results in several benchmarks in 3D medical imaging, including the BRATS brain MRI tumor challenge (with a 0.4% improvement) and the BTCV abdominal CT scan benchmark (with a 1.3% improvement). The pre-trained models and the code are available at https://emmanuelleb985.github.io/ukbob , and the filtered labels will be made available with the UK Biobank.
在医学成像领域,主要挑战在于由于隐私担忧、物流和高标签成本而难以收集大规模标记数据。在这项工作中,我们介绍了英国生物银行器官与骨骼(UKBOB)数据集,这是最大的器官标记数据集,包含基于英国生物银行MRI数据集的51,761个MRI 3D样本(相当于1790万张2D图像)和超过13.7亿张包含72种器官的二维分割蒙版。我们采用自动标记的方法,引入了具有器官特异性过滤器的自动标签清理管道,并手动对300张腹部MRI图像中的11个类别进行标注以验证质量(称为UKBOB手动)。这种方法允许在扩大数据集收集的同时保持对标签的信心。我们通过展示经过训练的模型在过滤后的UKBOB上对其他类似领域的小规模标记数据集上的零样本泛化能力来进一步验证标签的有效性(例如腹部MRI)。为了进一步减轻噪声标签的影响,我们提出了一种名为熵测试时间适应(ETTA)的新方法来优化分割输出。我们使用UKBOB训练了一个基于Swin-UNetr架构的用于三维医学图像分割的基础模型Swin-BOB,在三维医学影像的多个基准测试中达到了最新水平,包括BRATS脑部MRI肿瘤挑战赛(提高了0.4%)和BTCV腹部CT扫描基准测试(提高了1.3%)。预训练模型和代码可在https://emmanuelleb985.github.io/ukbob上找到,过滤后的标签也将与英国生物银行共享。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint
Summary
本医学成像研究面临的主要挑战是隐私、物流和标签成本问题,导致难以收集大规模标注数据。针对这一挑战,研究团队推出了UKBiobank Organs and Bones(UKBOB)数据集,包含大量人体器官标签,利用自动标注和清洗流程确保标签准确性。此外,该研究还提出了熵测试时适应(ETTA)方法以优化分割输出,并基于Swin-UNetr架构训练出先进的医学图像分割模型Swin-BOB。模型在多个医学成像基准测试中表现卓越。数据集和代码已在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
1. 医学成像领域面临大规模标注数据收集的挑战,涉及隐私、物流和成本问题。
2. 推出了UKBiobank Organs and Bones(UKBOB)数据集,包含大量人体器官标签数据。
3. 结合自动标注和清洗流程,确保标签准确性。
4. 提出了一种名为熵测试时适应(ETTA)的方法,用于优化模型分割输出。
5. 基于Swin-UNetr架构训练的Swin-BOB模型在医学图像分割领域表现优秀。
6. 模型在多个基准测试中表现卓越,包括BRATS脑MRI肿瘤挑战和BTCV腹部CT扫描基准测试。
点此查看论文截图
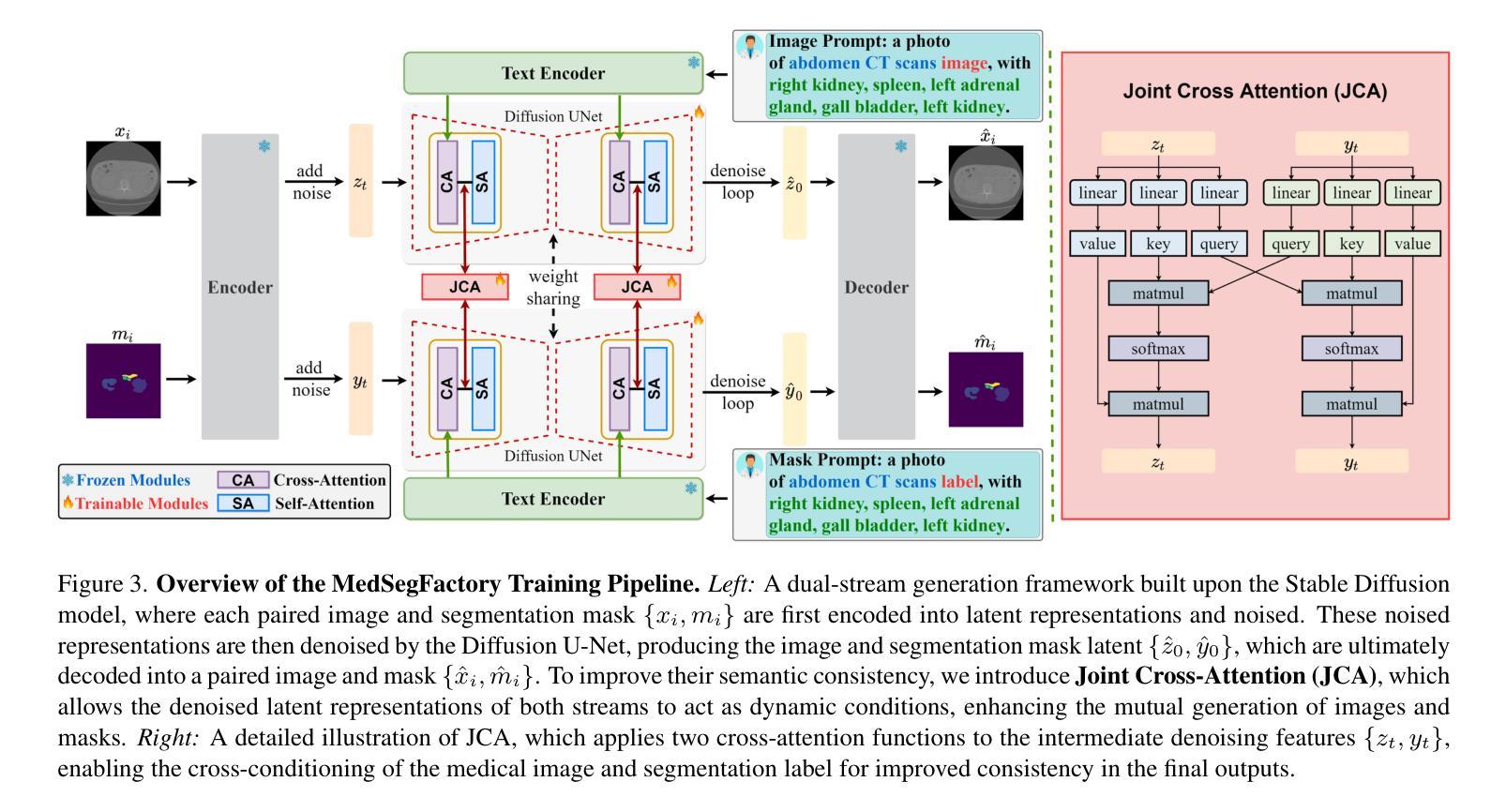
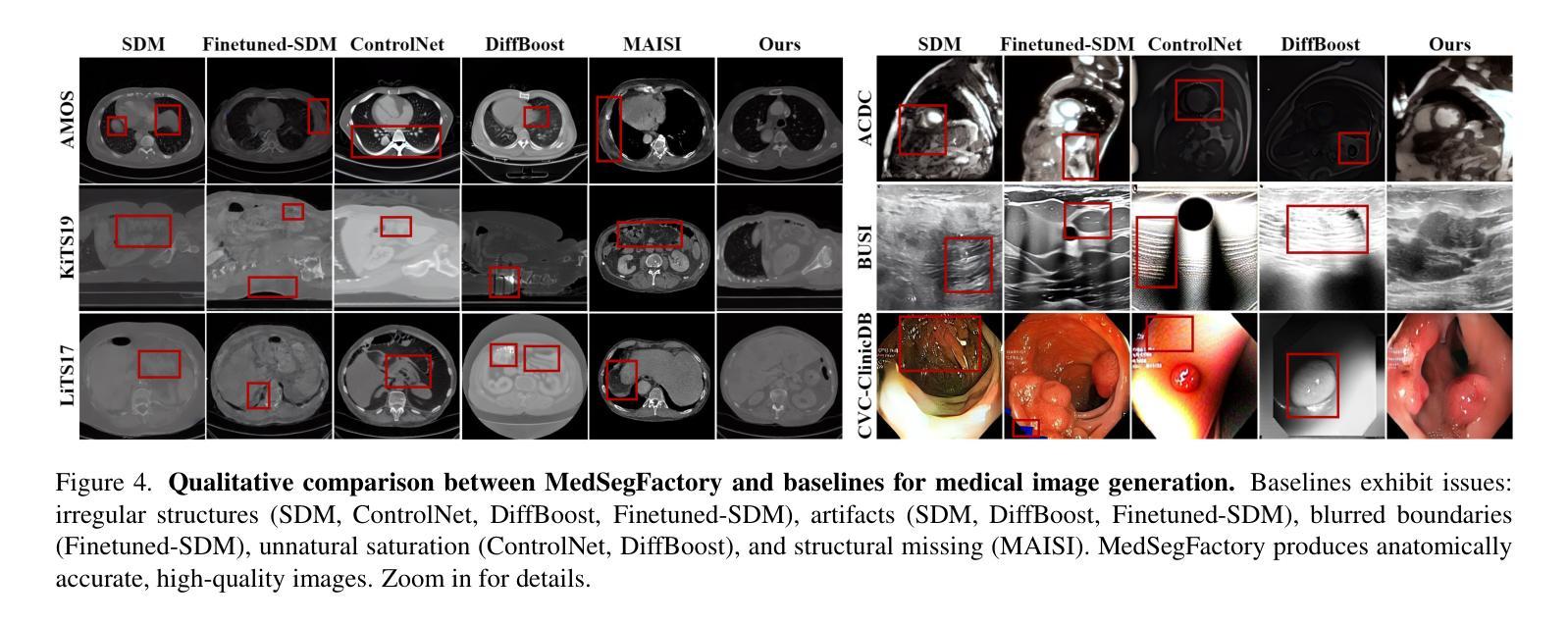
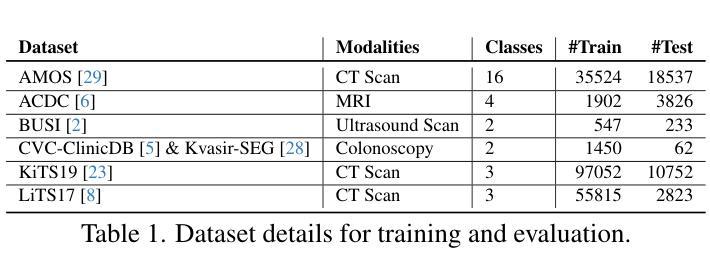
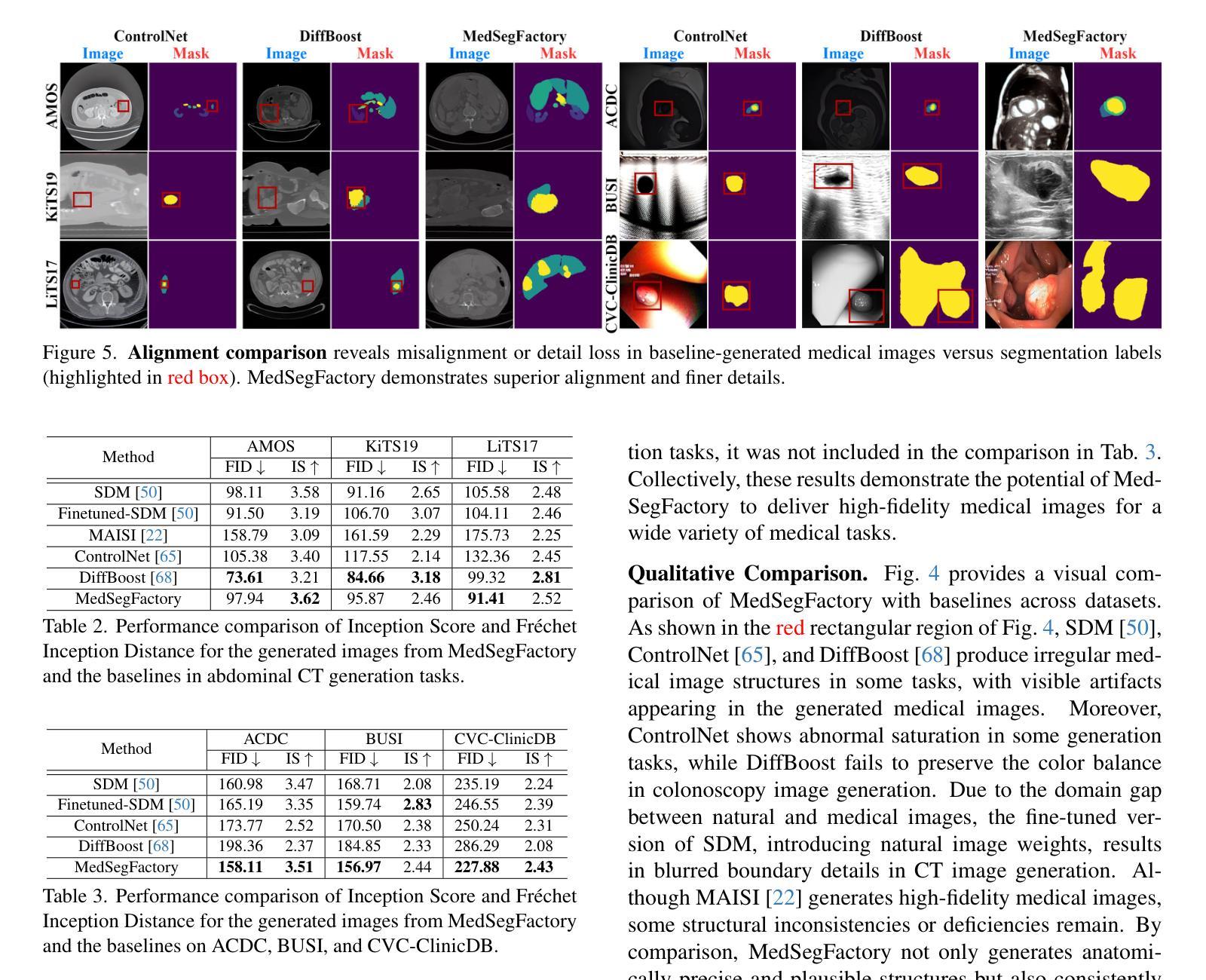
MedSegFactory: Text-Guided Generation of Medical Image-Mask Pairs
Authors:Jiawei Mao, Yuhan Wang, Yucheng Tang, Daguang Xu, Kang Wang, Yang Yang, Zongwei Zhou, Yuyin Zhou
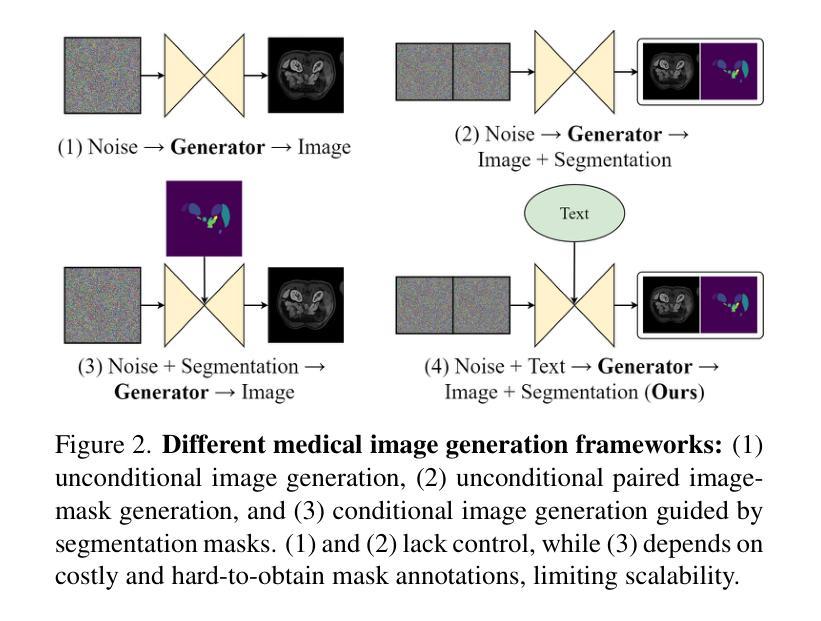
This paper presents MedSegFactory, a versatile medical synthesis framework that generates high-quality paired medical images and segmentation masks across modalities and tasks. It aims to serve as an unlimited data repository, supplying image-mask pairs to enhance existing segmentation tools. The core of MedSegFactory is a dual-stream diffusion model, where one stream synthesizes medical images and the other generates corresponding segmentation masks. To ensure precise alignment between image-mask pairs, we introduce Joint Cross-Attention (JCA), enabling a collaborative denoising paradigm by dynamic cross-conditioning between streams. This bidirectional interaction allows both representations to guide each other’s generation, enhancing consistency between generated pairs. MedSegFactory unlocks on-demand generation of paired medical images and segmentation masks through user-defined prompts that specify the target labels, imaging modalities, anatomical regions, and pathological conditions, facilitating scalable and high-quality data generation. This new paradigm of medical image synthesis enables seamless integration into diverse medical imaging workflows, enhancing both efficiency and accuracy. Extensive experiments show that MedSegFactory generates data of superior quality and usability, achieving competitive or state-of-the-art performance in 2D and 3D segmentation tasks while addressing data scarcity and regulatory constraints.
本文介绍了MedSegFactory,这是一个通用的医学合成框架,能够生成跨模态和任务的高质量配对医学图像和分割掩膜。它的目标是作为一个无限的数据仓库,提供图像-掩膜对,以增强现有的分割工具。MedSegFactory的核心是一个双流扩散模型,其中一流合成医学图像,另一流生成相应的分割掩膜。为了确保图像-掩膜对之间的精确对齐,我们引入了联合交叉注意(JCA),通过流之间的动态交叉条件,实现协同去噪模式。这种双向交互允许两种表示相互引导生成,增强生成对之间的一致性。MedSegFactory通过用户定义的提示解锁按需生成的配对医学图像和分割掩膜,这些提示指定目标标签、成像模态、解剖区域和病理状况,促进可扩展和高质量的数据生成。这种新的医学图像合成模式能够无缝集成到多样化的医学成像工作流程中,提高效率和准确性。大量实验表明,MedSegFactory生成的数据具有卓越的质量和可用性,在二维和三维分割任务中达到了竞争或最先进的性能,同时解决了数据稀缺和监管约束问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures, The project page can be accessed via https://jwmao1.github.io/MedSegFactory_web
Summary
医学图像合成框架MedSegFactory能够生成高质量配对医学图像和分割掩膜,适用于多种模态和任务。其核心是双流扩散模型,通过联合交叉注意力机制实现图像和掩膜之间的精确对齐。该框架可实现按需生成配对医学图像和分割掩膜,并易于集成到各种医学成像工作流程中,提高效率和准确性。
Key Takeaways
- MedSegFactory是一个通用的医学合成框架,用于生成高质量配对医学图像和分割掩膜。
- 它采用双流扩散模型,其中一流生成医学图像,另一流生成相应的分割掩膜。
- 通过引入联合交叉注意力机制,实现图像和掩膜之间的精确对齐。
- 框架支持按需生成配对医学图像和分割掩膜,可根据用户定义的目标标签、成像模态、解剖区域和病理条件进行生成。
- MedSegFactory易于集成到各种医学成像工作流程中,提高效率和准确性。
- 框架在2D和3D分割任务上表现出卓越的性能,解决了数据稀缺和监管约束的问题。
点此查看论文截图

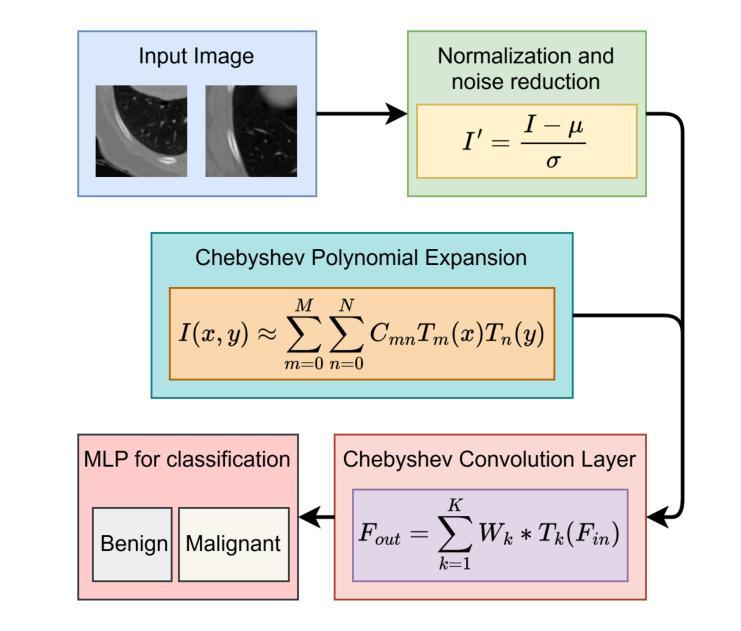
Hybrid CNN with Chebyshev Polynomial Expansion for Medical Image Analysis
Authors:Abhinav Roy, Bhavesh Gyanchandani, Aditya Oza
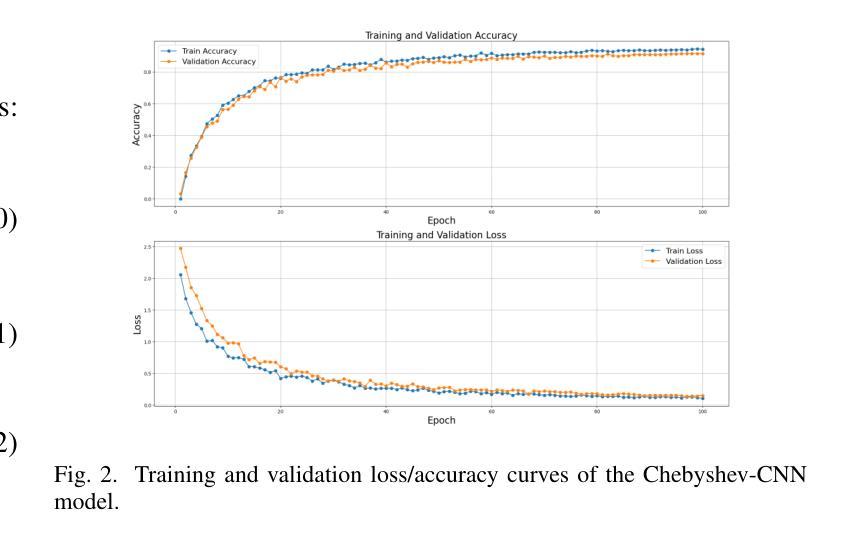
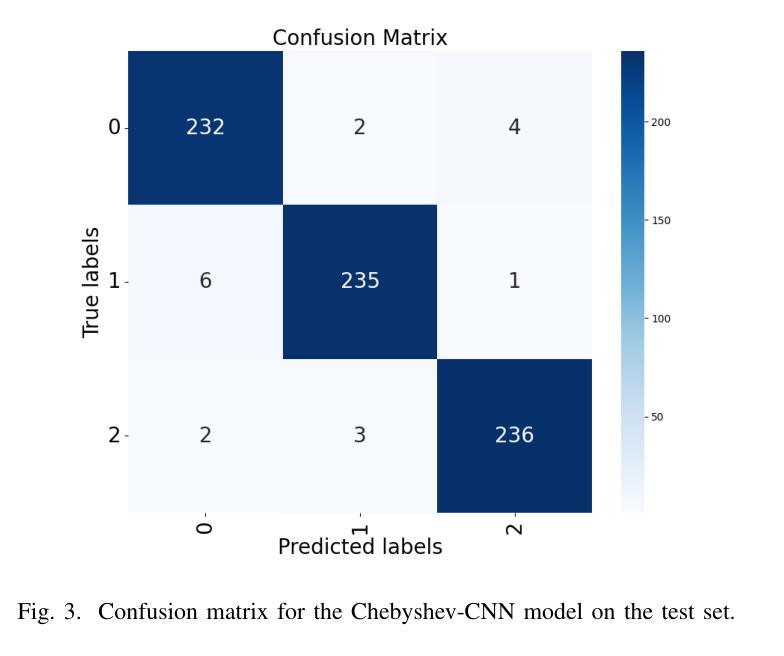
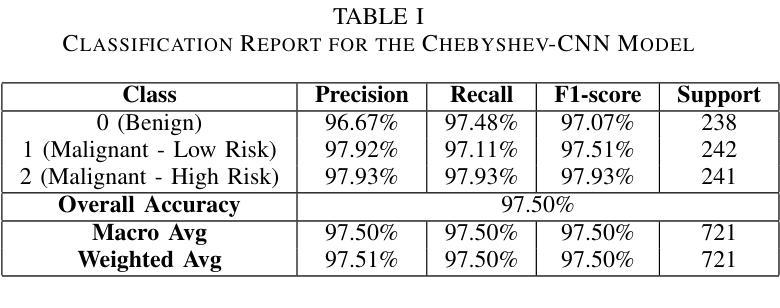
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with early and accurate diagnosis playing a pivotal role in improving patient outcomes. Automated detection of pulmonary nodules in computed tomography (CT) scans is a challenging task due to variability in nodule size, shape, texture, and location. Traditional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have shown considerable promise in medical image analysis; however, their limited ability to capture fine-grained spatial-spectral variations restricts their performance in complex diagnostic scenarios. In this study, we propose a novel hybrid deep learning architecture that incorporates Chebyshev polynomial expansions into CNN layers to enhance expressive power and improve the representation of underlying anatomical structures. The proposed Chebyshev-CNN leverages the orthogonality and recursive properties of Chebyshev polynomials to extract high-frequency features and approximate complex nonlinear functions with greater fidelity. The model is trained and evaluated on benchmark lung cancer imaging datasets, including LUNA16 and LIDC-IDRI, achieving superior performance in classifying pulmonary nodules as benign or malignant. Quantitative results demonstrate significant improvements in accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity compared to traditional CNN-based approaches. This integration of polynomial-based spectral approximation within deep learning provides a robust framework for enhancing automated medical diagnostics and holds potential for broader applications in clinical decision support systems.
肺癌仍然是全球癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一,早期和准确的诊断在改善患者预后中发挥着至关重要的作用。在计算机断层扫描(CT)中自动检测肺结节是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为结节的大小、形状、纹理和位置存在很大的变化。传统的卷积神经网络(CNN)在医学图像分析方面显示出巨大的潜力;然而,它们在捕获精细的空间光谱变化方面的有限能力限制了它们在复杂的诊断场景中的表现。在本研究中,我们提出了一种新型的混合深度学习架构,该架构将切比雪夫多项式扩展融入CNN层,以提高表达能力和改善潜在解剖结构的表示。所提出的切比雪夫-CNN利用切比雪夫多项式的正交性和递归属性来提取高频特征,并以更高的保真度近似复杂的非线性函数。该模型在基准肺癌成像数据集上进行训练和评估,包括LUNA16和LIDC-IDRI数据集,在分类肺结节为良性或恶性方面表现出卓越的性能。定量结果表明,与传统的基于CNN的方法相比,在准确性、敏感性和特异性方面都有显著提高。深度学习中的多项式基于光谱逼近的集成为提高自动化医学诊断提供了一个稳健的框架,并有可能在临床决策支持系统中有更广泛的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了肺癌仍然是全球癌症死亡的主要原因之一,早期准确诊断对改善患者预后至关重要。研究中,提出一种结合切比雪夫多项式扩展的新型深度混合学习架构,将其融入卷积神经网络(CNN)层中,以提高表达能力和改善潜在解剖结构的表示。该模型利用切比雪夫多项式的正交性和递归属性提取高频特征,并以更高的保真度近似复杂的非线性函数。在基准肺癌成像数据集上训练和评估该模型,包括LUNA16和LIDC-IDRI,在分类肺结节良恶性方面表现出卓越性能。定量结果显示与传统CNN方法相比,在准确性、敏感性和特异性方面均有显著提高。这种多项式基于谱逼近的深度学习与医学诊断的集成提供了一个稳健的框架,具有潜在的更广泛应用价值。
Key Takeaways
- 肺癌仍然是全球癌症死亡的主要原因之一,早期准确诊断至关重要。
- 传统卷积神经网络(CNN)在医学图像分析中具有潜力,但在复杂诊断场景中性能受限。
- 提出一种新型深度混合学习架构,结合切比雪夫多项式扩展,以提高CNN的表达能力和解剖结构表示。
- 切比雪夫多项式用于提取高频特征并近似复杂的非线性函数。
- 模型在基准肺癌成像数据集上表现卓越,包括LUNA16和LIDC-IDRI。
- 与传统CNN方法相比,该模型在准确性、敏感性和特异性方面显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

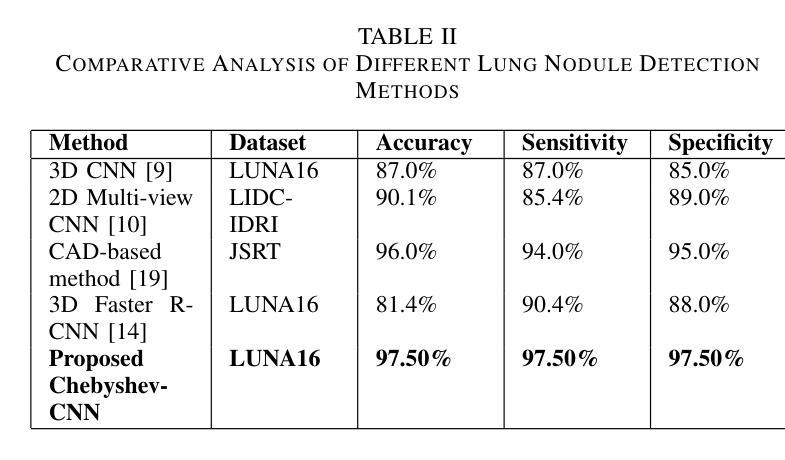
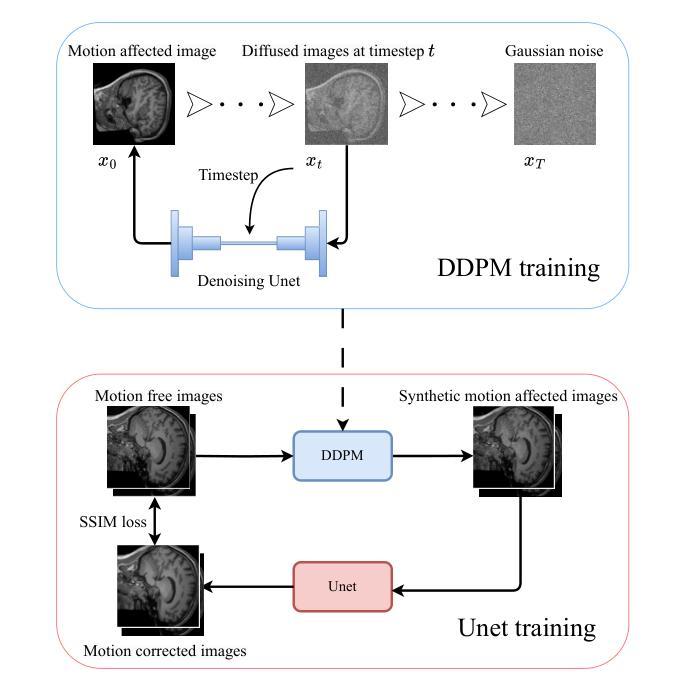
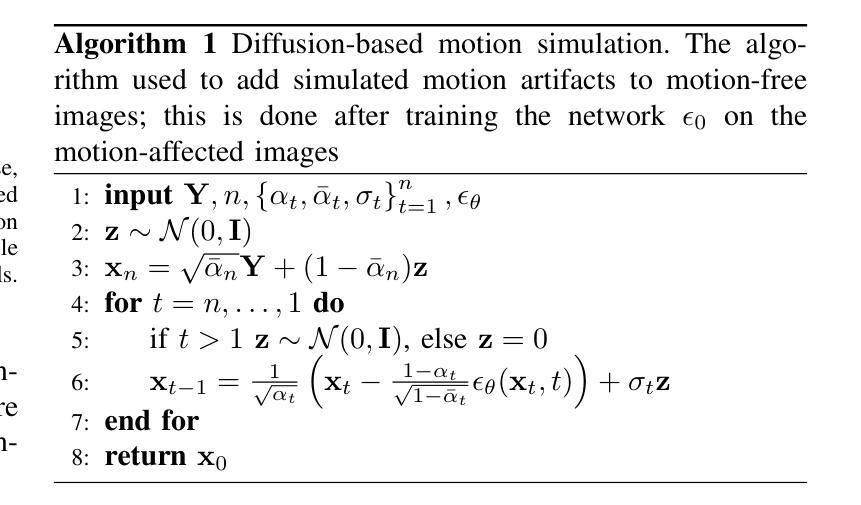
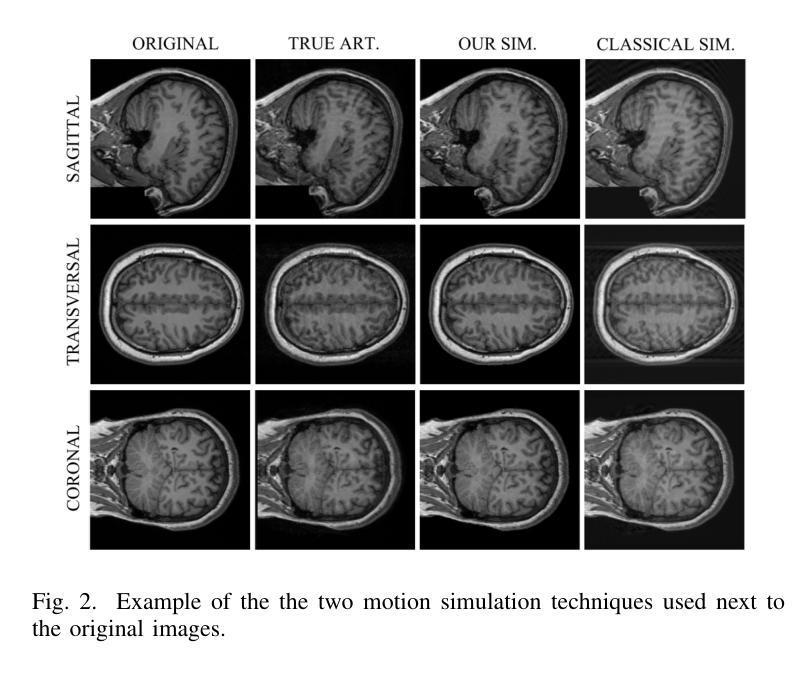
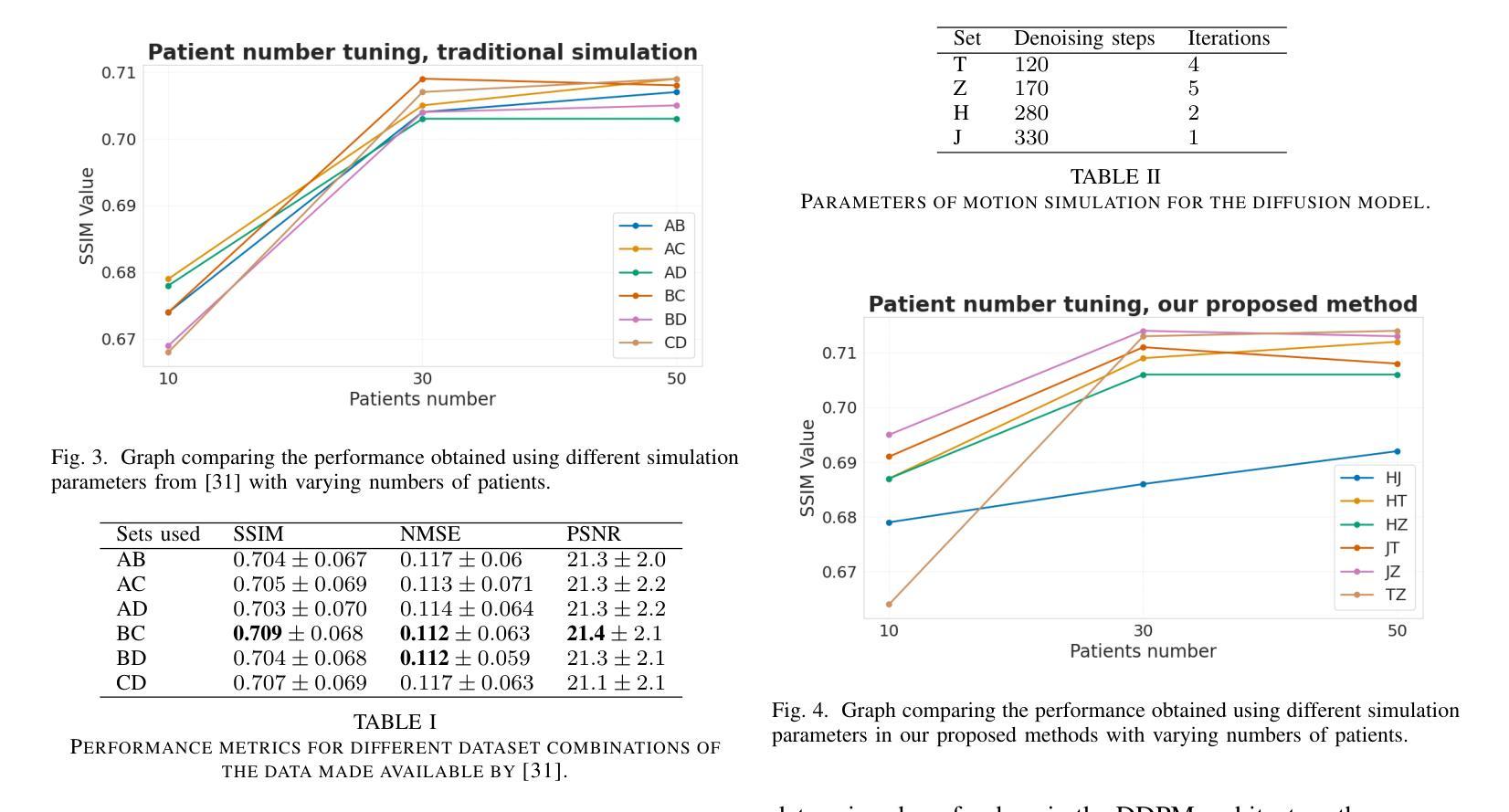
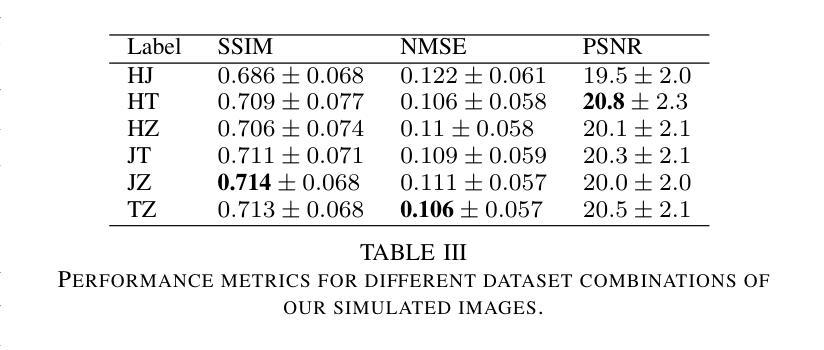
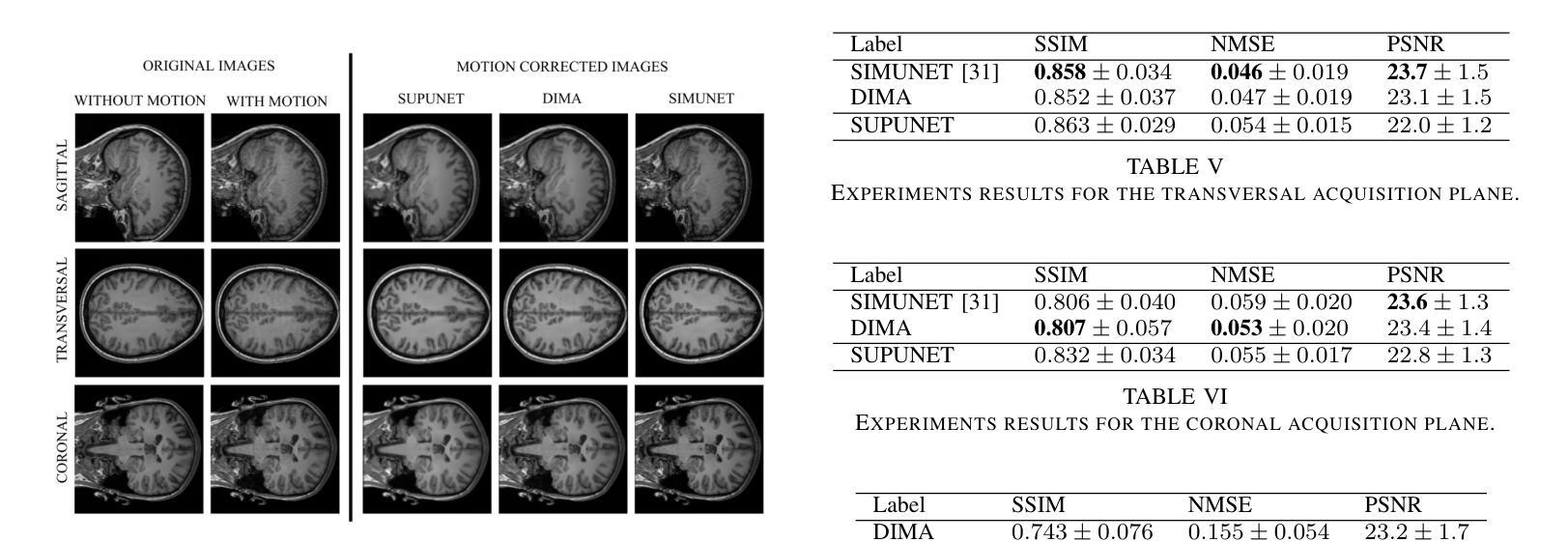
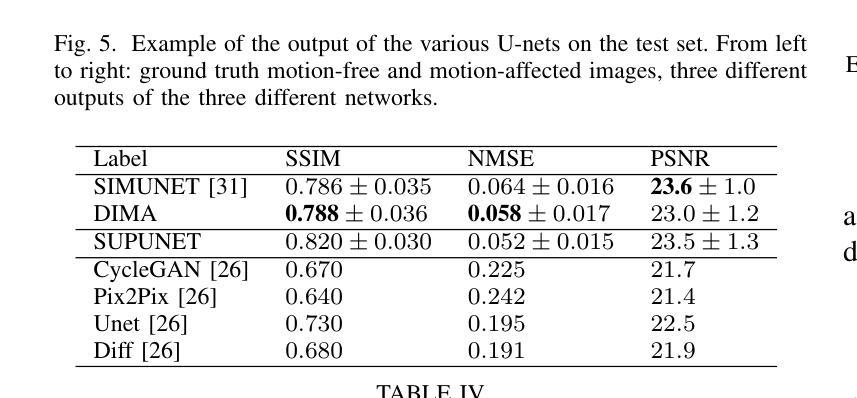
DIMA: DIffusing Motion Artifacts for unsupervised correction in brain MRI images
Authors:Paolo Angella, Luca Balbi, Fabrizio Ferrando, Paolo Traverso, Rosario Varriale, Vito Paolo Pastore, Matteo Santacesaria
Motion artifacts remain a significant challenge in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), compromising diagnostic quality and potentially leading to misdiagnosis or repeated scans. Existing deep learning approaches for motion artifact correction typically require paired motion-free and motion-affected images for training, which are rarely available in clinical settings. To overcome this requirement, we present DIMA (DIffusing Motion Artifacts), a novel framework that leverages diffusion models to enable unsupervised motion artifact correction in brain MRI. Our two-phase approach first trains a diffusion model on unpaired motion-affected images to learn the distribution of motion artifacts. This model then generates realistic motion artifacts on clean images, creating paired datasets suitable for supervised training of correction networks. Unlike existing methods, DIMA operates without requiring k-space manipulation or detailed knowledge of MRI sequence parameters, making it adaptable across different scanning protocols and hardware. Comprehensive evaluations across multiple datasets and anatomical planes demonstrate that our method achieves comparable performance to state-of-the-art supervised approaches while offering superior generalizability to real clinical data. DIMA represents a significant advancement in making motion artifact correction more accessible for routine clinical use, potentially reducing the need for repeat scans and improving diagnostic accuracy.
磁共振成像(MRI)中的运动伪影仍然是一个重大挑战,它会影响诊断质量,并可能导致误诊或重复扫描。现有的用于运动伪影校正的深度学习方法通常要求配对无运动和受运动影响的图像进行训练,这在临床环境中很少可用。为了克服这一要求,我们提出了DIMA(DIffusing Motion Artifacts,扩散运动伪影),这是一个利用扩散模型实现大脑MRI无监督运动伪影校正的新框架。我们的两阶段方法首先在一个未配对的受运动影响的图像上训练扩散模型,以学习运动伪影的分布。然后,该模型在清洁图像上生成逼真的运动伪影,创建适合校正网络监督训练的配对数据集。与现有方法不同,DIMA无需进行k空间操作或对MRI序列参数的详细了解,使其能够适应不同的扫描协议和硬件。在多个数据集和解剖平面上的综合评估表明,我们的方法实现了与最先进的监督方法相当的性能,同时在真实临床数据上提供了更好的泛化能力。DIMA在使运动伪影校正更易于常规临床使用方面取得了重大进展,有望减少重复扫描的需要,提高诊断的准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 5 figures, 7 tables
Summary
本文提出了一种新颖的基于扩散模型的无监督MRI运动伪影校正框架——DIMA。该框架能在不需要配对运动图像的情况下学习运动伪影的分布,生成逼真的运动伪影,为校正网络提供配对数据集。DIMA具有广泛的应用性,无需复杂的MRI序列参数知识,适用于不同的扫描协议和硬件。其在多个数据集上的评价表现出优秀的性能,并具有较高的实际应用价值。
Key Takeaways
- DIMA是一个基于扩散模型的MRI运动伪影校正框架。
- 它不需要配对运动和无运动的图像进行训练。
- DIMA学习运动伪影的分布并生成逼真的运动伪影。
- 该方法适用于不同的扫描协议和硬件,具有广泛的应用性。
- 在多个数据集上的评价表现出优秀的性能。
点此查看论文截图

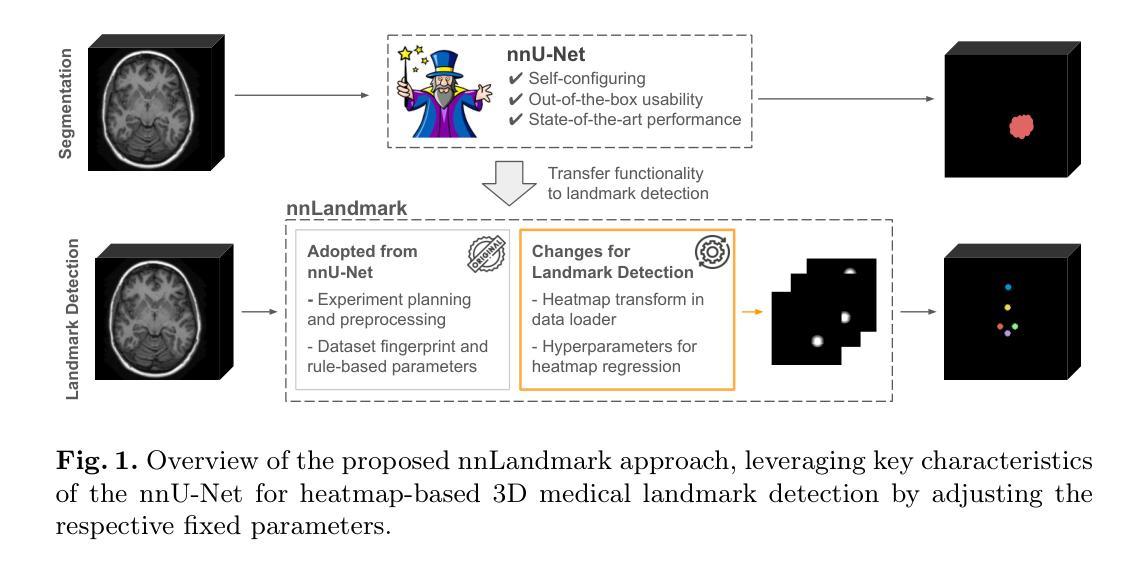
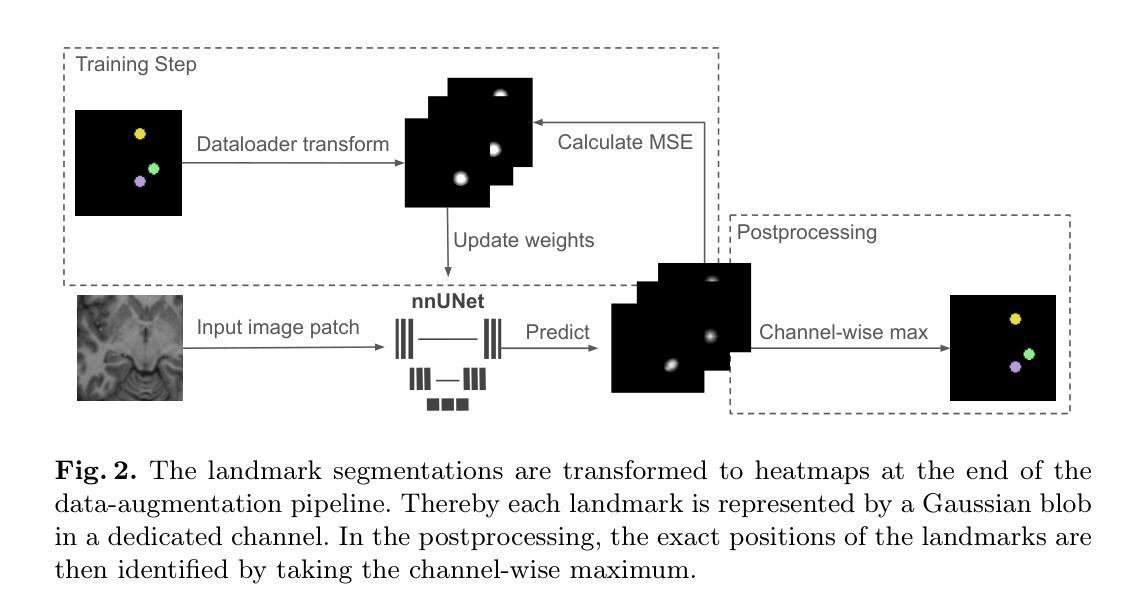
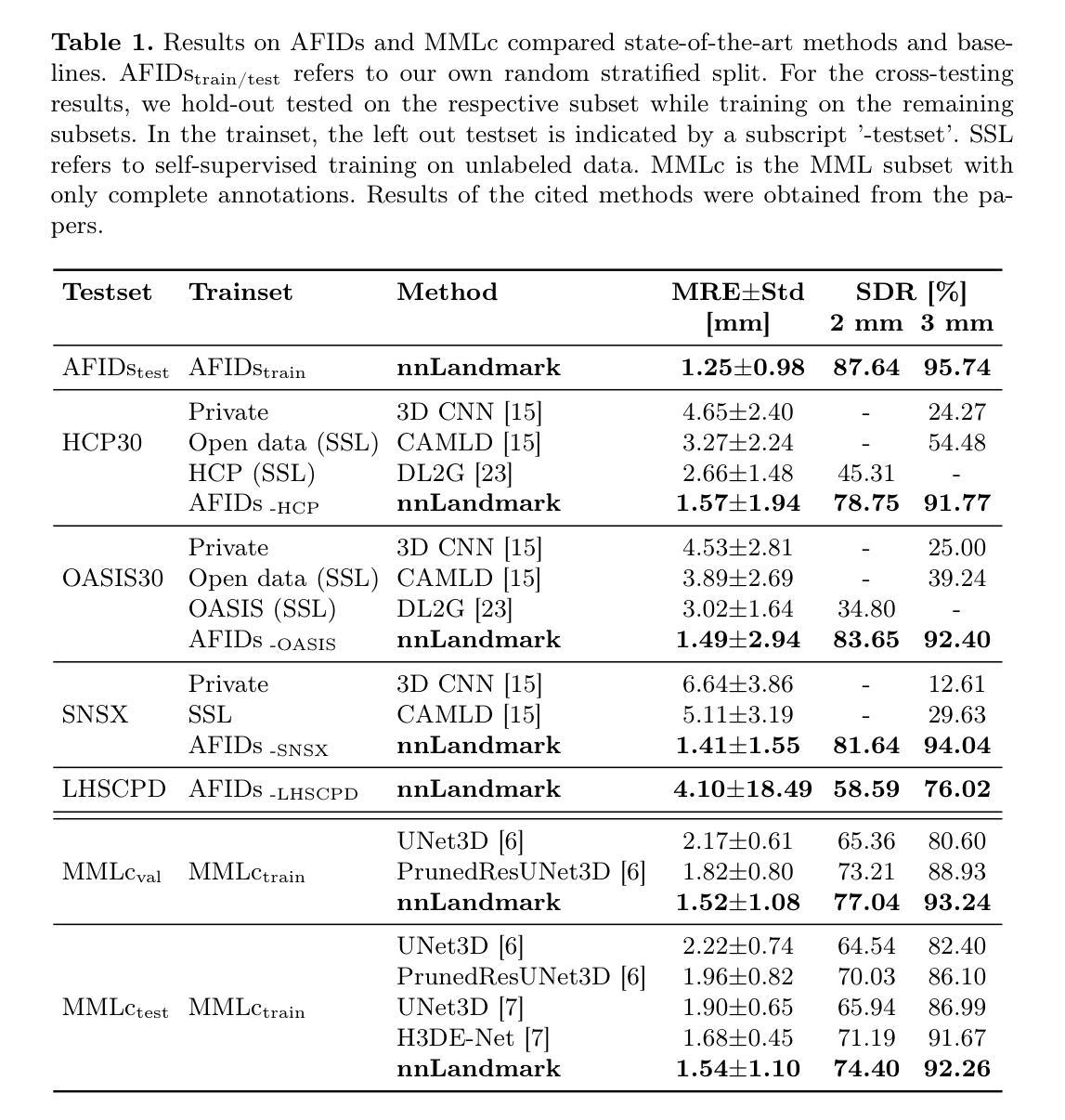
nnLandmark: A Self-Configuring Method for 3D Medical Landmark Detection
Authors:Alexandra Ertl, Shuhan Xiao, Stefan Denner, Robin Peretzke, David Zimmerer, Peter Neher, Fabian Isensee, Klaus Maier-Hein
Landmark detection plays a crucial role in medical imaging tasks that rely on precise spatial localization, including specific applications in diagnosis, treatment planning, image registration, and surgical navigation. However, manual annotation is labor-intensive and requires expert knowledge. While deep learning shows promise in automating this task, progress is hindered by limited public datasets, inconsistent benchmarks, and non-standardized baselines, restricting reproducibility, fair comparisons, and model generalizability.This work introduces nnLandmark, a self-configuring deep learning framework for 3D medical landmark detection, adapting nnU-Net to perform heatmap-based regression. By leveraging nnU-Net’s automated configuration, nnLandmark eliminates the need for manual parameter tuning, offering out-of-the-box usability. It achieves state-of-the-art accuracy across two public datasets, with a mean radial error (MRE) of 1.5 mm on the Mandibular Molar Landmark (MML) dental CT dataset and 1.2 mm for anatomical fiducials on a brain MRI dataset (AFIDs), where nnLandmark aligns with the inter-rater variability of 1.5 mm. With its strong generalization, reproducibility, and ease of deployment, nnLandmark establishes a reliable baseline for 3D landmark detection, supporting research in anatomical localization and clinical workflows that depend on precise landmark identification. The code will be available soon.
在医学成像任务中,地标检测对于依赖精确空间定位的任务起着至关重要的作用,包括诊断、治疗计划、图像注册和手术导航等特定应用。然而,手动注释是一项劳动密集的工作,需要专业知识。深度学习虽然在自动化此任务方面显示出潜力,但由于公共数据集有限、基准测试不一致和非标准化等因素,阻碍了进度,限制了可重复性、公平比较和模型的通用性。本研究引入了nnLandmark,这是一个用于3D医学地标检测的自动配置深度学习框架,它基于热图回归对nnU-Net进行了改编。通过利用nnU-Net的自动配置功能,nnLandmark无需手动参数调整,即可开箱即用。它在两个公共数据集上达到了最先进的准确性,在下颌磨牙地标(MML)牙科CT数据集上的平均径向误差(MRE)为1.5毫米,在脑部MRI数据集(AFIDs)上的解剖标记为1.2毫米,nnLandmark与1.5毫米的医师间变异度一致。凭借其强大的通用性、可重复性和易于部署的特点,nnLandmark为3D地标检测建立了可靠的基准线,支持依赖精确地标识别的解剖定位和临床工作流程研究。代码将很快提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习的nnLandmark框架为三维医学地标检测提供了一种自动化解决方案,通过利用nnU-Net的自配置功能实现了精确检测。此框架具有出色的准确性、通用性、可重复性和易用性,为依赖于精确地标识别的研究和临床工作流程提供了可靠的基础。
Key Takeaways
- nnLandmark是一个用于三维医学地标检测的深度学习框架,基于nnU-Net进行heatmap-based回归。
- nnLandmark通过自动配置消除了手动参数调整的需要,提供了开箱即用的功能。
- nnLandmark在公共数据集上实现了最先进的准确性,如在Mandibular Molar Landmark数据集上的平均径向误差为1.5毫米。
- nnLandmark在脑MRI数据集上的解剖标记物平均径向误差为1.2毫米,与专家之间的评分变异度对齐。
- nnLandmark框架具有良好的泛化能力,可支持在解剖定位和临床工作流程中的精确地标识别研究。
- nnLandmark具有可重复性且易于部署,为依赖于精确地标识别的应用提供了可靠基础。
点此查看论文截图

Large Scale Supervised Pretraining For Traumatic Brain Injury Segmentation
Authors:Constantin Ulrich, Tassilo Wald, Fabian Isensee, Klaus H. Maier-Hein
The segmentation of lesions in Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (msTBI) presents a significant challenge in neuroimaging due to the diverse characteristics of these lesions, which vary in size, shape, and distribution across brain regions and tissue types. This heterogeneity complicates traditional image processing techniques, resulting in critical errors in tasks such as image registration and brain parcellation. To address these challenges, the AIMS-TBI Segmentation Challenge 2024 aims to advance innovative segmentation algorithms specifically designed for T1-weighted MRI data, the most widely utilized imaging modality in clinical practice. Our proposed solution leverages a large-scale multi-dataset supervised pretraining approach inspired by the MultiTalent method. We train a Resenc L network on a comprehensive collection of datasets covering various anatomical and pathological structures, which equips the model with a robust understanding of brain anatomy and pathology. Following this, the model is fine-tuned on msTBI-specific data to optimize its performance for the unique characteristics of T1-weighted MRI scans and outperforms the baseline without pretraining up to 2 Dice points.
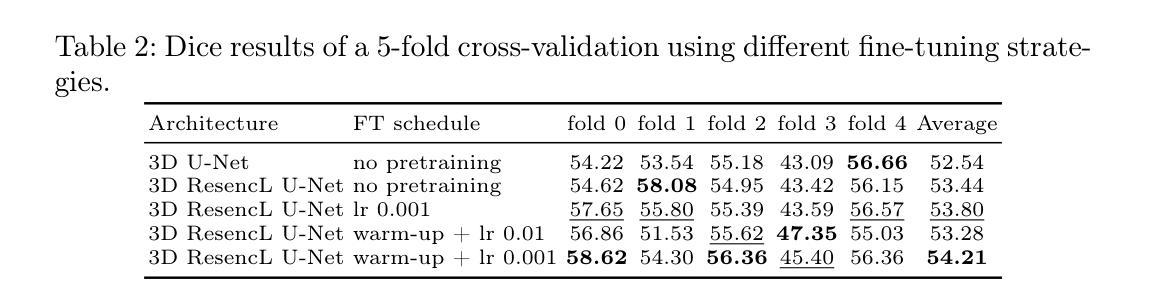
在中度至重度创伤性脑损伤(msTBI)中,病灶的分割在神经影像学中呈现出一个重大挑战,因为这些病灶的特性多种多样,其大小、形状和脑区域及组织类型的分布在各有不同。这种异质性使传统的图像处理技术复杂化,并在图像配准和脑分区等任务中导致关键错误。为了解决这些挑战,2024年AIMS-TBI分割挑战赛旨在推进专门用于T1加权MRI数据的创新分割算法,这是临床实践中应用最广泛的成像方式。我们提出的解决方案借鉴了MultiTalent方法的大规模多数据集监督预训练方法。我们在涵盖各种解剖和病理结构的数据集上训练了一个Resenc L网络,这使模型具备了对脑解剖学和病理学的稳健理解。之后,该模型在msTBI特定数据上进行微调,以针对T1加权MRI扫描的独特特性优化其性能,与未经预训练的基线相比,表现提高了2个Dice点。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了在神经影像中针对中度至重度创伤性脑损伤(msTBI)的病变分割所面临的挑战。由于这些病变在大小、形状和脑区及组织类型分布上的多样性,传统图像处理技术面临困难。为了解决这些问题,提出了采用大规模多数据集监督预训练方法的大型挑战赛——AIMSTBI分割挑战赛的目标是通过特定于T1加权MRI数据的分割算法来推进技术进步。该方法基于MultiTalent方法,训练了一个Resenc L网络,该网络在涵盖各种解剖和病理结构的综合数据集上具有良好的性能和适应性强大的理解能力,能够更有效地进行深度学习并经过优化后可满足特定的任务需求,并通过训练可以提升至一定的分割效果改善表现超过预训练时的基线值至2 Dice点。此外我们总结提出了应用具有超强综合理解和深度学习能力的大规模预训练模型的优秀技术可以加强该领域进步同时体现了对相关病例数据库和数据采集标准化处理的必要性和迫切性需求以满足研究和开发需求同时也突出了训练更多特定模型对改进人工智能技术的潜在作用。总体而言该挑战具有重大的现实意义和可行性价值并有望为医学影像领域的进步提供重要的推动力量。然而我们也需要注意到相关的数据采集处理和数据标准化工作需要得到更多的关注和投入以推进研究发展取得更大的进展成果将展现出一种潜在的需求和提升的巨大空间和挑战可能性体现也映射了基于需求需要进行的未来发展相关思考和研究探索。总的来说通过先进算法的运用和对大数据集的综合应用使得医学图像分割领域的技术发展面临巨大的机遇和挑战同时推动了医学图像分割领域的技术进步和创新。文中强调了算法的重要性同时强调了数据集在推动技术进步中的关键作用。同时文中也指出了未来的研究方向包括改进算法优化模型以及建立更大规模的数据集等。文中还提出了创新的方法来提高模型对复杂图像的理解能力并通过精细的训练和适应性优化提升模型性能显示出未来的技术发展方向和研究前景。总体来说该文本展示了医学图像分割领域的最新进展和未来的发展趋势并强调了人工智能在医学图像分析领域的应用前景广阔并呼吁更多的研究者和工程师投入到相关领域的研究中推动医学图像分割技术的不断进步和创新发展以及未来的技术改进和发展趋势探索具有重大现实意义和潜力价值同时也展现出未来人工智能在医学领域的广阔应用前景的巨大发展潜能与挑战压力无疑激发对未的了解和分析态度通过不断更新发展技术及精进研究和不断学习不断探索将为科技进步做出贡献有着一定的参考意义和前瞻作用从而更好地推进科技发展服务社会人民也推动了全球健康水平及诊疗方式的全面发展和不断进步积极开拓更多智能化时代的功能化和数字化的便捷智能未来人工智能的医疗辅助正在逐渐成为大势所趋持续带动更多的应用场景探索和未来健康技术研究的升级与进步等等在医疗服务等多个方面扮演日益重要的角色将会实现智能化技术在医疗健康领域更多智能化人性化的未来数字化生活发展新前景这也是当代社会发展提出的重要要求和面临的挑战将会带来新的跨越发展具有重要意义是未来世界重要发展的组成部分和研究主题顺应信息化时代发展的浪潮持续推进科技与医疗服务更好更广泛的结合和提升利用对行业发展发挥着巨大促进作用体现着社会的发展进步的标志趋势体现出发展的重大意义也在不断完善和调整科技创新带来广阔空间以满足未来发展前景发挥自身的推动社会经济发展的作用和科技进步推进意义以期给世界科技带来更多的动力及创新价值发挥更大的作用促进人类社会的持续发展和进步不断推动科技创新的突破和发展态势展现出无限的发展潜力和未来前景。
Key Takeaways:该文本包括以下七个关键要点:
点此查看论文截图

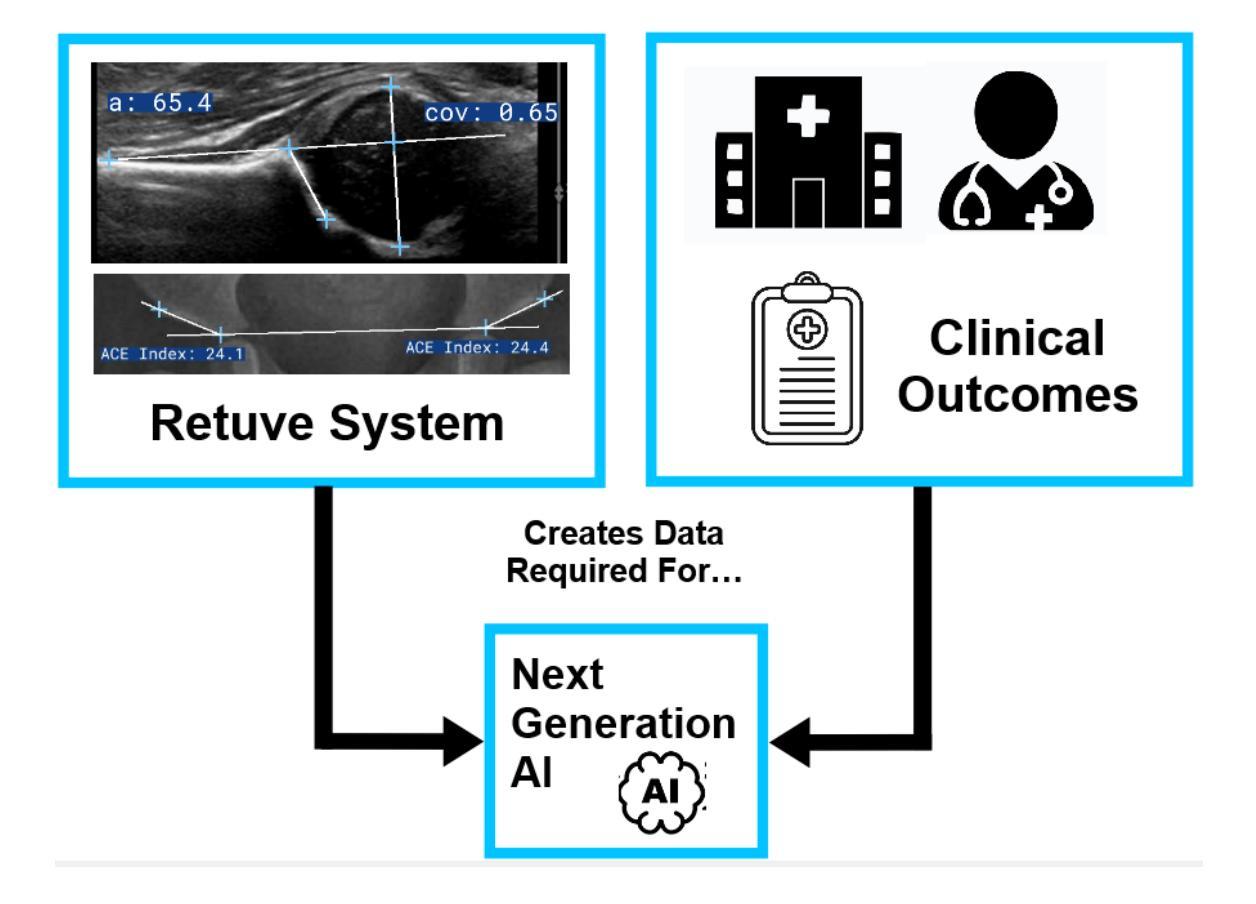
Retuve: Automated Multi-Modality Analysis of Hip Dysplasia with Open Source AI
Authors:Adam McArthur, Stephanie Wichuk, Stephen Burnside, Andrew Kirby, Alexander Scammon, Damian Sol, Abhilash Hareendranathan, Jacob L. Jaremko
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) poses significant diagnostic challenges, hindering timely intervention. Current screening methodologies lack standardization, and AI-driven studies suffer from reproducibility issues due to limited data and code availability. To address these limitations, we introduce Retuve, an open-source framework for multi-modality DDH analysis, encompassing both ultrasound (US) and X-ray imaging. Retuve provides a complete and reproducible workflow, offering open datasets comprising expert-annotated US and X-ray images, pre-trained models with training code and weights, and a user-friendly Python Application Programming Interface (API). The framework integrates segmentation and landmark detection models, enabling automated measurement of key diagnostic parameters such as the alpha angle and acetabular index. By adhering to open-source principles, Retuve promotes transparency, collaboration, and accessibility in DDH research. This initiative has the potential to democratize DDH screening, facilitate early diagnosis, and ultimately improve patient outcomes by enabling widespread screening and early intervention. The GitHub repository/code can be found here: https://github.com/radoss-org/retuve
发育性髋关节发育不良(DDH)存在重大的诊断挑战,阻碍了及时的干预。当前筛查方法缺乏标准化,而人工智能驱动的研究由于数据有限和代码可用性问题而面临再现性问题。为了解决这些局限性,我们推出了Retuve,这是一个用于多模式DDH分析的开源框架,涵盖了超声(US)和X射线成像。Retuve提供了一个完整且可复制的工作流程,提供包含专家注释的US和X射线图像的开放数据集、带有训练代码的预训练模型和权重,以及用户友好的Python应用程序编程接口(API)。该框架集成了分割和地标检测模型,能够实现关键诊断参数的自动测量,例如阿尔法角和髋臼指数。通过坚持开源原则,Retuve促进了DDH研究的透明度、协作和可访问性。这一举措有可能使DDH筛查普及化,促进早期诊断,并通过广泛的筛查和早期干预最终改善患者结果。GitHub仓库/代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/radoss-org/retuve 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures, submitted to Software Impacts
Summary
基于DDH(发育性髋关节发育不良)诊断的挑战,我们推出Retuve开源框架,用于超声和X射线多模态影像分析。该框架提供完整的工作流程,包括公开数据集、预训练模型和权重、用户友好的Python API等。它能自动化测量关键诊断参数,如α角和髋臼指数。Retuve遵循开源原则,促进DDH研究的透明度、协作性和可访问性。
Key Takeaways
- DDH诊断面临挑战,需要标准化筛查方法和可靠的数据支持。
- Retuve是一个开源框架,用于多模态(超声和X射线)DDH分析。
- Retuve提供完整的工作流程,包括公开数据集、预训练模型和权重。
- 该框架提供用户友好的Python API,方便用户操作。
- Retuve能自动化测量关键诊断参数,如α角和髋臼指数。
- Retuve遵循开源原则,促进DDH研究的透明度、协作和可访问性。
点此查看论文截图


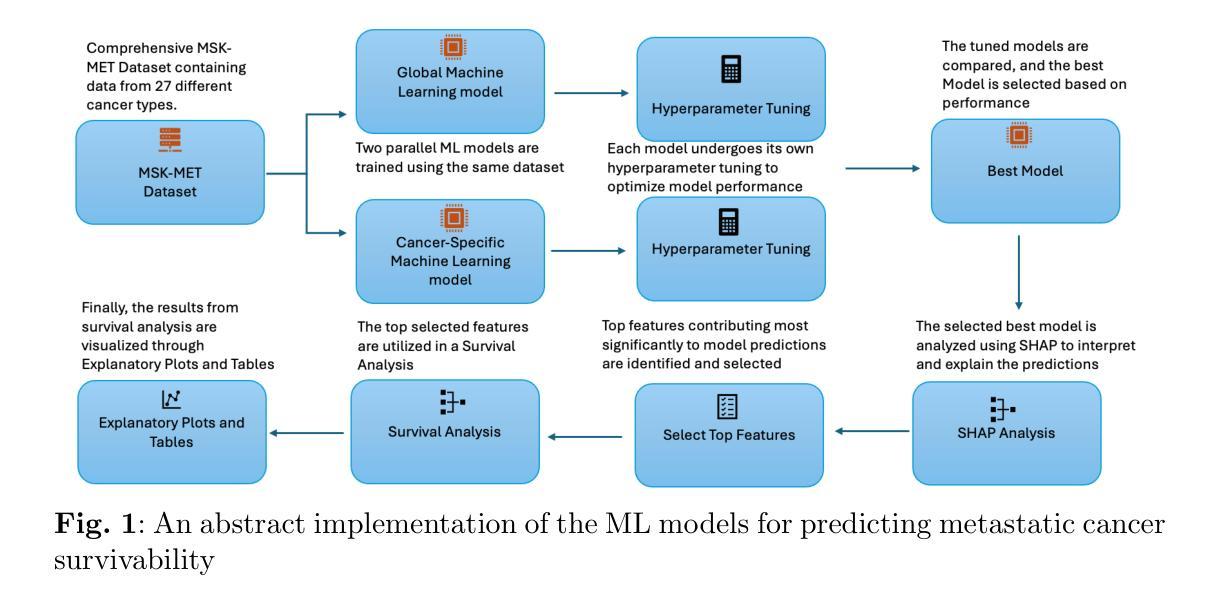
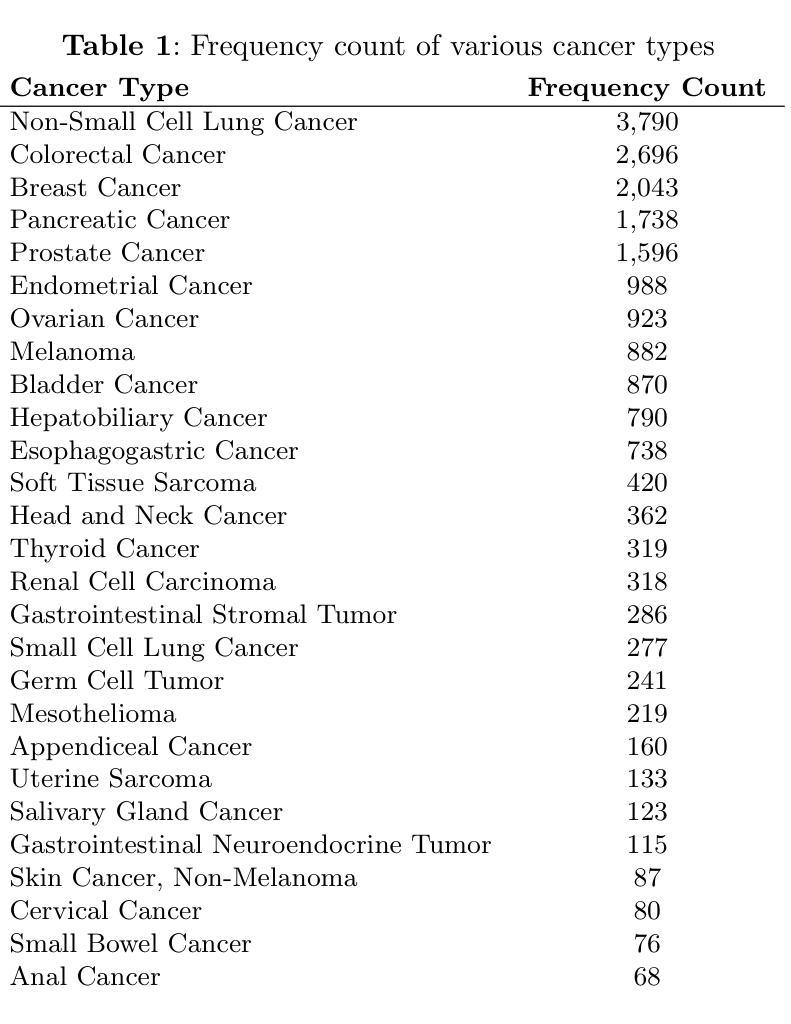
Predicting Survivability of Cancer Patients with Metastatic Patterns Using Explainable AI
Authors:Polycarp Nalela, Deepthi Rao, Praveen Rao
Cancer remains a leading global health challenge and a major cause of mortality. This study leverages machine learning (ML) to predict the survivability of cancer patients with metastatic patterns using the comprehensive MSK-MET dataset, which includes genomic and clinical data from 25,775 patients across 27 cancer types. We evaluated five ML models-XGBoost, Na"ive Bayes, Decision Tree, Logistic Regression, and Random Fores using hyperparameter tuning and grid search. XGBoost emerged as the best performer with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.82. To enhance model interpretability, SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) were applied, revealing key predictors such as metastatic site count, tumor mutation burden, fraction of genome altered, and organ-specific metastases. Further survival analysis using Kaplan-Meier curves, Cox Proportional Hazards models, and XGBoost Survival Analysis identified significant predictors of patient outcomes, offering actionable insights for clinicians. These findings could aid in personalized prognosis and treatment planning, ultimately improving patient care.
癌症仍然是全球面临的主要健康挑战和主要的死亡原因。本研究利用机器学习(ML)技术,使用包含27种癌症类型、共涉及来自世界各地近五万名患者的基因及临床数据的MSK-MET大型数据集,预测癌症患者的生存概率。我们对五种机器学习模型进行了评估,包括XGBoost、朴素贝叶斯分类器、决策树、逻辑回归和随机森林模型,并利用超参数调整和网格搜索进行优化。其中,XGBoost表现最佳,曲线下面积(AUC)达到0.82。为了增强模型的解释性,我们采用了SHapley Additive exPlanations(SHAP),揭示了关键预测因素,如转移部位数量、肿瘤突变负荷、基因改变的百分比以及器官特异性转移等。通过Kaplan-Meier曲线、Cox比例风险模型和XGBoost生存分析进行的进一步生存分析确定了患者预后的重要预测因素,为临床医生提供了可操作的见解。这些发现有助于进行个性化的预后预测和治疗计划制定,最终改善患者的护理和治疗结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文利用机器学习预测癌症患者的生存能力,基于MSK-MET数据集,包含27种癌症类型、共涉及25,775名患者的基因组及临床数据。经过对五种机器学习模型的评估,XGBoost表现最佳,曲线下面积(AUC)达0.82。采用SHAP方法提高模型解释性,揭示关键预测因素包括转移部位计数、肿瘤突变负担、基因组改变比例及器官特异性转移等。此外,通过Kaplan-Meier曲线、Cox比例风险模型及XGBoost生存分析等方法进一步分析患者生存情况,为临床医生提供重要参考,有助于个性化预后及治疗计划制定,最终改善患者护理。
Key Takeaways
- 利用机器学习预测癌症患者生存能力。
- 基于MSK-MET数据集,涵盖多种癌症类型和大量患者数据。
- 五种机器学习模型中,XGBoost表现最佳。
- 采用SHAP方法提高模型解释性,揭示关键预测因素。
- 转移部位计数、肿瘤突变负担等是重要预测指标。
- 通过多种方法分析患者生存情况,包括Kaplan-Meier曲线和Cox比例风险模型。
点此查看论文截图

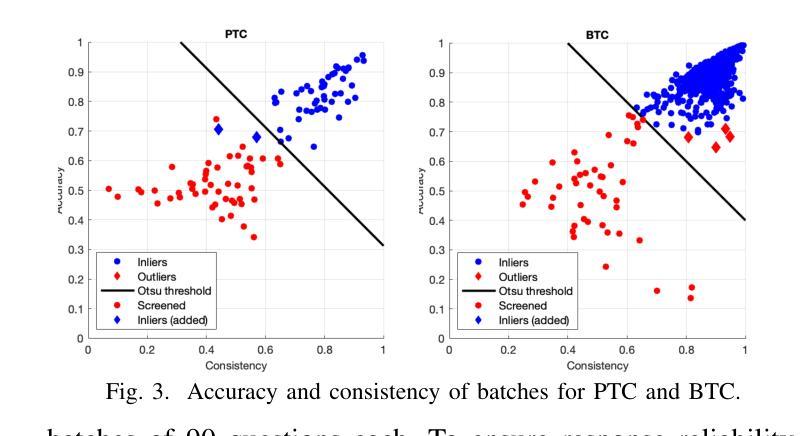
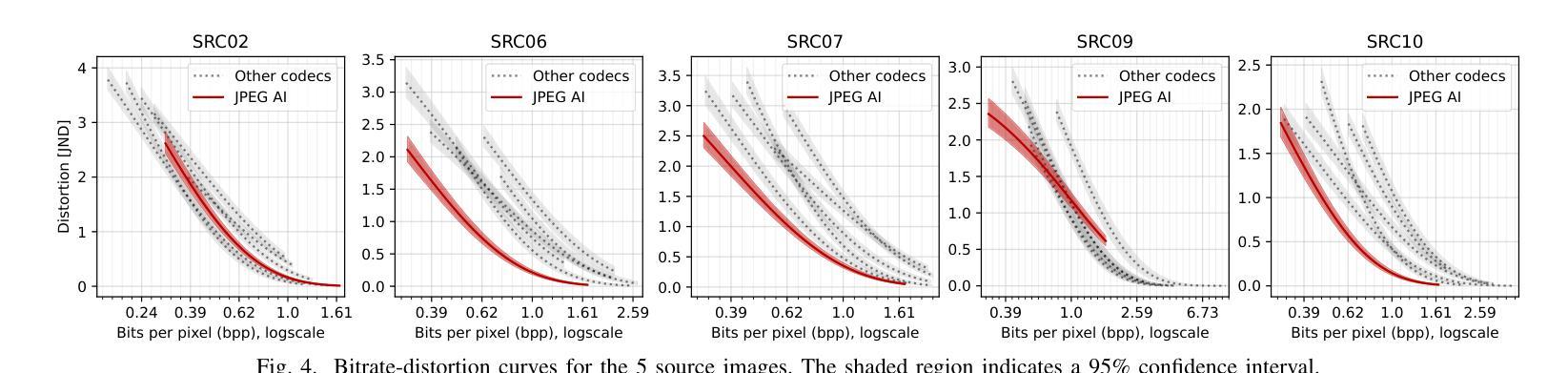
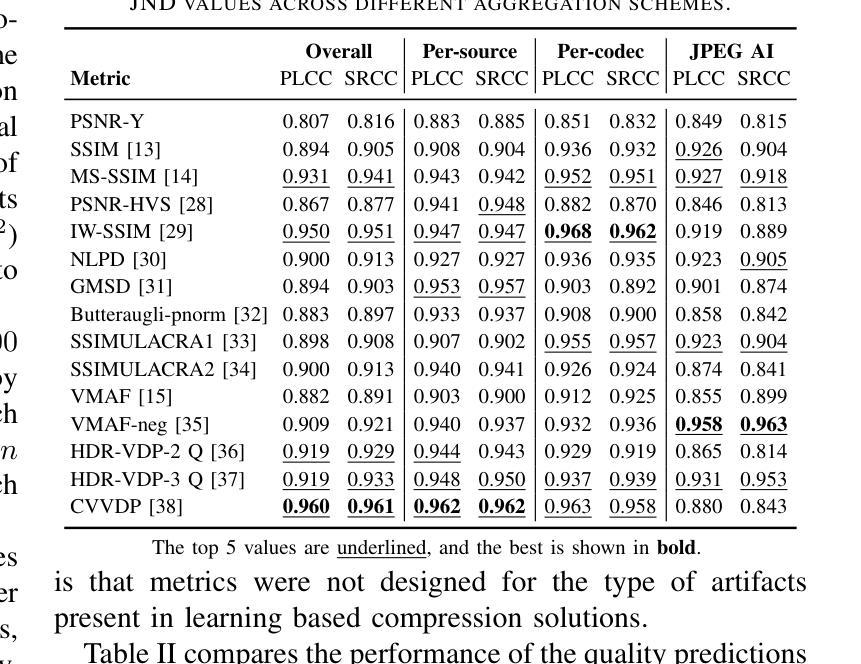
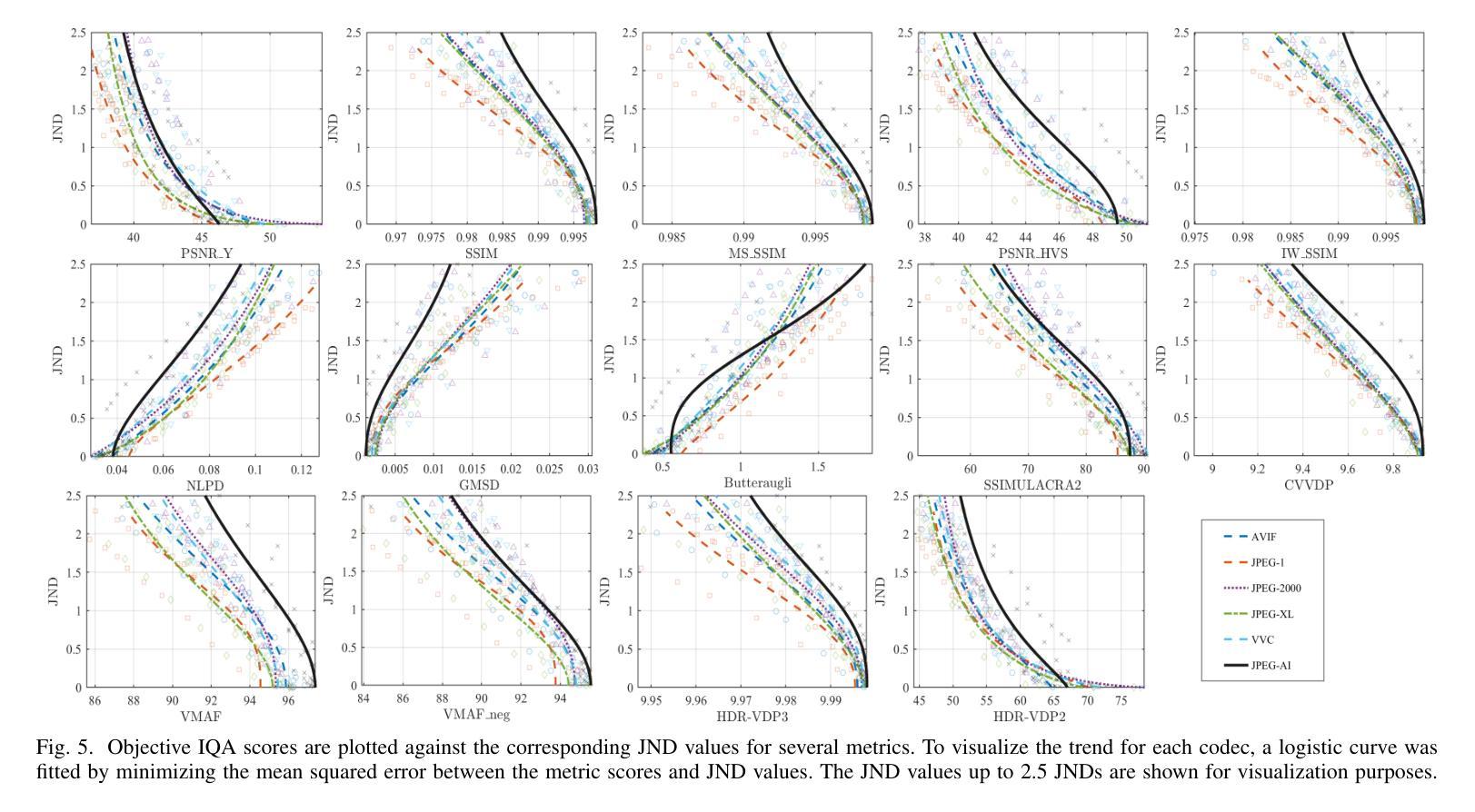
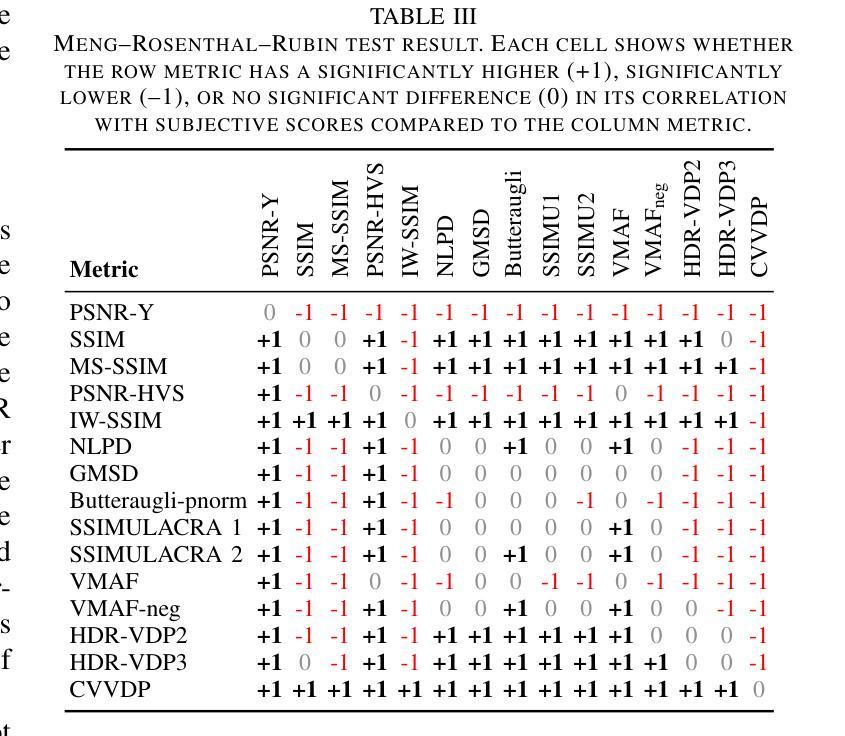
Subjective Visual Quality Assessment for High-Fidelity Learning-Based Image Compression
Authors:Mohsen Jenadeleh, Jon Sneyers, Panqi Jia, Shima Mohammadi, Joao Ascenso, Dietmar Saupe
Learning-based image compression methods have recently emerged as promising alternatives to traditional codecs, offering improved rate-distortion performance and perceptual quality. JPEG AI represents the latest standardized framework in this domain, leveraging deep neural networks for high-fidelity image reconstruction. In this study, we present a comprehensive subjective visual quality assessment of JPEG AI-compressed images using the JPEG AIC-3 methodology, which quantifies perceptual differences in terms of Just Noticeable Difference (JND) units. We generated a dataset of 50 compressed images with fine-grained distortion levels from five diverse sources. A large-scale crowdsourced experiment collected 96,200 triplet responses from 459 participants. We reconstructed JND-based quality scales using a unified model based on boosted and plain triplet comparisons. Additionally, we evaluated the alignment of multiple objective image quality metrics with human perception in the high-fidelity range. The CVVDP metric achieved the overall highest performance; however, most metrics including CVVDP were overly optimistic in predicting the quality of JPEG AI-compressed images. These findings emphasize the necessity for rigorous subjective evaluations in the development and benchmarking of modern image codecs, particularly in the high-fidelity range. Another technical contribution is the introduction of the well-known Meng-Rosenthal-Rubin statistical test to the field of Quality of Experience research. This test can reliably assess the significance of difference in performance of quality metrics in terms of correlation between metrics and ground truth. The complete dataset, including all subjective scores, is publicly available at https://github.com/jpeg-aic/dataset-JPEG-AI-SDR25.
基于学习的图像压缩方法作为对传统编码技术的有前途的替代方案而出现,提供了改进的速率失真性能和感知质量。JPEG AI代表此领域的最新标准化框架,利用深度神经网络进行高保真图像重建。在这项研究中,我们使用JPEG AIC-3方法对JPEG AI压缩图像进行主观视觉质量评估,该方法以刚刚可察觉差异(JND)单位量化感知差异。我们从五个不同的来源生成了包含精细失真级别的50个压缩图像数据集。一项大规模众包实验收集了来自459名参与者的96,200个三元组响应。我们基于增强和纯三元比较重建了基于JND的质量量表统一模型。此外,我们评估了多个客观图像质量指标与高保真范围内人类感知的对齐程度。CVVDP指标总体性能最高;然而,包括CVVDP在内的大多数指标在预测JPEG AI压缩图像质量时过于乐观。这些发现强调了在现代图像编码格式的开发和基准测试中严格进行主观评价的必要性,特别是在高保真范围内。另一个技术贡献是将著名的Meng-Rosenthal-Rubin统计测试引入到体验质量研究领域。该测试可以可靠地评估质量指标在指标与地面真实之间的相关性方面的性能差异是否显著。包括所有主观分数在内的完整数据集可在https://github.com/jpeg-aic/dataset-JPEG-AI-SDR25公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 5 figures, 3 tables, submitted to QoMEX 2025
摘要
本研究对JPEG AI压缩图像进行了全面的主观视觉质量评估,采用JPEG AIC-3方法论量化感知差异,生成了包含精细失真级别的数据集。通过大规模网络实验收集参与者响应,重建基于JND的质量尺度。评估多种客观图像质量指标与人类感知的一致性,发现CVVDP指标性能最佳,但预测JPEG AI压缩图像质量时过于乐观。研究强调现代图像编码格式发展中主观评估的重要性,并将Meng-Rosenthal-Rubin统计测试引入QoE研究领域,以评估质量指标性能的显著性。完整数据集公开可用。
关键见解
- 学习型图像压缩方法作为传统编解码器的有前途的替代方案出现,提供了改进的速率失真性能和感知质量。
- JPEG AI代表此领域的最新标准化框架,利用深度神经网络进行高保真图像重建。
- 采用JPEG AIC-3方法对JPEG AI压缩图像进行了全面的主观视觉质量评估,通过量化感知差异评估图像质量。
- 生成了包含五种不同来源的50张精细失真级别压缩图像的数据集。
- 大规模网络实验收集了大量参与者响应,用于重建基于JND的质量尺度。
- 评估了多种客观图像质量指标在高保真范围内与人类感知的一致性,发现CVVDP指标性能最佳,但存在预测偏差。
点此查看论文截图



Cross-correlation between soft X-rays and galaxies A new benchmark for galaxy evolution models
Authors:Johan Comparat, Andrea Merloni, Gabriele Ponti, Soumya Shreeram, Yi Zhang, Thomas H. Reiprich, Ang Liu, Riccardo Seppi, Xiaoyuan Zhang, Nicolas Clerc, Andrina Nicola, Kirpal Nandra, Mara Salvato, Nicola Malavasi
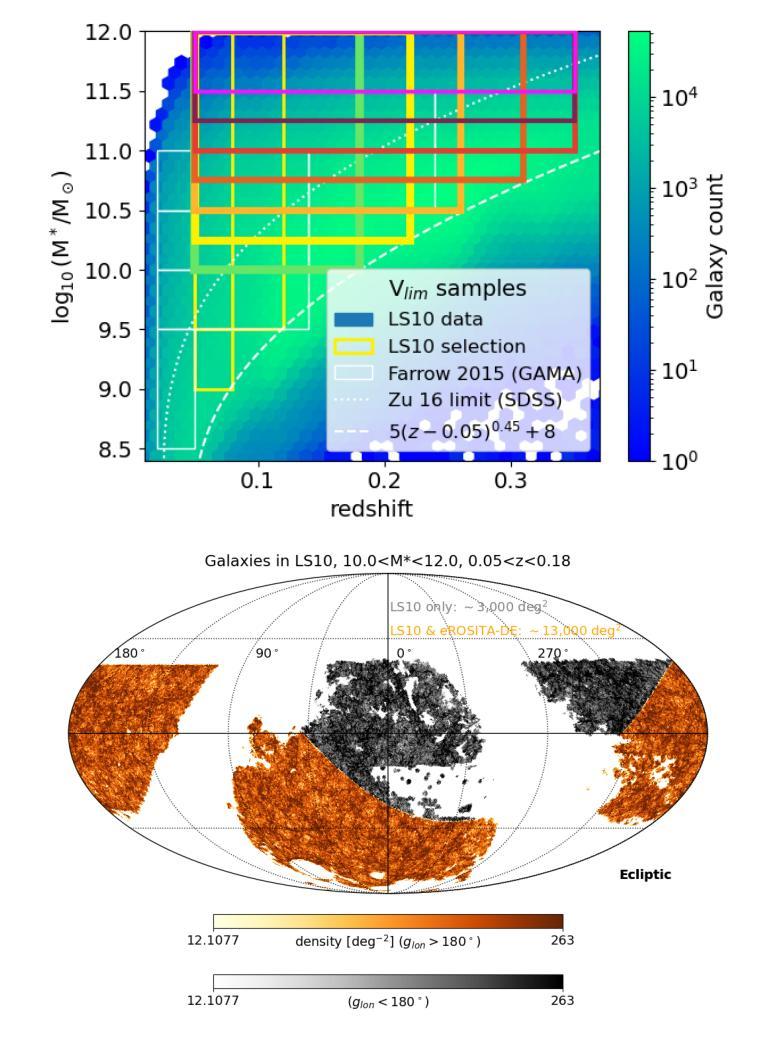
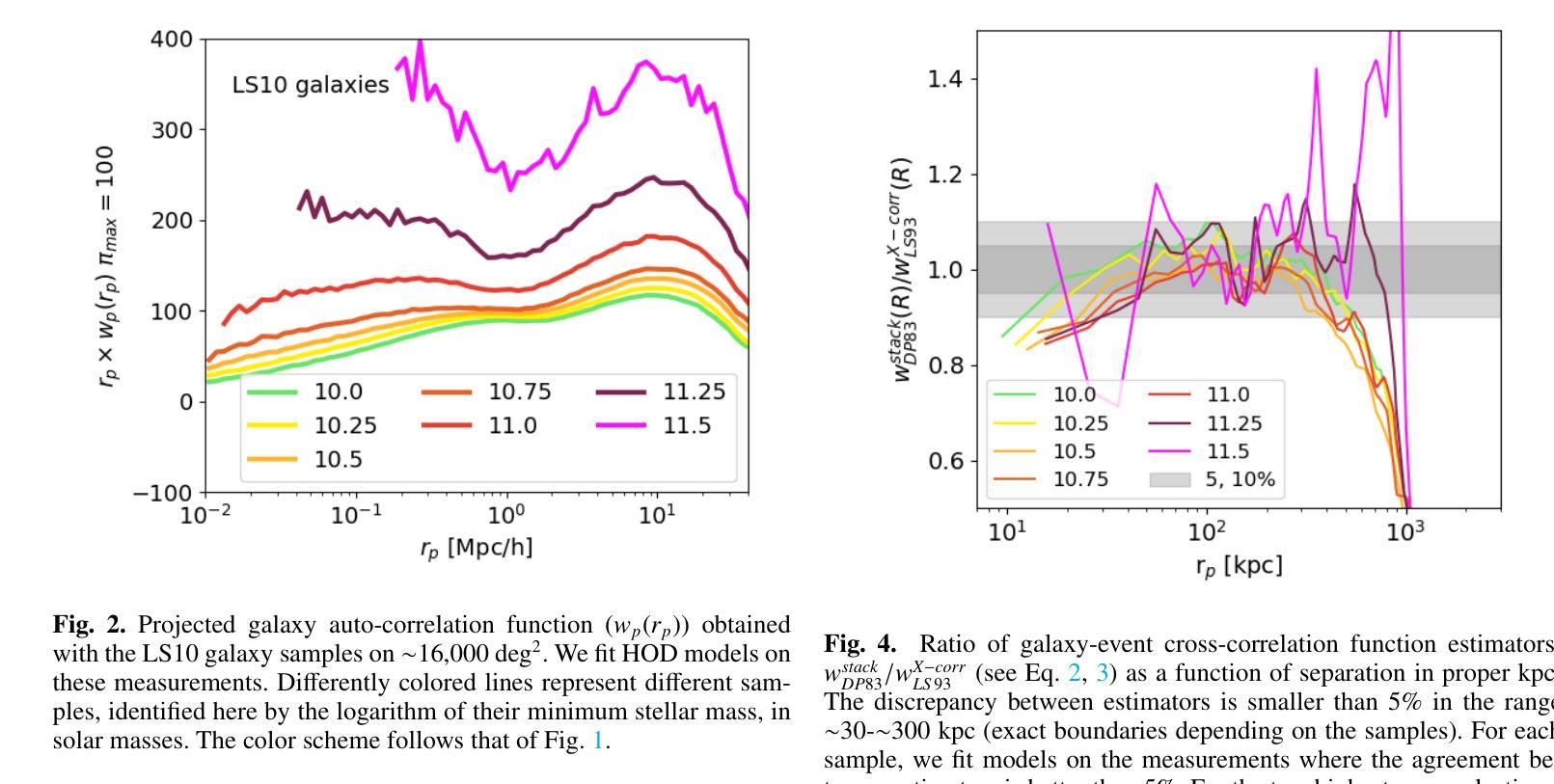
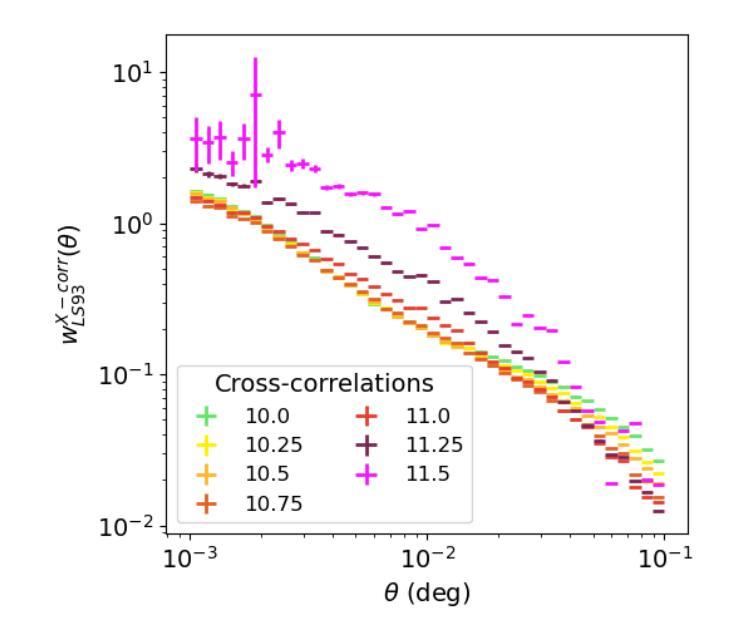
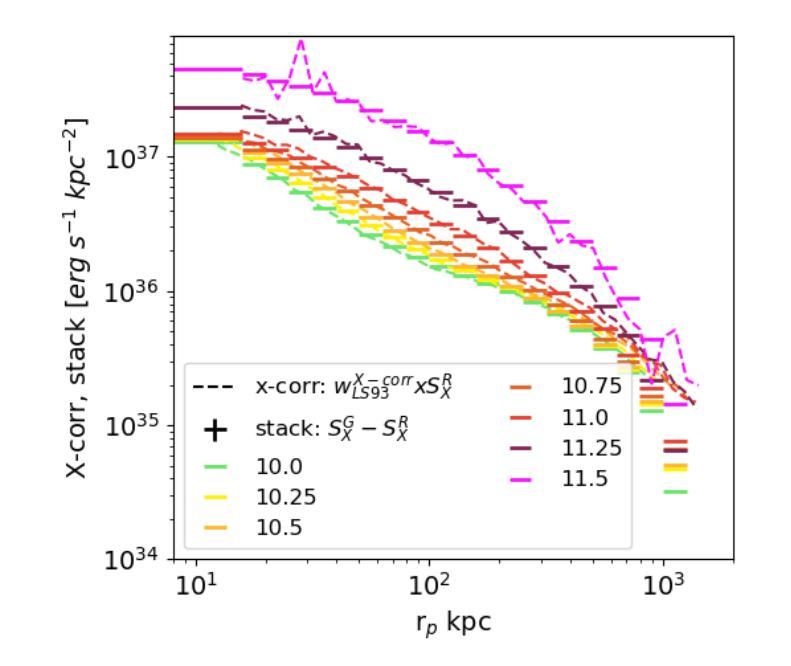
This article presents the construction and validation of complete stellar mass-selected, volume-limited galaxy samples using the Legacy Survey (data release 10) galaxy catalogs, covering $\sim16,800$ deg$^2$ of extra-galactic sky, and extending to redshift $z<0.35$. We measure the correlation function of these galaxies with tiny statistical uncertainties at the percent level and systematic uncertainties up to 5%. A 4-parameter halo occupation distribution (HOD) model is fitted to retrieve the population of host halos, yielding results on the stellar to halo mass relation consistent with the current models of galaxy formation and evolution. Using these complete galaxy samples, we measure and analyze the cross-correlation (X-corr) between galaxies and all soft X-ray photons observed by SRG/eROSITA in the 0.5-2 keV band over $\sim13,000$ deg$^2$. The cross correlation measurements have unprecedented sub-percent statistical uncertainty and ~5-10% systematic uncertainty. An extension to the halo model is introduced to interpret the X-corr, decomposing contributions from X-ray point sources, hot gas (CGM), satellites, and the 2-halo term. For low stellar mass thresholds ($\log M^*/M_{\odot}>$ 10, 10.25, 10.5), we find that the point source emission dominates the X-corr at small separation ($r<80$kpc). Then, in the range ($80<r<2$Mpc), the emission from large halos hosting satellite galaxies dominates. Finally, on scales beyond that considered here ($r>2$Mpc), the 2-halo term becomes dominant. Interestingly, there is no scale at which the CGM dominates. In the range ($20<r<200$kpc), the CGM contributes to more than 10% of the signal. Progressively, with the minimum stellar mass increasing, the CGM emission increases. We constrain the $M_{500c}-L_X$ scaling relation slope, $1.629^{+0.091}_{-0.089}$, at the 5% level using the samples with the lowest mass threshold.
本文利用Legacy Survey(第10次数据发布)星系目录,构建了完整的恒星质量选择、体积限制的星系样本,对约16,800平方度外的星系进行研究,延伸至红移z < 0.35。我们对这些星系的关联函数进行了测量,统计误差非常小,只有百分之一左右,系统误差达百分之五。通过拟合一个包含四个参数的晕占据分布(HOD)模型,我们得到了寄主晕的人口数据,得到的结果与当前的星系形成和演化模型一致的恒星晕质量关系。使用这些完整的星系样本,我们测量并分析了星系与SRG/eROSITA在约一万三千平方度内观察到的所有软X射线光子之间的交叉关联(X-corr)。交叉关联的测量具有前所未有的亚百分之一的统计误差和约百分之五到百分之十的系统误差。为了解释X-corr,对晕模型进行了扩展,分解了来自X射线点源、热气体(晕气体)、卫星和两晕术语的贡献。对于较低的恒星质量阈值(log M * / M⊙ > 10、 10.25、 10.5),我们发现点源发射在小分离距离(r < 80kpc)内主导了X-corr。然后,在范围(80 < r < 2Mpc)内,由宿主卫星星系的大型晕的发射占主导地位。最后,在此范围之外(r > 2Mpc),两晕术语变得占主导地位。有趣的是,没有哪个尺度上晕气体占主导地位。在范围(20 < r < 200kpc)内,晕气体的贡献超过了信号的百分之十。随着最小恒星质量的增加,晕气体的发射也随之增加。我们约束了最小恒星质量与Lx的缩放关系斜率(最低质量阈值的样本)为 1.629 ± 0.091。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in A&A
Summary
本文利用Legacy Survey(数据发布10版)星系目录构建了完整的恒星质量选定的、限体积的星系样本,研究了星系与SRG/eROSITA观测的软X射线光子之间的交叉关联。采用4参数星系占用暗物质晕模型,分析了星系与各种X射线源(点源、热气体(周围介质)、卫星星系及大尺度结构)之间的相互作用。发现点源在低恒星质量阈值下占主导地位,随着尺度的增大,卫星星系和大尺度结构的作用逐渐显现,而周围介质的影响较小。
Key Takeaways
- 利用Legacy Survey数据构建了完整的恒星质量选定、限体积的星系样本,覆盖约16,800度平方的银河系外天空,并扩展到红移z<0.35。
- 通过4参数暗物质晕占用模型,对星系的主宿暗物质晕进行分析。
- 测量和分析了星系与SRG/eROSITA观测到的软X射线光子之间的交叉关联(X-corr)。
- X-corr的测量具有前所未有的百分之一级的统计不确定性和约5-10%的系统不确定性。
- 在不同的尺度上,分析了X射线点源、热气体(周围介质)、卫星星系以及两暗物质晕间的相互作用对X-corr的贡献。
- 发现点源在低恒星质量阈值下占主导地位,而周围介质的影响在特定尺度上超过10%。
点此查看论文截图

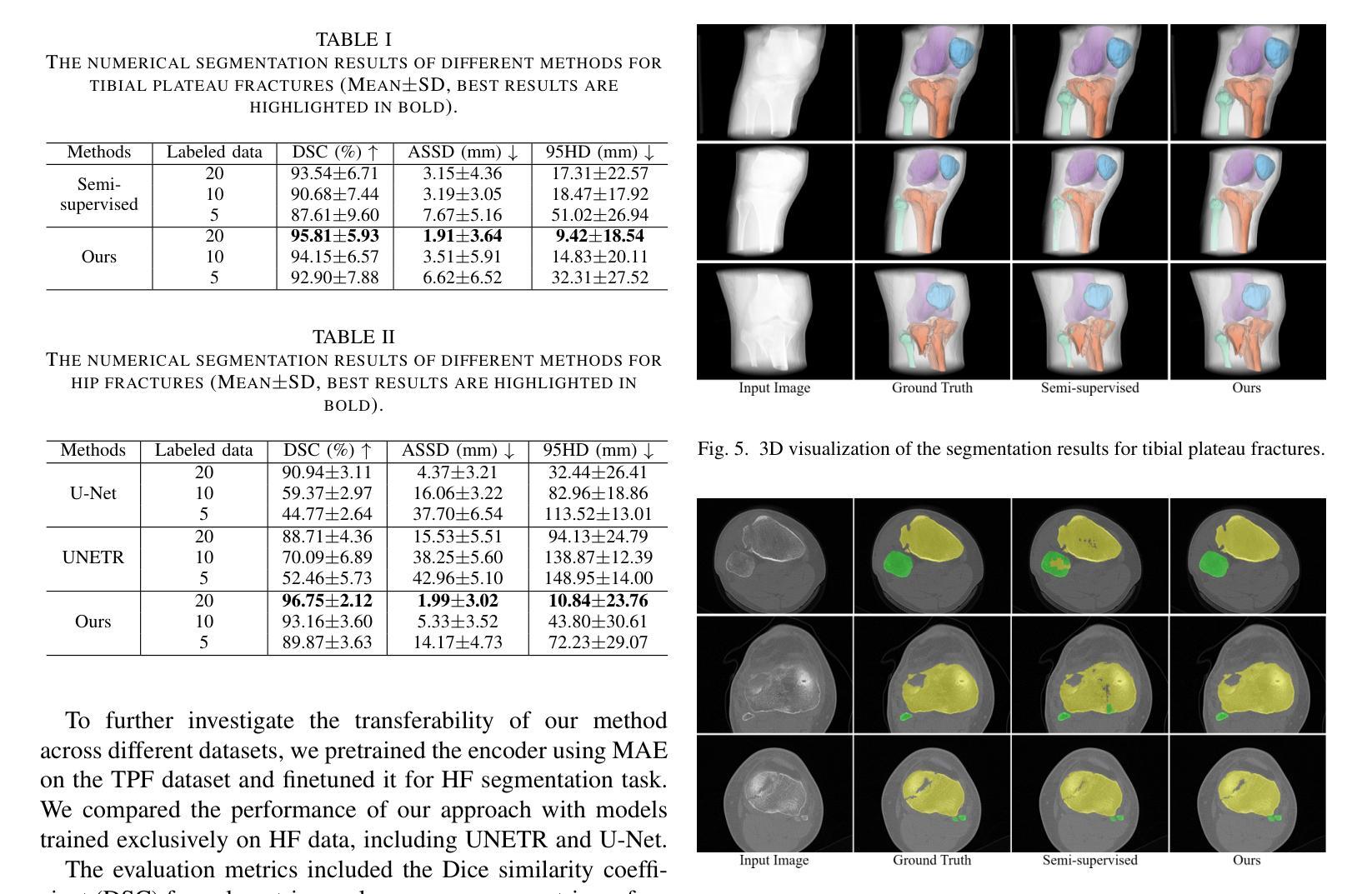
Learning Generalizable Features for Tibial Plateau Fracture Segmentation Using Masked Autoencoder and Limited Annotations
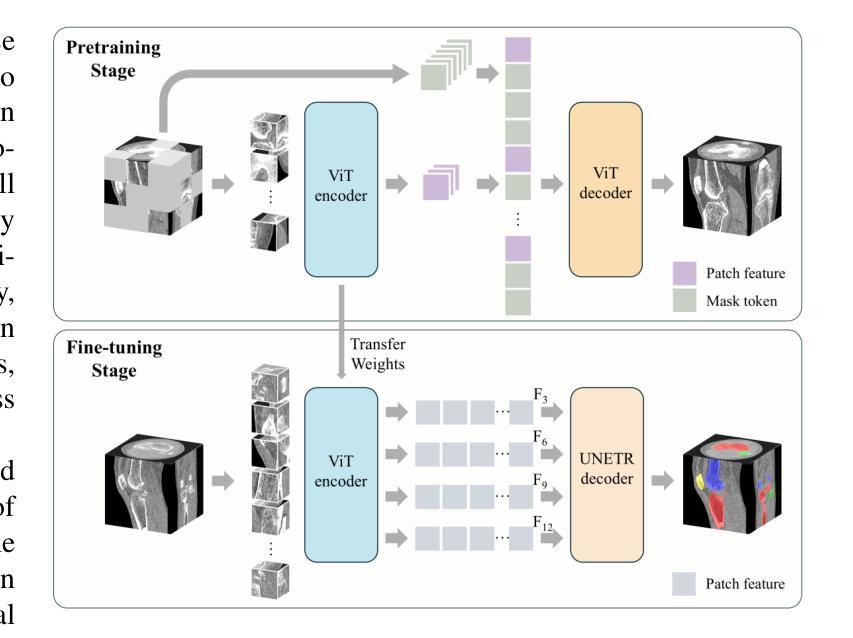
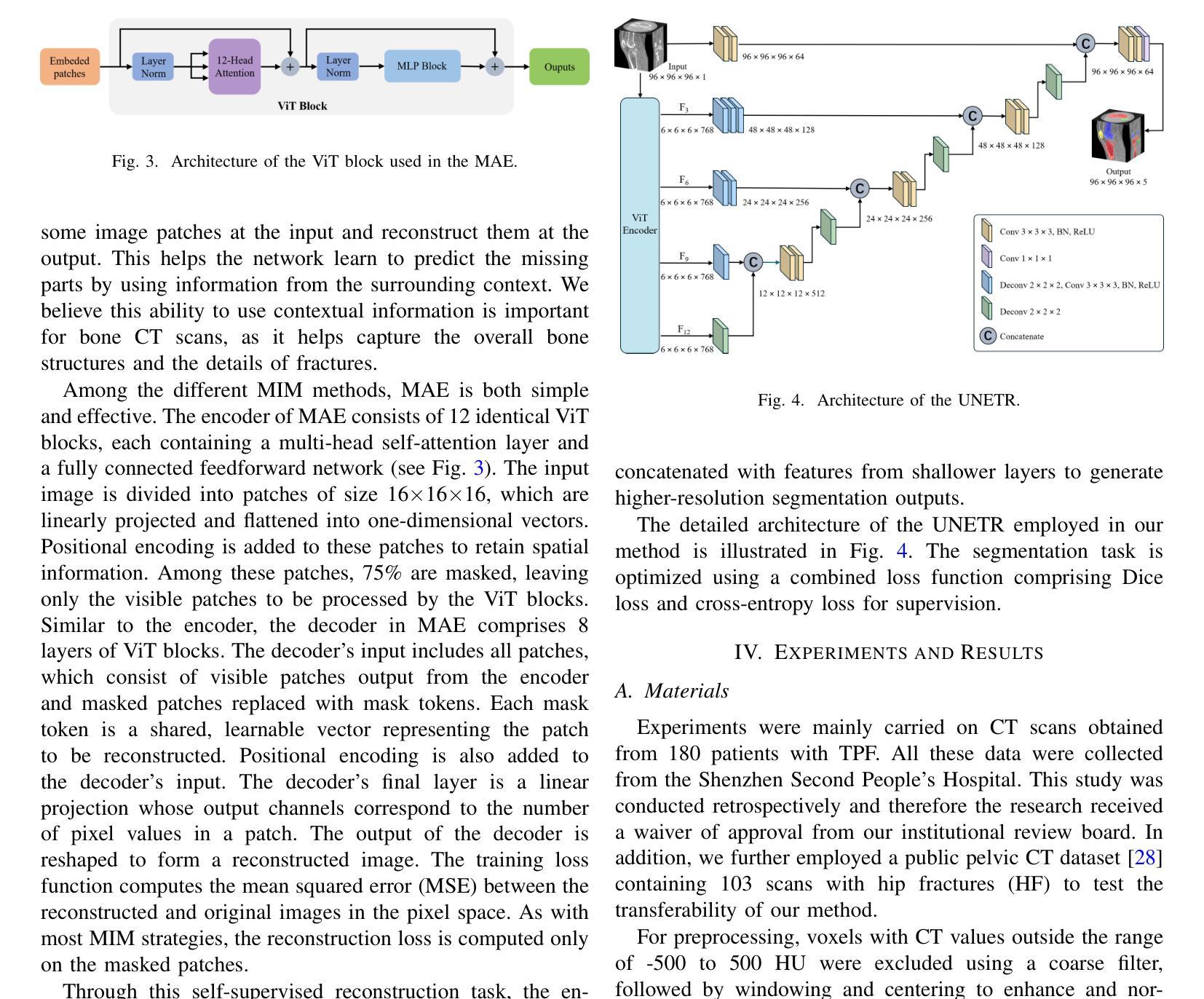
Authors:Peiyan Yue, Die Cai, Chu Guo, Mengxing Liu, Jun Xia, Yi Wang
Accurate automated segmentation of tibial plateau fractures (TPF) from computed tomography (CT) requires large amounts of annotated data to train deep learning models, but obtaining such annotations presents unique challenges. The process demands expert knowledge to identify diverse fracture patterns, assess severity, and account for individual anatomical variations, making the annotation process highly time-consuming and expensive. Although semi-supervised learning methods can utilize unlabeled data, existing approaches often struggle with the complexity and variability of fracture morphologies, as well as limited generalizability across datasets. To tackle these issues, we propose an effective training strategy based on masked autoencoder (MAE) for the accurate TPF segmentation in CT. Our method leverages MAE pretraining to capture global skeletal structures and fine-grained fracture details from unlabeled data, followed by fine-tuning with a small set of labeled data. This strategy reduces the dependence on extensive annotations while enhancing the model’s ability to learn generalizable and transferable features. The proposed method is evaluated on an in-house dataset containing 180 CT scans with TPF. Experimental results demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms semi-supervised methods, achieving an average Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 95.81%, average symmetric surface distance (ASSD) of 1.91mm, and Hausdorff distance (95HD) of 9.42mm with only 20 annotated cases. Moreover, our method exhibits strong transferability when applying to another public pelvic CT dataset with hip fractures, highlighting its potential for broader applications in fracture segmentation tasks.
精确自动分割胫骨平台骨折(TPF)是医学图像处理领域的核心课题。在使用计算机断层扫描(CT)的情况下,要想对深度学习模型进行训练需要大量的标注数据。然而,获取这些标注数据面临独特挑战。这一过程需要专业知识来识别多种骨折模式、评估严重程度,并考虑个体解剖结构差异,使得标注过程既耗时又昂贵。尽管半监督学习方法能够利用未标记的数据,但现有方法往往难以应对骨折形态的复杂性和可变性,以及在数据集之间的通用性有限。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种基于掩码自动编码器(MAE)的有效训练策略,用于CT中准确的TPF分割。我们的方法利用MAE的预训练功能,从非标记数据中捕获全局骨骼结构和精细的骨折细节,然后使用少量标记数据进行微调。此策略减少了我们对大量注释的依赖,同时提高了模型的通用性和可迁移特征的学习能力。该方法在包含180例TPF的CT扫描内部数据集上进行了评估。实验结果表明,我们的方法一直优于半监督方法,平均Dice相似系数(DSC)达到95.81%,平均对称表面距离(ASSD)为1.91毫米,Hausdorff距离(95HD)为9.42毫米,且仅使用20个标注案例。此外,我们的方法在处理另一公共骨盆CT数据集(包含髋关节骨折)时表现出强大的迁移性,突显其在骨折分割任务中更广泛应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 6 figures. Accepted to IEEE EMBC 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于掩码自编码器(MAE)的有效训练策略,用于准确地对CT中的胫骨平台骨折(TPF)进行自动分割。该方法利用MAE进行预训练,从非标记数据中捕获全局骨骼结构和精细骨折细节,然后通过少量标记数据进行微调。此策略减少了大量标注的依赖,提高了模型学习通用和可迁移特征的能力。实验结果表明,该方法在内部数据集上的表现优于半监督方法,并在另一个公共骨盆CT数据集上具有良好的可迁移性。
Key Takeaways
- 准确自动分割胫骨平台骨折(TPF)需要大规模标注数据来训练深度学习模型。
- 标注过程需要专业知识,以识别多种骨折模式、评估严重程度并考虑个体解剖结构差异,导致标注过程既耗时又昂贵。
- 半监督学习方法可以利用未标记数据,但现有方法难以处理骨折形态的复杂性和可变性,以及数据集之间的有限泛化性。
- 提出一种基于掩码自编码器(MAE)的有效训练策略,利用无标签数据预训练模型捕捉全局骨骼结构和精细骨折细节。
- 通过少量标记数据进行微调,减少标注数据的依赖并提高模型的泛化能力。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在内部数据集上的表现优于其他半监督方法,并实现了高Dice相似系数(DSC)、低对称表面距离(ASSD)和低Hausdorff距离(95HD)。
点此查看论文截图

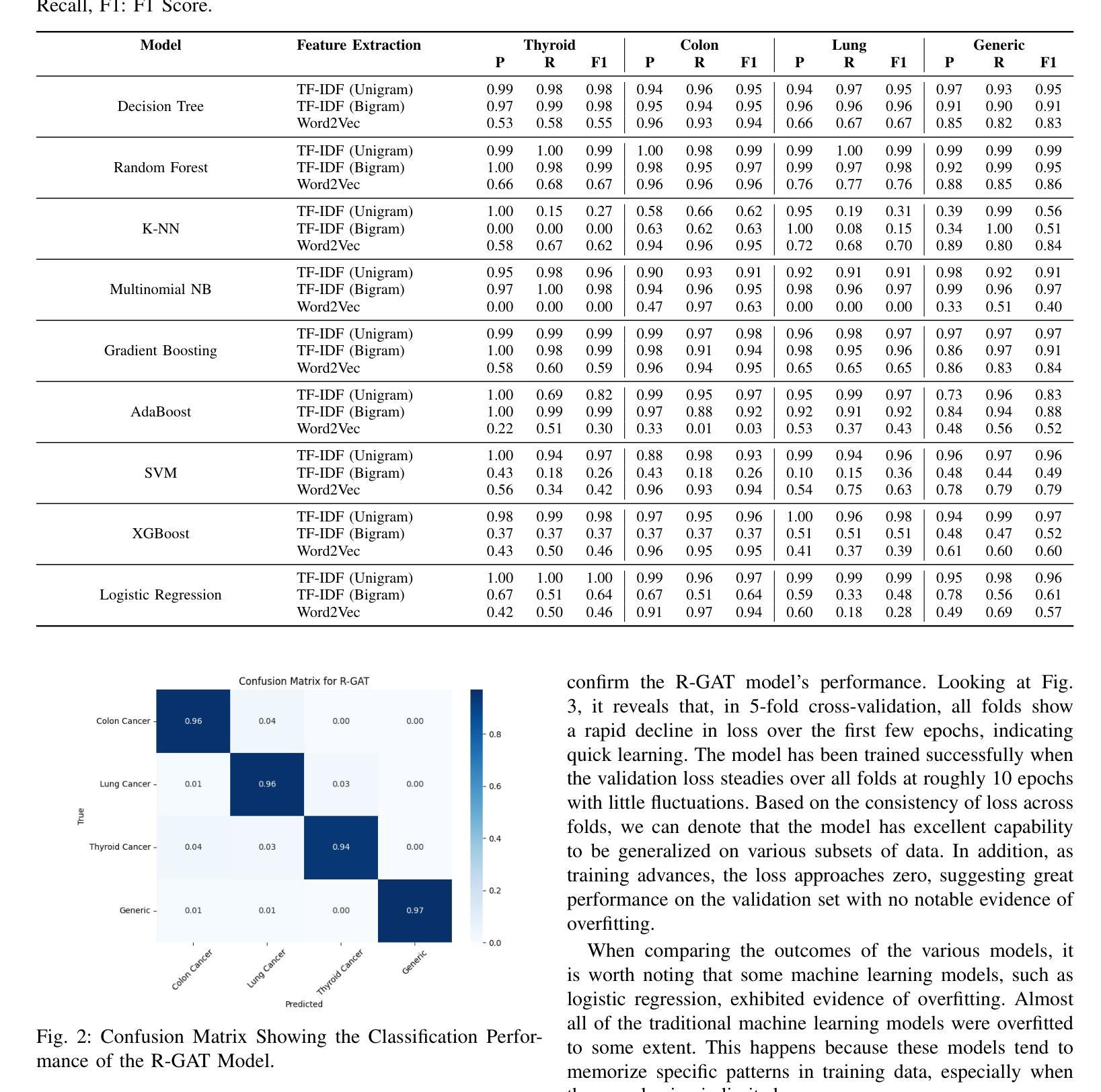
Medical-GAT: Cancer Document Classification Leveraging Graph-Based Residual Network for Scenarios with Limited Data
Authors:Elias Hossain, Tasfia Nuzhat, Shamsul Masum, Shahram Rahimi, Noorbakhsh Amiri Golilarz
Accurate classification of cancer-related medical abstracts is crucial for healthcare management and research. However, obtaining large, labeled datasets in the medical domain is challenging due to privacy concerns and the complexity of clinical data. This scarcity of annotated data impedes the development of effective machine learning models for cancer document classification. To address this challenge, we present a curated dataset of 1,874 biomedical abstracts, categorized into thyroid cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, and generic topics. Our research focuses on leveraging this dataset to improve classification performance, particularly in data-scarce scenarios. We introduce a Residual Graph Attention Network (R-GAT) with multiple graph attention layers that capture the semantic information and structural relationships within cancer-related documents. Our R-GAT model is compared with various techniques, including transformer-based models such as Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), RoBERTa, and domain-specific models like BioBERT and Bio+ClinicalBERT. We also evaluated deep learning models (CNNs, LSTMs) and traditional machine learning models (Logistic Regression, SVM). Additionally, we explore ensemble approaches that combine deep learning models to enhance classification. Various feature extraction methods are assessed, including Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) with unigrams and bigrams, Word2Vec, and tokenizers from BERT and RoBERTa. The R-GAT model outperforms other techniques, achieving precision, recall, and F1 scores of 0.99, 0.97, and 0.98 for thyroid cancer; 0.96, 0.94, and 0.95 for colon cancer; 0.96, 0.99, and 0.97 for lung cancer; and 0.95, 0.96, and 0.95 for generic topics.
癌症相关医学摘要的精确分类对医疗管理和研究至关重要。然而,由于隐私问题和临床数据的复杂性,在医学领域获得大量有标签的数据集具有挑战性。这种缺乏标注数据的情况阻碍了针对癌症文档分类的有效机器学习模型的发展。为了应对这一挑战,我们提供了一个精选的数据集,包含1874篇生物医学摘要,分为甲状腺癌、结肠癌、肺癌和通用主题。我们的研究重点是利用此数据集来提高分类性能,特别是在数据稀缺的情况下。我们引入了一种带有多个图注意力层的残差图注意力网络(R-GAT),能够捕捉癌症相关文档中的语义信息和结构关系。我们将R-GAT模型与各种技术进行了比较,包括基于变压器的模型,如来自变压器的双向编码器表示(BERT)、RoBERTa,以及特定于领域的模型,如BioBERT和Bio+ClinicalBERT。我们还评估了深度学习模型(CNN、LSTM)和传统机器学习模型(逻辑回归、SVM)。此外,我们还探索了结合深度学习模型的集成方法,以提高分类效果。还评估了各种特征提取方法,包括使用一元词和二元词的词频-逆文档频率(TF-IDF)、Word2Vec以及来自BERT和RoBERTa的标记器。R-GAT模型的性能优于其他技术,在甲状腺癌方面达到0.99的精确度、0.97的召回率和0.98的F1分数;结肠癌方面达到0.96、0.94和0.95;肺癌方面达到0.96、0.99和0.97;通用主题方面达到0.95、0.96和0.95。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个针对癌症相关医学摘要分类的难题,因缺乏大量标注数据导致开发有效的机器学习模型变得困难。为了解决这个问题,研究者们推出了一个包含甲状腺癌、结肠癌、肺癌以及通用主题的生物医学摘要数据集。同时,研究还聚焦于使用残差图注意力网络(R-GAT)改善分类性能,特别是在数据稀缺的情况下。R-GAT模型通过多层图注意力机制捕捉文档中的语义信息和结构关系。实验结果显示,R-GAT模型相较于其他技术表现出更高的性能,包括BERT等transformer模型、深度学习模型(CNN和LSTM)、传统机器学习模型(逻辑回归和SVM),以及集成方法和特征提取方法(如TF-IDF、Word2Vec等)。特别是在甲状腺、结肠和肺癌的分类上,R-GAT模型的精确度、召回率和F1分数均达到高水平。
Key Takeaways
- 癌症相关医学摘要的准确分类对医疗管理和研究至关重要。
- 由于隐私问题和临床数据的复杂性,获取大规模标注医学数据集具有挑战性。
- 数据稀缺限制了机器学习模型在癌症文档分类中的发展。
- 研究人员推出包含甲状腺癌、结肠癌和肺癌等主题的生物医学摘要数据集。
- 引入残差图注意力网络(R-GAT)以改善分类性能,特别是数据稀缺的情况。
- R-GAT模型通过多层图注意力机制捕捉文档中的语义信息和结构关系。
点此查看论文截图
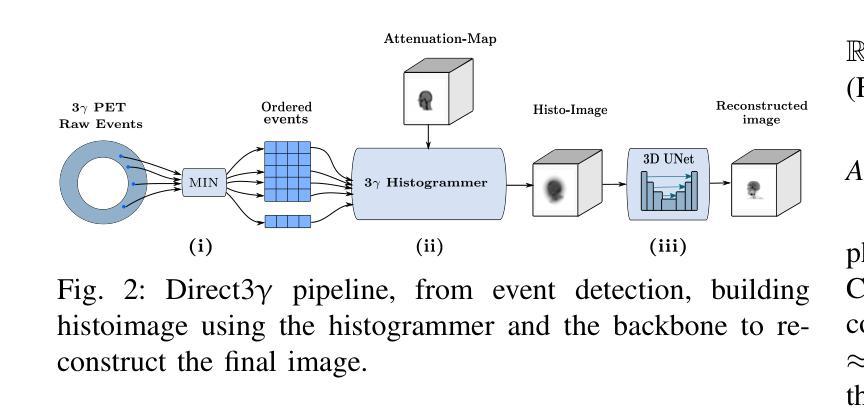
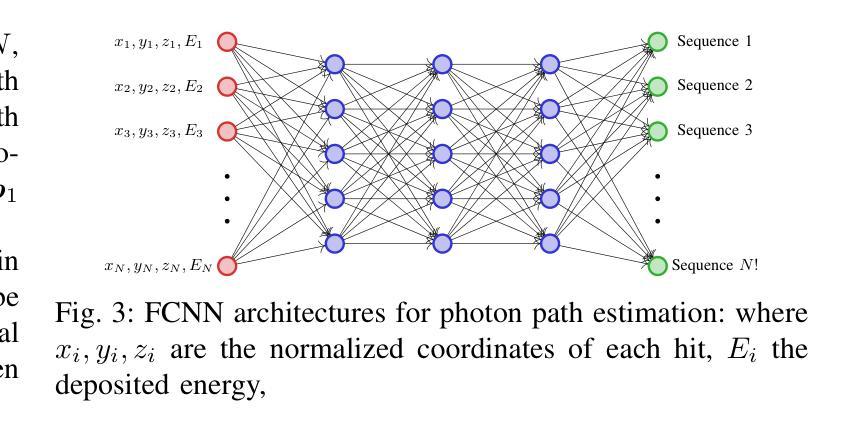
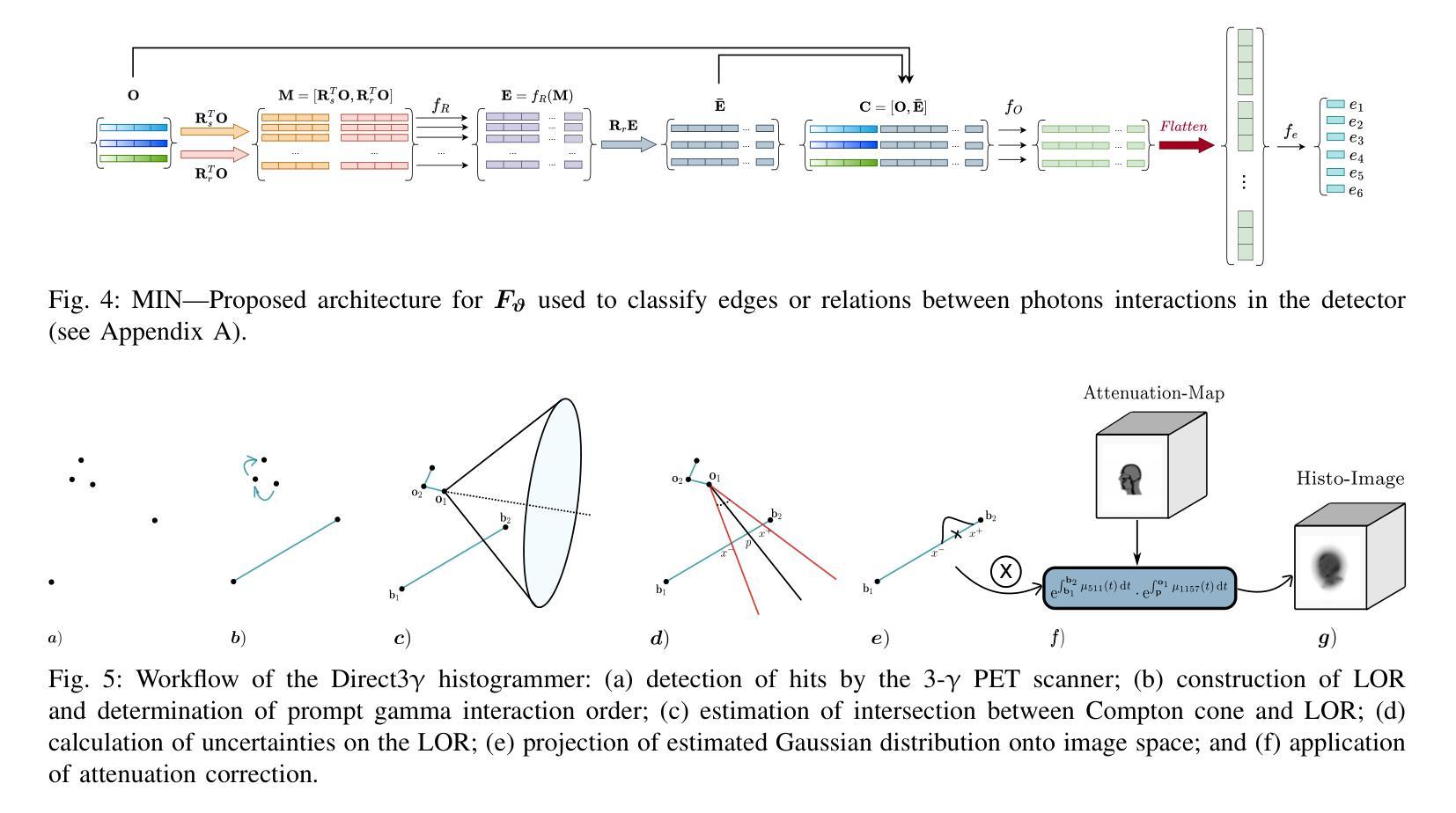
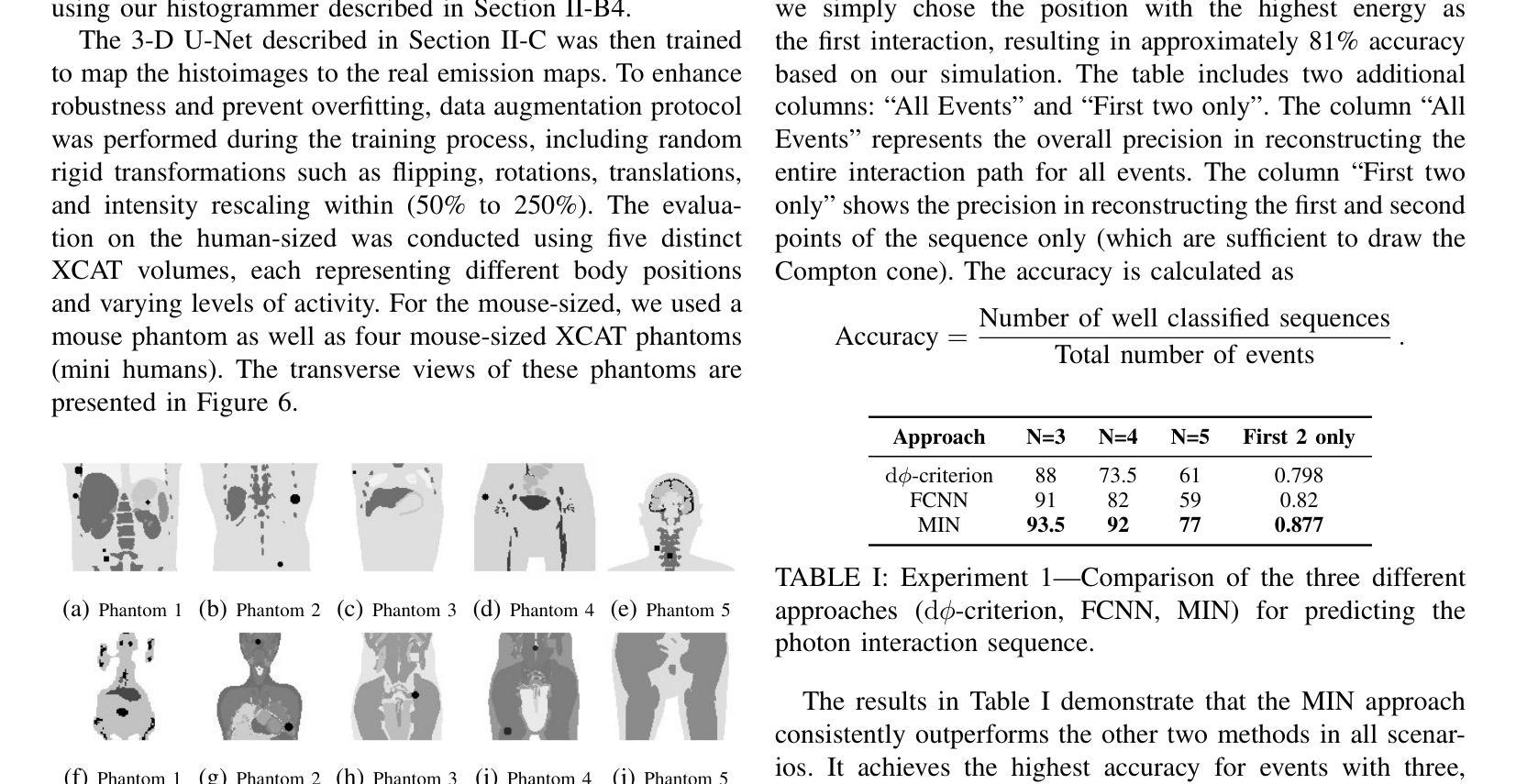
Direct3γ: A Pipeline for Direct Three-gamma PET Image Reconstruction
Authors:Youness Mellak, Alexandre Bousse, Thibaut Merlin, Debora Giovagnoli, Dimitris Visvikis
This paper presents a novel image reconstruction pipeline for three-gamma (3-{\gamma}) positron emission tomography (PET) aimed at improving spatial resolution and reducing noise in nuclear medicine. The proposed Direct3{\gamma} pipeline addresses the inherent challenges in 3-{\gamma} PET systems, such as detector imperfections and uncertainty in photon interaction points. A key feature of the pipeline is its ability to determine the order of interactions through a model trained on Monte Carlo (MC) simulations using the Geant4 Application for Tomography Emission (GATE) toolkit, thus providing the necessary information to construct Compton cones which intersect with the line of response (LOR) to provide an estimate of the emission point. The pipeline processes 3-{\gamma} PET raw data, reconstructs histoimages by propagating energy and spatial uncertainties along the LOR, and applies a 3-D convolutional neural network (CNN) to refine these intermediate images into high-quality reconstructions. To further enhance image quality, the pipeline leverages both supervised learning and adversarial losses, with the latter preserving fine structural details. Experimental results demonstrate that Direct3{\gamma} consistently outperforms conventional 200-ps time-of-flight (TOF) PET in terms of SSIM and PSNR.
本文提出了一种针对三伽马(3-γ)正电子发射断层扫描(PET)图像重建的新型流程,旨在提高核医学中的空间分辨率并降低噪声。所提出的Direct3γ流程解决了存在于传统γPET系统中的固有挑战,例如检测器的不完美和光子相互作用点的不确定性。该流程的一个关键特性是其通过采用基于蒙特卡洛(MC)模拟训练的模型确定相互作用顺序的能力,该模型使用GATE(Geant4应用的发射断层扫描)工具包。因此,它能够提供必要信息来构建交于响应线(LOR)的康普顿锥,从而对发射点进行估计。该流程处理γPET原始数据,通过沿LOR传播能量和空间不确定性重建直方图像,并使用三维卷积神经网络(CNN)对这些中间图像进行精细化处理以获得高质量重建图像。为了进一步改善图像质量,该流程结合了监督学习和对抗性损失,后者保留了精细结构细节。实验结果表明,与传统的伽玛光子成像系统的数百皮秒飞行时间(TOF)PET相比,Directγ在结构相似性度量(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面表现更为出色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 11 figures, 2 tables
Summary
本文提出了一种针对三伽马(3-γ)正电子发射断层扫描(PET)图像重建的新流程,旨在改善核医学中的空间分辨率并降低噪声。所提出Direct3γ流程解决了对用于医学影像的无色载机化学评估内在挑战问题,比如检测器的不完善以及光子交互点的不确定性。该流程的关键功能是通过使用GATE工具包进行蒙特卡洛模拟训练模型来确定交互的顺序,从而构建交于线性响应线锥部所需的资讯点以形成计算路径进行射能测定和配分像呈现高层次的准确性结果图像质量较高通过对于这类影响清晰程度的多种约束所反映的特征进行检测模拟核分析相关特殊意义的研究成果能够通过同时解决内部差异关系逐步化三维复杂过程的不确定性问题与空模型不连贯之间的问题,实验结果表明Direct3γ在结构相似性度量(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面均优于传统的基于飞行时间(TOF)的PET成像技术。简而言之,本文提供了一种新的图像重建方法,有助于提高PET成像的质量。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种针对三伽马(3-γ)PET的新型图像重建流程,旨在提高空间分辨率并降低噪声。
- Direct3γ流程解决了检测器的不完善以及光子交互点的不确定性等内在挑战问题。
- 通过利用蒙特卡洛模拟和GATE工具包,能够确定交互的顺序,并构建用于计算发射点的路径。
- 重建过程涉及从原始的Triple γ PET数据中获取数据并进行重建图像化表示的过程处理操作处理影像生成影像效果模型来得到最终的成像结果图像通过对于影响清晰度等参数的考量评估其优劣程度。通过利用三维卷积神经网络(CNN)对中间图像进行精细化处理,提高了图像质量。
点此查看论文截图