⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-11 更新
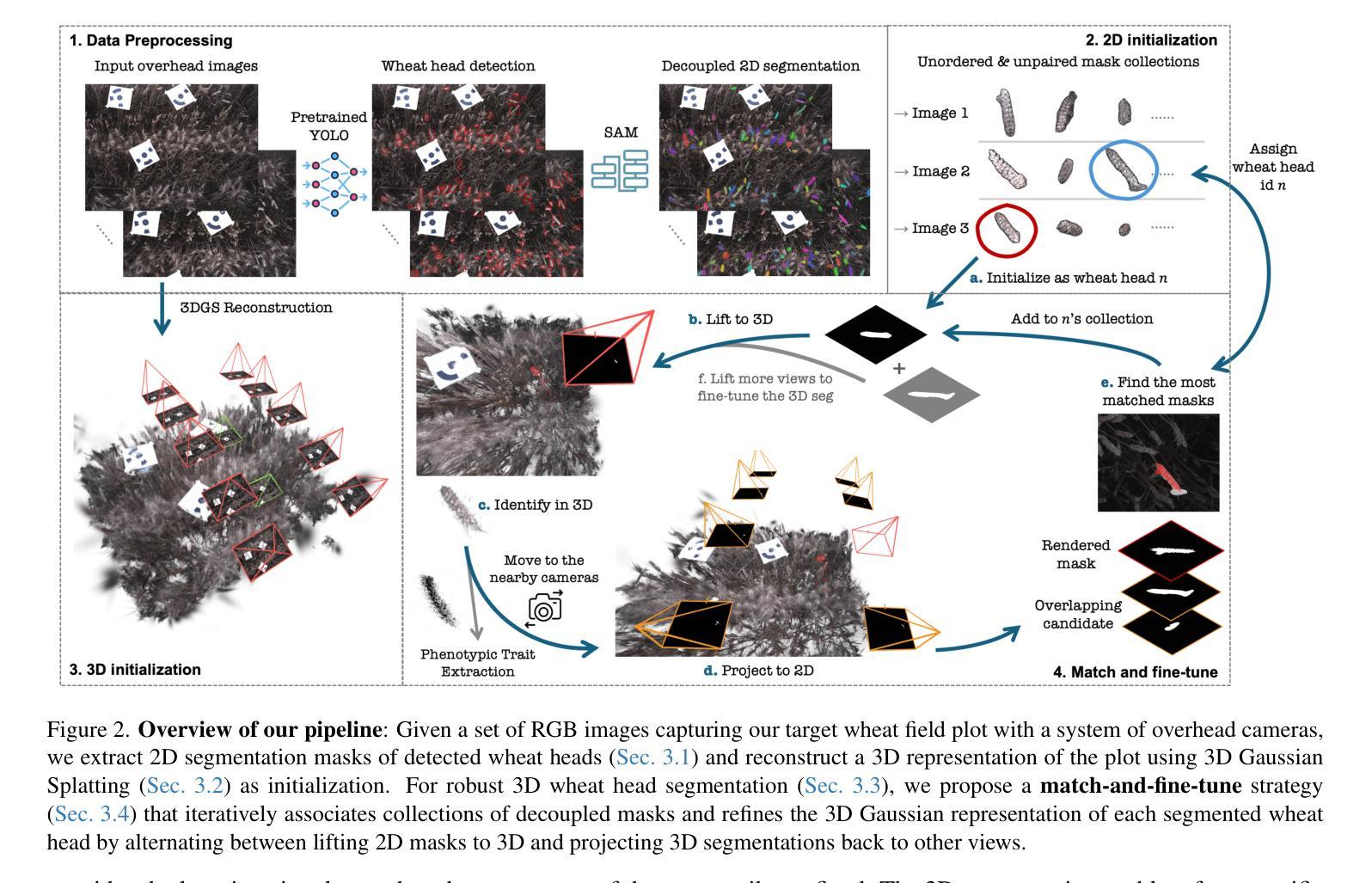
Wheat3DGS: In-field 3D Reconstruction, Instance Segmentation and Phenotyping of Wheat Heads with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Daiwei Zhang, Joaquin Gajardo, Tomislav Medic, Isinsu Katircioglu, Mike Boss, Norbert Kirchgessner, Achim Walter, Lukas Roth
Automated extraction of plant morphological traits is crucial for supporting crop breeding and agricultural management through high-throughput field phenotyping (HTFP). Solutions based on multi-view RGB images are attractive due to their scalability and affordability, enabling volumetric measurements that 2D approaches cannot directly capture. While advanced methods like Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) have shown promise, their application has been limited to counting or extracting traits from only a few plants or organs. Furthermore, accurately measuring complex structures like individual wheat heads-essential for studying crop yields-remains particularly challenging due to occlusions and the dense arrangement of crop canopies in field conditions. The recent development of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) offers a promising alternative for HTFP due to its high-quality reconstructions and explicit point-based representation. In this paper, we present Wheat3DGS, a novel approach that leverages 3DGS and the Segment Anything Model (SAM) for precise 3D instance segmentation and morphological measurement of hundreds of wheat heads automatically, representing the first application of 3DGS to HTFP. We validate the accuracy of wheat head extraction against high-resolution laser scan data, obtaining per-instance mean absolute percentage errors of 15.1%, 18.3%, and 40.2% for length, width, and volume. We provide additional comparisons to NeRF-based approaches and traditional Muti-View Stereo (MVS), demonstrating superior results. Our approach enables rapid, non-destructive measurements of key yield-related traits at scale, with significant implications for accelerating crop breeding and improving our understanding of wheat development.
自动化提取植物形态特征是支持通过高通量表型技术(HTFP)进行作物育种和农业管理的重要方法。基于多视角RGB图像解决方案因其可扩展性和经济性而具有吸引力,能够实现2D方法无法直接获取的容积测量。虽然先进的神经网络辐射场(NeRFs)等方法显示出了一定的潜力,但其应用仅限于对少数植物或器官进行计数或特征提取。此外,准确测量如小麦穗头等复杂结构对于研究作物产量至关重要,但由于田间条件下的遮挡和作物冠层密集排列,这仍然是一个巨大的挑战。最近开发的3D高斯平铺(3DGS)技术因其高质量重建和显式点基表示而成为了HTFP的一种有前途的替代方案。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为Wheat3DGS的新方法,该方法利用3DGS和分段任何模型(SAM)进行精确的3D实例分割和形态测量,可自动对数百个小麦穗头进行识别测量,这是3DGS在HTFP中的首次应用。我们通过与高分辨率激光扫描数据的对比验证了小麦穗头提取的准确性,针对长度、宽度和体积的实例平均绝对百分比误差分别为15.1%、18.3%和40.2%。我们还与NeRF方法和传统的多角度立体视觉技术进行了比较(MVS),展示了更优越的结果。我们的方法能够在大规模进行关键产量相关特征的快速无损测量,对于加速作物育种和加深我们对小麦发育的理解具有重要意义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Copyright 2025 IEEE. This is the author’s version of the work. It is posted here for your personal use. Not for redistribution. The definitive version is published in the 2025 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW)
Summary
本研究提出了Wheat3DGS方法,结合3DGS和SAM模型,实现小麦头部自动精确的3D实例分割和形态测量。通过对比验证,该方法在高通量表型分析中具有较高的准确性和优越性,为大规模快速测量关键产量性状提供了可能。
Key Takeaways
- 自动提取植物形态特征是支持作物育种和农业管理的重要技术。
- 基于多视角RGB图像的解决方案具有可扩展性和经济性,能够支持三维测量。
- 尽管神经网络辐射场(NeRFs)等先进方法显示出潜力,但其在作物表型分析中的应用仍然有限。
- 小麦头部等复杂结构的精确测量对于研究作物产量至关重要,但由于遮挡和田间作物冠层密集排列的影响,这是一个挑战。
- 3D高斯拼接(3DGS)提供了一种有前途的替代方案,用于高通量表型分析,其特点是高质量重建和基于点的显式表示。
- Wheat3DGS方法结合3DGS和SAM模型进行精确的3D实例分割和形态测量,实现了对数百个小麦头部的自动测量。
点此查看论文截图


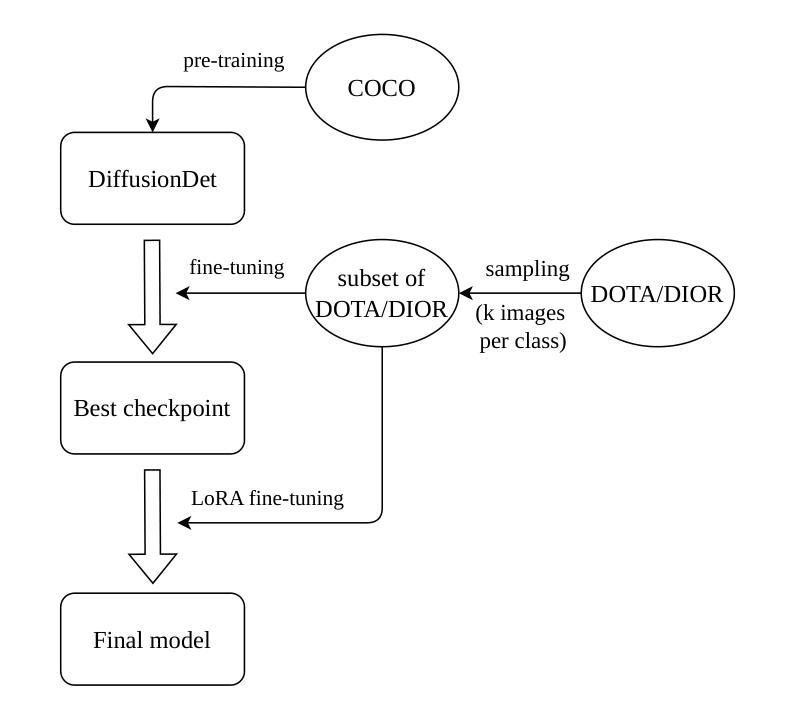
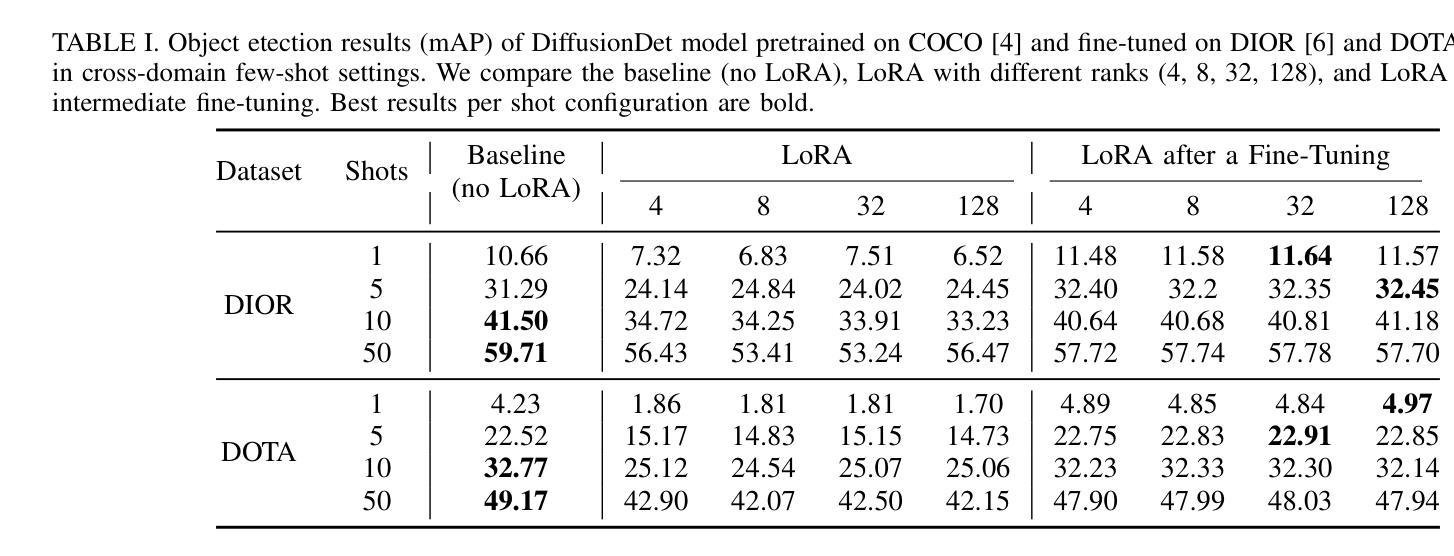
Analyzing the Impact of Low-Rank Adaptation for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection in Aerial Images
Authors:Hicham Talaoubrid, Anissa Mokraoui, Ismail Ben Ayed, Axel Prouvost, Sonimith Hang, Monit Korn, Rémi Harvey
This paper investigates the application of Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to small models for cross-domain few-shot object detection in aerial images. Originally designed for large-scale models, LoRA helps mitigate overfitting, making it a promising approach for resource-constrained settings. We integrate LoRA into DiffusionDet, and evaluate its performance on the DOTA and DIOR datasets. Our results show that LoRA applied after an initial fine-tuning slightly improves performance in low-shot settings (e.g., 1-shot and 5-shot), while full fine-tuning remains more effective in higher-shot configurations. These findings highlight LoRA’s potential for efficient adaptation in aerial object detection, encouraging further research into parameter-efficient fine-tuning strategies for few-shot learning. Our code is available here: https://github.com/HichTala/LoRA-DiffusionDet.
本文探讨了将低秩适应(LoRA)应用于小型模型,以进行跨域小样本空中图像目标检测的应用。LoRA最初是为大规模模型设计的,有助于缓解过拟合问题,使其在资源受限的环境中成为一种有前途的方法。我们将LoRA集成到DiffusionDet中,并在DOTA和DIOR数据集上评估其性能。结果表明,在初始微调后应用LoRA在低样本设置(例如,1个样本和5个样本)中略微提高了性能,而完全微调在更高样本配置中仍然更有效。这些发现突出了LoRA在航空目标检测中的高效适应性潜力,鼓励进一步研究面向小样本学习的参数高效微调策略。我们的代码位于:https://github.com/HichTala/LoRA-DiffusionDet。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了将低秩适应(LoRA)应用于小型模型进行跨域小样本空中图像目标检测的问题。文章指出,虽然LoRA最初是为大规模模型设计的,但它在缓解过拟合方面具有优势,对于资源受限的环境来说是一种很有前途的方法。文章将LoRA集成到DiffusionDet中,并在DOTA和DIOR数据集上进行了评估。结果表明,在初始微调后应用LoRA可以略微提高低样本环境下的性能(例如,一镜头和五镜头),而完全微调在更高的射击配置中仍然更有效。这为LoRA在航空目标检测中的高效适应提供了潜力,并鼓励进一步研究小样本学习的参数精细调整策略。代码已在GitHub上发布:https://github.com/HichTala/LoRA-DiffusionDet。
Key Takeaways
- 低秩适应(LoRA)方法被引入用于小型模型的跨域小样本空中图像目标检测。
- LoRA能够缓解模型的过拟合问题,尤其适用于资源受限的环境。
- LoRA集成到DiffusionDet模型中,并在DOTA和DIOR数据集上进行了性能评估。
- 在低样本环境下,应用LoRA后微调可略微提高性能。
- 完全微调在更高样本配置下仍然是最有效的方法。
- LoRA具有在航空目标检测中高效适应的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

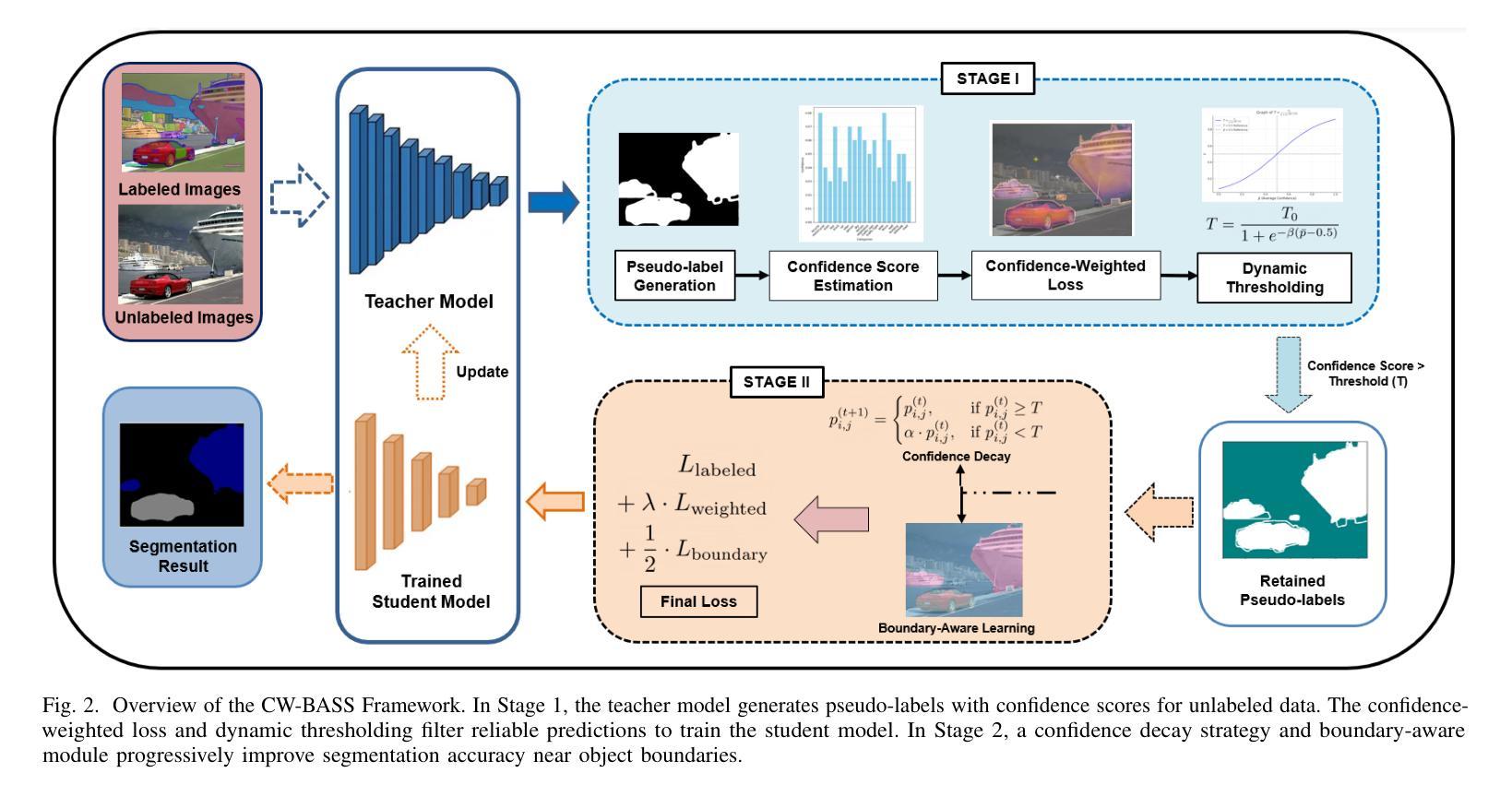
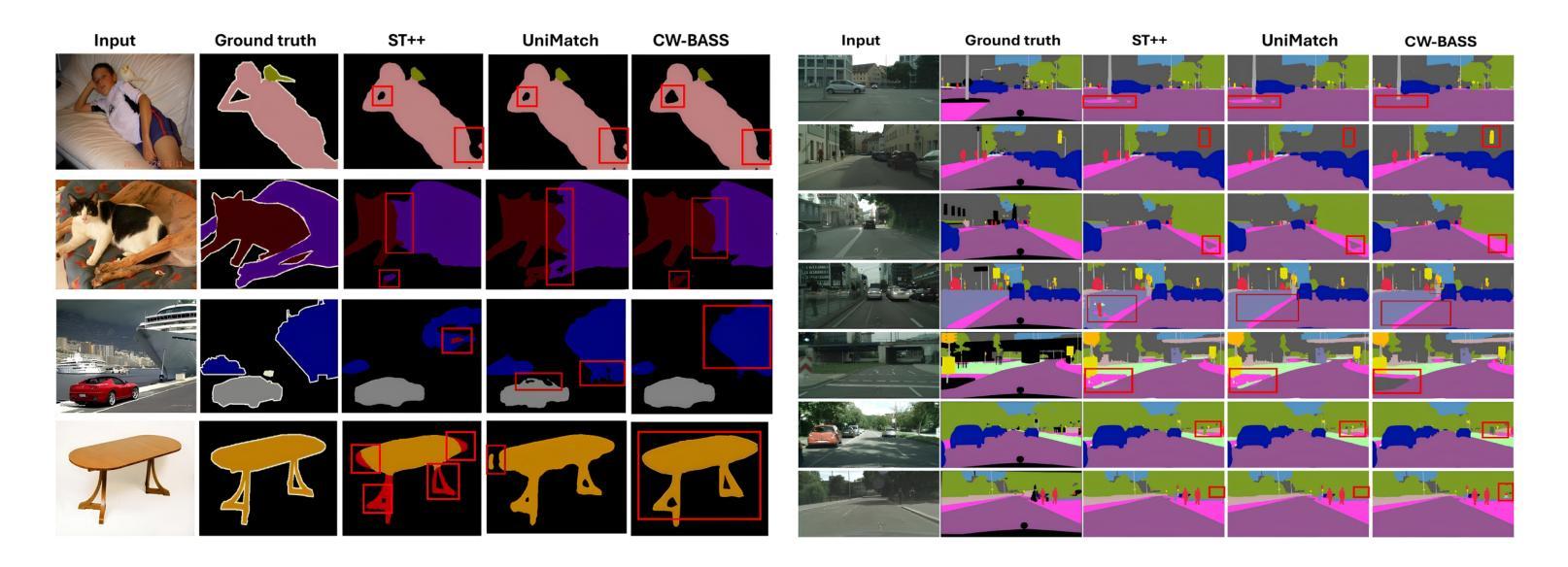
CW-BASS: Confidence-Weighted Boundary-Aware Learning for Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Ebenezer Tarubinga, Jenifer Kalafatovich, Seong-Whan Lee
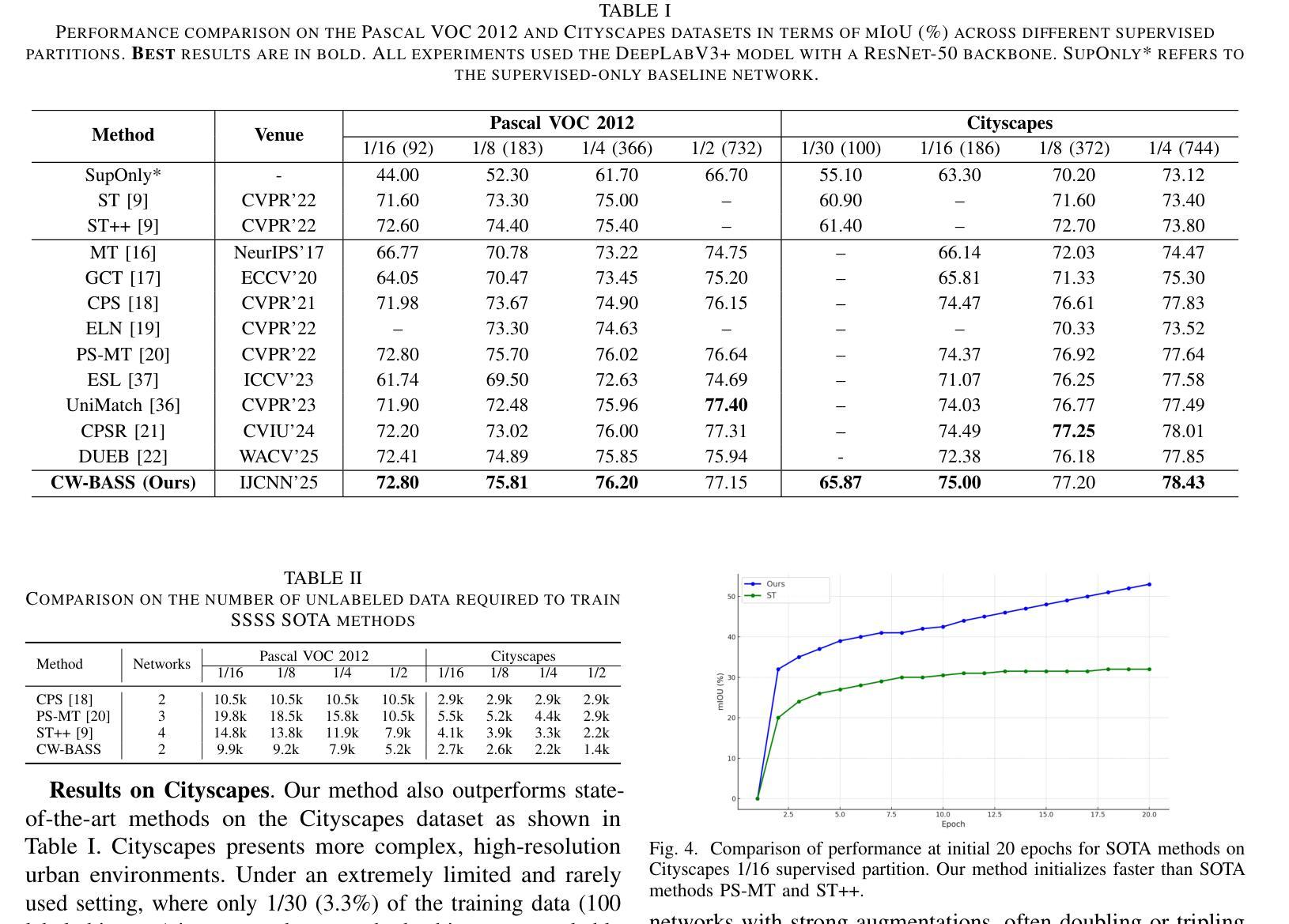
Semi-supervised semantic segmentation (SSSS) aims to improve segmentation performance by utilizing large amounts of unlabeled data with limited labeled samples. Existing methods often suffer from coupling, where over-reliance on initial labeled data leads to suboptimal learning; confirmation bias, where incorrect predictions reinforce themselves repeatedly; and boundary blur caused by limited boundary-awareness and ambiguous edge cues. To address these issues, we propose CW-BASS, a novel framework for SSSS. In order to mitigate the impact of incorrect predictions, we assign confidence weights to pseudo-labels. Additionally, we leverage boundary-delineation techniques, which, despite being extensively explored in weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS), remain underutilized in SSSS. Specifically, our method: (1) reduces coupling via a confidence-weighted loss that adjusts pseudo-label influence based on their predicted confidence scores, (2) mitigates confirmation bias with a dynamic thresholding mechanism that learns to filter out pseudo-labels based on model performance, (3) tackles boundary blur using a boundary-aware module to refine segmentation near object edges, and (4) reduces label noise through a confidence decay strategy that progressively refines pseudo-labels during training. Extensive experiments on Pascal VOC 2012 and Cityscapes demonstrate that CW-BASS achieves state-of-the-art performance. Notably, CW-BASS achieves a 65.9% mIoU on Cityscapes under a challenging and underexplored 1/30 (3.3%) split (100 images), highlighting its effectiveness in limited-label settings. Our code is available at https://github.com/psychofict/CW-BASS.
半监督语义分割(SSSS)旨在利用大量无标签数据和有限的有标签样本,提高分割性能。现有方法常常受到耦合、确认偏见和边界模糊等问题的影响。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了CW-BASS,这是一种新型的半监督语义分割框架。为了减轻错误预测的影响,我们对伪标签分配了置信权重。此外,我们还利用边界描绘技术,尽管这些技术在弱监督语义分割(WSSS)中得到了广泛的研究,但在SSSS中仍然没有得到充分利用。具体来说,我们的方法:(1)通过置信加权损失减少耦合,根据预测的置信分数调整伪标签的影响;(2)通过动态阈值机制减轻确认偏见,该机制能够基于模型性能过滤出伪标签;(3)使用边界感知模块解决边界模糊问题,以细化对象边缘附近的分割;(4)通过置信衰减策略减少标签噪声,该策略在训练过程中逐步优化伪标签。在Pascal VOC 2012和Cityscapes上的大量实验表明,CW-BASS达到了最新技术水平。尤其值得一提的是,在具有挑战性和被忽视的Cityscapes的1/30(3.3%)分割(100张图像)下,CW-BASS达到了65.9%的mIoU,突显其在有限标签设置中的有效性。我们的代码位于:https://github.com/psychofict/CW-BASS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IJCNN 2025
摘要
半监督语义分割(SSSS)旨在利用有限的标注样本和大量的无标签数据来提高分割性能。现有方法存在耦合、确认偏差和边界模糊等问题。为解决这些问题,我们提出了CW-BASS这一新型SSSS框架。通过为伪标签分配置信权重,减轻错误预测的影响,并利用边界划分技术来改进分割效果。具体方法包括:通过置信加权损失减少耦合,动态阈值机制缓解确认偏差,边界感知模块解决边界模糊问题,以及通过置信衰减策略减少标签噪声。在Pascal VOC 2012和Cityscapes上的实验表明,CW-BASS达到了最新技术水平,特别是在挑战性且鲜有研究涉及的Cityscapes 1/30(3.3%)分割上取得了65.9%的mIoU。代码已公开在链接。
关键发现
- SSSS旨在结合标注和无标签数据提高语义分割性能,但面临耦合、确认偏差和边界模糊等挑战。
- CW-BASS框架通过置信加权、动态阈值、边界感知模块和置信衰减策略应对这些挑战。
- CW-BASS在Pascal VOC 2012和Cityscapes数据集上实现先进性能。
- 在Cityscapes的1/30(3.3%)分割挑战中,CW-BASS取得了特别显著的65.9% mIoU结果。
- CW-BASS方法能有效在有限标注样本的情况下实现良好性能。
- 代码已公开,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图