⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-11 更新
nnLandmark: A Self-Configuring Method for 3D Medical Landmark Detection
Authors:Alexandra Ertl, Shuhan Xiao, Stefan Denner, Robin Peretzke, David Zimmerer, Peter Neher, Fabian Isensee, Klaus Maier-Hein
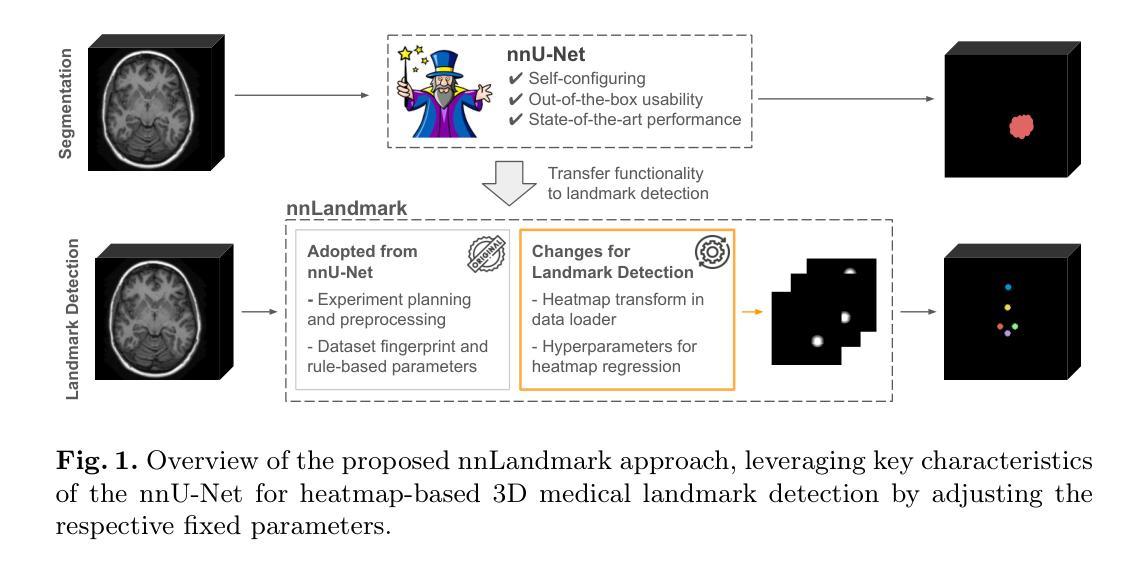
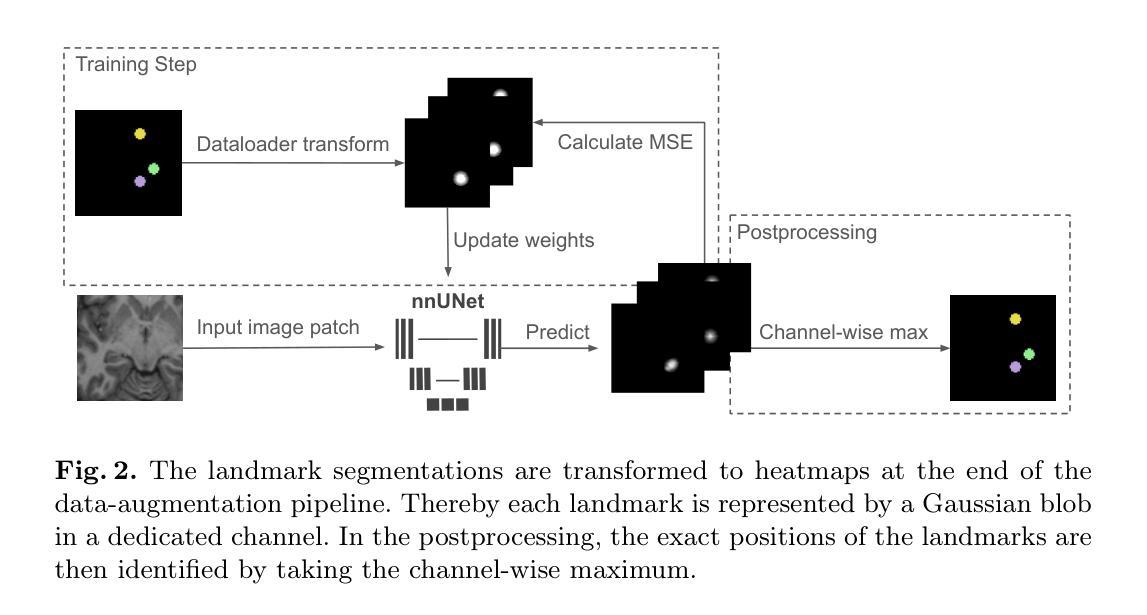
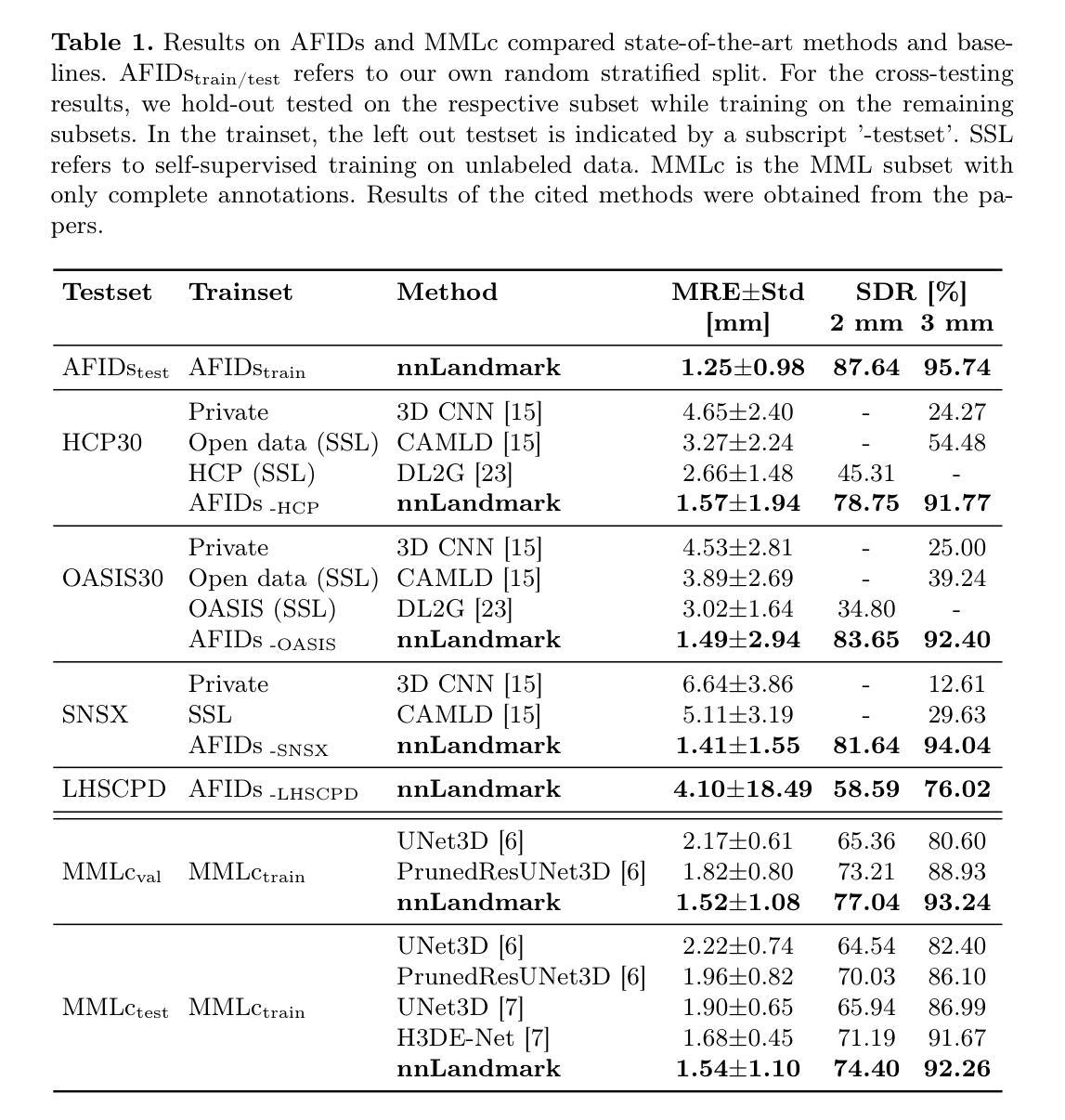
Landmark detection plays a crucial role in medical imaging tasks that rely on precise spatial localization, including specific applications in diagnosis, treatment planning, image registration, and surgical navigation. However, manual annotation is labor-intensive and requires expert knowledge. While deep learning shows promise in automating this task, progress is hindered by limited public datasets, inconsistent benchmarks, and non-standardized baselines, restricting reproducibility, fair comparisons, and model generalizability.This work introduces nnLandmark, a self-configuring deep learning framework for 3D medical landmark detection, adapting nnU-Net to perform heatmap-based regression. By leveraging nnU-Net’s automated configuration, nnLandmark eliminates the need for manual parameter tuning, offering out-of-the-box usability. It achieves state-of-the-art accuracy across two public datasets, with a mean radial error (MRE) of 1.5 mm on the Mandibular Molar Landmark (MML) dental CT dataset and 1.2 mm for anatomical fiducials on a brain MRI dataset (AFIDs), where nnLandmark aligns with the inter-rater variability of 1.5 mm. With its strong generalization, reproducibility, and ease of deployment, nnLandmark establishes a reliable baseline for 3D landmark detection, supporting research in anatomical localization and clinical workflows that depend on precise landmark identification. The code will be available soon.
地标检测在依赖精确空间定位的医学成像任务中起着至关重要的作用,包括诊断、治疗计划、图像注册和手术导航等特定应用。然而,手动注释需要大量劳动力并且需要专业知识。深度学习在自动化此任务方面显示出希望,但公共数据集的有限性、基准测试的不一致性和非标准化的基准线限制了可重复性、公平比较和模型的通用性,阻碍了进展。本文介绍了nnLandmark,这是一个用于3D医疗地标检测的自主学习框架,它采用nnU-Net进行基于热图的回归。通过利用nnU-Net的自动配置,nnLandmark消除了手动参数调整的需求,提供了开箱即用的可用性。它在两个公共数据集上达到了最先进的准确性,在下颌磨牙地标(MML)牙科CT数据集上的平均径向误差(MRE)为1.5毫米,在脑部MRI数据集(AFIDs)上的解剖标记为1.2毫米,nnLandmark与1.5毫米的医师间变异度一致。凭借其强大的通用性、可重复性和易于部署的特点,nnLandmark为3D地标检测建立了可靠的基准线,支持依赖精确地标识别的解剖定位和临床工作流程研究。代码将很快可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个基于深度学习的自适应配置框架nnLandmark,用于医学图像中的三维地标检测。该框架利用nnU-Net进行热图回归,无需手动参数调整,具有良好的通用性和易用性。在多个公开数据集上的实验结果表明,nnLandmark在地标检测任务中具有出色的性能,特别是在下颌磨牙地标(MML)和脑部MRI数据集(AFIDs)上的平均径向误差(MRE)达到了很高的精度。这为依赖于精确地标识别的解剖定位和临床工作流程研究提供了可靠的基准。
Key Takeaways
- nnLandmark是一个用于医学图像中三维地标检测的深度学习框架。
- 该框架基于nnU-Net进行热图回归,实现自我配置,无需手动参数调整。
- nnLandmark具有良好的通用性,易于使用,并实现了最先进的性能。
- 在下颌磨牙地标(MML)和脑部MRI数据集(AFIDs)上的实验表明,nnLandmark的平均径向误差(MRE)达到了很高的精度。
- nnLandmark与手动标注的地标识别结果一致,对齐的误差在可接受范围内。
- nnLandmark为解剖定位和依赖于精确地标识别的临床工作流程研究提供了可靠的基准。
点此查看论文截图