⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-11 更新
Wheat3DGS: In-field 3D Reconstruction, Instance Segmentation and Phenotyping of Wheat Heads with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Daiwei Zhang, Joaquin Gajardo, Tomislav Medic, Isinsu Katircioglu, Mike Boss, Norbert Kirchgessner, Achim Walter, Lukas Roth
Automated extraction of plant morphological traits is crucial for supporting crop breeding and agricultural management through high-throughput field phenotyping (HTFP). Solutions based on multi-view RGB images are attractive due to their scalability and affordability, enabling volumetric measurements that 2D approaches cannot directly capture. While advanced methods like Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) have shown promise, their application has been limited to counting or extracting traits from only a few plants or organs. Furthermore, accurately measuring complex structures like individual wheat heads-essential for studying crop yields-remains particularly challenging due to occlusions and the dense arrangement of crop canopies in field conditions. The recent development of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) offers a promising alternative for HTFP due to its high-quality reconstructions and explicit point-based representation. In this paper, we present Wheat3DGS, a novel approach that leverages 3DGS and the Segment Anything Model (SAM) for precise 3D instance segmentation and morphological measurement of hundreds of wheat heads automatically, representing the first application of 3DGS to HTFP. We validate the accuracy of wheat head extraction against high-resolution laser scan data, obtaining per-instance mean absolute percentage errors of 15.1%, 18.3%, and 40.2% for length, width, and volume. We provide additional comparisons to NeRF-based approaches and traditional Muti-View Stereo (MVS), demonstrating superior results. Our approach enables rapid, non-destructive measurements of key yield-related traits at scale, with significant implications for accelerating crop breeding and improving our understanding of wheat development.
在植物育种和农业管理中,通过高通量表型技术(HTFP)自动提取植物形态特征是至关重要的。基于多视角RGB图像的解决方案因其可扩展性和成本效益而具有吸引力,能够进行三维测量,而二维方法无法直接捕获这些信息。虽然神经辐射场(NeRFs)等先进方法已显示出潜力,但它们的应用仅限于从少数植物或器官中计数或提取特征。此外,准确测量如小麦穗等复杂结构仍然是一项特别挑战,因为它们在田间条件下存在遮挡和密集的排列,这对于研究作物产量至关重要。最近开发的3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)因其高质量重建和显式点基表示而成为HTFP的有前途的替代方案。在本文中,我们提出了Wheat3DGS,这是一种利用3DGS和Segment Anything Model(SAM)进行精确的三维实例分割和形态测量的新方法,可自动对数百个小麦穗进行形态测量。这是首次将3DGS应用于HTFP的案例。我们利用高分辨率激光扫描数据验证了小麦穗提取的准确性,长度、宽度和体积的绝对百分比误差分别为15.1%、18.3%和40.2%。我们还与基于NeRF的方法和传统的多角度视图立体声(MVS)进行了比较,证明了我们的方法具有更好的结果。我们的方法能够在大规模上进行快速、无损的关键产量相关特征的测量,对于加速作物育种和改进我们对小麦发育的理解具有重要的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Copyright 2025 IEEE. This is the author’s version of the work. It is posted here for your personal use. Not for redistribution. The definitive version is published in the 2025 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW)
摘要
基于多视角RGB图像的植物形态学特征自动化提取对于高通量表型分析(HTFP)在作物育种和农业管理中有着重要意义。最新开发的3D高斯展开(3DGS)方法以其高质量重建和显式点基表示而展现出应用前景。本文介绍了一种结合3DGS与SAM模型的新方法——小麦三时动态场景构建器(Wheat3DGS),它能实现对数百个麦穗进行精确的三维实体分割和形态测量,代表了首个将3DGS应用于高通量表型分析的应用。通过与高分辨率激光扫描数据的验证,小麦穗提取的精确度达到了长度、宽度和体积的平均绝对百分比误差分别为15.1%、18.3%和40.2%。与其他方法相比,本文提出的方法展现出卓越的性能。它为大规模快速、无损地测量关键产量性状提供了可能,对加速作物育种和改善对小麦发育的理解具有重要意义。
关键要点
- 高通量表型分析(HTFP)在作物育种和农业管理中至关重要。
- 基于多视角RGB图像的方法在植物形态学特征提取中因其可扩展性和成本效益而受到关注。
- 3D高斯展开(3DGS)作为一种新兴技术,以其高质量重建和显式点基表示展现出其在HTFP中的潜力。
- 文中介绍的小麦三时动态场景构建器(Wheat3DGS)结合了3DGS与SAM模型,实现了对数百个麦穗的精确三维实体分割和形态测量。
- Wheat3DGS方法的准确性通过对比实验得到了验证,展现出较低的误差率。
- 与其他方法(如NeRF和MVS)相比,Wheat3DGS表现出卓越的性能。
- 该方法对于大规模快速、无损地测量关键产量性状具有显著意义,可加速作物育种工作并增进对小麦发育的理解。
点此查看论文截图

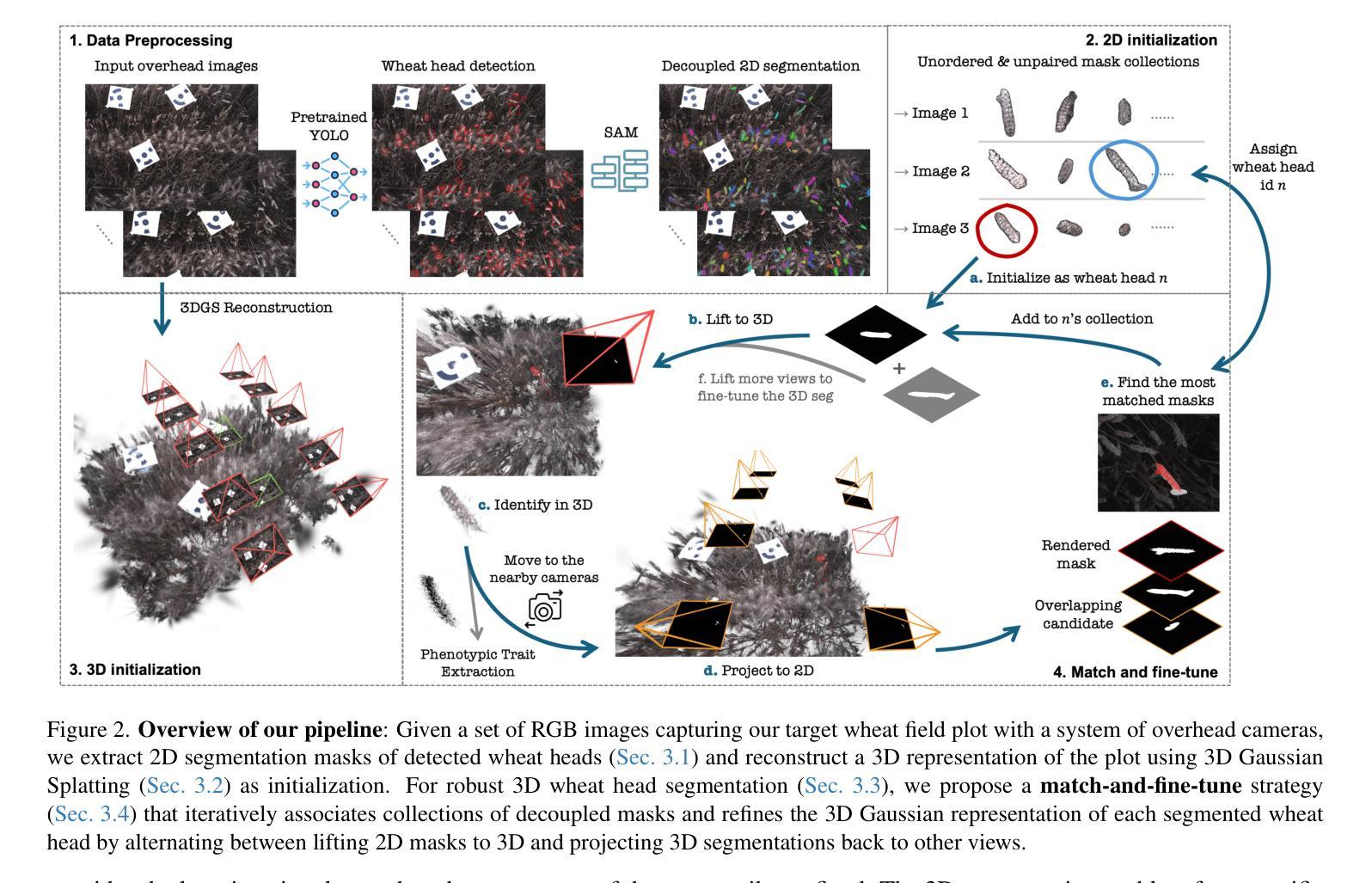

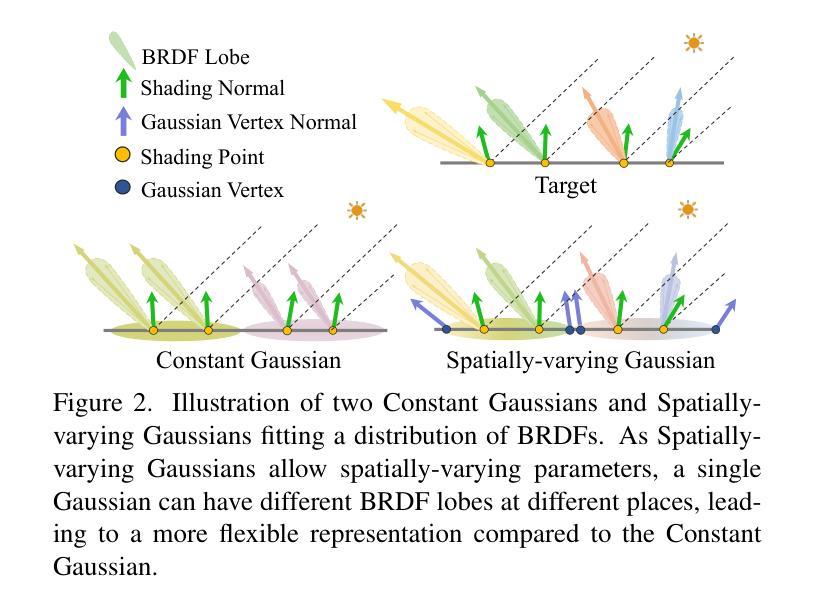
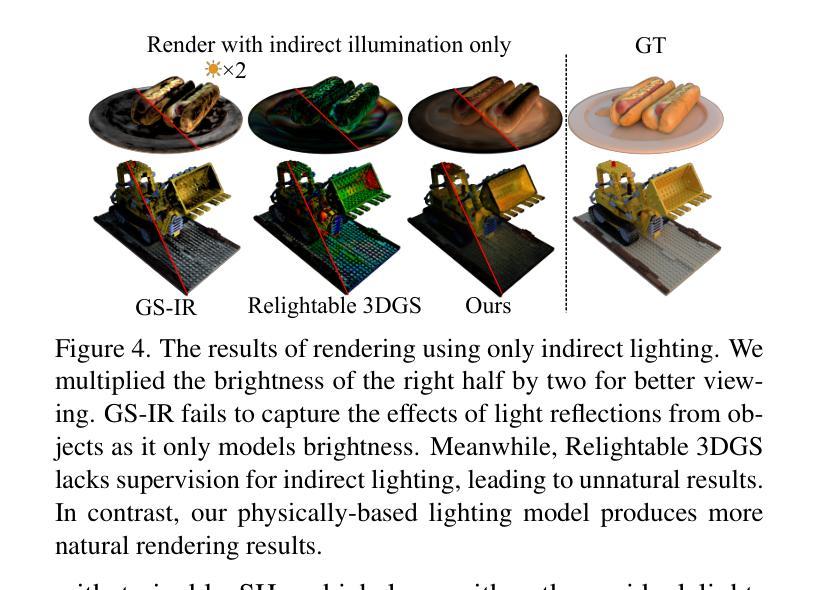
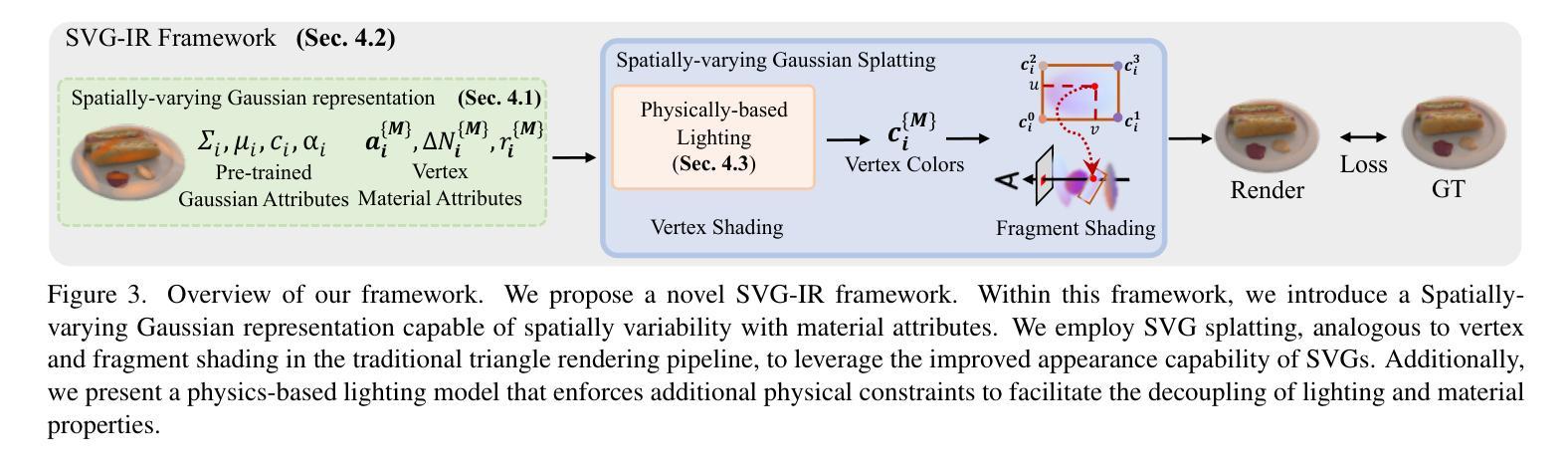
SVG-IR: Spatially-Varying Gaussian Splatting for Inverse Rendering
Authors:Hanxiao Sun, YuPeng Gao, Jin Xie, Jian Yang, Beibei Wang
Reconstructing 3D assets from images, known as inverse rendering (IR), remains a challenging task due to its ill-posed nature. 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated impressive capabilities for novel view synthesis (NVS) tasks. Methods apply it to relighting by separating radiance into BRDF parameters and lighting, yet produce inferior relighting quality with artifacts and unnatural indirect illumination due to the limited capability of each Gaussian, which has constant material parameters and normal, alongside the absence of physical constraints for indirect lighting. In this paper, we present a novel framework called Spatially-vayring Gaussian Inverse Rendering (SVG-IR), aimed at enhancing both NVS and relighting quality. To this end, we propose a new representation-Spatially-varying Gaussian (SVG)-that allows per-Gaussian spatially varying parameters. This enhanced representation is complemented by a SVG splatting scheme akin to vertex/fragment shading in traditional graphics pipelines. Furthermore, we integrate a physically-based indirect lighting model, enabling more realistic relighting. The proposed SVG-IR framework significantly improves rendering quality, outperforming state-of-the-art NeRF-based methods by 2.5 dB in peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and surpassing existing Gaussian-based techniques by 3.5 dB in relighting tasks, all while maintaining a real-time rendering speed.
从图像重建3D资产,也称为逆向渲染(IR),仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为它的不适定性。3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)在新型视图合成(NVS)任务中展示了令人印象深刻的能力。方法将其应用于重新照明,通过将辐射度分离为BRDF参数和照明,然而,由于每个高斯具有恒定的材料参数和法线,以及缺乏间接照明的物理约束,导致重新照明质量较差,出现伪影和不自然的间接照明。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为空间变化高斯逆向渲染(SVG-IR)的新型框架,旨在提高NVS和重新照明质量。为此,我们提出了一种新的表示方法-空间变化高斯(SVG),允许每个高斯具有空间变化的参数。这种增强的表示方法由类似于传统图形管道中的顶点/片段着色的SVG拼贴方案所补充。此外,我们整合了基于物理的间接照明模型,以实现更逼真的重新照明。所提出的SVG-IR框架显著提高了渲染质量,在峰值信噪比(PSNR)上比最新的NeRF方法高出2.5分贝,在重新照明任务上比现有的高斯技术高出3.5分贝,同时保持实时渲染速度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于图像的3D资产重建,即逆向渲染(IR),是一项具有挑战性的任务。本文提出了一种名为SVG-IR的新型框架,旨在提高新型视图合成和重新照明质量。我们提出了一种名为空间变化高斯(SVG)的新表示方法,并集成了一种基于物理的间接照明模型,以实现更逼真的重新照明效果。与现有的NeRF方法和高斯技术相比,SVG-IR框架在峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面分别提高了2.5dB和3.5dB,同时保持了实时渲染速度。
Key Takeaways
- 逆向渲染(IR)在重建三维资产时面临挑战,而新方法SVG-IR旨在改进视图合成和重新照明质量。
- 提出了一种新型的空间变化高斯(SVG)表示方法,每个高斯拥有可变参数,增强了表示能力。
- 引入了一种类似于传统图形处理管道中的顶点/片段着色的SVG喷涂方案。
- 集成基于物理的间接照明模型,实现了更逼真的重新照明效果。
点此查看论文截图

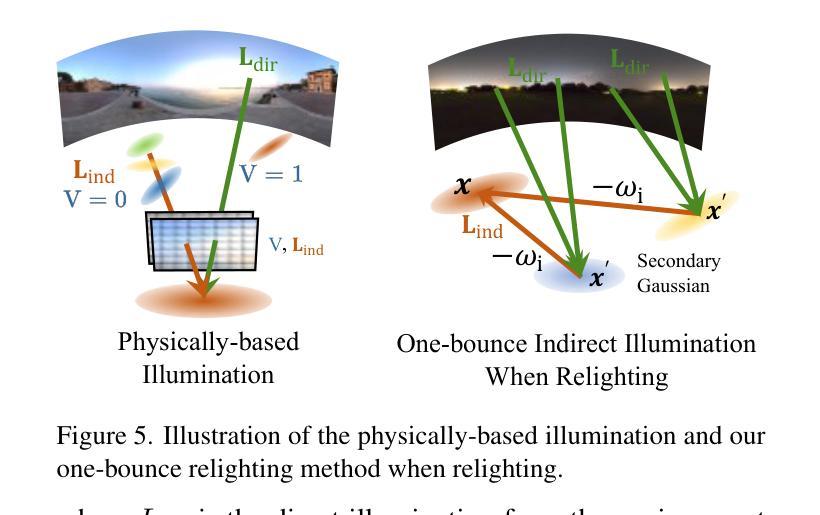
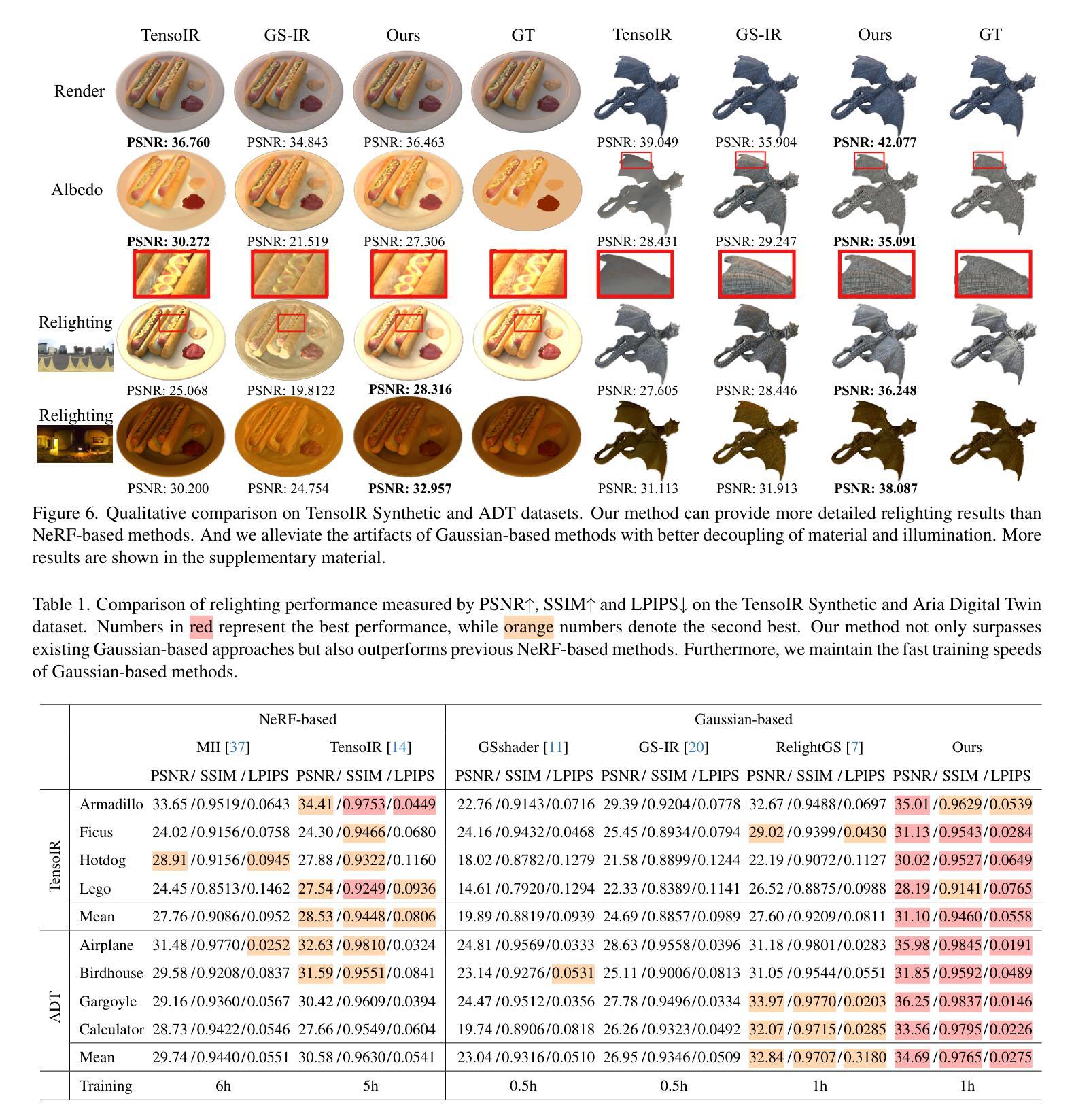
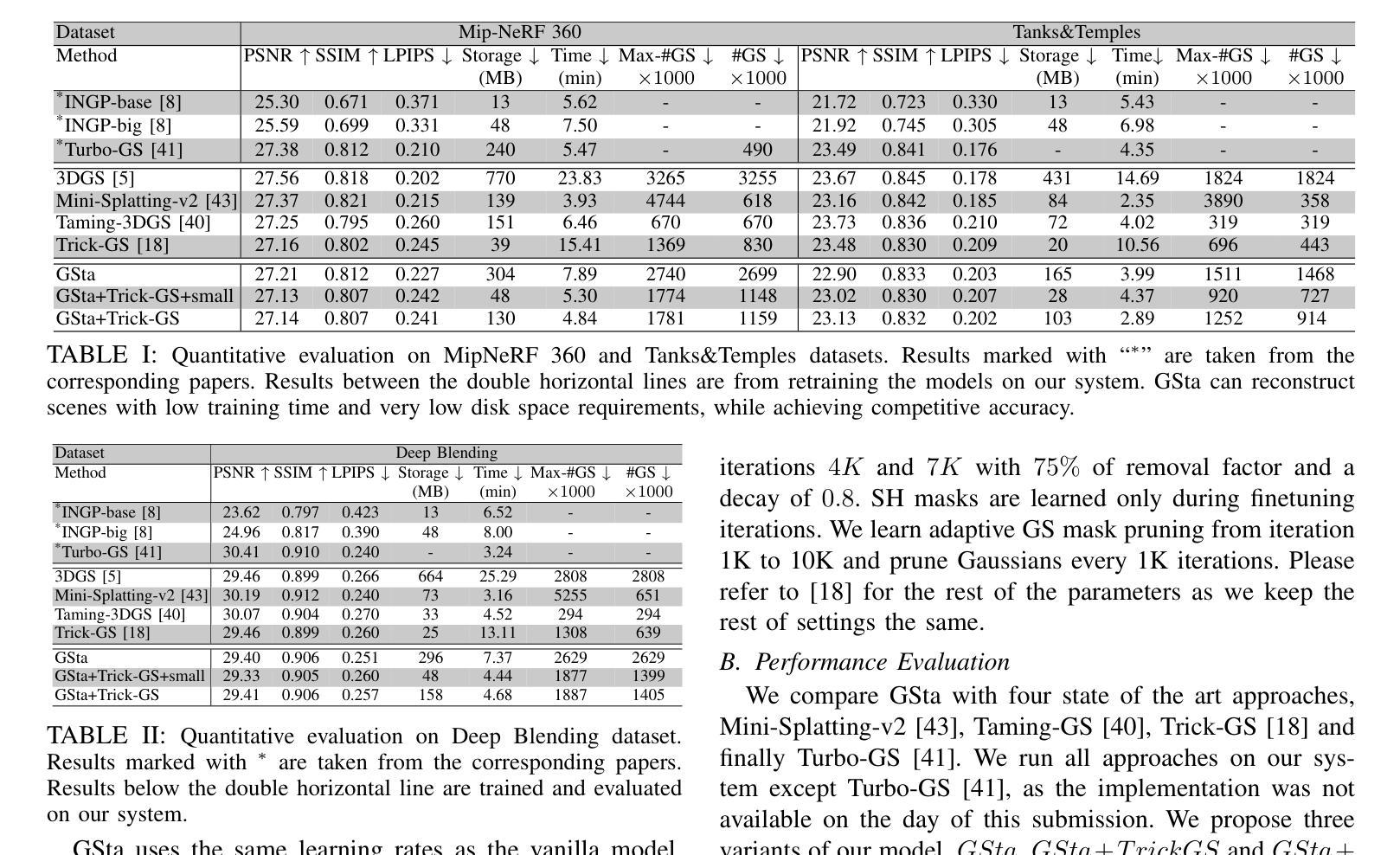
GSta: Efficient Training Scheme with Siestaed Gaussians for Monocular 3D Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Anil Armagan, Albert Saà-Garriga, Bruno Manganelli, Kyuwon Kim, M. Kerim Yucel
Gaussian Splatting (GS) is a popular approach for 3D reconstruction, mostly due to its ability to converge reasonably fast, faithfully represent the scene and render (novel) views in a fast fashion. However, it suffers from large storage and memory requirements, and its training speed still lags behind the hash-grid based radiance field approaches (e.g. Instant-NGP), which makes it especially difficult to deploy them in robotics scenarios, where 3D reconstruction is crucial for accurate operation. In this paper, we propose GSta that dynamically identifies Gaussians that have converged well during training, based on their positional and color gradient norms. By forcing such Gaussians into a siesta and stopping their updates (freezing) during training, we improve training speed with competitive accuracy compared to state of the art. We also propose an early stopping mechanism based on the PSNR values computed on a subset of training images. Combined with other improvements, such as integrating a learning rate scheduler, GSta achieves an improved Pareto front in convergence speed, memory and storage requirements, while preserving quality. We also show that GSta can improve other methods and complement orthogonal approaches in efficiency improvement; once combined with Trick-GS, GSta achieves up to 5x faster training, 16x smaller disk size compared to vanilla GS, while having comparable accuracy and consuming only half the peak memory. More visualisations are available at https://anilarmagan.github.io/SRUK-GSta.
高斯融合(GS)是一种流行的3D重建方法,它之所以受到广泛关注,主要是因为其收敛速度合理,能够真实地呈现场景并在短时间内进行渲染(新颖的)视图。然而,它存在存储和内存需求大的问题,其训练速度仍然落后于基于哈希网格的辐射场方法(例如Instant-NGP),这使得在机器人场景中部署它们变得尤为困难,而在这些场景中,3D重建对于准确操作至关重要。在本文中,我们提出了GSta,它可以根据高斯的位置和颜色梯度范数动态地识别训练过程中已经收敛良好的高斯。通过强制这些高斯进入休眠状态并在训练过程中停止其更新(冻结),我们在保持与最新技术竞争准确性的同时,提高了训练速度。我们还提出了一种基于计算部分训练图像峰值信噪比(PSNR值)的早期停止机制。结合其他改进,如集成学习率调度器,GSta在收敛速度、内存和存储要求方面实现了改进的帕累托前沿,同时保持了质量。我们还表明,GSta可以提高其他方法的效率并与其他正交方法进行互补;与Trick-GS结合后,GSta实现了高达5倍的培训速度提升,磁盘大小缩小了16倍,同时保持了相当的准确性和只有峰值内存的一半消耗。更多可视化内容请访问:https://anilarmagan.github.io/SRUK-GSta。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages. In submission to an IEEE conference
Summary
本文介绍了针对三维重建中的高斯插值(GS)方法存在的问题,提出了一种改进方法GSta。GSta通过动态识别已良好收敛的高斯分布,在训练过程中暂停其更新,以提高训练速度和准确性。同时,结合峰值信噪比(PSNR)值的早期停止机制和学习率调度器,GSta在收敛速度、内存和存储要求方面实现了帕累托前沿的改进,同时保证了质量。此外,GSta还可以与其他方法结合,进一步提高效率。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯插值(GS)是三维重建中的流行方法,但存在存储和内存要求大的问题,训练速度也相对较慢。
- GSta通过识别并暂停已良好收敛的高斯分布在训练中的更新,提高了训练速度和准确性。
- GSta结合了一种基于峰值信噪比(PSNR)的早期停止机制,进一步优化了训练过程。
- 通过集成学习率调度器,GSta在收敛速度、内存和存储要求方面取得了帕累托前沿的改进。
- GSta可以与其它方法结合,进一步提高效率,例如与Trick-GS结合时,可实现最高达5倍的训练速度提升和16倍的小磁盘存储。
- GSta的改进不仅体现在效率上,还能保证质量,达到与原始GS相当甚至更高的准确性。
点此查看论文截图
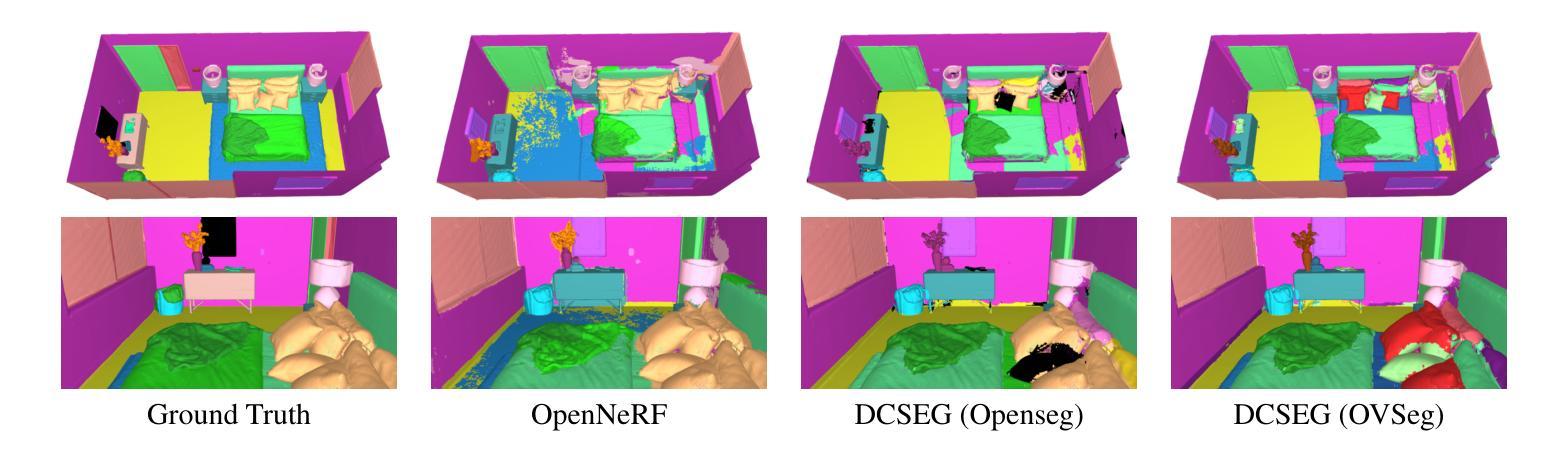
DCSEG: Decoupled 3D Open-Set Segmentation using Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Luis Wiedmann, Luca Wiehe, David Rozenberszki
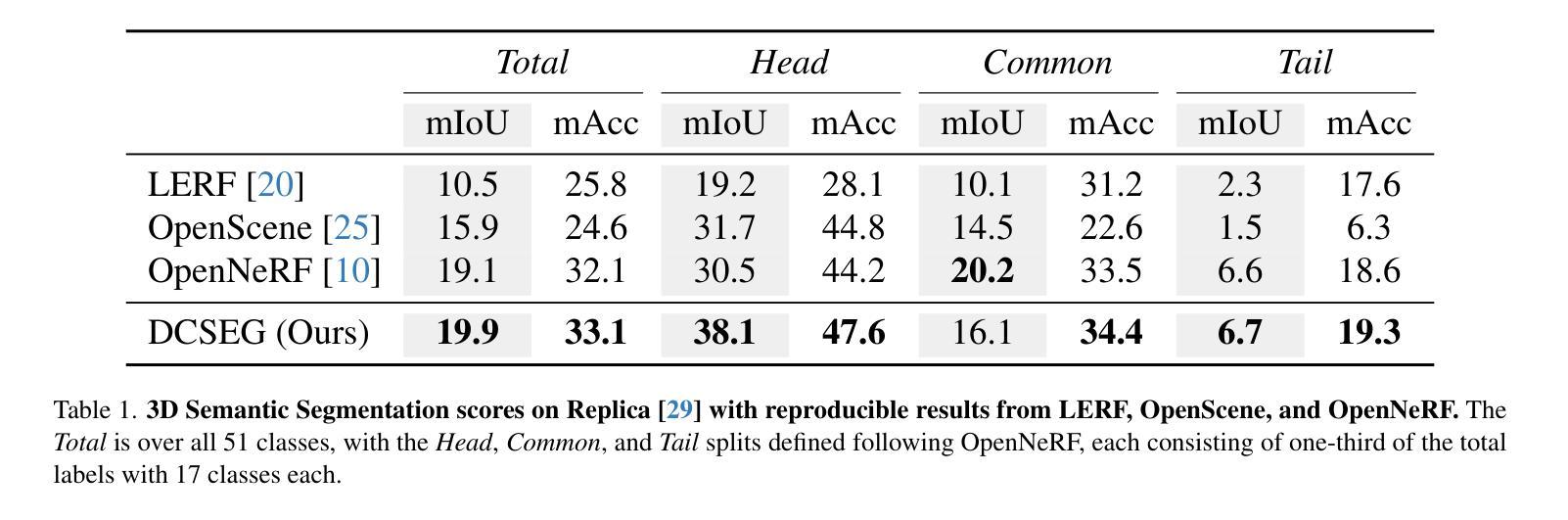
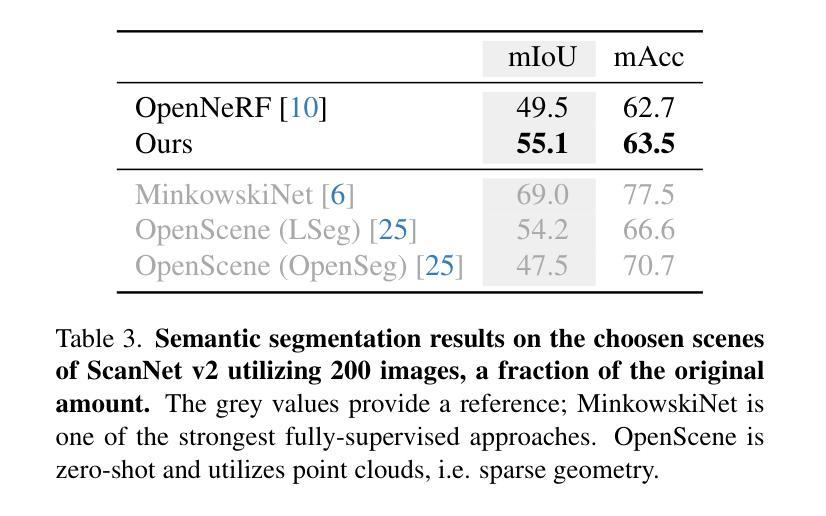
Open-set 3D segmentation represents a major point of interest for multiple downstream robotics and augmented/virtual reality applications. We present a decoupled 3D segmentation pipeline to ensure modularity and adaptability to novel 3D representations as well as semantic segmentation foundation models. We first reconstruct a scene with 3D Gaussians and learn class-agnostic features through contrastive supervision from a 2D instance proposal network. These 3D features are then clustered to form coarse object- or part-level masks. Finally, we match each 3D cluster to class-aware masks predicted by a 2D open-vocabulary segmentation model, assigning semantic labels without retraining the 3D representation. Our decoupled design (1) provides a plug-and-play interface for swapping different 2D or 3D modules, (2) ensures multi-object instance segmentation at no extra cost, and (3) leverages rich 3D geometry for robust scene understanding. We evaluate on synthetic and real-world indoor datasets, demonstrating improved performance over comparable NeRF-based pipelines on mIoU and mAcc, particularly for challenging or long-tail classes. We also show how varying the 2D backbone affects the final segmentation, highlighting the modularity of our framework. These results confirm that decoupling 3D mask proposal and semantic classification can deliver flexible, efficient, and open-vocabulary 3D segmentation.
开放式三维分割(Open-set 3D segmentation)为多个下游机器人学和增强/虚拟现实应用提供了一个重要的关注点。我们提出了一种解耦的三维分割管道,以确保模块化以及对新型三维表示和语义分割基础模型的适应性。首先,我们使用三维高斯(Gaussian)重建场景,并通过来自二维实例提议网络的对比监督学习类别无关的特征。这些三维特征随后被聚类以形成粗略的对象或部件级掩码。最后,我们将每个三维簇与由二维开放词汇分割模型预测的类别感知掩码相匹配,为三维表示分配语义标签而无需重新训练。我们的解耦设计(1)提供了一个即插即用的接口来交换不同的二维或三维模块,(2)确保多对象实例分割不增加额外成本,(3)利用丰富的三维几何进行稳健的场景理解。我们在合成和真实室内数据集上进行了评估,在mIoU和mAcc上展示了比类似的NeRF管道更高的性能,特别是对于具有挑战性或长尾类。我们还展示了改变二维主干如何影响最终分割,突出了我们框架的模块化特点。这些结果证实,将三维掩膜提议和语义分类解耦可以实现灵活、高效和开放词汇的三维分割。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be published in CVPR Workshop on Open-World 3D Scene Understanding with Foundation Models
摘要
三维开放集分割技术对于机器人技术和增强/虚拟现实应用具有重要意义。本文提出了一种解耦的三维分割管道,旨在确保模块化和适应新型三维表示以及语义分割基础模型。首先,通过三维高斯重建场景,并通过对比监督从二维实例提案网络学习类别无关特征。然后,对这些三维特征进行聚类,形成粗略的对象或部件级掩膜。最后,将每个三维簇与由二维开放词汇分割模型预测的类别感知掩膜相匹配,为三维表示分配语义标签而无需重新训练。解耦设计提供了插件式接口以交换不同的二维或三维模块,确保多对象实例分割无需额外成本,并利用丰富的三维几何实现稳健的场景理解。在合成和真实室内数据集上的评估表明,与基于NeRF的管道相比,该方法在mIoU和mAcc上表现出改进的性能,特别是在具有挑战性或长尾类别上。此外,还展示了改变二维主干网会影响最终的分割效果,凸显了框架的模块化特点。结果证实,解耦三维掩膜提案和语义分类可实现灵活、高效和开放词汇的三维分割。
关键见解
- 开放集三维分割在机器人技术和增强/虚拟现实应用中具有重要性。
- 提出一种解耦的三维分割管道,确保模块化和对新三维表示的适应性。
- 通过三维高斯重建场景并学习类别无关特征,随后进行特征聚类以形成掩膜。
- 通过匹配三维簇与二维开放词汇分割模型的类别感知掩膜,实现语义标签的分配,无需重新训练三维表示。
- 解耦设计提供了插件式接口以交换模块,实现多对象实例分割并利用三维几何实现稳健的场景理解。
- 在多个数据集上的评估表明,该方法在性能上优于基于NeRF的管道,尤其在处理具有挑战性和长尾类别时。
点此查看论文截图


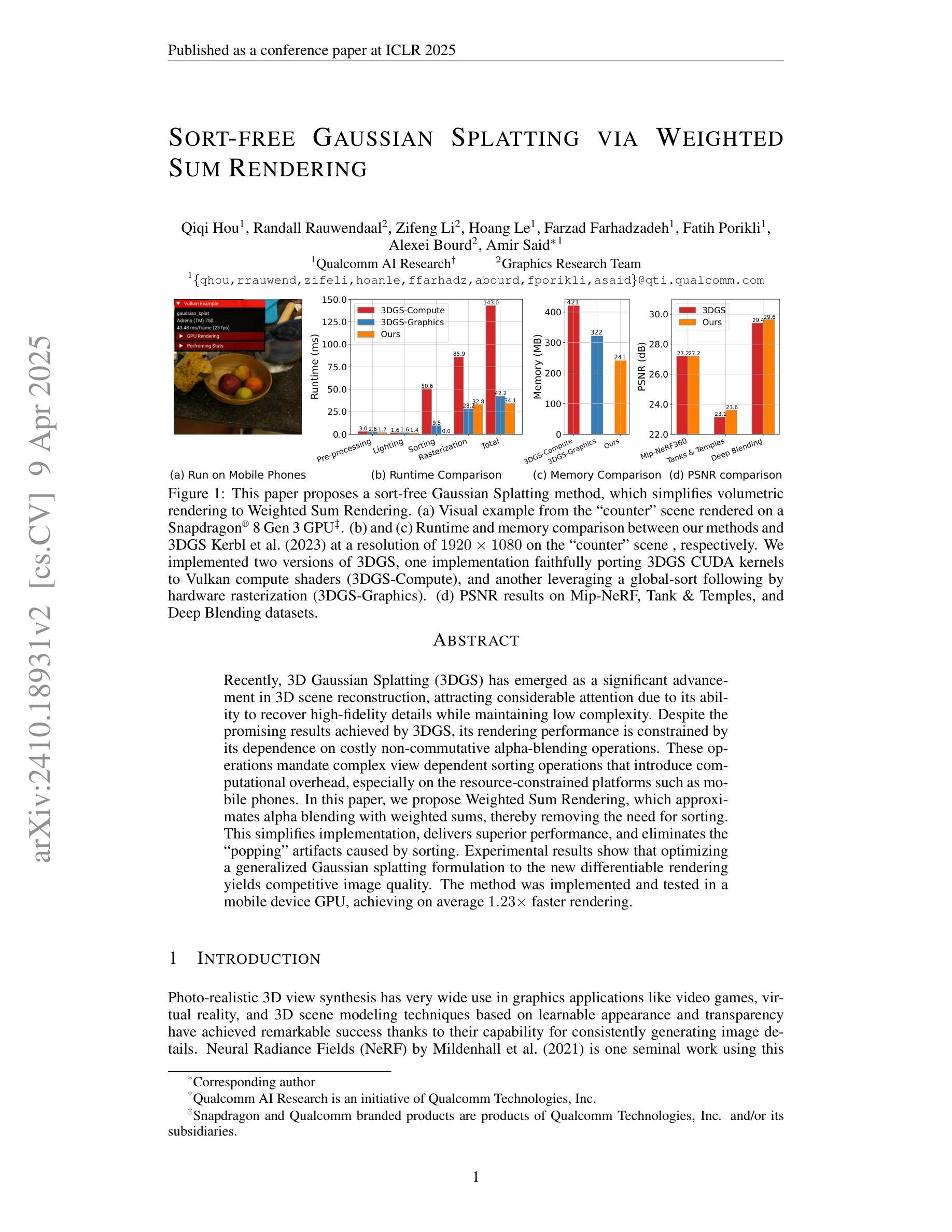
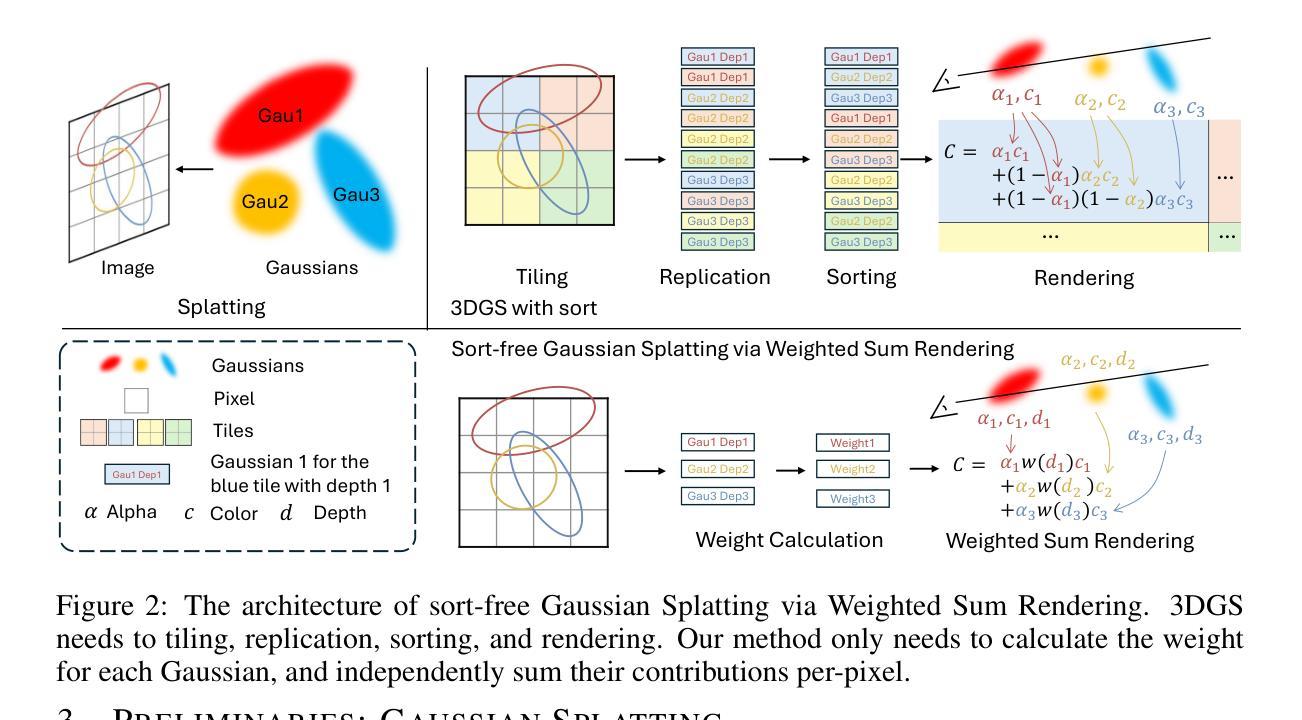
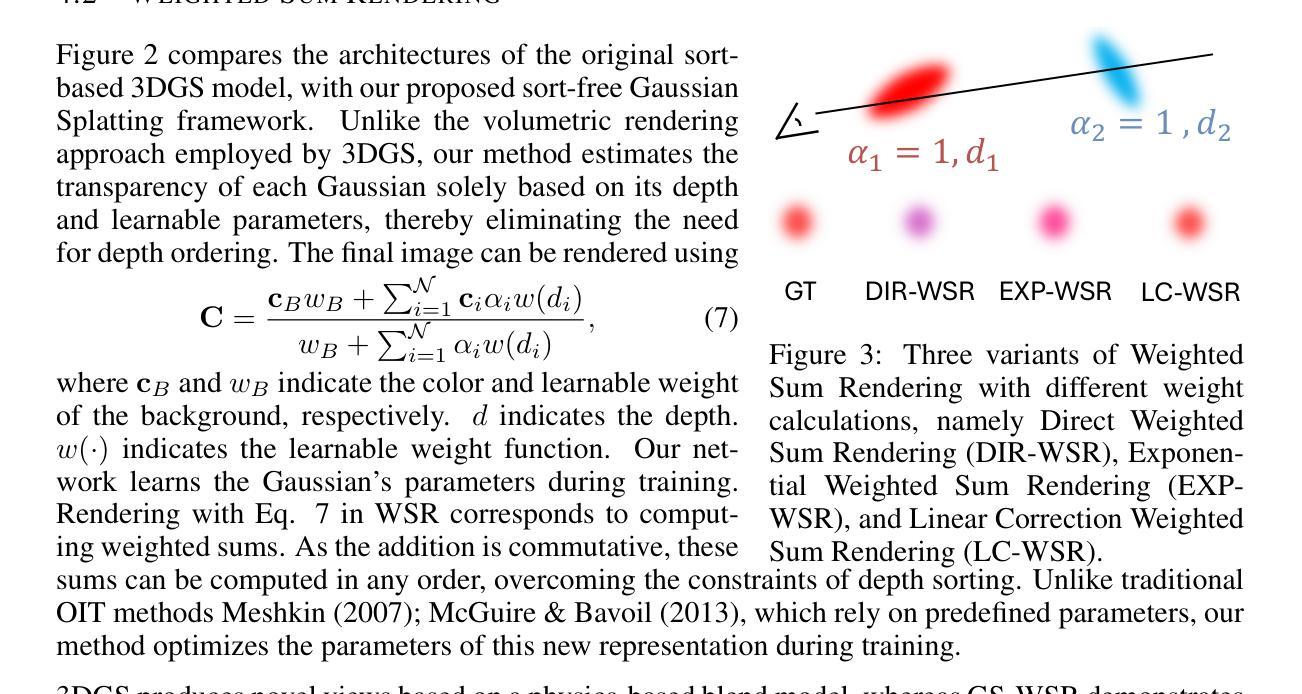
Sort-free Gaussian Splatting via Weighted Sum Rendering
Authors:Qiqi Hou, Randall Rauwendaal, Zifeng Li, Hoang Le, Farzad Farhadzadeh, Fatih Porikli, Alexei Bourd, Amir Said
Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a significant advancement in 3D scene reconstruction, attracting considerable attention due to its ability to recover high-fidelity details while maintaining low complexity. Despite the promising results achieved by 3DGS, its rendering performance is constrained by its dependence on costly non-commutative alpha-blending operations. These operations mandate complex view dependent sorting operations that introduce computational overhead, especially on the resource-constrained platforms such as mobile phones. In this paper, we propose Weighted Sum Rendering, which approximates alpha blending with weighted sums, thereby removing the need for sorting. This simplifies implementation, delivers superior performance, and eliminates the “popping” artifacts caused by sorting. Experimental results show that optimizing a generalized Gaussian splatting formulation to the new differentiable rendering yields competitive image quality. The method was implemented and tested in a mobile device GPU, achieving on average $1.23\times$ faster rendering.
最近,3D高斯延展(3DGS)作为3D场景重建的一项重要进展而出现,因其能够恢复高保真细节的同时保持低复杂度而备受关注。尽管3DGS取得了令人鼓舞的结果,但其渲染性能受到昂贵的非交换alpha混合运算的制约。这些操作需要进行复杂的视差相关排序操作,从而引入了计算开销,特别是在资源受限的平台(如手机)上。在本文中,我们提出了加权和渲染(Weighted Sum Rendering),它通过加权和来近似alpha混合,从而消除了排序的需要。这简化了实现,提高了性能,并消除了由排序引起的“跳跃”伪影。实验结果表明,将广义高斯延展公式优化为新的可微分渲染可产生具有竞争力的图像质量。该方法在手机设备GPU上实现并进行了测试,平均渲染速度提高了$1.23\times$。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了三维高斯拼贴技术(3DGS)在三维场景重建中的最新进展。虽然该技术能够恢复高质量细节并保持低复杂度,但其渲染性能受限于复杂的非交换alpha混合运算,导致计算开销较大。针对这一问题,本文提出加权求和渲染方法,通过近似alpha混合运算来简化实现,从而提高性能并消除排序造成的“跳跃”现象。实验结果表明,该方法实现了竞争性的图像质量。在手机等受限平台上实施和测试,平均渲染速度提高了1.23倍。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS作为一种重要的三维场景重建技术,具有恢复高保真细节和低复杂度的优势。
- 传统的3DGS受限于复杂的非交换alpha混合运算,导致计算开销大。
- 加权求和渲染方法的提出是为了解决这一问题,它通过近似alpha混合运算来简化实现和提高性能。
- 加权求和渲染消除了排序造成的“跳跃”现象。
- 实验结果表明,优化后的广义高斯拼贴公式实现了竞争性的图像质量。
- 该方法在手机等受限平台上实施和测试,性能表现优异,平均渲染速度提高了1.23倍。
点此查看论文截图
Atlas Gaussians Diffusion for 3D Generation
Authors:Haitao Yang, Yuan Dong, Hanwen Jiang, Dejia Xu, Georgios Pavlakos, Qixing Huang
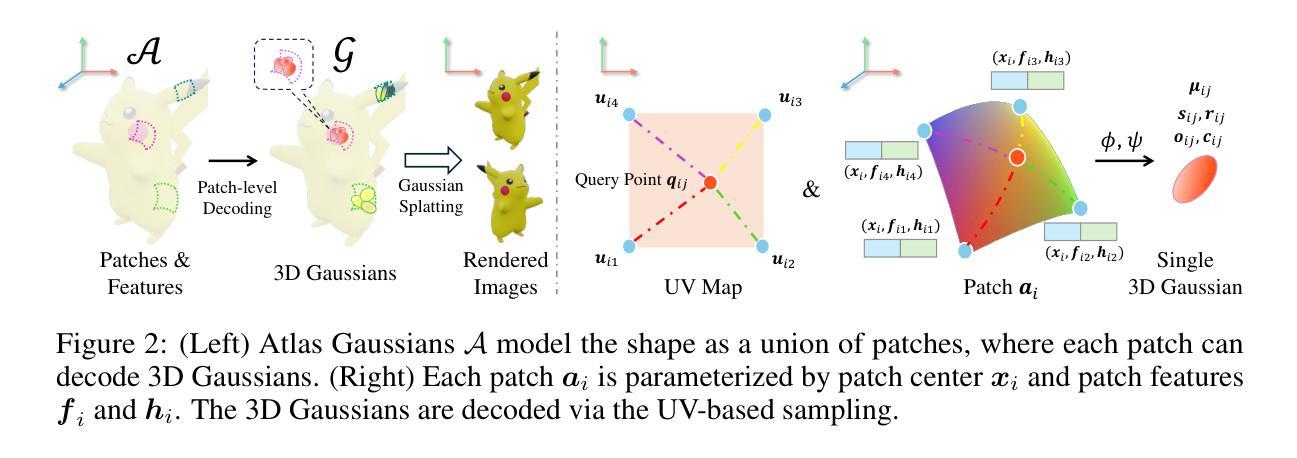
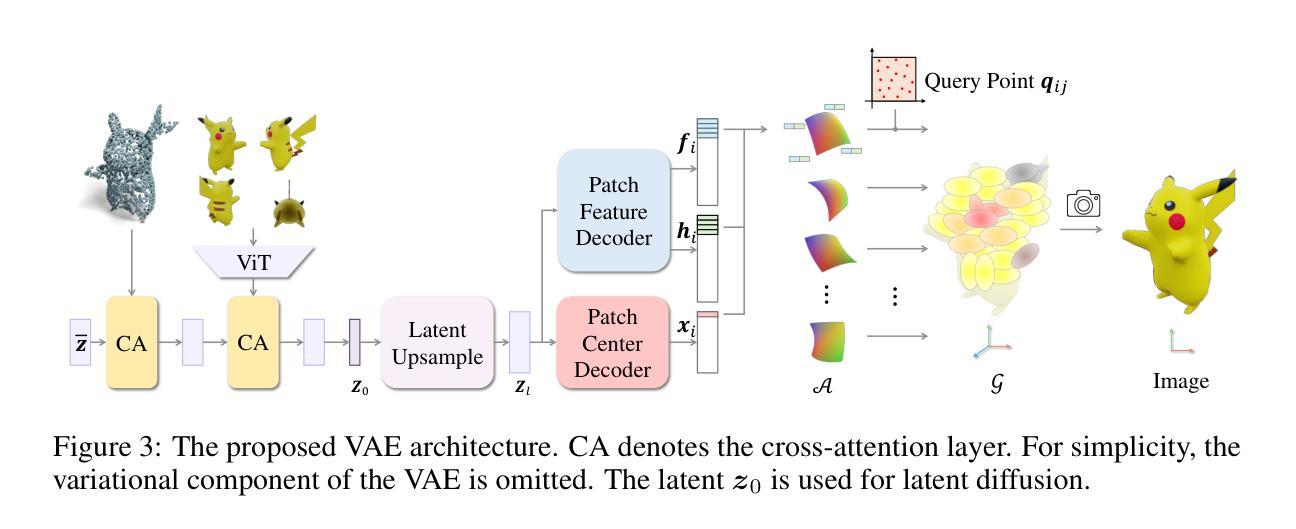
Using the latent diffusion model has proven effective in developing novel 3D generation techniques. To harness the latent diffusion model, a key challenge is designing a high-fidelity and efficient representation that links the latent space and the 3D space. In this paper, we introduce Atlas Gaussians, a novel representation for feed-forward native 3D generation. Atlas Gaussians represent a shape as the union of local patches, and each patch can decode 3D Gaussians. We parameterize a patch as a sequence of feature vectors and design a learnable function to decode 3D Gaussians from the feature vectors. In this process, we incorporate UV-based sampling, enabling the generation of a sufficiently large, and theoretically infinite, number of 3D Gaussian points. The large amount of 3D Gaussians enables the generation of high-quality details. Moreover, due to local awareness of the representation, the transformer-based decoding procedure operates on a patch level, ensuring efficiency. We train a variational autoencoder to learn the Atlas Gaussians representation, and then apply a latent diffusion model on its latent space for learning 3D Generation. Experiments show that our approach outperforms the prior arts of feed-forward native 3D generation. Project page: https://yanghtr.github.io/projects/atlas_gaussians.
使用潜在扩散模型已被证明在开发新型3D生成技术方面非常有效。为了利用潜在扩散模型,一个关键挑战是设计一种高保真和高效的表现方式,将潜在空间与3D空间联系起来。在本文中,我们介绍了Atlas Gaussians,一种用于前馈原生3D生成的新型表现方式。Atlas Gaussians将形状表示为局部补丁的并集,每个补丁可以解码为3D高斯。我们将补丁参数化为特征向量的序列,并设计了一个可学习的函数,从特征向量中解码出3D高斯。在此过程中,我们采用了基于UV的采样,能够生成足够大且理论上无限的3D高斯点数。大量的3D高斯能够生成高质量细节。此外,由于表现方式的局部感知性,基于变压器的解码过程在补丁级别上运行,确保了效率。我们训练了一个变分自动编码器来学习Atlas Gaussians的表现方式,然后在其潜在空间上应用潜在扩散模型进行3D生成学习。实验表明,我们的方法优于先前的原生3D生成的前馈方法。项目页面:[https://yanghtr.github.io/projects/atlas_gaussians(请自行访问以获取更多详细信息)]。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ICLR 2025 (Spotlight). Project page: https://yanghtr.github.io/projects/atlas_gaussians
Summary
本文引入了一种名为Atlas Gaussians的新型表现方法,用于实现前馈原生3D生成技术。该方法将形状表示为局部补丁的集合,每个补丁可解码为3D高斯。通过参数化补丁为特征向量序列,并设计解码函数从特征向量生成3D高斯,实现3D生成。此方法结合UV采样生成足够多的理论无限3D高斯点,提高生成细节质量。由于表现形式的局部感知性,基于变压器的解码程序在补丁级别运行,确保效率。
Key Takeaways
- 引入Atlas Gaussians表现方法,实现前馈原生3D生成技术。
- 将形状表示为局部补丁集合,每个补丁可解码为3D高斯。
- 参数化补丁为特征向量序列,设计解码函数从特征向量生成3D高斯。
- 结合UV采样生成大量理论无限的3D高斯点,提高生成质量。
- 局部感知性使得基于变压器的解码程序运行高效。
- 使用变分自编码器学习Atlas Gaussians表现方法,并在其潜在空间应用潜在扩散模型进行3D生成。
点此查看论文截图

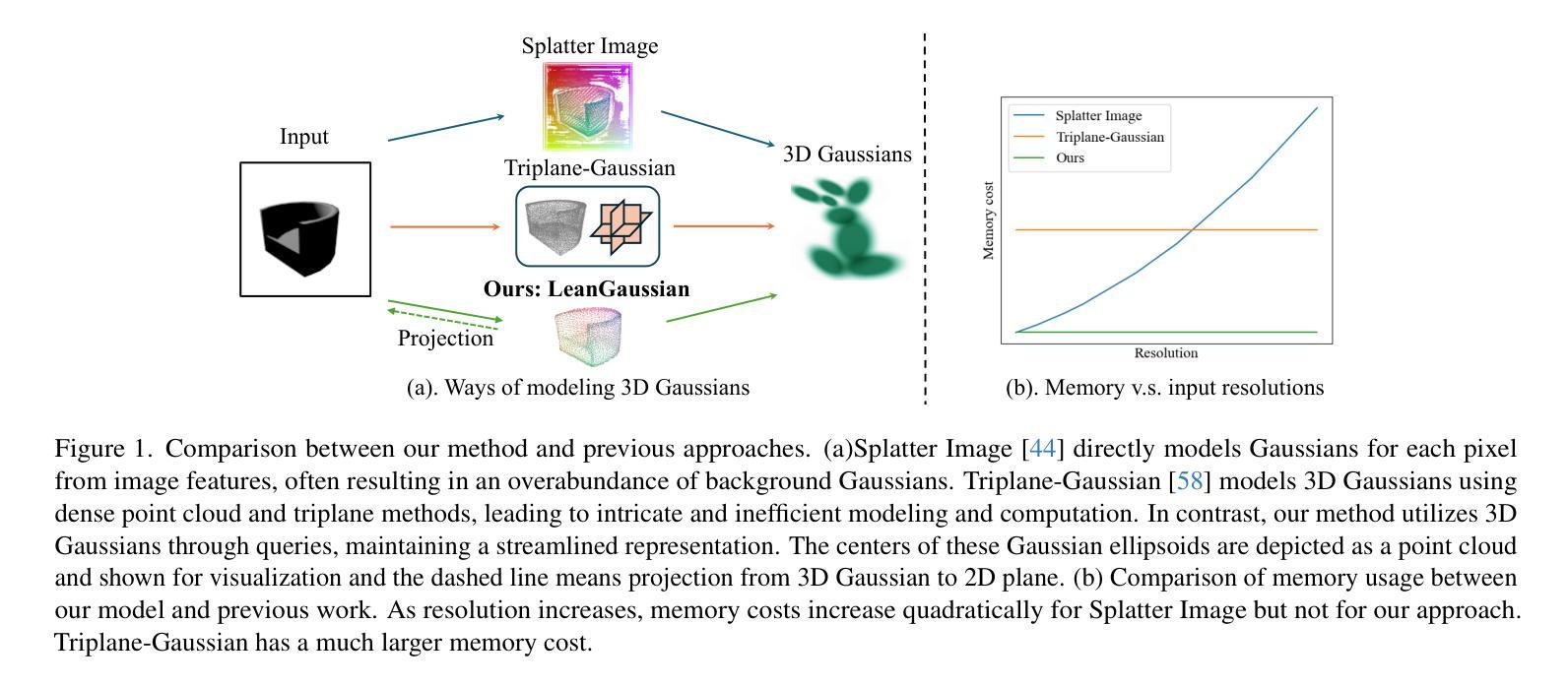
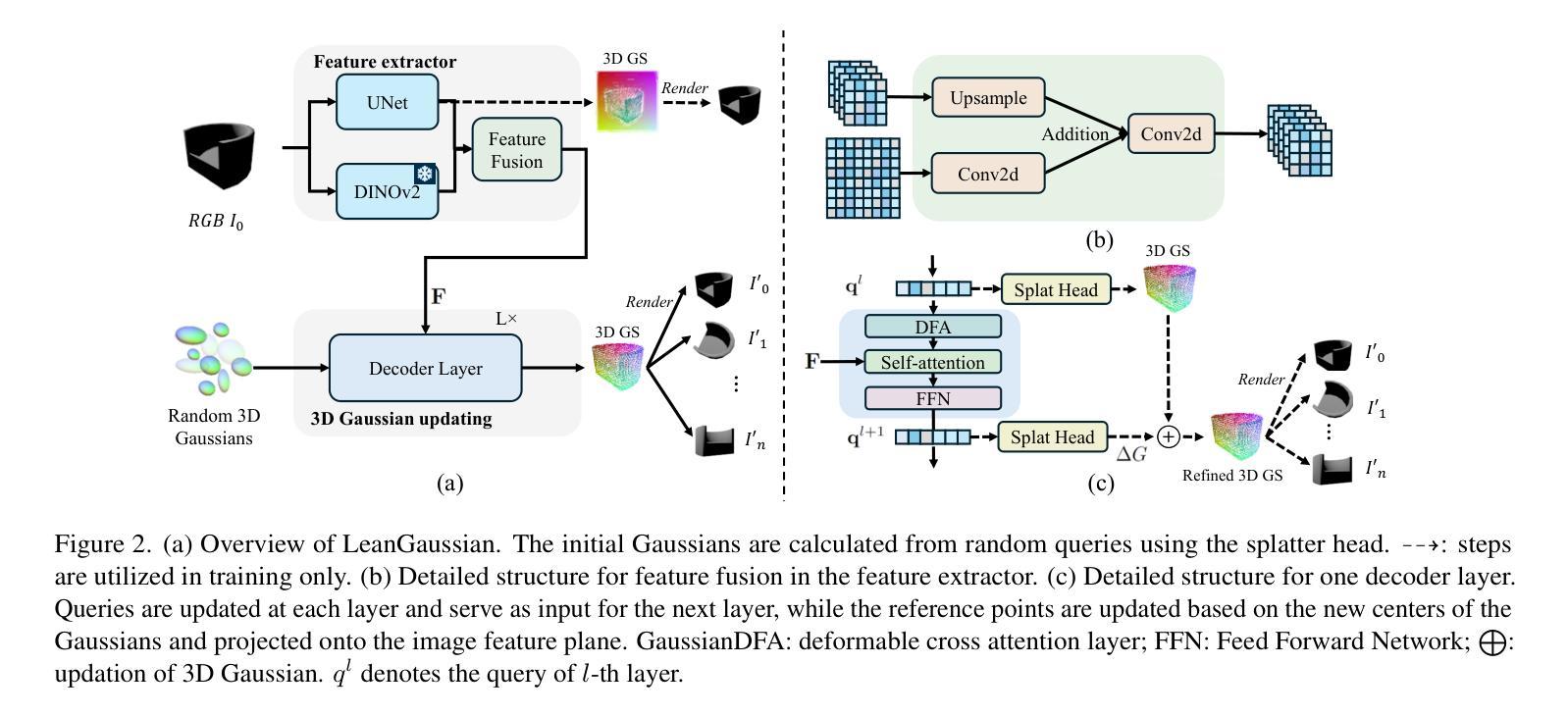
LeanGaussian: Breaking Pixel or Point Cloud Correspondence in Modeling 3D Gaussians
Authors:Jiamin Wu, Kenkun Liu, Han Gao, Xiaoke Jiang, Yao Yuan, Lei Zhang
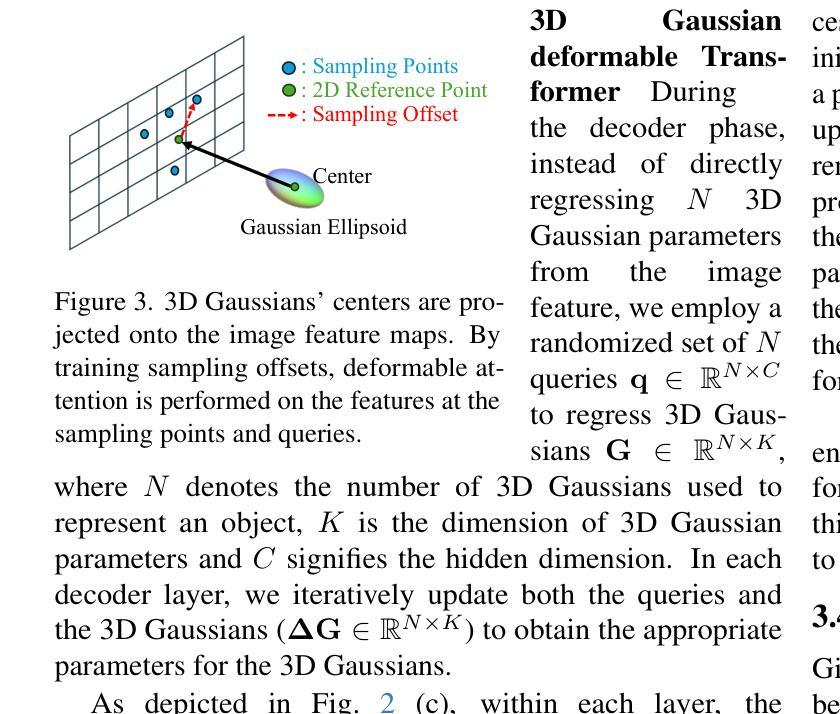
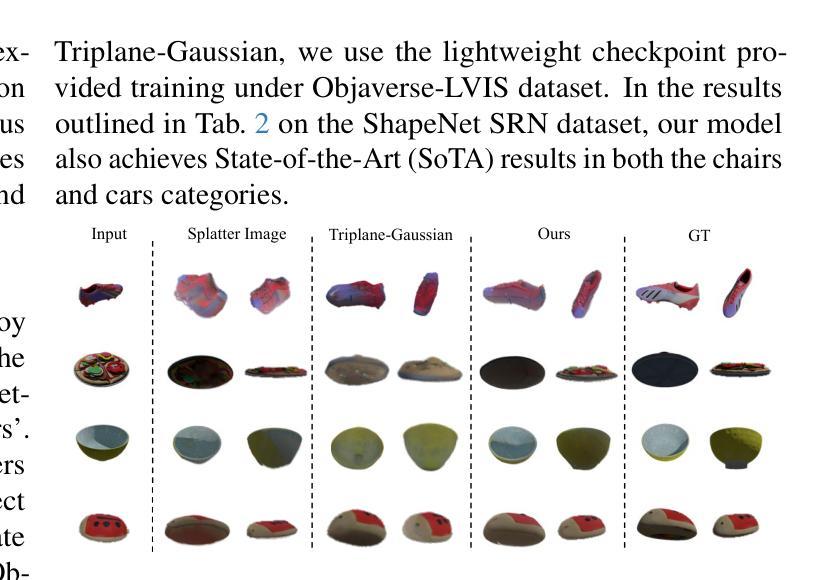
Recently, Gaussian splatting has demonstrated significant success in novel view synthesis. Current methods often regress Gaussians with pixel or point cloud correspondence, linking each Gaussian with a pixel or a 3D point. This leads to the redundancy of Gaussians being used to overfit the correspondence rather than the objects represented by the 3D Gaussians themselves, consequently wasting resources and lacking accurate geometries or textures. In this paper, we introduce LeanGaussian, a novel approach that treats each query in deformable Transformer as one 3D Gaussian ellipsoid, breaking the pixel or point cloud correspondence constraints. We leverage deformable decoder to iteratively refine the Gaussians layer-by-layer with the image features as keys and values. Notably, the center of each 3D Gaussian is defined as 3D reference points, which are then projected onto the image for deformable attention in 2D space. On both the ShapeNet SRN dataset (category level) and the Google Scanned Objects dataset (open-category level, trained with the Objaverse dataset), our approach, outperforms prior methods by approximately 6.1%, achieving a PSNR of 25.44 and 22.36, respectively. Additionally, our method achieves a 3D reconstruction speed of 7.2 FPS and rendering speed 500 FPS. Codes are available at https://github.com/jwubz123/LeanGaussian.
近期,高斯拼贴技术在新型视图合成领域取得了显著的成功。当前的方法通常通过像素或点云对应关系来回归高斯,将每个高斯与一个像素或一个3D点相关联。这导致使用大量冗余的高斯来过度拟合对应关系,而不是由3D高斯本身所表示的对象,从而浪费资源,并且缺乏准确的几何或纹理。在本文中,我们介绍了LeanGaussian,这是一种新型方法,它将可变形Transformer中的每个查询视为一个3D高斯椭圆体,打破了像素或点云对应关系的约束。我们利用可变形解码器逐层迭代地细化高斯,以图像特征作为键和值。值得注意的是,每个3D高斯的中心被定义为3D参考点,然后投影到图像上进行2D空间的可变形注意力。在ShapeNet SRN数据集(类别级别)和Google扫描对象数据集(开放类别级别,使用Objaverse数据集进行训练)上,我们的方法较之前的方法高出约6.1%,分别实现了PSNR值为25.44和22.36。此外,我们的方法达到3D重建速度为7.2 FPS和渲染速度500 FPS。代码可访问https://github.com/jwubz123/LeanGaussian。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出LeanGaussian方法,以3D高斯椭圆体处理变形Transformer中的查询,打破像素或点云对应的约束。利用可变形解码器逐层细化高斯,以图像特征为键和值。定义每个3D高斯的中心为3D参考点,然后将其投影到图像上进行二维空间的变形注意力。在ShapeNet SRN数据集(类别级别)和Google扫描对象数据集(开放类别级别,使用Objaverse数据集进行训练)上,LeanGaussian方法较之前的方法提高了约6.1%,分别实现了PSNR 25.44和22.36。此外,我们的方法实现了3D重建速度为每秒7.2帧,渲染速度为每秒500帧。代码可在https://github.com/jwubz123/LeanGaussian获取。
关键见解
- 当前方法在新型视图合成中使用高斯展开时主要关注像素或点云的对应关系,导致资源浪费和对物体表示的准确度不足。
- LeanGaussian方法引入变形Transformer和可变形解码器,将每个查询视为一个3D高斯椭圆体,提高了模型的灵活性和准确性。
- 该方法通过迭代细化高斯并引入图像特征作为键和值,增强了模型的性能。
- 定义了每个3D高斯的中心为3D参考点,并将其投影到图像上,以实现二维空间的变形注意力机制。
- 在两个主要数据集上进行了评估,包括ShapeNet SRN数据集和Google扫描对象数据集,显示LeanGaussian方法的性能明显优于其他方法。
- LeanGaussian方法的PSNR值在ShapeNet SRN数据集上为25.44,在Google扫描对象数据集上为22.36,显示出其优越的性能。
点此查看论文截图