⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-11 更新
A Unified Agentic Framework for Evaluating Conditional Image Generation
Authors:Jifang Wang, Xue Yang, Longyue Wang, Zhenran Xu, Yiyu Wang, Yaowei Wang, Weihua Luo, Kaifu Zhang, Baotian Hu, Min Zhang
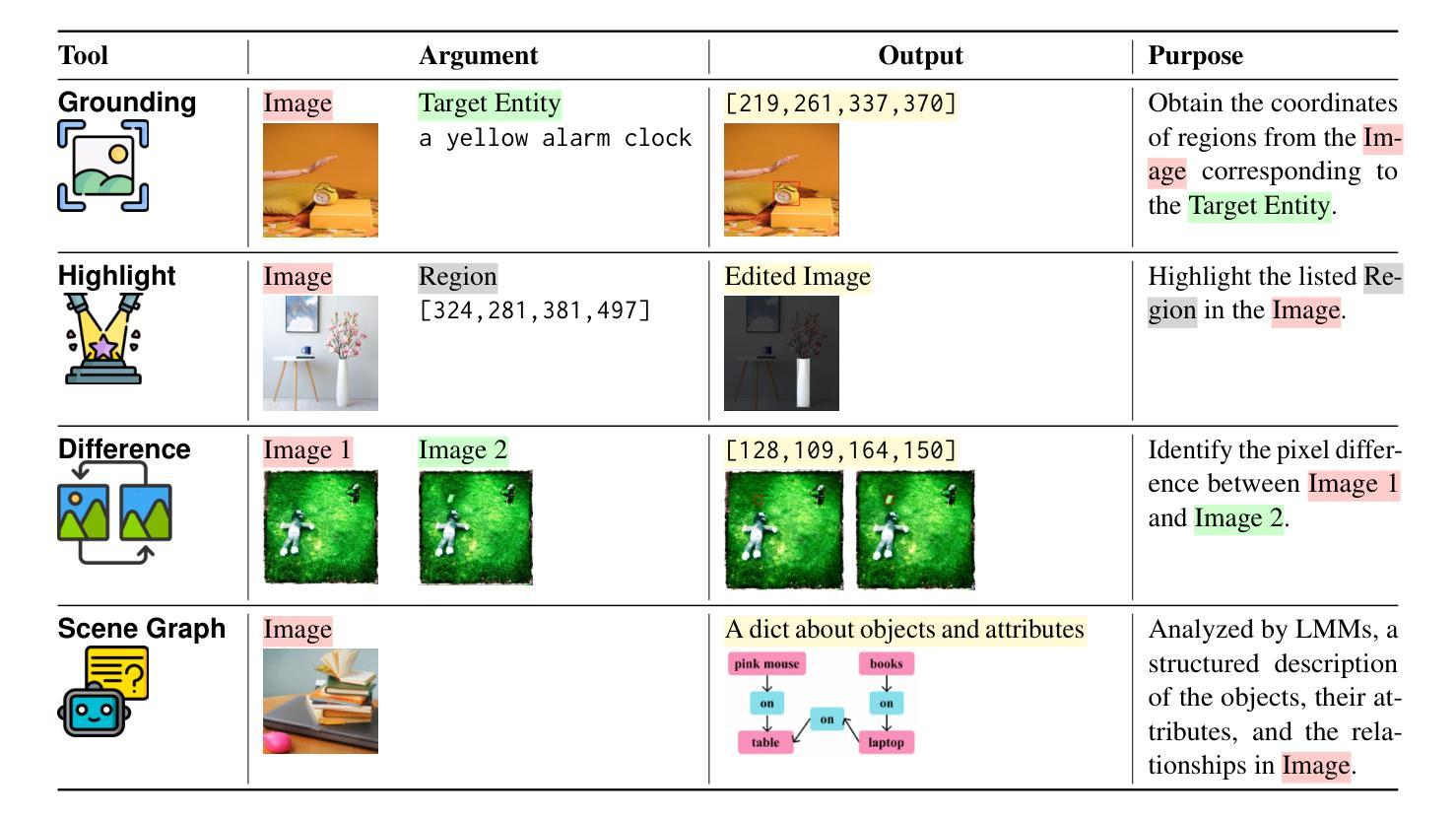
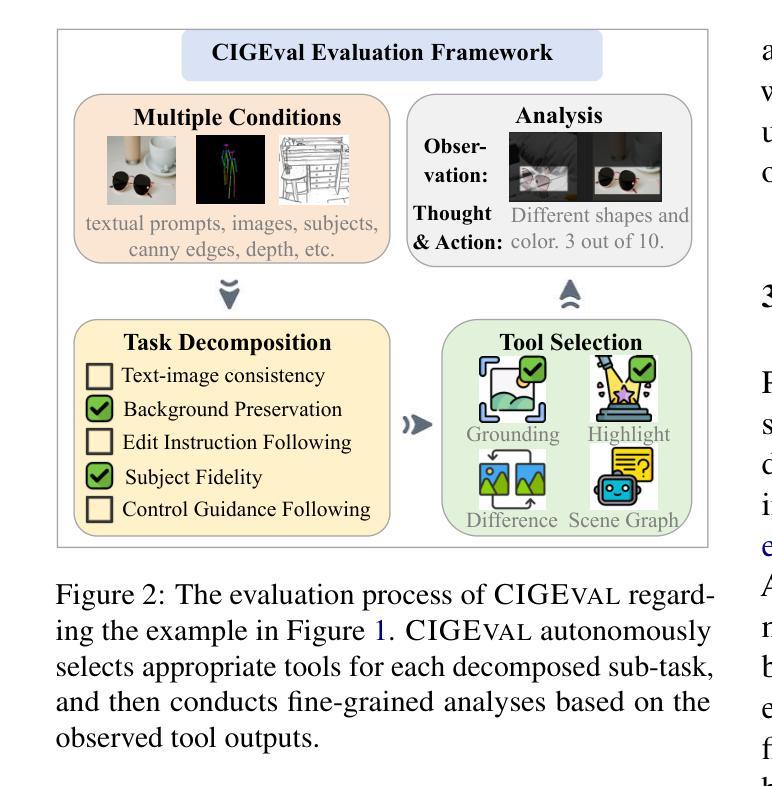
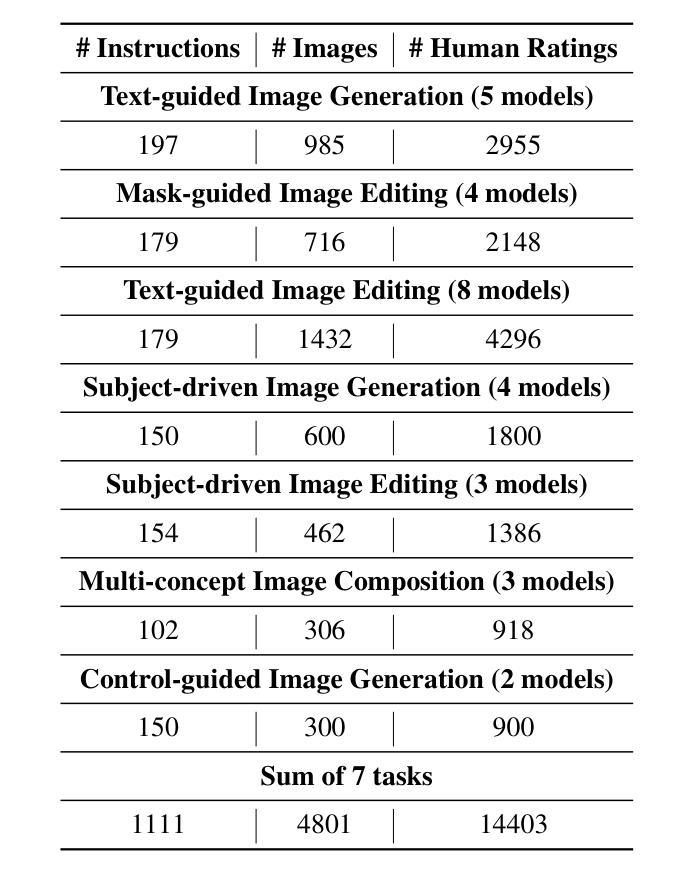
Conditional image generation has gained significant attention for its ability to personalize content. However, the field faces challenges in developing task-agnostic, reliable, and explainable evaluation metrics. This paper introduces CIGEval, a unified agentic framework for comprehensive evaluation of conditional image generation tasks. CIGEval utilizes large multimodal models (LMMs) as its core, integrating a multi-functional toolbox and establishing a fine-grained evaluation framework. Additionally, we synthesize evaluation trajectories for fine-tuning, empowering smaller LMMs to autonomously select appropriate tools and conduct nuanced analyses based on tool outputs. Experiments across seven prominent conditional image generation tasks demonstrate that CIGEval (GPT-4o version) achieves a high correlation of 0.4625 with human assessments, closely matching the inter-annotator correlation of 0.47. Moreover, when implemented with 7B open-source LMMs using only 2.3K training trajectories, CIGEval surpasses the previous GPT-4o-based state-of-the-art method. Case studies on GPT-4o image generation highlight CIGEval’s capability in identifying subtle issues related to subject consistency and adherence to control guidance, indicating its great potential for automating evaluation of image generation tasks with human-level reliability.
条件图像生成因其个性化内容的能力而受到广泛关注。然而,该领域在开发任务无关、可靠和可解释的评价指标方面面临挑战。本文介绍了CIGEval,这是一个用于条件图像生成任务综合评价的统一智能框架。CIGEval以大型多模态模型(LMMs)为核心,集成多功能工具箱并建立精细的评价框架。此外,我们合成评价轨迹进行微调,使较小的LMM能够自主选择适当的工具,并根据工具输出进行微妙分析。在七个突出的条件图像生成任务上的实验表明,CIGEval(GPT-4o版本)与人类评估的相关性高达0.4625,接近人工评估者之间的相关性0.47。而且,在使用7B开源LMM仅通过2.3K训练轨迹实现时,CIGEval超越了基于GPT-4o的先前最先进的方法。在GPT-4o图像生成方面的案例研究突出了CIGEval在识别与主题一致性和遵循控制指导相关的细微问题方面的能力,表明其在自动化图像生成任务评估中具有与人类水平可靠性相匹配的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress. GitHub: https://github.com/HITsz-TMG/Agentic-CIGEval
Summary
本文提出一种名为CIGEval的统一智能框架,用于全面评估条件图像生成任务。该框架利用大型多模态模型为核心,集成多功能工具箱并建立精细的评价框架。实验表明,CIGEval与人的评估高度相关,并能自主选择合适的工具进行细致的分析。
Key Takeaways
- CIGEval是一个用于条件图像生成任务的综合评估框架。
- 它利用大型多模态模型(LMMs)为核心,提供一个多功能的工具箱。
- CIGEval建立了精细的评价框架,可以合成评价轨迹进行微调。
- 实验证明,CIGEval与人类评估高度相关,并能自主选择合适的工具进行分析。
- CIGEval在仅使用2.3K训练轨迹的7B开源LMMs上超越了之前的GPT-4o基于状态的方法。
- 案例研究表明,CIGEval能够识别与主题一致性和遵循控制指导相关的细微问题。
点此查看论文截图

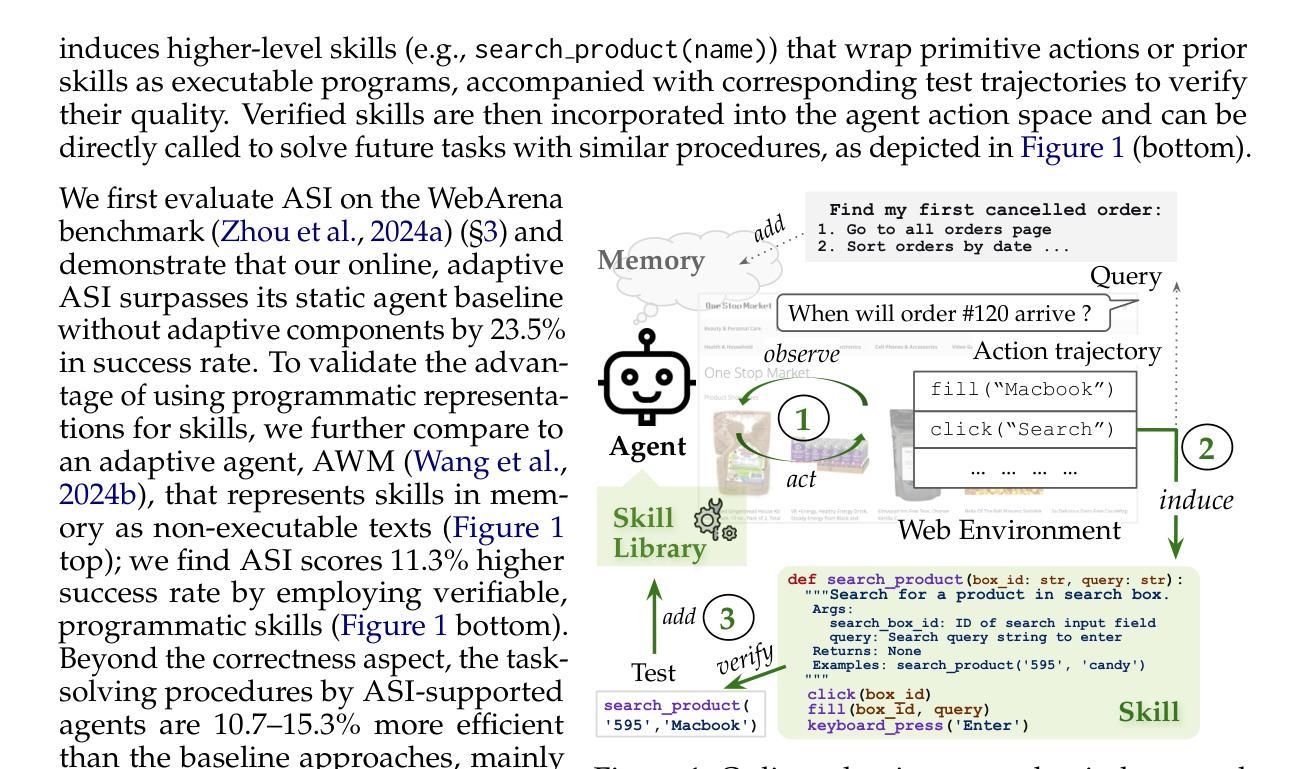
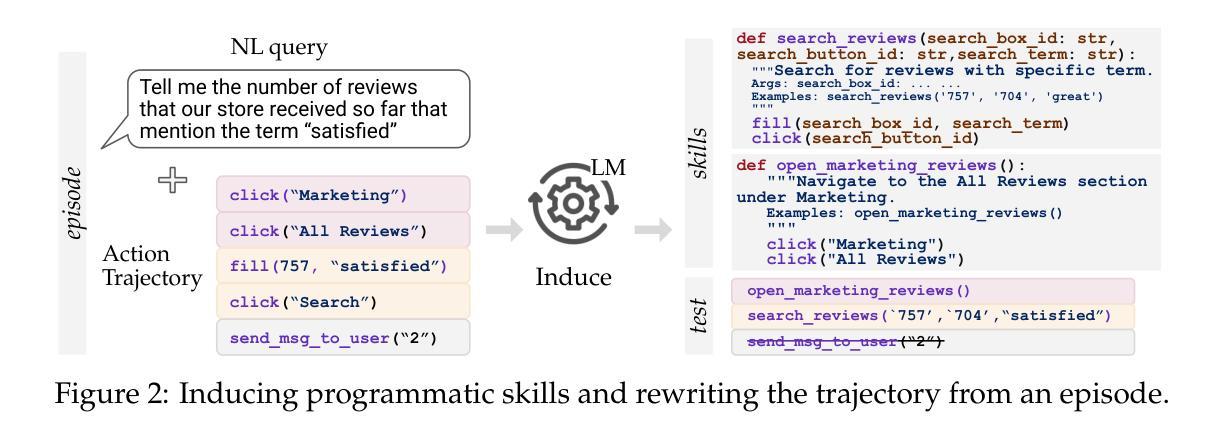
Inducing Programmatic Skills for Agentic Tasks
Authors:Zora Zhiruo Wang, Apurva Gandhi, Graham Neubig, Daniel Fried
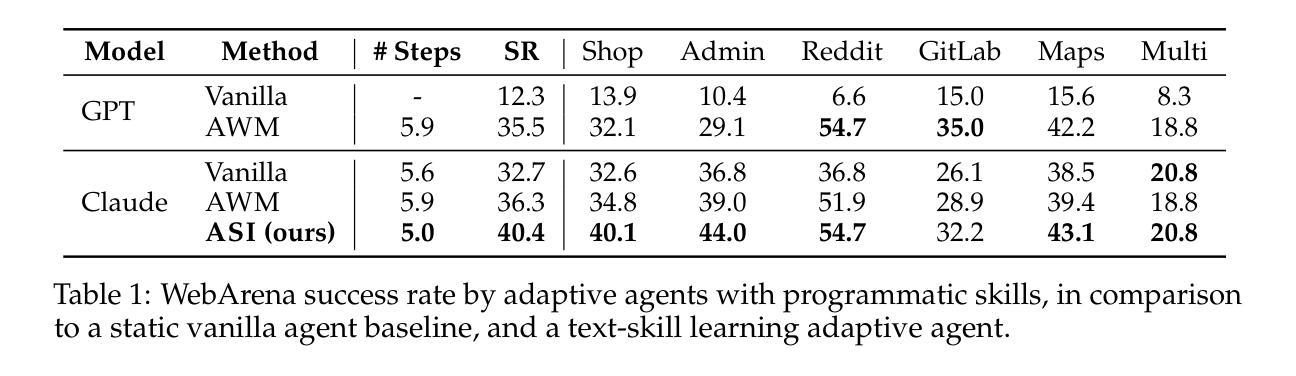
To succeed in common digital tasks such as web navigation, agents must carry out a variety of specialized tasks such as searching for products or planning a travel route. To tackle these tasks, agents can bootstrap themselves by learning task-specific skills online through interaction with the web environment. In this work, we demonstrate that programs are an effective representation for skills. We propose agent skill induction (ASI), which allows agents to adapt themselves by inducing, verifying, and utilizing program-based skills on the fly. We start with an evaluation on the WebArena agent benchmark and show that ASI outperforms the static baseline agent and its text-skill counterpart by 23.5% and 11.3% in success rate, mainly thanks to the programmatic verification guarantee during the induction phase. ASI also improves efficiency by reducing 10.7-15.3% of the steps over baselines, by composing primitive actions (e.g., click) into higher-level skills (e.g., search product). We then highlight the efficacy of ASI in remaining efficient and accurate under scaled-up web activities. Finally, we examine the generalizability of induced skills when transferring between websites, and find that ASI can effectively reuse common skills, while also updating incompatible skills to versatile website changes.
要在网络导航等常见数字任务中取得成功,代理必须完成各种专业任务,如搜索产品或规划旅行路线。为了应对这些任务,代理可以通过与在线网络环境互动来在线学习特定任务的技能,从而实现自我引导。在这项工作中,我们证明了程序是技能的有效表示。我们提出了代理技能感应(ASI),它允许代理在即时感应、验证和利用基于程序的技能时进行自我适应。我们以WebArena代理基准测试为起点,证明ASI在成功率上优于静态基线代理和其文本技能对应物,分别高出23.5%和11.3%,这主要得益于感应阶段的程序验证保证。ASI还通过组合基本动作(例如点击)形成更高级的技能(例如搜索产品),提高了效率,减少了基线步骤的10.7%-15.3%。然后,我们强调了ASI在扩大网络活动范围内保持高效和准确的有效性。最后,我们考察了感应技能在不同网站之间的可迁移性,发现ASI可以有效地重用常见技能,同时更新不兼容技能以适应网站的多变。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了在数字任务中,如网页导航等,智能体需要通过在线学习特定技能来适应环境。为此,本文提出了一种名为“智能体技能感应(ASI)”的方法,通过感应、验证和利用基于程序的技能来实现智能体的自我适应。在WebArena基准测试中,ASI相较于静态基准智能体和文本技能智能体,成功率提高了23.5%和11.3%,主要得益于感应阶段的程序验证保障。此外,ASI还能通过组合基础动作(如点击)为高级技能(如搜索产品),提高效率达10.7%~15.3%。同时,ASI在大型网络活动中也能保持高效和准确。最后,本文通过实验验证了感应技能的通用性,在网站间迁移时,ASI可以有效地复用通用技能,并更新不兼容技能以适应网站变化。
Key Takeaways:
- 智能体需要学习特定任务技能以适应数字任务环境。
- 提出了智能体技能感应(ASI)方法,使智能体能够自我适应并学习新技能。
- ASI在WebArena基准测试中表现出优异性能,成功率显著提高。
- ASI通过组合基础动作形成高级技能,从而提高效率。
- ASI在大型网络活动中保持高效和准确。
- 感应技能具有通用性,ASI可以在不同网站间迁移并有效复用技能。
点此查看论文截图


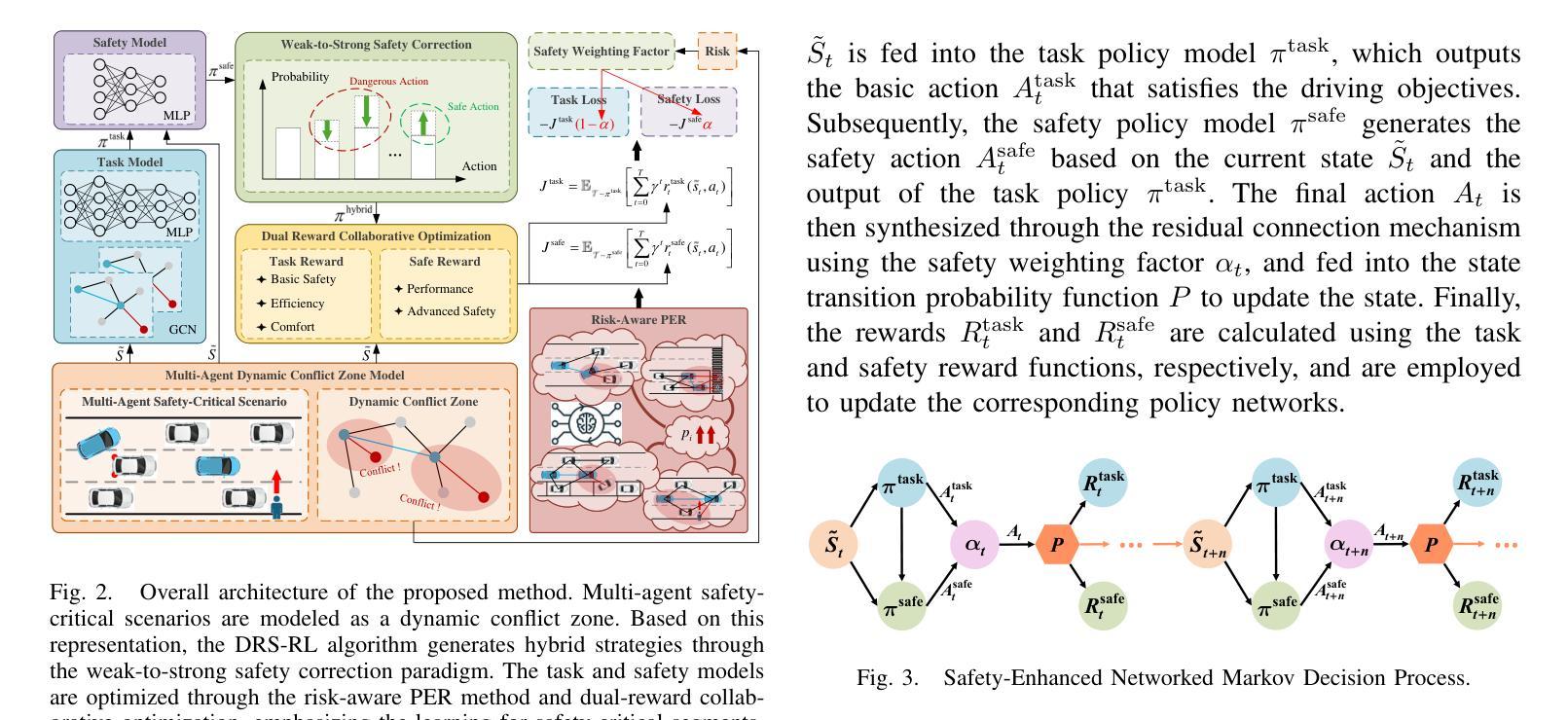
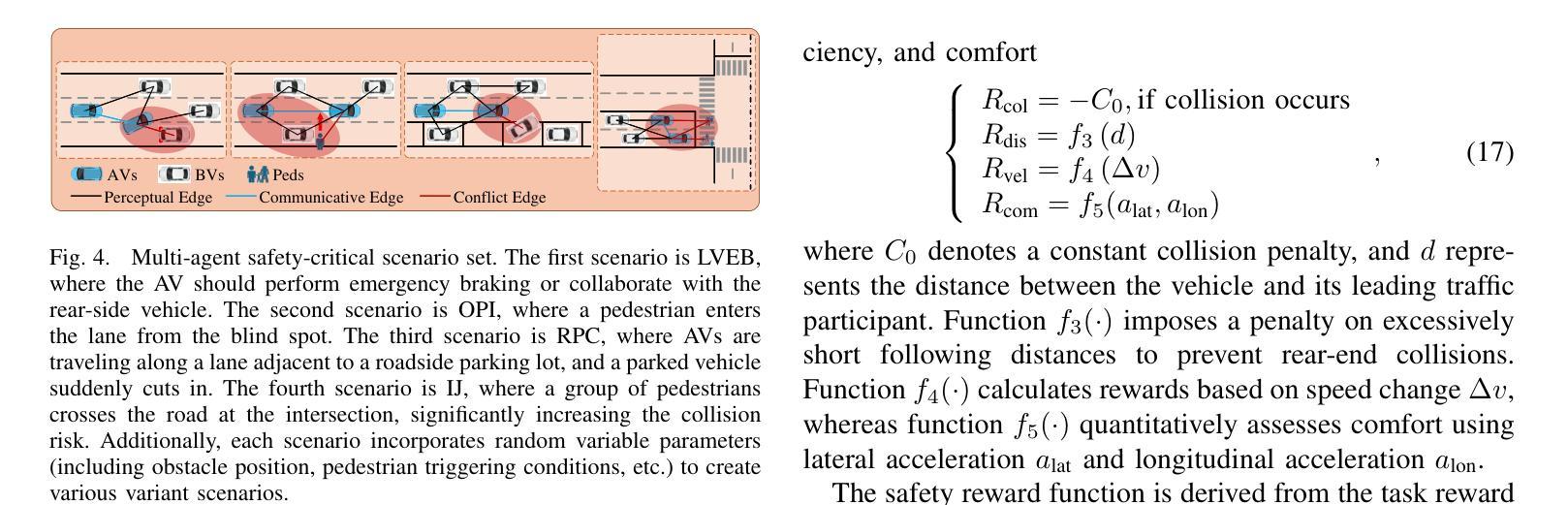
Dynamic Residual Safe Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Agent Safety-Critical Scenarios Decision-Making
Authors:Kaifeng Wang, Yinsong Chen, Qi Liu, Xueyuan Li, Xin Gao
In multi-agent safety-critical scenarios, traditional autonomous driving frameworks face significant challenges in balancing safety constraints and task performance. These frameworks struggle to quantify dynamic interaction risks in real-time and depend heavily on manual rules, resulting in low computational efficiency and conservative strategies. To address these limitations, we propose a Dynamic Residual Safe Reinforcement Learning (DRS-RL) framework grounded in a safety-enhanced networked Markov decision process. It’s the first time that the weak-to-strong theory is introduced into multi-agent decision-making, enabling lightweight dynamic calibration of safety boundaries via a weak-to-strong safety correction paradigm. Based on the multi-agent dynamic conflict zone model, our framework accurately captures spatiotemporal coupling risks among heterogeneous traffic participants and surpasses the static constraints of conventional geometric rules. Moreover, a risk-aware prioritized experience replay mechanism mitigates data distribution bias by mapping risk to sampling probability. Experimental results reveal that the proposed method significantly outperforms traditional RL algorithms in safety, efficiency, and comfort. Specifically, it reduces the collision rate by up to 92.17%, while the safety model accounts for merely 27% of the main model’s parameters.
在多智能体安全关键场景中,传统自动驾驶框架在平衡安全约束和任务性能方面面临重大挑战。这些框架在实时量化动态交互风险时遇到困难,并严重依赖于手动规则,导致计算效率低和过于保守的策略。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种基于增强安全网络马尔可夫决策过程的动态剩余安全强化学习(DRS-RL)框架。这是首次将强弱理论引入多智能体决策,通过强弱安全校正范式实现安全边界的轻量级动态校准。基于多智能体动态冲突区域模型,我们的框架准确捕捉了异质交通参与者之间的时空耦合风险,并超越了传统几何规则的静态约束。此外,一种风险感知优先经验回放机制通过将风险映射到采样概率来缓解数据分布偏差。实验结果表明,该方法在安全、效率和舒适性方面显著优于传统强化学习算法。具体而言,它可以将碰撞率降低高达92.17%,而安全模型仅占主模型参数的27%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在复杂多智能体安全场景中,传统自主驾驶框架在平衡安全约束和任务性能方面面临挑战。它们难以实时量化动态交互风险,并高度依赖手动规则,导致计算效率低下和策略保守。为解决这些问题,我们提出了基于安全增强网络马尔可夫决策过程的动态残余安全强化学习(DRS-RL)框架。该框架首次将强弱理论引入多智能体决策制定,通过强弱安全校正范式实现安全边界的轻量级动态校准。基于多智能体动态冲突区域模型,该框架准确捕捉不同交通参与者之间的时空耦合风险,并超越传统几何规则的静态约束。此外,风险感知优先经验回放机制通过风险映射采样概率缓解数据分布偏见。实验结果显示,该方法在安全性、效率和舒适性方面均优于传统强化学习算法。具体而言,它降低了高达92.17%的碰撞率,而安全模型仅占主模型参数的27%。
Key Takeaways
- 传统自主驾驶框架在多智能体安全场景中面临平衡安全约束和任务性能的难题。
- 实时量化动态交互风险是一大挑战。
- DRS-RL框架基于安全增强网络马尔可夫决策过程。
- 首次将强弱理论引入多智能体决策制定。
- 通过多智能体动态冲突区域模型准确捕捉时空耦合风险。
- 风险感知优先经验回放机制有助于缓解数据分布偏见。
点此查看论文截图