⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-11 更新
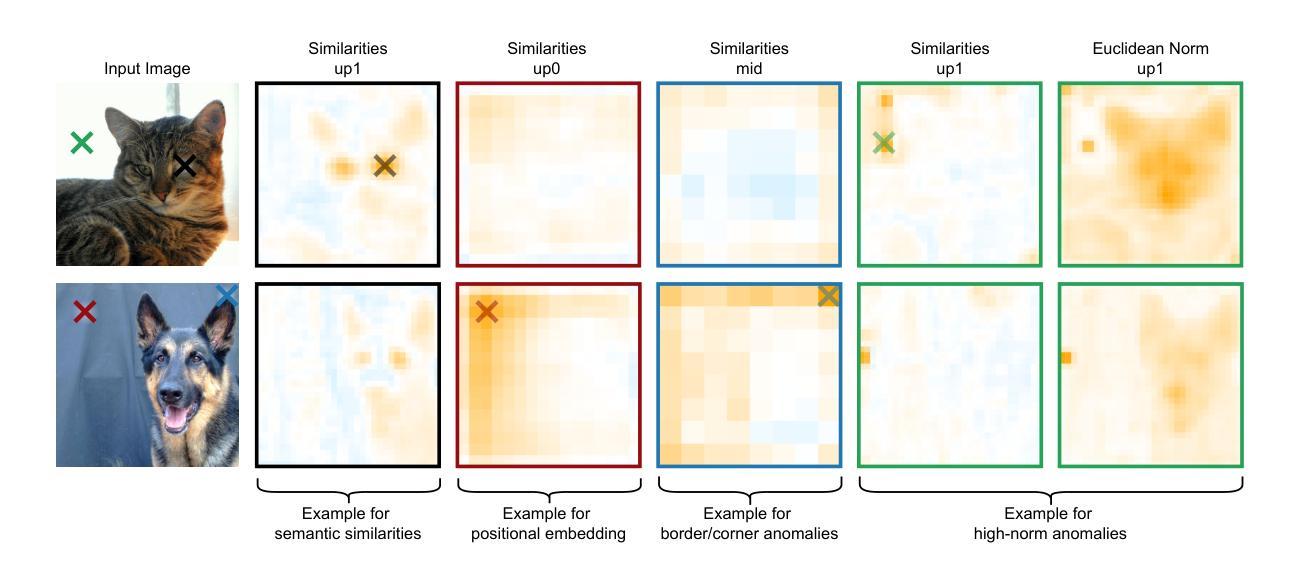
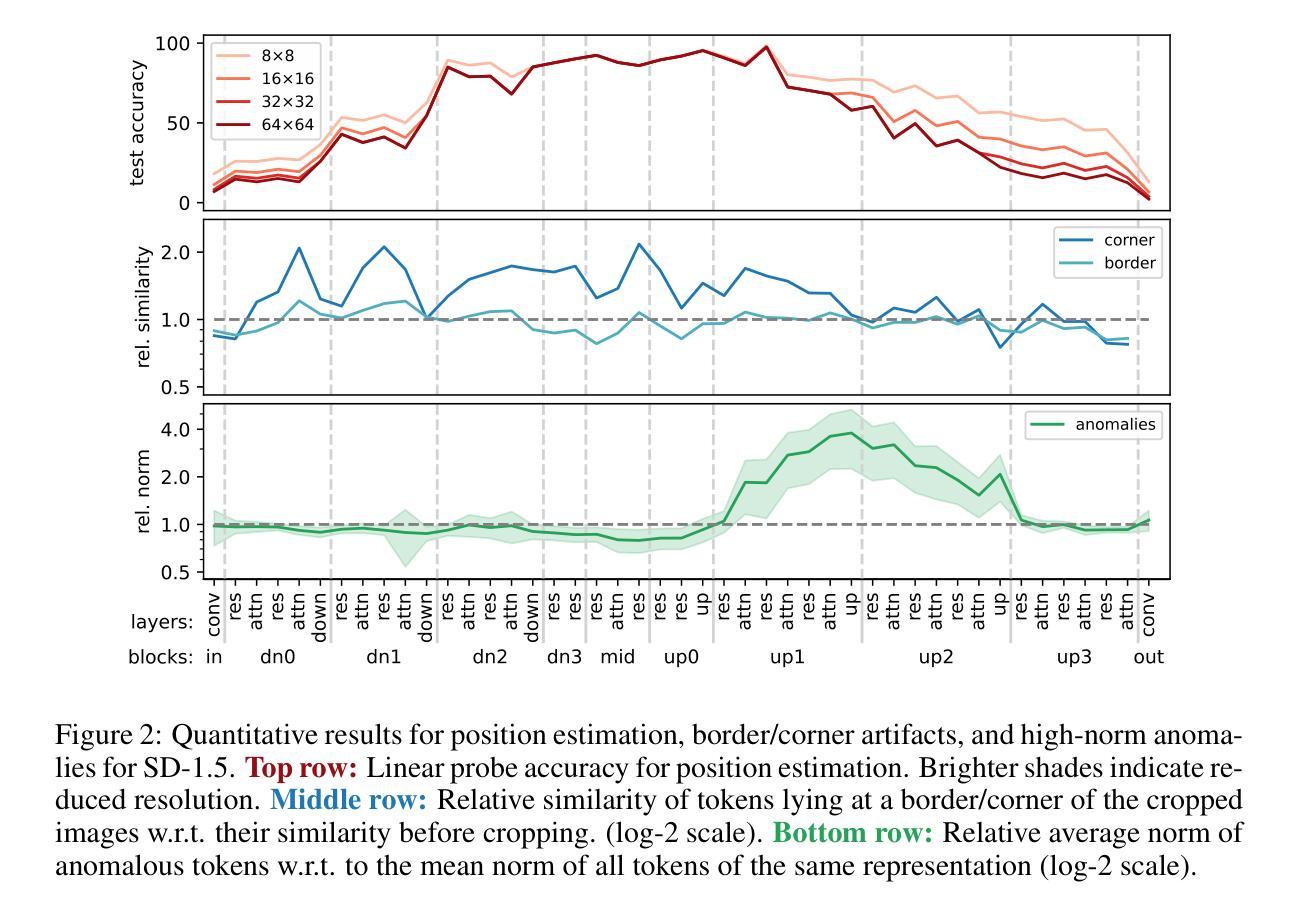
Latent Diffusion U-Net Representations Contain Positional Embeddings and Anomalies
Authors:Jonas Loos, Lorenz Linhardt
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in synthesizing realistic images, spurring interest in using their representations for various downstream tasks. To better understand the robustness of these representations, we analyze popular Stable Diffusion models using representational similarity and norms. Our findings reveal three phenomena: (1) the presence of a learned positional embedding in intermediate representations, (2) high-similarity corner artifacts, and (3) anomalous high-norm artifacts. These findings underscore the need to further investigate the properties of diffusion model representations before considering them for downstream tasks that require robust features. Project page: https://jonasloos.github.io/sd-representation-anomalies
扩散模型在合成逼真图像方面表现出卓越的能力,激发了人们对其表示法用于各种下游任务的兴趣。为了更好地了解这些表示的稳健性,我们通过分析流行的Stable Diffusion模型使用表示相似性规范和准则。我们的研究发现了三种现象:(1)中间表示中存在学习的位置嵌入;(2)高相似度角落伪影;(3)异常高规范伪影。这些发现强调了在考虑将扩散模型表示法用于需要稳健特征的下游任务之前,需要进一步研究其特性。项目页面:https://jonasloos.github.io/sd-representation-anomalies
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 Workshop on Deep Generative Models: Theory, Principle, and Efficacy
Summary
文本探讨了Diffusion模型在合成真实图像方面的出色表现,并分析了其对于多种下游任务的潜在应用价值。针对流行的Stable Diffusion模型,研究通过代表性相似性和范数进行深入分析,揭示了模型存在的学习位置嵌入、高相似性角落异常和高范数异常等三个现象。这些发现强调了进一步探究Diffusion模型特性对于需要稳健特征的下游任务的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion模型在合成真实图像方面表现出卓越的能力。
- Stable Diffusion模型的分析揭示了三个关键现象。
- 模型中存在学习的位置嵌入现象。
- 模型可能出现高相似性角落异常。
- 模型可能表现出异常的高范数特征。
- 在考虑使用Diffusion模型进行需要稳健特征的下游任务之前,需要进一步探究其特性。
点此查看论文截图

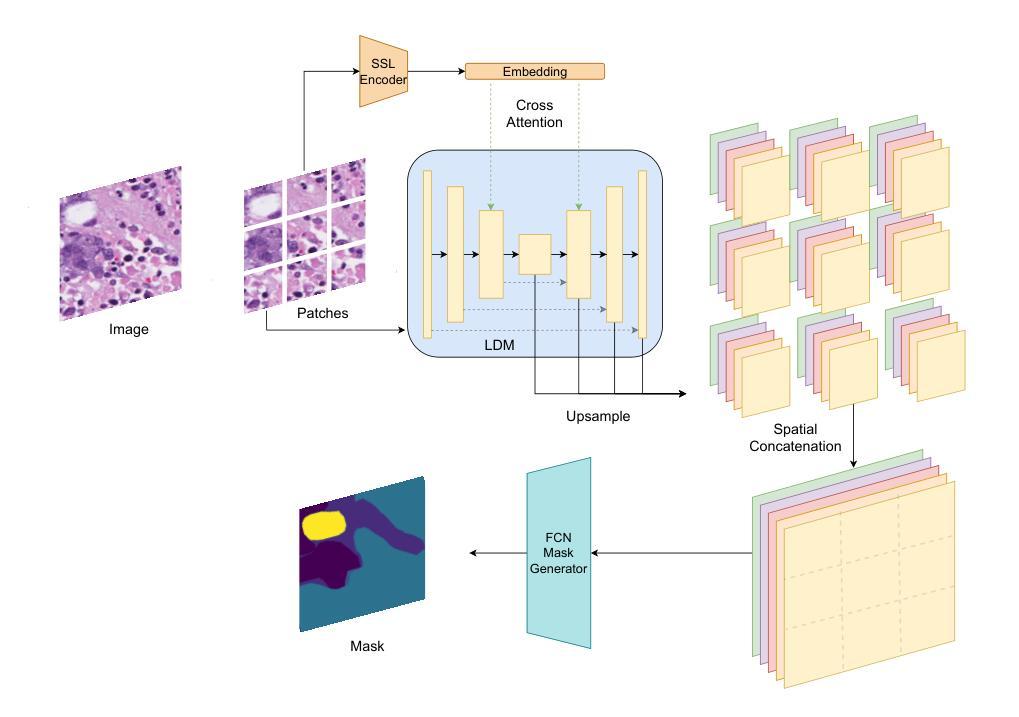
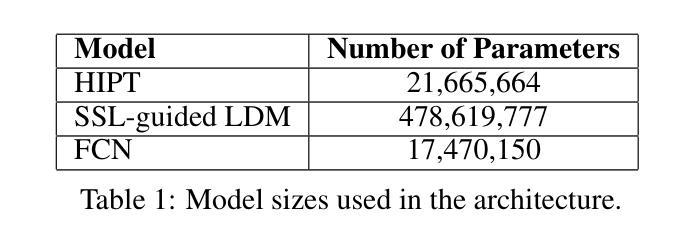
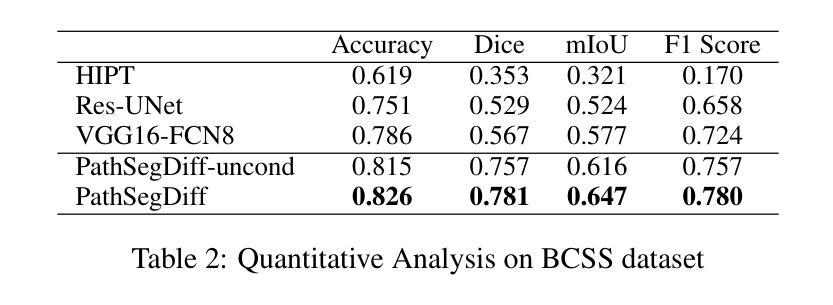
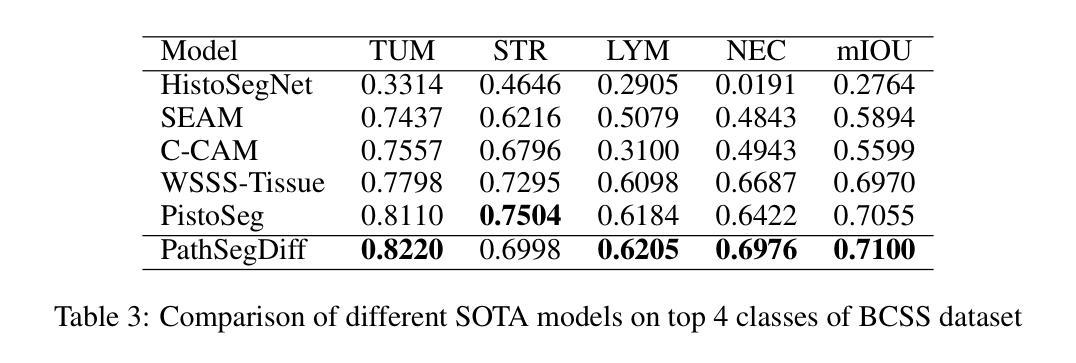
PathSegDiff: Pathology Segmentation using Diffusion model representations
Authors:Sachin Kumar Danisetty, Alexandros Graikos, Srikar Yellapragada, Dimitris Samaras
Image segmentation is crucial in many computational pathology pipelines, including accurate disease diagnosis, subtyping, outcome, and survivability prediction. The common approach for training a segmentation model relies on a pre-trained feature extractor and a dataset of paired image and mask annotations. These are used to train a lightweight prediction model that translates features into per-pixel classes. The choice of the feature extractor is central to the performance of the final segmentation model, and recent literature has focused on finding tasks to pre-train the feature extractor. In this paper, we propose PathSegDiff, a novel approach for histopathology image segmentation that leverages Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) as pre-trained featured extractors. Our method utilizes a pathology-specific LDM, guided by a self-supervised encoder, to extract rich semantic information from H&E stained histopathology images. We employ a simple, fully convolutional network to process the features extracted from the LDM and generate segmentation masks. Our experiments demonstrate significant improvements over traditional methods on the BCSS and GlaS datasets, highlighting the effectiveness of domain-specific diffusion pre-training in capturing intricate tissue structures and enhancing segmentation accuracy in histopathology images.
图像分割在计算病理学流程中非常重要,包括准确的疾病诊断、亚型分类、结果预测和生存预测。训练分割模型的一般方法依赖于预训练的特征提取器和配对图像和掩膜注释的数据集。这些被用来训练一个轻量级的预测模型,该模型将特征转化为像素级别的类别。特征提取器的选择对最终分割模型的性能至关重要,最近的文献主要集中在寻找预训练特征提取器的任务。在本文中,我们提出了PathSegDiff,这是一种新的病理图像分割方法,它利用潜在扩散模型(LDMs)作为预训练的特征提取器。我们的方法利用一个病理特定的LDM,由一个自监督编码器引导,从HE染色的病理图像中提取丰富的语义信息。我们使用一个简单的全卷积网络来处理从LDM提取的特征,并生成分割掩膜。我们的实验在BCSS和GlaS数据集上证明了传统方法的显著改进,突出了领域特定扩散预训练在捕捉复杂组织结构和提高病理图像分割准确性方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于潜在扩散模型(LDM)的病理图像分割新方法PathSegDiff。该方法利用病理特异性LDM和自监督编码器提取H&E染色病理图像的丰富语义信息,并通过全卷积网络生成分割掩膜。实验结果表明,与传统方法相比,该方法在BCSS和GlaS数据集上表现出显著优势,证明了领域特定扩散预训练在捕捉复杂组织结构和提高病理图像分割精度方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 图像分割在计算病理学管道中至关重要,包括准确疾病诊断、分型、结果预测和生存预测。
- 传统方法依赖于预训练的特征提取器和配对图像和掩膜注释数据集来训练轻量级预测模型。
- 特征提取器的选择对最终分割模型的性能至关重要。
- PathSegDiff是一种基于潜在扩散模型(LDM)的新方法,用于病理图像分割。
- PathSegDiff利用病理特异性LDM和自监督编码器提取病理图像的丰富语义信息。
- 实验结果表明,与传统方法相比,PathSegDiff在BCSS和GlaS数据集上表现出显著优势。
点此查看论文截图

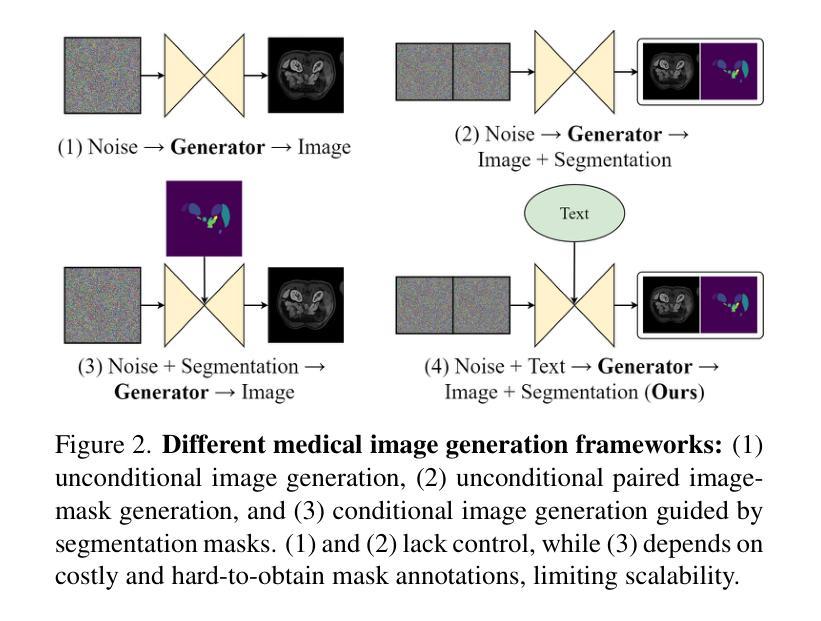
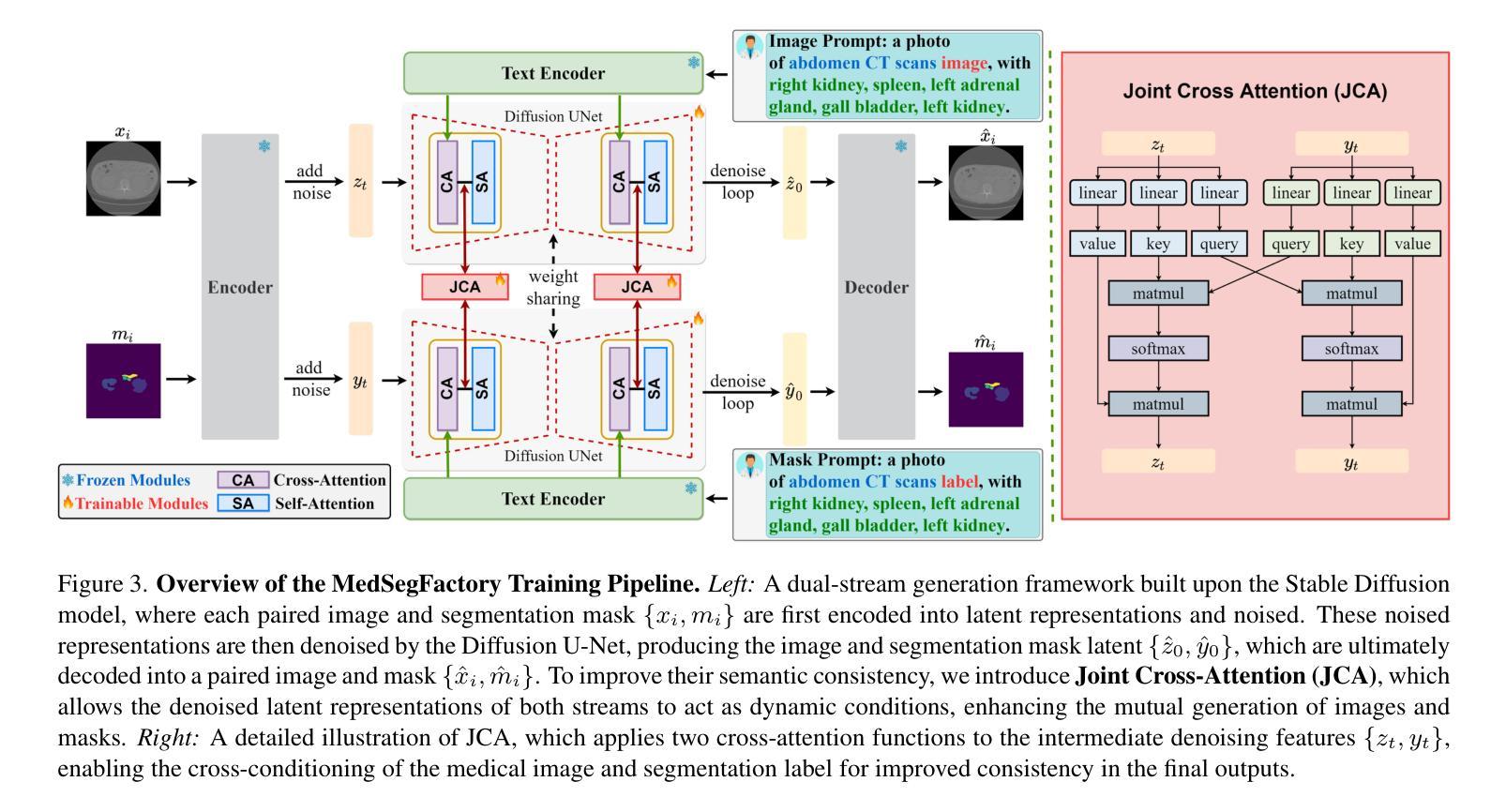
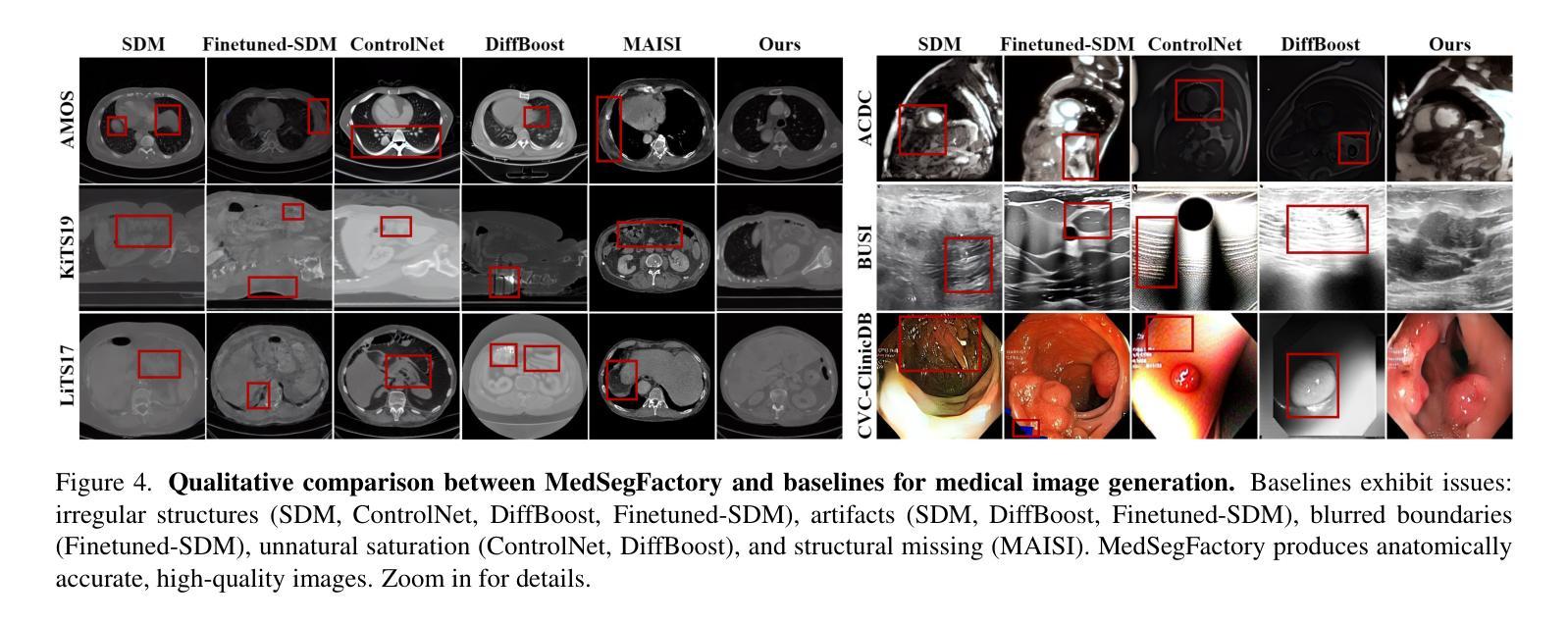
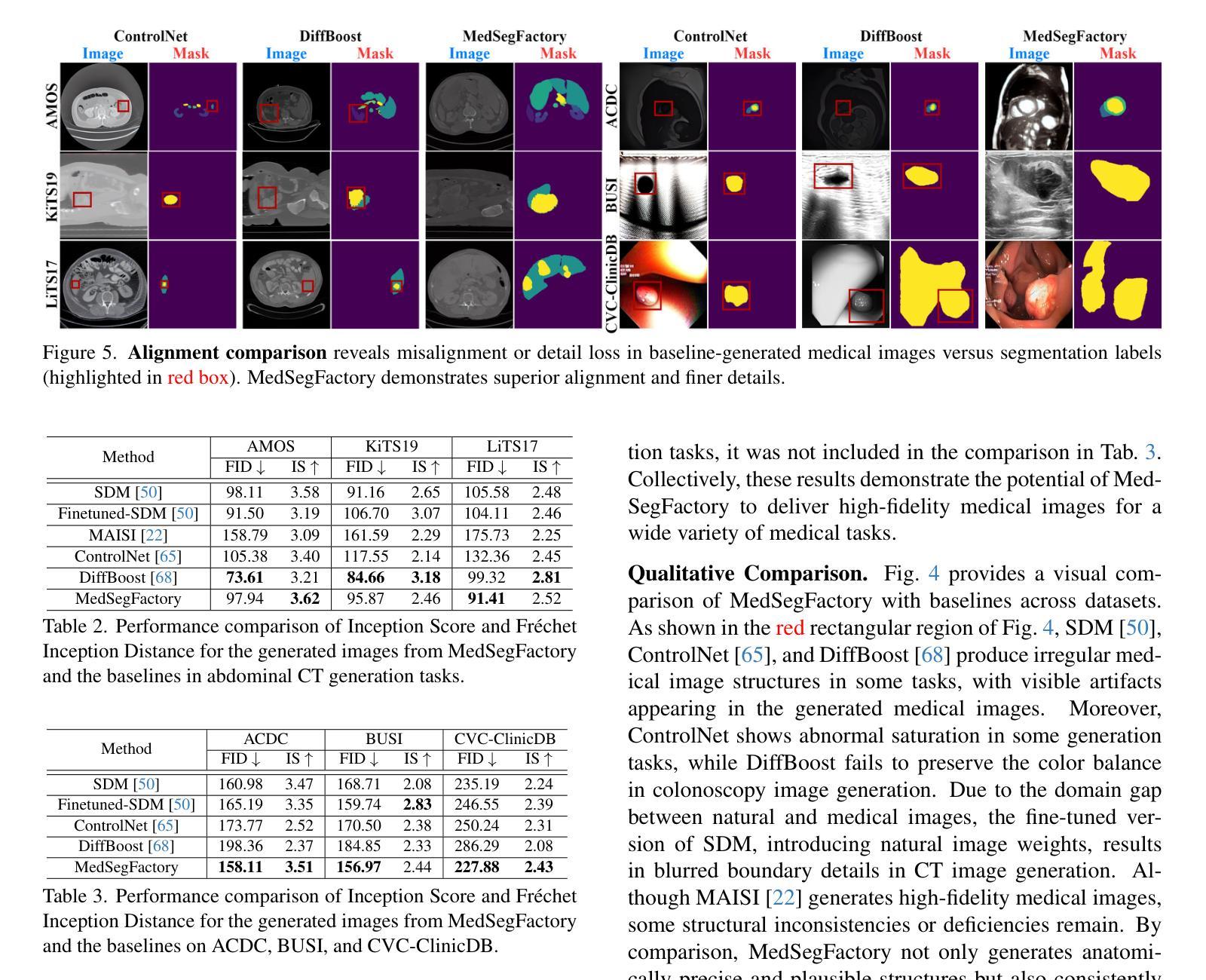
MedSegFactory: Text-Guided Generation of Medical Image-Mask Pairs
Authors:Jiawei Mao, Yuhan Wang, Yucheng Tang, Daguang Xu, Kang Wang, Yang Yang, Zongwei Zhou, Yuyin Zhou
This paper presents MedSegFactory, a versatile medical synthesis framework that generates high-quality paired medical images and segmentation masks across modalities and tasks. It aims to serve as an unlimited data repository, supplying image-mask pairs to enhance existing segmentation tools. The core of MedSegFactory is a dual-stream diffusion model, where one stream synthesizes medical images and the other generates corresponding segmentation masks. To ensure precise alignment between image-mask pairs, we introduce Joint Cross-Attention (JCA), enabling a collaborative denoising paradigm by dynamic cross-conditioning between streams. This bidirectional interaction allows both representations to guide each other’s generation, enhancing consistency between generated pairs. MedSegFactory unlocks on-demand generation of paired medical images and segmentation masks through user-defined prompts that specify the target labels, imaging modalities, anatomical regions, and pathological conditions, facilitating scalable and high-quality data generation. This new paradigm of medical image synthesis enables seamless integration into diverse medical imaging workflows, enhancing both efficiency and accuracy. Extensive experiments show that MedSegFactory generates data of superior quality and usability, achieving competitive or state-of-the-art performance in 2D and 3D segmentation tasks while addressing data scarcity and regulatory constraints.
本文介绍了MedSegFactory,这是一个通用的医学合成框架,能够生成跨模态和任务的高质量配对医学图像和分割掩膜。它的目标是作为一个无限的数据仓库,提供图像-掩膜对,以增强现有的分割工具。MedSegFactory的核心是一个双流扩散模型,其中一个流合成医学图像,另一个流生成相应的分割掩膜。为了确保图像-掩膜对之间的精确对齐,我们引入了联合交叉注意(JCA),通过流之间的动态交叉条件,实现协同去噪模式。这种双向交互允许两种表示相互引导生成,增强生成对之间的一致性。MedSegFactory通过用户定义的提示解锁按需生成的配对医学图像和分割掩膜,这些提示指定目标标签、成像模态、解剖区域和病理状况,促进可扩展和高质量的数据生成。这种新的医学图像合成模式能够无缝融入多样化的医学成像工作流程,提高效率和准确性。大量实验表明,MedSegFactory生成的数据具有卓越的质量和可用性,在二维和三维分割任务中达到了竞争或最先进的性能,同时解决了数据稀缺和监管约束问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures, The project page can be accessed via https://jwmao1.github.io/MedSegFactory_web
Summary
MedSegFactory是一个通用医疗合成框架,能生成跨模态和任务的配对高质量医疗图像和分割掩膜。它旨在作为一个无限的数据仓库,为现有的分割工具提供图像-掩膜对以增强其性能。该框架的核心是双重流扩散模型,一个流负责合成医疗图像,另一个流生成相应的分割掩膜。通过引入联合交叉注意(JCA)机制,确保图像-掩膜对之间的精确对齐。JCA实现了流之间的动态交叉条件,推动协同去噪模式。这种双向交互允许两个表示相互引导生成,提高生成对的一致性。MedSegFactory通过用户定义提示,按需生成配对医疗图像和分割掩膜,提示可指定目标标签、成像模式、解剖区域和病理状况等,促进了高质量数据的可扩展生成。这一新的医疗图像合成范式可无缝融入各种医疗成像工作流程,提高效率和准确性。实验表明,MedSegFactory生成的数据质量高、实用性强,在二维和三维分割任务上达到了竞争或领先水平,同时解决了数据稀缺和监管约束问题。
Key Takeaways
- MedSegFactory是一个医疗合成框架,能生成高质量配对医疗图像和分割掩膜。
- 框架采用双重流扩散模型,分别负责生成医疗图像和分割掩膜。
- 引入联合交叉注意(JCA)机制,确保图像和掩膜之间的精确对齐。
- 用户可以通过定义提示(如目标标签、成像模式等)按需生成数据。
- MedSegFactory能提高医疗成像工作流程的效率和准确性。
- 实验证明,MedSegFactory在数据生成的质量和实用性上表现优异,达到或超越现有水平。
点此查看论文截图

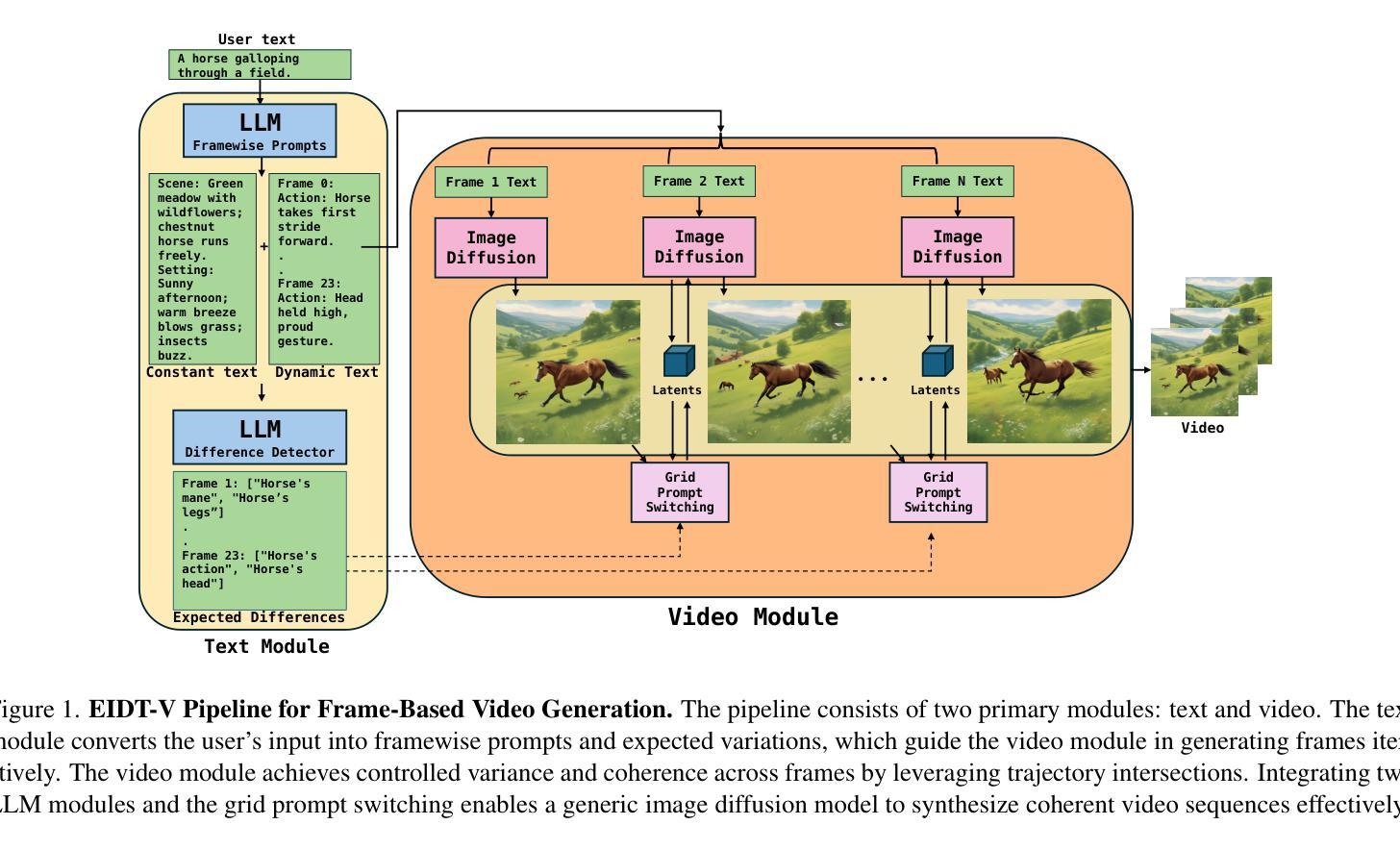
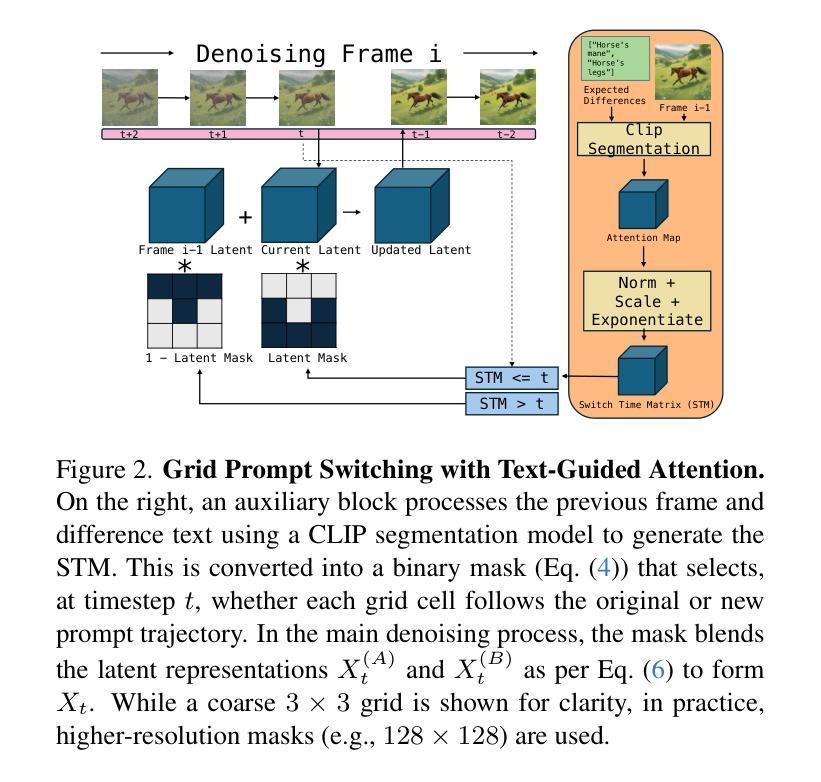
EIDT-V: Exploiting Intersections in Diffusion Trajectories for Model-Agnostic, Zero-Shot, Training-Free Text-to-Video Generation
Authors:Diljeet Jagpal, Xi Chen, Vinay P. Namboodiri
Zero-shot, training-free, image-based text-to-video generation is an emerging area that aims to generate videos using existing image-based diffusion models. Current methods in this space require specific architectural changes to image generation models, which limit their adaptability and scalability. In contrast to such methods, we provide a model-agnostic approach. We use intersections in diffusion trajectories, working only with the latent values. We could not obtain localized frame-wise coherence and diversity using only the intersection of trajectories. Thus, we instead use a grid-based approach. An in-context trained LLM is used to generate coherent frame-wise prompts; another is used to identify differences between frames. Based on these, we obtain a CLIP-based attention mask that controls the timing of switching the prompts for each grid cell. Earlier switching results in higher variance, while later switching results in more coherence. Therefore, our approach can ensure appropriate control between coherence and variance for the frames. Our approach results in state-of-the-art performance while being more flexible when working with diverse image-generation models. The empirical analysis using quantitative metrics and user studies confirms our model’s superior temporal consistency, visual fidelity and user satisfaction, thus providing a novel way to obtain training-free, image-based text-to-video generation.
零样本、无训练、基于图像的文本到视频生成是一个新兴领域,旨在利用现有的基于图像的扩散模型生成视频。目前该领域的方法需要对图像生成模型进行特定的架构更改,这限制了其适应性和可扩展性。与此类方法相比,我们提供了一种与模型无关的方法。我们只使用扩散轨迹的交点,只关注潜在值。仅使用轨迹的交点,我们无法获得局部帧级的一致性和多样性。因此,我们转而使用基于网格的方法。使用上下文训练的LLM生成连贯的帧级提示;另一个用于识别帧之间的差异。基于此,我们获得了基于CLIP的注意力掩码,该掩码控制每个网格单元提示切换的时机。提前切换会导致更高的方差,而延迟切换会导致更高的连贯性。因此,我们的方法可以在帧的连贯性和方差之间实现适当的控制。我们的方法达到了最先进的性能,在处理各种图像生成模型时更加灵活。使用定量指标和用户研究进行的实证分析证实了我们模型在时间上的一致性、视觉保真度和用户满意度方面的优越性,从而为无训练、基于图像的文本到视频生成提供了一种新颖的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于图像的无训练文本转视频生成方法。该方法利用扩散轨迹的交集,结合网格技术和大型语言模型(LLM),实现了在多种图像生成模型中的灵活应用。通过控制切换提示的时间,实现了帧间的一致性和多样性平衡。实证分析显示,该方法在时序一致性、视觉保真度和用户满意度上表现卓越。
Key Takeaways
- 利用图像扩散模型的交集实现零样本训练转视频生成。
- 采用网格技术以增强局部帧级的连贯性和多样性。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLM)生成连贯的帧级提示和识别帧间差异。
- 通过控制切换提示的时间,实现了帧间连贯性和多样性的平衡。
- 方法具有高度的模型适应性,可在多种图像生成模型中灵活应用。
- 实证分析显示,该方法在性能上达到最新水平,具有出色的时序一致性、视觉保真度和用户满意度。
点此查看论文截图


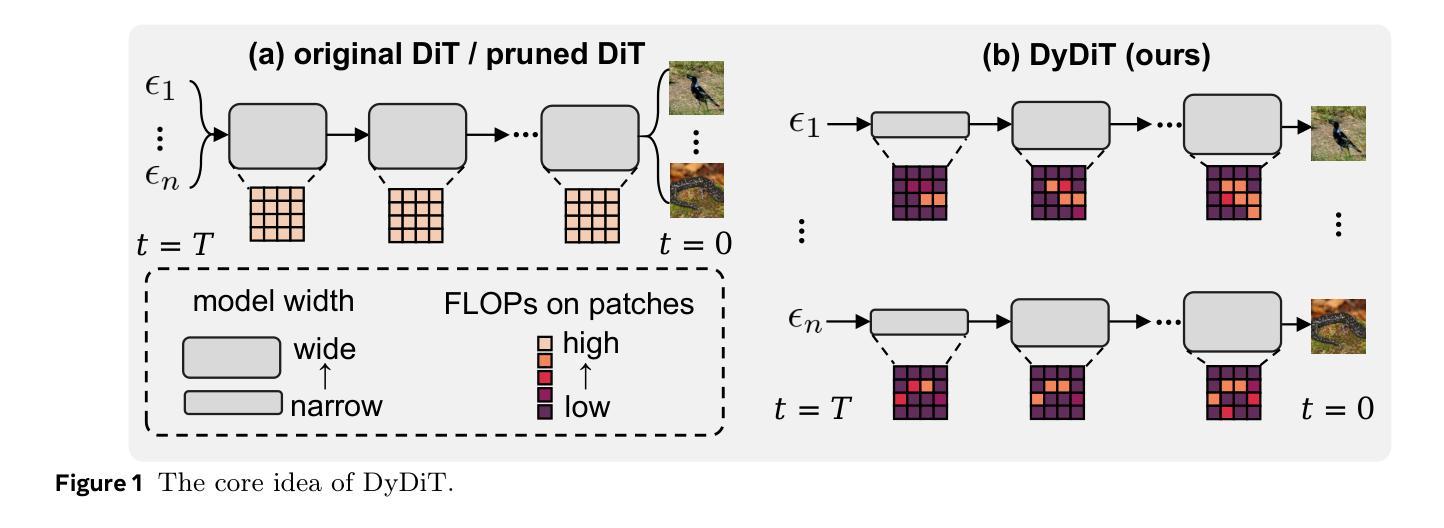
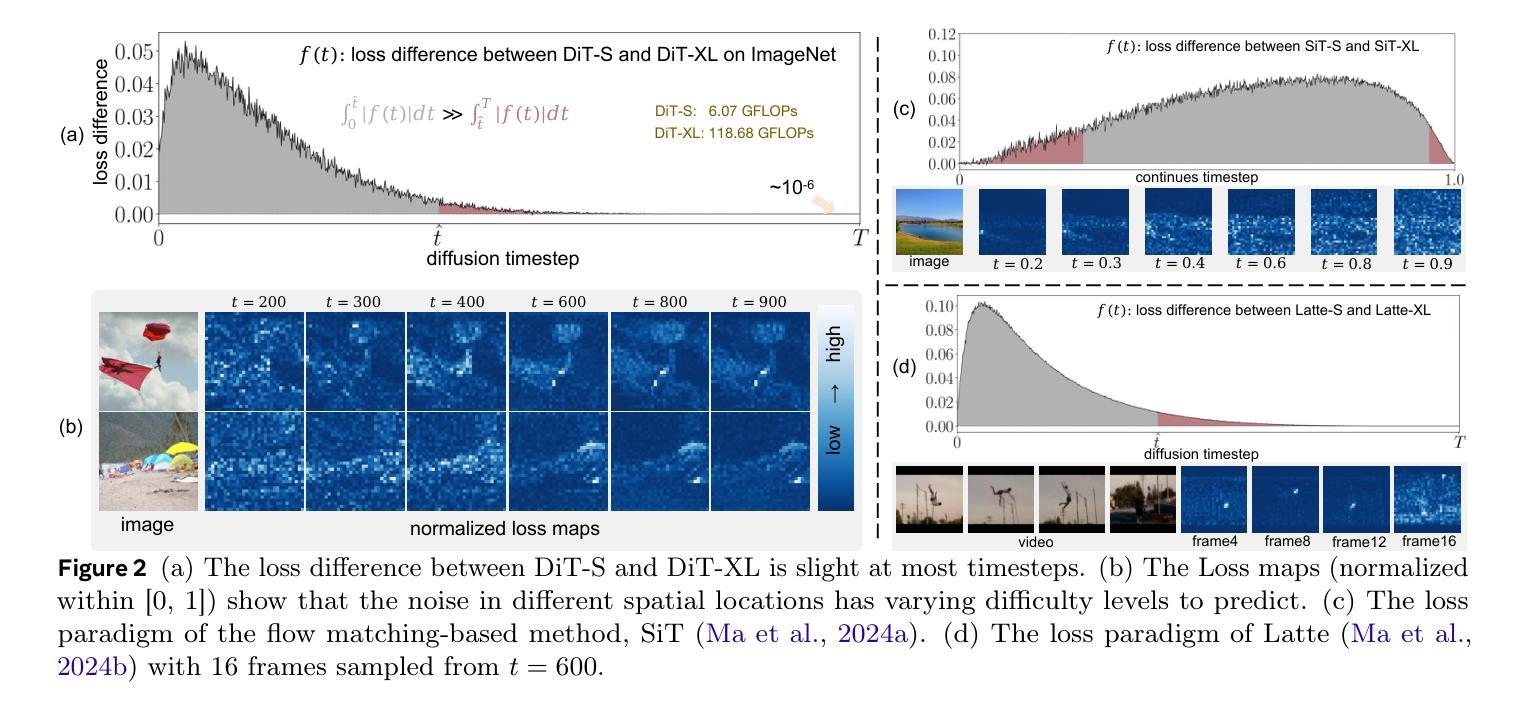
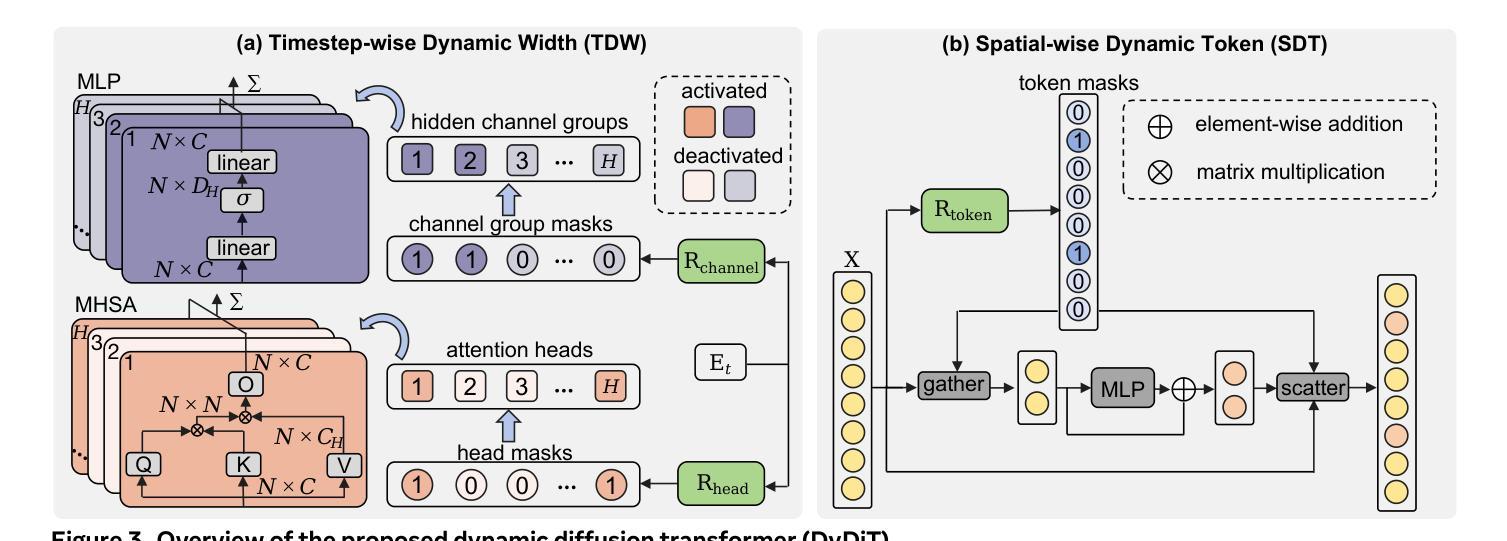
DyDiT++: Dynamic Diffusion Transformers for Efficient Visual Generation
Authors:Wangbo Zhao, Yizeng Han, Jiasheng Tang, Kai Wang, Hao Luo, Yibing Song, Gao Huang, Fan Wang, Yang You
Diffusion Transformer (DiT), an emerging diffusion model for visual generation, has demonstrated superior performance but suffers from substantial computational costs. Our investigations reveal that these costs primarily stem from the \emph{static} inference paradigm, which inevitably introduces redundant computation in certain \emph{diffusion timesteps} and \emph{spatial regions}. To overcome this inefficiency, we propose \textbf{Dy}namic \textbf{Di}ffusion \textbf{T}ransformer (DyDiT), an architecture that \emph{dynamically} adjusts its computation along both \emph{timestep} and \emph{spatial} dimensions. Specifically, we introduce a \emph{Timestep-wise Dynamic Width} (TDW) approach that adapts model width conditioned on the generation timesteps. In addition, we design a \emph{Spatial-wise Dynamic Token} (SDT) strategy to avoid redundant computation at unnecessary spatial locations. TDW and SDT can be seamlessly integrated into DiT and significantly accelerates the generation process. Building on these designs, we further enhance DyDiT in three key aspects. First, DyDiT is integrated seamlessly with flow matching-based generation, enhancing its versatility. Furthermore, we enhance DyDiT to tackle more complex visual generation tasks, including video generation and text-to-image generation, thereby broadening its real-world applications. Finally, to address the high cost of full fine-tuning and democratize technology access, we investigate the feasibility of training DyDiT in a parameter-efficient manner and introduce timestep-based dynamic LoRA (TD-LoRA). Extensive experiments on diverse visual generation models, including DiT, SiT, Latte, and FLUX, demonstrate the effectiveness of DyDiT.
扩散Transformer(DiT)是一种新兴的视觉生成扩散模型,它表现出卓越的性能,但计算成本较高。我们的调查表明,这些成本主要源于\emph{静态}推理范式,这种范式不可避免地会在某些\emph{扩散时间步}和\emph{空间区域}中引入冗余计算。为了克服这种低效,我们提出了\textbf{Dy}namic \textbf{Di}ffusion \textbf{T}ransformer(DyDiT),这是一种\emph{动态}调整其在\emph{时间步}和\emph{空间}维度上计算的结构。具体来说,我们引入了一种\emph{时间步动态宽度}(TDW)方法,根据生成时间步来适应模型宽度。此外,我们设计了一种\emph{空间动态令牌}(SDT)策略,以避免在不必要的空间位置进行冗余计算。TDW和SDT可以无缝集成到DiT中,并显著加速生成过程。基于这些设计,我们从三个方面进一步增强了DyDiT。首先,DyDiT可以无缝集成与流匹配生成技术,增强其通用性。此外,我们增强了DyDiT,以解决更复杂的视觉生成任务,包括视频生成和文本到图像生成,从而扩大了其在现实世界中的应用。最后,为了解决全精细调整的高成本并实现技术的民主化,我们研究了以参数高效的方式训练DyDiT的可行性,并引入了基于时间步的动态LoRA(TD-LoRA)。在包括DiT、SiT、Latte和FLUX等多种视觉生成模型上的广泛实验证明了DyDiT的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Extended journal version for ICLR. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2410.03456
摘要
扩散Transformer(DiT)作为视觉生成的扩散模型展现出卓越性能,但计算成本较高。研究发现,这些成本主要源于静态推理范式,它在某些扩散时间步长和空间区域中不可避免地引入了冗余计算。为了克服这一不足,我们提出了动态扩散Transformer(DyDiT),它能够在时序和空间维度上动态调整计算。具体来说,我们引入了时间步长动态宽度(TDW)方法,根据生成时间步长自适应调整模型宽度。此外,我们设计了空间动态令牌(SDT)策略,以避免不必要空间位置的冗余计算。TDW和SDT可以无缝集成到DiT中,显著加速生成过程。在此基础上,我们进一步从三个方面增强DyDiT。首先,DyDiT可以与基于流匹配的生成方法无缝集成,提高其通用性。其次,我们增强DyDiT以处理更复杂的视觉生成任务,包括视频生成和文本到图像生成,从而扩大其在现实世界中的应用。最后,为了解决全精细调整的高成本并实现技术普及,我们研究了以参数高效的方式训练DyDiT的可行性,并引入了基于时间步长的动态LoRA(TD-LoRA)。在多种视觉生成模型上的广泛实验证明了DyDiT的有效性。
关键见解
- 扩散Transformer(DiT)在视觉生成任务中表现出卓越性能,但存在高计算成本问题。
- 高计算成本主要源于静态推理范式,导致某些扩散时间步长和空间区域的冗余计算。
- 提出了动态扩散Transformer(DyDiT)架构,能够动态调整计算以适应时间步长和空间维度。
- 通过引入时间步长动态宽度(TDW)和空间动态令牌(SDT)策略,实现了在DiT中的无缝集成并显著加速生成过程。
- DyDiT与基于流匹配的生成方法无缝集成,提高其通用性,并能处理更复杂的视觉生成任务,如视频和文本到图像生成。
- 为了降低训练成本,研究了参数高效的训练方法,并引入了基于时间步长的动态LoRA(TD-LoRA)。
- 在多种视觉生成模型上的实验证明了DyDiT的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

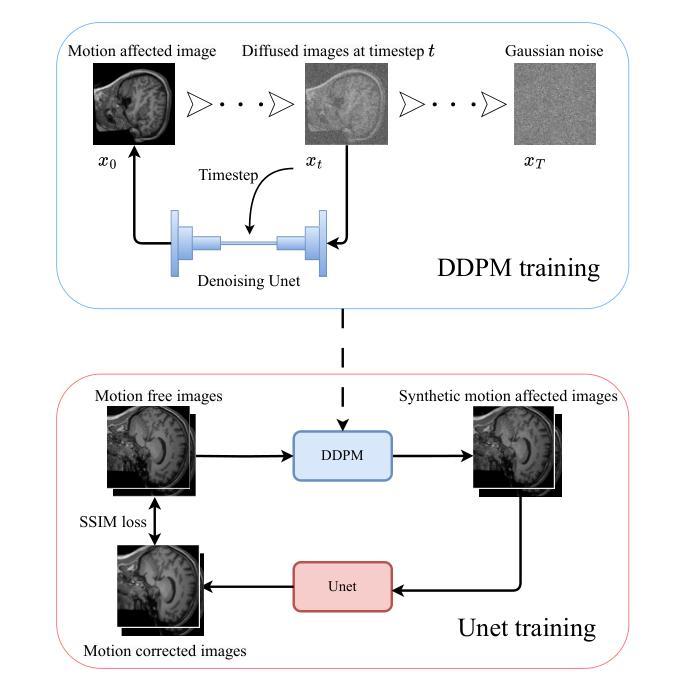
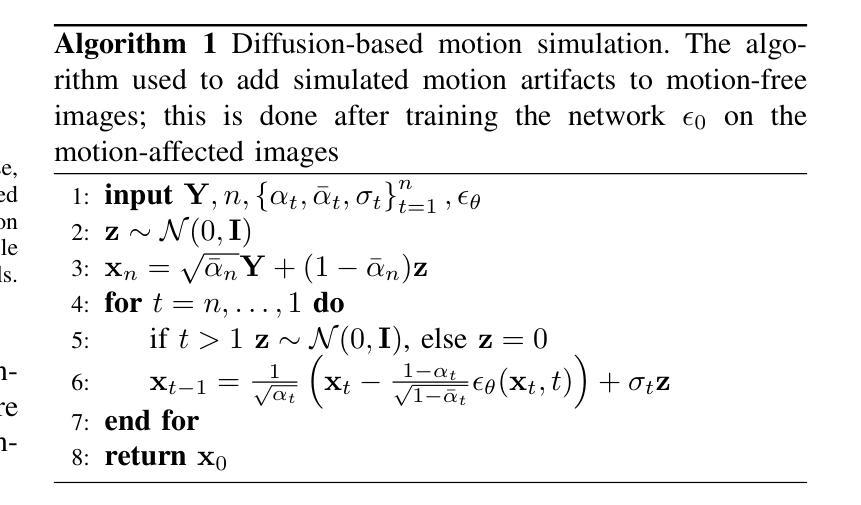
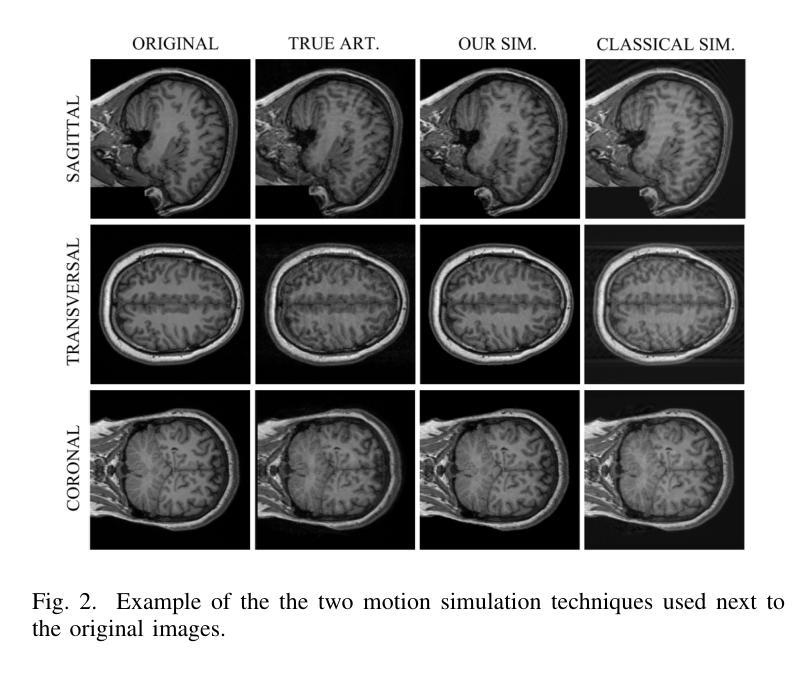
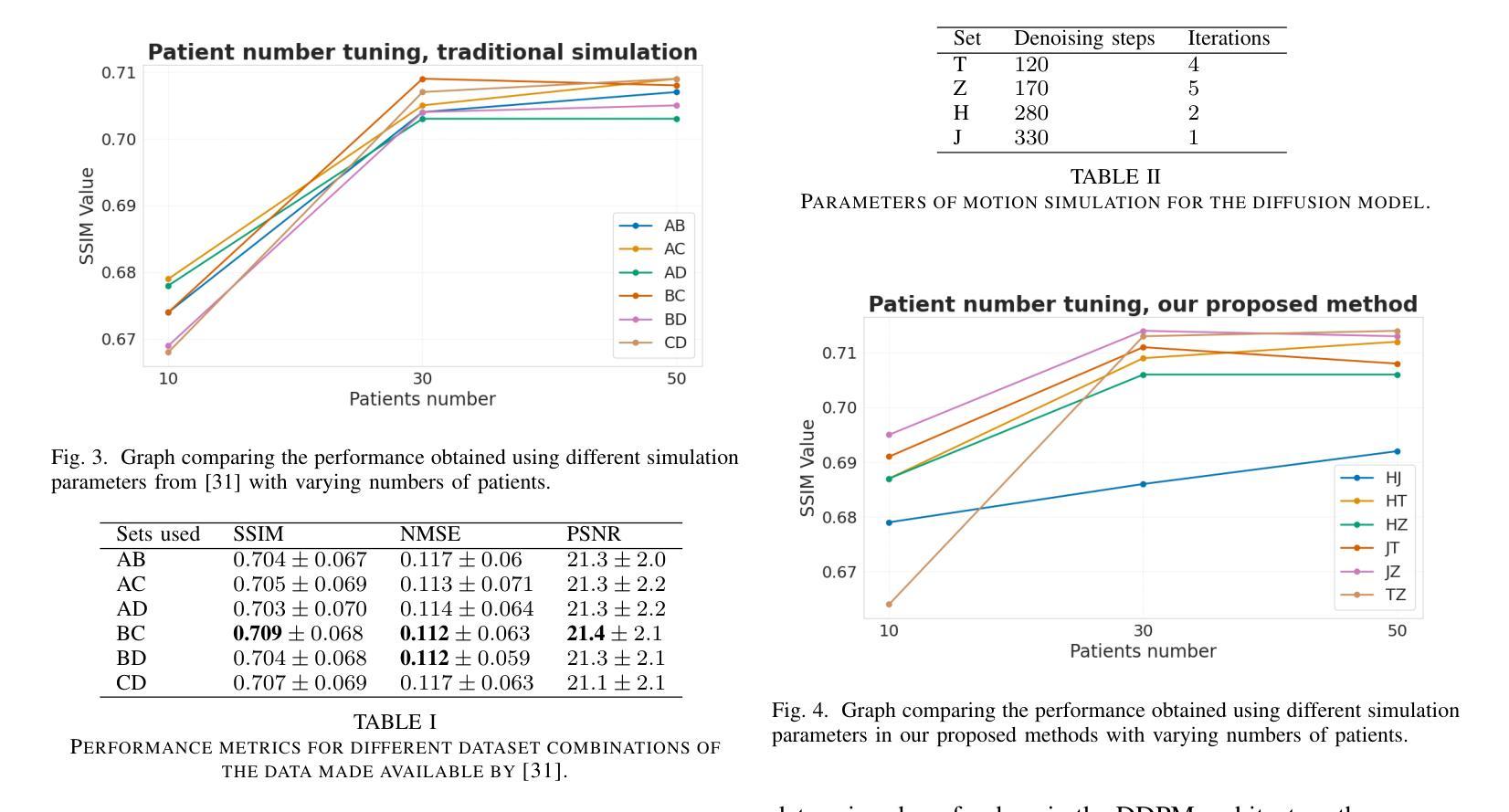
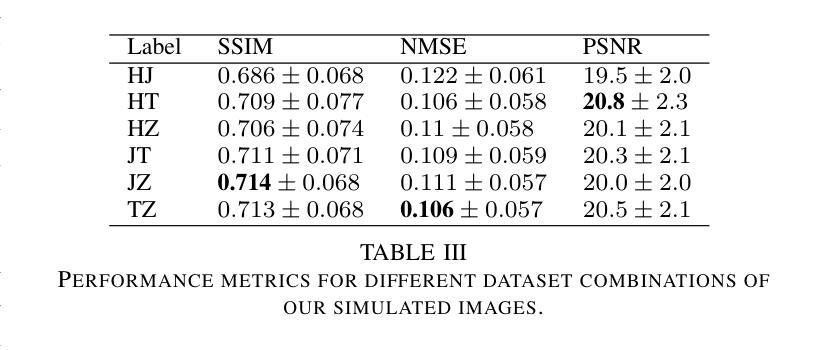
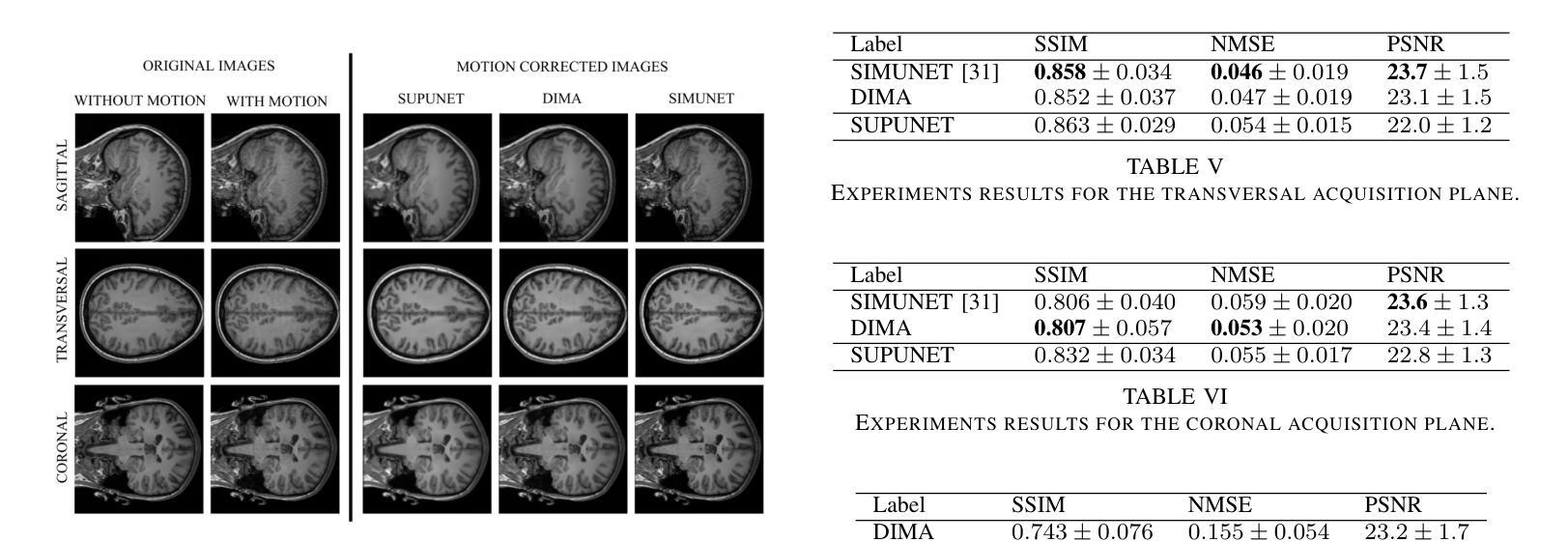
DIMA: DIffusing Motion Artifacts for unsupervised correction in brain MRI images
Authors:Paolo Angella, Luca Balbi, Fabrizio Ferrando, Paolo Traverso, Rosario Varriale, Vito Paolo Pastore, Matteo Santacesaria
Motion artifacts remain a significant challenge in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), compromising diagnostic quality and potentially leading to misdiagnosis or repeated scans. Existing deep learning approaches for motion artifact correction typically require paired motion-free and motion-affected images for training, which are rarely available in clinical settings. To overcome this requirement, we present DIMA (DIffusing Motion Artifacts), a novel framework that leverages diffusion models to enable unsupervised motion artifact correction in brain MRI. Our two-phase approach first trains a diffusion model on unpaired motion-affected images to learn the distribution of motion artifacts. This model then generates realistic motion artifacts on clean images, creating paired datasets suitable for supervised training of correction networks. Unlike existing methods, DIMA operates without requiring k-space manipulation or detailed knowledge of MRI sequence parameters, making it adaptable across different scanning protocols and hardware. Comprehensive evaluations across multiple datasets and anatomical planes demonstrate that our method achieves comparable performance to state-of-the-art supervised approaches while offering superior generalizability to real clinical data. DIMA represents a significant advancement in making motion artifact correction more accessible for routine clinical use, potentially reducing the need for repeat scans and improving diagnostic accuracy.
磁共振成像(MRI)中的运动伪影仍然是一个重大挑战,会影响诊断质量,并可能导致误诊或重复扫描。现有的用于运动伪影校正的深度学习方法通常要求配对无运动和受运动影响的图像进行训练,这在临床环境中很少可用。为了克服这一要求,我们提出了DIMA(扩散运动伪影),这是一个利用扩散模型实现磁共振成像中无监督运动伪影校正的新框架。我们的两阶段方法首先使用未配对的受运动影响的图像训练扩散模型,以学习运动伪影的分布。然后,该模型在干净的图像上生成逼真的运动伪影,创建适合监督校正网络训练的配对数据集。与现有方法不同,DIMA无需进行k空间操作或对MRI序列参数有深入了解,因此可适应不同的扫描协议和硬件。在多数据集和解剖平面的综合评估表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的监督方法的性能,同时在真实临床数据上提供了更好的泛化能力。DIMA在使运动伪影校正更易于常规临床使用方面取得了重大进展,有望减少重复扫描的需要,提高诊断的准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 5 figures, 7 tables
Summary
磁共振成像中的运动伪影是一大挑战,影响诊断质量,可能导致误诊或重复扫描。现有深度学习方法需要配对无运动影响的图像和运动影响的图像进行训练,这在临床环境中很少见。为解决这一问题,我们提出了DIMA(扩散运动伪影),一种利用扩散模型实现磁共振成像中大脑运动伪影的无监督校正的新框架。我们的两阶段方法首先训练一个扩散模型来学习运动伪影的分布。然后该模型在清洁图像上生成逼真的运动伪影,创建适合校正网络监督训练的配对数据集。不同于现有方法,DIMA不需要操作k空间或深入了解磁共振成像序列参数,具有不同扫描协议和硬件的适应性。在多数据集和解剖平面上的综合评估表明,我们的方法与最先进的监督方法相比取得了相当的性能,在实际临床数据上表现出更好的泛化能力。DIMA为常规临床使用中的运动伪影校正提供了更便捷的访问方式,可能减少重复扫描的需要,提高诊断准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 运动伪影是磁共振成像中的一大挑战,影响诊断质量。
- 现有深度学习方法通常需要配对的数据集进行训练,这在临床环境中难以实现。
- DIMA框架利用扩散模型进行无监督运动伪影校正,无需配对数据集。
- DIMA通过训练扩散模型学习运动伪影的分布,并在清洁图像上生成逼真的运动伪影。
- DIMA适用于不同的扫描协议和硬件,具有广泛的适应性。
- 综合评估显示,DIMA方法与最先进的监督方法性能相当,并在实际临床数据上表现出更好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

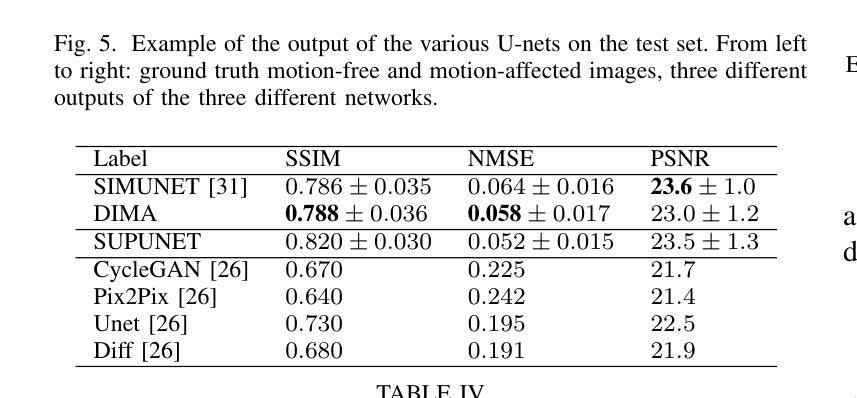
Compass Control: Multi Object Orientation Control for Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Rishbuh Parihar, Vaibhav Agrawal, Sachidanand VS, R. Venkatesh Babu
Existing approaches for controlling text-to-image diffusion models, while powerful, do not allow for explicit 3D object-centric control, such as precise control of object orientation. In this work, we address the problem of multi-object orientation control in text-to-image diffusion models. This enables the generation of diverse multi-object scenes with precise orientation control for each object. The key idea is to condition the diffusion model with a set of orientation-aware \textbf{compass} tokens, one for each object, along with text tokens. A light-weight encoder network predicts these compass tokens taking object orientation as the input. The model is trained on a synthetic dataset of procedurally generated scenes, each containing one or two 3D assets on a plain background. However, direct training this framework results in poor orientation control as well as leads to entanglement among objects. To mitigate this, we intervene in the generation process and constrain the cross-attention maps of each compass token to its corresponding object regions. The trained model is able to achieve precise orientation control for a) complex objects not seen during training and b) multi-object scenes with more than two objects, indicating strong generalization capabilities. Further, when combined with personalization methods, our method precisely controls the orientation of the new object in diverse contexts. Our method achieves state-of-the-art orientation control and text alignment, quantified with extensive evaluations and a user study.
现有文本到图像扩散模型的控制方法虽然强大,但无法实现明确的3D对象中心控制,例如无法精确控制对象的方向。在这项工作中,我们解决了文本到图像扩散模型中的多对象方向控制问题。这能够实现为每个对象提供精确方向控制的多样化多对象场景生成。主要思想是使用一组方向感知的指南针标记符来条件化扩散模型,每个对象一个,以及文本标记符。一个轻量级的编码器网络以对象方向作为输入来预测这些指南针标记符。该模型是在合成数据集上训练的,该数据集包含程序生成的场景,每个场景都包含一个或两个在纯色背景上的3D资产。然而,直接训练此框架会导致方向控制不佳以及对象之间的纠缠。为了缓解这个问题,我们在生成过程中进行干预,并约束每个指南针标记符的交叉注意力图到其对应的对象区域。训练好的模型能够对以下方面实现精确的方向控制:训练期间未见到的复杂对象以及具有超过两个对象的多个对象场景,这显示了强大的泛化能力。此外,当与个人化方法相结合时,我们的方法能够在各种背景下精确地控制新对象的方向。我们的方法实现了业界最佳的方向控制和文本对齐,这已通过广泛评估和用户体验得到了验证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://rishubhpar.github.io/compasscontrol
Summary
本文解决了文本到图像扩散模型中多对象方向控制的问题,通过引入方向感知指南针令牌,实现对每个对象精确的方向控制,生成多样化多对象场景。训练模型能够在复杂对象及多对象场景中实现精确的方向控制,并与个性化方法结合,实现新对象在多样化上下文中的精确方向控制。
Key Takeaways
- 引入指南针令牌以实现文本到图像扩散模型中多对象的精确方向控制。
- 通过轻量级编码器网络预测每个对象的指南针令牌。
- 模型在合成数据集上进行训练,包含单个或两个3D资产在平面背景上的场景。
- 通过干预生成过程并约束每个指南针令牌的跨注意力图,解决方向控制及对象纠缠问题。
- 模型对未见过的复杂对象及多对象场景实现精确方向控制,展现出强大的泛化能力。
- 与个性化方法结合,实现在多样化上下文中的新对象精确方向控制。
点此查看论文截图



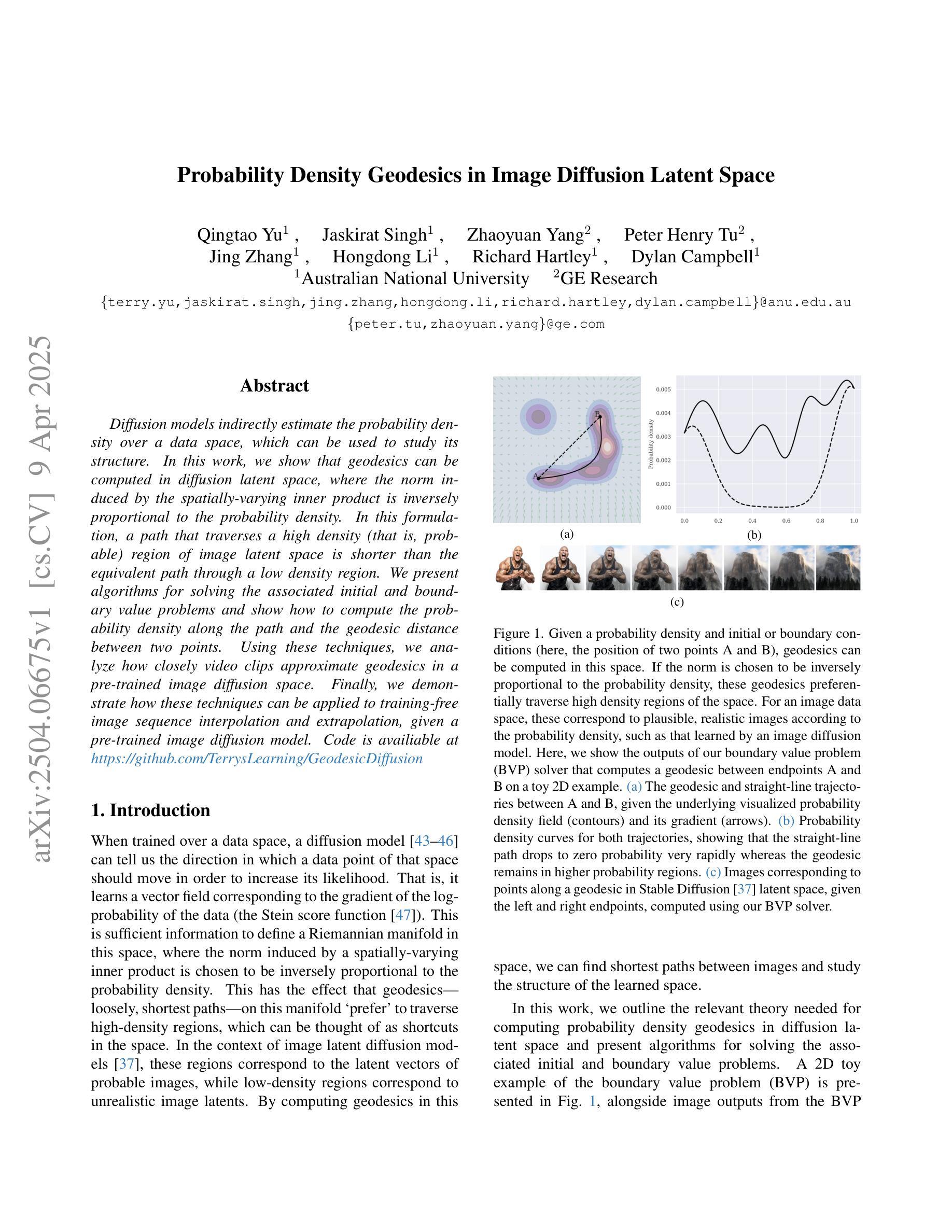
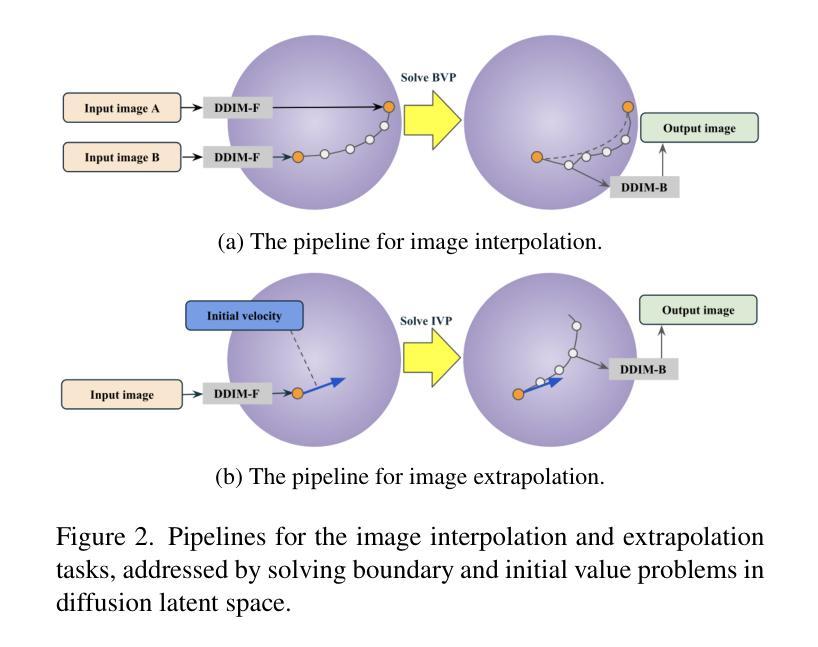
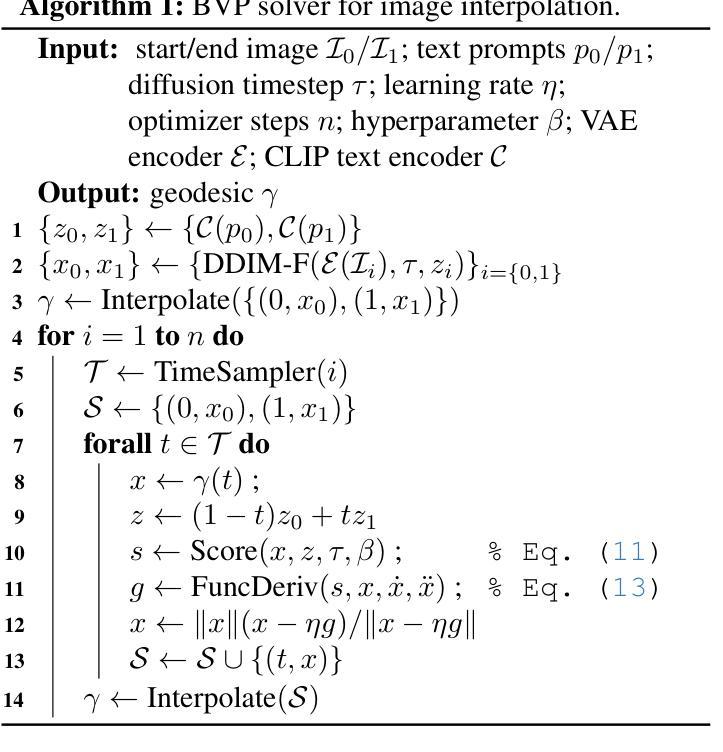
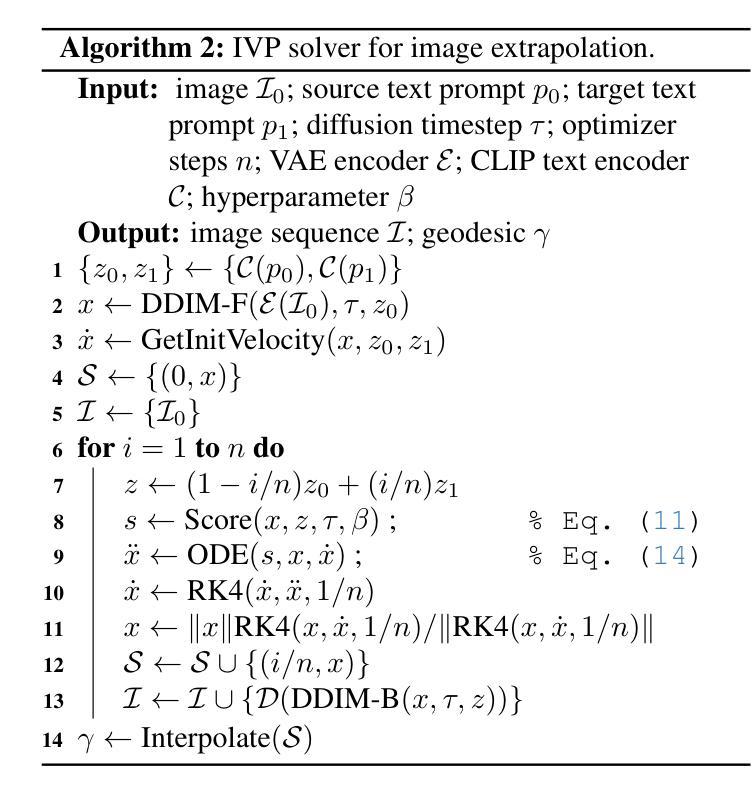
Probability Density Geodesics in Image Diffusion Latent Space
Authors:Qingtao Yu, Jaskirat Singh, Zhaoyuan Yang, Peter Henry Tu, Jing Zhang, Hongdong Li, Richard Hartley, Dylan Campbell
Diffusion models indirectly estimate the probability density over a data space, which can be used to study its structure. In this work, we show that geodesics can be computed in diffusion latent space, where the norm induced by the spatially-varying inner product is inversely proportional to the probability density. In this formulation, a path that traverses a high density (that is, probable) region of image latent space is shorter than the equivalent path through a low density region. We present algorithms for solving the associated initial and boundary value problems and show how to compute the probability density along the path and the geodesic distance between two points. Using these techniques, we analyze how closely video clips approximate geodesics in a pre-trained image diffusion space. Finally, we demonstrate how these techniques can be applied to training-free image sequence interpolation and extrapolation, given a pre-trained image diffusion model.
扩散模型通过间接估计数据空间的概率密度,可用于研究其结构。在这项工作中,我们展示了如何在扩散潜在空间中计算测地线,其中由空间变化的内积引起的范数与概率密度成反比。在这种表述中,遍历图像潜在空间的高密度(即可能的)区域的路径比通过低密度区域的等效路径更短。我们提出了解决相关初始值和边界值问题的算法,并展示了如何计算路径上的概率密度以及两点之间的测地距离。使用这些技术,我们分析了视频剪辑在预训练的图像扩散空间中如何近似测地线。最后,我们展示了如何在给定预训练的图像扩散模型的情况下,将这些技术应用于无训练图像序列的插值和外推。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025
Summary
扩散模型通过估计数据空间的概率密度来研究其结构。本研究中,我们在扩散潜在空间计算测地线,其中由空间变化内积诱导的范数与概率密度成反比。在高密度区域(即可能的)图像潜在空间中的路径比低密度区域的等效路径更短。我们提出了解决相关初始和边界值问题的算法,并展示了如何计算路径上的概率密度和两点之间的测地距离。利用这些技术,我们分析了视频剪辑在预训练图像扩散空间中的测地线路近似程度。最后,我们展示了如何在给定预训练图像扩散模型的情况下,将这些技术应用于无训练图像序列的插值和预测。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型能够估计数据空间的概率密度,用于研究其结构。
- 在扩散潜在空间中可以计算测地线,其中范数与概率密度成反比。
- 高密度区域的图像潜在空间路径比低密度区域更短。
- 提出了解决初始和边界值问题的算法来计算路径上的概率密度和两点之间的测地距离。
- 视频剪辑在预训练图像扩散空间中的路径可近似为测地线。
- 所提技术可用于无训练图像序列的插值。
点此查看论文截图
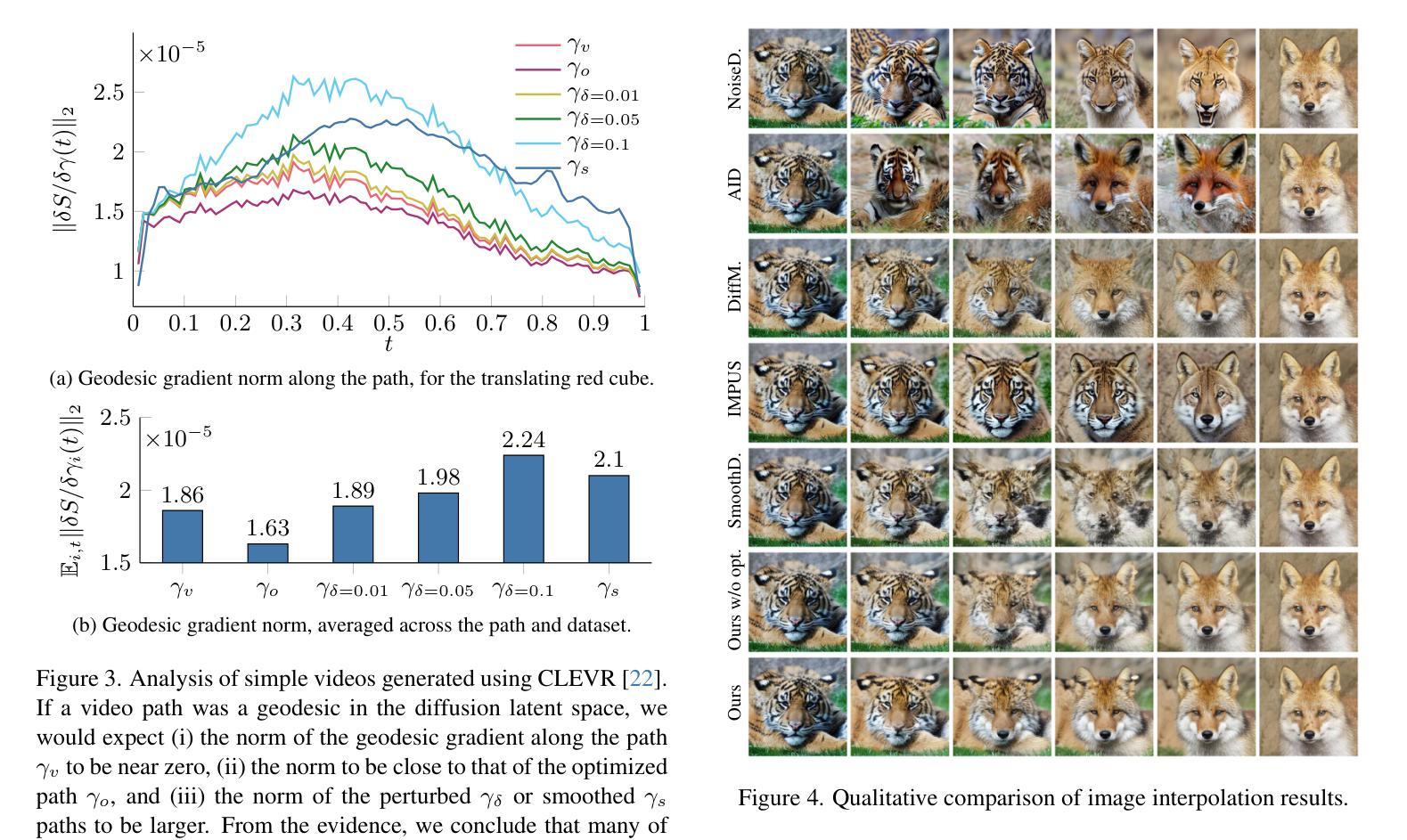
Meta-LoRA: Meta-Learning LoRA Components for Domain-Aware ID Personalization
Authors:Barış Batuhan Topal, Umut Özyurt, Zafer Doğan Budak, Ramazan Gokberk Cinbis
Recent advancements in text-to-image generative models, particularly latent diffusion models (LDMs), have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in synthesizing high-quality images from textual prompts. However, achieving identity personalization-ensuring that a model consistently generates subject-specific outputs from limited reference images-remains a fundamental challenge. To address this, we introduce Meta-Low-Rank Adaptation (Meta-LoRA), a novel framework that leverages meta-learning to encode domain-specific priors into LoRA-based identity personalization. Our method introduces a structured three-layer LoRA architecture that separates identity-agnostic knowledge from identity-specific adaptation. In the first stage, the LoRA Meta-Down layers are meta-trained across multiple subjects, learning a shared manifold that captures general identity-related features. In the second stage, only the LoRA-Mid and LoRA-Up layers are optimized to specialize on a given subject, significantly reducing adaptation time while improving identity fidelity. To evaluate our approach, we introduce Meta-PHD, a new benchmark dataset for identity personalization, and compare Meta-LoRA against state-of-the-art methods. Our results demonstrate that Meta-LoRA achieves superior identity retention, computational efficiency, and adaptability across diverse identity conditions. Our code, model weights, and dataset are released on barisbatuhan.github.io/Meta-LoRA.
近期文本到图像生成模型的进展,尤其是潜在扩散模型(LDMs),已经显示出从文本提示合成高质量图像方面的显著能力。然而,实现身份个性化——确保模型从有限的参考图像中一致地生成特定主题的输出——仍然是一个基本挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了Meta-Low-Rank Adaptation(Meta-LoRA),这是一个利用元学习将领域特定先验编码到基于LoRA的身份个性化的新型框架。我们的方法引入了一个结构化的三层LoRA架构,将身份无关的知识与身份特定的适应分离。在第一阶段,LoRA Meta-Down层在多个主题之间进行元训练,学习一个共享流形,以捕获与身份相关的通用特征。在第二阶段,仅优化LoRA-Mid和LoRA-Up层以针对给定主题进行专业化处理,这显著减少了适应时间,同时提高了身份保真度。为了评估我们的方法,我们引入了Meta-PHD,这是一个用于身份个性化的新基准数据集,并比较了Meta-LoRA与最先进的方法。我们的结果表明,Meta-LoRA在身份保留、计算效率和适应各种身份条件方面都具有优势。我们的代码、模型权重和数据集已在barisbatuhan.github.io/Meta-LoRA上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于文本到图像生成模型的最新进展,特别是潜在扩散模型(LDMs)。针对身份个性化问题,提出了一种新的框架Meta-LoRA,利用元学习将领域特定先验知识编码到基于LoRA的身份个性化中。该方法引入了一个结构化的三层LoRA架构,将身份无关的知识与身份特定的适应分离。在多个主体之间进行元训练,学习共享流形捕捉一般身份相关特征。然后在第二阶段,仅优化LoRA-Mid和LoRA-Up层以适应给定主体,提高了身份保真度和计算效率。为评估方法,引入了Meta-PHD新基准数据集,并与最新方法进行比较,结果表明Meta-LoRA在身份保留、计算效率和适应性方面表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像生成模型,特别是潜在扩散模型(LDMs),在合成高质量图像方面表现出卓越的能力。
- 身份个性化是确保模型从有限参考图像中一致生成特定主体输出的重要挑战。
- 提出了一种新的框架Meta-LoRA,利用元学习和LoRA架构进行身份个性化。
- Meta-LoRA通过分离身份无关知识和身份特定适应,提高了身份保真度和计算效率。
- 引入了Meta-PHD基准数据集,用于评估身份个性化方法的效果。
- 与现有方法相比,Meta-LoRA在身份保留、计算效率和适应性方面表现优越。
- 公开了代码、模型权重和数据集。
点此查看论文截图

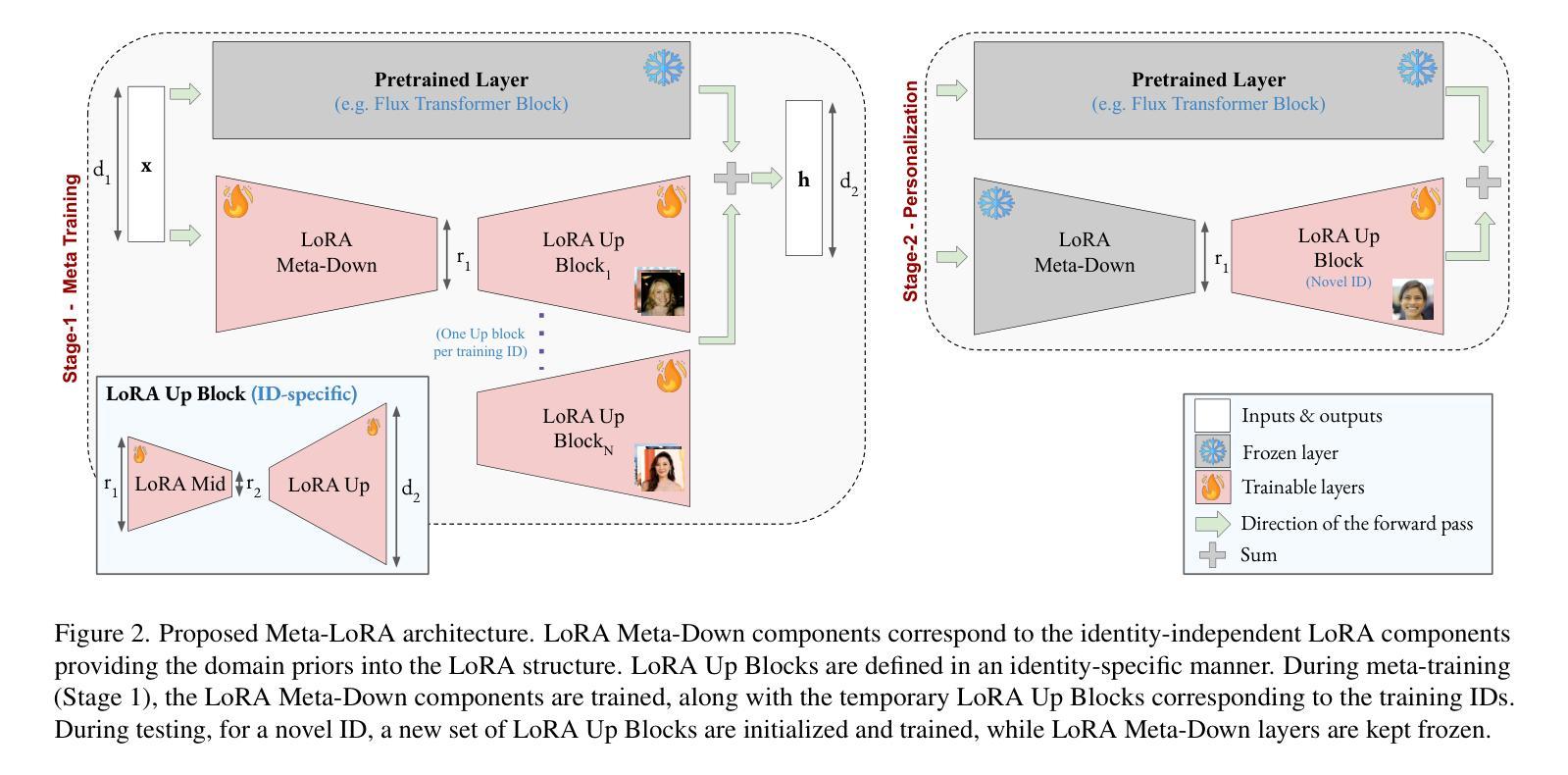
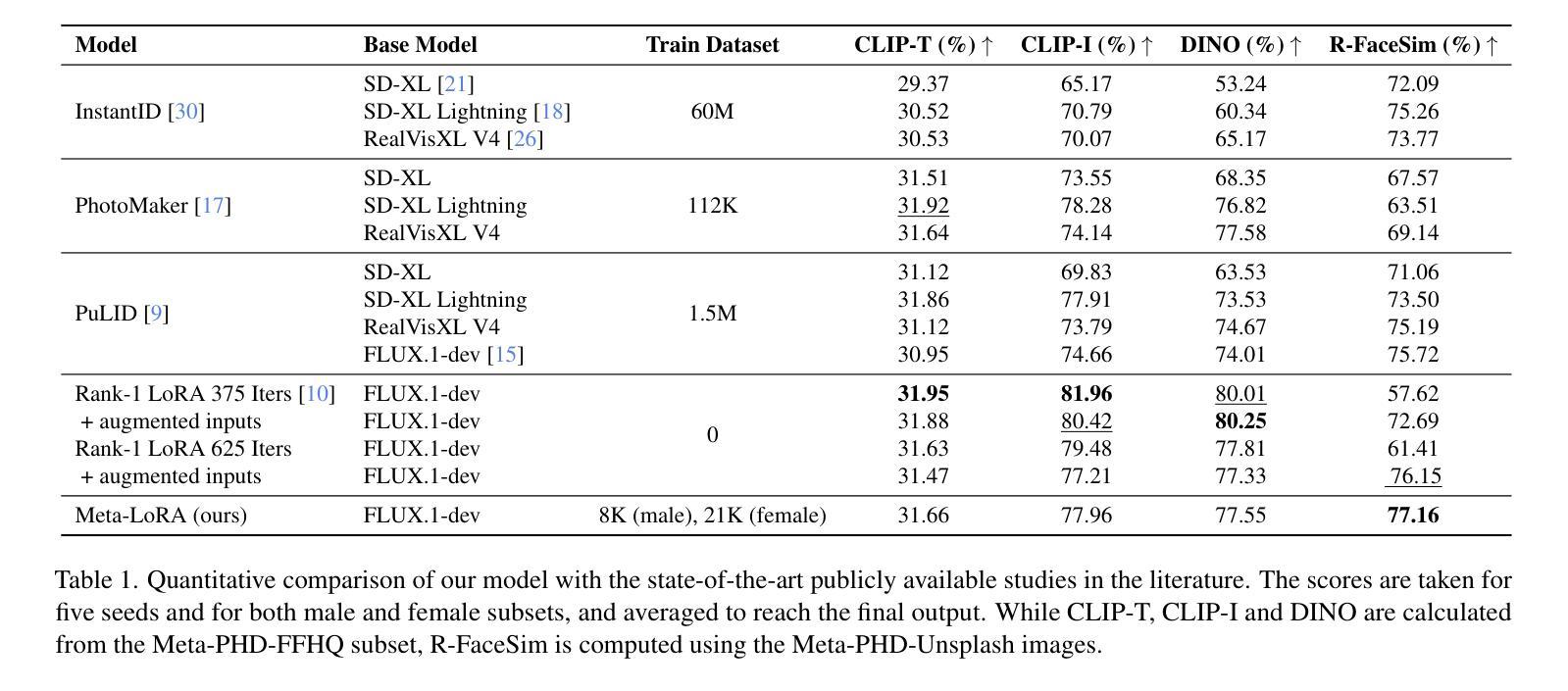
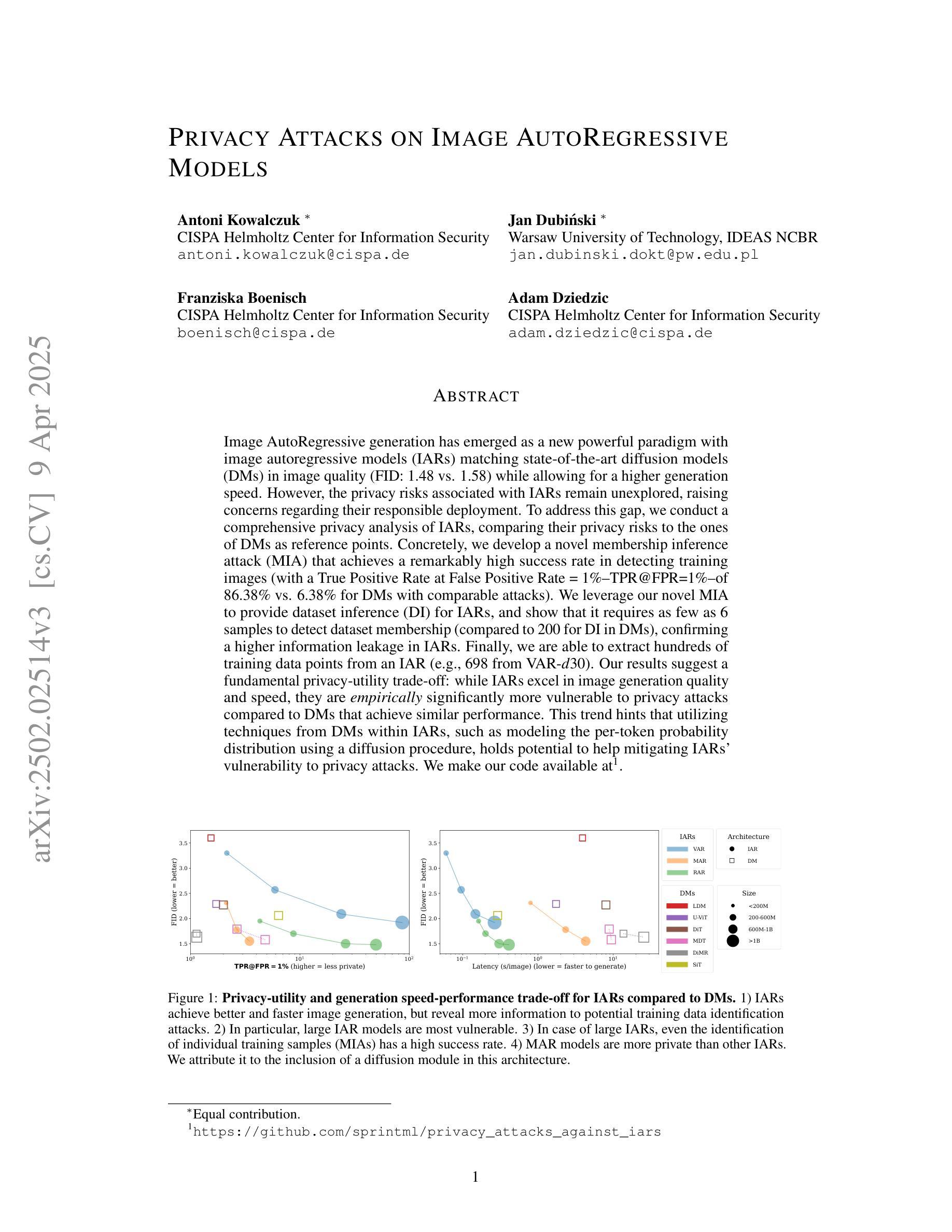
Privacy Attacks on Image AutoRegressive Models
Authors:Antoni Kowalczuk, Jan Dubiński, Franziska Boenisch, Adam Dziedzic
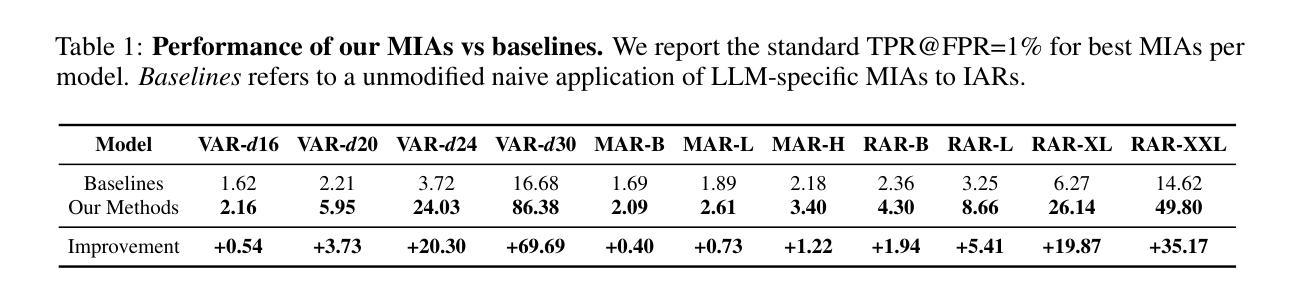
Image autoregressive generation has emerged as a powerful new paradigm, with image autoregressive models (IARs) matching state-of-the-art diffusion models (DMs) in image quality (FID: 1.48 vs. 1.58) while allowing for higher generation speed. However, the privacy risks associated with IARs remain unexplored, raising concerns about their responsible deployment. To address this gap, we conduct a comprehensive privacy analysis of IARs, comparing their privacy risks to those of DMs as a reference point. Specifically, we develop a novel membership inference attack (MIA) that achieves a remarkably high success rate in detecting training images, with a True Positive Rate at False Positive Rate = 1% (TPR@FPR=1%) of 86.38%, compared to just 6.38% for DMs using comparable attacks. We leverage our novel MIA to perform dataset inference (DI) for IARs and show that it requires as few as 6 samples to detect dataset membership, compared to 200 samples for DI in DMs. This confirms a higher level of information leakage in IARs. Finally, we are able to extract hundreds of training data points from an IAR (e.g., 698 from VAR-d30). Our results suggest a fundamental privacy-utility trade-off: while IARs excel in image generation quality and speed, they are empirically significantly more vulnerable to privacy attacks compared to DMs that achieve similar performance. This trend suggests that incorporating techniques from DMs into IARs, such as modeling the per-token probability distribution using a diffusion procedure, could help mitigate IARs’ vulnerability to privacy attacks. We make our code available at: https://github.com/sprintml/privacy_attacks_against_iars
图像自回归生成已经成为一种强大的新范式,图像自回归模型(IARs)在图像质量方面与最先进的扩散模型(DMs)相匹配(FID:1.48 vs. 1.58),同时允许更高的生成速度。然而,与IARs相关的隐私风险尚未得到探索,这引发了对其负责任部署的担忧。为了弥补这一空白,我们对IARs进行了全面的隐私分析,并将其隐私风险与DMs作为参考点进行比较。具体来说,我们开发了一种新的成员推理攻击(MIA),该攻击在检测训练图像方面取得了非常高的成功率,在假阳性率(FPR)= 1%的情况下,真阳性率(TPR)达到86.38%,相比之下,使用类似攻击的DMs仅为6.38%。我们利用新型MIA对IARs进行数据集推理(DI),结果表明只需6个样本即可检测数据集成员身份,而DMs进行DI则需要200个样本。这证实了IARs中存在更高程度的信息泄露。最后,我们能够从IAR中提取数百个训练数据点(例如,从VAR-d30中提取698个)。我们的结果表明存在基本的隐私效用权衡:虽然IAR在图像生成质量和速度方面表现出色,但它们实际上更容易受到隐私攻击,与表现相似的DMs相比,这表现出明显的脆弱性。这一趋势表明,将DMs的技术融入IARs中,例如使用扩散过程对每令牌概率分布进行建模,可能有助于减轻IARs对隐私攻击的脆弱性。我们已将代码放在https://github.com/sprintml/privacy_attacks_against_iars供公众查阅。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/sprintml/privacy_attacks_against_iars
Summary
图像自回归生成模型(IARs)作为一种新兴的强大范式,在图像质量方面与扩散模型(DMs)相匹配,同时允许更高的生成速度。然而,IARs的隐私风险尚未探索,引发了对其负责任部署的担忧。为了弥补这一空白,我们对IARs进行了全面的隐私分析,并将其与DMs的隐私风险进行比较。研究发现,IARs在信息泄露方面存在更高的风险,更易受到隐私攻击。尽管IARs在图像生成质量和速度方面表现出色,但与DMs相比,它们更容易受到隐私攻击。因此,建议将DMs的技术融入IARs中,以提高其抵御隐私攻击的能力。完整的研究结果已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 图像自回归生成模型(IARs)在图像质量上可与扩散模型(DMs)相匹配,但生成速度更快。
- IARs的隐私风险尚未得到充分探索,存在潜在的隐私泄露问题。
- 通过新型的成员推理攻击(MIA),发现IARs在检测训练图像方面的成功率非常高,达到86.38%。
- IARs的数据集推理(DI)仅需6个样本即可检测数据集成员,相比之下DMs需要200个样本。
- IARs更容易受到隐私攻击,表现出较高的信息泄露风险。
- 尽管IARs在图像生成方面表现出色,但与DMs相比,它们存在隐私与效用的权衡。
点此查看论文截图
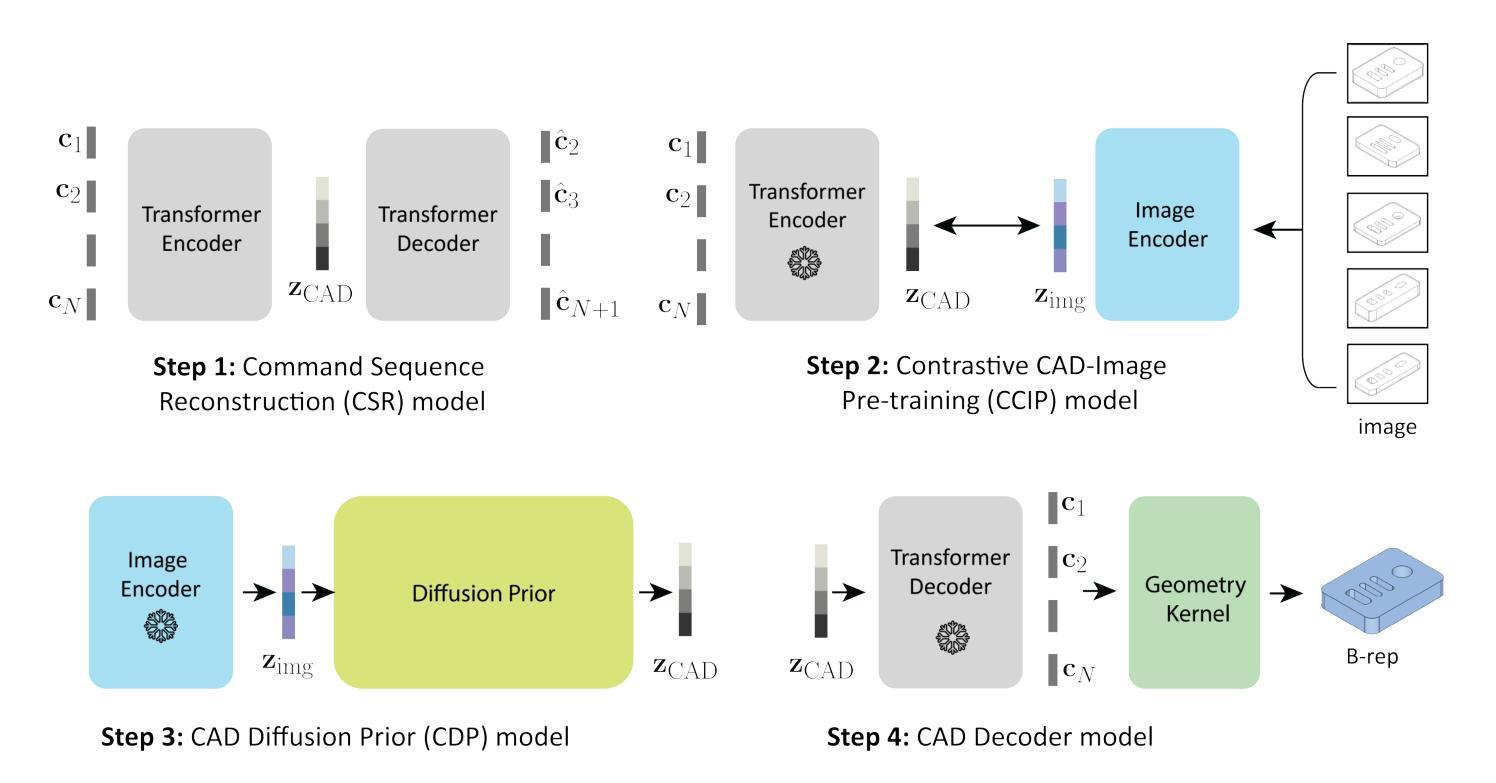
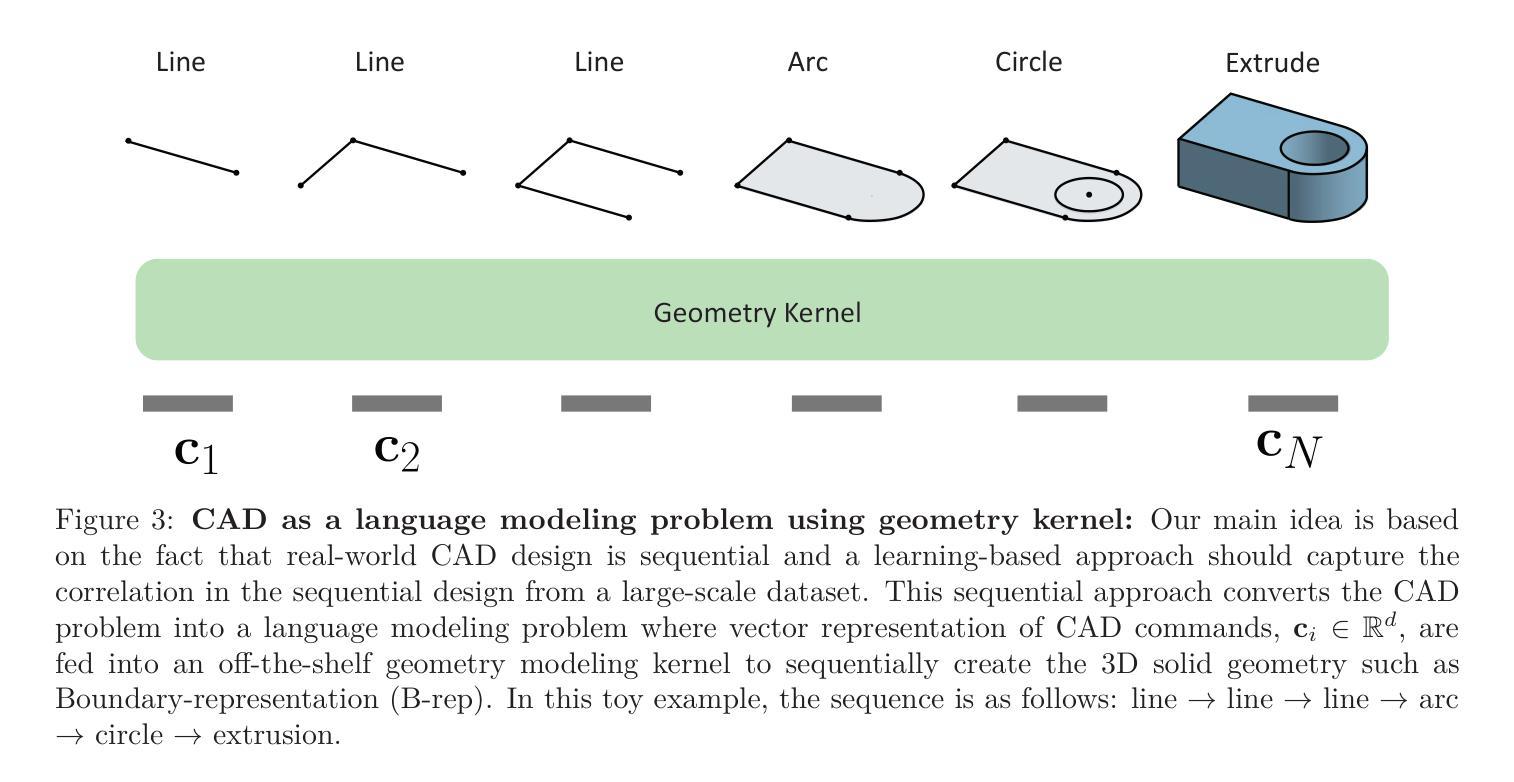
GenCAD: Image-Conditioned Computer-Aided Design Generation with Transformer-Based Contrastive Representation and Diffusion Priors
Authors:Md Ferdous Alam, Faez Ahmed
The creation of manufacturable and editable 3D shapes through Computer-Aided Design (CAD) remains a highly manual and time-consuming task, hampered by the complex topology of boundary representations of 3D solids and unintuitive design tools. While most work in the 3D shape generation literature focuses on representations like meshes, voxels, or point clouds, practical engineering applications demand the modifiability and manufacturability of CAD models and the ability for multi-modal conditional CAD model generation. This paper introduces GenCAD, a generative model that employs autoregressive transformers with a contrastive learning framework and latent diffusion models to transform image inputs into parametric CAD command sequences, resulting in editable 3D shape representations. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that GenCAD significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of the unconditional and conditional generations of CAD models. Additionally, the contrastive learning framework of GenCAD facilitates the retrieval of CAD models using image queries from large CAD databases, which is a critical challenge within the CAD community. Our results provide a significant step forward in highlighting the potential of generative models to expedite the entire design-to-production pipeline and seamlessly integrate different design modalities.
通过计算机辅助设计(CAD)创建可制造和可编辑的3D形状仍然是一项高度手动和时间密集的任务,受到3D实体边界表示复杂拓扑和非直观设计工具的限制。尽管3D形状生成文献中的大多数工作都集中在网格、体素或点云等表示方法上,但实用工程应用要求CAD模型的可修改性和可制造性,以及多模式条件CAD模型生成的能力。本文介绍了GenCAD,它是一种采用自回归变压器和对比学习框架以及潜在扩散模型的生成模型,能够将图像输入转换为参数化CAD命令序列,从而产生可编辑的3D形状表示。广泛评估表明,GenCAD在无条件和有条件的CAD模型生成方面显著优于现有最先进的方法。此外,GenCAD的对比学习框架有助于使用图像查询从大型CAD数据库中检索CAD模型,这是CAD社区内的关键挑战。我们的研究结果突显了生成模型在加快整个设计到生产流程并无缝集成不同设计模式方面的潜力,这标志着向前迈进了一大步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 13 figures
Summary
本论文提出一种名为GenCAD的生成模型,利用自回归变压器与对比学习框架及潜在扩散模型,将图像输入转换为参数化CAD命令序列,从而生成可编辑的3D形状表示。GenCAD显著优于现有最先进的方法,尤其是在CAD模型的无条件与有条件生成方面。此外,GenCAD的对比学习框架还能使用图像查询从大型CAD数据库中检索CAD模型,这是CAD社区内的一个关键挑战。研究成果展示了生成模型在加快整个设计到生产流程并整合不同设计模态方面的巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- GenCAD是一个利用自回归变压器和对比学习框架的生成模型,能够将图像转化为参数化CAD命令序列。
- GenCAD可以生成可编辑的3D形状表示,满足实际工程应用的需求。
- GenCAD在无条件与有条件生成CAD模型方面显著优于现有方法。
- GenCAD采用对比学习框架,可从大型CAD数据库中检索CAD模型。
- 检索功能解决了CAD设计中的关键挑战之一。
- 生成模型在加快设计到生产流程方面具有巨大潜力。
点此查看论文截图