⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-11 更新
Generalized Semantic Contrastive Learning via Embedding Side Information for Few-Shot Object Detection
Authors:Ruoyu Chen, Hua Zhang, Jingzhi Li, Li Liu, Zhen Huang, Xiaochun Cao
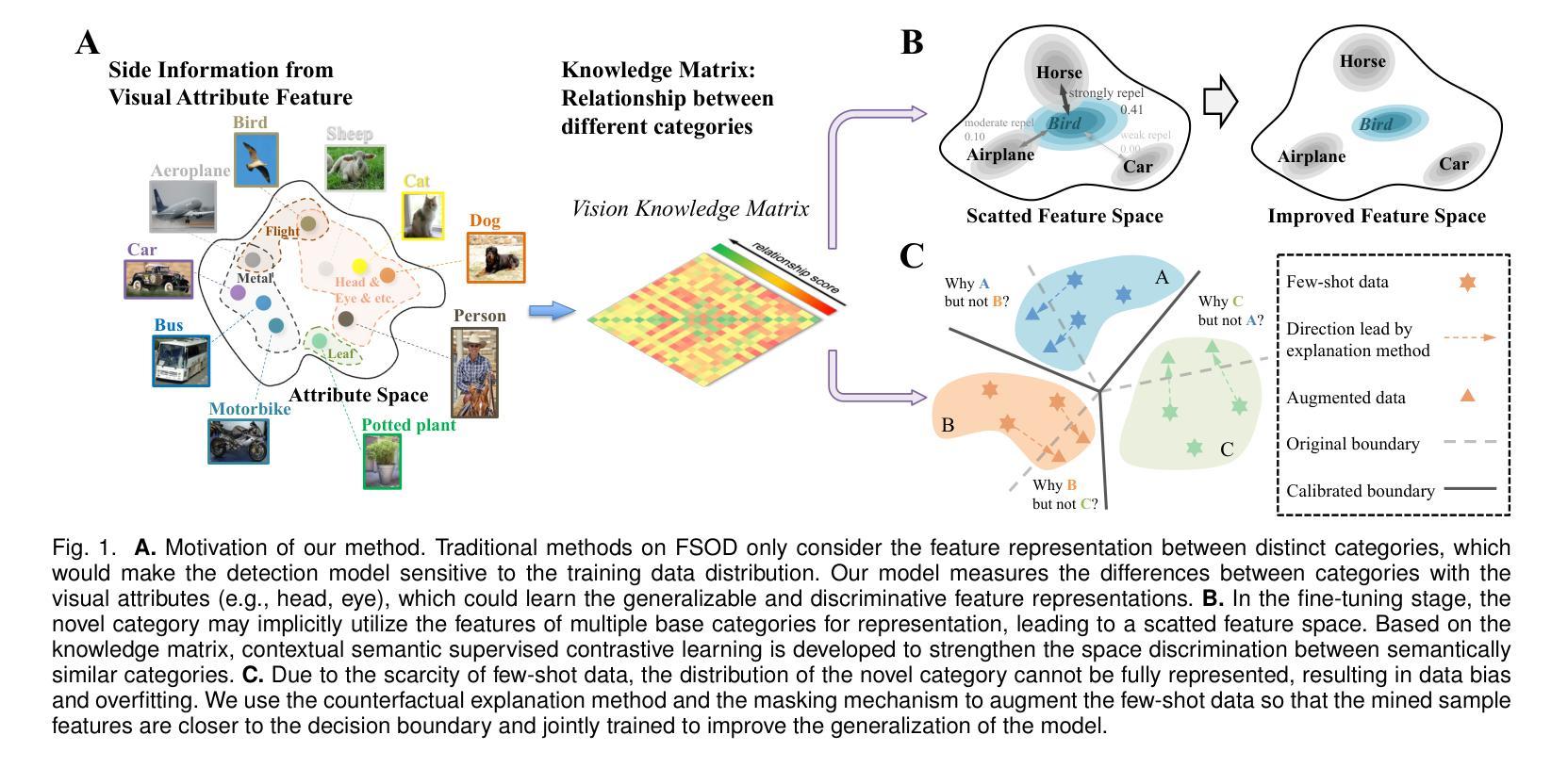
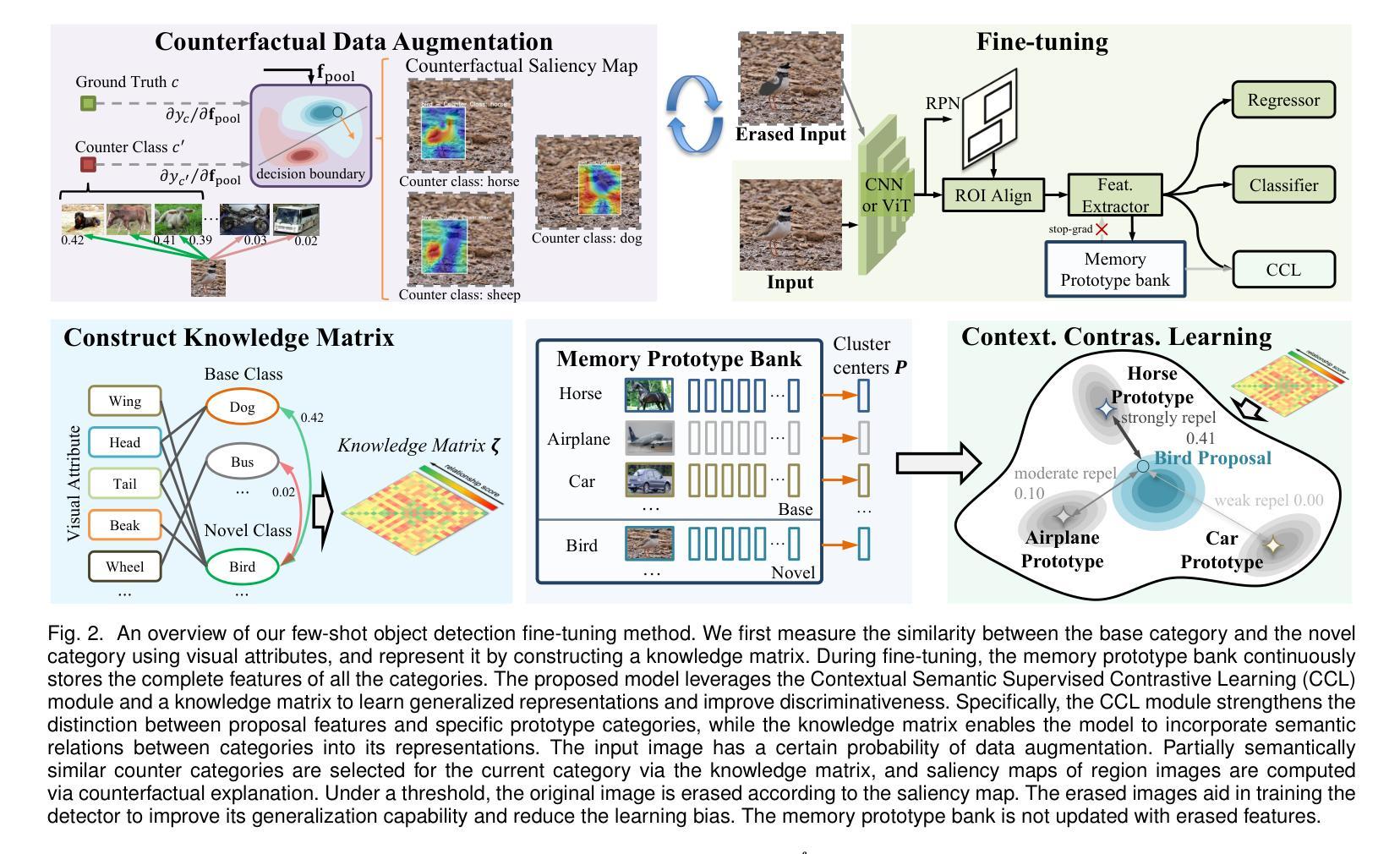
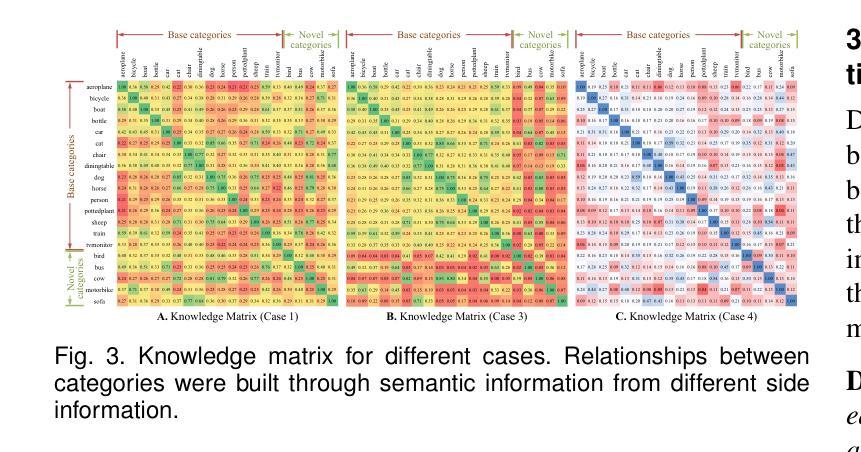
The objective of few-shot object detection (FSOD) is to detect novel objects with few training samples. The core challenge of this task is how to construct a generalized feature space for novel categories with limited data on the basis of the base category space, which could adapt the learned detection model to unknown scenarios. However, limited by insufficient samples for novel categories, two issues still exist: (1) the features of the novel category are easily implicitly represented by the features of the base category, leading to inseparable classifier boundaries, (2) novel categories with fewer data are not enough to fully represent the distribution, where the model fine-tuning is prone to overfitting. To address these issues, we introduce the side information to alleviate the negative influences derived from the feature space and sample viewpoints and formulate a novel generalized feature representation learning method for FSOD. Specifically, we first utilize embedding side information to construct a knowledge matrix to quantify the semantic relationship between the base and novel categories. Then, to strengthen the discrimination between semantically similar categories, we further develop contextual semantic supervised contrastive learning which embeds side information. Furthermore, to prevent overfitting problems caused by sparse samples, a side-information guided region-aware masked module is introduced to augment the diversity of samples, which finds and abandons biased information that discriminates between similar categories via counterfactual explanation, and refines the discriminative representation space further. Extensive experiments using ResNet and ViT backbones on PASCAL VOC, MS COCO, LVIS V1, FSOD-1K, and FSVOD-500 benchmarks demonstrate that our model outperforms the previous state-of-the-art methods, significantly improving the ability of FSOD in most shots/splits.
少量样本目标检测(FSOD)的目标是使用少量训练样本对新型目标进行检测。该任务的核心挑战是如何在基础类别空间的基础上,为新型类别构建一个通用的特征空间,使学习到的检测模型能够适应未知场景。然而,由于新型类别的样本量有限,仍存在两个问题:(1)新型类别的特征很容易隐含地由基础类别的特征表示,导致分类器边界无法分离;(2)新型类别的数据较少,不足以充分代表分布,模型微调容易出现过拟合。为了解决这些问题,我们引入侧面信息来缓解特征空间和样本观点产生的负面影响,并为FSOD制定一种新的通用特征表示学习方法。具体而言,我们首先利用嵌入侧面信息来构建知识矩阵,以量化基础类别和新型类别之间的语义关系。然后,为了加强语义相似类别之间的鉴别能力,我们进一步发展了上下文语义监督对比学习,其中嵌入了侧面信息。此外,为了防止因样本稀疏而导致的过拟合问题,我们引入了侧面信息引导的区域感知遮挡模块,以增加样本的多样性,该模块通过反事实解释来发现并摒弃相似类别之间的偏见信息,并进一步细化判别表示空间。在PASCAL VOC、MS COCO、LVIS V1、FSOD-1K和FSVOD-500基准测试上进行的使用ResNet和ViT骨架的广泛实验表明,我们的模型优于之前的最先进方法,在大多数射击/分割中显著提高了FSOD的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by T-PAMI (IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence)
Summary
该文本介绍了少样本目标检测(FSOD)的目标和挑战,并针对挑战引入了辅助信息来缓解特征空间和样本观点产生的负面影响,提出了一种新的广义特征表示学习方法。通过嵌入辅助信息构建知识矩阵来量化基础类别和新颖类别之间的语义关系,并开发上下文语义监督对比学习来增强相似类别之间的鉴别力。同时,引入辅助信息引导的区域感知掩模模块来增加样本的多样性,并通过反事实解释来发现和丢弃区分相似类别的偏见信息,进一步细化判别表示空间。实验证明,该模型在多个基准测试上优于先前的方法,显著提高了FSOD在大多数场景下的性能。
Key Takeaways
- FSOD的目标是检测新对象,在少量训练样本的情况下构建通用的特征空间以适应未知场景。
- 存在两个问题:新类别的特征容易被基础类别的特征所隐含表示,导致分类器边界不清晰;新类别数据不足,不能完全代表分布,模型微调容易过拟合。
- 引入辅助信息缓解特征空间和样本观点带来的负面影响。
- 通过嵌入辅助信息构建知识矩阵,量化基础类别和新颖类别之间的语义关系。
- 采用上下文语义监督对比学习,增强相似类别之间的鉴别力。
- 引入辅助信息引导的区域感知掩模模块增加样本多样性,通过反事实解释区分相似类别。
点此查看论文截图

RuOpinionNE-2024: Extraction of Opinion Tuples from Russian News Texts
Authors:Natalia Loukachevitch, Natalia Tkachenko, Anna Lapanitsyna, Mikhail Tikhomirov, Nicolay Rusnachenko
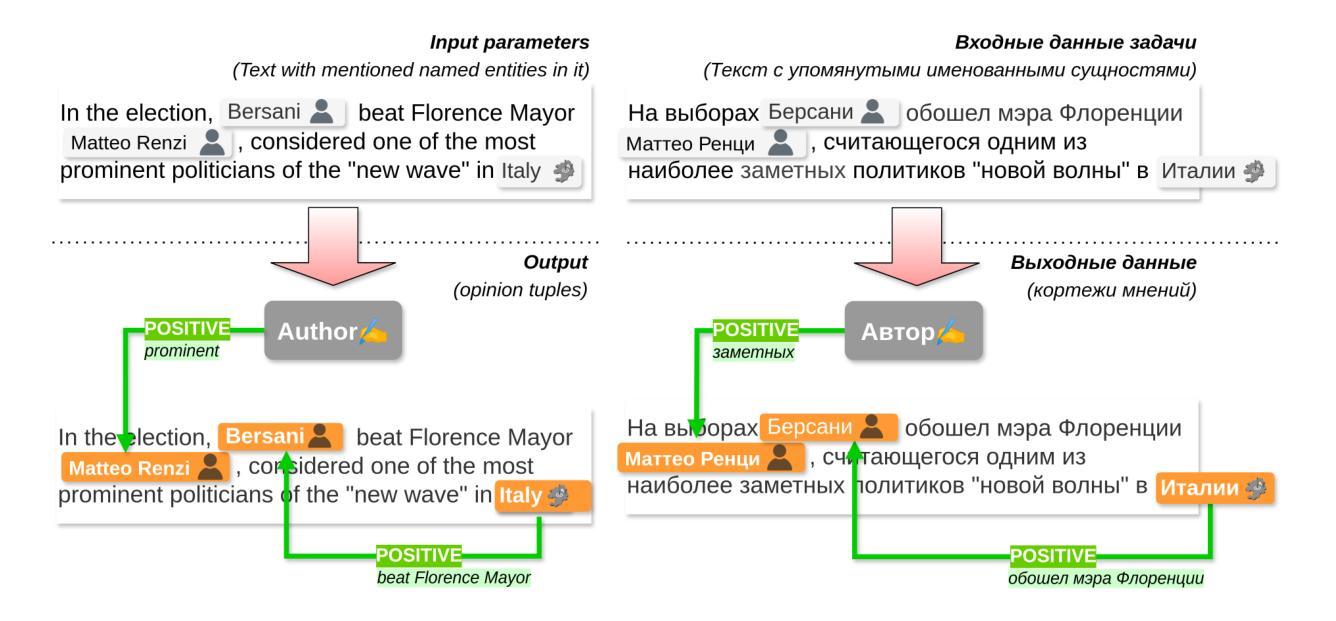
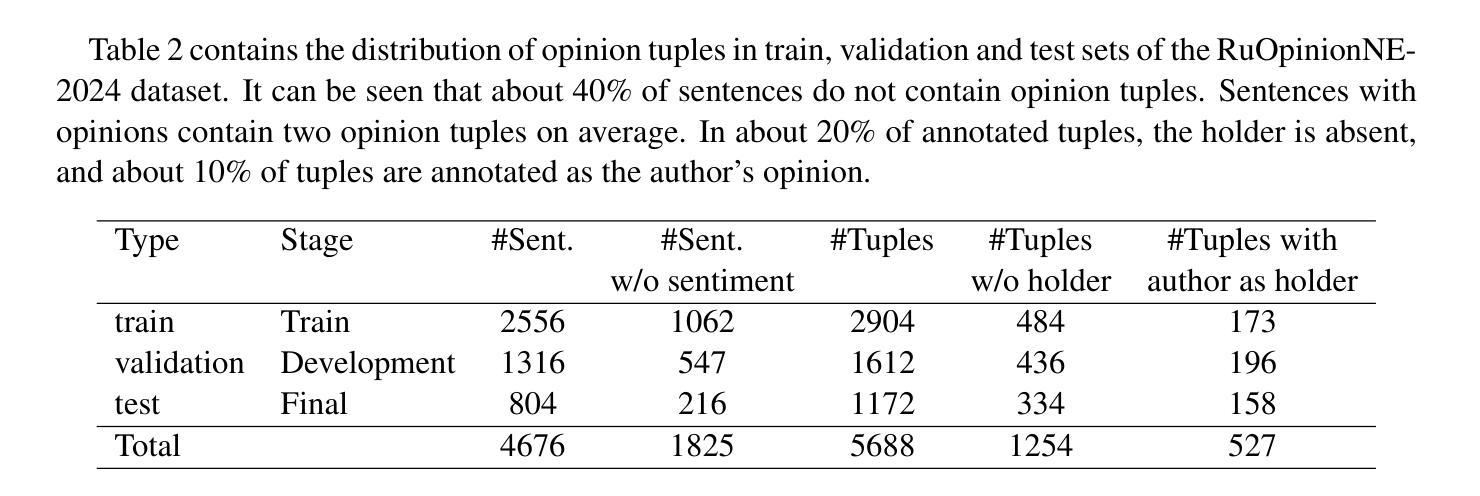
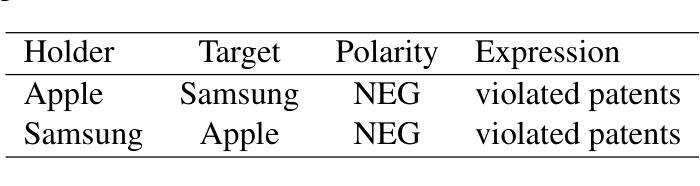
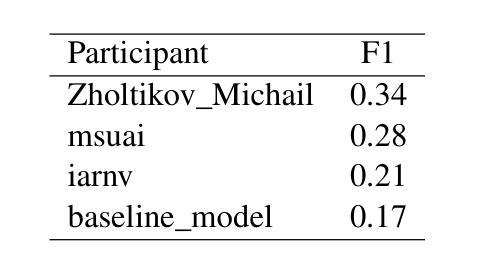
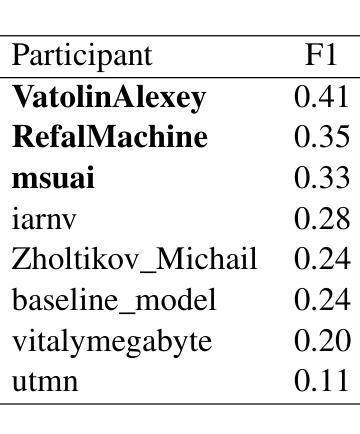
In this paper, we introduce the Dialogue Evaluation shared task on extraction of structured opinions from Russian news texts. The task of the contest is to extract opinion tuples for a given sentence; the tuples are composed of a sentiment holder, its target, an expression and sentiment from the holder to the target. In total, the task received more than 100 submissions. The participants experimented mainly with large language models in zero-shot, few-shot and fine-tuning formats. The best result on the test set was obtained with fine-tuning of a large language model. We also compared 30 prompts and 11 open source language models with 3-32 billion parameters in the 1-shot and 10-shot settings and found the best models and prompts.
本文介绍了从俄罗斯新闻文本中提取结构化意见的对话评价共享任务。该任务的目标是为给定的句子提取意见元组,这些元组由意见持有者、目标、表达和从持有者对目标的情感组成。该任务共收到超过100份提交。参赛者主要尝试使用大型语言模型进行零样本、少样本和微调格式的实验。测试集的最佳结果是通过微调大型语言模型获得的。我们还比较了1-shot和10-shot设置中的30个提示和11个开源语言模型(具有3亿至32亿个参数),并找到了最佳的模型和提示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF RuOpinionNE-2024 represent a proceeding of RuSentNE-2023. It contributes with extraction and evaluation of factual statements that support the assigned sentiment
Summary
本文介绍了俄罗斯新闻文本中的对话评价共享任务,该任务旨在从给定的句子中提取意见元组,包括情感持有者、目标、表达和持有者对目标的情感。该任务收到了超过100份提交,参赛者主要尝试使用大型语言模型进行零样本、小样例和微调。在测试集上获得最佳结果的模型是对大型语言模型的微调。此外,还对比了不同提示和开源语言模型的效果,找到了最佳模型和提示。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文介绍了关于从俄罗斯新闻文本中提取结构化意见的对话评价共享任务。
- 任务的目标是提取给定句子中的意见元组,包括情感持有者、目标、表达和相应情感。
- 任务收到了超过100份提交,参赛者主要使用大型语言模型进行尝试。
- 在测试集上,通过微调大型语言模型获得了最佳结果。
点此查看论文截图


FeedbackEval: A Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models in Feedback-Driven Code Repair Tasks
Authors:Dekun Dai, MingWei Liu, Anji Li, Jialun Cao, Yanlin Wang, Chong Wang, Xin Peng, Zibin Zheng
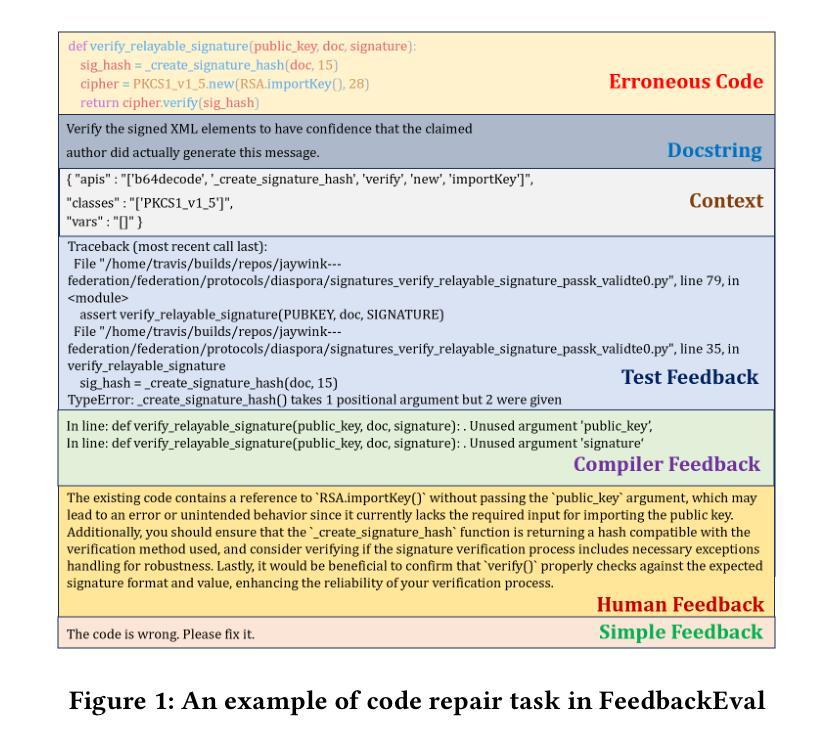
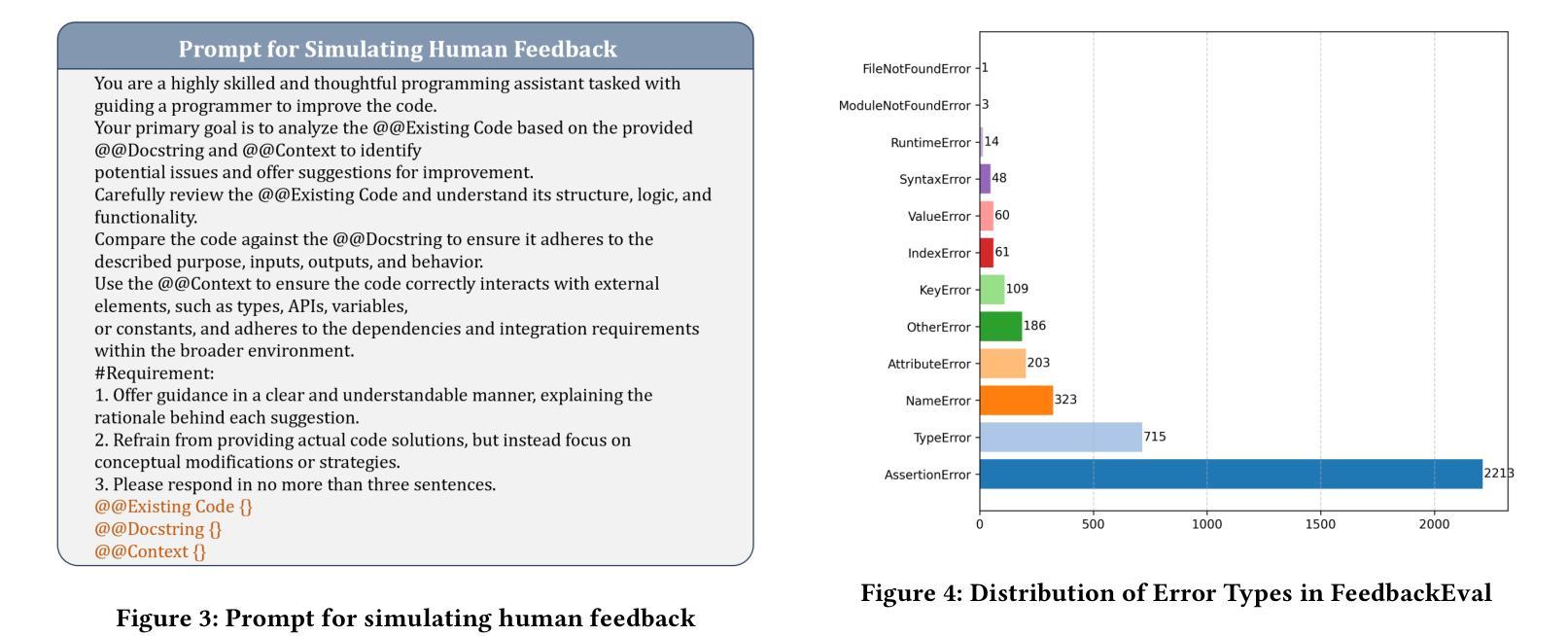
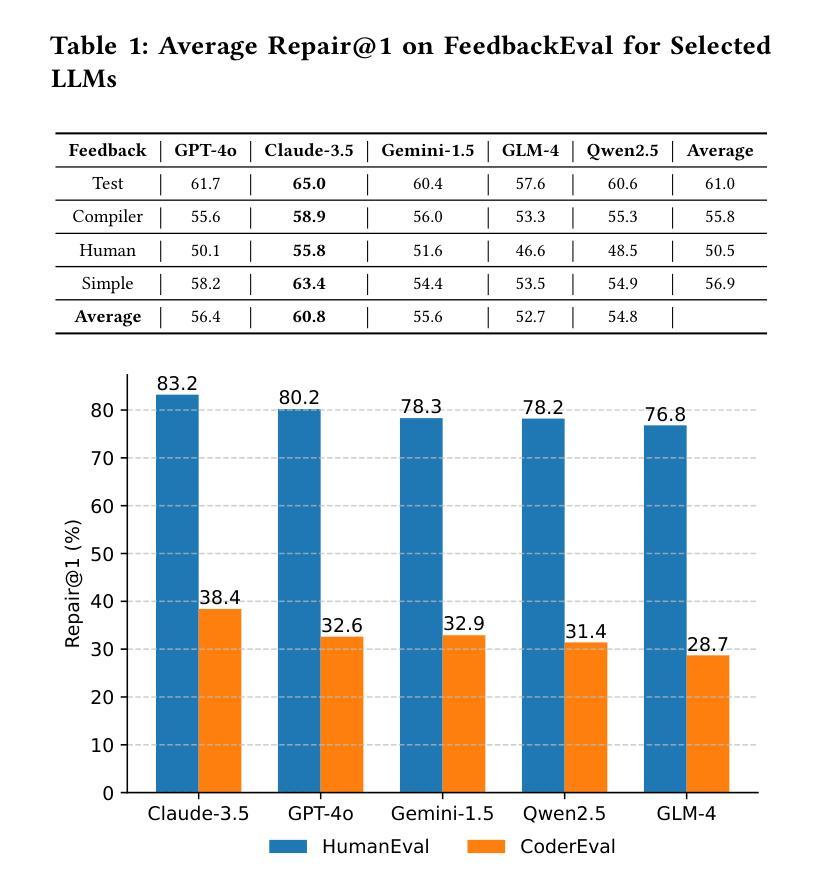
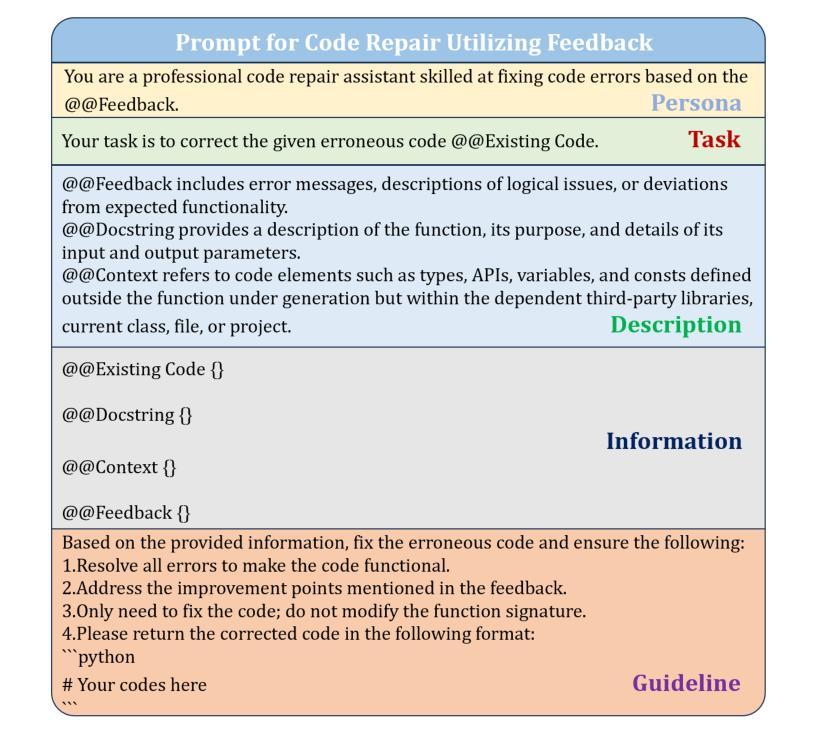
Code repair is a fundamental task in software development, facilitating efficient bug resolution and software maintenance. Although large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated considerable potential in automated code repair, their ability to comprehend and effectively leverage diverse types of feedback remains insufficiently understood. To bridge this gap, we introduce FeedbackEval, a systematic benchmark for evaluating LLMs’ feedback comprehension and performance in code repair tasks. We conduct a comprehensive empirical study on five state-of-the-art LLMs, including GPT-4o, Claude-3.5, Gemini-1.5, GLM-4, and Qwen2.5, to evaluate their behavior under both single-iteration and iterative code repair settings. Our results show that structured feedback, particularly in the form of test feedback, leads to the highest repair success rates, while unstructured feedback proves significantly less effective. Iterative feedback further enhances repair performance, though the marginal benefit diminishes after two or three rounds. Moreover, prompt structure is shown to be critical: incorporating docstrings, contextual information, and explicit guidelines substantially improves outcomes, whereas persona-based, chain-of-thought, and few-shot prompting strategies offer limited benefits in single-iteration scenarios. This work introduces a robust benchmark and delivers practical insights to advance the understanding and development of feedback-driven code repair using LLMs.
代码修复是软件开发中的一项基本任务,能够促进高效的错误解决和软件维护。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在自动代码修复中展现出了巨大的潜力,但它们理解和有效利用各种反馈的能力仍未能得到充分理解。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了FeedbackEval,这是一个用于评估LLM在代码修复任务中理解和利用反馈能力的系统性基准测试。我们对五个最新的大型语言模型进行了全面的实证研究,包括GPT-4o、Claude-3.5、Gemini-1.5、GLM-4和Qwen2.5,以评估它们在单轮和迭代代码修复设置下的行为。结果表明,结构化的反馈,尤其是测试反馈的形式,导致最高的修复成功率,而非结构化的反馈证明效果甚微。迭代反馈进一步提高了修复性能,但两轮或三轮后的边际效益逐渐减小。此外,提示的结构被证明是关键的:结合文档字符串、上下文信息和明确的指导方针可以大大改善结果,而基于角色的思考、思维链和少样本提示策略在单轮场景中提供的益处有限。这项工作建立了一个稳健的基准测试,并提供了实用的见解,以推动利用LLM进行反馈驱动的代码修复的理解和开发。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
代码修复是软件开发中的一项基本任务,能够促进有效的错误解决和软件维护。尽管大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动代码修复中展现出巨大潜力,但它们理解和有效利用多种反馈的能力尚待深入了解。为弥补这一差距,我们推出FeedbackEval,一个用于评估LLMs在代码修复任务中理解和利用反馈能力的系统基准测试。我们对五款最新LLMs进行了全面的实证研究,包括GPT-4o、Claude-3.5、Gemini-1.5、GLM-4和Qwen2.5,以评估它们在单轮和迭代代码修复环境下的表现。研究发现,结构化反馈,尤其是测试反馈,导致最高的修复成功率,而非结构化反馈证明效果甚微。迭代反馈进一步提高了修复性能,但两轮或三轮后的边际效益递减。此外,提示结构至关重要:融入docstring、上下文信息和明确指导大幅改善结果,而基于角色的、思维链和少样本提示策略在单轮场景中提供有限效益。本研究推出一个稳健的基准测试,为推进利用LLMs的反馈驱动代码修复的理解和开发提供实用见解。
Key Takeaways
- 反馈评价系统(FeedbackEval)对于评估大型语言模型(LLMs)在代码修复中的反馈理解和利用能力至关重要。
- 结构化反馈,特别是测试反馈,对代码修复的成功率有最大影响。
- 非结构化反馈在代码修复中的效果有限。
- 迭代反馈能提高修复性能,但边际效益在多次迭代后递减。
- 提示结构在代码修复中起到重要作用,融入特定元素如docstring、上下文信息和明确指导能大幅改善修复结果。
- 基于角色的、思维链和少样本提示策略在单轮代码修复场景中效果有限。
点此查看论文截图

ZIP: An Efficient Zeroth-order Prompt Tuning for Black-box Vision-Language Models
Authors:Seonghwan Park, Jaehyeon Jeong, Yongjun Kim, Jaeho Lee, Namhoon Lee
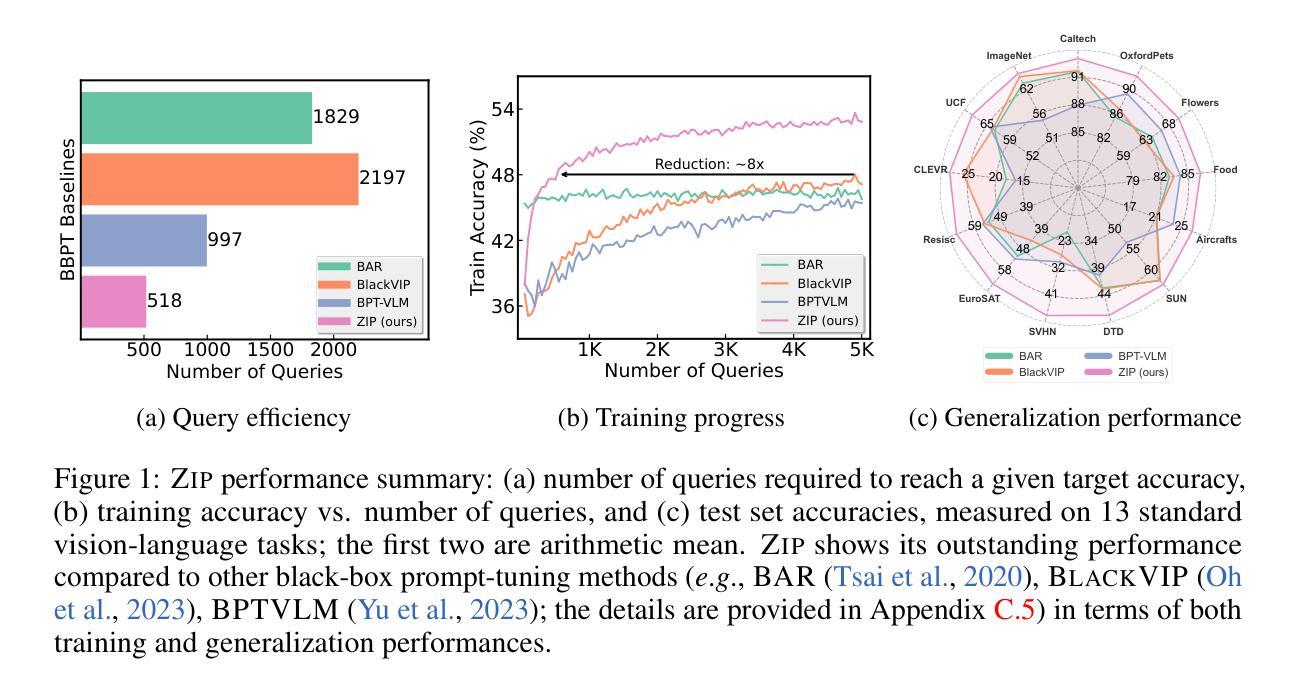
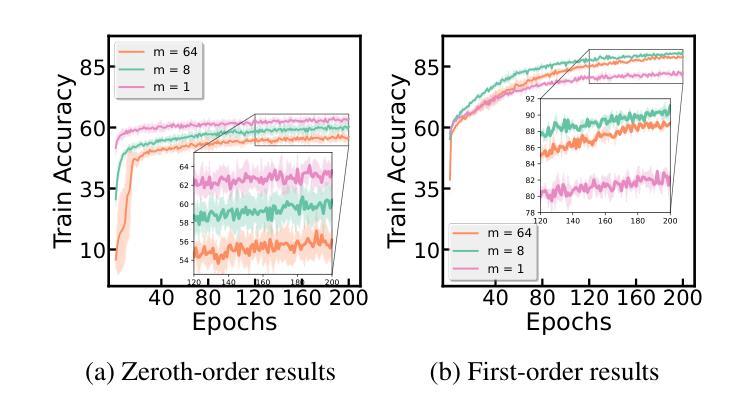
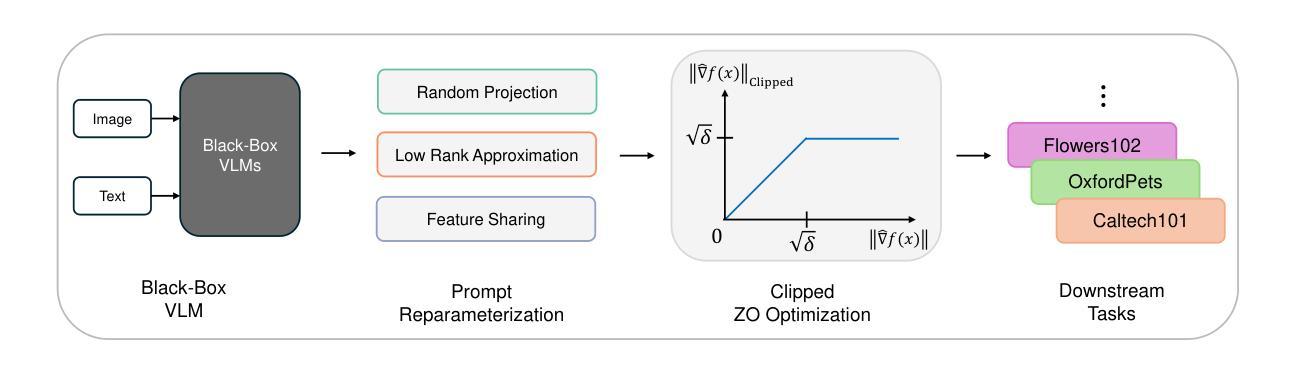
Recent studies have introduced various approaches for prompt-tuning black-box vision-language models, referred to as black-box prompt-tuning (BBPT). While BBPT has demonstrated considerable potential, it is often found that many existing methods require an excessive number of queries (i.e., function evaluations), which poses a significant challenge in real-world scenarios where the number of allowed queries is limited. To tackle this issue, we propose Zeroth-order Intrinsic-dimensional Prompt-tuning (ZIP), a novel approach that enables efficient and robust prompt optimization in a purely black-box setting. The key idea of ZIP is to reduce the problem dimensionality and the variance of zeroth-order gradient estimates, such that the training is done fast with far less queries. We achieve this by re-parameterizing prompts in low-rank representations and designing intrinsic-dimensional clipping of estimated gradients. We evaluate ZIP on 13+ vision-language tasks in standard benchmarks and show that it achieves an average improvement of approximately 6% in few-shot accuracy and 48% in query efficiency compared to the best-performing alternative BBPT methods, establishing a new state of the art. Our ablation analysis further shows that the proposed clipping mechanism is robust and nearly optimal, without the need to manually select the clipping threshold, matching the result of expensive hyperparameter search.
最近的研究已经引入了各种针对黑盒视觉语言模型的提示调整方法,被称为黑盒提示调整(BBPT)。虽然BBPT已经显示出巨大的潜力,但人们发现许多现有方法需要过多的查询(即功能评估),这在允许查询次数有限的现实场景中构成了一个巨大的挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了零阶内在维度提示调整(ZIP),这是一种在纯黑盒环境中实现高效且稳健的提示优化的新方法。ZIP的关键思想是通过降低问题维度和零阶梯度估计的方差来实现快速的训练以及更少的查询次数。我们通过以低秩表示重新参数化提示并设计内在维度的梯度估计裁剪来实现这一点。我们在标准基准测试中评估了ZIP在超过13个视觉语言任务上的性能,结果表明,与表现最佳的替代BBPT方法相比,它在小样本精度上平均提高了约6%,在查询效率上提高了48%,达到了新的技术水平。我们的消融分析进一步表明,所提出的裁剪机制是稳健且近乎最优的,无需手动选择裁剪阈值,就能匹配昂贵的超参数搜索的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对黑箱视觉语言模型的零阶固有维度提示优化方法(ZIP)。ZIP通过降低问题维度和零阶梯度估计的方差,实现了快速且高效的提示优化。通过重新参数化提示在低秩表示中,并设计固有维度梯度估计的裁剪机制,实现了在少量查询下的高效训练。在标准基准的13个视觉语言任务上评估显示,ZIP在少样本精度上平均提高了约6%,查询效率提高了48%,达到了新的技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 黑箱提示优化(BBPT)在视觉语言模型中显示出潜力,但需要大量的查询。
- ZIP方法通过降低问题维度和零阶梯度估计的方差来提高查询效率和训练速度。
- ZIP采用低秩表示重新参数化提示。
- ZIP通过设计固有维度梯度估计裁剪机制实现高效训练。
- 在多个视觉语言任务上评估,ZIP相比其他最佳BBPT方法,少样本精度提高约6%,查询效率提高48%。
- ZIP的裁剪机制稳健且近乎最优,无需手动选择裁剪阈值。
点此查看论文截图

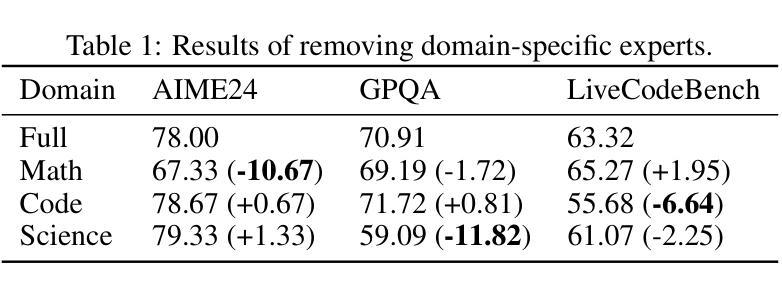
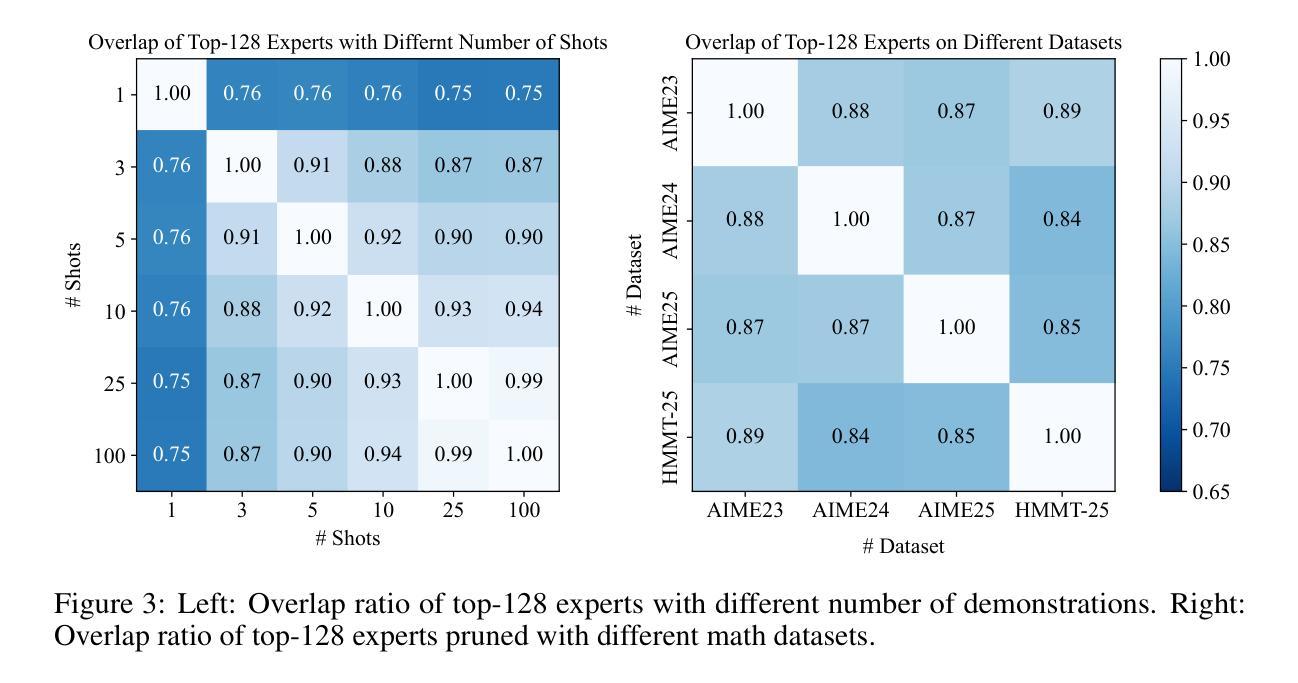
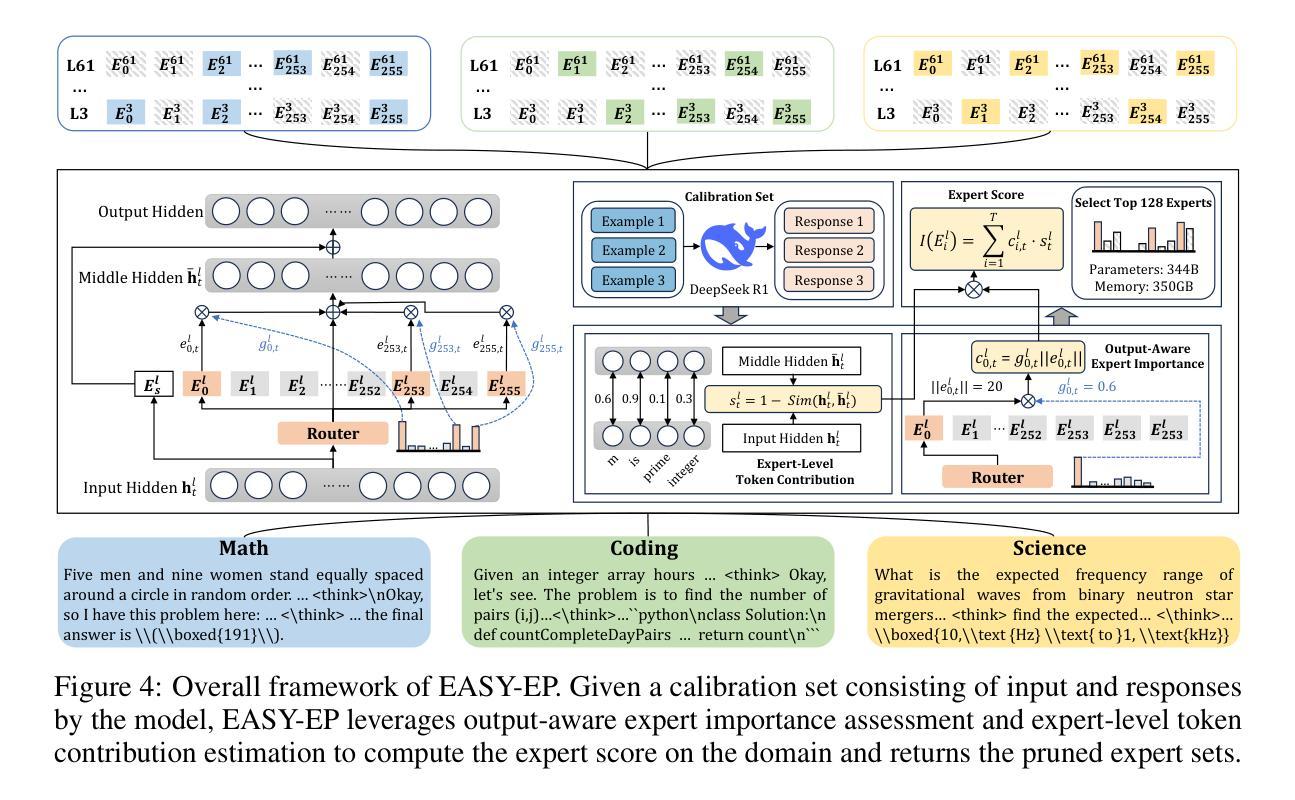
Domain-Specific Pruning of Large Mixture-of-Experts Models with Few-shot Demonstrations
Authors:Zican Dong, Han Peng, Peiyu Liu, Wayne Xin Zhao, Dong Wu, Feng Xiao, Zhifeng Wang
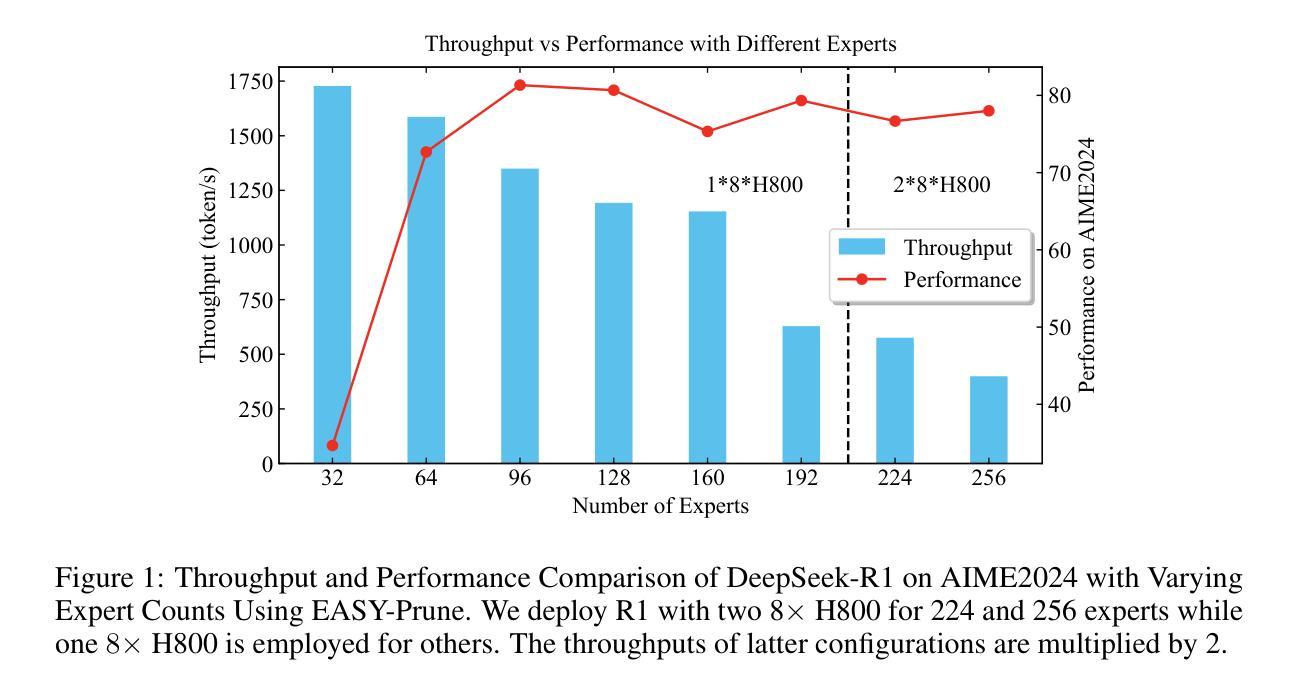
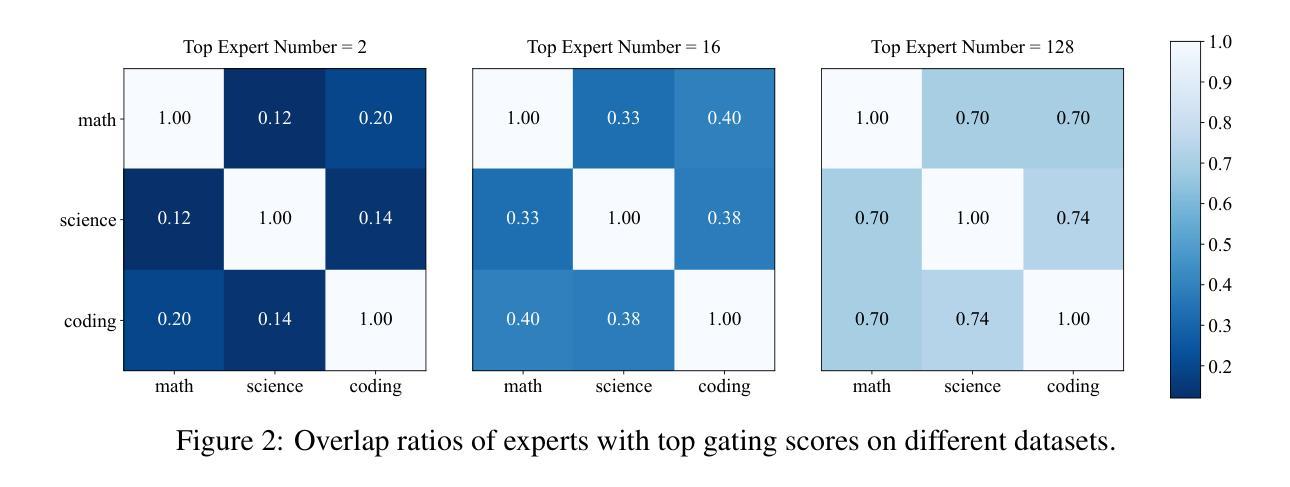
Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models achieve a favorable trade-off between performance and inference efficiency by activating only a subset of experts. However, the memory overhead of storing all experts remains a major limitation, especially in large-scale MoE models such as DeepSeek-R1 (671B). In this study, we investigate domain specialization and expert redundancy in large-scale MoE models and uncover a consistent behavior we term few-shot expert localization, with only a few demonstrations, the model consistently activates a sparse and stable subset of experts. Building on this observation, we propose a simple yet effective pruning framework, EASY-EP, that leverages a few domain-specific demonstrations to identify and retain only the most relevant experts. EASY-EP comprises two key components: output-aware expert importance assessment and expert-level token contribution estimation. The former evaluates the importance of each expert for the current token by considering the gating scores and magnitudes of the outputs of activated experts, while the latter assesses the contribution of tokens based on representation similarities after and before routed experts. Experiments show that our method can achieve comparable performances and $2.99\times$ throughput under the same memory budget with full DeepSeek-R1 with only half the experts. Our code is available at https://github.com/RUCAIBox/EASYEP.
混合专家(MoE)模型通过仅激活一部分专家,实现了性能与推理效率之间的良好平衡。然而,存储所有专家的内存开销仍然是其主要限制,特别是在大规模MoE模型(如DeepSeek-R1(671B))中。在这项研究中,我们调查了大规模MoE模型中的领域专业化与专家冗余,并发现了一个我们称之为“小样例专家定位”的一致行为。仅凭几个演示样本,模型就能始终激活一个稀疏且稳定的专家子集。基于这一观察,我们提出了一个简单有效的剪枝框架EASY-EP,它利用少量的领域特定演示来识别并保留最相关的专家。EASY-EP包含两个关键组件:输出感知的专家重要性评估专家和基于令牌贡献的专家级别评估。前者通过考虑门控分数和已激活专家的输出幅度来评估每个专家对当前令牌的重要性,后者则基于路由前后的表示相似性来评估令牌贡献。实验表明,我们的方法可以在相同的内存预算下,使用仅一半的专家实现与完整DeepSeek-R1相当的性能和2.99倍的吞吐量。我们的代码可在https://github.com/RUCAIBox/EASYEP找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了大型混合专家模型中的领域专业化和专家冗余问题,并提出了一种基于少量领域特定演示的简单有效的剪枝框架EASY-EP。该框架通过评估每个专家对当前标记的重要性以及标记对激活的专家贡献,来识别和保留最相关的专家。实验表明,在相同内存预算下,该方法可以实现与全DeepSeek-R1相当的性能和更高的吞吐量,并且只需要一半的专家数量。
Key Takeaways
- 大型混合专家模型(如DeepSeek-R1)存在存储所有专家的内存开销问题。
- 在仅使用少量演示的情况下,模型表现出一致的“少样本专家定位”行为,即激活的专家子集是稀疏且稳定的。
- 提出了一种新的专家剪枝框架EASY-EP,利用少量领域特定演示来优化模型。
- EASY-EP包含两个关键组件:输出感知的专家重要性评估和专家级别的令牌贡献估算。
- 通过评估每个专家对当前令牌的重要性以及令牌对激活的专家贡献,EASY-EP能够识别和保留最相关的专家。
- 实验表明,在相同的内存预算下,EASY-EP方法可以实现与全DeepSeek-R1相当的性能,并且吞吐量提高了$2.99\times$,同时只需要一半的专家数量。
- EASY-EP的代码已公开发布在https://github.com/RUCAIBox/EASYEP。
点此查看论文截图

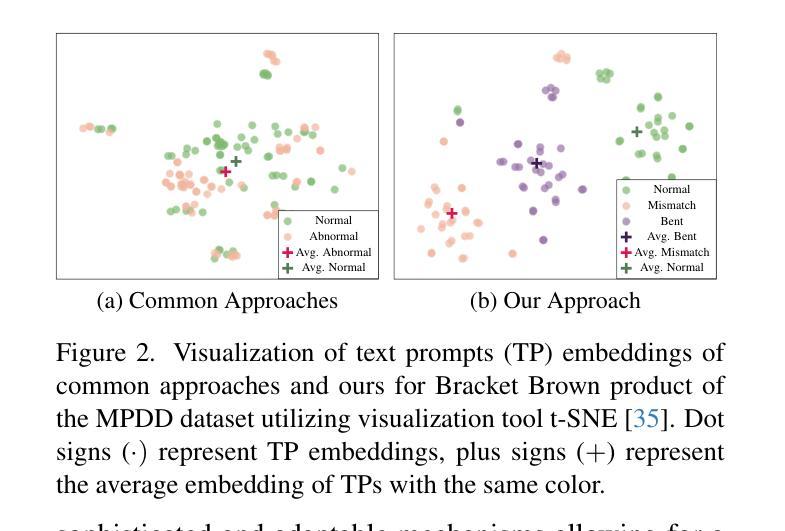
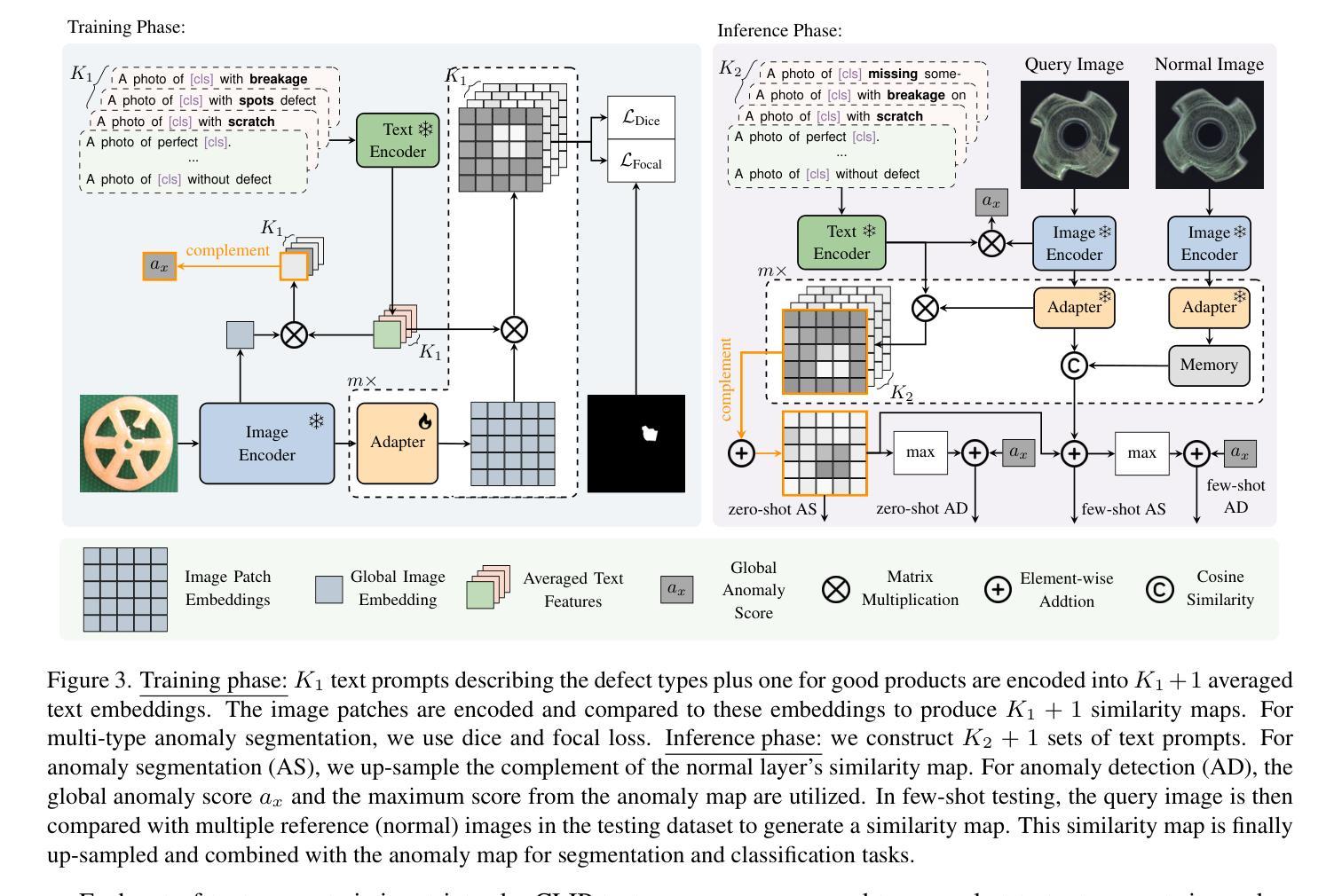
MultiADS: Defect-aware Supervision for Multi-type Anomaly Detection and Segmentation in Zero-Shot Learning
Authors:Ylli Sadikaj, Hongkuan Zhou, Lavdim Halilaj, Stefan Schmid, Steffen Staab, Claudia Plant
Precise optical inspection in industrial applications is crucial for minimizing scrap rates and reducing the associated costs. Besides merely detecting if a product is anomalous or not, it is crucial to know the distinct type of defect, such as a bent, cut, or scratch. The ability to recognize the “exact” defect type enables automated treatments of the anomalies in modern production lines. Current methods are limited to solely detecting whether a product is defective or not without providing any insights on the defect type, nevertheless detecting and identifying multiple defects. We propose MultiADS, a zero-shot learning approach, able to perform Multi-type Anomaly Detection and Segmentation. The architecture of MultiADS comprises CLIP and extra linear layers to align the visual- and textual representation in a joint feature space. To the best of our knowledge, our proposal, is the first approach to perform a multi-type anomaly segmentation task in zero-shot learning. Contrary to the other baselines, our approach i) generates specific anomaly masks for each distinct defect type, ii) learns to distinguish defect types, and iii) simultaneously identifies multiple defect types present in an anomalous product. Additionally, our approach outperforms zero/few-shot learning SoTA methods on image-level and pixel-level anomaly detection and segmentation tasks on five commonly used datasets: MVTec-AD, Visa, MPDD, MAD and Real-IAD.
在工业应用中,精确光学检测对于最小化废品率和降低相关成本至关重要。除了检测产品是否异常外,了解缺陷的特定类型,如弯曲、切割或划痕也非常关键。识别“精确”缺陷类型的能力,使现代生产线中的异常自动化处理成为可能。当前的方法仅限于检测产品是否缺陷,而无法提供关于缺陷类型的任何见解,尽管如此,仍需检测和识别多种缺陷。我们提出了MultiADS,这是一种零样本学习方法,能够进行多类型异常检测和分割。MultiADS架构包括CLIP和额外的线性层,以对视觉和文本表示进行联合特征空间的对齐。据我们所知,我们的提案是零样本学习中进行多类型异常分割任务的第一种方法。与其他基线方法相比,我们的方法具有以下特点:i)为每种不同的缺陷类型生成特定的异常掩膜,ii)学习区分缺陷类型,iii)同时识别异常产品中存在的多种缺陷类型。此外,我们的方法在五个常用数据集上,即在图像级和像素级的异常检测和分割任务上,超越了零/小样学习领域的最新方法。数据集包括MVTec-AD、Visa、MPDD、MAD和Real-IAD。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文强调了工业应用中精确光学检测的重要性,它不仅关乎产品的异常检测,更能区分缺陷的具体类型,如弯曲、切割或划痕等。现有的方法主要局限于检测产品是否缺陷,而MultiADS作为一种零样本学习方法,能够进行多类型异常检测和分割。它结合了CLIP技术和额外的线性层,在联合特征空间中实现对视觉和文本表示的匹配。据我们所知,MultiADS是首个在零样本学习中实现多类型异常分割任务的方法,可以生成针对每种缺陷的特定异常掩膜,同时识别和区分多个异常类型。该方法在五个常用数据集上优于零样本/少样本学习的最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- 精确光学检测在工业应用中至关重要,可最小化废品率和降低成本。
- 识别缺陷的精确类型是实现自动化处理的关键。
- 当前方法主要检测产品是否缺陷,但不提供关于缺陷类型的任何信息。
- MultiADS是一种零样本学习方法,能进行多类型异常检测和分割。
- MultiADS结合了CLIP技术和线性层,在联合特征空间中匹配视觉和文本表示。
- 据了解,MultiADS是首个在零样本学习中实现多类型异常分割任务的方法。
点此查看论文截图

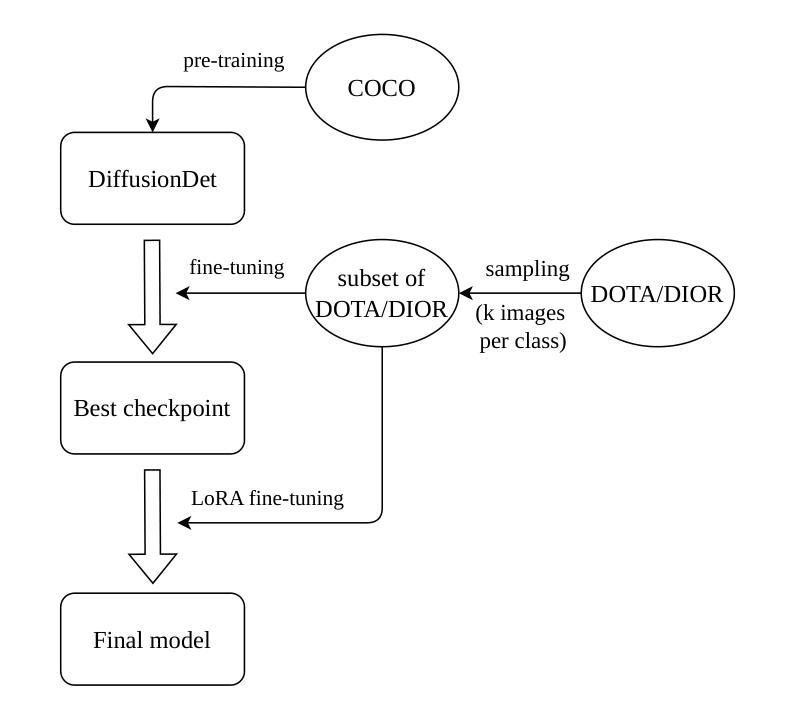
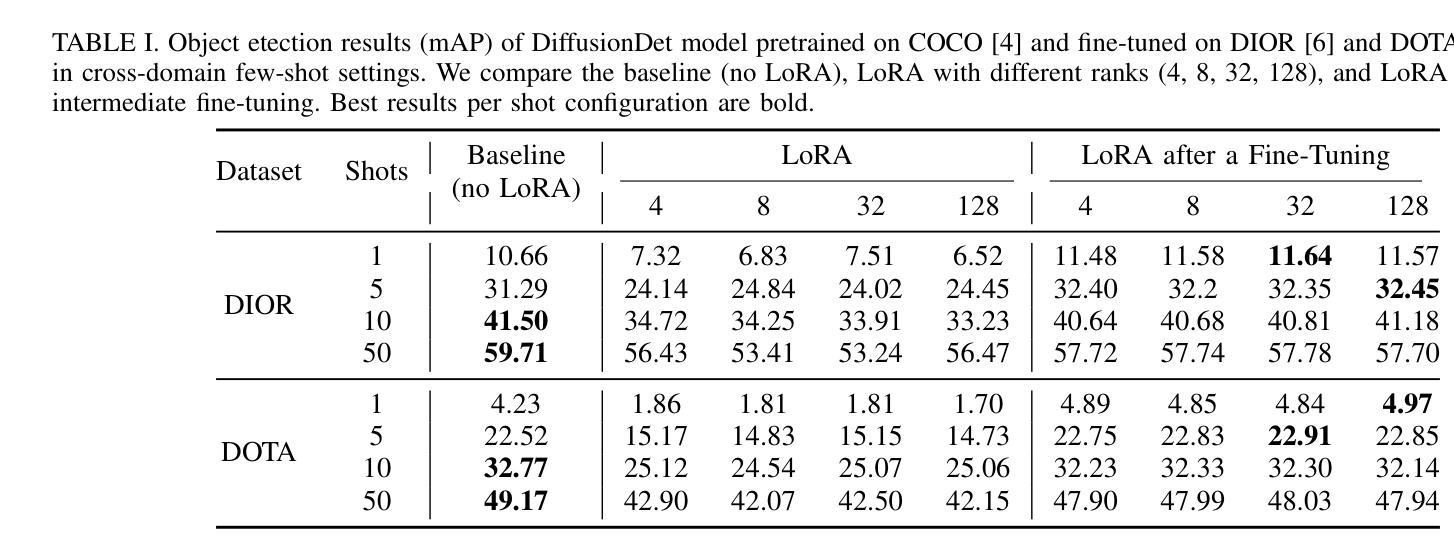
Analyzing the Impact of Low-Rank Adaptation for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection in Aerial Images
Authors:Hicham Talaoubrid, Anissa Mokraoui, Ismail Ben Ayed, Axel Prouvost, Sonimith Hang, Monit Korn, Rémi Harvey
This paper investigates the application of Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to small models for cross-domain few-shot object detection in aerial images. Originally designed for large-scale models, LoRA helps mitigate overfitting, making it a promising approach for resource-constrained settings. We integrate LoRA into DiffusionDet, and evaluate its performance on the DOTA and DIOR datasets. Our results show that LoRA applied after an initial fine-tuning slightly improves performance in low-shot settings (e.g., 1-shot and 5-shot), while full fine-tuning remains more effective in higher-shot configurations. These findings highlight LoRA’s potential for efficient adaptation in aerial object detection, encouraging further research into parameter-efficient fine-tuning strategies for few-shot learning. Our code is available here: https://github.com/HichTala/LoRA-DiffusionDet.
本文探讨了将低秩适应(LoRA)应用于小型模型进行跨域小样本空中图像目标检测的应用。LoRA最初是为大规模模型设计的,有助于缓解过拟合问题,使其成为资源受限环境中的有前途的方法。我们将LoRA集成到DiffusionDet中,并在DOTA和DIOR数据集上评估其性能。结果表明,在初始微调后应用LoRA在低样本设置(例如,1个样本和5个样本)中略微提高了性能,而完全微调在更高样本配置中仍然更有效。这些发现突出了LoRA在航空目标检测中的高效适应性潜力,鼓励对少样本学习的参数有效微调策略进行进一步研究。我们的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/HichTala/LoRA-DiffusionDet。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文探索了将低秩适应(LoRA)应用于小型模型,用于跨域少样本目标检测在航空图像中的表现。LoRA最初是为大规模模型设计的,有助于缓解过拟合问题,使其成为资源受限环境中的有前途的方法。该研究将LoRA集成到DiffusionDet中,并在DOTA和DIOR数据集上评估其性能。结果表明,在少样本设置(例如1-shot和5-shot)下,应用LoRA后稍微提高了性能,而完全微调在高样本配置中更为有效。这突显了LoRA在航空目标检测中的高效适应能力,鼓励针对少样本学习的参数有效微调策略进行进一步研究。
Key Takeaways
- LoRA被应用于小型模型进行跨域少样本目标检测在航空图像中的研究。
- LoRA有助于缓解模型过拟合问题,特别适用于资源受限的环境。
- LoRA集成到DiffusionDet模型中,并在DOTA和DIOR数据集上进行性能评估。
- 在少样本设置下,应用LoRA后性能有所提升。
- 完全微调在高样本配置中更为有效。
- LoRA具有在航空目标检测中的高效适应能力。
点此查看论文截图