⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-11 更新
PathSegDiff: Pathology Segmentation using Diffusion model representations
Authors:Sachin Kumar Danisetty, Alexandros Graikos, Srikar Yellapragada, Dimitris Samaras
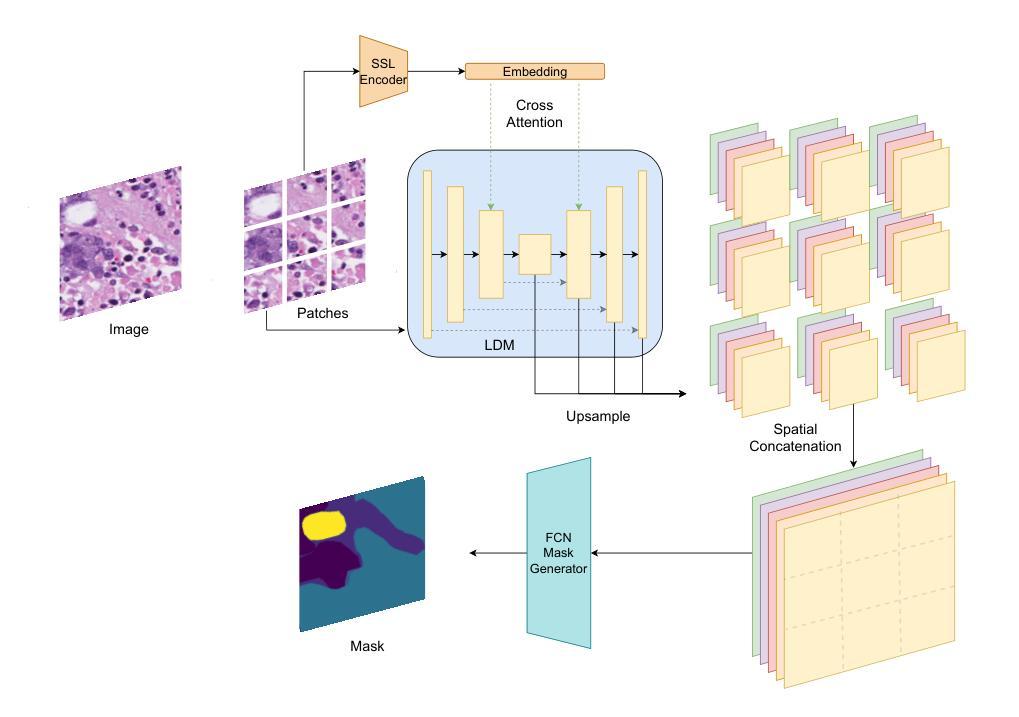
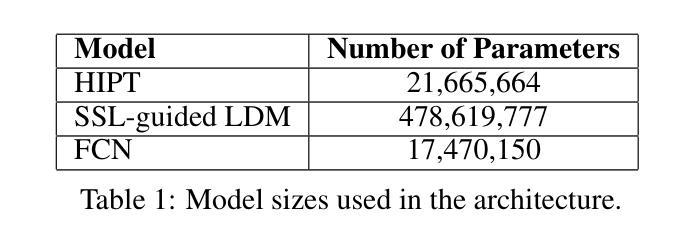
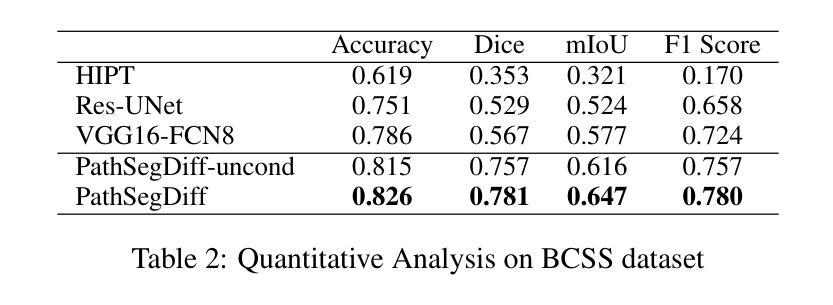
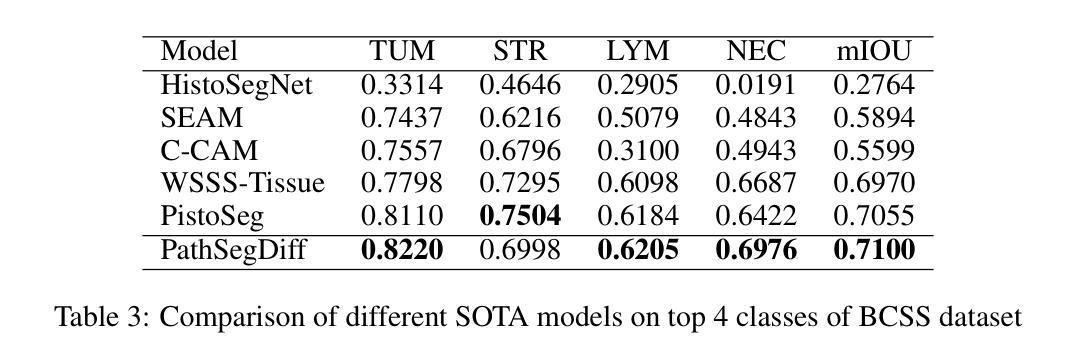
Image segmentation is crucial in many computational pathology pipelines, including accurate disease diagnosis, subtyping, outcome, and survivability prediction. The common approach for training a segmentation model relies on a pre-trained feature extractor and a dataset of paired image and mask annotations. These are used to train a lightweight prediction model that translates features into per-pixel classes. The choice of the feature extractor is central to the performance of the final segmentation model, and recent literature has focused on finding tasks to pre-train the feature extractor. In this paper, we propose PathSegDiff, a novel approach for histopathology image segmentation that leverages Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) as pre-trained featured extractors. Our method utilizes a pathology-specific LDM, guided by a self-supervised encoder, to extract rich semantic information from H&E stained histopathology images. We employ a simple, fully convolutional network to process the features extracted from the LDM and generate segmentation masks. Our experiments demonstrate significant improvements over traditional methods on the BCSS and GlaS datasets, highlighting the effectiveness of domain-specific diffusion pre-training in capturing intricate tissue structures and enhancing segmentation accuracy in histopathology images.
图像分割在计算病理学流程中至关重要,包括准确的疾病诊断、亚型分类、结果预测和生存预测。训练分割模型的常见方法依赖于预训练的特征提取器和配对图像和掩膜注释的数据集。这些用于训练轻量级的预测模型,将特征转化为像素级分类。特征提取器的选择对最终分割模型的性能至关重要,最近的文献主要集中在寻找预训练特征提取器的任务。在本文中,我们提出了PathSegDiff,这是一种利用潜在扩散模型(LDMs)作为预训练特征提取器的新颖方法,用于组织病理学图像分割。我们的方法利用一个病理专用的LDM,由一个自监督编码器引导,从HE染色的组织病理学图像中提取丰富的语义信息。我们使用一个简单、全卷积网络来处理从LDM中提取的特征,并生成分割掩膜。我们的实验在BCSS和GlaS数据集上证明了相较于传统方法的显著改进,突显了领域特定扩散预训练在捕捉复杂组织结构和提高组织病理学图像分割精度方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
病理图像分割对疾病诊断、分型、预后及生存预测等计算病理学流程至关重要。本文提出PathSegDiff方法,采用潜在扩散模型(LDMs)作为预训练特征提取器,结合自监督编码器,从H&E染色病理图像中提取丰富语义信息。实验证明,与传统方法相比,该方法在BCSS和GlaS数据集上显著提高分割准确性,凸显领域特定扩散预训练捕捉复杂组织结构的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 图像分割在计算病理学中具有重要作用,包括疾病诊断、分型、预后和生存预测。
- 预训练特征提取器的选择对分割模型性能至关重要。
- PathSegDiff方法利用潜在扩散模型(LDMs)作为病理图像的特征提取器。
- PathSegDiff采用自监督编码器引导病理特异性LDM,提取H&E染色病理图像中的丰富语义信息。
- 实验证明,与传统方法相比,PathSegDiff在BCSS和GlaS数据集上显著提高分割准确性。
- 领域特定的扩散预训练能有效捕捉病理图像中的复杂组织结构。
- PathSegDiff方法采用简单全卷积网络处理从LDM提取的特征并生成分割掩膜。
点此查看论文截图