⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-12 更新
Zero-Shot Low-dose CT Denoising via Sinogram Flicking
Authors:Yongyi Shi, Ge Wang
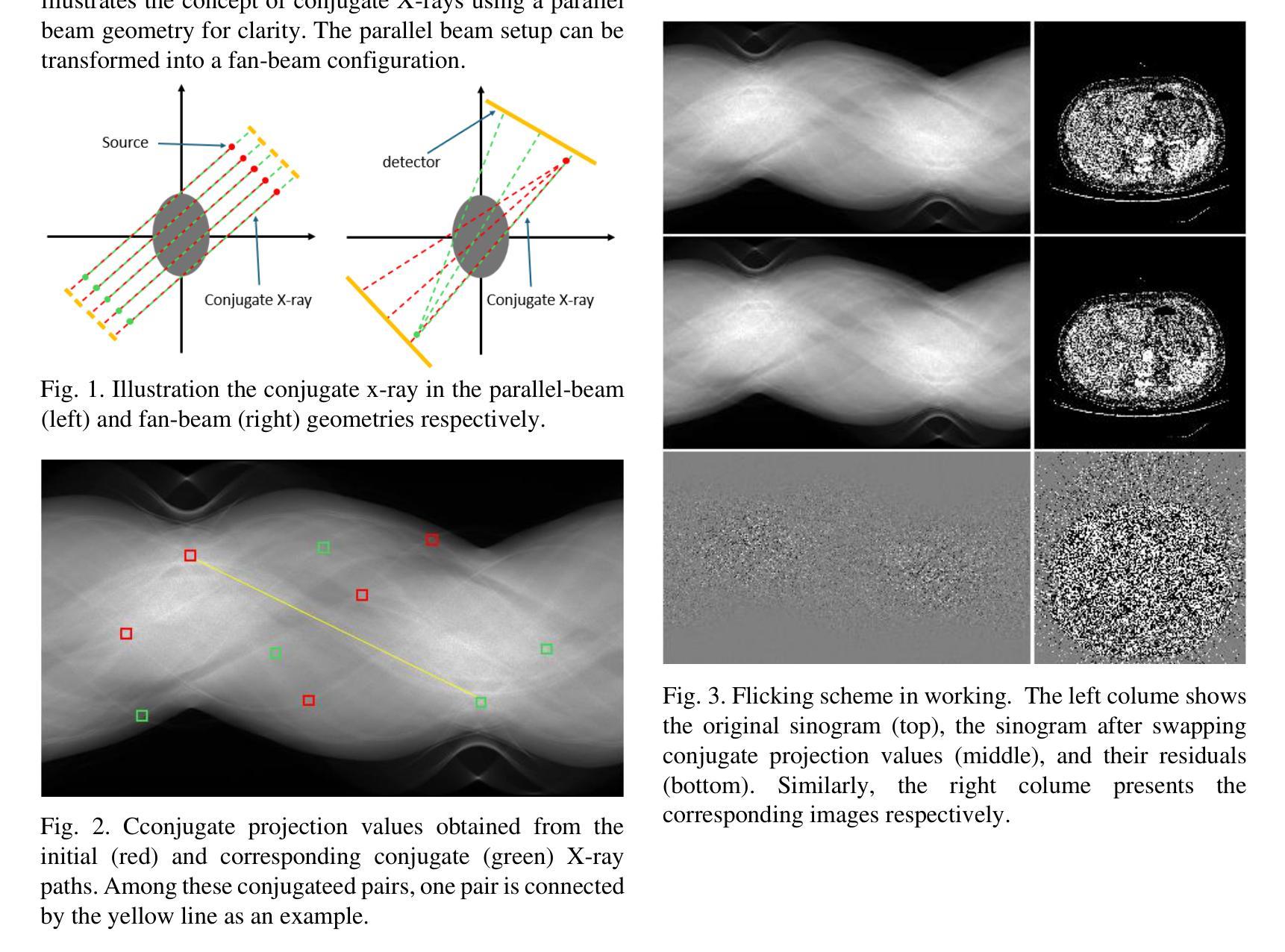
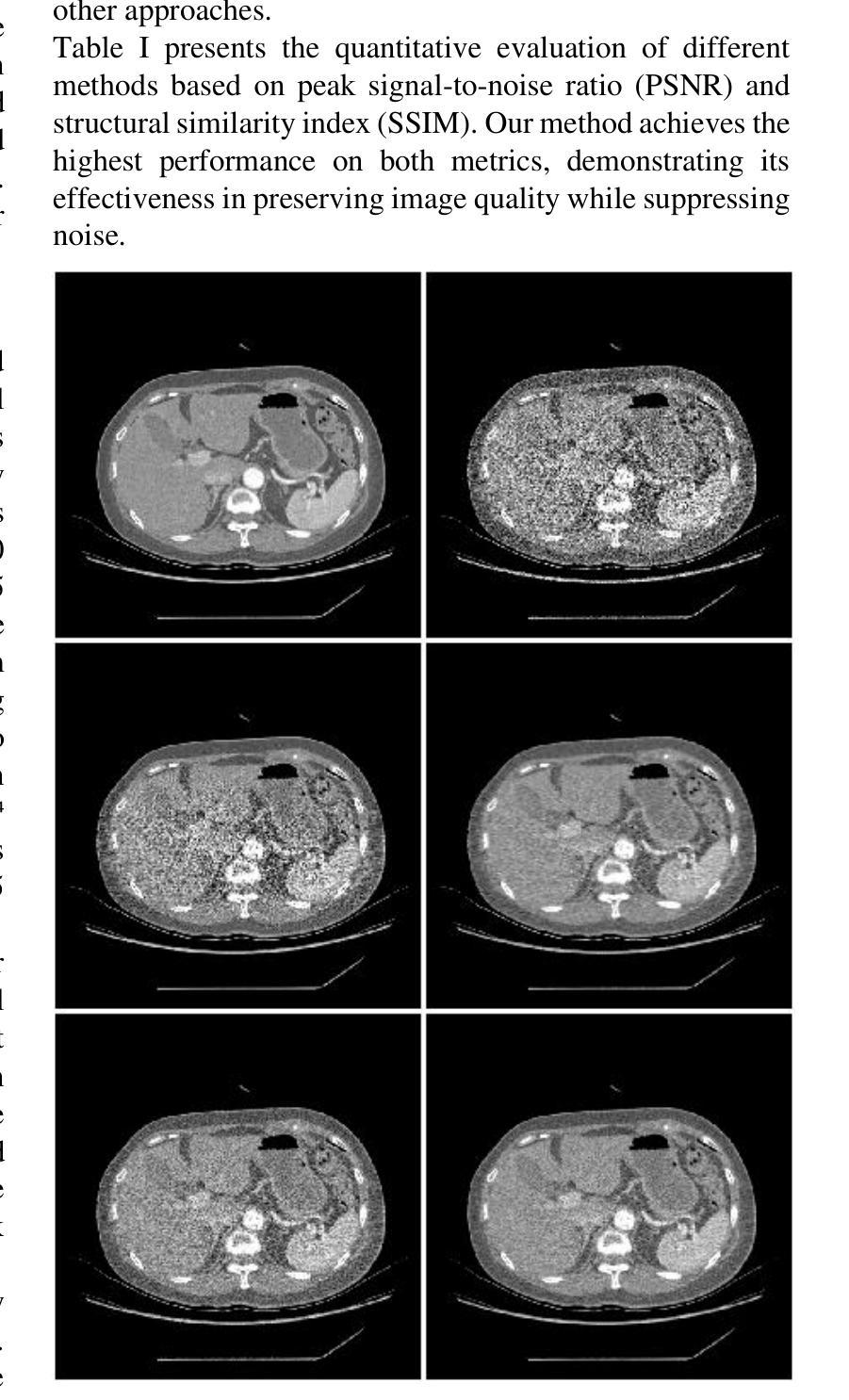
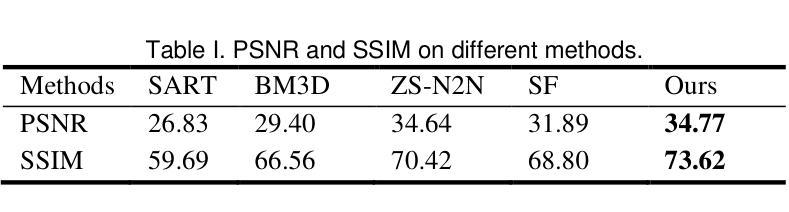
Many low-dose CT imaging methods rely on supervised learning, which requires a large number of paired noisy and clean images. However, obtaining paired images in clinical practice is challenging. To address this issue, zero-shot self-supervised methods train denoising networks using only the information within a single image, such as ZS-N2N. However, these methods often employ downsampling operations that degrade image resolution. Additionally, the training dataset is inherently constrained to the image itself. In this paper, we propose a zero-shot low-dose CT imaging method based on sinogram flicking, which operates within a single image but generates many copies via random conjugate ray matching. Specifically, two conjugate X-ray pencil beams measure the same path; their expected values should be identical, while their noise levels vary during measurements. By randomly swapping portions of the conjugate X-rays in the sinogram domain, we generate a large set of sinograms with consistent content but varying noise patterns. When displayed dynamically, these sinograms exhibit a flickering effect due to their identical structural content but differing noise patterns-hence the term sinogram flicking. We train the network on pairs of sinograms with the same content but different noise distributions using a lightweight model adapted from ZS-NSN. This process is repeated to obtain the final results. A simulation study demonstrates that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches such as ZS-N2N.
许多低剂量CT成像方法依赖于监督学习,这需要大量配对的有噪声和清洁图像。然而,在临床实践中获取配对图像具有挑战性。为了解决这一问题,零样本自监督方法仅使用单幅图像内的信息进行去噪网络训练,例如ZS-N2N。然而,这些方法通常采用降采样操作,会降低图像分辨率。此外,训练数据集本质上受限于图像本身。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于辛图闪烁的零剂量低剂量CT成像方法,它在单个图像内进行操作,但通过随机共轭射线匹配生成多个副本。具体来说,两条共轭的X射线铅笔光束测量相同的路径;它们的期望值应该相同,而噪声水平在测量过程中会有所不同。通过随机交换辛图中的共轭X射线的部分,我们生成了大量具有一致内容但噪声模式各异的辛图。由于它们具有相同的结构内容但噪声模式不同,当动态显示时,这些辛图会表现出闪烁效果——因此称为辛图闪烁。我们使用具有相同内容但噪声分布不同的辛图对进行网络训练,使用从ZS-NSN改编的轻量级模型。该过程会重复进行以获取最终结果。模拟研究表明,我们的方法优于最先进的方法,如ZS-N2N。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本摘要提供了一种基于零样本自监督学习方法的低剂量CT成像新技术。该技术通过随机交换正弦图域中的共轭射线部分,生成具有一致内容但不同噪声模式的多个正弦图副本。训练网络使用具有相同内容但不同噪声分布的正弦图对进行训练,并采用轻量级模型,从而在不依赖大量配对噪声和清洁图像的情况下提升图像去噪效果。模拟研究表明,该方法优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于零样本自监督学习方法的低剂量CT成像技术。
- 通过随机交换正弦图域中的共轭射线部分,生成具有一致内容但不同噪声模式的正弦图副本。
- 训练网络使用具有相同内容但不同噪声分布的正弦图对进行训练。
- 采用了轻量级模型以适应这种训练方法,实现了高效去噪。
- 该技术能有效解决临床实践中配对图像获取困难的问题。
- 模拟研究表明,该技术相较于现有技术如ZS-N2N有更好的表现。
点此查看论文截图

Nonlocal Retinex-Based Variational Model and its Deep Unfolding Twin for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Authors:Daniel Torres, Joan Duran, Julia Navarro, Catalina Sbert
Images captured under low-light conditions present significant limitations in many applications, as poor lighting can obscure details, reduce contrast, and hide noise. Removing the illumination effects and enhancing the quality of such images is crucial for many tasks, such as image segmentation and object detection. In this paper, we propose a variational method for low-light image enhancement based on the Retinex decomposition into illumination, reflectance, and noise components. A color correction pre-processing step is applied to the low-light image, which is then used as the observed input in the decomposition. Moreover, our model integrates a novel nonlocal gradient-type fidelity term designed to preserve structural details. Additionally, we propose an automatic gamma correction module. Building on the proposed variational approach, we extend the model by introducing its deep unfolding counterpart, in which the proximal operators are replaced with learnable networks. We propose cross-attention mechanisms to capture long-range dependencies in both the nonlocal prior of the reflectance and the nonlocal gradient-based constraint. Experimental results demonstrate that both methods compare favorably with several recent and state-of-the-art techniques across different datasets. In particular, despite not relying on learning strategies, the variational model outperforms most deep learning approaches both visually and in terms of quality metrics.
在低光照条件下捕捉的图像在许多应用中存在显著局限性,因为光线不足会掩盖细节、降低对比度和隐藏噪声。去除照明效果、提高此类图像的质量对于图像分割和对象检测等许多任务至关重要。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于Retinex分解(分解出照明、反射和噪声成分)的低光照图像增强变分方法。对低光照图像应用了颜色校正预处理步骤,然后将其作为观察输入用于分解。此外,我们的模型集成了一种新型的非局部梯度型保真度项,旨在保留结构细节。我们还提出了一种自动伽马校正模块。基于所提出的变分方法,我们通过引入其深度展开对应物来扩展模型,其中近端算子被可学习的网络所替代。我们提出了交叉注意机制,以捕获反射的非局部先验和基于非局部梯度的约束中的长距离依赖关系。实验结果表明,两种方法在不同数据集上均优于最近的一些最先进技术。尤其值得一提的是,尽管不依赖于学习策略,变分模型在视觉和质量指标方面均优于大多数深度学习方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于Retinex分解的低光图像增强变分方法,通过分解图像为照明、反射和噪声成分,提高低光图像的视觉质量。方法包含颜色校正预处理步骤,并采用新型非局部梯度型保真度项以保留结构细节。此外,引入自动伽马校正模块,并采用深度学习技术实现模型展开,通过交叉注意力机制捕捉反射的非局部先验和基于梯度的约束的长期依赖性。实验结果显示,该方法与最新技术相比表现优异,尤其在视觉和质量指标方面,即使不依赖学习策略,变分模型也能超越大多数深度学习方法。
Key Takeaways
- 低光图像在多种应用中存在显著局限性,如图像分割和对象检测等。
- 提出一种基于Retinex分解的低光图像增强变分方法,旨在提高图像质量并去除照明影响。
- 采用颜色校正预处理步骤和非局部梯度型保真度项以保留结构细节。
- 引入自动伽马校正模块进行进一步优化。
- 结合深度学习技术实现模型的展开化,并通过交叉注意力机制捕捉长期依赖性。
- 实验结果显示该方法与现有技术相比表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

PRAD: Periapical Radiograph Analysis Dataset and Benchmark Model Development
Authors:Zhenhuan Zhou, Yuchen Zhang, Ruihong Xu, Xuansen Zhao, Tao Li
Deep learning (DL), a pivotal technology in artificial intelligence, has recently gained substantial traction in the domain of dental auxiliary diagnosis. However, its application has predominantly been confined to imaging modalities such as panoramic radiographs and Cone Beam Computed Tomography, with limited focus on auxiliary analysis specifically targeting Periapical Radiographs (PR). PR are the most extensively utilized imaging modality in endodontics and periodontics due to their capability to capture detailed local lesions at a low cost. Nevertheless, challenges such as resolution limitations and artifacts complicate the annotation and recognition of PR, leading to a scarcity of publicly available, large-scale, high-quality PR analysis datasets. This scarcity has somewhat impeded the advancement of DL applications in PR analysis. In this paper, we present PRAD-10K, a dataset for PR analysis. PRAD-10K comprises 10,000 clinical periapical radiograph images, with pixel-level annotations provided by professional dentists for nine distinct anatomical structures, lesions, and artificial restorations or medical devices, We also include classification labels for images with typical conditions or lesions. Furthermore, we introduce a DL network named PRNet to establish benchmarks for PR segmentation tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that PRNet surpasses previous state-of-the-art medical image segmentation models on the PRAD-10K dataset. The codes and dataset will be made publicly available.
深度学习(DL)是人工智能中的一项关键技术,最近在牙科辅助诊断领域获得了大量的关注。然而,它的应用主要集中在全景放射影像和锥形束计算机断层扫描等成像模式上,对于根尖周放射影像(PR)的辅助分析关注有限。由于PR能够以低成本捕获详细的局部病变,因此在牙髓学和牙周病学中是最广泛使用的成像方式。然而,分辨率限制和伪影等挑战使PR的标注和识别变得复杂,导致公开可用的大规模高质量PR分析数据集稀缺。这种稀缺状况在一定程度上阻碍了DL在PR分析中的应用发展。在本文中,我们介绍了用于PR分析的PRAD-10K数据集。PRAD-10K包含10,000张临床根尖周放射影像图像,由专业牙医提供像素级标注,涵盖九种不同的解剖结构、病变以及人工修复体或医疗设备。我们还为典型状况或病变的图像提供了分类标签。此外,我们还引入了一个名为PRNet的DL网络,为PR分割任务建立基准测试。实验结果表明,PRNet在PRAD-10K数据集上的性能超过了之前最先进的医学图像分割模型。代码和数据集将公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages & Under Review
Summary
深度学习技术在牙科辅助诊断领域的应用逐渐受到关注,尤其在全景射影和锥形束计算机断层扫描等成像方式中。然而,针对根尖周射影(PR)的辅助分析尚显不足。PR是牙髓病学和牙周病学中最广泛使用的成像方式,能够低成本地捕获局部详细病变。但PR分析面临分辨率限制和伪影等挑战,高质量的大型公开数据集较为稀缺,制约了深度学习在PR分析中的应用。本文提出了PRAD-10K数据集和PRNet网络,为PR分析提供基准测试。PRAD-10K包含10,000张临床根尖周射影图像,由专业牙医提供像素级注释,涵盖九种不同的解剖结构、病变和人工修复体或医疗设备。PRNet在PRAD-10K数据集上的表现超过其他先进的医学图像分割模型。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在牙科辅助诊断中的应用逐渐受到关注,特别是在全景射影和锥形束计算机断层扫描领域。
- 根尖周射影(PR)是最常用的牙髓病学和牙周病学成像方式,但由于分辨率限制和伪影等问题,其分析面临挑战。
- 目前缺乏公开的大型高质量PR分析数据集,限制了深度学习在PR分析中的应用。
- 本文提出了PRAD-10K数据集,包含专业牙医提供的像素级注释,涵盖多种解剖结构、病变等。
- 同时介绍了PRNet网络,该网络在PRAD-10K数据集上的表现优于其他医学图像分割模型。
- 本文将公开数据集和代码,为PR分析提供基准测试。
点此查看论文截图

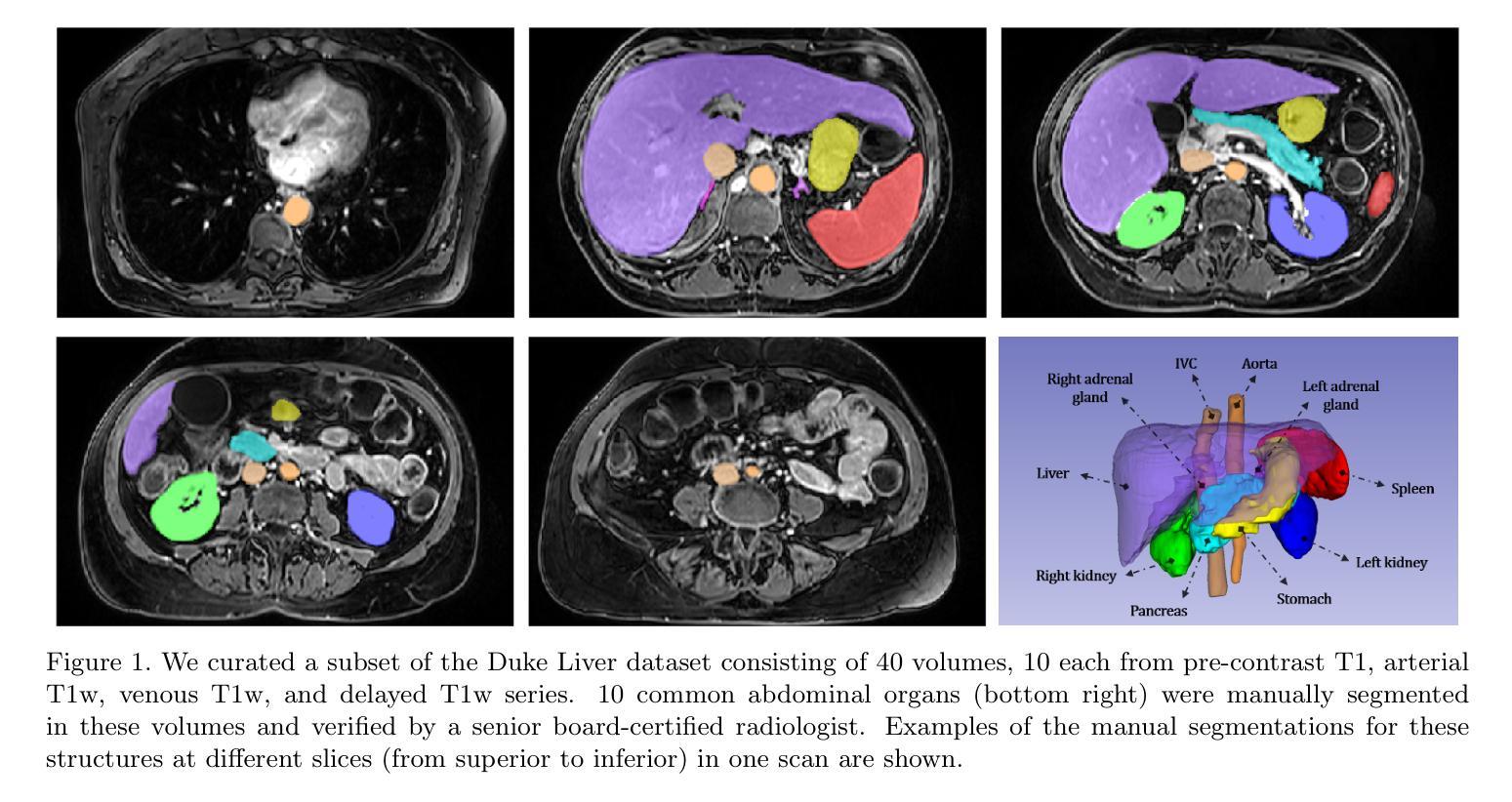
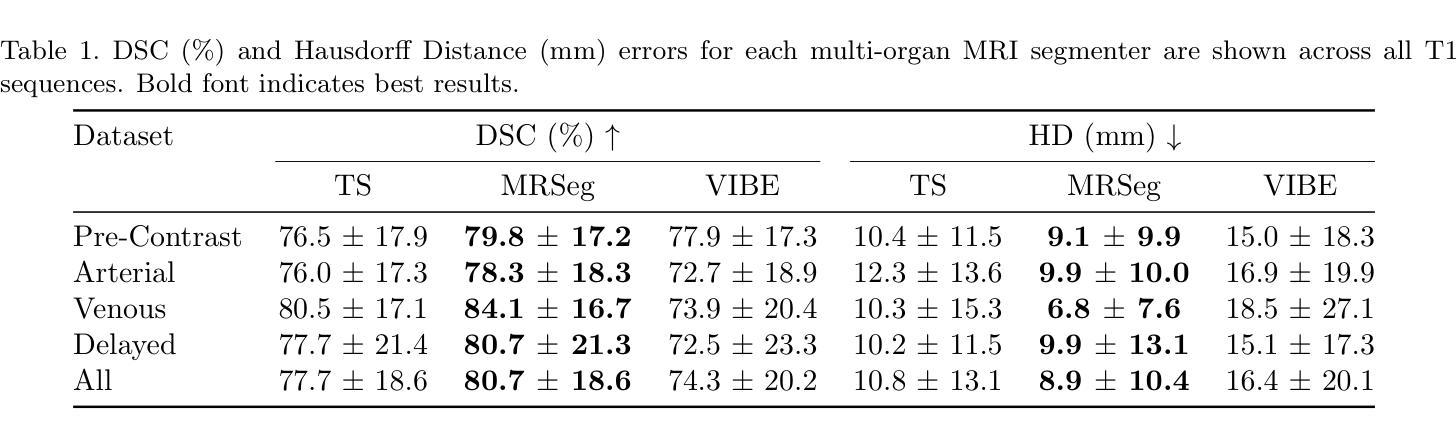
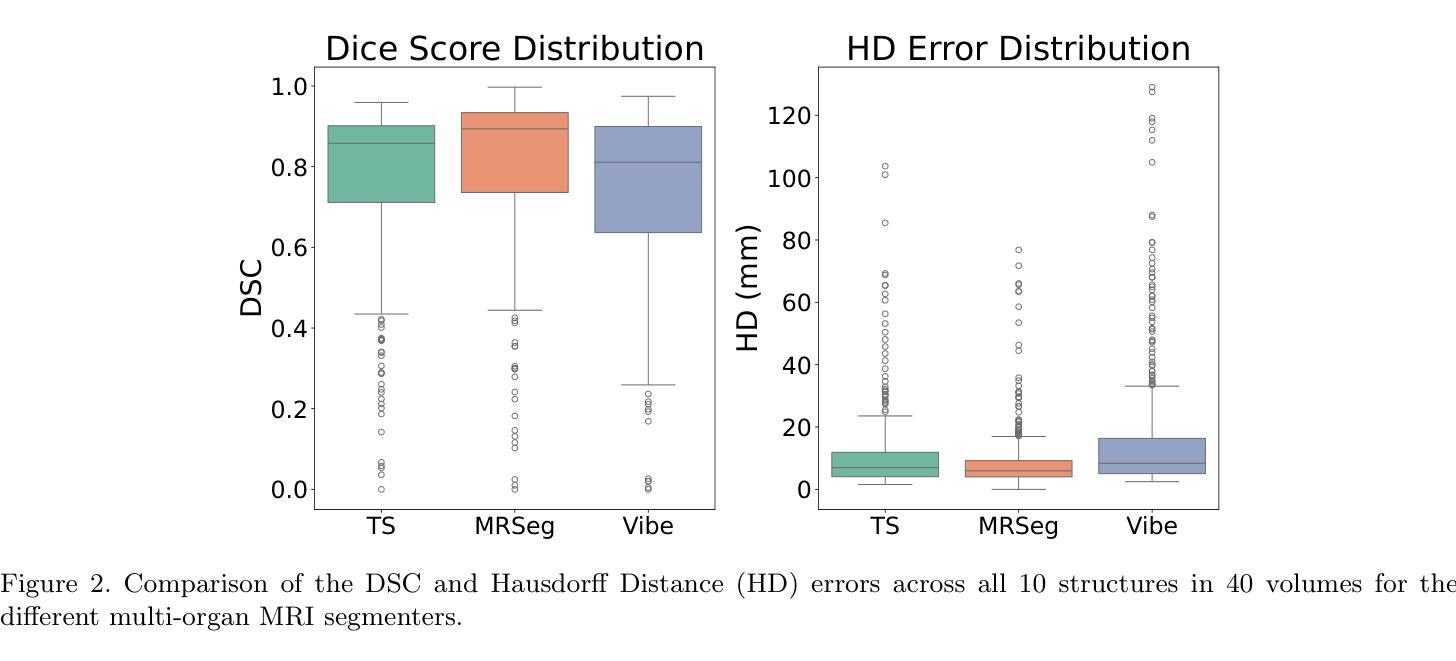
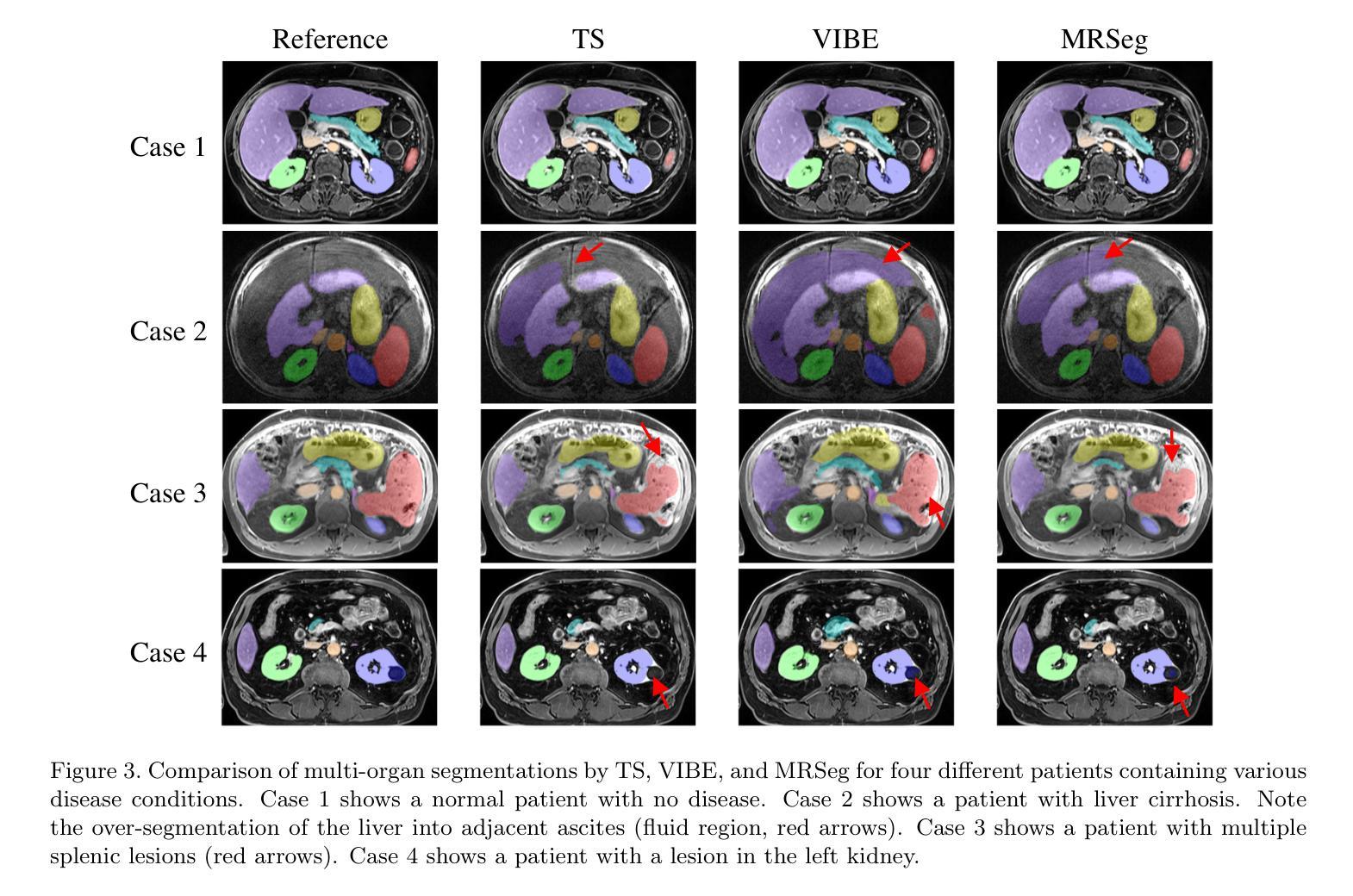
Benchmarking Multi-Organ Segmentation Tools for Multi-Parametric T1-weighted Abdominal MRI
Authors:Nicole Tran, Anisa Prasad, Yan Zhuang, Tejas Sudharshan Mathai, Boah Kim, Sydney Lewis, Pritam Mukherjee, Jianfei Liu, Ronald M. Summers
The segmentation of multiple organs in multi-parametric MRI studies is critical for many applications in radiology, such as correlating imaging biomarkers with disease status (e.g., cirrhosis, diabetes). Recently, three publicly available tools, such as MRSegmentator (MRSeg), TotalSegmentator MRI (TS), and TotalVibeSegmentator (VIBE), have been proposed for multi-organ segmentation in MRI. However, the performance of these tools on specific MRI sequence types has not yet been quantified. In this work, a subset of 40 volumes from the public Duke Liver Dataset was curated. The curated dataset contained 10 volumes each from the pre-contrast fat saturated T1, arterial T1w, venous T1w, and delayed T1w phases, respectively. Ten abdominal structures were manually annotated in these volumes. Next, the performance of the three public tools was benchmarked on this curated dataset. The results indicated that MRSeg obtained a Dice score of 80.7 $\pm$ 18.6 and Hausdorff Distance (HD) error of 8.9 $\pm$ 10.4 mm. It fared the best ($p < .05$) across the different sequence types in contrast to TS and VIBE.
在多参数MRI研究中,多器官分割对于放射学中的许多应用至关重要,例如将成像生物标志物与疾病状态(如肝硬化、糖尿病等)进行关联。最近,提出了三种公开工具,包括MRSegmentator(MRSeg)、TotalSegmentator MRI(TS)和TotalVibeSegmentator(VIBE),用于MRI中的多器官分割。然而,这些工具在特定MRI序列类型上的性能尚未得到量化。
在这项工作中,从公共Duke肝脏数据集中挑选了40个体积的子集。该精选数据集包含来自预饱和脂肪T1、动脉T1w、静脉T1w和延迟T1w阶段的各10个体积,并在这些体积中手动标注了10个腹部结构。接下来,在这组精选数据集上对这三种公开工具的性能进行了基准测试。结果表明,MRSeg的Dice得分为80.7±18.6,Hausdorff Distance(HD)误差为8.9±10.4毫米。与TS和VIBE相比,它在不同的序列类型中表现最佳(p < .05)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at SPIE Medical Imaging 2025
Summary
多参数MRI研究中多器官分割对放射学应用至关重要,如将影像生物标志物与疾病状态相关联(如肝硬化、糖尿病等)。近期推出三款公开工具MRSegmentator、TotalSegmentator MRI和TotalVibeSegmentator用于MRI多器官分割,但这些工具在特定MRI序列上的表现尚未量化。本研究选用公共Duke Liver Dataset的40体积子集,包含不同阶段的T1加权图像,对腹部10个结构进行手动标注,以评估这三款工具的表现。结果显示,MRSeg的Dice得分为80.7±18.6,Hausdorff Distance误差为8.9±10.4mm,在不同序列中表现最佳。
Key Takeaways
- 多参数MRI研究中多器官分割对放射学应用非常重要。
- 存在多款公开工具用于MRI多器官分割,包括MRSegmentator、TotalSegmentator MRI和TotalVibeSegmentator。
- 这些工具在特定MRI序列上的表现尚未得到充分评估。
- 研究选用Duke Liver Dataset的40体积子集进行评估。
- 研究对腹部10个结构进行了手动标注。
- MRSeg在多种MRI序列上表现最佳,Dice得分为80.7±18.6,Hausdorff Distance误差为8.9±10.4mm。
点此查看论文截图

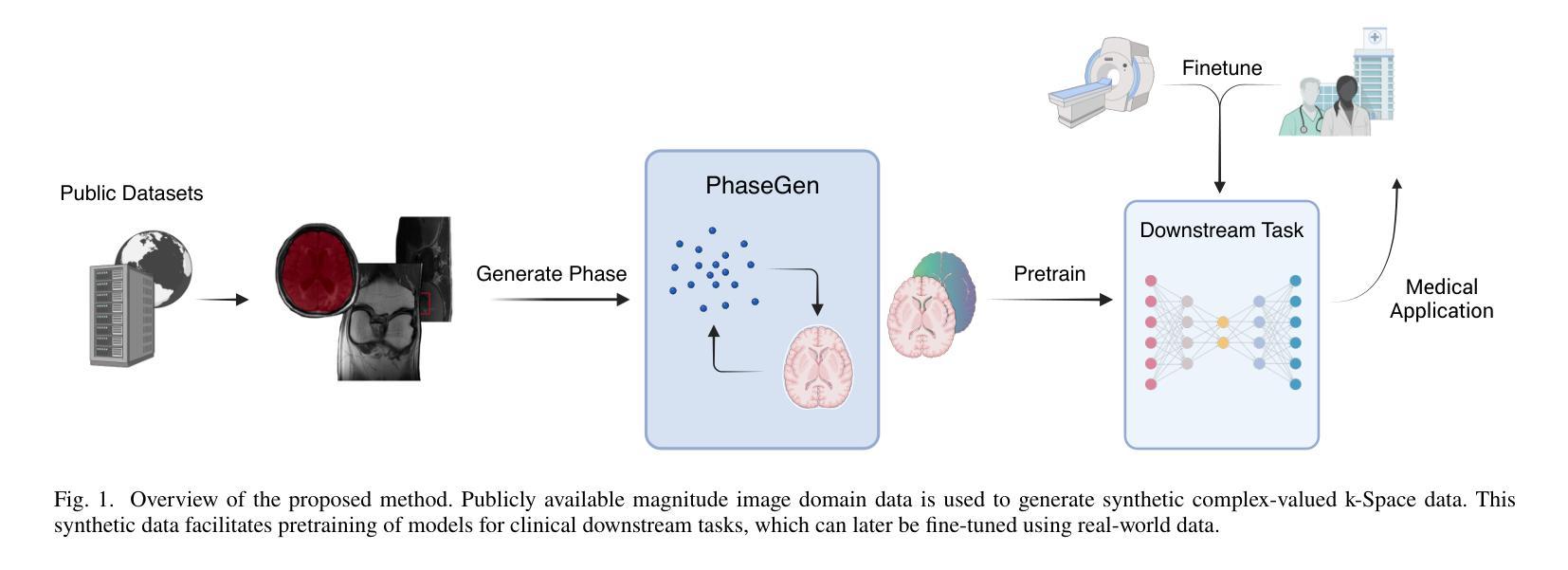
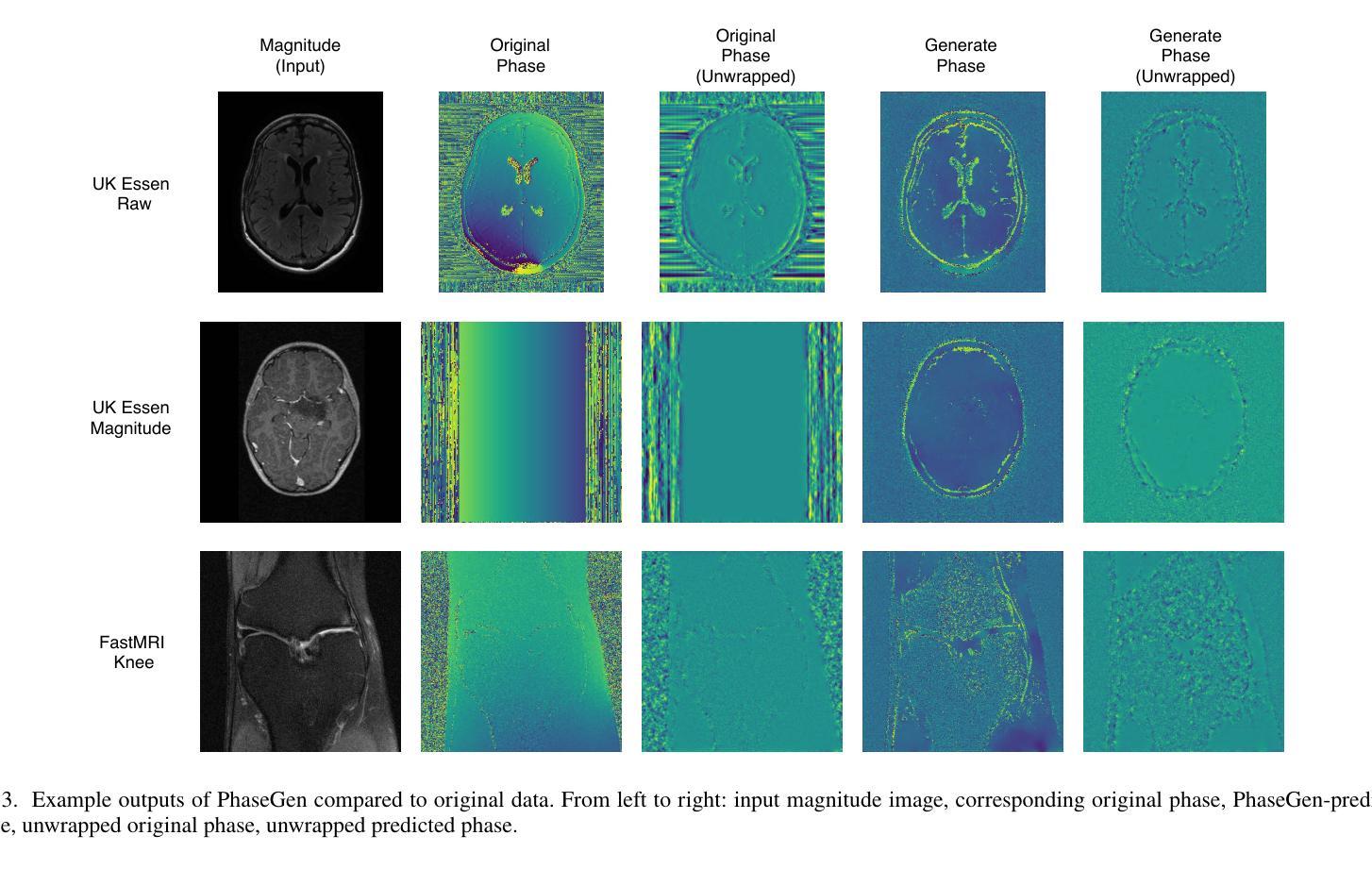
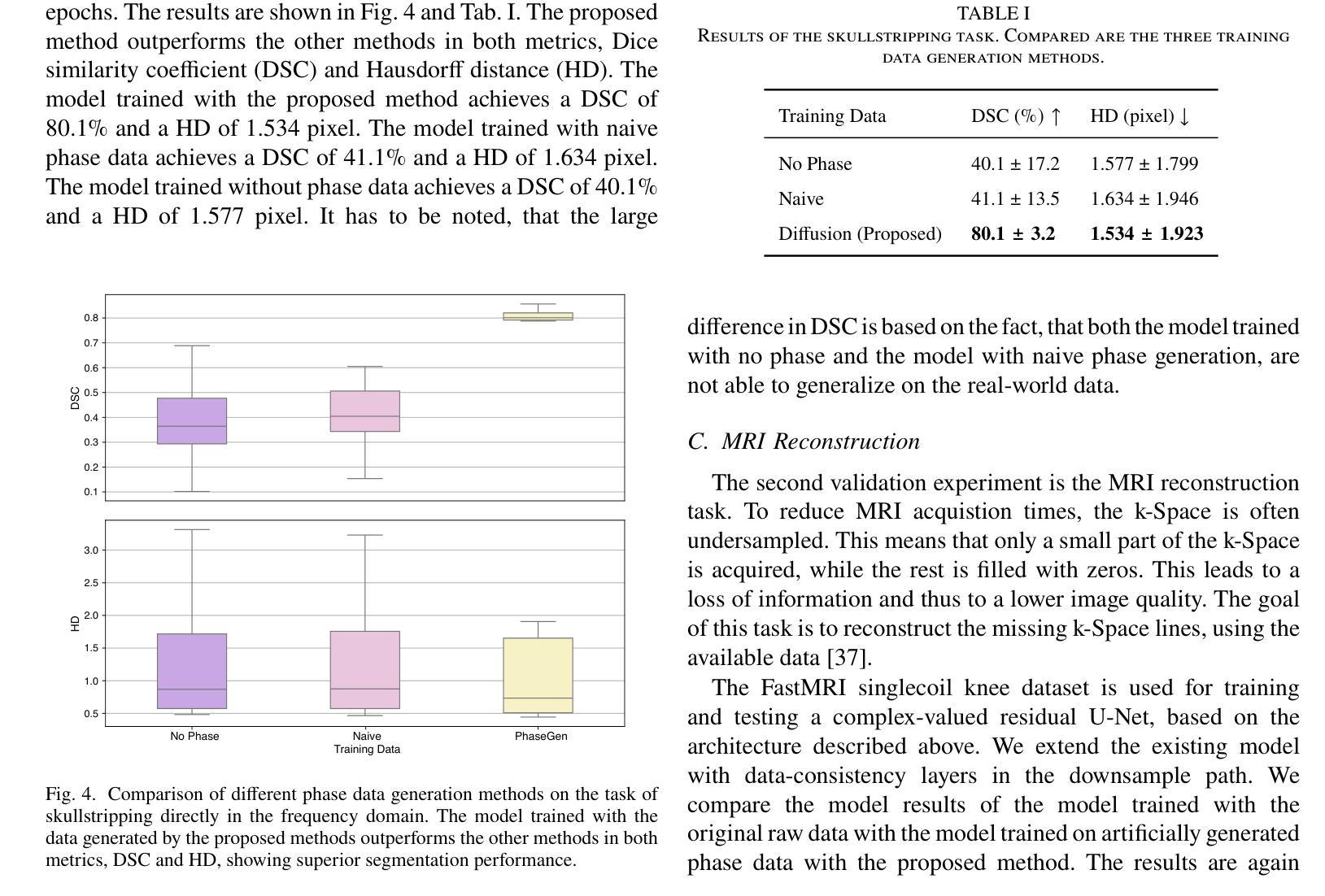
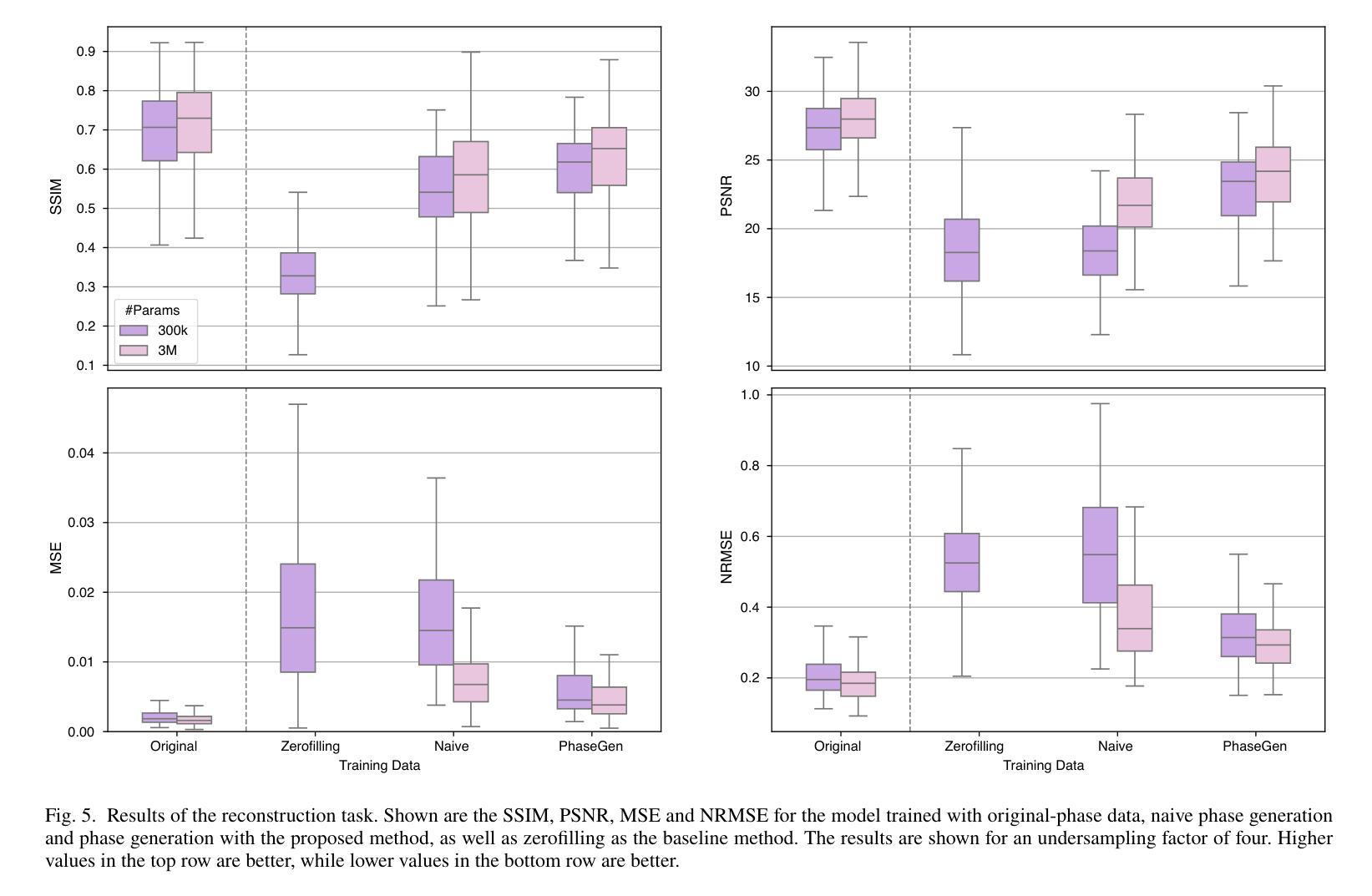
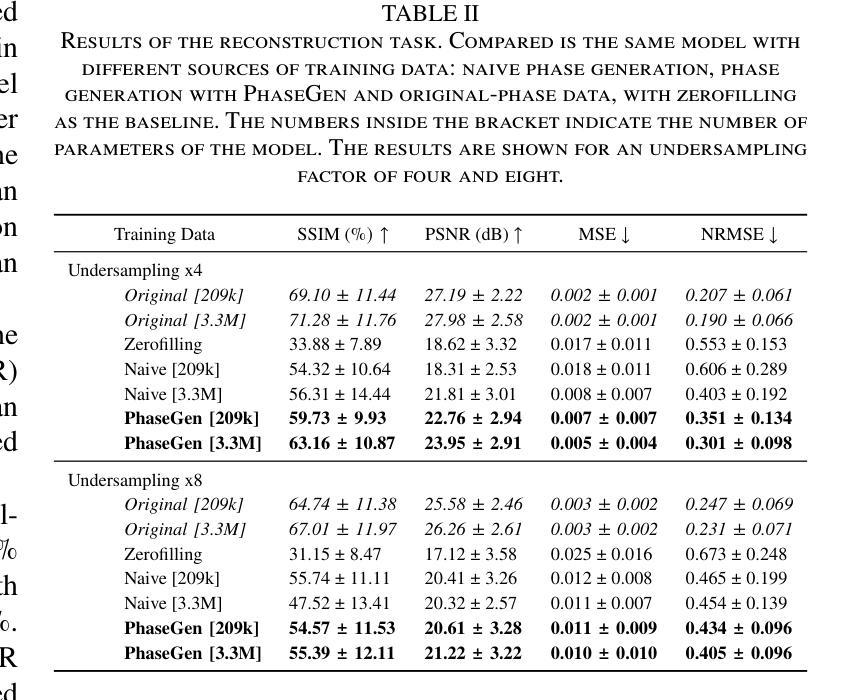
PhaseGen: A Diffusion-Based Approach for Complex-Valued MRI Data Generation
Authors:Moritz Rempe, Fabian Hörst, Helmut Becker, Marco Schlimbach, Lukas Rotkopf, Kevin Kröninger, Jens Kleesiek
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) raw data, or k-Space data, is complex-valued, containing both magnitude and phase information. However, clinical and existing Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based methods focus only on magnitude images, discarding the phase data despite its potential for downstream tasks, such as tumor segmentation and classification. In this work, we introduce $\textit{PhaseGen}$, a novel complex-valued diffusion model for generating synthetic MRI raw data conditioned on magnitude images, commonly used in clinical practice. This enables the creation of artificial complex-valued raw data, allowing pretraining for models that require k-Space information. We evaluate PhaseGen on two tasks: skull-stripping directly in k-Space and MRI reconstruction using the publicly available FastMRI dataset. Our results show that training with synthetic phase data significantly improves generalization for skull-stripping on real-world data, with an increased segmentation accuracy from $41.1%$ to $80.1%$, and enhances MRI reconstruction when combined with limited real-world data. This work presents a step forward in utilizing generative AI to bridge the gap between magnitude-based datasets and the complex-valued nature of MRI raw data. This approach allows researchers to leverage the vast amount of avaliable image domain data in combination with the information-rich k-Space data for more accurate and efficient diagnostic tasks. We make our code publicly $\href{https://github.com/TIO-IKIM/PhaseGen}{\text{available here}}$.
核磁共振成像(MRI)原始数据或k-空间数据是复数形式的,包含幅度和相位信息。然而,现有的临床和基于人工智能(AI)的方法仅关注幅度图像,尽管相位数据对下游任务(如肿瘤分割和分类)具有潜力,但仍将其丢弃。在这项工作中,我们介绍了$\textit{PhaseGen}$,这是一种新型的复数扩散模型,可以根据幅度图像生成模拟MRI原始数据,这在临床实践中是常见的。这能够创建人工的复数原始数据,允许对需要k-空间信息的模型进行预训练。我们在两个任务上对PhaseGen进行了评估:直接在k-空间中进行颅骨剥离,以及使用公开可用的FastMRI数据集进行MRI重建。我们的结果表明,使用合成相位数据进行训练显著提高了在现实数据上进行颅骨剥离的泛化能力,分割准确度从41.1%提高到80.1%,并且在与有限的现实数据相结合时,增强了MRI重建的效果。这项工作展示了如何利用生成式人工智能来弥补基于幅度的数据集与MRI原始数据的复数性质之间的差距。这种方法允许研究人员结合大量可用的图像域数据和丰富的k-空间数据,以更准确、更高效地执行诊断任务。我们的代码可在https://github.com/TIO-IKIM/PhaseGen获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究介绍了一种新型复杂值扩散模型PhaseGen,能够基于幅度图像生成模拟的MRI原始数据。该模型可应用于生成模拟MRI k-Space数据,从而满足对原始k-Space信息的训练需求。实验结果表明,利用合成相位数据进行训练可有效提高在现实数据上的颅骨剥离分段准确性,并提升MRI重建质量。这项研究为利用生成人工智能弥补了基于幅度数据集与复杂值MRI原始数据之间的差距提供了方向。
Key Takeaways
- PhaseGen是一种复杂值扩散模型,可从幅度图像生成模拟MRI原始数据。
- 该模型能够在k-Space生成人工数据,为需要k-Space信息的模型提供预训练机会。
- 通过颅骨剥离实验证明,使用合成相位数据进行训练显著提高分段准确性。
- 结合有限现实数据,MRI重建质量得到提升。
- 该研究首次利用生成AI来缩小基于幅度的数据集与MRI原始数据的差异。
- 公开可用的PhaseGen代码为研究者利用大量图像域数据和丰富的k-Space信息提供了工具。
点此查看论文截图


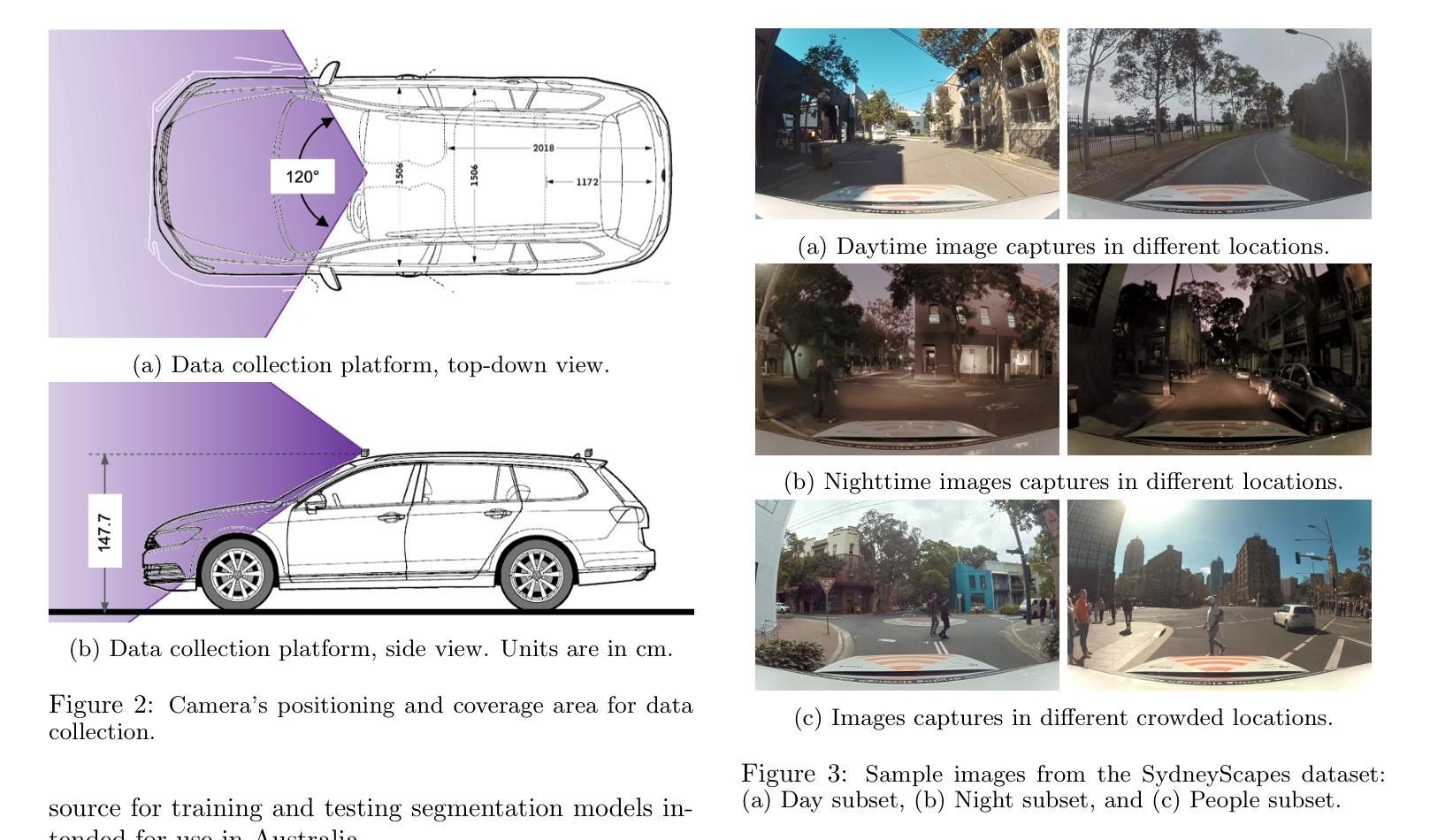
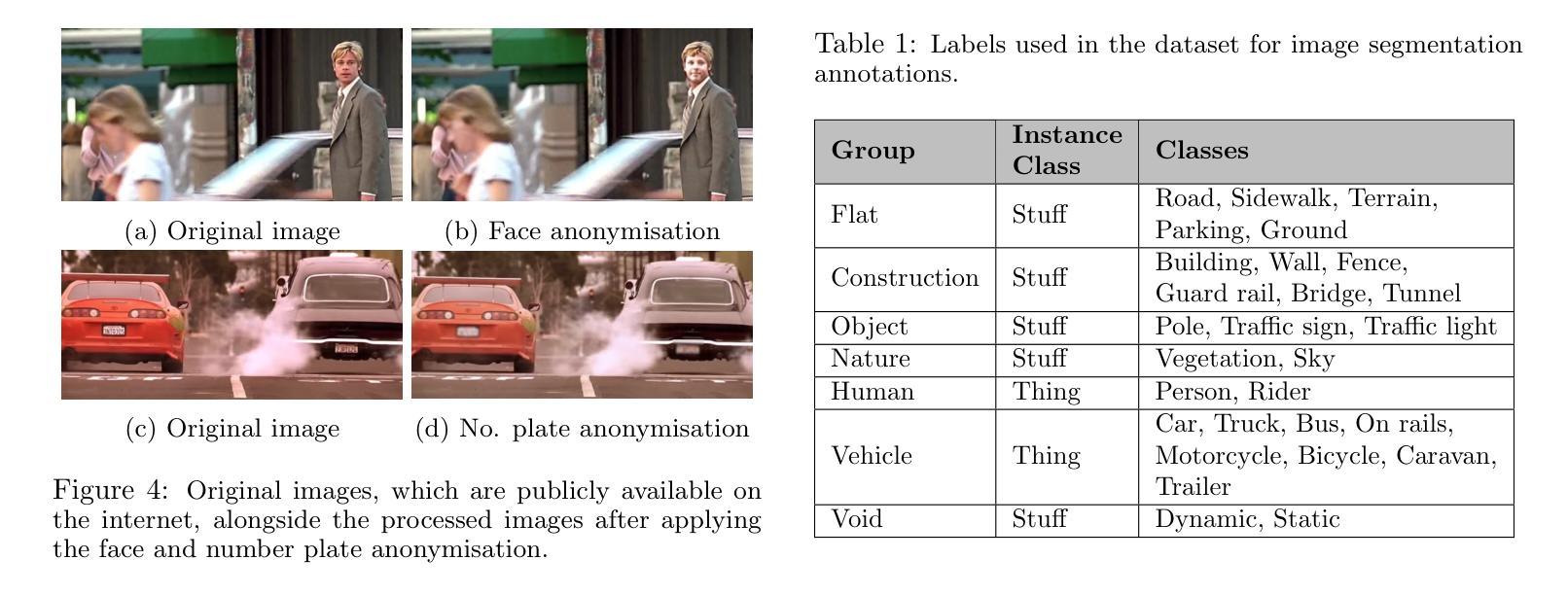
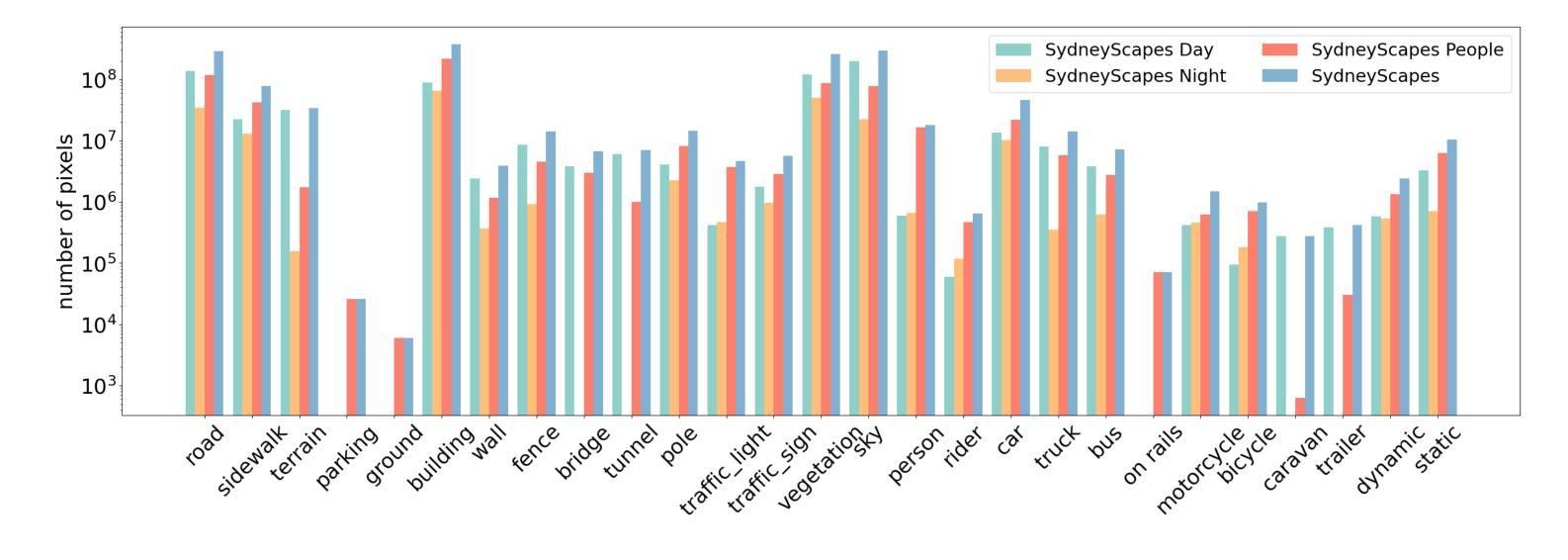
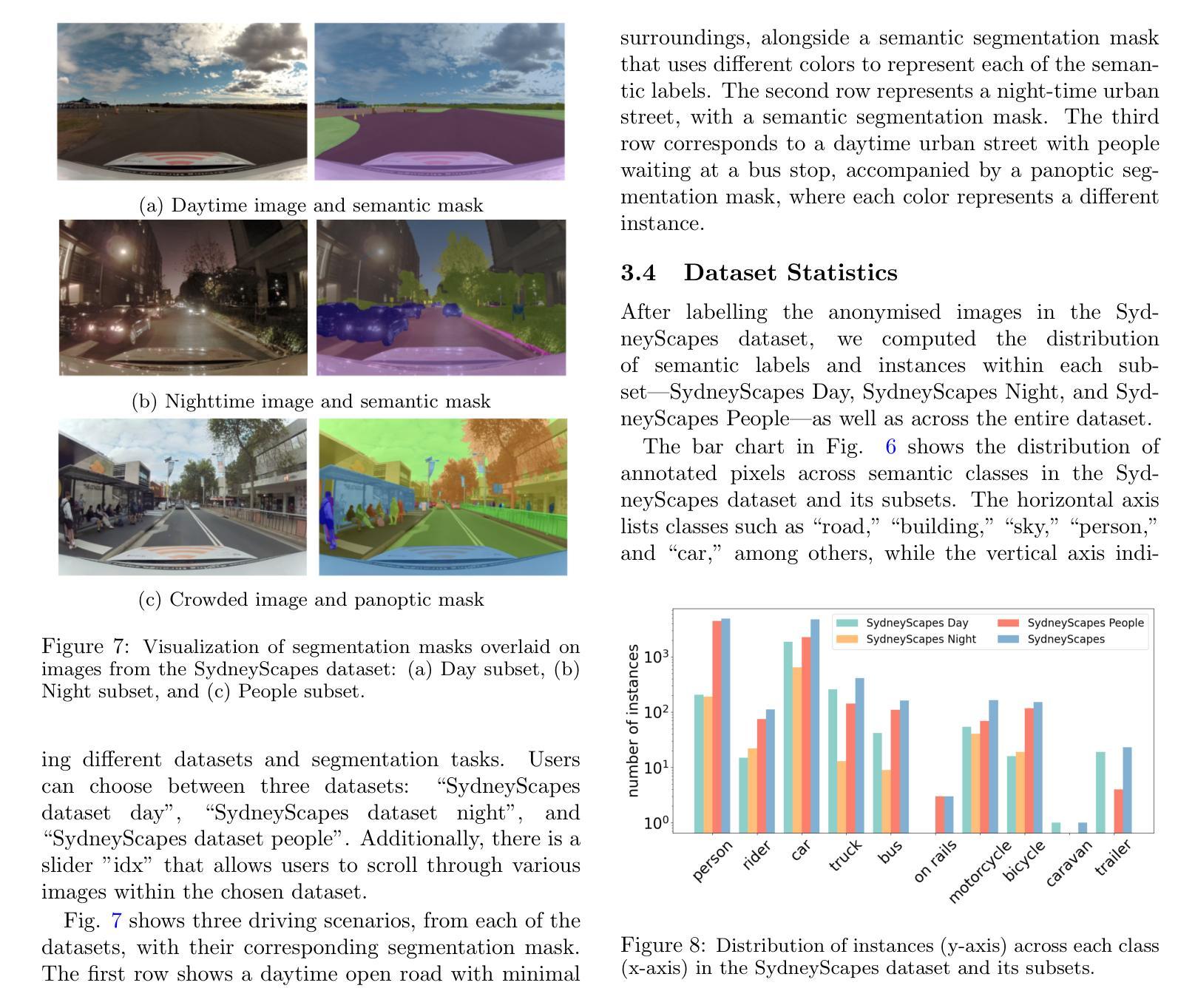
SydneyScapes: Image Segmentation for Australian Environments
Authors:Hongyu Lyu, Julie Stephany Berrio, Mao Shan, Stewart Worrall
Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) are being partially deployed and tested across various global locations, including China, the USA, Germany, France, Japan, Korea, and the UK, but with limited demonstrations in Australia. The integration of machine learning (ML) into AV perception systems highlights the need for locally labelled datasets to develop and test algorithms in specific environments. To address this, we introduce SydneyScapes - a dataset tailored for computer vision tasks of image semantic, instance, and panoptic segmentation. This dataset, collected from Sydney and surrounding cities in New South Wales (NSW), Australia, consists of 756 images with high-quality pixel-level annotations. It is designed to assist AV industry and researchers by providing annotated data and tools for algorithm development, testing, and deployment in the Australian context. Additionally, we offer benchmarking results using state-of-the-art algorithms to establish reference points for future research and development. The dataset is publicly available at https://hdl.handle.net/2123/33051.
自动驾驶车辆(AVs)正在全球各地,包括中国、美国、德国、法国、日本、韩国和英国进行部分部署和测试,但在澳大利亚的演示非常有限。机器学习(ML)融入AV感知系统凸显了针对特定环境开发和测试算法时对本地标注数据集的需求。为解决这一问题,我们推出了SydneyScapes数据集,该数据集专为图像语义分割、实例分割和全视野分割等计算机视觉任务量身定制。该数据集收集自澳大利亚新南威尔士州悉尼及其周边城市,包含756张高质量像素级注释图像。其目的是为自动驾驶行业和研究者提供注释数据和工具,以协助其在澳大利亚环境下进行算法开发、测试和部署。此外,我们还使用最先进的算法提供了基准测试结果,为未来的研究和发展建立参考点。数据集可通过https://hdl.handle.net/2123/33051公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自动驾驶车辆在全球范围内正在部署和测试,其中中国、美国等地已经广泛应用,澳大利亚的演示仍然有限。为了解决自动驾驶感知系统中机器学习算法在特定环境下开发和测试的需求,推出了SydneyScapes数据集,该数据集包含针对图像语义、实例和全景分割的计算机视觉任务的数据。数据集从澳大利亚新南威尔士州的悉尼及周边城市收集,包含756张高质量像素级注释的图像。数据集用于帮助自动驾驶行业和研究者进行算法开发、测试和部署在澳大利亚的环境中。此外还提供最新的算法基准测试结果以供未来研究参考,该数据集已公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶车辆在全球范围内正在部署和测试,但澳大利亚的演示仍然有限。
- 机器学习的集成对自动驾驶感知系统的算法开发在特定环境下有需求。
- SydneyScapes数据集是专为计算机视觉任务设计的,包括图像语义、实例和全景分割。
- SydneyScapes数据集从悉尼和新南威尔士州周边城市收集,包含高质量像素级注释的图像。
- 该数据集旨在帮助自动驾驶行业和研究人员在澳大利亚环境下进行算法开发、测试和部署。
- SydneyScapes数据集提供了最新的算法基准测试结果,为未来研究提供参考。
点此查看论文截图

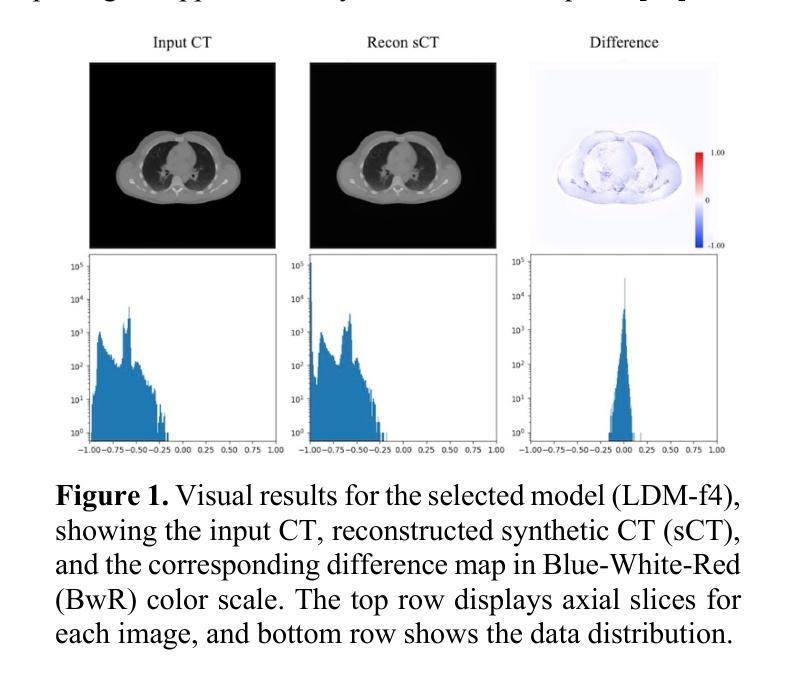
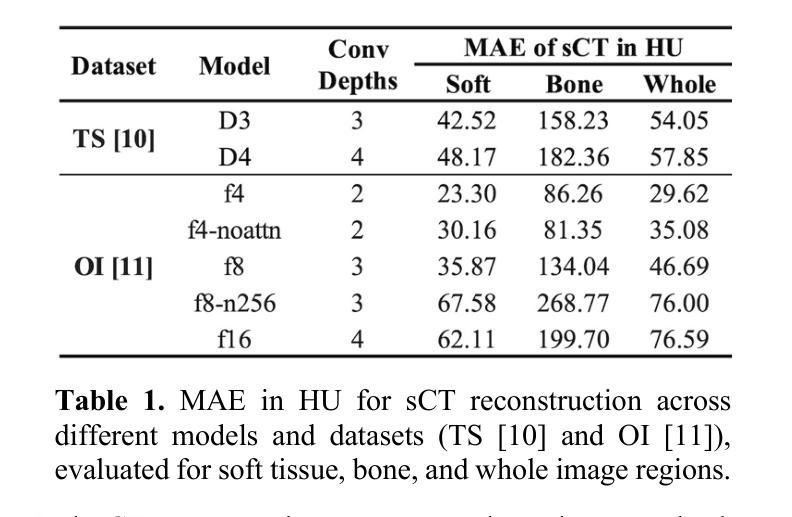
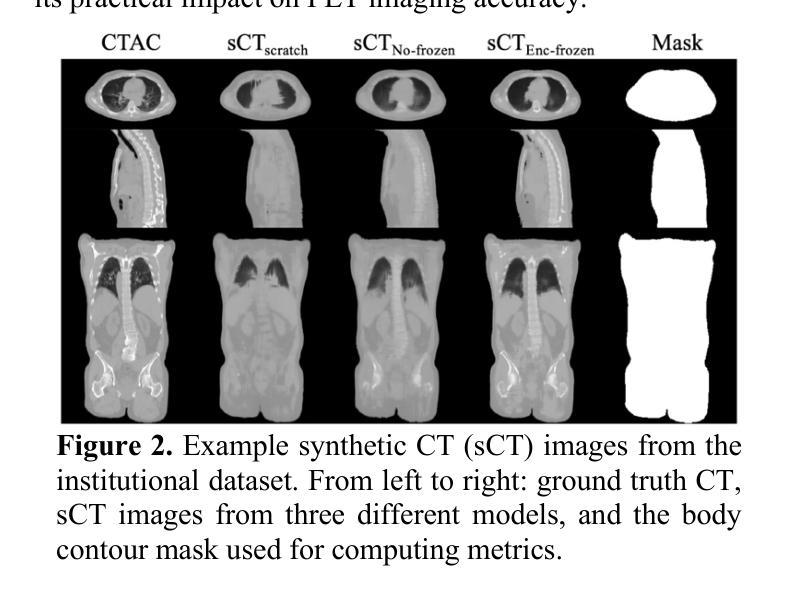
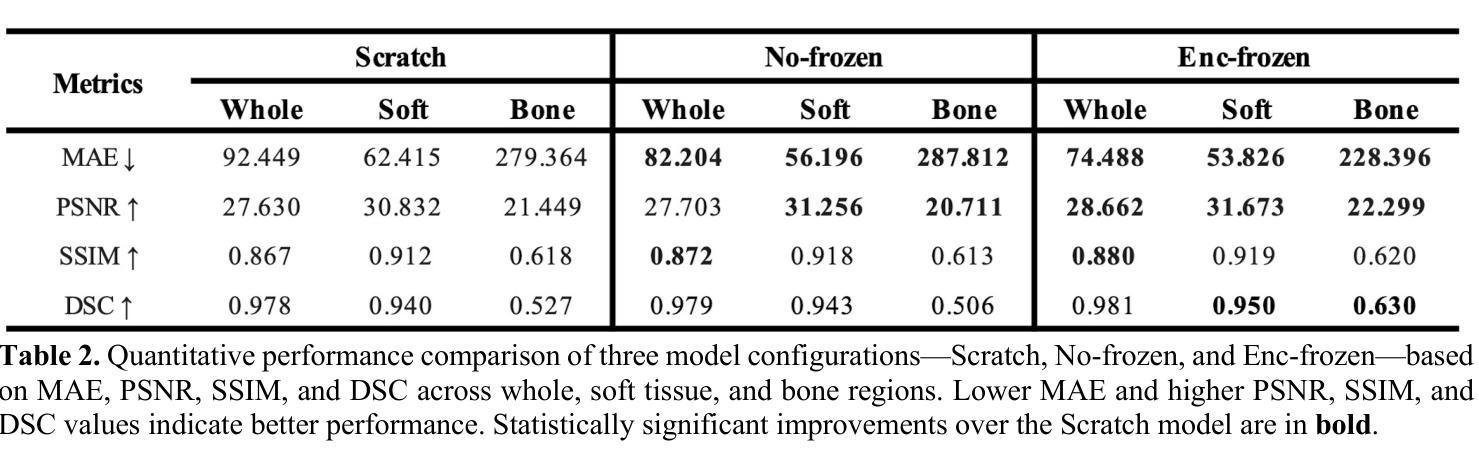
Synthetic CT Generation from Time-of-Flight Non-Attenutaion-Corrected PET for Whole-Body PET Attenuation Correction
Authors:Weijie Chen, James Wang, Alan McMillan
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging requires accurate attenuation correction (AC) to account for photon loss due to tissue density variations. In PET/MR systems, computed tomography (CT), which offers a straightforward estimation of AC is not available. This study presents a deep learning approach to generate synthetic CT (sCT) images directly from Time-of-Flight (TOF) non-attenuation corrected (NAC) PET images, enhancing AC for PET/MR. We first evaluated models pre-trained on large-scale natural image datasets for a CT-to-CT reconstruction task, finding that the pre-trained model outperformed those trained solely on medical datasets. The pre-trained model was then fine-tuned using an institutional dataset of 35 TOF NAC PET and CT volume pairs, achieving the lowest mean absolute error (MAE) of 74.49 HU and highest peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) of 28.66 dB within the body contour region. Visual assessments demonstrated improved reconstruction of both bone and soft tissue structures from TOF NAC PET images. This work highlights the effectiveness of using pre-trained deep learning models for medical image translation tasks. Future work will assess the impact of sCT on PET attenuation correction and explore additional neural network architectures and datasets to further enhance performance and practical applications in PET imaging.
正电子发射断层扫描(PET)成像需要精确的衰减校正(AC)来弥补因组织密度变化而损失的光子。在PET/MR系统中,提供AC直接估算的计算机断层扫描(CT)并不可用。本研究提出了一种基于深度学习的方法,直接从飞行时间(TOF)非衰减校正(NAC)PET图像生成合成CT(sCT)图像,以增强PET/MR的AC。我们首先评估了在大型自然图像数据集上预训练的模型进行CT-to-CT重建任务的效果,发现预训练模型优于仅使用医疗数据集训练的模型。然后,我们对预训练模型使用机构提供的35对TOF NAC PET和CT体积数据进行微调,在体轮廓区域内达到最低的平均绝对误差(MAE)为74.49 HU和最高的峰值信噪比(PSNR)为28.66 dB。视觉评估表明,从TOF NAC PET图像中重建的骨骼和软组织结构均有所改善。这项工作强调了使用预训练深度学习模型进行医学图像翻译任务的有效性。未来的工作将评估sCT对PET衰减校正的影响,并探索其他神经网络架构和数据集,以进一步提高性能并在PET成像中的实际应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 2 figures, ISBI 2025
Summary
本研究利用深度学习技术,直接从飞行时间非衰减校正PET图像生成合成CT(sCT)图像,以提高PET/MR的衰减校正。研究评估了预训练于大规模自然图像数据集的模型,发现其较仅训练于医疗数据集的模型表现更佳。经机构数据集微调后,模型在体腔区域内达到最低平均绝对误差74.49 HU及最高峰值信噪比28.66 dB。视觉评估显示,从TOF NAC PET图像重建的骨骼和软组织结构有所改善。
Key Takeaways
- PET成像需要进行衰减校正以补偿因组织密度变化导致的光子损失。
- 在PET/MR系统中,通常使用的CT并不提供衰减校正的直观估计。
- 本研究采用深度学习技术,直接从非衰减校正PET图像生成合成CT图像,以提高PET/MR的衰减校正效果。
- 研究评估了预训练于大规模自然图像数据集的模型性能,发现其表现优于仅使用医疗数据集的模型。
- 经过机构数据集的微调,模型在体腔区域达到了较低的平均绝对误差和较高的峰值信噪比。
- 视觉评估显示,模型能够从非衰减校正PET图像中改善骨骼和软组织结构的重建。
点此查看论文截图

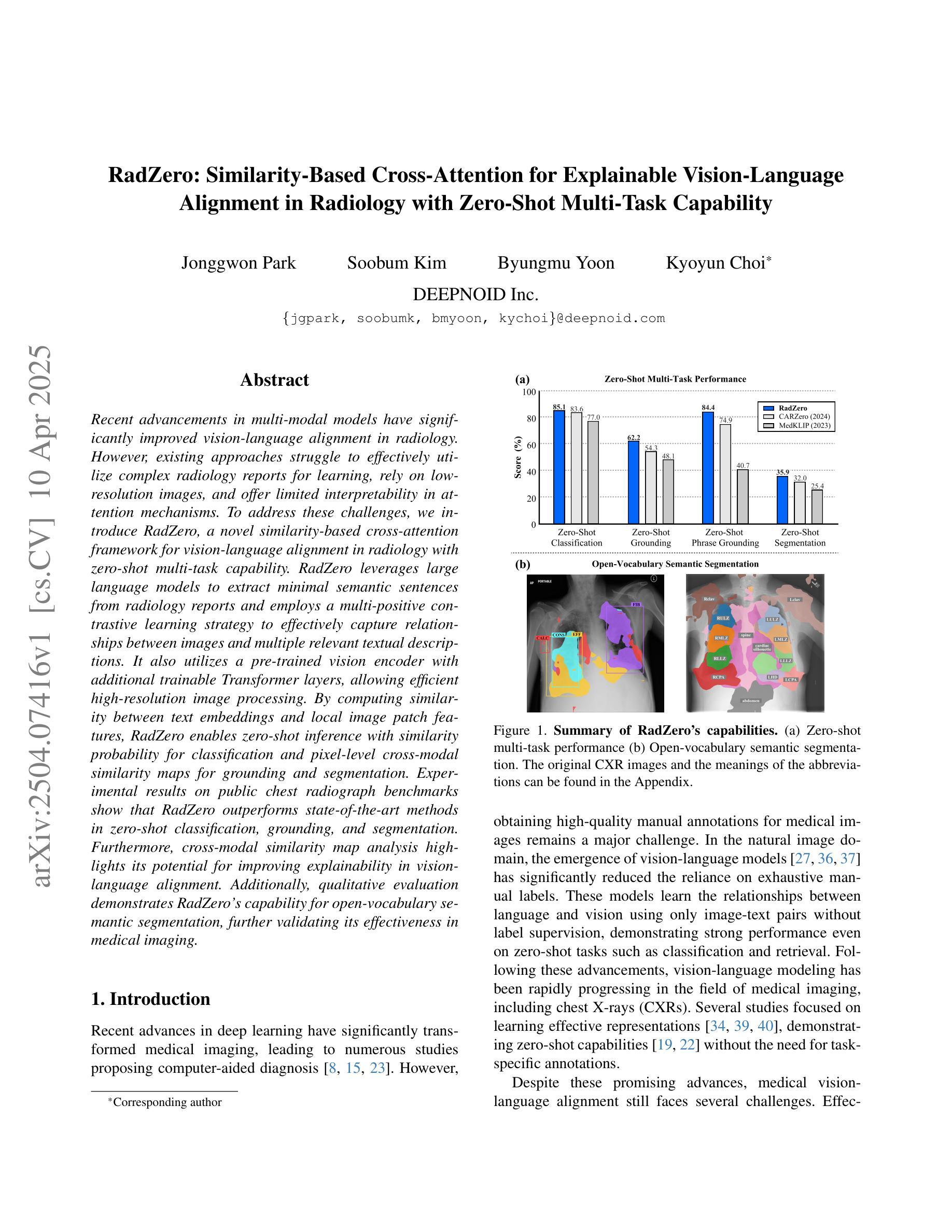
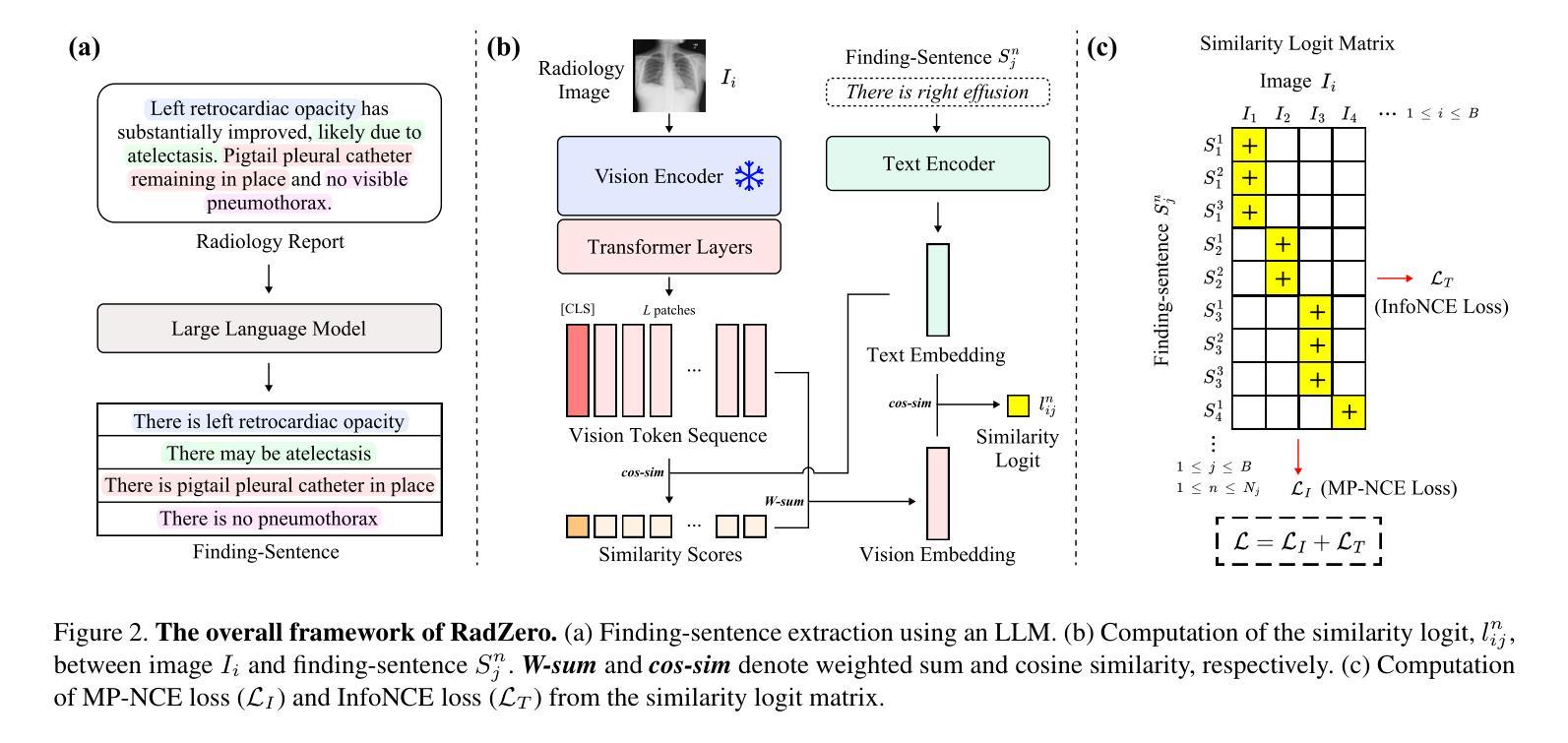
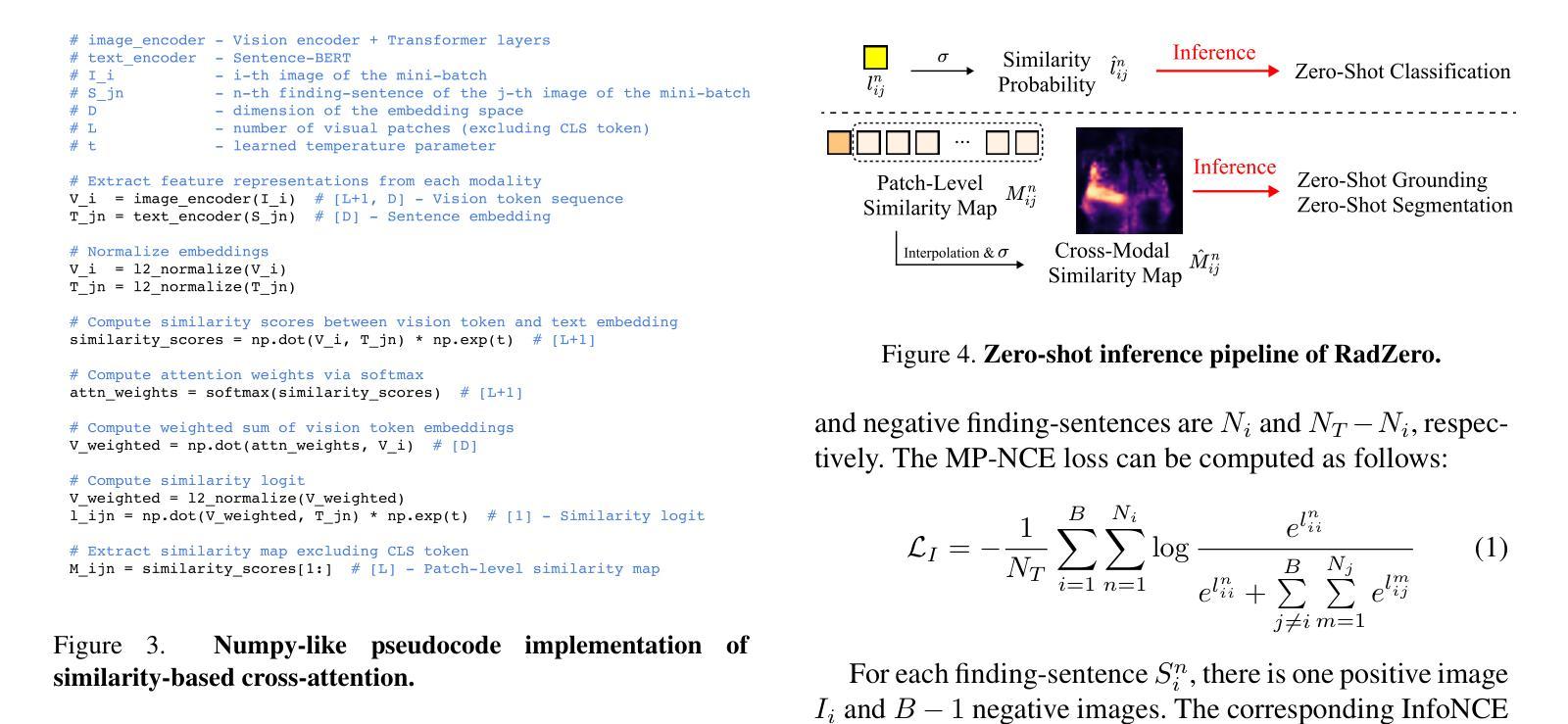
RadZero: Similarity-Based Cross-Attention for Explainable Vision-Language Alignment in Radiology with Zero-Shot Multi-Task Capability
Authors:Jonggwon Park, Soobum Kim, Byungmu Yoon, Kyoyun Choi
Recent advancements in multi-modal models have significantly improved vision-language alignment in radiology. However, existing approaches struggle to effectively utilize complex radiology reports for learning, rely on low-resolution images, and offer limited interpretability in attention mechanisms. To address these challenges, we introduce RadZero, a novel similarity-based cross-attention framework for vision-language alignment in radiology with zero-shot multi-task capability. RadZero leverages large language models to extract minimal semantic sentences from radiology reports and employs a multi-positive contrastive learning strategy to effectively capture relationships between images and multiple relevant textual descriptions. It also utilizes a pre-trained vision encoder with additional trainable Transformer layers, allowing efficient high-resolution image processing. By computing similarity between text embeddings and local image patch features, RadZero enables zero-shot inference with similarity probability for classification and pixel-level cross-modal similarity maps for grounding and segmentation. Experimental results on public chest radiograph benchmarks show that RadZero outperforms state-of-the-art methods in zero-shot classification, grounding, and segmentation. Furthermore, cross-modal similarity map analysis highlights its potential for improving explainability in vision-language alignment. Additionally, qualitative evaluation demonstrates RadZero’s capability for open-vocabulary semantic segmentation, further validating its effectiveness in medical imaging.
在医学图像的多模态模型方面,最近的进展极大地改善了视觉与语言的对齐在放射学领域的应用。然而,现有的方法难以有效地利用复杂的放射学报告进行学习,依赖于低分辨率的图像,并且在注意力机制中的解释性有限。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了RadZero,这是一种基于相似性交叉注意力框架的放射学视觉与语言对齐方法,具有零样本多任务能力。RadZero利用大型语言模型从放射学报告中提取最小的语义句子,并采用多阳性对比学习策略有效地捕获图像与多个相关文本描述之间的关系。它还利用预训练的视觉编码器以及额外的可训练Transformer层,实现高效的高分辨率图像处理。通过计算文本嵌入和局部图像补丁特征之间的相似性,RadZero能够实现零样本推理,使用相似性概率进行分类,以及像素级的跨模态相似性地图用于定位和方向分割。在公共胸部X射线基准测试上的实验结果表明,RadZero在零样本分类、定位和分割方面的性能超过了最先进的方法。此外,跨模态相似性地图分析凸显了其在视觉与语言对齐的解释性方面的潜力。此外,定性评估证明了RadZero在开放词汇语义分割方面的能力,进一步验证了其在医学影像中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
RadZero是一种基于相似性交叉注意机制的全新框架,用于解决放射学中的视觉语言对齐问题。它采用多模态模型,克服现有方法的局限性,如难以利用复杂放射学报告进行学习、依赖低分辨率图像以及注意力机制的可解释性有限等挑战。RadZero具有零样本多任务能力,利用大型语言模型从放射学报告中提取关键语义句子,并采用多阳性对比学习策略有效捕捉图像与多个相关文本描述之间的关系。通过计算文本嵌入和局部图像补丁特征之间的相似性,RadZero实现了零样本推断,可用于分类和像素级别的跨模态相似性映射,为定位和分析提供有力支持。实验结果表明,RadZero在公共胸部X光影像基准测试中表现优异,展现出其在零样本分类、定位和分割方面的优势。此外,跨模态相似性映射分析突显其在提高视觉语言对齐的可解释性方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- RadZero是一个基于相似性交叉注意机制的框架,用于改进放射学中的视觉语言对齐。
- 现有方法面临的挑战包括复杂报告利用困难、低分辨率图像依赖和有限的可解释性。
- RadZero具备零样本多任务能力,运用大型语言模型提取关键语义信息。
- 采用多阳性对比学习策略有效捕捉图像与文本之间的关系。
- 通过计算文本嵌入和图像补丁特征之间的相似性实现零样本推断。
- RadZero在分类、定位和分割方面表现优异,实验结果显示其优越性。
点此查看论文截图
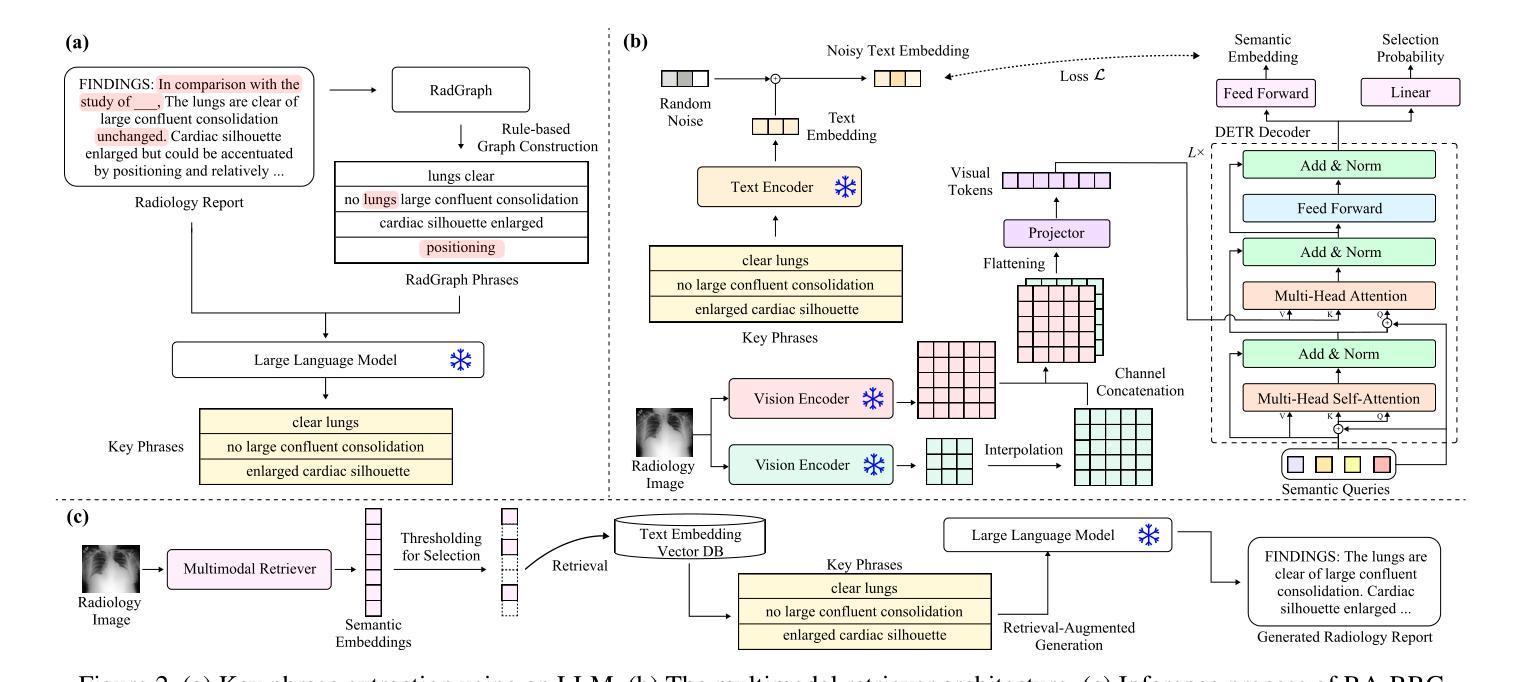
Leveraging LLMs for Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Radiology Report Generation via Key Phrase Extraction
Authors:Kyoyun Choi, Byungmu Yoon, Soobum Kim, Jonggwon Park
Automated radiology report generation (RRG) holds potential to reduce radiologists’ workload, especially as recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) enable the development of multimodal models for chest X-ray (CXR) report generation. However, multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) are resource-intensive, requiring vast datasets and substantial computational cost for training. To address these challenges, we propose a retrieval-augmented generation approach that leverages multimodal retrieval and LLMs to generate radiology reports while mitigating hallucinations and reducing computational demands. Our method uses LLMs to extract key phrases from radiology reports, effectively focusing on essential diagnostic information. Through exploring effective training strategies, including image encoder structure search, adding noise to text embeddings, and additional training objectives, we combine complementary pre-trained image encoders and adopt contrastive learning between text and semantic image embeddings. We evaluate our approach on MIMIC-CXR dataset, achieving state-of-the-art results on CheXbert metrics and competitive RadGraph F1 metric alongside MLLMs, without requiring LLM fine-tuning. Our method demonstrates robust generalization for multi-view RRG, making it suitable for comprehensive clinical applications.
自动放射学报告生成(RRG)具有减少放射科医生工作量的潜力,尤其是随着大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展,使得用于胸部X射线(CXR)报告生成的跨模态模型的开发成为可能。然而,跨模态LLM(MLLM)资源密集,需要大量的数据集和大量的计算成本进行训练。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种增强检索的生成方法,该方法利用跨模态检索和LLM生成放射学报告,同时减轻虚构现象并降低计算需求。我们的方法使用LLM从放射学报告中提取关键短语,有效地关注关键诊断信息。通过探索有效的训练策略,包括图像编码器结构搜索、向文本嵌入添加噪声以及额外的训练目标,我们结合了预训练的图像编码器的互补性,并在文本和语义图像嵌入之间采用对比学习。我们在MIMIC-CXR数据集上评估了我们的方法,在CheXbert指标上取得了最新成果,在RadGraph F1指标上与MLLM相比具有竞争力,且无需对LLM进行微调。我们的方法在多视图RRG中表现出稳健的泛化能力,使其成为全面的临床应用的理想选择。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了自动化生成放射学报告(RRG)的潜力,特别是随着大型语言模型(LLMs)的最新进展,为生成胸部X射线(CXR)报告的多模态模型开发提供了可能。针对多模态LLMs资源密集、需要大量数据集和高昂的计算成本的问题,提出了一种检索增强生成方法。该方法利用多模态检索和LLMs生成放射学报告,减少幻觉现象并降低计算需求。通过有效训练策略,结合预训练图像编码器,采用文本和语义图像嵌入之间的对比学习,在MIMIC-CXR数据集上取得了优异的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化放射学报告生成具有减少放射科医生工作量的潜力。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在放射学报告生成中的应用为这一领域带来了新可能。
- 多模态LLMs存在资源密集和计算成本高昂的问题。
- 提出了一种检索增强生成方法,通过结合多模态检索和LLMs来生成报告,减少幻觉现象并降低计算需求。
- 该方法使用LLMs提取关键短语,聚焦于重要的诊断信息。
- 通过一系列有效的训练策略,包括图像编码器结构搜索、文本嵌入添加噪声和额外的训练目标,该方法在MIMIC-CXR数据集上取得了优异的结果。
点此查看论文截图
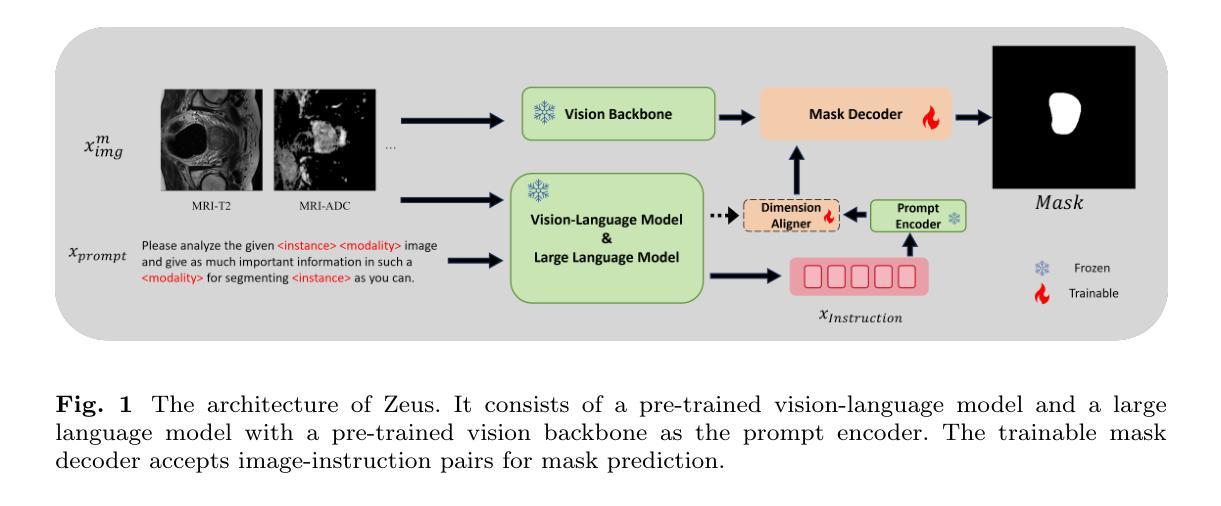
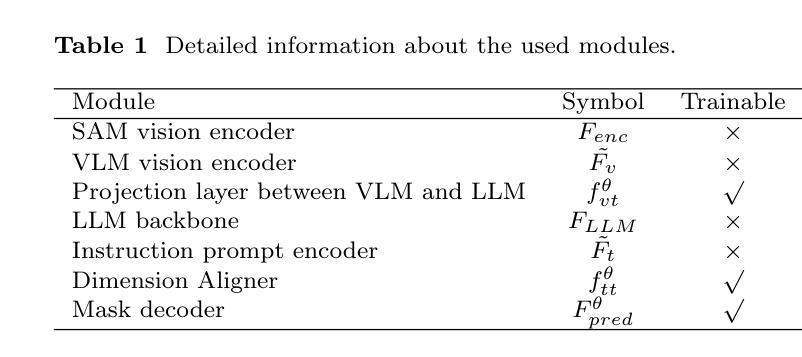
Zeus: Zero-shot LLM Instruction for Union Segmentation in Multimodal Medical Imaging
Authors:Siyuan Dai, Kai Ye, Guodong Liu, Haoteng Tang, Liang Zhan
Medical image segmentation has achieved remarkable success through the continuous advancement of UNet-based and Transformer-based foundation backbones. However, clinical diagnosis in the real world often requires integrating domain knowledge, especially textual information. Conducting multimodal learning involves visual and text modalities shown as a solution, but collecting paired vision-language datasets is expensive and time-consuming, posing significant challenges. Inspired by the superior ability in numerous cross-modal tasks for Large Language Models (LLMs), we proposed a novel Vision-LLM union framework to address the issues. Specifically, we introduce frozen LLMs for zero-shot instruction generation based on corresponding medical images, imitating the radiology scanning and report generation process. {To better approximate real-world diagnostic processes}, we generate more precise text instruction from multimodal radiology images (e.g., T1-w or T2-w MRI and CT). Based on the impressive ability of semantic understanding and rich knowledge of LLMs. This process emphasizes extracting special features from different modalities and reunion the information for the ultimate clinical diagnostic. With generated text instruction, our proposed union segmentation framework can handle multimodal segmentation without prior collected vision-language datasets. To evaluate our proposed method, we conduct comprehensive experiments with influential baselines, the statistical results and the visualized case study demonstrate the superiority of our novel method.}
医学图像分割领域随着基于UNet和Transformer的基础骨干网络的不断发展,已经取得了显著的成果。然而,现实世界的临床诊断往往需要结合领域知识,尤其是文本信息。进行多模态学习涉及视觉和文本模态,被证明是一种解决方案,但收集配对的视觉语言数据集既昂贵又耗时,这构成了重大挑战。受大型语言模型(LLM)在多个跨模态任务中的卓越能力的启发,我们提出了一个新的Vision-LLM联合框架来解决这些问题。具体来说,我们引入冻结的LLM进行零射击指令生成,这些指令基于相应的医学图像,模仿放射学扫描和报告生成过程。为了更好地近似真实世界的诊断过程,我们从多模态放射学图像(如T1加权或T2加权MRI和CT)生成更精确的文本指令。基于LLM令人印象深刻的语义理解能力和丰富的知识。这个过程强调从不同模态中提取特殊特征,并将这些信息融合进行最终的临床诊断。使用生成的文本指令,我们提出的联合分割框架可以进行多模态分割,而无需事先收集视觉语言数据集。为了评估我们提出的方法,我们与有影响力的基线进行了全面的实验,统计结果和可视化案例研究证明了我们新方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 4 figures, In Press by a journal
Summary
医学图像分割领域因UNet和Transformer基础骨干的持续进步而取得显著成果。然而,现实世界的临床诊断需要结合领域知识,尤其是文本信息。虽然多模态学习融合了视觉和文本模态,但收集配对视语言数据集既昂贵又耗时,挑战重重。受大型语言模型(LLM)在跨模态任务中出色能力的启发,提出新型Vision-LLM联合框架,引入冻结的LLM进行零射击指令生成,基于相应医学图像进行模仿放射扫描和报告生成过程。该框架从多模态放射图像生成精确文本指令,以更好地模拟现实诊断过程。结合LLM的语义理解和丰富知识,该框架强调从不同模态提取特殊特征并重新整合信息以进行最终临床诊断。借助生成的文本指令,该联合分割框架无需预先收集视语言数据集即可处理多模态分割。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割领域持续利用UNet和Transformer基础骨干技术取得进展。
- 临床诊断需结合领域知识和文本信息。
- 多模态学习融合视觉和文本模态,但收集配对视语言数据集具有挑战。
- 引入冻结的LLM进行零射击指令生成,基于医学图像模仿放射扫描和报告生成过程。
- 框架生成精确文本指令以模拟现实诊断过程。
- 框架结合LLM的语义理解和丰富知识,强调特征提取和信息整合。
点此查看论文截图

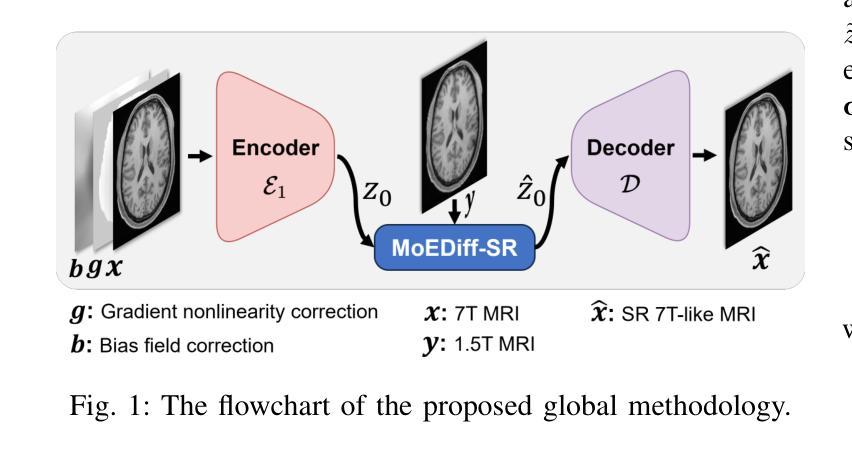
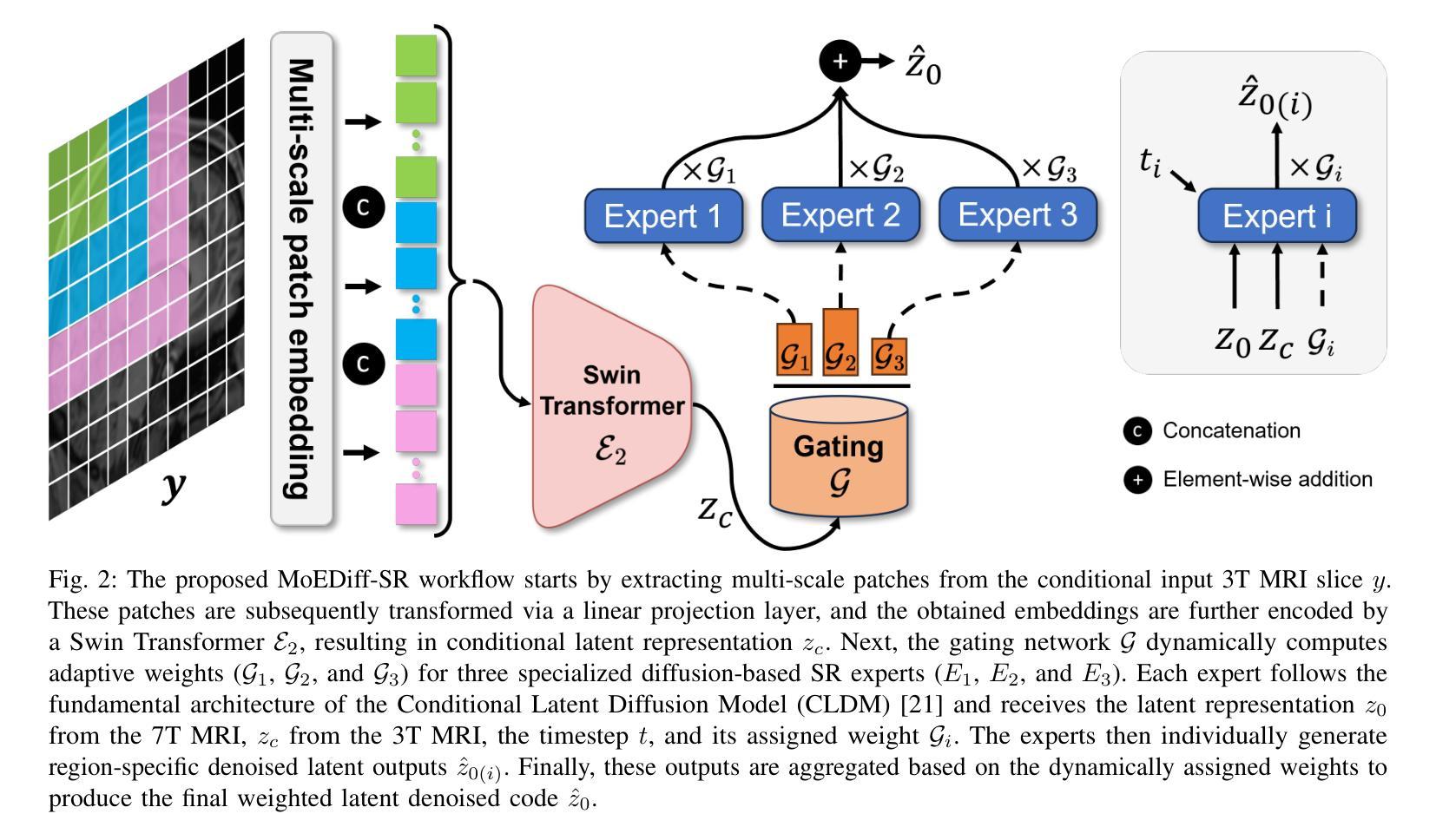
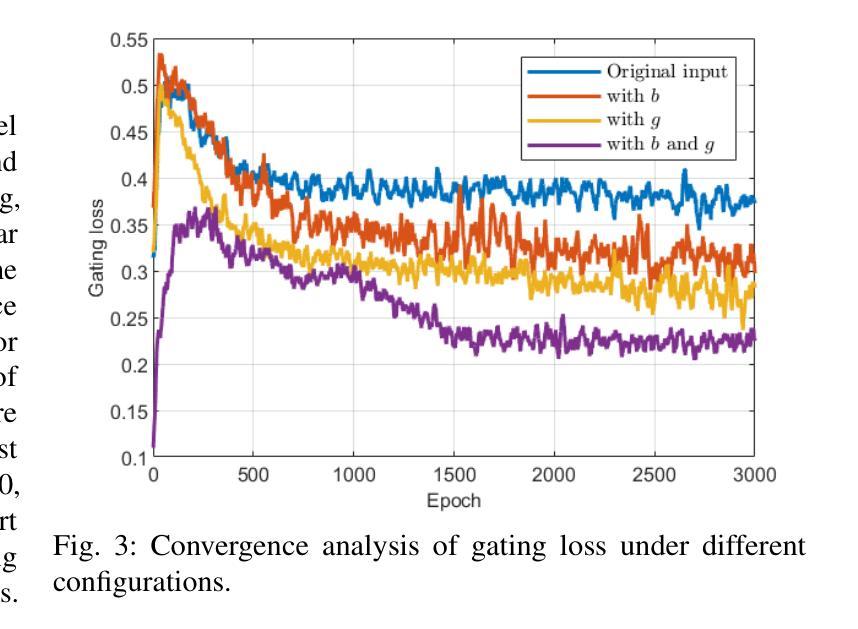
MoEDiff-SR: Mixture of Experts-Guided Diffusion Model for Region-Adaptive MRI Super-Resolution
Authors:Zhe Wang, Yuhua Ru, Aladine Chetouani, Fang Chen, Fabian Bauer, Liping Zhang, Didier Hans, Rachid Jennane, Mohamed Jarraya, Yung Hsin Chen
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) at lower field strengths (e.g., 3T) suffers from limited spatial resolution, making it challenging to capture fine anatomical details essential for clinical diagnosis and neuroimaging research. To overcome this limitation, we propose MoEDiff-SR, a Mixture of Experts (MoE)-guided diffusion model for region-adaptive MRI Super-Resolution (SR). Unlike conventional diffusion-based SR models that apply a uniform denoising process across the entire image, MoEDiff-SR dynamically selects specialized denoising experts at a fine-grained token level, ensuring region-specific adaptation and enhanced SR performance. Specifically, our approach first employs a Transformer-based feature extractor to compute multi-scale patch embeddings, capturing both global structural information and local texture details. The extracted feature embeddings are then fed into an MoE gating network, which assigns adaptive weights to multiple diffusion-based denoisers, each specializing in different brain MRI characteristics, such as centrum semiovale, sulcal and gyral cortex, and grey-white matter junction. The final output is produced by aggregating the denoised results from these specialized experts according to dynamically assigned gating probabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that MoEDiff-SR outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of quantitative image quality metrics, perceptual fidelity, and computational efficiency. Difference maps from each expert further highlight their distinct specializations, confirming the effective region-specific denoising capability and the interpretability of expert contributions. Additionally, clinical evaluation validates its superior diagnostic capability in identifying subtle pathological features, emphasizing its practical relevance in clinical neuroimaging. Our code is available at https://github.com/ZWang78/MoEDiff-SR.
在低场强(例如3T)的磁共振成像(MRI)中,其空间分辨率有限,难以捕获对临床诊断和神经影像学研究至关重要的精细解剖结构。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了MoEDiff-SR,这是一种受专家混合(MoE)引导的区域自适应MRI超分辨率(SR)扩散模型。与传统的基于扩散的SR模型不同,这些模型在整个图像上应用统一的去噪过程,MoEDiff-SR在细粒度标记级别动态选择专业去噪专家,确保区域特定的适应性和增强的SR性能。具体来说,我们的方法首先使用基于Transformer的特征提取器来计算多尺度补丁嵌入,捕获全局结构信息和局部纹理细节。提取的特征嵌入随后被输入到MoE门控网络中,该网络为多个基于扩散的去噪器分配自适应权重,每个去噪器都专门处理不同的脑部MRI特征,如中心半卵圆中心、沟和回状皮层以及灰白质交界处。最终输出是通过根据动态分配的门控概率聚合这些专业专家的去噪结果而产生的。实验结果表明,MoEDiff-SR在图像质量指标、感知保真度和计算效率方面均优于现有最先进的方法。来自每个专家的差异图进一步突出了它们的特殊专长,证实了有效的区域特定去噪能力和专家贡献的可解释性。此外,临床评估验证了其在识别细微病理特征方面的卓越诊断能力,强调其在临床神经影像学中的实际相关性。我们的代码位于https://github.com/ZWang78/MoEDiff-SR。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MoEDiff-SR是一种基于专家混合(MoE)引导的区域自适应MRI超分辨率(SR)技术,解决了低磁场强度MRI空间分辨率受限的问题。它采用动态选择特定去噪专家的方式,确保区域适应性和增强SR性能。实验结果显示,MoEDiff-SR在图像质量指标、感知保真度和计算效率方面超越了现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- MoEDiff-SR解决了低场强MRI空间分辨率低的问题,该技术有助于提高区域自适应的MRI超分辨率(SR)。
- MoEDiff-SR利用专家混合(MoE)的方法动态选择去噪专家,不同于传统的扩散模型对全图进行统一处理。
- 技术利用转换器特征提取器计算多尺度斑块嵌入,捕获全局结构信息和局部纹理细节。
- 通过MoE门控网络分配权重给多个扩散去噪器,针对MRI不同特性(如大脑的不同部位)有不同的去噪器负责。
- 专家分工产生的高质量差异映射揭示了各领域的专长,增强了区域特定去噪能力和专家贡献的可解释性。
- 临床评估验证了其在识别细微病理特征方面的卓越诊断能力,证明了其在临床神经影像中的实际应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

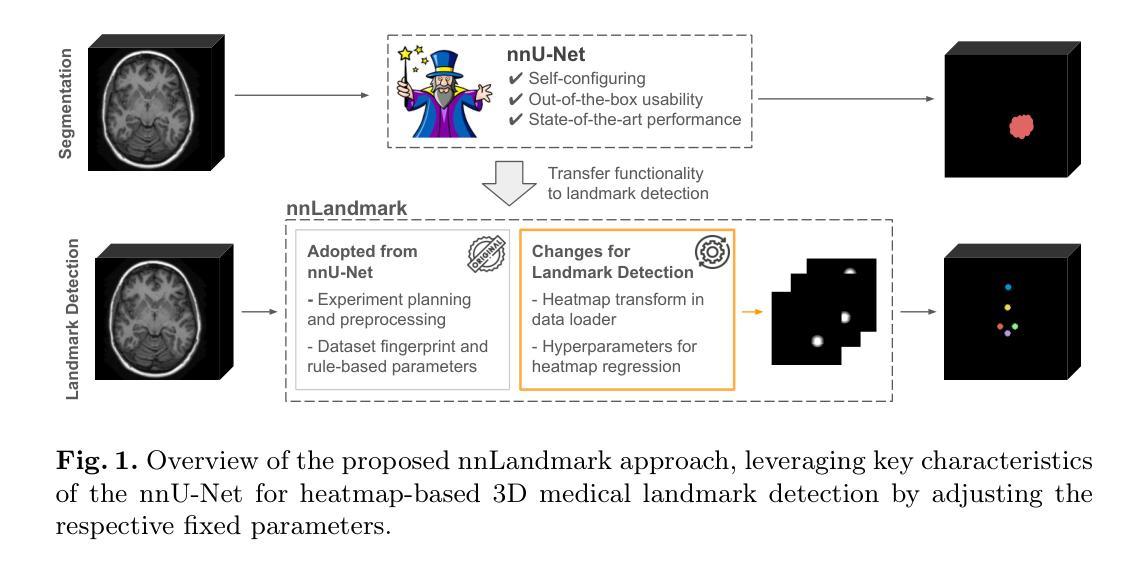
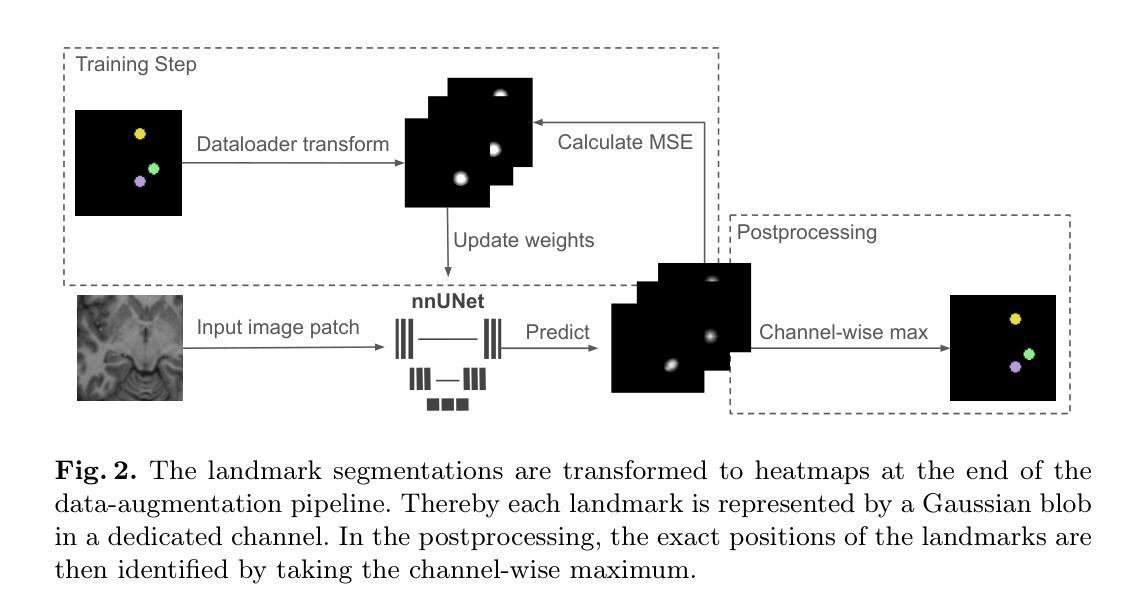
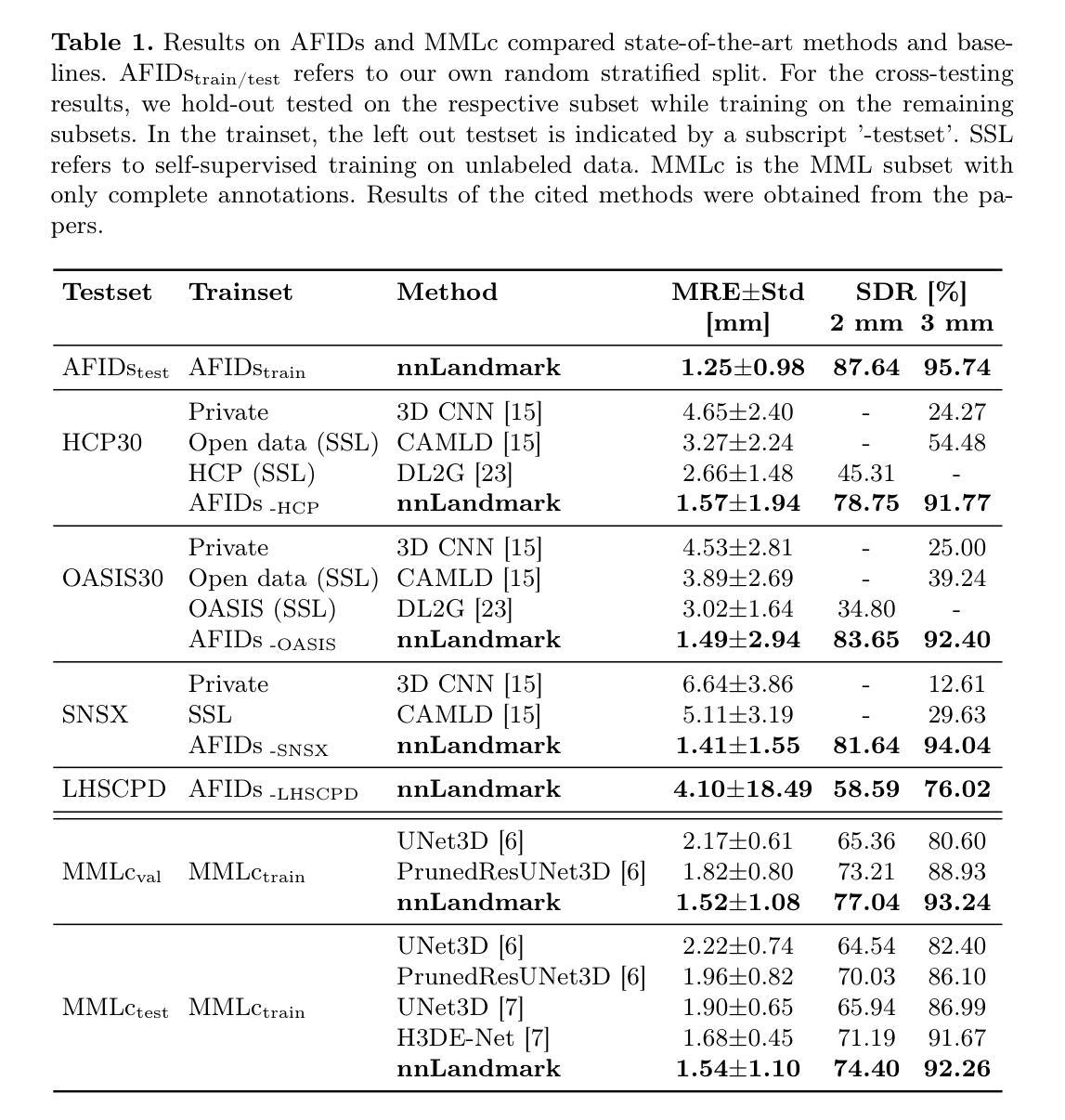
nnLandmark: A Self-Configuring Method for 3D Medical Landmark Detection
Authors:Alexandra Ertl, Shuhan Xiao, Stefan Denner, Robin Peretzke, David Zimmerer, Peter Neher, Fabian Isensee, Klaus Maier-Hein
Landmark detection plays a crucial role in medical imaging tasks that rely on precise spatial localization, including specific applications in diagnosis, treatment planning, image registration, and surgical navigation. However, manual annotation is labor-intensive and requires expert knowledge. While deep learning shows promise in automating this task, progress is hindered by limited public datasets, inconsistent benchmarks, and non-standardized baselines, restricting reproducibility, fair comparisons, and model generalizability. This work introduces nnLandmark, a self-configuring deep learning framework for 3D medical landmark detection, adapting nnU-Net to perform heatmap-based regression. By leveraging nnU-Net’s automated configuration, nnLandmark eliminates the need for manual parameter tuning, offering out-of-the-box usability. It achieves state-of-the-art accuracy across two public datasets, with a mean radial error (MRE) of 1.5 mm on the Mandibular Molar Landmark (MML) dental CT dataset and 1.2 mm for anatomical fiducials on a brain MRI dataset (AFIDs), where nnLandmark aligns with the inter-rater variability of 1.5 mm. With its strong generalization, reproducibility, and ease of deployment, nnLandmark establishes a reliable baseline for 3D landmark detection, supporting research in anatomical localization and clinical workflows that depend on precise landmark identification. The code will be available soon.
地标检测在依赖精确空间定位的医学成像任务中起着至关重要的作用,包括诊断、治疗计划、图像注册和手术导航等特定应用。然而,手动标注是一项劳动密集型工作,需要专业知识。深度学习虽然有望自动化这项任务,但公共数据集的局限性、基准测试的不一致性以及非标准化的基线限制了可重复性、公平比较和模型的泛化能力。这项工作引入了nnLandmark,这是一个用于3D医学地标检测的自我配置的深度学习框架,它采用nnU-Net进行基于热图的回归。通过利用nnU-Net的自动配置,nnLandmark消除了对手动参数调整的需求,提供了开箱即用的可用性。它在两个公共数据集上达到了最先进的准确性,在下颌磨牙地标(MML)牙科CT数据集上的平均径向误差(MRE)为1.5毫米,在基于MRI的解剖标记数据集(AFIDs)上的平均径向误差为1.2毫米,其中nnLandmark与1.5毫米的医师间变异度一致。凭借其强大的泛化能力、可重复性和易于部署的特点,nnLandmark为3D地标检测建立了可靠的基线,支持依赖精确地标识别的解剖定位和临床工作流程的研究。代码很快将可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像中的地标检测在诊断、治疗计划、图像注册和手术导航等应用中具有关键作用。手动标注是一项耗时且需要专业知识的工作。深度学习在地标自动检测中显示出潜力,但受到公开数据集限制等因素影响进展。本文介绍的nnLandmark框架采用深度学习自适应配置技术,实现医学图像中三维地标检测的自动化配置,并实现了高精度效果。其在牙科CT和脑部MRI数据集上的平均径向误差达到了行业领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 地标检测在医学成像中具有关键作用,对于依赖精确空间定位的应用尤为重要。
- 手动标注是一个耗时的过程,并且需要专业知识和经验。
- 深度学习在地标自动检测领域具有潜力,但受限于公开数据集不足和缺乏标准化的基准测试。
- nnLandmark是一个基于深度学习的自适应配置框架,用于医学图像中的三维地标检测。
- nnLandmark消除了手动参数调整的需要,提高了易用性。
- nnLandmark在牙科CT和脑部MRI数据集上实现了最先进的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

Subjective Visual Quality Assessment for High-Fidelity Learning-Based Image Compression
Authors:Mohsen Jenadeleh, Jon Sneyers, Panqi Jia, Shima Mohammadi, Joao Ascenso, Dietmar Saupe
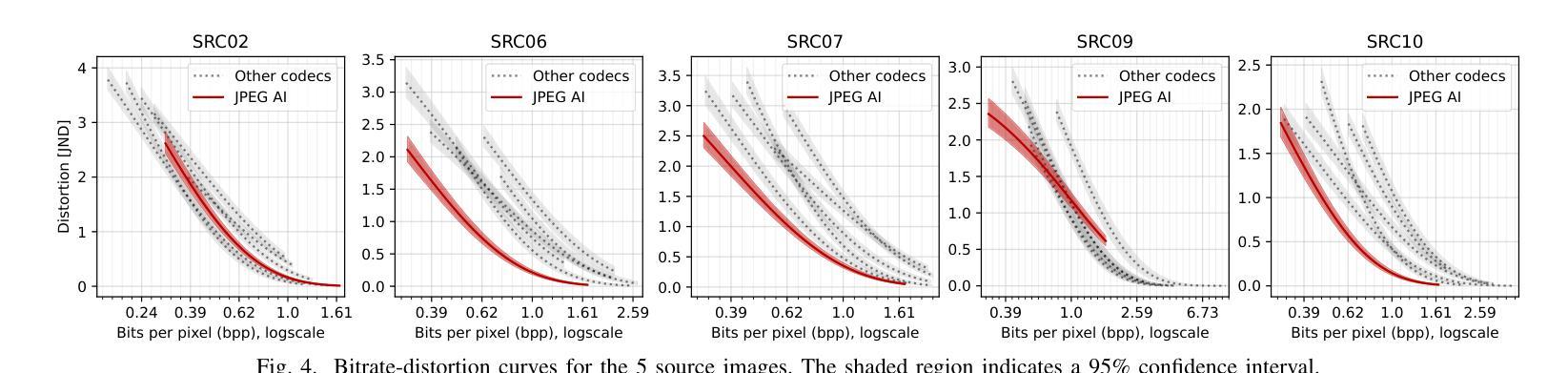
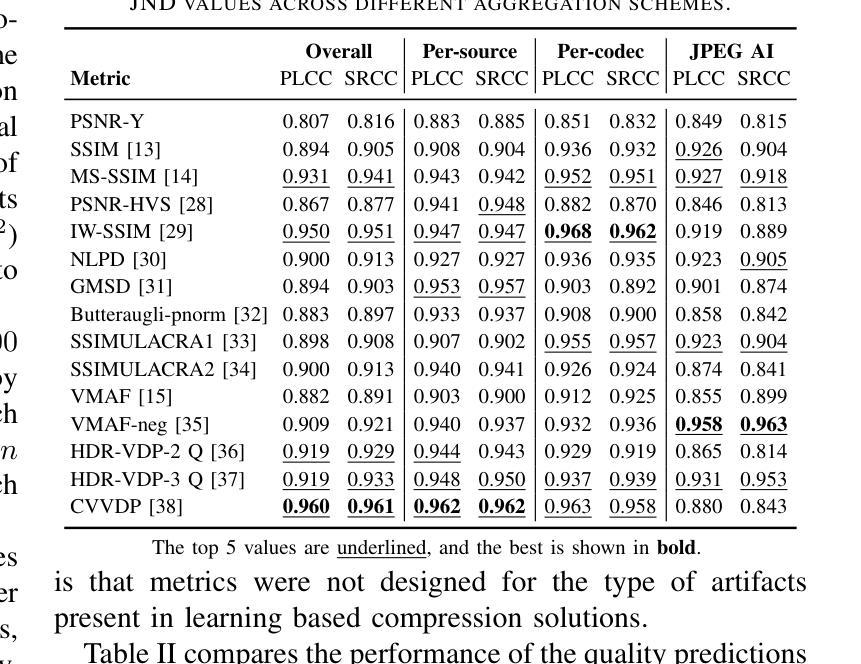
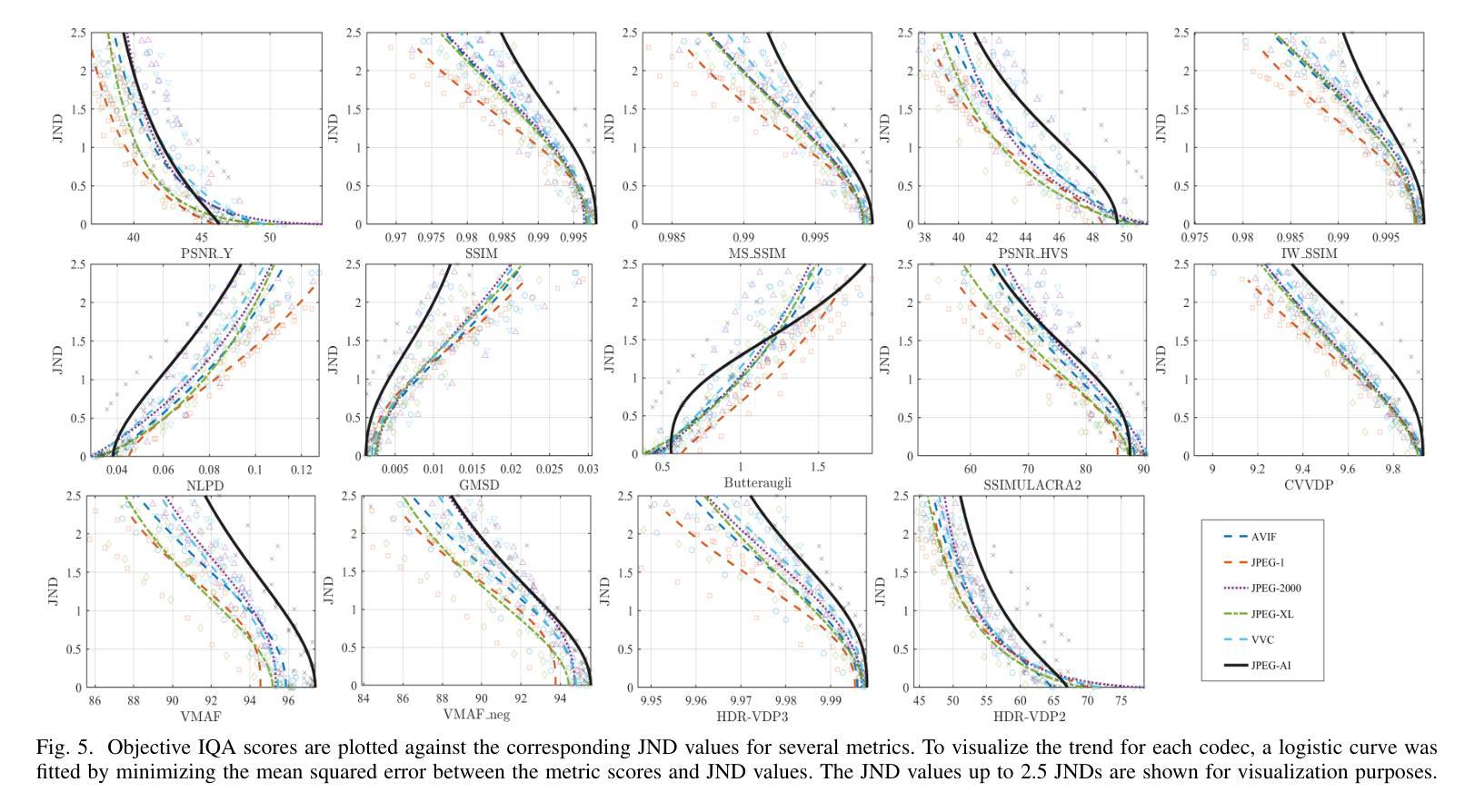
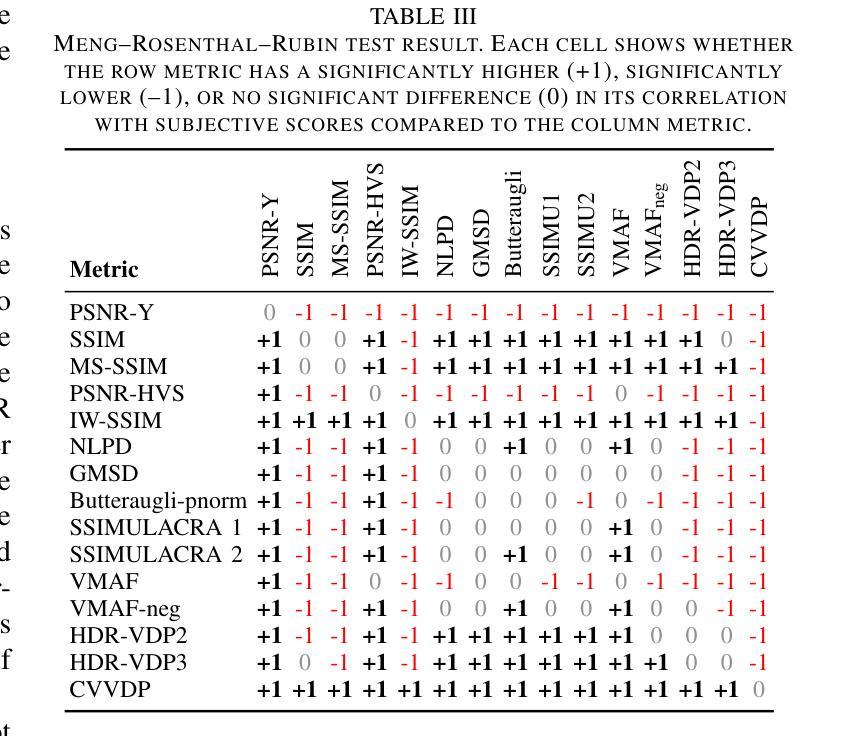
Learning-based image compression methods have recently emerged as promising alternatives to traditional codecs, offering improved rate-distortion performance and perceptual quality. JPEG AI represents the latest standardized framework in this domain, leveraging deep neural networks for high-fidelity image reconstruction. In this study, we present a comprehensive subjective visual quality assessment of JPEG AI-compressed images using the JPEG AIC-3 methodology, which quantifies perceptual differences in terms of Just Noticeable Difference (JND) units. We generated a dataset of 50 compressed images with fine-grained distortion levels from five diverse sources. A large-scale crowdsourced experiment collected 96,200 triplet responses from 459 participants. We reconstructed JND-based quality scales using a unified model based on boosted and plain triplet comparisons. Additionally, we evaluated the alignment of multiple objective image quality metrics with human perception in the high-fidelity range. The CVVDP metric achieved the overall highest performance; however, most metrics including CVVDP were overly optimistic in predicting the quality of JPEG AI-compressed images. These findings emphasize the necessity for rigorous subjective evaluations in the development and benchmarking of modern image codecs, particularly in the high-fidelity range. Another technical contribution is the introduction of the well-known Meng-Rosenthal-Rubin statistical test to the field of Quality of Experience research. This test can reliably assess the significance of difference in performance of quality metrics in terms of correlation between metrics and ground truth. The complete dataset, including all subjective scores, is publicly available at https://github.com/jpeg-aic/dataset-JPEG-AI-SDR25.
基于学习的图像压缩方法作为传统编码器的有前途的替代方案而出现,提供了改进的速率失真性能和感知质量。JPEG AI代表此领域的最新标准化框架,利用深度神经网络进行高保真图像重建。在这项研究中,我们使用JPEG AIC-3方法论对JPEG AI压缩图像进行主观视觉质量评估,该方法以刚刚可察觉差异(JND)单位量化感知差异。我们生成了一个包含来自五个不同源的50张压缩图像的数据集,这些图像具有精细的失真级别。大规模的众包实验收集了来自459名参与者的96,200个三元组响应。我们基于增强的和普通三元组比较重建了基于JND的质量量表。此外,我们还评估了多个客观图像质量指标与高保真范围内的人类感知的一致性。CVVDP指标总体性能最佳;然而,包括CVVDP在内的大多数指标在预测JPEG AI压缩图像的质量时过于乐观。这些发现强调了在现代图像编码器的开发和基准测试中严格进行主观评价的必要性,特别是在高保真范围内。另一个技术贡献是将著名的Meng-Rosenthal-Rubin统计测试引入到体验质量研究领域。该测试可以可靠地评估质量指标性能差异的显著性,以指标与基准之间的相关性为准。所有主观分数均包含在完整数据集中,可在https://github.com/jpeg-aic/dataset-JPEG-AI-SDR25公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 5 figures, 3 tables, submitted to QoMEX 2025
Summary
基于学习的图像压缩方法已成为传统编码技术的有前途的替代方案,提供了改进的速率失真性能和感知质量。本研究对JPEG AI压缩图像进行了全面的主观视觉质量评估,采用JPEG AIC-3方法论量化感知差异。实验生成了50张具有精细失真级别的压缩图像数据集,并通过大规模众包实验收集了参与者的反应。研究发现,在高质量范围内,大多数客观图像质量指标在预测JPEG AI压缩图像质量时过于乐观。因此,在现代图像编码技术开发和评估中,特别是在高质量范围内,需要严格的客观评估。此外,本研究还将Meng-Rosenthal-Rubin统计测试引入用户体验研究领域,以评估质量指标性能差异的显著性。
Key Takeaways
- 学习型图像压缩方法已显示出对传统编码技术的优势,表现在改善速率失真性能和感知质量方面。
- JPEG AI代表该领域的最新标准化框架,利用深度神经网络进行高保真图像重建。
- 本研究通过JPEG AIC-3方法论对JPEG AI压缩图像进行了全面的主观视觉质量评估。
- 生成了包含50张具有精细失真级别的压缩图像数据集,并通过大规模众包实验收集参与者反应。
- 在高保真范围内,大多数客观图像质量指标预测JPEG AI压缩图像质量时表现过于乐观。
- 严格的客观评估对于现代图像编码技术的开发和评估至关重要。
- 引入Meng-Rosenthal-Rubin统计测试来评估质量指标性能差异的显著性。
点此查看论文截图



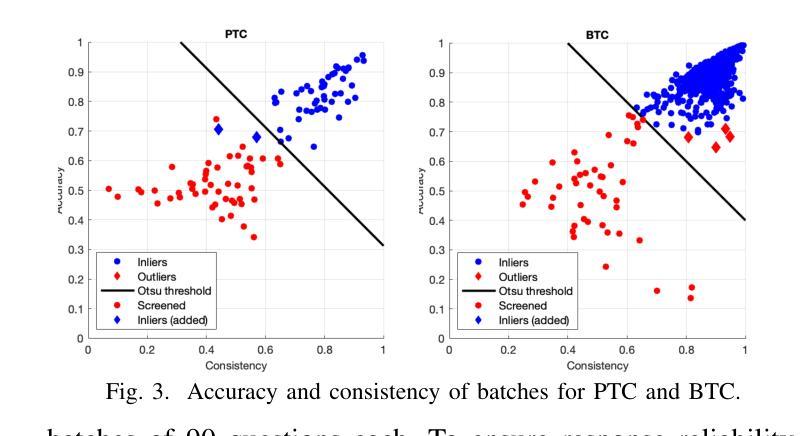
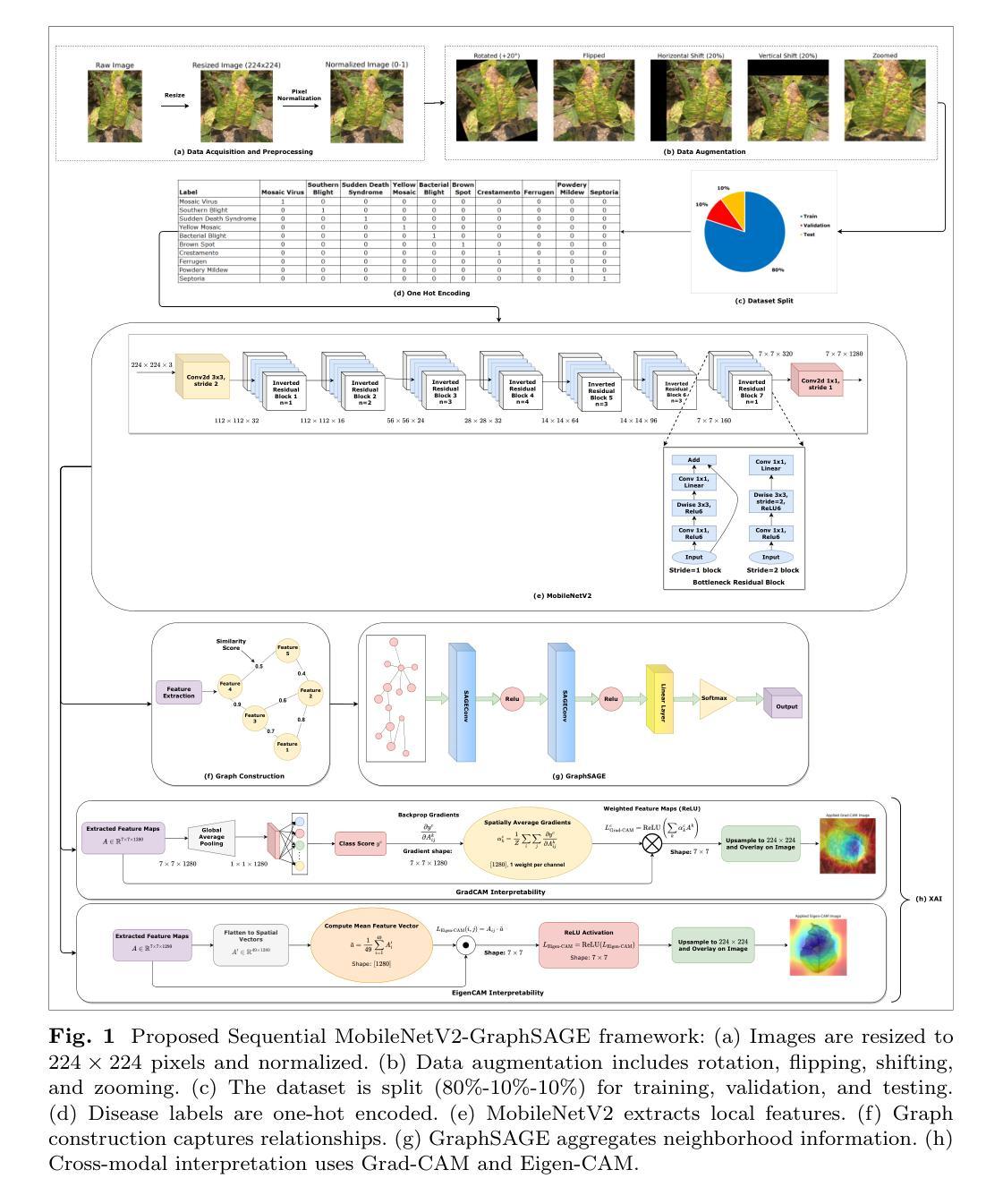
Soybean Disease Detection via Interpretable Hybrid CNN-GNN: Integrating MobileNetV2 and GraphSAGE with Cross-Modal Attention
Authors:Md Abrar Jahin, Soudeep Shahriar, M. F. Mridha, Md. Jakir Hossen, Nilanjan Dey
Soybean leaf disease detection is critical for agricultural productivity but faces challenges due to visually similar symptoms and limited interpretability in conventional methods. While Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) excel in spatial feature extraction, they often neglect inter-image relational dependencies, leading to misclassifications. This paper proposes an interpretable hybrid Sequential CNN-Graph Neural Network (GNN) framework that synergizes MobileNetV2 for localized feature extraction and GraphSAGE for relational modeling. The framework constructs a graph where nodes represent leaf images, with edges defined by cosine similarity-based adjacency matrices and adaptive neighborhood sampling. This design captures fine-grained lesion features and global symptom patterns, addressing inter-class similarity challenges. Cross-modal interpretability is achieved via Grad-CAM and Eigen-CAM visualizations, generating heatmaps to highlight disease-influential regions. Evaluated on a dataset of ten soybean leaf diseases, the model achieves $97.16%$ accuracy, surpassing standalone CNNs ($\le95.04%$) and traditional machine learning models ($\le77.05%$). Ablation studies validate the sequential architecture’s superiority over parallel or single-model configurations. With only 2.3 million parameters, the lightweight MobileNetV2-GraphSAGE combination ensures computational efficiency, enabling real-time deployment in resource-constrained environments. The proposed approach bridges the gap between accurate classification and practical applicability, offering a robust, interpretable tool for agricultural diagnostics while advancing CNN-GNN integration in plant pathology research.
大豆叶病检测对农业生产力至关重要,但由于症状视觉相似性和传统方法的有限解释性,它面临着挑战。尽管卷积神经网络(CNN)在空间特征提取方面表现出色,但它们往往忽略了图像间的关系依赖性,从而导致误分类。本文提出了一种可解释的混合序贯CNN-图神经网络(GNN)框架,该框架协同MobileNetV2进行局部特征提取和GraphSAGE进行关系建模。该框架构建了一个图,其中节点代表叶图像,边由基于余弦相似性的邻接矩阵和自适应邻域采样定义。这种设计捕捉了精细的病变特征和全局症状模式,解决了类间相似性的挑战。通过Grad-CAM和Eigen-CAM可视化实现跨模态解释性,生成热图以突出显示影响疾病的区域。在包含十种大豆叶病的数据集上进行评估,该模型达到了97.16%的准确率,超过了单独的CNN(≤95.04%)和传统机器学习模型(≤77.05%)。消融研究验证了序贯架构优于并行或单一模型配置。仅有230万个参数的轻量级MobileNetV2-GraphSAGE组合确保了计算效率,可在资源受限的环境中实现实时部署。所提出的方法弥合了准确分类与实际适用之间的鸿沟,为农业诊断提供了一个稳健、可解释的工具,同时推动了CNN-GNN在植物病理学研究中的集成。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种可解释的混合序贯CNN-图神经网络(GNN)框架,用于大豆叶病检测。该框架结合MobileNetV2进行局部特征提取和GraphSAGE进行关系建模,通过构建图像图来捕捉精细病变特征和全局症状模式,解决类间相似性的挑战。模型在十种大豆叶病数据集上取得了97.16%的准确率,超越单一CNN和传统机器学习模型。其架构具有轻量、高效的特点,适用于资源受限环境。该模型为农业诊断提供了一个强大、可解释的工具,推动了CNN-GNN在植物病理学研究中的融合。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了混合序贯CNN-图神经网络(GNN)框架用于大豆叶病检测。
- 结合MobileNetV2进行局部特征提取和GraphSAGE进行关系建模。
- 通过构建图像图来捕捉精细病变特征和全局症状模式。
- 模型实现了跨模态解释性,通过Grad-CAM和Eigen-CAM可视化生成热图突出疾病影响区域。
- 在十种大豆叶病数据集上取得了97.16%的准确率,超越其他模型。
- 模型具有轻量、高效的特点,适用于资源受限环境。
点此查看论文截图

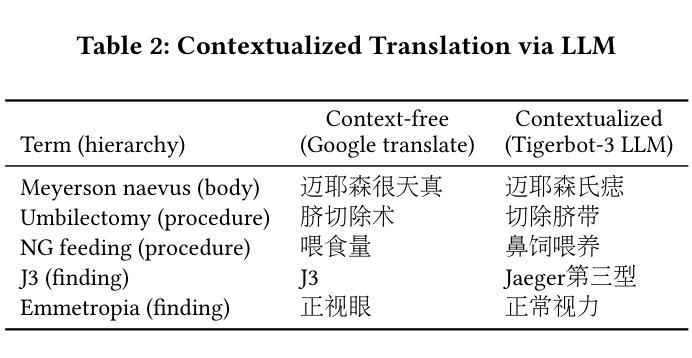
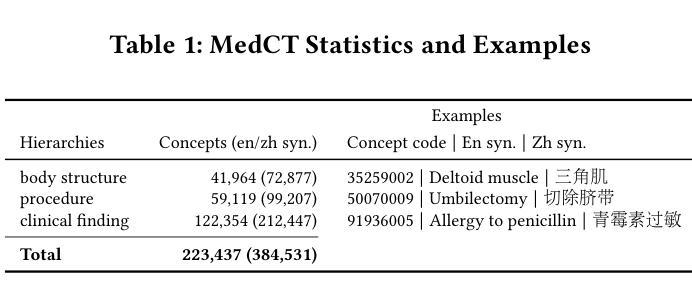
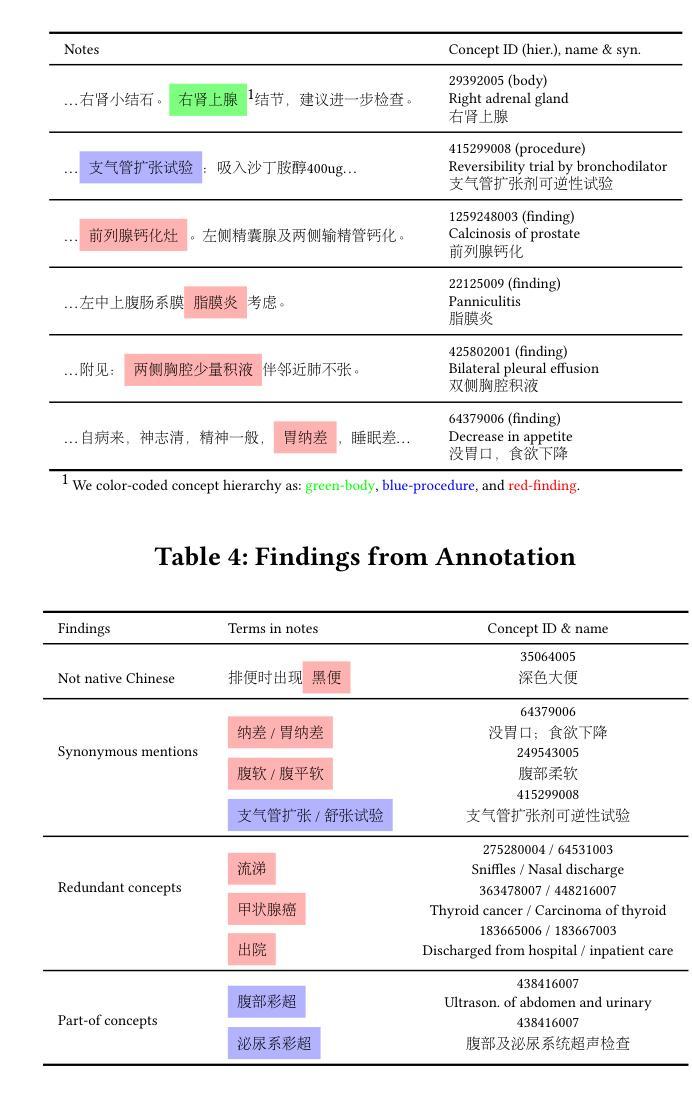
MedCT: A Clinical Terminology Graph for Generative AI Applications in Healthcare
Authors:Ye Chen, Dongdong Huang, Haoyun Xu, Cong Fu, Lin Sheng, Qingli Zhou, Yuqiang Shen, Kai Wang
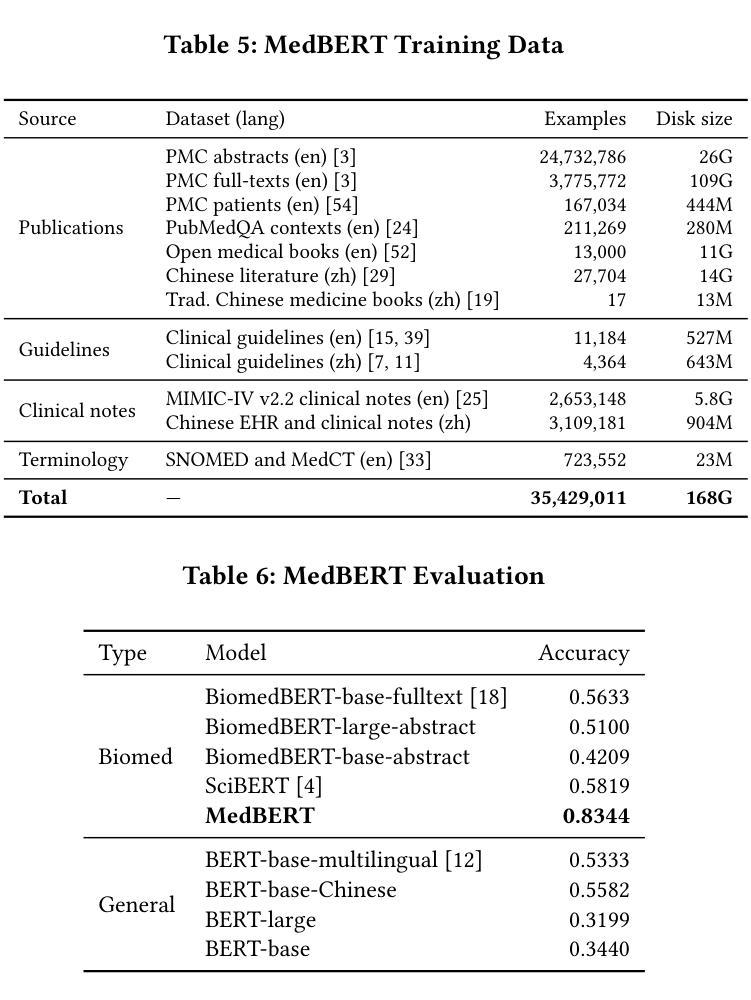
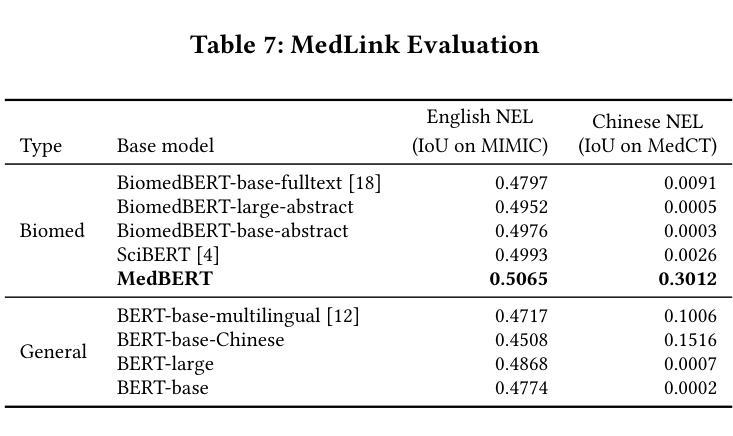
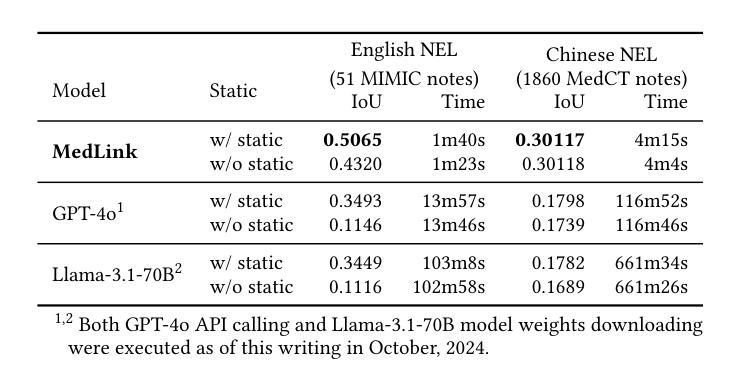
We introduce the world’s first clinical terminology for the Chinese healthcare community, namely MedCT, accompanied by a clinical foundation model MedBERT and an entity linking model MedLink. The MedCT system enables standardized and programmable representation of Chinese clinical data, successively stimulating the development of new medicines, treatment pathways, and better patient outcomes for the populous Chinese community. Moreover, the MedCT knowledge graph provides a principled mechanism to minimize the hallucination problem of large language models (LLMs), therefore achieving significant levels of accuracy and safety in LLM-based clinical applications. By leveraging the LLMs’ emergent capabilities of generativeness and expressiveness, we were able to rapidly built a production-quality terminology system and deployed to real-world clinical field within three months, while classical terminologies like SNOMED CT have gone through more than twenty years development. Our experiments show that the MedCT system achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in semantic matching and entity linking tasks, not only for Chinese but also for English. We also conducted a longitudinal field experiment by applying MedCT and LLMs in a representative spectrum of clinical tasks, including electronic health record (EHR) auto-generation and medical document search for diagnostic decision making. Our study shows a multitude of values of MedCT for clinical workflows and patient outcomes, especially in the new genre of clinical LLM applications. We present our approach in sufficient engineering detail, such that implementing a clinical terminology for other non-English societies should be readily reproducible. We openly release our terminology, models and algorithms, along with real-world clinical datasets for the development.
我们为中文医疗社区引入了世界上首个临床术语——MedCT,它配备了临床基础模型MedBERT和实体链接模型MedLink。MedCT系统能够实现中文临床数据的标准化和可编程表示,进而刺激新药研发、治疗路径的探索,为人口众多的中文社区带来更好的患者疗效。此外,MedCT知识图谱提供了一种有原则的机制,以最小化大型语言模型(LLM)的幻觉问题,从而在基于LLM的临床应用中实现显著水平和准确性及安全性。通过利用LLM的生成能力和表现力,我们能够在三个月内快速构建了一个生产质量术语系统并部署到现实世界中的临床领域,而像SNOMED CT这样的经典术语却经历了超过二十年的发展。我们的实验表明,MedCT系统在语义匹配和实体链接任务上达到了最新(SOTA)的性能,不仅适用于中文,也适用于英文。我们还通过在一系列具有代表性的临床任务中应用MedCT和LLM进行了纵向实地实验,包括自动生成电子健康记录(EHR)和用于诊断决策的医疗文件搜索。我们的研究表明,MedCT在临床工作流程和患者疗效方面具有多种价值,特别是在新型临床LLM应用中。我们以足够的工程细节呈现了我们方法,使得为其他非英语社会实施临床术语应该很容易复制。我们公开发布我们的术语、模型和算法,以及用于开发的真实世界临床数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted into ICCS 2025 and published in Springer’s LNCS Series
摘要
本文介绍了针对中文医疗社区的世界首个临床术语系统MedCT,它配备了临床基础模型MedBERT和实体链接模型MedLink。MedCT系统能够实现中文临床数据的标准化和可编程表示,刺激新药研发、治疗路径的优化,以及针对庞大中文社区的更好患者治疗效果的实现。此外,MedCT知识图谱提供了减少大型语言模型(LLMs)的幻想问题的原则机制,从而在LLM临床应用中实现了高准确性和安全性。通过利用LLMs的生成能力和表现力,我们能够在三个月内快速构建生产质量术语系统并部署到现实临床环境中,而像SNOMED CT这样的经典术语则经历了超过二十年的发展。实验表明,MedCT系统在语义匹配和实体链接任务上达到了最新水平,不仅适用于中文,也适用于英文。我们还通过应用MedCT和LLMs于一系列具有代表性的临床任务进行了纵向实地实验,包括自动生成电子健康记录和用于诊断决策的医疗文件搜索。研究表明,MedCT对临床工作流程和患者治疗效果具有多重价值,特别是在新型临床LLM应用中。我们的方法有足够的工程细节,使得为其他非英语社会实施临床术语系统变得容易复制。我们公开发布了术语、模型和算法,以及用于开发的真实临床数据集。
关键见解
- 引入针对中文医疗社区的世界首个临床术语系统MedCT,具备标准化和可编程表示中文临床数据的能力。
- MedCT系统刺激新药研发、优化治疗路径,并改善患者治疗效果。
- MedCT知识图谱有效减少大型语言模型的幻想问题,提高准确性和安全性。
- 利用大型语言模型的生成能力和表现力,快速构建并部署生产质量术语系统。
- MedCT系统在语义匹配和实体链接任务上表现优异,适用于中文和英文。
- 实地实验证明MedCT对临床工作流程和患者治疗效果具有显著价值,特别是在新型临床LLM应用中。
点此查看论文截图


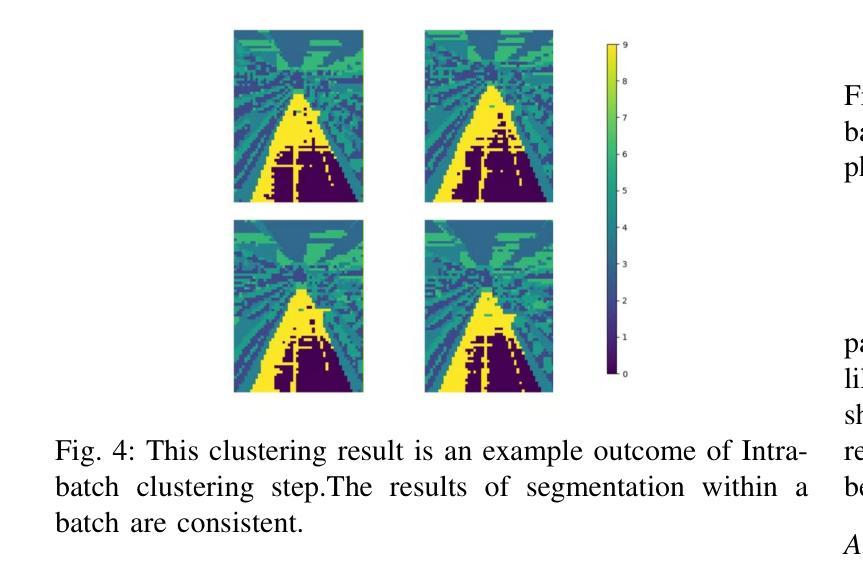
BYOCL: Build Your Own Consistent Latent with Hierarchical Representative Latent Clustering
Authors:Jiayue Dai, Yunya Wang, Yihan Fang, Yuetong Chen, Butian Xiong
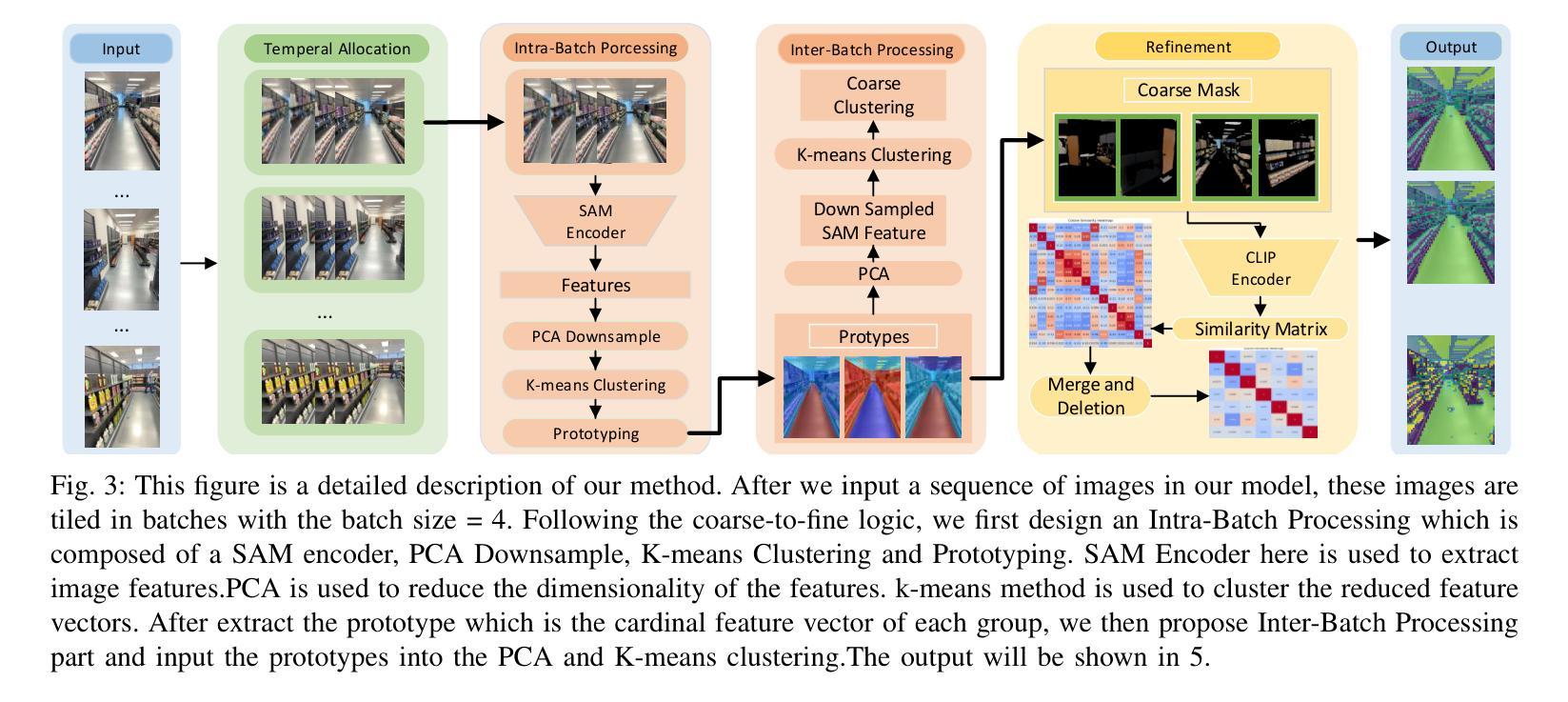
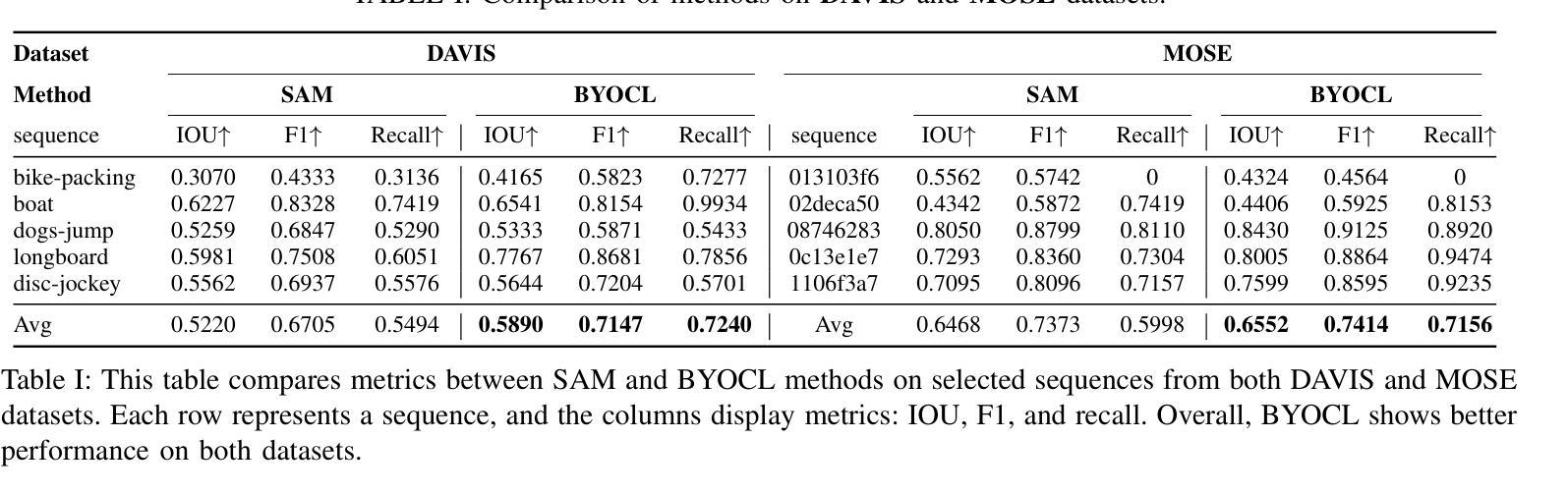
To address the semantic inconsistency issue with SAM or other single-image segmentation models handling image sequences, we introduce BYOCL. This novel model outperforms SAM in extensive experiments, showcasing its Hierarchical prototype capabilities across CLIP and other representations. BYOCL significantly reduces time and space consumption by dividing inputs into smaller batches, achieving exponential time reduction compared to previous methods. Our approach leverages the SAM image encoder for feature extraction, followed by Intra-Batch and Inter-Batch clustering algorithms. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BYOCL far exceeds the previous state-of-the-art single image segmentation model. Our work is the first to apply consistent segmentation using foundation models without requiring training, utilizing plug-and-play modules for any latent space, making our method highly efficientModels are available at \href{https://github.com/cyt1202/BYOCL.git
为了解决SAM或其他处理图像序列的单图像分割模型中的语义不一致问题,我们引入了BYOCL。这一新型模型在大量实验中表现出优于SAM的性能,展示了其在CLIP和其他表示法中的分层原型能力。BYOCL通过将输入分成较小的批次,显著减少了时间和空间消耗,与前人方法相比实现了指数级的时间减少。我们的方法利用SAM图像编码器进行特征提取,随后使用批内和批间聚类算法。大量实验表明,BYOCL远远超过了之前的最先进的单图像分割模型。我们的工作是首次应用基础模型进行一致分割,无需训练,利用即插即用模块适应任何潜在空间,使我们的方法高度有效。模型可通过链接https://github.com/cyt1202/BYOCL.git获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 5 figures
Summary
基于SAM或其他单图像分割模型在处理图像序列时存在的语义不一致问题,我们引入了BYOCL模型。该新型模型在广泛实验中表现出优异性能,展现了其跨CLIP和其他表征的分层原型能力。BYOCL通过将输入划分为较小的批次,显著减少了时间和空间消耗,与前人方法相比实现了指数级的时间减少。该模型利用SAM图像编码器进行特征提取,随后采用Intra-Batch和Inter-Batch聚类算法。广泛实验证明,BYOCL远超之前最先进的单图像分割模型,并且是首次应用无需训练的基础模型进行一致分割,利用任意潜在空间的即插即用模块,使该方法具有高度高效性。
Key Takeaways
- BYOCL模型解决了SAM和其他单图像分割模型在处理图像序列时的语义不一致问题。
- BYOCL通过划分输入为较小的批次,显著减少了时间和空间的消耗。
- BYOCL模型利用SAM图像编码器进行特征提取,并采用Intra-Batch和Inter-Batch聚类算法。
- 广泛实验证明BYOCL模型性能超越了之前的单图像分割模型。
- BYOCL模型是首个应用基础模型进行一致分割的模型,无需训练。
- BYOCL模型具有高度的灵活性,可以适应任意潜在空间,即插即用。
- BYOCL模型提高了单图像分割模型的效率。
点此查看论文截图


Multi-view Hybrid Graph Convolutional Network for Volume-to-mesh Reconstruction in Cardiovascular MRI
Authors:Nicolás Gaggion, Benjamin A. Matheson, Yan Xia, Rodrigo Bonazzola, Nishant Ravikumar, Zeike A. Taylor, Diego H. Milone, Alejandro F. Frangi, Enzo Ferrante
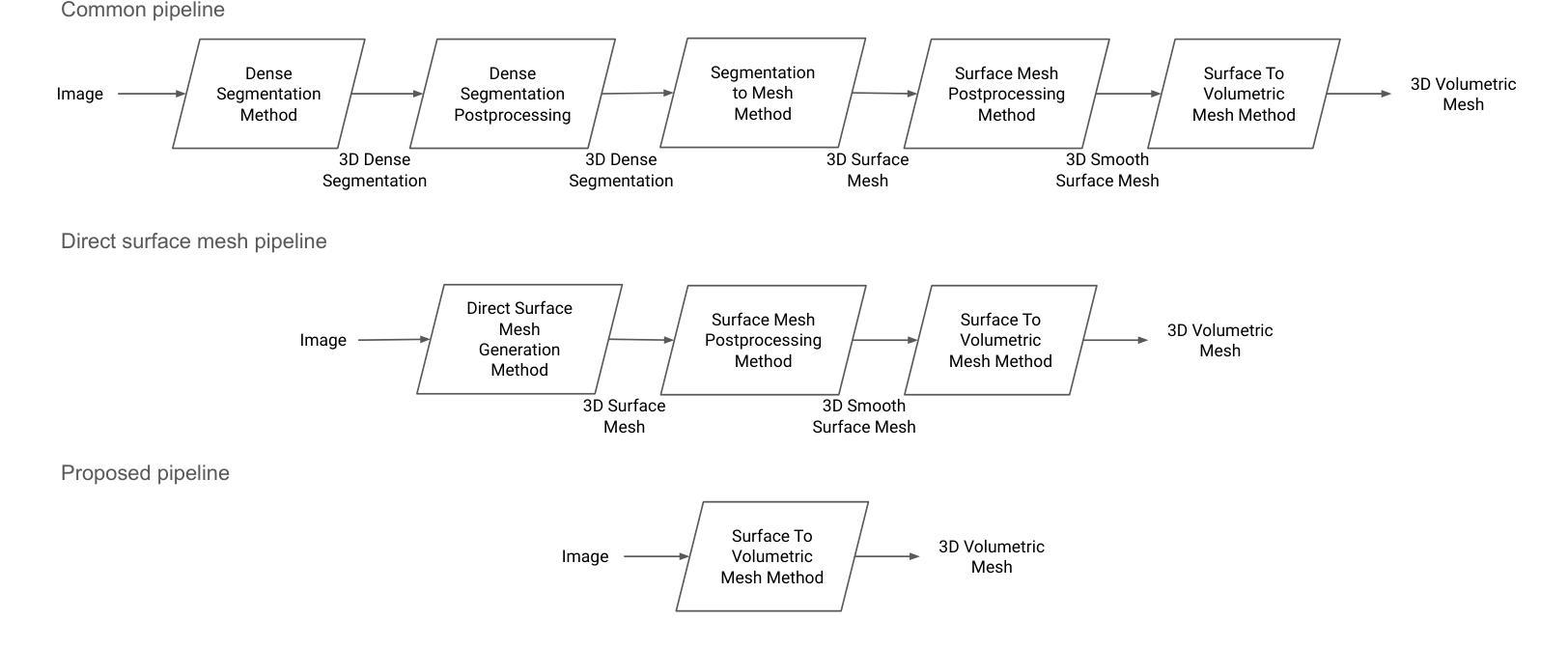
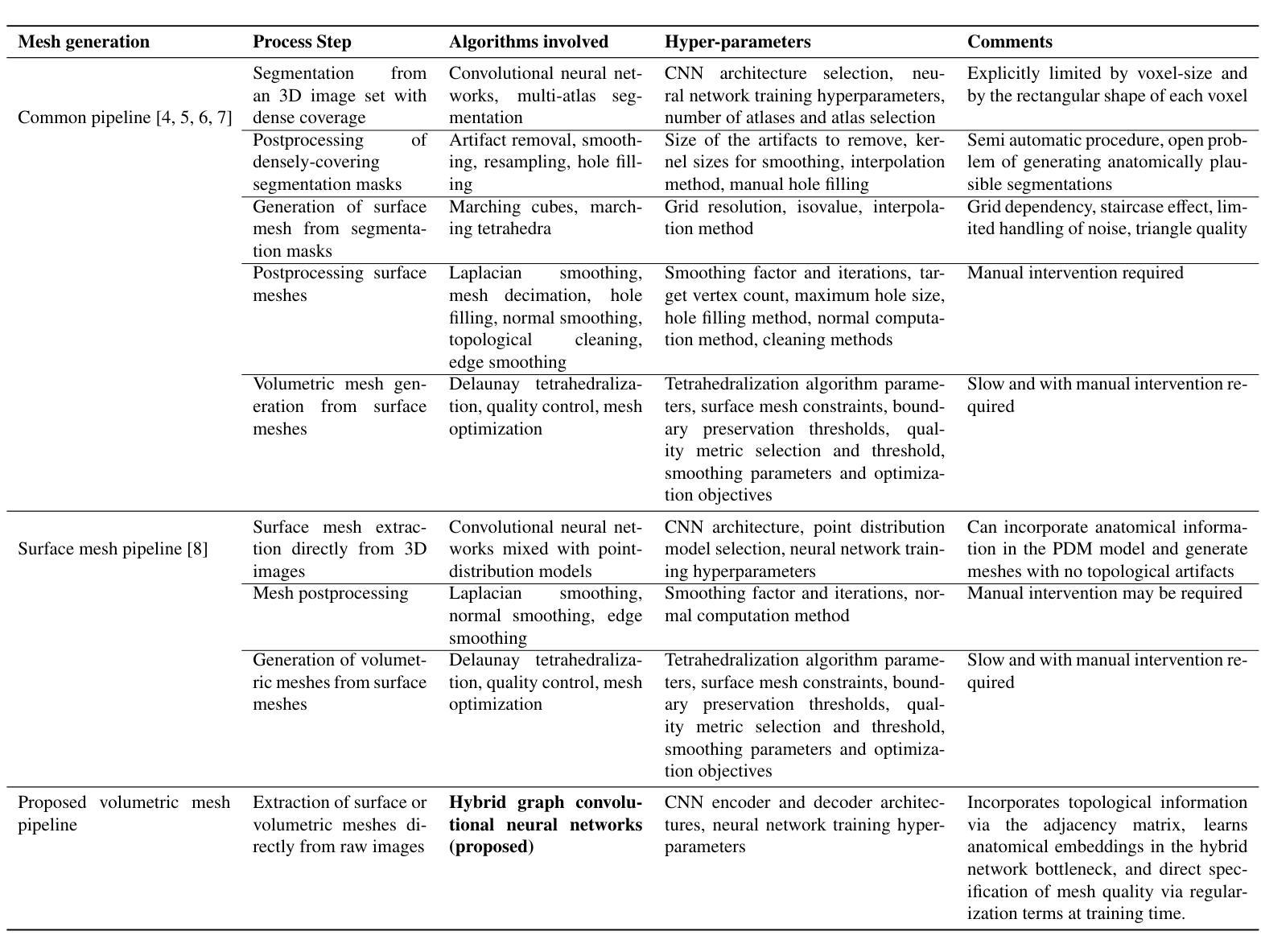
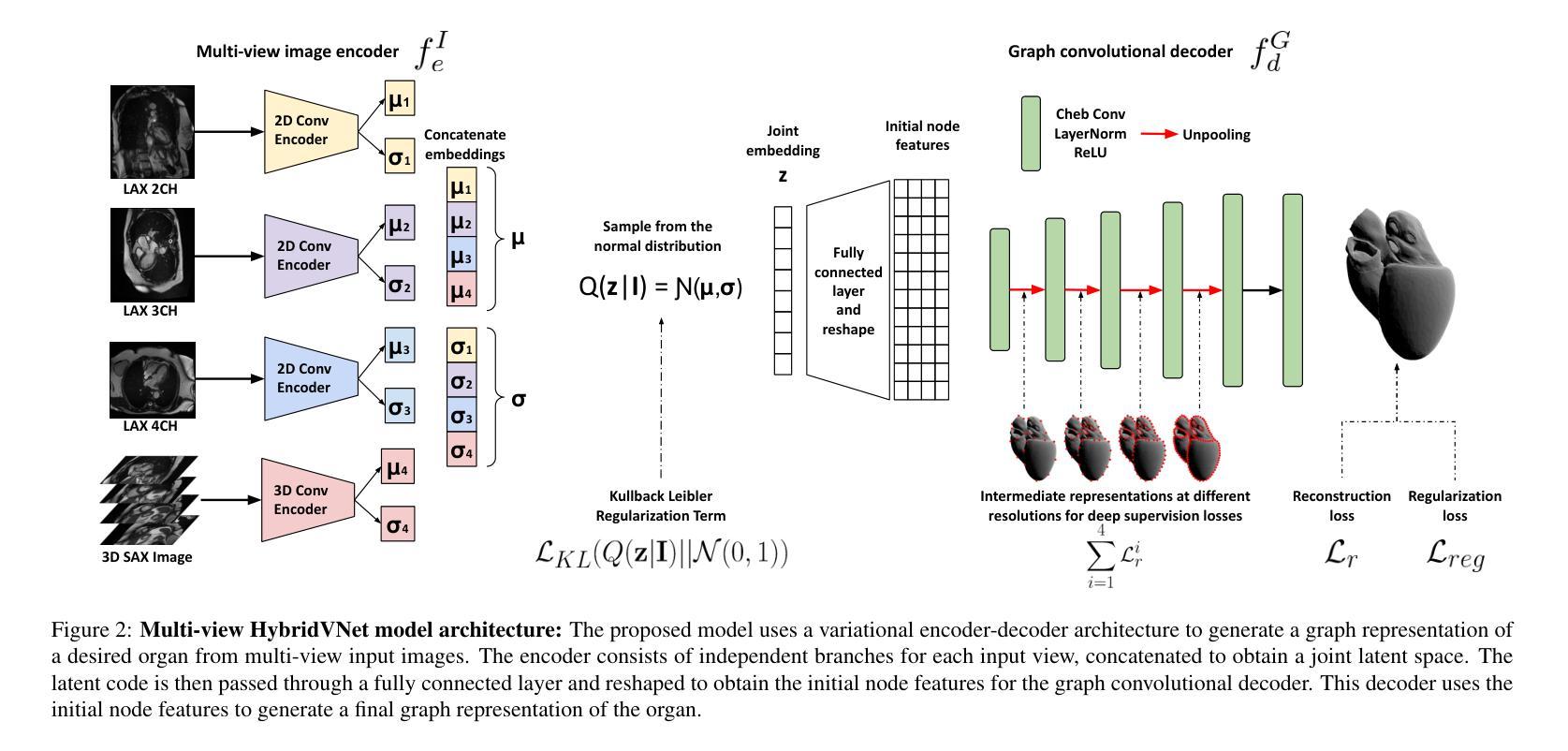
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging is emerging as a crucial tool to examine cardiac morphology and function. Essential to this endeavour are anatomical 3D surface and volumetric meshes derived from CMR images, which facilitate computational anatomy studies, biomarker discovery, and in-silico simulations. Traditional approaches typically follow complex multi-step pipelines, first segmenting images and then reconstructing meshes, making them time-consuming and prone to error propagation. In response, we introduce HybridVNet, a novel architecture for direct image-to-mesh extraction seamlessly integrating standard convolutional neural networks with graph convolutions, which we prove can efficiently handle surface and volumetric meshes by encoding them as graph structures. To further enhance accuracy, we propose a multi-view HybridVNet architecture which processes both long axis and short axis CMR, showing that it can increase the performance of cardiac MR mesh generation. Our model combines traditional convolutional networks with variational graph generative models, deep supervision and mesh-specific regularisation. Experiments on a comprehensive dataset from the UK Biobank confirm the potential of HybridVNet to significantly advance cardiac imaging and computational cardiology by efficiently generating high-fidelity meshes from CMR images. Multi-view HybridVNet outperforms the state-of-the-art, achieving improvements of up to $\sim$27% reduction in Mean Contour Distance (from 1.86 mm to 1.35 mm for the LV Myocardium), up to $\sim$18% improvement in Hausdorff distance (from 4.74 mm to 3.89mm, for the LV Endocardium), and up to $\sim$8% in Dice Coefficient (from 0.78 to 0.84, for the LV Myocardium), highlighting its superior accuracy.
心血管磁共振成像正成为一种用于检查心脏形态和功能的重要工具。在这一工作中,从CMR图像中得出的解剖三维表面和体积网格尤为关键,这些网格促进了计算解剖学研究、生物标志物发现和计算机模拟。传统方法通常遵循复杂的多步管道,首先分割图像,然后重建网格,这使得它们耗时且容易出错。作为回应,我们引入了HybridVNet,这是一种直接图像到网格提取的新型架构,无缝集成了标准卷积神经网络和图卷积。我们已经证明它能够有效地处理表面和体积网格,通过将它们编码为图形结构来实现这一点。为了进一步提高准确性,我们提出了一种多视角HybridVNet架构,该架构既处理长轴CMR又处理短轴CMR,表明它可以提高心脏MR网格生成的性能。我们的模型结合了传统卷积网络、变图生成模型、深度监督和网格特定正则化。在英国生物银行综合数据集上的实验证实了HybridVNet的潜力,它可以通过从CMR图像高效生成高保真网格来推动心脏成像和计算心脏病学的发展。多视角HybridVNet表现优于最新技术,平均轮廓距离减少了约27%(左心室心肌从1.86毫米降至1.35毫米),豪斯多夫距离提高了约18%(左心室内膜从4.74毫米降至3.89毫米),迪杰斯特拉系数提高了约8%(左心室心肌从0.78提高到0.84),突显了其卓越准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
心血管磁共振成像(CMR)是检查心脏形态和功能的重要工具。本研究引入HybridVNet,一种直接图像到网格提取的新架构,集成标准卷积神经网络和图卷积,能高效处理表面和体积网格。为进一步提高准确性,提出多视角HybridVNet架构,处理长轴和短轴CMR图像,结合传统卷积网络、变分图生成模型、深度监督和网格特定正则化。实验证明,HybridVNet在心脏MR网格生成方面具有巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 心血管磁共振成像(CMR)是检查心脏形态和功能的关键工具。
- CMR图像中的解剖3D表面和体积网格对于计算解剖学、生物标志物发现和计算机模拟至关重要。
- 传统的图像到网格提取方法复杂且耗时,易出错。
- HybridVNet架构能直接从CMR图像中提取网格,集成卷积神经网络和图卷积。
- 多视角HybridVNet架构能提高心脏MR网格生成的性能。
- HybridVNet结合传统卷积网络、变分图生成模型、深度监督和网格特定正则化。
点此查看论文截图