⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-12 更新
P2Object: Single Point Supervised Object Detection and Instance Segmentation
Authors:Pengfei Chen, Xuehui Yu, Xumeng Han, Kuiran Wang, Guorong Li, Lingxi Xie, Zhenjun Han, Jianbin Jiao
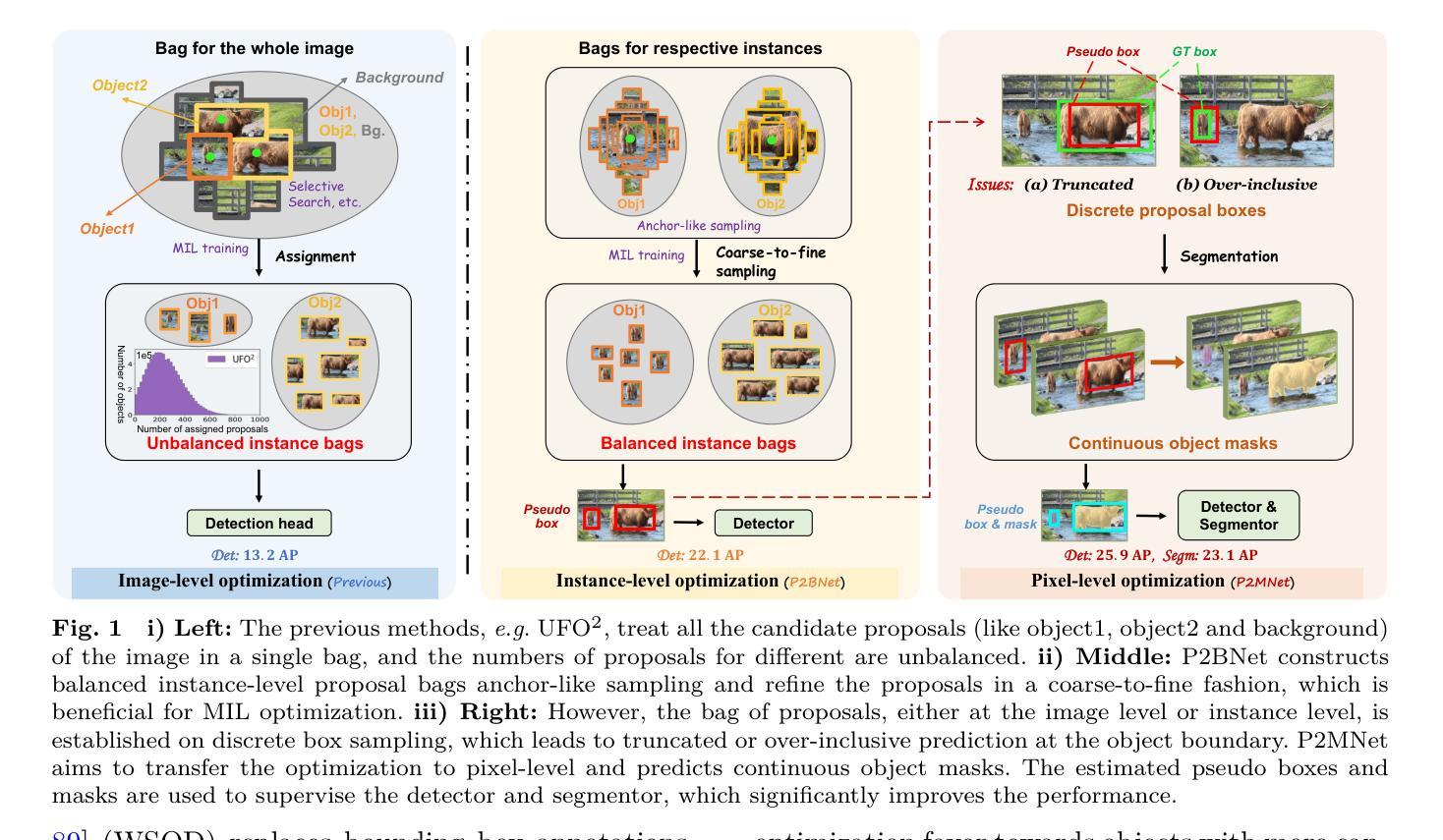
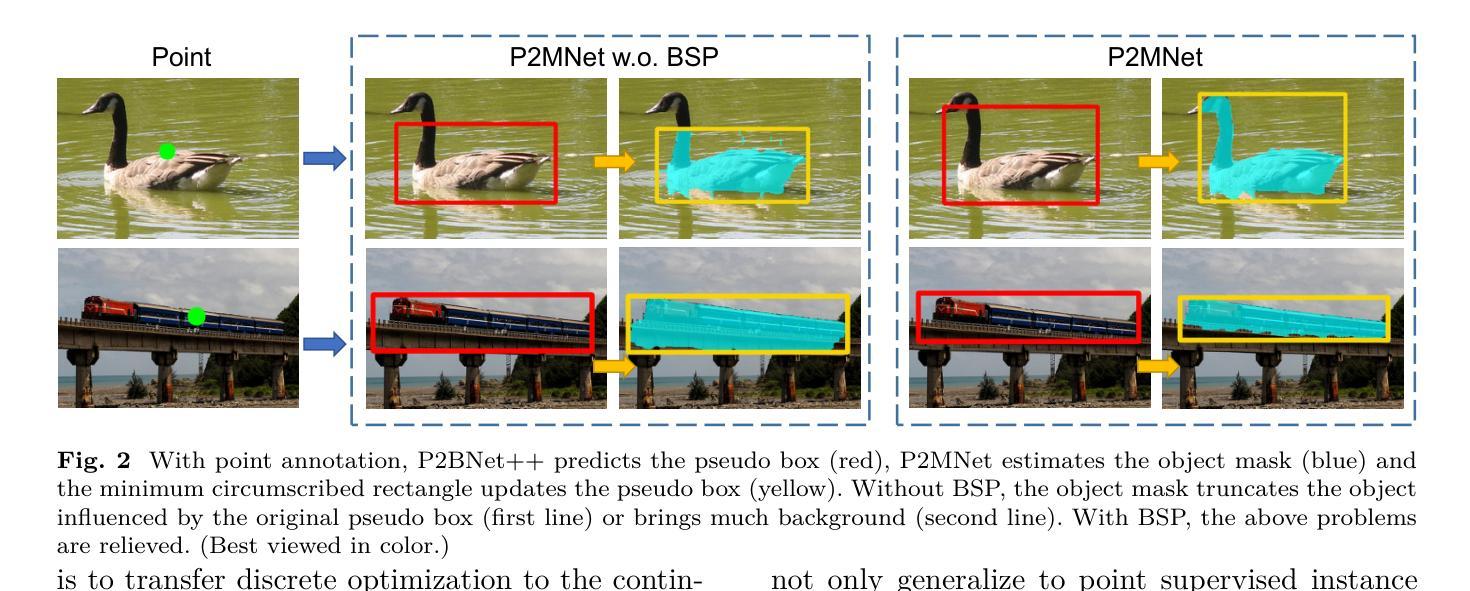
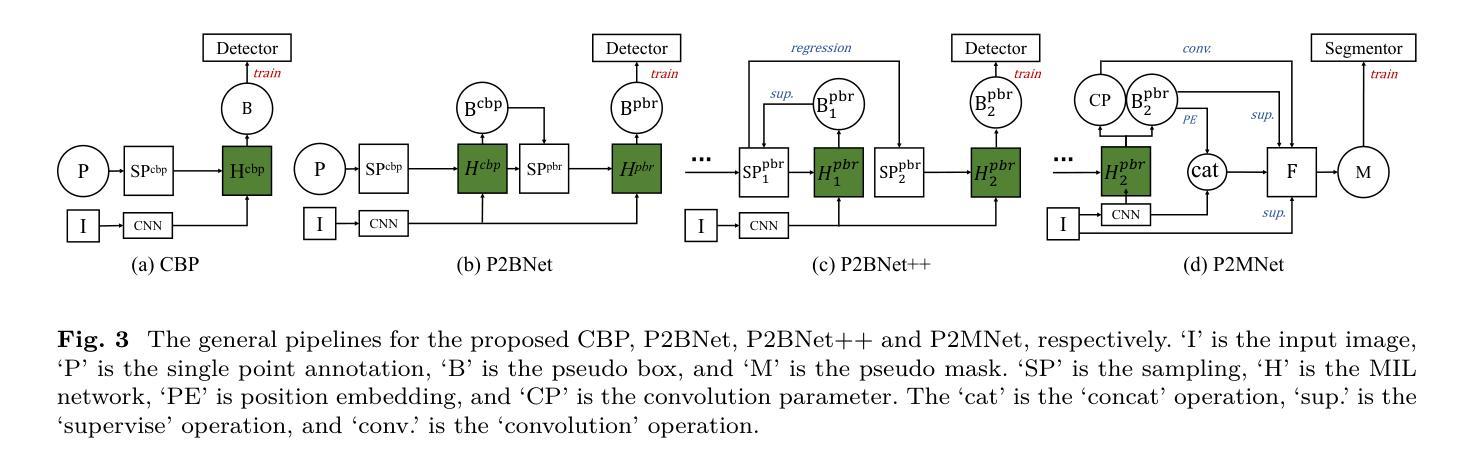
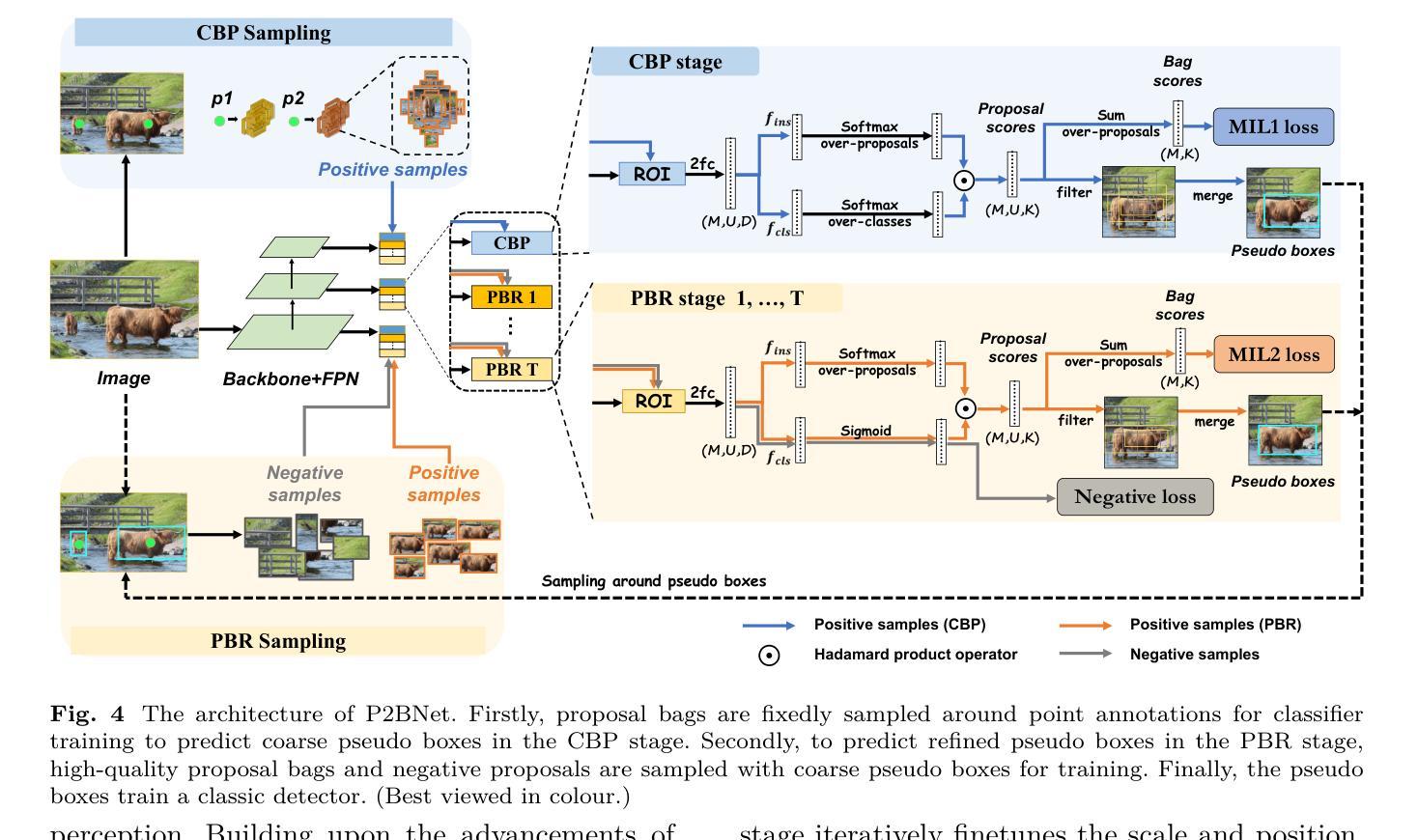
Object recognition using single-point supervision has attracted increasing attention recently. However, the performance gap compared with fully-supervised algorithms remains large. Previous works generated class-agnostic \textbf{\textit{proposals in an image}} offline and then treated mixed candidates as a single bag, putting a huge burden on multiple instance learning (MIL). In this paper, we introduce Point-to-Box Network (P2BNet), which constructs balanced \textbf{\textit{instance-level proposal bags}} by generating proposals in an anchor-like way and refining the proposals in a coarse-to-fine paradigm. Through further research, we find that the bag of proposals, either at the image level or the instance level, is established on discrete box sampling. This leads the pseudo box estimation into a sub-optimal solution, resulting in the truncation of object boundaries or the excessive inclusion of background. Hence, we conduct a series exploration of discrete-to-continuous optimization, yielding P2BNet++ and Point-to-Mask Network (P2MNet). P2BNet++ conducts an approximately continuous proposal sampling strategy by better utilizing spatial clues. P2MNet further introduces low-level image information to assist in pixel prediction, and a boundary self-prediction is designed to relieve the limitation of the estimated boxes. Benefiting from the continuous object-aware \textbf{\textit{pixel-level perception}}, P2MNet can generate more precise bounding boxes and generalize to segmentation tasks. Our method largely surpasses the previous methods in terms of the mean average precision on COCO, VOC, SBD, and Cityscapes, demonstrating great potential to bridge the performance gap compared with fully supervised tasks.
使用单点监督进行对象识别最近引起了越来越多的关注。然而,与完全监督的算法相比,性能差距仍然很大。之前的工作离线生成图像中的类无关(通用)提案,然后将混合候选者视为单个袋子,给多实例学习(MIL)带来了巨大的负担。在本文中,我们介绍了点框网络(P2BNet),它通过类似锚点的方式生成提案,并在粗略到精细的范式中细化提案,从而构建平衡的实例级提案袋。通过进一步研究,我们发现无论是图像级还是实例级的提案袋,都是以离散框采样为基础建立的。这导致伪框估计陷入次优解,导致对象边界被截断或过度包含背景。因此,我们进行了一系列从离散到连续的优化的探索,从而推出了P2BNet++和点遮罩网络(P2MNet)。P2BNet++通过更好地利用空间线索,实现了近似连续的提案采样策略。P2MNet进一步引入低级别的图像信息来帮助像素预测,并设计了一个边界自预测来缓解估计框的限制。受益于持续的面向对象像素级感知,P2MNet可以生成更精确边界框并将其推广至分割任务。我们的方法在COCO、VOC、SBD和Cityscapes上的平均精度均值大大超过了之前的方法,显示出在缩小与全监督任务性能差距方面的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IJCV
Summary
本文介绍了利用单点监督的对象识别技术,针对现有方法存在的问题,提出了Point-to-Box网络(P2BNet)和Point-to-Mask网络(P2MNet)。通过构建平衡的实例级提案包,采用从粗到细的提案细化策略,提高了对象识别的性能。P2BNet++对离散提案采样策略进行了近似连续优化,而P2MNet引入了低级别图像信息辅助像素预测,并设计了边界自预测来缓解估计框的限制。这些方法在COCO、VOC、SBD和Cityscapes等多个数据集上的平均精度均值方面都超过了以前的方法,展现出在缩小与全监督任务性能差距方面的巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 对象识别中,单点监督技术受到关注,但与全监督算法的性能差距仍然较大。
- 此前的方法生成类无关的提案,并将其作为单一包处理,给多实例学习(MIL)带来了巨大负担。
- 引入Point-to-Box网络(P2BNet)和Point-to-Mask网络(P2MNet),通过构建平衡的实例级提案包和提高像素级别的感知能力,提高了对象识别的性能。
- P2BNet++采用近似连续的提案采样策略,更好地利用空间线索。
- P2MNet引入低级别图像信息辅助像素预测,并设计边界自预测来缓解估计框的限制。
- 方法在多个数据集上的表现超过以前的方法,显示出缩小与全监督任务性能差距的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

Adaptive Detection of Fast Moving Celestial Objects Using a Mixture of Experts and Physical-Inspired Neural Network
Authors:Peng Jia, Ge Li, Bafeng Cheng, Yushan Li, Rongyu Sun
Fast moving celestial objects are characterized by velocities across the celestial sphere that significantly differ from the motions of background stars. In observational images, these objects exhibit distinct shapes, contrasting with the typical appearances of stars. Depending on the observational method employed, these celestial entities may be designated as near-Earth objects or asteroids. Historically, fast moving celestial objects have been observed using ground-based telescopes, where the relative stability of stars and Earth facilitated effective image differencing techniques alongside traditional fast moving celestial object detection and classification algorithms. However, the growing prevalence of space-based telescopes, along with their diverse observational modes, produces images with different properties, rendering conventional methods less effective. This paper presents a novel algorithm for detecting fast moving celestial objects within star fields. Our approach enhances state-of-the-art fast moving celestial object detection neural networks by transforming them into physical-inspired neural networks. These neural networks leverage the point spread function of the telescope and the specific observational mode as prior information; they can directly identify moving fast moving celestial objects within star fields without requiring additional training, thereby addressing the limitations of traditional techniques. Additionally, all neural networks are integrated using the mixture of experts technique, forming a comprehensive fast moving celestial object detection algorithm. We have evaluated our algorithm using simulated observational data that mimics various observations carried out by space based telescope scenarios and real observation images. Results demonstrate that our method effectively detects fast moving celestial objects across different observational modes.
快速运动的天体特征在于其在天体球面上的速度与背景恒星的运动存在显著差异。在观测图像中,这些天体呈现出独特的形状,与恒星的典型外观形成鲜明对比。根据所采用观测方法的不同,这些天体可能被指定为近地天体或小行星。历史上,人们使用地面望远镜观测快速运动的天体,恒星的相对稳定性和地球的特性促进了有效的图像差分技术与传统的快速运动天体检测与分类算法的融合使用。然而,基于太空的望远镜的普及率不断增长及其多样的观测模式产生了具有不同属性的图像,使得传统方法的有效性降低。本文提出了一种检测星域内快速运动天体的新型算法。我们的方法通过将其转化为受物理启发的神经网络,增强了最先进的快速运动天体检测神经网络的功能。这些神经网络利用望远镜的点扩散函数和特定的观测模式作为先验信息;它们可以直接识别星域内的快速运动天体,无需额外的训练,从而解决了传统技术的局限性。此外,所有神经网络均采用混合专家技术集成,形成了全面的快速运动天体检测算法。我们利用模拟观测数据(模仿太空望远镜场景的观测结果)和实际观测图像评估了我们的算法。结果表明,我们的方法在多种观测模式下均能有效检测快速运动的天体。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the AJ
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型算法,用于在星空背景下检测快速移动的天体。该算法通过物理启发神经网络提升现有技术,利用望远镜的点扩散函数和特定观测模式作为先验信息,无需额外训练即可直接识别星空中的快速移动天体,解决了传统技术的局限性。通过模拟观测数据和真实观测图像的评估,验证了该方法在不同观测模式下的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 快速移动天体具有与背景恒星显著不同的运动速度,在观测图像中呈现出独特形状。
- 传统检测分类算法对地面望远镜相对稳定的图像有效。
- 空间望远镜的普及及其多种观测模式产生了具有不同属性的图像,使传统方法效率降低。
- 本文提出了一种新型算法,通过物理启发神经网络提升现有技术检测快速移动天体。
- 该算法利用望远镜的点扩散函数和观测模式作为先验信息,无需额外训练即可识别移动天体。
- 通过模拟和真实观测数据评估,该算法在不同观测模式下均表现出有效检测能力。
点此查看论文截图
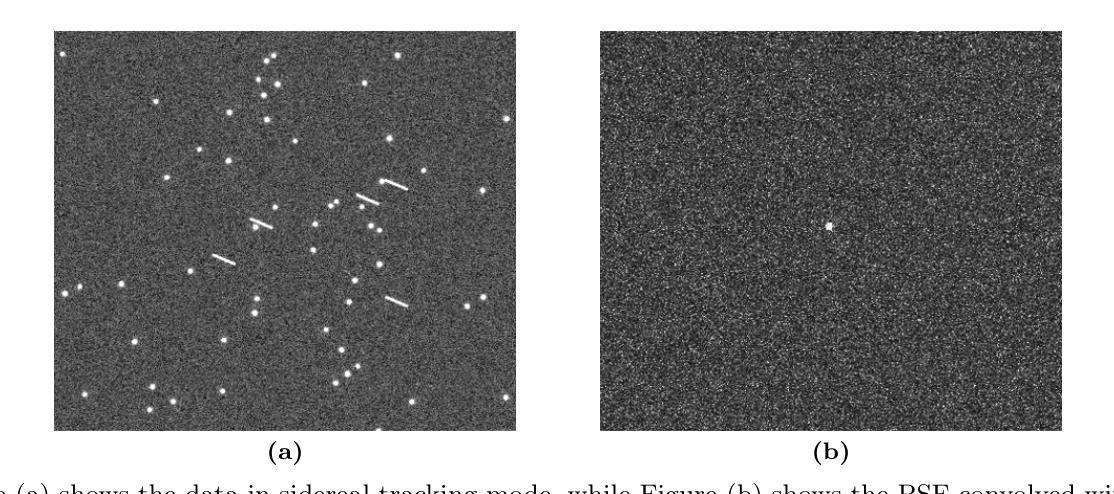


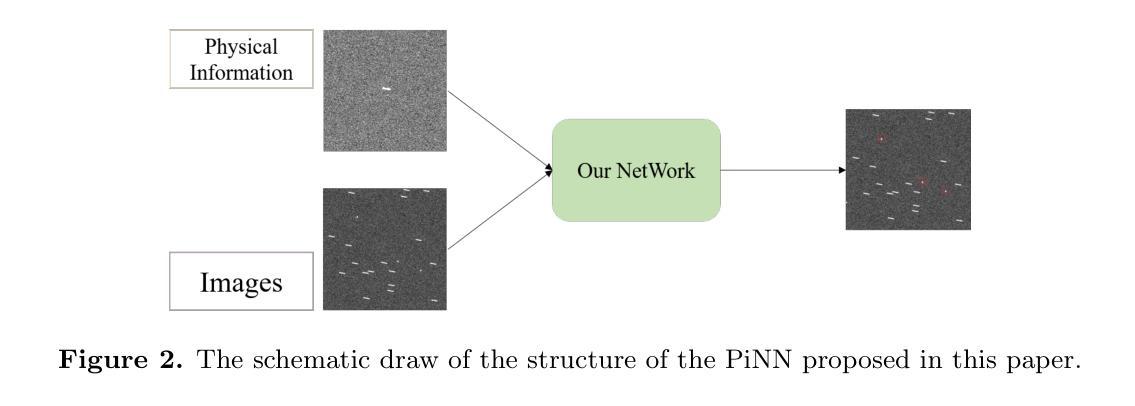

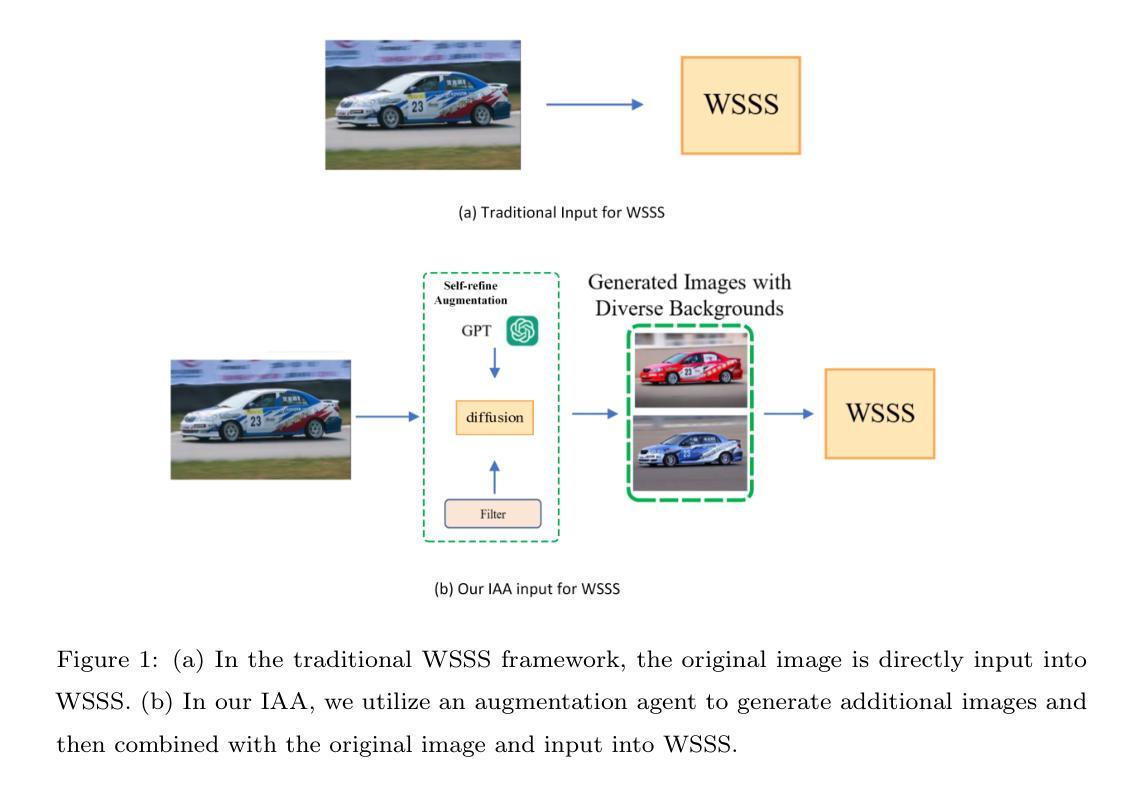
Image Augmentation Agent for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wangyu Wu, Xianglin Qiu, Siqi Song, Zhenhong Chen, Xiaowei Huang, Fei Ma, Jimin Xiao
Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) has achieved remarkable progress using only image-level labels. However, most existing WSSS methods focus on designing new network structures and loss functions to generate more accurate dense labels, overlooking the limitations imposed by fixed datasets, which can constrain performance improvements. We argue that more diverse trainable images provides WSSS richer information and help model understand more comprehensive semantic pattern. Therefore in this paper, we introduce a novel approach called Image Augmentation Agent (IAA) which shows that it is possible to enhance WSSS from data generation perspective. IAA mainly design an augmentation agent that leverages large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models to automatically generate additional images for WSSS. In practice, to address the instability in prompt generation by LLMs, we develop a prompt self-refinement mechanism. It allow LLMs to re-evaluate the rationality of generated prompts to produce more coherent prompts. Additionally, we insert an online filter into diffusion generation process to dynamically ensure the quality and balance of generated images. Experimental results show that our method significantly surpasses state-of-the-art WSSS approaches on the PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 datasets.
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)仅使用图像级标签取得了显著的进步。然而,大多数现有的WSSS方法主要关注设计新的网络结构和损失函数来生成更精确的密集标签,而忽视了固定数据集所带来的限制,这些限制可能会限制性能的提升。我们认为,提供更多可训练图像的多样性可以为WSSS提供更丰富的信息,并帮助模型理解更全面的语义模式。因此,在本文中,我们介绍了一种新的方法,称为图像增强代理(IAA),它表明从数据生成的角度增强WSSS是可能的。IAA主要设计了一个增强代理,利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型自动为WSSS生成额外的图像。在实践中,为了解决LLMs在提示生成中的不稳定性问题,我们开发了一种提示自我完善机制。它允许LLMs重新评估生成的提示的合理性,以产生更连贯的提示。此外,我们在扩散生成过程中插入了一个在线过滤器,以动态确保生成图像的质量和平衡。实验结果表明,我们的方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上显著超越了最新的WSSS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
使用图像级标签进行弱监督语义分割(WSSS)已经取得了显著进展。然而,现有方法多关注设计新网络结构和损失函数以生成更准确的密集标签,忽视了固定数据集带来的限制。本文提出一种名为Image Augmentation Agent(IAA)的新方法,从数据生成角度提升WSSS性能。IAA设计了一个利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型自动生成额外图像的方法。为解决LLMs在提示生成中的不稳定问题,开发了一种提示自我完善机制,并插入在线过滤器以确保生成图像的质量和平衡。实验结果表明,该方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上超越了现有WSSS方法。
Key Takeaways
- WSSS在利用图像级标签进行语义分割方面已取得显著进展。
- 现有方法主要关注网络结构和损失函数的设计,忽视了数据集限制对性能的影响。
- 本文提出一种名为IAA的新方法,从数据生成角度提升WSSS性能。
- IAA利用大型语言模型和扩散模型自动生成额外图像。
- IAA采用提示自我完善机制解决语言模型在提示生成中的不稳定问题。
- 在线过滤器用于确保生成图像的质量和平衡。
点此查看论文截图

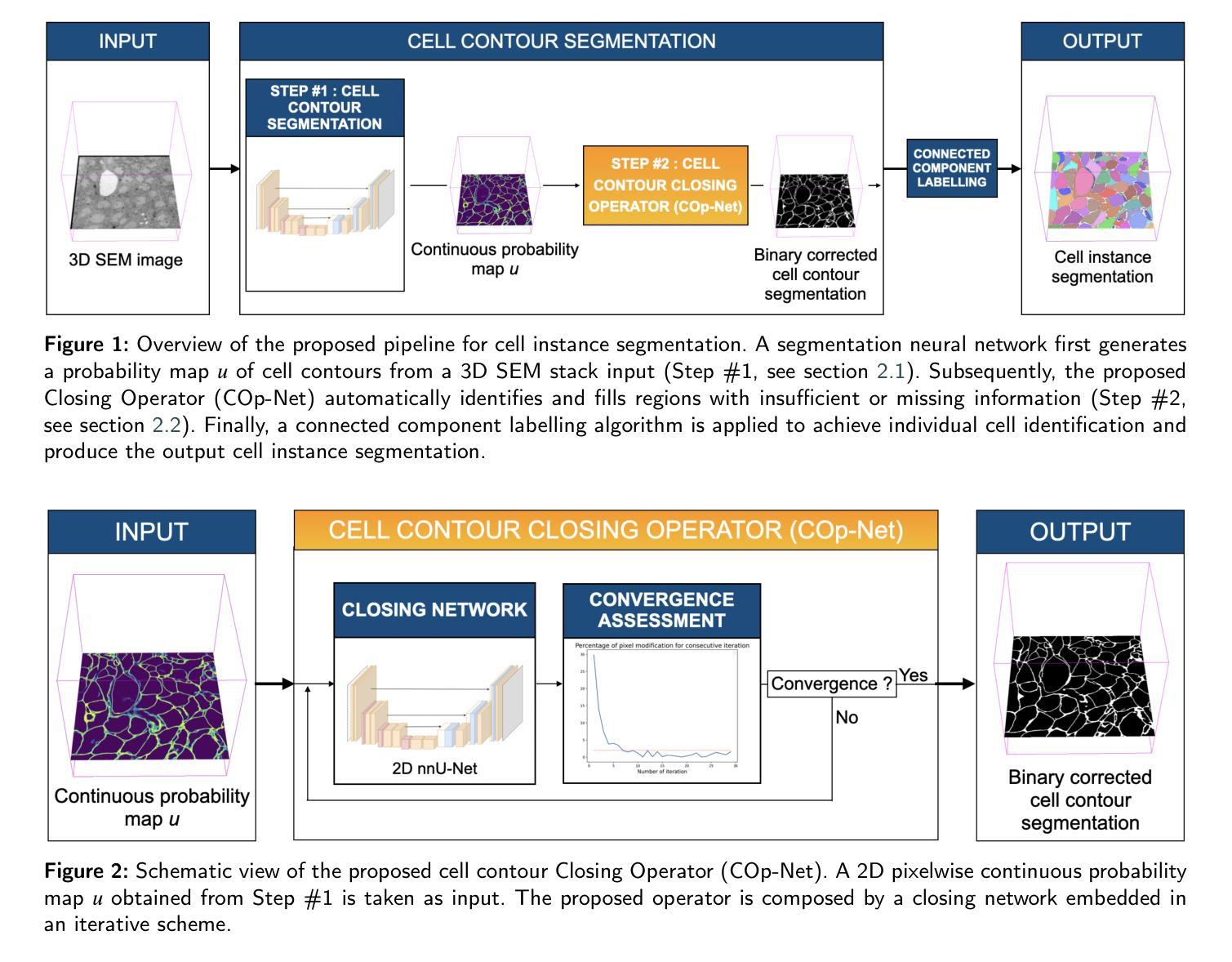
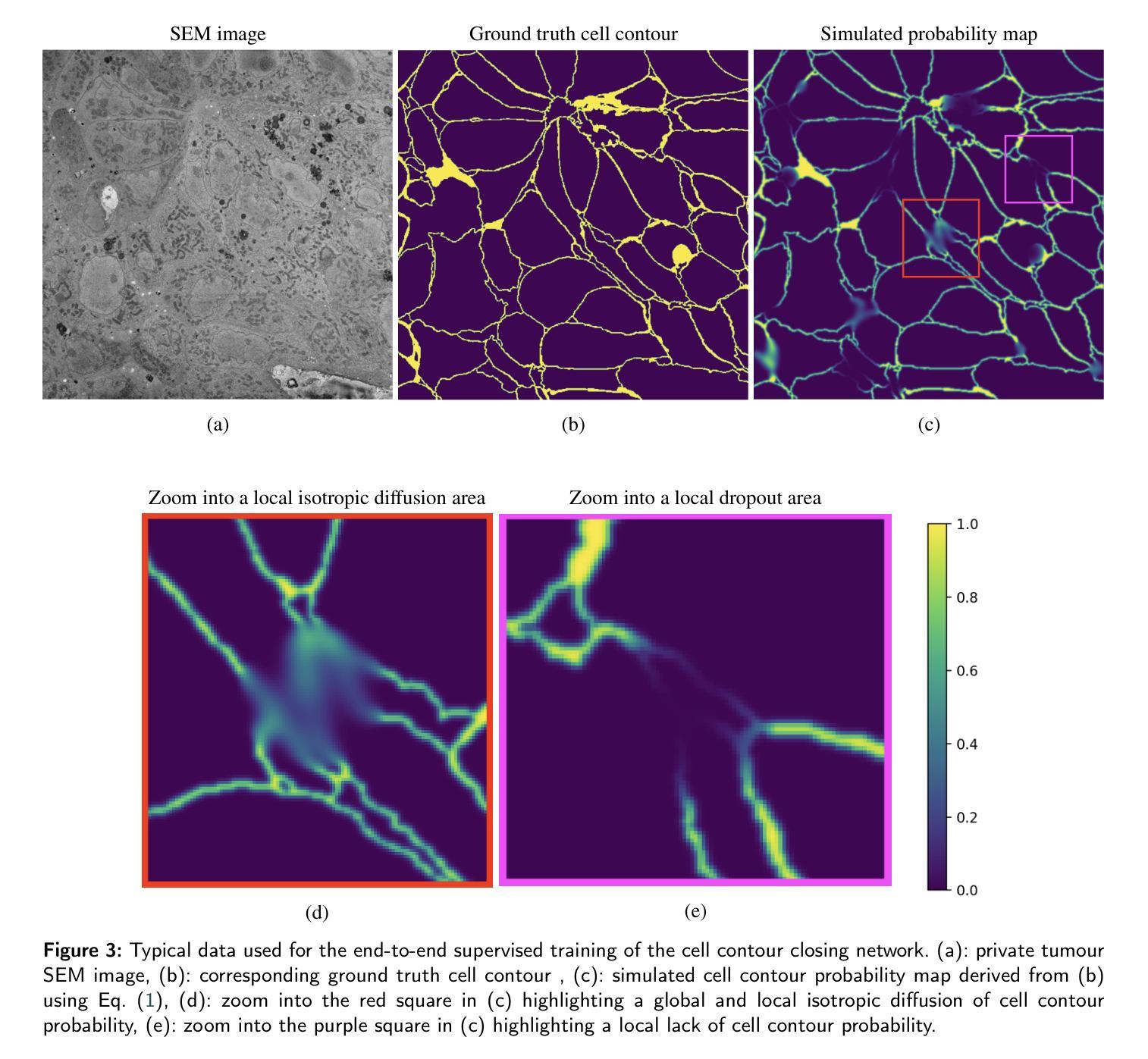
Enhancing Cell Instance Segmentation in Scanning Electron Microscopy Images via a Deep Contour Closing Operator
Authors:Florian Robert, Alexia Calovoulos, Laurent Facq, Fanny Decoeur, Etienne Gontier, Christophe F. Grosset, Baudouin Denis de Senneville
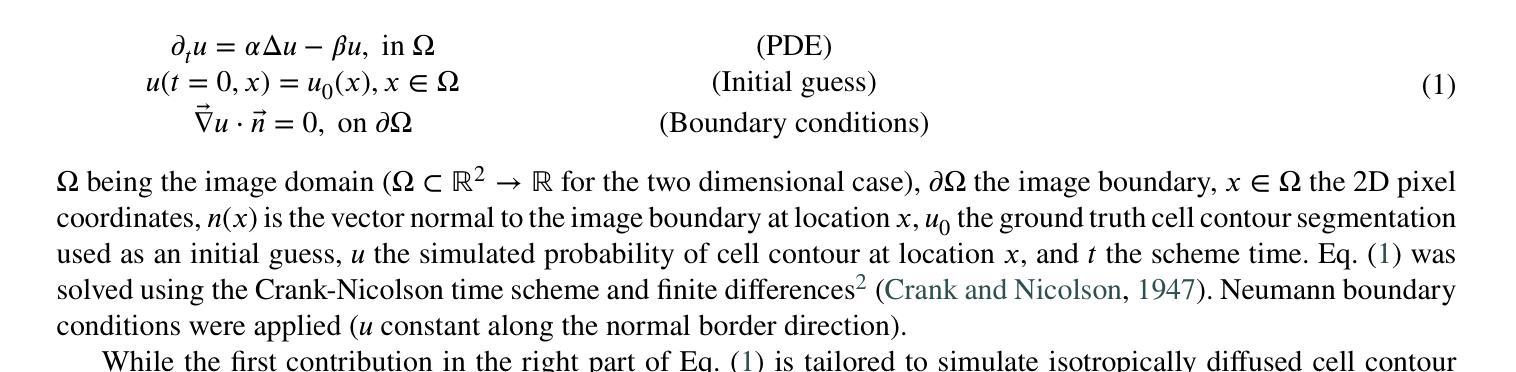
Accurately segmenting and individualizing cells in SEM images is a highly promising technique for elucidating tissue architecture in oncology. While current AI-based methods are effective, errors persist, necessitating time-consuming manual corrections, particularly in areas where the quality of cell contours in the image is poor and requires gap filling. This study presents a novel AI-driven approach for refining cell boundary delineation to improve instance-based cell segmentation in SEM images, also reducing the necessity for residual manual correction. A CNN COp-Net is introduced to address gaps in cell contours, effectively filling in regions with deficient or absent information. The network takes as input cell contour probability maps with potentially inadequate or missing information and outputs corrected cell contour delineations. The lack of training data was addressed by generating low integrity probability maps using a tailored PDE. We showcase the efficacy of our approach in augmenting cell boundary precision using both private SEM images from PDX hepatoblastoma tissues and publicly accessible images datasets. The proposed cell contour closing operator exhibits a notable improvement in tested datasets, achieving respectively close to 50% (private data) and 10% (public data) increase in the accurately-delineated cell proportion compared to state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, the need for manual corrections was significantly reduced, therefore facilitating the overall digitalization process. Our results demonstrate a notable enhancement in the accuracy of cell instance segmentation, particularly in highly challenging regions where image quality compromises the integrity of cell boundaries, necessitating gap filling. Therefore, our work should ultimately facilitate the study of tumour tissue bioarchitecture in onconanotomy field.
在扫描电子显微镜(SEM)图像中准确分割和个性化细胞是一种在肿瘤学中阐明组织结构的极具前景的技术。尽管当前的基于人工智能的方法很有效,但仍然存在错误,需要进行耗时的手动更正,特别是在图像中细胞轮廓质量较差且需要进行间隙填充的区域。本研究提出了一种新型的AI驱动方法来改进细胞边界描绘,以提高SEM图像中的基于实例的细胞分割,并减少剩余手动更正的需要。引入了一种CNN COp-Net来解决细胞轮廓中的间隙问题,有效地填充了信息不足或缺失的区域。该网络以可能不足或缺失信息的细胞轮廓概率图作为输入,并输出校正后的细胞轮廓描绘。通过采用定制的偏微分方程生成低完整性概率图来解决训练数据不足的问题。我们展示了使用来自PDX肝母细胞瘤组织的私有SEM图像和可公开访问的图像数据集,我们的方法在增强细胞边界精度方面的有效性。所提出的细胞轮廓闭合算子在测试数据集上表现出显著的改进,与最先进的方法相比,私有数据的准确描绘细胞比例增加了近50%,公共数据增加了约10%。此外,手动更正的需求大大降低,从而促进了整体数字化过程。我们的结果显著提高了细胞实例分割的准确性,特别是在图像质量损害细胞边界完整性的极具挑战的区域,需要进行间隙填充。因此,我们的工作最终应有助于肿瘤组织生物结构学的研究在肿瘤解剖学领域的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 8 figures, 2 tables
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型AI驱动的方法,用于优化SEM图像中的细胞边界描绘,提高基于实例的细胞分割精度,并减少剩余的手动修正需求。研究引入了CNN COp-Net,用于解决细胞轮廓中的间隙问题,有效填充信息缺失或不足的区域。该方法提高了私有和公开可用的SEM图像数据集中肝细胞瘤组织的细胞边界精度,并显著减少了手动修正的需求。
Key Takeaways
- AI方法在细胞分割中虽有效,但仍存在误差,需耗时手动修正,特别是在图像质量差的区域,需要填补间隙。
- 本研究提出了一种新型的AI驱动方法,用于优化细胞边界描绘,提高基于实例的细胞分割精度。
- 引入CNN COp-Net解决细胞轮廓中的间隙问题,有效填充信息缺失区域。
- 通过私有和公开数据集的测试,该方法提高了细胞边界描绘的精确度。
- 与现有方法相比,该方法在私有数据集和公开数据集上分别实现了接近50%和10%的准确描绘细胞比例增长。
- 该方法显著减少了手动修正的需求,促进了数字化过程的整体进展。
点此查看论文截图

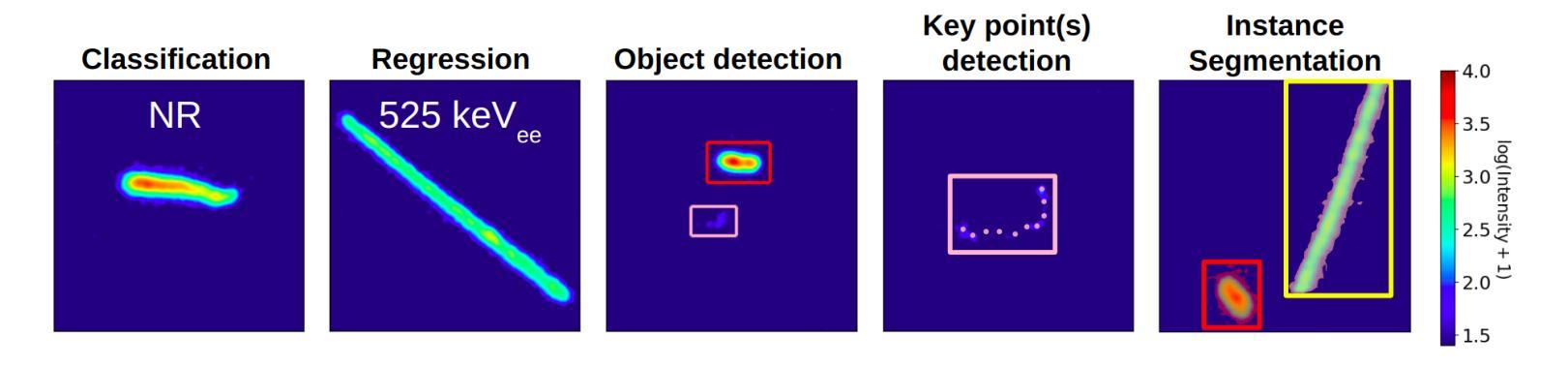
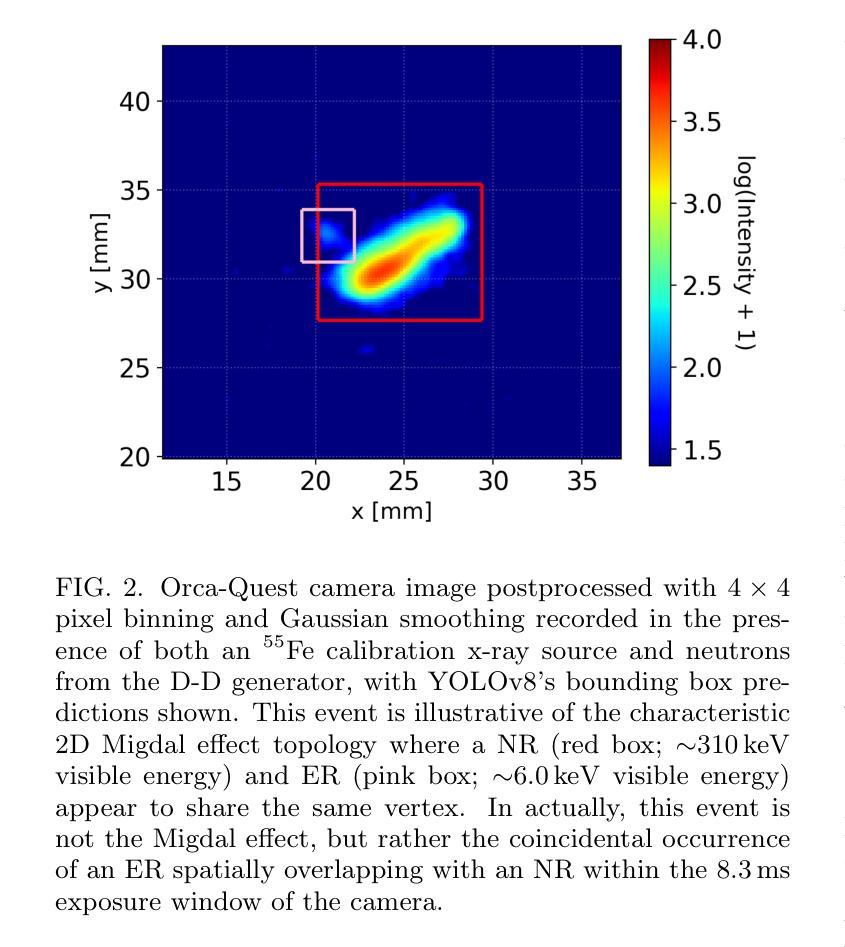
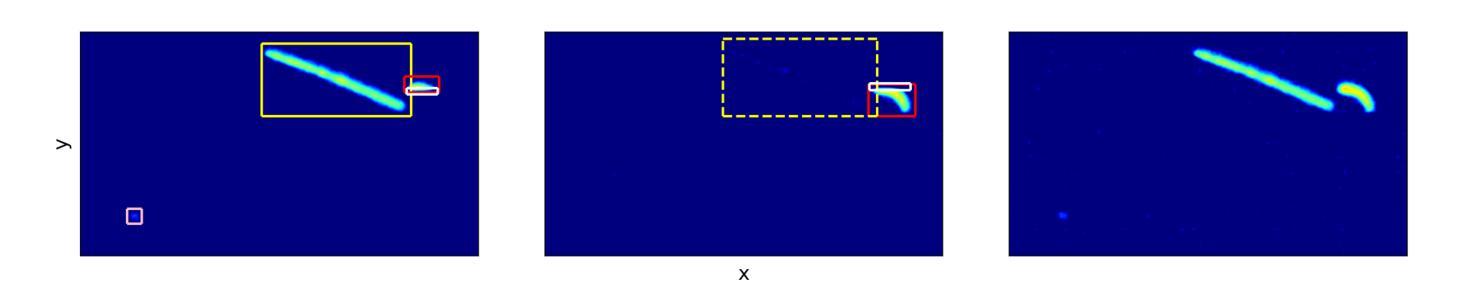
Transforming a rare event search into a not-so-rare event search in real-time with deep learning-based object detection
Authors:J. Schueler, H. M. Araújo, S. N. Balashov, J. E. Borg, C. Brew, F. M. Brunbauer, C. Cazzaniga, A. Cottle, C. D. Frost, F. Garcia, D. Hunt, A. C. Kaboth, M. Kastriotou, I. Katsioulas, A. Khazov, P. Knights, H. Kraus, V. A. Kudryavtsev, S. Lilley, A. Lindote, M. Lisowska, D. Loomba, M. I. Lopes, E. Lopez Asamar, P. Luna Dapica, P. A. Majewski, T. Marley, C. McCabe, L. Millins, A. F. Mills, M. Nakhostin, R. Nandakumar, T. Neep, F. Neves, K. Nikolopoulos, E. Oliveri, L. Ropelewski, V. N. Solovov, T. J. Sumner, J. Tarrant, E. Tilly, R. Turnley, R. Veenhof
Deep learning-based object detection algorithms enable the simultaneous classification and localization of any number of objects in image data. Many of these algorithms are capable of operating in real-time on high resolution images, attributing to their widespread usage across many fields. We present an end-to-end object detection pipeline designed for real-time rare event searches for the Migdal effect, using high-resolution image data from a state-of-the-art scientific CMOS camera in the MIGDAL experiment. The Migdal effect in nuclear scattering, crucial for sub-GeV dark matter searches, has yet to be experimentally confirmed, making its detection a primary goal of the MIGDAL experiment. Our pipeline employs the YOLOv8 object detection algorithm and is trained on real data to enhance the detection efficiency of nuclear and electronic recoils, particularly those exhibiting overlapping tracks that are indicative of the Migdal effect. When deployed online on the MIGDAL readout PC, we demonstrate our pipeline to process and perform the rare event search on 2D image data faster than the peak 120 frame per second acquisition rate of the CMOS camera. Applying these same steps offline, we demonstrate that we can reduce a sample of 20 million camera frames to around 1000 frames while maintaining nearly all signal that YOLOv8 is able to detect, thereby transforming a rare search into a much more manageable search. Our studies highlight the potential of pipelines similar to ours significantly improving the detection capabilities of experiments requiring rapid and precise object identification in high-throughput data environments.
基于深度学习的目标检测算法可以同时实现对图像数据中任何数量的对象的分类和定位。许多这些算法能够在高分辨率图像上进行实时操作,这促使它们被广泛应用于许多领域。我们针对实时搜索米格尔效应中的稀有事件,设计了一个端到端的对象检测流程,该流程使用MIGDAL实验中的先进科学CMOS相机拍摄的高分辨率图像数据。米格尔效应在核散射中的重要性对于亚吉电子伏暗物质搜索至关重要,但尚未得到实验证实,因此其检测成为MIGDAL实验的主要目标。我们的流程采用YOLOv8目标检测算法,并在真实数据上进行训练,以提高对核和电子反冲的检测效率,尤其是那些表现出重叠轨迹(指示米格尔效应)的核和电子反冲。当在MIGDAL读出计算机上在线部署时,我们证明了我们的流程能够在二维图像数据上执行稀有事件搜索的速度超过了CMOS相机的峰值每秒120帧的采集速率。将相同的步骤应用于线下场景时,我们证明了可以将20万个相机帧的样本减少到大约一千帧,同时几乎保留了YOLOv8能够检测到的所有信号,从而将艰难的稀有事件搜索转化为更易管理的搜索。我们的研究表明,与我们类似的流程具有巨大潜力,能够显著提高需要在高吞吐量数据环境中快速准确识别对象的实验的检测能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:基于深度学习技术的物体检测算法可以同时实现对图像数据中任何数量的物体的分类和定位。我们提出了一种端到端的物体检测流程,旨在用于实时搜索罕见事件,如Migdal效应,该流程使用MIGDAL实验中先进科学CMOS相机拍摄的高分辨率图像数据。该流程采用YOLOv8物体检测算法,并经过真实数据训练,以提高对核和电子回冲的检测效率,特别是在显示Migdal效应特征的重叠轨迹上。在线部署在MIGDAL读出PC上时,我们的流程处理并进行了罕见事件的搜索操作,运行速度超过了CMOS相机的峰值采集帧率(最高为每秒采集120帧)。当将这些步骤应用于离线样本时,我们证明了可以将大约2千万帧的相机样本减少到大约一千帧,同时几乎保留了YOLOv8检测到的所有信号。这大大提高了稀有搜索的识别能力,并展示了类似流程在需要快速精确识别物体的实验中的潜力。这些实验通常涉及处理大量数据。我们的研究强调了这一方法的重要性和潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- 深度学习物体检测算法可以同时分类和定位图像中的物体。
- 针对Migdal效应设计了实时物体检测流程,应用于先进科学CMOS相机的高分辨率图像数据。
- 采用YOLOv8算法进行物体检测,经过真实数据训练以增强检测效率。
- 在处理图像数据方面具有较高性能,实现了与CMOS相机采集帧率的匹配和超越。
- 可以通过离线应用将大量数据样本减少至更小范围,同时保留关键信号信息。
- 该方法显著提高了稀有事件的搜索能力,并优化了数据处理效率。
点此查看论文截图