⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-12 更新
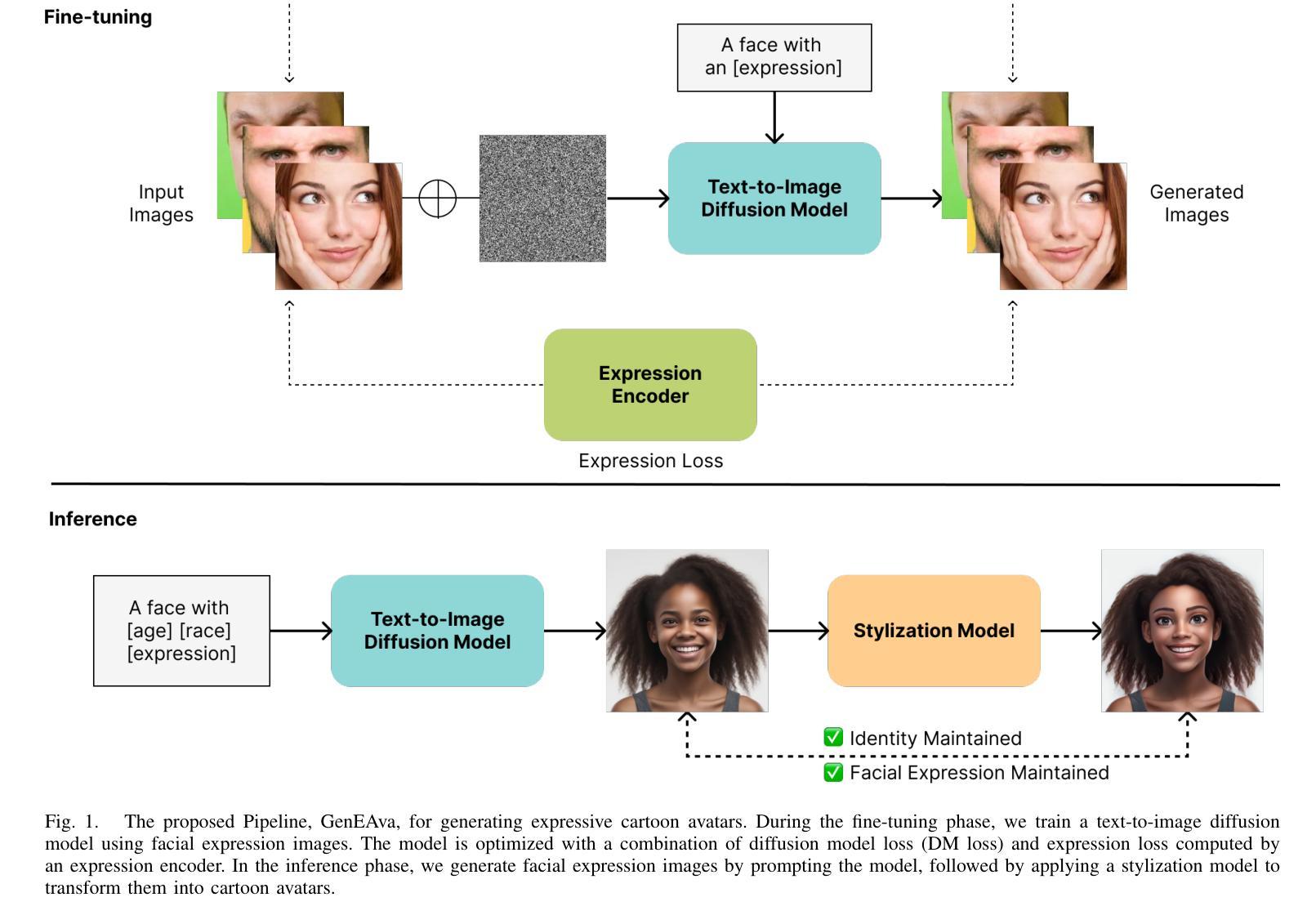
GenEAva: Generating Cartoon Avatars with Fine-Grained Facial Expressions from Realistic Diffusion-based Faces
Authors:Hao Yu, Rupayan Mallick, Margrit Betke, Sarah Adel Bargal
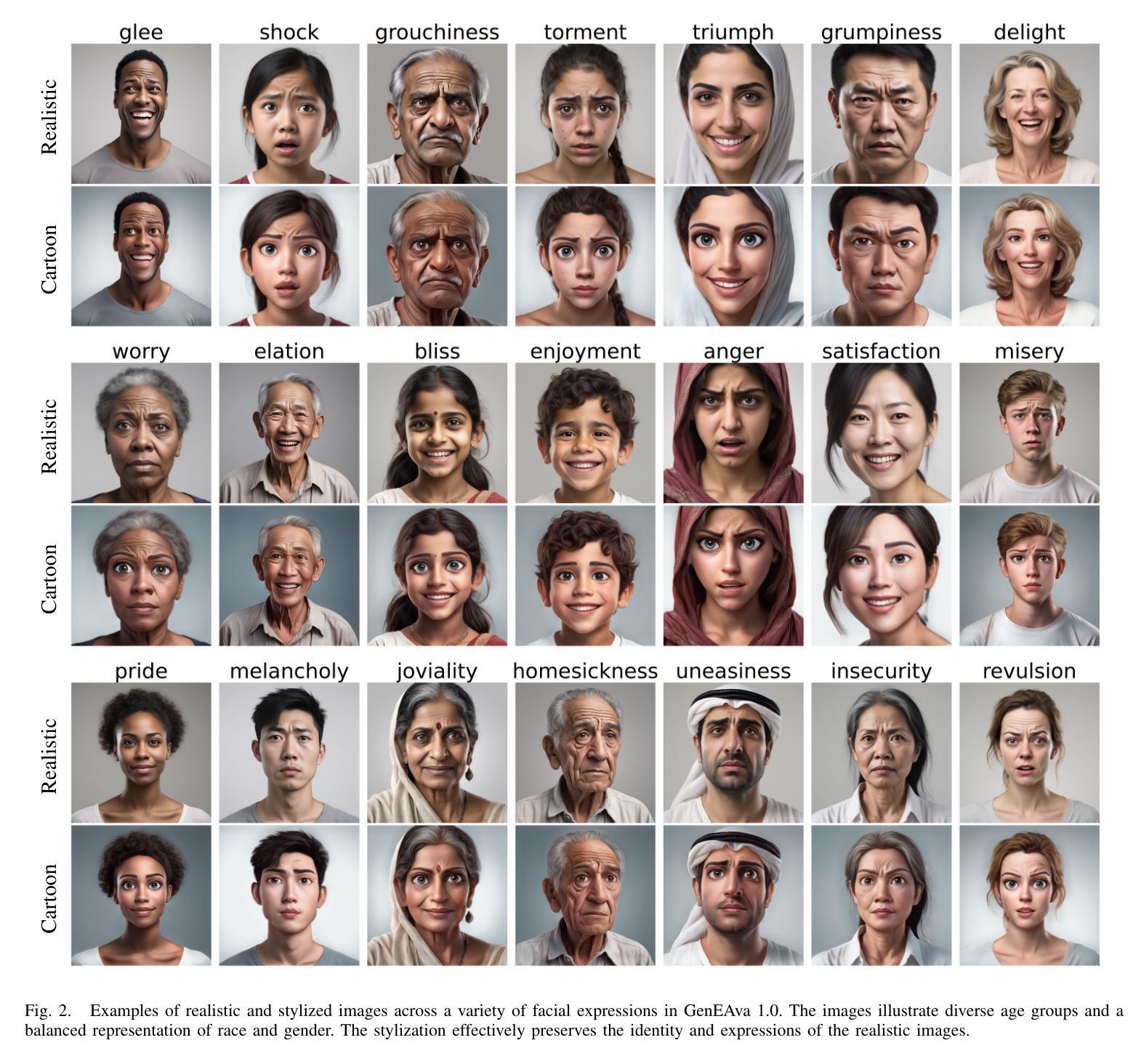
Cartoon avatars have been widely used in various applications, including social media, online tutoring, and gaming. However, existing cartoon avatar datasets and generation methods struggle to present highly expressive avatars with fine-grained facial expressions and are often inspired from real-world identities, raising privacy concerns. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework, GenEAva, for generating high-quality cartoon avatars with fine-grained facial expressions. Our approach fine-tunes a state-of-the-art text-to-image diffusion model to synthesize highly detailed and expressive facial expressions. We then incorporate a stylization model that transforms these realistic faces into cartoon avatars while preserving both identity and expression. Leveraging this framework, we introduce the first expressive cartoon avatar dataset, GenEAva 1.0, specifically designed to capture 135 fine-grained facial expressions, featuring 13,230 expressive cartoon avatars with a balanced distribution across genders, racial groups, and age ranges. We demonstrate that our fine-tuned model generates more expressive faces than the state-of-the-art text-to-image diffusion model SDXL. We also verify that the cartoon avatars generated by our framework do not include memorized identities from fine-tuning data. The proposed framework and dataset provide a diverse and expressive benchmark for future research in cartoon avatar generation.
卡通头像已广泛应用于各种应用程序,包括社交媒体、在线教学和游戏。然而,现有的卡通头像数据集和生成方法难以呈现具有高度表情和精细面部表情的头像,并且通常受到真实身份的启发,这引发了隐私担忧。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型框架GenEAva,用于生成具有精细面部表情的高质量卡通头像。我们的方法通过微调最先进的文本到图像扩散模型来合成高度详细和富有表现力的面部表情。然后,我们融入了一种风格化模型,将这些逼真的面孔转化为卡通头像,同时保留身份和表情。借助这一框架,我们推出了首个富有表现力的卡通头像数据集GenEAva 1.0,专门设计用于捕捉135种精细面部表情,包含13,230个富有表现力的卡通头像,在性别、种族和年龄范围内具有平衡分布。我们证明,我们的微调模型比最先进的文本到图像扩散模型SDXL生成的表情更加丰富。我们还验证了由我们框架生成的卡通头像不包括微调数据中的记忆身份。所提出的框架和数据集为卡通头像生成的未来研究提供了一个多样化和富有表现力的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为GenEAva的新型框架,用于生成高质量且表情细腻的卡通头像。该框架通过微调先进的文本到图像扩散模型,合成高度详细的表情。接着,采用风格化模型将这些真实面孔转化为卡通头像,同时保留身份和表情。基于此框架,推出了首个表情丰富的卡通头像数据集GenEAva 1.0,专门捕捉135种细腻表情,包含13,230个表情丰富的卡通头像,均衡分布在性别、种族和年龄范围中。实验证明,该框架生成的卡通头像比SDXL模型更富有表现力,且不包含微调数据中的记忆身份。
Key Takeaways
- 现有卡通头像数据集和生成方法难以呈现高度细腻的表情,并受到隐私问题的关注。
- 提出了一种新型框架GenEAva,用于生成高质量且表情细腻的卡通头像。
- 通过微调先进的文本到图像扩散模型,合成高度详细的表情。
- 引入风格化模型将真实面孔转化为卡通头像,同时保留身份和表情。
- 推出首个表情丰富的卡通头像数据集GenEAva 1.0,包含多种性别、种族和年龄范围的细腻表情。
- 对比实验显示GenEAva框架生成的卡通头像比SDXL模型更具表现力。
点此查看论文截图


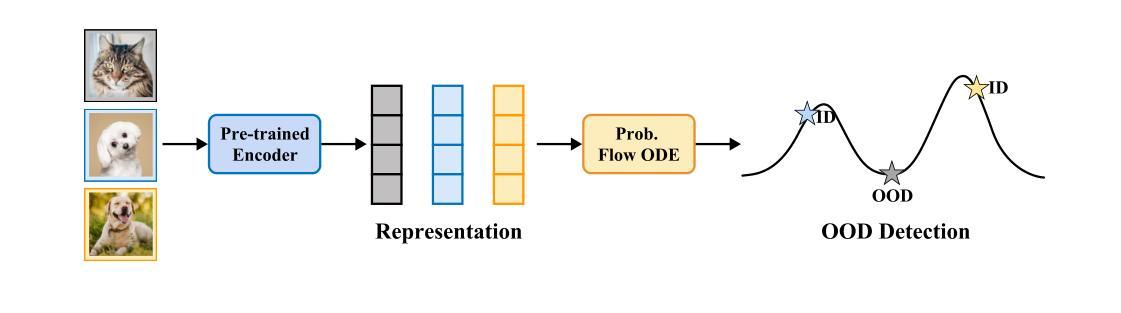
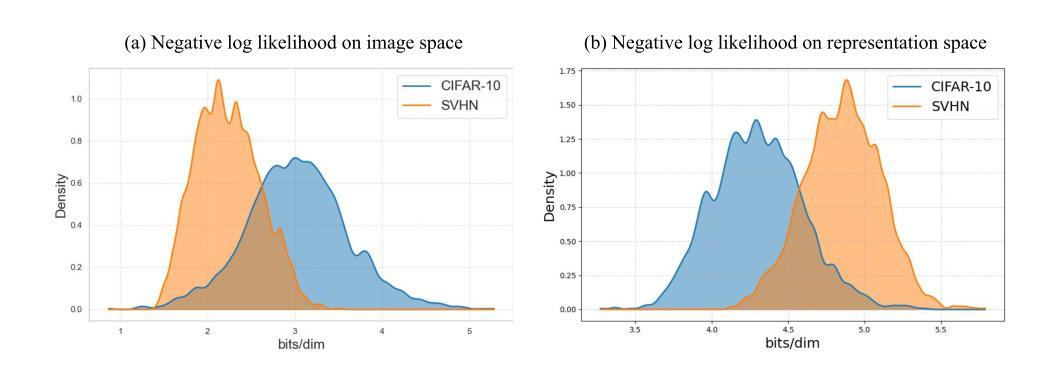
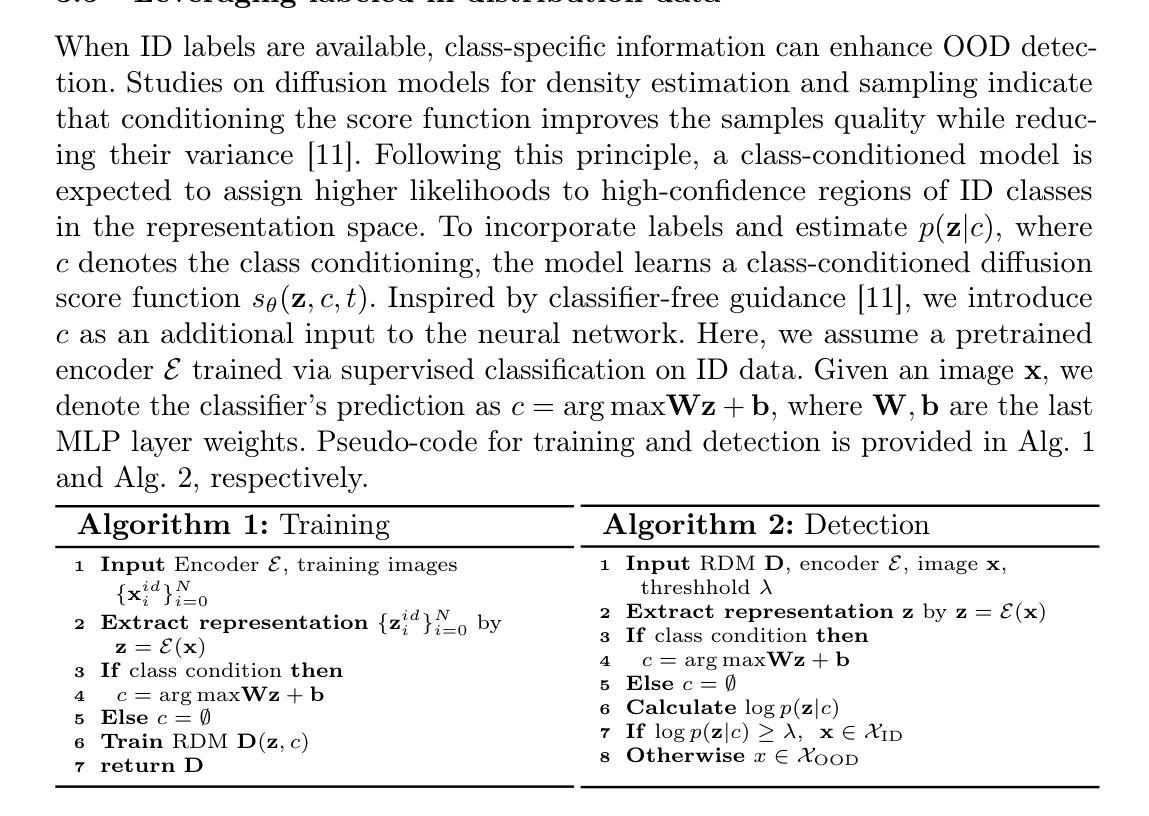
Revisiting Likelihood-Based Out-of-Distribution Detection by Modeling Representations
Authors:Yifan Ding, Arturas Aleksandrauskas, Amirhossein Ahmadian, Jonas Unger, Fredrik Lindsten, Gabriel Eilertsen
Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is critical for ensuring the reliability of deep learning systems, particularly in safety-critical applications. Likelihood-based deep generative models have historically faced criticism for their unsatisfactory performance in OOD detection, often assigning higher likelihood to OOD data than in-distribution samples when applied to image data. In this work, we demonstrate that likelihood is not inherently flawed. Rather, several properties in the images space prohibit likelihood as a valid detection score. Given a sufficiently good likelihood estimator, specifically using the probability flow formulation of a diffusion model, we show that likelihood-based methods can still perform on par with state-of-the-art methods when applied in the representation space of pre-trained encoders. The code of our work can be found at $\href{https://github.com/limchaos/Likelihood-OOD.git}{\texttt{https://github.com/limchaos/Likelihood-OOD.git}}$.
异常检测(OOD检测)对于确保深度学习系统的可靠性至关重要,特别是在安全关键的应用程序中。基于可能性的深度生成模型在历史上面临着对异常检测性能不满意的批评,在应用于图像数据时,这些模型往往会为异常数据分配较高的可能性,高于内部分布的样本。在这项工作中,我们证明了可能性本身并非存在问题。相反,图像空间中的几个属性阻止了可能性作为有效的检测分数。给定一个足够好的可能性估计器,特别是使用扩散模型的概率流公式,我们证明了基于可能性的方法仍然可以应用在预训练编码器的表示空间中,并且表现可与最先进的检测器不相上下。我们的工作代码可在 https://github.com/limchaos/Likelihood-OOD.git 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文指出,在足够好的概率流估计器(基于扩散模型)的支持下,对预训练编码器的表示空间应用基于可能性的方法,可以表现出与最新技术相当的性能,打破了以往认为基于可能性的深度生成模型在图像数据中进行OOD检测性能不佳的观点。证明了可能性的固有优势并强调适当使用方法和工具的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 出于分布检测(OOD)对确保深度学习系统可靠性的重要性,特别是在安全关键应用中的重要性。
- 传统的基于可能性的深度生成模型在图像数据中进行OOD检测的表现不尽如人意,常常被批评对OOD数据的可能性赋予过高的评价。
- 文章指出,问题并非在于可能性本身的缺陷,而是图像空间中的某些特性阻止了可能性作为有效的检测分数。
- 利用扩散模型的概率流公式作为估计器时,如果足够好,基于可能性的方法可以在预训练编码器的表示空间应用时表现出卓越性能。
- 该研究提供了一个有效的GitHub代码库链接,便于其他研究者获取和使用其方法。
- 文章强调了选择合适的方法和工具的重要性,在深度学习系统的设计和应用过程中应注重适应性和创新。
点此查看论文截图

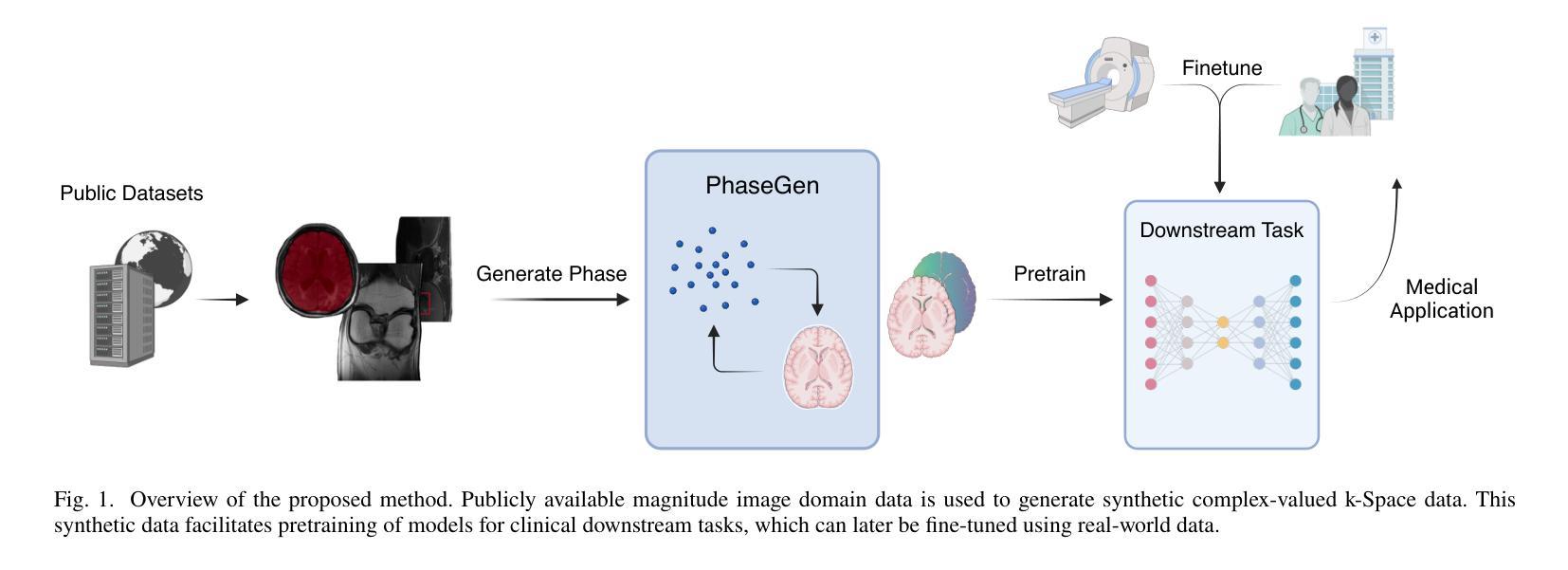
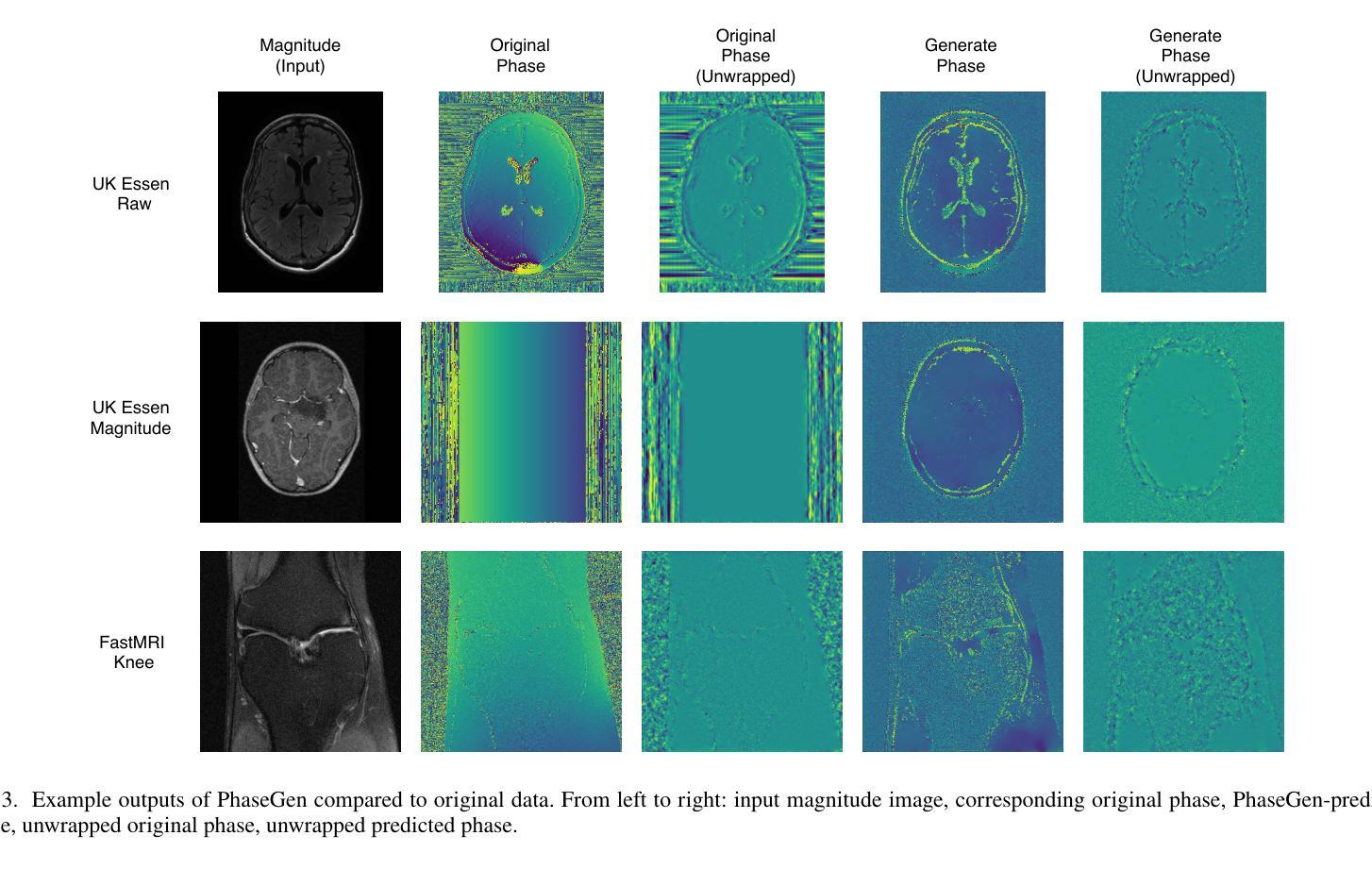
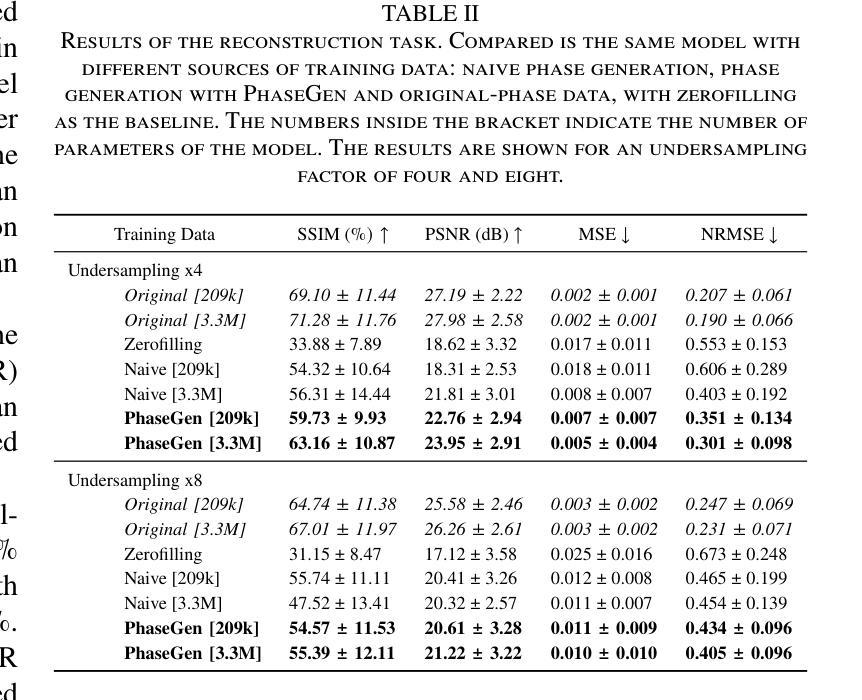
PhaseGen: A Diffusion-Based Approach for Complex-Valued MRI Data Generation
Authors:Moritz Rempe, Fabian Hörst, Helmut Becker, Marco Schlimbach, Lukas Rotkopf, Kevin Kröninger, Jens Kleesiek
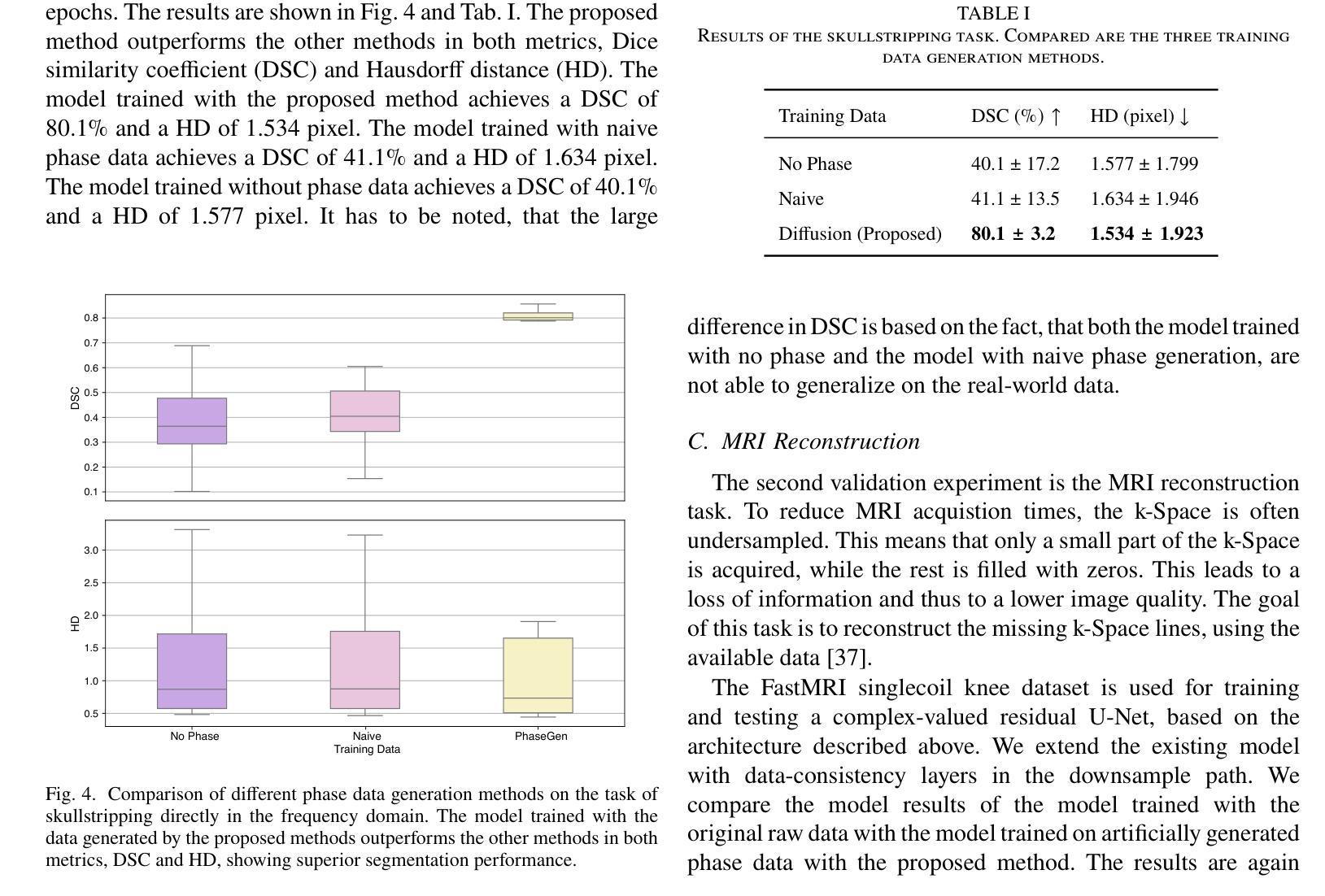
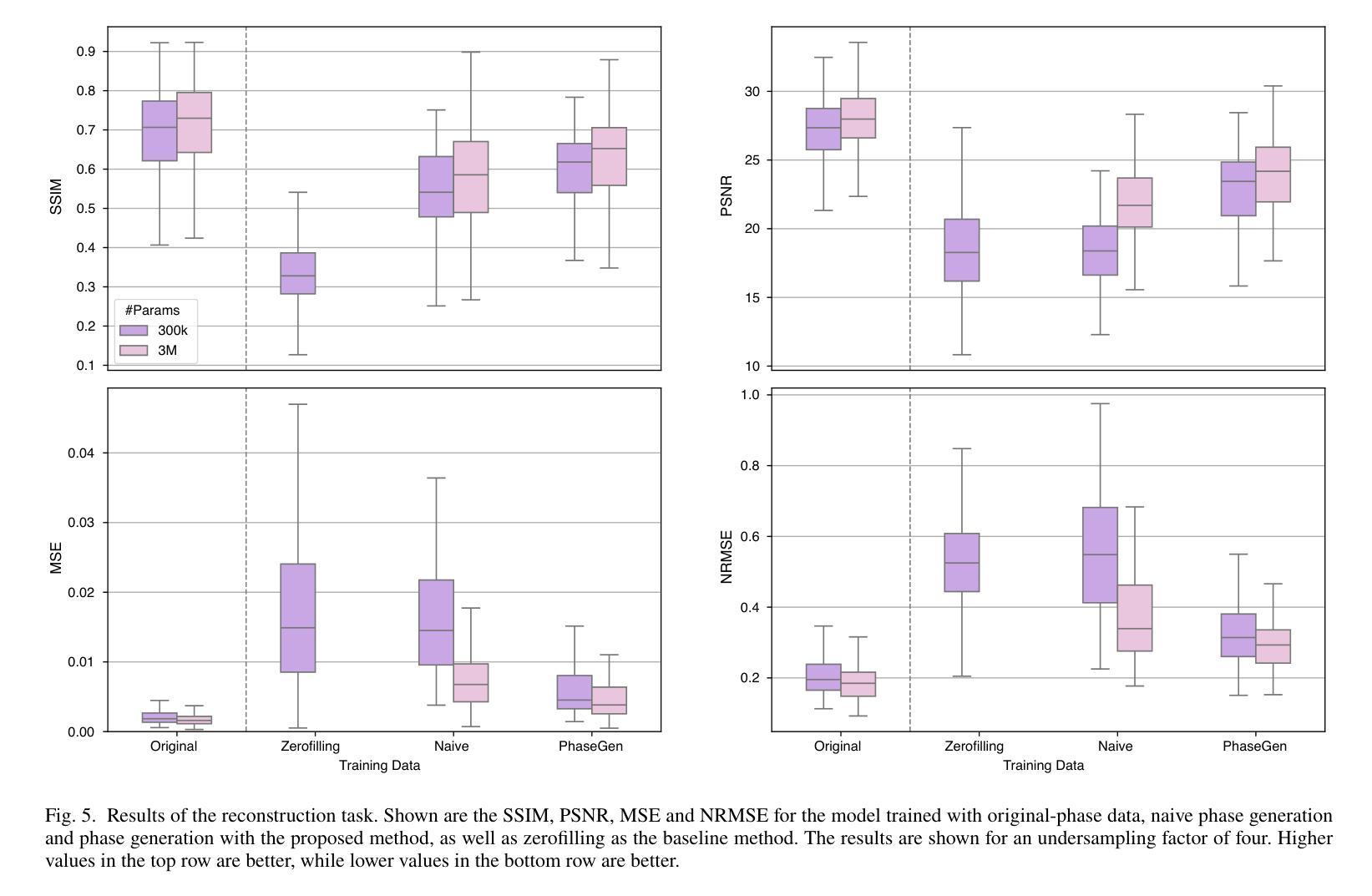
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) raw data, or k-Space data, is complex-valued, containing both magnitude and phase information. However, clinical and existing Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based methods focus only on magnitude images, discarding the phase data despite its potential for downstream tasks, such as tumor segmentation and classification. In this work, we introduce $\textit{PhaseGen}$, a novel complex-valued diffusion model for generating synthetic MRI raw data conditioned on magnitude images, commonly used in clinical practice. This enables the creation of artificial complex-valued raw data, allowing pretraining for models that require k-Space information. We evaluate PhaseGen on two tasks: skull-stripping directly in k-Space and MRI reconstruction using the publicly available FastMRI dataset. Our results show that training with synthetic phase data significantly improves generalization for skull-stripping on real-world data, with an increased segmentation accuracy from $41.1%$ to $80.1%$, and enhances MRI reconstruction when combined with limited real-world data. This work presents a step forward in utilizing generative AI to bridge the gap between magnitude-based datasets and the complex-valued nature of MRI raw data. This approach allows researchers to leverage the vast amount of avaliable image domain data in combination with the information-rich k-Space data for more accurate and efficient diagnostic tasks. We make our code publicly $\href{https://github.com/TIO-IKIM/PhaseGen}{\text{available here}}$.
磁共振成像(MRI)原始数据,也称为k-Space数据,是复数形式的,包含幅度和相位信息。然而,现有的临床和基于人工智能(AI)的方法只关注幅度图像,尽管相位数据对下游任务(如肿瘤分割和分类)具有潜力,但仍然被丢弃。在这项工作中,我们介绍了$\textit{PhaseGen}$,这是一种新型的复数扩散模型,能够根据在临床实践中常用的幅度图像生成合成MRI原始数据。这使得可以创建人工的复数原始数据,允许对需要k-Space信息的模型进行预训练。我们在两个任务上对PhaseGen进行了评估:直接在k-Space中进行颅骨剥离和使用公开可用的FastMRI数据集进行MRI重建。我们的结果表明,使用合成相位数据进行训练可以显著提高在现实数据上进行颅骨剥离的泛化能力,分割准确度从41.1%提高到80.1%,并且在与有限现实数据结合时,可以增强MRI重建。这项工作利用生成性人工智能弥合了基于幅度的数据集和MRI原始数据的复数性质之间的差距。这种方法允许研究人员结合大量可用的图像域数据和丰富的k-Space信息,以进行更准确和高效的诊断任务。我们的代码公开$\href{https://github.com/TIO-IKIM/PhaseGen}{\text{可在此处获取}}$.
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为PhaseGen的新型复杂值扩散模型,该模型可根据幅度图像生成合成MRI原始数据。这项技术在临床实践中常用,能够创建人工复杂值原始数据,为需要k-Space信息的模型提供预训练。在FastMRI公开数据集上进行的两项任务评估表明,使用合成相位数据进行训练显著提高了在现实数据上的颅骨剥离分割准确度,从41.1%提高到80.1%,并在结合有限现实数据时进行MRI重建时表现出增强的性能。这项工作利用生成性人工智能缩小了基于幅度的数据集和复杂值MRI原始数据之间的差距,允许研究人员结合丰富的k-Space数据和大量的图像域数据,以进行更准确和高效的诊断任务。
Key Takeaways
- PhaseGen是一种复杂值扩散模型,能够根据幅度图像生成合成MRI原始数据。
- 临床和现有的人工智能方法主要关注幅度图像,忽视了相位数据在肿瘤分割和分类等下游任务中的潜力。
- PhaseGen的引入使得创建人工复杂值原始数据成为可能,为需要k-Space信息的模型提供了预训练的机会。
- 在FastMRI数据集上进行评估,显示合成相位数据训练在颅骨剥离分割和MRI重建任务上显著提高性能。
- 该方法缩小了基于幅度的数据集和MRI原始数据的差距,促进了更准确的诊断。
- PhaseGen代码已公开发布,链接为[链接地址]。
点此查看论文截图


Conditional Data Synthesis Augmentation
Authors:Xinyu Tian, Xiaotong Shen
Reliable machine learning and statistical analysis rely on diverse, well-distributed training data. However, real-world datasets are often limited in size and exhibit underrepresentation across key subpopulations, leading to biased predictions and reduced performance, particularly in supervised tasks such as classification. To address these challenges, we propose Conditional Data Synthesis Augmentation (CoDSA), a novel framework that leverages generative models, such as diffusion models, to synthesize high-fidelity data for improving model performance across multimodal domains including tabular, textual, and image data. CoDSA generates synthetic samples that faithfully capture the conditional distributions of the original data, with a focus on under-sampled or high-interest regions. Through transfer learning, CoDSA fine-tunes pre-trained generative models to enhance the realism of synthetic data and increase sample density in sparse areas. This process preserves inter-modal relationships, mitigates data imbalance, improves domain adaptation, and boosts generalization. We also introduce a theoretical framework that quantifies the statistical accuracy improvements enabled by CoDSA as a function of synthetic sample volume and targeted region allocation, providing formal guarantees of its effectiveness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CoDSA consistently outperforms non-adaptive augmentation strategies and state-of-the-art baselines in both supervised and unsupervised settings.
可靠的人工智能机器学习和统计分析依赖于多样且分布良好的训练数据。然而,现实世界的数据集往往规模有限,并在关键子群体中表现出现象表征不足,导致预测出现偏差和性能下降,特别是在如分类这样的监督任务中。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了条件数据合成增强(CoDSA)这一新型框架。该框架利用生成模型(如扩散模型)合成高保真数据,以改善跨多模式域(包括表格、文本和图像数据)的模型性能。CoDSA生成合成样本,忠实捕捉原始数据的条件分布,重点关注欠采样或高兴趣区域。通过迁移学习,CoDSA对预训练的生成模型进行微调,以增强合成数据的真实性和稀疏区域的样本密度。这一过程保留了跨模态关系,缓解了数据不平衡问题,提高了域适应性和泛化能力。我们还引入了一个理论框架,量化由CoDSA启用的统计精度改进与合成样本量和目标区域分配的函数关系,为其提供有效的正式保证。大量实验表明,在监督和非监督环境中,CoDSA始终优于非自适应增强策略和最新的基线方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
该文本提出了条件数据合成增强(CoDSA)框架,利用生成模型(如扩散模型)合成高质量数据,以改善包括表格、文本和图像数据等多模式领域的模型性能。CoDSA生成的数据样本能够忠实捕捉原始数据的条件分布,重点关注欠采样或高兴趣区域。通过迁移学习,CoDSA对预训练的生成模型进行微调,以提高合成数据的真实性和稀疏区域的样本密度。此框架能够保留跨模态关系,缓解数据不平衡问题,改善领域适应性和提高泛化能力。实验证明,CoDSA在监督和半监督设置中始终优于非自适应增强策略和最新基线。
关键见解
- 真实世界的数据集在大小和代表性方面常常有限,会导致模型预测偏差和性能下降。
- CoDSA框架利用生成模型(如扩散模型)合成高质量数据,以改善模型性能。
- CoDSA能够关注欠采样或高兴趣区域,并生成忠实于原始数据条件分布的合成样本。
- 通过迁移学习,CoDSA能够增强合成数据的真实性和提高稀疏区域的样本密度。
- CoDSA能够保留跨模态关系,缓解数据不平衡问题,改善领域适应性。
- CoDSA提供了一个理论框架,量化合成样本体积和目标区域分配所带来的统计精度改进。
- 实验证明,CoDSA在多个设置中均优于其他增强策略和基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

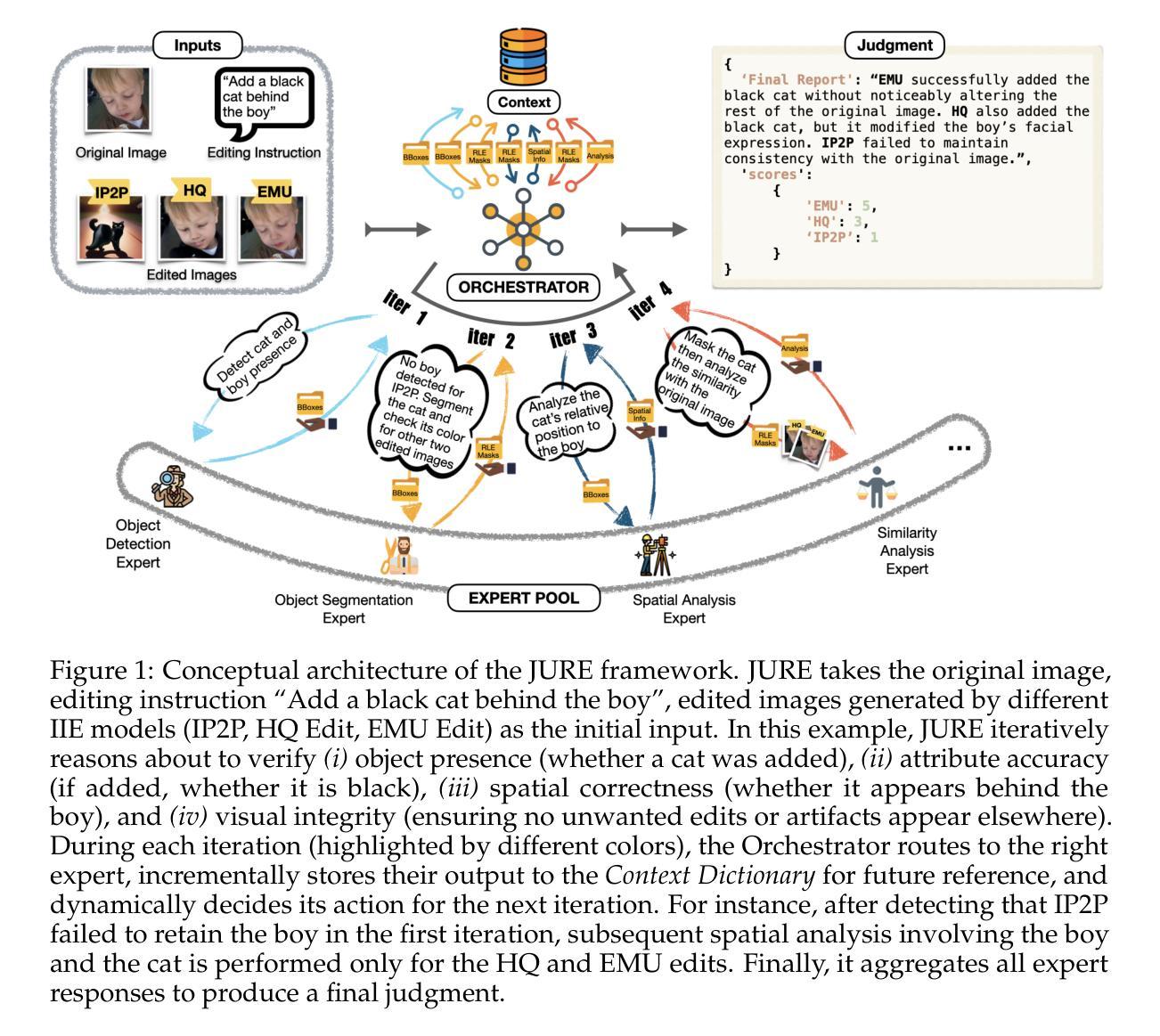
Routing to the Right Expertise: A Trustworthy Judge for Instruction-based Image Editing
Authors:Chenxi Sun, Hongzhi Zhang, Qi Wang, Fuzheng Zhang
Instruction-based Image Editing (IIE) models have made significantly improvement due to the progress of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) and diffusion models, which can understand and reason about complex editing instructions. In addition to advancing current IIE models, accurately evaluating their output has become increasingly critical and challenging. Current IIE evaluation methods and their evaluation procedures often fall short of aligning with human judgment and often lack explainability. To address these limitations, we propose JUdgement through Routing of Expertise (JURE). Each expert in JURE is a pre-selected model assumed to be equipped with an atomic expertise that can provide useful feedback to judge output, and the router dynamically routes the evaluation task of a given instruction and its output to appropriate experts, aggregating their feedback into a final judge. JURE is trustworthy in two aspects. First, it can effortlessly provide explanations about its judge by examining the routed experts and their feedback. Second, experimental results demonstrate that JURE is reliable by achieving superior alignment with human judgments, setting a new standard for automated IIE evaluation. Moreover, JURE’s flexible design is future-proof - modular experts can be seamlessly replaced or expanded to accommodate advancements in IIE, maintaining consistently high evaluation quality. Our evaluation data and results are available at https://github.com/Cyyyyyrus/JURE.git.
基于指令的图像编辑(IIE)模型由于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)和扩散模型的进展而取得了显著改进,这些模型能够理解和推理复杂的编辑指令。除了推进当前的IIE模型外,准确评估它们的输出也变得日益关键和具有挑战性。当前的IIE评估方法及其流程往往与人类判断不符,并且缺乏可解释性。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了通过专业路由进行评判(JURE)。在JURE中的每个专家都是预先选择好的模型,假设具备原子专业知识,可以为判断输出提供有用的反馈,路由器会动态地将给定指令的评估任务及其输出路由到合适的专家,并汇总他们的反馈以做出最终判断。JURE在两个方面值得信赖。首先,通过检查路由的专家及其反馈,它可以轻松地对其判断提供解释。其次,实验结果表明,与人类判断相比,JURE更加可靠,为自动化IIE评估树立了新标准。此外,JURE的设计具有前瞻性,模块化专家可以轻松替换或扩展以适应IIE的进步,从而保持始终如一的高评估质量。我们的评估数据和结果可在https://github.com/Cyyyyyrus/JURE.git上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于指令的图像编辑(IIE)模型因多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)和扩散模型的进展而得到显著改善,能够理解并处理复杂的编辑指令。针对当前IIE模型评估方法与其程序与人类判断的对齐不足和缺乏解释性的问题,提出通过路由专业知识进行评判(JURE)。JURE中的专家被视为拥有原子专业知识,可提供有用的反馈来评估输出,路由器会动态地将给定指令及其输出的评估任务路由到合适的专家,并汇集他们的反馈作出最终判断。JURE在两个方面值得信赖:一是可以轻松解释其判断依据;二是与人类判断对齐的可靠性高,为自动化IIE评估设定了新的标准。此外,JURE灵活的设计能够适应未来的IIE进展,保持一贯的评估质量。
Key Takeaways
- IIE模型由于多模态大型语言模型和扩散模型的进步而有所提升,能够理解和处理复杂的编辑指令。
- 当前IIE模型的评估方法经常无法与人类判断对齐,且缺乏解释性。
- 提出通过路由专业知识进行评判(JURE)的方法来解决这一问题。
- JURE中的专家提供原子专业知识来评估输出。
- 路由器动态地将指令和输出路由到合适的专家进行评估。
- JURE具备解释性、与人类判断对齐的可靠性,为未来IIE模型的进展提供了灵活的评估框架。
- JURE的评价数据和结果可在https://github.com/Cyyyyyrus/JURE.git上找到。
点此查看论文截图

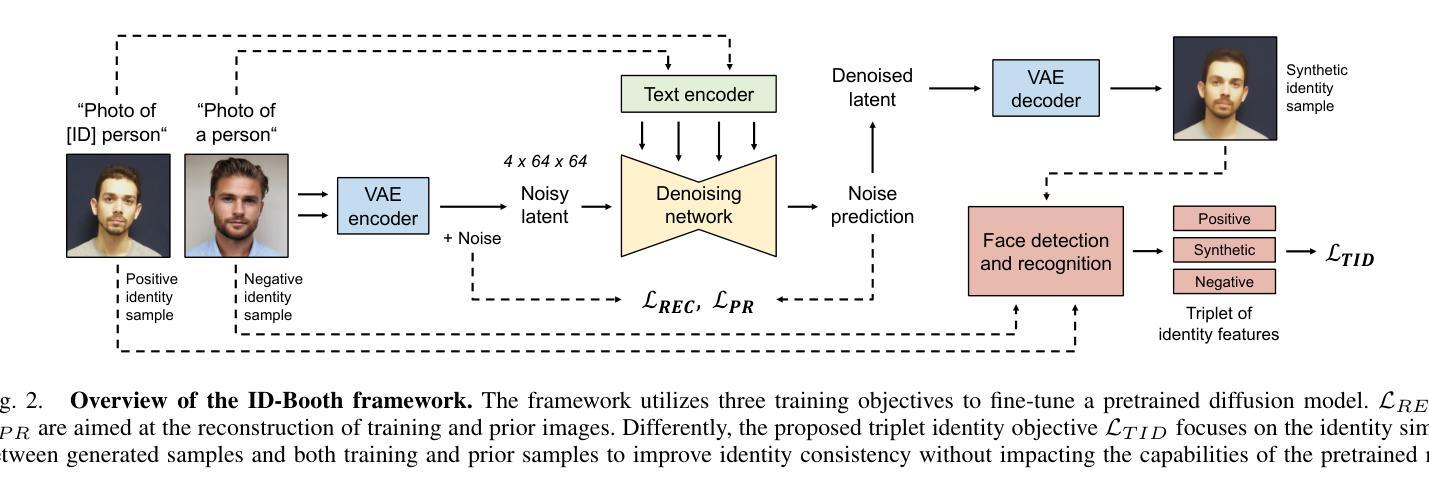
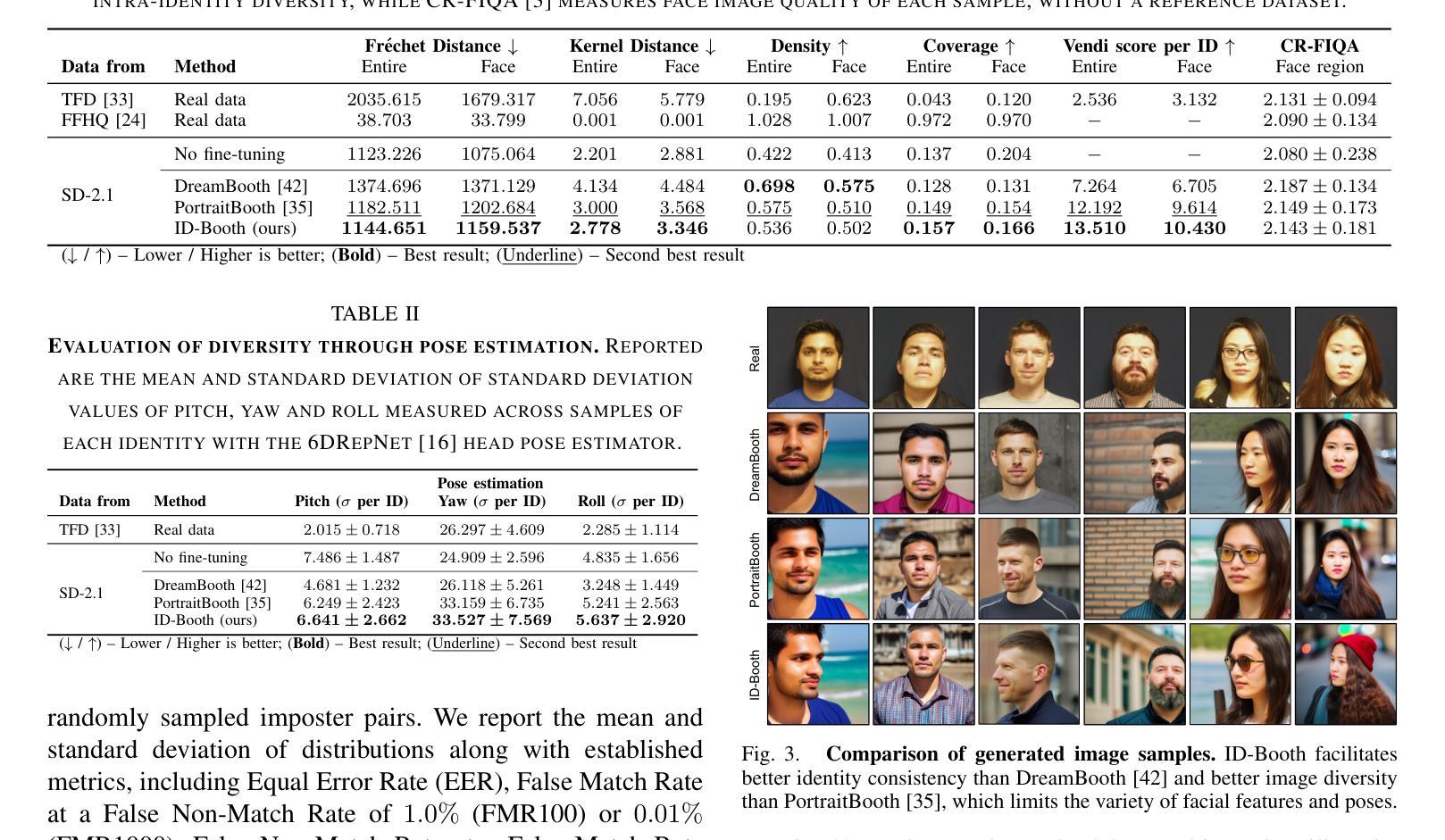
ID-Booth: Identity-consistent Face Generation with Diffusion Models
Authors:Darian Tomašević, Fadi Boutros, Chenhao Lin, Naser Damer, Vitomir Štruc, Peter Peer
Recent advances in generative modeling have enabled the generation of high-quality synthetic data that is applicable in a variety of domains, including face recognition. Here, state-of-the-art generative models typically rely on conditioning and fine-tuning of powerful pretrained diffusion models to facilitate the synthesis of realistic images of a desired identity. Yet, these models often do not consider the identity of subjects during training, leading to poor consistency between generated and intended identities. In contrast, methods that employ identity-based training objectives tend to overfit on various aspects of the identity, and in turn, lower the diversity of images that can be generated. To address these issues, we present in this paper a novel generative diffusion-based framework, called ID-Booth. ID-Booth consists of a denoising network responsible for data generation, a variational auto-encoder for mapping images to and from a lower-dimensional latent space and a text encoder that allows for prompt-based control over the generation procedure. The framework utilizes a novel triplet identity training objective and enables identity-consistent image generation while retaining the synthesis capabilities of pretrained diffusion models. Experiments with a state-of-the-art latent diffusion model and diverse prompts reveal that our method facilitates better intra-identity consistency and inter-identity separability than competing methods, while achieving higher image diversity. In turn, the produced data allows for effective augmentation of small-scale datasets and training of better-performing recognition models in a privacy-preserving manner. The source code for the ID-Booth framework is publicly available at https://github.com/dariant/ID-Booth.
最近生成建模技术的进步使得能够生成适用于各种领域的高质量合成数据,包括人脸识别。在这里,最先进的生成模型通常依赖于对功能强大的预训练扩散模型进行条件设定和微调,以促进所需身份的逼真图像合成。然而,这些模型在训练过程中往往不考虑主体的身份,导致生成图像与预期身份之间的一致性较差。相比之下,采用基于身份的训练目标的方法往往会在身份的各个方面过度拟合,从而降低了可以生成的图像多样性。为了解决这个问题,我们在本文中提出了一种新型的基于扩散的生成框架,称为ID-Booth。ID-Booth由一个负责数据生成的降噪网络、一个用于将图像映射到低维潜在空间及其反向映射的变分自动编码器和一个文本编码器组成,该文本编码器允许基于提示控制生成过程。该框架利用了一种新型的三重身份训练目标,能够在保持预训练扩散模型的合成能力的同时,实现身份一致的图像生成。利用最先进的潜在扩散模型和多种提示进行的实验表明,我们的方法在身份内部一致性和身份间可分性方面优于其他方法,同时实现了较高的图像多样性。因此,生成的数据允许有效地扩充小规模数据集,并以保护隐私的方式训练性能更好的识别模型。ID-Booth框架的源代码可在https://github.com/dariant/ID-Booth公开获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG) 2025, 14 pages
摘要
本文介绍了一种基于扩散模型的新型生成式框架ID-Booth,用于生成具有身份一致性的高质量合成数据。该框架通过去噪网络负责数据生成,使用变分自动编码器实现图像与低维潜在空间之间的映射,并通过文本编码器实现基于提示的生成过程控制。实验结果表明,与其他方法相比,ID-Booth具有更好的身份一致性、更高的图像多样性和更好的跨身份分离能力。此外,该框架产生的数据可用于有效地增强小规模数据集,并以隐私保护的方式训练性能更好的识别模型。
要点
- 最新进展的生成建模技术可以通过扩散模型生成高质量合成数据,这些数据适用于各种领域,包括人脸识别。
- 当前先进技术通常依赖于对预训练的扩散模型进行条件设定和微调来合成具有现实感的图像。但这些模型在训练期间不考虑身份,导致生成身份与实际意图之间的不一致。
- 采用身份为基础的训练目标的方法可能会过于适应身份的各个方面,从而降低可生成的图像多样性。
- ID-Booth框架通过结合去噪网络、变分自动编码器和文本编码器解决了上述问题。它采用新颖的三重身份训练目标,实现了身份一致的图像生成并保留了预训练的扩散模型的合成能力。
- 实验表明,与其他方法相比,ID-Booth在身份一致性和图像多样性方面表现更佳。此外,它产生的数据能有效增强小规模数据集并训练出性能更佳的识别模型。框架的源代码已公开提供。
- ID-Booth框架能够以一种隐私保护的方式生成合成数据,从而提高人脸识别等任务的性能。
点此查看论文截图

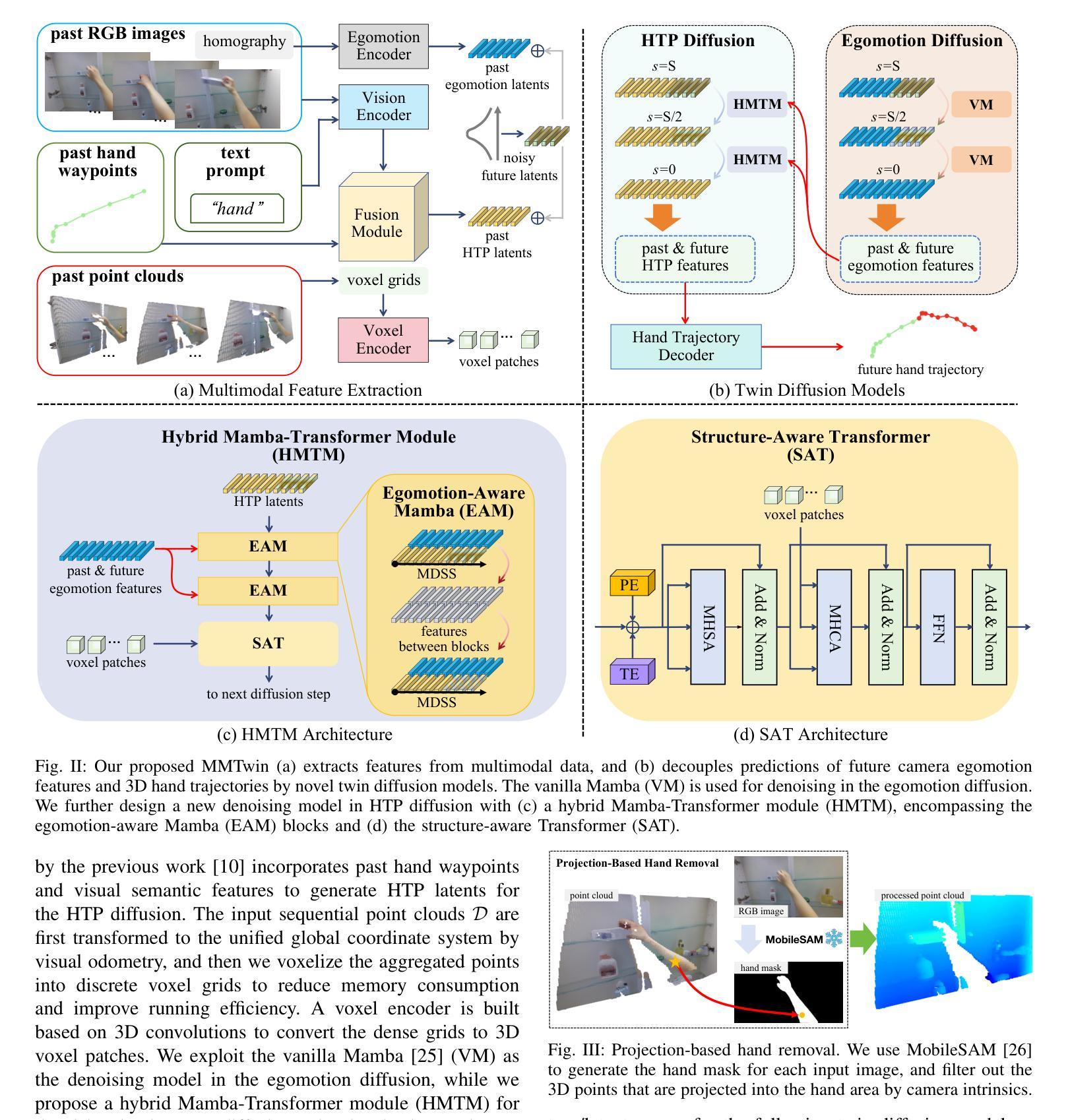
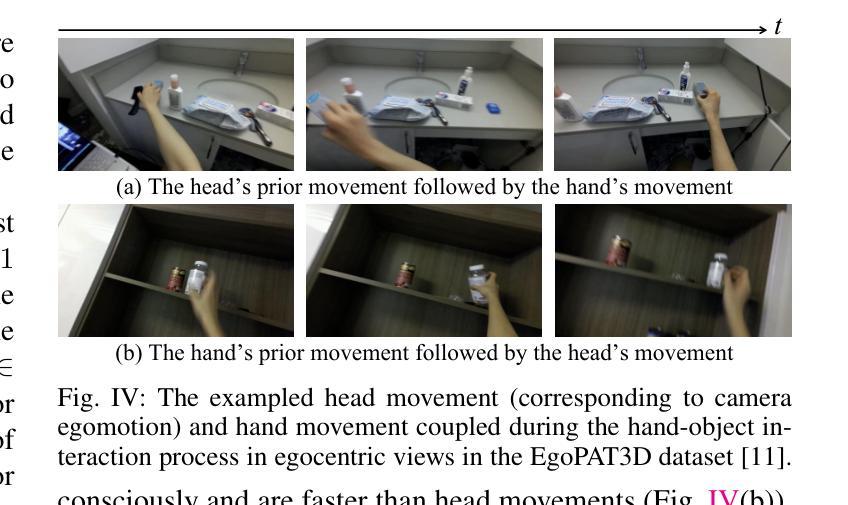
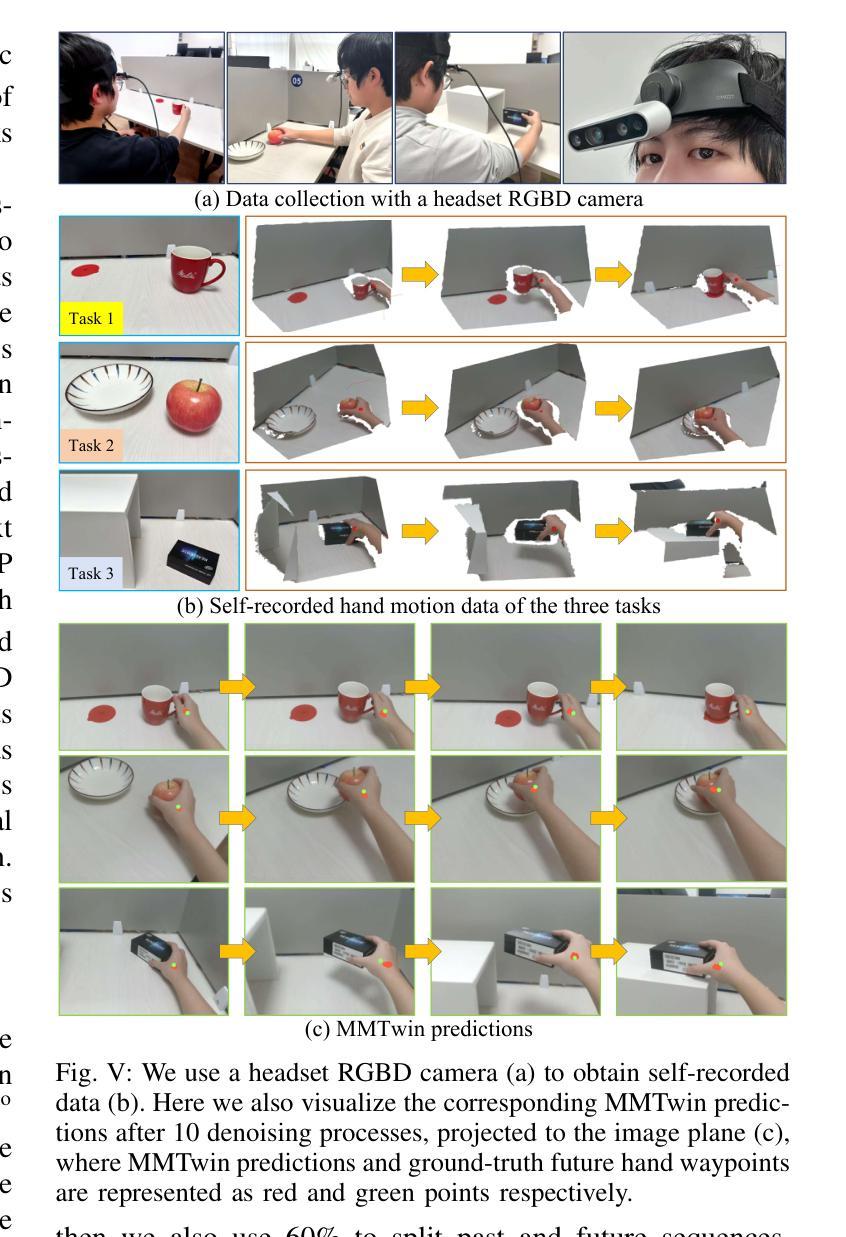
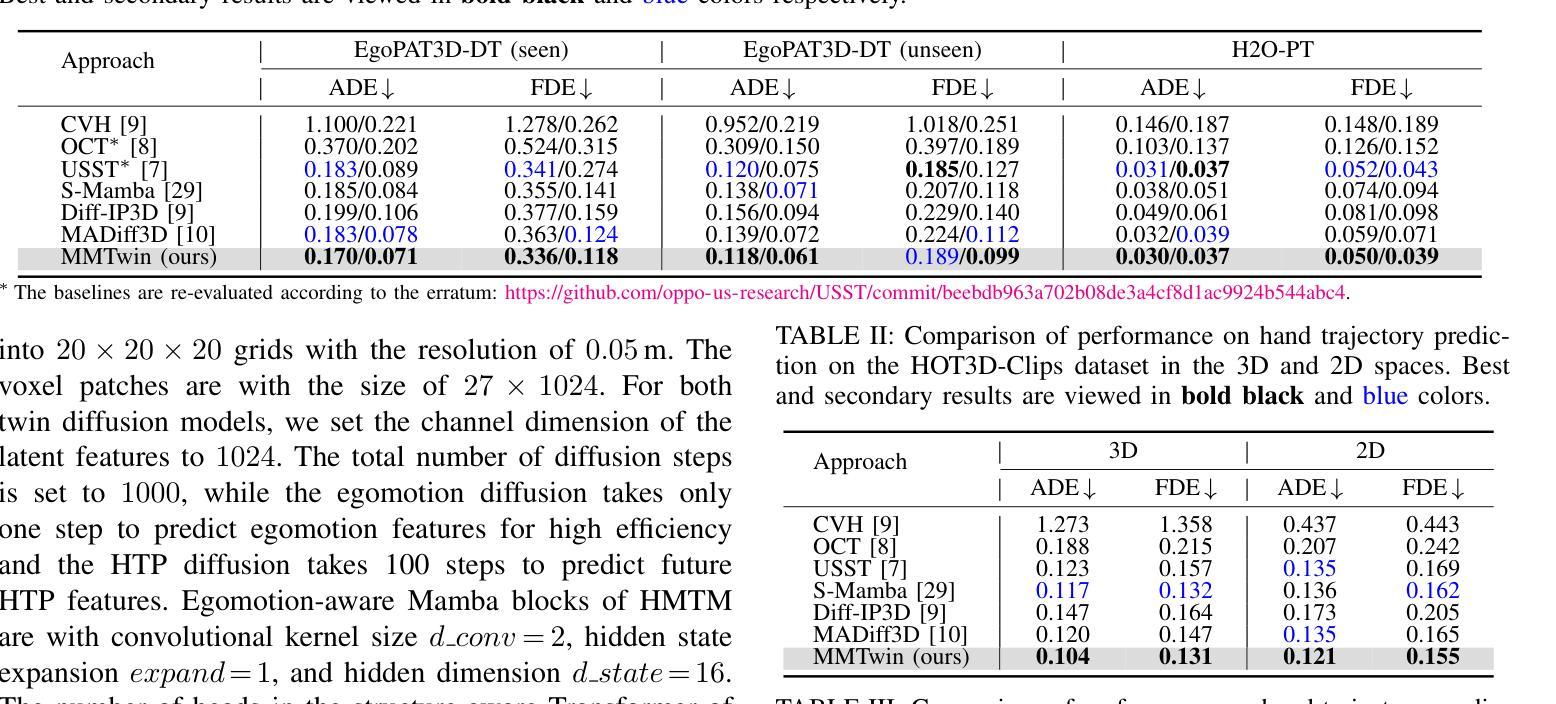
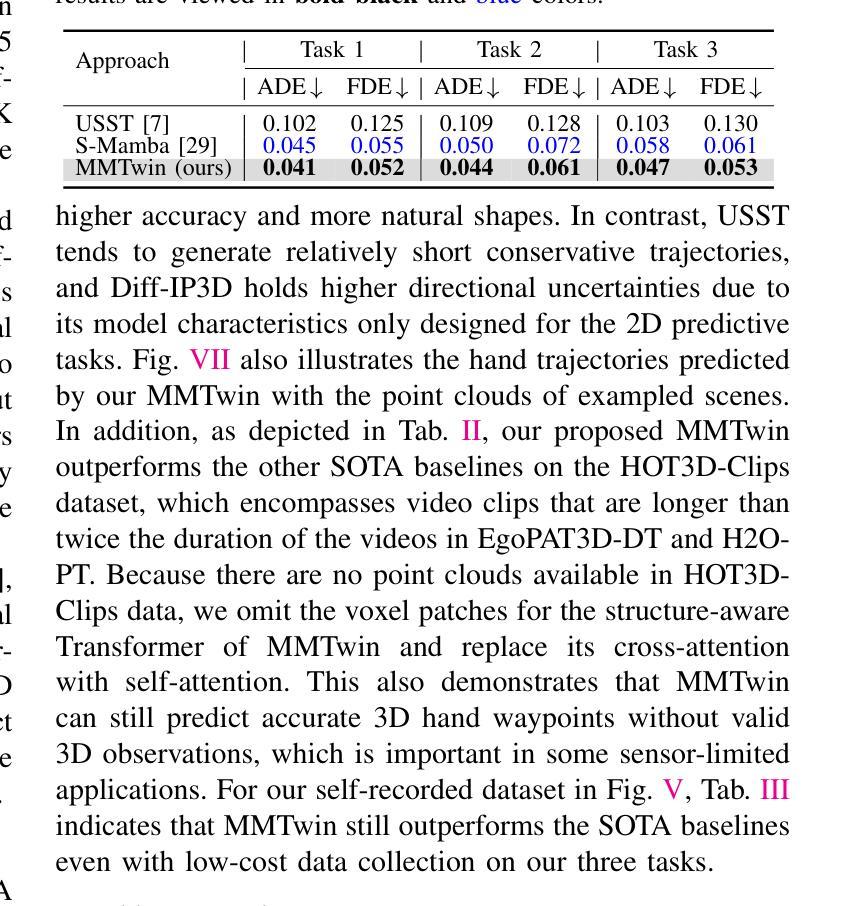
Novel Diffusion Models for Multimodal 3D Hand Trajectory Prediction
Authors:Junyi Ma, Wentao Bao, Jingyi Xu, Guanzhong Sun, Xieyuanli Chen, Hesheng Wang
Predicting hand motion is critical for understanding human intentions and bridging the action space between human movements and robot manipulations. Existing hand trajectory prediction (HTP) methods forecast the future hand waypoints in 3D space conditioned on past egocentric observations. However, such models are only designed to accommodate 2D egocentric video inputs. There is a lack of awareness of multimodal environmental information from both 2D and 3D observations, hindering the further improvement of 3D HTP performance. In addition, these models overlook the synergy between hand movements and headset camera egomotion, either predicting hand trajectories in isolation or encoding egomotion only from past frames. To address these limitations, we propose novel diffusion models (MMTwin) for multimodal 3D hand trajectory prediction. MMTwin is designed to absorb multimodal information as input encompassing 2D RGB images, 3D point clouds, past hand waypoints, and text prompt. Besides, two latent diffusion models, the egomotion diffusion and the HTP diffusion as twins, are integrated into MMTwin to predict camera egomotion and future hand trajectories concurrently. We propose a novel hybrid Mamba-Transformer module as the denoising model of the HTP diffusion to better fuse multimodal features. The experimental results on three publicly available datasets and our self-recorded data demonstrate that our proposed MMTwin can predict plausible future 3D hand trajectories compared to the state-of-the-art baselines, and generalizes well to unseen environments. The code and pretrained models will be released at https://github.com/IRMVLab/MMTwin.
预测手部运动对于理解人类意图以及建立人类运动和机器人操作之间的动作空间桥梁至关重要。现有的手部轨迹预测(HTP)方法基于过去的以自我为中心的观测来预测未来手部在三维空间中的轨迹点。然而,这些模型仅设计用于处理二维以自我为中心的视频输入。它们无法意识到来自二维和三维观察的多元环境信息,阻碍了三维HTP性能的进一步提高。此外,这些模型忽视了手部动作与头戴式相机自主运动之间的协同作用,要么单独预测手部轨迹,要么仅从过去几帧中编码自主运动。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了用于多模态三维手部轨迹预测的新型扩散模型MMTwin。MMTwin被设计成吸收多模态信息作为输入,包括二维RGB图像、三维点云、过去的手部轨迹点和文本提示。此外,两个潜在扩散模型——自主运动扩散和HTP扩散作为双胞胎模型被集成到MMTwin中,以同时预测相机自主运动和未来手部轨迹。我们提出了一种新型的混合Mamba-Transformer模块作为HTP扩散的去噪模型,以更好地融合多模态特征。在三个公开数据集和我们自行录制的数据上的实验结果表明,与我们提出的MMTwin相比,最先进的基线模型可以预测更合理的未来三维手部轨迹,并且能很好地推广到未见过的环境。代码和预训练模型将在https://github.com/IRMVLab/MMTwin上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
提出一种基于多模态信息的三维手轨迹预测扩散模型MMTwin,可融合二维RGB图像、三维点云、过去的手轨迹和文本提示等多种信息。采用两个潜式扩散模型:egomotion扩散和HTP扩散,同时预测相机运动和未来手轨迹。采用新型混合Mamba-Transformer模块作为HTP扩散的去噪模型,实现多模态特征融合。在公开数据集和自我录制数据上的实验表明,MMTwin能预测可信的未来三维手轨迹,具有良好的泛化性能。
关键见解
- 现有手轨迹预测方法主要基于过去二维观察数据,缺乏多模态环境信息的融合。
- 提出一种新型扩散模型MMTwin,用于多模态三维手轨迹预测,能够融合包括二维RGB图像、三维点云等环境信息。
- MMTwin包含两个潜式扩散模型:egomotion扩散和HTP扩散,分别预测相机运动和未来手轨迹。
- 采用混合Mamba-Transformer模块作为去噪模型,实现多模态特征的有效融合。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明MMTwin能够预测未来可信的三维手轨迹,相较于现有方法具有优势。
- MMTwin具有良好的泛化性能,能够适应未见过环境的手轨迹预测任务。
点此查看论文截图

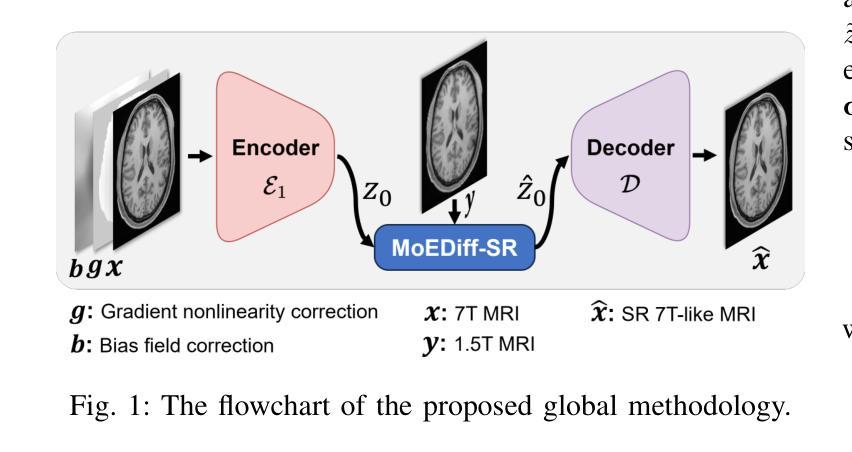
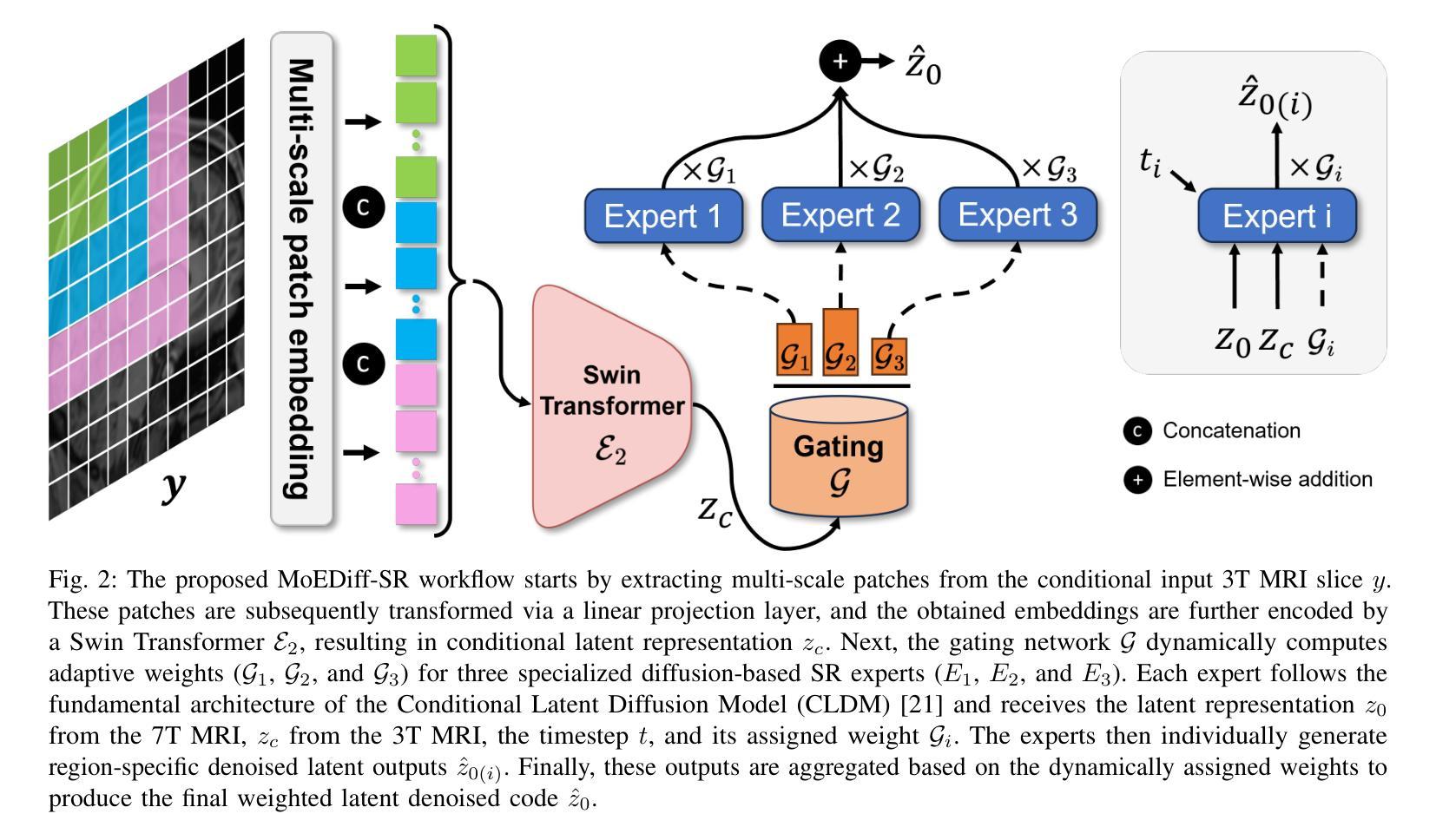
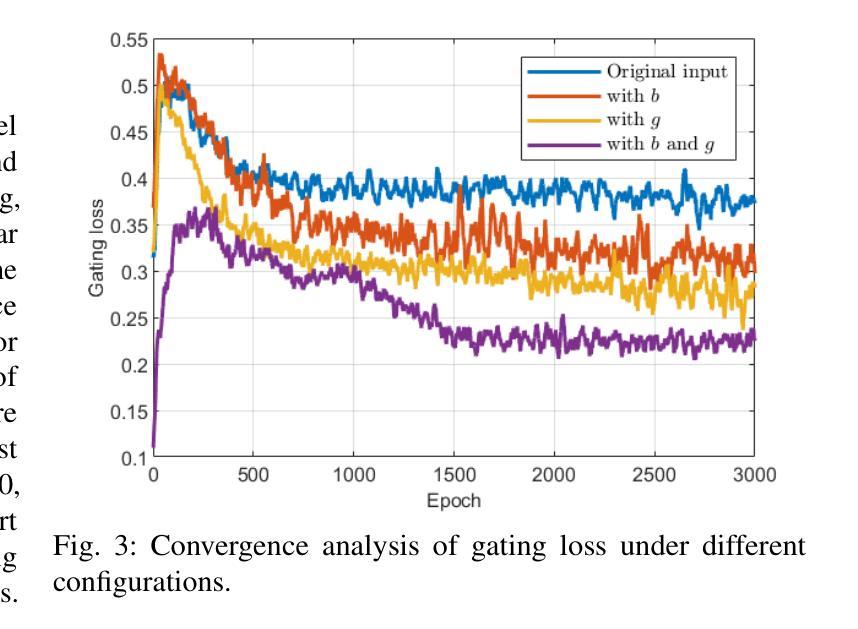
MoEDiff-SR: Mixture of Experts-Guided Diffusion Model for Region-Adaptive MRI Super-Resolution
Authors:Zhe Wang, Yuhua Ru, Aladine Chetouani, Fang Chen, Fabian Bauer, Liping Zhang, Didier Hans, Rachid Jennane, Mohamed Jarraya, Yung Hsin Chen
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) at lower field strengths (e.g., 3T) suffers from limited spatial resolution, making it challenging to capture fine anatomical details essential for clinical diagnosis and neuroimaging research. To overcome this limitation, we propose MoEDiff-SR, a Mixture of Experts (MoE)-guided diffusion model for region-adaptive MRI Super-Resolution (SR). Unlike conventional diffusion-based SR models that apply a uniform denoising process across the entire image, MoEDiff-SR dynamically selects specialized denoising experts at a fine-grained token level, ensuring region-specific adaptation and enhanced SR performance. Specifically, our approach first employs a Transformer-based feature extractor to compute multi-scale patch embeddings, capturing both global structural information and local texture details. The extracted feature embeddings are then fed into an MoE gating network, which assigns adaptive weights to multiple diffusion-based denoisers, each specializing in different brain MRI characteristics, such as centrum semiovale, sulcal and gyral cortex, and grey-white matter junction. The final output is produced by aggregating the denoised results from these specialized experts according to dynamically assigned gating probabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that MoEDiff-SR outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of quantitative image quality metrics, perceptual fidelity, and computational efficiency. Difference maps from each expert further highlight their distinct specializations, confirming the effective region-specific denoising capability and the interpretability of expert contributions. Additionally, clinical evaluation validates its superior diagnostic capability in identifying subtle pathological features, emphasizing its practical relevance in clinical neuroimaging. Our code is available at https://github.com/ZWang78/MoEDiff-SR.
在低场强(例如3T)的磁共振成像(MRI)中,由于空间分辨率有限,捕获对临床诊断和神经影像研究至关重要的精细解剖细节具有挑战性。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了MoEDiff-SR,这是一种受专家混合(MoE)引导的区域自适应MRI超分辨率(SR)扩散模型。与传统的基于扩散的SR模型不同,后者在整个图像上应用统一的去噪过程,MoEDiff-SR在精细的标记级别动态选择专业的去噪专家,确保区域特定的适应性和增强的SR性能。具体来说,我们的方法首先采用基于Transformer的特征提取器来计算多尺度补丁嵌入,捕捉全局结构信息和局部纹理细节。提取的特征嵌入随后被输入到MoE门控网络中,该网络为多个基于扩散的去噪器分配自适应权重,每个去噪器都专注于不同的脑部MRI特征,例如半卵中心、沟和回状皮层以及灰白质交界处。最终输出是通过根据动态分配的门控概率聚合这些专业专家的去噪结果而产生的。实验结果表明,MoEDiff-SR在图像质量指标、感知保真度和计算效率方面优于现有的最先进方法。来自每个专家的差异映射进一步突出了其独特的专业特点,证实了其在特定区域的去噪能力和专家贡献的可解释性。此外,临床评估验证了其在识别细微病理特征方面的优越诊断能力,强调其在临床神经影像中的实际相关性。我们的代码可在[https://github.com/ZWang78/MoEDiff-SR找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MoEDiff-SR,一种基于专家混合(MoE)引导扩散模型的区域自适应MRI超分辨率(SR)技术,旨在解决低场强MRI空间分辨率有限的挑战。该技术通过动态选择专门的去噪专家,在细粒度令牌级别进行区域特定适应,确保SR性能的提升。实验结果表明,MoEDiff-SR在图像质量指标、感知保真度和计算效率方面均优于现有先进技术。此外,临床评估验证了其在识别细微病理特征方面的卓越诊断能力。
Key Takeaways
- MoEDiff-SR是一种基于专家混合(MoE)的扩散模型,用于区域自适应MRI超分辨率(SR)。
- 传统扩散模型在整个图像上应用均匀去噪过程,而MoEDiff-SR则通过动态选择去噪专家进行区域特定适应。
- MoEDiff-SR使用基于Transformer的特征提取器计算多尺度补丁嵌入,捕捉全局结构信息和局部纹理细节。
- MoE门控网络根据多个专注于不同大脑MRI特性的专业扩散去噪器(如中枢半卵圆中心、脑沟和脑回皮层、灰白质交界处)进行自适应权重分配。
- 实验结果表明,MoEDiff-SR在图像质量、感知保真度和计算效率方面优于现有先进技术。
- 专家差异图突出了各自的专业特点,验证了区域特定去噪能力和专家贡献的可解释性。
点此查看论文截图

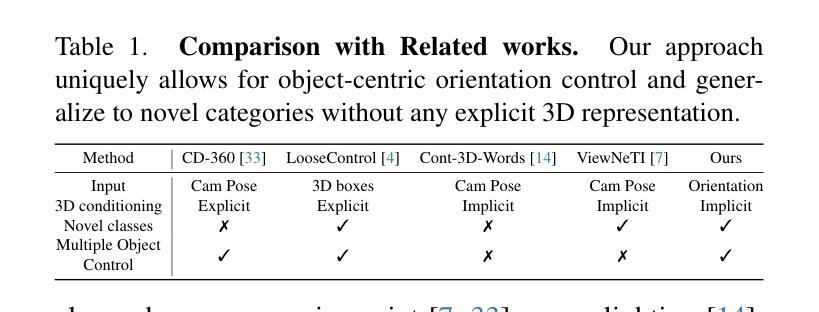
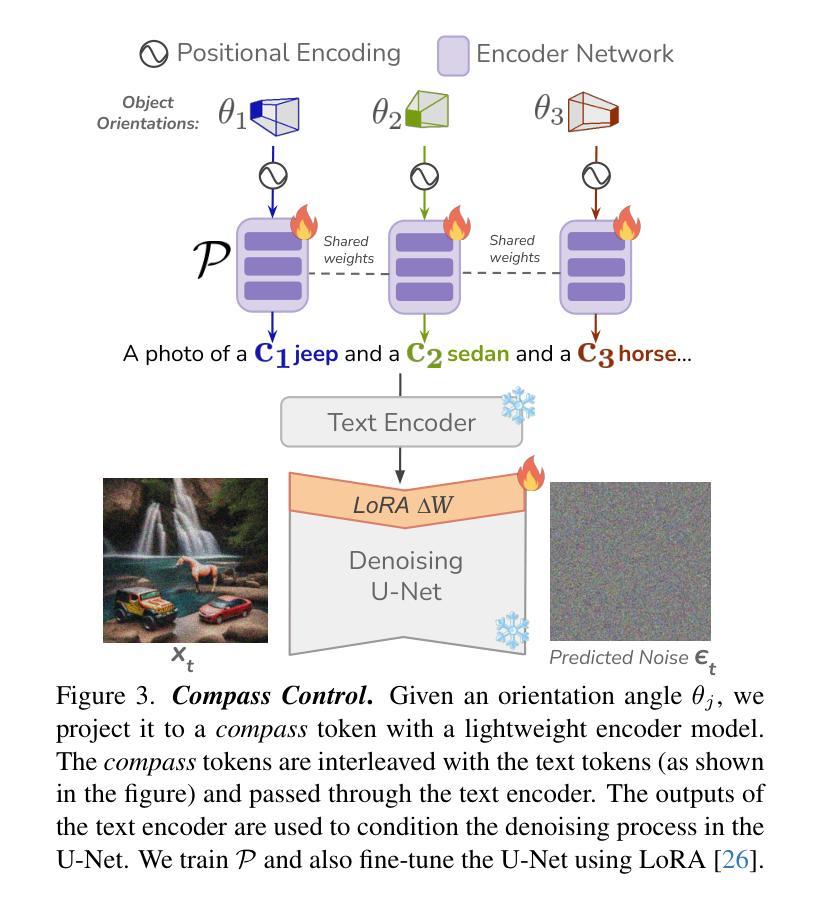
Compass Control: Multi Object Orientation Control for Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Rishubh Parihar, Vaibhav Agrawal, Sachidanand VS, R. Venkatesh Babu
Existing approaches for controlling text-to-image diffusion models, while powerful, do not allow for explicit 3D object-centric control, such as precise control of object orientation. In this work, we address the problem of multi-object orientation control in text-to-image diffusion models. This enables the generation of diverse multi-object scenes with precise orientation control for each object. The key idea is to condition the diffusion model with a set of orientation-aware \textbf{compass} tokens, one for each object, along with text tokens. A light-weight encoder network predicts these compass tokens taking object orientation as the input. The model is trained on a synthetic dataset of procedurally generated scenes, each containing one or two 3D assets on a plain background. However, direct training this framework results in poor orientation control as well as leads to entanglement among objects. To mitigate this, we intervene in the generation process and constrain the cross-attention maps of each compass token to its corresponding object regions. The trained model is able to achieve precise orientation control for a) complex objects not seen during training and b) multi-object scenes with more than two objects, indicating strong generalization capabilities. Further, when combined with personalization methods, our method precisely controls the orientation of the new object in diverse contexts. Our method achieves state-of-the-art orientation control and text alignment, quantified with extensive evaluations and a user study.
现有文本到图像扩散模型的控制方法虽然强大,但无法实现明确的3D对象中心控制,例如无法精确控制对象的方向。在这项工作中,我们解决了文本到图像扩散模型中的多对象方向控制问题。这能够实现为每个对象提供精确方向控制的多样化多对象场景生成。关键思想是使用一组方向感知的指南针令牌(一个用于每个对象)以及文本令牌来调控扩散模型。一个轻量级的编码器网络以对象方向作为输入来预测这些指南针令牌。该模型是在合成数据集上进行训练的,该数据集包含程序生成的场景,每个场景包含一个或两个位于平面背景上的3D资产。然而,直接训练该框架会导致方向控制不佳以及对象之间的纠缠。为了缓解这个问题,我们在生成过程中进行干预,并限制每个指南针令牌的跨注意力图到其对应的对象区域。训练后的模型能够对以下方面实现精确的方向控制:a)训练中未见过的复杂对象;b)具有超过两个对象的多对象场景,显示出强大的泛化能力。此外,当与个人化方法相结合时,我们的方法能够在多种上下文中精确控制新对象的方向。我们的方法在方向控制和文本对齐方面达到了最新水平,这通过广泛的评估和一项用户研究得到了量化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 Camera Ready. Project page: https://rishubhpar.github.io/compasscontrol
Summary
本文解决了文本到图像扩散模型中的多目标方向控制问题,通过引入一组面向方向性的指南针标记和轻量级编码器网络,实现了每个对象的精确方向控制,从而生成了多样化的多目标场景。模型经过合成数据集训练,通过对生成过程的干预和约束交叉注意力图,实现了对复杂对象和新场景中多个对象的精确方向控制。结合个性化方法,该方法能够精确控制不同背景下的新对象的方向。本文的方法实现了最先进的方向控制和文本对齐。
Key Takeaways
- 引入指南针标记实现文本到图像扩散模型中的多目标方向控制。
- 通过轻量级编码器网络预测指南针标记,以控制对象方向。
- 模型在合成数据集上进行训练,包含单个或两个3D资产在纯背景上的场景。
- 通过干预生成过程和约束交叉注意力图,解决方向控制不准确和对象纠缠的问题。
- 模型实现对复杂对象和新场景中多个对象的精确方向控制,展现强大泛化能力。
- 结合个性化方法,能够精确控制不同背景下的新对象的方向。
点此查看论文截图



Hyperbolic Diffusion Recommender Model
Authors:Meng Yuan, Yutian Xiao, Wei Chen, Chu Zhao, Deqing Wang, Fuzhen Zhuang
Diffusion models (DMs) have emerged as the new state-of-the-art family of deep generative models. To gain deeper insights into the limitations of diffusion models in recommender systems, we investigate the fundamental structural disparities between images and items. Consequently, items often exhibit distinct anisotropic and directional structures that are less prevalent in images. However, the traditional forward diffusion process continuously adds isotropic Gaussian noise, causing anisotropic signals to degrade into noise, which impairs the semantically meaningful representations in recommender systems. Inspired by the advancements in hyperbolic spaces, we propose a novel \textit{\textbf{H}yperbolic} \textit{\textbf{D}iffusion} \textit{\textbf{R}ecommender} \textit{\textbf{M}odel} (named HDRM). Unlike existing directional diffusion methods based on Euclidean space, the intrinsic non-Euclidean structure of hyperbolic space makes it particularly well-adapted for handling anisotropic diffusion processes. In particular, we begin by formulating concepts to characterize latent directed diffusion processes within a geometrically grounded hyperbolic space. Subsequently, we propose a novel hyperbolic latent diffusion process specifically tailored for users and items. Drawing upon the natural geometric attributes of hyperbolic spaces, we impose structural restrictions on the space to enhance hyperbolic diffusion propagation, thereby ensuring the preservation of the intrinsic topology of user-item graphs. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of HDRM.
扩散模型(DMs)已经成为最新的深度生成模型家族。为了更深入地了解扩散模型在推荐系统中的局限性,我们研究了图像和项目之间根本的结构性差异。因此,项目通常表现出不同的各向异性和方向性结构,这些在图像中并不常见。然而,传统的正向扩散过程不断添加各向同性的高斯噪声,导致各向异性的信号降为噪声,从而损害了推荐系统中的语义表示。受超曲面空间发展的启发,我们提出了一种新型的Hyperbolic Diffusion Recommender Model,简称HDRM模型。与基于欧几里得空间的现有方向性扩散方法不同,超曲面空间的内在非欧几里得结构使其特别适合于处理各向异性扩散过程。具体来说,我们首先制定概念,以表征几何接地超曲面空间内的潜在定向扩散过程。随后,我们针对用户和项目提出了一种新型的超曲面潜在扩散过程。利用超曲面空间的自然几何属性,我们对空间施加结构性限制,以增强超曲面扩散传播,从而确保用户-项目图的内在拓扑结构得以保留。在三个基准数据集上的大量实验证明了HDRM模型的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型(DMs)在深度生成模型中处于前沿地位。为了在推荐系统中更深入地了解扩散模型的局限性,研究者对比了图像和物品之间的基本结构差异。物品常具有独特的定向结构,而传统的前向扩散过程添加的是同向高斯噪声,这会损害语义表示。受双曲空间发展的启发,提出了新型的“超扩散推荐模型”(HDRM)。不同于基于欧几里得空间的定向扩散方法,双曲空间的非欧几里得结构更适合处理定向扩散过程。HDRM在几何双曲空间中描述了潜在定向扩散过程的特点,并针对用户和物品提出了新型的双曲潜在扩散过程。在三个基准数据集上的实验验证了HDRM的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在深度生成模型中占据领先地位,但在推荐系统中有局限性。
- 物品与图像在结构上有差异,物品常具有独特的定向结构。
- 传统的前向扩散过程添加同向高斯噪声,不利于推荐系统中的语义表示。
- 受双曲空间发展的启发,提出了超扩散推荐模型(HDRM)。
- 双曲空间的非欧几里得结构更适合处理定向扩散过程。
- HDRM在几何双曲空间中描述了潜在定向扩散过程的特点。
点此查看论文截图

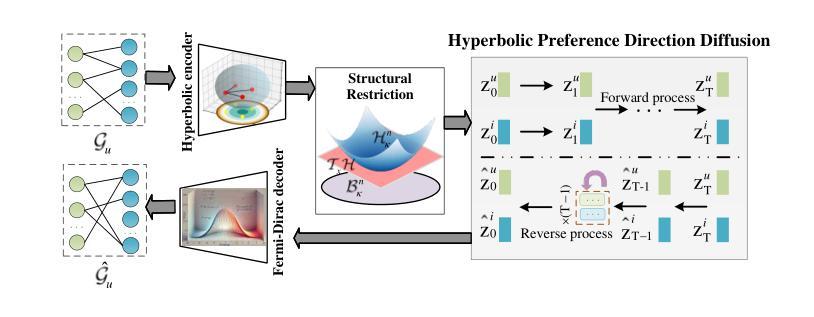
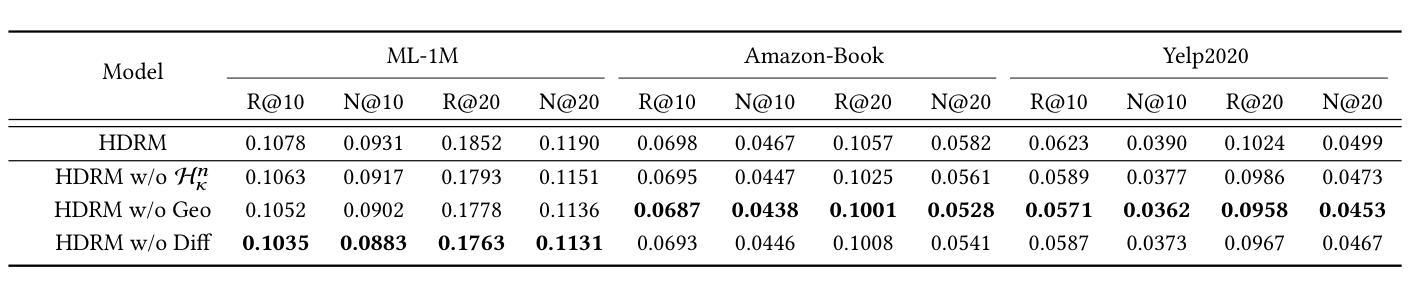
Image Augmentation Agent for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wangyu Wu, Xianglin Qiu, Siqi Song, Zhenhong Chen, Xiaowei Huang, Fei Ma, Jimin Xiao
Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) has achieved remarkable progress using only image-level labels. However, most existing WSSS methods focus on designing new network structures and loss functions to generate more accurate dense labels, overlooking the limitations imposed by fixed datasets, which can constrain performance improvements. We argue that more diverse trainable images provides WSSS richer information and help model understand more comprehensive semantic pattern. Therefore in this paper, we introduce a novel approach called Image Augmentation Agent (IAA) which shows that it is possible to enhance WSSS from data generation perspective. IAA mainly design an augmentation agent that leverages large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models to automatically generate additional images for WSSS. In practice, to address the instability in prompt generation by LLMs, we develop a prompt self-refinement mechanism. It allow LLMs to re-evaluate the rationality of generated prompts to produce more coherent prompts. Additionally, we insert an online filter into diffusion generation process to dynamically ensure the quality and balance of generated images. Experimental results show that our method significantly surpasses state-of-the-art WSSS approaches on the PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 datasets.
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)仅使用图像级标签取得了显著的进步。然而,大多数现有的WSSS方法主要集中在设计新的网络结构和损失函数来生成更准确的密集标签,忽视了固定数据集所带来的限制,这些限制可能会限制性能的提升。我们认为,提供更多可训练图像的多样性可以为WSSS提供更丰富的信息,并帮助模型理解更全面的语义模式。因此,在本文中,我们介绍了一种新方法,称为图像增强代理(IAA),它表明从数据生成的角度增强WSSS是可能的。IAA主要设计了一个增强代理,利用大型语言模型(LLM)和扩散模型自动为WSSS生成额外的图像。在实践中,为了解决LLM提示生成中的不稳定问题,我们开发了一种提示自我优化机制。它允许LLM重新评估生成的提示的合理性,以产生更连贯的提示。此外,我们在扩散生成过程中插入了一个在线过滤器,以动态确保生成图像的质量和平衡。实验结果表明,我们的方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上显著超越了最先进的WSSS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Image Augmentation Agent(IAA)的方法,从数据生成的角度提升弱监督语义分割(WSSS)的性能。该方法利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型自动生成额外的图像,增强WSSS的训练图像多样性。同时,为解决LLMs在生成提示时的不稳定性问题,设计了一种提示自我优化机制,并通过在线过滤器确保生成图像的质量和平衡性。在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法显著超越了现有的WSSS方法。
Key Takeaways
- WSSS方法主要关注设计新的网络结构和损失函数以生成更准确的密集标签,但固定数据集的局限性限制了性能提升。
- 提出了一种名为Image Augmentation Agent(IAA)的新方法,从数据生成角度提升WSSS性能。
- IAA利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型自动生成额外图像,增加训练图像的多样性。
- 设计了提示自我优化机制,解决LLMs在生成提示时的不稳定性问题。
- 通过在线过滤器确保生成图像的质量和平衡性。
- 实验结果表明,IAA方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上显著超越了现有的WSSS方法。
点此查看论文截图

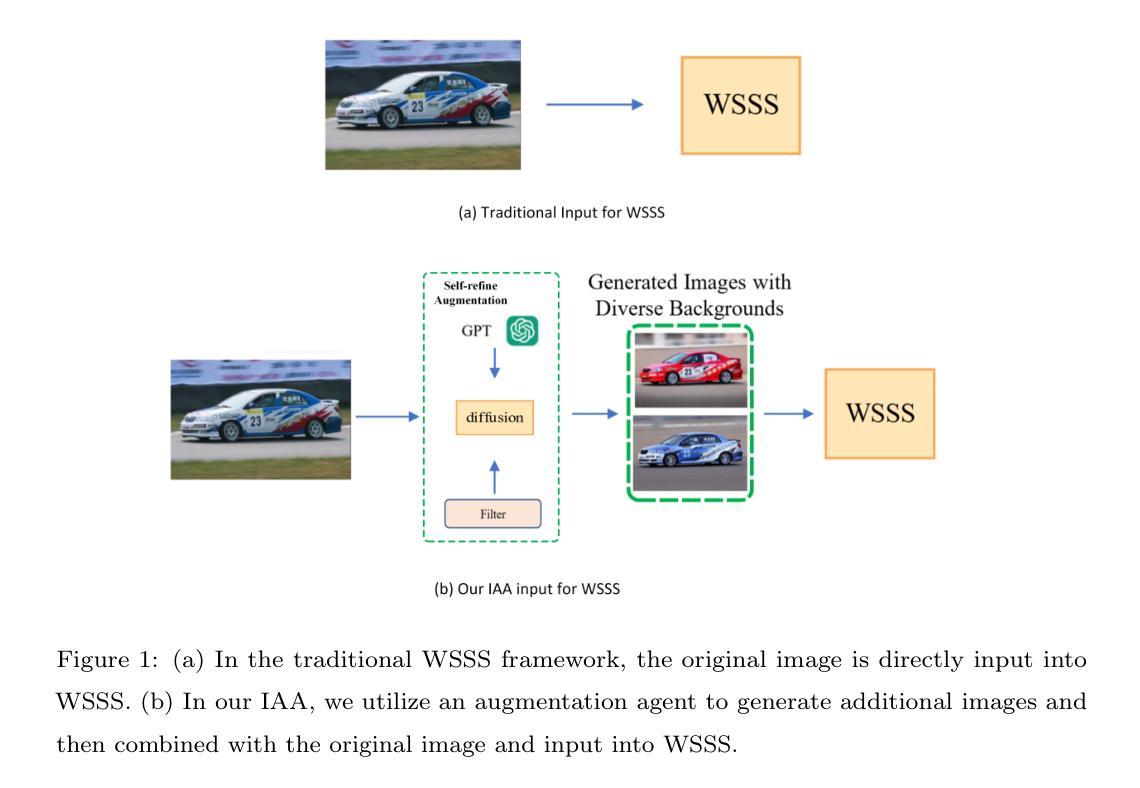
Distillation of Discrete Diffusion through Dimensional Correlations
Authors:Satoshi Hayakawa, Yuhta Takida, Masaaki Imaizumi, Hiromi Wakaki, Yuki Mitsufuji
Diffusion models have demonstrated exceptional performances in various fields of generative modeling, but suffer from slow sampling speed due to their iterative nature. While this issue is being addressed in continuous domains, discrete diffusion models face unique challenges, particularly in capturing dependencies between elements (e.g., pixel relationships in image, sequential dependencies in language) mainly due to the computational cost of processing high-dimensional joint distributions. In this paper, (i) we propose “mixture” models for discrete diffusion that are capable of treating dimensional correlations while remaining scalable, and (ii) we provide a set of loss functions for distilling the iterations of existing models. Two primary theoretical insights underpin our approach: First, conventional models with element-wise independence can well approximate the data distribution, but essentially require {\it many sampling steps}. Second, our loss functions enable the mixture models to distill such many-step conventional models into just a few steps by learning the dimensional correlations. Our experimental results show the effectiveness of the proposed method in distilling pretrained discrete diffusion models across image and language domains. The code used in the paper is available at https://github.com/sony/di4c .
扩散模型在生成建模的各个领域都表现出了卓越的性能,但由于其迭代性质,采样速度较慢。虽然这个问题正在连续域中得到解决,但离散扩散模型面临着独特的挑战,特别是在捕获元素之间的依赖关系方面(例如,图像中的像素关系,语言中的序列依赖),这主要是由于处理高维联合分布的计算成本造成的。在本文中,(i)我们为离散扩散提出了“混合”模型,这种模型能够在处理维度关联的同时保持可扩展性;(ii)我们为现有模型的迭代提供了一组损失函数。我们的方法基于两个主要的理论见解:首先,具有元素独立性的传统模型可以很好地近似数据分布,但基本上需要多次采样步骤。其次,我们的损失函数使混合模型能够通过学习维度相关性,将多次步骤的传统模型提炼为仅几步。我们的实验结果表明,该方法在图像和语言领域的预训练离散扩散模型提炼中非常有效。论文中使用的代码可在https://github.com/sony/di4c中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 39 pages, GitHub link added
摘要
扩散模型在生成建模的各个领域都表现出卓越的性能,但由于其迭代性质,采样速度较慢。虽然连续域的问题正在得到解决,离散扩散模型在捕捉元素间依赖关系方面面临独特挑战,例如在图像中的像素关系和语言中的序列依赖关系,这主要归因于处理高维联合分布的计算成本。本文提出混合模型来处理离散扩散的维度相关性,同时保持可扩展性,并提供一套损失函数来提炼现有模型的迭代过程。我们的方法基于两个主要理论见解:一是传统元素独立模型可以很好地近似数据分布,但需要多次采样步骤;二是我们的损失函数使混合模型能够通过学习维度相关性,将多次步骤的传统模型提炼为少数步骤。实验结果表明,该方法在图像和语言领域的预训练离散扩散模型提炼中效果显著。代码可在https://github.com/sony/di4c找到。
关键见解
- 扩散模型在生成建模的多个领域表现优秀,但采样速度慢。
- 离散扩散模型在捕捉元素间依赖关系时面临挑战,特别是高维联合分布的处理成本高昂。
- 本文提出混合模型处理离散扩散的维度相关性,兼顾性能与可扩展性。
- 引入损失函数来优化现有模型的迭代过程,减少采样步骤。
- 方法基于两个理论见解:传统模型需要多次采样步骤,而我们的损失函数能减少这些步骤。
- 实验证明,该方法在图像和语言领域的预训练离散扩散模型提炼中效果显著。
- 相关代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

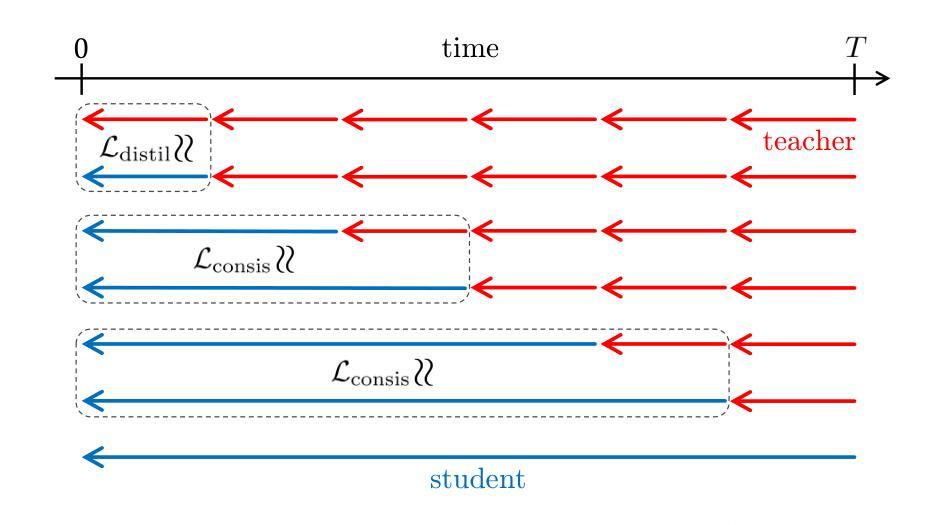
KnobGen: Controlling the Sophistication of Artwork in Sketch-Based Diffusion Models
Authors:Pouyan Navard, Amin Karimi Monsefi, Mengxi Zhou, Wei-Lun Chao, Alper Yilmaz, Rajiv Ramnath
Recent advances in diffusion models have significantly improved text-to-image (T2I) generation, but they often struggle to balance fine-grained precision with high-level control. Methods like ControlNet and T2I-Adapter excel at following sketches by seasoned artists but tend to be overly rigid, replicating unintentional flaws in sketches from novice users. Meanwhile, coarse-grained methods, such as sketch-based abstraction frameworks, offer more accessible input handling but lack the precise control needed for detailed, professional use. To address these limitations, we propose KnobGen, a dual-pathway framework that democratizes sketch-based image generation by seamlessly adapting to varying levels of sketch complexity and user skill. KnobGen uses a Coarse-Grained Controller (CGC) module for high-level semantics and a Fine-Grained Controller (FGC) module for detailed refinement. The relative strength of these two modules can be adjusted through our knob inference mechanism to align with the user’s specific needs. These mechanisms ensure that KnobGen can flexibly generate images from both novice sketches and those drawn by seasoned artists. This maintains control over the final output while preserving the natural appearance of the image, as evidenced on the MultiGen-20M dataset and a newly collected sketch dataset.
最近扩散模型(Diffusion Models)的进展极大地推动了文本到图像(T2I)生成技术的发展,但这些模型在平衡精细粒度的精度与高级控制方面常遇到困难。例如,ControlNet和T2I-Adapter这类方法擅长遵循资深艺术家的草图,但它们往往过于僵化,会复制新手用户草图中的无意缺陷。同时,基于粗略草图的方法,如基于草图抽象框架的方法,虽然提供了更易于处理的输入,但却缺乏用于专业用途所需的精确控制。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了KnobGen——一个双路径框架,它通过无缝适应不同级别的草图复杂性和用户技能来实现基于草图的图像生成的民主化。KnobGen使用粗粒度控制器(CGC)模块用于高级语义和细粒度控制器(FGC)模块用于详细调整。这两种模块的相对强度可以通过我们的旋钮推断机制进行调整,以符合用户的特定需求。这些机制确保了KnobGen能够灵活地生成从新手草图到资深艺术家所绘草图生成的图像。这保持了对最终输出的控制,同时保持了图像的自然外观,这在MultiGen-20M数据集和新收集的草图数据集上得到了证实。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025 Workshop on CVEU
Summary
扩散模型在文本转图像生成方面的最新进展已在提高精细粒度精度与高级控制之间达到平衡。提出的KnobGen框架通过双路径设计,实现了对不同复杂度草图和用户技能的适应性调整。该框架包含粗粒度控制器和细粒度控制器模块,通过旋钮推理机制调整两者的相对强度,以满足用户的特定需求。确保生成图像既符合新手草图,又能适应专业艺术家的绘图,从而在控制最终输出和保持图像自然外观之间取得平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本转图像生成取得显著进展,但需平衡精细粒度精度与高级控制。
- KnobGen框架通过双路径设计应对不同复杂度草图和用户技能的差异。
- KnobGen包含粗粒度控制器和细粒度控制器模块,分别负责高级语义和详细修饰。
- 通过旋钮推理机制调整两个控制器的相对强度。
- KnobGen能够适应新手和专业艺术家的草图,生成相应的图像。
- KnobGen在保持图像自然外观的同时,提供了对最终输出的精细控制。
点此查看论文截图


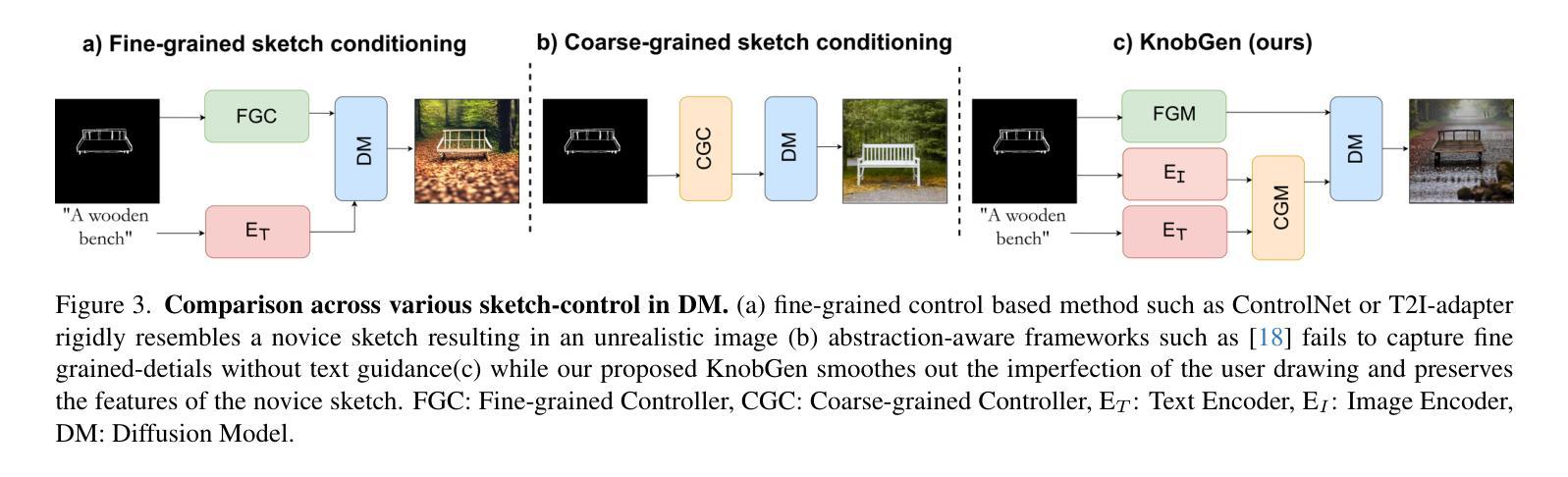


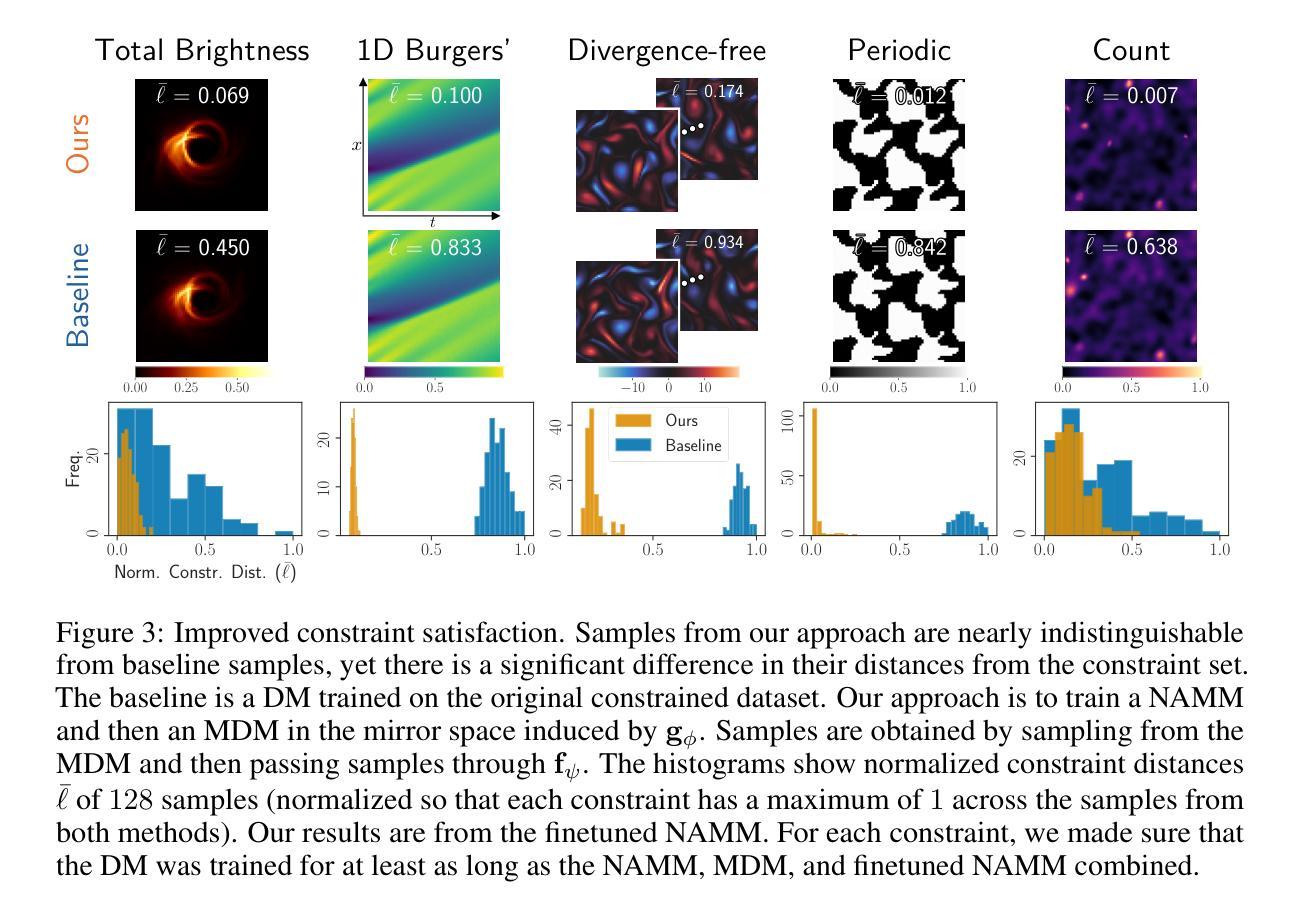
Neural Approximate Mirror Maps for Constrained Diffusion Models
Authors:Berthy T. Feng, Ricardo Baptista, Katherine L. Bouman
Diffusion models excel at creating visually-convincing images, but they often struggle to meet subtle constraints inherent in the training data. Such constraints could be physics-based (e.g., satisfying a PDE), geometric (e.g., respecting symmetry), or semantic (e.g., including a particular number of objects). When the training data all satisfy a certain constraint, enforcing this constraint on a diffusion model makes it more reliable for generating valid synthetic data and solving constrained inverse problems. However, existing methods for constrained diffusion models are restricted in the constraints they can handle. For instance, recent work proposed to learn mirror diffusion models (MDMs), but analytical mirror maps only exist for convex constraints and can be challenging to derive. We propose neural approximate mirror maps (NAMMs) for general, possibly non-convex constraints. Our approach only requires a differentiable distance function from the constraint set. We learn an approximate mirror map that transforms data into an unconstrained space and a corresponding approximate inverse that maps data back to the constraint set. A generative model, such as an MDM, can then be trained in the learned mirror space and its samples restored to the constraint set by the inverse map. We validate our approach on a variety of constraints, showing that compared to an unconstrained diffusion model, a NAMM-based MDM substantially improves constraint satisfaction. We also demonstrate how existing diffusion-based inverse-problem solvers can be easily applied in the learned mirror space to solve constrained inverse problems.
扩散模型在生成视觉上有说服力的图像方面表现出色,但在满足训练数据中的微妙约束时常常遇到困难。这些约束可能是基于物理的(例如,满足偏微分方程)、几何的(例如,保持对称性)或语义的(例如,包含特定数量的对象)。当训练数据都满足某个约束时,对扩散模型强制实施此约束使其生成有效合成数据和解决约束逆问题更加可靠。然而,现有的约束扩散模型方法在处理约束方面存在局限性。例如,最近的工作提出了学习镜像扩散模型(MDMs),但解析镜像映射只存在于凸约束中,并且推导可能具有挑战性。我们针对一般、可能是非凸约束,提出了神经近似镜像映射(NAMMs)。我们的方法只需要一个可区分的距离函数来自约束集。我们学习一个将数据转换到无约束空间的近似镜像映射,以及一个相应的近似逆映射将数据返回到约束集。然后,可以在学习的镜像空间中训练如MDM这样的生成模型,并通过逆映射将其样本恢复到约束集。我们通过多种约束验证了我们的方法,结果表明,与无约束的扩散模型相比,基于NAMM的MDM在约束满足方面有了实质性的改进。我们还演示了如何在学习的镜像空间中轻松应用现有的基于扩散的逆问题求解器来解决约束逆问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
本文提出一种针对扩散模型的新方法,通过神经近似镜像映射(NAMMs)处理各类约束,包括物理、几何和语义约束。该方法在约束满足的训练数据基础上,提高扩散模型生成有效合成数据和解决约束逆问题的能力。通过在镜像空间学习映射,使扩散模型能在该空间进行训练,并通过逆向映射将数据恢复到约束集内。实验证明,此方法显著提高了约束满足的程度。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成视觉上令人信服的图像方面表现出色,但在满足训练数据中的微妙约束方面经常遇到困难。
- 当训练数据满足特定约束时,对扩散模型强制执行此约束可提高其生成有效合成数据和解决约束逆问题的能力。
- 现有处理约束的扩散模型方法受到限制,只能处理特定类型的约束。
- 提出了一种新的方法——神经近似镜像映射(NAMMs),用于处理一般、可能是非凸的约束。
- 该方法只需要一个可区分的距离函数来自约束集。
- 通过学习将数据转换为无约束空间,并学习相应的逆向映射将数据返回到约束集,实现了在镜像空间中的扩散模型训练。
点此查看论文截图

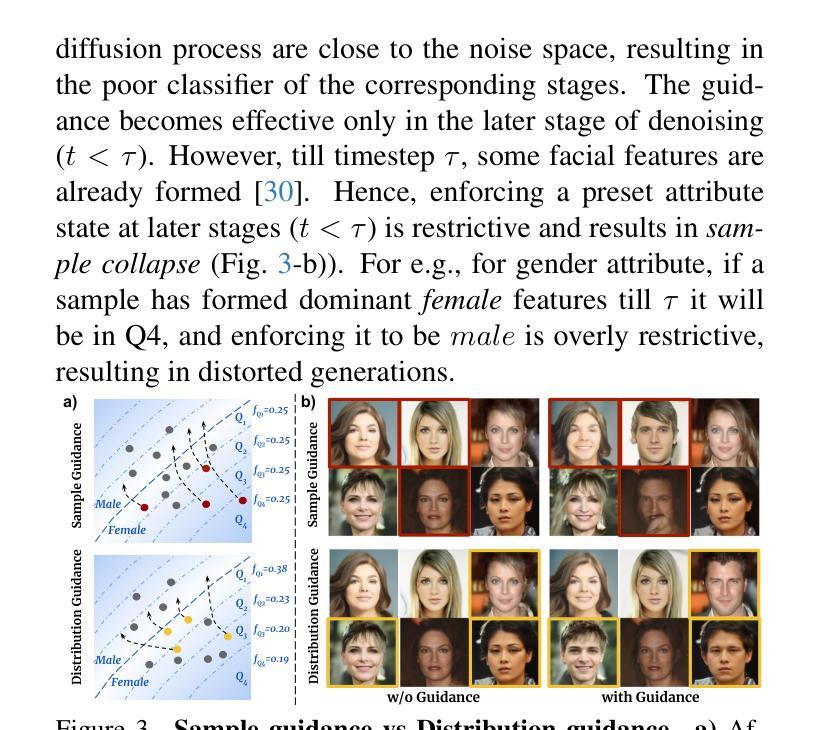
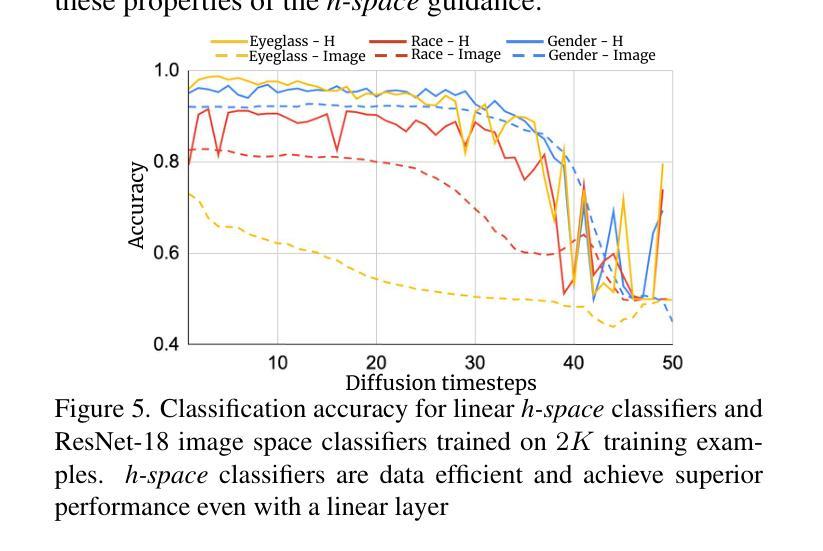
Balancing Act: Distribution-Guided Debiasing in Diffusion Models
Authors:Rishubh Parihar, Abhijnya Bhat, Abhipsa Basu, Saswat Mallick, Jogendra Nath Kundu, R. Venkatesh Babu
Diffusion Models (DMs) have emerged as powerful generative models with unprecedented image generation capability. These models are widely used for data augmentation and creative applications. However, DMs reflect the biases present in the training datasets. This is especially concerning in the context of faces, where the DM prefers one demographic subgroup vs others (eg. female vs male). In this work, we present a method for debiasing DMs without relying on additional data or model retraining. Specifically, we propose Distribution Guidance, which enforces the generated images to follow the prescribed attribute distribution. To realize this, we build on the key insight that the latent features of denoising UNet hold rich demographic semantics, and the same can be leveraged to guide debiased generation. We train Attribute Distribution Predictor (ADP) - a small mlp that maps the latent features to the distribution of attributes. ADP is trained with pseudo labels generated from existing attribute classifiers. The proposed Distribution Guidance with ADP enables us to do fair generation. Our method reduces bias across single/multiple attributes and outperforms the baseline by a significant margin for unconditional and text-conditional diffusion models. Further, we present a downstream task of training a fair attribute classifier by rebalancing the training set with our generated data.
扩散模型(DMs)作为强大的生成模型,具有前所未有的图像生成能力。这些模型广泛应用于数据增强和创意应用。然而,DMs会反映出训练数据集存在的偏见。在人脸的背景下,DM更倾向于某一人口统计亚组而非其他亚组(例如,女性与男性),这特别令人担忧。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种不需要额外数据或模型重新训练的方法来对DMs进行去偏处理。具体来说,我们提出了分布指导(Distribution Guidance)的方法,强制生成的图像遵循规定的属性分布。为此,我们建立在这样一个关键见解之上:去噪UNet的潜在特征包含丰富的人口统计语义,可以被用来引导去偏生成。我们训练了属性分布预测器(ADP)——一个可以将潜在特征映射到属性分布的小型多层感知器(mlp)。ADP使用来自现有属性分类器的伪标签进行训练。提出的带有ADP的分布指导使我们能够实现公平生成。我们的方法降低了单一/多个属性上的偏见,并且在无条件和文本条件扩散模型上都大幅超越了基线方法。此外,我们还提出了通过利用我们的生成数据对训练集进行重新平衡来训练公平属性分类器的下游任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2024. Project Page : https://ab-34.github.io/balancing_act/
Summary
扩散模型(DMs)是一种强大的生成模型,具有前所未有的图像生成能力,广泛应用于数据增强和创意应用。然而,DMs会反映出训练数据集中的偏见,特别是在面部数据上,更倾向于某一人群(如女性与男性)。本研究提出了一种无需额外数据或模型重训的去除DM偏见的方法——分布指导。我们利用去噪UNet的潜在特征具有丰富的种族语义这一关键见解,并以此来实现去偏生成。我们训练了一个属性分布预测器(ADP),一个可以将潜在特征映射到属性分布的小mlp。ADP使用来自现有属性分类器的伪标签进行训练。通过ADP实现的分布指导和属性分布预测器,我们的方法能够在单一或多属性上减少偏见,并在无条件和文本条件扩散模型上显著优于基线。此外,我们还提出了使用生成数据重新平衡训练集来训练公平属性分类器的下游任务。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)具有强大的图像生成能力,广泛应用于数据增强和创意应用。
- DMs会反映出训练数据中的偏见,特别是在面部数据上。
- 本研究提出了一种新的去除DM偏见的方法——分布指导。
- 分布指导利用去噪UNet的潜在特征来实现去偏生成。
- 提出了属性分布预测器(ADP),将潜在特征映射到属性分布。
- ADP使用伪标签进行训练,显著优于基线方法。
点此查看论文截图