⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-12 更新
MARS: a Multimodal Alignment and Ranking System for Few-Shot Segmentation
Authors:Nico Catalano, Stefano Samele, Paolo Pertino, Matteo Matteucci
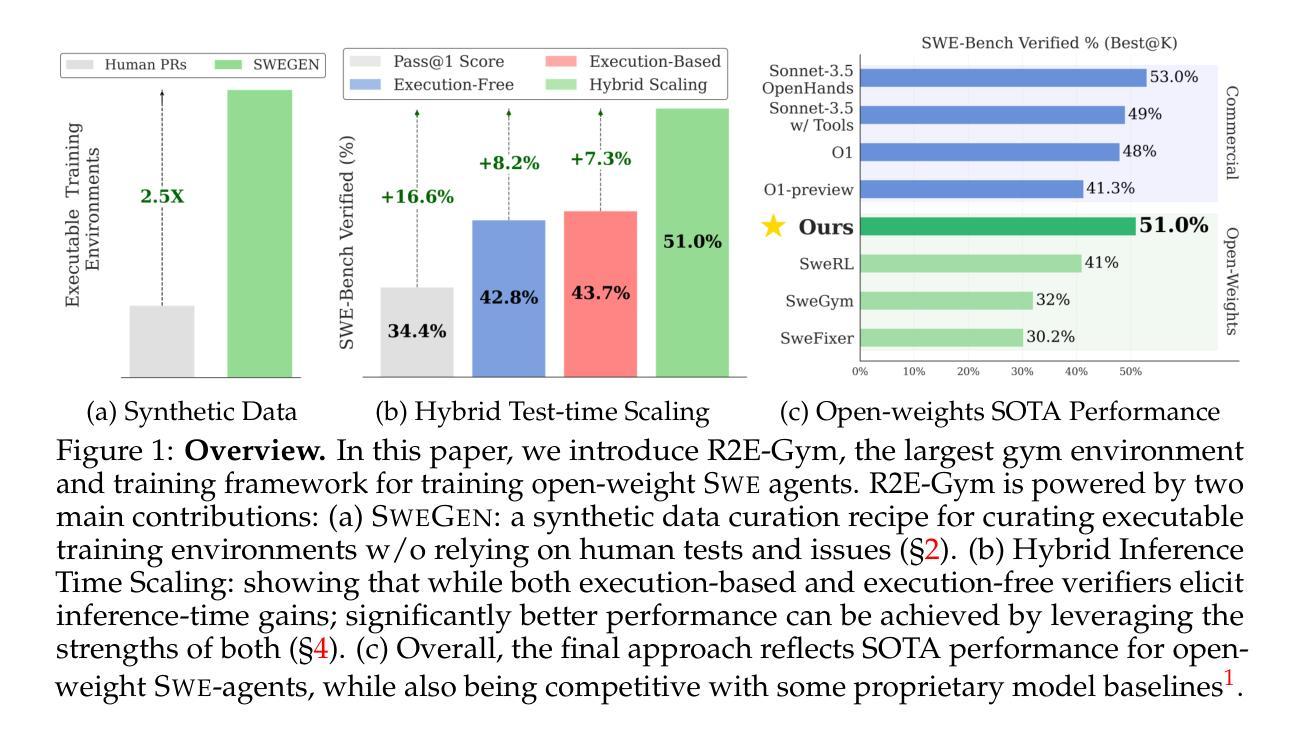
Current Few Shot Segmentation literature lacks a mask selection method that goes beyond visual similarity between the query and example images, leading to suboptimal predictions. We present MARS, a plug-and-play ranking system that leverages multimodal cues to filter and merge mask proposals robustly. Starting from a set of mask predictions for a single query image, we score, filter, and merge them to improve results. Proposals are evaluated using multimodal scores computed at local and global levels. Extensive experiments on COCO-20i, Pascal-5i, LVIS-92i, and FSS-1000 demonstrate that integrating all four scoring components is crucial for robust ranking, validating our contribution. As MARS can be effortlessly integrated with various mask proposal systems, we deploy it across a wide range of top-performer methods and achieve new state-of-the-art results on multiple existing benchmarks. Code will be available upon acceptance.
当前的小样本分割文献缺乏一种超越查询图像和示例图像之间视觉相似性的掩膜选择方法,导致预测结果不理想。我们提出了MARS,这是一个即插即用的排名系统,它利用多模式线索来稳健地过滤和合并掩膜提案。从单个查询图像的掩膜预测集合开始,我们对它们进行评分、过滤和合并,以提高结果。提案是使用在局部和全局级别计算的多模式分数进行评估的。在COCO-20i、Pascal-5i、LVIS-92i和FSS-1000上的大量实验表明,整合所有四个评分组件对于稳健排名至关重要,验证了我们所做的贡献。由于MARS可以轻松地与各种掩膜提案系统集成,因此我们将其部署在多种高性能方法中,并在多个现有基准测试上实现了最新的最新结果。代码将在接受后提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对现有Few Shot Segmentation文献中缺乏超越查询图像和示例图像之间视觉相似性的掩膜选择方法的问题,提出了一种名为MARS的即插即用排名系统。该系统利用多模态线索来过滤和合并掩膜提议,以提高预测结果的鲁棒性。通过对单一查询图像的多个掩膜预测进行评分、过滤和合并,结合局部和全局的多模态评分对提议进行评估。在多个基准数据集上的实验验证了整合所有四个评分组件对于稳健排名的重要性,并证实了MARS的贡献。由于MARS可以轻松地与各种掩膜提议系统相结合,因此将其部署在多种顶级性能方法中,并在多个现有基准数据集上实现了新的最先进的成果。
Key Takeaways
- 当前Few Shot Segmentation文献在掩膜选择方法上有所欠缺,主要基于视觉相似性,导致预测结果不理想。
- MARS系统是一种利用多模态线索的即插即用排名系统,旨在改进掩膜提议的过滤和合并过程。
- MARS通过评分、过滤和合并针对单一查询图像的多个掩膜预测来提高结果。
- 提议的评价结合了局部和全局的多模态评分。
- 在多个基准数据集上的实验表明,整合所有四个评分组件对于实现稳健的排名至关重要。
- MARS可以轻松地与各种掩膜提议系统结合,提高了其在实际应用中的通用性。
点此查看论文截图

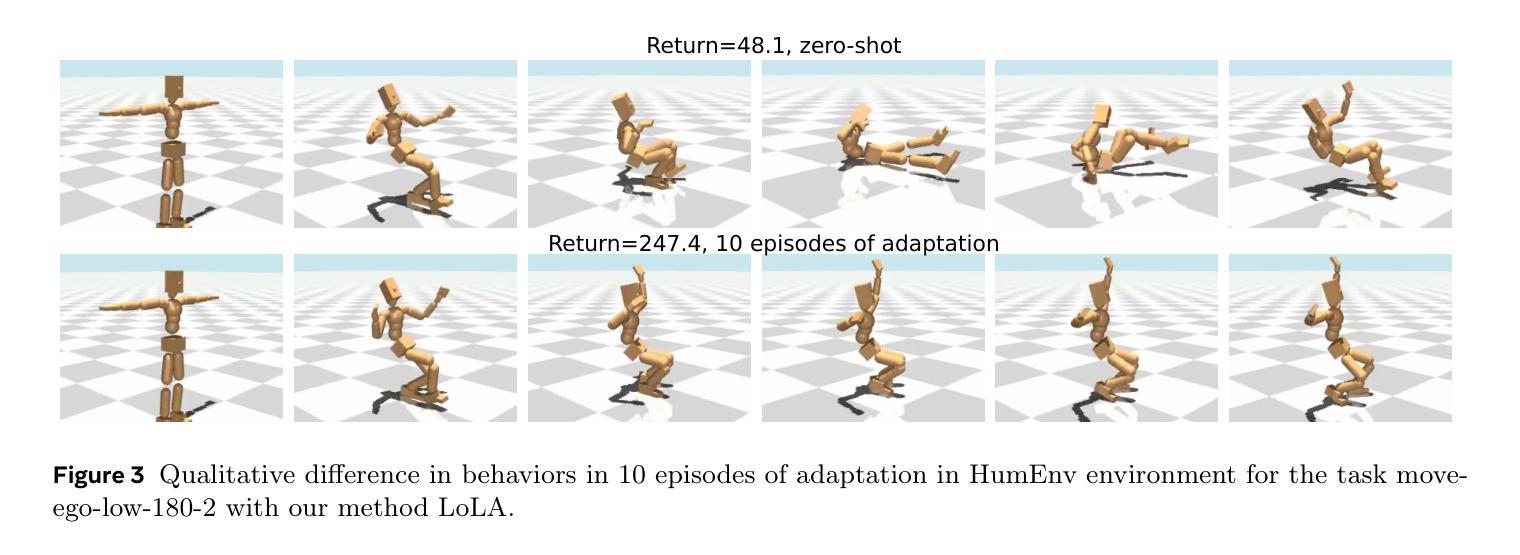
Fast Adaptation with Behavioral Foundation Models
Authors:Harshit Sikchi, Andrea Tirinzoni, Ahmed Touati, Yingchen Xu, Anssi Kanervisto, Scott Niekum, Amy Zhang, Alessandro Lazaric, Matteo Pirotta
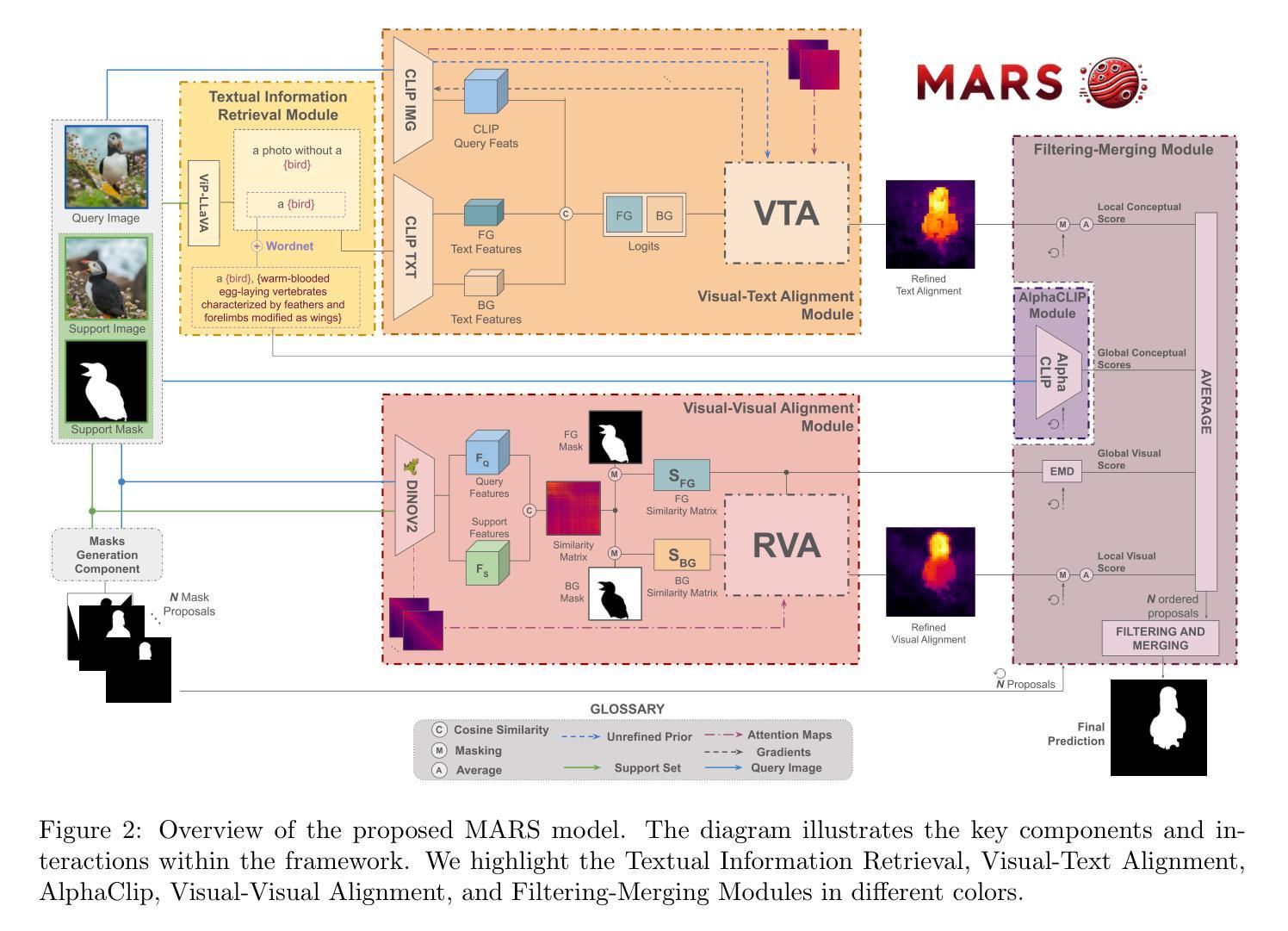
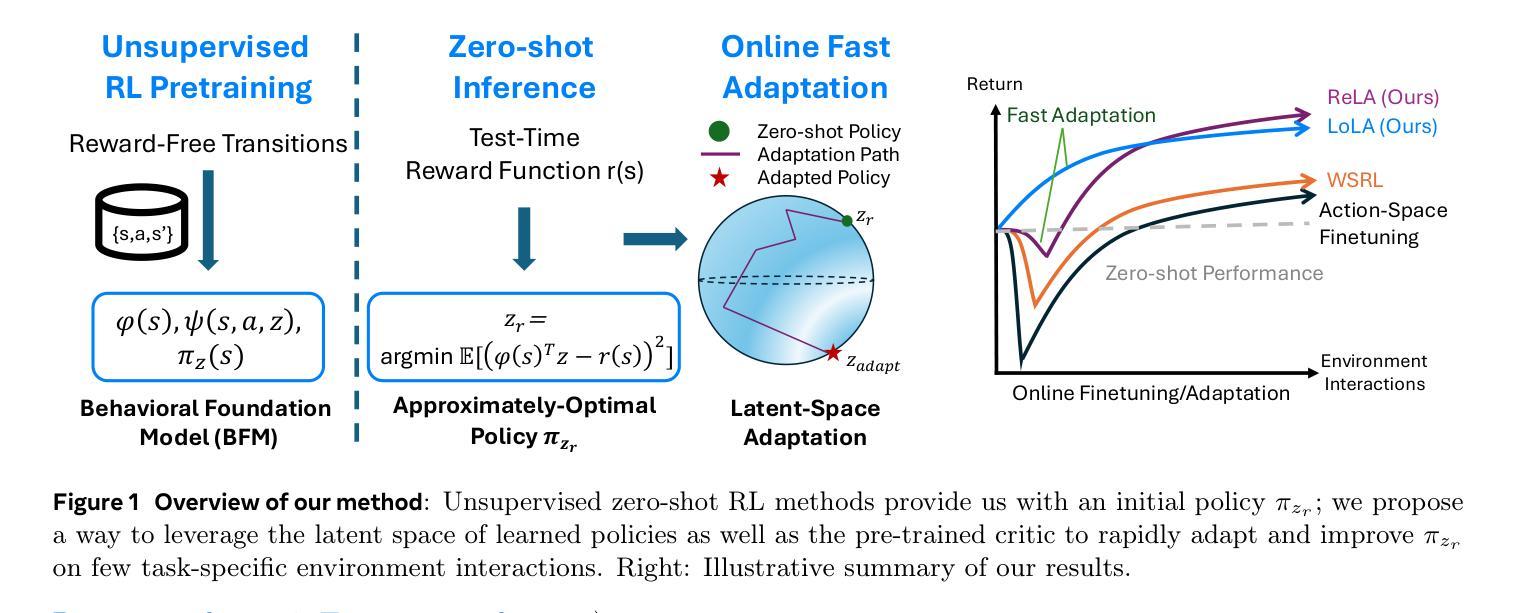
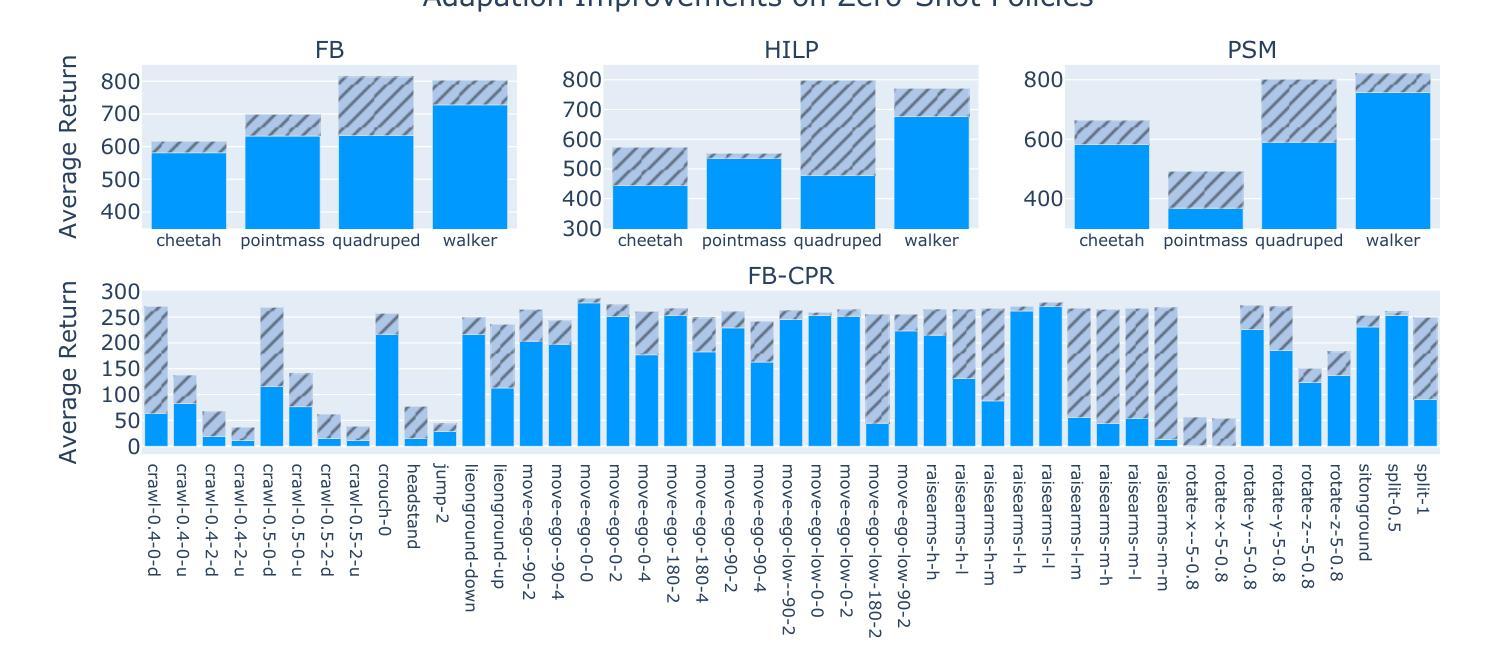
Unsupervised zero-shot reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for pretraining behavioral foundation models (BFMs), enabling agents to solve a wide range of downstream tasks specified via reward functions in a zero-shot fashion, i.e., without additional test-time learning or planning. This is achieved by learning self-supervised task embeddings alongside corresponding near-optimal behaviors and incorporating an inference procedure to directly retrieve the latent task embedding and associated policy for any given reward function. Despite promising results, zero-shot policies are often suboptimal due to errors induced by the unsupervised training process, the embedding, and the inference procedure. In this paper, we focus on devising fast adaptation strategies to improve the zero-shot performance of BFMs in a few steps of online interaction with the environment while avoiding any performance drop during the adaptation process. Notably, we demonstrate that existing BFMs learn a set of skills containing more performant policies than those identified by their inference procedure, making them well-suited for fast adaptation. Motivated by this observation, we propose both actor-critic and actor-only fast adaptation strategies that search in the low-dimensional task-embedding space of the pre-trained BFM to rapidly improve the performance of its zero-shot policies on any downstream task. Notably, our approach mitigates the initial “unlearning” phase commonly observed when fine-tuning pre-trained RL models. We evaluate our fast adaptation strategies on top of four state-of-the-art zero-shot RL methods in multiple navigation and locomotion domains. Our results show that they achieve 10-40% improvement over their zero-shot performance in a few tens of episodes, outperforming existing baselines.
无监督零样本强化学习(RL)已经成为预训练行为基础模型(BFMs)的强大范式,它使智能体能够以零样本方式解决通过奖励函数指定的各种下游任务,即无需额外的测试时间学习和规划。这是通过学习与相应近优行为一起的自我监督任务嵌入,并融入推理程序来直接检索给定奖励函数的潜在任务嵌入和相关策略来实现的。尽管结果充满希望,但由于无监督训练过程、嵌入和推理程序所引起的错误,零样本策略通常表现不佳。在本文中,我们专注于设计快速适应策略,以提高行为基础模型在少量在线环境交互步骤中的零样本性能,同时避免适应过程中的任何性能下降。值得注意的是,我们证明现有的BFMs学习到的技能集包含比其推理程序所确定的更有效策略更多的高性能策略,使它们非常适合快速适应。受这一观察结果的启发,我们提出了基于actor-critic和actor-only的快速适应策略,在预训练BFM的低维任务嵌入空间中搜索,以迅速提高其在任何下游任务上的零样本策略性能。值得注意的是,我们的方法缓解了微调预训练RL模型时通常观察到的初始“遗忘”阶段。我们在四种最先进的零样本RL方法之上评估了我们的快速适应策略,涉及多个导航和移动领域。结果表明,它们在几十集内实现了对其零样本性能的10-40%的提升,超过了现有基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages
Summary
该论文探讨了无监督零步强化学习(RL)中的预训练行为基础模型(BFMs)的快速适应策略。通过预训练过程中的自监督任务嵌入和相关近似最优行为,模型能够在无需额外测试时间学习和规划的情况下,以零步方式解决各种下游任务。文章聚焦于设计快速适应策略来提升BFMs的零步性能,这些策略能够在与环境的少量在线交互步骤中发挥作用,同时避免适应过程中的性能下降。实验表明,所提出的方法在多个导航和动作领域实现了相较于零步性能的显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- 无监督零步强化学习能够通过预训练生成一种行为基础模型(BFMs),该模型能够解决多种下游任务。
- BFMs通过自我监督任务嵌入和对应的近似最优行为进行训练,能实现对任意奖励函数的直接推断。
- 零步策略常因无监督训练过程、嵌入和推断程序产生的错误而表现不佳。
- 文章提出了针对BFMs的快速适应策略,旨在提升其在少量在线交互步骤中的零步性能。
- 观察发现,现有BFMs学习到的技能集包含比推断程序更高效的策略,适合快速适应。
- 提出了基于actor-critic和actor-only的快速适应策略,通过搜索预训练BFM的低维任务嵌入空间来迅速提升其在下游任务上的零步策略性能。
点此查看论文截图

Few-Shot Adaptation of Grounding DINO for Agricultural Domain
Authors:Rajhans Singh, Rafael Bidese Puhl, Kshitiz Dhakal, Sudhir Sornapudi
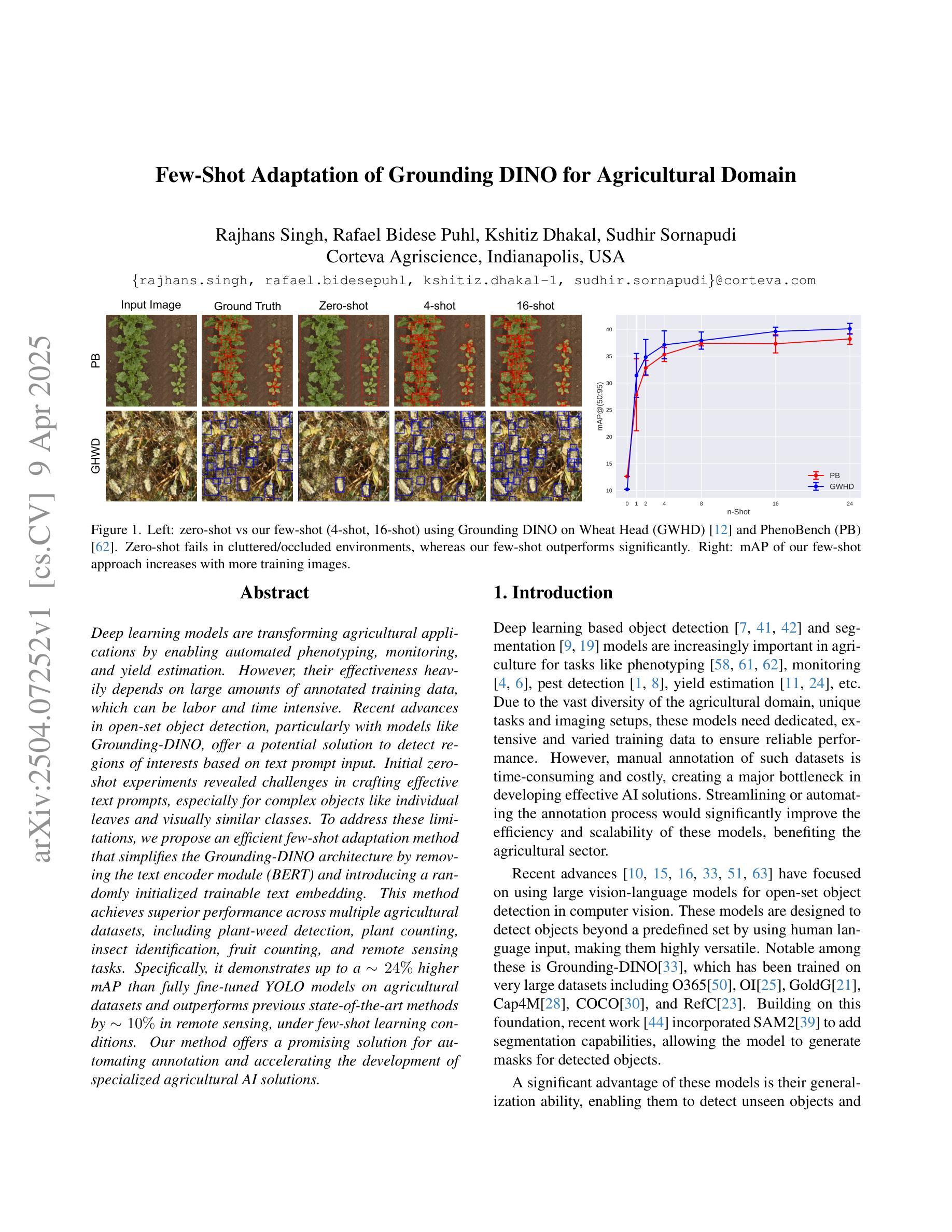
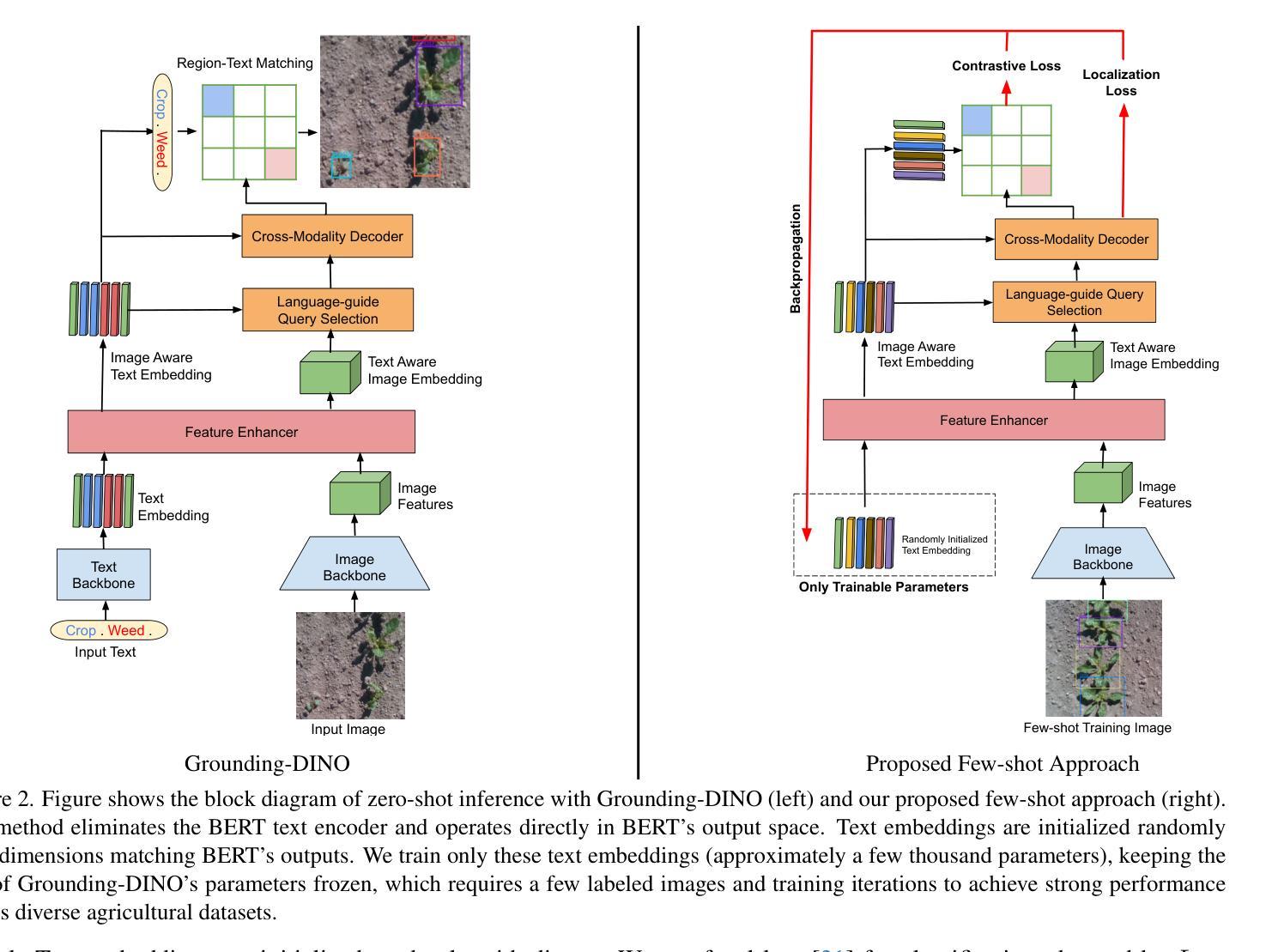
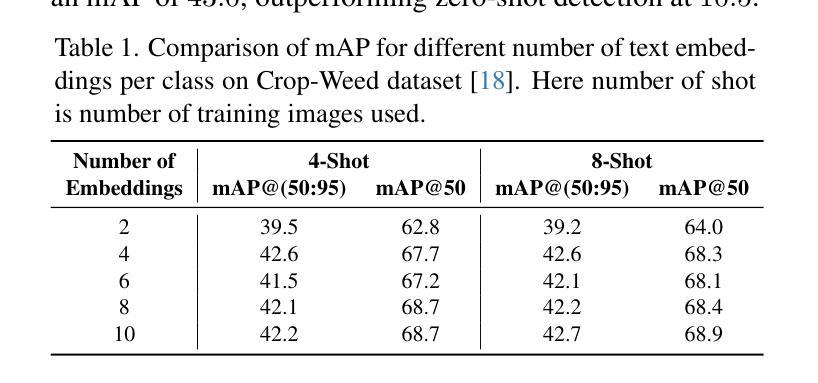
Deep learning models are transforming agricultural applications by enabling automated phenotyping, monitoring, and yield estimation. However, their effectiveness heavily depends on large amounts of annotated training data, which can be labor and time intensive. Recent advances in open-set object detection, particularly with models like Grounding-DINO, offer a potential solution to detect regions of interests based on text prompt input. Initial zero-shot experiments revealed challenges in crafting effective text prompts, especially for complex objects like individual leaves and visually similar classes. To address these limitations, we propose an efficient few-shot adaptation method that simplifies the Grounding-DINO architecture by removing the text encoder module (BERT) and introducing a randomly initialized trainable text embedding. This method achieves superior performance across multiple agricultural datasets, including plant-weed detection, plant counting, insect identification, fruit counting, and remote sensing tasks. Specifically, it demonstrates up to a $\sim24%$ higher mAP than fully fine-tuned YOLO models on agricultural datasets and outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods by $\sim10%$ in remote sensing, under few-shot learning conditions. Our method offers a promising solution for automating annotation and accelerating the development of specialized agricultural AI solutions.
深度学习模型通过实现自动化表型分析、监测和产量估算,正在改变农业应用。然而,它们的有效性在很大程度上依赖于大量的注释训练数据,这可能需要大量的劳动和时间。最近开放集目标检测的进展,特别是像Grounding-DINO这样的模型,提供了一种基于文本提示输入检测感兴趣区域的潜在解决方案。初步的零样本实验表明,在构建有效的文本提示方面存在挑战,特别是对于个体叶片和视觉相似类别等复杂对象。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种有效的少样本适应方法,它通过移除Grounding-DINO架构中的文本编码器模块(BERT),并引入一个随机初始化的可训练文本嵌入来简化模型。该方法在多个农业数据集上表现出卓越的性能,包括植物杂草检测、植物计数、昆虫识别、水果计数和遥感任务。具体来说,它在农业数据集上比完全微调过的YOLO模型高出约24%的mAP,并在少样本学习条件下,遥感任务上比以前的先进方法高出约10%。我们的方法为自动化注释和加速专业化农业AI解决方案的开发提供了有前景的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习模型正在通过实现自动化表型分析、监控和产量估计来变革农业应用。然而,其有效性严重依赖于大量的注释训练数据,这可能是劳动密集型的和时间密集型的。最近开放集合对象检测的进步,特别是Grounding-DINO等模型,提供了一种基于文本提示输入检测感兴趣区域的潜在解决方案。为了解决文本提示在复杂对象(如单个叶子)和视觉相似类别方面的局限性,我们提出了一种有效的few-shot适应方法,简化Grounding-DINO架构,移除文本编码器模块(BERT),并引入随机初始化的可训练文本嵌入。该方法在多个农业数据集上表现优越,包括植物杂草检测、植物计数、昆虫识别、水果计数和遥感任务。特别是,在农业数据集上,它的平均精度(mAP)比完全微调过的YOLO模型高出约24%,并且在遥感领域少样本学习条件下优于以前的最先进方法约10%。我们的方法为解决自动化注释和加速专业农业人工智能解决方案的开发提供了有前途的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型正在农业应用中发挥重要作用,但在实际应用中受限于大规模注释训练数据的获取难度。
- Grounding-DINO模型在基于文本提示的感兴趣区域检测方面具有潜力。
- 解决复杂对象和视觉相似类别的文本提示挑战是当前的限制。
- 提出了一种简化的few-shot适应方法,通过移除文本编码器模块并引入可训练文本嵌入来提高性能。
- 该方法在多个农业数据集上表现优越,包括植物杂草检测、植物计数等任务。
- 在农业数据集上的平均精度比YOLO模型高出约24%,并显著优于遥感领域的现有方法。
点此查看论文截图