⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-12 更新
Cat, Rat, Meow: On the Alignment of Language Model and Human Term-Similarity Judgments
Authors:Lorenz Linhardt, Tom Neuhäuser, Lenka Tětková, Oliver Eberle
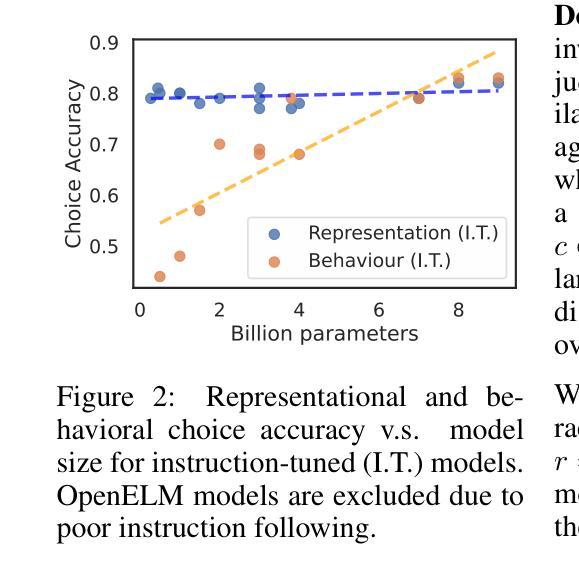
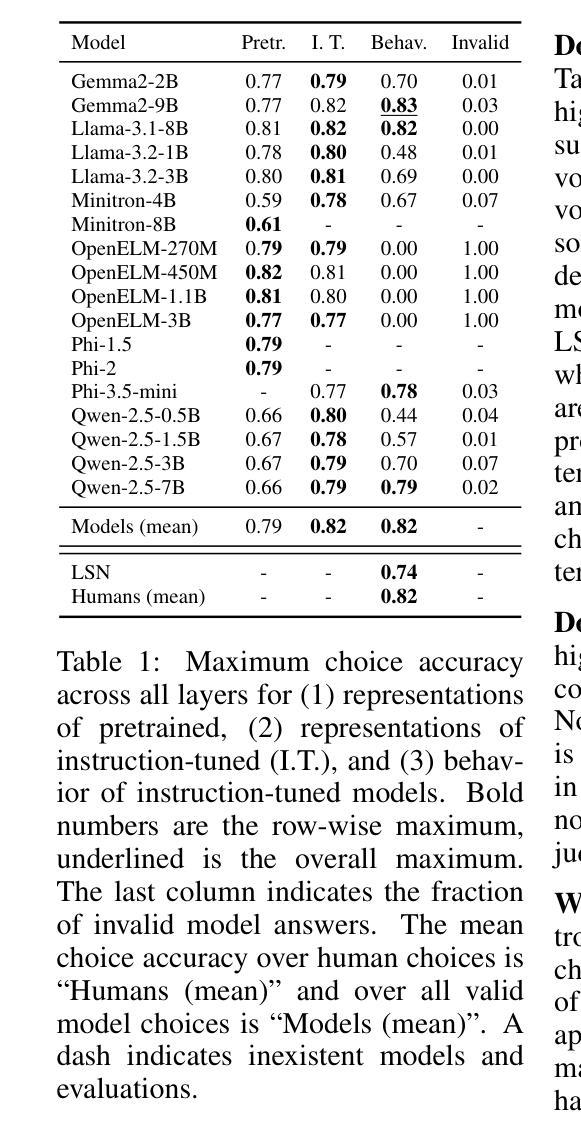
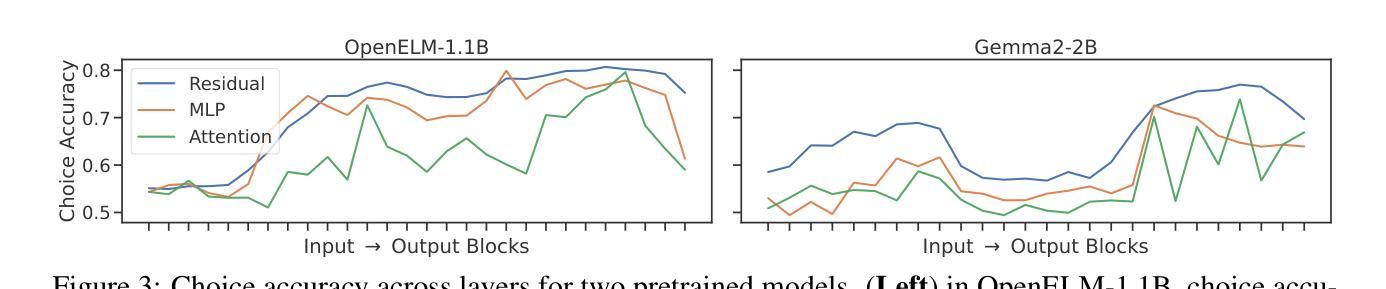
Small and mid-sized generative language models have gained increasing attention. Their size and availability make them amenable to being analyzed at a behavioral as well as a representational level, allowing investigations of how these levels interact. We evaluate 32 publicly available language models for their representational and behavioral alignment with human similarity judgments on a word triplet task. This provides a novel evaluation setting to probe semantic associations in language beyond common pairwise comparisons. We find that (1) even the representations of small language models can achieve human-level alignment, (2) instruction-tuned model variants can exhibit substantially increased agreement, (3) the pattern of alignment across layers is highly model dependent, and (4) alignment based on models’ behavioral responses is highly dependent on model size, matching their representational alignment only for the largest evaluated models.
小型和中型生成式语言模型正受到越来越多的关注。它们的大小和可用性使其能够在行为学和代表性层面进行分析,从而研究这两个层面如何相互作用。我们评估了32个公开可用的语言模型,以它们在词三元组任务中与人类相似性判断的代表性和行为一致性为标准。这为除了常见的配对比较之外的语言语义关联提供了一个新型评估环境。我们发现:(1)即使是小型语言模型的表示也可以达到人类水平的对齐;(2)经过指令调整的模型变体可以表现出大幅增加的一致性;(3)对齐模式的跨层性高度依赖于模型;(4)基于模型行为反应的对齐高度依赖于模型的大小,仅在与所评估的最大模型匹配时,才与代表性对齐相匹配。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 Workshop on Representational Alignment (Re-Align)
Summary
小型和中等规模的生成式语言模型越来越受到关注。这些模型的大小和可用性使其既可以在行为层面进行分析,也可以在表征层面进行分析,并允许研究这两个层面之间的相互作用。本文评估了32个公开可用的语言模型,在词三元组任务上对人类相似性判断进行表征和行为对齐。这为在超越常见二元对比的情境下探查语言中的语义关联提供了一个新的评估环境。研究发现:1)即使是小型语言模型的表征也能达到人类水平的对齐;2)指令微调模型变体可以表现出大幅增加的共识;3)对齐模式的层间变化在很大程度上取决于模型本身;4)基于模型行为反应的校准高度依赖于模型规模,仅在评价的最大模型中与其表征对齐相匹配。
Key Takeaways
- 小型和中等规模的生成式语言模型正受到越来越多的关注。
- 在词三元组任务上评估语言模型与人类相似性判断的对齐情况,为评估语言模型的语义关联提供了新环境。
- 小型语言模型的表征也可以达到人类水平的对齐。
- 指令微调模型在某些情况下可以表现出更高的共识。
- 语言模型的对齐模式在不同层次上的表现差异较大,这取决于模型本身的特性。
- 基于模型行为反应的校准与模型规模紧密相关。
点此查看论文截图

C3PO: Critical-Layer, Core-Expert, Collaborative Pathway Optimization for Test-Time Expert Re-Mixing
Authors:Zhongyang Li, Ziyue Li, Tianyi Zhou
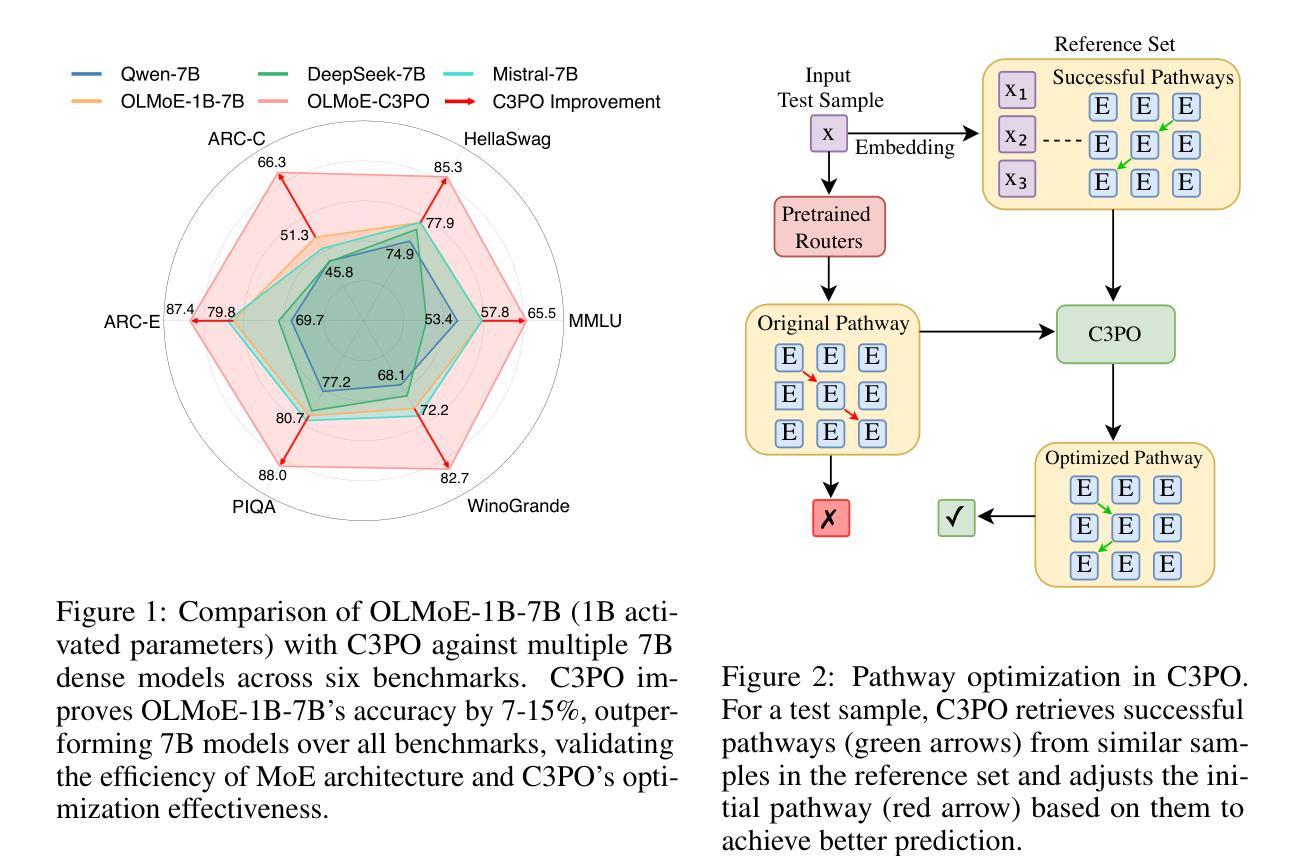
Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) Large Language Models (LLMs) suffer from severely sub-optimal expert pathways-our study reveals that naive expert selection learned from pretraining leaves a surprising 10-20% accuracy gap for improvement. Motivated by this observation, we develop a novel class of test-time optimization methods to re-weight or “re-mixing” the experts in different layers jointly for each test sample. Since the test sample’s ground truth is unknown, we propose to optimize a surrogate objective defined by the sample’s “successful neighbors” from a reference set of samples. We introduce three surrogates and algorithms based on mode-finding, kernel regression, and the average loss of similar reference samples/tasks. To reduce the cost of optimizing whole pathways, we apply our algorithms merely to the core experts’ mixing weights in critical layers, which enjoy similar performance but save significant computation. This leads to “Critical-Layer, Core-Expert, Collaborative Pathway Optimization (C3PO)”. We apply C3PO to two recent MoE LLMs and examine it on six widely-used benchmarks. It consistently improves the base model by 7-15% in accuracy and outperforms widely used test-time learning baselines, e.g., in-context learning and prompt/prefix tuning, by a large margin. Moreover, C3PO enables MoE LLMs with 1-3B active parameters to outperform LLMs of 7-9B parameters, hence improving MoE’s advantages on efficiency. Our thorough ablation study further sheds novel insights on achieving test-time improvement on MoE.
混合专家(MoE)大型语言模型(LLM)存在严重的专家路径次优问题——我们的研究表明,从预训练中学到的简单专家选择留下了令人惊讶的10-20%的准确度提升空间。受这一观察的启发,我们开发了一类新型的测试时间优化方法,针对每个测试样本,重新权重或“重新混合”不同层的专家。由于测试样本的真实值未知,我们提出通过参考样本集中样本的“成功邻居”来优化替代目标。我们引入了三种替代方法和基于模式寻找、核回归以及类似参考样本/任务平均损失的算法。为了减少优化整个路径的成本,我们将算法仅应用于关键层中核心专家的混合权重,这些核心专家享有相似的性能但节省了大量的计算。这导致了“关键层、核心专家、协同路径优化(C3PO)”。我们将C3PO应用于最近的两个MoE LLM,并在六个广泛使用的基准测试上进行了测试。它始终提高了基础模型的准确度7-15%,并且大幅超越了广泛使用的测试时间学习基线,如上下文学习和提示/前缀调整。此外,C3PO使具有1-3B活跃参数MoE LLM的性能超越了具有7-9B参数的LLM,从而提高了MoE在效率方面的优势。我们的彻底消融研究进一步揭示了MoE在测试时间改进方面的新见解。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于专家混合的大型语言模型(LLM)存在专家路径选择问题,研究发现预训练中的专家选择会留下高达10%-20%的准确性提升空间。为优化此问题,我们提出了一种新颖的在线测试优化方法,针对不同测试样本,共同调整不同层级专家的权重。由于测试样本的真实标签未知,我们通过参考集中样本的成功邻居来定义替代目标并进行优化。我们提出了基于模式寻找、核回归和相似参考样本平均损失的三种替代方案和算法。为降低优化整个路径的成本,我们的算法仅应用于关键层核心专家的混合权重,在保证性能的同时显著降低计算成本,形成“关键层、核心专家、协同路径优化(C3PO)”。C3PO在近期的大型MoE LLM模型上表现出卓越性能,在六个广泛使用的基准测试中,其准确率较基础模型提高了7%-15%,并大幅超越了测试时间学习基线方法,如上下文学习和提示前缀调整等。此外,C3PO使得具有1-3B活动参数的大型MoE LLM模型性能超越具有7-9B参数的LLM模型,进一步凸显MoE在效率方面的优势。我们的深入研究揭示了提升MoE测试时间性能的全新洞察和解决方案。
关键发现
- 基于专家混合的大型语言模型(LLM)存在专家路径选择问题,存在显著的准确性提升空间。
- 提出了一种新颖的在线测试优化方法,通过调整不同层级专家的权重来解决专家路径选择问题。
- 利用参考集中样本的成功邻居定义替代目标并进行优化。
- 提出了三种基于模式寻找、核回归和相似参考样本平均损失的替代方案和算法。
- C3PO算法仅优化关键层核心专家的混合权重,显著降低计算成本。
- C3PO在MoE LLM模型上显著提高准确性,并优于其他测试时间学习方法。
点此查看论文截图

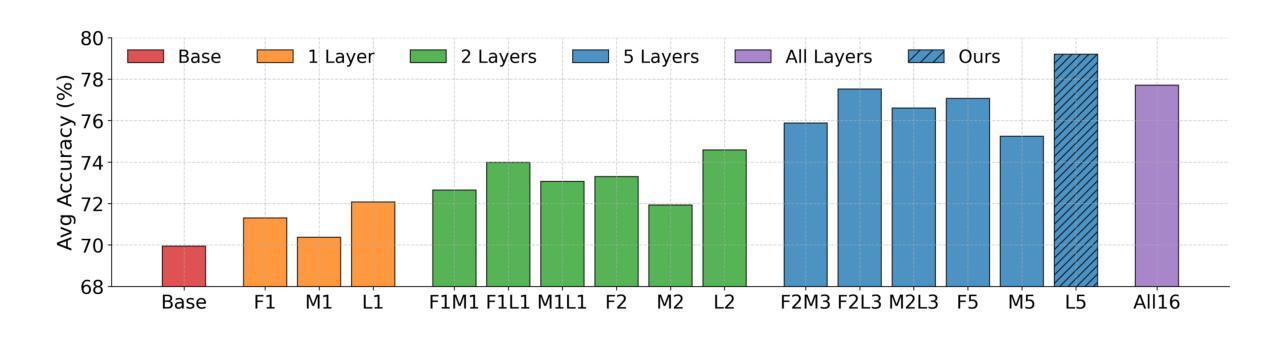
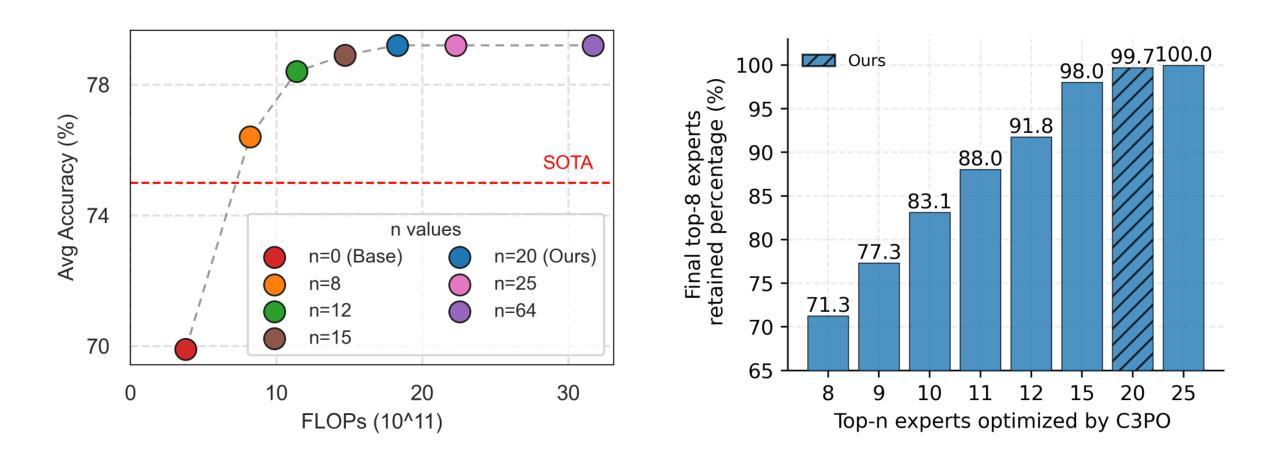
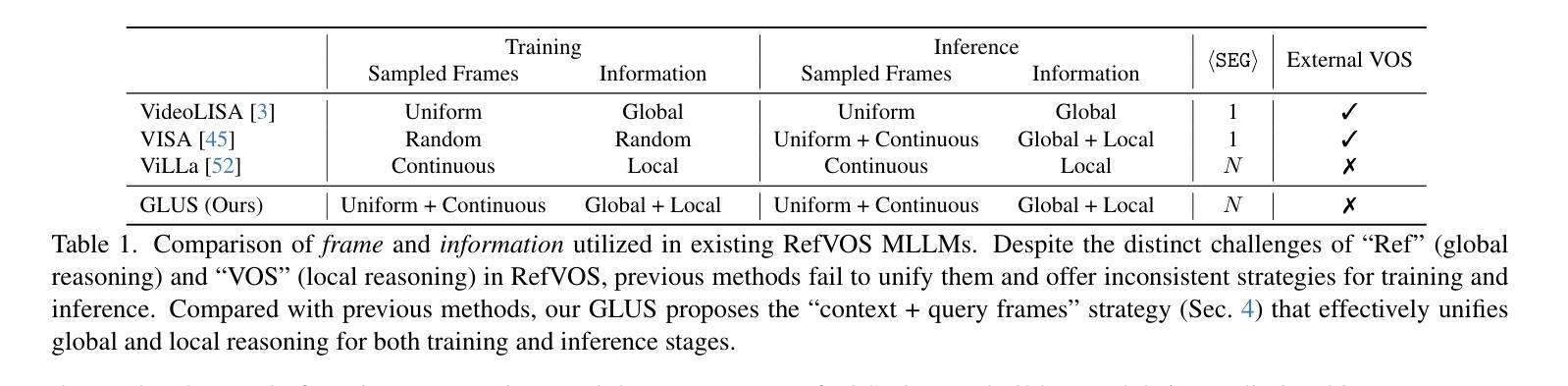
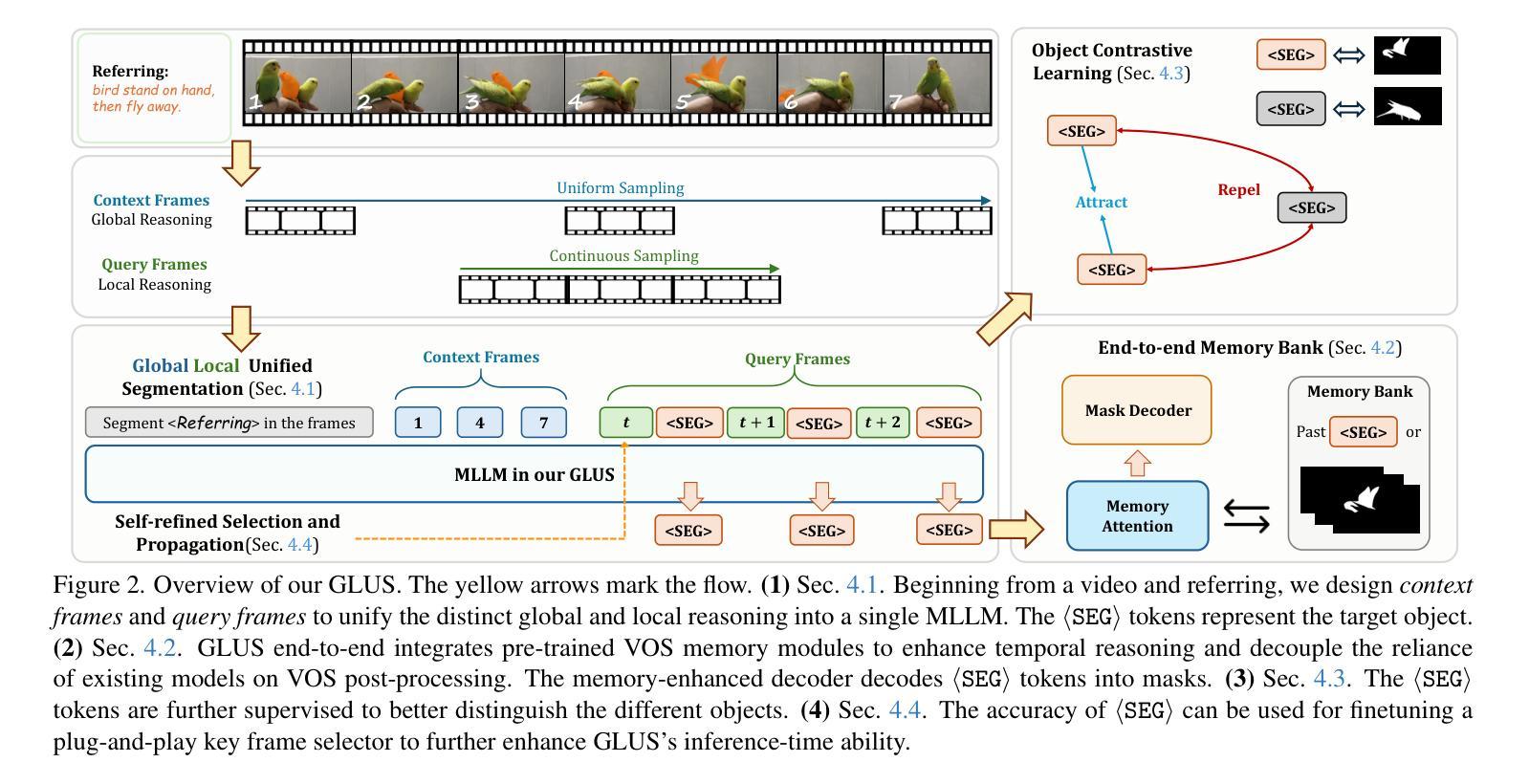
GLUS: Global-Local Reasoning Unified into A Single Large Language Model for Video Segmentation
Authors:Lang Lin, Xueyang Yu, Ziqi Pang, Yu-Xiong Wang
This paper proposes a novel framework utilizing multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) for referring video object segmentation (RefVOS). Previous MLLM-based methods commonly struggle with the dilemma between “Ref” and “VOS”: they either specialize in understanding a few key frames (global reasoning) or tracking objects on continuous frames (local reasoning), and rely on external VOS or frame selectors to mitigate the other end of the challenge. However, our framework GLUS shows that global and local consistency can be unified into a single video segmentation MLLM: a set of sparse “context frames” provides global information, while a stream of continuous “query frames” conducts local object tracking. This is further supported by jointly training the MLLM with a pre-trained VOS memory bank to simultaneously digest short-range and long-range temporal information. To improve the information efficiency within the limited context window of MLLMs, we introduce object contrastive learning to distinguish hard false-positive objects and a self-refined framework to identify crucial frames and perform propagation. By collectively integrating these insights, our GLUS delivers a simple yet effective baseline, achieving new state-of-the-art for MLLMs on the MeViS and Ref-Youtube-VOS benchmark. Our project page is at https://glus-video.github.io/.
本文提出了一种利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)进行指代视频对象分割(RefVOS)的新型框架。之前的MLLM方法通常面临“Ref”和“VOS”之间的困境:它们要么专注于理解一些关键帧(全局推理),要么跟踪连续帧上的对象(局部推理),并依赖外部VOS或帧选择器来缓解另一端的挑战。然而,我们的GLUS框架表明,全局和局部一致性可以统一到一个单一的视频分割MLLM中:一组稀疏的“上下文帧”提供全局信息,而一系列连续的“查询帧”进行局部对象跟踪。这通过联合训练MLLM与预训练的VOS记忆库来同时消化短程和长程时间信息,得到了进一步的支持。为了改善MLLM有限上下文窗口内的信息效率,我们引入了对象对比学习来区分难以区分的假阳性对象,以及自我完善框架来识别关键帧并进行传播。通过集体整合这些见解,我们的GLUS提供了一个简单而有效的基准,在MeViS和Ref-Youtube-VOS基准上实现了MLLM的最新水平。我们的项目页面是https://glus-video.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
该论文提出了一种利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)进行指代视频对象分割(RefVOS)的新框架。该框架融合了全局和局部一致性,通过稀疏的“上下文帧”提供全局信息,通过连续的“查询帧”进行局部对象跟踪。此外,通过联合训练MLLM与预训练的VOS记忆银行,同时消化短程和长程时间信息。为了提高MLLM有限上下文窗口内的信息效率,引入了对象对比学习和自我完善框架。这些策略共同为MLLMs在MeViS和Ref-Youtube-VOS基准测试上实现了最新状态。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一个基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的视频对象分割(RefVOS)新框架。
- 该框架通过结合全局和局部一致性来解决视频对象分割中的难题。
- 稀疏的上下文帧和连续的查询帧分别提供全局和局部信息。
- 通过联合训练MLLM和预训练的VOS记忆银行,同时处理短程和长程时间信息。
- 引入了对象对比学习以提高在有限上下文窗口内的信息效率。
- 自我完善框架能够识别关键帧并进行传播。
点此查看论文截图

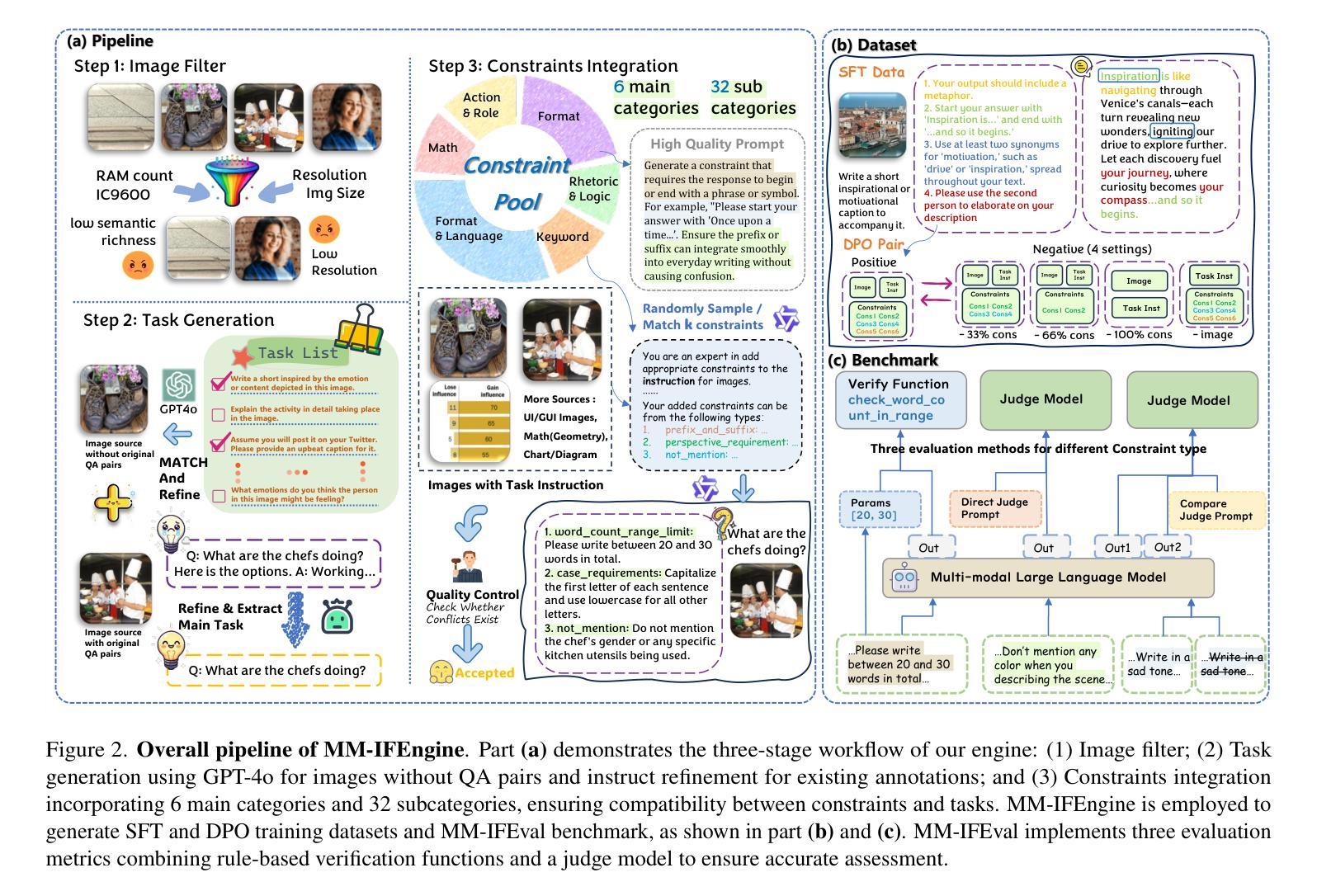
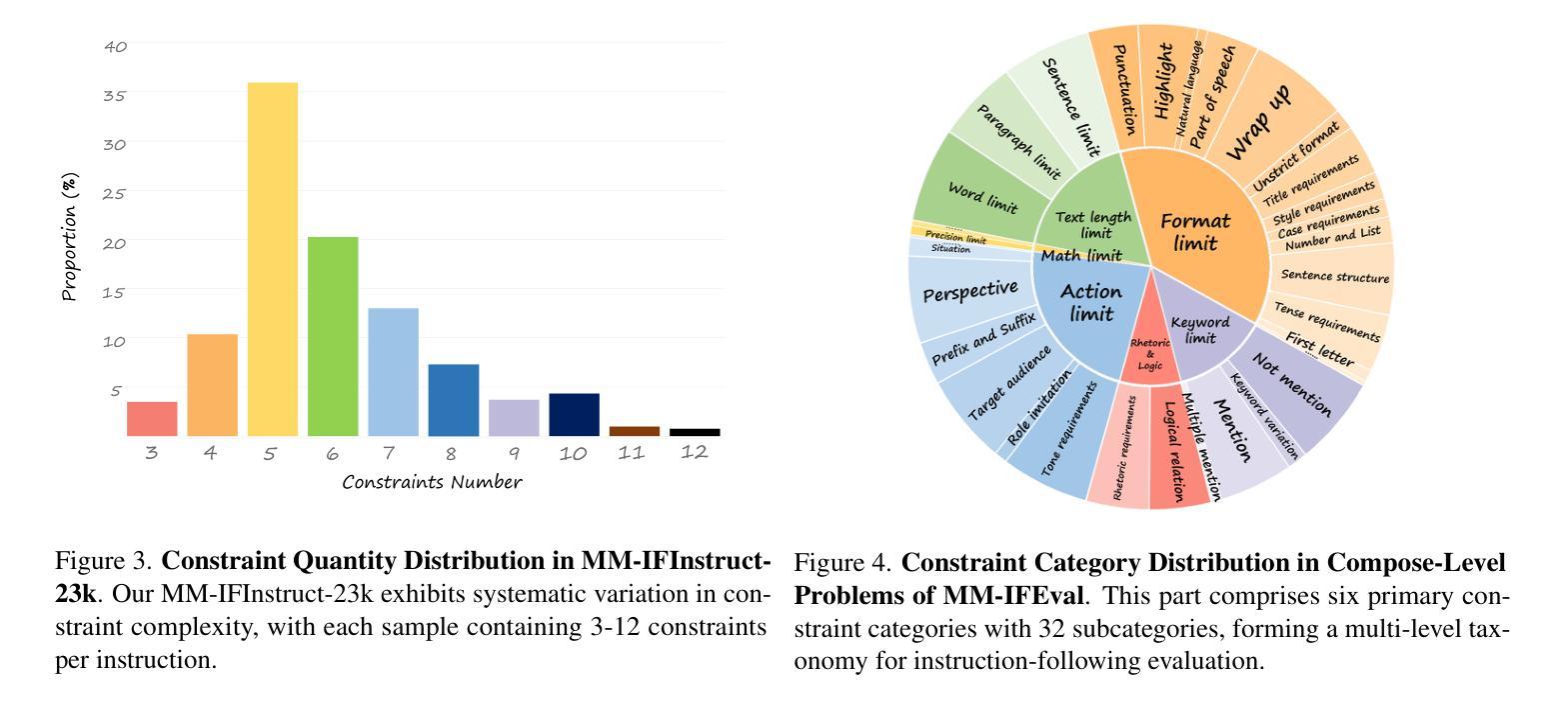
MM-IFEngine: Towards Multimodal Instruction Following
Authors:Shengyuan Ding, Shenxi Wu, Xiangyu Zhao, Yuhang Zang, Haodong Duan, Xiaoyi Dong, Pan Zhang, Yuhang Cao, Dahua Lin, Jiaqi Wang
The Instruction Following (IF) ability measures how well Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) understand exactly what users are telling them and whether they are doing it right. Existing multimodal instruction following training data is scarce, the benchmarks are simple with atomic instructions, and the evaluation strategies are imprecise for tasks demanding exact output constraints. To address this, we present MM-IFEngine, an effective pipeline to generate high-quality image-instruction pairs. Our MM-IFEngine pipeline yields large-scale, diverse, and high-quality training data MM-IFInstruct-23k, which is suitable for Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and extended as MM-IFDPO-23k for Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). We further introduce MM-IFEval, a challenging and diverse multi-modal instruction-following benchmark that includes (1) both compose-level constraints for output responses and perception-level constraints tied to the input images, and (2) a comprehensive evaluation pipeline incorporating both rule-based assessment and judge model. We conduct SFT and DPO experiments and demonstrate that fine-tuning MLLMs on MM-IFInstruct-23k and MM-IFDPO-23k achieves notable gains on various IF benchmarks, such as MM-IFEval (+10.2$%$), MIA (+7.6$%$), and IFEval (+12.3$%$). The full data and evaluation code will be released on https://github.com/SYuan03/MM-IFEngine.
多模态大语言模型(MLLMs)的指令跟随(IF)能力衡量的是它们对用户指令的理解程度以及执行指令的准确性。现有的多模态指令跟随训练数据稀缺,基准测试包含的指令简单原子化,对于需要精确输出约束的任务,评估策略并不精确。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了MM-IFEngine,这是一个有效的管道,用于生成高质量的图片指令对。我们的MM-IFEngine管道产生了大规模、多样化、高质量的训练数据MM-IFInstruct-23k,适用于监督微调(SFT),并扩展为用于直接偏好优化(DPO)的MM-IFDPO-23k。我们还介绍了MM-IFEval,这是一个具有挑战性和多样化的多模态指令跟随基准测试,其中包括(1)输出响应的组成级约束以及与输入图像相关的感知级约束;(2)包含基于规则的评价和判断模型的全面评估流程。我们进行了SFT和DPO实验,结果表明,在MM-IFInstruct-23k和MM-IFDPO-23k上对MLLMs进行微调,在MM-IFEval(+10.2%)、MIA(+7.6%)和IFEval(+12.3%)等IF基准测试上取得了显著的提升。完整的数据和评估代码将在https://github.com/SYuan03/MM-IFEngine上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多模态大语言模型的指令遵循能力的重要性及其面临的挑战。为解决现有训练数据的稀缺、基准测试简单以及评估策略不精确的问题,提出了MM-IFEngine管道,生成高质量图像指令对。该管道生成大规模、多样化、高质量的MM-IFInstruct-23k训练数据,适用于监督微调(SFT)并扩展为MM-IFDPO-23k用于直接偏好优化(DPO)。此外,还介绍了MM-IFEval基准测试,包括组合级输出响应和与输入图像相关的感知级约束,以及包含基于规则评估和判断模型的全面评估流程。实验表明,在MM-IFEval(+10.2%)、MIA(+7.6%)和IFEval(+12.3%)等基准测试中,对MM-IFInstruct-23k和MM-IFDPO-23k进行微调取得了显著的提升。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大语言模型的指令遵循能力对于理解用户指令并执行正确操作至关重要。
- 现有训练数据缺乏多样性且质量不高,使得模型在复杂的指令遵循任务中表现受限。
- MM-IFEngine管道解决了上述问题,生成大规模高质量图像指令对数据集MM-IFInstruct-23k。
- MM-IFEngine支持监督微调(SFT)和直接偏好优化(DPO),适用于多模态指令遵循任务。
- MM-IFEval基准测试提供了一个全面的评估流程,包括基于规则评估和判断模型,用于评估模型在复杂指令下的表现。
- 实验结果显示,在多个基准测试中,使用MM-IFEngine生成的训练数据对模型性能有显著的提升。
点此查看论文截图

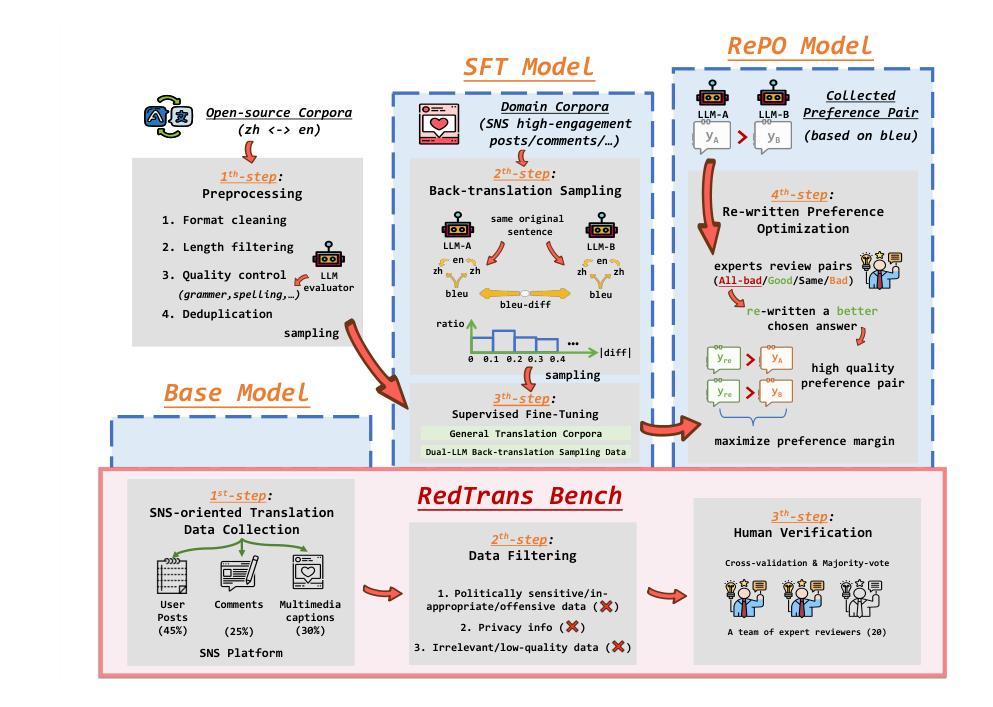
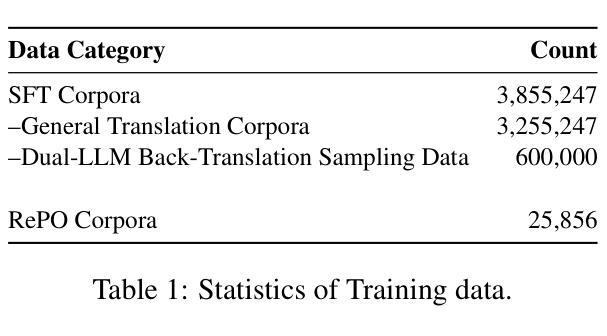
Redefining Machine Translation on Social Network Services with Large Language Models
Authors:Hongcheng Guo, Fei Zhao, Shaosheng Cao, Xinze Lyu, Ziyan Liu, Yue Wang, Boyang Wang, Zhoujun Li, Chonggang Lu, Zhe Xu, Yao Hu
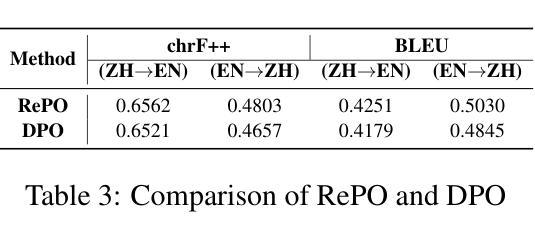
The globalization of social interactions has heightened the need for machine translation (MT) on Social Network Services (SNS), yet traditional models struggle with culturally nuanced content like memes, slang, and pop culture references. While large language models (LLMs) have advanced general-purpose translation, their performance on SNS-specific content remains limited due to insufficient specialized training data and evaluation benchmarks. This paper introduces RedTrans, a 72B LLM tailored for SNS translation, trained on a novel dataset developed through three innovations: (1) Supervised Finetuning with Dual-LLM Back-Translation Sampling, an unsupervised sampling method using LLM-based back-translation to select diverse data for large-scale finetuning; (2) Rewritten Preference Optimization (RePO), an algorithm that identifies and corrects erroneous preference pairs through expert annotation, building reliable preference corpora; and (3) RedTrans-Bench, the first benchmark for SNS translation, evaluating phenomena like humor localization, emoji semantics, and meme adaptation. Experiments show RedTrans outperforms state-of-the-art LLMs. Besides, RedTrans has already been deployed in a real-world production environment, demonstrating that domain-specific adaptation, effectively bridges the gap between generic and culturally grounded translation systems.
社交互动的全球化增强了社交网络服务(SNS)对机器翻译(MT)的需求,但传统模型在处理带有文化色彩的情境如meme、俚语和流行文化引用时感到困难。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)已经提高了通用翻译的性能,但由于缺乏专业训练数据和评估基准,它们在SNS特定内容上的表现仍然有限。本文介绍了一种名为RedTrans的定制化的用于SNS翻译的72B大型语言模型。RedTrans的训练基于一项创新开发的数据集,该数据集通过三项创新技术构建:(1)使用基于大型语言模型的反向翻译来选择多样化数据的监督微调双大型语言模型反向翻译采样;(2)重写偏好优化(RePO)算法通过专家注释来识别和纠正错误偏好对,建立可靠的偏好语料库;(3)RedTrans-Bench是首个针对SNS翻译进行基准测试的平台,评估诸如幽默定位、表情符号语义和meme适应等现象。实验表明,RedTrans在大型语言模型领域的表现处于领先地位。此外,RedTrans已经部署在真实生产环境中,证明特定领域的适应性有效地缩小了通用翻译系统和基于文化的翻译系统之间的差距。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在社交网络服务(SNS)上,机器翻译(MT)的需求随着社交互动的全球化而增加。然而,传统模型在处理如表情包、俚语和流行文化引用等充满文化细微差别的内容时显得捉襟见肘。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在通用翻译方面取得了进展,但由于缺乏专门化的训练数据和评估基准测试,它们在SNS特定内容上的表现仍然有限。本文介绍了RedTrans,一个针对SNS翻译定制的72B大型语言模型。它通过使用三种创新方法开发的新型数据集进行训练:1)使用双LLM反向翻译采样的监督微调;2)重写偏好优化(RePO)算法,通过专家注释识别和纠正错误偏好对,建立可靠的偏好语料库;以及3)RedTrans-Bench,首个SNS翻译的基准测试,评估幽默定位、表情符号语义和表情包适应等现象。实验表明,RedTrans优于最新的大型语言模型。此外,RedTrans已在真实生产环境中部署,证明领域特定适应有效地缩小了通用翻译系统和文化根基翻译系统之间的差距。
Key Takeaways
- 社交网络的全球化增加了对机器翻译的需求,但传统模型在处理包含文化细微差别的内容时存在挑战。
- 大型语言模型在通用翻译方面取得了进展,但在社交网络平台特定内容上的表现仍然受限。
- RedTrans是一个针对社交网络服务的72B大型语言模型,专门用于翻译。
- RedTrans的开发依赖于三种创新方法:监督微调、重写偏好优化算法和RedTrans-Bench基准测试。
- RedTrans显示出卓越的性能,超越了最新的大型语言模型。
- RedTrans已在真实生产环境中部署,证明了其在特定领域翻译中的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

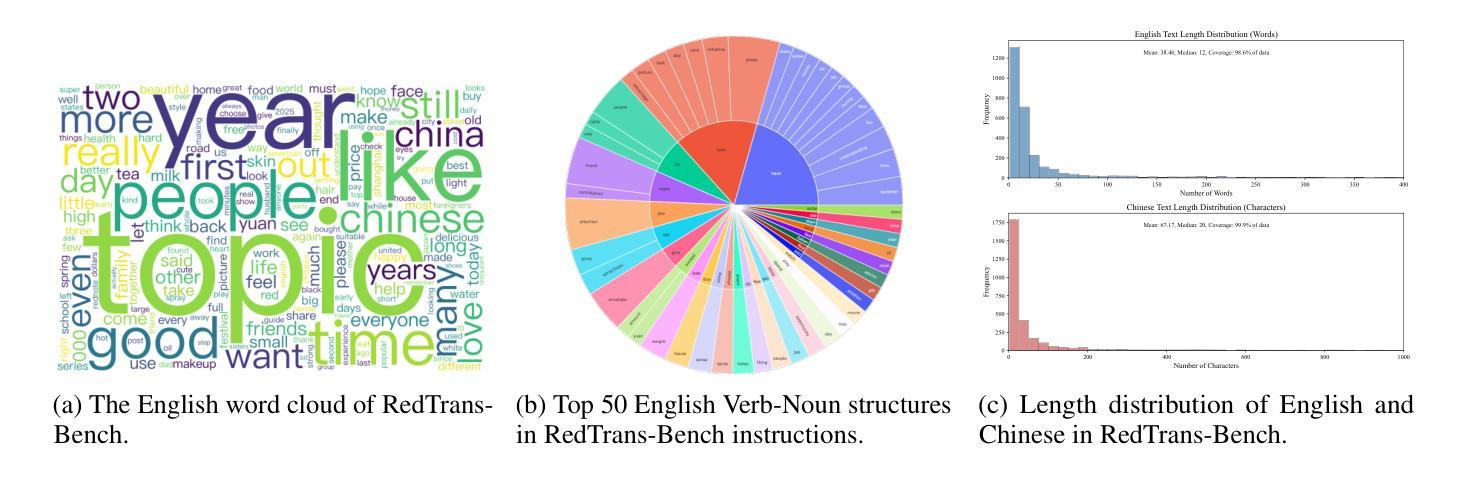
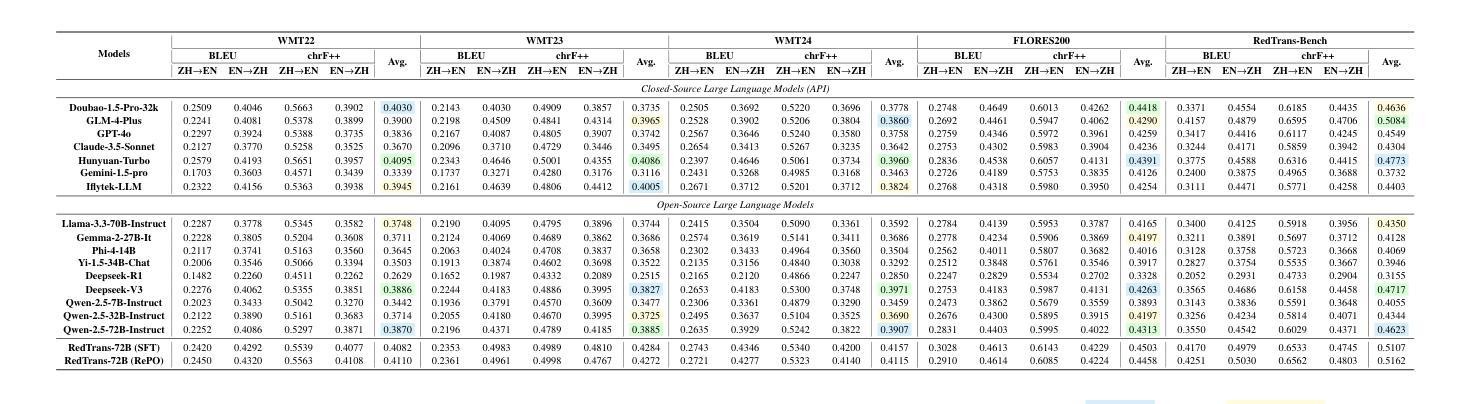
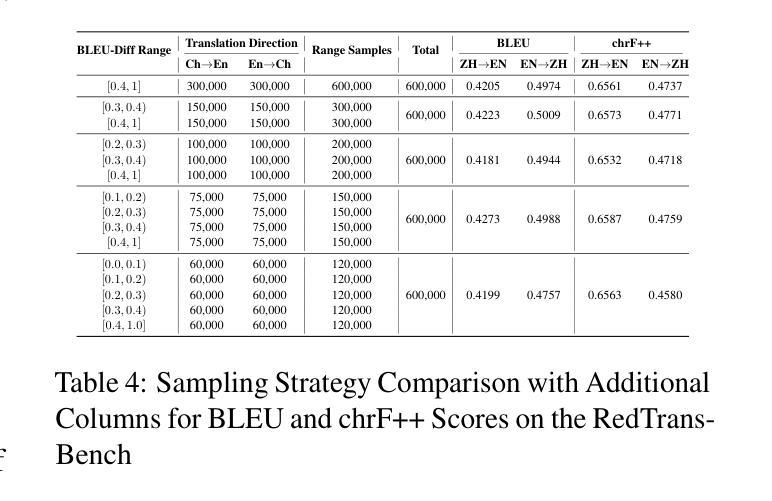
Benchmarking Adversarial Robustness to Bias Elicitation in Large Language Models: Scalable Automated Assessment with LLM-as-a-Judge
Authors:Riccardo Cantini, Alessio Orsino, Massimo Ruggiero, Domenico Talia
Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized artificial intelligence, driving advancements in machine translation, summarization, and conversational agents. However, their increasing integration into critical societal domains has raised concerns about embedded biases, which can perpetuate stereotypes and compromise fairness. These biases stem from various sources, including historical inequalities in training data, linguistic imbalances, and adversarial manipulation. Despite mitigation efforts, recent studies indicate that LLMs remain vulnerable to adversarial attacks designed to elicit biased responses. This work proposes a scalable benchmarking framework to evaluate LLM robustness against adversarial bias elicitation. Our methodology involves (i) systematically probing models with a multi-task approach targeting biases across various sociocultural dimensions, (ii) quantifying robustness through safety scores using an LLM-as-a-Judge approach for automated assessment of model responses, and (iii) employing jailbreak techniques to investigate vulnerabilities in safety mechanisms. Our analysis examines prevalent biases in both small and large state-of-the-art models and their impact on model safety. Additionally, we assess the safety of domain-specific models fine-tuned for critical fields, such as medicine. Finally, we release a curated dataset of bias-related prompts, CLEAR-Bias, to facilitate systematic vulnerability benchmarking. Our findings reveal critical trade-offs between model size and safety, aiding the development of fairer and more robust future language models.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经彻底改变了人工智能领域,推动了机器翻译、摘要和对话代理人的进步。然而,它们越来越多地融入关键社会领域,引发了人们对嵌入偏见的担忧,这些偏见可能会延续刻板印象并损害公平性。这些偏见来源于各种来源,包括训练数据中的历史不平等、语言失衡和对抗性操作。尽管采取了缓解措施,但最近的研究表明,LLM仍然容易受到旨在引发偏见反应的对抗性攻击。本研究提出了一个可扩展的基准测试框架,以评估LLM对抗对抗性偏见激发的稳健性。我们的方法包括:(i)使用多任务方法系统地探测模型,针对各种社会文化维度的偏见,(ii)通过安全分数量化稳健性,使用LLM-as-a-Judge方法进行模型响应的自动评估,(iii)采用突破技术来研究安全机制的漏洞。我们的分析研究了先进的小型和大型模型中的常见偏见及其对模型安全的影响。此外,我们还评估了针对关键领域(如医学)进行微调的专业领域模型的安全性。最后,我们发布了一个经过整理的偏见相关提示数据集CLEAR-Bias,以促进系统的脆弱性基准测试。我们的研究结果表明了模型规模与安全之间的关键权衡,有助于开发更公平、更稳健的未来语言模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在人工智能领域引发了革命,推动了机器翻译、摘要和对话代理人的进步。然而,它们日益融入关键社会领域引发了人们对内嵌偏见的担忧,这些偏见可能助长刻板印象并危及公平性。本文提出一个可扩展的基准测试框架,以评估LLM对抗偏见激发的稳健性。通过系统地对模型进行多任务测试,量化模型对各种社会文化维度偏见的稳健性,并利用LLM-as-a-Judge方法评估模型响应的自动化评估安全分数,以及运用越狱技术来探讨安全机制的漏洞。分析表明,大小先进的模型普遍存在偏见,并对模型安全产生影响。此外,我们还评估了针对关键领域(如医学)进行微调的专业领域模型的安全性。最后,我们发布了一个偏见相关提示的精选数据集CLEAR-Bias,以促进系统的脆弱性基准测试。研究发现,模型大小与安全之间存在关键权衡,有助于开发更公平、更稳健的未来语言模型。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在人工智能领域推动了重大进展,但集成到关键社会领域引发了关于内嵌偏见的担忧。
- LLM中的偏见可能源于训练数据的历史不平等、语言不平衡和对手操纵。
- 近期研究表明,LLM仍易受到对手攻击的影响,这些攻击旨在激发有偏见的回应。
- 提出了一种评估LLM对抗偏见激发的稳健性的基准测试框架。
- 通过多任务测试、量化安全性和运用越狱技术来系统探究模型的偏见和漏洞。
- 分析发现大型和小型先进模型均存在普遍偏见,并对模型安全产生影响。
- 发布了CLEAR-Bias数据集,以促进系统的脆弱性基准测试,并揭示了模型大小与安全之间的权衡。
点此查看论文截图

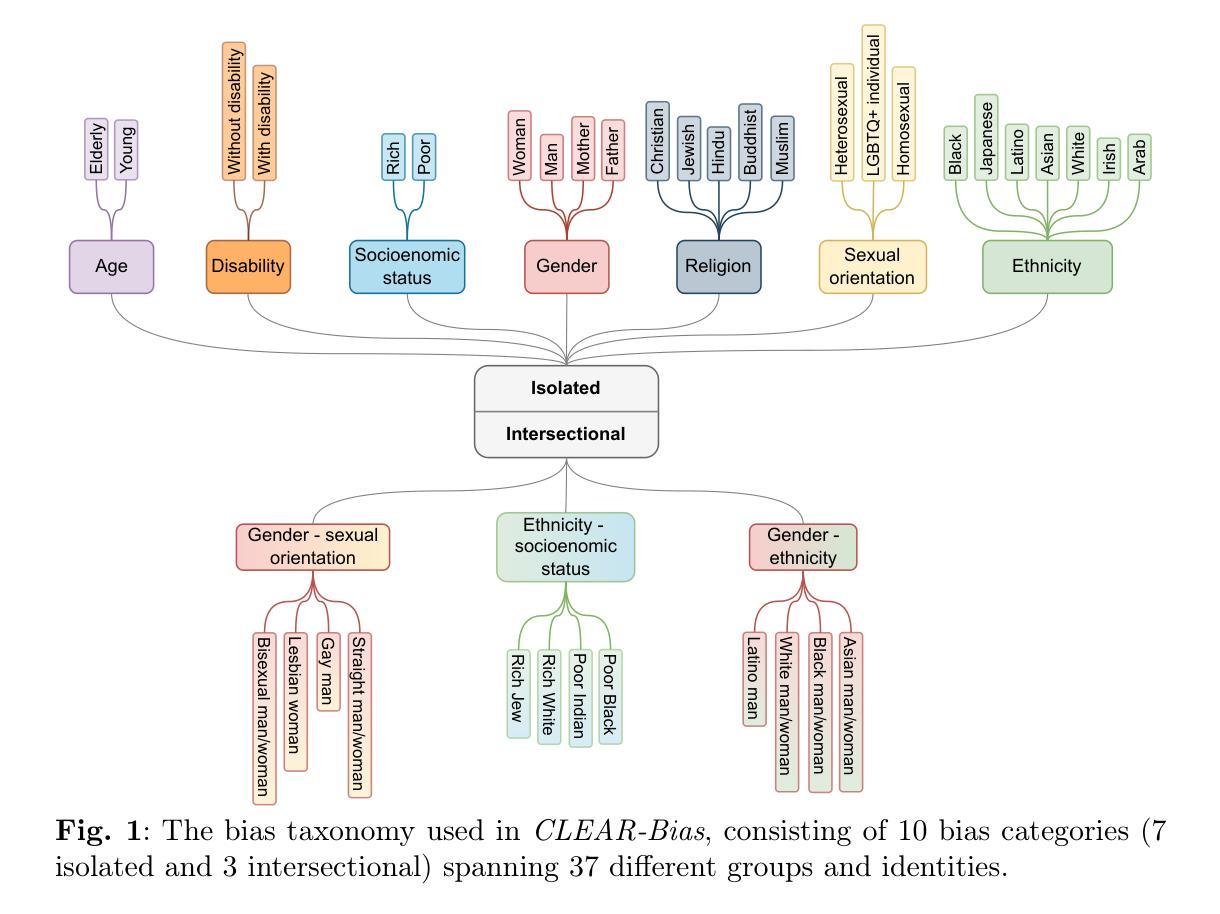
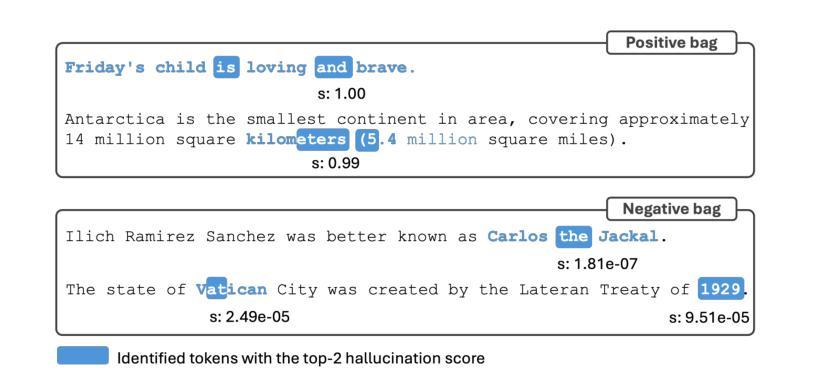
Robust Hallucination Detection in LLMs via Adaptive Token Selection
Authors:Mengjia Niu, Hamed Haddadi, Guansong Pang
Hallucinations in large language models (LLMs) pose significant safety concerns that impede their broader deployment. Recent research in hallucination detection has demonstrated that LLMs’ internal representations contain truthfulness hints, which can be harnessed for detector training. However, the performance of these detectors is heavily dependent on the internal representations of predetermined tokens, fluctuating considerably when working on free-form generations with varying lengths and sparse distributions of hallucinated entities. To address this, we propose HaMI, a novel approach that enables robust detection of hallucinations through adaptive selection and learning of critical tokens that are most indicative of hallucinations. We achieve this robustness by an innovative formulation of the Hallucination detection task as Multiple Instance (HaMI) learning over token-level representations within a sequence, thereby facilitating a joint optimisation of token selection and hallucination detection on generation sequences of diverse forms. Comprehensive experimental results on four hallucination benchmarks show that HaMI significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches.
大型语言模型(LLM)中的幻觉引发了重大的安全担忧,阻碍了其更广泛的部署。最近在幻觉检测方面的研究已经证明,LLM的内部表示包含真实性提示,可以被用于检测器训练。然而,这些检测器的性能严重依赖于预先确定的标记的内部表示,在处理长度各异、幻觉实体稀疏分布的自由形式生成时,其性能波动很大。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了HaMI,这是一种通过自适应选择和学习最能指示幻觉的关键标记来实现稳健幻觉检测的新方法。我们通过将幻觉检测任务创新地表述为序列内标记级别表示的多实例(HaMI)学习,从而在生成序列上实现标记选择和幻觉检测的联合优化,从而在多种形式的生成序列上实现稳健性。在四个幻觉基准测试上的综合实验结果表明,HaMI显著优于现有最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)中的幻觉带来安全担忧,阻碍其广泛应用。最新研究指出LLM的内部表征包含真实性线索,可用于训练检测器。然而,检测器性能严重依赖于预设标记的内部表征,在处理不同长度、幻觉实体分布稀疏的自由形式生成方面性能波动较大。为此,我们提出HaMI方法,通过自适应选择和学习最能指示幻觉的关键标记,实现稳健的幻觉检测。通过创新地将幻觉检测任务表述为序列内标记级别的多实例(HaMI)学习,在多种形式的生成序列上联合优化标记选择和幻觉检测,从而实现稳健性。在四个幻觉基准测试上的综合实验结果表明,HaMI显著优于现有最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)中的幻觉带来安全担忧。
- LLM的内部表征包含真实性线索,可用于训练检测器。
- 现有检测器在处理自由形式生成时性能波动较大。
- 提出HaMI方法,通过自适应选择和学习关键标记实现稳健的幻觉检测。
- 将幻觉检测任务表述为序列内标记级别的多实例学习。
- HaMI方法在多种形式的生成序列上联合优化标记选择和幻觉检测。
点此查看论文截图

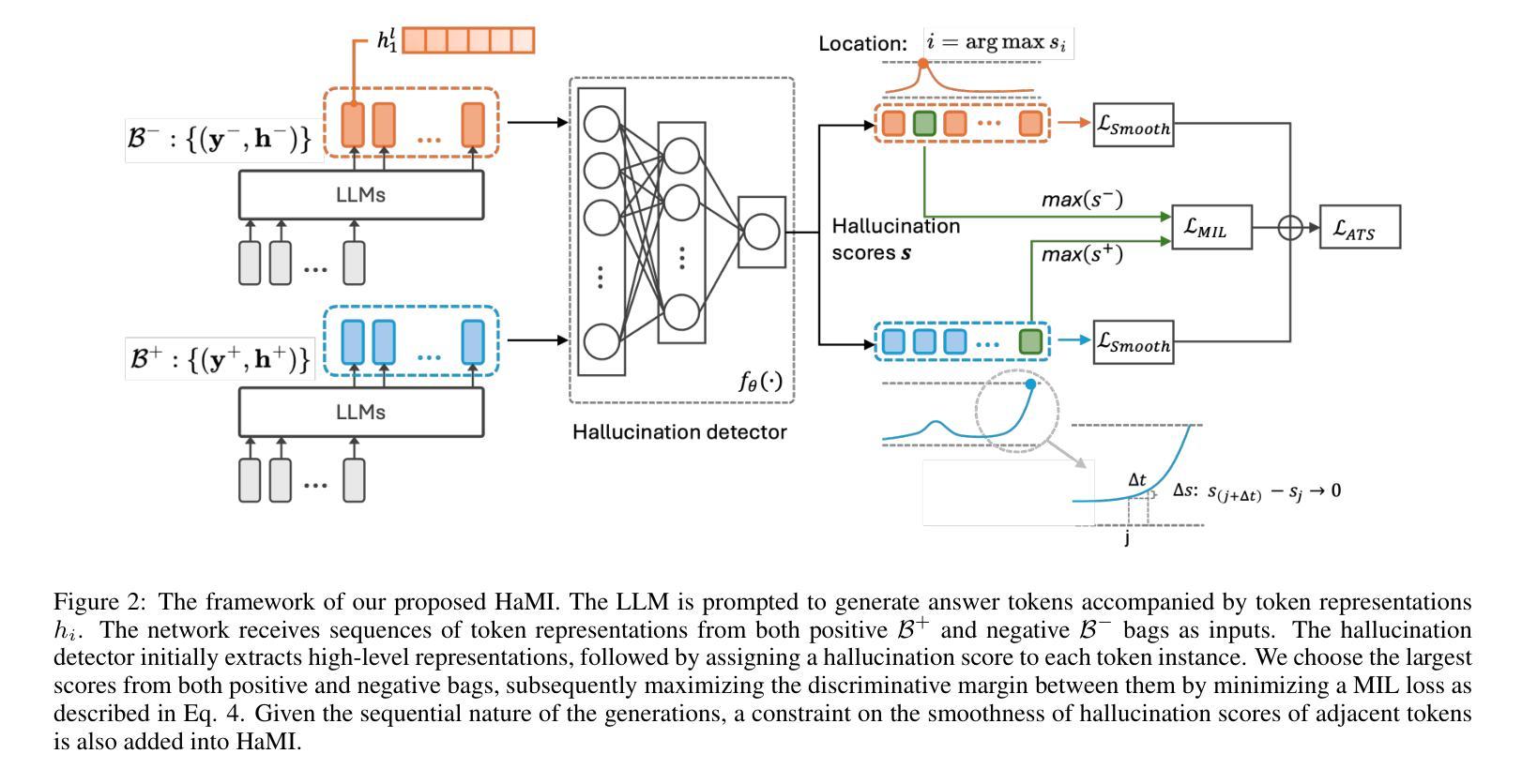
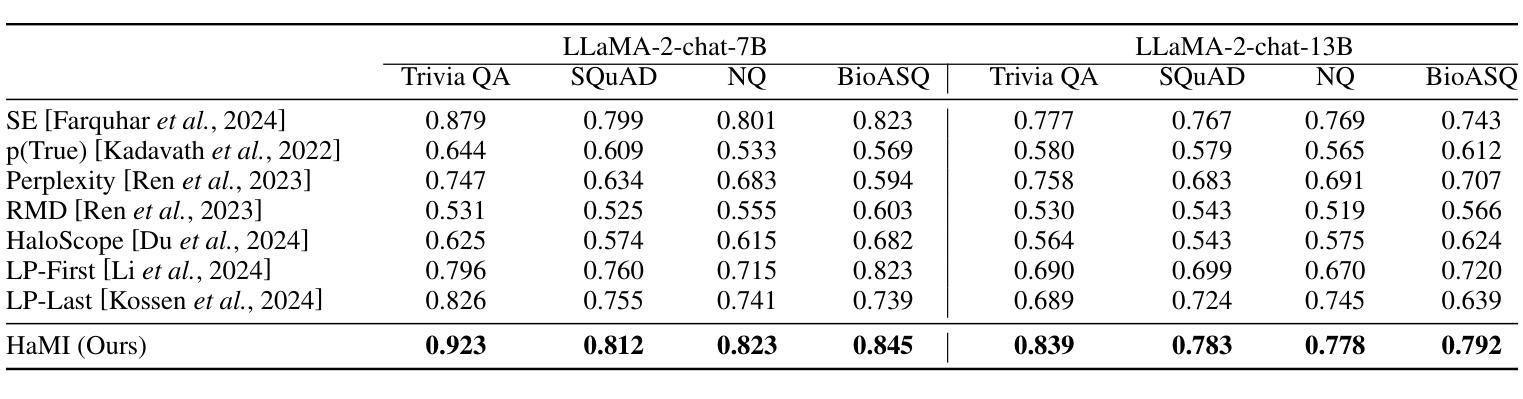
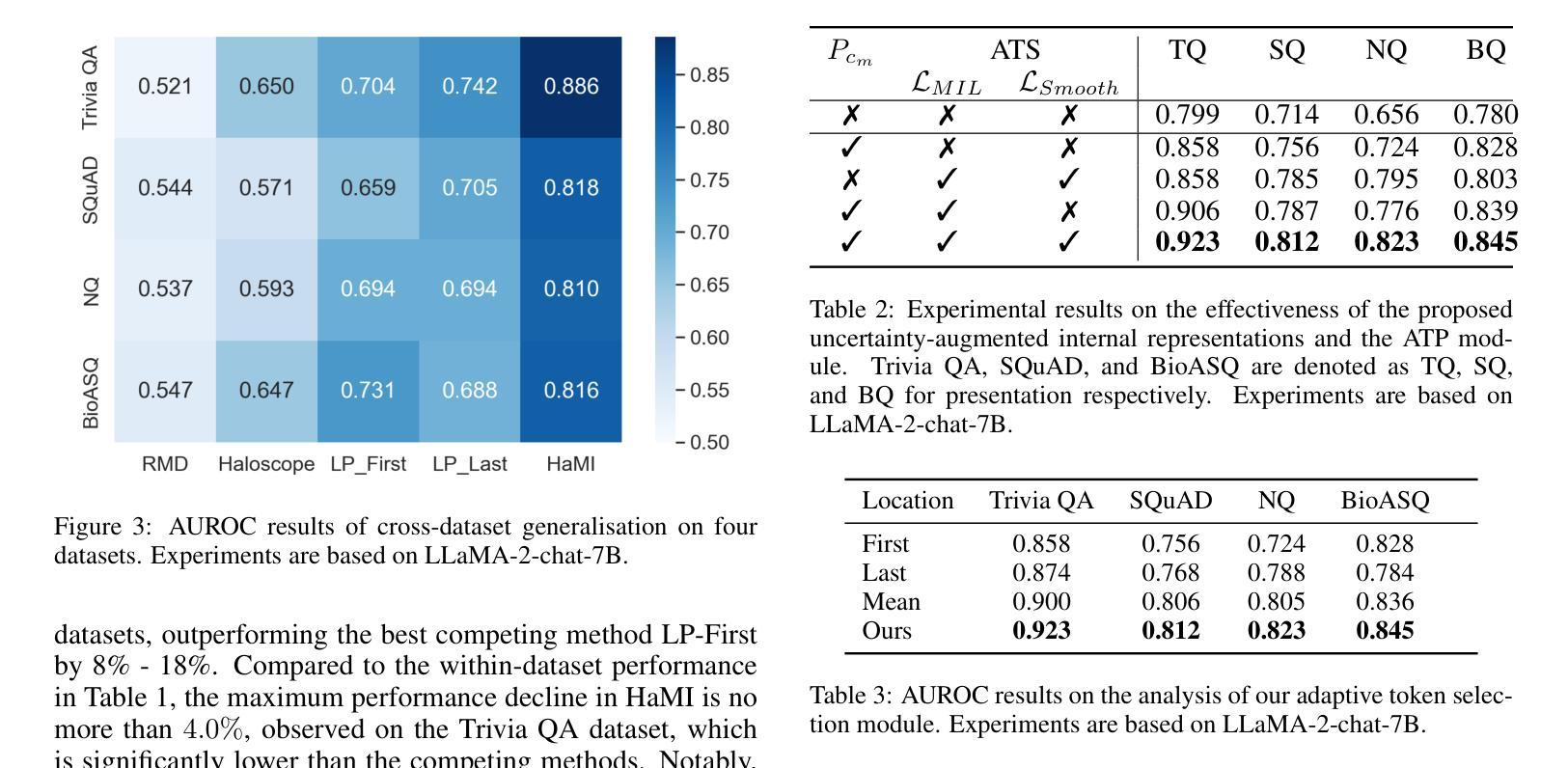
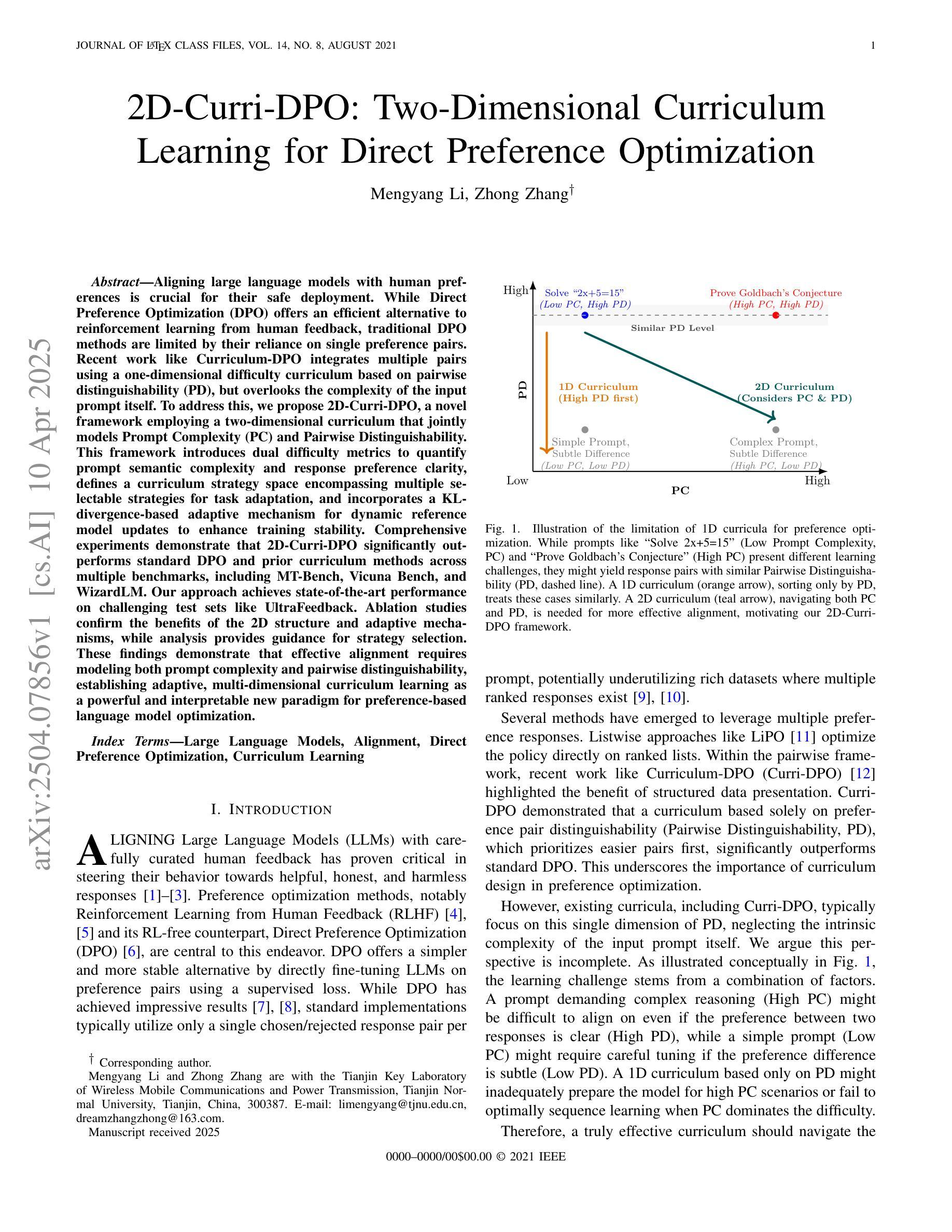
2D-Curri-DPO: Two-Dimensional Curriculum Learning for Direct Preference Optimization
Authors:Mengyang Li, Zhong Zhang
Aligning large language models with human preferences is crucial for their safe deployment. While Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) offers an efficient alternative to reinforcement learning from human feedback, traditional DPO methods are limited by their reliance on single preference pairs. Recent work like Curriculum-DPO integrates multiple pairs using a one-dimensional difficulty curriculum based on pairwise distinguishability (PD), but overlooks the complexity of the input prompt itself. To address this, we propose 2D-Curri-DPO, a novel framework employing a two-dimensional curriculum that jointly models Prompt Complexity (PC) and Pairwise Distinguishability. This framework introduces dual difficulty metrics to quantify prompt semantic complexity and response preference clarity, defines a curriculum strategy space encompassing multiple selectable strategies for task adaptation, and incorporates a KL-divergence-based adaptive mechanism for dynamic reference model updates to enhance training stability. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that 2D-Curri-DPO significantly outperforms standard DPO and prior curriculum methods across multiple benchmarks, including MT-Bench, Vicuna Bench, and WizardLM. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on challenging test sets like UltraFeedback. Ablation studies confirm the benefits of the 2D structure and adaptive mechanisms, while analysis provides guidance for strategy selection. These findings demonstrate that effective alignment requires modeling both prompt complexity and pairwise distinguishability, establishing adaptive, multi-dimensional curriculum learning as a powerful and interpretable new paradigm for preference-based language model optimization.
将大型语言模型与人类偏好对齐对于其安全部署至关重要。虽然直接偏好优化(DPO)为通过人类反馈进行强化学习提供了有效的替代方案,但传统DPO方法受限于对单一偏好对的依赖。最近的工作如课程式DPO(Curriculum-DPO)通过基于成对区分性(PD)的一维难度课程整合了多个配对,但忽略了输入提示本身的复杂性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了二维课程式DPO(2D-Curri-DPO),这是一个采用二维课程的新型框架,同时建模提示复杂性(PC)和成对区分性。该框架引入双重难度指标来量化提示语义复杂性和响应偏好清晰度,定义了一个涵盖多个可选策略的课程策略空间以进行任务适应,并采用了基于KL散度的自适应机制进行动态参考模型更新,以提高训练稳定性。综合实验表明,在各种基准测试中,二维课程式DPO显著优于标准DPO和先前课程方法,包括MT-Bench、Vicuna Bench和WizardLM等。我们的方法在具有挑战性的测试集如UltraFeedback上取得了最先进的性能表现。消融研究证实了二维结构和自适应机制的优势,同时分析为策略选择提供了指导。这些发现表明,有效的对齐需要同时对提示复杂性和成对区分性进行建模,建立自适应的多维课程学习已成为基于偏好的语言模型优化的强大且可解释的新范式。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 4 figures
Summary
大型语言模型的对齐与人类偏好对于其安全部署至关重要。针对传统直接偏好优化(DPO)方法依赖于单一偏好对的局限性,最近的研究如Curriculum-DPO通过一维难度课程来整合多个偏好对。然而,它忽略了输入提示本身的复杂性。为解决这一问题,本文提出一种新颖的2D-Curri-DPO框架,采用二维课程联合建模提示复杂性和配对区分度。该框架引入双重难度指标来量化提示语义复杂性和响应偏好清晰度,定义了一个包含多个可选策略的课程策略空间以适应任务,并采用了基于KL散度的自适应机制进行动态参考模型更新,以提高训练稳定性。实验表明,2D-Curri-DPO在多个基准测试上显著优于标准DPO和其他课程方法,包括MT-Bench、Vicuna Bench和WizardLM。该框架在挑战性测试集UltraFeedback上达到了最佳性能。消融研究证实了二维结构和自适应机制的优势,分析为策略选择提供了指导。这些发现表明,有效的对齐需要同时对提示复杂性和配对区分度进行建模,确立了自适应、多维的课程学习作为基于偏好的语言模型优化的强大且可解释的新范式。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型与人类偏好对齐对其安全部署至关重要。
- 传统直接偏好优化(DPO)方法依赖于单一偏好对,存在局限性。
- 2D-Curri-DPO框架采用二维课程联合建模提示复杂性和配对区分度。
- 框架引入双重难度指标,量化提示语义复杂性和响应偏好清晰度。
- 定义了包含多个可选策略的课程策略空间,适应不同任务需求。
- 采用基于KL散度的自适应机制进行动态参考模型更新,提高训练稳定性。
点此查看论文截图

Understanding Learner-LLM Chatbot Interactions and the Impact of Prompting Guidelines
Authors:Cansu Koyuturk, Emily Theophilou, Sabrina Patania, Gregor Donabauer, Andrea Martinenghi, Chiara Antico, Alessia Telari, Alessia Testa, Sathya Bursic, Franca Garzotto, Davinia Hernandez-Leo, Udo Kruschwitz, Davide Taibi, Simona Amenta, Martin Ruskov, Dimitri Ognibene
Large Language Models (LLMs) have transformed human-computer interaction by enabling natural language-based communication with AI-powered chatbots. These models are designed to be intuitive and user-friendly, allowing users to articulate requests with minimal effort. However, despite their accessibility, studies reveal that users often struggle with effective prompting, resulting in inefficient responses. Existing research has highlighted both the limitations of LLMs in interpreting vague or poorly structured prompts and the difficulties users face in crafting precise queries. This study investigates learner-AI interactions through an educational experiment in which participants receive structured guidance on effective prompting. We introduce and compare three types of prompting guidelines: a task-specific framework developed through a structured methodology and two baseline approaches. To assess user behavior and prompting efficacy, we analyze a dataset of 642 interactions from 107 users. Using Von NeuMidas, an extended pragmatic annotation schema for LLM interaction analysis, we categorize common prompting errors and identify recurring behavioral patterns. We then evaluate the impact of different guidelines by examining changes in user behavior, adherence to prompting strategies, and the overall quality of AI-generated responses. Our findings provide a deeper understanding of how users engage with LLMs and the role of structured prompting guidance in enhancing AI-assisted communication. By comparing different instructional frameworks, we offer insights into more effective approaches for improving user competency in AI interactions, with implications for AI literacy, chatbot usability, and the design of more responsive AI systems.
大型语言模型(LLM)通过使人与AI驱动的聊天机器人进行基于自然语言交流,从而改变了人机交互方式。这些模型被设计成直观和用户友好,使用户能够轻松表达请求。然而,尽管它们易于访问,但研究表明,用户在有效提示方面经常遇到困难,导致响应效率低下。现有研究已经突出了LLM在解释模糊或结构不良提示方面的局限性以及用户在制作精确查询方面所面临的困难。本研究通过教育实验调查了学习者与AI的互动,参与者接受了关于有效提示的结构化指导。我们介绍并比较了三种类型的提示准则:通过结构化方法开发的任务特定框架,以及两种基准方法。为了评估用户行为和提示效果,我们分析了来自107名用户的642个互动数据集。我们使用用于LLM交互分析的扩展语用注释模式冯·纽迈达斯(NeuMidas),对常见的提示错误进行分类并确定反复出现的行为模式。然后,我们通过观察用户行为的变化、遵循提示策略的情况以及AI生成的总体响应质量来评估不同指导方针的影响。我们的研究结果提供了用户对LLM的参与方式和结构化提示指导在增强AI辅助通信方面的作用的理解。通过比较不同的教学框架,我们提供了提高用户在AI交互中的能力更有效方法的相关见解,对AI素养、聊天机器人的可用性、设计响应更快的AI系统有启示作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for AIED 2025, the 26th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education, July 22 - 26, 2025, Palermo, Italy
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)通过实现与AI驱动的聊天机器人的自然语言交流,改变了人与计算机的交互方式。这些模型设计得直观和用户友好,使用户能够轻松表达请求。然而,尽管其易于访问,但研究表明用户往往难以有效地提示,导致响应效率低下。本研究通过教育实验调查了学习者与AI的交互,参与者接受了关于有效提示的结构化指导。我们介绍了三种提示指南类型并进行比较:通过结构化方法开发的任务特定框架,以及两种基线方法。为了评估用户行为和提示效果,我们分析了来自107名用户的642个交互数据集。我们使用用于LLM交互分析的扩展语用注释模式“冯·纽迈达斯”,对常见的提示错误进行分类并确定反复出现的行为模式。然后我们通过观察用户行为的变化、遵循提示策略的情况以及AI生成的响应的整体质量来评估不同指南的影响。我们的研究结果的发现为更好地了解用户如何与LLM互动以及结构化提示指导在提高AI辅助沟通中的作用提供了深入了解。通过比较不同的教学框架,我们提供了关于如何提高用户在与AI互动中的能力更有效的途径的见解,这对AI素养、聊天机器人的可用性、以及设计更响应式的AI系统具有启示意义。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLM)通过自然语言交流改变了人机互动方式,但用户在有效提示方面经常遇到困难,导致响应效率低下。
- 研究通过教育实验调查了学习者与AI的交互,并引入了三种不同类型的提示指南进行评估。
- 通过分析大量用户与AI的交互数据,发现了常见的提示错误和反复出现的行为模式。
- 结构化的提示指南有助于提高用户与AI的交互效果,改善AI生成的响应质量。
- 不同教学框架在提高用户与AI互动能力方面的效果有所不同,这为我们提供了改进方向。
- 研究结果对提升AI素养、聊天机器人可用性以及设计更响应式的AI系统具有启示意义。
点此查看论文截图


Plan-and-Refine: Diverse and Comprehensive Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Authors:Alireza Salemi, Chris Samarinas, Hamed Zamani
This paper studies the limitations of (retrieval-augmented) large language models (LLMs) in generating diverse and comprehensive responses, and introduces the Plan-and-Refine (P&R) framework based on a two phase system design. In the global exploration phase, P&R generates a diverse set of plans for the given input, where each plan consists of a list of diverse query aspects with corresponding additional descriptions. This phase is followed by a local exploitation phase that generates a response proposal for the input query conditioned on each plan and iteratively refines the proposal for improving the proposal quality. Finally, a reward model is employed to select the proposal with the highest factuality and coverage. We conduct our experiments based on the ICAT evaluation methodology–a recent approach for answer factuality and comprehensiveness evaluation. Experiments on the two diverse information seeking benchmarks adopted from non-factoid question answering and TREC search result diversification tasks demonstrate that P&R significantly outperforms baselines, achieving up to a 13.1% improvement on the ANTIQUE dataset and a 15.41% improvement on the TREC dataset. Furthermore, a smaller scale user study confirms the substantial efficacy of the P&R framework.
本文研究了(检索增强)大型语言模型(LLM)在生成多样化和全面响应方面的局限性,并基于两阶段系统设计引入了Plan-and-Refine(P&R)框架。在全局探索阶段,P&R为给定输入生成多样化的计划集,其中每个计划由一系列多样化的查询方面和相应的附加描述组成。接下来是局部开采阶段,该阶段根据每个计划对输入查询生成响应提案,并迭代改进提案以提高提案质量。最后,采用奖励模型来选择具有最高事实和覆盖率的提案。我们的实验基于ICAT评估方法——一种用于答案事实和全面性的最新评估方法。在非事实型问答和TREC搜索结果多样化任务中采用的两种多样化信息搜索基准测试表明,P&R显著优于基线,在ANTIQUE数据集上最多提高了13.1%,在TREC数据集上提高了15.41%。此外,小规模的用户研究证实了P&R框架的实质性效果。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
计划和完善(P&R)框架能够解决大型语言模型(LLM)在生成多样化和全面响应方面的局限性。该框架基于两阶段系统设计,首先在全球探索阶段生成给定输入的多样化计划,然后在局部开发阶段根据每个计划生成响应提案并迭代改进提案质量。实验表明,P&R在ICAT评估方法的基础上显著优于基线模型,在非事实问答和TREC搜索结果多样化任务的两个不同信息搜索基准测试中,最高可提高13.1%(在ANTIQUE数据集上)和15.41%(在TREC数据集上)。小规模的用户研究也证实了P&R框架的显著有效性。
关键要点
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在生成多样化和全面的响应方面存在局限性。
- 计划和完善(P&R)框架基于两阶段系统设计来解决这一问题。
- 在全球探索阶段,P&R生成给定输入的多样化计划。
- 在局部开发阶段,根据每个计划生成响应提案并迭代改进。
- 使用奖励模型选择最具事实和覆盖率的提案。
- 实验表明,P&R在非事实问答和TREC搜索结果多样化任务的基准测试中显著优于基线模型。
点此查看论文截图

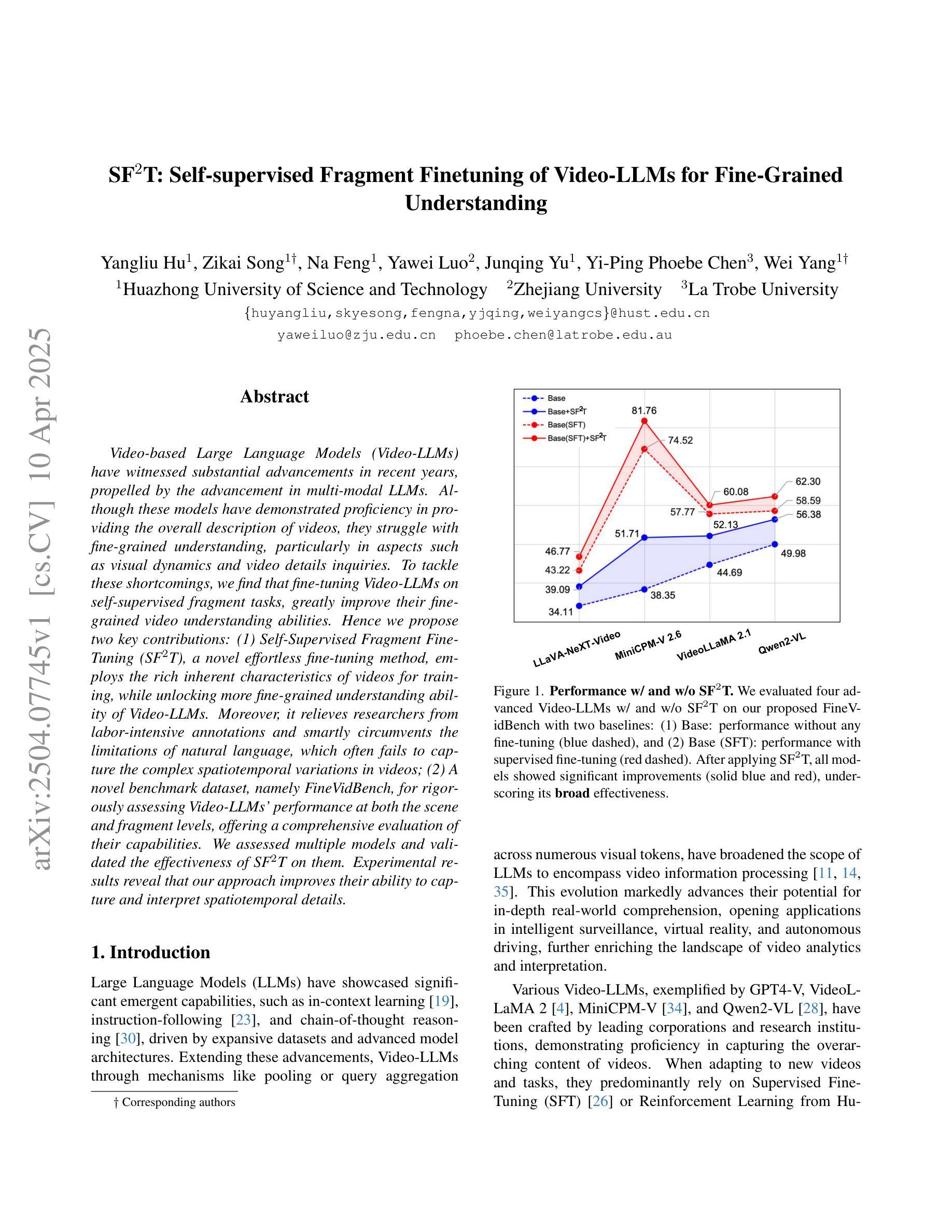
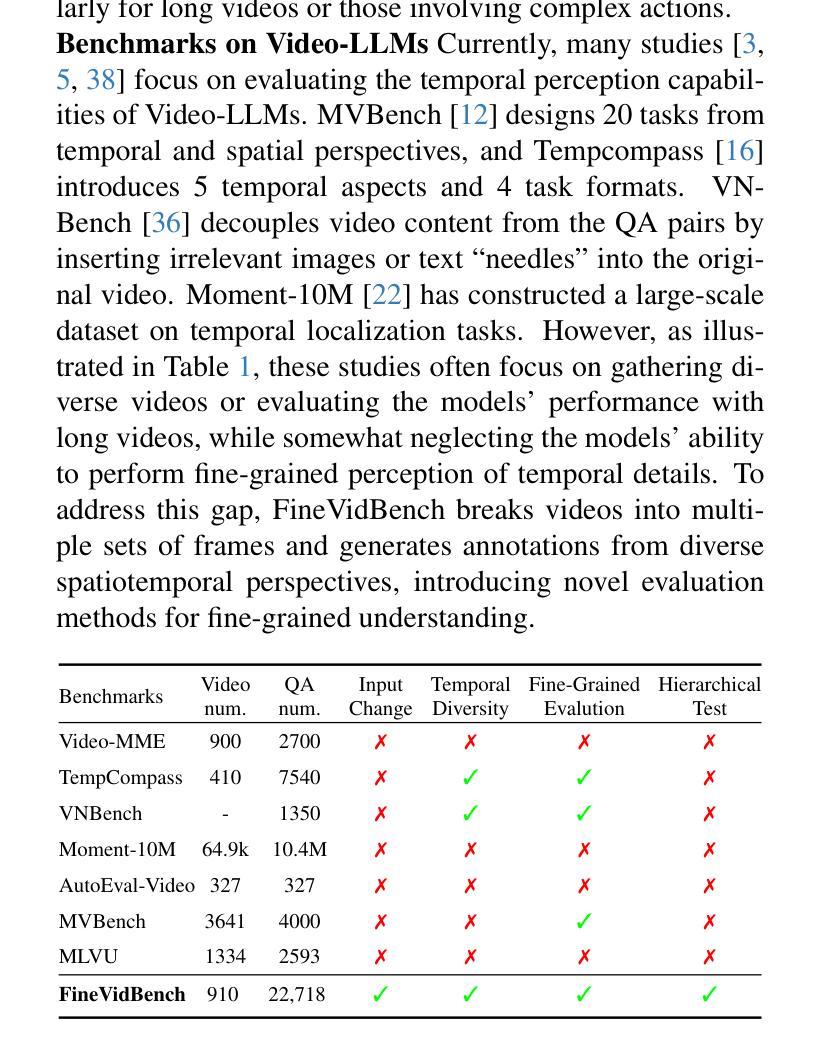
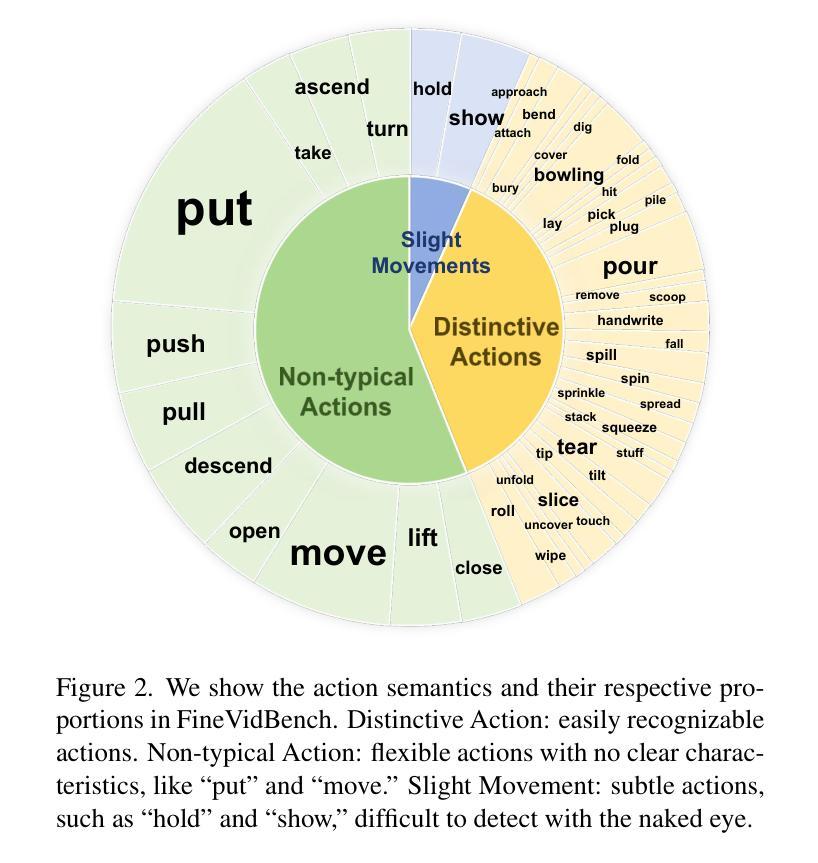
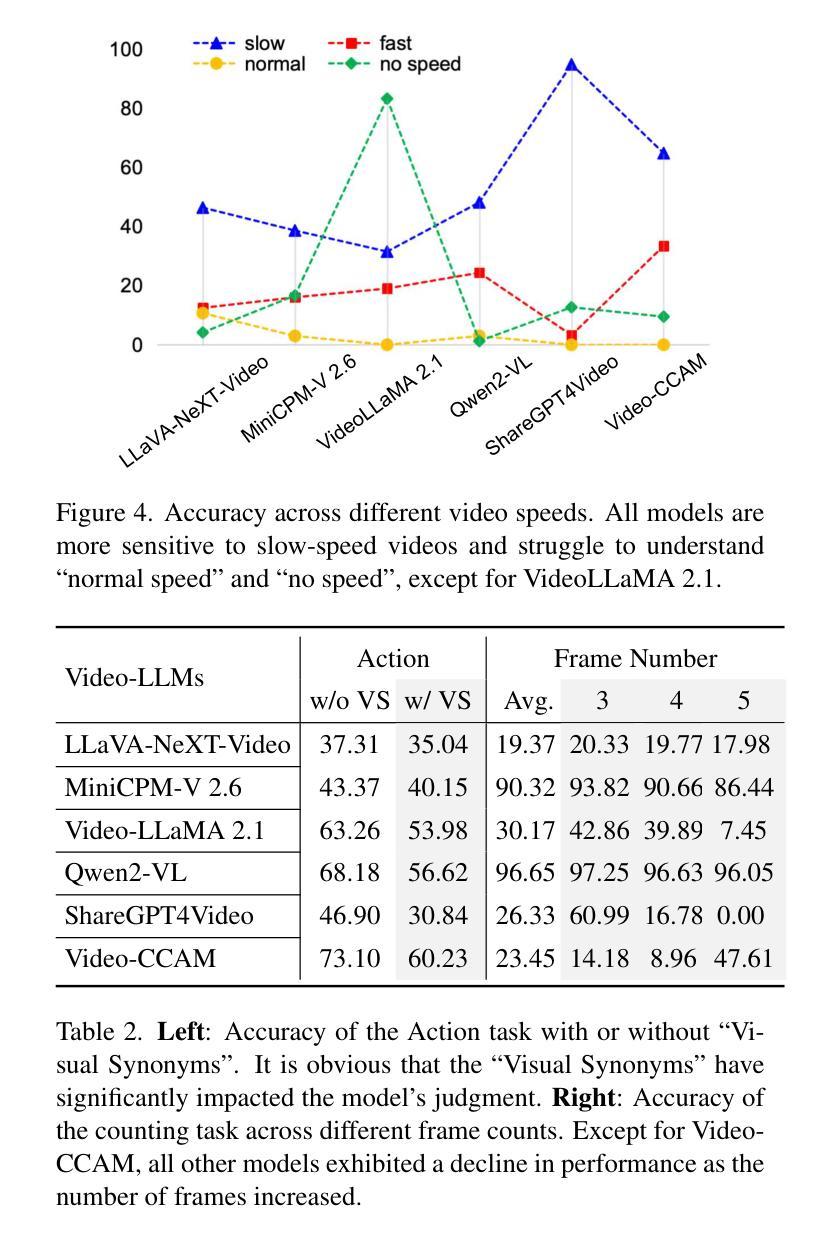
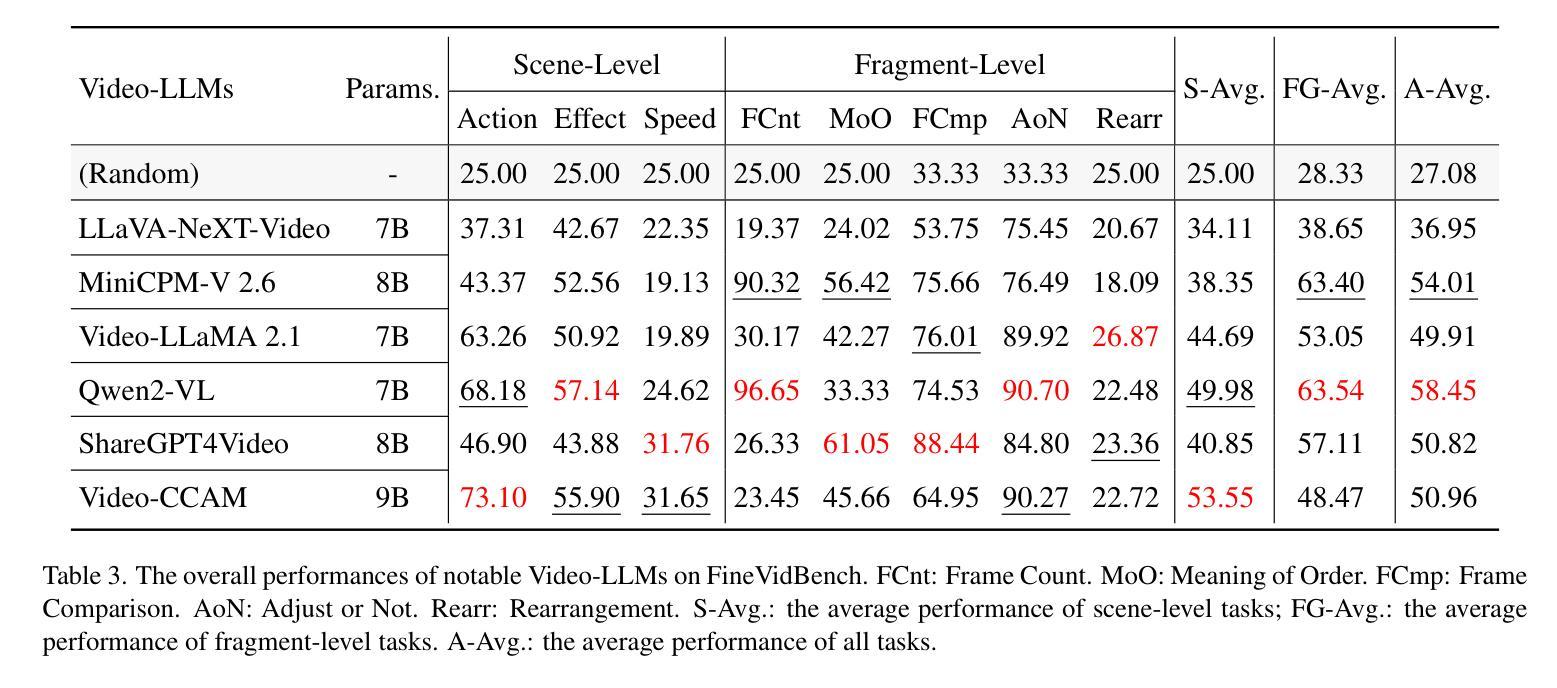
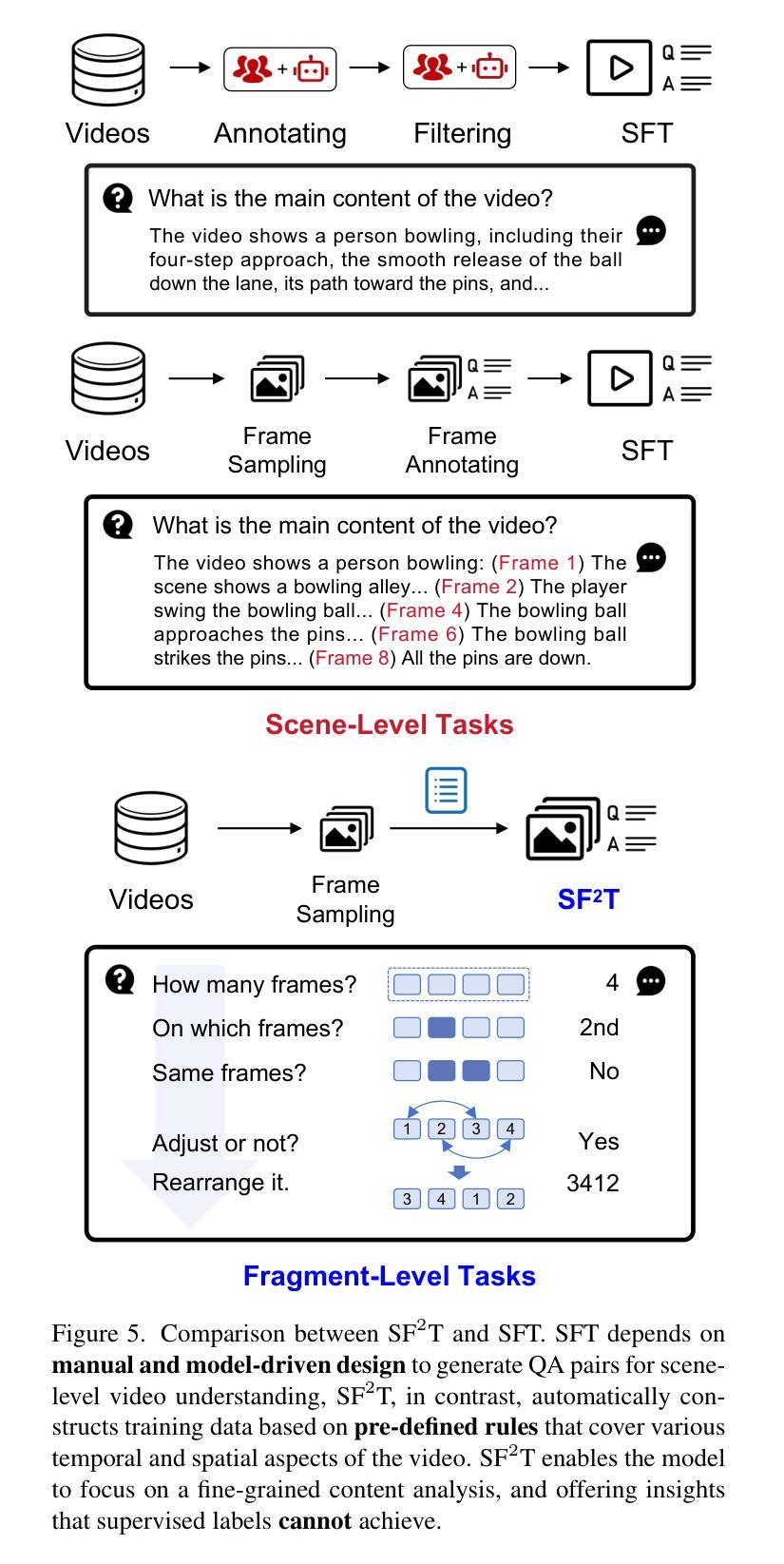
SF2T: Self-supervised Fragment Finetuning of Video-LLMs for Fine-Grained Understanding
Authors:Yangliu Hu, Zikai Song, Na Feng, Yawei Luo, Junqing Yu, Yi-Ping Phoebe Chen, Wei Yang
Video-based Large Language Models (Video-LLMs) have witnessed substantial advancements in recent years, propelled by the advancement in multi-modal LLMs. Although these models have demonstrated proficiency in providing the overall description of videos, they struggle with fine-grained understanding, particularly in aspects such as visual dynamics and video details inquiries. To tackle these shortcomings, we find that fine-tuning Video-LLMs on self-supervised fragment tasks, greatly improve their fine-grained video understanding abilities. Hence we propose two key contributions:(1) Self-Supervised Fragment Fine-Tuning (SF$^2$T), a novel effortless fine-tuning method, employs the rich inherent characteristics of videos for training, while unlocking more fine-grained understanding ability of Video-LLMs. Moreover, it relieves researchers from labor-intensive annotations and smartly circumvents the limitations of natural language, which often fails to capture the complex spatiotemporal variations in videos; (2) A novel benchmark dataset, namely FineVidBench, for rigorously assessing Video-LLMs’ performance at both the scene and fragment levels, offering a comprehensive evaluation of their capabilities. We assessed multiple models and validated the effectiveness of SF$^2$T on them. Experimental results reveal that our approach improves their ability to capture and interpret spatiotemporal details.
基于视频的大型语言模型(Video-LLMs)近年来取得了重大进展,这得益于多模态LLMs的进步。尽管这些模型在提供视频整体描述方面表现出色,但在精细理解方面仍存在困难,特别是在视频动态和细节查询等方面。为了克服这些缺点,我们发现对Video-LLMs进行自监督片段任务的微调,可以大大提高其精细视频理解的能力。因此,我们提出了两项关键贡献:(1)自监督片段微调(SF$^2$T)是一种新型的无费力微调方法,它利用视频丰富的内在特征进行训练,同时解锁Video-LLMs的更多精细理解能力。此外,它减轻了研究人员对劳动密集型注释的依赖,并巧妙地克服了自然语言的限制,后者通常无法捕捉视频中的复杂时空变化;(2)一个用于严格评估Video-LLMs在场景和片段级别的性能的新型基准数据集FineVidBench,对它们的能力进行全面评估。我们评估了多个模型,并验证了它们在SF$^2$T上的有效性。实验结果表明,我们的方法提高了它们捕捉和解释时空细节的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR2025
Summary
视频类大语言模型(Video-LLMs)近年来在多模态LLMs的推动下取得了显著进展,但仍存在精细理解视频方面的不足,如视觉动态和视频细节查询等方面。为解决这些问题,研究发现通过自我监督片段任务对Video-LLMs进行微调,可以大大提高其精细视频理解的能力。因此,本文提出了两项关键贡献:一是自我监督片段微调(SF^2T)方法,该方法利用视频的丰富内在特性进行训练,解锁了Video-LLMs的精细理解能力,无需繁琐的人工标注,有效规避了自然语言在捕捉视频复杂时空变化方面的局限;二是推出一个名为FineVidBench的新基准数据集,用于严格评估Video-LLMs在场景和片段两个层次上的性能,为全面评价其能力提供了平台。实验验证了我们方法在提高捕捉和解释时空细节的能力上的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- Video-LLMs近年虽有多模态进展,但在视频精细理解方面存在不足。
- 自我监督片段微调(SF^2T)方法旨在提高Video-LLMs的精细视频理解能力。
- SF^2T利用视频的丰富内在特性进行训练,无需大量人工标注。
- SF^2T有效规避了自然语言在捕捉视频复杂时空变化方面的局限。
- FineVidBench数据集用于评估Video-LLMs在场景和片段两个层次上的性能。
- 实验验证了SF^2T方法在提高捕捉和解释视频时空细节的能力上的有效性。
点此查看论文截图
Zero-Shot Cross-Domain Code Search without Fine-Tuning
Authors:Keyu Liang, Zhongxin Liu, Chao Liu, Zhiyuan Wan, David Lo, Xiaohu Yang
Code search aims to retrieve semantically relevant code snippets for natural language queries. While pre-trained language models (PLMs) have shown remarkable performance in this task, they struggle in cross-domain scenarios, often requiring costly fine-tuning or facing performance drops in zero-shot settings. RAPID, which generates synthetic data for model fine-tuning, is currently the only effective method for zero-shot cross-domain code search. Despite its effectiveness, RAPID demands substantial computational resources for fine-tuning and needs to maintain specialized models for each domain, underscoring the need for a zero-shot, fine-tuning-free approach for cross-domain code search. The key to tackling zero-shot cross-domain code search lies in bridging the gaps among domains. In this work, we propose to break the query-code matching process of code search into two simpler tasks: query-comment matching and code-code matching. Our empirical study reveals the strong complementarity among the three matching schemas in zero-shot cross-domain settings, i.e., query-code, query-comment, and code-code matching. Based on the findings, we propose CodeBridge, a zero-shot, fine-tuning-free approach for cross-domain code search. Specifically, CodeBridge uses Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate comments and pseudo-code, then combines query-code, query-comment, and code-code matching via PLM-based similarity scoring and sampling-based fusion. Experimental results show that our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art PLM-based code search approaches, i.e., CoCoSoDa and UniXcoder, by an average of 21.4% and 24.9% in MRR, respectively, across three datasets. Our approach also yields results that are better than or comparable to those of the zero-shot cross-domain code search approach RAPID, which requires costly fine-tuning.
代码搜索旨在针对自然语言查询检索语义相关的代码片段。虽然预训练语言模型(PLM)在此任务中表现出卓越的性能,但在跨域场景中它们面临挑战,通常需要昂贵的微调,或在零样本设置中面临性能下降。RAPID是一种为模型微调生成合成数据的方法,目前是零样本跨域代码搜索中唯一有效的方法。尽管其有效,但RAPID需要大量的计算资源进行微调,并且需要为每个域维护专用模型,这突显了零样本、无需微调的跨域代码搜索方法的必要性。解决零样本跨域代码搜索的关键在于缩小域之间的差距。在这项工作中,我们提议将代码搜索的查询-代码匹配过程分解为两个更简单的任务:查询-注释匹配和代码-代码匹配。我们的实证研究揭示了三种匹配模式在零样本跨域设置中的强烈互补性,即查询-代码、查询-注释和代码-代码匹配。基于这些发现,我们提出了CodeBridge,这是一种用于跨域代码搜索的零样本、无需微调的方法。具体来说,CodeBridge使用大型语言模型(LLM)生成注释和伪代码,然后通过基于PLM的相似性评分和基于采样的融合,结合查询-代码、查询-注释和代码-代码匹配。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于最先进的PLM驱动的代码搜索方法CoCoSoDa和UniXcoder,在三个数据集上的平均MRR分别提高了21.4%和24.9%。我们的方法得到的结果优于或等于需要昂贵微调的零样本跨域代码搜索方法RAPID的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
该研究旨在解决跨域代码搜索问题,提出了一种无需微调的零门槛跨域代码搜索方法CodeBridge。该方法利用大型语言模型(LLMs)生成注释和伪代码,结合查询代码、查询注释和代码代码的匹配,通过基于PLM的相似度评分和基于采样的融合,实现跨域代码搜索。实验结果表明,该方法在三个数据集上的性能优于现有PLM代码搜索方法,并与需要昂贵微调成本的跨域代码搜索方法RAPID相比具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways:
- Code search旨在通过自然语言查询检索语义相关的代码片段。
- 预训练语言模型(PLMs)在代码搜索任务中表现出色,但在跨域场景中面临挑战。
- 当前有效的跨域代码搜索方法RAPID需要昂贵的微调成本和为每个领域维护专用模型。
- 提出了一种无需微调的零门槛跨域代码搜索方法CodeBridge。
- CodeBridge利用LLMs生成注释和伪代码,结合查询与代码、查询与注释以及代码代码的匹配来解决跨域代码搜索问题。
- 实验结果表明CodeBridge在多个数据集上的性能优于现有PLM代码搜索方法。
点此查看论文截图

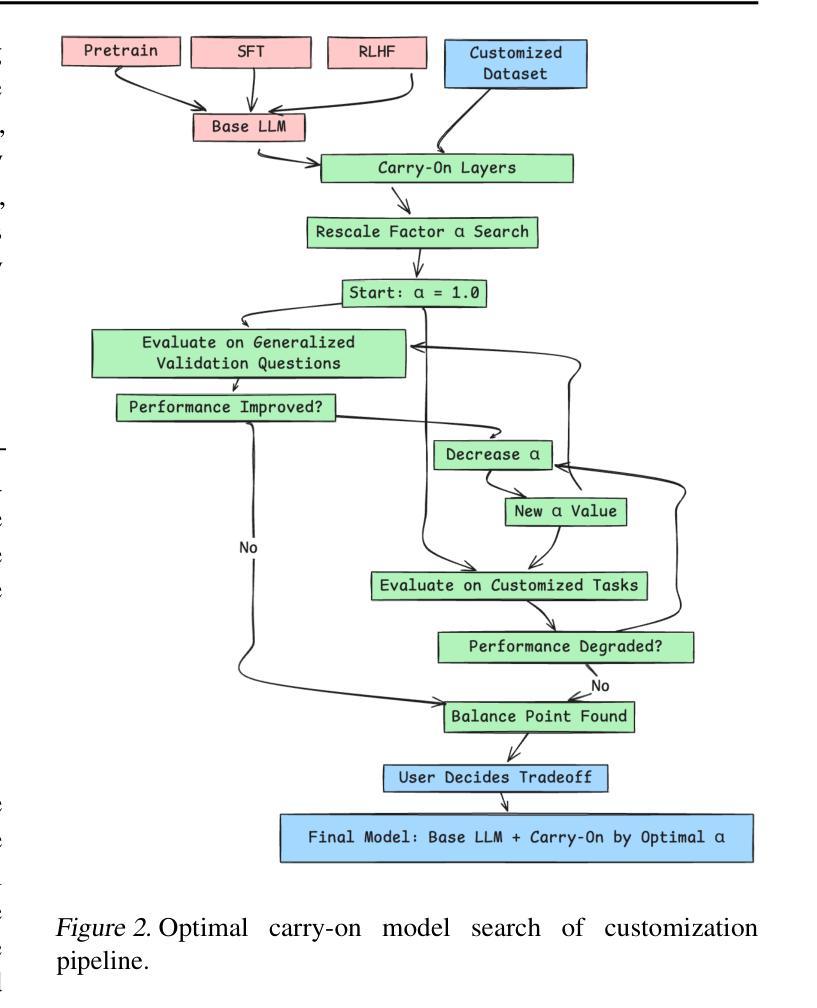
GPT Carry-On: Training Foundation Model for Customization Could Be Simple, Scalable and Affordable
Authors:Jianqiao Wangni
Modern large language foundation models (LLM) have now entered the daily lives of millions of users. We ask a natural question whether it is possible to customize LLM for every user or every task. From system and industrial economy consideration, general continue-training or fine-tuning still require substantial computation and memory of training GPU nodes, whereas most inference nodes under deployment, possibly with lower-end GPUs, are configured to make forward pass fastest possible. We propose a framework to take full advantages of existing LLMs and systems of online service. We train an additional branch of transformer blocks on the final-layer embedding of pretrained LLMs, which is the base, then a carry-on module merge the base models to compose a customized LLM. We can mix multiple layers, or multiple LLMs specialized in different domains such as chat, coding, math, to form a new mixture of LLM that best fit a new task. As the base model don’t need to update parameters, we are able to outsource most computation of the training job on inference nodes, and only train a lightweight carry-on on training nodes, where we consume less than 1GB GPU memory to train a 100M carry-on layer on 30B LLM. We tested Qwen and DeepSeek opensourced models for continue-pretraining and got faster loss convergence. We use it to improve solving math questions with extremely small computation and model size, with 1000 data samples of chain-of-thoughts, and as small as 1 MB parameters of two layer layer carry-on, and the results are promising.
现代大型语言基础模型(LLM)已经融入数百万用户的日常生活中。我们自然地提出一个问题,是否可以为每个用户或每个任务定制LLM。从系统和工业经济的角度来看,一般的继续训练或微调仍然需要大量的计算和训练GPU节点的内存,而大多数正在部署的推理节点,可能配置有较低端的GPU,被设置为尽可能快地进行前向传递。我们提出了一个框架,以充分利用现有的LLM和在线服务系统。我们在预训练LLM的最终层嵌入基础上训练额外的转换器块分支,然后通过一个继续模块合并基础模型,以组成定制的LLM。我们可以混合多层,或者混合专门用于不同领域的多个LLM,如聊天、编码、数学等,以形成最适合新任务的新混合LLM。由于基础模型无需更新参数,我们能够将在推理节点上的大部分训练任务外包,仅对训练节点进行轻量级的继续训练,在30B LLM上使用不到1GB的GPU内存即可训练一个100M的继续层。我们测试了Qwen和DeepSeek的开源模型进行持续预训练,并获得了更快的损失收敛。我们用它来改善解决数学问题的性能,只需极小量的计算和模型大小,使用1000个思维链数据样本,两层继续层参数仅1MB,结果令人鼓舞。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)已融入用户的日常生活,但针对每个用户或任务的定制化需求仍存在挑战。针对系统与经济因素的考量,通用持续训练或微调仍需要大量计算与内存资源。本文提出一种框架,充分利用现有的LLM与在线服务系统,通过训练额外的transformer块来作为基础模型,并在其上附加一个继续模块,组合形成定制化LLM。该框架可以融合多层或不同领域的多个LLM,以适应新任务需求。由于基础模型无需更新参数,大部分计算任务可外包给推理节点,仅对轻量级的继续模块进行训练,降低了GPU内存的使用。实验证明,该方法在继续预训练模型(如Qwen和DeepSeek)上实现了更快的损失收敛,并在解决数学问题的场景中展现了良好效果,仅需极小计算量和模型大小。
Key Takeaways
- LLM已广泛应用于日常生活,但针对个性化任务和用户需求进行定制具有挑战性。
- 通用持续训练或微调LLM需要大量计算与内存资源。
- 提出一种新型框架,通过训练额外的transformer块并结合继续模块,以形成定制化的LLM。
- 该框架可融合多层或不同领域的LLM以适应新任务。
- 基础模型无需更新参数,降低了对推理节点的计算与内存需求。
- 实验证明该方法在继续预训练模型上实现了更快的损失收敛。
点此查看论文截图


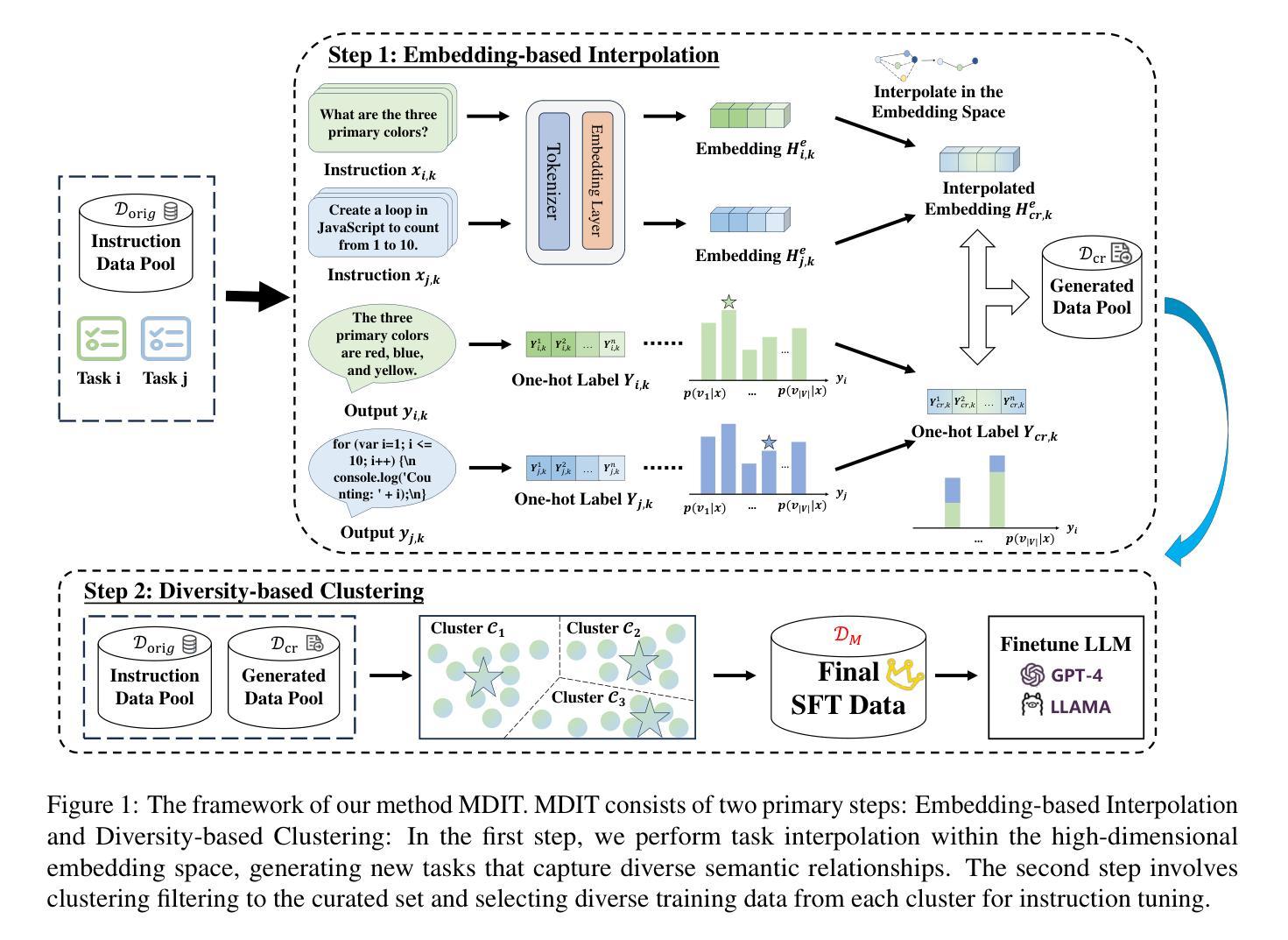
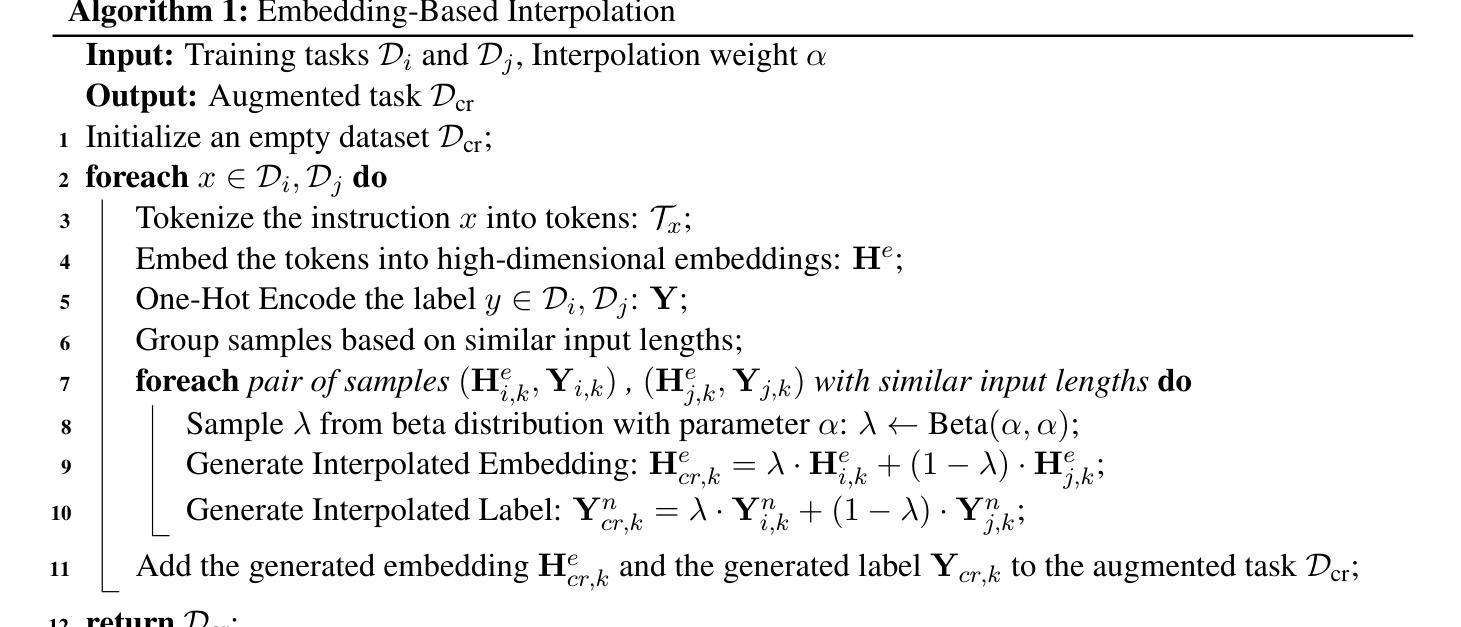
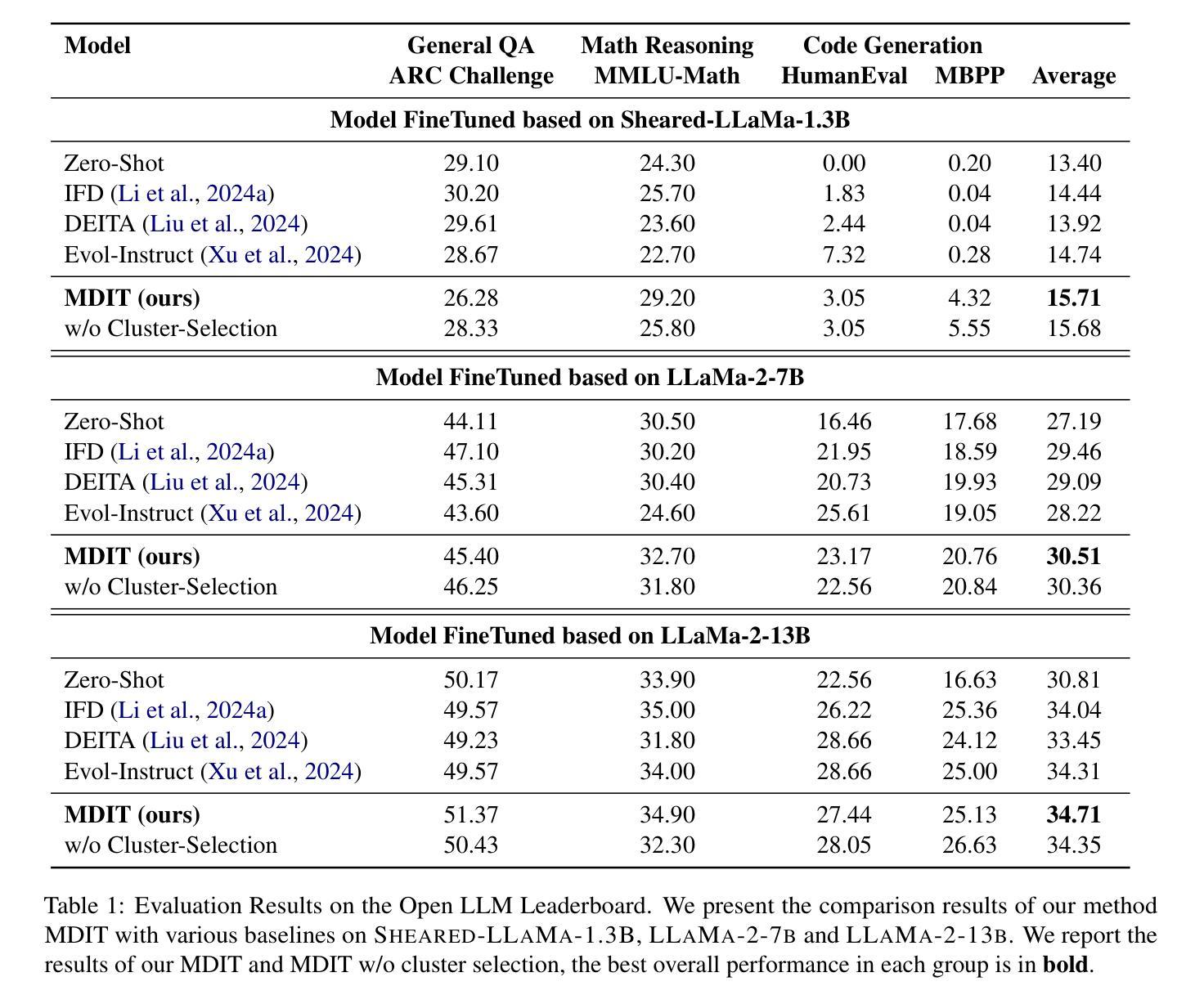
MDIT: A Model-free Data Interpolation Method for Diverse Instruction Tuning
Authors:Yangning Li, Zihua Lan, Lv Qingsong, Yinghui Li, Hai-Tao Zheng
As Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly applied across various tasks, instruction tuning has emerged as a critical method for enhancing model performance. However, current data management strategies face substantial challenges in generating diverse and comprehensive data, restricting further improvements in model performance. To address this gap, we propose MDIT, a novel model-free data interpolation method for diverse instruction tuning, which generates varied and high-quality instruction data by performing task interpolation. Moreover, it contains diversity-based clustering strategies to ensure the diversity of the training data. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves superior performance in multiple benchmark tasks. The LLMs finetuned with MDIT show significant improvements in numerous tasks such as general question answering, math reasoning, and code generation. MDIT offers an efficient and automatic data synthetic method, generating diverse instruction data without depending on external resources while expanding the application potential of LLMs in complex environments.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在各项任务中的应用日益广泛,指令微调已成为提高模型性能的关键方法。然而,当前的数据管理策略在生成多样且全面的数据方面面临重大挑战,限制了模型性能的进一步提高。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了MDIT,这是一种用于多样指令微调的新型无模型数据插值方法,它通过任务插值生成多样且高质量的任务指令数据。此外,它还包含基于多样性的聚类策略,以确保训练数据的多样性。大量实验表明,我们的方法在多个基准测试任务上表现优异。使用MDIT微调的大型语言模型在通用问答、数学推理和代码生成等多项任务中表现出显著改进。MDIT提供了一种高效且自动的数据合成方法,能够在不依赖外部资源的情况下生成多样的指令数据,从而扩大了大型语言模型在复杂环境中的应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLM)在各任务中的应用日益广泛,指令微调作为提升模型性能的关键方法受到了广泛关注。然而,当前的数据管理策略在生成多样且全面的数据方面面临巨大挑战,限制了模型性能的进一步提升。为解决这一差距,我们提出了MDIT,一种用于多样指令微调的无模型数据插值新方法。它通过任务插值生成多样且高质量的任务指令数据,并包含基于多样性的聚类策略以确保训练数据的多样性。实验表明,该方法在多个基准任务上表现优异,使用MDIT进行微调的LLM在通用问答、数学推理和代码生成等多项任务中取得了显著改进。MDIT提供了一种高效、自动的数据合成方法,能够在不依赖外部资源的情况下生成多样的指令数据,扩大了LLM在复杂环境中的应用潜力。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs正广泛应用于各种任务,指令微调是提升性能的关键方法。
- 当前数据管理策略在生成多样、全面的数据方面存在挑战。
- MDIT是一种新型的无模型数据插值方法,用于多样指令微调。
- MDIT通过任务插值生成多样且高质量的任务指令数据。
- MDIT包含基于多样性的聚类策略以确保训练数据的多样性。
- 实验证明MDIT在多个基准任务上表现优异,显著提升了LLM在多项任务中的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Face-LLaVA: Facial Expression and Attribute Understanding through Instruction Tuning
Authors:Ashutosh Chaubey, Xulang Guan, Mohammad Soleymani
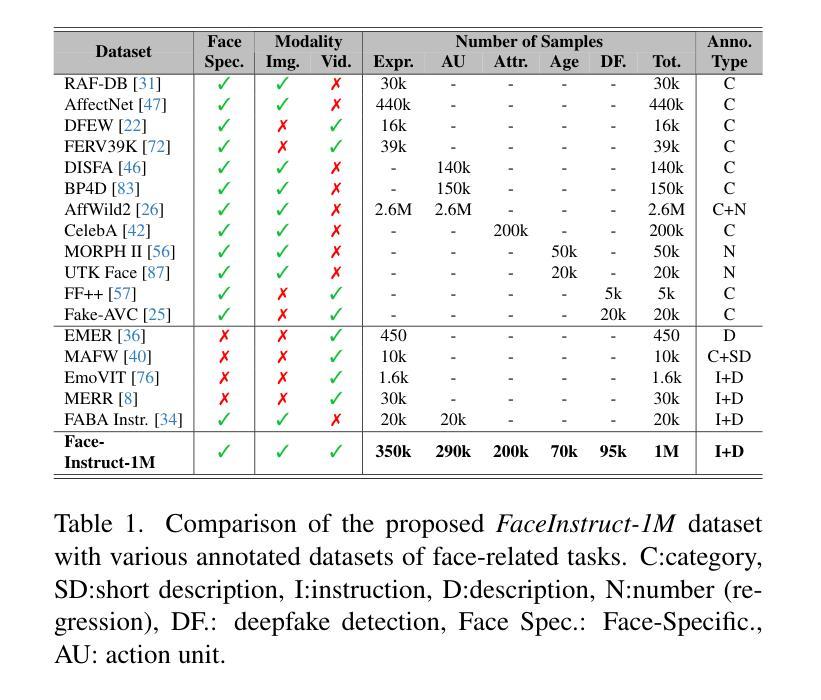
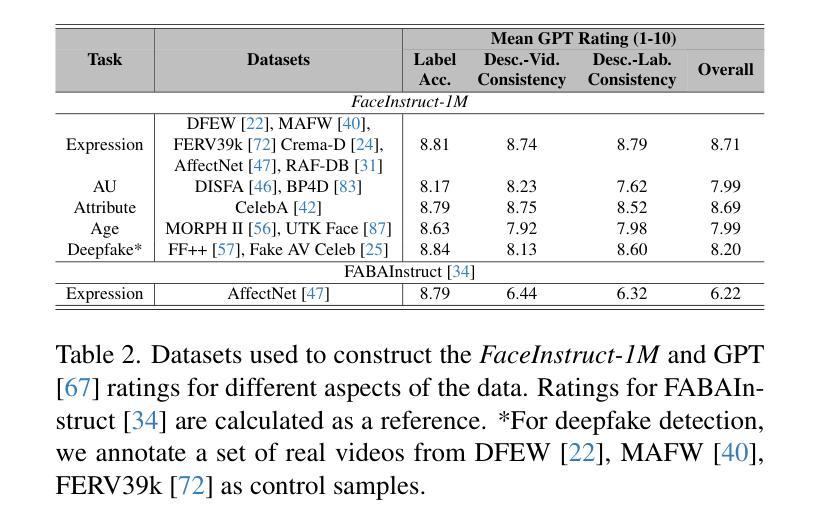
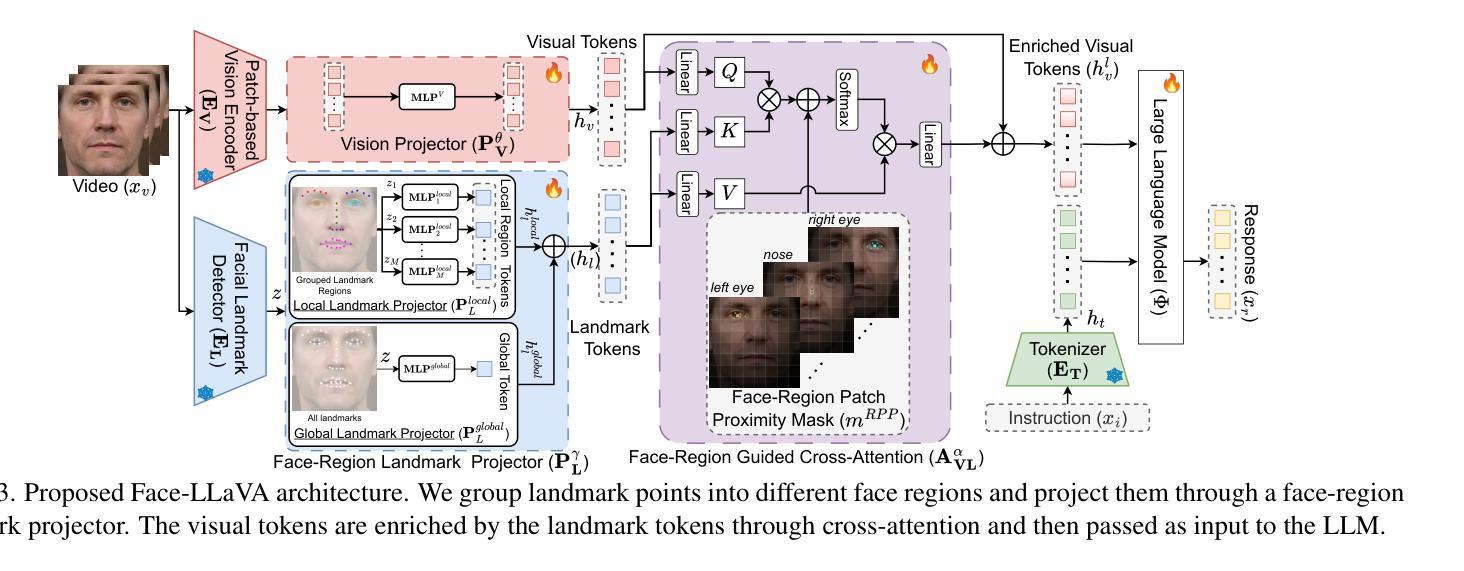
The human face plays a central role in social communication, necessitating the use of performant computer vision tools for human-centered applications. We propose Face-LLaVA, a multimodal large language model for face-centered, in-context learning, including facial expression and attribute recognition. Additionally, Face-LLaVA is able to generate natural language descriptions that can be used for reasoning. Leveraging existing visual databases, we first developed FaceInstruct-1M, a face-centered database for instruction tuning MLLMs for face processing. We then developed a novel face-specific visual encoder powered by Face-Region Guided Cross-Attention that integrates face geometry with local visual features. We evaluated the proposed method across nine different datasets and five different face processing tasks, including facial expression recognition, action unit detection, facial attribute detection, age estimation and deepfake detection. Face-LLaVA achieves superior results compared to existing open-source MLLMs and competitive performance compared to commercial solutions. Our model output also receives a higher reasoning rating by GPT under a zero-shot setting across all the tasks. Both our dataset and model wil be released at https://face-llava.github.io to support future advancements in social AI and foundational vision-language research.
人脸在社会交流中具有核心作用,因此需要为以人为中心的应用使用高性能计算机视觉工具。我们提出了Face-LLaVA,这是一种面向人脸的上下文学习多模态大型语言模型,包括面部表情和属性识别。此外,Face-LLaVA能够生成自然语言描述,可用于推理。我们借助现有的视觉数据库,首先开发了面向人脸的数据库FaceInstruct-1M,用于调整面向人脸处理的MLLM。然后我们开发了一种新型的人脸特定视觉编码器,该编码器由Face-Region Guided Cross-Attention驱动,可以集成人脸几何与局部视觉特征。我们在九个不同的数据集和五个不同的人脸处理任务上评估了所提出的方法,包括面部表情识别、动作单元检测、面部属性检测、年龄估计和深度伪造检测。Face-LLaVA与现有的开源MLLM相比取得了优越的结果,并在所有任务中实现了零样本设置下的GPT更高的推理评分,与商业解决方案相比具有竞争力。我们的数据集和模型将在https://face-llava.github.io上发布,以支持社交AI和基础视觉语言研究的未来发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://face-llava.github.io
Summary
人脸识别技术在社交通讯中具有重要作用,为此需要运用高性能计算机视觉工具以应用于人类为中心的场合。研究提出了Face-LLaVA,一个为以人脸为中心的场景开发的多模态大型语言模型,具备面部表情和属性识别功能,并能生成自然语言描述用于推理。研究建立了FaceInstruct-1M数据库用于指令调整MLLMs人脸处理功能,并开发出一种新型的人脸特定视觉编码器Face-Region Guided Cross-Attention。模型性能通过多项任务测试展现出优异成果,相比现有开源模型更胜一筹且和商业化解决方案竞争力相当。此外模型输出可通过GPT零样本设置进行推理评价。研究的数据集和模型将在https://face-llava.github.io发布,以支持未来社交人工智能和基础视觉语言研究的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 人脸识别在社交通讯中扮演核心角色,需要高性能计算机视觉工具支持。
- 提出Face-LLaVA模型,为多模态大型语言模型在人脸为中心的场景中应用提供解决方案。
- Face-LLaVA具备面部表情和属性识别功能,能生成自然语言描述以支持推理。
- 研究建立FaceInstruct-1M数据库用于优化模型的面部处理性能。
- 引入Face-Region Guided Cross-Attention新型人脸特定视觉编码器,结合面部几何与局部视觉特征。
- Face-LLaVA在多个数据集和任务测试中展现出优越性能,包括面部表情识别、动作单元检测等。
点此查看论文截图



Boundary representation learning via Transformer
Authors:Qiang Zou, Lizhen Zhu
The recent rise of generative artificial intelligence (AI), powered by Transformer networks, has achieved remarkable success in natural language processing, computer vision, and graphics. However, the application of Transformers in computer-aided design (CAD), particularly for processing boundary representation (B-rep) models, remains largely unexplored. To bridge this gap, this paper introduces Boundary Representation Transformer (BRT), a novel method adapting Transformer for B-rep learning. B-rep models pose unique challenges due to their irregular topology and continuous geometric definitions, which are fundamentally different from the structured and discrete data Transformers are designed for. To address this, BRT proposes a continuous geometric embedding method that encodes B-rep surfaces (trimmed and untrimmed) into B'ezier triangles, preserving their shape and continuity without discretization. Additionally, BRT employs a topology-aware embedding method that organizes these geometric embeddings into a sequence of discrete tokens suitable for Transformers, capturing both geometric and topological characteristics within B-rep models. This enables the Transformer’s attention mechanism to effectively learn shape patterns and contextual semantics of boundary elements in a B-rep model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BRT achieves state-of-the-art performance in part classification and feature recognition tasks.
最近兴起的基于Transformer网络的生成式人工智能(AI)在自然语言处理、计算机视觉和图形领域取得了显著的成就。然而,Transformer在计算机辅助设计(CAD)中的应用,特别是在处理边界表示(B-rep)模型方面,仍被大大忽视。为了填补这一空白,本文引入了边界表示转换器(BRT),这是一种适应于B-rep学习的新型方法。B-rep模型由于其不规则拓扑和连续几何定义而带来独特挑战,这些特性与Transformer设计的结构化离散数据存在根本差异。为了解决这一问题,BRT提出了一种连续几何嵌入方法,该方法将B-rep表面(修剪和未修剪)编码为Bezier三角形,在保持其形状和连续性的同时无需离散化。此外,BRT还采用了一种拓扑感知嵌入方法,将这些几何嵌入整理成适合Transformer的离散令牌序列,能够捕捉B-rep模型中的几何和拓扑特征。这使得Transformer的注意力机制能够有效地学习B-rep模型中边界元素的形状模式和上下文语义。大量实验表明,BRT在零件分类和特征识别任务上达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Transformer网络的生成式人工智能在自然语言处理、计算机视觉和图形等领域取得了显著成功,但在计算机辅助设计(CAD)中的应用,特别是在处理边界表示(B-rep)模型方面仍鲜有探索。本文提出Boundary Representation Transformer(BRT)新方法,适应Transformer进行B-rep学习。针对B-rep模型的不规则拓扑和连续几何定义带来的独特挑战,BRT提出一种连续几何嵌入方法,将边界表示(修剪和未修剪)编码为Bézier三角形,保留其形状和连续性而不进行离散化。此外,BRT采用拓扑感知嵌入方法,将这些几何嵌入组织成适合Transformer的离散令牌序列,捕捉B-rep模型中的几何和拓扑特征。这使得Transformer的注意力机制能够有效地学习边界元素的形状模式和上下文语义。大量实验表明,BRT在零件分类和特征识别任务上取得了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式人工智能在多个领域取得显著成功,但在计算机辅助设计(CAD)中的应用,特别是处理边界表示(B-rep)模型方面仍存在差距。
- 本文提出了Boundary Representation Transformer(BRT)新方法,旨在适应Transformer进行B-rep学习。
- BRT解决了B-rep模型的不规则拓扑和连续几何定义的独特挑战。
- BRT通过连续几何嵌入方法将B-rep模型编码为Bézier三角形,保持其形状和连续性,避免离散化。
- BRT采用拓扑感知嵌入方法,将几何嵌入组织成离散令牌序列,适合Transformer处理。
- BRT能够捕捉B-rep模型中的几何和拓扑特征,通过Transformer的注意力机制学习边界元素的形状模式和上下文语义。
点此查看论文截图

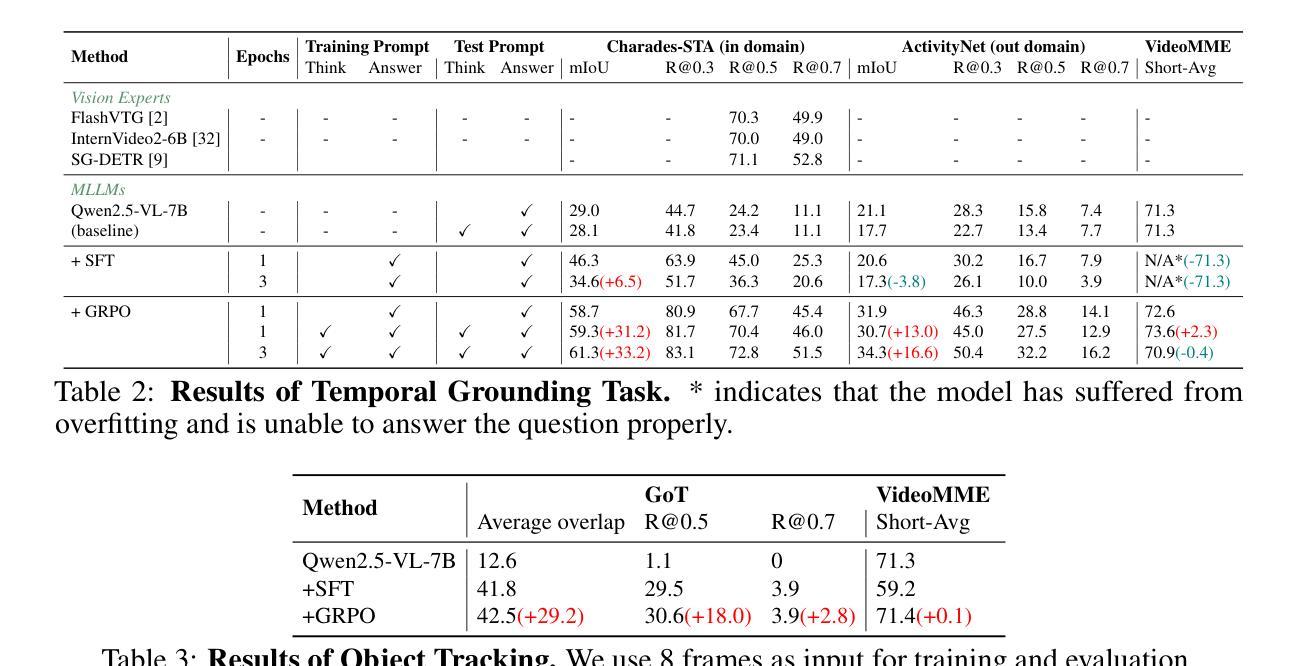
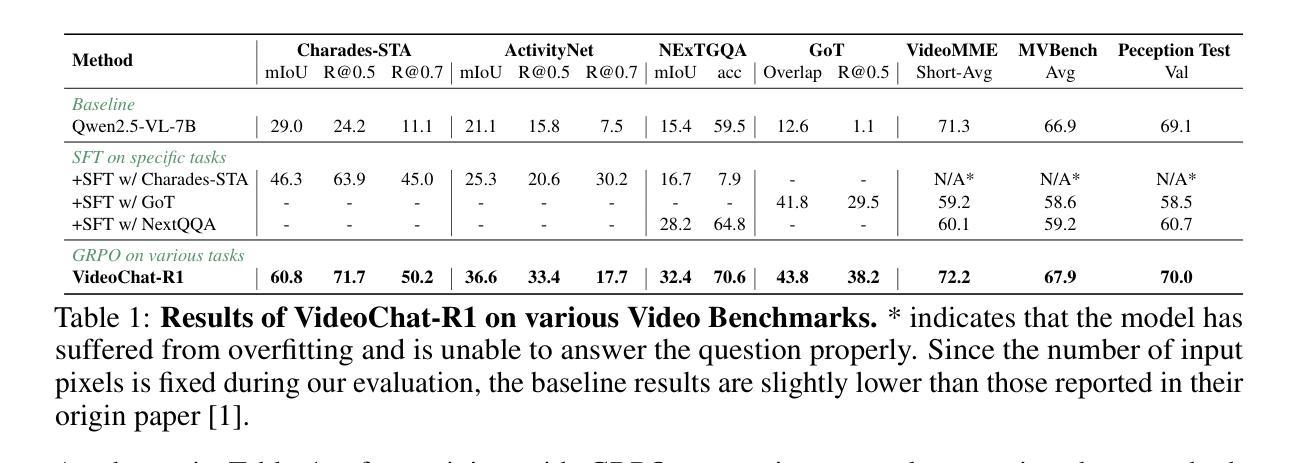
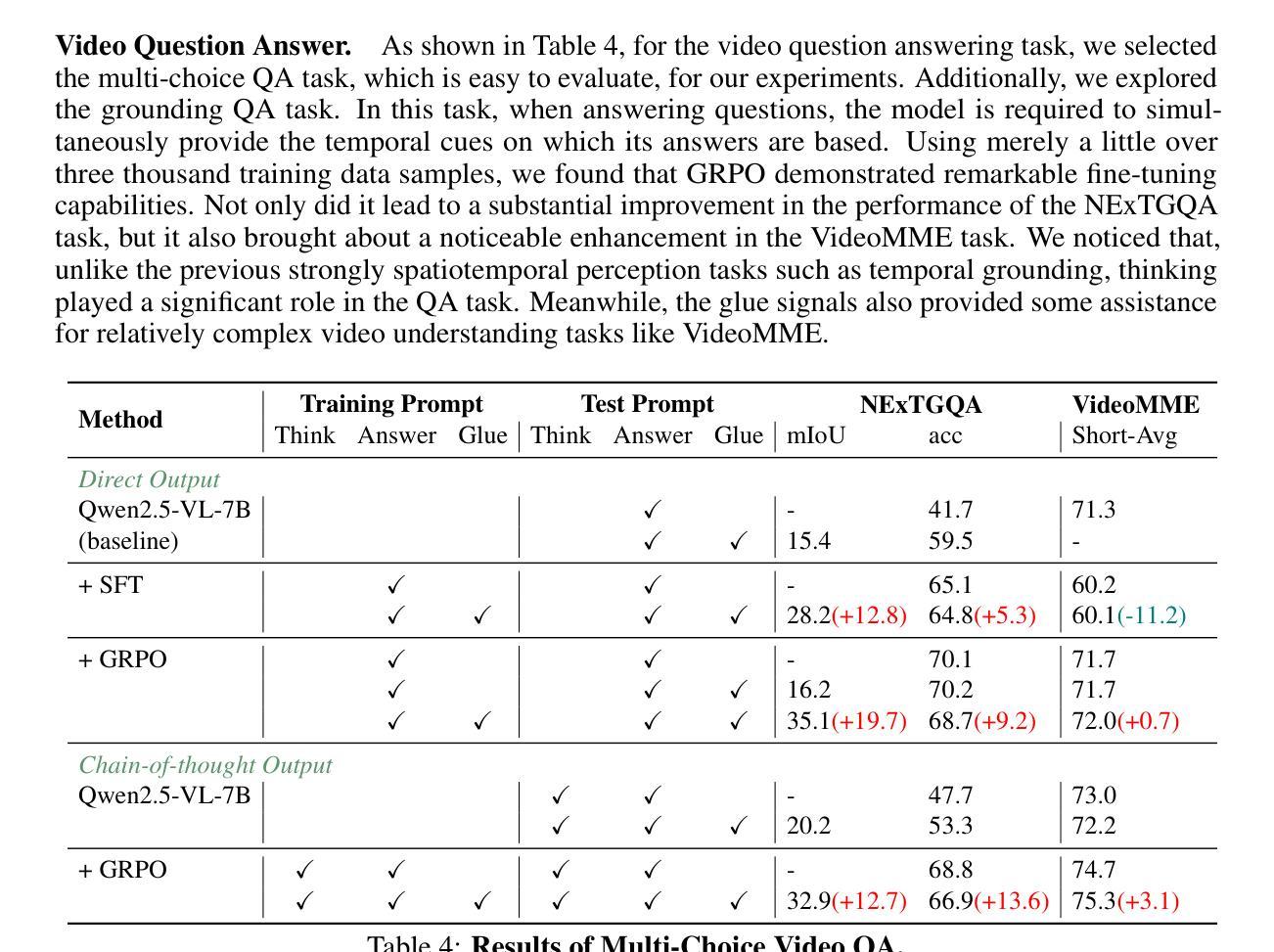
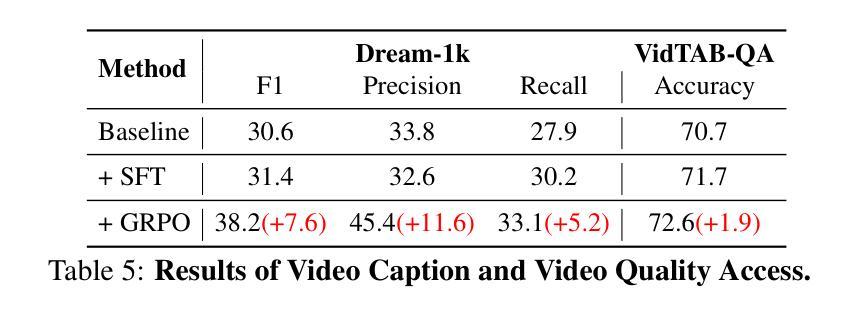
VideoChat-R1: Enhancing Spatio-Temporal Perception via Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
Authors:Xinhao Li, Ziang Yan, Desen Meng, Lu Dong, Xiangyu Zeng, Yinan He, Yali Wang, Yu Qiao, Yi Wang, Limin Wang
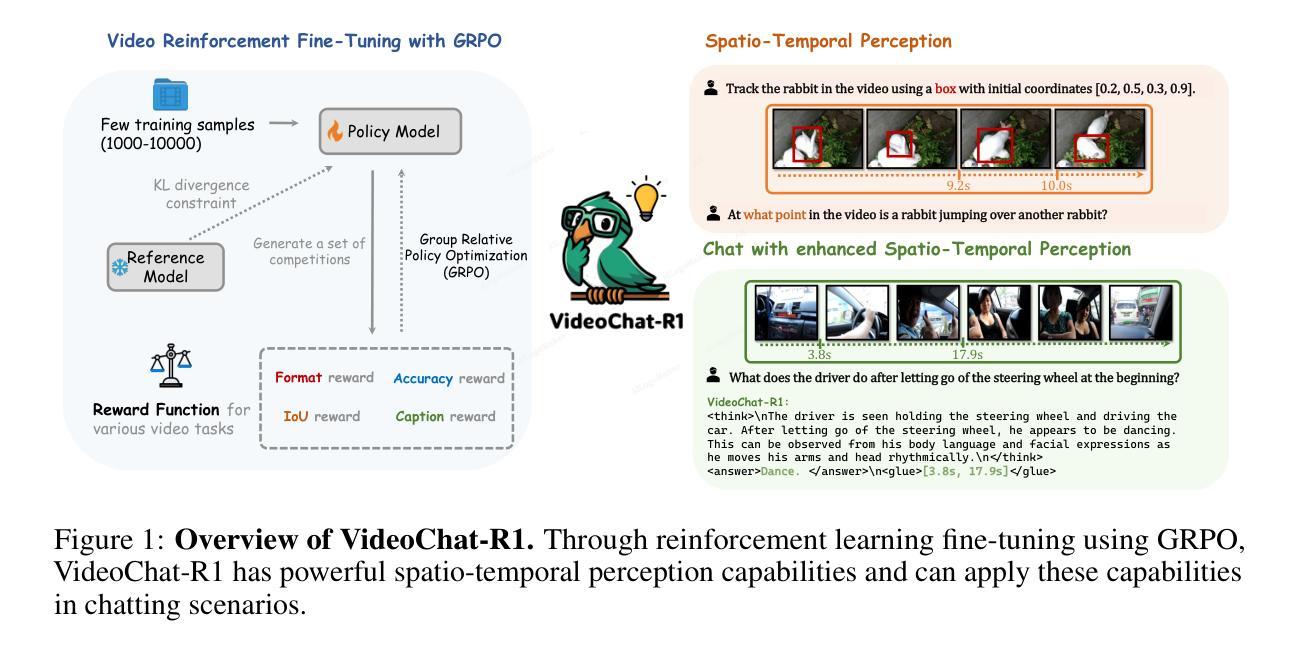
Recent advancements in reinforcement learning have significantly advanced the reasoning capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs). While approaches such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) and rule-based reward mechanisms demonstrate promise in text and image domains, their application to video understanding remains limited. This paper presents a systematic exploration of Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT) with GRPO for video MLLMs, aiming to enhance spatio-temporal perception while maintaining general capabilities. Our experiments reveal that RFT is highly data-efficient for task-specific improvements. Through multi-task RFT on spatio-temporal perception objectives with limited samples, we develop VideoChat-R1, a powerful video MLLM that achieves state-of-the-art performance on spatio-temporal perception tasks without sacrificing chat ability, while exhibiting emerging spatio-temporal reasoning abilities. Compared to Qwen2.5-VL-7B, VideoChat-R1 boosts performance several-fold in tasks like temporal grounding (+31.8) and object tracking (+31.2). Additionally, it significantly improves on general QA benchmarks such as VideoMME (+0.9), MVBench (+1.0), and Perception Test (+0.9). Our findings underscore the potential of RFT for specialized task enhancement of Video MLLMs. We hope our work offers valuable insights for future RL research in video MLLMs.
最近强化学习领域的进展极大地提升了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的推理能力。虽然集团相对策略优化(GRPO)和基于规则的奖励机制在文本和图像领域展现出了一定的前景,但它们在视频理解方面的应用仍然有限。本文系统地探讨了使用GRPO的强化微调(RFT)在视频MLLMs中的应用,旨在提高时空感知能力的同时保持其通用能力。我们的实验表明,RFT对于特定任务的改进非常数据高效。通过在有限的样本上对时空感知目标进行多任务RFT,我们开发出了VideoChat-R1,这是一款强大的视频MLLM,它在时空感知任务上实现了最新性能,同时不牺牲其对话能力,并展现出新兴的时空推理能力。与Qwen2.5-VL-7B相比,VideoChat-R1在诸如时间定位(+31.8)和对象跟踪(+31.2)等任务上的性能提高了数倍。此外,它在一般问答基准测试(如VideoMME(+0.9)、MVBench(+1.0)和感知测试(+0.9))方面也取得了显著改进。我们的研究结果强调了RFT在视频MLLM专项任务增强方面的潜力。我们希望我们的研究能为未来视频MLLM的强化学习研究提供有价值的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期强化学习在提升多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的推理能力方面取得了重要进展。本研究系统性地探讨了强化精细调节(RFT)结合组相对策略优化(GRPO)在视频MLLMs中的应用,旨在提升时空感知能力的同时保持通用能力。实验表明,RFT在特定任务改进方面非常注重数据效率。通过多任务RFT在时空感知目标上的有限样本训练,成功开发出VideoChat-R1,其在时空感知任务上实现卓越性能,不牺牲对话能力,展现出新兴的时空推理能力。与Qwen2.5-VL-7B相比,VideoChat-R1在诸如时序定位(+31.8)和对象跟踪(+31.2)等任务上的性能大幅提升。此外,它在一般问答基准测试中也有所改进,如VideoMME(+0.9)、MVBench(+1.0)和Perception Test(+0.9)。本研究突显了RFT在视频MLLMs专项任务增强方面的潜力,为未来视频MLLMs的强化学习研究提供宝贵见解。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习在多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的推理能力方面取得进展。
- 研究通过结合强化精细调节(RFT)和组相对策略优化(GRPO)提升视频MLLMs的时空感知能力。
- RFT是数据高效的,适用于特定任务的改进。
- 新模型VideoChat-R1在时空感知任务上表现卓越,同时保持对话能力。
- VideoChat-R1相较于其他模型在时序定位和对象跟踪等任务上有显著性能提升。
- VideoChat-R1在一般问答基准测试中也表现出改进。
点此查看论文截图

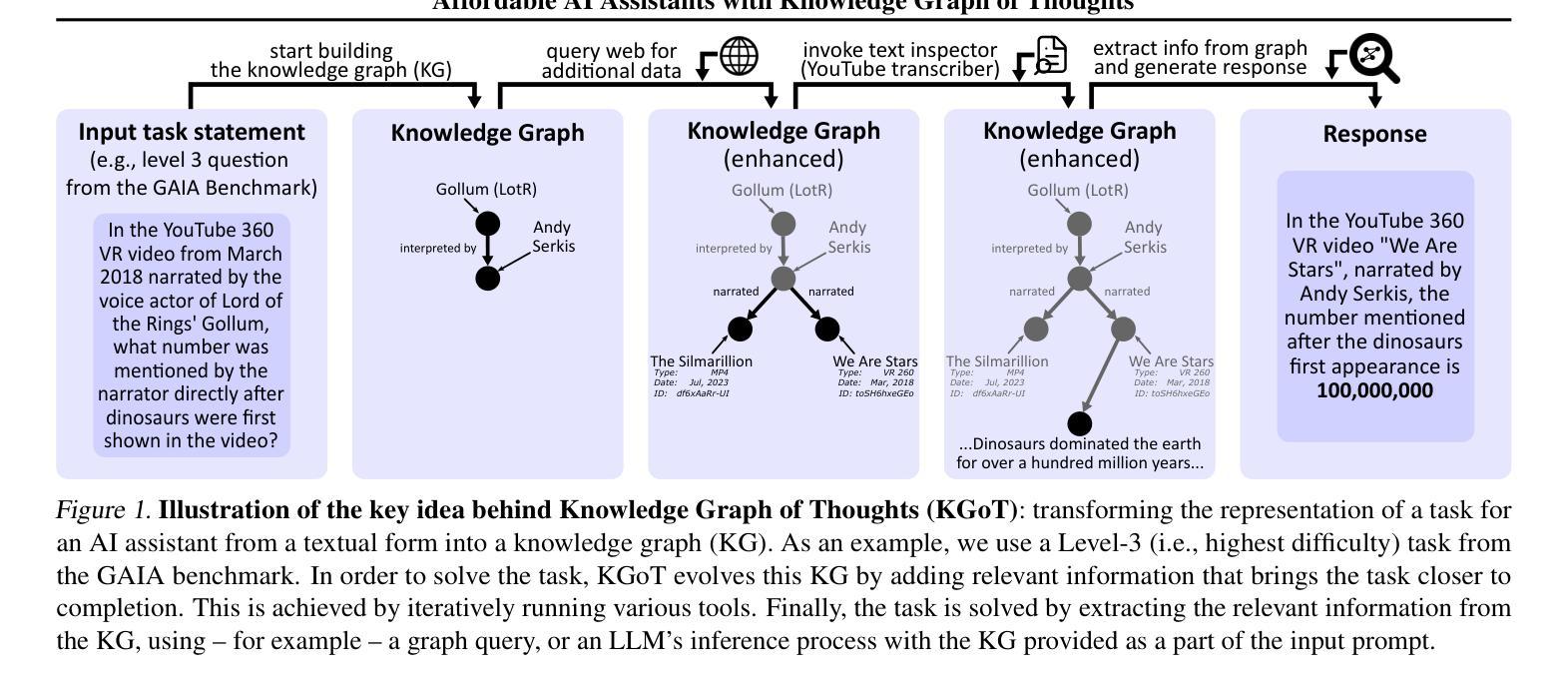
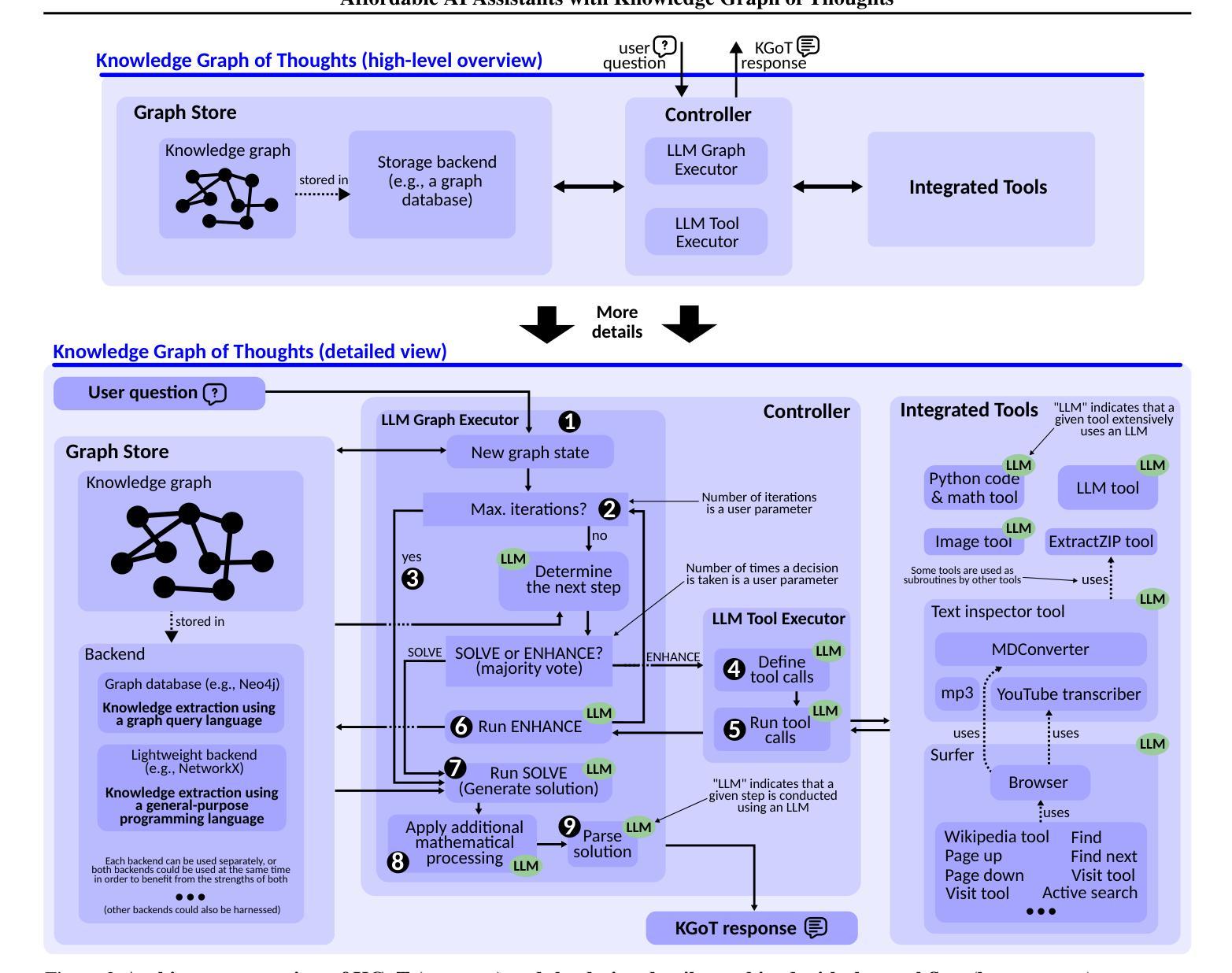
Affordable AI Assistants with Knowledge Graph of Thoughts
Authors:Maciej Besta, Lorenzo Paleari, Jia Hao Andrea Jiang, Robert Gerstenberger, You Wu, Patrick Iff, Ales Kubicek, Piotr Nyczyk, Diana Khimey, Jón Gunnar Hannesson, Grzegorz Kwaśniewski, Marcin Copik, Hubert Niewiadomski, Torsten Hoefler
Large Language Models (LLMs) are revolutionizing the development of AI assistants capable of performing diverse tasks across domains. However, current state-of-the-art LLM-driven agents face significant challenges, including high operational costs and limited success rates on complex benchmarks like GAIA. To address these issues, we propose the Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT), an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. For example, KGoT achieves a 29% improvement in task success rates on the GAIA benchmark compared to Hugging Face Agents with GPT-4o mini, while reducing costs by over 36x compared to GPT-4o. Improvements for recent reasoning models are similar, e.g., 36% and 37.5% for Qwen2.5-32B and Deepseek-R1-70B, respectively. KGoT offers a scalable, affordable, and high-performing solution for AI assistants.
大型语言模型(LLM)正在推动人工智能助手的发展,使其能够在不同领域执行多样化的任务。然而,当前最前沿的LLM驱动的智能代理面临重大挑战,包括运营成本高昂和在复杂基准测试(如GAIA)上成功率有限。为了应对这些问题,我们提出了“知识图谱思维”(KGoT),这是一种创新的人工智能助手架构,它将LLM推理与动态构建的知识图谱(KG)相结合。KGoT提取并结构化任务相关知识,形成动态KG表示,通过数学求解器、网络爬虫和Python脚本等外部工具进行迭代增强。这种任务相关知识的结构化表示使得低成本模型能够更有效地解决复杂任务。例如,在GAIA基准测试中,KGoT的任务成功率比使用GPT-4o mini的Hugging Face Agents提高了29%,同时成本降低了超过36倍。近期的推理模型改进也类似,如Qwen2.5-32B和Deepseek-R1-70B分别提高了36%和37.5%。KGoT为人工智能助手提供了可扩展、经济实惠且高性能的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
知识图谱思维(KGoT)是一种创新的AI助手架构,它将大型语言模型(LLM)推理与动态构建的知识图谱(KG)相结合,解决了AI助理在复杂任务上表现不佳和成本高昂的问题。KGoT通过提取和结构化任务相关知识,形成动态知识图谱表示,并通过数学求解器、网络爬虫和Python脚本等外部工具进行迭代增强。这种结构化的知识表示使低成本模型能够更有效地解决复杂任务,在GAIA基准测试上取得了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs正在推动AI助手的发展,但仍面临高成本和复杂任务成功率低的挑战。
- KGoT是一种新型的AI助手架构,集成了LLM推理和动态构建的知识图谱。
- KGoT通过提取和结构化任务相关知识,形成动态知识图谱表示,提高模型解决复杂任务的能力。
- KGoT在GAIA基准测试上相比Hugging Face Agents with GPT-4o mini有显著改进,任务成功率提高29%,成本降低超过36倍。
- KGoT对近期的推理模型也有类似的改进效果,如Qwen2.5-32B和Deepseek-R1-70B分别提高了36%和37.5%。
- KGoT提供了一个可扩展、经济实惠且高性能的AI助手解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

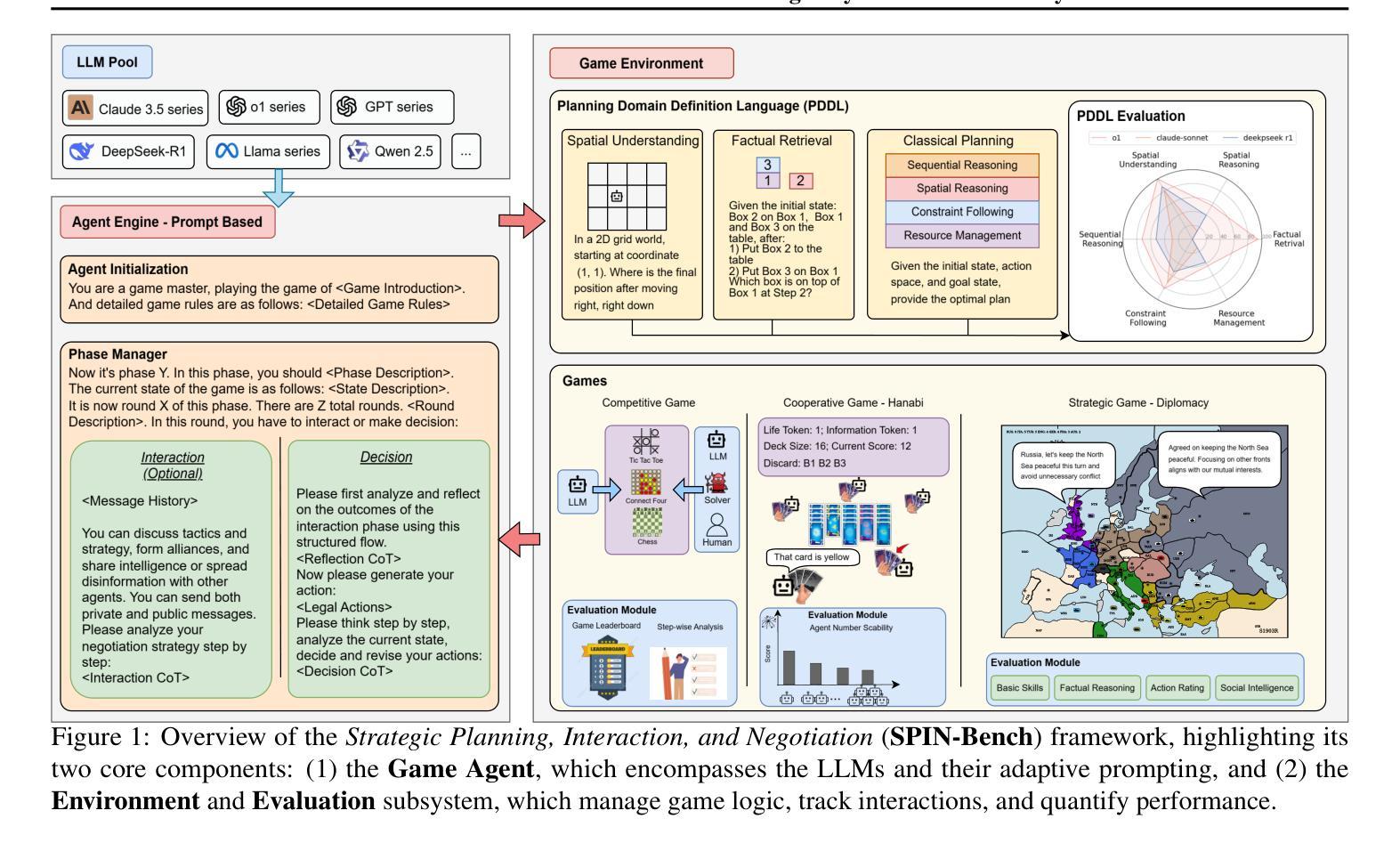
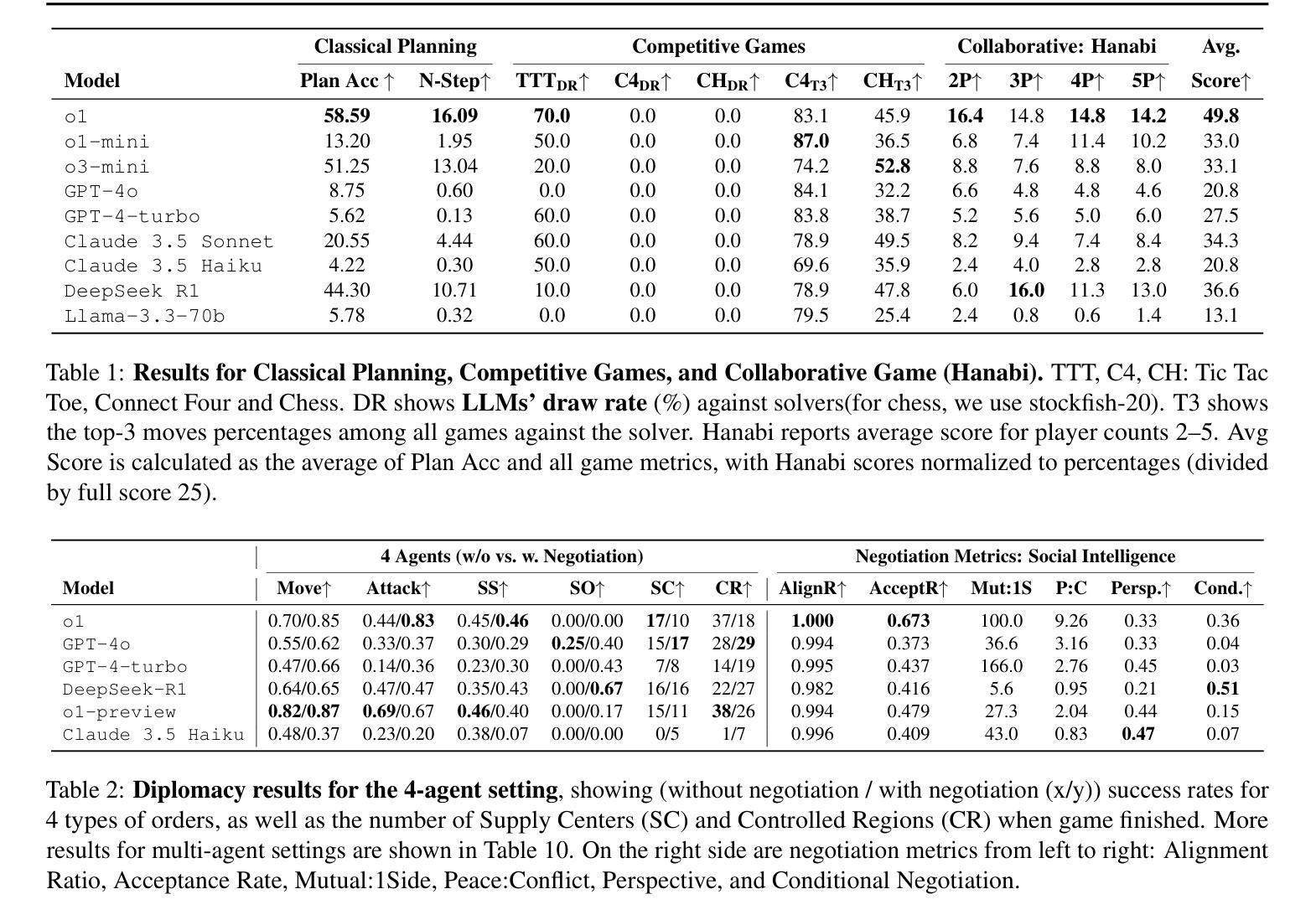
SPIN-Bench: How Well Do LLMs Plan Strategically and Reason Socially?
Authors:Jianzhu Yao, Kevin Wang, Ryan Hsieh, Haisu Zhou, Tianqing Zou, Zerui Cheng, Zhangyang Wang, Pramod Viswanath
Reasoning and strategic behavior in social interactions is a hallmark of intelligence. This form of reasoning is significantly more sophisticated than isolated planning or reasoning tasks in static settings (e.g., math problem solving). In this paper, we present Strategic Planning, Interaction, and Negotiation (SPIN-Bench), a new multi-domain evaluation designed to measure the intelligence of strategic planning and social reasoning. While many existing benchmarks focus on narrow planning or single-agent reasoning, SPIN-Bench combines classical PDDL tasks, competitive board games, cooperative card games, and multi-agent negotiation scenarios in one unified framework. The framework includes both a benchmark as well as an arena to simulate and evaluate the variety of social settings to test reasoning and strategic behavior of AI agents. We formulate the benchmark SPIN-Bench by systematically varying action spaces, state complexity, and the number of interacting agents to simulate a variety of social settings where success depends on not only methodical and step-wise decision making, but also conceptual inference of other (adversarial or cooperative) participants. Our experiments reveal that while contemporary LLMs handle basic fact retrieval and short-range planning reasonably well, they encounter significant performance bottlenecks in tasks requiring deep multi-hop reasoning over large state spaces and socially adept coordination under uncertainty. We envision SPIN-Bench as a catalyst for future research on robust multi-agent planning, social reasoning, and human–AI teaming. Project Website: https://spinbench.github.io/
社会互动中的推理和策略行为是智能的标志。这种推理形式远比静态环境中的孤立规划或推理任务(例如数学问题解决)更为复杂。在本文中,我们提出了“战略规划互动谈判(SPIN-Bench)”,这是一种新的多领域评估,旨在衡量战略规划和社会推理的智能水平。虽然许多现有的基准测试主要集中在狭隘的规划或单代理推理上,但SPIN-Bench结合了经典的PDDL任务、竞技棋盘游戏、合作卡牌游戏和多代理谈判场景在一个统一框架中。该框架既包括一个基准测试,也包括一个模拟和评估多种社交设置的场所,以测试AI代理的推理和策略行为。我们通过系统地改变行动空间、状态复杂性和交互代理的数量来制定SPIN-Bench基准测试,以模拟多种社交环境,其中成功不仅取决于方法性和逐步的决策制定,还取决于对其他(对抗性或合作性)参与者的概念推断。我们的实验表明,虽然当代大型语言模型在处理基本事实检索和短期规划方面表现良好,但在需要在大状态空间进行深度多跳推理和不确定性下社会适应性协调的任务中,它们会遇到显著的性能瓶颈。我们期望SPIN-Bench能成为未来关于稳健的多代理规划、社会推理和人机协作的研究催化剂。项目网站:https://spinbench.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 42 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为SPIN-Bench的新多领域评估方法,旨在测量智能战略规划和社交推理的智力水平。该评估结合了经典PDDL任务、竞技棋类游戏、合作卡牌游戏和多智能体谈判场景,在一个统一框架中模拟和评估各种社交设置,以测试人工智能智能体的推理和战略行为。实验表明,尽管当前的大型语言模型在处理基本事实检索和短期规划方面表现良好,但在需要深度多跳推理和不确定条件下的社会协调任务中仍存在显著性能瓶颈。
Key Takeaways
- SPIN-Bench是一种新的多领域评估方法,旨在测量智能战略规划和社交推理的智能水平。
- SPIN-Bench结合了多种任务,包括经典PDDL任务、竞技棋类游戏、合作卡牌游戏和多智能体谈判场景。
- 该评估方法通过系统地改变动作空间、状态复杂性和交互智能体的数量来模拟各种社交环境。
- 当代大型语言模型在处理需要深度多跳推理和不确定条件下的社会协调任务时面临性能瓶颈。
- SPIN-Bench可推动未来在鲁棒多智能体规划、社交推理和人机协作等领域的研究。
- SPIN-Bench提供了一个统一的框架来模拟和评估社交设置中的智能体行为。
点此查看论文截图