⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-12 更新
Heart Failure Prediction using Modal Decomposition and Masked Autoencoders for Scarce Echocardiography Databases
Authors:Andrés Bell-Navas, María Villalba-Orero, Enrique Lara-Pezzi, Jesús Garicano-Mena, Soledad Le Clainche
Heart diseases constitute the main cause of international human defunction. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 18 million deaths happen each year due to precisely heart diseases. In particular, heart failures (HF) press the healthcare industry to develop systems for their early, rapid and effective prediction. In this work, an automatic system which analyses in real-time echocardiography video sequences is proposed for the challenging and more specific task of prediction of heart failure times. This system is based on a novel deep learning framework, and works in two stages. The first one transforms the data included in a database of echocardiography video sequences into a machine learning-compatible collection of annotated images which can be used in the training phase of any kind of machine learning-based framework, including a deep learning one. This initial stage includes the use of the Higher Order Dynamic Mode Decomposition (HODMD) algorithm for both data augmentation and feature extraction. The second stage is focused on building and training a Vision Transformer (ViT). Self-supervised learning (SSL) methods, which have been so far barely explored in the literature about heart failure prediction, are applied to effectively train the ViT from scratch, even with scarce databases of echocardiograms. The designed neural network analyses images from echocardiography sequences to estimate the time in which a heart failure will happen. The results obtained show the efficacy of the HODMD algorithm and the superiority of the proposed system with respect to several established ViT and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architectures.
心脏病是国际人类功能障碍的主要诱因。据世界卫生组织(WHO)统计,每年约有1800万人因心脏病而死亡。特别是,心力衰竭(HF)迫使医疗行业需要开发系统进行早期、快速和有效的预测。在这项工作中,提出了一种自动分析实时超声心动图视频序列的系统,用于预测心力衰竭时间的更具挑战性的特定任务。该系统基于新型深度学习框架,分为两个阶段工作。第一阶段将包含在超声心动图视频序列数据库中的数据转换为可用于任何基于机器学习框架的训练阶段的注释图像集合,包括深度学习。这一阶段包括使用高阶动态模式分解(HODMD)算法进行数据增强和特征提取。第二阶段专注于构建和训练视觉转换器(ViT)。应用自监督学习方法(SSL),迄今为止在关于心力衰竭预测的文献中几乎未被探索,以有效地从头开始训练ViT,即使使用稀有的超声心动图数据库也是如此。所设计的神经网络分析超声心动图序列的图像,以估计心力衰竭发生的时间。获得的结果显示了HODMD算法的有效性以及所提出的系统相对于几种成熟的ViT和卷积神经网络(CNN)架构的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 37 pages, 7 figures. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2404.19579
Summary
本文提出了一种基于深度学习的自动系统,用于实时分析超声心动图视频序列,以预测心脏衰竭的时间。系统分为两个阶段,第一阶段使用高阶动态模式分解(HODMD)算法进行数据增强和特征提取,第二阶段是构建和训练视觉转换器(ViT)。采用自监督学习方法对ViT进行训练,即使在稀缺的超声心动图数据库中也能取得优异结果。
Key Takeaways
- 心脏疾病是国际人类功能缺陷的主要原因,每年约有1800万人因此死亡。
- 心脏衰竭是医疗保健行业亟需解决的问题,需要开发早期、快速和有效的预测系统。
- 提出的自动系统基于深度学习,能够实时分析超声心动图视频序列进行心脏衰竭预测。
- 系统分为两个阶段:第一阶段使用HODMD算法进行数据增强和特征提取,第二阶段是构建和训练视觉转换器(ViT)。
- 采用自监督学习方法,可在稀缺的超声心动图数据库中训练ViT。
- 预测心脏衰竭时间的系统相较于传统的ViT和卷积神经网络(CNN)架构具有优越性。
- 此研究为心脏衰竭预测提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图

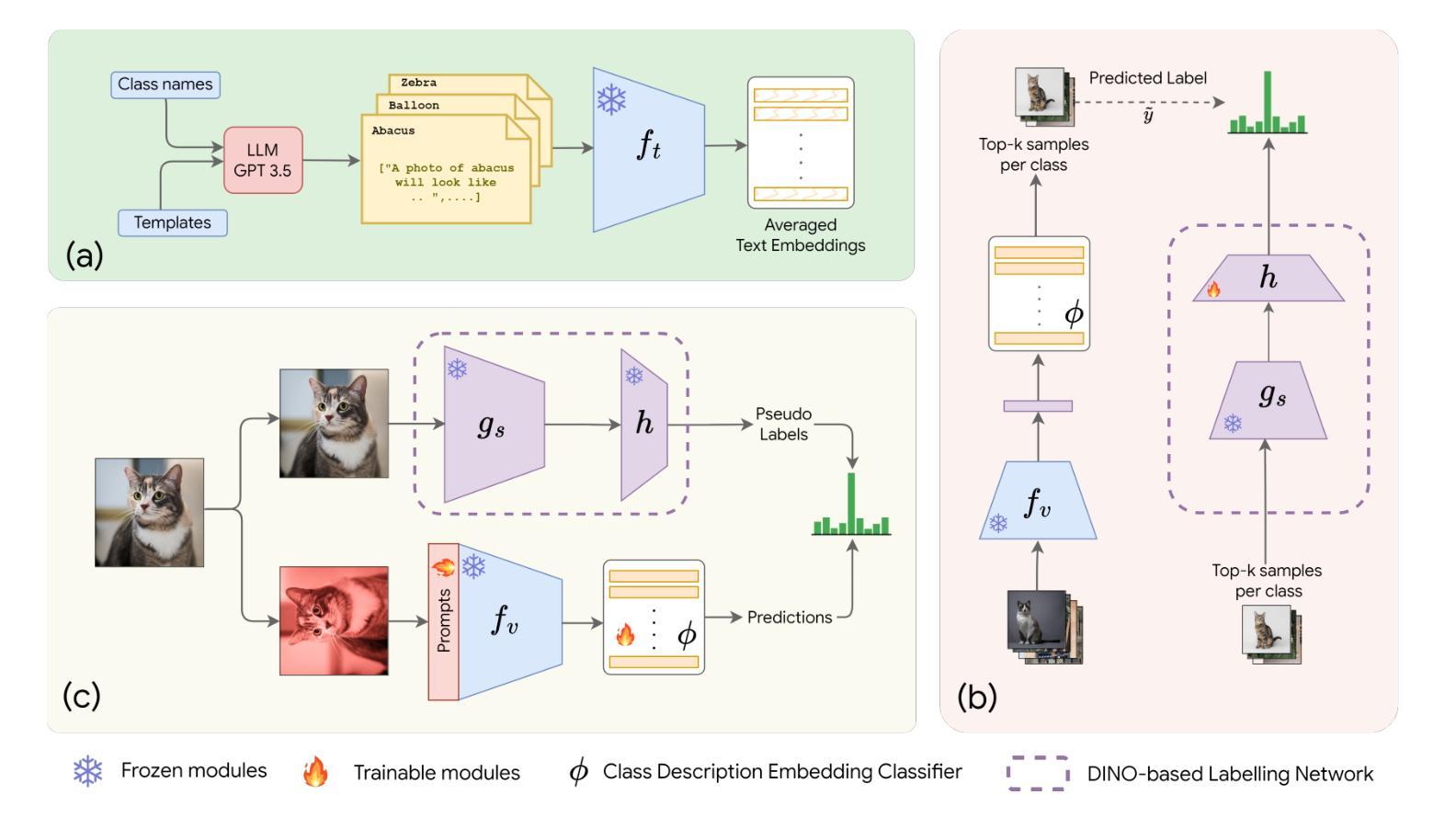
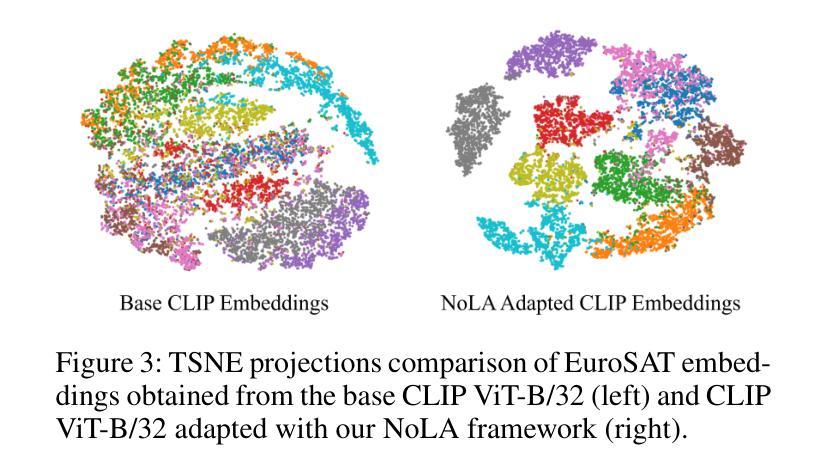
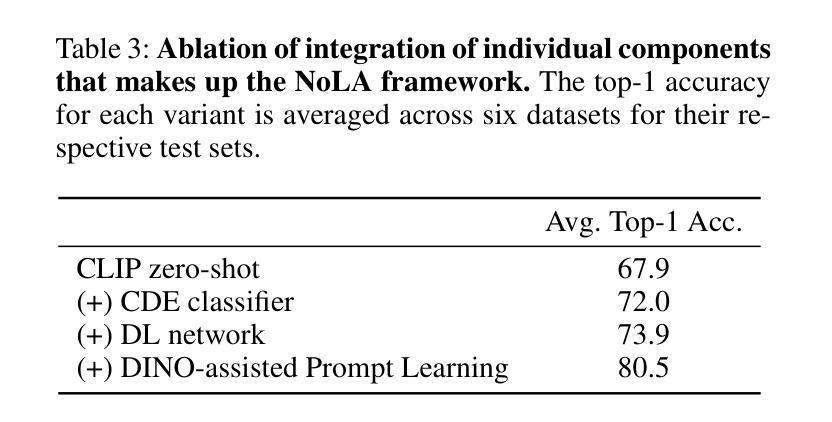
CLIP meets DINO for Tuning Zero-Shot Classifier using Unlabeled Image Collections
Authors:Mohamed Fazli Imam, Rufael Fedaku Marew, Jameel Hassan, Mustansar Fiaz, Alham Fikri Aji, Hisham Cholakkal
In the era of foundation models, CLIP has emerged as a powerful tool for aligning text & visual modalities into a common embedding space. However, the alignment objective used to train CLIP often results in subpar visual features for fine-grained tasks. In contrast, SSL-pretrained models like DINO excel at extracting rich visual features due to their specialized training paradigm. Yet, these SSL models require an additional supervised linear probing step, which relies on fully labeled data which is often expensive and difficult to obtain at scale. In this paper, we propose a label-free prompt-tuning method that leverages the rich visual features of self-supervised learning models (DINO) and the broad textual knowledge of large language models (LLMs) to largely enhance CLIP-based image classification performance using unlabeled images. Our approach unfolds in three key steps: (1) We generate robust textual feature embeddings that more accurately represent object classes by leveraging class-specific descriptions from LLMs, enabling more effective zero-shot classification compared to CLIP’s default name-specific prompts. (2) These textual embeddings are then used to produce pseudo-labels to train an alignment module that integrates the complementary strengths of LLM description-based textual embeddings & DINO’s visual features. (3) Finally, we prompt-tune CLIP’s vision encoder through DINO-assisted supervision using the trained alignment module. This three-step process allows us to harness the best of visual & textual foundation models, resulting in a powerful and efficient approach that surpasses state-of-the-art label-free classification methods. Notably, our framework, NoLA (No Labels Attached), achieves an average absolute gain of 3.6% over the state-of-the-art LaFTer across 11 diverse image classification datasets. Our code & models can be found at https://github.com/fazliimam/NoLA.
在基础模型时代,CLIP已成为将文本和视觉模式对齐到通用嵌入空间的有力工具。然而,用于训练CLIP的对齐目标通常会导致对精细粒度任务产生次优的视觉特征。相比之下,SSL预训练的模型(如DINO)由于其特殊的训练范式而擅长提取丰富的视觉特征。然而,这些SSL模型需要额外的有监督线性探测步骤,这依赖于全面标记的数据,而这些数据通常价格昂贵且难以大规模获取。
在本文中,我们提出了一种无标签提示调整方法,该方法利用自监督学习模型的丰富视觉特征(DINO)和大语言模型(LLM)的广泛文本知识,使用无标签图像极大地提高了基于CLIP的图像分类性能。我们的方法分为三个关键步骤:
(1)我们通过利用LLM提供的特定类别的描述来生成更准确地代表对象类别的稳健文本特征嵌入,从而实现与CLIP的默认名称特定提示相比更有效的零样本分类。
(2)然后,这些文本嵌入用于生成伪标签,以训练一个集成LLM基于描述的文本嵌入和DINO视觉特征的互补优点的对齐模块。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种无标签提示调整方法,该方法利用自监督学习模型的丰富视觉特征和大型语言模型的广泛文本知识,大大提高了基于CLIP的图像分类性能。该方法通过三个关键步骤实现:1)生成更准确地代表对象类的稳健文本特征嵌入;2)使用这些文本嵌入生成伪标签,以训练融合LLM描述基于的文本嵌入和DINO视觉特征的对齐模块;3)通过DINO辅助监督提示调整CLIP的视觉编码器。此方法结合了视觉和文本基础模型的优点,是一种强大而高效的方法,在无标签图像分类任务上超越了现有技术,平均绝对增益达3.6%。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP已逐渐成为将文本和视觉模式对齐到通用嵌入空间的有力工具,但在精细粒度任务中,其视觉特征提取表现不佳。
- SSL预训练模型(如DINO)由于专门的训练范式,擅长提取丰富的视觉特征。
- DINO等SSL模型需要额外的有监督线性探测步骤,这依赖于昂贵且难以大规模获取的全标签数据。
- 本文提出了一种无标签提示调整方法,结合了自监督学习模型的视觉特征和大型语言模型的文本知识,提高了CLIP的图像分类性能。
- 该方法通过生成更准确的文本特征嵌入、训练对齐模块并使用DINO辅助监督提示调整CLIP视觉编码器三个关键步骤实现。
- 该方法在无标签图像分类任务上超越了现有技术,平均绝对增益为3.6%。
点此查看论文截图