⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-15 更新
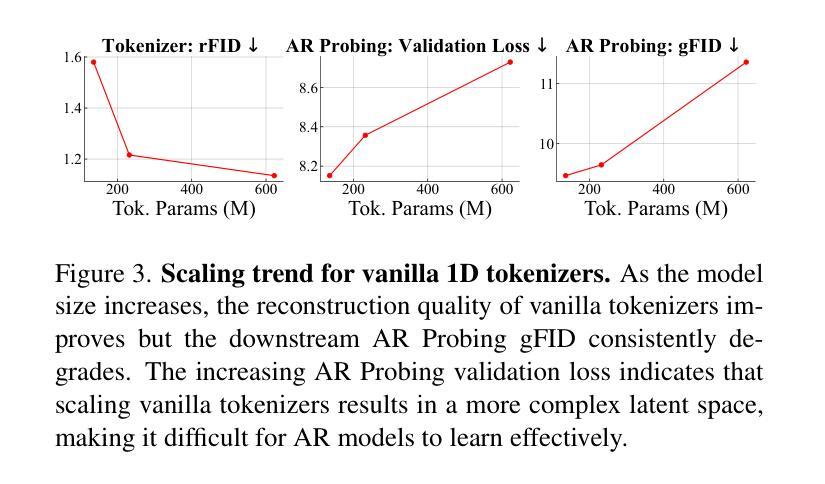
GigaTok: Scaling Visual Tokenizers to 3 Billion Parameters for Autoregressive Image Generation
Authors:Tianwei Xiong, Jun Hao Liew, Zilong Huang, Jiashi Feng, Xihui Liu
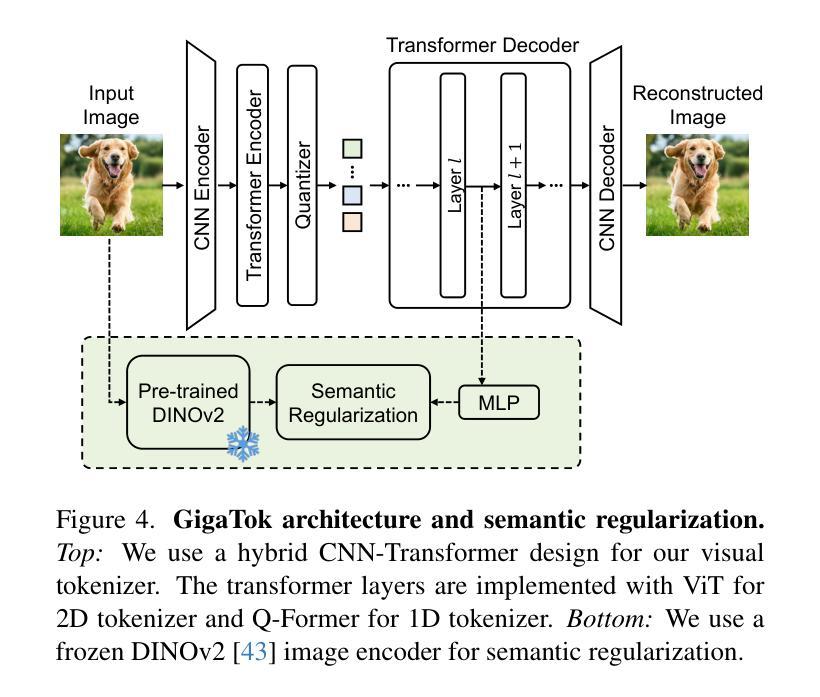
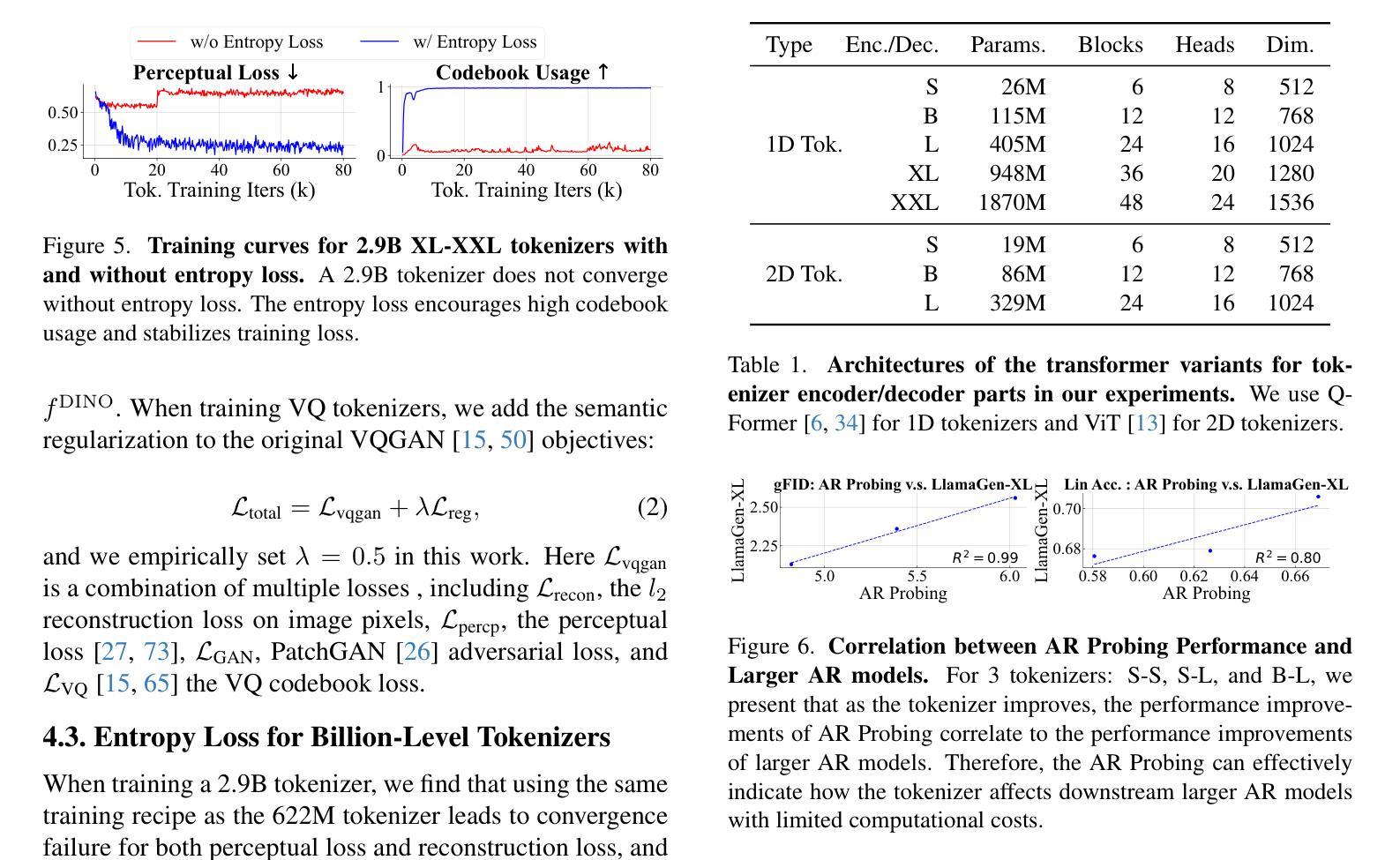
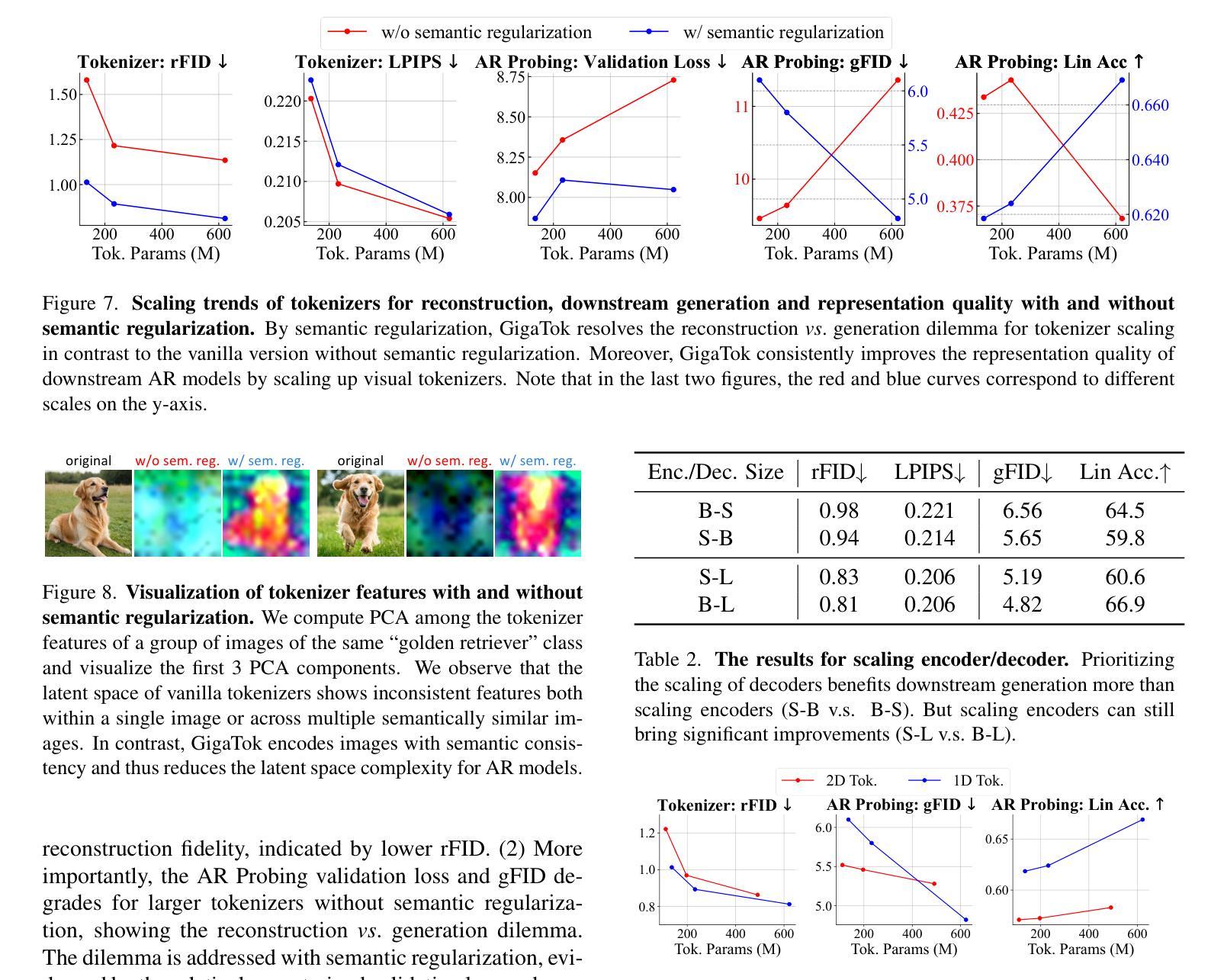
In autoregressive (AR) image generation, visual tokenizers compress images into compact discrete latent tokens, enabling efficient training of downstream autoregressive models for visual generation via next-token prediction. While scaling visual tokenizers improves image reconstruction quality, it often degrades downstream generation quality – a challenge not adequately addressed in existing literature. To address this, we introduce GigaTok, the first approach to simultaneously improve image reconstruction, generation, and representation learning when scaling visual tokenizers. We identify the growing complexity of latent space as the key factor behind the reconstruction vs. generation dilemma. To mitigate this, we propose semantic regularization, which aligns tokenizer features with semantically consistent features from a pre-trained visual encoder. This constraint prevents excessive latent space complexity during scaling, yielding consistent improvements in both reconstruction and downstream autoregressive generation. Building on semantic regularization, we explore three key practices for scaling tokenizers:(1) using 1D tokenizers for better scalability, (2) prioritizing decoder scaling when expanding both encoder and decoder, and (3) employing entropy loss to stabilize training for billion-scale tokenizers. By scaling to $\bf{3 \space billion}$ parameters, GigaTok achieves state-of-the-art performance in reconstruction, downstream AR generation, and downstream AR representation quality.
在自回归(AR)图像生成中,视觉分词器将图像压缩成紧凑的离散潜在令牌,通过下一个令牌的预测实现对下游自回归模型进行高效的视觉生成训练。虽然扩大视觉分词器可以提高图像重建质量,但它往往会降低下游生成质量——这是现有文献中尚未充分解决的问题。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了GigaTok,这是一种在扩大视觉分词器的同时,可以同时提高图像重建、生成和表示学习的方法。我们发现潜在空间的复杂性增长是重建与生成困境背后的关键因素。为了缓解这一问题,我们提出了语义正则化,它能够将分词器特征与来自预训练视觉编码器的语义一致特征对齐。这种约束在扩大时防止了潜在空间复杂性过高,从而在重建和下游自回归生成方面都取得了持续的改进。基于语义正则化,我们探索了扩大分词器的三个关键实践:(1)使用一维分词器以提高可扩展性,(2)在扩大编码器和解码器时优先扩展解码器,(3)采用熵损失来稳定数十亿规模分词器的训练。通过扩展到$\bf{3 \space billion}$个参数,GigaTok在重建、下游AR生成和下游AR表示质量方面达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF project page: https://silentview.github.io/GigaTok
Summary
本文介绍了在自回归图像生成中,视觉令牌器在压缩图像到离散潜在令牌时面临的挑战。随着令牌器规模的扩大,图像重建质量提高,但生成质量下降。为解决这一问题,本文提出了GigaTok方法,通过语义正则化对齐令牌器特征与预训练视觉编码器的语义一致特征,以缓解潜在空间的复杂性增长。在此基础上,探索了三个扩展令牌器的重要实践,包括使用1D令牌器提高可扩展性、优先扩展解码器,以及采用熵损失稳定大规模令牌器的训练。通过扩展到3亿参数,GigaTok在重建、下游自回归生成和下游自回归表示质量方面达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉令牌器在自回归图像生成中压缩图像到离散潜在令牌,提高训练效率。
- 扩大视觉令牌器规模虽能提高图像重建质量,但会导致下游生成质量下降。
- GigaTok方法通过语义正则化解决这一挑战,改善图像重建和生成质量。
- 语义正则化对齐令牌器特征与预训练视觉编码器的语义一致特征,缓解潜在空间复杂性增长。
- GigaTok探索了三个扩展令牌器的实践:使用1D令牌器、优先扩展解码器、采用熵损失稳定训练。
- GigaTok扩展到3亿参数后,在重建、下游自回归生成和表示质量方面达到最先进性能。
点此查看论文截图


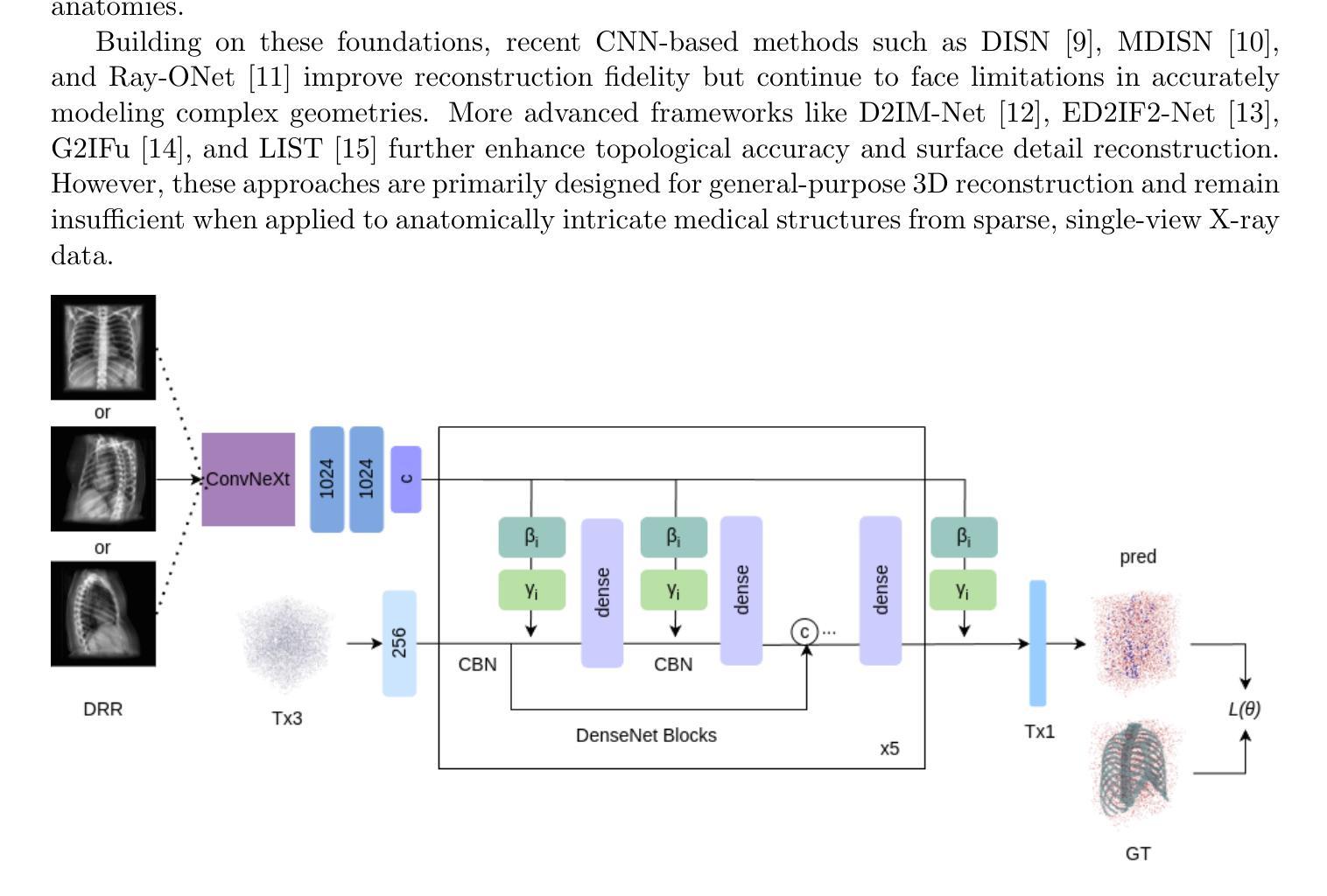
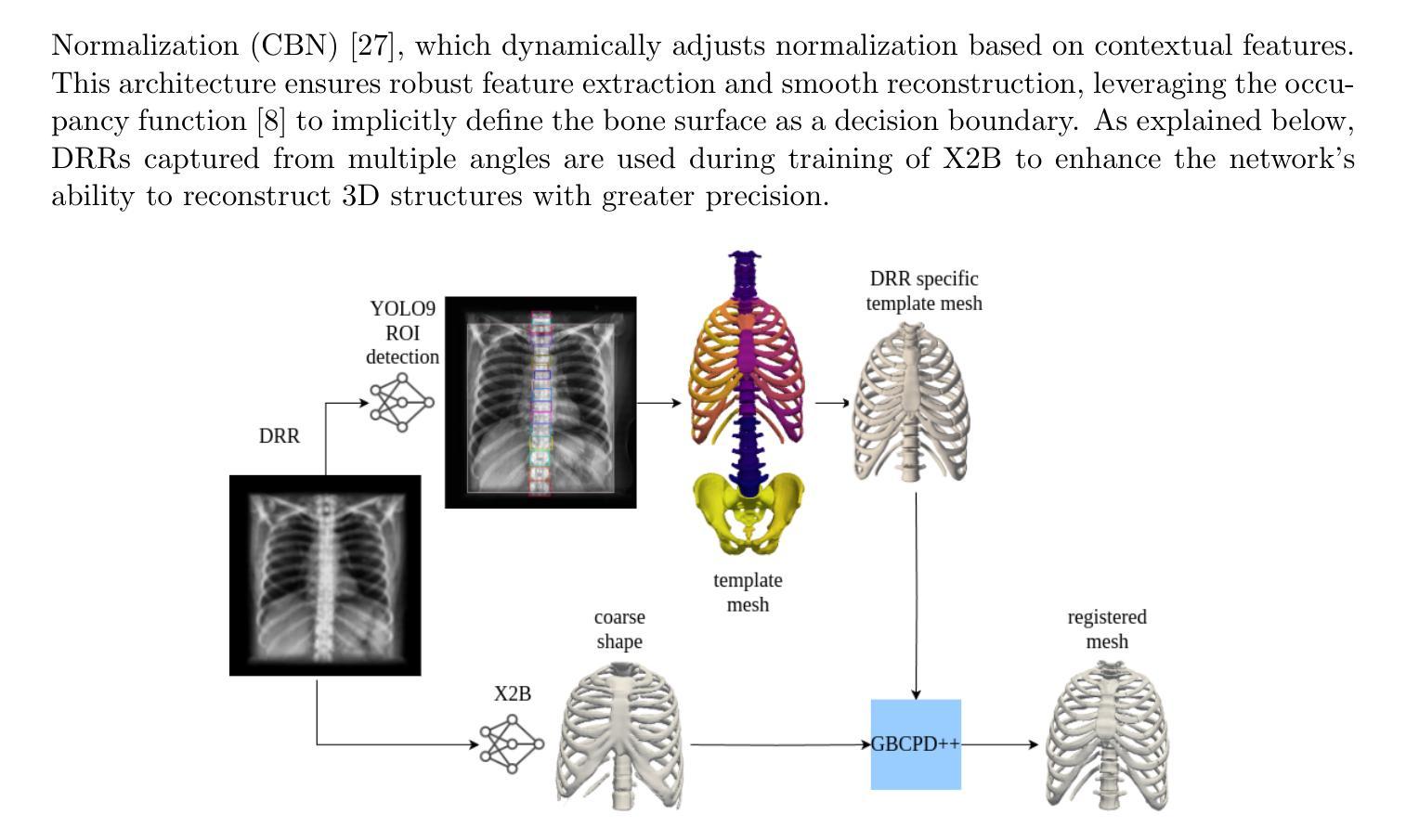
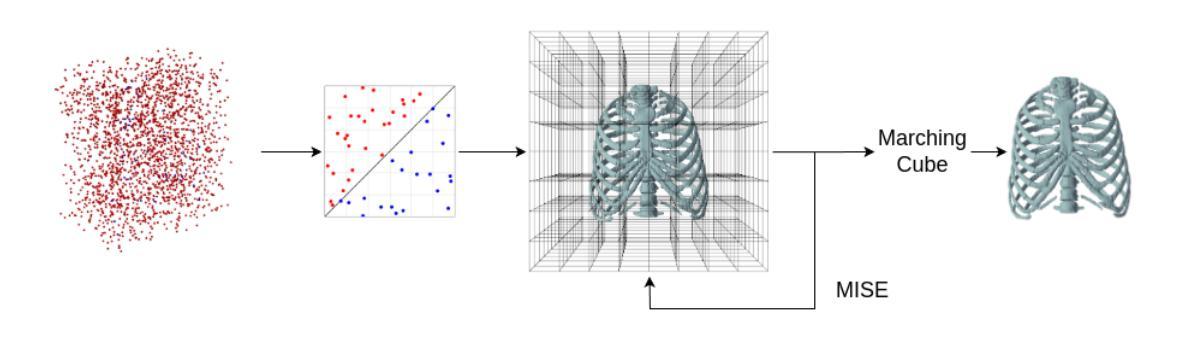
X2BR: High-Fidelity 3D Bone Reconstruction from a Planar X-Ray Image with Hybrid Neural Implicit Methods
Authors:Gokce Guven, H. Fatih Ugurdag, Hasan F. Ates
Accurate 3D bone reconstruction from a single planar X-ray remains a challenge due to anatomical complexity and limited input data. We propose X2BR, a hybrid neural implicit framework that combines continuous volumetric reconstruction with template-guided non-rigid registration. The core network, X2B, employs a ConvNeXt-based encoder to extract spatial features from X-rays and predict high-fidelity 3D bone occupancy fields without relying on statistical shape models. To further refine anatomical accuracy, X2BR integrates a patient-specific template mesh, constructed using YOLOv9-based detection and the SKEL biomechanical skeleton model. The coarse reconstruction is aligned to the template using geodesic-based coherent point drift, enabling anatomically consistent 3D bone volumes. Experimental results on a clinical dataset show that X2B achieves the highest numerical accuracy, with an IoU of 0.952 and Chamfer-L1 distance of 0.005, outperforming recent baselines including X2V and D2IM-Net. Building on this, X2BR incorporates anatomical priors via YOLOv9-based bone detection and biomechanical template alignment, leading to reconstructions that, while slightly lower in IoU (0.875), offer superior anatomical realism, especially in rib curvature and vertebral alignment. This numerical accuracy vs. visual consistency trade-off between X2B and X2BR highlights the value of hybrid frameworks for clinically relevant 3D reconstructions.
从单个平面X射线进行精确的3D骨骼重建仍然是一个挑战,主要是由于解剖结构的复杂性和输入数据的有限性。我们提出了X2BR,这是一种混合神经隐式框架,它将连续的体积重建与模板引导的非刚性注册结合起来。核心网络X2B采用基于ConvNeXt的编码器,从X射线中提取空间特征,并预测高保真3D骨骼占用场,而无需依赖统计形状模型。为了进一步提高解剖准确性,X2BR整合了针对患者的特定模板网格,该网格是使用YOLOv9检测器和SKEL生物力学骨骼模型构建的。粗重建与模板通过基于测地线的相干点漂移进行对齐,从而实现解剖上一致的3D骨骼体积。在临床数据集上的实验结果表明,X2B在数值上达到了最高精度,交并比(IoU)为0.952,Chamfer-L1距离为0.005,超过了最近的基线包括X2V和D2IM-Net。在此基础上,X2BR通过YOLOv9骨检测和生物力学模板对齐融入了解剖先验知识,虽然略微降低IoU(为0.875),但在解剖真实性方面提供了优势,尤其在肋骨弯曲和椎体对齐方面。X2B与X2BR之间的数值精度与视觉一致性的权衡突出了混合框架在临床相关3D重建中的价值。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种混合神经网络隐式框架X2BR,结合连续体积重建和模板引导的非刚性配准,从单一的平面X射线实现精确的三维骨骼重建。核心网络X2B依靠ConvNeXt-based编码器提取X射线空间特征并预测高精度三维骨骼占用场,无需依赖统计形状模型。为进一步提高解剖精度,X2BR集成特定患者模板网格,通过YOLOv9检测和SKEL生物力学骨骼模型构建。粗重建与模板通过测地线相干点漂移对齐,生成解剖上一致的三维骨骼体积。实验结果显示,X2B在数值精度上达到最高水平,交并比(IoU)为0.952,Chamfer-L1距离为0.005,超越近期基线包括X2V和D2IM-Net。在此基础上,X2BR通过YOLOv9骨检测和生物力学模板对齐融入解剖先验知识,虽交并比略降至0.875,但在肋骨曲率和椎体对齐方面展现出优越的解剖现实性。这表明X2BR这种混合框架在具有临床相关性的三维重建中实现了数值精度与视觉一致性的权衡。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种混合神经网络隐式框架X2BR,用于从单一平面X射线实现三维骨骼重建。
- 核心网络X2B能预测高精度三维骨骼占用场,不依赖统计形状模型。
- 通过集成特定患者模板网格和与模板对齐,提高了重建的解剖精度和一致性。
- X2BR结合了YOLOv9骨检测和生物力学模板,以融入解剖先验知识。
- X2B在数值精度上表现最佳,而X2BR在解剖现实性方面有所优势,尤其在肋骨曲率和椎体对齐方面。
- X2BR框架在数值精度与视觉一致性之间达到了权衡。
点此查看论文截图

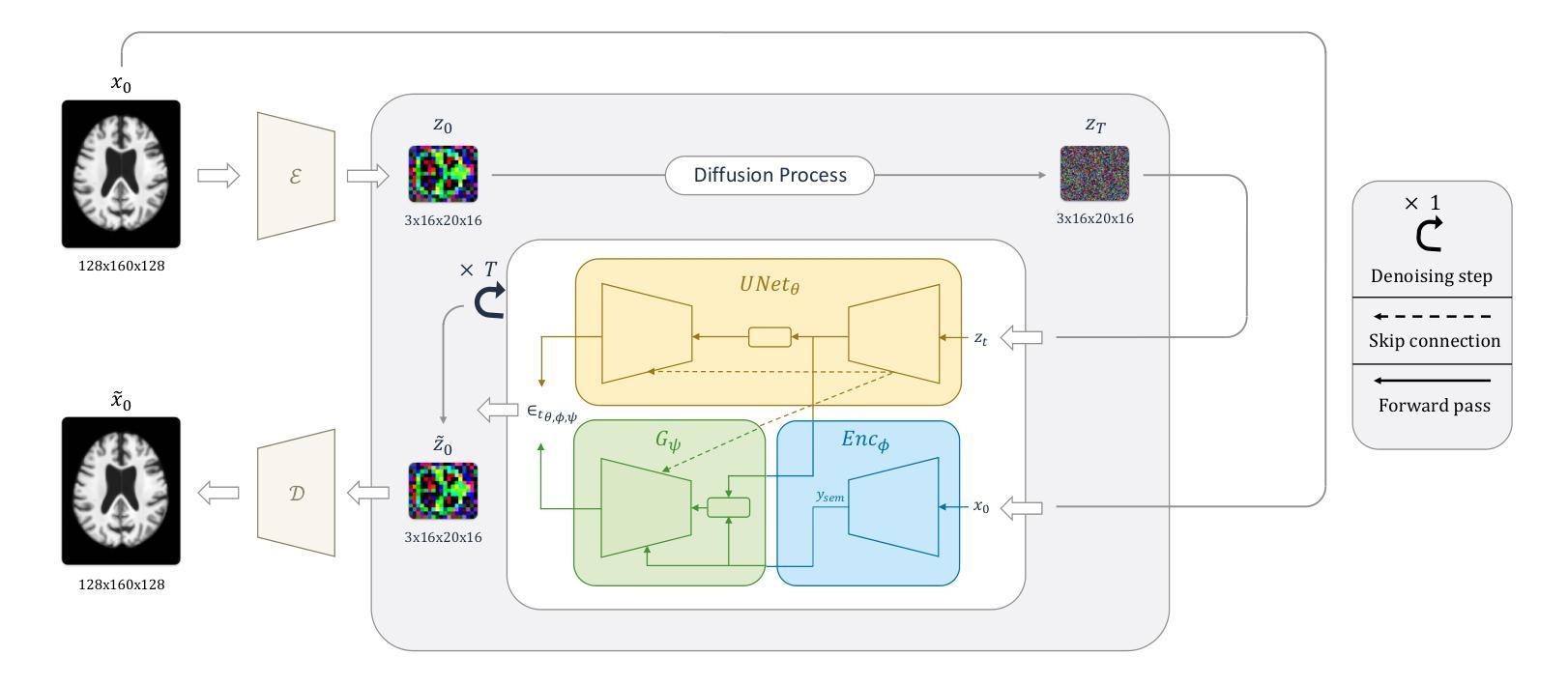
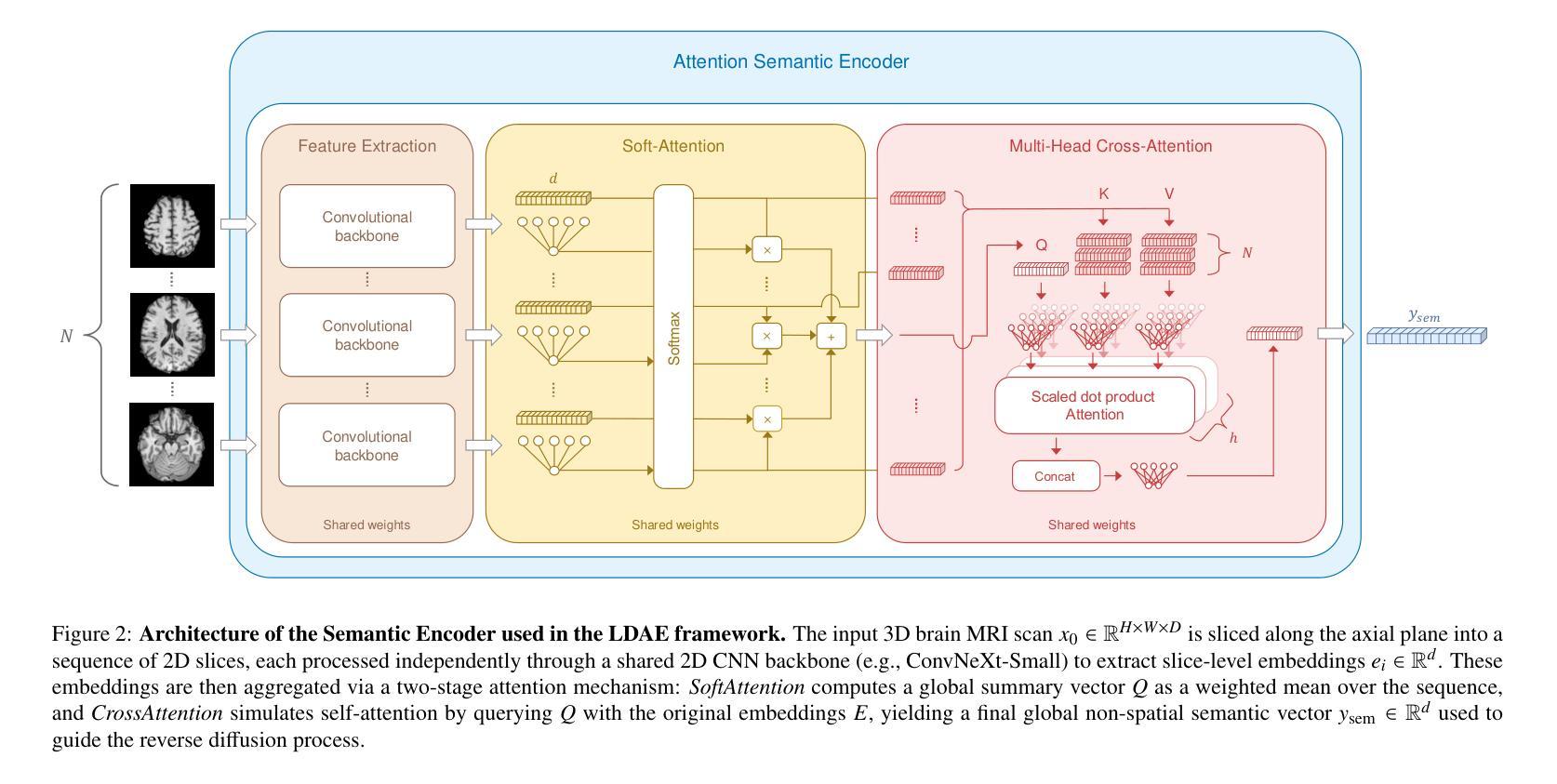
Latent Diffusion Autoencoders: Toward Efficient and Meaningful Unsupervised Representation Learning in Medical Imaging
Authors:Gabriele Lozupone, Alessandro Bria, Francesco Fontanella, Frederick J. A. Meijer, Claudio De Stefano, Henkjan Huisman
This study presents Latent Diffusion Autoencoder (LDAE), a novel encoder-decoder diffusion-based framework for efficient and meaningful unsupervised learning in medical imaging, focusing on Alzheimer disease (AD) using brain MR from the ADNI database as a case study. Unlike conventional diffusion autoencoders operating in image space, LDAE applies the diffusion process in a compressed latent representation, improving computational efficiency and making 3D medical imaging representation learning tractable. To validate the proposed approach, we explore two key hypotheses: (i) LDAE effectively captures meaningful semantic representations on 3D brain MR associated with AD and ageing, and (ii) LDAE achieves high-quality image generation and reconstruction while being computationally efficient. Experimental results support both hypotheses: (i) linear-probe evaluations demonstrate promising diagnostic performance for AD (ROC-AUC: 90%, ACC: 84%) and age prediction (MAE: 4.1 years, RMSE: 5.2 years); (ii) the learned semantic representations enable attribute manipulation, yielding anatomically plausible modifications; (iii) semantic interpolation experiments show strong reconstruction of missing scans, with SSIM of 0.969 (MSE: 0.0019) for a 6-month gap. Even for longer gaps (24 months), the model maintains robust performance (SSIM > 0.93, MSE < 0.004), indicating an ability to capture temporal progression trends; (iv) compared to conventional diffusion autoencoders, LDAE significantly increases inference throughput (20x faster) while also enhancing reconstruction quality. These findings position LDAE as a promising framework for scalable medical imaging applications, with the potential to serve as a foundation model for medical image analysis. Code available at https://github.com/GabrieleLozupone/LDAE
本研究提出了潜在扩散自编码器(LDAE),这是一种基于扩散的新型编码器-解码器框架,可在医学成像中进行高效且有意义的无监督学习,重点关注使用ADNI数据库的大脑MRI对阿尔茨海默病(AD)进行个案研究。不同于在图像空间运行的常规扩散自编码器,LDAE在压缩的潜在表示中应用扩散过程,提高了计算效率,使3D医学成像表示学习变得可行。为了验证所提出的方法,我们探索了两个关键假设:(i)LDAE能够有效地捕获与AD和衰老相关的3D大脑MRI的有意义语义表示;(ii)LDAE在计算效率高的同时实现了高质量的图片生成和重建。实验结果支持了这两个假设:(i)线性探测评估显示AD的诊断性能令人鼓舞(ROC-AUC:90%,ACC:84%),年龄预测(MAE:4.1岁,RMSE:5.2岁);(ii)学习到的语义表示能够实现属性操作,从而产生解剖上合理的修改;(iii)语义插值实验显示了强大的缺失扫描重建能力,对于6个月的间隔,SSIM为0.969(MSE:0.0019)。即使对于更长的间隔(24个月),该模型仍能保持稳健的性能(SSIM> 0.93,MSE <0.004),表明其能够捕捉时间进展趋势;(iv)与常规扩散自编码器相比,LDAE显著提高了推理吞吐量(快20倍),同时提高了重建质量。这些发现使LDAE成为医学成像应用程序中一个有前途的框架,并有可能成为医学图像分析的基础模型。代码可在https://github.com/GabrieleLozupone/LDAE找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 9 figures, 7 tables
Summary
本研究提出了潜在扩散自编码器(LDAE)这一新的编码器-解码器扩散框架,用于医学成像中的高效和有意义无监督学习,以阿尔茨海默病(AD)为例,使用ADNI数据库的脑MR进行研究。LDAE在压缩的潜在表示中应用扩散过程,提高了计算效率,使三维医学成像表示学习变得可行。实验结果显示,LDAE在AD和年龄预测方面表现出良好诊断性能,并且实现了高质量图像生成和重建。此外,LDAE还能进行属性操作、解剖上合理的修改以及强大的重建缺失扫描。与常规扩散自编码器相比,LDAE提高了推理速度并增强了重建质量,为医学成像应用提供了有前途的框架。
Key Takeaways
- LDAE是一种新的编码器-解码器扩散框架,用于医学成像中的无监督学习。
- LDAE在压缩的潜在表示中应用扩散过程,提高了计算效率。
- LDAE在AD和年龄预测方面表现出良好的诊断性能。
- LDAE实现了高质量图像生成和重建,并可以进行属性操作。
- LDAE能进行解剖上合理的修改和强大的重建缺失扫描。
- LDAE与常规扩散自编码器相比,提高了推理速度。
点此查看论文截图

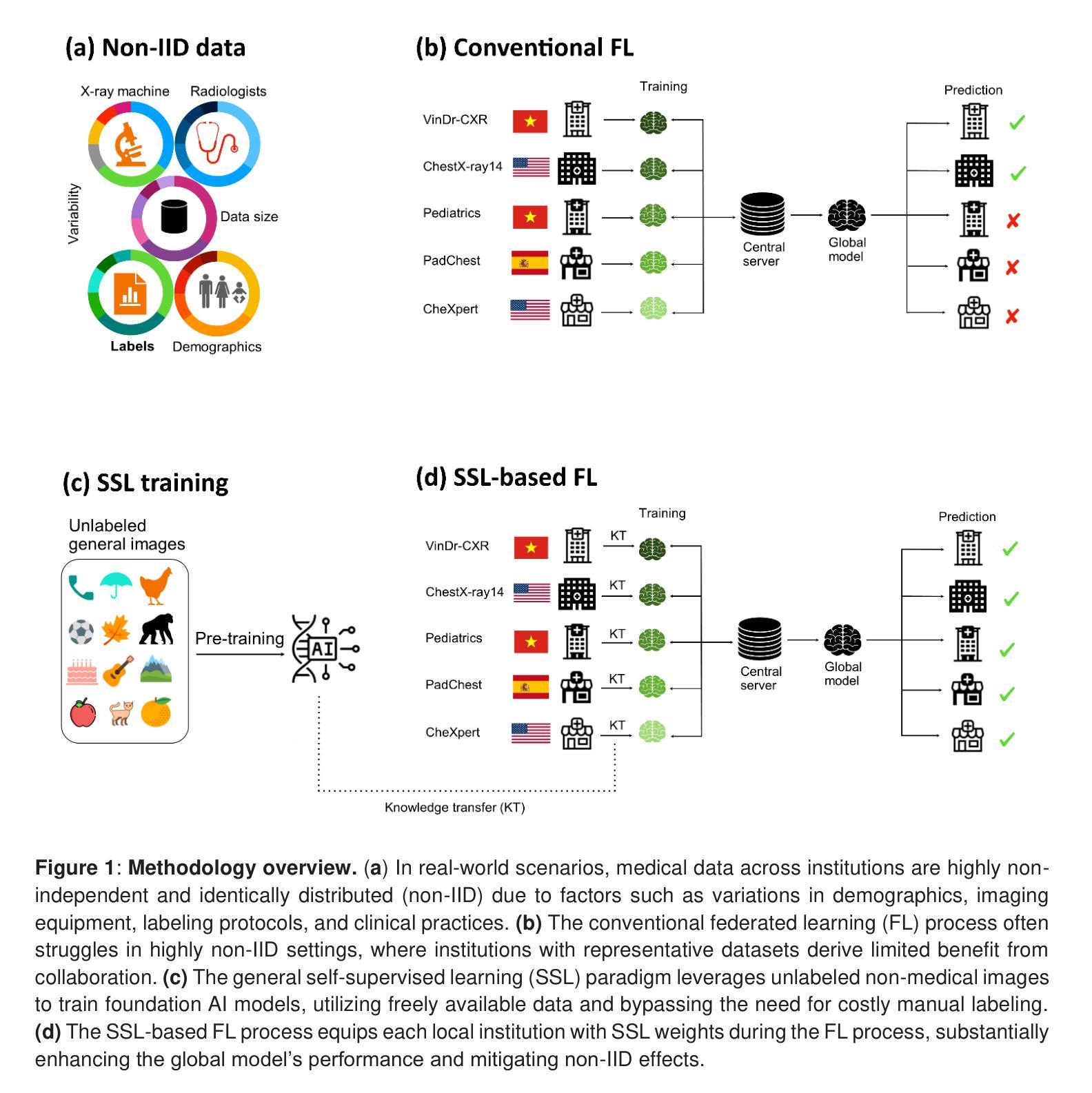
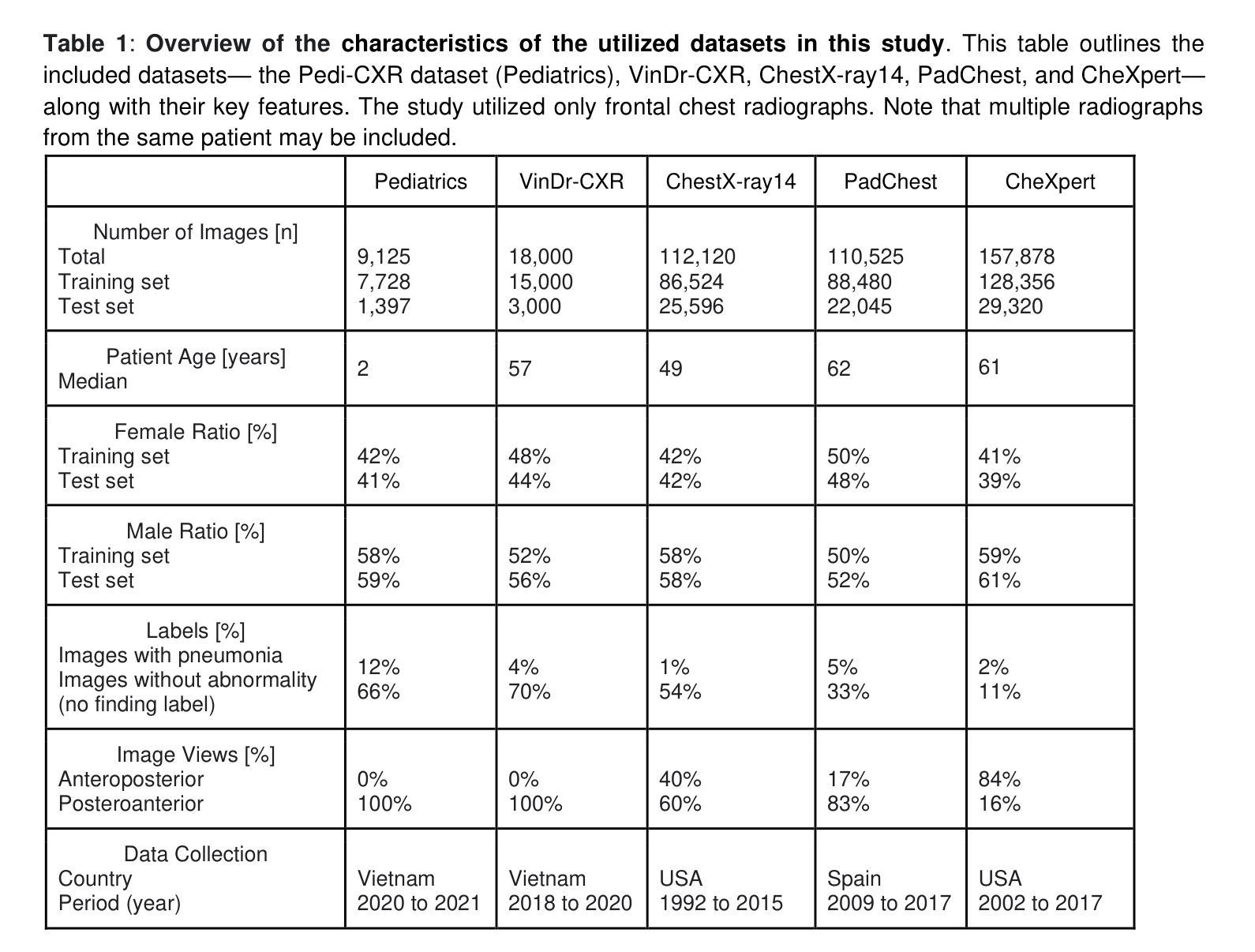
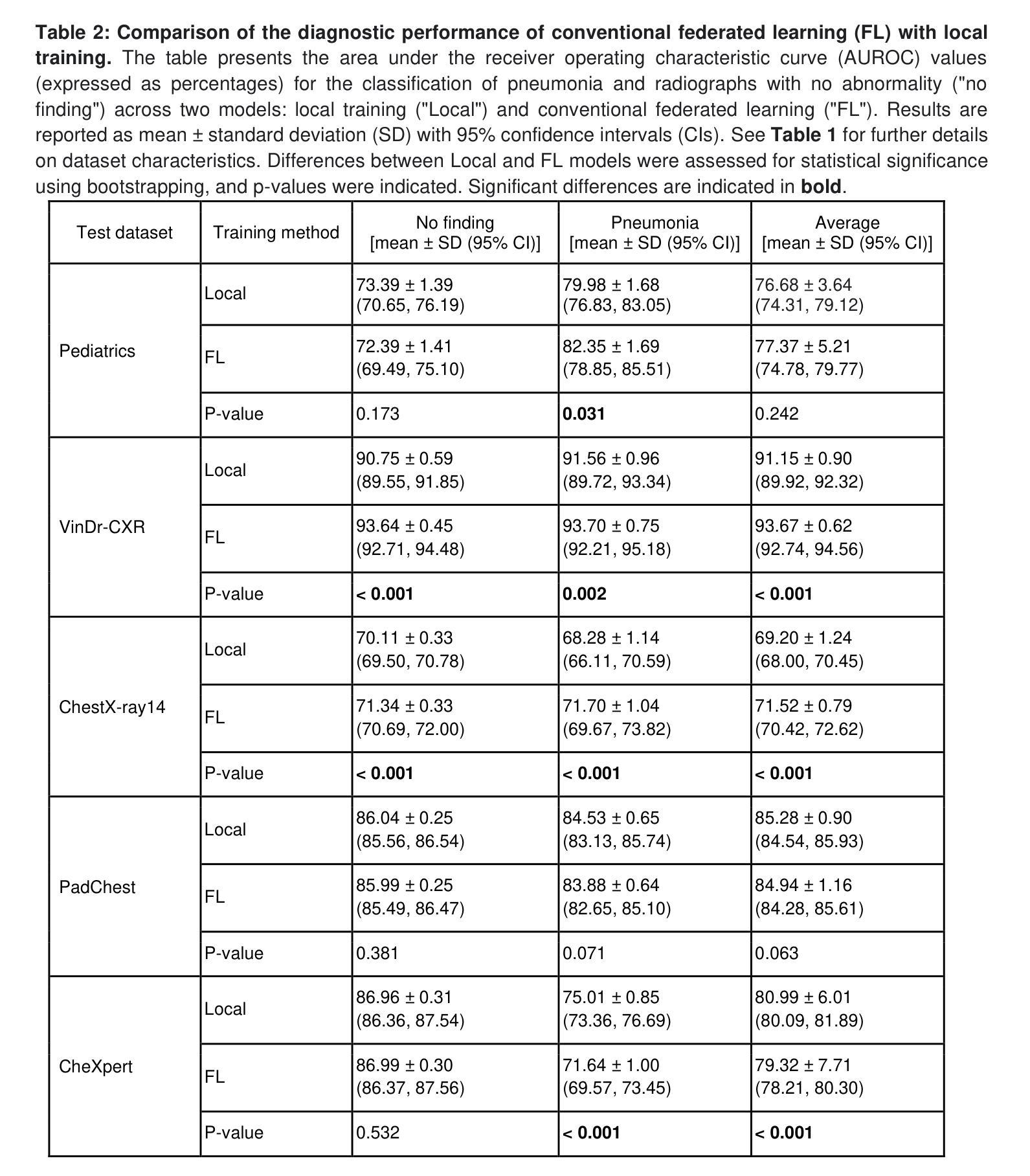
Boosting multi-demographic federated learning for chest x-ray analysis using general-purpose self-supervised representations
Authors:Mahshad Lotfinia, Arash Tayebiarasteh, Samaneh Samiei, Mehdi Joodaki, Soroosh Tayebi Arasteh
Reliable artificial intelligence (AI) models for medical image analysis often depend on large and diverse labeled datasets. Federated learning (FL) offers a decentralized and privacy-preserving approach to training but struggles in highly non-independent and identically distributed (non-IID) settings, where institutions with more representative data may experience degraded performance. Moreover, existing large-scale FL studies have been limited to adult datasets, neglecting the unique challenges posed by pediatric data, which introduces additional non-IID variability. To address these limitations, we analyzed n=398,523 adult chest radiographs from diverse institutions across multiple countries and n=9,125 pediatric images, leveraging transfer learning from general-purpose self-supervised image representations to classify pneumonia and cases with no abnormality. Using state-of-the-art vision transformers, we found that FL improved performance only for smaller adult datasets (P<0.001) but degraded performance for larger datasets (P<0.064) and pediatric cases (P=0.242). However, equipping FL with self-supervised weights significantly enhanced outcomes across pediatric cases (P=0.031) and most adult datasets (P<0.008), except the largest dataset (P=0.052). These findings underscore the potential of easily deployable general-purpose self-supervised image representations to address non-IID challenges in clinical FL applications and highlight their promise for enhancing patient outcomes and advancing pediatric healthcare, where data scarcity and variability remain persistent obstacles.
可靠的人工智能(AI)模型进行医学图像分析通常依赖于大量多样且有标签的数据集。联合学习(FL)提供了一种去中心化和保护隐私的训练方法,但在高度非独立同分布(non-IID)的环境中表现挣扎,在这种环境中,拥有更具代表性数据的机构可能会遇到性能下降的问题。此外,现有的大规模联合学习研究仅限于成人数据集,忽视了儿童数据带来的独特挑战,这引入了额外的非IID变化。为了解决这个问题,我们分析了来自多个国家的不同机构中的398,523张成人胸部放射图像和9,125张儿童图像,利用通用自监督图像表示的迁移学习来分类肺炎和无异常情况的病例。使用最先进的视觉转换器,我们发现联合学习只对较小的成人数据集的性能有所提升(P<0.001),而对较大的数据集(P<0.064)和儿童病例(P=0.242)的性能却有所下降。然而,将联合学习与自监督权重相结合,显著提高了儿童病例(P=0.031)和大多数成人数据集(P<0.008)的结果,但未能改善最大数据集的结果(P=0.052)。这些发现强调了易于部署的通用自监督图像表示在解决临床联合学习应用中的非IID挑战方面的潜力,并突显了其在改善患者成果和推进儿科医疗保健方面的前景,其中数据稀缺和变化性仍是持续存在的障碍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了联邦学习在医学图像分析中的应用,尤其是在处理不同来源的数据时的性能表现。研究发现,在小型成人数据集上,联邦学习能提高模型性能;但在大型数据集和儿科病例上,其性能有所下降。通过引入自监督图像表示技术,能够在很大程度上提升联邦学习在儿科病例和多数成人数据集上的表现。这为解决临床联邦学习中非独立同分布数据的挑战提供了潜力,并有望改善患者结果,特别是在数据稀缺和变化性较大的儿科医疗领域。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习在医学图像分析中面临非独立同分布数据的挑战,尤其是在大型数据集和儿科病例方面。
- 在小型成人数据集上,联邦学习能提高模型性能。但在大型数据集和儿科病例上,其性能可能下降。
- 自监督图像表示技术能显著提升联邦学习在儿科病例和多数成人数据集上的表现。
- 自监督图像表示技术有助于解决临床联邦学习中非独立同分布数据的挑战。
- 该技术有望改善患者结果,特别是在数据稀缺和变化性较大的儿科医疗领域。
- 研究表明,引入自监督权重能增强联邦学习的效果。
点此查看论文截图

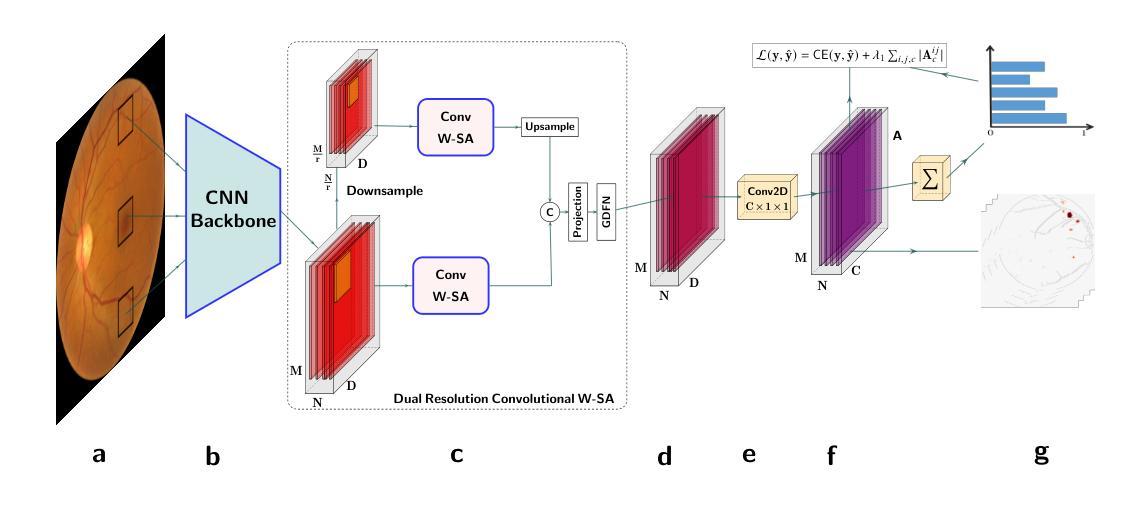
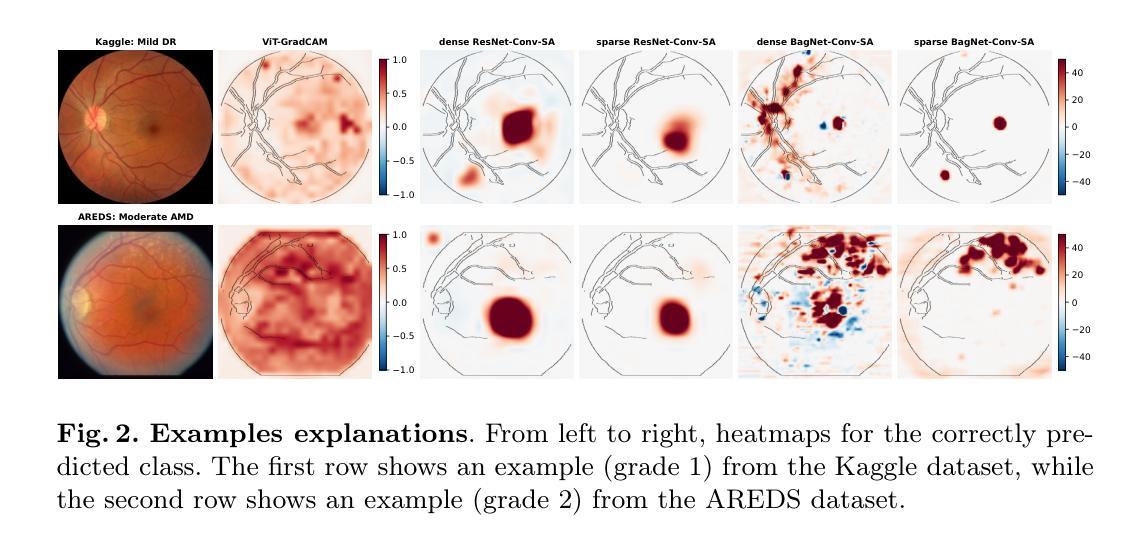
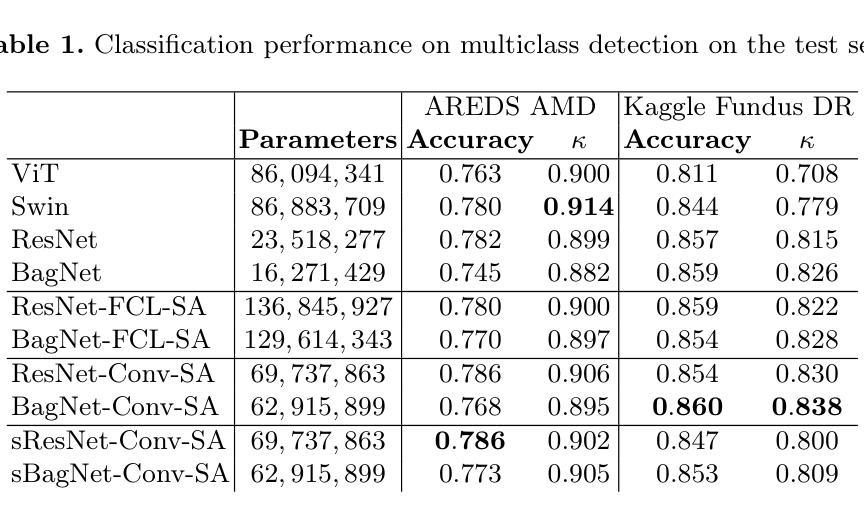
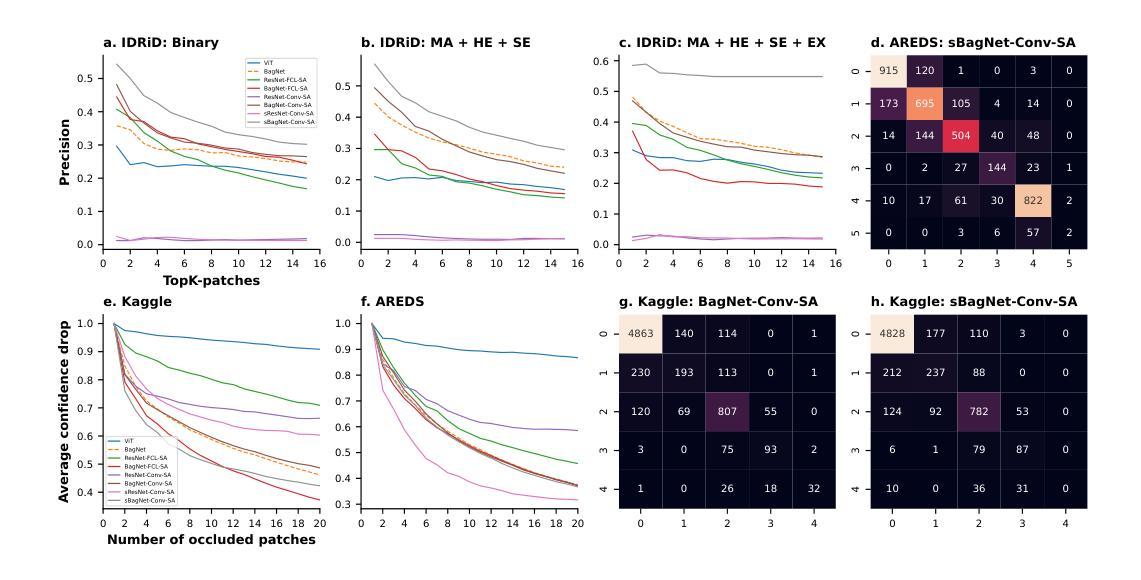
A Hybrid Fully Convolutional CNN-Transformer Model for Inherently Interpretable Medical Image Classification
Authors:Kerol Djoumessi, Samuel Ofosu Mensah, Philipp Berens
In many medical imaging tasks, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) efficiently extract local features hierarchically. More recently, vision transformers (ViTs) have gained popularity, using self-attention mechanisms to capture global dependencies, but lacking the inherent spatial localization of convolutions. Therefore, hybrid models combining CNNs and ViTs have been developed to combine the strengths of both architectures. However, such hybrid CNN-ViT models are difficult to interpret, which hinders their application in medical imaging. In this work, we introduce an interpretable-by-design hybrid fully convolutional CNN-Transformer architecture for medical image classification. Unlike widely used post-hoc saliency methods for ViTs, our approach generates faithful and localized evidence maps that directly reflect the model’s decision process. We evaluated our method on two medical image classification tasks using color fundus images. Our model not only achieves state-of-the-art predictive performance compared to both black-box and interpretable models but also provides class-specific sparse evidence maps in a single forward pass. The code is available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Expl-CNN-Transformer/.
在许多医学成像任务中,卷积神经网络(CNN)能够高效地分层提取局部特征。最近,使用自注意力机制的视觉转换器(ViT)越来越受欢迎,能够捕捉全局依赖性,但缺乏卷积的固有空间定位能力。因此,已经开发出了结合CNN和ViT的混合模型,以结合两种架构的优点。然而,这样的混合CNN-ViT模型难以解释,这阻碍了它们在医学成像中的应用。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种可设计的混合全卷积CNN-Transformer架构,用于医学图像分类。与广泛使用的针对ViT的后期显著性方法不同,我们的方法生成忠实且定位准确的证据映射,直接反映模型的决策过程。我们使用彩色眼底图像对两个医学图像分类任务评估了我们的方法。我们的模型不仅与黑箱和可解释模型相比实现了最先进的预测性能,而且还在单次前向传递中提供了特定类别的稀疏证据映射。代码可在:https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Expl-CNN-Transformer/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种专为解释性设计的混合全卷积CNN-Transformer架构,用于医学图像分类。该架构结合了卷积神经网络和视觉变压器的优点,生成忠实且定位的证据图,直接反映模型的决策过程。在医学图像分类任务中,该模型不仅实现了最先进的预测性能,与黑盒和可解释模型相比,还提供了单次前向传递的类特定稀疏证据图。
Key Takeaways
- CNNs和ViTs在医学成像中的优缺点:CNNs能高效地提取局部特征,而ViTs使用自注意力机制捕捉全局依赖性,但缺乏CNN的固有空间定位能力。
- 混合CNN-ViT模型的出现:为了结合两者的优点,已经开发出了混合CNN-ViT模型。
- 当前混合模型的可解释性问题:尽管混合CNN-ViT模型在性能上表现出色,但它们的解释性较差,这阻碍了它们在医学成像中的应用。
- 本文提出的解决方案:介绍了一种可解释的混合全卷积CNN-Transformer架构,该架构旨在直接反映模型的决策过程。
- 证据图的生成:该架构生成忠实且定位的证据图,这些证据图能展示模型如何结合局部和全局信息做出决策。
- 模型的性能:在医学图像分类任务中,该模型实现了最先进的预测性能,与现有模型相比具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

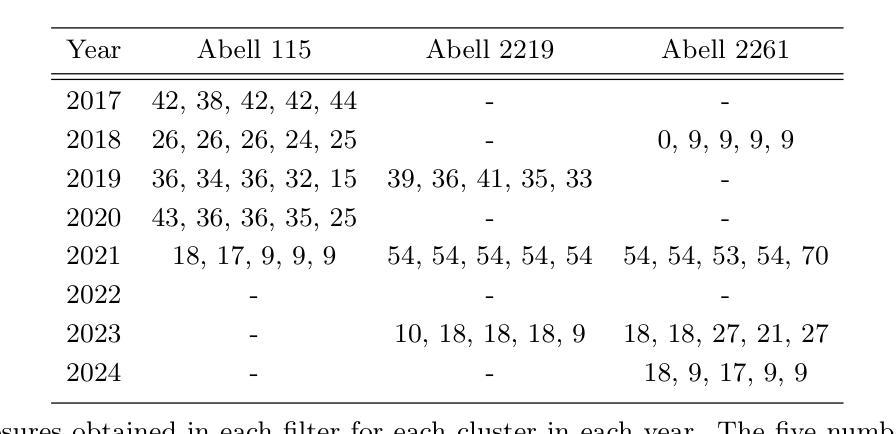
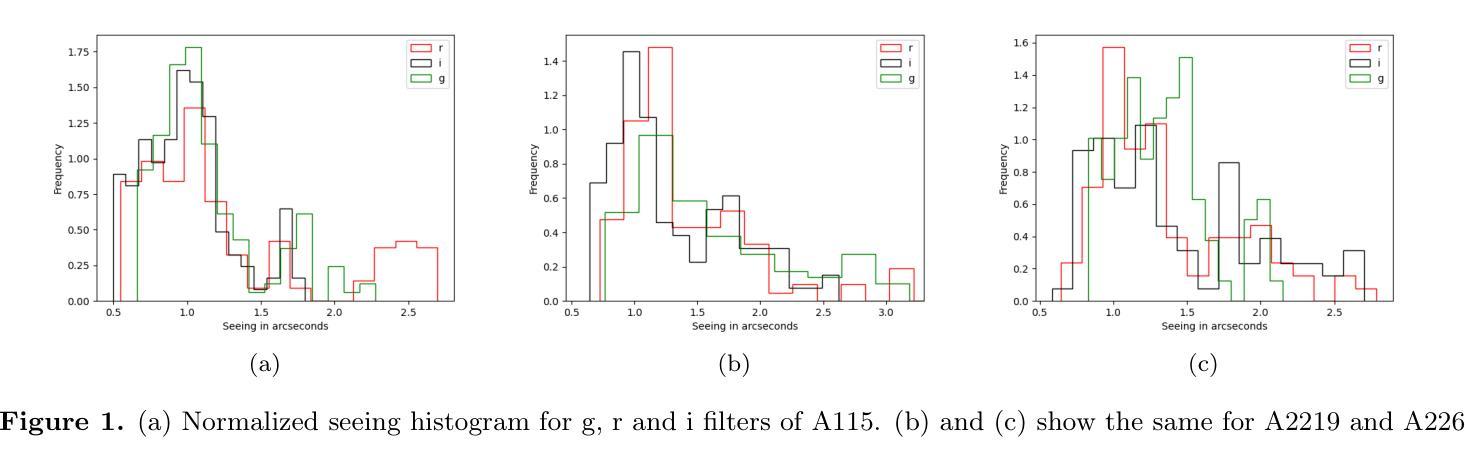
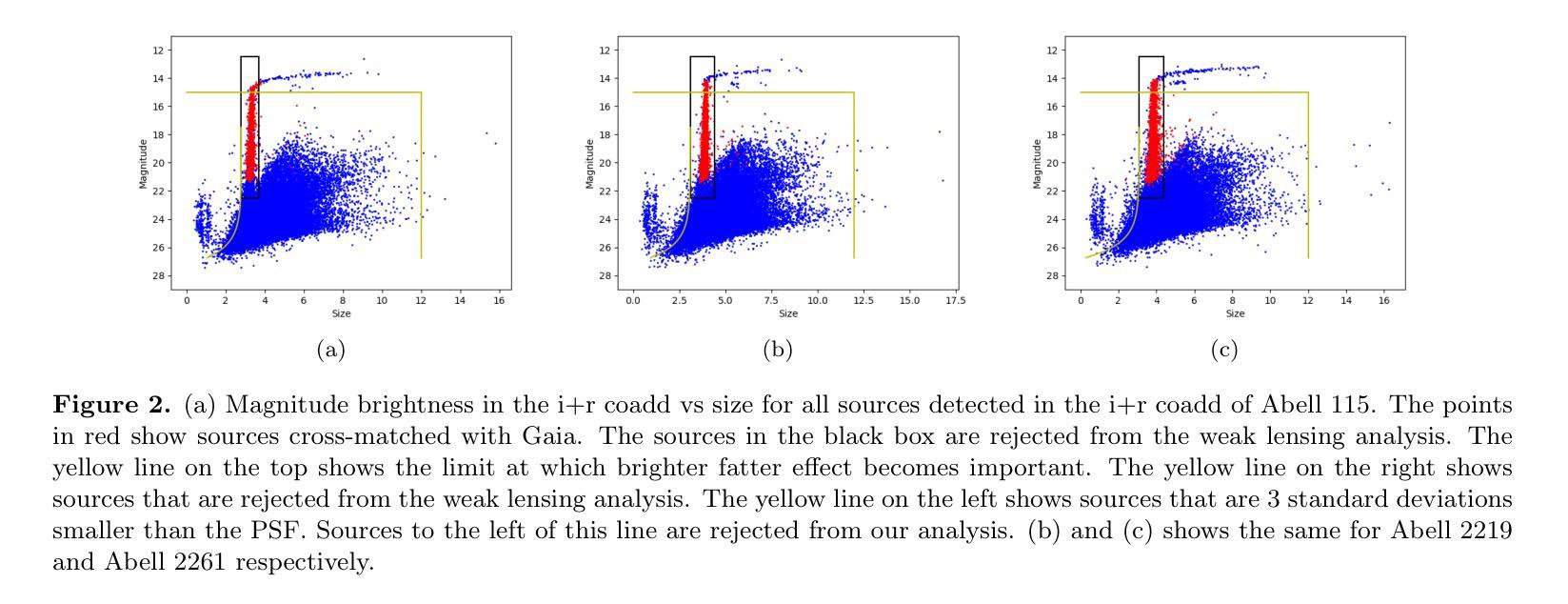
Weak lensing analysis of A115, A2219 and A2261: Detection of galaxy groups and filaments around clusters
Authors:Anirban Dutta, John Peterson, Matteo Cianfaglione, Glenn Sembroski
We present a weak lensing and multi-wavelength analysis of three galaxy clusters: A115, A2219, and A2261. Weak lensing is performed using shape measurements made in short 60s exposure images obtained using WIYN-ODI. Forced measurement is used to measure low Signal to Noise (SNR) sources in individual exposures. We find the weak lensing significance map recovers the galaxy clusters and most galaxy groups in the wide 40$’$ $\times$ 40$’$ field. Significant parts of the filamentary structures over this field, as indicated by the galaxy number density map, were also successfully recovered in lensing significance maps. We find the amount of structure recovery depends on both the depth and average seeing of the images. In particular, we detect a $>$ 9 Mpc long structure that contains the cluster A2219. We compare our weak lensing maps with Chandra, XMM, and LOFAR observations and find that A115 and A2219 show clear signs of ongoing mergers. In particular, we find a significant separation of hot ICM and the weak lensing contours in A115. On the other hand, while A2261 appears relaxed, based on radio and X-ray analysis, we find that it is likely interacting with a structure 700 kpc SW of the main cluster. We also successfully recovered mass structures in two regions around A2261 indicated by diffuse X-ray emission in XMM images.
我们对三个星系团A115、A2219和A2261进行了弱引力透镜和多波长分析。弱引力透镜分析是利用WIYN-ODI获取的60秒曝光图像中的形状测量来进行的。强制测量用于测量单个曝光中的低信噪比源。我们发现弱引力透镜显著性地图恢复了宽达40’×40’视野中的星系团和大多数星系团。由星系数密度图指示的此字段的大部分丝状结构,也在透镜显著性地图中成功恢复。我们发现结构恢复的数量取决于图像的深度和平均视宁度。尤其地,我们检测到一个包含星系团A2219的超过9Mpc长的结构。我们将弱引力透镜地图与Chandra、XMM和LOFAR观测结果进行比较,发现A115和A2219显示出正在进行中的合并迹象。特别是,我们发现A115中的热ICM和弱透镜轮廓有明显的分离。另一方面,虽然A2261在射电和X射线分析中看起来处于松弛状态,但我们发现它可能与主星系团西南700kpc处的结构相互作用。我们还成功恢复了XMM图像中围绕A2261的两个区域的弥散X射线发射所指示的质量结构。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in PASP
Summary
本研究通过对A115、A2219和A2261三个星系团进行弱引力透镜和多波长的分析。利用WIYN-ODI获取的60秒曝光图像进行形状测量,成功恢复了大部分星系群结构。结果显示弱引力透镜显著图与星系数密度图吻合,尤其在发现超过9百万秒差距的结构包含A2219星系团。与Chandra、XMM和LOFAR观测对比,发现A115和A2219存在明显的合并迹象,而看似平静的A2261可能与附近结构有交互作用。
Key Takeaways
- 通过对三个星系团A115、A2219和A2261的弱引力透镜和多波长分析,成功恢复了大部分星系群结构。
- 弱引力透镜显著图与星系数密度图相吻合,揭示了星系团及其周围的细丝状结构。
- 图像深度和平均视宁度影响结构恢复的程度。
- 检测到一个超过9百万秒差距的结构,包含A2219星系团。
- 与其他观测数据对比,发现A115和A2219正在经历合并。
- A2261虽看似平静,但可能与附近的结构有交互作用。
点此查看论文截图

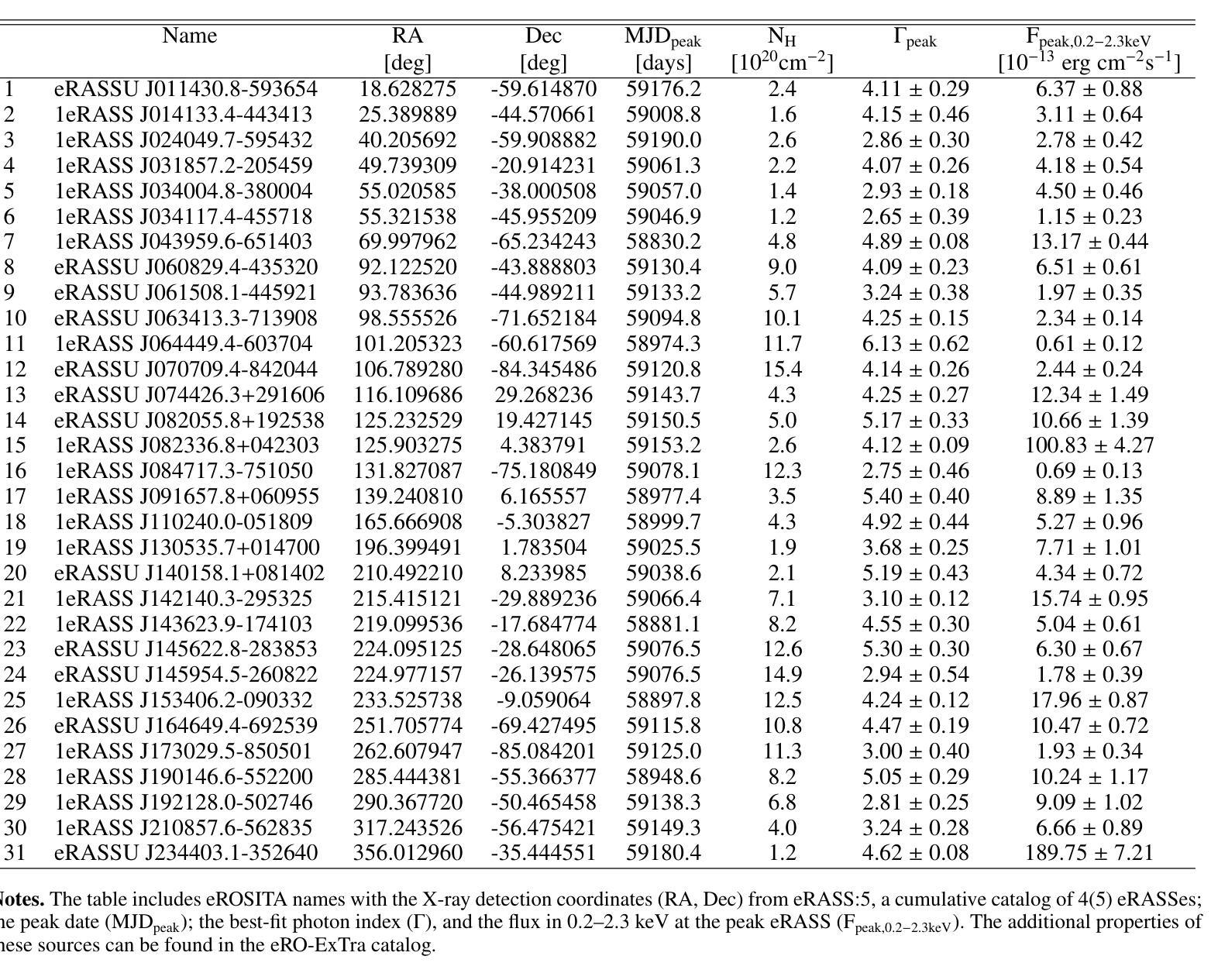
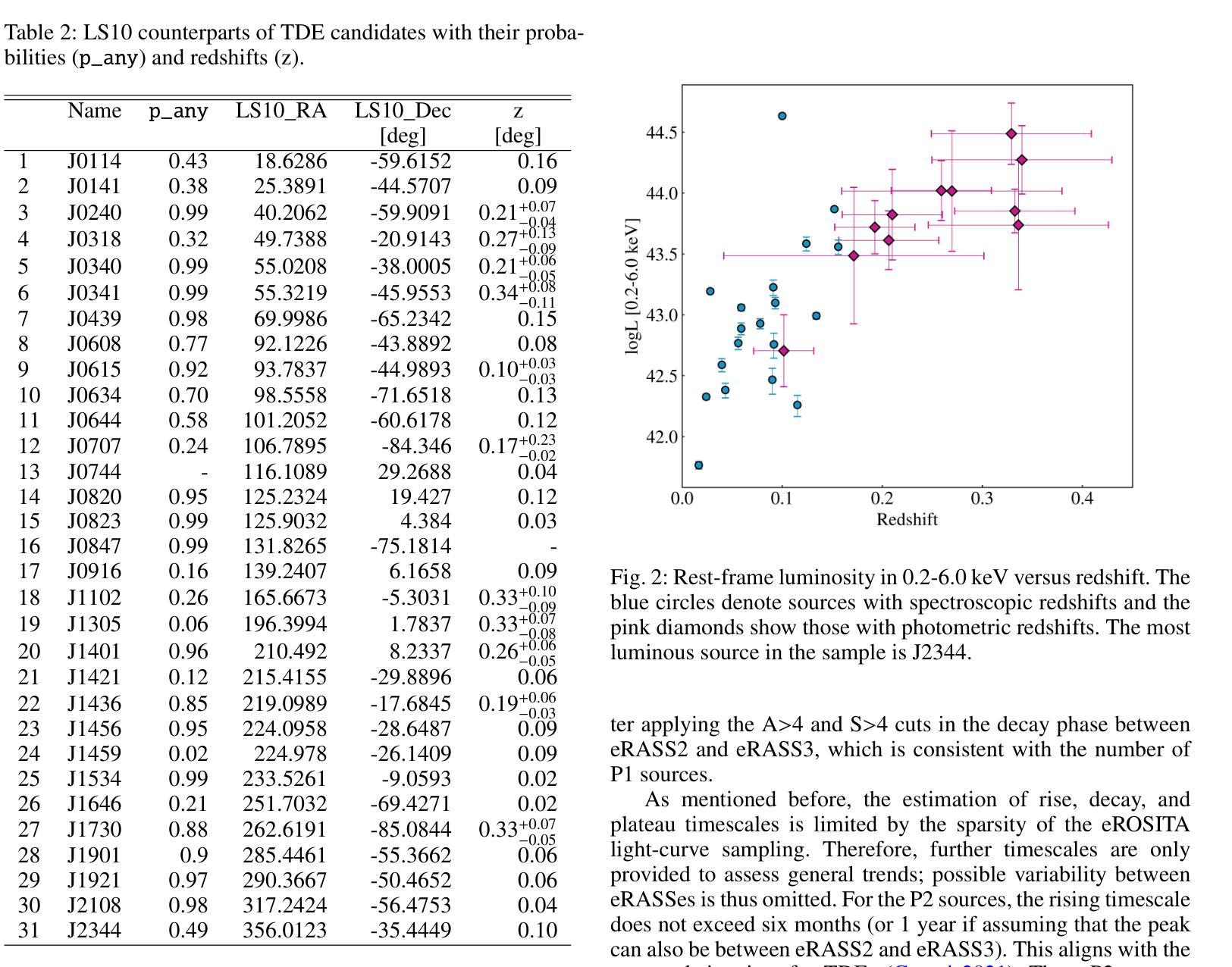
The population of tidal disruption events discovered with eROSITA
Authors:Iuliia Grotova, Arne Rau, Pietro Baldini, Adelle J. Goodwin, Zhu Liu, Andrea Merloni, Mara Salvato, Gemma E. Anderson, Riccardo Arcodia, Johannes Buchner, Mirko Krumpe, Adam Malyali, Megan Masterson, James C. A. Miller-Jones, Kirpal Nandra, Raphael Shirley
This paper presents a systematic study of X-ray-selected canonical tidal disruption events (TDEs) discovered in the western Galactic hemisphere of the first two eROSITA all-sky surveys (eRASS1 and eRASS2) performed between Dec 2019 and Dec 2020. We compiled a TDE sample from the catalog of eROSITA’s extragalactic transients and variables eRO-ExTra, which includes X-ray sources with a variability significance and fractional amplitude over four between eRASS1 and eRASS2, not associated with known AGNs. Each X-ray source is associated with an optical counterpart from the Legacy Survey DR10. Canonical TDEs were selected based on their X-ray light-curve properties (single flare or decline), soft X-ray spectra ($\Gamma>3$), and the absence of archival X-ray variability and AGN signatures in their host photometry and spectroscopy. The sample includes 31 X-ray-selected TDE candidates with redshifts of $0.02< z<0.34$ and luminosities of $5.7 \times 10^{41}<L_X<5.3 \times 10^{44}$ erg/s in the 0.2-6.0 keV rest frame, of which 30 are canonical TDEs and one is an off-nuclear TDE candidate. The derived X-ray luminosity function is best fit by a double power law with a luminosity break at $10^{44}$ erg/s, corresponding to the Eddington-limiting prediction. This corresponds to a TDE volumetric rate of $ (2.3^{+1.2}_{-0.9})\times10^{-7},Mpc^{-3} yr^{-1}$ ($\approx1.2\times 10^{-5}$ events per galaxy per year). TDE host galaxies show a green-valley overdensity. In addition, 20%, 30%, and 15% of the sample exhibit flares in the optical, mid-infrared (mid-IR), or radio bands, respectively. We discuss the differences between X-ray, optical, and mid-IR TDE populations and the origins of multiwavelength flares in the context of the obscuring envelope and stream-stream collision models. Finally, we highlight TDE subpopulations that are not included in the canonical sample and should be explored in the future.
本文系统地研究了在第一期和第二期eROSITA全天空调查(eRASS1和eRASS2)中,在西银道区域发现的通过X射线选定的典型潮汐撕裂事件(TDEs)。这些调查是在2019年12月至2020年12月之间进行的。我们从eROSITA的类星体外在事件和变量(ERO-ExTra)目录编译了一个TDE样本,其中包括在eRASS1和eRASS2之间四次调查中具有变率显著性和分数振幅的X射线源,这些源并未与已知的活动星系核(AGNs)相关联。每个X射线源都与Legacy Survey DR10的一个光学对应体相关联。典型TDE的选择基于其X射线光曲线特性(单次爆发或下降)、软X射线光谱(γ>3),以及在其宿主的光度测量和光谱中缺乏归档的X射线变率和AGNs的迹象。样本包括31个通过X射线选定的TDE候选者,红移范围为$0.02<z<0.34$,在静止帧的0.2-6.0keV下,光度范围为$5.7\times 10^{41}<Lx<5.3\times 10^{44}$erg/s,其中30个是典型TDEs,一个是离核TDE候选者。推导出的X射线光度函数最适合用双幂律拟合,光度中断在$10^{44}$erg/s处,这与爱丁顿极限预测相对应。这对应于TDE的体积率为$(2.3^{+1.2}_{-0.9})\times 10^{-7},Mpc^{-3} yr^{-1}$(每年每个星系约有$1.2\times 10^{-5}$个事件)。TDE宿主星系显示出绿谷密度过高。此外,样本中有20%、30%和15%分别在光学、中红外或射频波段表现出爆发。我们讨论了X射线、光学和中红外TDE人群之间的差异以及多波长爆发的起源,这些起源涉及隐蔽包络和流碰撞模型。最后,我们强调了不包括在典型样本中的TDE亚群,未来应对其进行探索研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 12 figures. Accepted for publication in A&A
摘要
本研究对首批两个eROSITA全天空调查(eRASS1和eRASS2)中发现的X射线选择的标准潮汐瓦解事件(TDEs)进行了系统研究。通过eROSITA的银河系外瞬态和变量源目录eRO-ExTra,我们筛选出了与已知活动星系核(AGNs)无关的X射线源,这些源在eRASS1和eRASS2之间的四次调查中表现出显著的变性和振幅变化。基于X射线光变曲线特性、软X射线光谱以及宿主的光学和光谱学中无归档的X射线变性和AGNs特征,我们选择了标准的TDEs。样本中包含31个X射线选择的TDE候选者,红移范围在$0.02< z<0.34$之间,在静止帧的0.2-6.0 keV内,光度为$5.7 \times 10^{41}<L_X<5.3 \times 10^{44}$ erg/s。样本中大多数为标准的TDEs,一个为离核TDE候选者。推导出的X射线光度函数最适合用双幂律拟合,光度断裂在$10^{44}$ erg/s处,与埃丁顿极限预测相符。这对应着每$Mpc^3$每年$ (2.3^{+1.2}_{-0.9})\times10^{-7}$的TDE体积率(即每年每星系约$1.2\times 10^{-5}$个事件)。TDE宿主星系显示出绿色山谷过密。此外,样本中有20%、30%、和15%的TDE在光学、中红外或射频波段表现出耀斑活动。我们讨论了X射线、光学和中红外TDE群体的差异以及多波长耀斑的起源,包括遮蔽包层和流-流碰撞模型。最后,我们强调了未来应探索的不包含在标准样本中的TDE亚群。
关键发现
- 通过对eROSITA首次两次全天空调查中的TDEs进行系统研究,发现了31个X射线选择的TDE候选者。
- 推导出的X射线光度函数符合双幂律分布,光度断裂点与埃丁顿极限预测相符。
- TDE宿主星系在绿色山谷区域有过密现象。
- 逾20%的样本在光学、中红外或射频波段展现出耀斑活动。
- 探讨了X射线、光学和中红外TDE群体的差异及多波长耀斑的起源。
- 发现并讨论了未被当前标准样本涵盖的TDE亚群,为未来研究提供了方向。
点此查看论文截图


A Modular Edge Device Network for Surgery Digitalization
Authors:Vincent Schorp, Frédéric Giraud, Gianluca Pargätzi, Michael Wäspe, Lorenzo von Ritter-Zahony, Marcel Wegmann, Nicola A. Cavalcanti, John Garcia Henao, Nicholas Bünger, Dominique Cachin, Sebastiano Caprara, Philipp Fürnstahl, Fabio Carrillo
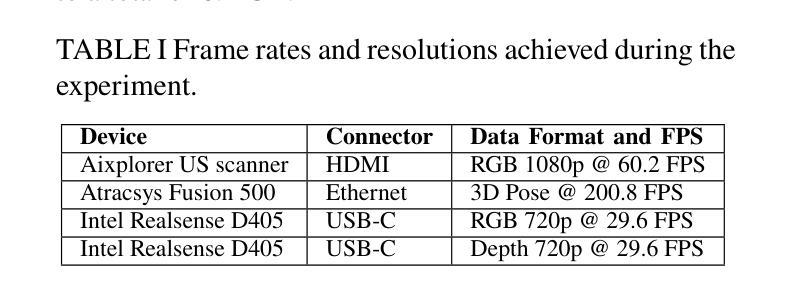
Future surgical care demands real-time, integrated data to drive informed decision-making and improve patient outcomes. The pressing need for seamless and efficient data capture in the OR motivates our development of a modular solution that bridges the gap between emerging machine learning techniques and interventional medicine. We introduce a network of edge devices, called Data Hubs (DHs), that interconnect diverse medical sensors, imaging systems, and robotic tools via optical fiber and a centralized network switch. Built on the NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX, each DH supports multiple interfaces (HDMI, USB-C, Ethernet) and encapsulates device-specific drivers within Docker containers using the Isaac ROS framework and ROS2. A centralized user interface enables straightforward configuration and real-time monitoring, while an Nvidia DGX computer provides state-of-the-art data processing and storage. We validate our approach through an ultrasound-based 3D anatomical reconstruction experiment that combines medical imaging, pose tracking, and RGB-D data acquisition.
未来的手术护理需要实时、集成的数据来推动决策的科学性和改善患者结果。手术室中对无缝、高效数据采集的迫切需求促使我们开发了一种模块化解决方案,以弥新兴的机器学习和介入医学之间的差距。我们引入了一种边缘设备网络,称为数据中心(DHs),它通过光纤和集中式网络交换机连接各种医疗传感器、成像系统和机器人工具。每个数据中心基于NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX构建,支持多个接口(HDMI、USB-C、以太网),并使用Isaac ROS框架和ROS2在Docker容器中封装设备特定驱动程序。一个集中的用户界面可实现简单的配置和实时监控,而Nvidia DGX计算机则提供最新颖的数据处理和存储功能。我们通过基于超声的3D解剖重建实验验证了我们的方法,该实验结合了医学影像、姿态跟踪和RGB-D数据采集。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for the Hamlyn Symposium, London, June 2025
Summary
未来手术护理需求实时集成数据以推动决策并改善患者结果。为解决手术室中无缝高效数据采集的迫切需求,我们开发了一种模块化解决方案,该方案能够弥接新兴机器学习技术与介入医学之间的鸿沟。我们推出名为数据中心的边缘设备网络,通过光纤和中央网络交换机互联各种医疗传感器、成像系统和机器人工具。每个数据中心基于NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX构建,支持多个接口(HDMI、USB-C、以太网),并在Docker容器中使用Isaac ROS框架和ROS2封装设备特定驱动程序。集中式用户界面可实现简易配置和实时监控,而NVIDIA DGX计算机则提供先进的数据处理和存储功能。我们通过结合医学成像、姿态追踪和RGB-D数据采集的超声三维重建实验验证了我们的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 未来手术护理需要实时集成数据以提高决策效率和改善患者结果。
- 开发了一种模块化解决方案,将新兴机器学习技术与介入医学相结合。
- 引入名为数据中心的边缘设备网络,可以互联医疗传感器、成像系统和机器人工具。
- 数据中心基于NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX构建,提供多种接口支持并在Docker容器中封装设备驱动程序。
- 集中式用户界面简化了配置和实时监控过程。
- NVIDIA DGX计算机提供了先进的数据处理和存储功能。
点此查看论文截图

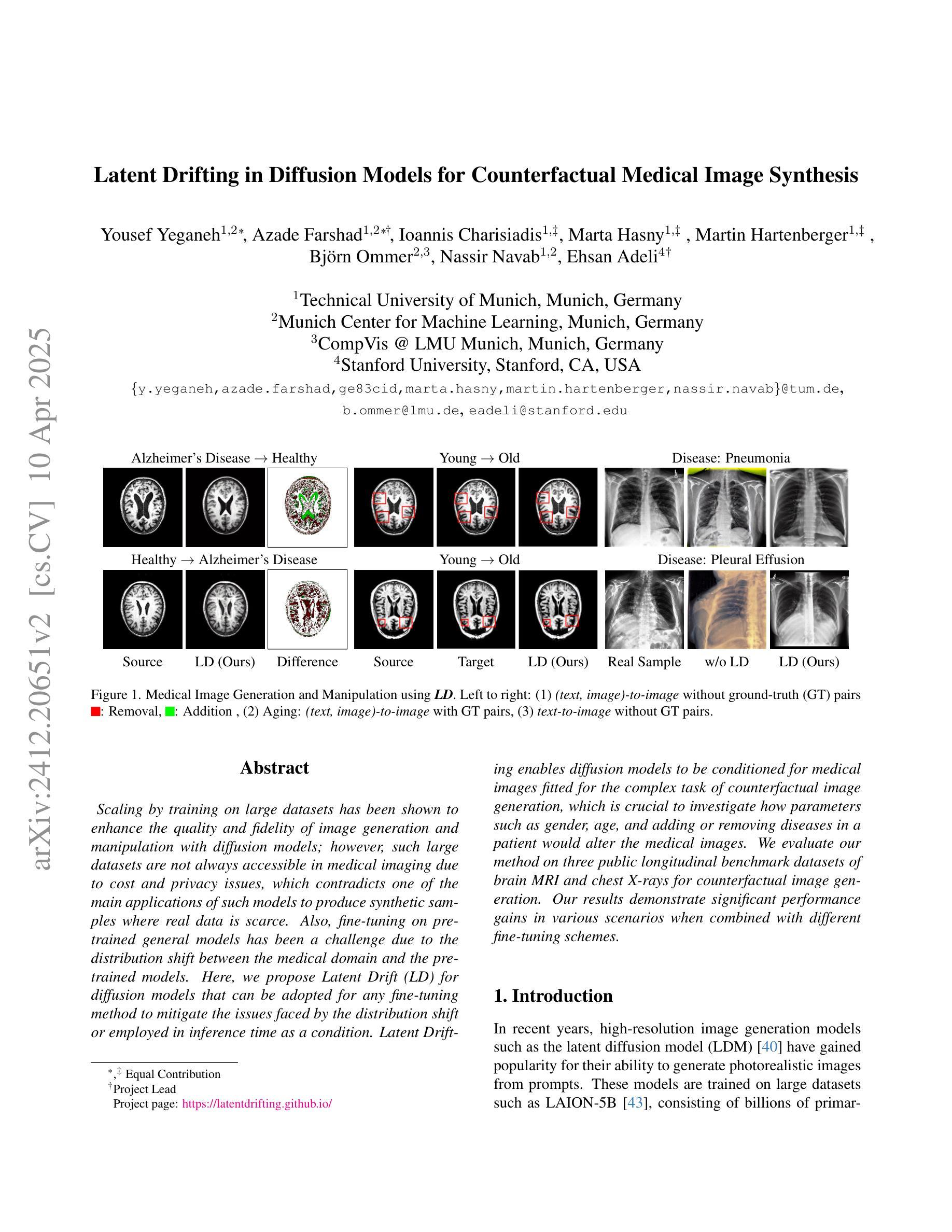
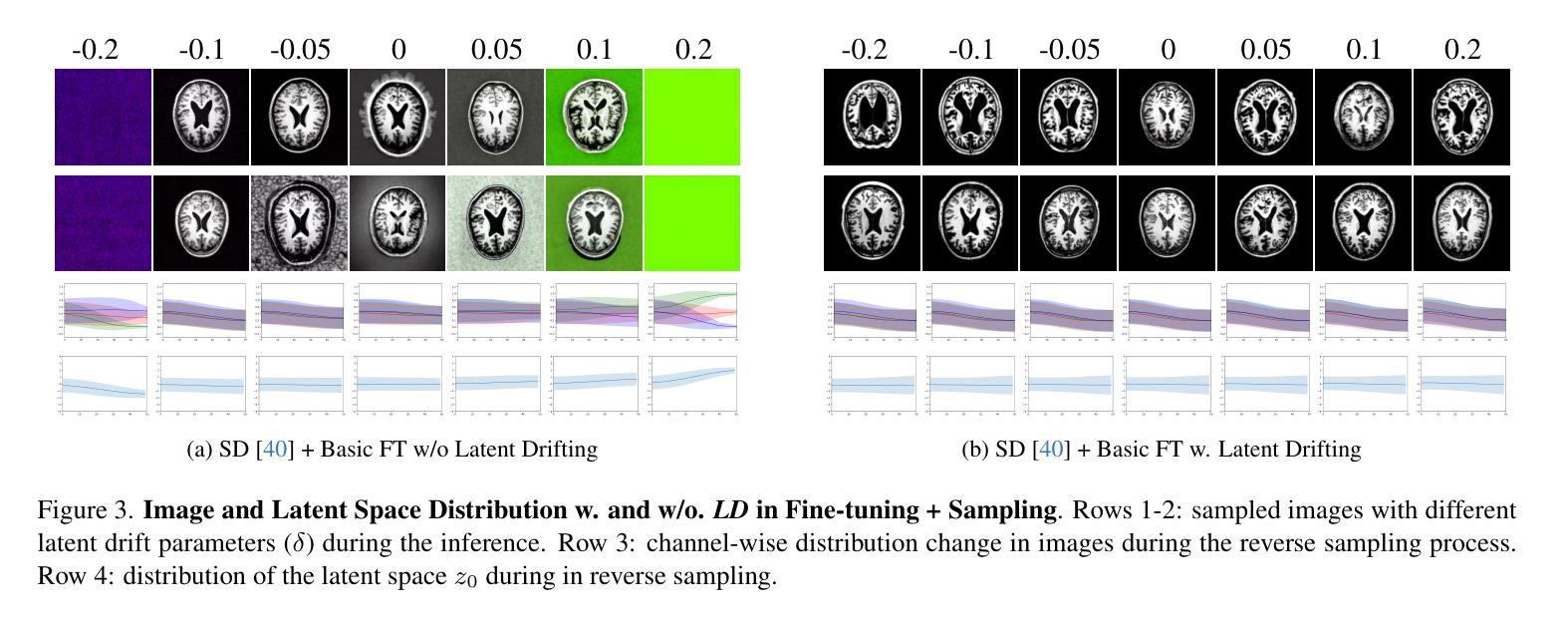
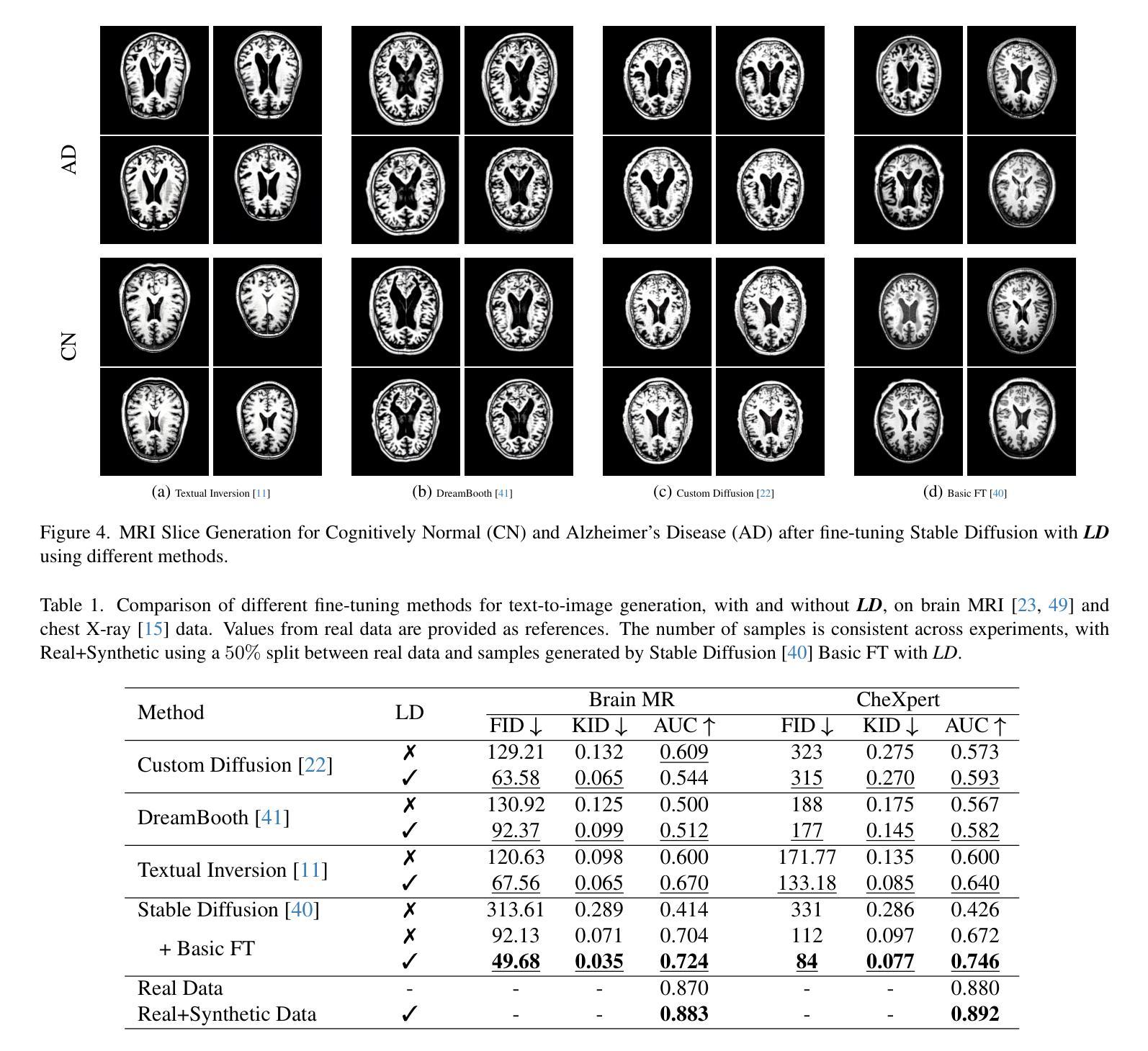
Latent Drifting in Diffusion Models for Counterfactual Medical Image Synthesis
Authors:Yousef Yeganeh, Azade Farshad, Ioannis Charisiadis, Marta Hasny, Martin Hartenberger, Björn Ommer, Nassir Navab, Ehsan Adeli
Scaling by training on large datasets has been shown to enhance the quality and fidelity of image generation and manipulation with diffusion models; however, such large datasets are not always accessible in medical imaging due to cost and privacy issues, which contradicts one of the main applications of such models to produce synthetic samples where real data is scarce. Also, fine-tuning pre-trained general models has been a challenge due to the distribution shift between the medical domain and the pre-trained models. Here, we propose Latent Drift (LD) for diffusion models that can be adopted for any fine-tuning method to mitigate the issues faced by the distribution shift or employed in inference time as a condition. Latent Drifting enables diffusion models to be conditioned for medical images fitted for the complex task of counterfactual image generation, which is crucial to investigate how parameters such as gender, age, and adding or removing diseases in a patient would alter the medical images. We evaluate our method on three public longitudinal benchmark datasets of brain MRI and chest X-rays for counterfactual image generation. Our results demonstrate significant performance gains in various scenarios when combined with different fine-tuning schemes.
通过在大规模数据集上进行训练,已经证明可以提高扩散模型在图像生成和操纵方面的质量和保真度。然而,在医学成像中,由于成本和隐私问题,并非总能获取到这样的大规模数据集,这与此类模型在真实数据稀缺的情况下产生合成样本的主要应用相矛盾。此外,由于医学领域与预训练模型之间的分布转移问题,对预训练的通用模型进行微调一直是一个挑战。在这里,我们为扩散模型提出了潜在漂移(LD)技术,该技术可以被任何微调方法所采用,以缓解由分布转移所面临的问题,或在推理时间作为条件被采用。潜在漂移技术使得扩散模型能够对医学图像进行适配,适应复杂的反事实图像生成任务,这对于研究参数如性别、年龄以及给患者添加或移除疾病后如何改变医学图像至关重要。我们在三个公开的纵向基准数据集上对我们的方法进行了评估,这些数据集包括用于反事实图像生成的脑MRI和胸部X射线。我们的结果表明,在不同的微调方案组合下,在各种场景中均实现了显著的性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025 (highlight)
Summary
训练大规模数据集能提高扩散模型在图像生成和操纵方面的质量和保真度,但在医学成像领域,由于成本和隐私问题,并不总能获取到如此大规模的数据集。此外,由于医学领域与预训练模型之间的分布转移问题,微调预训练的通用模型也面临挑战。为此,我们提出了扩散模型的Latent Drift(LD)方法,可应用于任何微调方法来缓解分布转移问题或在推理时间作为条件使用。Latent Drifting使扩散模型能够进行医疗图像的条件适配,适用于复杂任务如反事实图像生成,这对于研究参数如性别、年龄以及增加或减少患者疾病等如何改变医疗图像至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型通过在大规模数据集上进行训练,可以提高图像生成和操纵的质量。
- 在医学成像领域,获取大规模数据集存在成本和隐私方面的挑战。
- 分布转移问题是将预训练模型应用于医学领域时面临的挑战之一。
- 提出了Latent Drift(LD)方法,可以缓解分布转移问题,并应用于任何微调方法。
- Latent Drifting使扩散模型能够进行医疗图像的条件适配,适用于复杂任务如反事实图像生成。
- 反事实图像生成有助于研究参数变化如何影响医疗图像。
点此查看论文截图