⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-15 更新
DRAFT-ing Architectural Design Decisions using LLMs
Authors:Rudra Dhar, Adyansh Kakran, Amey Karan, Karthik Vaidhyanathan, Vasudeva Varma
Architectural Knowledge Management (AKM) is crucial for software development but remains challenging due to the lack of standardization and high manual effort. Architecture Decision Records (ADRs) provide a structured approach to capture Architecture Design Decisions (ADDs), but their adoption is limited due to the manual effort involved and insufficient tool support. Our previous work has shown that Large Language Models (LLMs) can assist in generating ADDs. However, simply prompting the LLM does not produce quality ADDs. Moreover, using third-party LLMs raises privacy concerns, while self-hosting them poses resource challenges. To this end, we experimented with different approaches like few-shot, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and fine-tuning to enhance LLM’s ability to generate ADDs. Our results show that both techniques improve effectiveness. Building on this, we propose Domain Specific Retreival Augumented Few Shot Fine Tuninng, DRAFT, which combines the strengths of all these three approaches for more effective ADD generation. DRAFT operates in two phases: an offline phase that fine-tunes an LLM on generating ADDs augmented with retrieved examples and an online phase that generates ADDs by leveraging retrieved ADRs and the fine-tuned model. We evaluated DRAFT against existing approaches on a dataset of 4,911 ADRs and various LLMs and analyzed them using automated metrics and human evaluations. Results show DRAFT outperforms all other approaches in effectiveness while maintaining efficiency. Our findings indicate that DRAFT can aid architects in drafting ADDs while addressing privacy and resource constraints.
架构知识管理(AKM)在软件开发中至关重要,但由于缺乏标准化和高度依赖人工操作,仍面临挑战。架构决策记录(ADR)提供了一种捕捉架构设计决策(ADD)的结构化方法,但由于涉及大量手动操作和工具支持不足,其采用受到限制。我们之前的工作表明,大型语言模型(LLM)可以辅助生成ADD。然而,仅仅提示LLM并不能产生高质量的ADD。此外,使用第三方LLM会引发隐私担忧,而自行托管则带来资源挑战。为此,我们尝试了不同的方法,如小样本、检索增强生成(RAG)和微调,以增强LLM生成ADD的能力。结果表明,这两种技术都提高了有效性。在此基础上,我们提出了领域特定检索增强小样本微调(DRAFT),它结合了这三种方法的优点,更有效地生成ADD。DRAFT分为两个阶段:一个是在生成ADD时通过微调LLM并使用检索到的例子进行增强的离线阶段;另一个是利用检索到的ADR和微调模型生成ADD的在线阶段。我们在包含4911条ADR的数据集上评估了DRAFT与其他现有方法,并通过自动化指标和人类评估进行了分析。结果表明,在有效性和效率方面,DRAFT都优于其他所有方法。我们的研究结果表明,DRAFT可以帮助架构师起草ADD,同时解决隐私和资源约束问题。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在软件开发中,架构知识管理(AKM)至关重要,但仍面临标准化缺失和高度依赖人工的挑战。架构决策记录(ADRs)为捕捉架构设计决策(ADDs)提供了一种结构化方法,但由于涉及大量手动操作和工具支持不足,其采用受到限制。先前的研究表明大型语言模型(LLM)可以辅助生成ADDs,但简单的提示并不能产生高质量的ADDs。为解决这一问题,研究团队尝试了多种方法,如少样本、检索增强生成(RAG)和微调,以提升LLM生成ADDs的能力。在此基础上,提出了结合这三种方法优点的领域特定检索增强少样本微调(DRAFT)。它通过离线阶段对LLM进行微调,利用检索到的例子辅助生成ADDs,以及在线阶段通过利用检索到的ADRs和已微调模型生成ADDs。评估显示,相较于其他方法,DRAFT在有效性和效率方面表现更佳,并能帮助架构师起草ADDs,同时解决隐私和资源约束问题。
Key Takeaways
- 架构知识管理(AKM)在软件开发中非常重要,但标准化和自动化程度不足使其具有挑战性。
- 架构决策记录(ADRs)是捕捉架构设计决策(ADDs)的结构化方法,但实施中面临手动操作复杂和工具支持不足的问题。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)可用于辅助生成ADDs,但简单提示效果不佳。
- 尝试了少样本、检索增强生成(RAG)和微调等方法来提升LLM生成ADDs的能力。
- 提出了结合多种方法的领域特定检索增强少样本微调(DRAFT)方案。
- DRAFT通过离线微调LLM并结合检索到的例子来生成ADDs,再在线利用检索到的ADRs和已微调模型生成ADDs。
点此查看论文截图

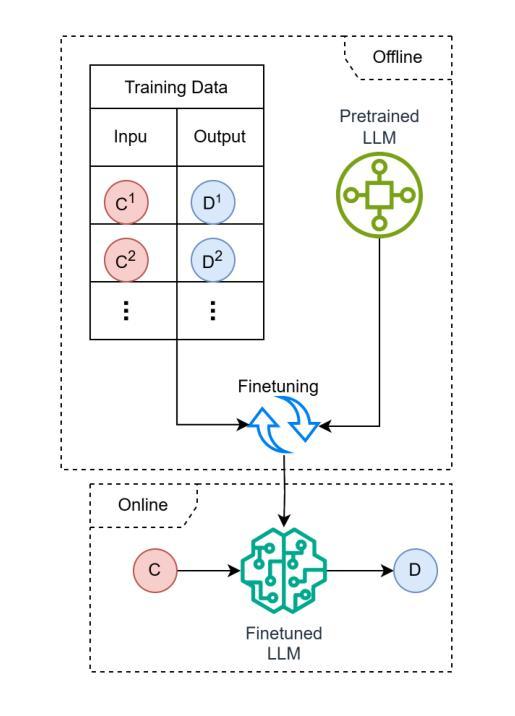
Investigating Vision-Language Model for Point Cloud-based Vehicle Classification
Authors:Yiqiao Li, Jie Wei, Camille Kamga
Heavy-duty trucks pose significant safety challenges due to their large size and limited maneuverability compared to passenger vehicles. A deeper understanding of truck characteristics is essential for enhancing the safety perspective of cooperative autonomous driving. Traditional LiDAR-based truck classification methods rely on extensive manual annotations, which makes them labor-intensive and costly. The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) trained on massive datasets presents an opportunity to leverage their few-shot learning capabilities for truck classification. However, existing vision-language models (VLMs) are primarily trained on image datasets, which makes it challenging to directly process point cloud data. This study introduces a novel framework that integrates roadside LiDAR point cloud data with VLMs to facilitate efficient and accurate truck classification, which supports cooperative and safe driving environments. This study introduces three key innovations: (1) leveraging real-world LiDAR datasets for model development, (2) designing a preprocessing pipeline to adapt point cloud data for VLM input, including point cloud registration for dense 3D rendering and mathematical morphological techniques to enhance feature representation, and (3) utilizing in-context learning with few-shot prompting to enable vehicle classification with minimally labeled training data. Experimental results demonstrate encouraging performance of this method and present its potential to reduce annotation efforts while improving classification accuracy.
重型卡车由于其庞大的体积和与乘用车相比有限的机动性,对安全构成了重大挑战。加深对卡车特性的了解对于提高合作自动驾驶的安全性至关重要。传统的基于激光雷达的卡车分类方法依赖于大量的手动注释,这使得它们劳动密集且成本高昂。大规模数据集训练的的大型语言模型的快速发展,利用它们的少样本学习能力进行卡车分类成为可能。然而,现有的视觉语言模型主要是基于图像数据集进行训练的,这使得直接处理点云数据具有挑战性。本研究介绍了一个新型框架,该框架结合了路边激光雷达点云数据和视觉语言模型,以实现高效准确的卡车分类,支持合作和安全的驾驶环境。本研究引入了三项关键创新:(1)利用现实世界的激光雷达数据集进行模型开发,(2)设计预处理管道以适应点云数据用于视觉语言模型的输入,包括点云注册进行密集三维渲染和数学形态技术以增强特征表示,(3)利用具有少量提示的上下文学习来进行车辆分类,以使用最少量的标注训练数据进行分类。实验结果表明,该方法具有令人鼓舞的性能,具有减少注释工作同时提高分类精度的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages,3 figures, 1 table, CVPR DriveX workshop
Summary
这篇文本介绍了重型卡车在驾驶安全方面的挑战,以及如何利用大型语言模型(LLMs)的少样本学习能力对卡车进行分类以提升驾驶安全。研究提出了一种结合路边激光雷达点云数据和视觉语言模型(VLMs)的新框架,通过设计预处理流程以适应点云数据输入,并利用少量标注数据进行车辆分类。该方法的性能表现良好,具有减少标注工作、提高分类准确性的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 重型卡车由于其大型尺寸和与乘用车相比的有限机动性,存在重大安全挑战。
- 对卡车特性的深入了解对于提高合作自动驾驶的安全性至关重要。
- 传统基于激光雷达的卡车分类方法依赖大量手动注释,既耗时又昂贵。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的少样本学习能力可用于卡车分类。
- 结合路边激光雷达点云数据和视觉语言模型(VLMs)的新框架被提出,以促进高效和准确的卡车分类。
- 框架中的关键创新包括:使用真实世界的激光雷达数据集进行模型开发、设计适应点云数据的预处理管道,以及利用少量样本提示进行上下文学习。
点此查看论文截图


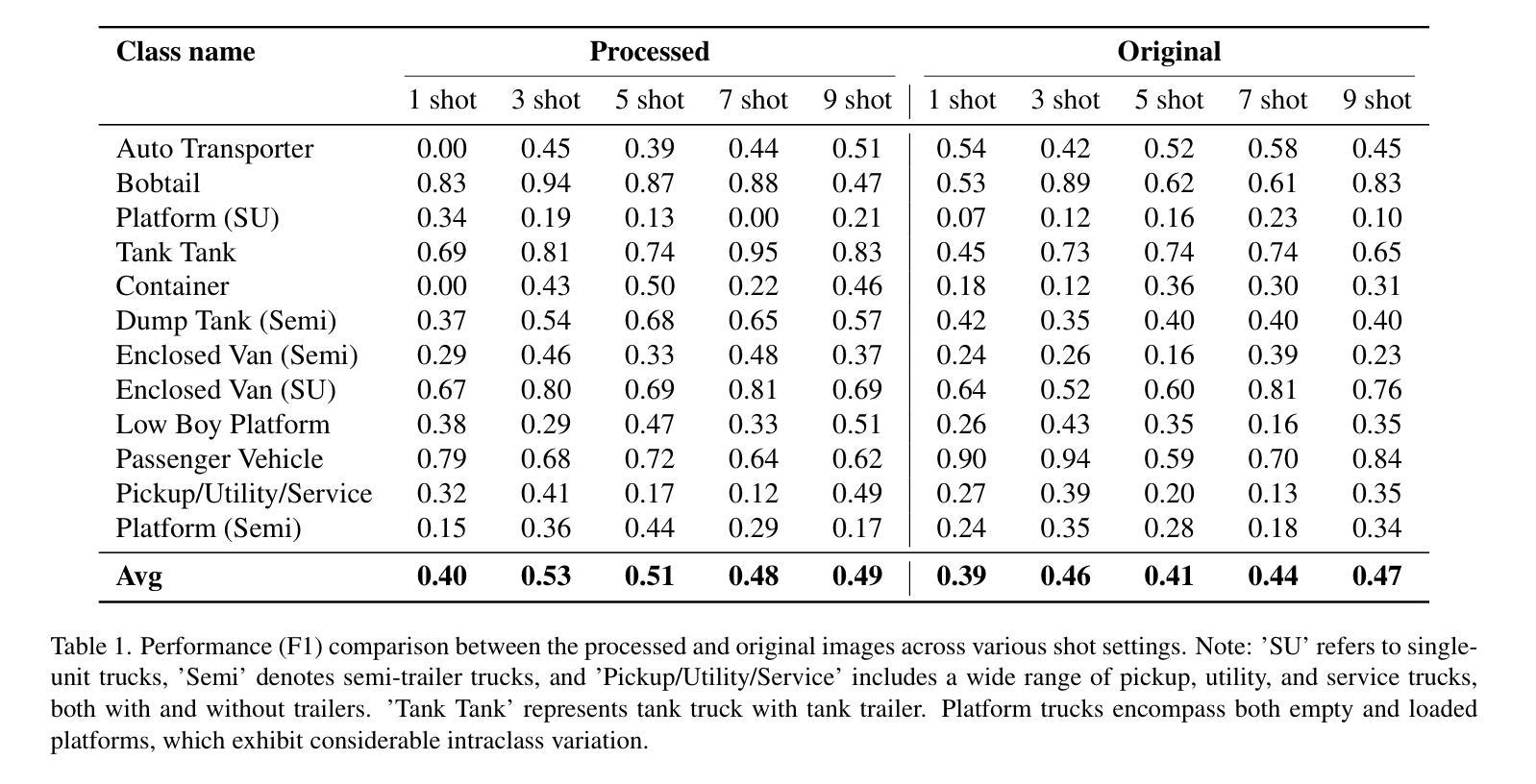
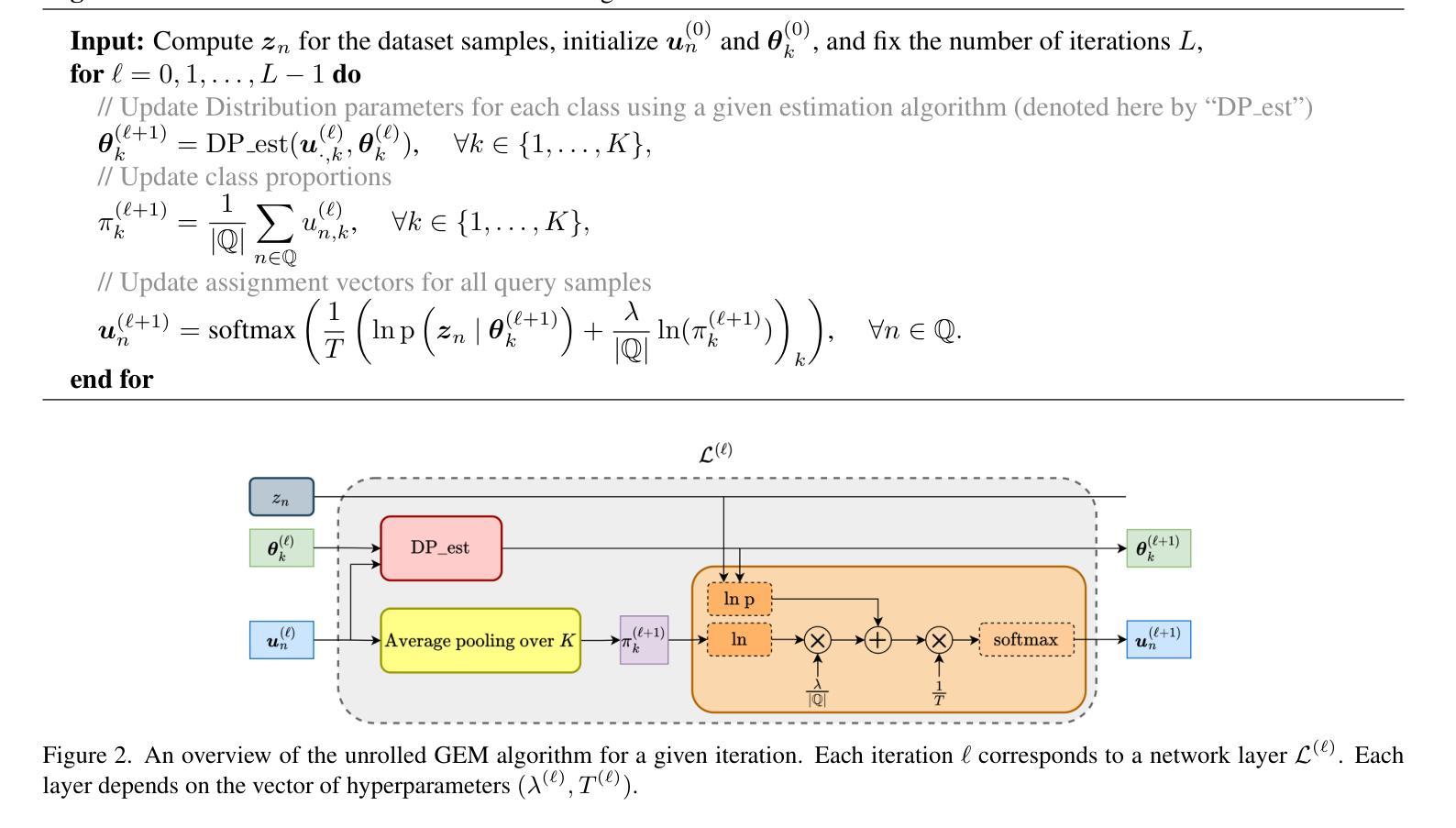
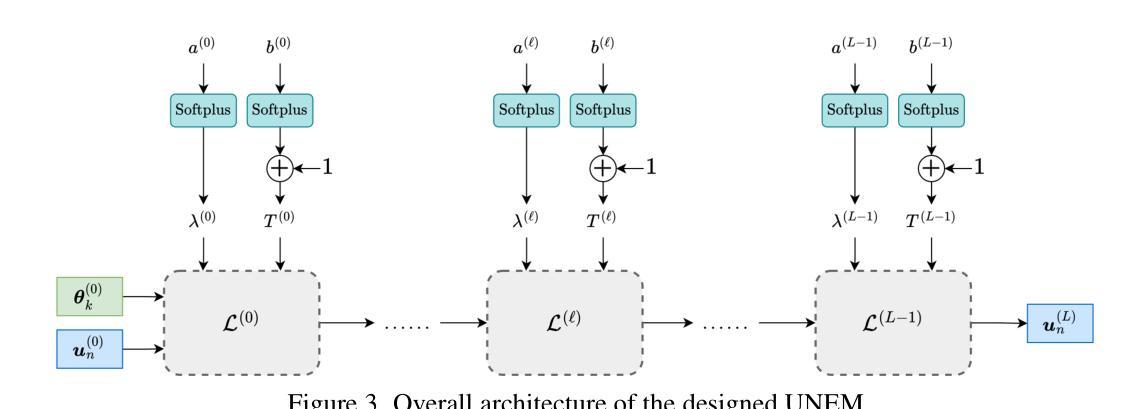
UNEM: UNrolled Generalized EM for Transductive Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Long Zhou, Fereshteh Shakeri, Aymen Sadraoui, Mounir Kaaniche, Jean-Christophe Pesquet, Ismail Ben Ayed
Transductive few-shot learning has recently triggered wide attention in computer vision. Yet, current methods introduce key hyper-parameters, which control the prediction statistics of the test batches, such as the level of class balance, affecting performances significantly. Such hyper-parameters are empirically grid-searched over validation data, and their configurations may vary substantially with the target dataset and pre-training model, making such empirical searches both sub-optimal and computationally intractable. In this work, we advocate and introduce the unrolling paradigm, also referred to as “learning to optimize”, in the context of few-shot learning, thereby learning efficiently and effectively a set of optimized hyper-parameters. Specifically, we unroll a generalization of the ubiquitous Expectation-Maximization (EM) optimizer into a neural network architecture, mapping each of its iterates to a layer and learning a set of key hyper-parameters over validation data. Our unrolling approach covers various statistical feature distributions and pre-training paradigms, including recent foundational vision-language models and standard vision-only classifiers. We report comprehensive experiments, which cover a breadth of fine-grained downstream image classification tasks, showing significant gains brought by the proposed unrolled EM algorithm over iterative variants. The achieved improvements reach up to 10% and 7.5% on vision-only and vision-language benchmarks, respectively.
转导式小样本学习近期在计算机视觉领域引起了广泛关注。然而,当前的方法引入了关键超参数,这些超参数控制测试批次的预测统计信息,如类别平衡水平,对性能产生重大影响。这些超参数是通过验证数据进行经验网格搜索的,并且它们的配置可能会随着目标数据集和预训练模型的不同而显著变化,这使得这种经验搜索既非最优也计算不可行。在这项工作中,我们提倡并在小样本学习的背景下引入“展开范式”,也称为“学习优化”,从而高效有效地学习一组优化超参数。具体来说,我们将普遍的期望最大化(EM)优化器推广并展开为神经网络架构,将其每个迭代映射到一层,并在验证数据上学习一组关键超参数。我们的展开方法涵盖了各种统计特征分布和预训练范式,包括最新的基础视觉语言模型和标准的仅视觉分类器。我们报告了全面的实验,涵盖了多种精细的下游图像分类任务,显示了所提出的展开EM算法相对于迭代变体所带来的显著收益。在仅视觉和视觉语言基准测试中,实现的改进分别高达10%和7.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR2025
Summary
本文关注transductive few-shot learning在计算机视觉领域的应用,提出将通用期望最大化(EM)优化器转化为神经网络架构的方法,将迭代过程中的每一步映射到神经网络的一层,并通过验证数据学习优化的一组关键超参数,以提高few-shot learning的性能。实验表明,该方法在多种下游图像分类任务上取得了显著的提升。
Key Takeaways
- Transductive few-shot learning在计算机视觉领域受到广泛关注。
- 当前方法的关键超参数对测试集性能有重大影响,且需要通过验证数据进行经验网格搜索。
- 本文提出将期望最大化(EM)优化器转化为神经网络架构的方法,将迭代过程映射到神经网络层。
- 通过验证数据学习优化的一组关键超参数,提高few-shot learning的性能。
- 方法涵盖多种统计特征分布和预训练模式,包括最新的视觉语言模型和标准的仅视觉分类器。
- 实验结果显示,在多种下游图像分类任务上,所提方法取得了显著的提升,最高提升幅度达到10%和7.5%。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Fine-Tuning of Single-Cell Foundation Models Enables Zero-Shot Molecular Perturbation Prediction
Authors:Sepideh Maleki, Jan-Christian Huetter, Kangway V. Chuang, David Richmond, Gabriele Scalia, Tommaso Biancalani
Predicting transcriptional responses to novel drugs provides a unique opportunity to accelerate biomedical research and advance drug discovery efforts. However, the inherent complexity and high dimensionality of cellular responses, combined with the extremely limited available experimental data, makes the task challenging. In this study, we leverage single-cell foundation models (FMs) pre-trained on tens of millions of single cells, encompassing multiple cell types, states, and disease annotations, to address molecular perturbation prediction. We introduce a drug-conditional adapter that allows efficient fine-tuning by training less than 1% of the original foundation model, thus enabling molecular conditioning while preserving the rich biological representation learned during pre-training. The proposed strategy allows not only the prediction of cellular responses to novel drugs, but also the zero-shot generalization to unseen cell lines. We establish a robust evaluation framework to assess model performance across different generalization tasks, demonstrating state-of-the-art results across all settings, with significant improvements in the few-shot and zero-shot generalization to new cell lines compared to existing baselines.
预测新型药物的转录反应为加速生物医学研究和推进药物发现努力提供了独特的机会。然而,由于细胞反应的固有复杂性和高维度性,以及可用的实验数据极为有限,这使得该任务具有挑战性。在这项研究中,我们利用基于单细胞的预训练模型(FMs),这些模型基于数千万个单细胞进行训练,涵盖了多种细胞类型、状态和疾病注释,来解决分子扰动预测问题。我们引入了一种药物条件适配器,通过训练原始预训练模型不到1%的参数,实现了高效的微调,从而在实现分子调节的同时,保留了预训练期间学到的丰富的生物表征。所提出的策略不仅允许预测新型药物的细胞反应,而且能够在未见过的细胞系中实现零样本泛化。我们建立了一个稳健的评估框架,以评估模型在不同泛化任务上的性能,在所有设置中都取得了最先进的结果,与现有基准相比,在新细胞系的少样本和零样本泛化方面取得了显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究利用预训练在数亿单细胞上的单细胞基础模型(FMs)进行分子扰动预测,解决细胞响应预测新药的任务。通过引入药物条件适配器,实现高效微调,仅训练原始基础模型的不到1%,能在保持预训练丰富生物学表征的同时实现分子调控。该方法不仅能预测细胞对新药的反应,还能实现零样本泛化到未见过的细胞系。建立了稳健的评估框架,全面评估模型性能,并在所有设置中取得最佳结果,与现有基线相比,在新细胞系的少样本和零样本泛化方面有明显改进。
Key Takeaways
- 利用单细胞基础模型(FMs)进行分子扰动预测,以应对新药预测的复杂性和高维度挑战。
- 通过引入药物条件适配器,实现高效微调预训练模型,进行分子调控。
- 实现零样本泛化到未见过的细胞系预测,对新药的细胞反应进行预测。
- 建立稳健的评估框架全面评估模型性能。
- 在不同泛化任务中取得最佳结果,显示模型的有效性和先进性。
- 与现有方法相比,模型在少样本和零样本泛化到新细胞系上表现更优。
- 研究成果为加速生物医学研究和药物发现提供了独特的机会。
点此查看论文截图

7B Fully Open Source Moxin-LLM – From Pretraining to GRPO-based Reinforcement Learning Enhancement
Authors:Pu Zhao, Xuan Shen, Zhenglun Kong, Yixin Shen, Sung-En Chang, Timothy Rupprecht, Lei Lu, Enfu Nan, Changdi Yang, Yumei He, Weiyan Shi, Xingchen Xu, Yu Huang, Wei Jiang, Wei Wang, Yue Chen, Yong He, Yanzhi Wang
Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have undergone a significant transformation, marked by a rapid rise in both their popularity and capabilities. Leading this evolution are proprietary LLMs like GPT-4 and GPT-o1, which have captured widespread attention in the AI community due to their remarkable performance and versatility. Simultaneously, open-source LLMs, such as LLaMA, have made great contributions to the ever-increasing popularity of LLMs due to the ease to customize and deploy the models across diverse applications. Although open-source LLMs present unprecedented opportunities for innovation and research, the commercialization of LLMs has raised concerns about transparency, reproducibility, and safety. Many open-source LLMs fail to meet fundamental transparency requirements by withholding essential components like training code and data, which may hinder further innovations on LLMs. To mitigate this issue, we introduce Moxin 7B, a fully open-source LLM developed, adhering to principles of open science, open source, open data, and open access. We release the pre-training code and configurations, training and fine-tuning datasets, and intermediate and final checkpoints, aiming to make continuous commitments to fully open-source LLMs. After pre-training and obtaining the base model, we finetune the Moxin Base model with SOTA post-training framework and instruction data to obtain Moxin Instruct model. To improve the reasoning capability, we further finetune our Instruct model with chain-of-thought data distilled from DeepSeek R1, and then use Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), an efficient and effective reinforcement learning algorithm following DeepSeek R1, to finetune our model, leading to the Moxin Reasoning model. Experiments show that our models achieve superior performance in various evaluations such as zero-shot evaluation, few-shot evaluation, and CoT evaluation.
最近,大型语言模型(LLM)经历了重大变革,其普及和能力都迅速增长。引领这一变革的是专有大型语言模型,如GPT-4和GPT-o1,它们由于出色的性能和多功能性,在人工智能领域引起了广泛关注。同时,开源大型语言模型,如LLaMA,由于对模型进行定制和跨多种应用的部署的便捷性,为大型语言模型日益普及做出了巨大贡献。尽管开源大型语言模型为创新和科研带来了前所未有的机会,但大型语言模型的商业化引发了关于透明度、可重复性和安全的担忧。许多开源的大型语言模型未能满足基本的透明度要求,隐瞒了关键组件,如训练代码和数据,这可能阻碍大型语言模型的进一步创新。为了缓解这个问题,我们引入了Moxin 7B,这是一个遵循公开科学、开源、开放数据和开放访问原则的全开源大型语言模型。我们发布了预训练代码和配置、训练和微调数据集以及中间和最终检查点,致力于完全开源的大型语言模型的持续承诺。在预训练并获取基础模型后,我们使用最先进的后训练框架和指令数据对Moxin Base模型进行微调,以获得Moxin Instruct模型。为了提高推理能力,我们进一步使用来自DeepSeek R1的蒸馏思维链数据对Instruct模型进行微调,并使用跟随DeepSeek R1的高效且有效的强化学习算法——Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)来微调我们的模型,从而得到Moxin Reasoning模型。实验表明,我们的模型在零样本评估、少样本评估和思维链评估等各种评估中均取得了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)正经历一次重大变革,其中以GPT-4和GPT-o1等专有LLM以及LLaMA等开源LLM为代表。然而,开源LLM的商业化引发了透明度、可复制性和安全性等方面的担忧。为此,我们推出遵循公开科学、开源、开放数据和开放访问原则的全新开源LLM——Moxin 7B,并公开预训练代码、配置、训练及微调数据集和中间及最终检查点。通过一系列微调和优化,我们成功开发出Moxin Instruct和Moxin Reasoning模型,实验显示,这些模型在零样本、少样本和CoT评估中表现卓越。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)正在经历重大变革,包括GPT-4和GPT-o1在内的专有LLM以及LLaMA等开源LLM引领了这一趋势。
- 开源LLM的商业化引发了关于透明度、可复制性和安全性的担忧。
- Moxin 7B是一个全新的开源LLM,遵循公开科学、开源、开放数据和开放访问的原则。
- Moxin 7B公开了预训练代码、配置、训练及微调数据集和中间及最终检查点。
- 通过使用SOTA后训练框架和指令数据微调,成功开发出Moxin Instruct模型。
- 通过使用链式思维数据和Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)算法进一步微调,成功开发出Moxin Reasoning模型。
点此查看论文截图


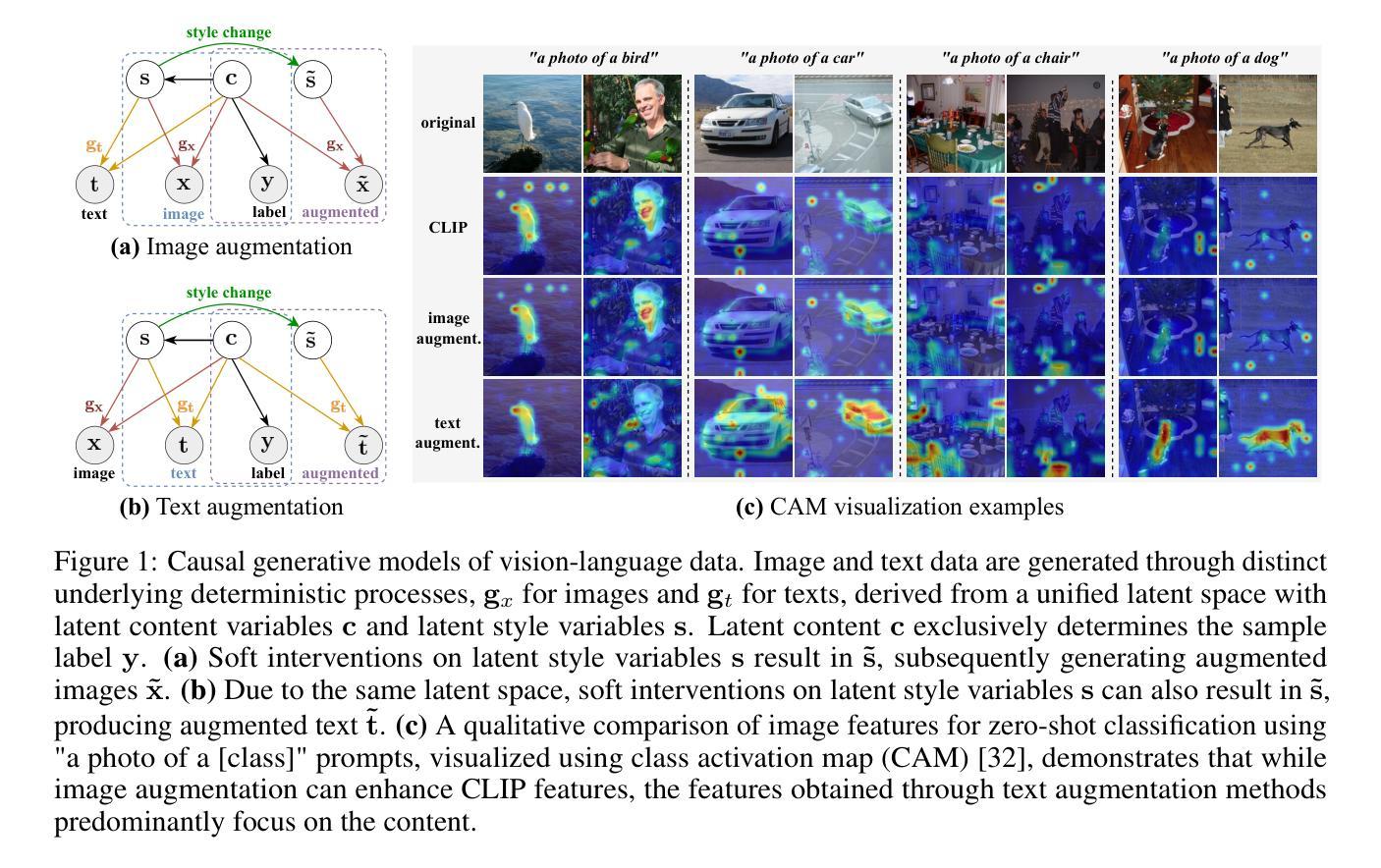
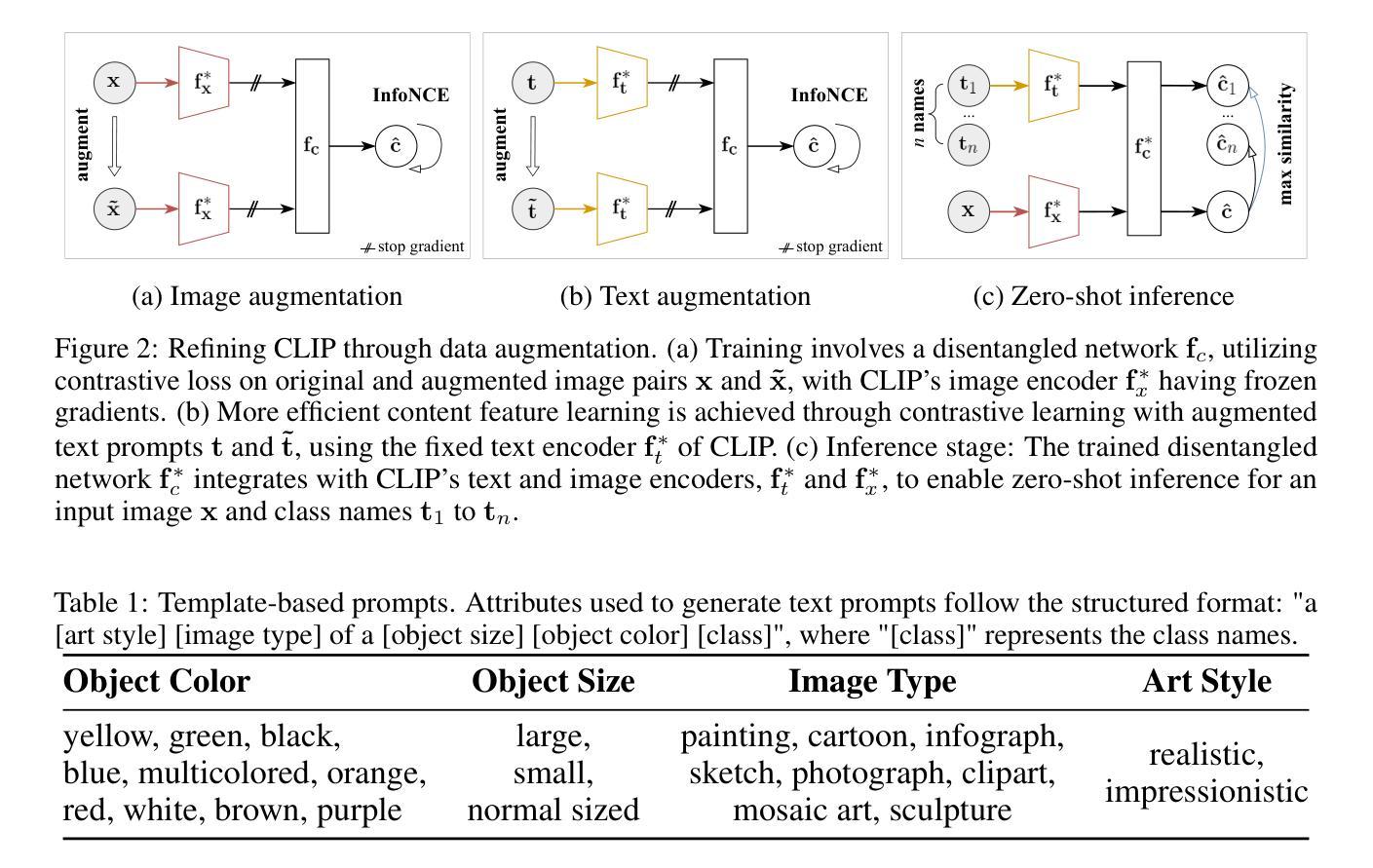
CLAP: Isolating Content from Style through Contrastive Learning with Augmented Prompts
Authors:Yichao Cai, Yuhang Liu, Zhen Zhang, Javen Qinfeng Shi
Contrastive vision-language models, such as CLIP, have garnered considerable attention for various downstream tasks, mainly due to the remarkable generalization ability of the learned features. However, the features they learn often blend content and style information, which somewhat limits their generalization capabilities under distribution shifts. To address this limitation, we adopt a causal generative perspective for multimodal data and propose contrastive learning with data augmentation to disentangle content features from the original representations. To achieve this, we begin by exploring image augmentation techniques and develop a method to seamlessly integrate them into pre-trained CLIP-like models to extract pure content features. Taking a step further, and recognizing the inherent semantic richness and logical structure of text data, we explore the use of text augmentation to isolate latent content from style features. This enables CLIP-like models’ encoders to concentrate on latent content information, refining the representations learned by pre-trained CLIP-like models. Our extensive experiments across diverse datasets demonstrate significant improvements in zero-shot and few-shot classification tasks, alongside enhanced robustness to various perturbations. These results underscore the effectiveness of our proposed methods in refining vision-language representations and advancing the state of the art in multimodal learning.
对比视觉语言模型,如CLIP,已引起广泛关注,主要用于各种下游任务,主要是由于所学特征的显著泛化能力。然而,它们学习的特征往往融合了内容和风格信息,这在某种程度上限制了其在分布变化下的泛化能力。为了解决这一局限性,我们从因果生成的角度看待多模态数据,并提出采用对比学习与数据增强来从原始表示中分离内容特征。为此,我们首先探索图像增强技术,并开发了一种方法,将其无缝集成到预训练的CLIP类模型中,以提取纯粹的内容特征。更进一步,我们认识到文本数据的内在语义丰富性和逻辑结构,探索使用文本增强来隔离潜在内容与风格特征。这可以让CLIP类模型的编码器专注于潜在内容信息,对预训练的CLIP类模型所学的表示进行精炼。我们在多个数据集上的广泛实验表明,零样本和少样本分类任务有了显著改进,对各种扰动的稳健性也得到提高。这些结果凸显了我们提出的方法在精炼视觉语言表示和推动多模态学习最新技术方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as a conference paper at ECCV 2024
Summary
视觉语言模型如CLIP等因其学习的特征的强大泛化能力而受到广泛关注,但所学特征常常融合了内容和风格信息,这在一定程度上限制了其在分布变化下的泛化能力。为解决此问题,本文采用因果生成视角和多模态数据对比学习进行数据增强,旨在从原始表示中分离内容特征。通过对图像增强技术的研究并探索文本增强对隔离潜在内容和风格特征的作用,本文实现了对预训练CLIP模型的优化。实验证明,该方法在零样本和少样本分类任务上取得了显著改进,并增强了对各种扰动的鲁棒性。展示了其在精炼视觉语言表征方面的有效性及其在多媒体学习方面的前沿性。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP等对比视觉语言模型具有显著的泛化能力,但面临分布变化下的泛化限制。
- 融合内容和风格信息的问题限制了模型的性能。
- 采用因果生成视角和多模态数据对比学习进行数据增强,旨在分离内容特征。
- 通过图像增强技术和文本增强方法提升模型性能。
- 该方法能显著提高零样本和少样本分类任务的性能。
- 模型对各种扰动的鲁棒性得到增强。
点此查看论文截图