⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-15 更新
Hypergraph Vision Transformers: Images are More than Nodes, More than Edges
Authors:Joshua Fixelle
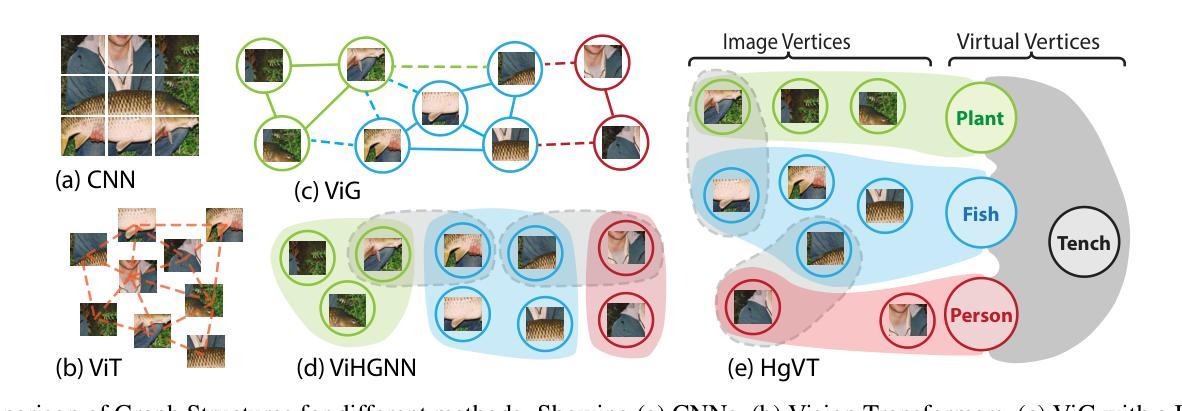
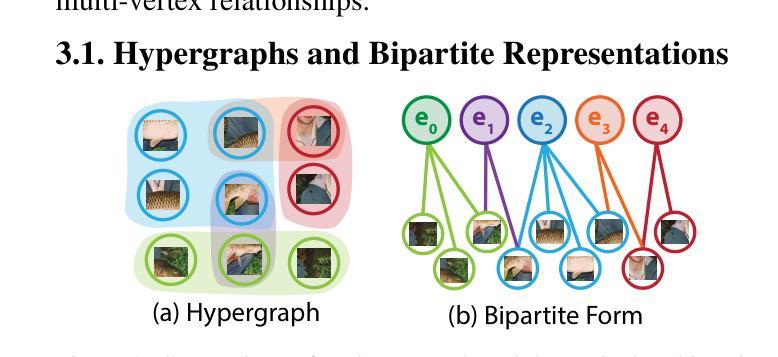
Recent advancements in computer vision have highlighted the scalability of Vision Transformers (ViTs) across various tasks, yet challenges remain in balancing adaptability, computational efficiency, and the ability to model higher-order relationships. Vision Graph Neural Networks (ViGs) offer an alternative by leveraging graph-based methodologies but are hindered by the computational bottlenecks of clustering algorithms used for edge generation. To address these issues, we propose the Hypergraph Vision Transformer (HgVT), which incorporates a hierarchical bipartite hypergraph structure into the vision transformer framework to capture higher-order semantic relationships while maintaining computational efficiency. HgVT leverages population and diversity regularization for dynamic hypergraph construction without clustering, and expert edge pooling to enhance semantic extraction and facilitate graph-based image retrieval. Empirical results demonstrate that HgVT achieves strong performance on image classification and retrieval, positioning it as an efficient framework for semantic-based vision tasks.
计算机视觉领域的最新进展突显了Vision Transformers(ViTs)在各种任务中的可扩展性,但在平衡适应性、计算效率和建模高阶关系方面仍存在挑战。Vision Graph Neural Networks(ViGs)通过利用基于图的方法提供了一种替代方案,但受到用于边缘生成的聚类算法的计算瓶颈的阻碍。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Hypergraph Vision Transformer(HgVT),它将分层二部超图结构融入视觉转换器框架,以捕捉高阶语义关系同时保持计算效率。HgVT利用群体和多样性正则化进行无需聚类的动态超图构建,并利用专家边缘池化增强语义提取并促进基于图的图像检索。经验结果表明,HgVT在图像分类和检索方面表现出强大的性能,使其成为基于语义的视觉任务的高效框架。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
基于计算机视觉的最新进展,Vision Transformers(ViTs)已在各种任务中展现出其可扩展性。然而,如何在适应性、计算效率和建模高阶关系之间取得平衡仍是挑战。Vision Graph Neural Networks(ViGs)通过利用基于图的方法提供替代方案,但受到聚类算法用于边缘生成时的计算瓶颈的限制。为解决这些问题,我们提出Hypergraph Vision Transformer(HgVT),它将分层二部超图结构融入视觉变压器框架中,以捕捉高阶语义关系并保持计算效率。HgVT利用种群和多样性正则化进行动态超图构建而无需聚类,并采用专家边缘池化增强语义提取并促进基于图的图像检索。实证结果表明,HgVT在图像分类和检索方面表现出强大的性能,成为基于语义的视觉任务的有效框架。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 已广泛适用于各种计算机视觉任务,但仍需平衡适应性、计算效率和建模高阶关系。
- Vision Graph Neural Networks (ViGs) 利用图的方法提供替代方案,但受聚类算法的计算瓶颈限制。
- Hypergraph Vision Transformer (HgVT) 结合了视觉变压器框架和分层二部超图结构,以捕捉高阶语义关系。
- HgVT 通过种群和多样性正则化进行动态超图构建,无需聚类。
- HgVT 采用专家边缘池化增强语义提取,并促进基于图的图像检索。
- HgVT 在图像分类和检索方面表现出强大的性能。
- HgVT 为基于语义的视觉任务提供了一个有效的框架。
点此查看论文截图

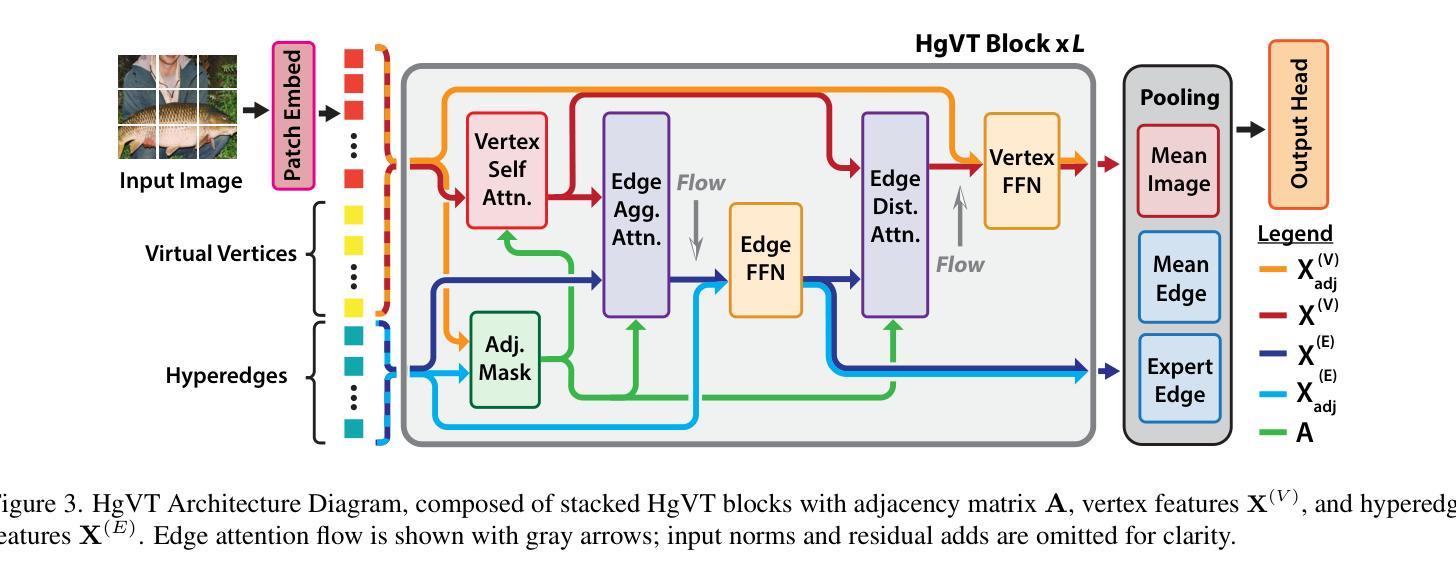
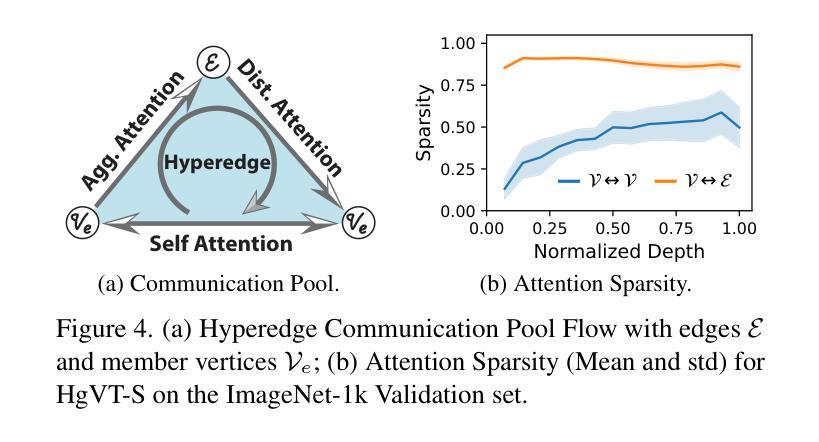
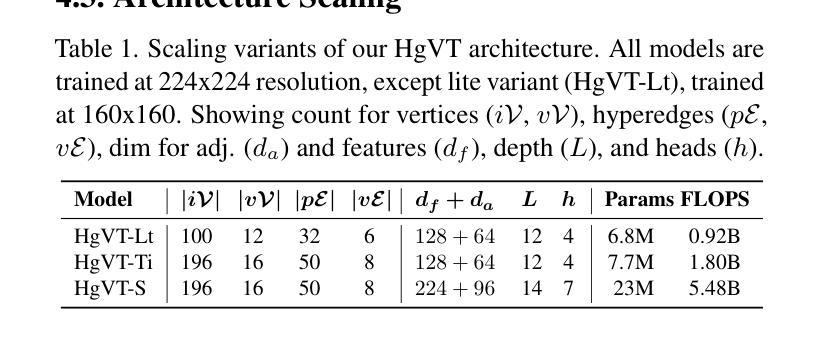
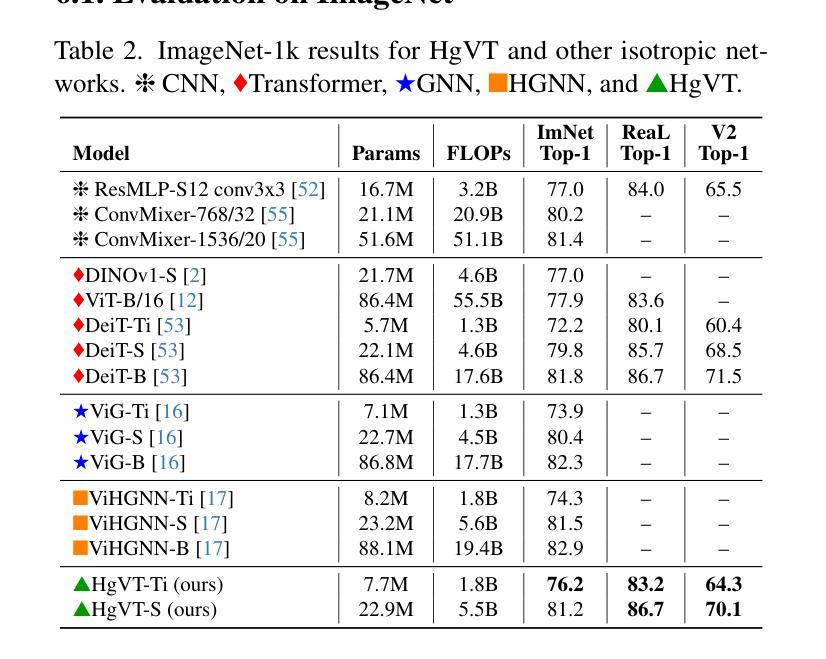
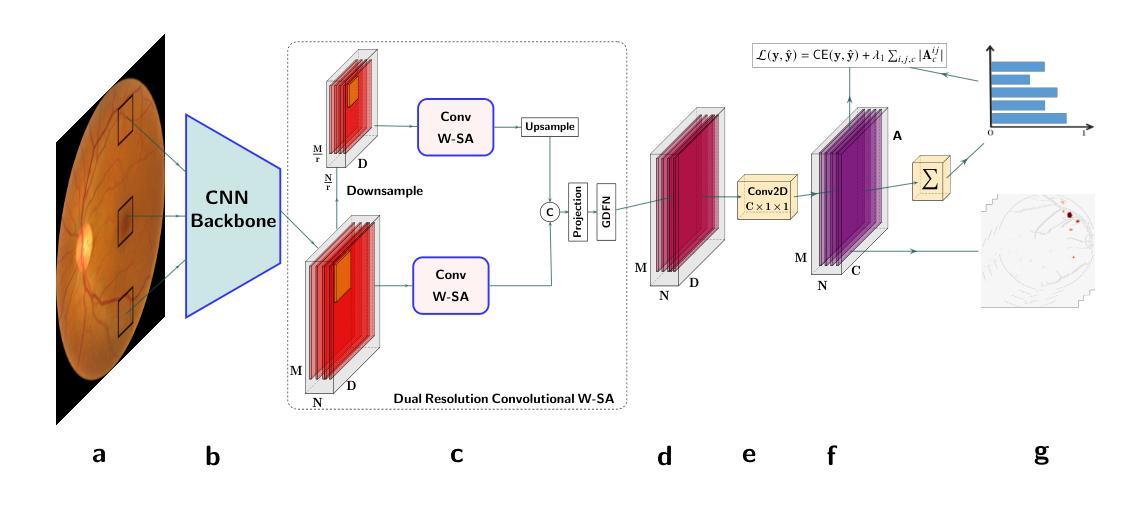
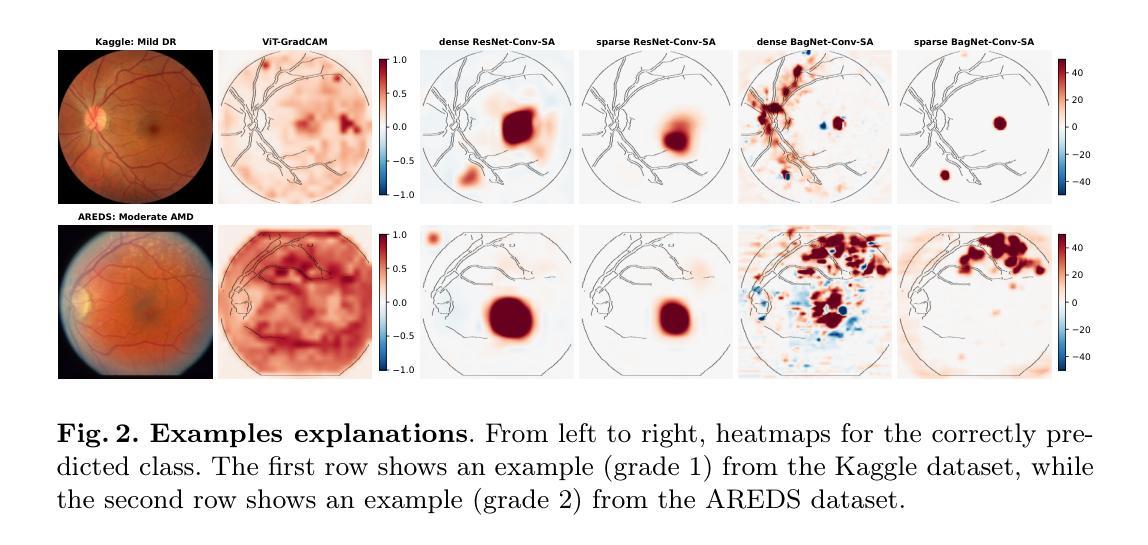
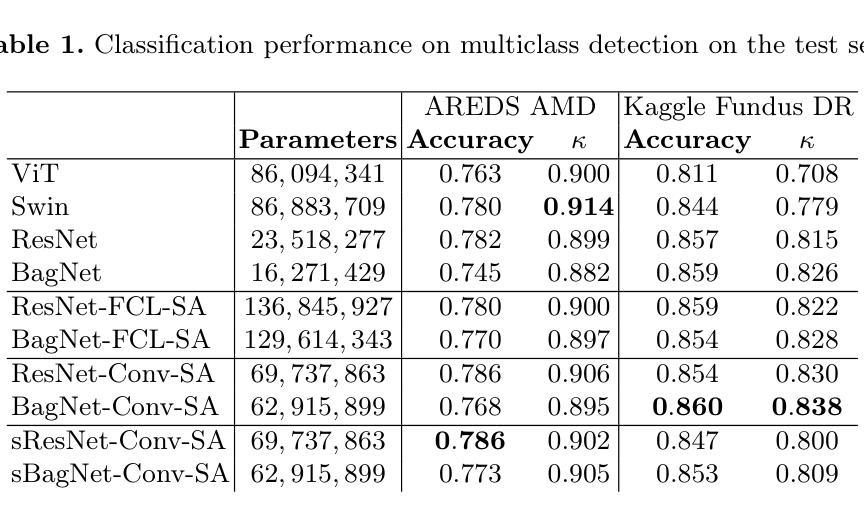
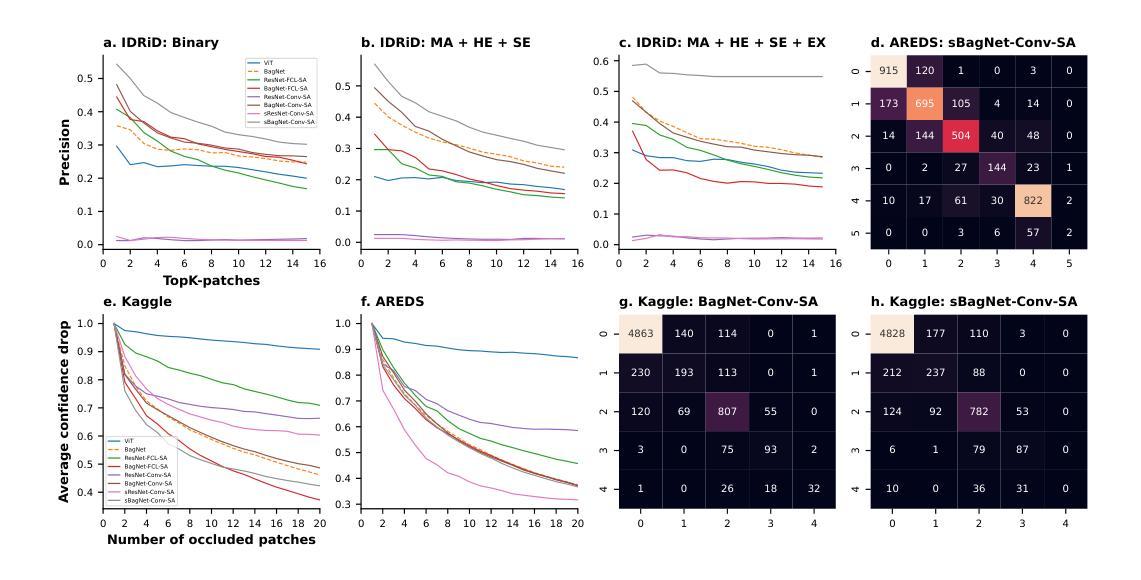
A Hybrid Fully Convolutional CNN-Transformer Model for Inherently Interpretable Medical Image Classification
Authors:Kerol Djoumessi, Samuel Ofosu Mensah, Philipp Berens
In many medical imaging tasks, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) efficiently extract local features hierarchically. More recently, vision transformers (ViTs) have gained popularity, using self-attention mechanisms to capture global dependencies, but lacking the inherent spatial localization of convolutions. Therefore, hybrid models combining CNNs and ViTs have been developed to combine the strengths of both architectures. However, such hybrid CNN-ViT models are difficult to interpret, which hinders their application in medical imaging. In this work, we introduce an interpretable-by-design hybrid fully convolutional CNN-Transformer architecture for medical image classification. Unlike widely used post-hoc saliency methods for ViTs, our approach generates faithful and localized evidence maps that directly reflect the model’s decision process. We evaluated our method on two medical image classification tasks using color fundus images. Our model not only achieves state-of-the-art predictive performance compared to both black-box and interpretable models but also provides class-specific sparse evidence maps in a single forward pass. The code is available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Expl-CNN-Transformer/.
在许多医学成像任务中,卷积神经网络(CNN)能够高效地分层提取局部特征。最近,使用自注意力机制的视觉转换器(ViT)开始流行起来,能够捕捉全局依赖性,但缺乏卷积的固有空间定位能力。因此,已经开发出了结合CNN和ViT优点的混合模型。然而,这样的混合CNN-ViT模型难以解释,阻碍了它们在医学成像中的应用。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种可设计的解释性混合全卷积CNN-Transformer架构,用于医学图像分类。与广泛用于ViT的后验显著性方法不同,我们的方法生成忠实且定位的证据图,直接反映模型的决策过程。我们在两项医学图像分类任务(使用彩色眼底图像)上评估了我们的方法。我们的模型不仅与黑箱和可解释模型相比实现了最先进的预测性能,而且还在单次前向传递中提供了特定类别的稀疏证据图。代码可在:https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Expl-CNN-Transformer/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对医疗图像分类的可解释性设计混合全卷积CNN-Transformer架构。该模型结合了CNN和ViT的优点,能生成忠实且定位准确的证据图,直接反映模型的决策过程。在彩色眼底图像分类任务上,该模型不仅实现了与黑箱模型和可解释模型相比的先进预测性能,而且能在单次前向传递过程中提供类特定的稀疏证据图。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了混合CNN-Transformer模型,该模型结合了卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)的优点。
- 该模型具有内在的空间定位能力,能够生成反映模型决策过程的忠实和定位准确的证据图。
- 模型在医疗图像分类任务上实现了最先进的预测性能。
- 模型相比其他黑箱和可解释模型具有优势。
- 模型能生成类特定的稀疏证据图,有助于理解和解释模型的决策过程。
- 该模型的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

Investigating Vision-Language Model for Point Cloud-based Vehicle Classification
Authors:Yiqiao Li, Jie Wei, Camille Kamga
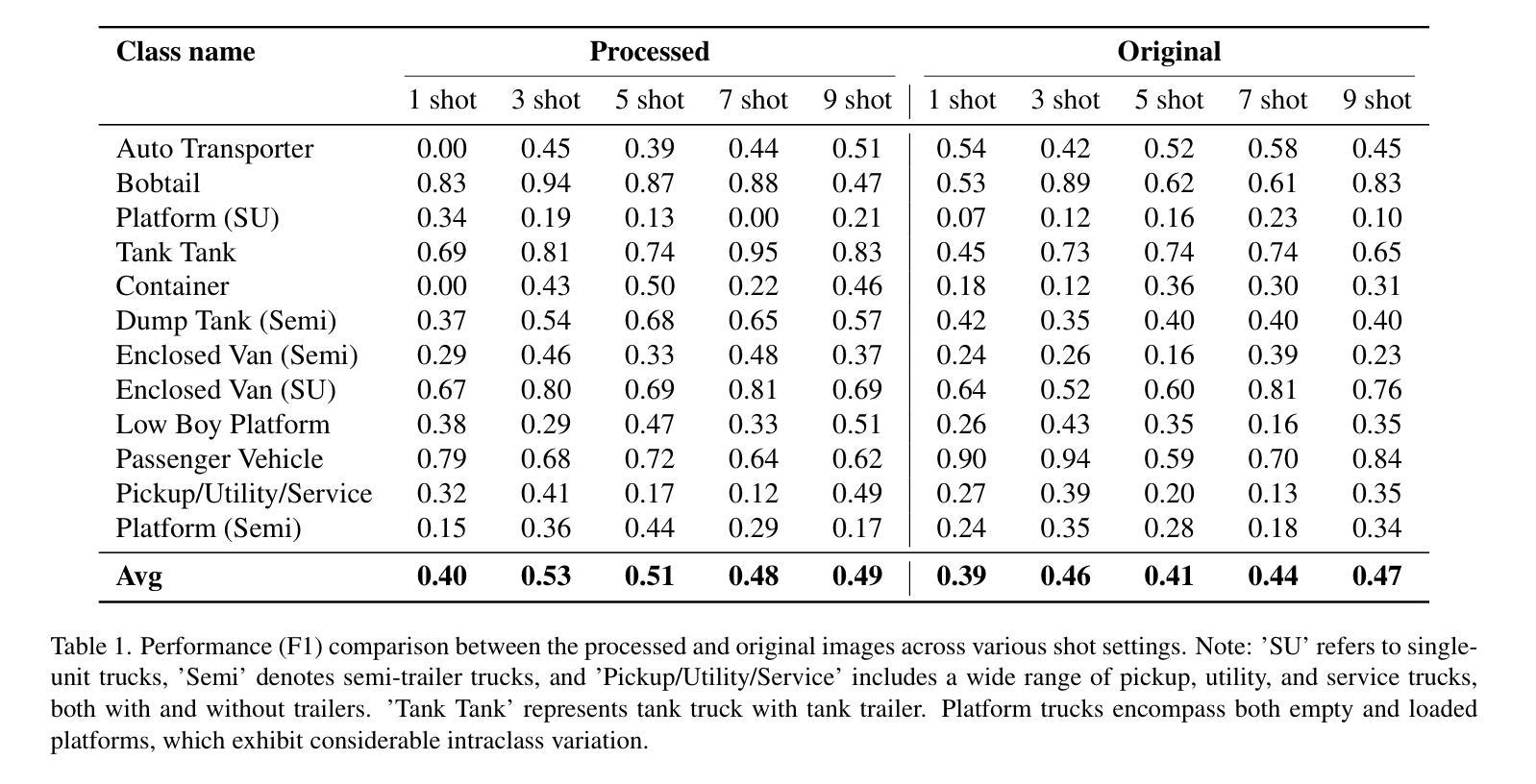
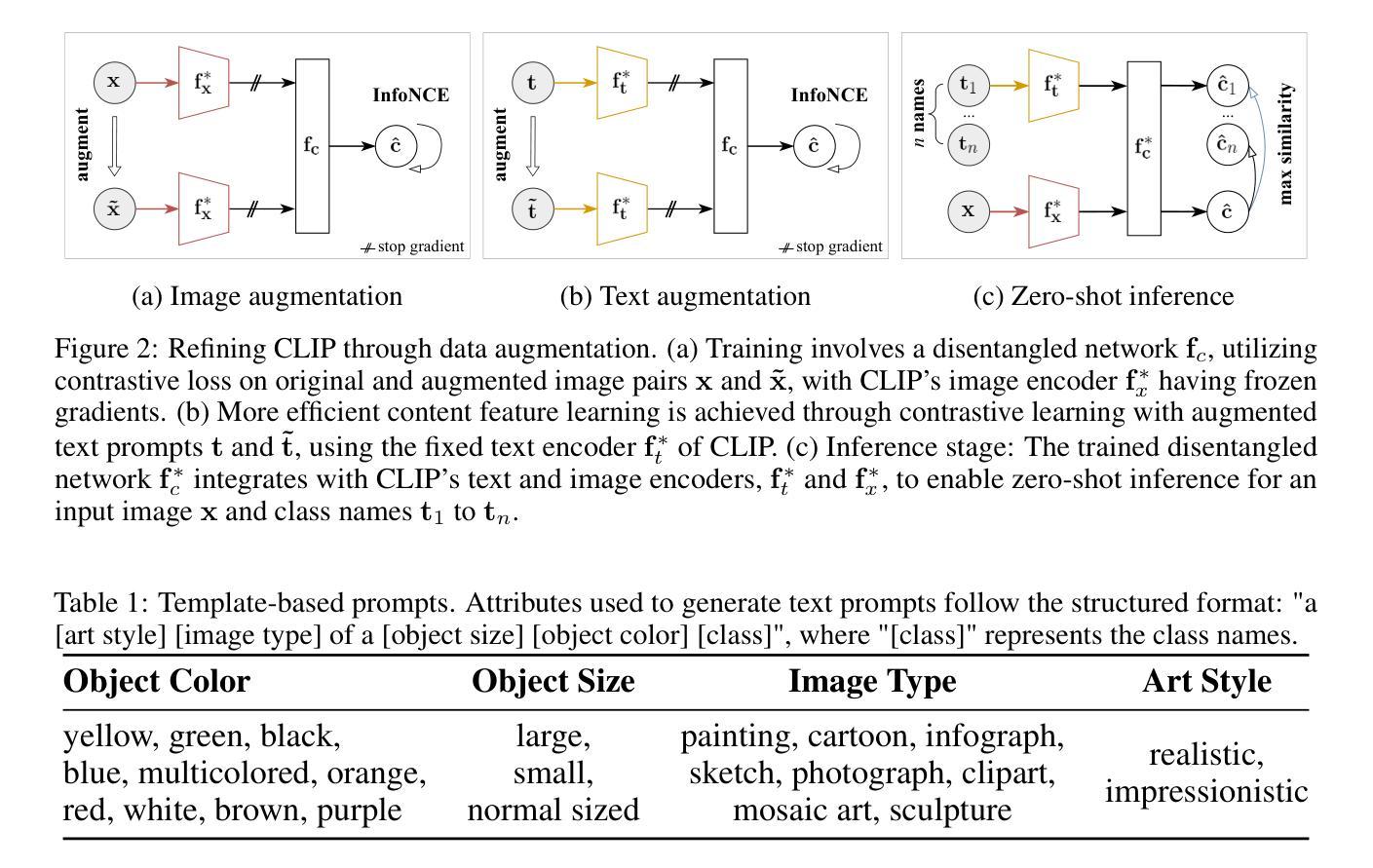
Heavy-duty trucks pose significant safety challenges due to their large size and limited maneuverability compared to passenger vehicles. A deeper understanding of truck characteristics is essential for enhancing the safety perspective of cooperative autonomous driving. Traditional LiDAR-based truck classification methods rely on extensive manual annotations, which makes them labor-intensive and costly. The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) trained on massive datasets presents an opportunity to leverage their few-shot learning capabilities for truck classification. However, existing vision-language models (VLMs) are primarily trained on image datasets, which makes it challenging to directly process point cloud data. This study introduces a novel framework that integrates roadside LiDAR point cloud data with VLMs to facilitate efficient and accurate truck classification, which supports cooperative and safe driving environments. This study introduces three key innovations: (1) leveraging real-world LiDAR datasets for model development, (2) designing a preprocessing pipeline to adapt point cloud data for VLM input, including point cloud registration for dense 3D rendering and mathematical morphological techniques to enhance feature representation, and (3) utilizing in-context learning with few-shot prompting to enable vehicle classification with minimally labeled training data. Experimental results demonstrate encouraging performance of this method and present its potential to reduce annotation efforts while improving classification accuracy.
重型卡车由于其庞大的体积和与乘用车相比有限的机动性,构成了重大的安全挑战。对于增强协同自动驾驶的安全性视角而言,对卡车特性的深入了解至关重要。传统的基于激光雷达的卡车分类方法依赖于大量的手动注释,这使得它们劳动密集型且成本高昂。在大量数据集上训练的大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,为我们利用它们的少量样本学习能力进行卡车分类提供了机会。然而,现有的视觉语言模型(VLM)主要训练在图像数据集上,这使得直接处理点云数据具有挑战性。本研究介绍了一个新型框架,该框架整合了路边激光雷达点云数据与VLM,以促进高效准确的卡车分类,支持协同安全的驾驶环境。本研究引入了三项关键创新:(1)利用现实世界激光雷达数据集进行模型开发,(2)设计预处理管道以适应VLM输入的点云数据,包括点云注册进行密集三维渲染和数学形态技术以增强特征表示,(3)使用基于上下文的少量样本提示进行即时学习,以实现用最少标记的训练数据进行车辆分类。实验结果表明该方法的性能令人鼓舞,并展示了其在减少注释工作同时提高分类精度的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages,3 figures, 1 table, CVPR DriveX workshop
Summary
本文介绍了大型货车由于其庞大的体积和有限的机动性所带来的安全挑战。为了提升协同自动驾驶的安全性,对货车特性的深入了解至关重要。传统基于激光雷达的货车分类方法依赖大量手动注释,既耗费人力又成本高昂。本研究利用大规模数据集训练的的大型语言模型,提出一种结合路边激光雷达点云数据和视觉语言模型的新型框架,以实现高效准确的货车分类,支持协同安全驾驶环境。本研究的三大创新点为:利用真实世界的激光雷达数据集进行模型开发、设计适应点云数据的预处理管道以供视觉语言模型输入和利用少量样本进行上下文学习以实现最小标注训练数据的车辆分类。实验结果证明了该方法的良好性能,展现出在减少标注工作同时提高分类精度的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型货车因其体积和机动性限制,存在显著的安全挑战。
- 深入了解货车特性对于提高协同自动驾驶的安全性至关重要。
- 传统基于激光雷达的货车分类方法成本高昂且耗时。
- 大型语言模型具有强大的学习能力,可应用于货车分类以提高效率和准确性。
- 本研究结合了路边激光雷达点云数据和视觉语言模型,形成新型框架。
- 预处理管道是关键,用于适应点云数据供视觉语言模型输入。
点此查看论文截图