⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-16 更新
Giant and anisotropic magnetostriction in $β$-O$_{2}$ at 110 T
Authors:Akihiko Ikeda, Yuya Kubota, Yuto Ishii, Xuguang Zhou, Shiyue Peng, Hiroaki Hayashi, Yasuhiro H. Matsuda, Kosuke Noda, Tomoya Tanaka, Kotomi Shimbori, Kenta Seki, Hideaki Kobayashi, Dilip Bhoi, Masaki Gen, Kamini Gautam, Mitsuru Akaki, Shiro Kawachi, Shusuke Kasamatsu, Toshihiro Nomura, Yuichi Inubushi, Makina Yabashi
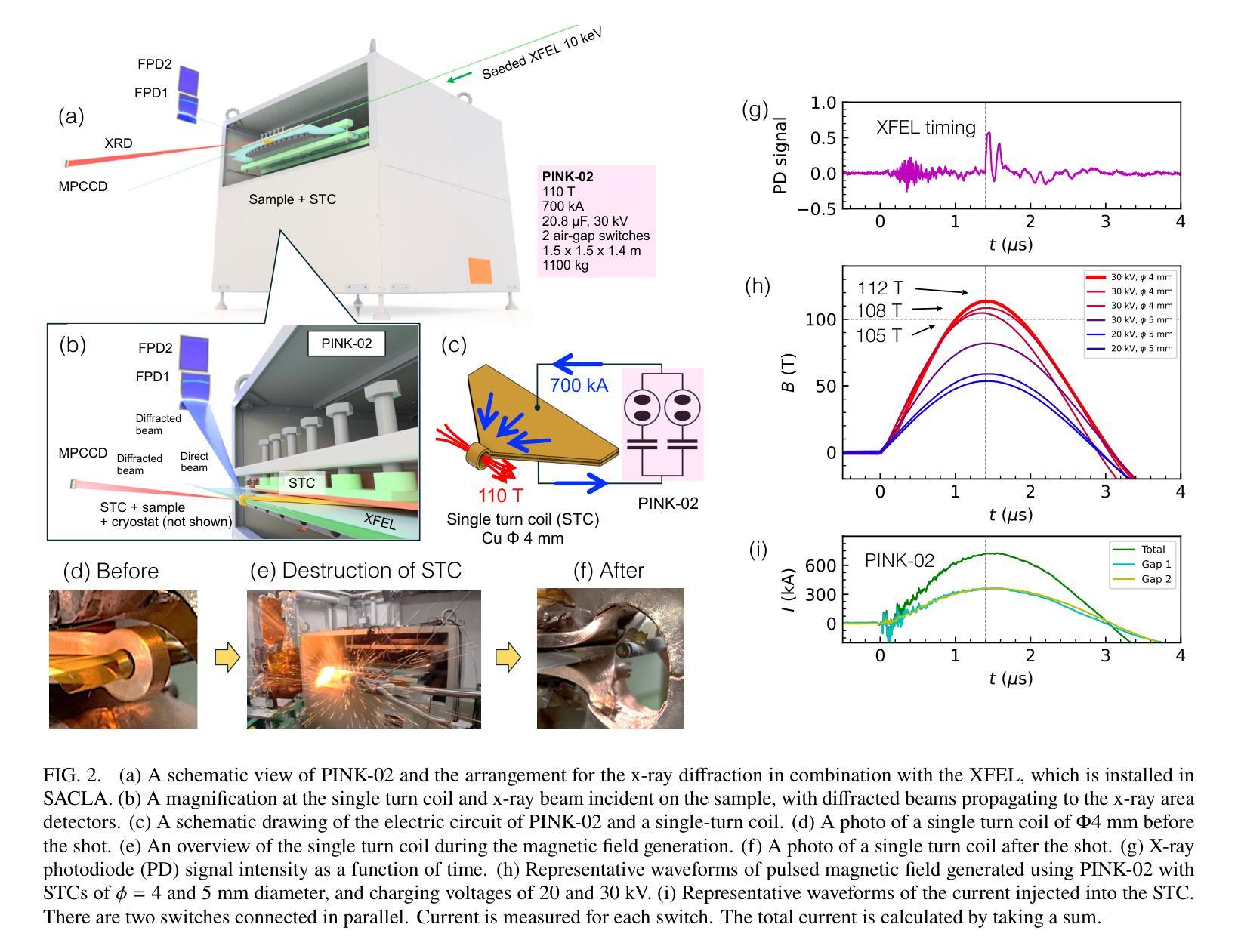
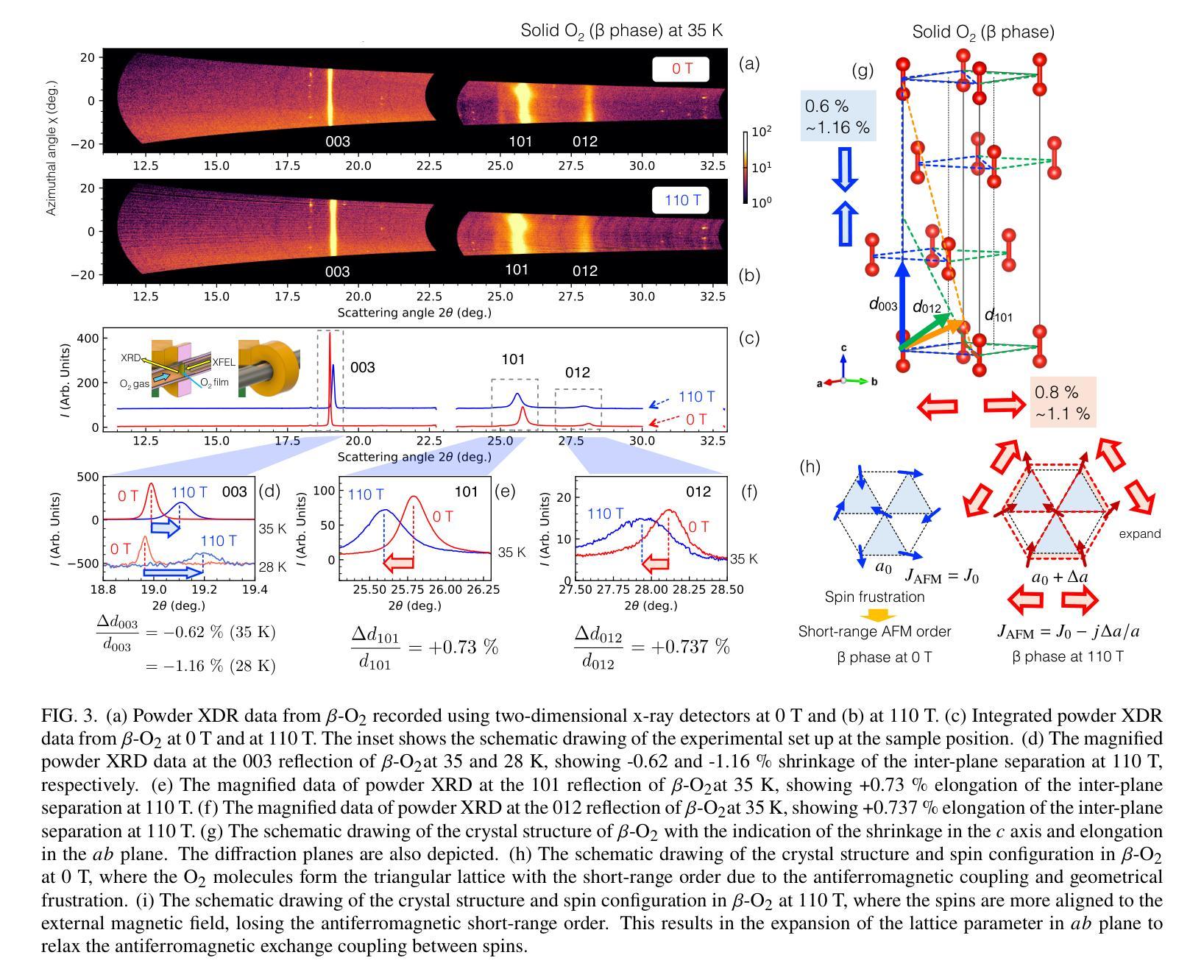
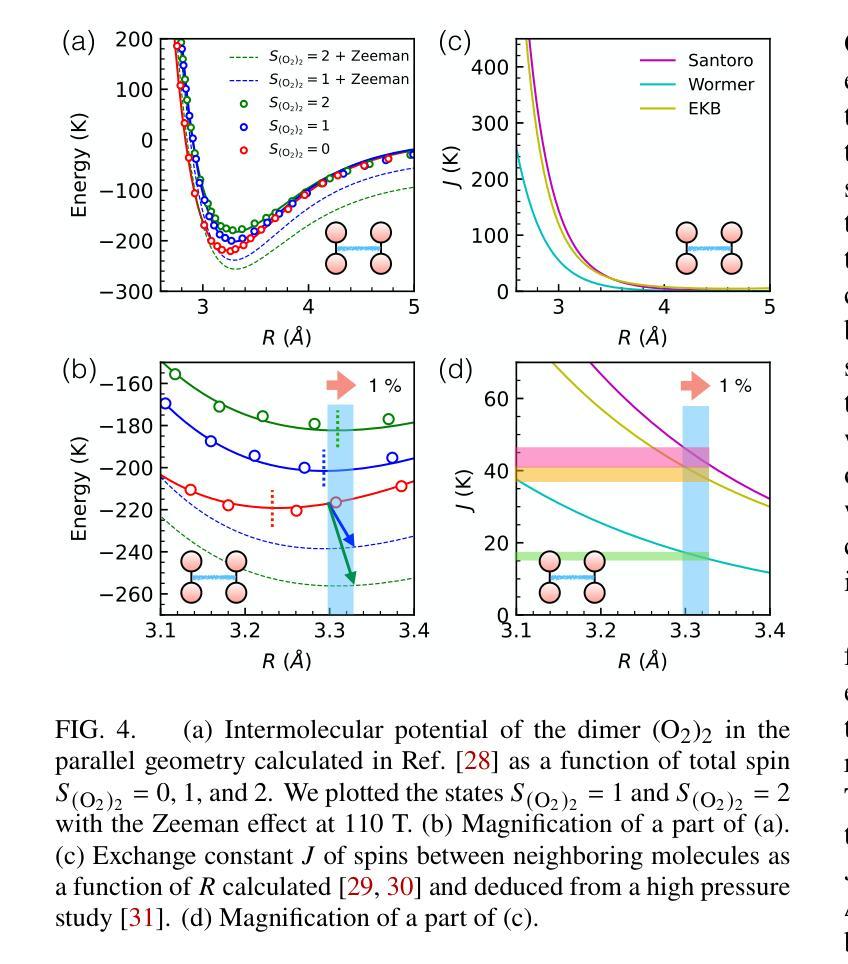
Magnetostriction is a crystal’s deformation under magnetic fields, usually in the range of $10^{-6}$ - $10^{-3}$, where the lattice change occurs with the change of spin and orbital state through spin-lattice couplings. In strong magnetic fields beyond 100 T, the significant Zeeman energy competes with the lattice interactions, where one can expect considerable magnetostriction. However, directly observing magnetostriction above 100 T is challenging, because generating magnetic fields beyond 100 T accompanies the destruction of the coil with a single-shot $\mu$-second pulse. Here, we observed the giant and anisotropic magnetostriction of $\sim$1 % at 110 T in the spin-controlled crystal of $\beta$-O${2}$, by combining the single-shot diffraction of x-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) and the state-of-the-art portable 100 T generator. The magnetostriction of $\sim$1 % is the largest class as a deformation of the unit cell. It is a response of the soft lattice of $\beta$-O${2}$ originating, not only in the competing van der Waals force and exchange interaction, but also the soft state of spin and lattice frustrated on the triangular network. Meanwhile, the anisotropy originates from the strong two-dimensionality of the spin system. Giant magnetostriction in crystals should become more ubiquitous and diverse beyond 100 T, where our XFEL experiment above 100 T opens a novel pathway for their exploration, providing fundamental insights into the roles of spin in stabilizing crystal structures.
磁致伸缩是晶体在磁场下的变形,通常范围在$10^{-6}$-$10^{-3}$之间,此时晶格变化伴随着自旋和轨道态的改变,通过自旋晶格耦合来实现。在超过100T的强磁场下,显著的塞曼能与晶格相互作用相竞争,可以预期会有相当大的磁致伸缩。然而,直接在超过100T的磁场下观察磁致伸缩是具有挑战性的,因为产生超过100T的磁场通常伴随着单次微秒脉冲对线圈的破坏。在这里,我们通过结合X射线自由电子激光(XFEL)的单次衍射拍摄和先进便携式100T生成器,在$\beta$-O2的自旋控制晶体中观察到约为1%的巨大且各向异性的磁致伸缩,该磁致伸缩发生在110T的磁场下。约1%的磁致伸缩是单元内变形最大的类别之一。这是$\beta$-O2软晶格的一种响应,不仅源于范德华力和交换相互作用的竞争,还源于自旋和晶格在三角网络上的受挫的软态。同时,各向异性源于自旋系统的强二维性。在超过100T的磁场下,晶体中的巨大磁致伸缩应该更加普遍和多样,我们的超过100T的XFEL实验为探索它们开辟了一条新途径,为自旋在稳定晶体结构中的作用提供了基本见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures
摘要
本论文探讨了磁致伸缩现象,即在强磁场下晶体的变形行为。研究利用X射线自由电子激光器和先进的100T发电机,观察到β-O2晶体在强磁场下的巨大且各向异性的磁致伸缩现象,变形达约百分之一。这一现象源于β-O2晶格的软性特征,表现为范德华力和交换作用的竞争以及旋和晶格在三角网络上的挫败状态。该实验为强磁场下的晶体磁致伸缩研究开辟了新途径,揭示了旋在稳定晶体结构中的作用。
关键见解
- 磁致伸缩是晶体在磁场下的变形行为,通常在$10^{-6}$至$10^{-3}$范围内发生,伴随着晶格变化。
- 在超过100T的强磁场下,显著的塞曼能量与晶格相互作用竞争,可能导致显著的磁致伸缩。
- β-O2晶体在强磁场下表现出巨大的磁致伸缩现象,变形达约百分之一。
- 这种巨大磁致伸缩源于β-O2晶格的软性特征以及范德华力和交换作用的竞争。
- 磁致伸缩的各向异性源于旋系统的强二维性。
- 在超过100T的强磁场下,晶体的磁致伸缩现象可能更为普遍和多样。
点此查看论文截图

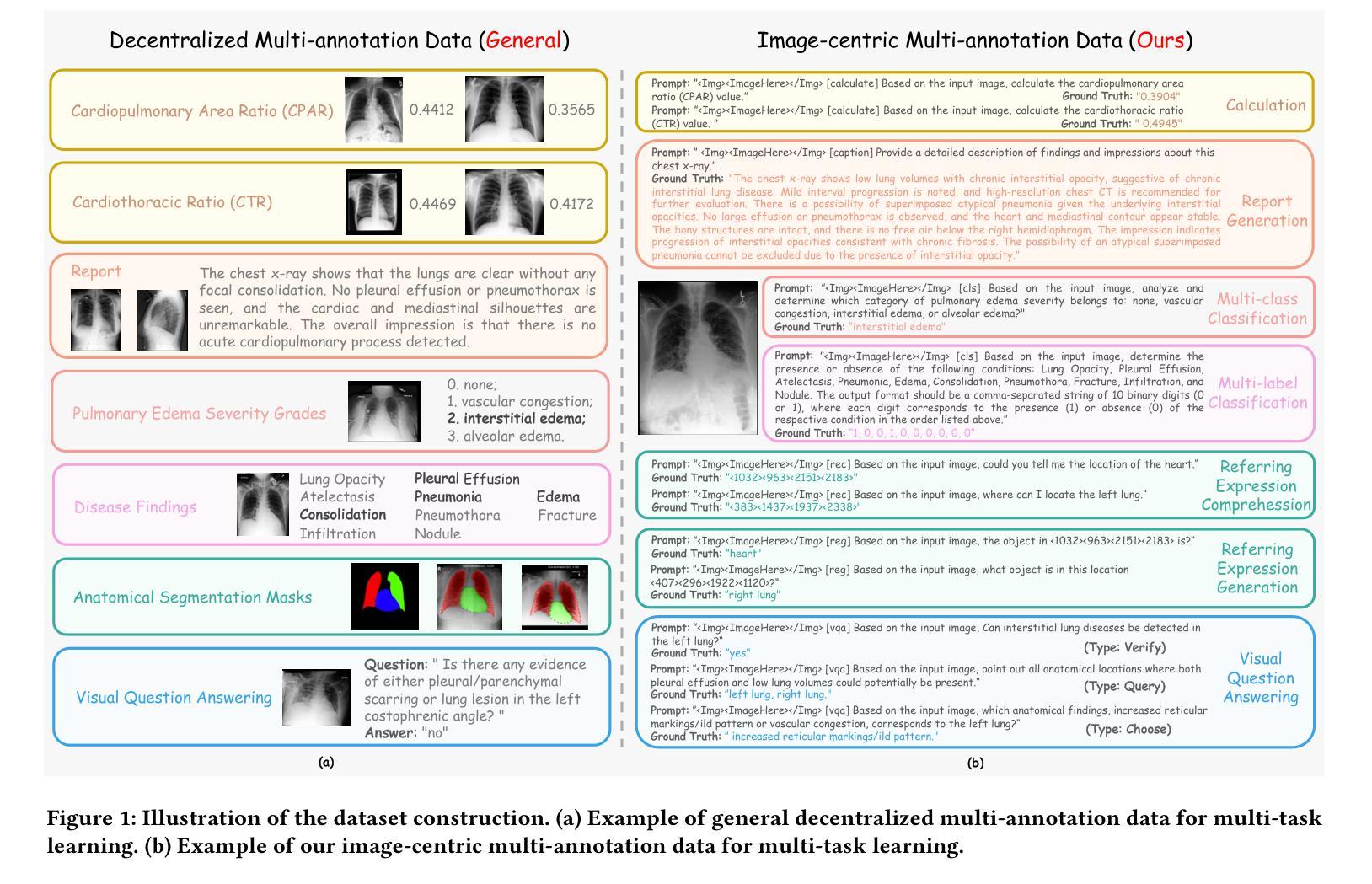
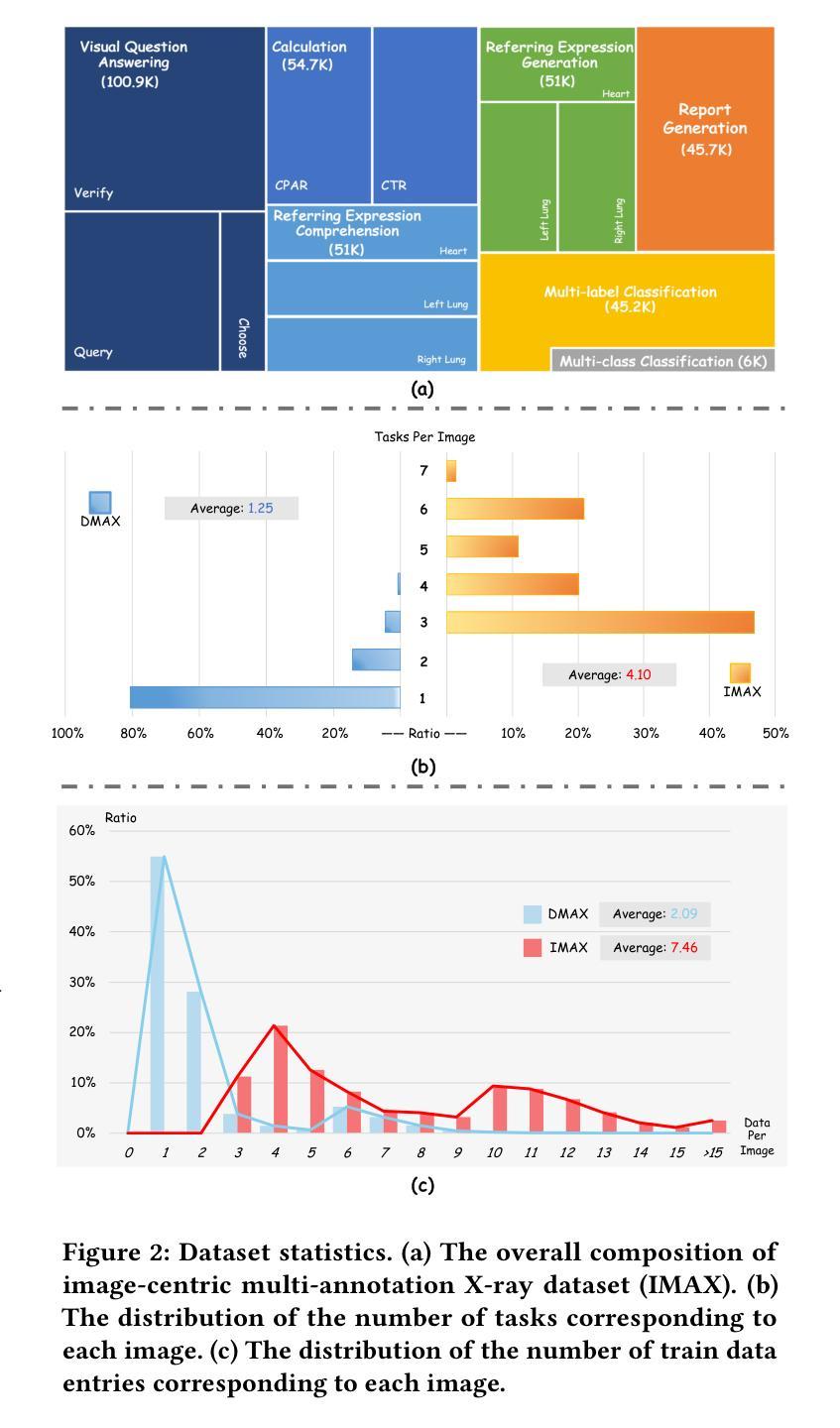
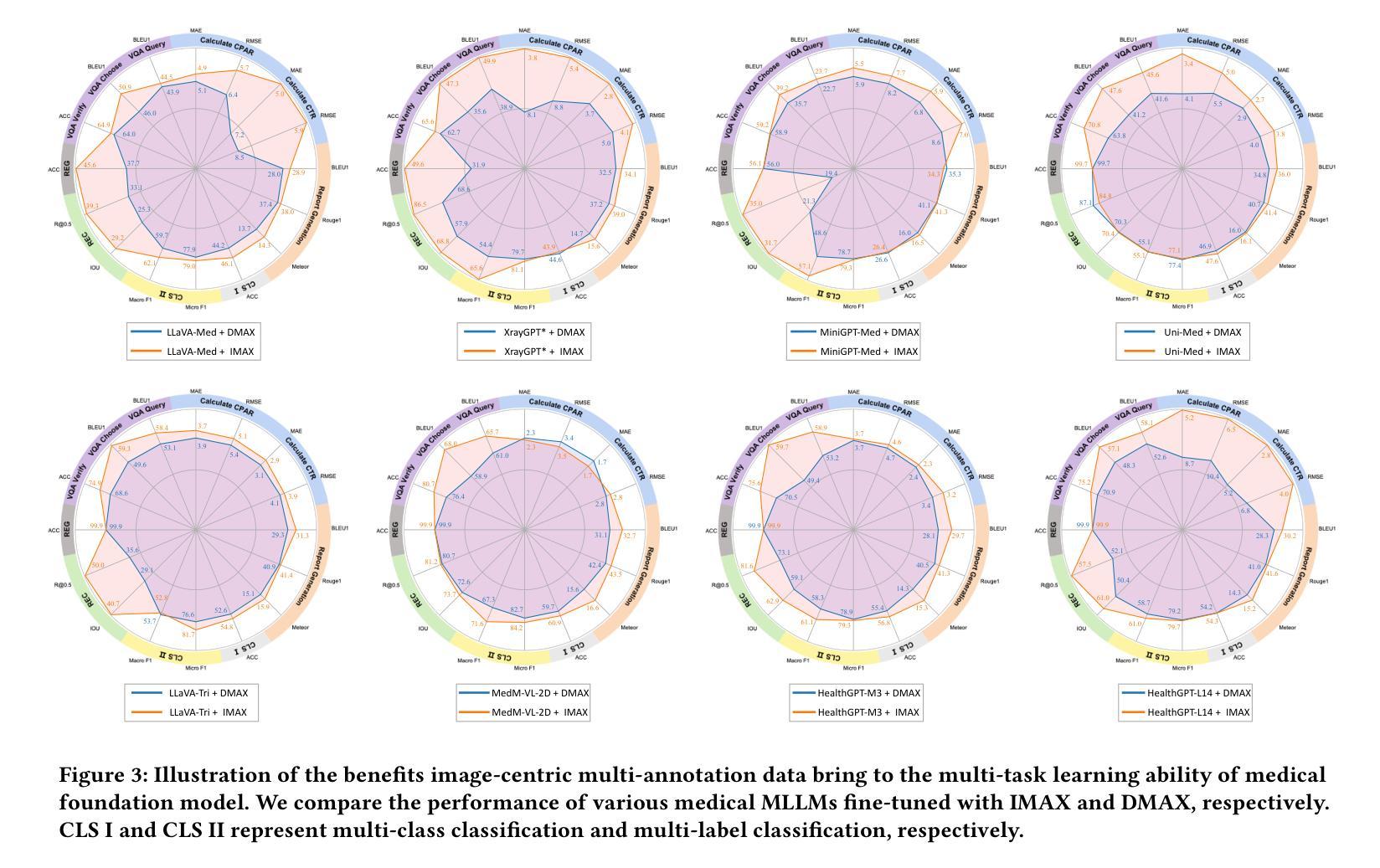
Enhancing Multi-task Learning Capability of Medical Generalist Foundation Model via Image-centric Multi-annotation Data
Authors:Xun Zhu, Fanbin Mo, Zheng Zhang, Jiaxi Wang, Yiming Shi, Ming Wu, Chuang Zhang, Miao Li, Ji Wu
The emergence of medical generalist foundation models has revolutionized conventional task-specific model development paradigms, aiming to better handle multiple tasks through joint training on large-scale medical datasets. However, recent advances prioritize simple data scaling or architectural component enhancement, while neglecting to re-examine multi-task learning from a data-centric perspective. Critically, simply aggregating existing data resources leads to decentralized image-task alignment, which fails to cultivate comprehensive image understanding or align with clinical needs for multi-dimensional image interpretation. In this paper, we introduce the image-centric multi-annotation X-ray dataset (IMAX), the first attempt to enhance the multi-task learning capabilities of medical multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) from the data construction level. To be specific, IMAX is featured from the following attributes: 1) High-quality data curation. A comprehensive collection of more than 354K entries applicable to seven different medical tasks. 2) Image-centric dense annotation. Each X-ray image is associated with an average of 4.10 tasks and 7.46 training entries, ensuring multi-task representation richness per image. Compared to the general decentralized multi-annotation X-ray dataset (DMAX), IMAX consistently demonstrates significant multi-task average performance gains ranging from 3.20% to 21.05% across seven open-source state-of-the-art medical MLLMs. Moreover, we investigate differences in statistical patterns exhibited by IMAX and DMAX training processes, exploring potential correlations between optimization dynamics and multi-task performance. Finally, leveraging the core concept of IMAX data construction, we propose an optimized DMAX-based training strategy to alleviate the dilemma of obtaining high-quality IMAX data in practical scenarios.
医疗通用基础模型的兴起已经彻底改变了传统的针对特定任务模型的开发范式,旨在通过大规模医疗数据集上的联合训练来更好地处理多个任务。然而,最近的进展侧重于简单的数据扩展或架构组件增强,而忽略从以数据为中心的角度重新审视多任务学习。关键问题是,简单聚合现有数据资源会导致分散的图像任务对齐,这无法培养全面的图像理解,也无法满足多维图像解读的临床需求。在本文中,我们介绍了以图像为中心的多注释X光数据集(IMAX),这是首次尝试从数据构建层面提高医疗多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的多任务学习能力。具体来说,IMAX具有以下属性:1)高质量的数据采集。全面收集了适用于七种不同医疗任务的超过354K条数据。2)以图像为中心密集注释。每个X光片都与平均4.10个任务和7.46个训练条目相关联,确保每张图像的多任务表示丰富性。与一般的分散多注释X光数据集(DMAX)相比,IMAX在七个开源的先进医疗MLLMs上持续显示出显著的多任务平均性能提升,范围从3.20%到21.05%。此外,我们研究了IMAX和DMAX训练过程中统计模式的差异,探索了优化动力与多任务性能之间的潜在关联。最后,利用IMAX数据构建的核心概念,我们提出了一种基于DMAX的优化训练策略,以缓解在实际场景中获取高质量IMAX数据的困境。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学通用基础模型的出现已经彻底改变了传统的针对特定任务模型的开发范式,旨在通过大规模医学数据集的联合训练更好地处理多个任务。然而,最近的进展侧重于简单的数据扩展或架构组件增强,而忽略了从数据中心的角度重新审查多任务学习。本文介绍了以图像为中心的多注解X光射线数据集(IMAX),这是第一次尝试从数据构建层面提升医学多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的多任务学习能力。IMAX数据集具有以下特点:一是高质量的数据采集,涵盖七种不同医疗任务的超过35.4万条记录;二是以图像为中心密集注解,确保每张图像的多任务表示丰富性。与一般的分散多注解X光射线数据集(DMAX)相比,IMAX在七个开源的先进医疗MLLMs上持续展现出显著的多任务平均性能提升。同时,本文对IMAX和DMAX训练过程中的统计模式差异进行了探究,并基于IMAX数据构建的核心概念,提出了优化DMAX的训练策略,以缓解在实际场景中获取高质量IMAX数据的困境。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗通用基础模型能够通过大规模医学数据集的联合训练处理多个任务。
- 现有方法主要关注数据扩展和架构优化,忽视从数据中心的角度重新考察多任务学习。
- 引入IMAX数据集,以高质量数据采集和图像为中心密集注解为特点,旨在提高医学语言模型的多任务学习能力。
- IMAX相比常规数据集在多个医疗任务上表现出显著性能提升。
- 通过比较IMAX和DMAX的训练过程,揭示了统计模式的差异,并探索了优化策略。
- 提出基于DMAX的优化训练策略,以应对实际场景中获取高质量IMAX数据的挑战。
点此查看论文截图

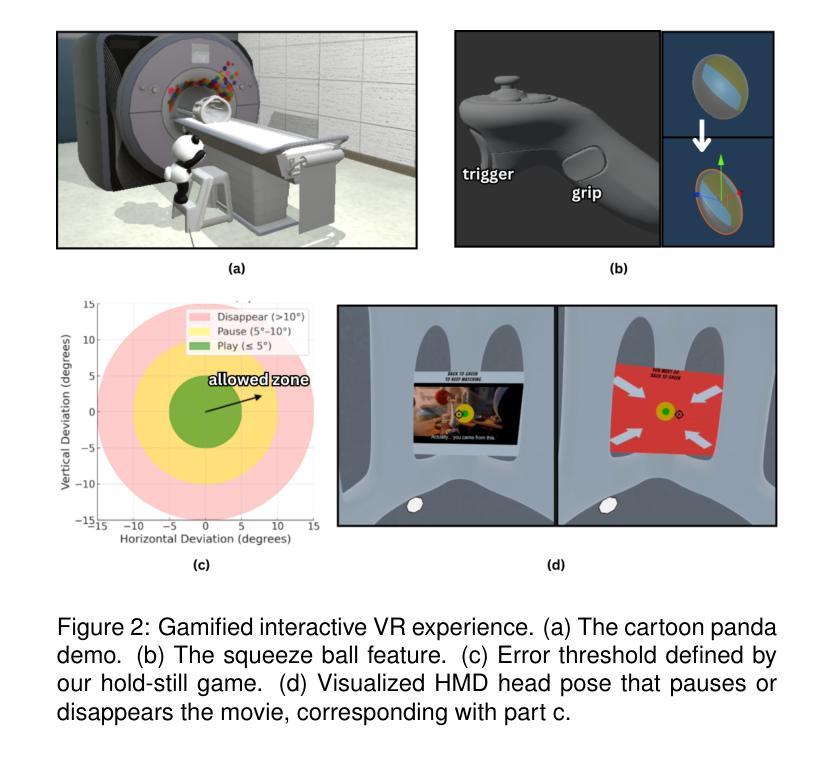
VR MRI Training for Adolescents: A Comparative Study of Gamified VR, Passive VR, 360 Video, and Traditional Educational Video
Authors:Yue Yang, Mengyao Guo, Emmanuel A Corona, Bruce Daniel, Christoph Leuze, Fred Baik
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can be a stressful experience for pediatric patients due to the loud acoustic environment, enclosed scanner bore, and a prolonged requirement to remain still. While sedation is commonly used to manage anxiety and motion, it carries clinical risks and logistical burdens. Traditional preparatory approaches, such as instructional videos and mock scans, often lack engagement for older children and adolescents. In this study, we present a comparative evaluation of four MRI preparation modalities: (1) a gamified virtual reality (VR) simulation that trains stillness through real-time feedback; (2) a passive VR experience replicating the MRI environment without interactivity; (3) a 360 degree first-person video of a real MRI procedure; and (4) a standard 2D educational video. Using a within-subjects design (N = 11, ages 10-16), we assess each method’s impact on head motion data, anxiety reduction, procedural preparedness, usability, cognitive workload, and subjective preference. Results show that the gamified VR condition has significantly lower head motion (p < 0.001) and yielded the highest preparedness scores (p < 0.05). Head motion data were significantly correlated with learning outcomes (p < 0.01), suggesting that behavioral performance in VR strongly indicates procedural readiness. While all modalities reduced anxiety and were rated usable, interactive VR was preferred by most participants and demonstrated unique advantages in promoting engagement and behavioral rehearsal. We conclude with design recommendations for designing immersive simulations and integrating VR training into pediatric imaging workflows.
磁共振成像(MRI)对儿科患者来说可能是一种令人压力的体验,因为其噪音大、扫描舱密闭且需要长时间保持静止不动。虽然经常使用镇静剂来控制焦虑和移动,但它存在一定的临床风险和操作不便的问题。传统的预先教育方法,如教学视频和模拟扫描,对于年龄较大的儿童和青少年往往缺乏吸引力。在这项研究中,我们对四种MRI准备方法进行了比较评估:(1)游戏化虚拟现实(VR)模拟训练,通过实时反馈训练静止不动;(2)被动VR体验,复制MRI环境而不具备交互性;(3)真实MRI过程的360度第一人称视频;(4)标准的二维教育视频。通过一项受试对象内部设计(N=11,年龄介于10至16岁之间),我们评估了每种方法对头部运动数据、焦虑减少、程序准备情况、可用性、认知工作量和主观偏好的影响。结果表明,游戏化VR条件下的头部运动显著降低(p < 0.001),并且获得了最高的准备度得分(p < 0.05)。头部运动数据与学习效果之间存在显著相关性(p < 0.01),这表明虚拟现实中的行为表现强烈预示着程序就绪程度。虽然所有模式都减少了焦虑并被认为是可用的,但大多数参与者更喜欢交互式VR,它独特地促进参与度和行为排练的优势也得到了展示。最后我们给出了设计沉浸式模拟并将VR训练融入儿科成像工作流程的设计建议。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Download our application at https://www.meta.com/experiences/stanford-mri-simulator/8205539289482347/
摘要
MRI的复杂体验对于儿科患者而言充满压力,由于其环境中的声音较大、扫描仪孔径密闭以及需要长时间保持静止的要求。虽然镇静剂常用于管理焦虑和动作,但它存在临床风险和后勤负担。传统的前置方法,如教学视频和模拟扫描,往往缺乏与年长儿童和青少年的互动。本研究对四种MRI准备模式进行了比较评估:(1)游戏化虚拟现实(VR)模拟通过实时反馈训练保持静止;(2)无交互性的被动VR体验复制MRI环境;(3)真实的MRI程序的第一人称视频;(4)标准二维教育视频。我们评估每种方法对头部运动数据、减少焦虑、程序准备度、可用性和主观偏好的影响。结果显示,游戏化VR条件下头部运动显著降低(p < 0.001),且准备度得分最高(p < 0.05)。头部运动数据与学习效果显著相关(p < 0.01),表明VR中的行为表现强烈预示程序就绪状态。虽然所有模式都减少了焦虑并被评定为可用,但交互式VR被大多数参与者所喜欢,在促进参与和行为的重复训练方面表现出独特的优势。最后我们给出了设计沉浸式模拟和将VR训练融入儿科成像工作流程的设计建议。
关键见解
- 儿科患者在MRI过程中的压力主要来源于声音、环境和长时间保持静止的要求。
- 传统的MRI预备方法如教学视频和模拟扫描在某些情况下缺乏与患者的互动。
- 游戏化虚拟现实(VR)模拟在减少头部运动和提高患者准备度方面表现出显著效果。
- VR中的行为表现与程序就绪状态之间存在显著相关性。
- 交互式VR在促进患者参与和重复训练方面展现出优势。
点此查看论文截图


Transformer-Based Representation Learning for Robust Gene Expression Modeling and Cancer Prognosis
Authors:Shuai Jiang, Saeed Hassanpour
Transformer-based models have achieved remarkable success in natural language and vision tasks, but their application to gene expression analysis remains limited due to data sparsity, high dimensionality, and missing values. We present GexBERT, a transformer-based autoencoder framework for robust representation learning of gene expression data. GexBERT learns context-aware gene embeddings by pretraining on large-scale transcriptomic profiles with a masking and restoration objective that captures co-expression relationships among thousands of genes. We evaluate GexBERT across three critical tasks in cancer research: pan-cancer classification, cancer-specific survival prediction, and missing value imputation. GexBERT achieves state-of-the-art classification accuracy from limited gene subsets, improves survival prediction by restoring expression of prognostic anchor genes, and outperforms conventional imputation methods under high missingness. Furthermore, its attention-based interpretability reveals biologically meaningful gene patterns across cancer types. These findings demonstrate the utility of GexBERT as a scalable and effective tool for gene expression modeling, with translational potential in settings where gene coverage is limited or incomplete.
基于Transformer的模型在自然语言和视觉任务中取得了显著的成功,但其在基因表达分析中的应用仍受限于数据的稀疏性、高维度和缺失值。我们提出了GexBERT,这是一个基于Transformer的自编码器框架,用于基因表达数据的稳健表示学习。GexBERT通过在大规模转录组图谱上进行预训练来学习上下文感知的基因嵌入,通过掩码和恢复目标来捕获数千个基因之间的共表达关系。我们在癌症研究的三个关键任务中评估了GexBERT:泛癌分类、特定癌症生存预测和缺失值估算。GexBERT在有限的基因子集上达到了最先进的分类精度,通过恢复预后锚基因的表达提高了生存预测能力,并在高缺失率的情况下优于传统的估算方法。此外,其基于注意力的可解释性揭示了不同癌症类型中生物意义明确的基因模式。这些发现证明了GexBERT作为基因表达建模的可扩展和有效工具,在基因覆盖有限或不完全的情况下具有翻译潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Transformer的模型在自然语言和视觉任务中取得了显著的成功,但在基因表达分析中的应用受到限制。本研究提出了GexBERT模型,它是一个基于Transformer的自编码器框架,用于学习基因表达数据的鲁棒表示。通过在大规模转录组谱上进行预训练,学习上下文感知的基因嵌入,通过掩码和恢复目标来捕获数千个基因之间的共表达关系。在癌症研究中的三个关键任务中进行了评估,包括泛癌分类、特定癌症生存预测和缺失值插补。GexBERT取得了最先进的分类准确性,从有限的基因子集中恢复表达关键的预后锚基因,提高了生存预测能力,并且在高缺失率的情况下优于传统的插补方法。此外,其基于注意力的解释性揭示了不同癌症类型中生物意义明确的基因模式。研究表明,GexBERT作为基因表达建模的可扩展和有效工具具有实用性,特别是在基因覆盖有限或不完全的情况下具有翻译潜力。
Key Takeaways
- GexBERT是一个基于Transformer的自编码器框架,用于基因表达数据的鲁棒表示学习。
- GexBERT通过预训练学习上下文感知的基因嵌入,捕捉基因间的共表达关系。
- 在泛癌分类任务中,GexBERT取得了最先进的分类准确性,即使使用有限的基因子集。
- GexBERT能恢复关键预后锚基因的表达,提高癌症生存预测的准确性。
- 在高缺失率的情况下,GexBERT的插补性能优于传统方法。
- GexBERT具有基于注意力的解释性,能揭示生物意义明确的基因模式。
点此查看论文截图

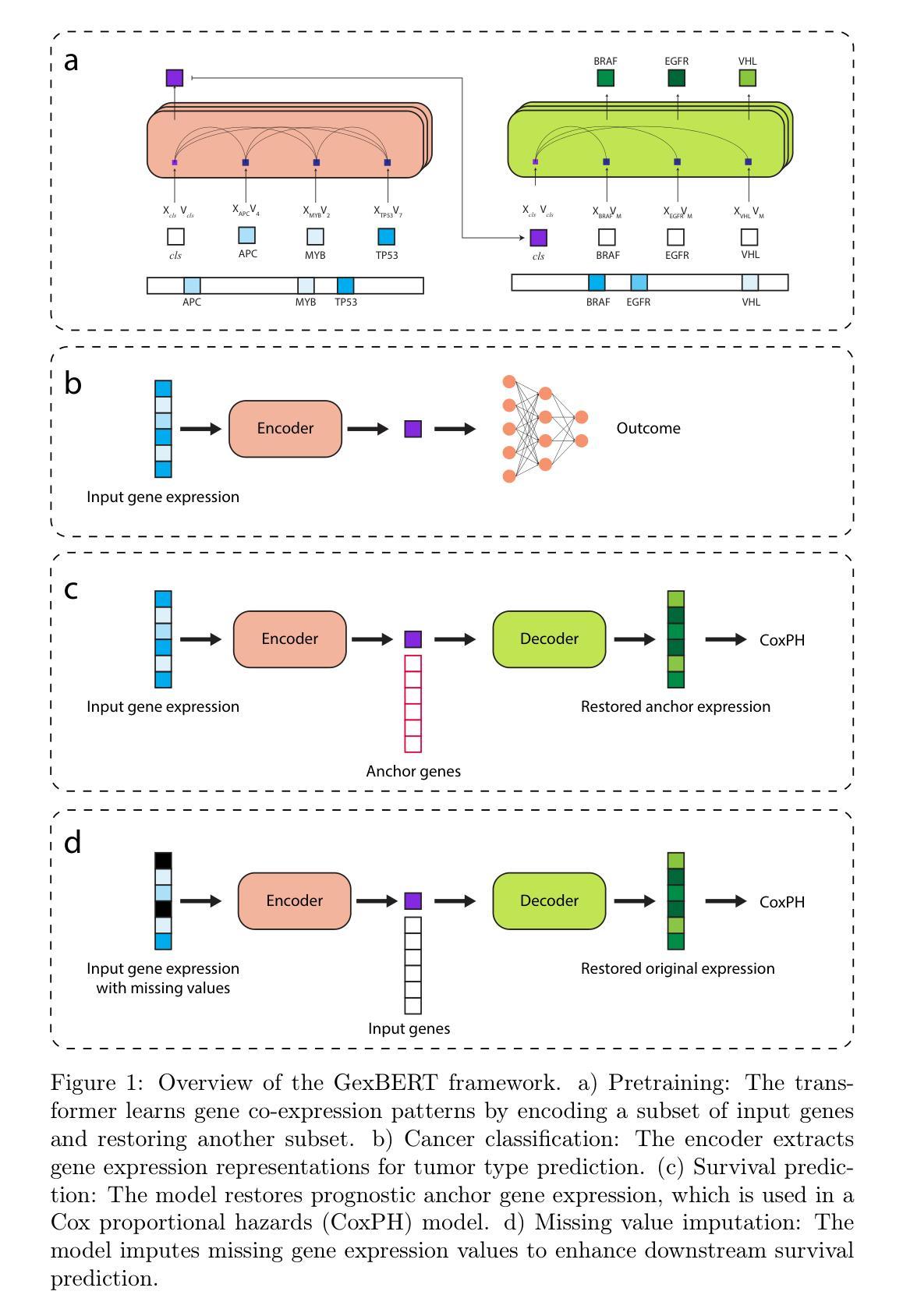
ToolTipNet: A Segmentation-Driven Deep Learning Baseline for Surgical Instrument Tip Detection
Authors:Zijian Wu, Shuojue Yang, Yueming Jin, Septimiu E Salcudean
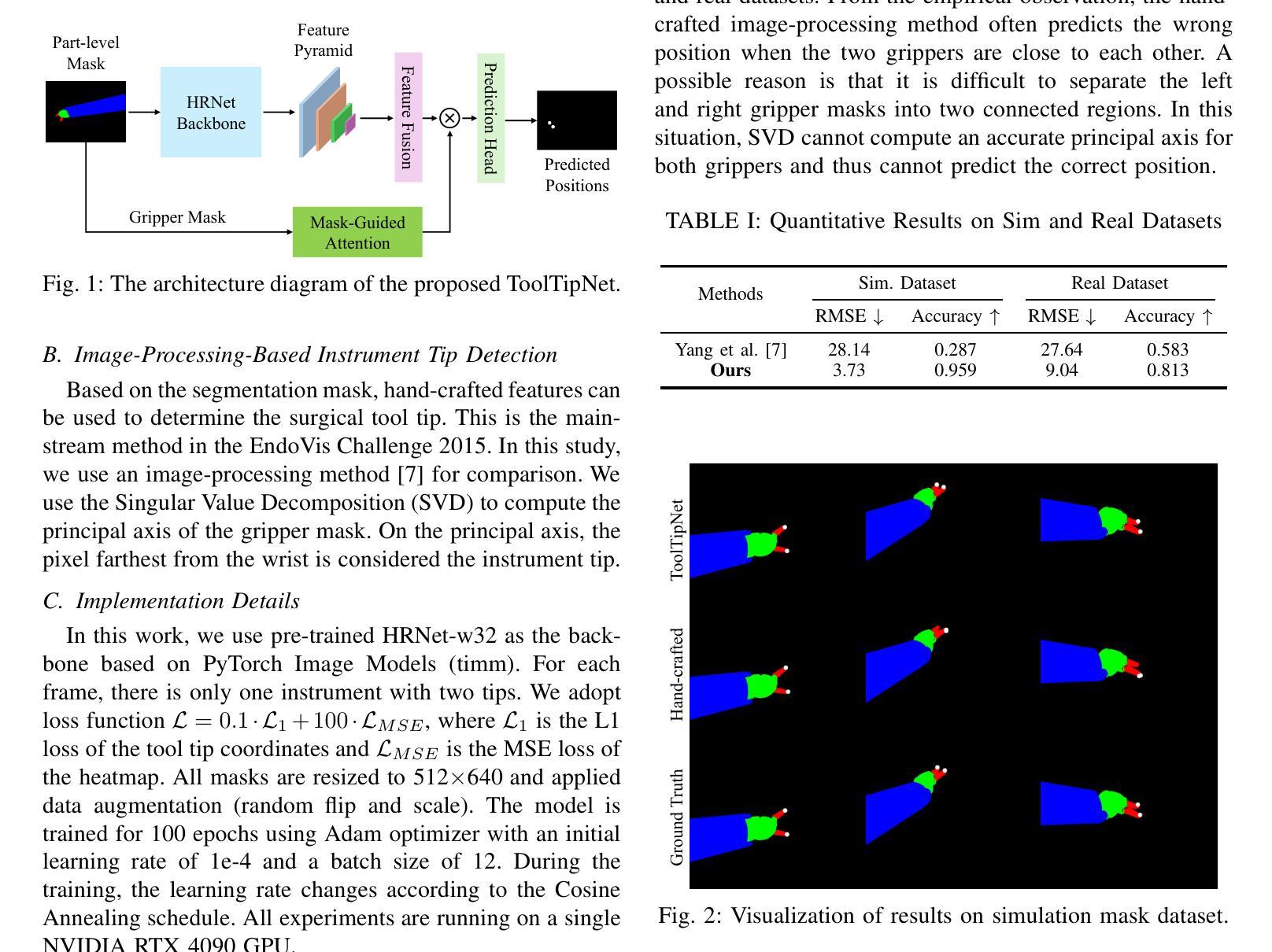
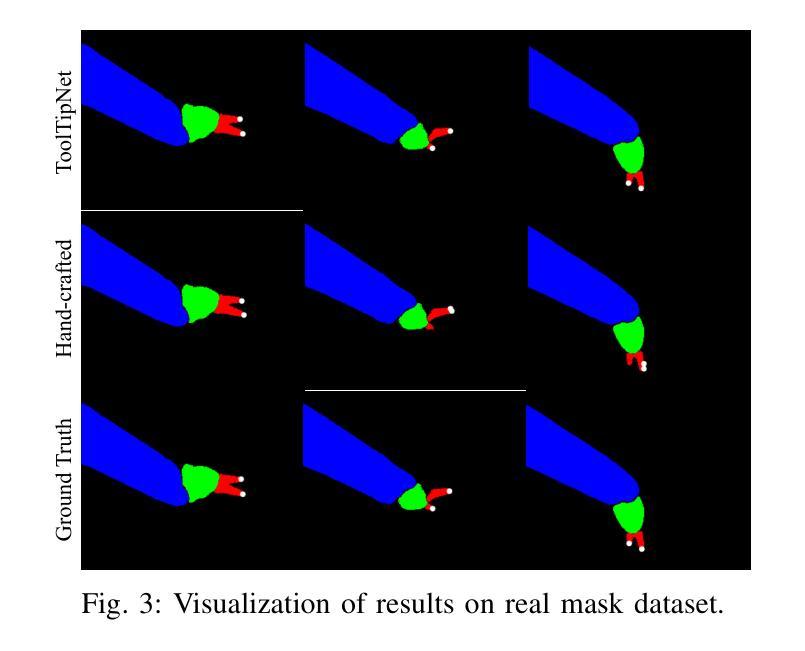
In robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (RALP), the location of the instrument tip is important to register the ultrasound frame with the laparoscopic camera frame. A long-standing limitation is that the instrument tip position obtained from the da Vinci API is inaccurate and requires hand-eye calibration. Thus, directly computing the position of the tool tip in the camera frame using the vision-based method becomes an attractive solution. Besides, surgical instrument tip detection is the key component of other tasks, like surgical skill assessment and surgery automation. However, this task is challenging due to the small size of the tool tip and the articulation of the surgical instrument. Surgical instrument segmentation becomes relatively easy due to the emergence of the Segmentation Foundation Model, i.e., Segment Anything. Based on this advancement, we explore the deep learning-based surgical instrument tip detection approach that takes the part-level instrument segmentation mask as input. Comparison experiments with a hand-crafted image-processing approach demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method on simulated and real datasets.
在机器人辅助腹腔镜下根治性前列腺切除术(RALP)中,仪器尖端的位置对于将超声框架与腹腔镜摄像机框架进行注册非常重要。一个长期存在的问题是从达芬奇API获得的仪器尖端位置不准确,需要进行手眼校准。因此,直接使用基于视觉的方法计算工具尖端在摄像机框架中的位置成为一个有吸引力的解决方案。此外,手术器械尖端检测是其他任务的关键组成部分,如手术技能评估和手术自动化。然而,由于工具尖点小且手术器械具有灵活性,此任务具有挑战性。由于分割基础模型的兴起,即分割任何事物,手术器械分割变得相对容易。基于此发展,我们探索了基于深度学习的手术器械尖端检测方案,该方案以部分级仪器分割掩膜作为输入。与手工图像处理方法进行的对比实验表明,该方法在模拟和真实数据集上的表现均优于手工图像处理方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在机器人辅助腹腔镜前列腺根治术(RALP)中,仪器尖端位置的重要性及其在超声框架与腹腔镜摄像机框架中的注册问题。由于从da Vinci API获取的仪器尖端位置不准确,需要手眼校准。因此,采用基于视觉的方法直接计算工具尖端在摄像机框架中的位置成为一种有吸引力的解决方案。此外,手术器械尖端检测是手术技能评估和手术自动化等任务的关键组成部分。然而,由于工具尖端尺寸小以及手术器械的关节活动,此任务极具挑战性。借助Segmentation Foundation Model(如Segment Anything),手术器械分段变得相对容易。基于此发展,本文探讨了基于深度学习的手术器械尖端检测方案,该方案以部分级别的仪器分段掩膜为输入。与手工图像处理方法相比,对比实验表明该方法在模拟和实际数据集上表现更佳。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人辅助腹腔镜前列腺根治术(RALP)中,仪器尖端位置的准确性对于手术过程至关重要。
- 当前从da Vinci API获取的仪器尖端位置数据存在不准确的长期限制,需要手眼校准。
- 基于视觉的方法为计算工具尖端在摄像机框架中的位置提供了有吸引力的解决方案。
- 手术器械尖端检测是手术技能评估和手术自动化任务的关键。
- 手术器械尖端检测面临工具尖端尺寸小和器械关节活动的挑战。
- Segmentation Foundation Model(如Segment Anything)的发展使得手术器械分段变得相对容易。
点此查看论文截图

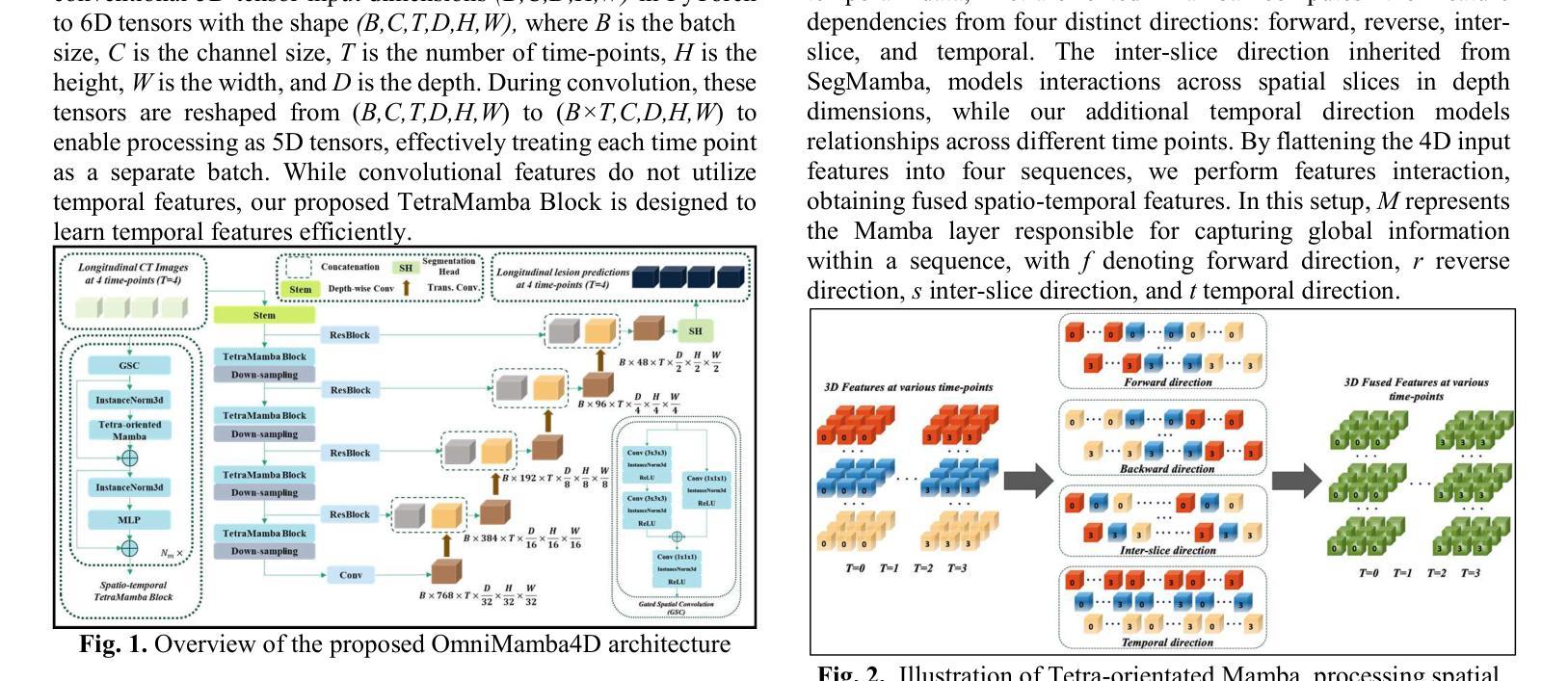
OmniMamba4D: Spatio-temporal Mamba for longitudinal CT lesion segmentation
Authors:Justin Namuk Kim, Yiqiao Liu, Rajath Soans, Keith Persson, Sarah Halek, Michal Tomaszewski, Jianda Yuan, Gregory Goldmacher, Antong Chen
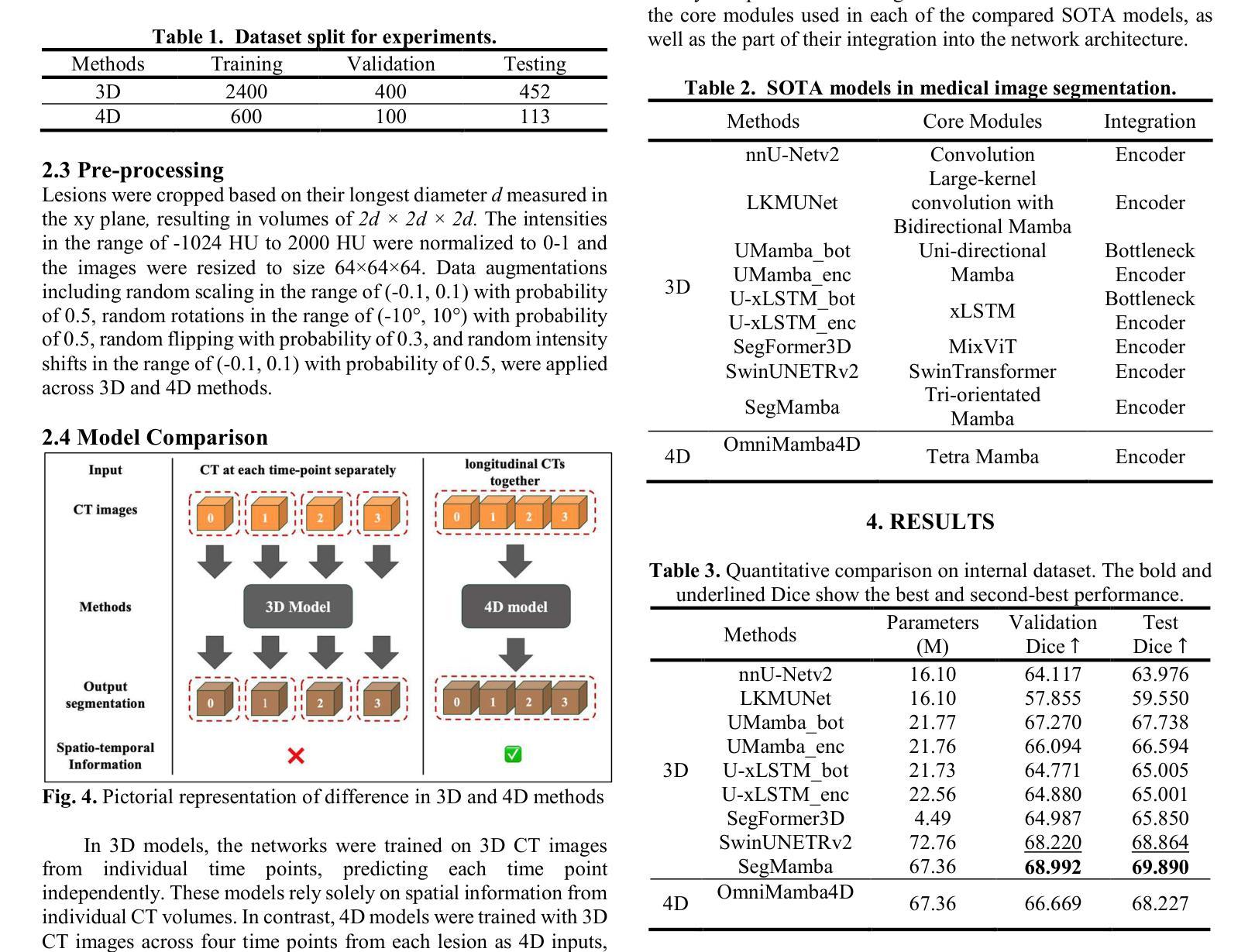
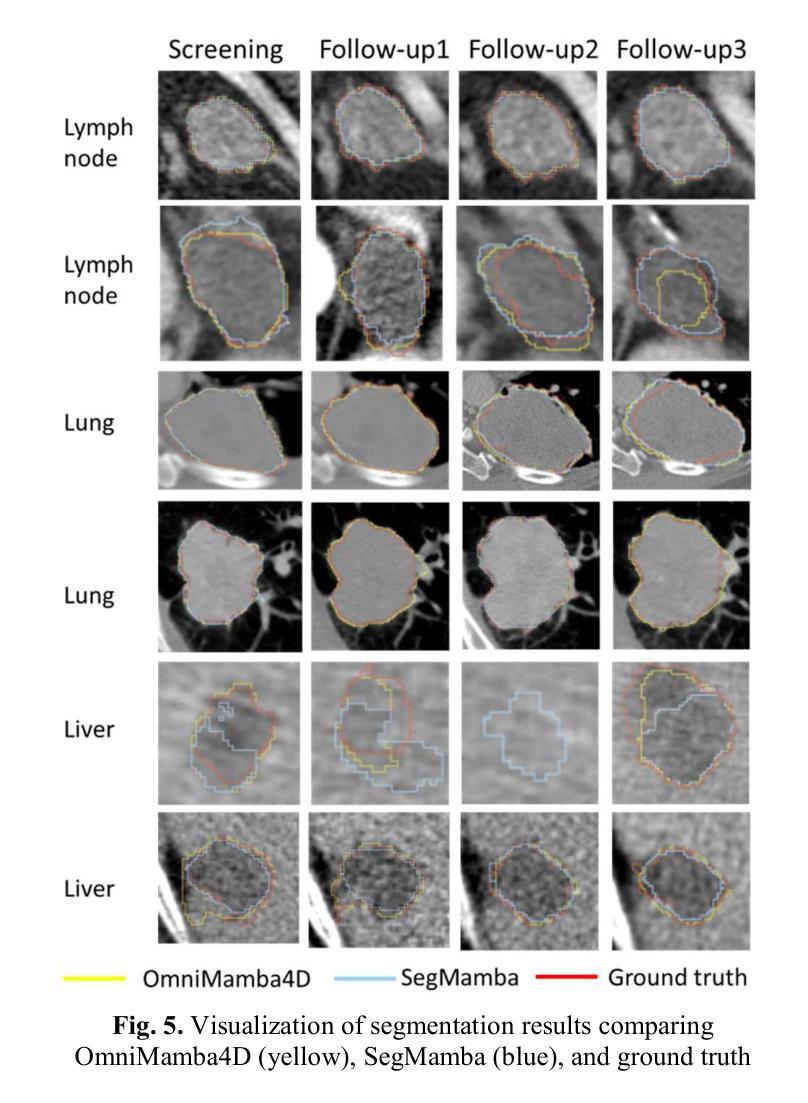
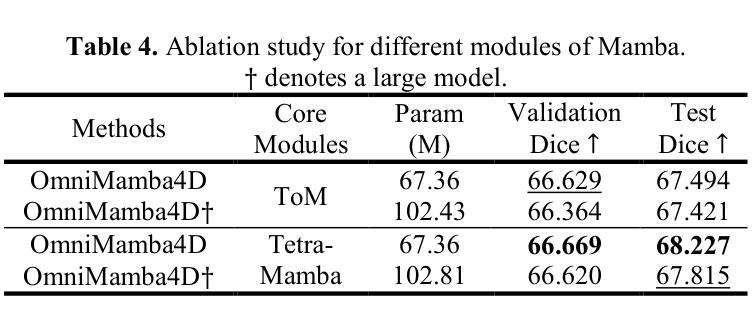
Accurate segmentation of longitudinal CT scans is important for monitoring tumor progression and evaluating treatment responses. However, existing 3D segmentation models solely focus on spatial information. To address this gap, we propose OmniMamba4D, a novel segmentation model designed for 4D medical images (3D images over time). OmniMamba4D utilizes a spatio-temporal tetra-orientated Mamba block to effectively capture both spatial and temporal features. Unlike traditional 3D models, which analyze single-time points, OmniMamba4D processes 4D CT data, providing comprehensive spatio-temporal information on lesion progression. Evaluated on an internal dataset comprising of 3,252 CT scans, OmniMamba4D achieves a competitive Dice score of 0.682, comparable to state-of-the-arts (SOTA) models, while maintaining computational efficiency and better detecting disappeared lesions. This work demonstrates a new framework to leverage spatio-temporal information for longitudinal CT lesion segmentation.
准确地对纵向CT扫描进行分割对于监测肿瘤进展和评估治疗效果非常重要。然而,现有的3D分割模型仅专注于空间信息。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了OmniMamba4D,这是一种专为4D医学图像(随时间变化的3D图像)设计的全新分割模型。OmniMamba4D利用时空四面体定向的Mamba块,有效地捕捉空间和时态特征。与传统的仅分析单一时间点的3D模型不同,OmniMamba4D处理4D CT数据,提供关于病灶进展的全面时空信息。在包含3252次CT扫描的内部数据集上进行评估,OmniMamba4D取得了竞争力的Dice评分0.682,与最先进的模型相比,同时保持了计算效率,并能更好地检测消失的病变。这项工作展示了一个利用时空信息进行纵向CT病灶分割的新框架。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2025
摘要
OmniMamba4D是一种针对四维医学图像(随时间变化的3D图像)的分割模型。该模型利用时空四向Mamba块,有效捕捉空间和时间特征。与传统的仅分析单一时间点的3D模型不同,OmniMamba4D处理四维CT数据,提供关于病灶进展的综合时空信息。在包含3,252个CT扫描的内部数据集上评估,OmniMamba4D的Dice分数达到0.682,与最新模型相当,同时保持计算效率和更好的消失病灶检测能力。该研究展示了利用时空信息进行纵向CT病灶分割的新框架。
要点
- OmniMamba4D是一种针对四维医学图像(3D图像随时间变化)的分割模型。
- 该模型利用时空四向Mamba块,有效捕捉空间和时间的特征。
- OmniMamba4D能够处理四维CT数据,提供关于病灶进展的综合时空信息。
- 与仅分析单一时间点的传统3D模型不同,OmniMamba4D具备更全面的分析功能。
- 在内部数据集上评估,OmniMamba4D的Dice分数达到0.682,表现具有竞争力。
- OmniMamba4D的Dice分数与最新模型相当,同时保持计算效率和更好的消失病灶检测能力。
点此查看论文截图

Q-ball mechanism of electron transport properties of high-T$_c$ superconductors
Authors:S. I. Mukhin
Proposed recently by the author Q-ball mechanism of the pseudogap state and high-Tc superconductivity in cuprates (2022) was supported by micro X-ray diffraction data in HgBa$2$CuO${4+y}$ (2023). In the present paper it is demonstrated that T-linear temperature dependence of electrical resistivity arises naturally in the Q-ball gas phase, that may explain corresponding experimental data in the “strange metal” phase of high-T$_c$ cuprates, as reviewed by Barisic et al. (2013). In the present theory it arises due to scattering of electrons on the Q-balls gas of condensed charge/spin fluctuations. Close to the lowest temperature boundary of the “strange metal” phase, at which Q-ball radius diverges, electrical resistivity caused by a slide of the Q-balls as a whole is calculated using fluctuation paraconductivity calculation method by Alex Abrikosov (1987). The diamagnetic response of Q-balls gas is calculated as well and shows good accord with experimental data by L.Li et al. (2010) in the “strange metal” phase. In total, obtained results demonstrate different properties of the correlated electrons systems that arise due to formation of Q-balls possessing internal bosonic frequency $\Omega=2\pi nT$ in Matsubara time and, thus, forming the quantum thermodynamic time polycrystals. Presented theory may give a clue concerning a possible mechanism of the experimentally measured properties of high-T$_c$ cuprates in the “strange metal” phase of their phase diagram. We believe , these results provide support to the quantum thermodynamic time crystal model of the Euclidean Q-balls considered in the present paper.
作者近期提出的伪间隙态和高温超导体的Q球机制(2022年)得到了汞巴铜酸盐(HgBa_2CuO_{4+y})(2023年)中的微X射线衍射数据的支持。本文展示了线性温度依赖的电阻率自然产生于Q球气态相,这可以解释巴里斯等人(Barisic et al., 2013)所回顾的高温超导体铜酸盐的“奇异金属”相中的相应实验数据。根据现有理论,它产生于电子在凝聚的电荷/自旋波动的Q球气体上的散射。在“奇异金属”相的最低温度边界附近,在此边界上,Q球的半径发散,由于Q球作为一个整体的滑动导致的电阻率是通过亚历克斯·阿布里科索夫(Alex Abrikosov)的涨落超导计算法(1987年)来计算的。此外,还计算了Q球气体的抗磁性响应,这与李立等人在“奇异金属”相中的实验数据(Li et al., 2010)吻合良好。总的来说,所获得的结果展示了相关电子系统的不同特性,这些特性是由于形成了内部具有玻色频率Ω=2πnT的Q球而产生的,从而在Matsubara时间中形成量子热力学时间多晶。本文提出的理论可能为高温超导体铜酸盐在相图中的“奇异金属”相的实验测量特性提供了一种可能的机制。我们相信,这些结果为本文中考虑的欧几里得Q球的量子热力学时间晶体模型提供了支持。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
最近由Q-ball机制提出的伪间隙态和高温超导性的理论,得到了汞基铜酸盐中微X射线衍射数据的支持。本文展示了线性温度依赖性的电阻率自然产生于Q-ball气态相,这解释了高温铜酸盐“奇异金属”相的实验数据。在该理论中,电阻率产生于电子与凝聚态电荷/自旋波动的Q-ball气体的散射。在“奇异金属”相的最低温度边界附近,Q-ball半径发散时,利用Alex Abrikosov的涨落超导电性计算方法计算了因整个Q-ball滑动而产生的电阻率。此外,还计算了Q-ball气体的抗磁性响应,与实验数据相符良好。总之,本研究揭示了关联电子系统因形成内部具有玻色频率的Q-ball而产生的不同特性,在Matsubara时间中形成量子热力学时间多晶体。本研究为“奇异金属”相高温铜酸盐的实验特性提供了可能的机制线索,并为我们对量子热力学时间晶体模型的探讨提供了支持。
关键见解
- Q-ball机制理论得到微X射线衍射数据的支持,证实伪间隙态和高温超导性的关系。
- 展示了电阻率的T-线性温度依赖性在Q-ball气态相中的自然产生,这解释了“奇异金属”相中高温铜酸盐的实验数据。
- 电阻率产生于电子与凝聚态电荷/自旋波动的Q-ball气体的散射。
- 在“奇异金属”相的最低温度边界附近,计算了因整个Q-ball滑动而产生的电阻率,展示了良好的理论预测性。
- Q-ball气体的抗磁性响应与实验数据相符,进一步验证了理论的准确性。
- 研究揭示了关联电子系统因形成Q-ball而产生的特性,这些Q-ball在Matsubara时间中形成量子热力学时间多晶体。
点此查看论文截图

Mixture-of-Shape-Experts (MoSE): End-to-End Shape Dictionary Framework to Prompt SAM for Generalizable Medical Segmentation
Authors:Jia Wei, Xiaoqi Zhao, Jonghye Woo, Jinsong Ouyang, Georges El Fakhri, Qingyu Chen, Xiaofeng Liu
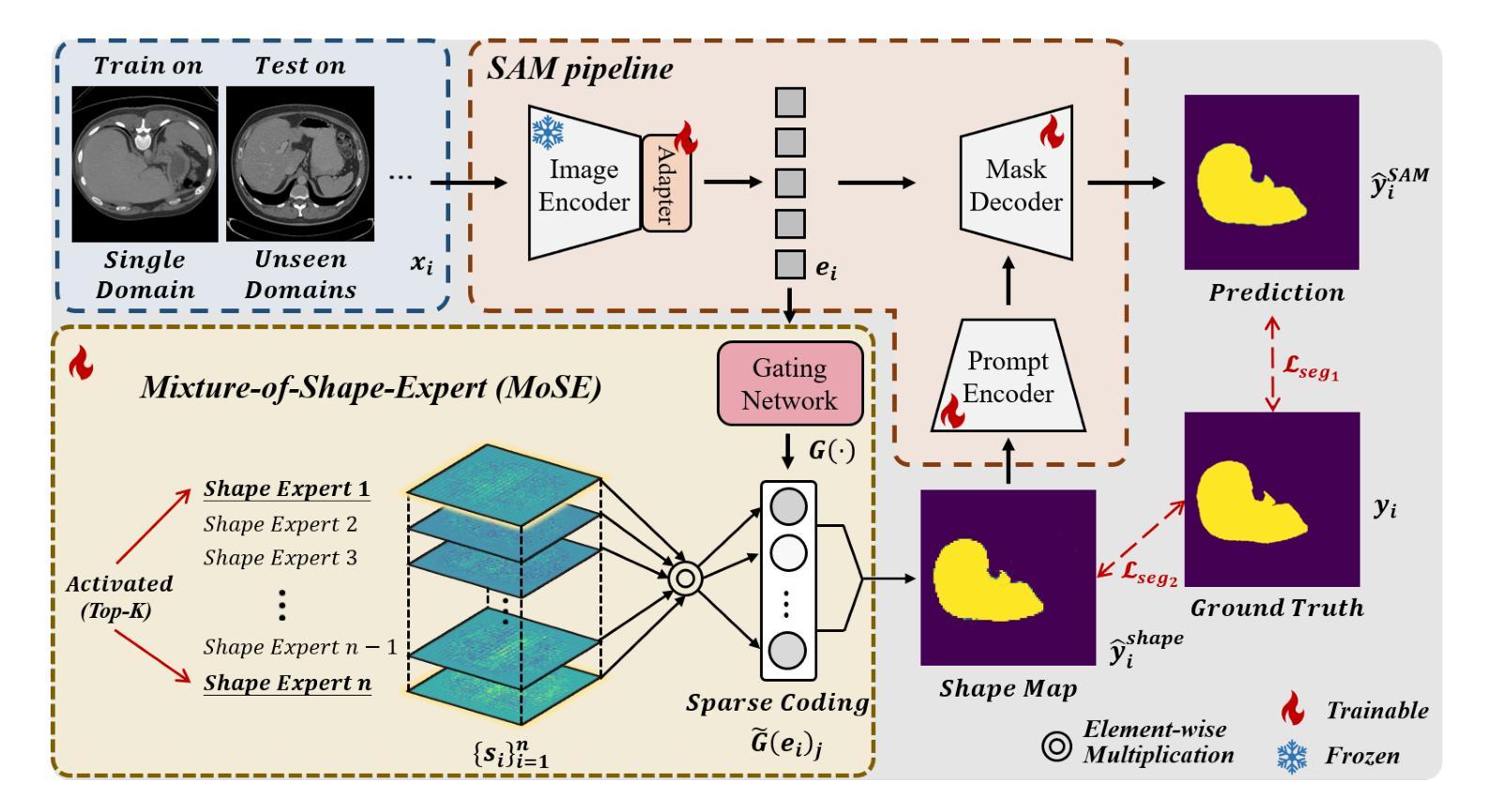
Single domain generalization (SDG) has recently attracted growing attention in medical image segmentation. One promising strategy for SDG is to leverage consistent semantic shape priors across different imaging protocols, scanner vendors, and clinical sites. However, existing dictionary learning methods that encode shape priors often suffer from limited representational power with a small set of offline computed shape elements, or overfitting when the dictionary size grows. Moreover, they are not readily compatible with large foundation models such as the Segment Anything Model (SAM). In this paper, we propose a novel Mixture-of-Shape-Experts (MoSE) framework that seamlessly integrates the idea of mixture-of-experts (MoE) training into dictionary learning to efficiently capture diverse and robust shape priors. Our method conceptualizes each dictionary atom as a shape expert, which specializes in encoding distinct semantic shape information. A gating network dynamically fuses these shape experts into a robust shape map, with sparse activation guided by SAM encoding to prevent overfitting. We further provide this shape map as a prompt to SAM, utilizing the powerful generalization capability of SAM through bidirectional integration. All modules, including the shape dictionary, are trained in an end-to-end manner. Extensive experiments on multiple public datasets demonstrate its effectiveness.
单域泛化(SDG)在医学图像分割中近期吸引了越来越多的关注。对于SDG来说,一种有前景的策略是利用不同成像协议、扫描仪供应商和临床站点之间的语义形状先验的一致性。然而,现有的编码形状先验的字典学习方法常常受到离线计算形状元素集较小的代表性不足的困扰,或者在字典大小增加时产生过拟合现象。此外,它们与大型的基石模型如“Anything分割模型”(SAM)并不兼容。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的混合形状专家(MoSE)框架,它将混合专家(MoE)训练的理念无缝地集成到字典学习中,以有效地捕获多样化和稳健的形状先验。我们的方法将每个字典原子概念化为一个形状专家,专门用于编码不同的语义形状信息。门控网络动态地融合这些形状专家到一个稳健的形状图中,通过SAM编码引导稀疏激活以防止过拟合。我们进一步将这个形状图作为SAM的提示,通过双向集成利用SAM的强大泛化能力。所有模块,包括形状字典,都是端到端进行训练的。在多个公共数据集上的广泛实验证明了其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025 workshop
Summary
该论文关注医学图像分割中的单域泛化(SDG)问题,并提出了一种新颖的Mixture-of-Shape-Experts(MoSE)框架。该框架结合了混合专家(MoE)训练的思想,以更有效地捕捉多样且稳健的形状先验。MoSE将每个字典原子概念化为一个形状专家,专门用于编码不同的语义形状信息。通过动态融合这些形状专家,形成一个稳健的形状图,并借助SAM编码进行稀疏激活以防止过拟合。此外,该研究还将形状图作为SAM的提示,利用SAM的强大泛化能力实现双向集成。所有模块包括形状字典均以端到端的方式进行训练,在多个公共数据集上的实验证明了其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 文章关注医学图像分割中的单域泛化问题。
- 现有编码形状先验的字典学习方法存在局限性,如代表性不足和过拟合问题。
- 提出了一种新颖的Mixture-of-Shape-Experts(MoSE)框架,结合混合专家训练思想提升形状先验捕捉效率。
- MoSE将每个字典原子视为一个形状专家,专门编码语义形状信息。
- 通过动态融合形状专家形成稳健的形状图,借助SAM编码防止过拟合。
- 将形状图作为SAM的提示,利用SAM的强大泛化能力实现双向集成。
点此查看论文截图

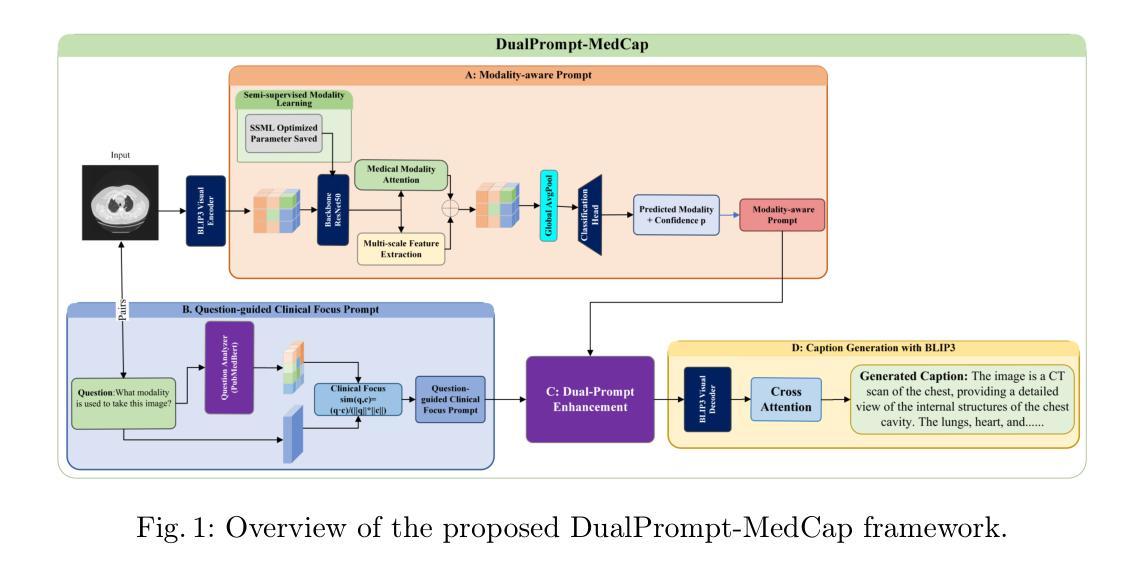
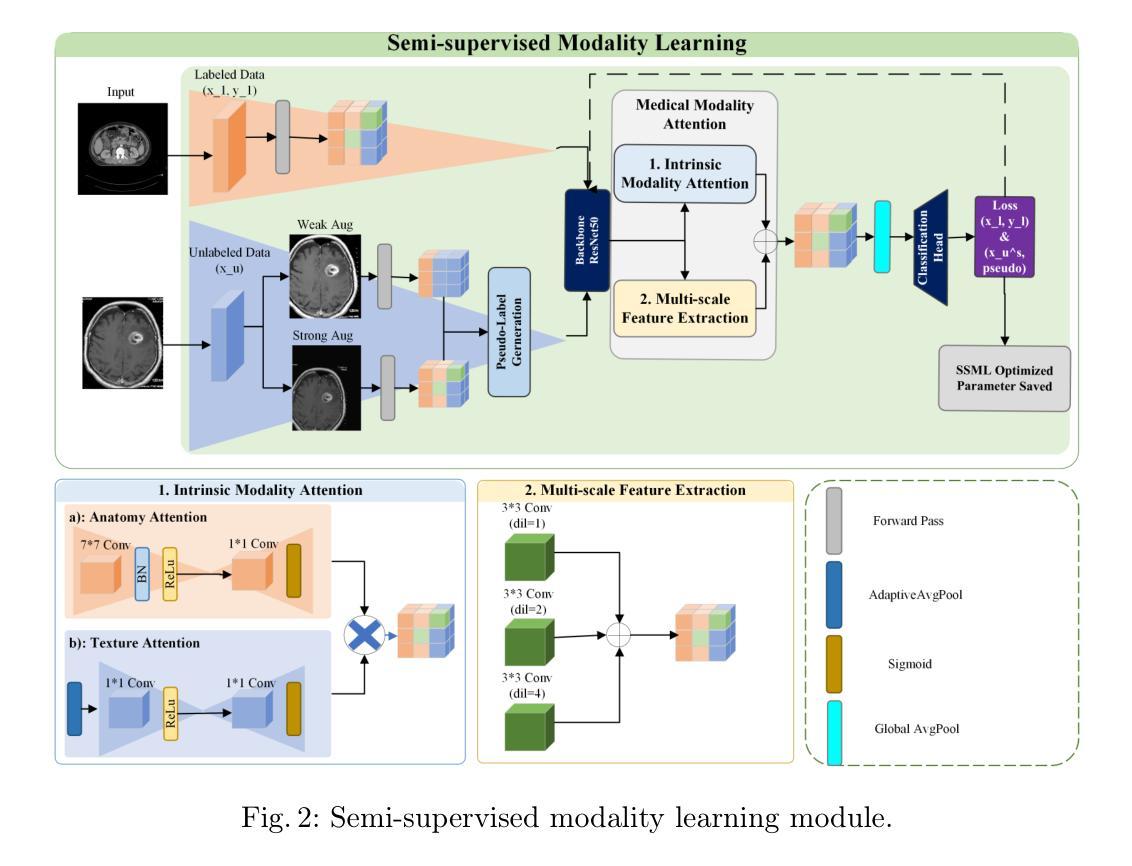
DualPrompt-MedCap: A Dual-Prompt Enhanced Approach for Medical Image Captioning
Authors:Yining Zhao, Ali Braytee, Mukesh Prasad
Medical image captioning via vision-language models has shown promising potential for clinical diagnosis assistance. However, generating contextually relevant descriptions with accurate modality recognition remains challenging. We present DualPrompt-MedCap, a novel dual-prompt enhancement framework that augments Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) through two specialized components: (1) a modality-aware prompt derived from a semi-supervised classification model pretrained on medical question-answer pairs, and (2) a question-guided prompt leveraging biomedical language model embeddings. To address the lack of captioning ground truth, we also propose an evaluation framework that jointly considers spatial-semantic relevance and medical narrative quality. Experiments on multiple medical datasets demonstrate that DualPrompt-MedCap outperforms the baseline BLIP-3 by achieving a 22% improvement in modality recognition accuracy while generating more comprehensive and question-aligned descriptions. Our method enables the generation of clinically accurate reports that can serve as medical experts’ prior knowledge and automatic annotations for downstream vision-language tasks.
通过视觉语言模型进行医学图像描述已经显示出在辅助临床诊断中的潜力。然而,生成具有准确模态识别能力的上下文相关描述仍然是一个挑战。我们提出了DualPrompt-MedCap,这是一种新型的双提示增强框架,它通过两个专业组件增强大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs):(1)一个基于半监督分类模型在医学问答对上预训练的模态感知提示;(2)一个利用生物医学语言模型嵌入的问题引导提示。为了解决缺乏描述性真实标签的问题,我们还提出了一个评估框架,该框架同时考虑空间语义相关性和医学叙述质量。在多个医学数据集上的实验表明,DualPrompt-MedCap相较于基线BLIP-3在模态识别准确度上提高了22%,同时生成了更全面、更符合问题方向的描述。我们的方法能够生成临床准确的报告,可作为医学专家的先验知识和下游视觉语言任务的自动注释。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 figures, 2 tables
摘要
基于视觉语言模型,医学图像描述在临床诊断辅助中展现出巨大潜力。然而,生成具有准确模态识别的上下文相关描述仍具有挑战性。本文提出DualPrompt-MedCap,一种新型双提示增强框架,通过两个专业组件增强大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs):(1)基于医学问答对半监督分类模型预训练的模态感知提示;(2)利用生物医学语言模型嵌入的问题引导提示。为解决缺乏描述性真实标签的问题,我们还提出了一个评估框架,该框架联合考虑空间语义相关性和医学叙事质量。在多个医学数据集上的实验表明,DualPrompt-MedCap相较于基线BLIP-3模型在模态识别准确率上提高了22%,同时生成更全面、更符合问题导向的描述。我们的方法能够生成临床准确的报告,可作为医学专家的先验知识和下游视觉语言任务的自动注释。
关键见解
- 医学图像描述在临床诊断辅助中具有巨大潜力。
- 生成具有准确模态识别的上下文相关描述是一大挑战。
- DualPrompt-MedCap框架通过两个专业组件增强大型视觉语言模型:模态感知提示和问题引导提示。
- 模态感知提示基于医学问答对半监督分类模型预训练。
- 问题引导提示利用生物医学语言模型嵌入。
- 提出一个联合考虑空间语义相关性和医学叙事质量的评估框架。
- 在多个医学数据集上,DualPrompt-MedCap相较于基线模型显著提高模态识别准确率,生成更全面、问题导向的描述,能生成临床准确的报告。
点此查看论文截图

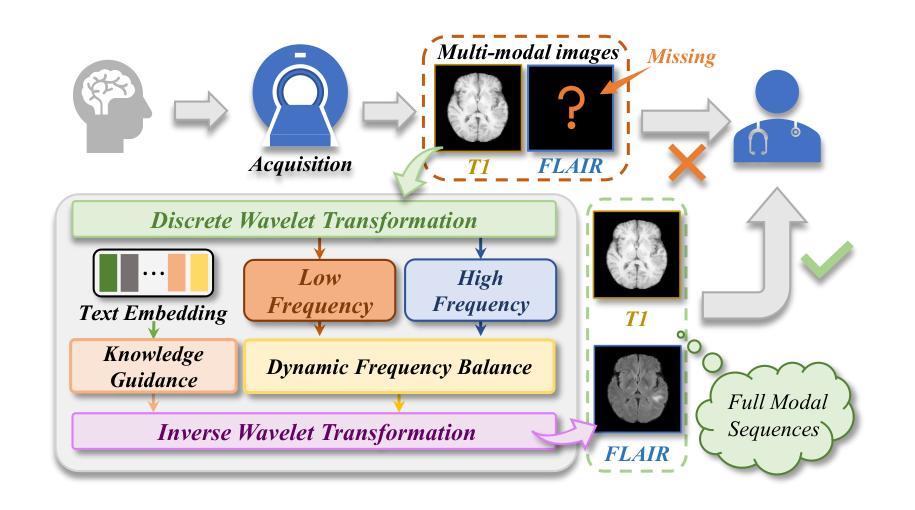
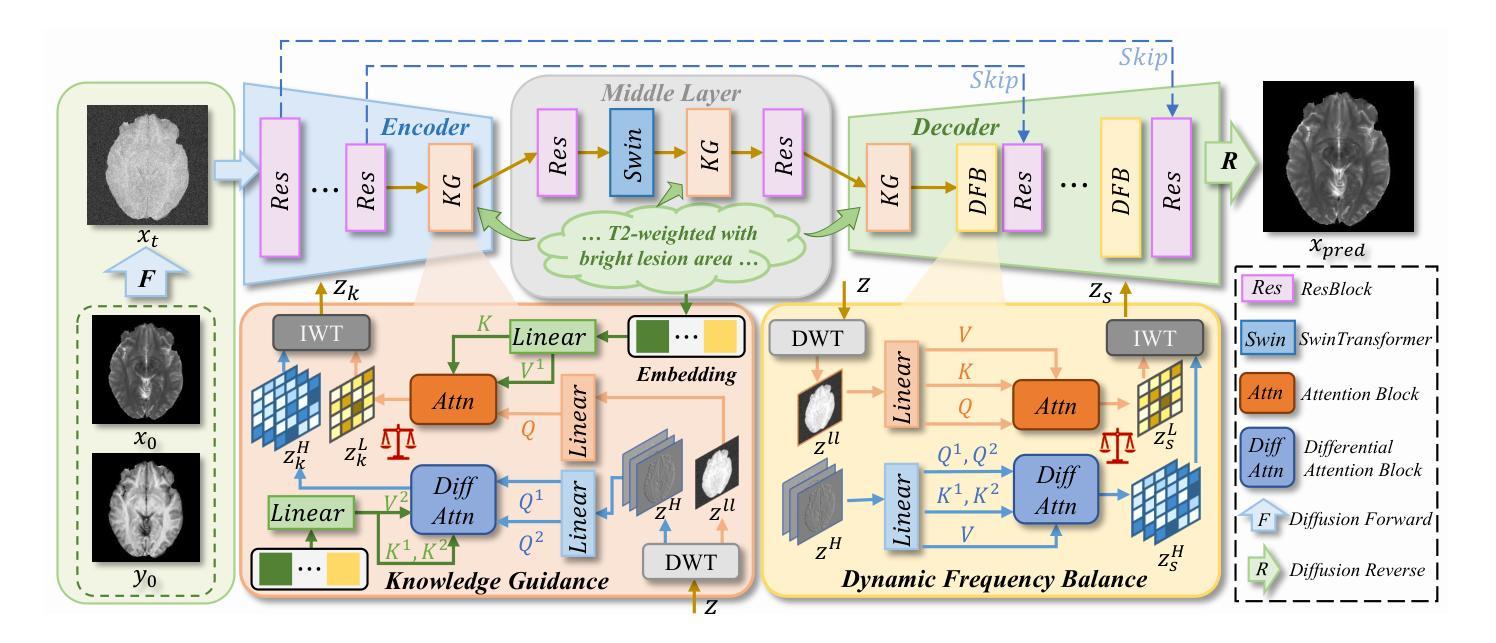
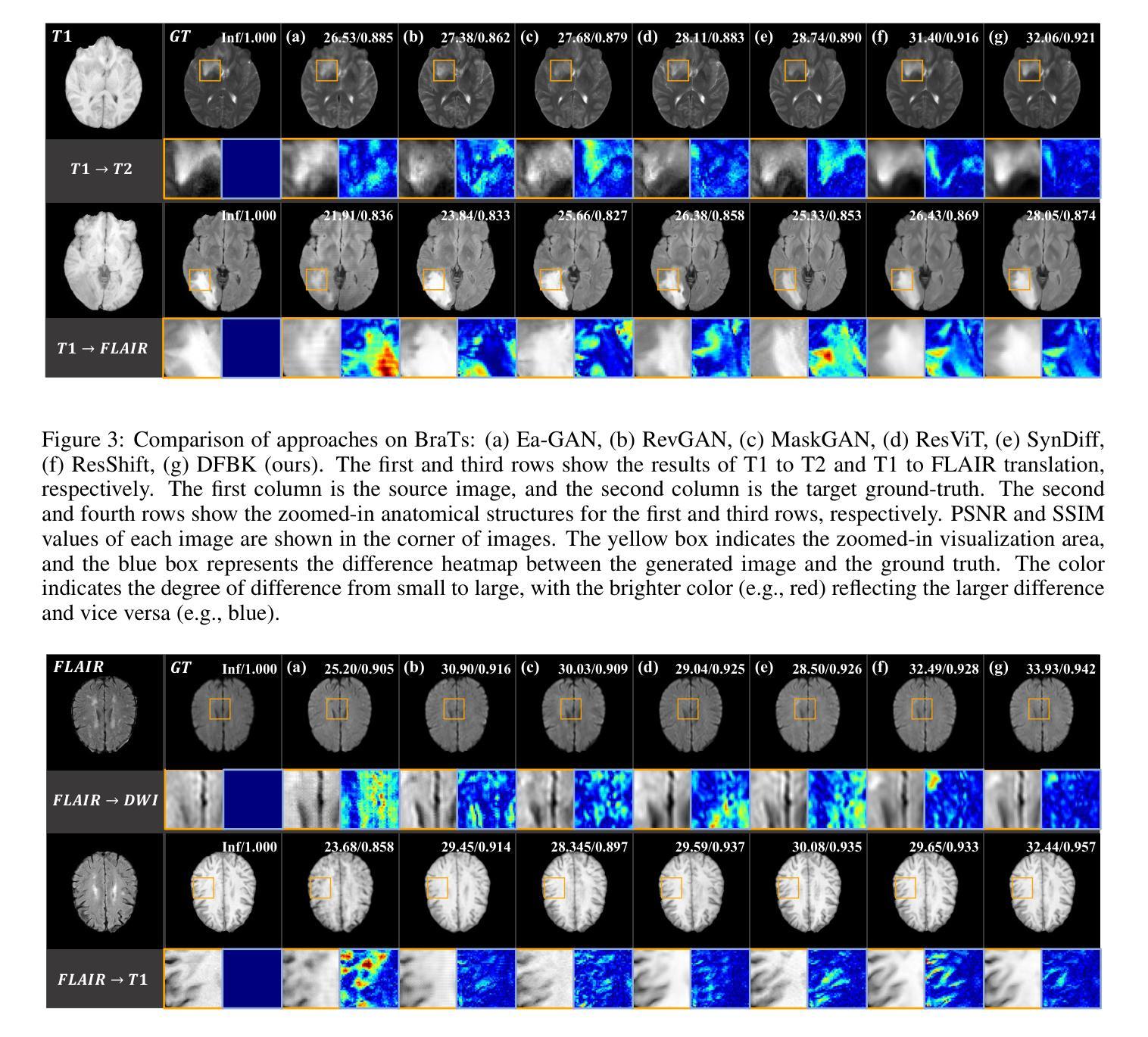
Structure-Accurate Medical Image Translation based on Dynamic Frequency Balance and Knowledge Guidance
Authors:Jiahua Xu, Dawei Zhou, Lei Hu, Zaiyi Liu, Nannan Wang, Xinbo Gao
Multimodal medical images play a crucial role in the precise and comprehensive clinical diagnosis. Diffusion model is a powerful strategy to synthesize the required medical images. However, existing approaches still suffer from the problem of anatomical structure distortion due to the overfitting of high-frequency information and the weakening of low-frequency information. Thus, we propose a novel method based on dynamic frequency balance and knowledge guidance. Specifically, we first extract the low-frequency and high-frequency components by decomposing the critical features of the model using wavelet transform. Then, a dynamic frequency balance module is designed to adaptively adjust frequency for enhancing global low-frequency features and effective high-frequency details as well as suppressing high-frequency noise. To further overcome the challenges posed by the large differences between different medical modalities, we construct a knowledge-guided mechanism that fuses the prior clinical knowledge from a visual language model with visual features, to facilitate the generation of accurate anatomical structures. Experimental evaluations on multiple datasets show the proposed method achieves significant improvements in qualitative and quantitative assessments, verifying its effectiveness and superiority.
多模态医学图像在精确全面的临床诊断中起着至关重要的作用。扩散模型是合成所需医学图像的一种强大策略。然而,现有方法仍然存在因高频信息过拟合和低频信息减弱而导致的解剖结构失真问题。因此,我们提出了一种基于动态频率平衡和知识引导的新方法。具体来说,我们首先通过小波变换分解模型的关键特征来提取低频和高频成分。然后,设计了一个动态频率平衡模块,该模块可以自适应地调整频率,以增强全局低频特征和有效的高频细节,同时抑制高频噪声。为了进一步克服不同医学模态之间差异较大的挑战,我们构建了一个知识引导机制,该机制将来自视觉语言模型的先验临床知识与视觉特征相结合,有助于生成准确的解剖结构。在多个数据集上的实验评估表明,该方法在定性和定量评估方面取得了显著的改进,验证了其有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Medical image translation, Diffusion model, 16 pages
Summary
基于动态频率平衡和知识引导的方法在多模态医学图像合成中提高了诊断精确度。该方法通过小波变换分解模型的关键特征,提取高低频成分,并设计动态频率平衡模块自适应调整频率,增强全局低频特征和有效高频细节,同时抑制高频噪声。此外,为了克服不同医学模态之间的差异,构建了知识引导机制,融合了来自视觉语言模型的先验临床知识,有助于生成准确的解剖结构。实验评估表明,该方法在多个数据集上实现了显著的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态医学图像在临床诊断中扮演重要角色,扩散模型是合成医学图像的有效策略。
- 现有方法存在解剖结构扭曲问题,主要是由于高频信息的过拟合和低频信息的减弱。
- 提出了基于动态频率平衡和知识引导的新方法,通过小波变换分解模型的关键特征。
- 动态频率平衡模块可自适应调整频率,增强低频和有效高频细节,抑制高频噪声。
- 知识引导机制融合了视觉语言模型的先验临床知识,有助于生成准确的解剖结构。
- 实验评估表明,该方法在多个数据集上实现了定性和定量评估的显著改善。
点此查看论文截图


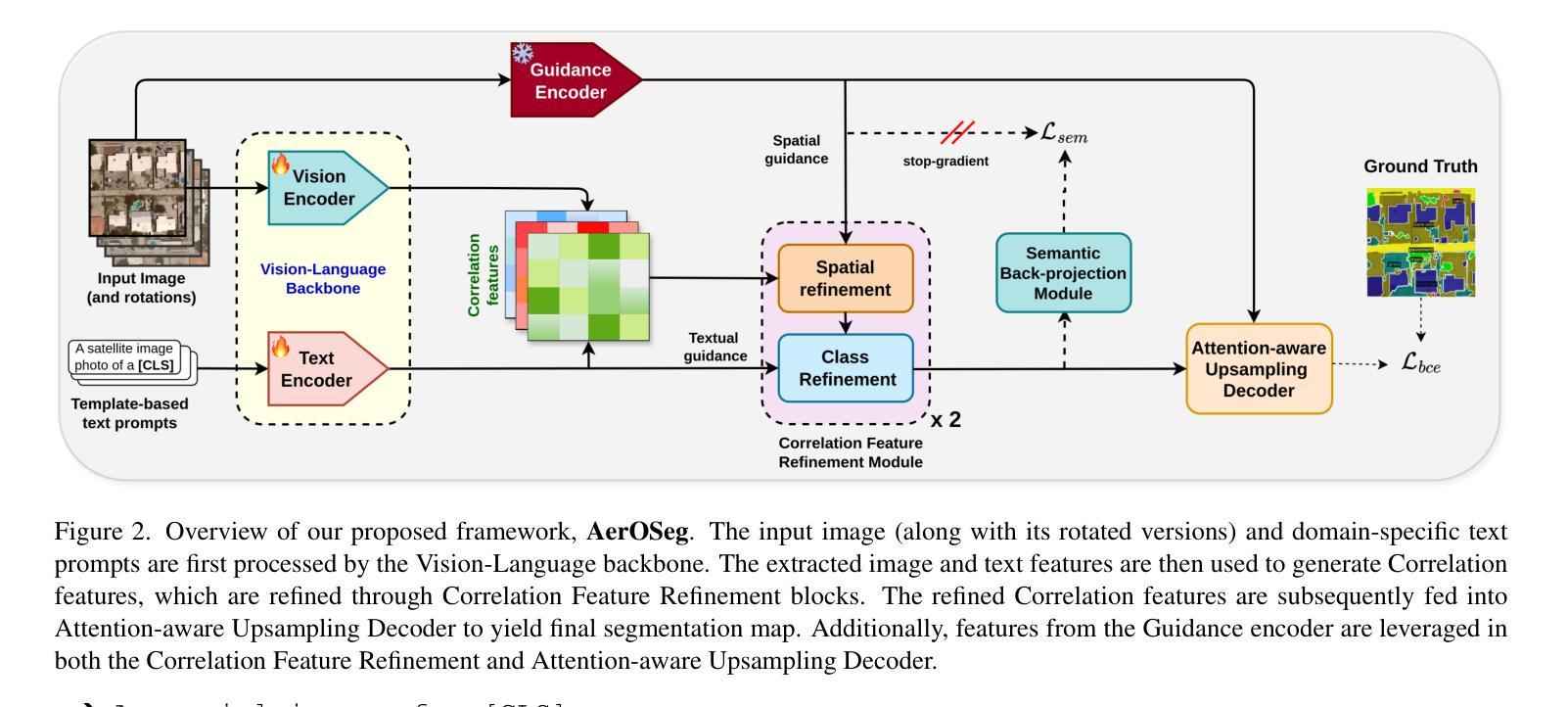
AerOSeg: Harnessing SAM for Open-Vocabulary Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Authors:Saikat Dutta, Akhil Vasim, Siddhant Gole, Hamid Rezatofighi, Biplab Banerjee
Image segmentation beyond predefined categories is a key challenge in remote sensing, where novel and unseen classes often emerge during inference. Open-vocabulary image Segmentation addresses these generalization issues in traditional supervised segmentation models while reducing reliance on extensive per-pixel annotations, which are both expensive and labor-intensive to obtain. Most Open-Vocabulary Segmentation (OVS) methods are designed for natural images but struggle with remote sensing data due to scale variations, orientation changes, and complex scene compositions. This necessitates the development of OVS approaches specifically tailored for remote sensing. In this context, we propose AerOSeg, a novel OVS approach for remote sensing data. First, we compute robust image-text correlation features using multiple rotated versions of the input image and domain-specific prompts. These features are then refined through spatial and class refinement blocks. Inspired by the success of the Segment Anything Model (SAM) in diverse domains, we leverage SAM features to guide the spatial refinement of correlation features. Additionally, we introduce a semantic back-projection module and loss to ensure the seamless propagation of SAM’s semantic information throughout the segmentation pipeline. Finally, we enhance the refined correlation features using a multi-scale attention-aware decoder to produce the final segmentation map. We validate our SAM-guided Open-Vocabulary Remote Sensing Segmentation model on three benchmark remote sensing datasets: iSAID, DLRSD, and OpenEarthMap. Our model outperforms state-of-the-art open-vocabulary segmentation methods, achieving an average improvement of 2.54 h-mIoU.
图像分割超越预定义类别是遥感中的关键挑战,其中在推理过程中经常出现新的和未见过的类别。开放词汇图像分割解决了传统监督分割模型的泛化问题,同时减少了对面元注释的依赖,这些注释既昂贵又耗劳力才能获得。大多数开放词汇分割(OVS)方法旨在用于自然图像,但由于尺度变化、方向变化和复杂的场景组合,它们在遥感数据上表现挣扎。因此,有必要开发专门用于遥感的OVS方法。在这种情况下,我们提出了AerOSeg,这是一种用于遥感数据的新型OVS方法。首先,我们使用输入图像的多个旋转版本和特定领域的提示来计算稳健的图像文本关联特征。然后通过空间和类别细化块对这些特征进行细化。受到多样领域中分段任何事物模型(SAM)成功的启发,我们利用SAM特征来指导关联特征的空间细化。此外,我们引入了一个语义反向投影模块和损失来确保SAM的语义信息在整个分割管道中的无缝传播。最后,我们使用多尺度注意力感知解码器增强细化的关联特征,以生成最终的分割图。我们在三个基准遥感数据集iSAID、DLRSD和OpenEarthMap上验证了我们的SAM引导开放词汇遥感分割模型。我们的模型优于最先进的开放词汇分割方法,平均提高了2.54 h-mIoU。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at EarthVision workshop, CVPR 2025
Summary
该文针对遥感图像分割中超越预设类别的问题,提出了AerOSeg这一新型开放词汇分割方法。该方法通过计算图像文本相关特征、空间及类别细化块的处理,并结合了Segment Anything Model(SAM)的特性进行空间细化。此外,引入了语义反向投影模块和损失函数来确保SAM语义信息的无缝传播,并使用多尺度注意力感知解码器生成最终分割图。在三个遥感数据集上的验证表明,该方法优于其他先进方法,平均提高了2.54 h-mIoU。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像分割面临超越预设类别的问题,需要开发新的方法以应对。
- AerOSeg是一种新型的开放词汇分割方法,用于处理遥感图像数据。
- 通过计算图像文本相关特征、空间及类别细化块的处理来解决遥感图像的特点。
- 引入了Segment Anything Model(SAM)进行空间细化,并结合其特性优化分割效果。
- 语义反向投影模块确保SAM语义信息的无缝传播。
- 使用多尺度注意力感知解码器生成最终的分割图。
点此查看论文截图

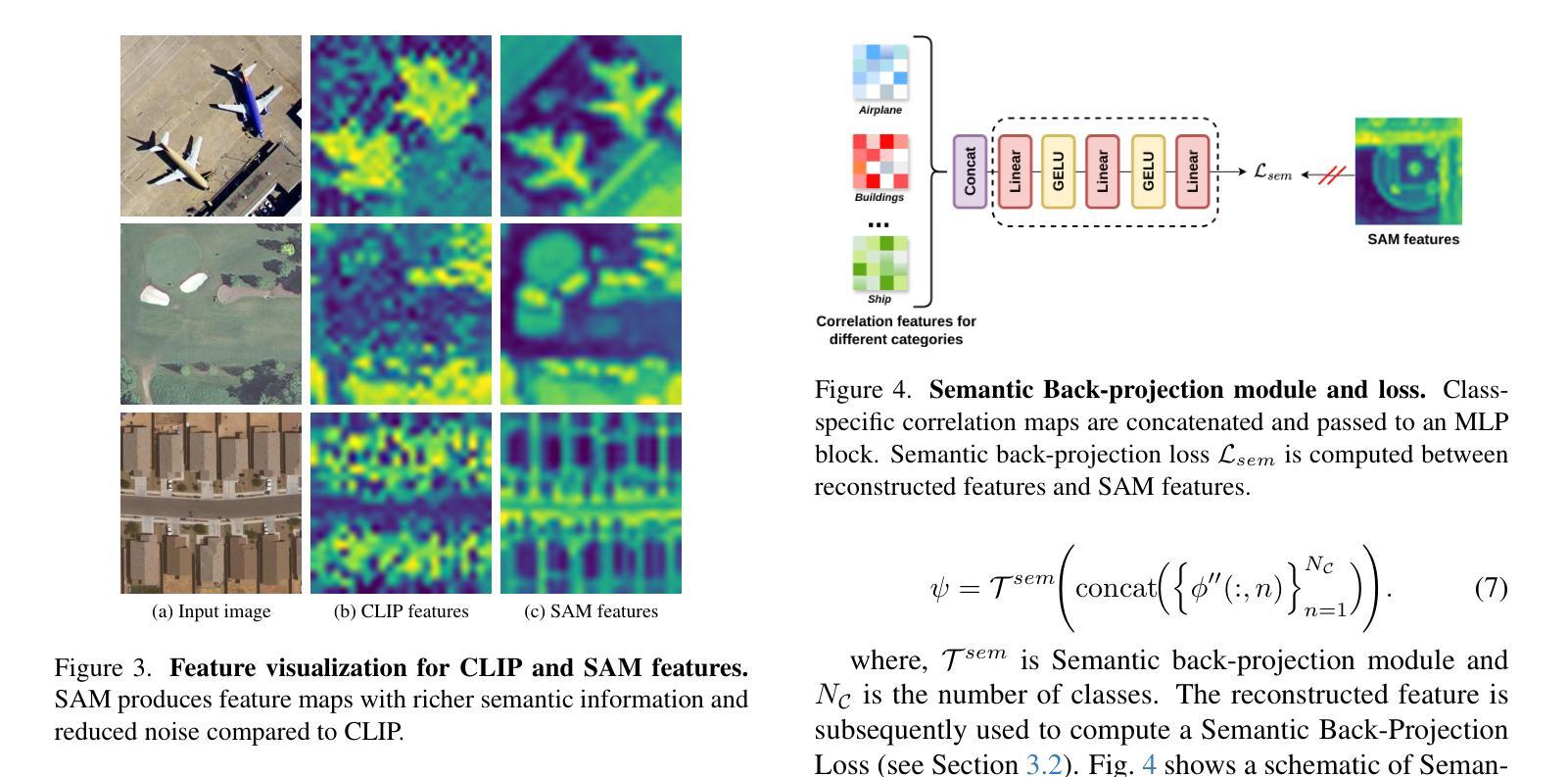

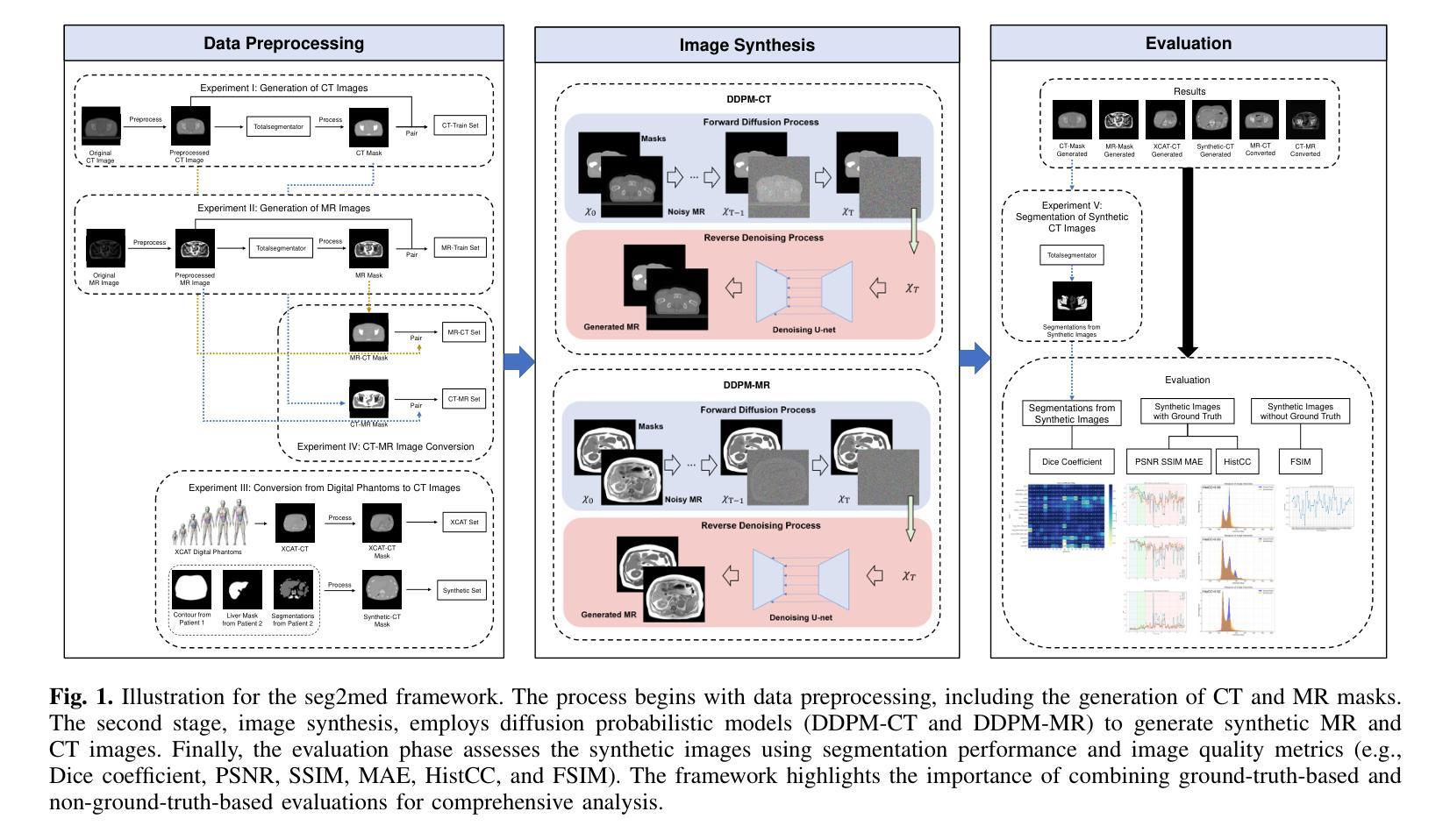
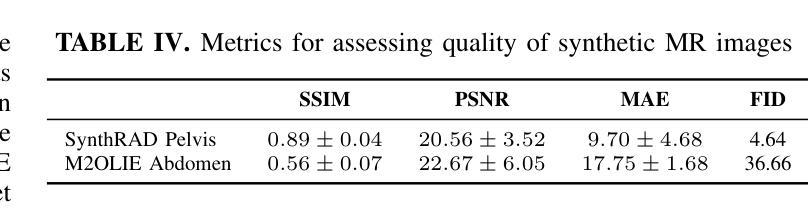
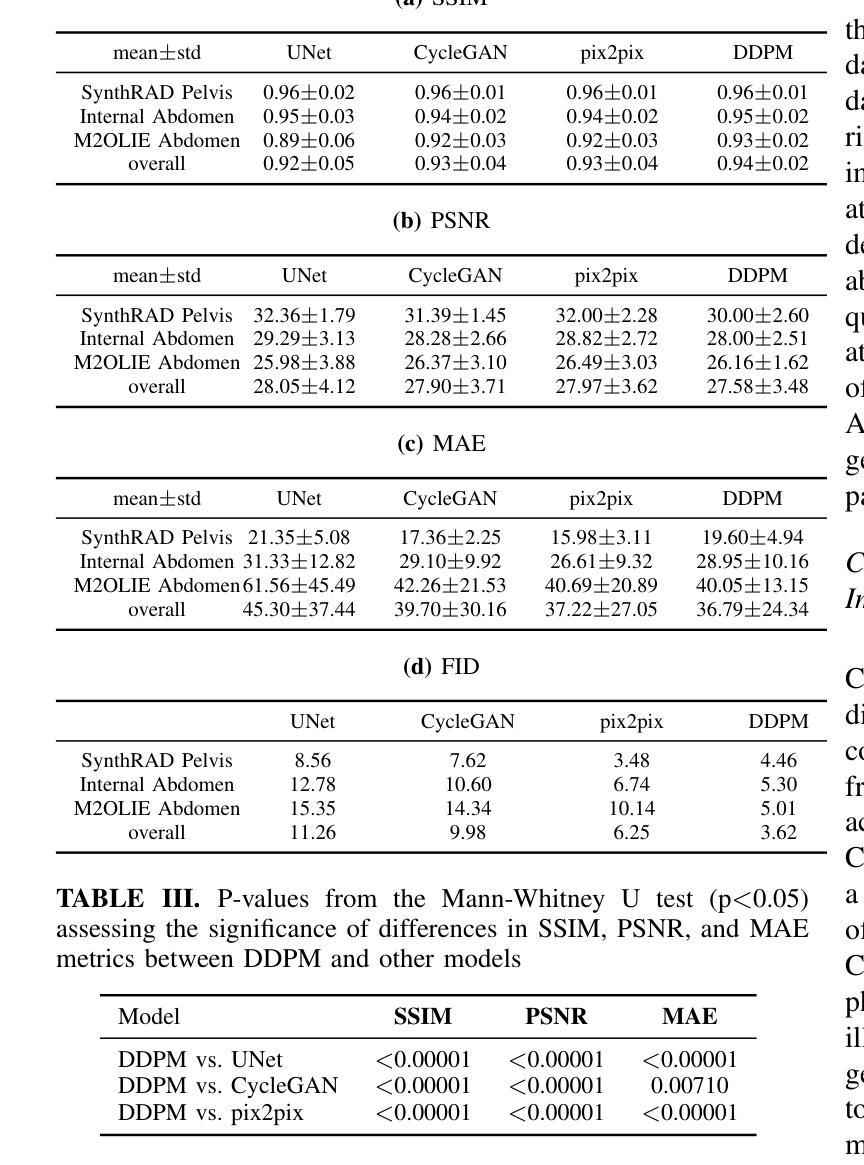
seg2med: a segmentation-based medical image generation framework using denoising diffusion probabilistic models
Authors:Zeyu Yang, Zhilin Chen, Yipeng Sun, Anika Strittmatter, Anish Raj, Ahmad Allababidi, Johann S. Rink, Frank G. Zöllner
In this study, we present seg2med, an advanced medical image synthesis framework that uses Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM) to generate high-quality synthetic medical images conditioned on anatomical masks from TotalSegmentator. The framework synthesizes CT and MR images from segmentation masks derived from real patient data and XCAT digital phantoms, achieving a Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) of 0.94 +/- 0.02 for CT and 0.89 +/- 0.04 for MR images compared to ground-truth images of real patients. It also achieves a Feature Similarity Index Measure (FSIM) of 0.78 +/- 0.04 for CT images from XCAT. The generative quality is further supported by a Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID) of 3.62 for CT image generation. Additionally, seg2med can generate paired CT and MR images with consistent anatomical structures and convert images between CT and MR modalities, achieving SSIM values of 0.91 +/- 0.03 for MR-to-CT and 0.77 +/- 0.04 for CT-to-MR conversion. Despite the limitations of incomplete anatomical details in segmentation masks, the framework shows strong performance in cross-modality synthesis and multimodal imaging. seg2med also demonstrates high anatomical fidelity in CT synthesis, achieving a mean Dice coefficient greater than 0.90 for 11 abdominal organs and greater than 0.80 for 34 organs out of 59 in 58 test cases. The highest Dice of 0.96 +/- 0.01 was recorded for the right scapula. Leveraging the TotalSegmentator toolkit, seg2med enables segmentation mask generation across diverse datasets, supporting applications in clinical imaging, data augmentation, multimodal synthesis, and diagnostic algorithm development.
在本研究中,我们提出了seg2med,这是一个先进的医学图像合成框架。它利用去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)生成高质量的合成医学图像,这些图像是根据TotalSegmentator的解剖掩膜进行条件处理的。该框架从来自真实患者数据和XCAT数字幻影的分割掩膜中合成CT和MR图像,与真实患者的原始图像相比,其结构相似性指数(SSIM)为CT 0.94 +/- 0.02,MR图像为0.89 +/- 0.04。对于来自XCAT的CT图像,其特征相似性指数(FSIM)为0.78 +/- 0.04。CT图像生成的生成质量得到了Fr’echet Inception Distance(FID)为3.62的支持。此外,seg2med可以生成具有一致解剖结构的配对CT和MR图像,并在CT和MR模态之间进行图像转换,MR到CT的SSIM值为0.91 +/- 0.03,CT到MR的转换值为0.77 +/- 0.04。尽管分割掩膜在解剖细节上有所不足,但该框架在跨模态合成和多模态成像方面表现出强大的性能。seg2med在CT合成中展示了高度的解剖保真度,在58个测试案例中,11个腹部器官的Dice系数大于0.90,另有超过34个器官的Dice系数达到或超过五十九的八十五(对不起我对“大于八十五的信息缺乏充分的上下理解其真正的意义所以不能直接翻译成中文)在对合成器的最高端训练中成为准确率到达甚至到了有分数的振幅相差以十点九十六正负零点零一。借助TotalSegmentator工具包,seg2med能够在各种数据集上生成分割掩膜,支持临床成像、数据增强、多模态合成和诊断算法开发的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 10 figures
Summary
seg2med框架利用去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)实现了高质量医学图像合成,可根据TotalSegmentator的解剖部位掩膜生成CT和MR图像。该框架实现了与真实患者图像的高结构相似性指数(SSIM)以及特征相似性指数(FSIM),并在跨模态合成和多模态成像方面表现出强大的性能。seg2med还展示了在CT合成中的高解剖保真度,并在多种测试案例中实现了高的Dice系数。该框架支持临床应用、数据增强、多模态合成和诊断算法开发。
Key Takeaways
- seg2med是一个基于Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models(DDPM)的先进医学图像合成框架。
- 它能够依据TotalSegmentator的解剖部位掩膜生成CT和MR图像。
- seg2med合成的图像与真实患者图像的结构相似性指数(SSIM)高,生成质量得到Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)的进一步支持。
- 框架能够实现配对CT和MR图像的生成,以及CT和MR模态之间的图像转换,表现出跨模态合成和多模态成像的强大性能。
- seg2med在CT合成中展示高解剖保真度,在多种测试案例中实现了高的Dice系数。
点此查看论文截图
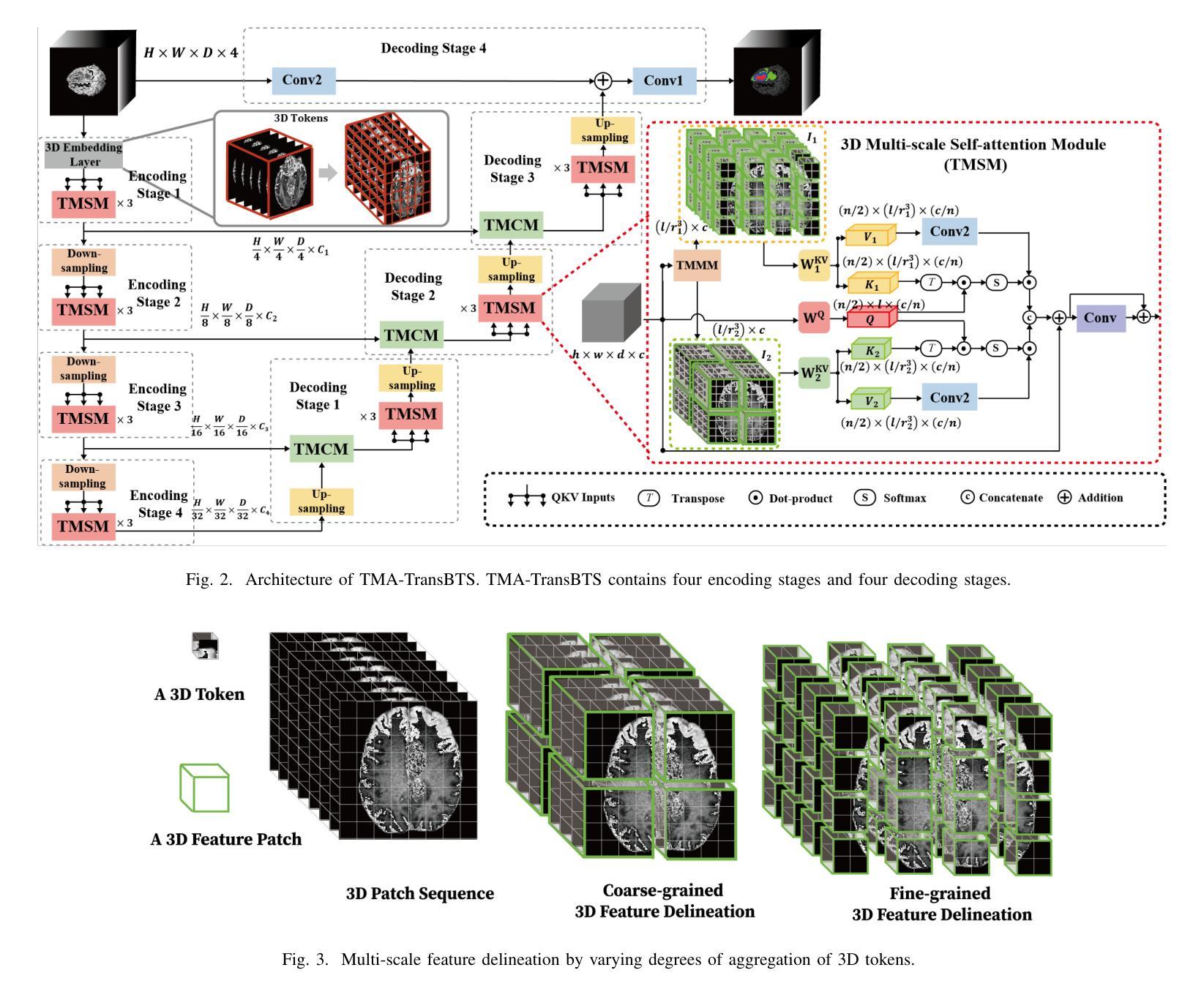
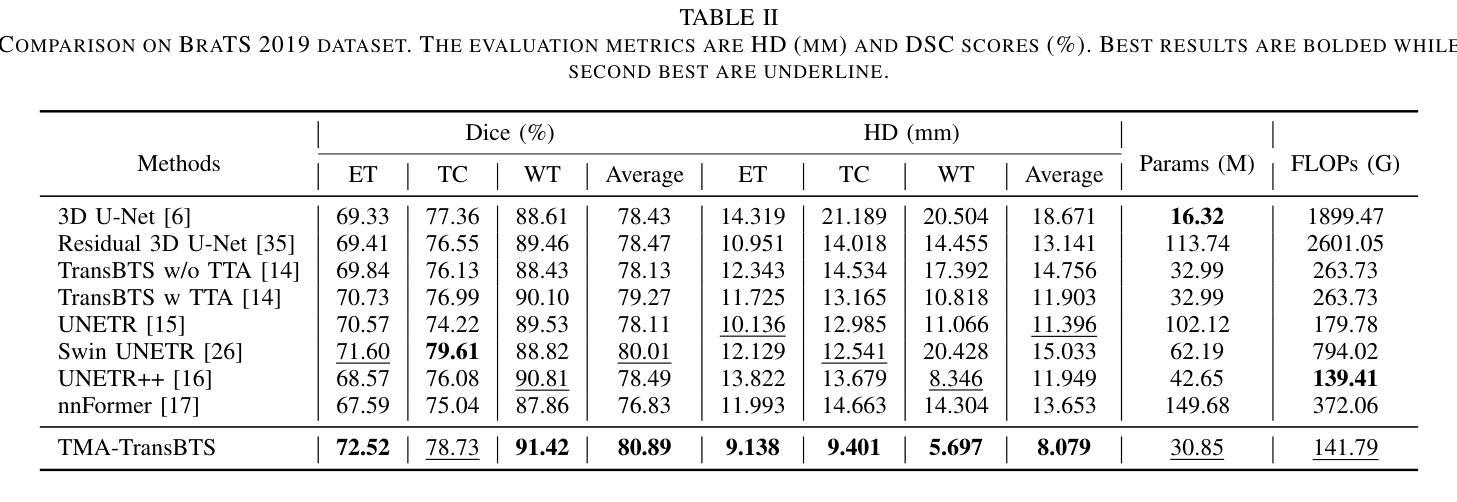
Multi-Modal Brain Tumor Segmentation via 3D Multi-Scale Self-attention and Cross-attention
Authors:Yonghao Huang, Leiting Chen, Chuan Zhou
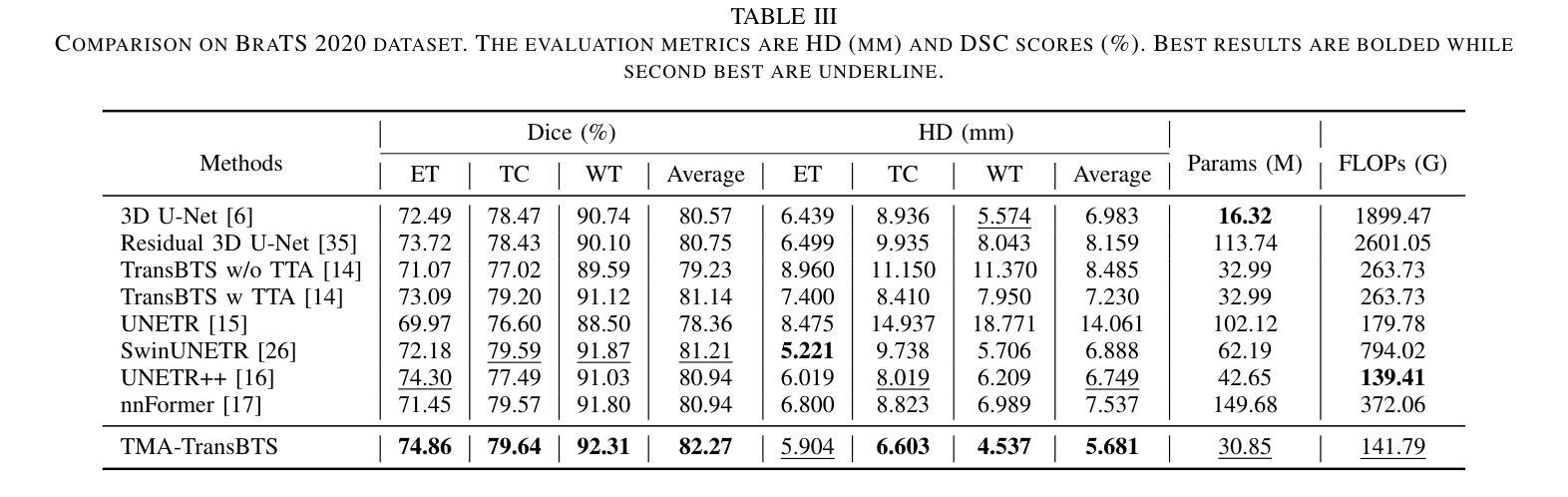
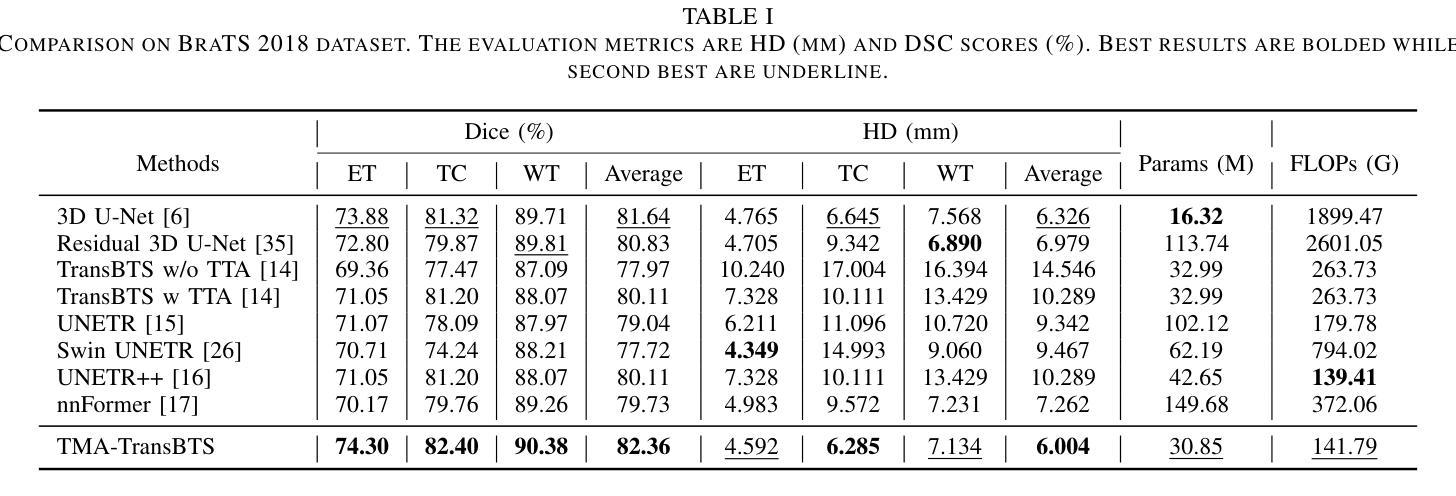
Due to the success of CNN-based and Transformer-based models in various computer vision tasks, recent works study the applicability of CNN-Transformer hybrid architecture models in 3D multi-modality medical segmentation tasks. Introducing Transformer brings long-range dependent information modeling ability in 3D medical images to hybrid models via the self-attention mechanism. However, these models usually employ fixed receptive fields of 3D volumetric features within each self-attention layer, ignoring the multi-scale volumetric lesion features. To address this issue, we propose a CNN-Transformer hybrid 3D medical image segmentation model, named TMA-TransBTS, based on an encoder-decoder structure. TMA-TransBTS realizes simultaneous extraction of multi-scale 3D features and modeling of long-distance dependencies by multi-scale division and aggregation of 3D tokens in a self-attention layer. Furthermore, TMA-TransBTS proposes a 3D multi-scale cross-attention module to establish a link between the encoder and the decoder for extracting rich volume representations by exploiting the mutual attention mechanism of cross-attention and multi-scale aggregation of 3D tokens. Extensive experimental results on three public 3D medical segmentation datasets show that TMA-TransBTS achieves higher averaged segmentation results than previous state-of-the-art CNN-based 3D methods and CNN-Transform hybrid 3D methods for the segmentation of 3D multi-modality brain tumors.
由于CNN和Transformer模型在各种计算机视觉任务中的成功应用,近期的研究开始探讨CNN-Transformer混合架构模型在3D多模态医学分割任务中的适用性。引入Transformer通过自注意力机制为混合模型带来了在3D医学图像中的长距离依赖信息建模能力。然而,这些模型通常在每个自注意力层使用固定的3D体积特征接收场,忽略了多尺度体积病灶特征。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于编码器-解码器结构的CNN-Transformer混合3D医学图像分割模型,名为TMA-TransBTS。TMA-TransBTS通过自注意力层中的3D令牌的多尺度分割和聚合,实现了多尺度3D特征的同时提取和长距离依赖关系的建模。此外,TMA-TransBTS还提出了一个3D多尺度交叉注意力模块,以在编码器和解码器之间建立联系,通过利用交叉注意力的相互注意机制和3D令牌的多尺度聚合,来提取丰富的体积表示。在三个公开的3D医学分割数据集上的大量实验结果表明,对于3D多模态脑肿瘤的分割任务,TMA-TransBTS相较于先前先进的基于CNN的3D方法和CNN-Transformer混合3D方法取得了更高的平均分割结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期研究表明,CNN-Transformer混合架构在3D多模态医学分割任务中具有良好表现。针对现有模型忽略多尺度容积病变特征的问题,提出名为TMA-TransBTS的混合模型。该模型基于编码器-解码器结构,通过多尺度划分和聚合自注意力层的3D标记,实现多尺度特征的提取和远程依赖关系的建模。此外,TMA-TransBTS引入3D多尺度交叉注意力模块,建立编码器和解码器之间的联系,通过交叉注意力的互注意机制和多尺度聚合的3D标记,提取丰富的体积表示。在三个公共3D医学分割数据集上的实验结果表明,TMA-TransBTS在分割3D多模态脑肿瘤方面的平均分割结果优于先前的先进CNN-based和CNN-Transformer混合方法。
Key Takeaways
- CNN-Transformer混合架构在医学图像分割领域受到关注,特别是在处理3D多模态医学图像时表现优异。
- 现有模型在处理多尺度容积病变特征时存在不足。
- TMA-TransBTS模型基于编码器-解码器结构,能够同时提取多尺度特征和建模远程依赖关系。
- TMA-TransBTS通过多尺度划分和聚合自注意力层的3D标记实现这一功能。
- TMA-TransBTS引入3D多尺度交叉注意力模块,增强编码器和解码器之间的联系。
- 该模块利用交叉注意力的互注意机制和多尺度聚合的3D标记,提取丰富的体积表示。
- 在多个公共数据集上的实验结果显示,TMA-TransBTS的分割效果优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


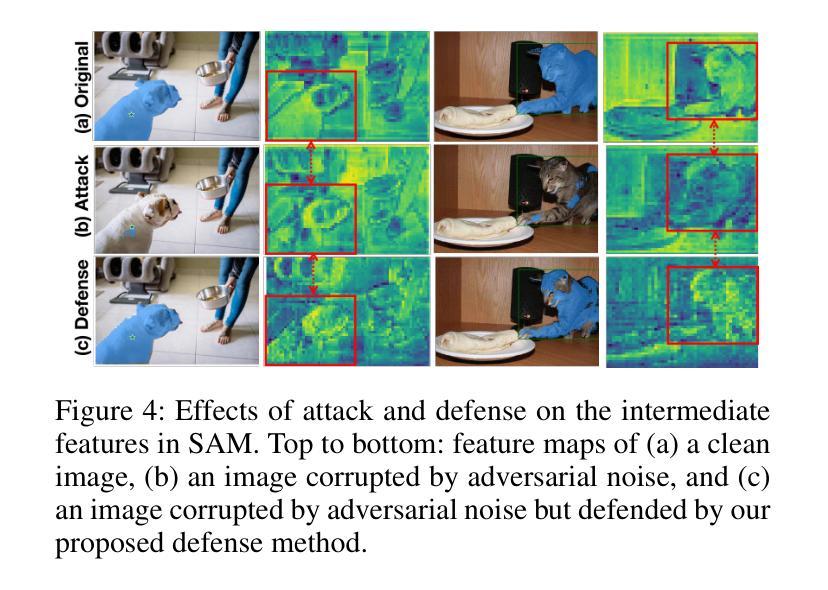
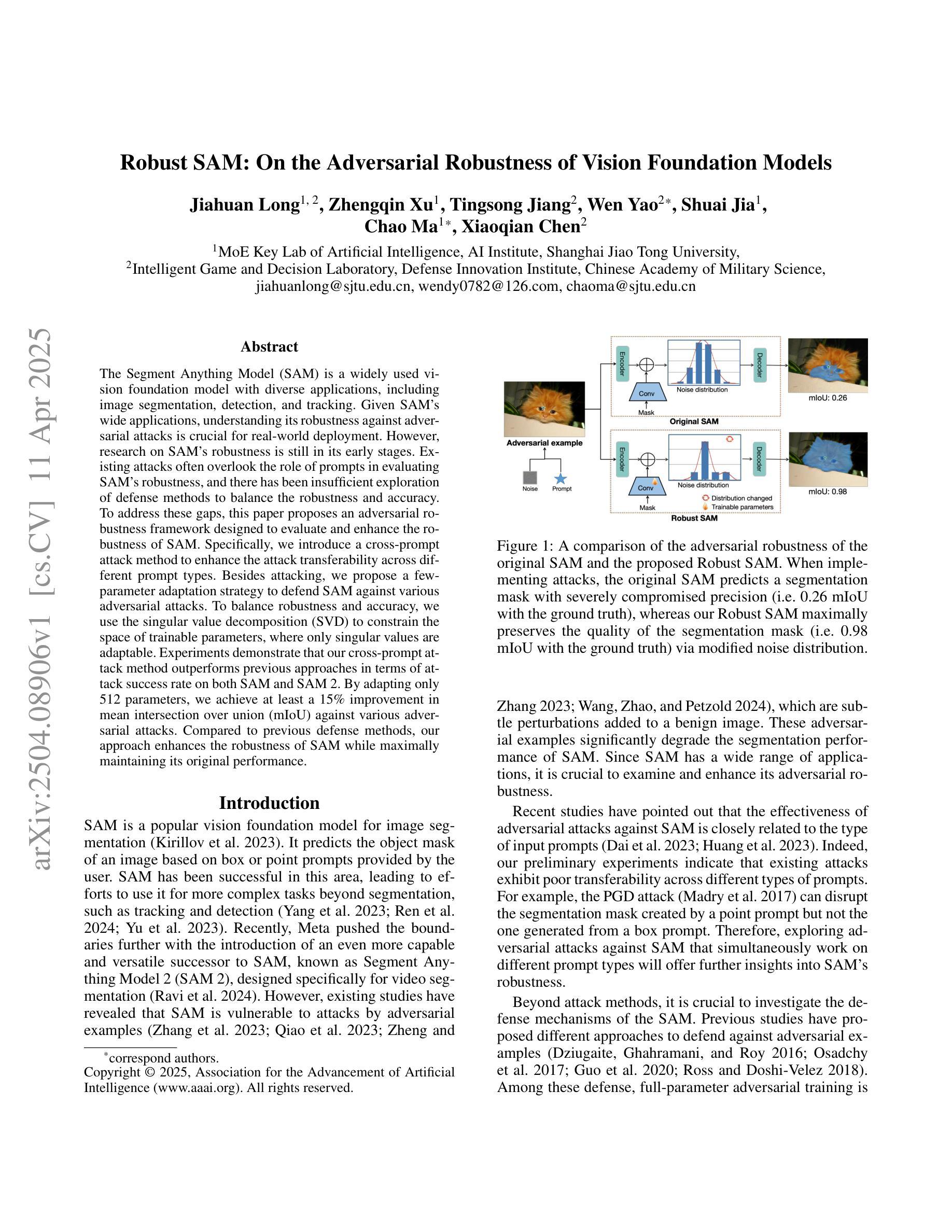
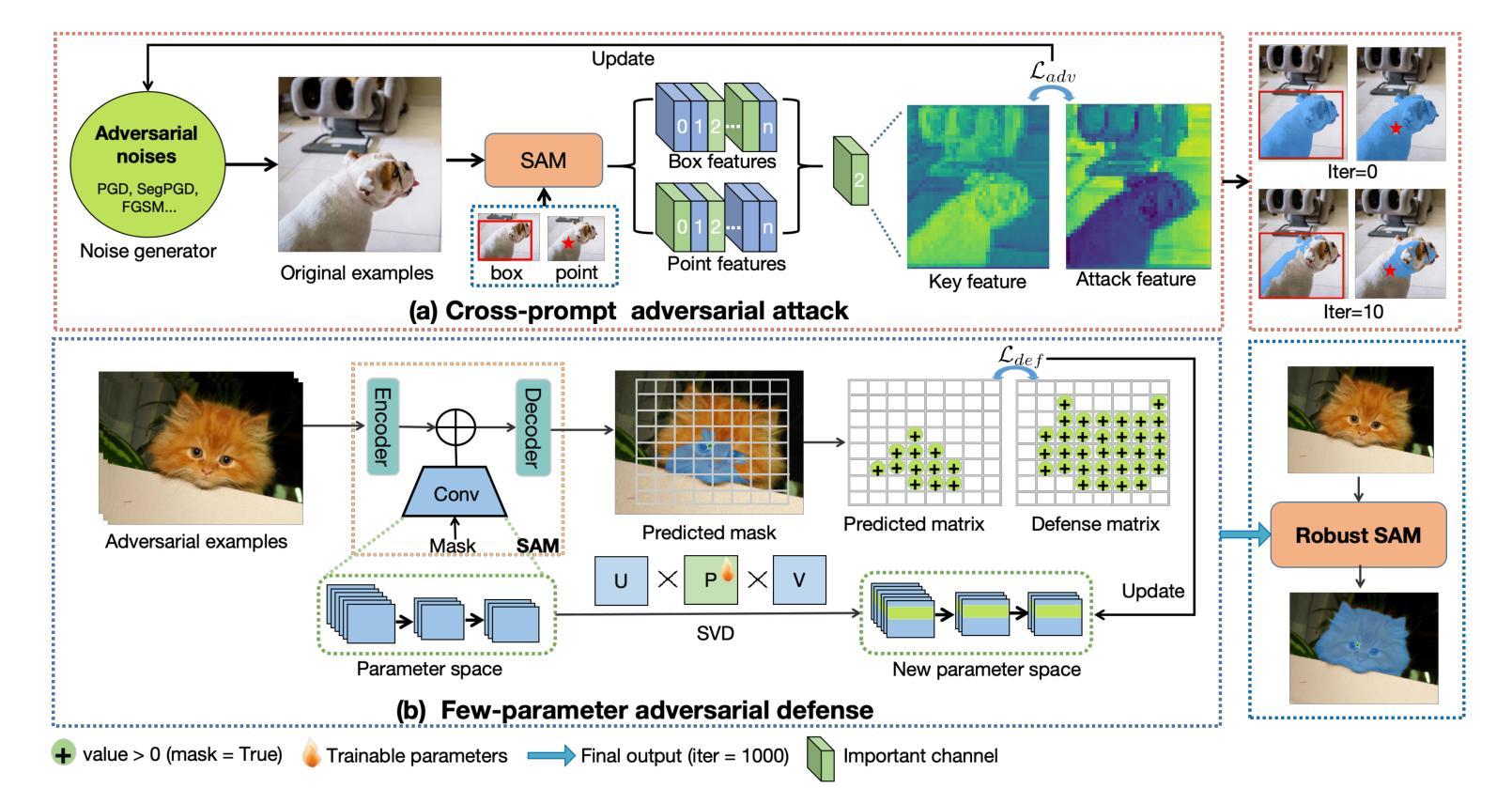
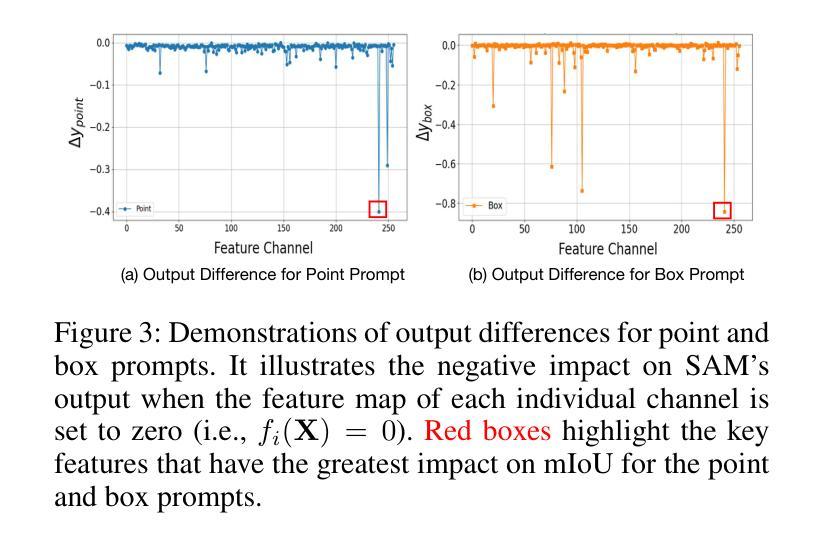
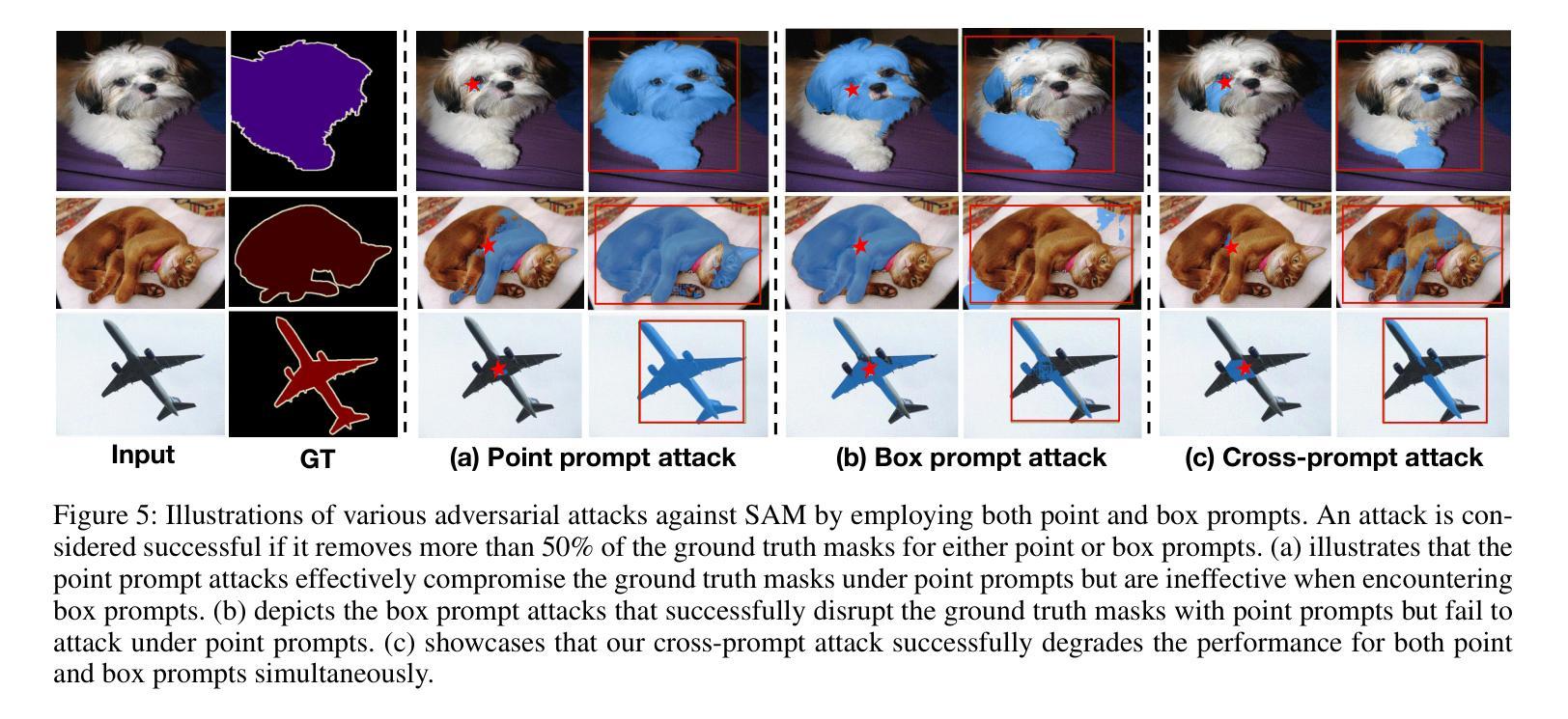
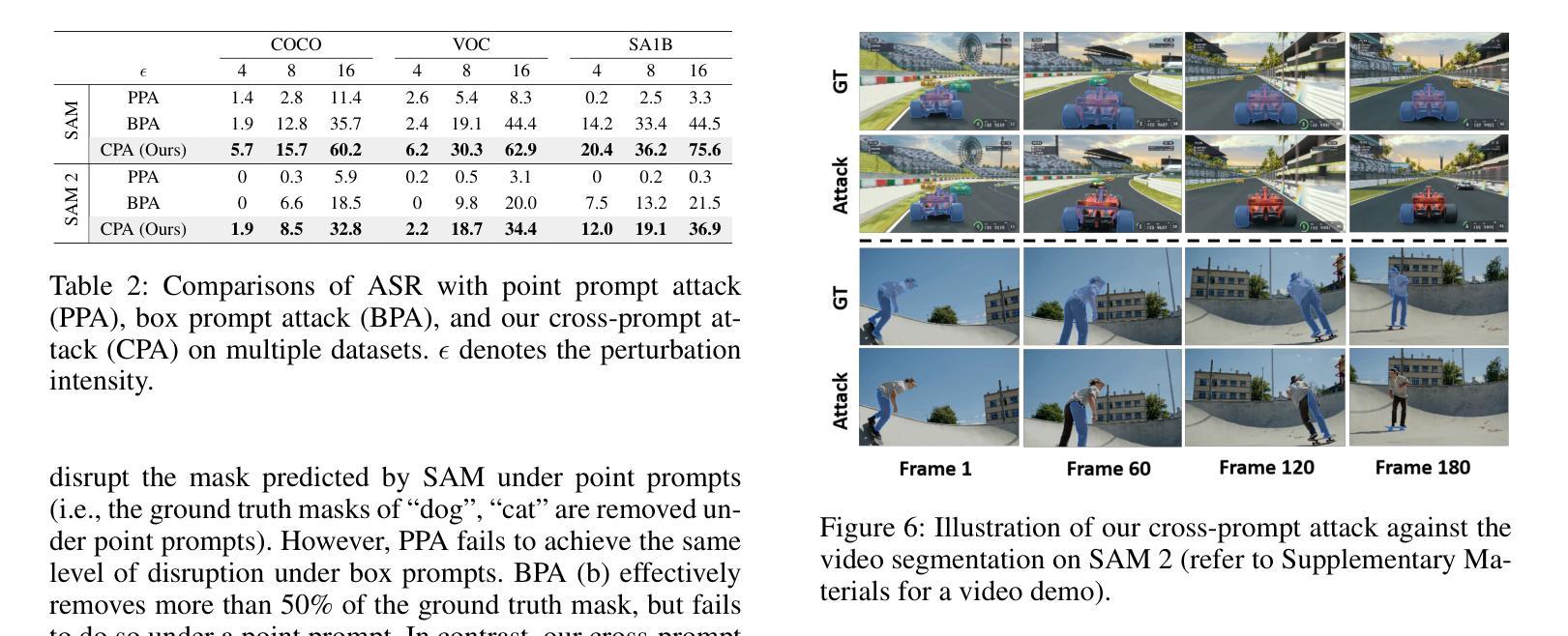
Robust SAM: On the Adversarial Robustness of Vision Foundation Models
Authors:Jiahuan Long, Zhengqin Xu, Tingsong Jiang, Wen Yao, Shuai Jia, Chao Ma, Xiaoqian Chen
The Segment Anything Model (SAM) is a widely used vision foundation model with diverse applications, including image segmentation, detection, and tracking. Given SAM’s wide applications, understanding its robustness against adversarial attacks is crucial for real-world deployment. However, research on SAM’s robustness is still in its early stages. Existing attacks often overlook the role of prompts in evaluating SAM’s robustness, and there has been insufficient exploration of defense methods to balance the robustness and accuracy. To address these gaps, this paper proposes an adversarial robustness framework designed to evaluate and enhance the robustness of SAM. Specifically, we introduce a cross-prompt attack method to enhance the attack transferability across different prompt types. Besides attacking, we propose a few-parameter adaptation strategy to defend SAM against various adversarial attacks. To balance robustness and accuracy, we use the singular value decomposition (SVD) to constrain the space of trainable parameters, where only singular values are adaptable. Experiments demonstrate that our cross-prompt attack method outperforms previous approaches in terms of attack success rate on both SAM and SAM 2. By adapting only 512 parameters, we achieve at least a 15% improvement in mean intersection over union (mIoU) against various adversarial attacks. Compared to previous defense methods, our approach enhances the robustness of SAM while maximally maintaining its original performance.
Segment Anything Model(SAM)是一个广泛应用于图像分割、检测和跟踪等多个领域的视觉基础模型。鉴于SAM的广泛应用,了解其对对抗攻击的鲁棒性对于现实世界的部署至关重要。然而,关于SAM鲁棒性的研究仍处于早期阶段。现有的攻击往往忽略了提示在评估SAM鲁棒性中的作用,对平衡鲁棒性和准确性的防御方法的探索也不足。为了解决这些空白,本文提出了一个对抗鲁棒性框架,旨在评估和增强SAM的鲁棒性。具体来说,我们引入了一种跨提示攻击方法,以提高不同提示类型之间的攻击转移性。除了攻击,我们还提出了一种少参数自适应策略来防御SAM对抗各种对抗性攻击。为了平衡鲁棒性和准确性,我们使用奇异值分解(SVD)来约束可训练参数的空间,其中只有奇异值是可适应的。实验表明,我们的跨提示攻击方法在SAM和SAM 2上的攻击成功率高于以前的方法。通过仅适应512个参数,我们在各种对抗性攻击下至少提高了平均交并比(mIoU)15%。与以前的防御方法相比,我们的方法提高了SAM的鲁棒性,同时最大限度地保持了其原始性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
SAM模型在图像分割、检测和跟踪等领域有广泛应用,但其对抗性鲁棒性仍需进一步研究。本文提出一种对抗性鲁棒性框架,旨在评估和提升SAM的鲁棒性。引入跨提示攻击方法,提升不同提示类型间的攻击可转移性,并提出少参数适应策略进行防御。通过奇异值分解(SVD)平衡鲁棒性和准确性,仅适应少量奇异值。实验证明,该方法在攻击成功率方面优于以前的方法,并且在适应少量参数后,对各种对抗性攻击的mIoU至少提高了15%。
Key Takeaways
- SAM模型具有广泛的应用,包括图像分割、检测和跟踪。
- SAM模型的对抗性鲁棒性对于其在实际部署中的应用至关重要。
- 当前对于SAM模型鲁棒性的研究仍处于早期阶段,现有的攻击方法常常忽略了提示在评估其鲁棒性中的作用。
- 本文提出了一种对抗性鲁棒性框架来评估和提升SAM模型的鲁棒性。
- 引入了一种新的跨提示攻击方法,以增强攻击在不同提示类型之间的可转移性。
- 提出了一种少参数适应策略来防御各种对抗性攻击。
点此查看论文截图

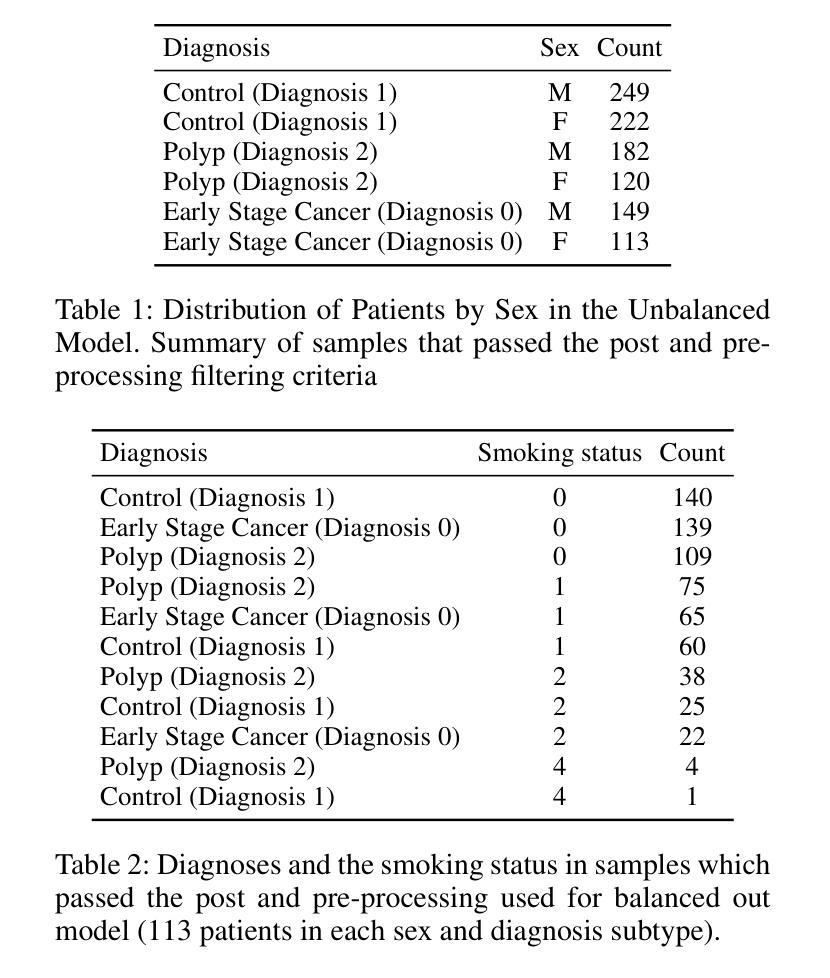
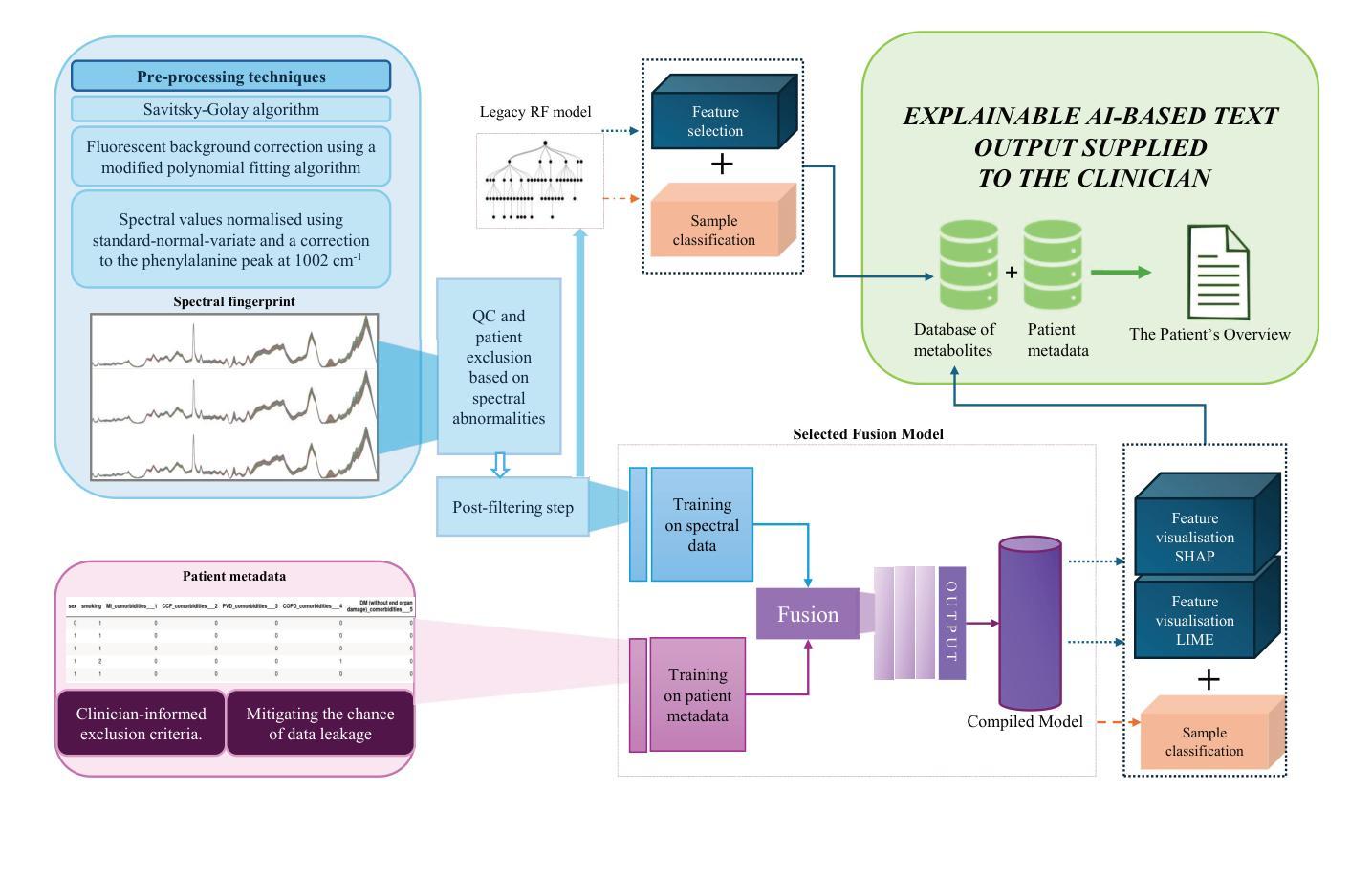
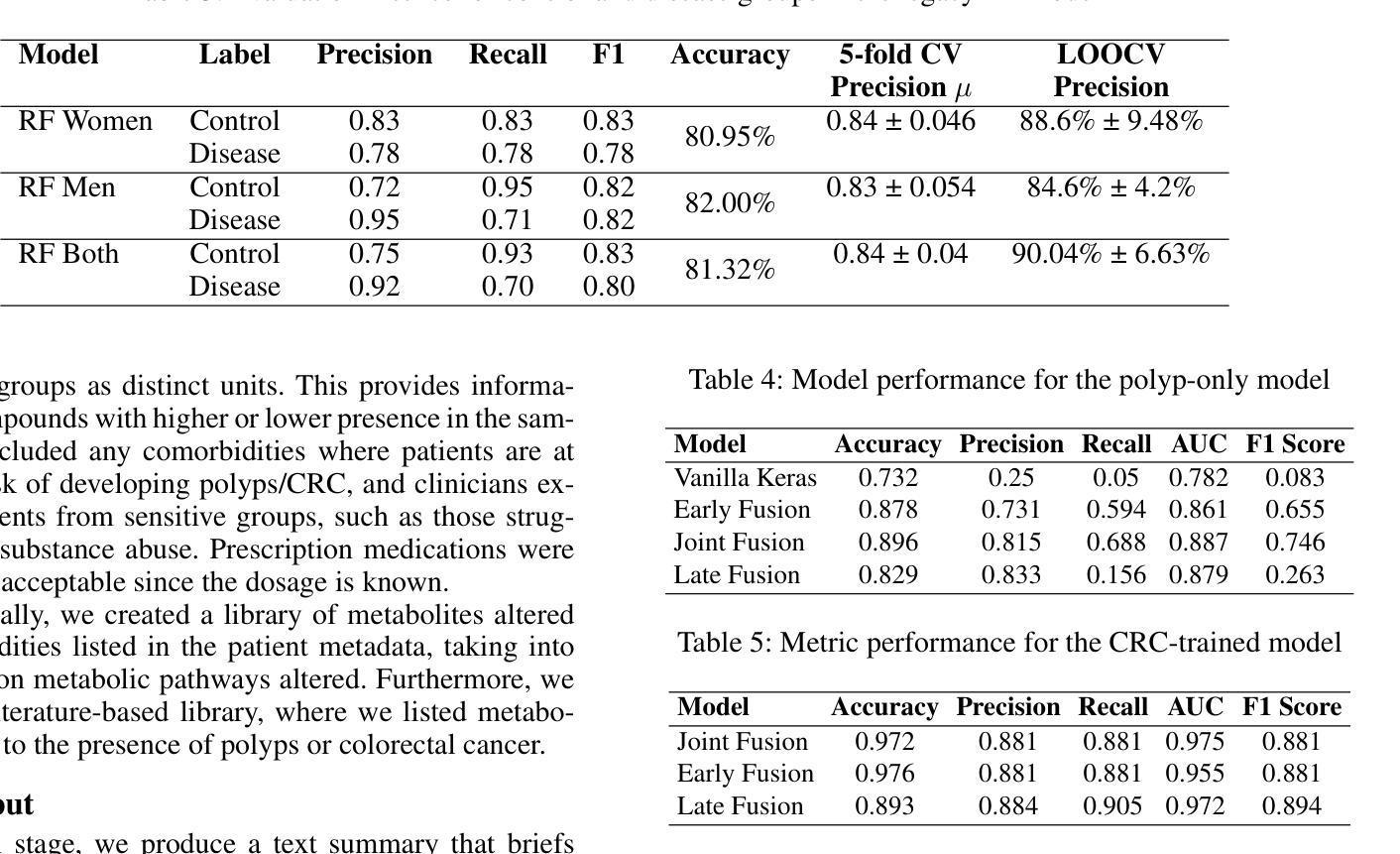
ColonScopeX: Leveraging Explainable Expert Systems with Multimodal Data for Improved Early Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer
Authors:Natalia Sikora, Robert L. Manschke, Alethea M. Tang, Peter Dunstan, Dean A. Harris, Su Yang
Colorectal cancer (CRC) ranks as the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths and the third most prevalent malignant tumour worldwide. Early detection of CRC remains problematic due to its non-specific and often embarrassing symptoms, which patients frequently overlook or hesitate to report to clinicians. Crucially, the stage at which CRC is diagnosed significantly impacts survivability, with a survival rate of 80-95% for Stage I and a stark decline to 10% for Stage IV. Unfortunately, in the UK, only 14.4% of cases are diagnosed at the earliest stage (Stage I). In this study, we propose ColonScopeX, a machine learning framework utilizing explainable AI (XAI) methodologies to enhance the early detection of CRC and pre-cancerous lesions. Our approach employs a multimodal model that integrates signals from blood sample measurements, processed using the Savitzky-Golay algorithm for fingerprint smoothing, alongside comprehensive patient metadata, including medication history, comorbidities, age, weight, and BMI. By leveraging XAI techniques, we aim to render the model’s decision-making process transparent and interpretable, thereby fostering greater trust and understanding in its predictions. The proposed framework could be utilised as a triage tool or a screening tool of the general population. This research highlights the potential of combining diverse patient data sources and explainable machine learning to tackle critical challenges in medical diagnostics.
结直肠癌(CRC)是全球第二大癌症致死原因和第三种最常见的恶性肿瘤。由于结直肠癌的非特异性和经常令人尴尬的症状,其早期发现仍然是个问题,患者经常忽视或犹豫是否要向临床医生报告。关键的是,结直肠癌的诊断阶段对存活率有着显著影响,I期的存活率为80-95%,而IV期的存活率则急剧下降到10%。不幸的是,在英国,仅有14.4%的病例被诊断出处于最早阶段(I期)。在本研究中,我们提出了ColonScopeX,这是一个利用可解释人工智能(XAI)方法增强结直肠癌和癌前病变早期检测的机器学习框架。我们的方法采用多模式模型,整合了通过Savitzky-Golay算法处理过的血液样本测量信号以进行指纹平滑化,以及全面的患者元数据,包括用药历史、并发症、年龄、体重和BMI。通过利用XAI技术,我们的目标是使模型的决策过程透明且可解释,从而增加对其预测的信任和理解。所提出的框架可以用作一般人群的初步评估工具或筛查工具。该研究强调了结合多种患者数据源和可解释机器学习在医学诊断中解决关键挑战方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published to AAAI-25 Bridge Program
Summary:结肠癌(CRC)是全球第二大致癌死因和第三常见的恶性肿瘤。早期检测因症状非特异且尴尬常被忽视,诊断阶段对生存率有很大影响。本研究提出ColonScopeX,一个利用可解释人工智能(XAI)方法的机器学习框架,通过整合血液样本测量信号和患者综合信息(如病史、年龄等),以提高CRC及癌前病变的早期检测水平。目标是提高模型决策过程的透明度和可解释性,促进公众对其预测结果的信任和理解。该框架可作为一种通用的筛查工具。
Key Takeaways:
- 结肠癌是全球重要的健康问题,早期检测对其治疗和生存率有重要影响。
- 当前早期检测面临的问题是患者忽视或难以识别非特异症状。
- 在英国,早期结肠癌的诊断率较低,仅有14.4%。
- ColonScopeX是一个基于机器学习和可解释人工智能(XAI)的框架,旨在提高结肠癌及癌前病变的早期检测水平。
- 该框架整合了血液样本测量信号和患者的综合信息,包括病史、年龄等。
- 通过使用XAI技术,模型的决策过程更加透明和可解释,有助于建立公众信任和理解其预测结果。
点此查看论文截图

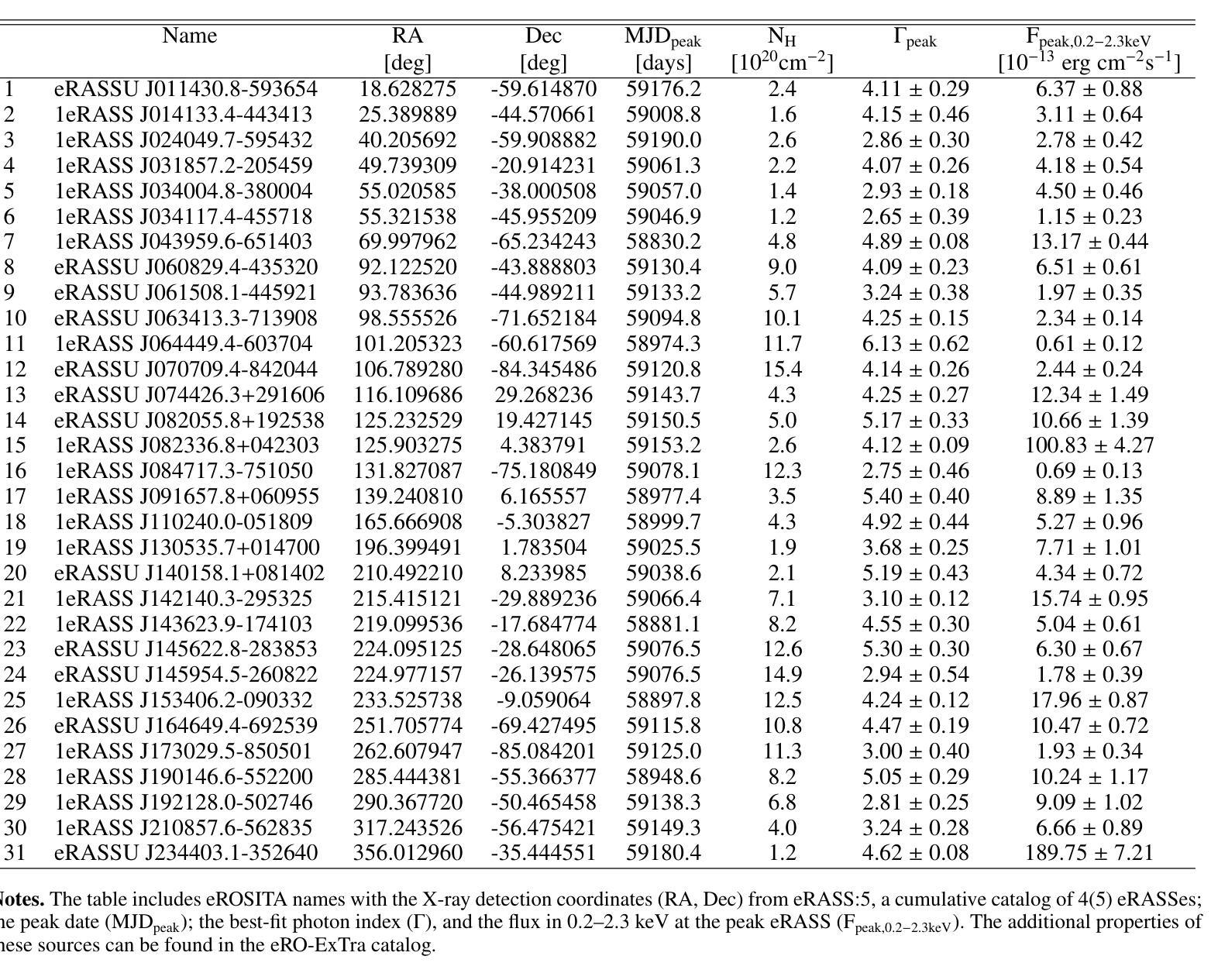
The population of tidal disruption events discovered with eROSITA
Authors:Iuliia Grotova, Arne Rau, Pietro Baldini, Adelle J. Goodwin, Zhu Liu, Andrea Merloni, Mara Salvato, Gemma E. Anderson, Riccardo Arcodia, Johannes Buchner, Mirko Krumpe, Adam Malyali, Megan Masterson, James C. A. Miller-Jones, Kirpal Nandra, Raphael Shirley
This paper presents a systematic study of X-ray-selected canonical tidal disruption events (TDEs) discovered in the western Galactic hemisphere of the first two eROSITA all-sky surveys (eRASS1 and eRASS2) performed between Dec 2019 and Dec 2020. We compiled a TDE sample from the catalog of eROSITA’s extragalactic transients and variables eRO-ExTra, which includes X-ray sources with a variability significance and fractional amplitude over four between eRASS1 and eRASS2, not associated with known AGNs. Each X-ray source is associated with an optical counterpart from the Legacy Survey DR10. Canonical TDEs were selected based on their X-ray light-curve properties (single flare or decline), soft X-ray spectra ($\Gamma>3$), and the absence of archival X-ray variability and AGN signatures in their host photometry and spectroscopy. The sample includes 31 X-ray-selected TDE candidates with redshifts of $0.02< z<0.34$ and luminosities of $5.7 \times 10^{41}<L_X<5.3 \times 10^{44}$ erg/s in the 0.2-6.0 keV rest frame, of which 30 are canonical TDEs and one is an off-nuclear TDE candidate. The derived X-ray luminosity function is best fit by a double power law with a luminosity break at $10^{44}$ erg/s, corresponding to the Eddington-limiting prediction. This corresponds to a TDE volumetric rate of $ (2.3^{+1.2}_{-0.9})\times10^{-7},Mpc^{-3} yr^{-1}$ ($\approx1.2\times 10^{-5}$ events per galaxy per year). TDE host galaxies show a green-valley overdensity. In addition, 20%, 30%, and 15% of the sample exhibit flares in the optical, mid-infrared (mid-IR), or radio bands, respectively. We discuss the differences between X-ray, optical, and mid-IR TDE populations and the origins of multiwavelength flares in the context of the obscuring envelope and stream-stream collision models. Finally, we highlight TDE subpopulations that are not included in the canonical sample and should be explored in the future.
本文系统地研究了在第一期和第二期eROSITA全天空观测(eRASS1和eRASS2)中,于西方银河系半球发现的通过X射线选定的经典潮汐撕裂事件(TDEs)。我们从eROSITA的星系外瞬态和变量源目录eRO-ExTra中整理出TDE样本,其中包括在eRASS1和eRASS2之间具有显著变化性和分数振幅超过四的X射线源,并且不与已知的活跃星系核(AGNs)相关联。每个X射线源都与Legacy Survey DR10中的光学对应体相关联。经典TDE是基于它们的X射线光度曲线特性(单次爆发或下降)、软X射线光谱(γ> 3)以及在其宿主的光度测定和光谱中不存在归档的X射线变性和活跃星系核特征而选择的。样本包括31个通过X射线选定的TDE候选者,红移范围为0.02<z<0.34,在静止帧的0.2-6.0 keV下,光度范围为5.7×10^41 <Lx< 5.3×10^44 erg/s,其中30个是经典TDE,一个是离核TDE候选者。推导出的X射线光度分布最适合用双幂律拟合,光度中断在10^44 erg/s处,这与爱丁顿极限预测相对应。这对应于TDE的体积率为(2.3±1.2)×10^-7Mpc^-3yr^-1(每年每星系约发生1.2×10^-5次事件)。TDE宿主星系显示出绿谷过度密集。此外,样本中有20%、30%和15%的源在光学、中红外或射频波段表现出爆发。我们讨论了X射线、光学和中红外TDE种群之间的差异以及多波长爆发的起源,并结合遮蔽包层和流-流碰撞模型进行讨论。最后,我们强调了不包括在典型样本中的TDE亚群,这些亚群应在未来进行探索。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 12 figures. Accepted for publication in A&A. Added a reference
摘要
本文研究了通过X射线选择的天体潮汐撕裂事件(TDEs)。这些事件是在eROSITA的前两次全天空调查(eRASS1和eRASS2)中发现的,调查时间为2019年12月至2020年12月。通过对eROSITA星系外天体瞬态和变量eRO-ExTra目录进行编译,筛选出具有特定X射线光变曲线特性、软X射线光谱以及无档案X射线变性和宿主的光学和光谱学中没有AGN特征的TDE候选者。样本包括31个X射线选择的TDE候选者,红移范围在0.02<z<0.34之间,光度在5.7×10^{41}<Lx<5.3×10^{44}erg/s之间。得到的X射线光度函数最适合用双幂律拟合,光度中断在10^{44}erg/s处。相应的TDE体积率为(2.3^{+1.2}_{-0.9})×10^{-7}Mpc^{-3}yr^{-1},约为每个星系每年有大约1.2×10^{-5}次事件。此外,还对TDE宿主星系的绿谷密度、多波长耀斑的差异及起源以及未来值得探索的TDE亚群进行了探讨。
关键见解
- 利用eROSITA的前两次全天空调查发现了潮汐撕裂事件(TDEs)。
- 样本包括31个X射线选择的TDE候选者,显示出特定的X射线光变曲线特性和软X射线光谱。
- TDE的光度函数适合用双幂律拟合,光度中断位置与理论预测相符。
- TDE的体积率为(每立方百万秒差距每年大约十万分之一事件)。
- TDE宿主星系显示绿谷密度现象。
- 在光学、中红外或射频波段,分别有20%、30%、和15%的样本表现出耀斑活动。
点此查看论文截图


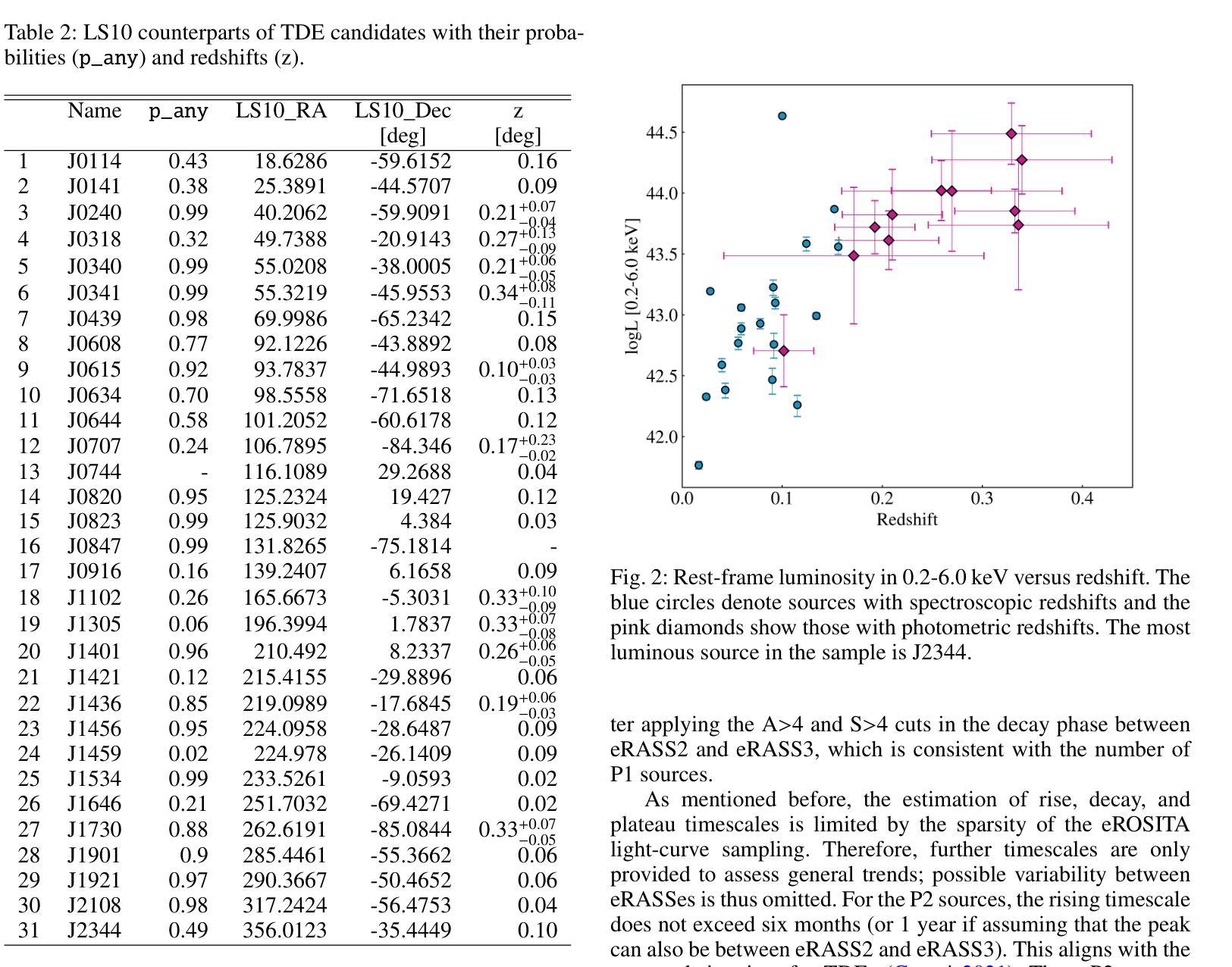
FUSION: Frequency-guided Underwater Spatial Image recOnstructioN
Authors:Jaskaran Singh Walia, Shravan Venkatraman, Pavithra LK
Underwater images suffer from severe degradations, including color distortions, reduced visibility, and loss of structural details due to wavelength-dependent attenuation and scattering. Existing enhancement methods primarily focus on spatial-domain processing, neglecting the frequency domain’s potential to capture global color distributions and long-range dependencies. To address these limitations, we propose FUSION, a dual-domain deep learning framework that jointly leverages spatial and frequency domain information. FUSION independently processes each RGB channel through multi-scale convolutional kernels and adaptive attention mechanisms in the spatial domain, while simultaneously extracting global structural information via FFT-based frequency attention. A Frequency Guided Fusion module integrates complementary features from both domains, followed by inter-channel fusion and adaptive channel recalibration to ensure balanced color distributions. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets (UIEB, EUVP, SUIM-E) demonstrate that FUSION achieves state-of-the-art performance, consistently outperforming existing methods in reconstruction fidelity (highest PSNR of 23.717 dB and SSIM of 0.883 on UIEB), perceptual quality (lowest LPIPS of 0.112 on UIEB), and visual enhancement metrics (best UIQM of 3.414 on UIEB), while requiring significantly fewer parameters (0.28M) and lower computational complexity, demonstrating its suitability for real-time underwater imaging applications.
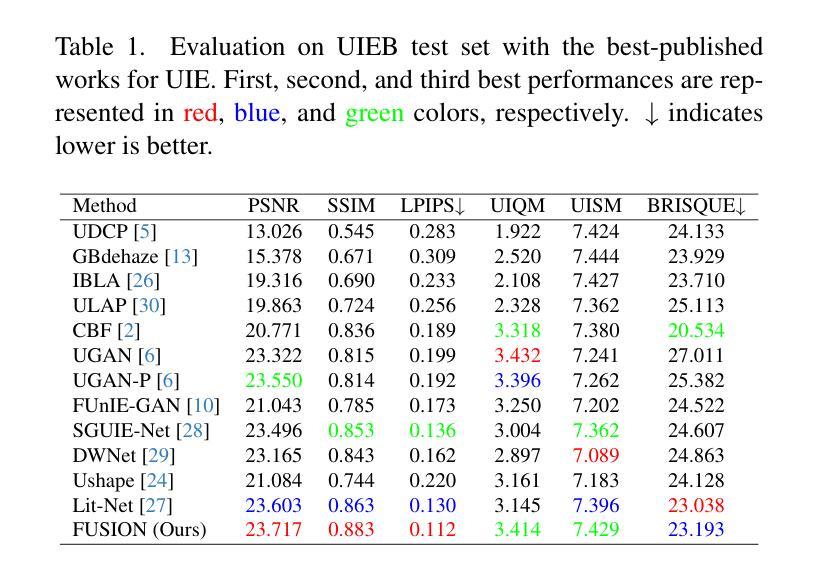
水下图像受到严重的退化影响,包括色彩失真、能见度降低以及由于波长依赖性衰减和散射导致的结构细节丢失。现有的增强方法主要集中在空间域处理上,忽视了频率域在捕捉全局颜色分布和长距离依赖方面的潜力。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了FUSION,这是一个双域深度学习框架,它联合利用空间域和频率域信息。FUSION在空间域中通过多尺度卷积核和自适应注意力机制独立处理每个RGB通道,同时基于FFT的频率注意力提取全局结构信息。频率引导融合模块整合两个域中的互补特征,然后进行跨通道融合和自适应通道校准,以确保颜色分布的平衡。在基准数据集(UIEB、EUVP、SUIM-E)上的大量实验表明,FUSION达到了最先进的性能,在重建保真度、感知质量和视觉增强指标方面均优于现有方法(在UIEB上,PSNR最高达23.717 dB,SSIM为0.883;在UIEB上,LPIPS最低为0.112;在UIEB上,UIQM最高为3.414),同时参数更少(仅0.28M)且计算复杂度更低,证明其适用于实时水下成像应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为FUSION的深度学习框架,该框架结合空间域和频域信息,用于提升水下图像的质量。FUSION能在空间域独立处理RGB通道,并引入多尺度卷积核和自适应注意力机制,同时利用FFT算法提取频域中的全局结构信息。通过频率引导融合模块,融合两个域的特征,然后进行跨通道融合和自适应通道校准,确保颜色分布的平衡。实验表明,FUSION在多个基准数据集上取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 水下图像存在严重的失真问题,包括颜色失真、能见度降低和结构细节丢失。
- 现有增强方法主要关注空间域处理,忽视了频域在全球颜色分布和长距离依赖方面的潜力。
- FUSION框架结合空间域和频域信息,以改进水下图像质量。
- FUSION在空间域独立处理RGB通道,并引入多尺度卷积核和自适应注意力机制。
- FUSION利用FFT算法提取频域中的全局结构信息。
- 通过频率引导融合模块和两个域的特征融合,实现跨通道融合和自适应通道校准。
点此查看论文截图

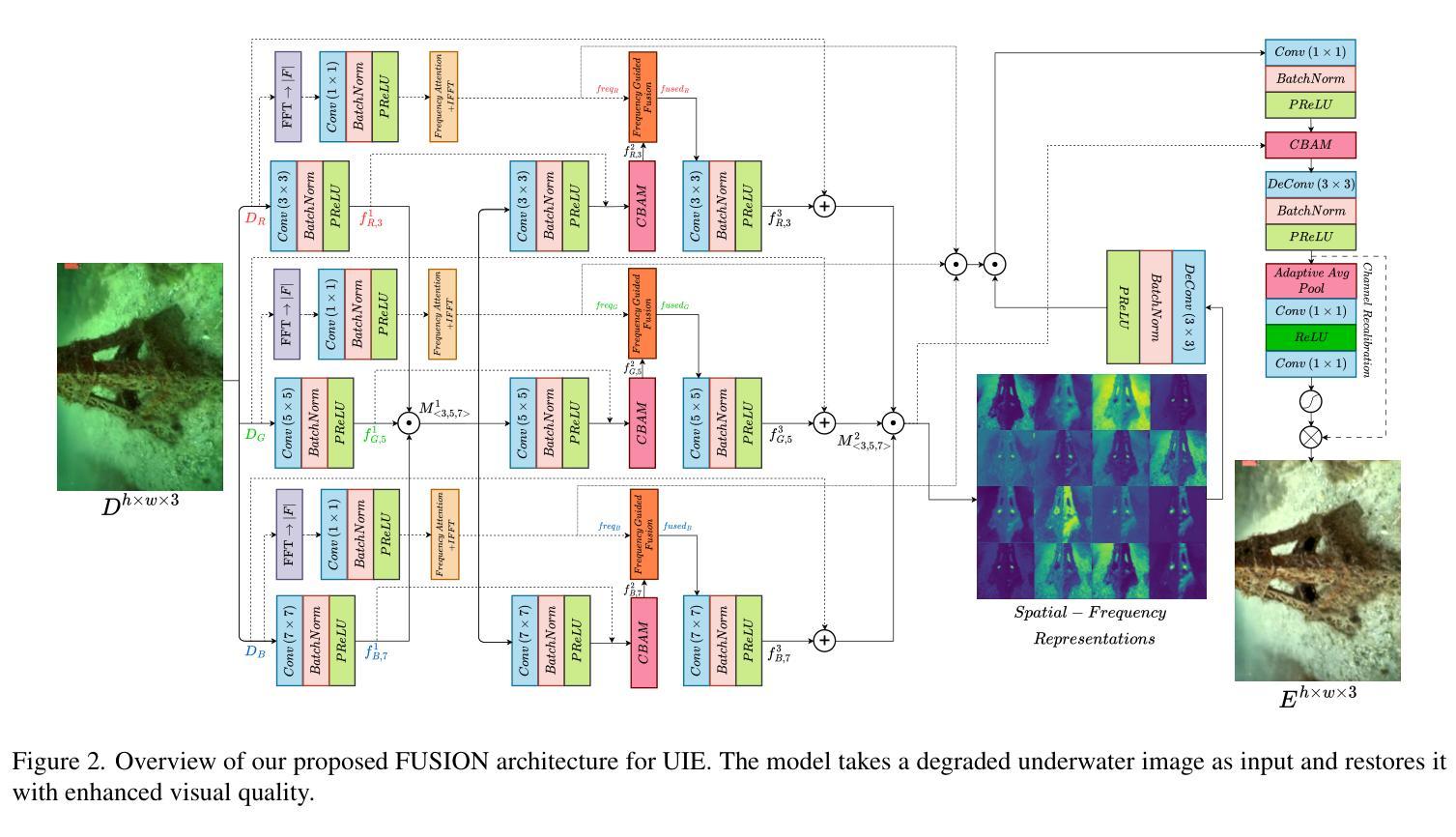
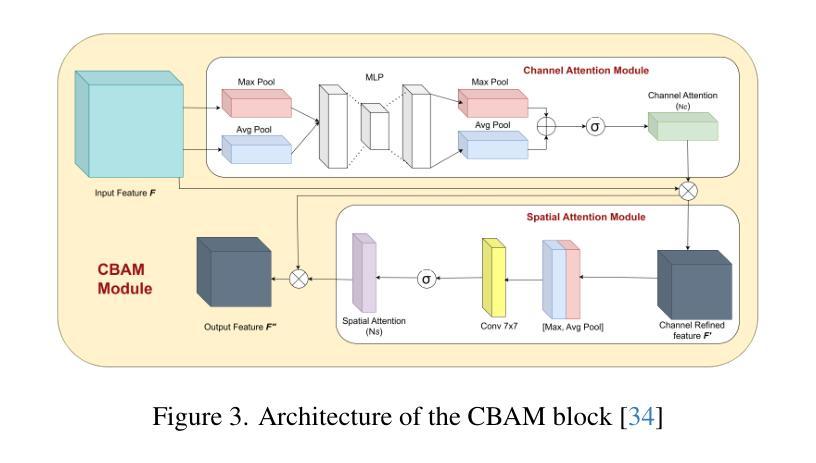


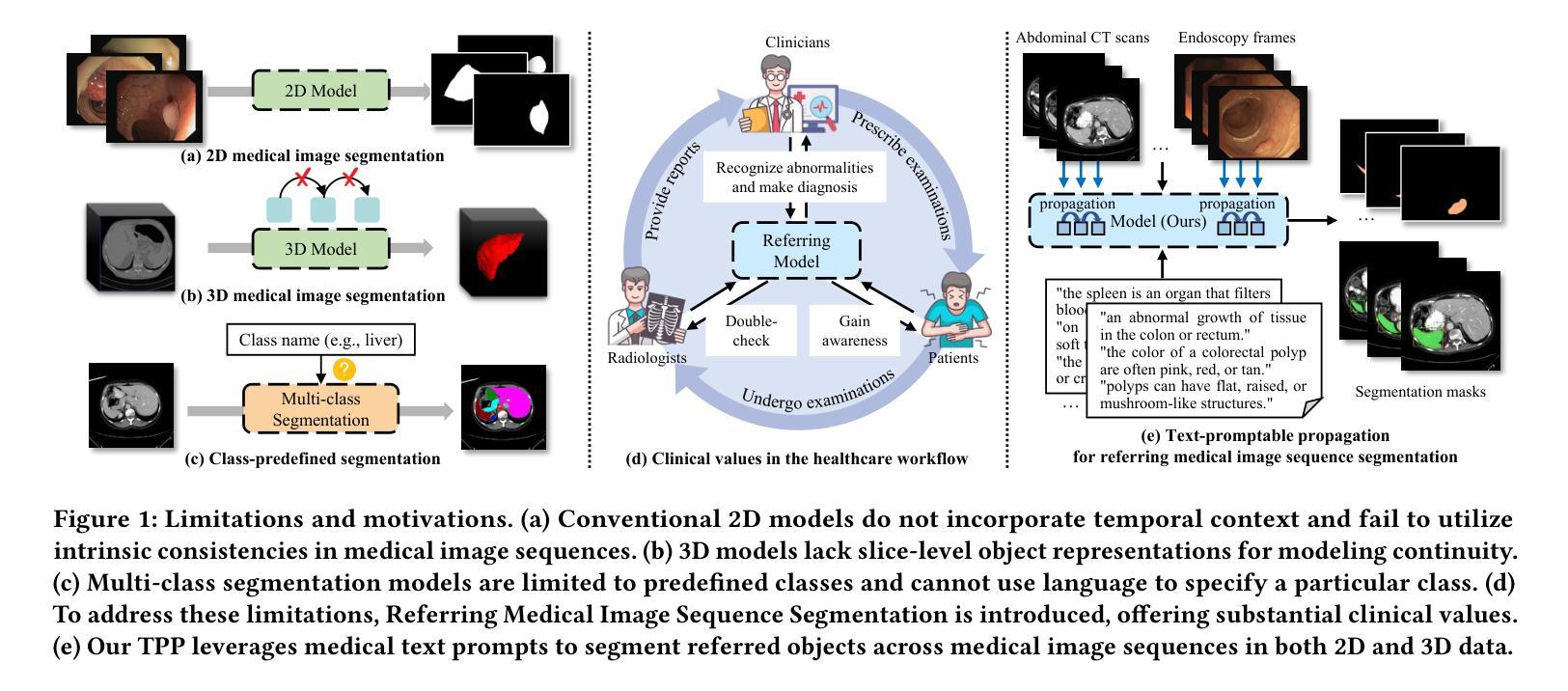
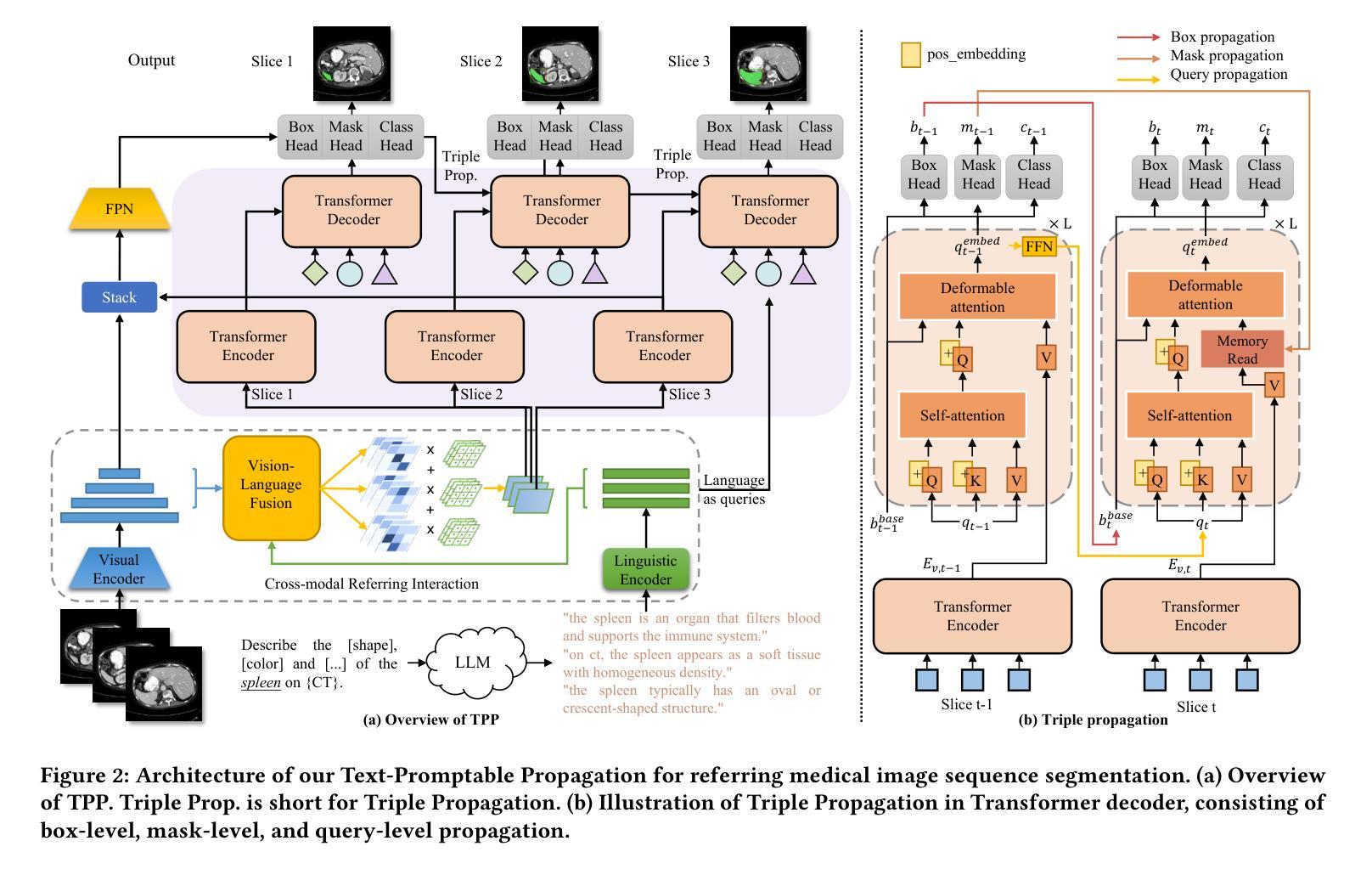
Text-Promptable Propagation for Referring Medical Image Sequence Segmentation
Authors:Runtian Yuan, Mohan Chen, Jilan Xu, Ling Zhou, Qingqiu Li, Yuejie Zhang, Rui Feng, Tao Zhang, Shang Gao
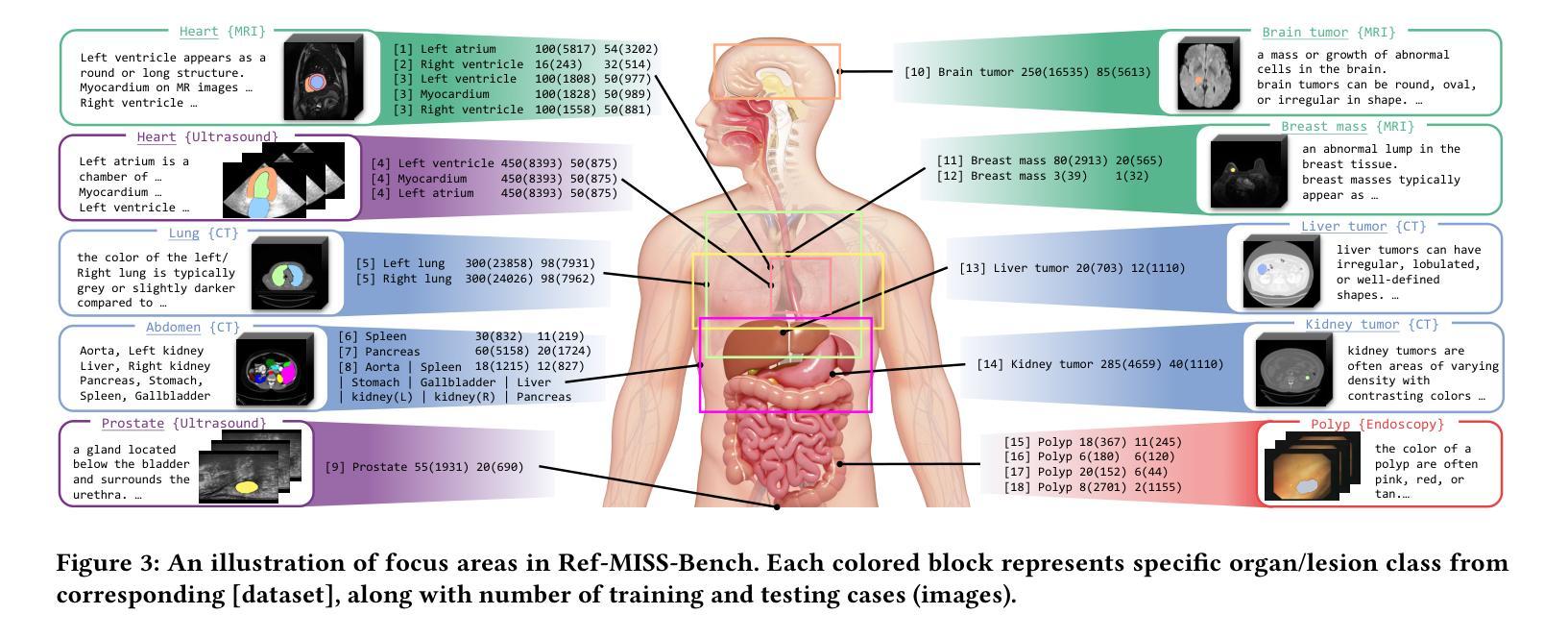
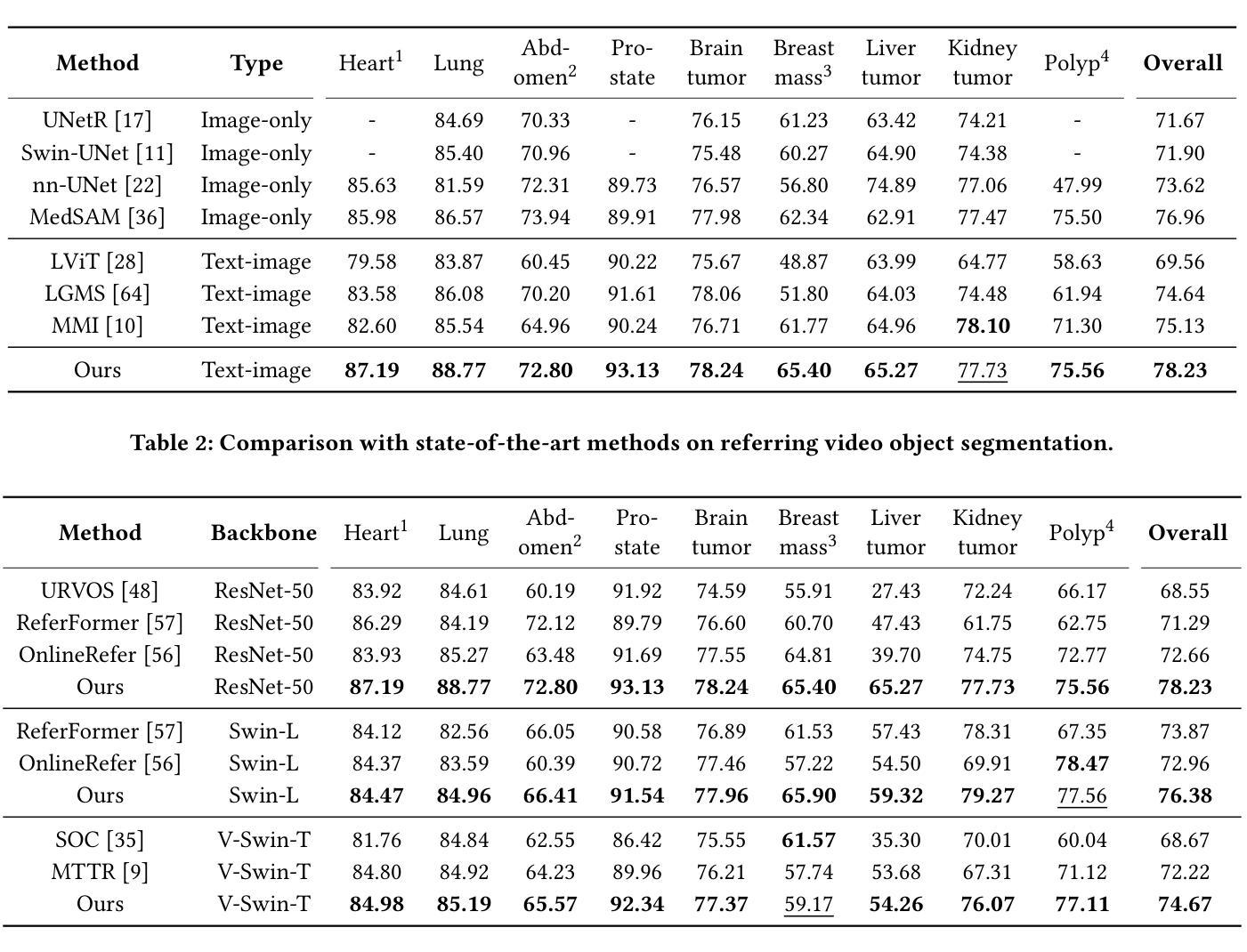
Referring Medical Image Sequence Segmentation (Ref-MISS) is a novel and challenging task that aims to segment anatomical structures in medical image sequences (\emph{e.g.} endoscopy, ultrasound, CT, and MRI) based on natural language descriptions. This task holds significant clinical potential and offers a user-friendly advancement in medical imaging interpretation. Existing 2D and 3D segmentation models struggle to explicitly track objects of interest across medical image sequences, and lack support for nteractive, text-driven guidance. To address these limitations, we propose Text-Promptable Propagation (TPP), a model designed for referring medical image sequence segmentation. TPP captures the intrinsic relationships among sequential images along with their associated textual descriptions. Specifically, it enables the recognition of referred objects through cross-modal referring interaction, and maintains continuous tracking across the sequence via Transformer-based triple propagation, using text embeddings as queries. To support this task, we curate a large-scale benchmark, Ref-MISS-Bench, which covers 4 imaging modalities and 20 different organs and lesions. Experimental results on this benchmark demonstrate that TPP consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both medical segmentation and referring video object segmentation.
医学图像序列分割引用(Ref-MISS)是一项新颖且具有挑战性的任务,旨在根据自然语言描述对医学图像序列(如内窥镜、超声、CT和MRI)进行解剖结构分割。这一任务在临床医学上具有巨大潜力,并为医学影像解读提供了用户友好的进步。现有的二维和三维分割模型难以在医学图像序列中明确跟踪感兴趣的目标,并且缺乏交互式的文本驱动指导支持。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了文本提示传播(TPP)模型,专为引用医学图像序列分割设计。TPP捕捉序列图像之间的内在关系及其相关的文本描述。具体来说,它通过跨模态引用交互识别目标对象,并通过基于Transformer的三重传播在序列中保持持续跟踪,使用文本嵌入作为查询。为了支持此任务,我们整理了一个大规模基准数据集Ref-MISS-Bench,涵盖4种成像模式和20种不同的器官和病变。在该基准数据集上的实验结果表明,TPP在医学分割和引用视频对象分割方面都始终优于现有最新技术的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像序列分割是一项新的挑战任务,旨在基于自然语言描述对医学图像序列(如内窥镜、超声、CT和MRI)进行解剖结构分割。现有模型难以在医学图像序列中显式跟踪感兴趣对象,并缺乏文本驱动的交互式指导支持。为此,我们提出了Text-Promptable Propagation(TPP)模型,该模型用于医学图像序列分割的引用。TPP能够捕获序列图像之间的内在关系及其相关文本描述,通过跨模态引用交互识别目标对象,并通过基于Transformer的三重传播在序列中持续跟踪对象,文本嵌入作为查询。同时,我们为此任务构建了大规模基准数据集Ref-MISS-Bench,涵盖四种成像模式和二十种不同器官和病变。实验结果表明,TPP在医学分割和引用视频对象分割方面都优于最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- Ref-MISS是一项新的医学图像序列分割任务,旨在基于自然语言描述进行解剖结构分割。
- 现有模型在医学图像序列中跟踪感兴趣对象方面存在困难。
- TPP模型被提出来解决这一问题,能够捕获序列图像间的内在关系及其文本描述。
- TPP通过跨模态引用交互识别目标对象,并在序列中持续跟踪对象。
- 我们构建了大规模基准数据集Ref-MISS-Bench来支持此任务。
- Ref-MISS-Bench涵盖四种成像模式和二十种不同的器官和病变。
点此查看论文截图

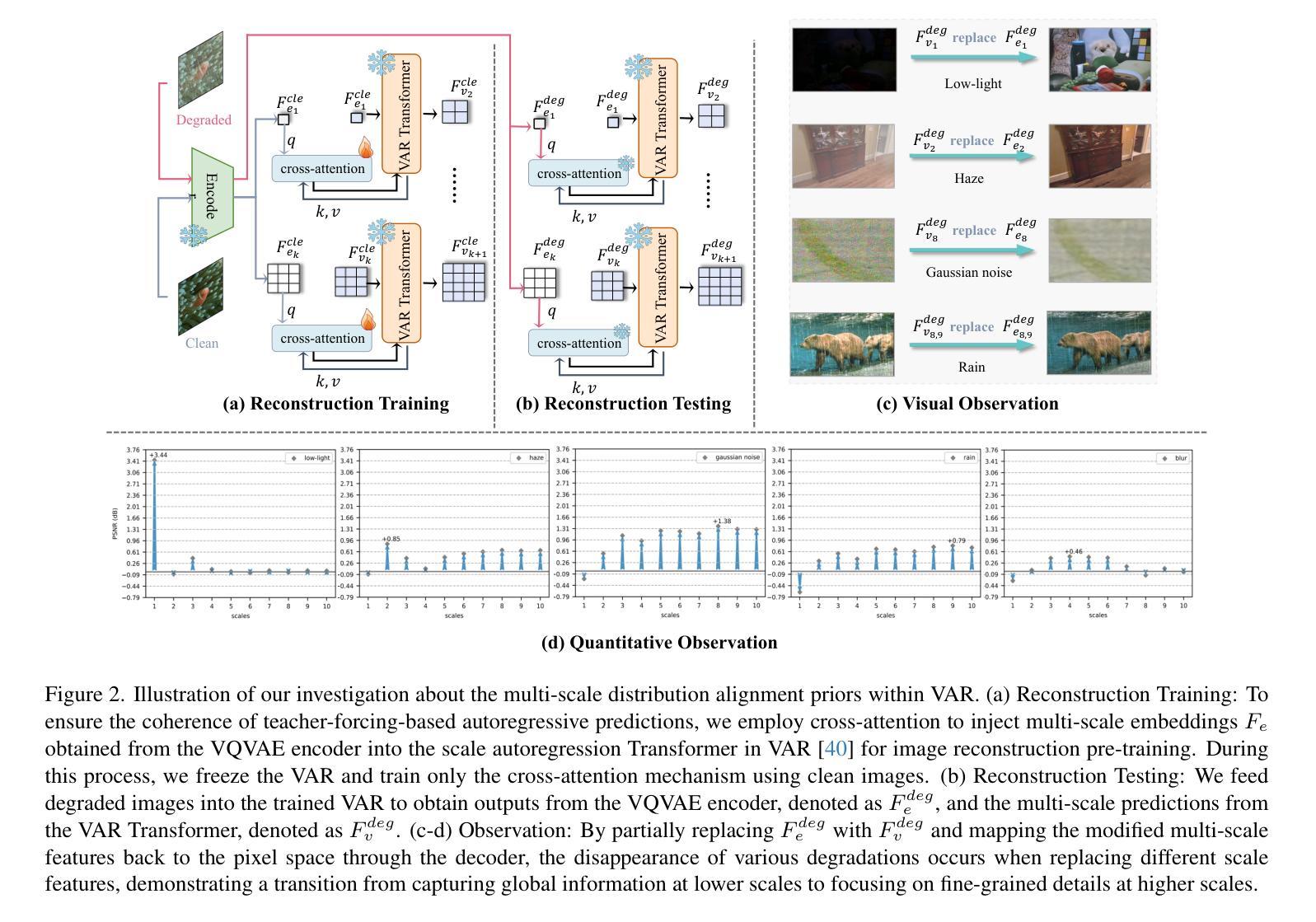
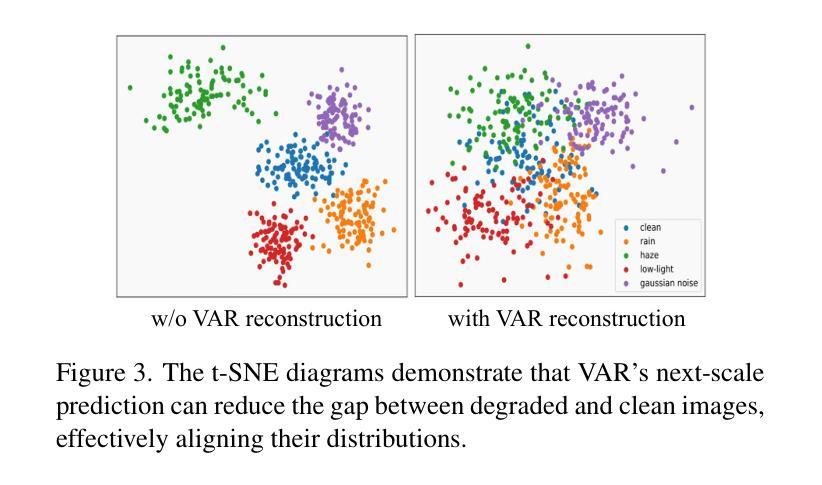
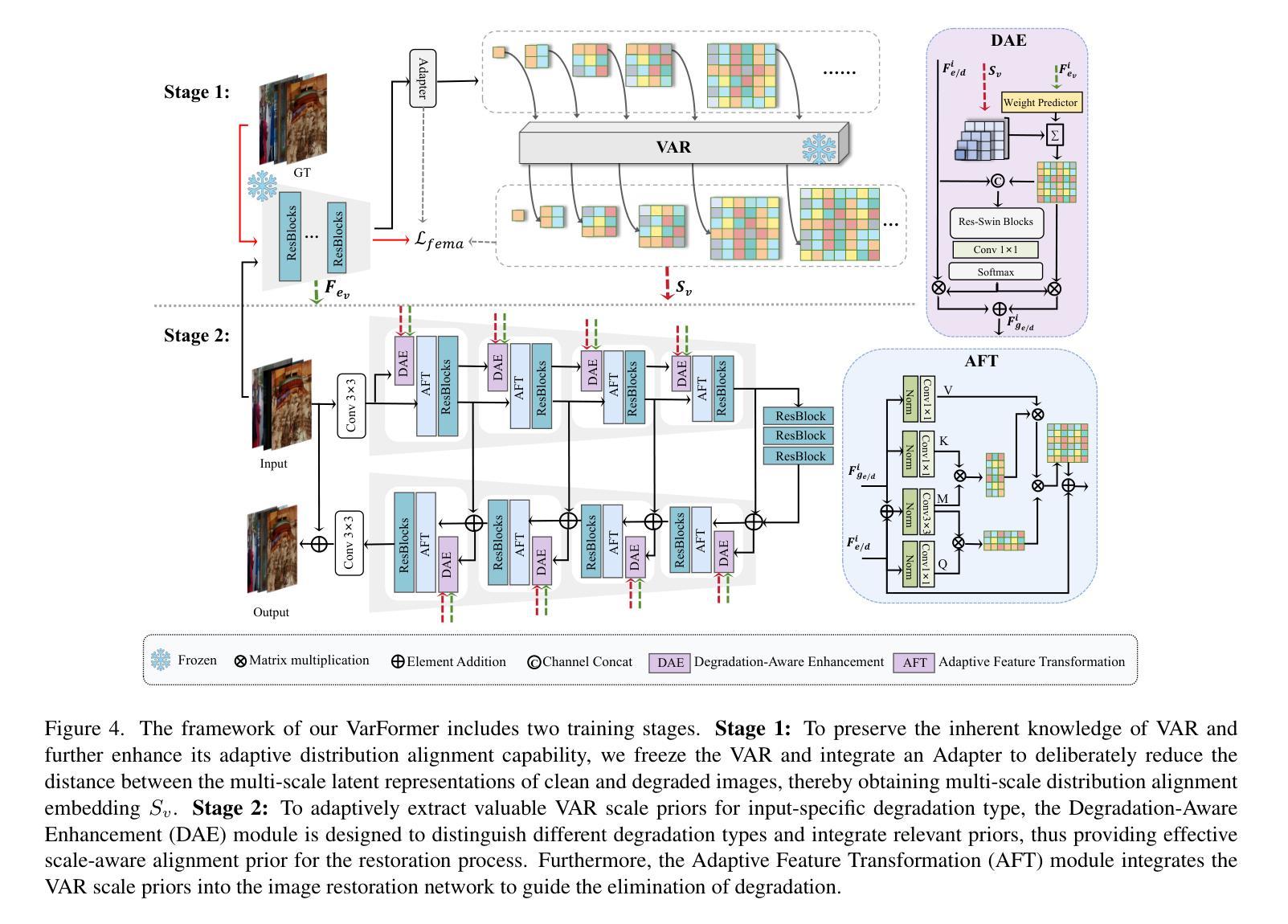
Navigating Image Restoration with VAR’s Distribution Alignment Prior
Authors:Siyang Wang, Feng Zhao
Generative models trained on extensive high-quality datasets effectively capture the structural and statistical properties of clean images, rendering them powerful priors for transforming degraded features into clean ones in image restoration. VAR, a novel image generative paradigm, surpasses diffusion models in generation quality by applying a next-scale prediction approach. It progressively captures both global structures and fine-grained details through the autoregressive process, consistent with the multi-scale restoration principle widely acknowledged in the restoration community. Furthermore, we observe that during the image reconstruction process utilizing VAR, scale predictions automatically modulate the input, facilitating the alignment of representations at subsequent scales with the distribution of clean images. To harness VAR’s adaptive distribution alignment capability in image restoration tasks, we formulate the multi-scale latent representations within VAR as the restoration prior, thus advancing our delicately designed VarFormer framework. The strategic application of these priors enables our VarFormer to achieve remarkable generalization on unseen tasks while also reducing training computational costs. Extensive experiments underscores that our VarFormer outperforms existing multi-task image restoration methods across various restoration tasks.
训练在大量高质量数据集上的生成模型,能够有效地捕捉干净图像的结构和统计特性,使其成为将退化特征转换为干净特征进行图像恢复的强大先验信息。VAR作为一种新型的图像生成范式,通过应用下一尺度预测方法,在生成质量上超越了扩散模型。它通过自回归过程逐步捕捉全局结构和精细细节,这与恢复界广泛认可的多尺度恢复原则相一致。此外,我们观察到,在利用VAR进行图像重建的过程中,尺度预测会自动调制输入,促进后续尺度的表示与干净图像分布的对齐。为了利用VAR在图像恢复任务中的自适应分布对齐能力,我们将VAR内的多尺度潜在表示作为恢复先验,从而推进了我们精心设计的VarFormer框架。这些先验知识的战略应用使我们的VarFormer在未见过的任务上实现了显著的泛化能力,同时降低了训练的计算成本。大量实验证明,我们的VarFormer在各种恢复任务上超越了现有的多任务图像恢复方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
生成模型经过大规模高质量数据集训练后,能有效捕捉清晰图像的结构和统计特性,在图像修复中将退化特征转换为清晰特征时表现出强大的先验能力。一种新的图像生成范式VAR,通过应用下一尺度预测方法,在生成质量上超越了扩散模型。VAR通过自回归过程逐步捕捉全局结构和精细细节,符合修复界广泛认可的多尺度修复原则。此外,在利用VAR进行图像重建的过程中,观察到尺度预测可自动调制输入,有助于后续尺度表示与干净图像分布的对齐。为了利用VAR在图像修复任务中的自适应分布对齐能力,将VAR内的多尺度潜在表示作为修复先验,从而提出精心设计的VarFormer框架。这些先验知识的战略应用使VarFormer在未见任务上实现了卓越泛化,同时降低了训练计算成本。广泛实验表明,VarFormer在多种修复任务上优于现有多任务图像修复方法。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型经过高质量数据集训练后,能有效捕捉清晰图像的结构和统计特性。
- VAR作为一种新的图像生成范式,在生成质量上超越了扩散模型。
- VAR通过自回归过程逐步捕捉全局结构和精细细节,符合多尺度修复原则。
- VAR在图像重建过程中能实现尺度预测自动调制输入,促进后续尺度表示与干净图像分布的对齐。
- VarFormer利用VAR的多尺度潜在表示作为修复先验,提高了图像修复的泛化能力和效率。
- VarFormer框架通过战略应用这些先验知识,实现了在未见任务上的卓越性能,同时降低了训练计算成本。
- 广泛实验证明,VarFormer在多种图像修复任务上优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


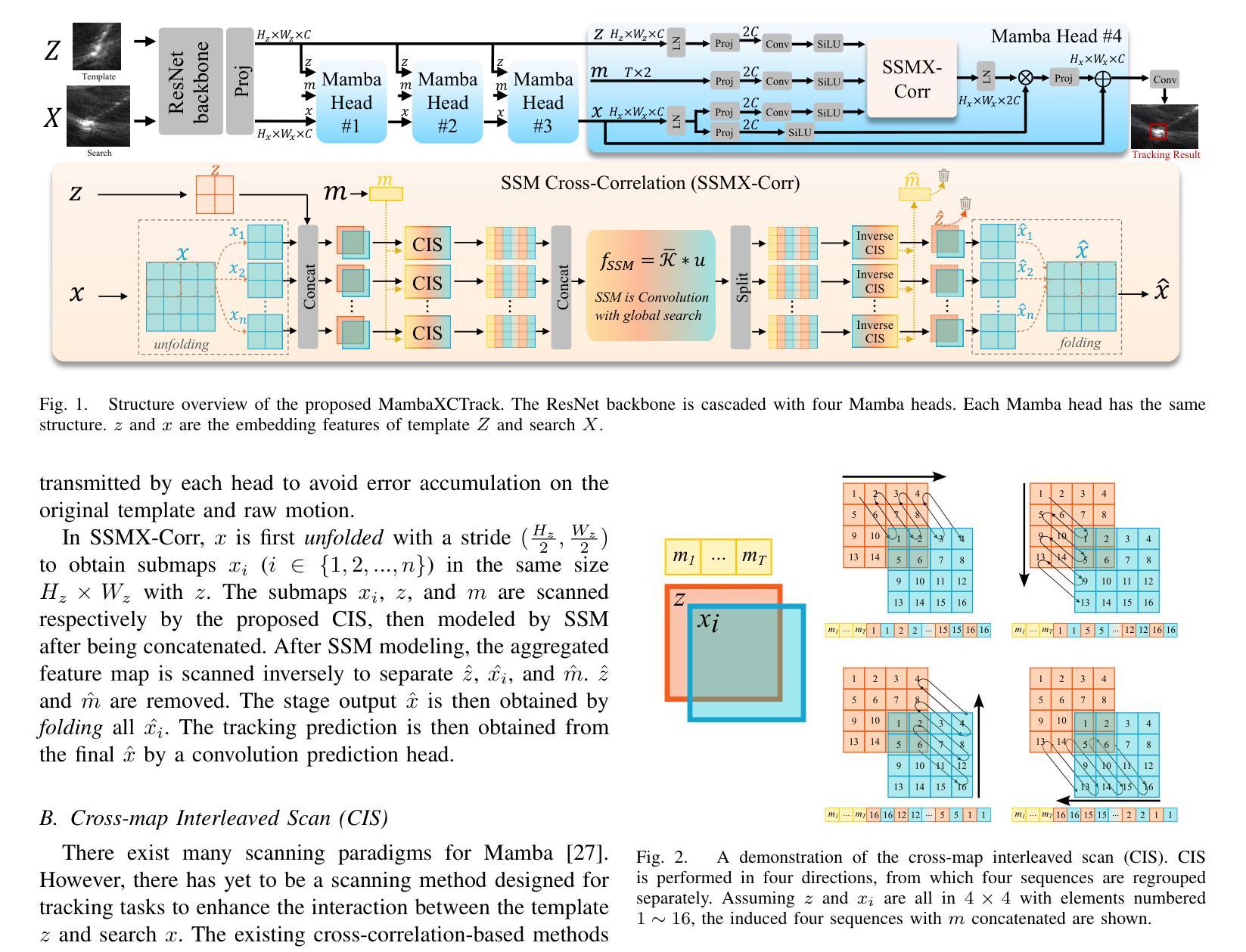
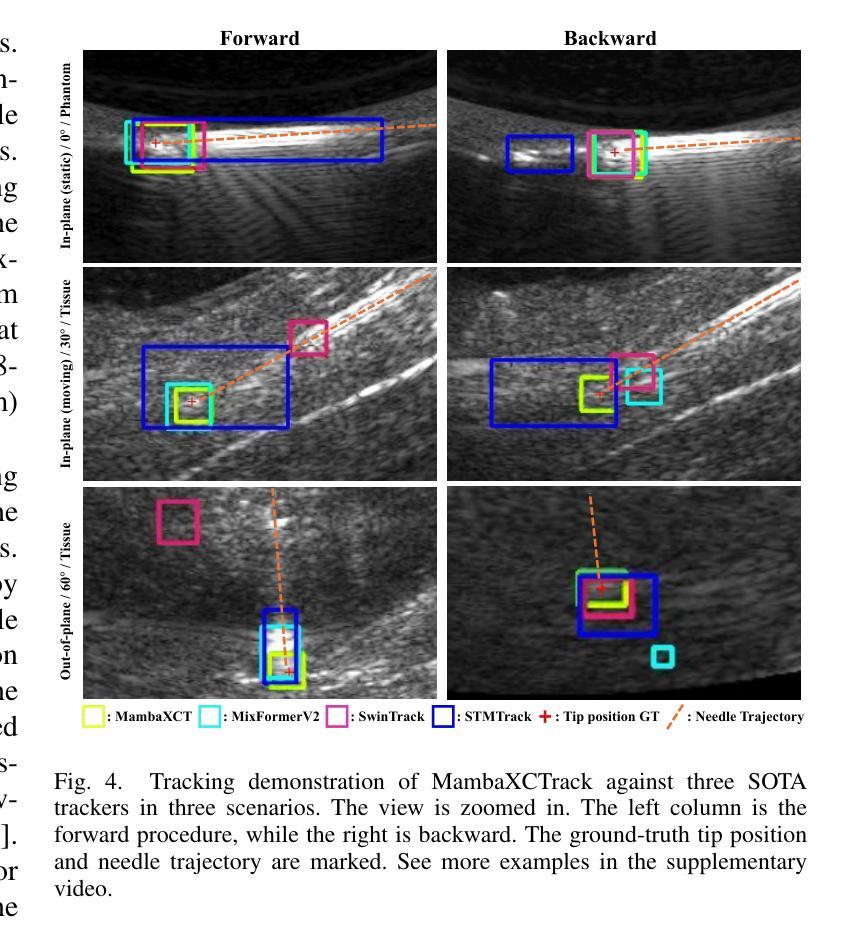
MambaXCTrack: Mamba-based Tracker with SSM Cross-correlation and Motion Prompt for Ultrasound Needle Tracking
Authors:Yuelin Zhang, Long Lei, Wanquan Yan, Tianyi Zhang, Raymond Shing-Yan Tang, Shing Shin Cheng
Ultrasound (US)-guided needle insertion is widely employed in percutaneous interventions. However, providing feedback on the needle tip position via US imaging presents challenges due to noise, artifacts, and the thin imaging plane of US, which degrades needle features and leads to intermittent tip visibility. In this paper, a Mamba-based US needle tracker MambaXCTrack utilizing structured state space models cross-correlation (SSMX-Corr) and implicit motion prompt is proposed, which is the first application of Mamba in US needle tracking. The SSMX-Corr enhances cross-correlation by long-range modeling and global searching of distant semantic features between template and search maps, benefiting the tracking under noise and artifacts by implicitly learning potential distant semantic cues. By combining with cross-map interleaved scan (CIS), local pixel-wise interaction with positional inductive bias can also be introduced to SSMX-Corr. The implicit low-level motion descriptor is proposed as a non-visual prompt to enhance tracking robustness, addressing the intermittent tip visibility problem. Extensive experiments on a dataset with motorized needle insertion in both phantom and tissue samples demonstrate that the proposed tracker outperforms other state-of-the-art trackers while ablation studies further highlight the effectiveness of each proposed tracking module.
超声(US)引导下的针插入术在经皮介入中得到了广泛应用。然而,通过超声成像提供针尖位置反馈却面临诸多挑战,这主要是由于噪声、伪影和超声成像平面较薄等原因导致针的特征退化,以及针尖可见性间歇性消失。本文提出了基于Mamba的超声针跟踪器MambaXCTrack,它利用结构化状态空间模型的互相关(SSMX-Corr)和隐式运动提示,这是Mamba在超声针跟踪中的首次应用。SSMX-Corr通过长程建模和模板与搜索地图之间远距离语义特征的全局搜索,增强了互相关,通过隐式学习潜在的远距离语义线索,有利于在噪声和伪影的情况下进行跟踪。通过与跨图交织扫描(CIS)相结合,还可以将具有位置诱导偏见的局部像素级交互引入到SSMX-Corr中。提出了一种隐式低级运动描述符作为非视觉提示,以增强跟踪的稳健性,解决针尖间歇性可见性问题。在模拟和组织样本中的电动针插入数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,所提出的跟踪器优于其他最先进的跟踪器,而消融研究进一步突出了每个所提出的跟踪模块的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by RAL
Summary
本论文提出了一种基于Mamba的超声针追踪技术MambaXCTrack,该技术采用结构化状态空间模型的互相关(SSMX-Corr)和隐式运动提示,为超声引导下的针插入提供了反馈。SSMX-Corr通过长程建模和模板与搜索图之间远距离语义特征的全局搜索,提高了互相关性能,并在噪声和伪影下通过隐式学习潜在远距离语义线索来增强跟踪效果。结合跨图交织扫描(CIS),还可以将带有位置诱导偏见的局部像素级交互引入到SSMX-Corr中。此外,提出了隐式低级运动描述符作为非视觉提示,以提高跟踪的稳健性,解决针尖间歇性可见的问题。在模拟和组织样本上的电动针插入数据集上的大量实验表明,所提出的追踪器优于其他最新追踪器,而消融研究进一步突出了所提出追踪模块的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 超声引导下的针插入在经皮介入中广泛应用,但提供关于针尖位置的反馈是一个挑战。
- 论文提出了一种基于Mamba的超声针追踪技术MambaXCTrack,该技术采用结构化状态空间模型的互相关(SSMX-Corr)。
- SSMX-Corr通过长程建模和全局搜索增强互相关性能,并在噪声和伪影下提高跟踪效果。
- 结合跨图交织扫描(CIS)可以增强局部像素级交互。
- 提出了隐式低级运动描述符作为非视觉提示,解决针尖间歇性可见的问题。
- 在模拟和组织样本上的实验表明,所提出的追踪器优于其他最新技术。
点此查看论文截图