⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-16 更新
FLOSS: Free Lunch in Open-vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Yasser Benigmim, Mohammad Fahes, Tuan-Hung Vu, Andrei Bursuc, Raoul de Charette
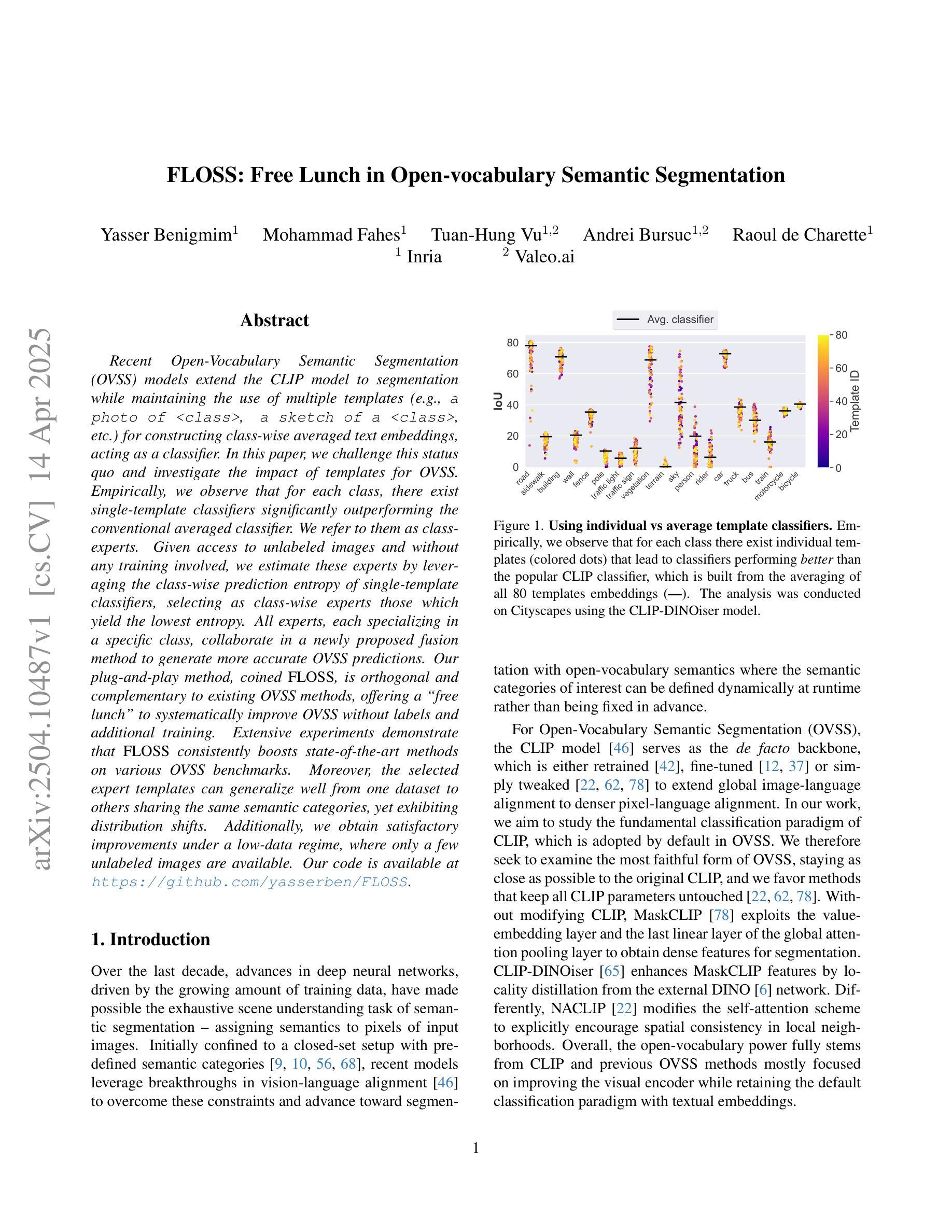
Recent Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation (OVSS) models extend the CLIP model to segmentation while maintaining the use of multiple templates (e.g., a photo of
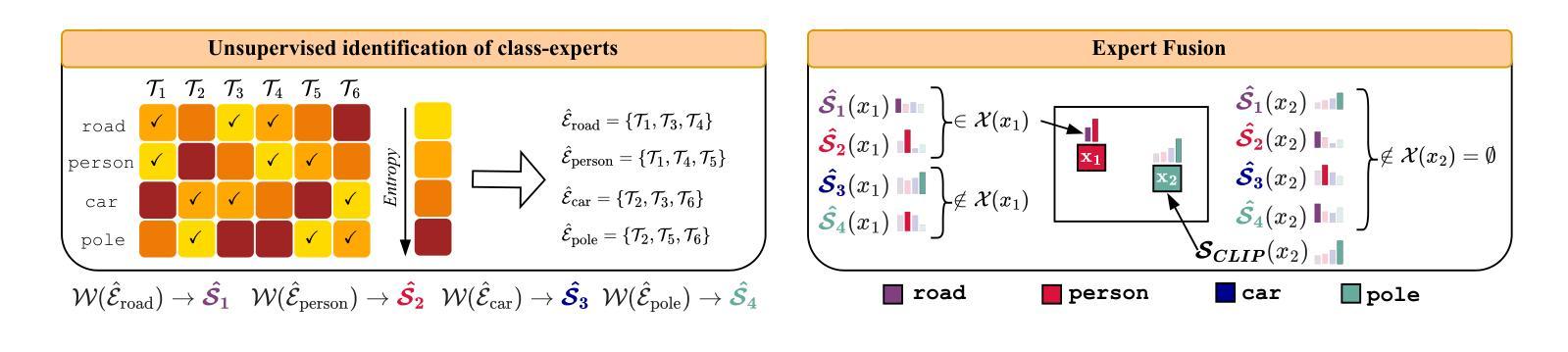
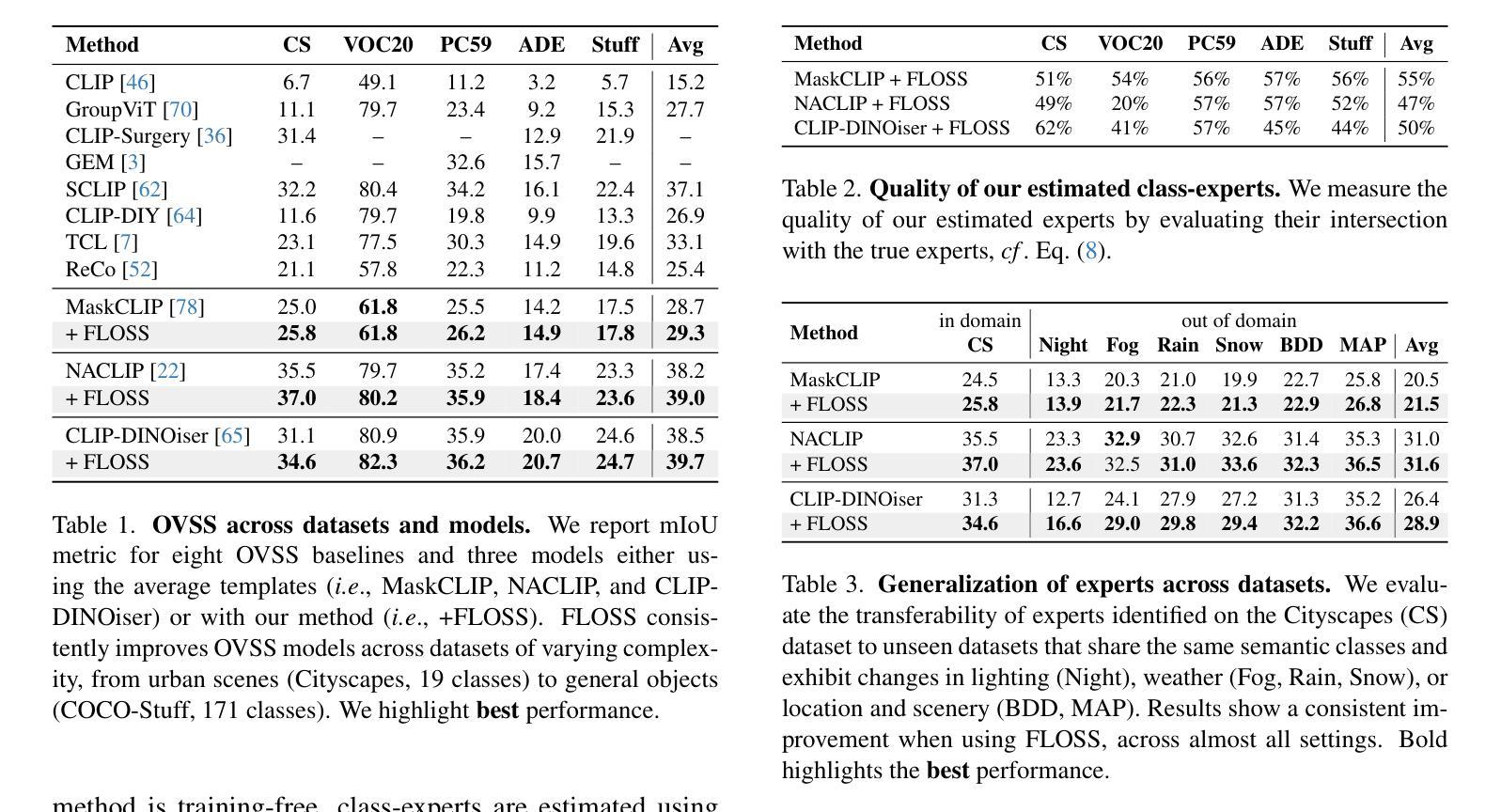
近期,开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)模型将CLIP模型拓展到分割领域,同时保持使用多种模板(例如,<类别>的照片、<类别>的草图等)来构建类平均文本嵌入,作为分类器。在本文中,我们挑战这一现状,并研究模板对OVSS的影响。从实证观察来看,对于每个类别,都存在单模板分类器,其性能显著优于传统的平均分类器。我们将其称为类专家。给定无标签图像且无需任何训练的情况下,我们通过利用单模板分类器的类预测熵来估算这些专家,选择产生最低熵的作为类专家。所有专家,每一个都专注于特定的类别,在一个新提出的融合方法中合作,以生成更准确的OVSS预测。我们提出的即插即用方法,称为FLOSS,与现有的OVSS方法正交且互补,为无标签和额外训练的OVSS系统改进提供了“免费午餐”。大量实验表明,FLOSS在各种OVSS基准测试中始终提升了最新方法的效果。此外,所选的专家模板可以在同一语义类别但存在分布变化的多个数据集之间进行很好的泛化。而且,在只有少量无标签图像的情况下,我们也获得了令人满意的改进。我们的代码可在https://github.com/yasserben/FLOSS中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://yasserben.github.io/FLOSS/
Summary
本文挑战了当前开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)模型使用多模板构建类平均文本嵌入作为分类器的做法。研究发现,对于每个类别,存在单一模板分类器显著优于传统平均分类器,称为类专家。在不使用标签图像和任何训练的情况下,通过利用类专家预测熵的估计来选择这些专家。所有类专家合作在一个新提出的融合方法中,生成更准确的OVSS预测。提出的即插即用方法FLOSS与现有OVSS方法正交且互补,可系统地提高OVSS性能,无需标签和额外训练。实验表明,FLOSS在各种OVSS基准测试中均提升了最新技术水平,且所选专家模板可在具有语义类别共享但分布转移的数据集之间很好地推广。在少量无标签图像的情况下,也获得了令人满意的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)模型采用多模板构建类平均文本嵌入作为分类器。
- 对于每个类别,存在单一模板分类器(类专家)表现优于传统平均分类器。
- 利用预测熵估计类专家,无需额外训练。
- 所有类专家通过新提出的融合方法合作,生成更准确预测。
- FLOSS方法即插即用,与现有OVSS方法互补,能提高性能而无需标签和额外训练。
- FLOSS在多种OVSS基准测试中表现优越,且专家模板可跨数据集推广。
- 在少量无标签图像情况下,FLOSS也表现出满意的改进。
点此查看论文截图
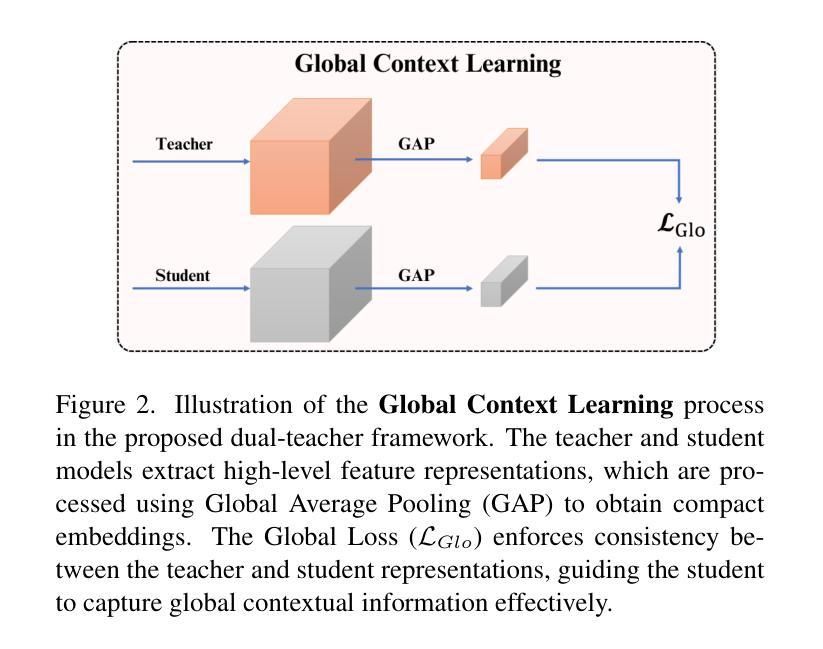
IGL-DT: Iterative Global-Local Feature Learning with Dual-Teacher Semantic Segmentation Framework under Limited Annotation Scheme
Authors:Dinh Dai Quan Tran, Hoang-Thien Nguyen. Thanh-Huy Nguyen, Gia-Van To, Tien-Huy Nguyen, Quan Nguyen
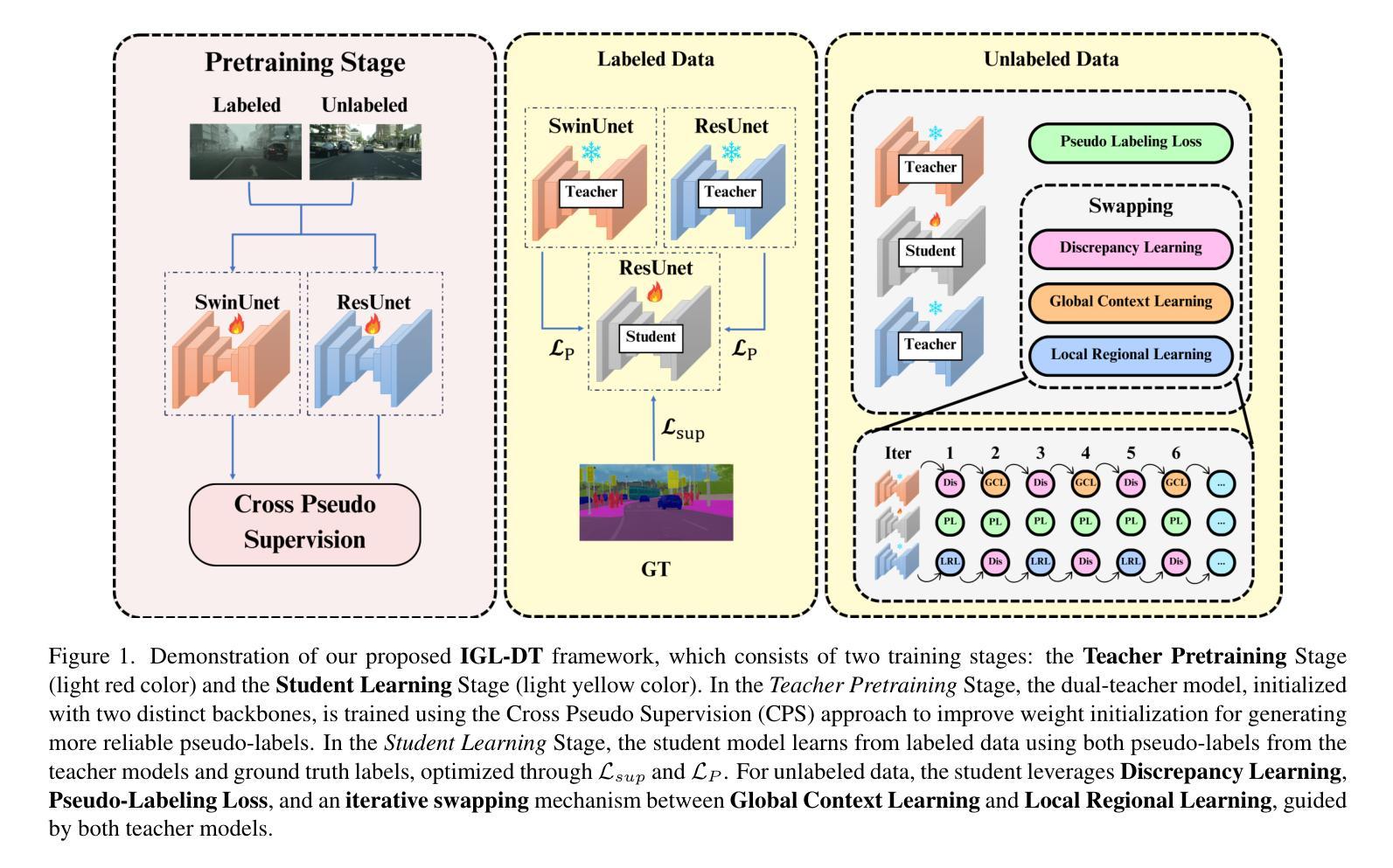
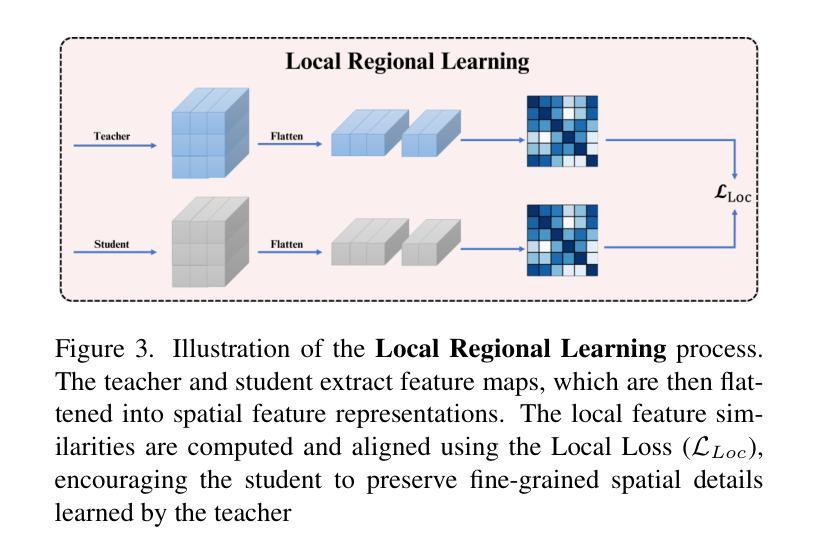
Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation (SSSS) aims to improve segmentation accuracy by leveraging a small set of labeled images alongside a larger pool of unlabeled data. Recent advances primarily focus on pseudo-labeling, consistency regularization, and co-training strategies. However, existing methods struggle to balance global semantic representation with fine-grained local feature extraction. To address this challenge, we propose a novel tri-branch semi-supervised segmentation framework incorporating a dual-teacher strategy, named IGL-DT. Our approach employs SwinUnet for high-level semantic guidance through Global Context Learning and ResUnet for detailed feature refinement via Local Regional Learning. Additionally, a Discrepancy Learning mechanism mitigates over-reliance on a single teacher, promoting adaptive feature learning. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, achieving superior segmentation performance across various data regimes.
半监督语义分割(SSSS)旨在利用少量标记图像和大量未标记数据来提高分割精度。最近的进展主要集中在伪标签、一致性正则化和协同训练策略上。然而,现有方法在平衡全局语义表示和精细局部特征提取方面存在困难。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种新的三分支半监督分割框架,采用双教师策略,名为IGL-DT。我们的方法采用SwinUnet进行高级语义指导的全局上下文学习,以及ResUnet进行详细特征精修的局部区域学习。此外,差异学习机制减轻了对单一教师的过度依赖,促进了自适应特征学习。在基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法优于最新方法,在各种数据状态下实现了优越的分割性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文介绍了半监督语义分割(SSSS)技术,该技术通过利用少量标记图像和大量未标记数据来提高分割准确性。为解决现有方法在全局语义表示与精细局部特征提取之间的平衡问题,提出了一种新型的三分支半监督分割框架IGL-DT,采用双教师策略,结合SwinUnet进行全局上下文学习和ResUnet进行局部区域学习,同时引入差异学习机制,减轻对单一教师的过度依赖,促进自适应特征学习。在基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,该方法优于最新技术,在各种数据条件下实现优越的分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督语义分割技术旨在通过结合标记和未标记数据提高分割准确性。
- 现有方法面临在全局语义和局部特征提取之间的平衡问题。
- 提出了一种新型三分支半监督分割框架IGL-DT,结合双教师策略。
- IGL-DT使用SwinUnet进行全局上下文学习,ResUnet进行局部区域学习。
- 差异学习机制用于减轻对单一教师的依赖,促进自适应特征学习。
- 在基准数据集上的实验表明,IGL-DT方法优于其他最新技术。
点此查看论文截图

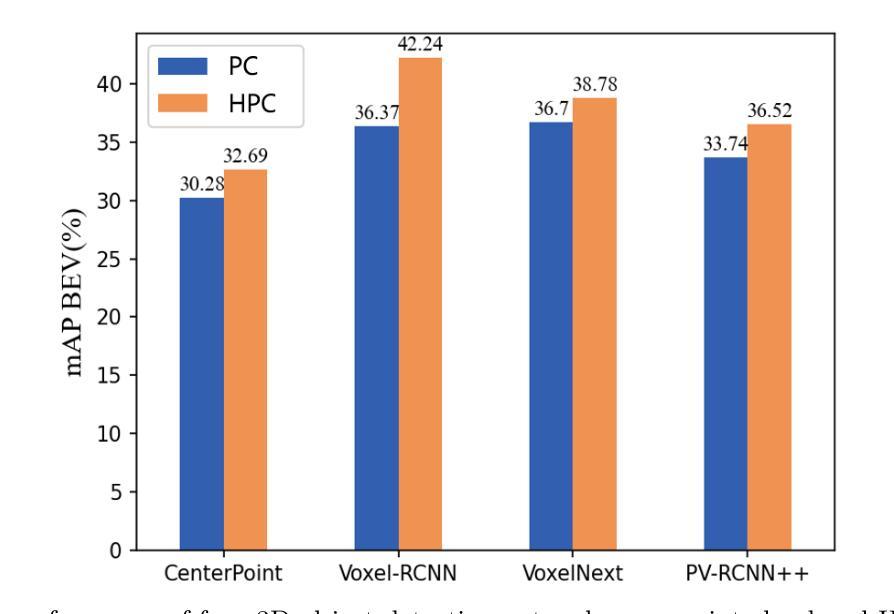
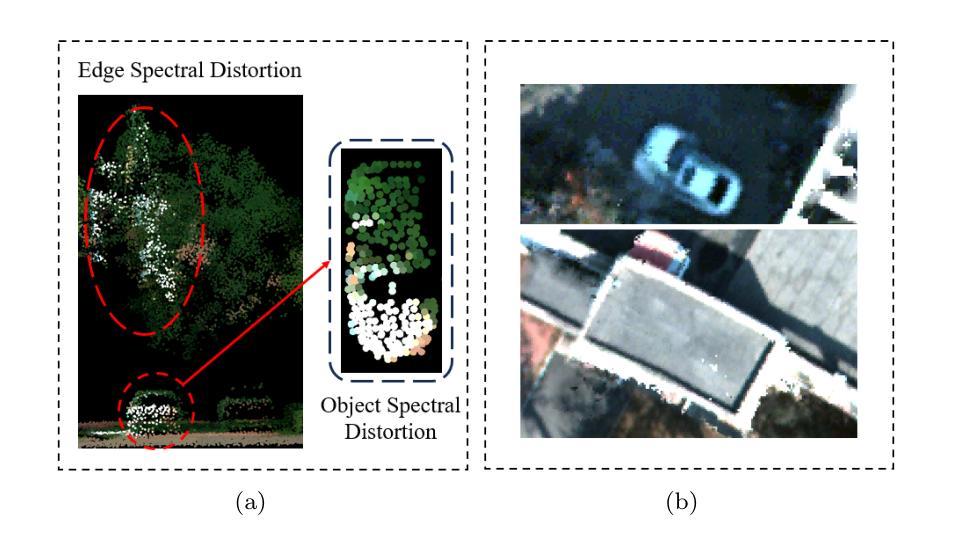
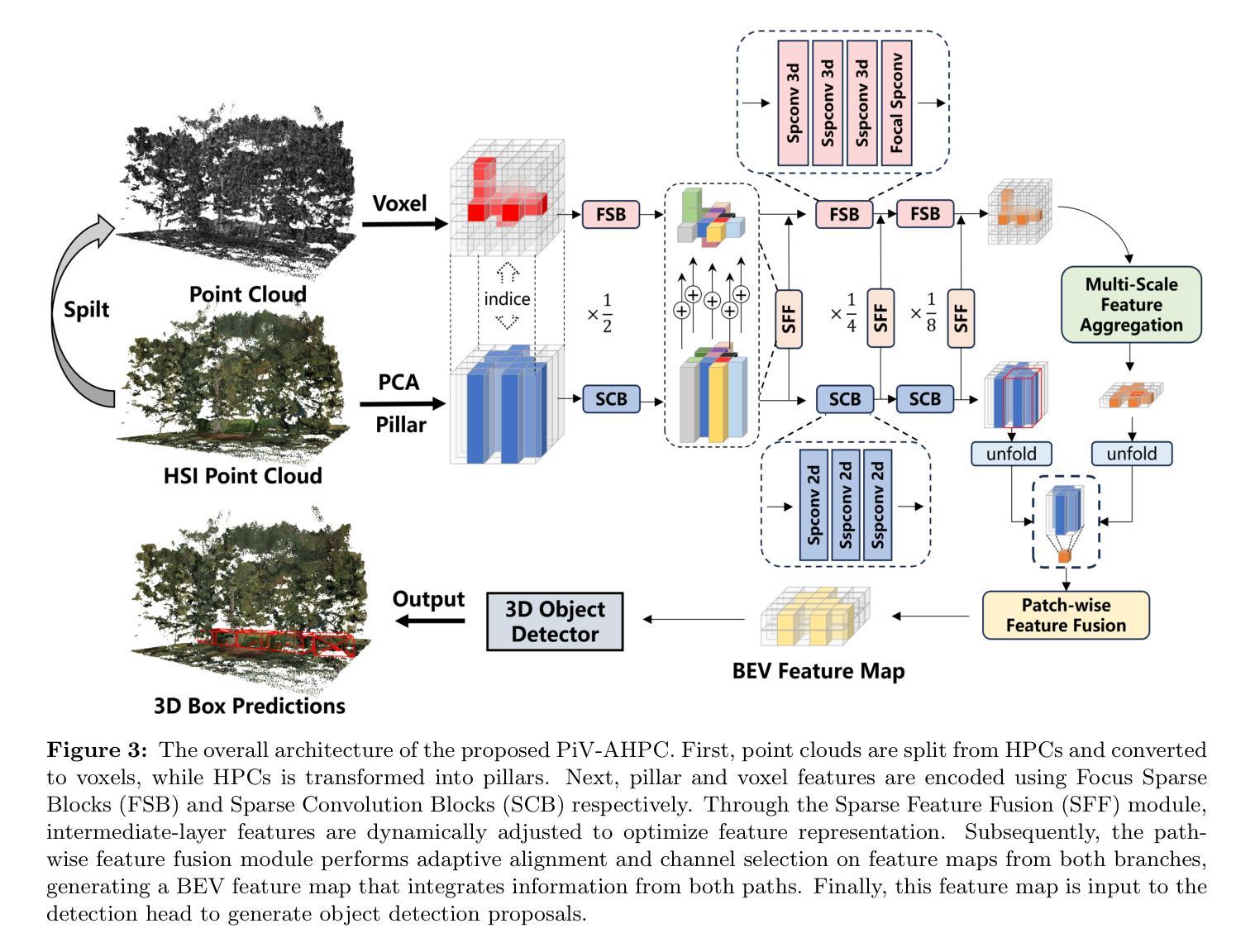
Pillar-Voxel Fusion Network for 3D Object Detection in Airborne Hyperspectral Point Clouds
Authors:Yanze Jiang, Yanfeng Gu, Xian Li
Hyperspectral point clouds (HPCs) can simultaneously characterize 3D spatial and spectral information of ground objects, offering excellent 3D perception and target recognition capabilities. Current approaches for generating HPCs often involve fusion techniques with hyperspectral images and LiDAR point clouds, which inevitably lead to geometric-spectral distortions due to fusion errors and obstacle occlusions. These adverse effects limit their performance in downstream fine-grained tasks across multiple scenarios, particularly in airborne applications. To address these issues, we propose PiV-AHPC, a 3D object detection network for airborne HPCs. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt at this HPCs task. Specifically, we first develop a pillar-voxel dual-branch encoder, where the former captures spectral and vertical structural features from HPCs to overcome spectral distortion, while the latter emphasizes extracting accurate 3D spatial features from point clouds. A multi-level feature fusion mechanism is devised to enhance information interaction between the two branches, achieving neighborhood feature alignment and channel-adaptive selection, thereby organically integrating heterogeneous features and mitigating geometric distortion. Extensive experiments on two airborne HPCs datasets demonstrate that PiV-AHPC possesses state-of-the-art detection performance and high generalization capability.
高光谱点云(HPCs)可以同时表征地面物体的三维空间信息和光谱信息,提供出色的三维感知和目标识别能力。目前生成HPCs的方法通常涉及高光谱图像和激光雷达点云的融合技术,由于融合误差和障碍物遮挡,不可避免地会导致几何光谱失真。这些不利影响在多场景下游的精细任务中限制了其性能,特别是在空中应用方面。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了PiV-AHPC,这是一个用于空中HPCs的三维对象检测网络。据我们所知,这是HPCs任务上的首次尝试。具体来说,我们首先开发了一个柱体-体素双分支编码器,前者从HPCs中提取光谱和垂直结构特征以克服光谱失真,而后者则侧重于从点云中提取准确的三维空间特征。设计了一种多层次特征融合机制,以增强两个分支之间的信息交互,实现邻域特征对齐和通道自适应选择,从而有机地融合异质特征并减轻几何失真。在两个空中HPCs数据集上的大量实验表明,PiV-AHPC具有最先进的检测性能和高泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对空中超光谱点云(HPCs)的目标检测问题。为解决现有融合技术带来的几何和光谱失真问题,提出一种名为PiV-AHPC的3D对象检测网络。该网络包含双分支编码器,能够分别捕捉点云的光谱和垂直结构特征以及空间特征。并通过多级特征融合机制增强信息交互,实现了邻域特征对齐和通道自适应选择,有效整合了异构特征并减轻了几何失真。在两种空中HPCs数据集上的实验表明,PiV-AHPC具有最先进的检测性能和高泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了空中超光谱点云(HPCs)的目标检测问题及其面临的挑战。
- HPCs可以同时表征地面对象的三维空间信息和光谱信息,为三维感知和目标识别提供了出色的能力。
- 当前生成HPCs的方法通常涉及与激光雷达点云融合的技术,这会导致几何和光谱失真。
- 提出了一种名为PiV-AHPC的3D对象检测网络,旨在解决空中HPCs的几何和光谱失真问题。
- PiV-AHPC包含一个双分支编码器,能够分别提取点云的光谱和结构特征以及空间特征。
- 通过多级特征融合机制增强信息交互,实现特征对齐和通道自适应选择。
点此查看论文截图

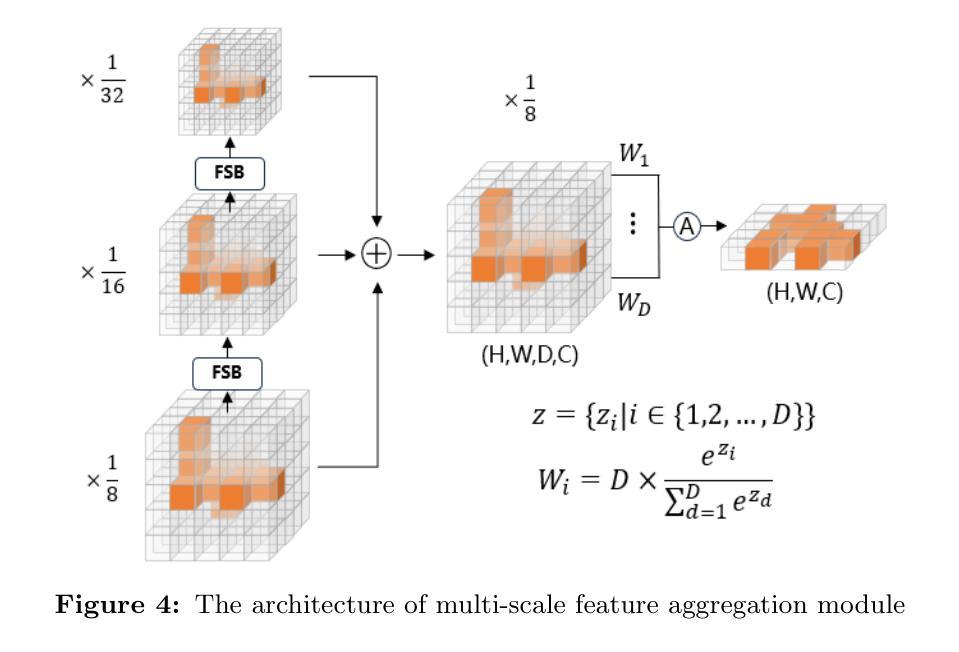
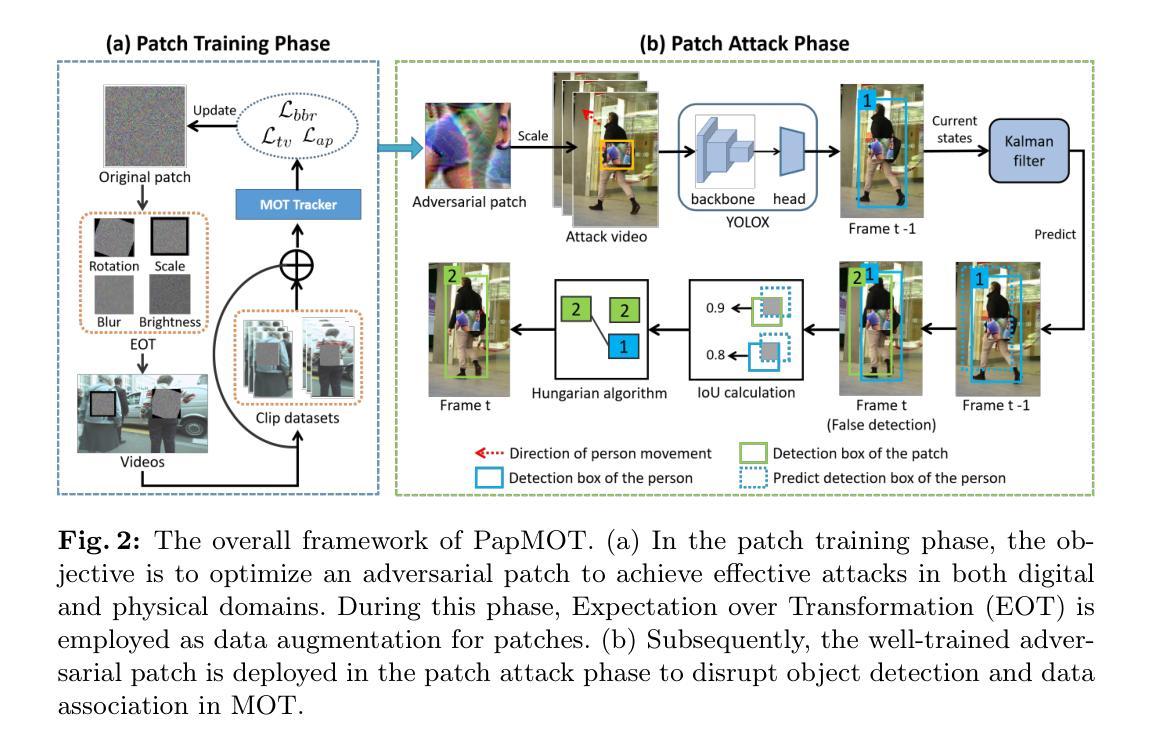
PapMOT: Exploring Adversarial Patch Attack against Multiple Object Tracking
Authors:Jiahuan Long, Tingsong Jiang, Wen Yao, Shuai Jia, Weijia Zhang, Weien Zhou, Chao Ma, Xiaoqian Chen
Tracking multiple objects in a continuous video stream is crucial for many computer vision tasks. It involves detecting and associating objects with their respective identities across successive frames. Despite significant progress made in multiple object tracking (MOT), recent studies have revealed the vulnerability of existing MOT methods to adversarial attacks. Nevertheless, all of these attacks belong to digital attacks that inject pixel-level noise into input images, and are therefore ineffective in physical scenarios. To fill this gap, we propose PapMOT, which can generate physical adversarial patches against MOT for both digital and physical scenarios. Besides attacking the detection mechanism, PapMOT also optimizes a printable patch that can be detected as new targets to mislead the identity association process. Moreover, we introduce a patch enhancement strategy to further degrade the temporal consistency of tracking results across video frames, resulting in more aggressive attacks. We further develop new evaluation metrics to assess the robustness of MOT against such attacks. Extensive evaluations on multiple datasets demonstrate that our PapMOT can successfully attack various architectures of MOT trackers in digital scenarios. We also validate the effectiveness of PapMOT for physical attacks by deploying printed adversarial patches in the real world.
在连续的视频流中跟踪多个物体对许多计算机视觉任务都至关重要。它涉及检测和关联物体及其在连续帧中的相应身份。尽管在多目标跟踪(MOT)方面取得了重大进展,但最近的研究表明现有MOT方法容易受到对抗性攻击的威胁。然而,所有这些攻击都属于向输入图像注入像素级噪声的数字攻击,因此在物理场景中无效。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了PapMOT,它能够针对数字场景和物理场景中的MOT生成物理对抗性补丁。除了攻击检测机制外,PapMOT还优化了一种可检测为全新目标点的可打印补丁,以误导身份关联过程。此外,我们还引入了补丁增强策略,以进一步降低视频帧之间跟踪结果的时序一致性,从而进行更激烈的攻击。我们还进一步开发了新的评价指标来评估MOT对这些攻击的鲁棒性。在多个数据集上的广泛评估表明,我们的PapMOT在数字场景中成功攻击了各种结构的MOT跟踪器。我们还通过在实际世界中部署打印的对抗性补丁来验证PapMOT针对物理攻击的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ECCV 2024
Summary
多目标跟踪(MOT)在计算机视觉任务中至关重要,涉及连续视频流中对象的检测和身份关联。现有MOT方法易受数字攻击的影响,这些攻击通过向输入图像注入像素级噪声来实施。为填补数字与物理场景之间攻击的空白,我们提出了PapMOT,它可针对MOT生成对抗性补丁,同时攻击检测机制和身份关联过程。此外,我们还引入了一种补丁增强策略,进一步降低视频帧间跟踪结果的时间一致性,实现更猛烈的攻击。我们开发了新评估指标,以评估MOT对此类攻击的鲁棒性。在多个数据集上的广泛评估表明,PapMOT在数字场景下成功攻击了各种架构的MOT跟踪器。通过在实际世界中部署印刷对抗性补丁,我们也验证了PapMOT在物理攻击方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 多目标跟踪(MOT)在计算机视觉中至关重要,涉及连续视频中的对象检测和身份关联。
- 现有MOT方法易受数字攻击影响,这些攻击通过向输入图像注入像素级噪声实施。
- PapMOT填补数字与物理场景间攻击的空白,生成对抗性补丁以同时攻击检测机制和身份关联过程。
- PapMOT引入补丁增强策略,降低视频帧间跟踪结果的时间一致性,实现更猛烈的攻击。
- 我们开发了新评估指标来评估MOT对这类攻击的鲁棒性。
- 在多个数据集上的广泛评估显示,PapMOT在数字场景下成功攻击多种MOT跟踪器。
点此查看论文截图


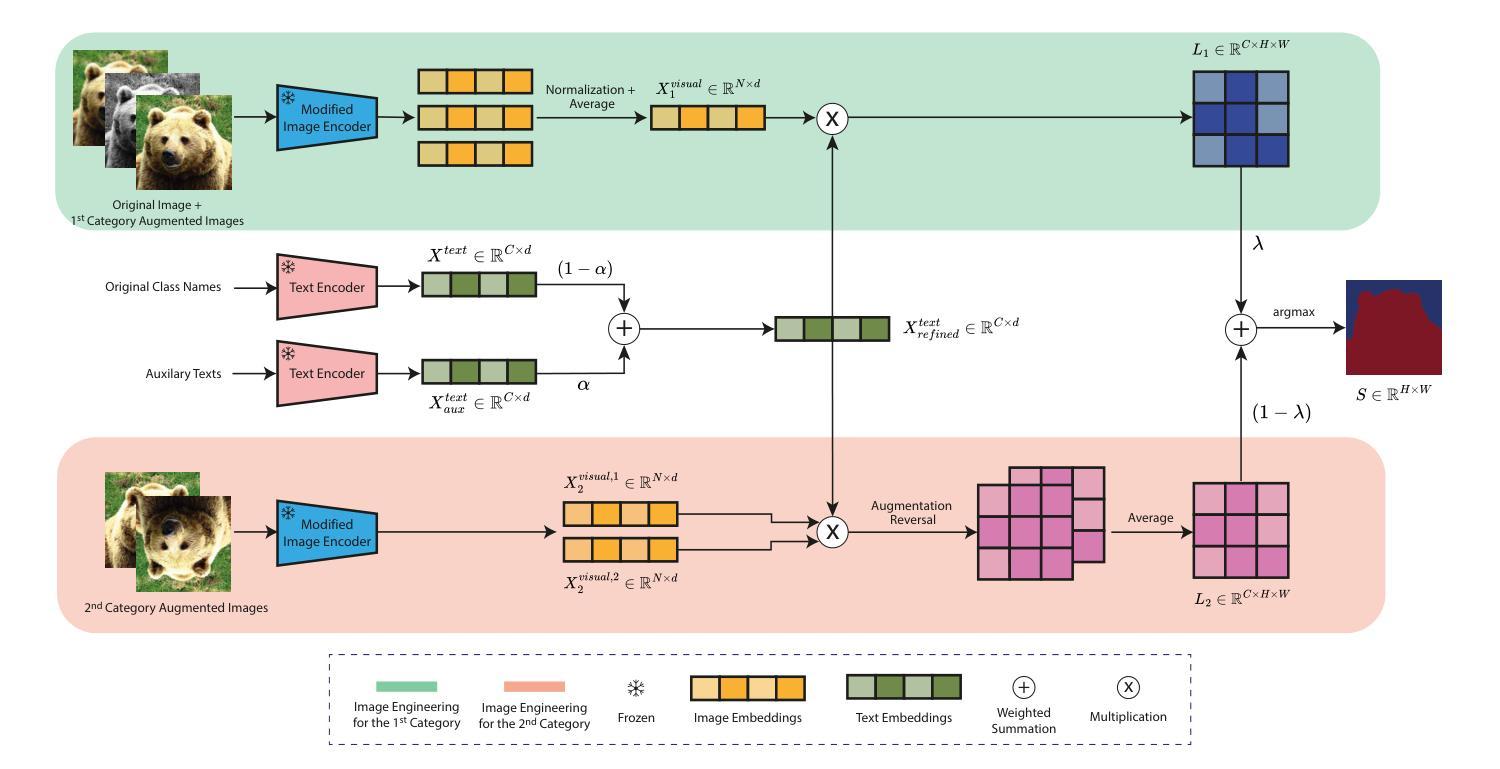
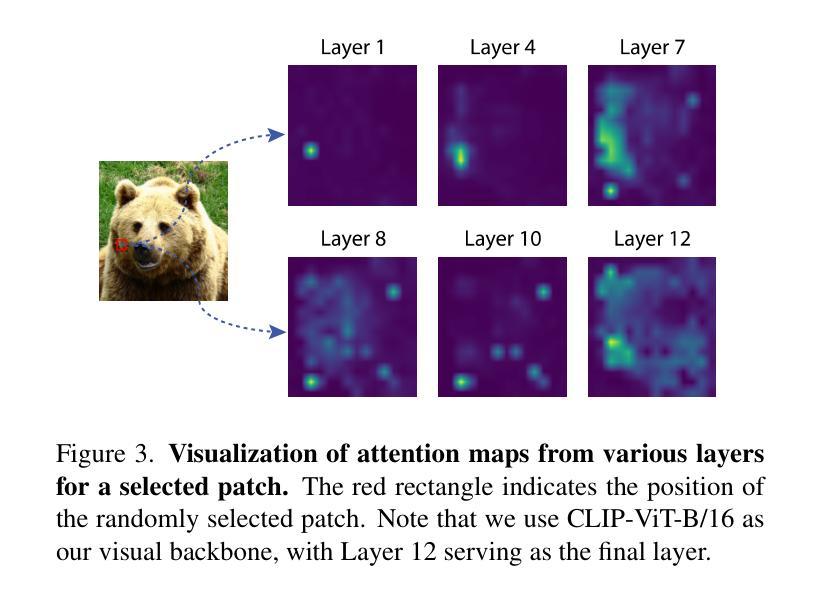
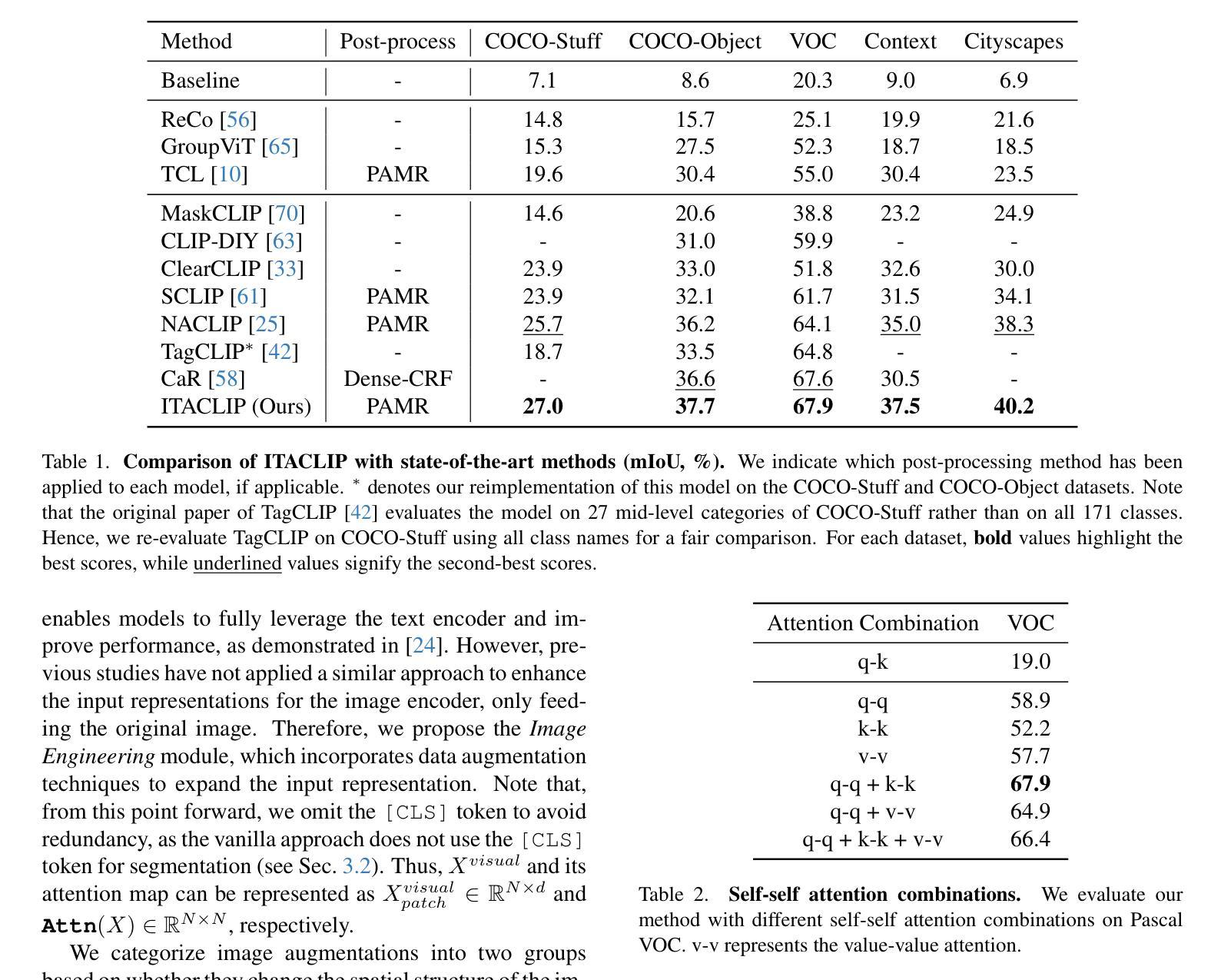
ITACLIP: Boosting Training-Free Semantic Segmentation with Image, Text, and Architectural Enhancements
Authors:M. Arda Aydın, Efe Mert Çırpar, Elvin Abdinli, Gozde Unal, Yusuf H. Sahin
Recent advances in foundational Vision Language Models (VLMs) have reshaped the evaluation paradigm in computer vision tasks. These foundational models, especially CLIP, have accelerated research in open-vocabulary computer vision tasks, including Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation (OVSS). Although the initial results are promising, the dense prediction capabilities of VLMs still require further improvement. In this study, we enhance the semantic segmentation performance of CLIP by introducing new modules and modifications: 1) architectural changes in the last layer of ViT and the incorporation of attention maps from the middle layers with the last layer, 2) Image Engineering: applying data augmentations to enrich input image representations, and 3) using Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate definitions and synonyms for each class name to leverage CLIP’s open-vocabulary capabilities. Our training-free method, ITACLIP, outperforms current state-of-the-art approaches on segmentation benchmarks such as COCO-Stuff, COCO-Object, Pascal Context, and Pascal VOC. Our code is available at https://github.com/m-arda-aydn/ITACLIP.
最近,基础视觉语言模型(VLMs)的进展重新塑造了计算机视觉任务的评估范式。尤其是CLIP等模型,加速了开放词汇计算机视觉任务的研究,包括开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)。虽然初步结果令人鼓舞,但VLMs的密集预测能力仍需进一步改进。本研究通过引入新模块和修改,提高了CLIP的语义分割性能:1)对ViT最后一层进行架构更改,并结合中间层的注意力图与最后一层;2)图像工程:应用数据增强来丰富输入图像表示;3)利用大型语言模型(LLM)为每一类名称生成定义和同义词,以利用CLIP的开放词汇能力。我们的无训练方法ITACLIP在COCO-Stuff、COCO-Object、Pascal Context和Pascal VOC等分割基准测试上超越了当前最先进的方法。我们的代码可在https://github.com/m-arda-aydn/ITACLIP找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期,基于Vision Language Models(VLMs)的进步重新塑造了计算机视觉任务的评估模式。特别是CLIP等模型推动了开放词汇计算机视觉任务的研究,如Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation(OVSS)。尽管初步结果具有前景,但VLMs的密集预测能力仍需改进。本研究通过引入新模块和修改增强CLIP的语义分割性能:1)修改ViT的最后一层并融入中间层的注意力图;2)图像工程:应用数据增强丰富输入图像表示;3)利用大型语言模型(LLMs)为每类名称生成定义和同义词,以利用CLIP的开放词汇能力。本研究提出的无训练方法ITACLIP在COCO-Stuff、COCO-Object、Pascal Context和Pascal VOC等分割基准测试中优于当前最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Language Models (VLMs) 的发展改变了计算机视觉任务的评估模式。
- CLIP等模型推动了开放词汇计算机视觉任务的研究。
- VLMs在密集预测方面仍需进一步改进。
- 本研究通过修改ViT的最后一层并融入中间层的注意力图增强CLIP的语义分割性能。
- 图像工程通过数据增强丰富输入图像表示。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLMs)生成类定义和同义词,以利用CLIP的开放词汇能力。
点此查看论文截图