⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-16 更新
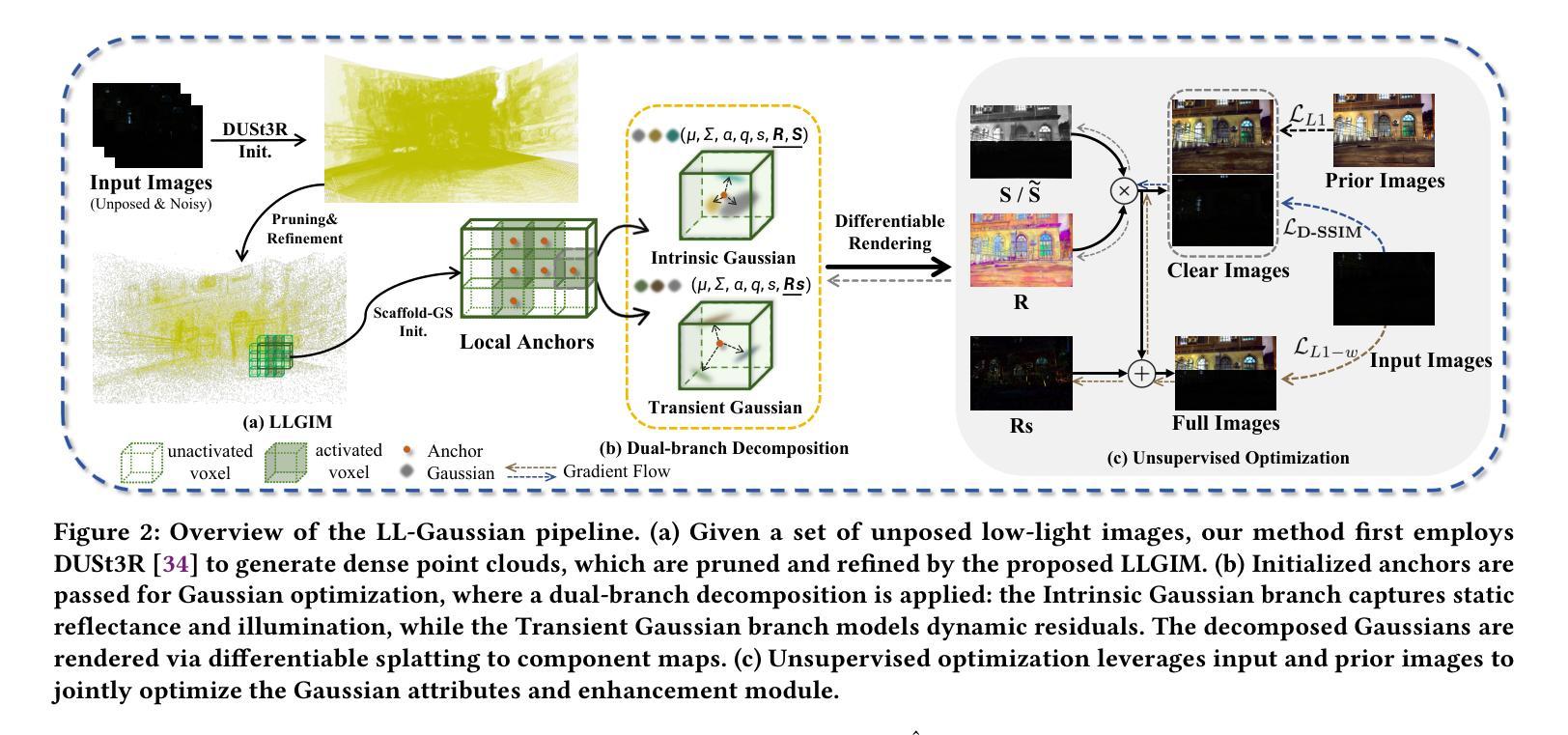
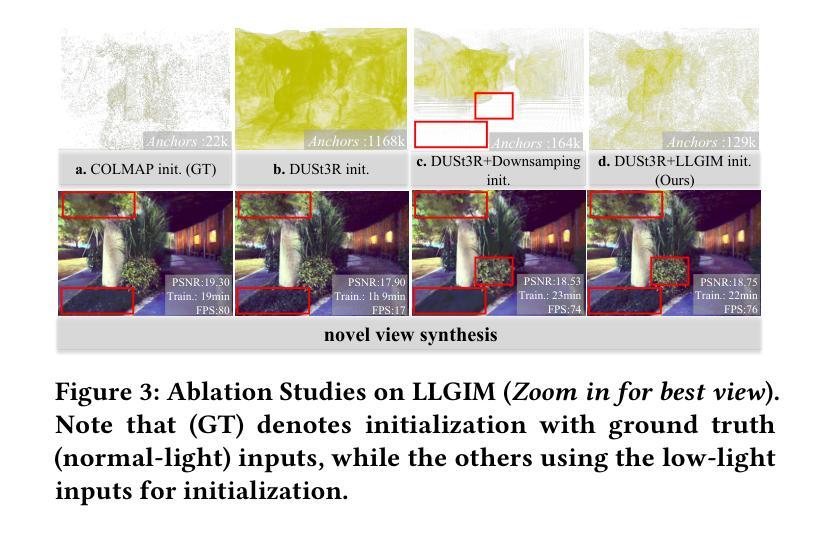
LL-Gaussian: Low-Light Scene Reconstruction and Enhancement via Gaussian Splatting for Novel View Synthesis
Authors:Hao Sun, Fenggen Yu, Huiyao Xu, Tao Zhang, Changqing Zou
Novel view synthesis (NVS) in low-light scenes remains a significant challenge due to degraded inputs characterized by severe noise, low dynamic range (LDR) and unreliable initialization. While recent NeRF-based approaches have shown promising results, most suffer from high computational costs, and some rely on carefully captured or pre-processed data–such as RAW sensor inputs or multi-exposure sequences–which severely limits their practicality. In contrast, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) enables real-time rendering with competitive visual fidelity; however, existing 3DGS-based methods struggle with low-light sRGB inputs, resulting in unstable Gaussian initialization and ineffective noise suppression. To address these challenges, we propose LL-Gaussian, a novel framework for 3D reconstruction and enhancement from low-light sRGB images, enabling pseudo normal-light novel view synthesis. Our method introduces three key innovations: 1) an end-to-end Low-Light Gaussian Initialization Module (LLGIM) that leverages dense priors from learning-based MVS approach to generate high-quality initial point clouds; 2) a dual-branch Gaussian decomposition model that disentangles intrinsic scene properties (reflectance and illumination) from transient interference, enabling stable and interpretable optimization; 3) an unsupervised optimization strategy guided by both physical constrains and diffusion prior to jointly steer decomposition and enhancement. Additionally, we contribute a challenging dataset collected in extreme low-light environments and demonstrate the effectiveness of LL-Gaussian. Compared to state-of-the-art NeRF-based methods, LL-Gaussian achieves up to 2,000 times faster inference and reduces training time to just 2%, while delivering superior reconstruction and rendering quality.
在低光照场景中的新型视图合成(NVS)仍然是一个重大挑战,因为退化输入的特征包括严重噪声、低动态范围(LDR)和不可靠的初始化。虽然最近的基于NeRF的方法已经显示出有希望的结果,但大多数方法的计算成本很高,有些方法依赖于精心捕获或预处理的数据,如RAW传感器输入或多曝光序列,这严重限制了其实用性。相比之下,3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)能够实现具有竞争视觉保真度的实时渲染;然而,现有的基于3DGS的方法在处理低光sRGB输入时遇到困难,导致高斯初始化不稳定且噪声抑制无效。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了LL-Gaussian,这是一个从低光sRGB图像进行3D重建和增强的新型框架,能够实现伪正常光新型视图合成。我们的方法引入了三个关键创新点:1)端到端的低光高斯初始化模块(LLGIM),它利用基于学习的MVS方法的密集先验来生成高质量初始点云;2)双分支高斯分解模型,将场景的内在属性(反射率和照明)从瞬态干扰中分离出来,实现稳定和可解释的优化;3)一种无监督优化策略,由物理约束和扩散先验共同引导分解和增强。此外,我们贡献了一个在极端低光环境中收集的挑战性数据集,并展示了LL-Gaussian的有效性。与最先进的基于NeRF的方法相比,LL-Gaussian实现了高达2000倍更快的推理速度,并将训练时间减少到仅2%,同时提供卓越的重建和渲染质量。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对低光场景中的新视角合成(NVS),现有方法面临噪声严重、动态范围低及初始化不稳定等问题。尽管基于NeRF的方法展现出潜力,但它们计算成本高且依赖精细捕捉或预处理的数据,限制了实用性。相比之下,3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)可实现实时渲染并具备竞争性的视觉保真度,但处理低光sRGB输入时表现不稳定。为此,我们提出LL-Gaussian框架,用于从低光sRGB图像进行3D重建和增强,实现伪正常光新视角合成。该方法引入三项关键创新:1)端到端的低光高斯初始化模块(LLGIM),利用基于学习的MVS方法的密集先验生成高质量初始点云;2)双分支高斯分解模型,将场景固有属性(反射和照明)与瞬态干扰分离,实现稳定和可解释的优化;3)由物理约束和扩散先验引导的无监督优化策略,共同引导分解和增强。此外,我们贡献了在极端低光环境中收集的挑战性数据集,并展示了LL-Gaussian的有效性。与先进的NeRF方法相比,LL-Gaussian推理速度最快可达2000倍,训练时间减少至仅2%,同时提供优越的重构和渲染质量。
要点摘要
- 低光场景中的新视角合成(NVS)面临诸多挑战,包括噪声、动态范围和初始化问题。
- 基于NeRF的方法虽具有潜力,但计算成本高且依赖特定数据,实用性受限。
- 3DGS方法可实现实时渲染,但在处理低光sRGB输入时表现不稳定。
- LL-Gaussian框架通过三项关键创新解决这些问题:低光高斯初始化模块、双分支高斯分解模型和无监督优化策略。
- LL-Gaussian在极端低光环境中收集的挑战性数据集上表现优异。
- 与其他方法相比,LL-Gaussian具有更快的推理速度和减少的训练时间。
点此查看论文截图

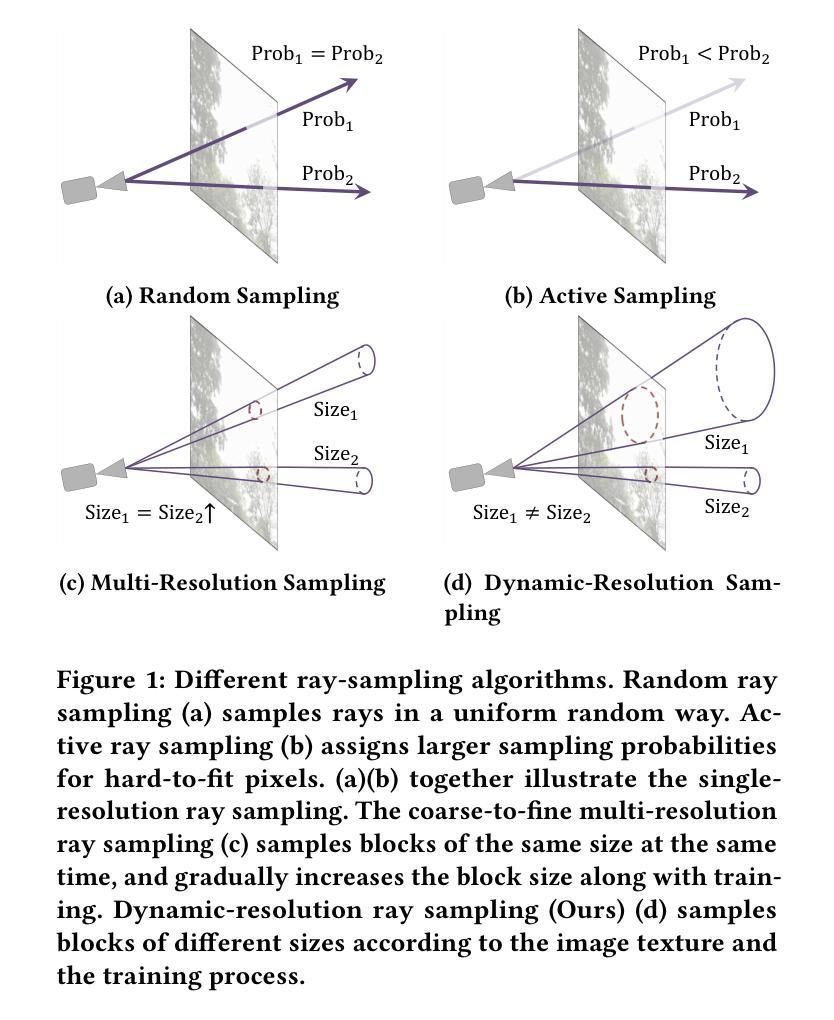
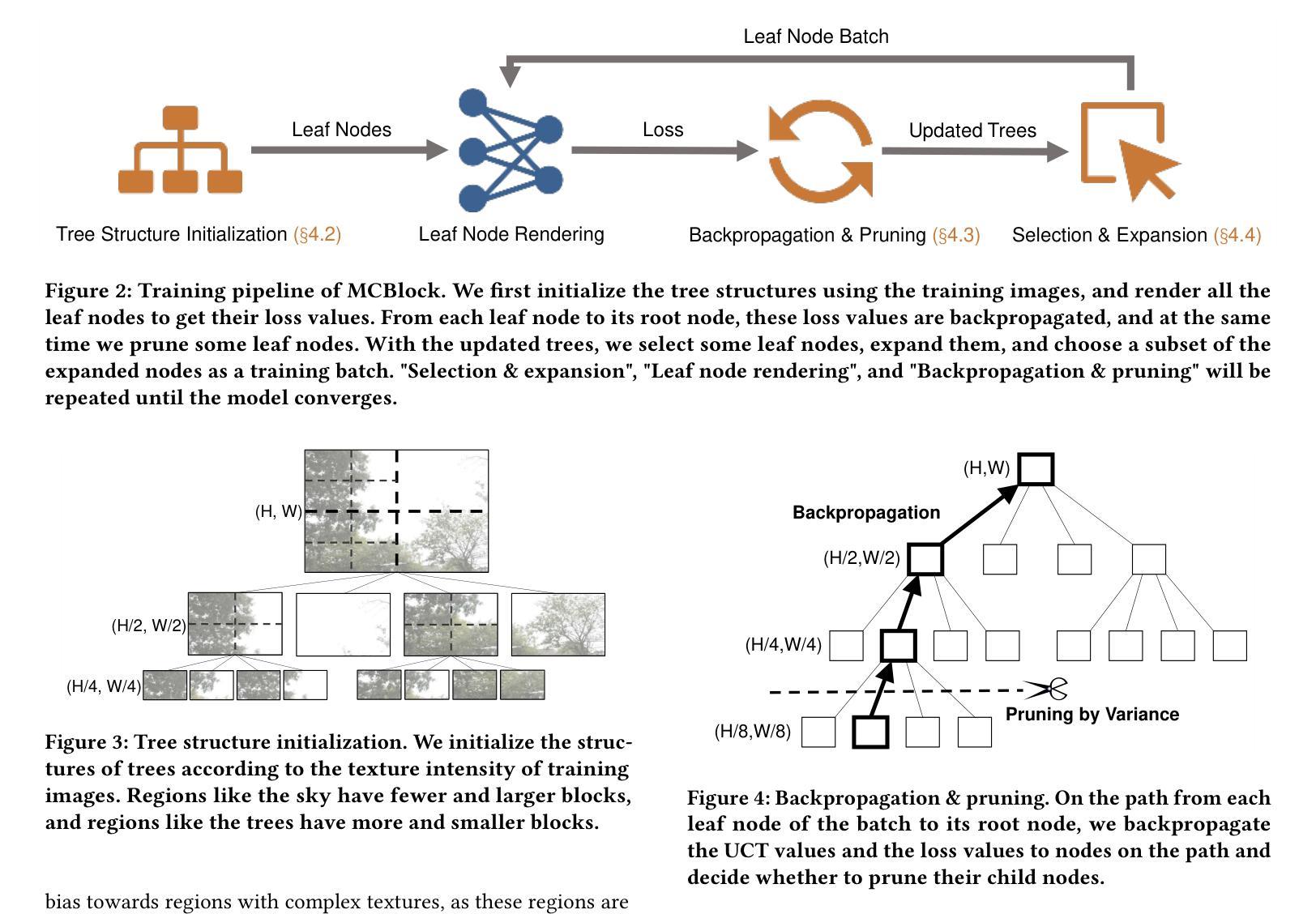
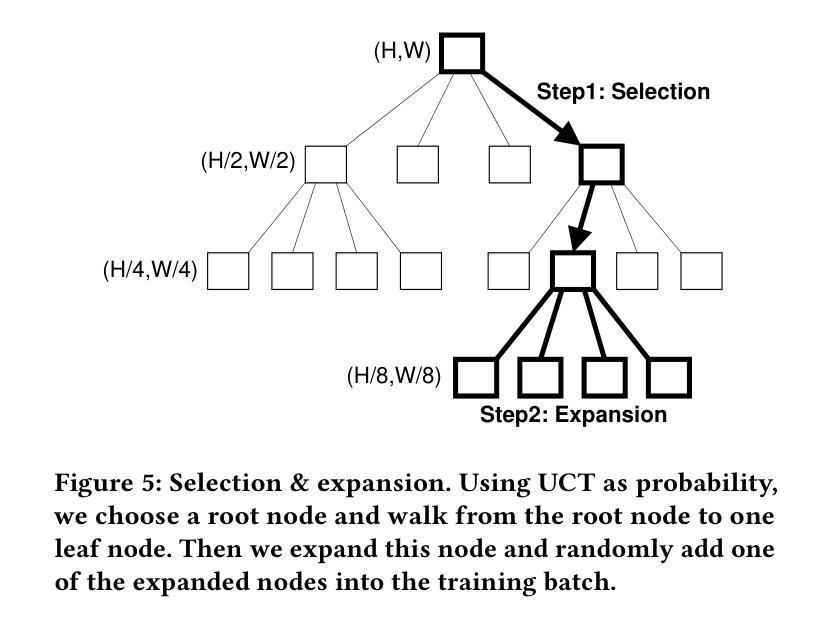
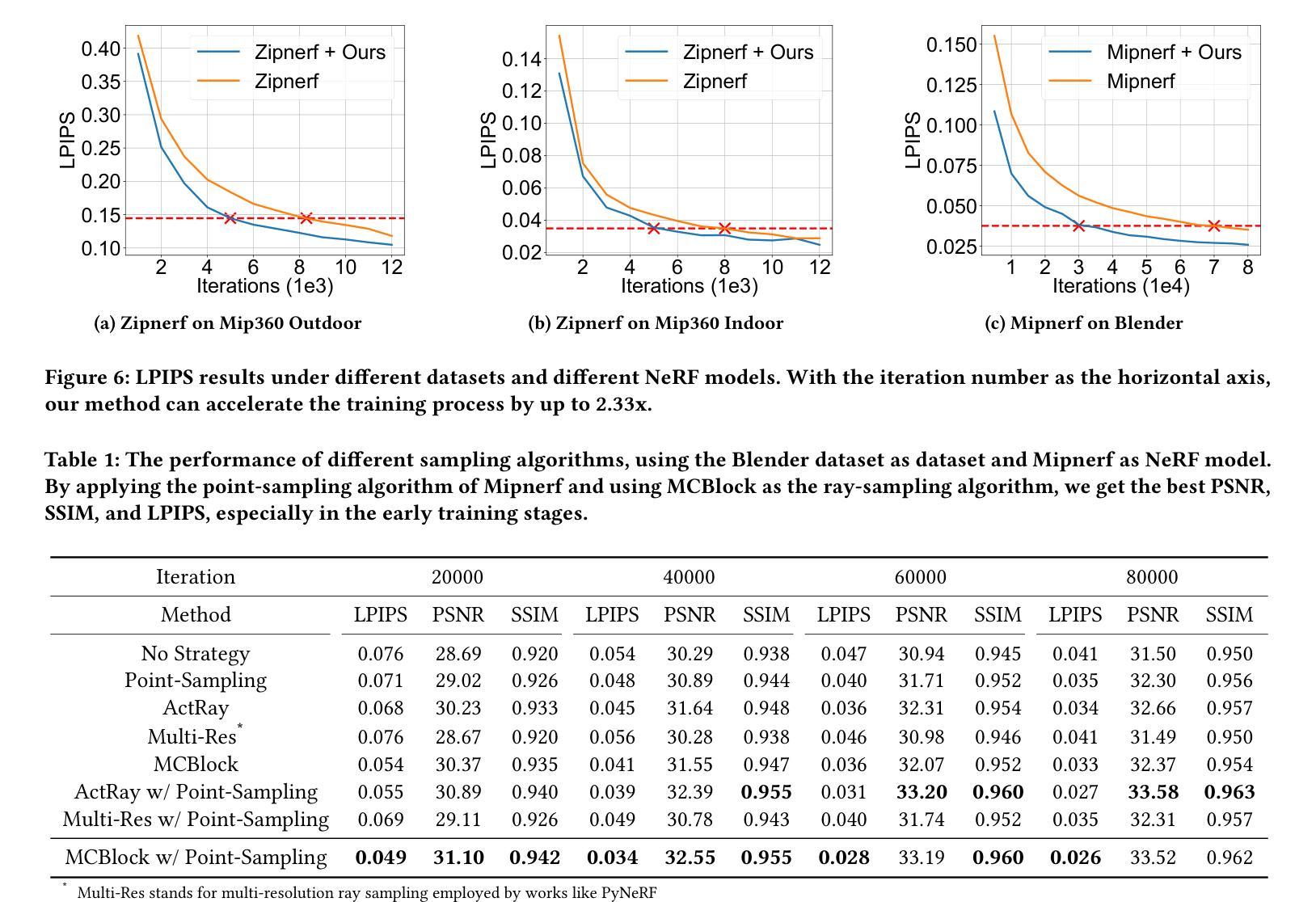
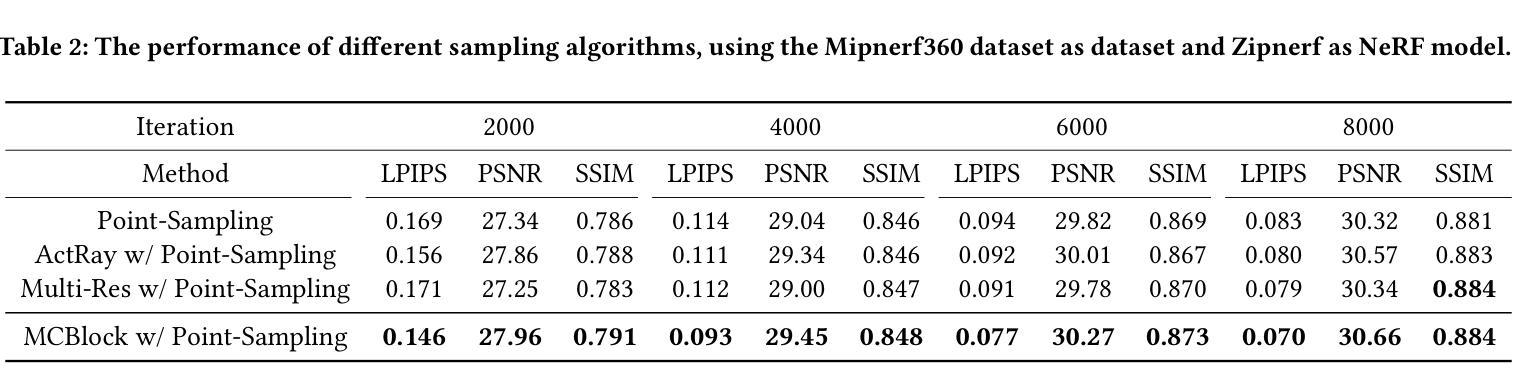
MCBlock: Boosting Neural Radiance Field Training Speed by MCTS-based Dynamic-Resolution Ray Sampling
Authors:Yunpeng Tan, Junlin Hao, Jiangkai Wu, Liming Liu, Qingyang Li, Xinggong Zhang
Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) is widely known for high-fidelity novel view synthesis. However, even the state-of-the-art NeRF model, Gaussian Splatting, requires minutes for training, far from the real-time performance required by multimedia scenarios like telemedicine. One of the obstacles is its inefficient sampling, which is only partially addressed by existing works. Existing point-sampling algorithms uniformly sample simple-texture regions (easy to fit) and complex-texture regions (hard to fit), while existing ray-sampling algorithms sample these regions all in the finest granularity (i.e. the pixel level), both wasting GPU training resources. Actually, regions with different texture intensities require different sampling granularities. To this end, we propose a novel dynamic-resolution ray-sampling algorithm, MCBlock, which employs Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to partition each training image into pixel blocks with different sizes for active block-wise training. Specifically, the trees are initialized according to the texture of training images to boost the initialization speed, and an expansion/pruning module dynamically optimizes the block partition. MCBlock is implemented in Nerfstudio, an open-source toolset, and achieves a training acceleration of up to 2.33x, surpassing other ray-sampling algorithms. We believe MCBlock can apply to any cone-tracing NeRF model and contribute to the multimedia community.
神经辐射场(NeRF)以其高保真度的新型视图合成而广为人知。然而,即使是最先进的NeRF模型——高斯拼贴(Gaussian Splatting),其训练也需要数分钟时间,远远不能满足远程医疗等多媒体场景对实时性能的要求。其中一个障碍是其低效的采样方式,现有研究对此只进行了部分解决。现有的点采样算法对简单纹理区域(易于拟合)和复杂纹理区域(难以拟合)进行统一采样,而现有的射线采样算法则在这些区域中以最精细的粒度(即像素级别)进行采样,两者都浪费了GPU训练资源。实际上,不同纹理强度的区域需要不同的采样粒度。为此,我们提出了一种新型动态分辨率射线采样算法MCBlock,该算法采用蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)将每一张训练图像分割成不同大小的像素块进行活动块级训练。具体来说,树根据训练图像的纹理进行初始化以加速初始化速度,一个扩展/修剪模块动态优化块分割。MCBlock在Nerfstudio这个开源工具包中实现,实现了高达2.33倍的训练加速,超越了其他射线采样算法。我们相信MCBlock可以应用于任何锥追踪NeRF模型,并为多媒体领域做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经网络辐射场(NeRF)以高保真度新颖视图合成为人所熟知,但其现有技术如高斯拼接仍存在训练时间长的问题,难以满足多媒体场景如远程医疗的实时性能要求。针对这一问题,提出了一种动态分辨率射线采样算法MCBlock,采用蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)对训练图像进行不同大小的像素块分割,实现活动块级训练。此算法可加速训练,达到2.33倍,并适用于任何锥追踪NeRF模型,对多媒体领域有所贡献。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF在高保真新颖视图合成方面的优势及其面临的实时性能挑战。
- 现有采样方法(包括点采样和射线采样)在GPU资源利用方面存在的问题。
- MCBlock算法采用蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)进行像素块分割,实现动态分辨率射线采样。
- MCBlock算法能够在训练图像上实现活动块级训练。
- MCBlock算法在训练加速方面取得了显著成果,达到2.33倍。
- MCBlock算法适用于任何锥追踪NeRF模型。
点此查看论文截图

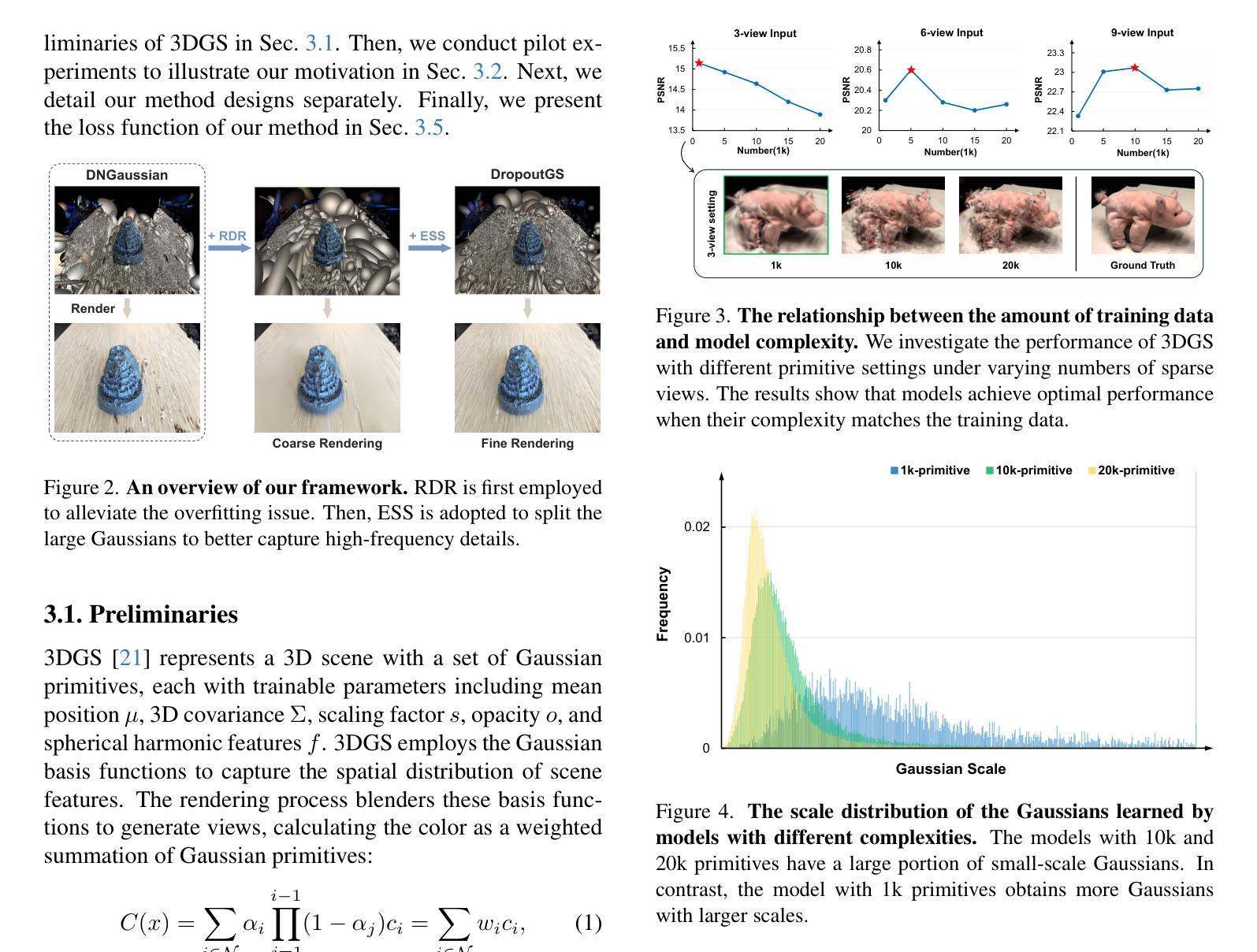
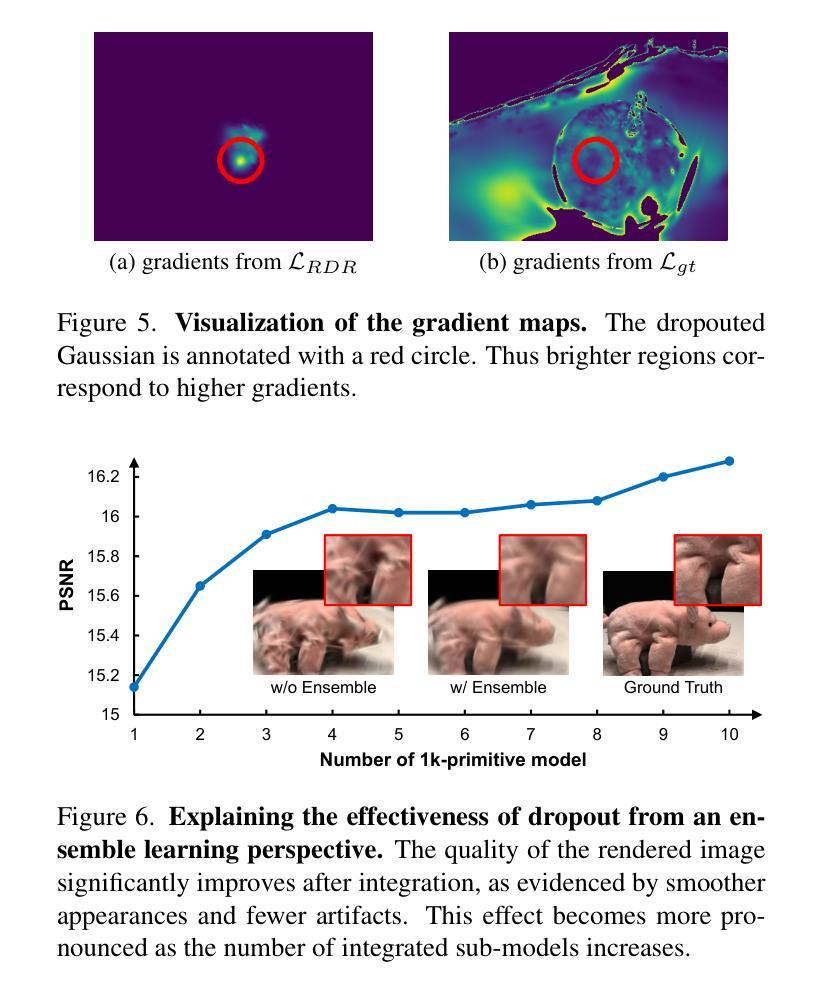
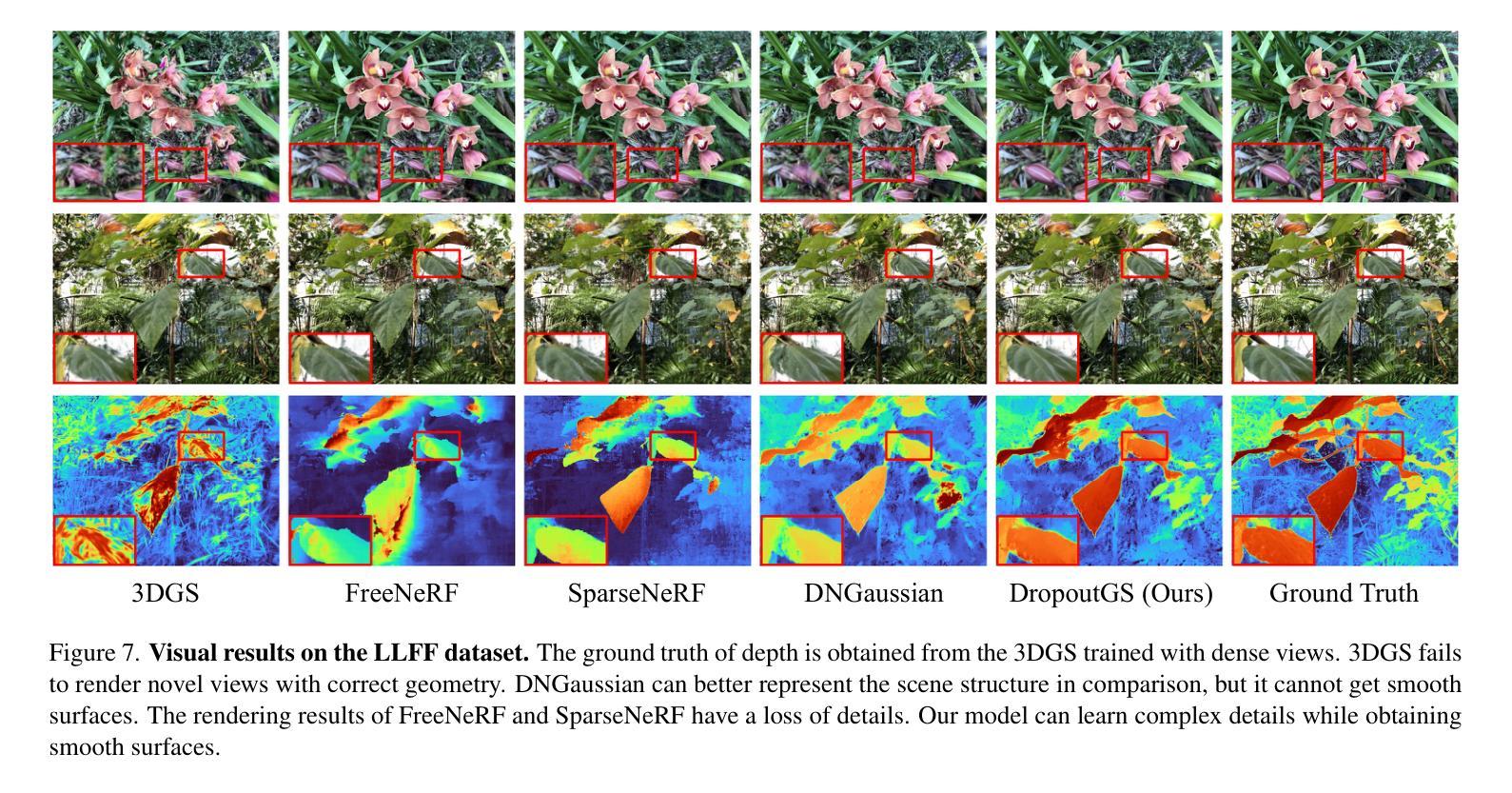
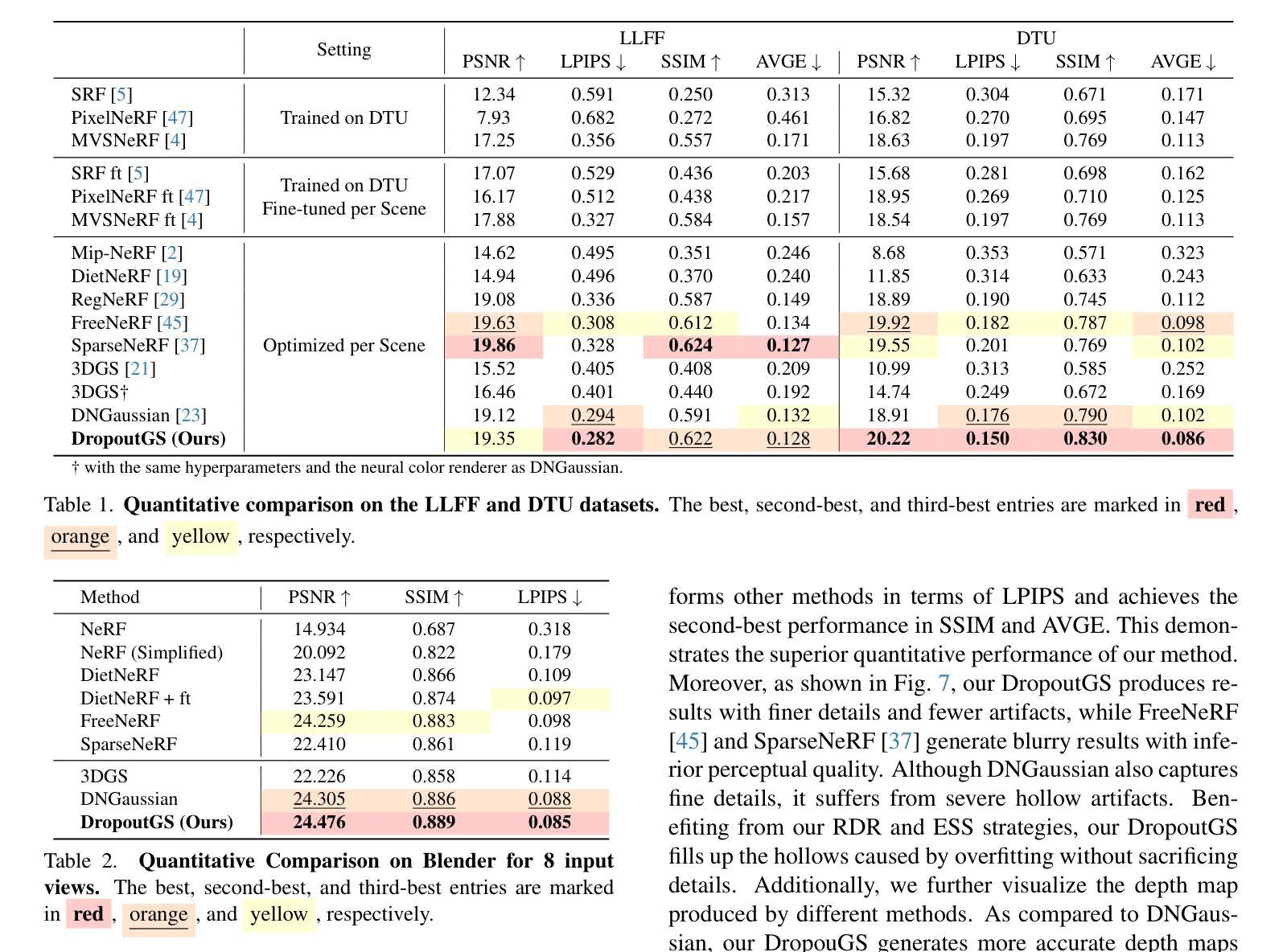
DropoutGS: Dropping Out Gaussians for Better Sparse-view Rendering
Authors:Yexing Xu, Longguang Wang, Minglin Chen, Sheng Ao, Li Li, Yulan Guo
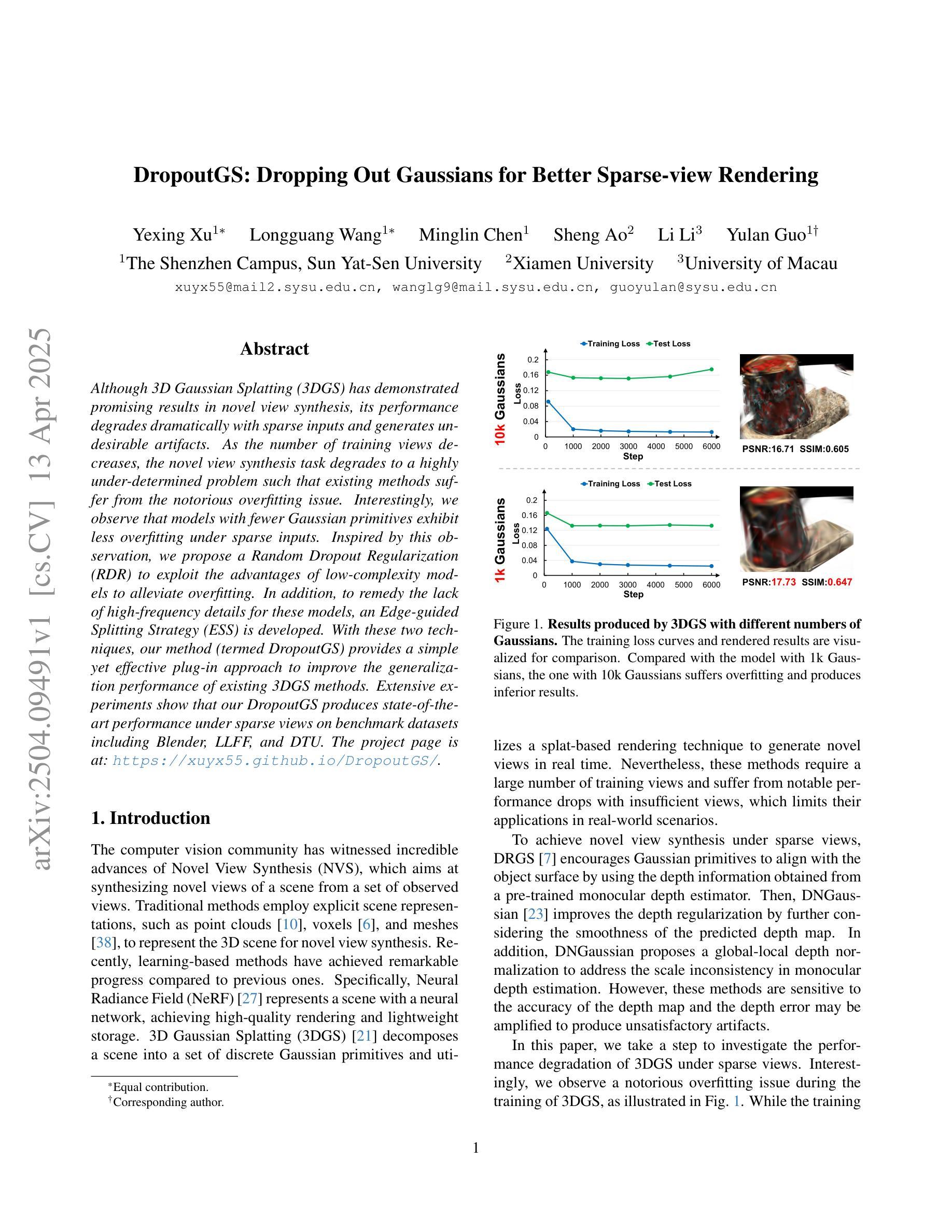
Although 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated promising results in novel view synthesis, its performance degrades dramatically with sparse inputs and generates undesirable artifacts. As the number of training views decreases, the novel view synthesis task degrades to a highly under-determined problem such that existing methods suffer from the notorious overfitting issue. Interestingly, we observe that models with fewer Gaussian primitives exhibit less overfitting under sparse inputs. Inspired by this observation, we propose a Random Dropout Regularization (RDR) to exploit the advantages of low-complexity models to alleviate overfitting. In addition, to remedy the lack of high-frequency details for these models, an Edge-guided Splitting Strategy (ESS) is developed. With these two techniques, our method (termed DropoutGS) provides a simple yet effective plug-in approach to improve the generalization performance of existing 3DGS methods. Extensive experiments show that our DropoutGS produces state-of-the-art performance under sparse views on benchmark datasets including Blender, LLFF, and DTU. The project page is at: https://xuyx55.github.io/DropoutGS/.
尽管三维高斯模糊技术(3DGS)在新型视图合成领域取得了有前景的结果,但在稀疏输入情况下其性能会显著下降,并产生不良伪影。随着训练视图数量的减少,新型视图合成任务降级为一个高度欠定问题,导致现有方法受到严重的过拟合问题影响。有趣的是,我们观察到具有更少高斯基元的模型在稀疏输入情况下表现出较少的过拟合现象。受此观察启发,我们提出了一种随机失活正则化(RDR)方法,以利用低复杂度模型的优势来缓解过拟合问题。此外,为了弥补这些模型缺乏高频细节的问题,我们开发了一种边缘引导分裂策略(ESS)。通过这两种技术,我们的方法(称为DropoutGS)提供了一种简单而有效的插件方法,以提高现有3DGS方法的泛化性能。大量实验表明,我们的DropoutGS在包括Blender、LLFF和DTU在内的基准数据集上,稀疏视图下的性能达到了最新水平。项目页面为:https://xuyx55.github.io/DropoutGS/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
在基于高斯喷绘技术的三维渲染过程中,尽管稀疏输入可能会导致算法性能显著下降并产生不良伪影,但减少高斯原始模型数量可以降低过拟合现象。为此,本研究提出了随机丢弃正则化(RDR)方法,并结合边缘引导分割策略(ESS),以提升现有技术的泛化性能。DropoutGS作为一种简单有效的插件方法,能够在稀疏视图下实现先进性能。该项目已在多个基准数据集上进行了广泛实验验证。
Key Takeaways
- 稀疏输入导致现有三维高斯喷绘技术性能下降并产生伪影。
- 减少模型中的高斯原始数量可降低过拟合现象。
- 随机丢弃正则化(RDR)方法用于利用低复杂度模型的优势缓解过拟合问题。
- 为弥补模型缺乏高频细节的问题,开发了边缘引导分割策略(ESS)。
- DropoutGS方法结合了RDR和ESS技术,提高了现有三维高斯喷绘技术的泛化性能。
点此查看论文截图
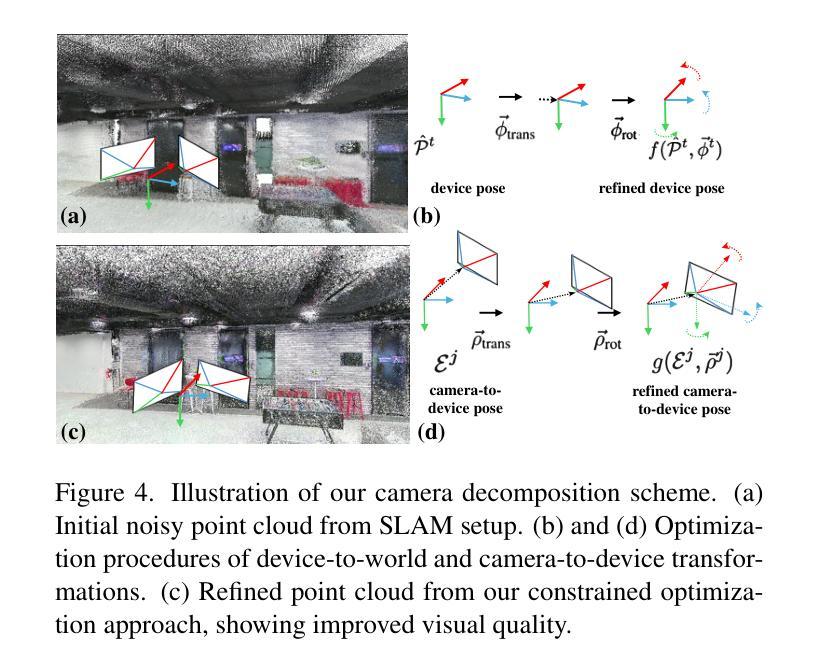
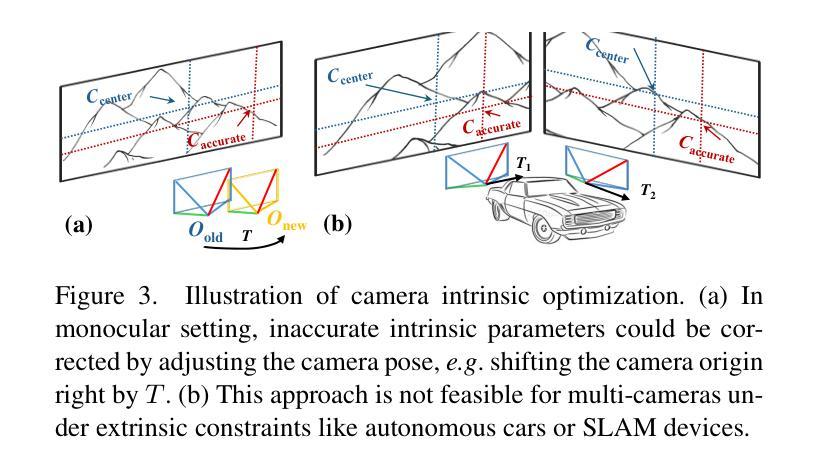
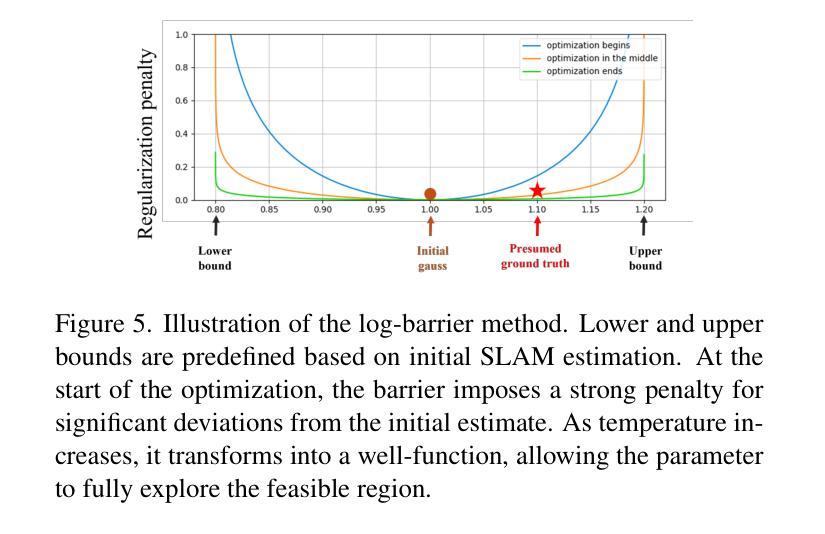
A Constrained Optimization Approach for Gaussian Splatting from Coarsely-posed Images and Noisy Lidar Point Clouds
Authors:Jizong Peng, Tze Ho Elden Tse, Kai Xu, Wenchao Gao, Angela Yao
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) is a powerful reconstruction technique, but it needs to be initialized from accurate camera poses and high-fidelity point clouds. Typically, the initialization is taken from Structure-from-Motion (SfM) algorithms; however, SfM is time-consuming and restricts the application of 3DGS in real-world scenarios and large-scale scene reconstruction. We introduce a constrained optimization method for simultaneous camera pose estimation and 3D reconstruction that does not require SfM support. Core to our approach is decomposing a camera pose into a sequence of camera-to-(device-)center and (device-)center-to-world optimizations. To facilitate, we propose two optimization constraints conditioned to the sensitivity of each parameter group and restricts each parameter’s search space. In addition, as we learn the scene geometry directly from the noisy point clouds, we propose geometric constraints to improve the reconstruction quality. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms the existing (multi-modal) 3DGS baseline and methods supplemented by COLMAP on both our collected dataset and two public benchmarks.
3D高斯展开(3DGS)是一种强大的重建技术,但它需要以精确的相机姿态和高保真点云作为初始值。通常,初始化是从运动结构(SfM)算法中提取的;然而,SfM耗时较长,限制了3DGS在真实场景和大规模场景重建中的应用。我们引入了一种用于同时估计相机姿态和进行三维重建的约束优化方法,该方法不需要SfM的支持。我们的方法的核心是将相机姿态分解成一系列相机到(设备)中心和(设备)中心到世界的优化。为了简化操作,我们提出了两种针对每个参数组敏感性的优化约束,并限制了每个参数的搜索空间。此外,由于我们直接从噪声点云学习场景几何,因此提出了几何约束以提高重建质量。实验表明,该方法在收集的数据集和两个公共基准测试上显著优于现有的(多模态)3DGS基准方法和由COLMAP辅助的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
3DGS技术需依赖准确的相机姿态与高保真点云进行初始化,通常依赖于从运动恢复结构(SfM)算法实现。但SfM耗时较长,限制了其在真实场景和大规模场景重建中的应用。为此,研究者提出一种约束优化方法,该方法能够同时估计相机姿态并进行三维重建,无需SfM支持。其核心是将相机姿态分解为一系列相机到设备中心和设备中心到世界的优化序列,提出两种针对每种参数组敏感性的优化约束,并限制每个参数的搜索空间。此外,直接从噪声点云学习场景几何,提出几何约束以提高重建质量。实验表明,该方法在收集的数据集和两个公开基准测试上显著优于现有的多模态3DGS方法和补充COLMAP的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术需要初始化相机姿态和高保真点云。
- 通常使用SfM算法进行初始化,但这种方法耗时较长,限制了其在真实场景和大规模场景重建中的应用。
- 研究者提出了一种新的约束优化方法,可同时估计相机姿态并进行三维重建,无需SfM支持。
- 该方法通过分解相机姿态优化过程,并引入针对参数组的敏感性优化约束。
- 为了提高从噪声点云中的重建质量,引入了几何约束。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在数据集的公开基准测试中显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

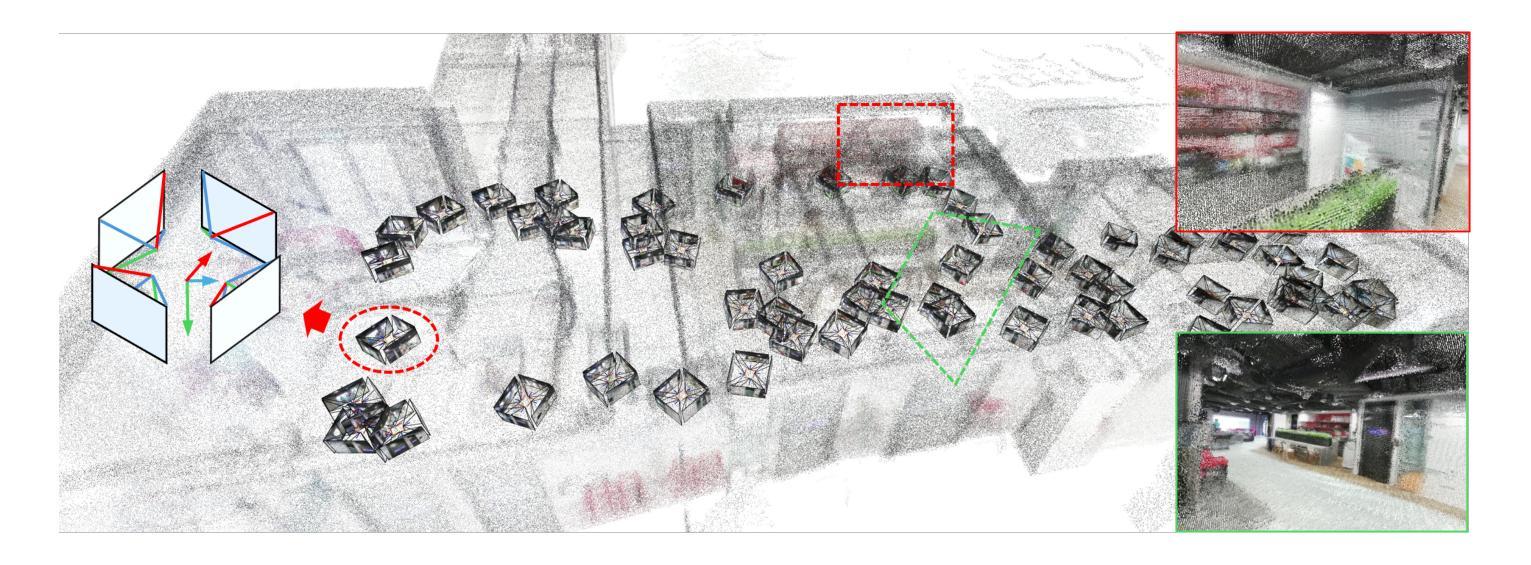

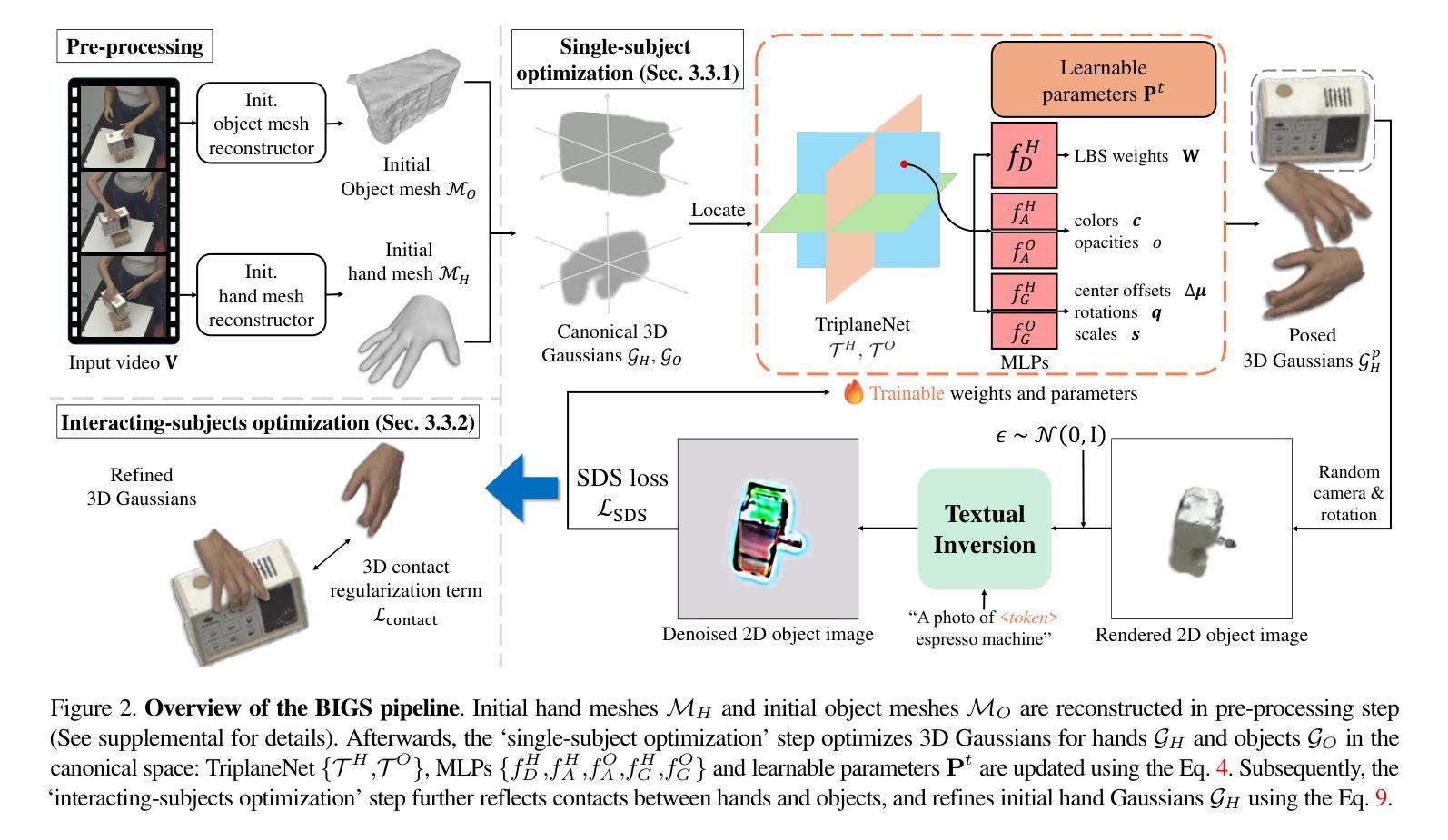
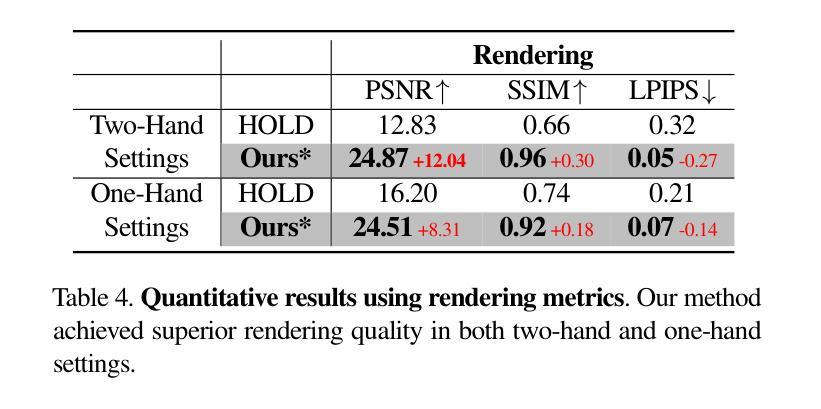
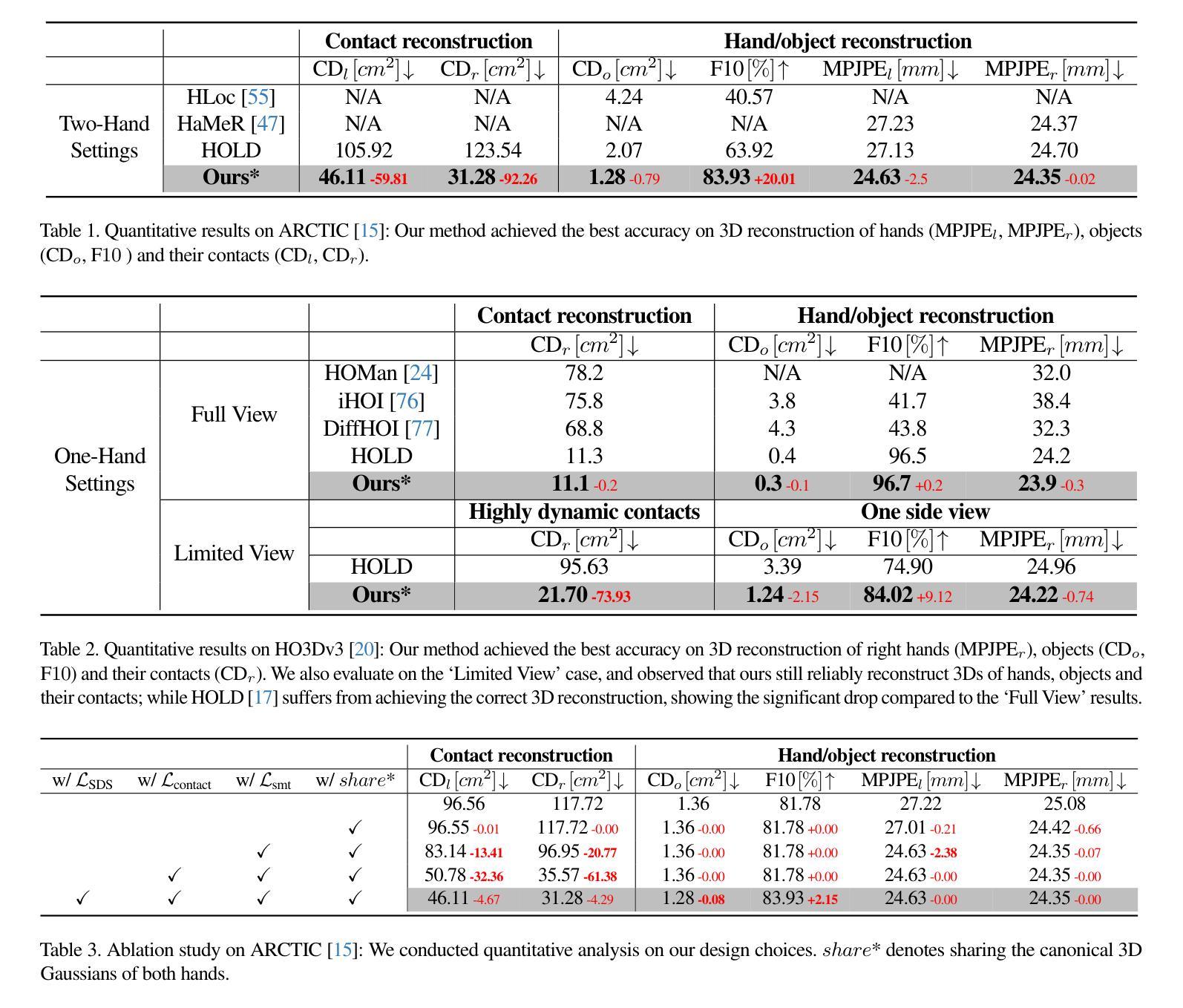
BIGS: Bimanual Category-agnostic Interaction Reconstruction from Monocular Videos via 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jeongwan On, Kyeonghwan Gwak, Gunyoung Kang, Junuk Cha, Soohyun Hwang, Hyein Hwang, Seungryul Baek
Reconstructing 3Ds of hand-object interaction (HOI) is a fundamental problem that can find numerous applications. Despite recent advances, there is no comprehensive pipeline yet for bimanual class-agnostic interaction reconstruction from a monocular RGB video, where two hands and an unknown object are interacting with each other. Previous works tackled the limited hand-object interaction case, where object templates are pre-known or only one hand is involved in the interaction. The bimanual interaction reconstruction exhibits severe occlusions introduced by complex interactions between two hands and an object. To solve this, we first introduce BIGS (Bimanual Interaction 3D Gaussian Splatting), a method that reconstructs 3D Gaussians of hands and an unknown object from a monocular video. To robustly obtain object Gaussians avoiding severe occlusions, we leverage prior knowledge of pre-trained diffusion model with score distillation sampling (SDS) loss, to reconstruct unseen object parts. For hand Gaussians, we exploit the 3D priors of hand model (i.e., MANO) and share a single Gaussian for two hands to effectively accumulate hand 3D information, given limited views. To further consider the 3D alignment between hands and objects, we include the interacting-subjects optimization step during Gaussian optimization. Our method achieves the state-of-the-art accuracy on two challenging datasets, in terms of 3D hand pose estimation (MPJPE), 3D object reconstruction (CDh, CDo, F10), and rendering quality (PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS), respectively.
重建手物交互(HOI)的3D模型是一个具有许多应用基础性问题。尽管最近有所进展,但目前还没有从单目RGB视频中实现双手无关类别的交互重建的全面流程,其中两只手和一个未知对象在相互交互。之前的工作解决了有限的手物交互情况,其中对象模板是预先已知的,或者只涉及一只手进行交互。双手交互重建会出现严重的遮挡问题,这是由于两只手和一个对象之间的复杂交互造成的。为了解决这个问题,我们首先推出了BIGS(双手交互3D高斯模板),这种方法可以从单目视频中重建手和未知对象的3D高斯模型。为了稳健地获取对象的高斯模型,避免严重的遮挡问题,我们利用预训练的扩散模型的先验知识,结合得分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失,来重建未见到的对象部分。对于手的高斯模型,我们利用手的3D先验知识(即MANO模型),并为两只手共享一个单一的高斯模型,以在有限的视角内有效地累积手的3D信息。为了进一步考虑手和物体之间的3D对齐,我们在高斯优化过程中包含了交互主体的优化步骤。我们的方法在具有挑战性的两个数据集上实现了最先进的准确性,在三维手姿态估计(MPJPE)、三维物体重建(CDh、CDo、F10)和渲染质量(PSNR、SSIM、LPIPS)等方面均取得了优异成绩。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
针对手-对象交互(HOI)的三维重建是一个具有众多应用前景的基础问题。针对双目手与未知对象交互的复杂情况,本研究提出了一种名为BIGS(双手交互三维高斯喷射)的方法,实现了从单目视频中重建双手与未知对象的三维高斯模型。该方法利用预训练扩散模型的先验知识,结合评分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失,有效重建了被遮挡的对象部分;同时利用手模型的3D先验信息,为双手共享单一高斯模型以累积有限视角下的手部三维信息。本研究在两项具有挑战性的数据集上达到了领先的准确度,在手部姿态估计和对象重建等多个方面表现优秀。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对手与未知对象交互的三维重建问题,提出了一个全新的方法BIGS。
- 该方法能够从单目视频中重建双手与未知对象的三维高斯模型。
- 利用预训练扩散模型的先验知识和评分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失技术解决了因手部交互导致的严重遮挡问题。
- 通过利用手部模型的3D先验信息,为双手共享单一高斯模型以优化信息累积。
- 在优化高斯模型时考虑了手和对象之间的三维对齐关系。
- 在两个具有挑战性的数据集上实现了卓越的准确性,包括手部姿态估计和对象重建等方面。
点此查看论文截图

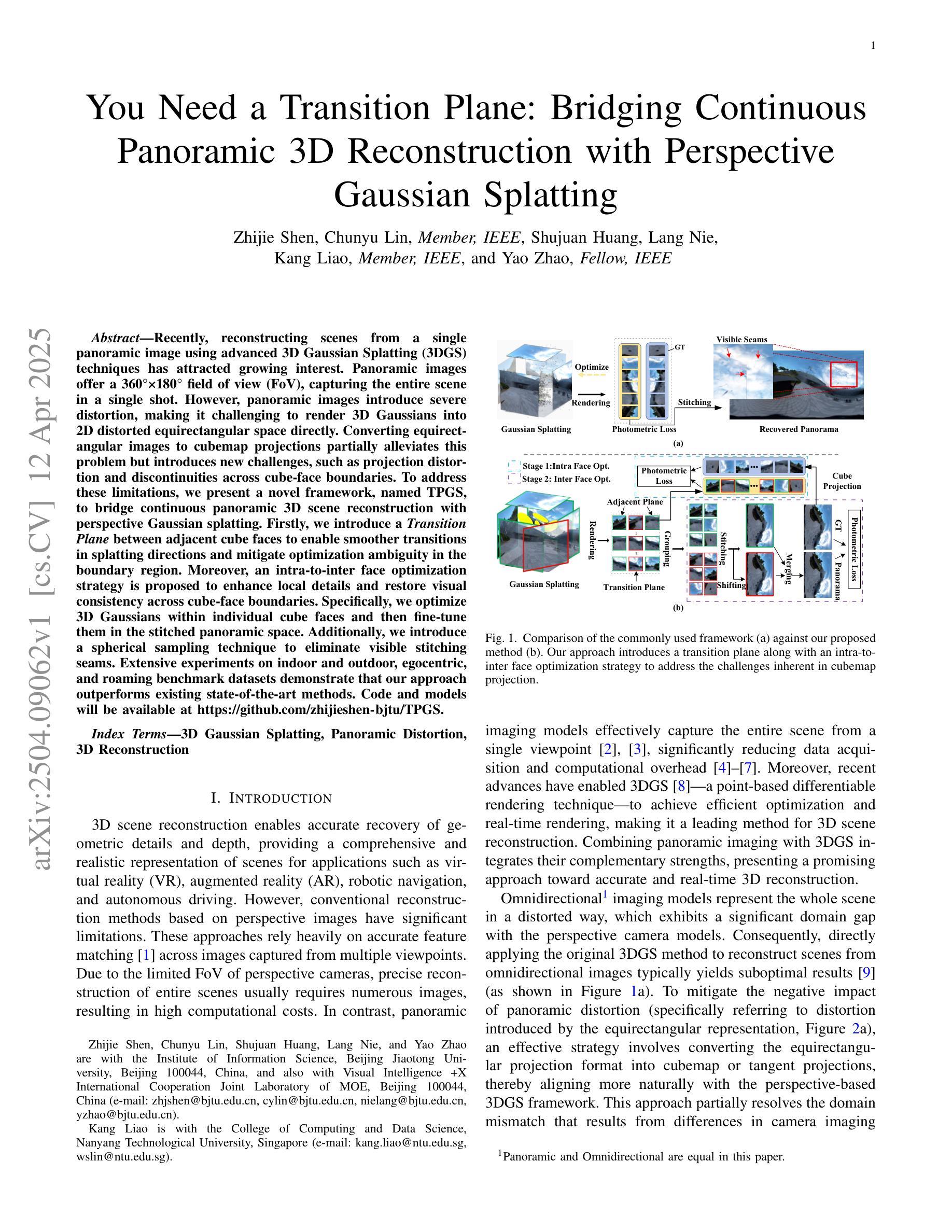
You Need a Transition Plane: Bridging Continuous Panoramic 3D Reconstruction with Perspective Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Zhijie Shen, Chunyu Lin, Shujuan Huang, Lang Nie, Kang Liao, Yao Zhao
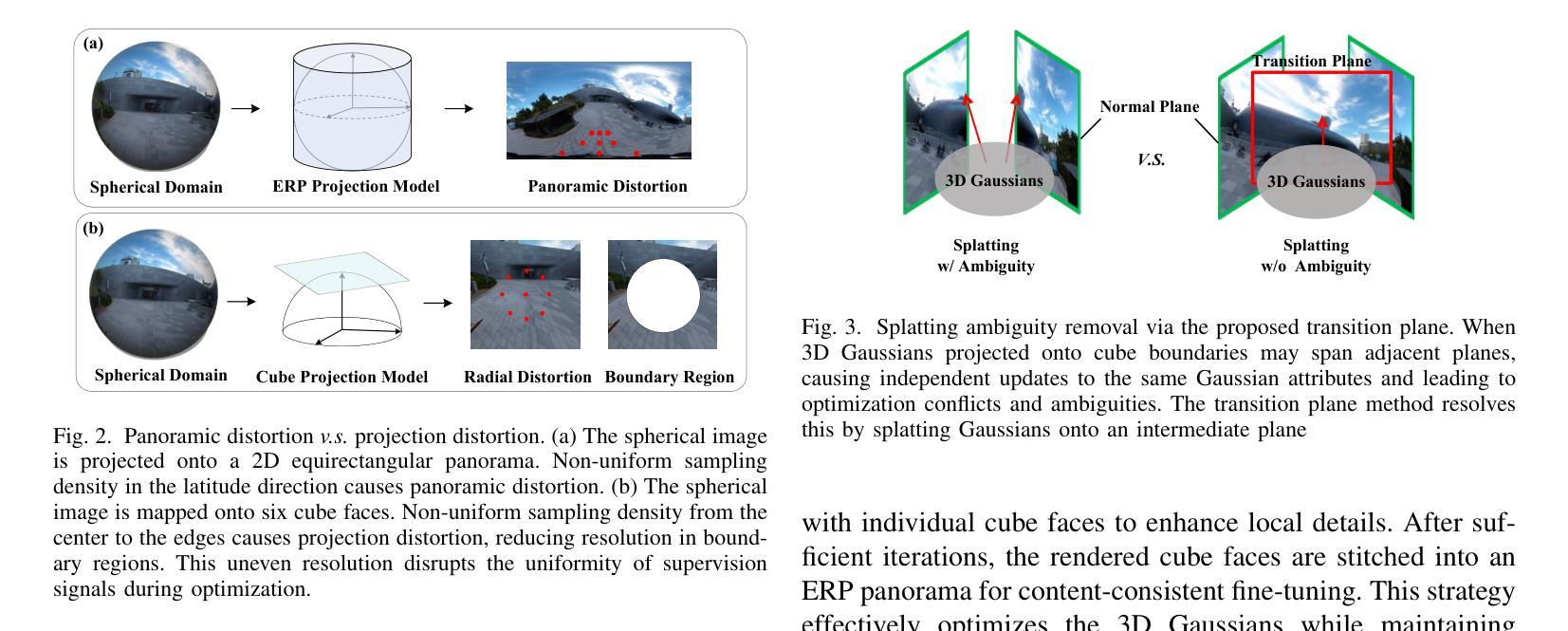
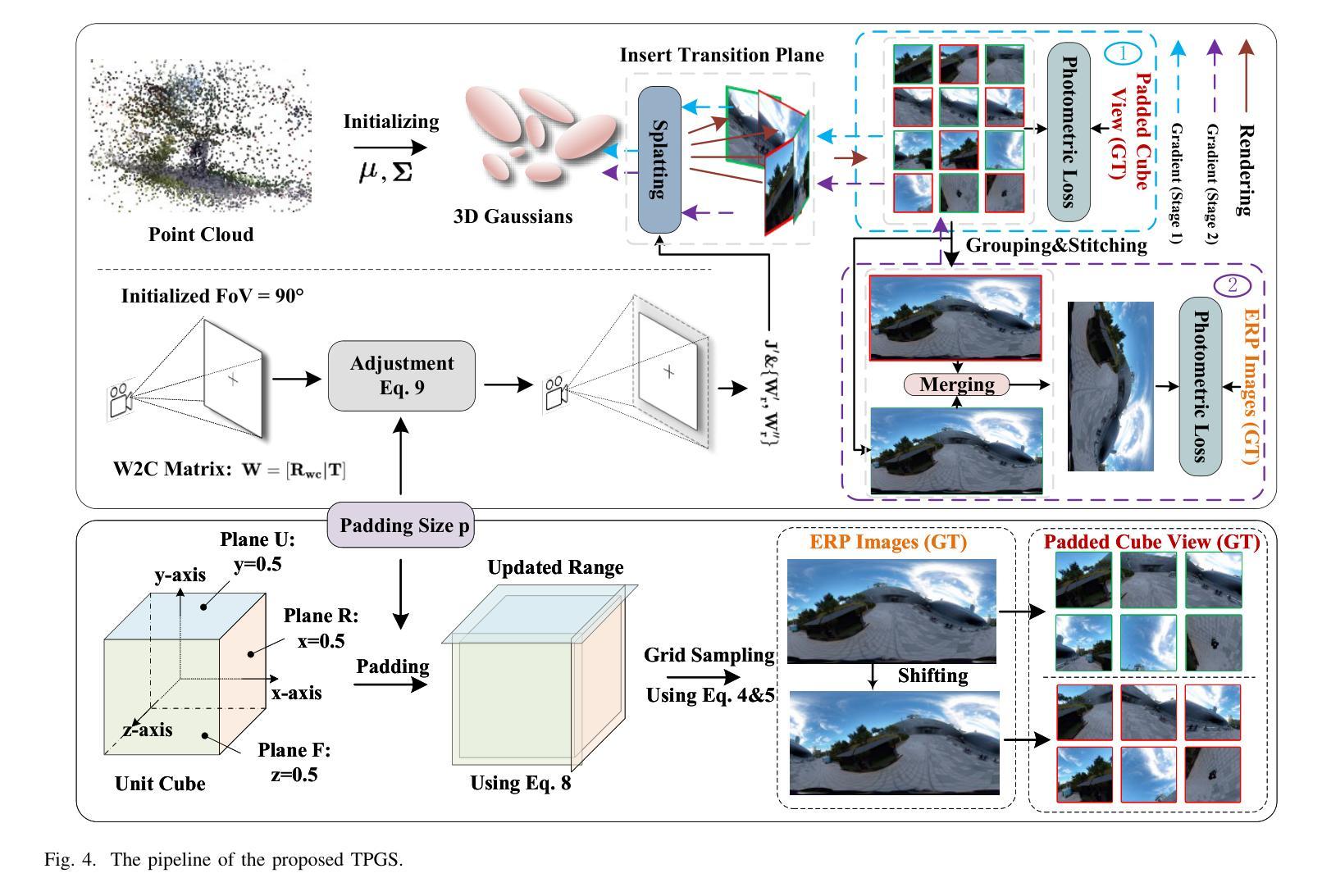
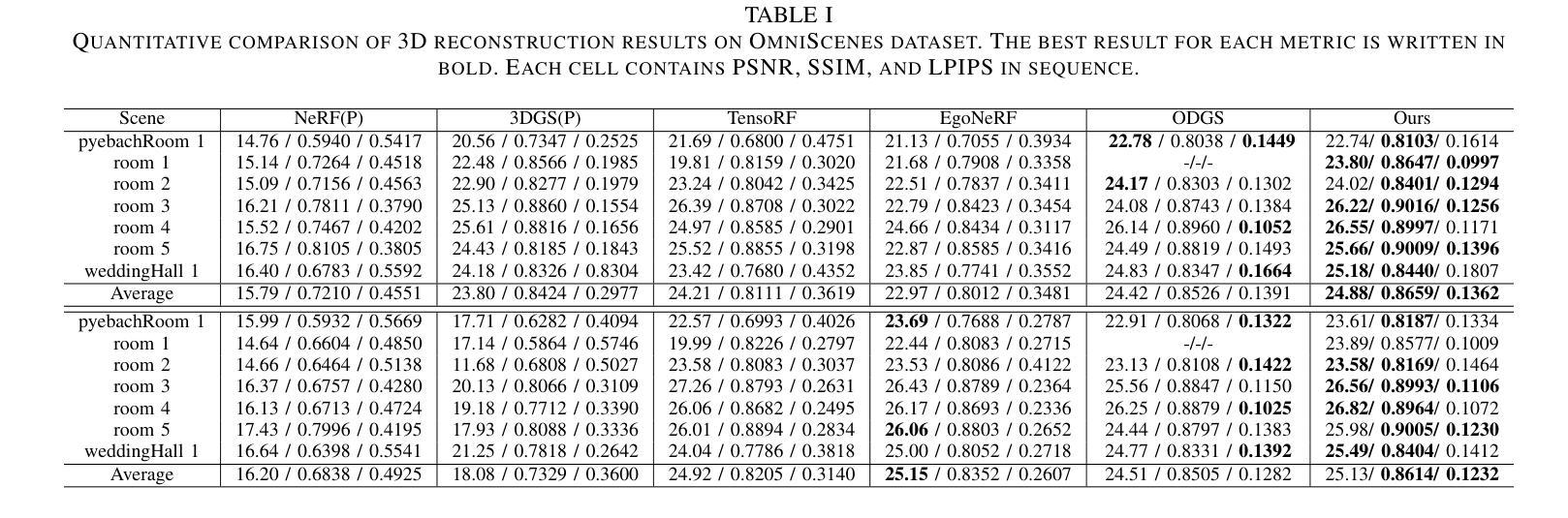
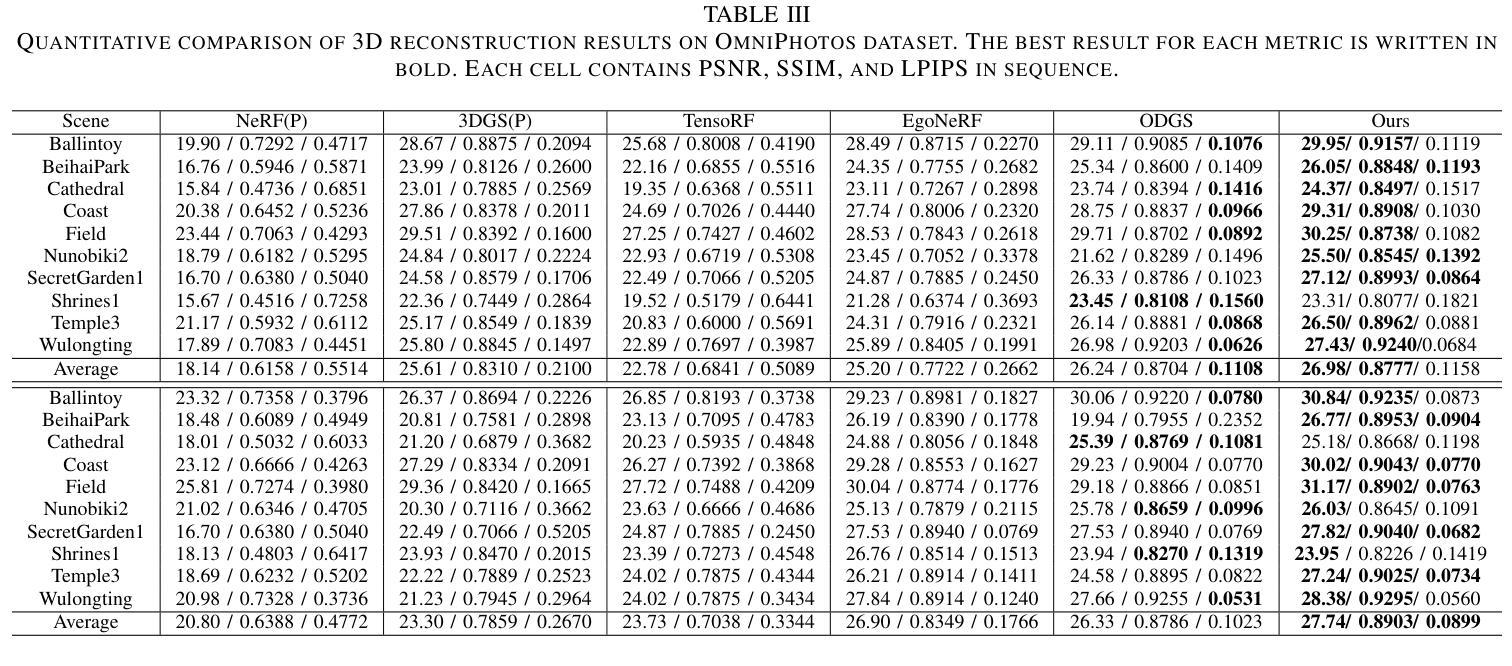
Recently, reconstructing scenes from a single panoramic image using advanced 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) techniques has attracted growing interest. Panoramic images offer a 360$\times$ 180 field of view (FoV), capturing the entire scene in a single shot. However, panoramic images introduce severe distortion, making it challenging to render 3D Gaussians into 2D distorted equirectangular space directly. Converting equirectangular images to cubemap projections partially alleviates this problem but introduces new challenges, such as projection distortion and discontinuities across cube-face boundaries. To address these limitations, we present a novel framework, named TPGS, to bridge continuous panoramic 3D scene reconstruction with perspective Gaussian splatting. Firstly, we introduce a Transition Plane between adjacent cube faces to enable smoother transitions in splatting directions and mitigate optimization ambiguity in the boundary region. Moreover, an intra-to-inter face optimization strategy is proposed to enhance local details and restore visual consistency across cube-face boundaries. Specifically, we optimize 3D Gaussians within individual cube faces and then fine-tune them in the stitched panoramic space. Additionally, we introduce a spherical sampling technique to eliminate visible stitching seams. Extensive experiments on indoor and outdoor, egocentric, and roaming benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods. Code and models will be available at https://github.com/zhijieshen-bjtu/TPGS.
最近,利用先进的3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)技术从单个全景图像重建场景已经引起了人们的极大兴趣。全景图像提供了360°×180°的视野(FoV),能够单次拍摄捕捉整个场景。然而,全景图像引入了严重的失真,使得直接将3D高斯渲染到2D扭曲的等距空间具有挑战性。将等距图像转换为立方体映射投影部分缓解了这个问题,但带来了新的挑战,例如投影失真和立方体面部边界处的间断。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种名为TPGS的新型框架,以建立连续全景3D场景重建与透视高斯拼贴之间的桥梁。首先,我们在相邻的立方体面部之间引入了一个过渡平面,以实现在拼贴方向上的平滑过渡,并减轻边界区域的优化模糊性。此外,我们提出了一种从内部到外部面部优化策略,以增强局部细节并恢复立方体面部边界处的视觉一致性。具体来说,我们优化单个立方体面部内的3D高斯,然后在拼接的全景空间中进行微调。此外,我们引入了一种球形采样技术以消除可见的接缝。在室内和室外、以自我为中心的以及漫游基准数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法优于现有最先进的方法。代码和模型将在https://github.com/zhijieshen-bjtu/TPGS上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于先进的3D高斯展开(3DGS)技术,从单一全景图像重建场景已引起广泛关注。全景图像引入的失真使得将3D高斯渲染到2D等距空间具有挑战性。本文提出一种新型框架TPGS,通过透视高斯展开桥接连续全景3D场景重建,引入过渡平面优化相邻立方体面部之间的过渡,并提出面内至面间优化策略,增强局部细节并恢复立方体面部边界处的视觉一致性。此外,采用球形采样技术消除可见接缝。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术在从单一全景图像重建场景中的应用受到关注。
- 全景图像引入的严重失真使得渲染具有挑战性。
- TPGS框架通过透视高斯展开解决连续全景3D场景重建问题。
- 引入过渡平面以优化相邻立方体面部之间的过渡。
- 提出面内至面间的优化策略,增强局部细节和视觉一致性。
- 球形采样技术用于消除可见接缝。
点此查看论文截图
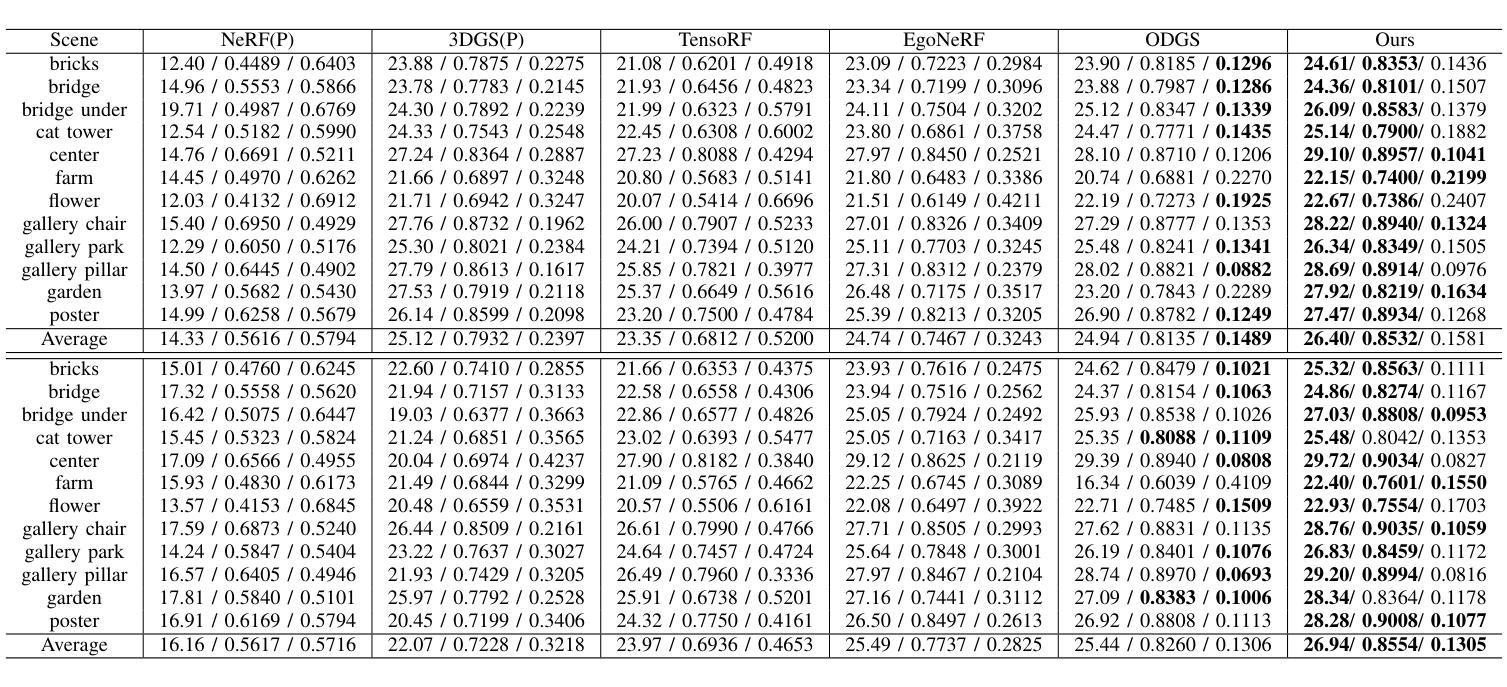
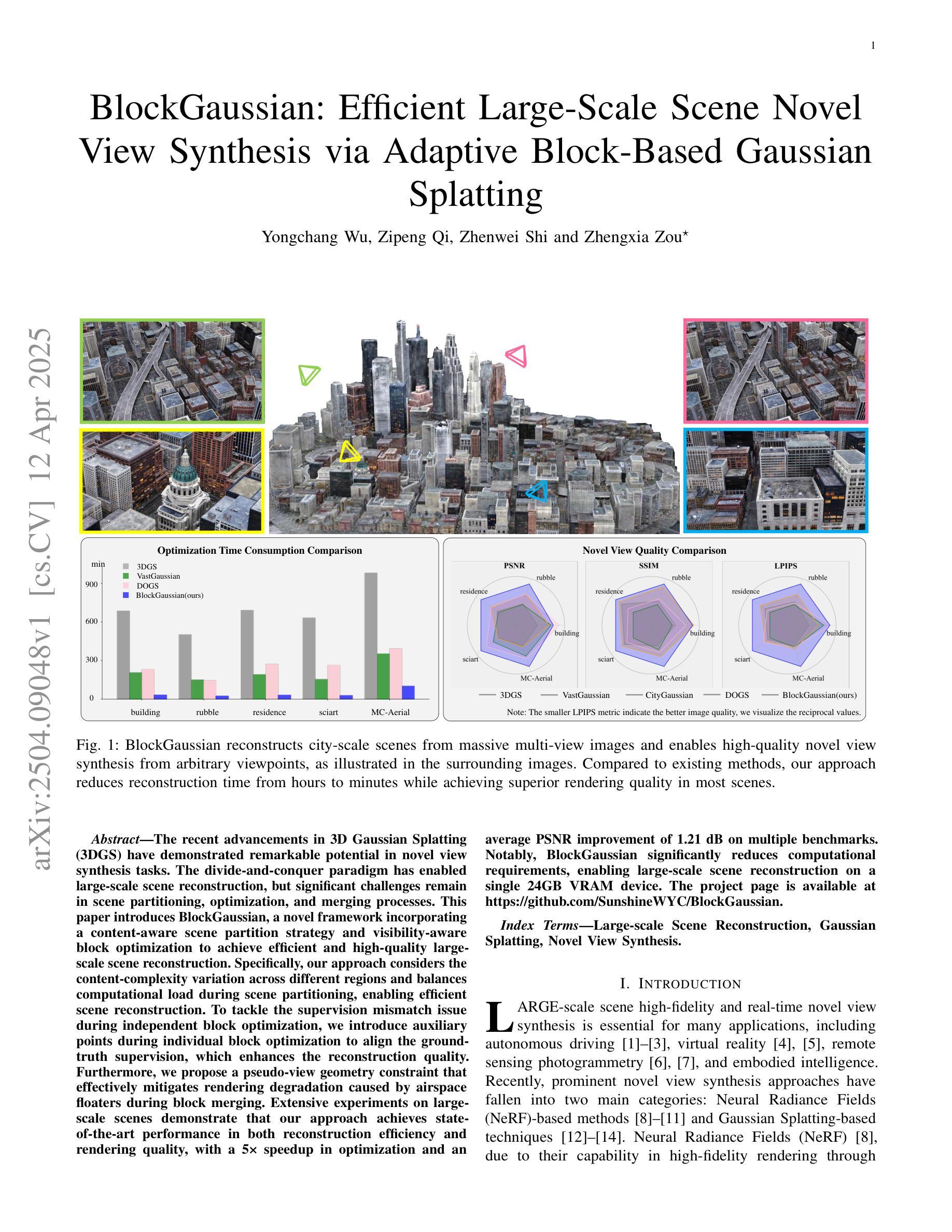
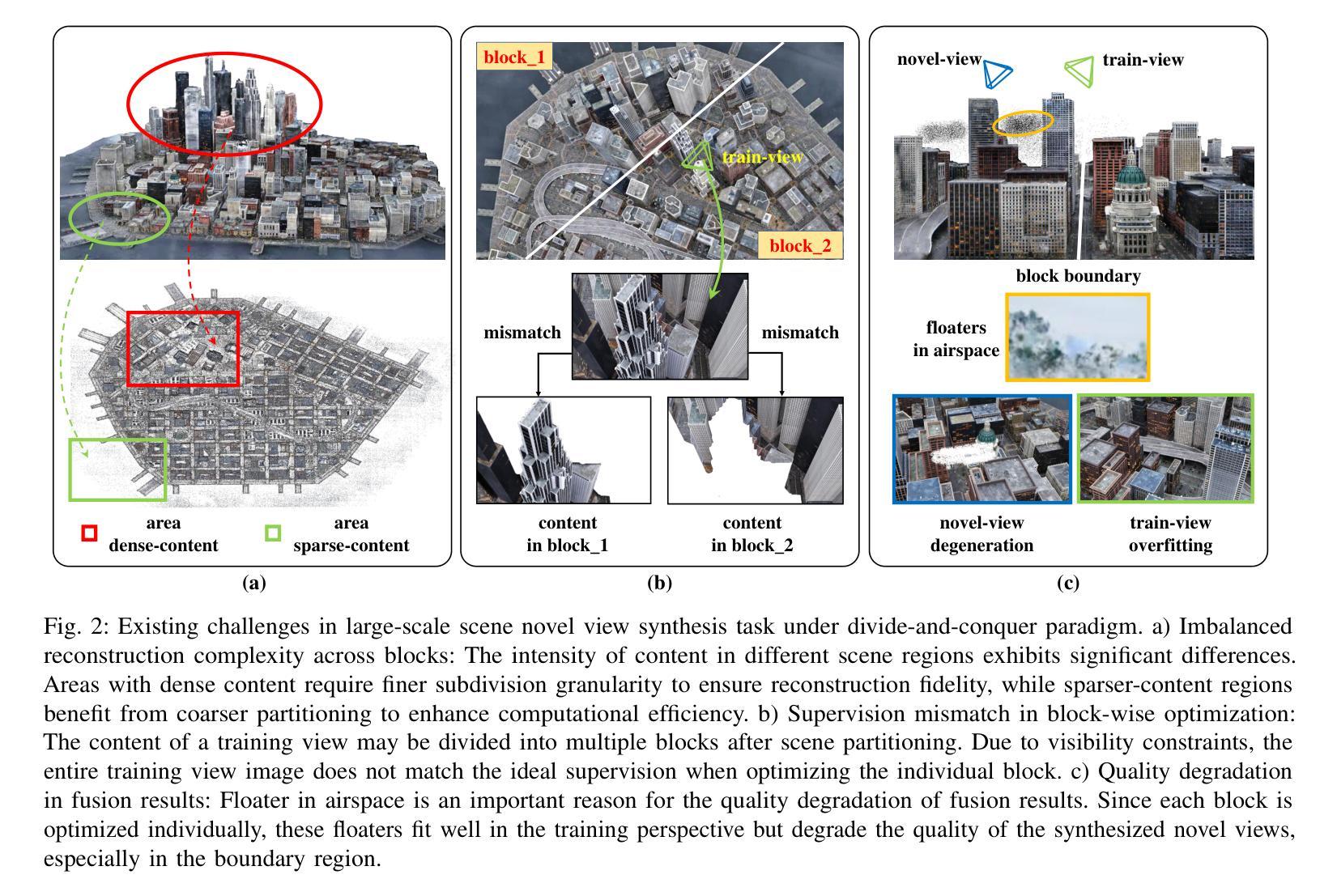
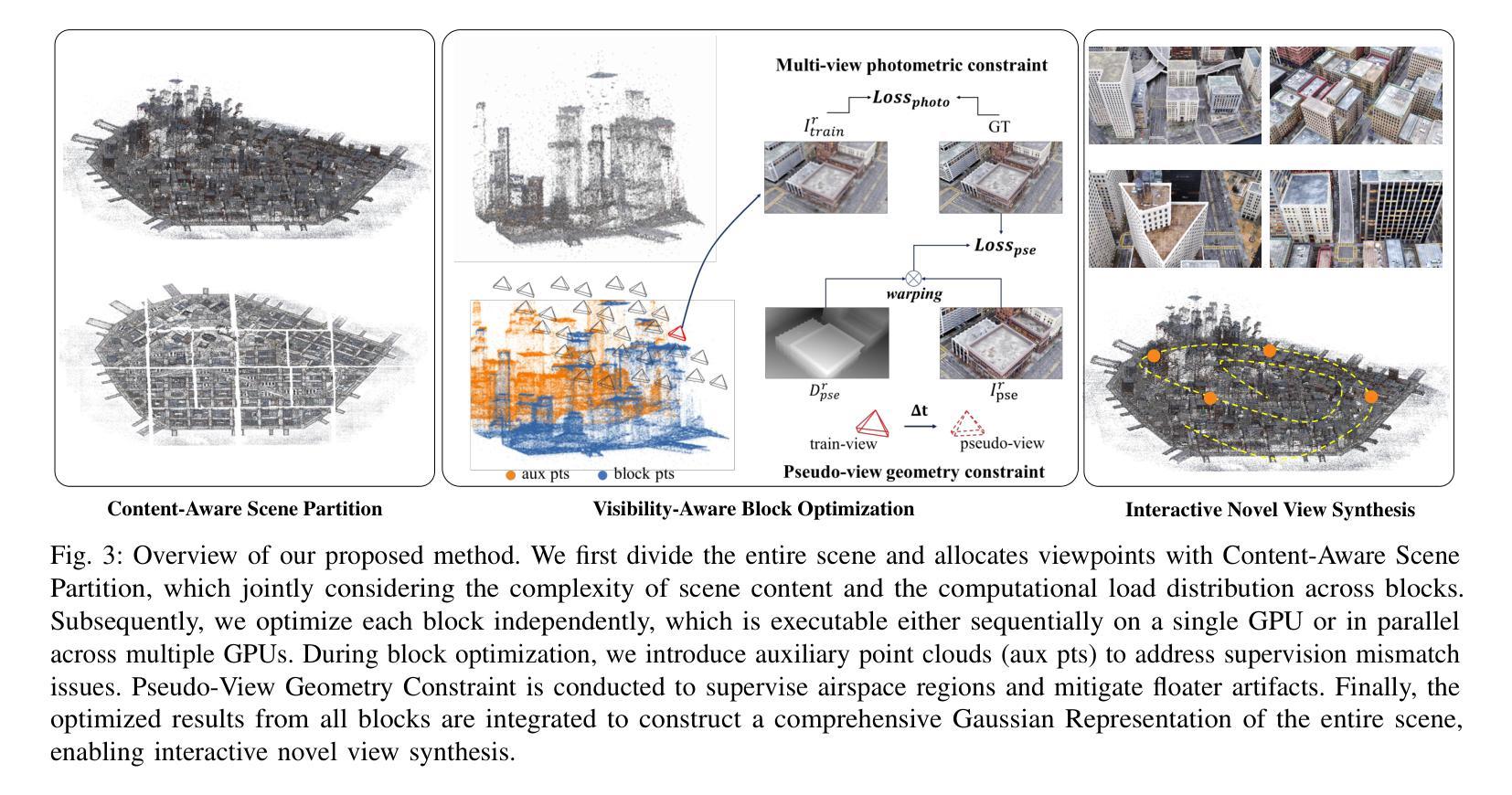
BlockGaussian: Efficient Large-Scale Scene NovelView Synthesis via Adaptive Block-Based Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yongchang Wu, Zipeng Qi, Zhenwei Shi, Zhengxia Zou
The recent advancements in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have demonstrated remarkable potential in novel view synthesis tasks. The divide-and-conquer paradigm has enabled large-scale scene reconstruction, but significant challenges remain in scene partitioning, optimization, and merging processes. This paper introduces BlockGaussian, a novel framework incorporating a content-aware scene partition strategy and visibility-aware block optimization to achieve efficient and high-quality large-scale scene reconstruction. Specifically, our approach considers the content-complexity variation across different regions and balances computational load during scene partitioning, enabling efficient scene reconstruction. To tackle the supervision mismatch issue during independent block optimization, we introduce auxiliary points during individual block optimization to align the ground-truth supervision, which enhances the reconstruction quality. Furthermore, we propose a pseudo-view geometry constraint that effectively mitigates rendering degradation caused by airspace floaters during block merging. Extensive experiments on large-scale scenes demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in both reconstruction efficiency and rendering quality, with a 5x speedup in optimization and an average PSNR improvement of 1.21 dB on multiple benchmarks. Notably, BlockGaussian significantly reduces computational requirements, enabling large-scale scene reconstruction on a single 24GB VRAM device. The project page is available at https://github.com/SunshineWYC/BlockGaussian
近期在三维高斯延展(3DGS)方面的进展表明,它在新型视图合成任务中表现出显著潜力。分而治之的模式使大规模场景重建成为可能,但在场景分割、优化和合并过程中仍存在重大挑战。本文介绍了BlockGaussian,这是一个结合内容感知场景分割策略和可见性感知块优化的新型框架,以实现高效高质量的大规模场景重建。具体来说,我们的方法考虑了不同区域的内容复杂性变化,并在场景分割过程中平衡计算负载,以实现高效的场景重建。为了解决独立块优化过程中的监督不匹配问题,我们在单个块优化过程中引入了辅助点来对齐地面真实监督,从而提高重建质量。此外,我们提出了一种伪视图几何约束,有效减轻了块合并过程中因空中漂浮物造成的渲染质量下降。大规模场景上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在重建效率和渲染质量方面都达到了最新技术水平,优化速度提高了5倍,多个基准测试的平均PSNR提高了1.21分贝。值得注意的是,BlockGaussian显著降低了计算要求,能够在单个24GB VRAM设备上实现大规模场景重建。项目页面可通过https://github.com/SunshineWYC/BlockGaussian访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/SunshineWYC/BlockGaussian
Summary
3DGS技术的新进展在新型视图合成任务中展现出巨大潜力。BlockGaussian框架采用分而治之的策略实现大规模场景重建,引入内容感知的场景分割策略和可见性感知的块优化技术,提高了场景重建的效率和品质。该框架还解决了独立块优化中的监督不匹配问题,并提出伪视图几何约束以缓解块合并过程中因空中漂浮物导致的渲染退化问题。实验证明,该框架在重建效率和渲染质量方面达到领先水平,优化速度提升5倍,多项基准测试的平均PSNR值提高1.21 dB。
Key Takeaways
- BlockGaussian框架利用分而治之策略实现大规模场景重建。
- 引入内容感知的场景分割策略,考虑内容复杂度的变化,平衡计算负载。
- 采用可见性感知的块优化技术,解决独立块优化中的监督不匹配问题。
- 引入辅助点进行个体块优化,提高重建质量。
- 提出伪视图几何约束,有效缓解因空中漂浮物导致的渲染退化问题。
- 实验证明,BlockGaussian框架在重建效率和渲染质量方面表现卓越。
- 该框架优化速度提升5倍,多项基准测试的平均PSNR值提高1.21 dB。
点此查看论文截图
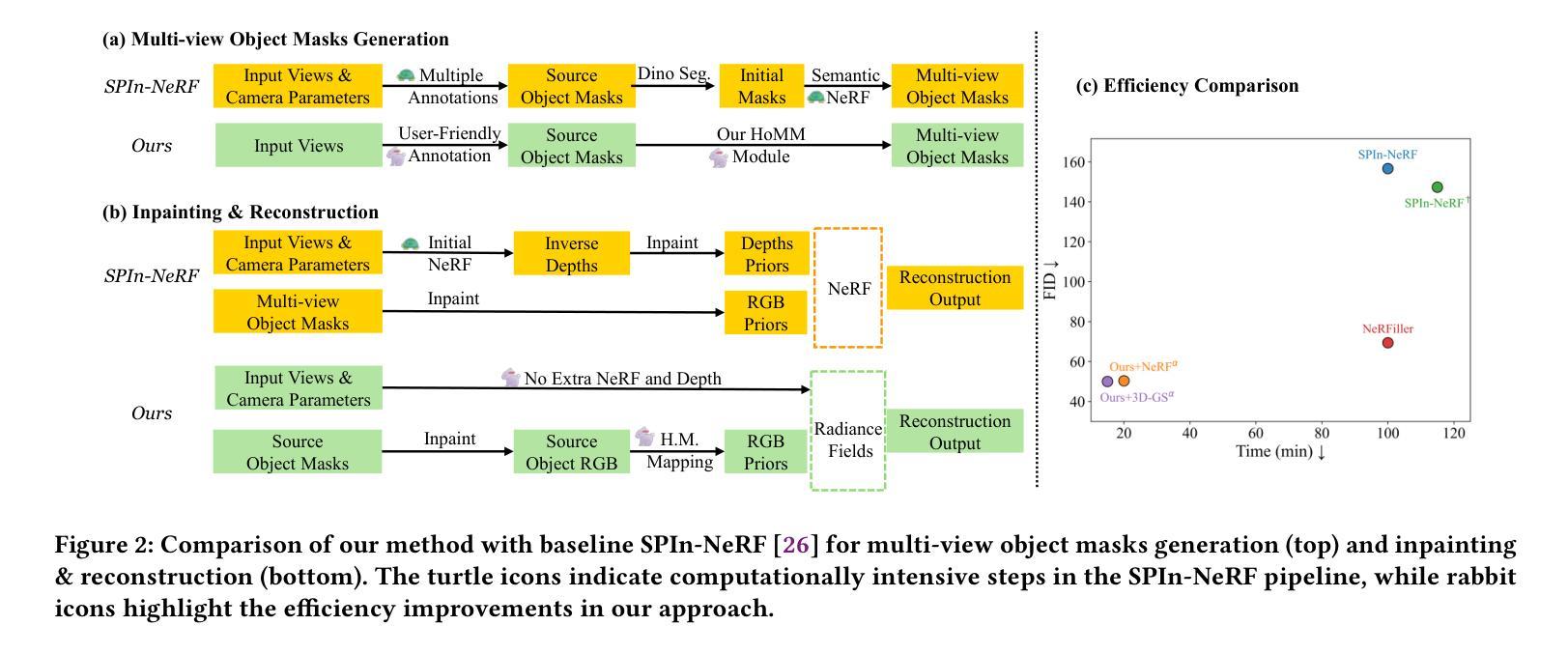
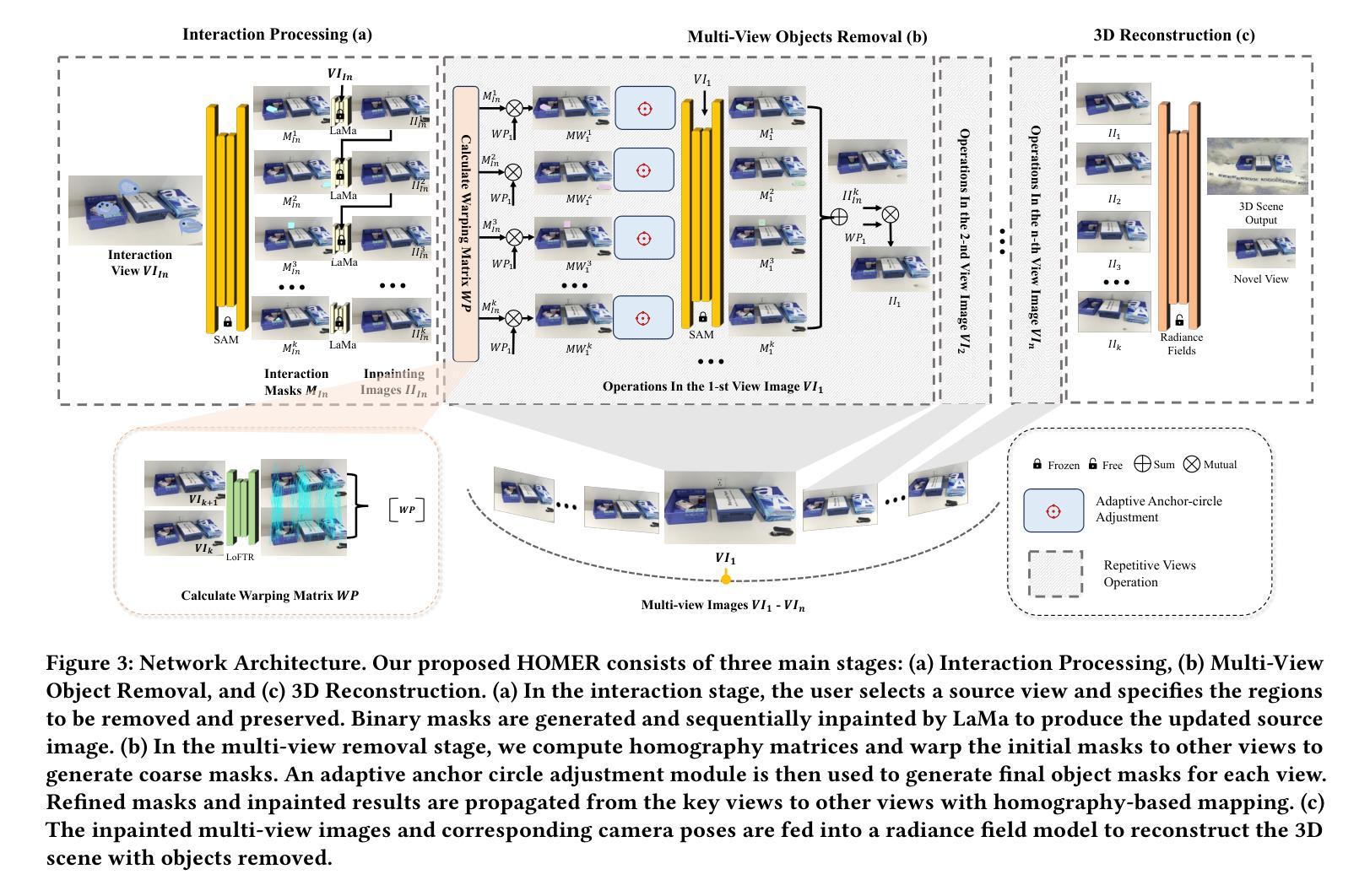
HOMER: Homography-Based Efficient Multi-view 3D Object Removal
Authors:Jingcheng Ni, Weiguang Zhao, Daniel Wang, Ziyao Zeng, Chenyu You, Alex Wong, Kaizhu Huang
3D object removal is an important sub-task in 3D scene editing, with broad applications in scene understanding, augmented reality, and robotics. However, existing methods struggle to achieve a desirable balance among consistency, usability, and computational efficiency in multi-view settings. These limitations are primarily due to unintuitive user interaction in the source view, inefficient multi-view object mask generation, computationally expensive inpainting procedures, and a lack of applicability across different radiance field representations. To address these challenges, we propose a novel pipeline that improves the quality and efficiency of multi-view object mask generation and inpainting. Our method introduces an intuitive region-based interaction mechanism in the source view and eliminates the need for camera poses or extra model training. Our lightweight HoMM module is employed to achieve high-quality multi-view mask propagation with enhanced efficiency. In the inpainting stage, we further reduce computational costs by performing inpainting only on selected key views and propagating the results to other views via homography-based mapping. Our pipeline is compatible with a variety of radiance field frameworks, including NeRF and 3D Gaussian Splatting, demonstrating improved generalizability and practicality in real-world scenarios. Additionally, we present a new 3D multi-object removal dataset with greater object diversity and viewpoint variation than existing datasets. Experiments on public benchmarks and our proposed dataset show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance while reducing runtime to one-fifth of that required by leading baselines.
3D物体移除是3D场景编辑中的一个重要子任务,广泛应用于场景理解、增强现实和机器人技术。然而,现有方法在多角度设置中的一致性、可用性和计算效率之间很难达到理想平衡。这些局限性主要是由于源视图中的用户交互不够直观、多视图对象蒙版生成效率低下、昂贵的修复程序计算以及缺乏跨不同辐射场表示的应用性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种改进多视图对象蒙版生成和修复质量及效率的新流程。我们的方法在源视图中引入了一种直观的基于区域的交互机制,无需相机姿态或额外的模型训练。我们采用轻量级的HoMM模块实现高效的高质量多视图蒙版传播。在修复阶段,我们通过在选定的关键视图上进行修复,并通过基于几何映射的传播将结果传播到其他视图,从而进一步降低计算成本。我们的流程与各种辐射场框架兼容,包括NeRF和3D高斯平铺,显示出在真实世界场景中的改进通用性和实用性。此外,我们提出了一个新的3D多物体移除数据集,与现有数据集相比,该数据集具有更大的物体多样性和视角变化。在公共基准测试和我们提出的数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能,同时将运行时间减少到现有基线所需时间的五分之一。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新颖的管道,旨在改进多视角物体移除的质量和效率。通过引入基于区域的交互机制和高效的多视角掩膜生成技术,该方法无需相机姿态和额外模型训练。同时,采用轻量级的HoMM模块实现高质量的多视角掩膜传播,并在选定的关键视图上执行填充操作,通过基于同构性的映射将结果传播到其他视图,降低计算成本。此外,该方法兼容多种辐射场框架,包括NeRF和3D高斯斑片技术,并在现实场景中表现出良好的通用性和实用性。实验结果表明,该方法在公共基准测试集和提出的新数据集上取得了最先进的性能,并将运行时间缩短到现有基线技术的五分之一。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了在多视角场景中物体移除的重要性和应用。
- 指出了现有方法的局限性和面临的挑战,如用户交互不直观、多视角物体掩膜生成效率低等。
- 提出了一种新颖的管道,包括基于区域的交互机制、高效的多视角掩膜生成和填充技术。
- 引入了轻量级的HoMM模块,实现了高质量的多视角掩膜传播和高效的填充操作。
- 方法兼容多种辐射场框架,包括NeRF和3D高斯斑片技术。
- 提出了一种新的多视角物体移除数据集,具有更大的物体多样性和视角变化。
点此查看论文截图

SplatMAP: Online Dense Monocular SLAM with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yue Hu, Rong Liu, Meida Chen, Peter Beerel, Andrew Feng
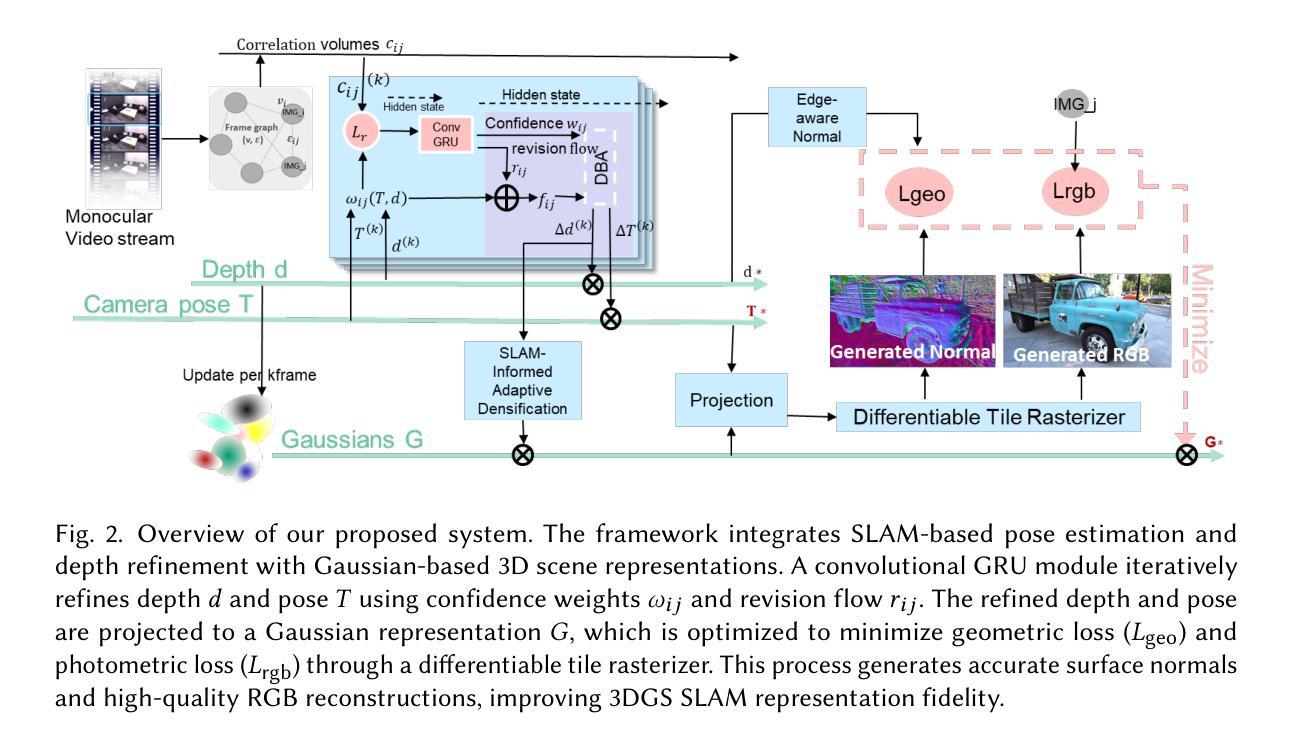
Achieving high-fidelity 3D reconstruction from monocular video remains challenging due to the inherent limitations of traditional methods like Structure-from-Motion (SfM) and monocular SLAM in accurately capturing scene details. While differentiable rendering techniques such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) address some of these challenges, their high computational costs make them unsuitable for real-time applications. Additionally, existing 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) methods often focus on photometric consistency, neglecting geometric accuracy and failing to exploit SLAM’s dynamic depth and pose updates for scene refinement. We propose a framework integrating dense SLAM with 3DGS for real-time, high-fidelity dense reconstruction. Our approach introduces SLAM-Informed Adaptive Densification, which dynamically updates and densifies the Gaussian model by leveraging dense point clouds from SLAM. Additionally, we incorporate Geometry-Guided Optimization, which combines edge-aware geometric constraints and photometric consistency to jointly optimize the appearance and geometry of the 3DGS scene representation, enabling detailed and accurate SLAM mapping reconstruction. Experiments on the Replica and TUM-RGBD datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, achieving state-of-the-art results among monocular systems. Specifically, our method achieves a PSNR of 36.864, SSIM of 0.985, and LPIPS of 0.040 on Replica, representing improvements of 10.7%, 6.4%, and 49.4%, respectively, over the previous SOTA. On TUM-RGBD, our method outperforms the closest baseline by 10.2%, 6.6%, and 34.7% in the same metrics. These results highlight the potential of our framework in bridging the gap between photometric and geometric dense 3D scene representations, paving the way for practical and efficient monocular dense reconstruction.
从单目视频中实现高保真3D重建仍然是一个挑战,这主要是由于传统方法(如结构从运动(SfM)和单目SLAM)在准确捕捉场景细节方面的固有局限性。虽然像神经辐射场(NeRF)这样的可微分渲染技术解决了一些这些挑战,但它们的高计算成本使它们不适合实时应用。此外,现有的3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)方法通常侧重于光度一致性,忽视了几何精度,并且未能利用SLAM的动态深度和姿态更新来进行场景细化。我们提出了一个整合密集SLAM与3DGS的框架,用于实时高保真密集重建。我们的方法引入了SLAM信息自适应致密化,利用SLAM的密集点云动态更新和致密化高斯模型。此外,我们结合了几何引导优化,它将边缘感知几何约束和光度一致性相结合,以联合优化3DGS场景表示的外观和几何形状,从而实现详细而准确的SLAM映射重建。在Replica和TUM-RGBD数据集上的实验证明了我们的方法的有效性,在单目系统中实现了最先进的成果。具体来说,我们的方法在Replica上实现了PSNR为36.864,SSIM为0.985,LPIPS为0.040的指标,分别比之前的最佳成果提高了10.7%,6.4%和49.4%。在TUM-RGBD上,我们的方法在相同的指标上比最接近的基线高出10.2%,6.6%和34.7%。这些结果凸显了我们框架在桥接光度表示和几何密集3D场景表示之间的潜力,为实用和高效的单目密集重建铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个融合密集SLAM与3DGS的新框架,用于实时高精度三维重建。该框架引入SLAM信息自适应密集化技术,结合边缘感知几何约束和光度一致性优化,实现了高精度的SLAM映射重建。在Replica和TUM-RGBD数据集上的实验表明,该方法在单目系统中取得了最先进的成果。
Key Takeaways
- 传统方法如SfM和单目SLAM在捕捉场景细节时存在局限性。
- 可微渲染技术如NeRF虽能解决部分挑战,但计算成本高,不适合实时应用。
- 现有3DGS方法主要关注光度一致性,忽视几何精度,未能利用SLAM的动态深度和姿态更新进行场景优化。
- 提出融合密集SLAM与3DGS的新框架,实现实时高精度三维重建。
- 引入SLAM信息自适应密集化技术,利用密集点云动态更新和加密高斯模型。
- 结合边缘感知几何约束和光度一致性优化,实现场景表示的几何和外观联合优化。
- 在Replica和TUM-RGBD数据集上的实验表明,该方法取得了显著成果,实现了与单目系统的最先进的成果。
点此查看论文截图


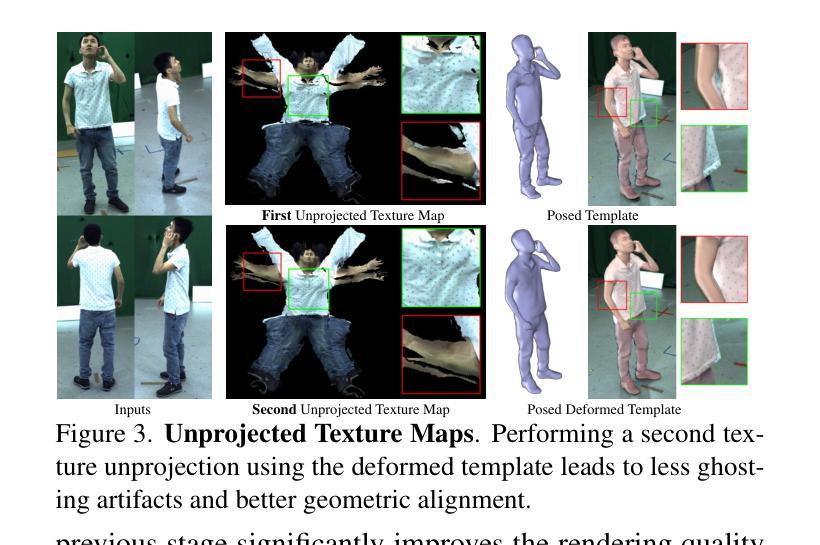
Real-time Free-view Human Rendering from Sparse-view RGB Videos using Double Unprojected Textures
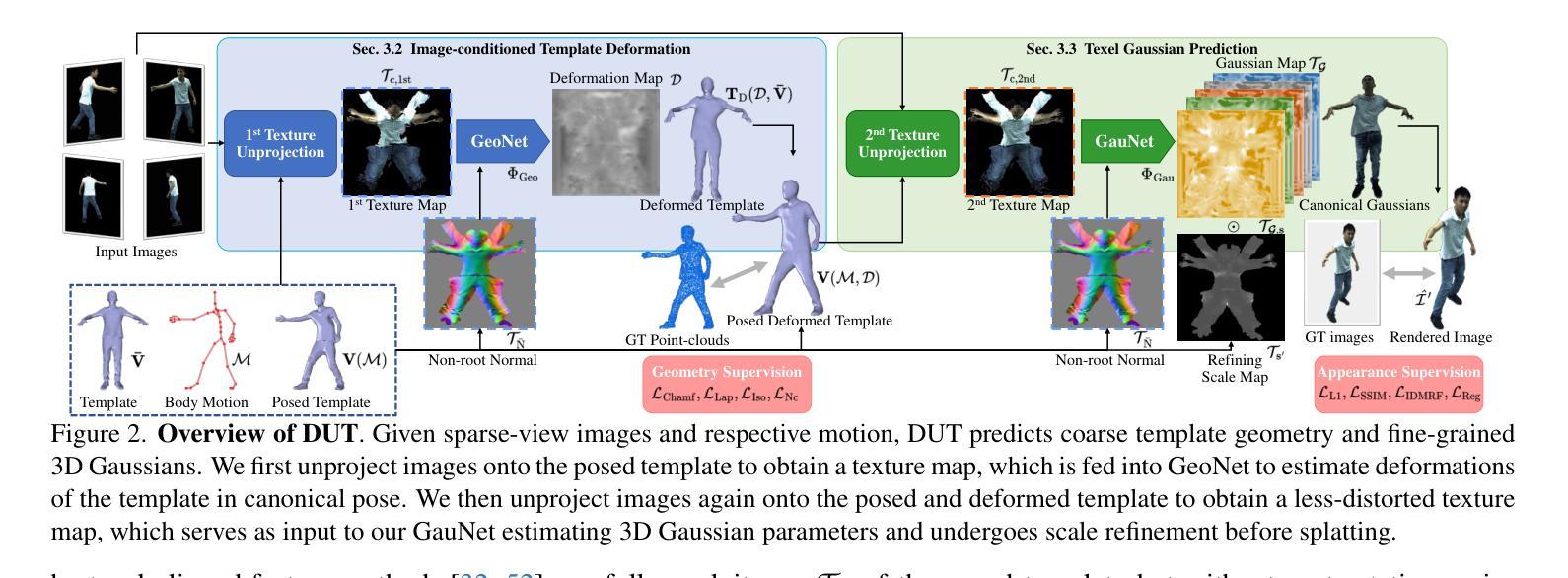
Authors:Guoxing Sun, Rishabh Dabral, Heming Zhu, Pascal Fua, Christian Theobalt, Marc Habermann
Real-time free-view human rendering from sparse-view RGB inputs is a challenging task due to the sensor scarcity and the tight time budget. To ensure efficiency, recent methods leverage 2D CNNs operating in texture space to learn rendering primitives. However, they either jointly learn geometry and appearance, or completely ignore sparse image information for geometry estimation, significantly harming visual quality and robustness to unseen body poses. To address these issues, we present Double Unprojected Textures, which at the core disentangles coarse geometric deformation estimation from appearance synthesis, enabling robust and photorealistic 4K rendering in real-time. Specifically, we first introduce a novel image-conditioned template deformation network, which estimates the coarse deformation of the human template from a first unprojected texture. This updated geometry is then used to apply a second and more accurate texture unprojection. The resulting texture map has fewer artifacts and better alignment with input views, which benefits our learning of finer-level geometry and appearance represented by Gaussian splats. We validate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed method in quantitative and qualitative experiments, which significantly surpasses other state-of-the-art methods. Project page: https://vcai.mpi-inf.mpg.de/projects/DUT/
从稀疏视角的RGB输入进行实时自由视角的人体渲染是一项具有挑战性的任务,这主要是因为传感器稀疏和严格的时间预算限制。为了保证效率,最近的方法利用在纹理空间操作的二维卷积神经网络来学习渲染原始数据。然而,它们要么联合学习几何和外观,要么完全忽略稀疏图像的几何估计信息,这严重损害了视觉质量和对未见过的身体姿态的鲁棒性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了双未投影纹理(Double Unprojected Textures)方法,其核心是将粗略的几何变形估计从外观合成中分离出来,从而实现实时鲁棒且逼真的4K渲染。具体来说,我们首先引入了一种新型图像条件模板变形网络,从第一个未投影纹理估计人体模板的粗略变形。然后,使用这个更新的几何体来进行第二次更准确的纹理反投影。得到的纹理映射具有较少的伪影,与输入视角对齐更好,这有利于我们学习由高斯点表示的更精细级别的几何和外观。我们通过定量和定性实验验证了所提出方法的有效性和效率,显著超越了其他最先进的方法。项目页面:https://vcai.mpi-inf.mpg.de/projects/DUT/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025, Project page: https://vcai.mpi-inf.mpg.de/projects/DUT/
Summary
实时从稀疏RGB输入进行自由视角人类渲染是一项具有挑战性的任务,由于传感器稀疏和时间限制。最近的方法利用二维卷积神经网络在纹理空间学习渲染原理,但存在联合学习几何和外观或忽略稀疏图像信息估计几何的问题,严重影响了视觉质量和对未见姿态的鲁棒性。为解决这些问题,我们提出双重未投影纹理(Double Unprojected Textures)方法,核心在于将粗略的几何变形估计与外观合成解耦,实现实时鲁棒的光子级渲染。我们引入图像条件模板变形网络,从第一个未投影纹理估计人体模板的粗略变形。更新的几何用于应用第二次更准确的纹理未投影。结果纹理图具有较少的伪影,与输入视图对齐更好,有利于我们学习由高斯点表示的精细级别的几何和外观。
Key Takeaways
- 实时自由视角人类渲染是项具有挑战性的任务,主要由于传感器稀疏和时间限制。
- 最近的方法利用二维卷积神经网络在纹理空间学习渲染原理。
- 现有方法存在联合学习几何和外观或忽略稀疏图像信息的问题,影响视觉质量和鲁棒性。
- 提出双重未投影纹理方法,核心在于将几何变形估计与外观合成解耦。
- 引入图像条件模板变形网络,从第一个未投影纹理估计人体模板的变形。
- 更新后的几何用于更准确的纹理二次未投影,减少伪影,提高与输入视图的对齐。
- 方法有利于提高对精细级别几何和外观的学习,显著超越其他先进方法。
点此查看论文截图


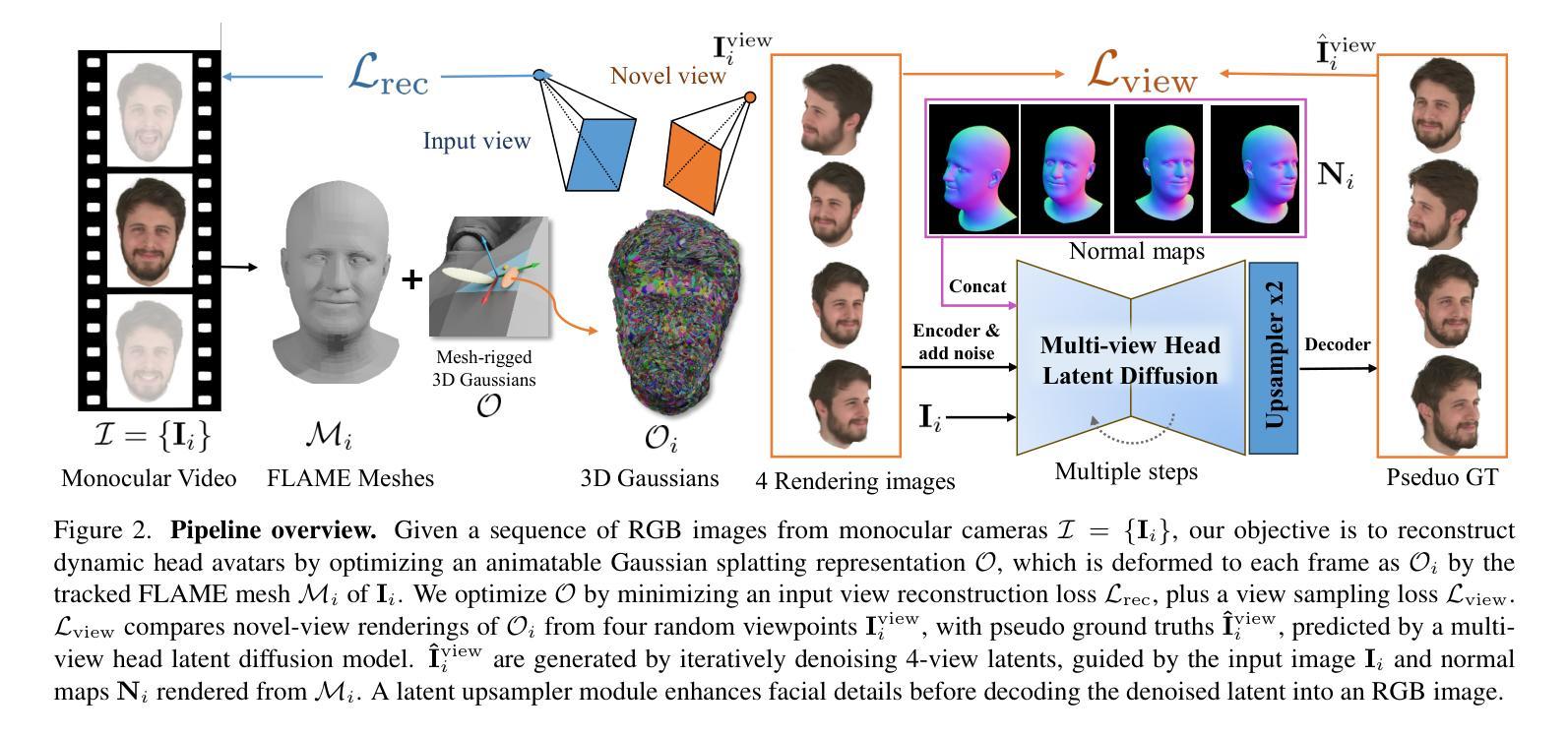
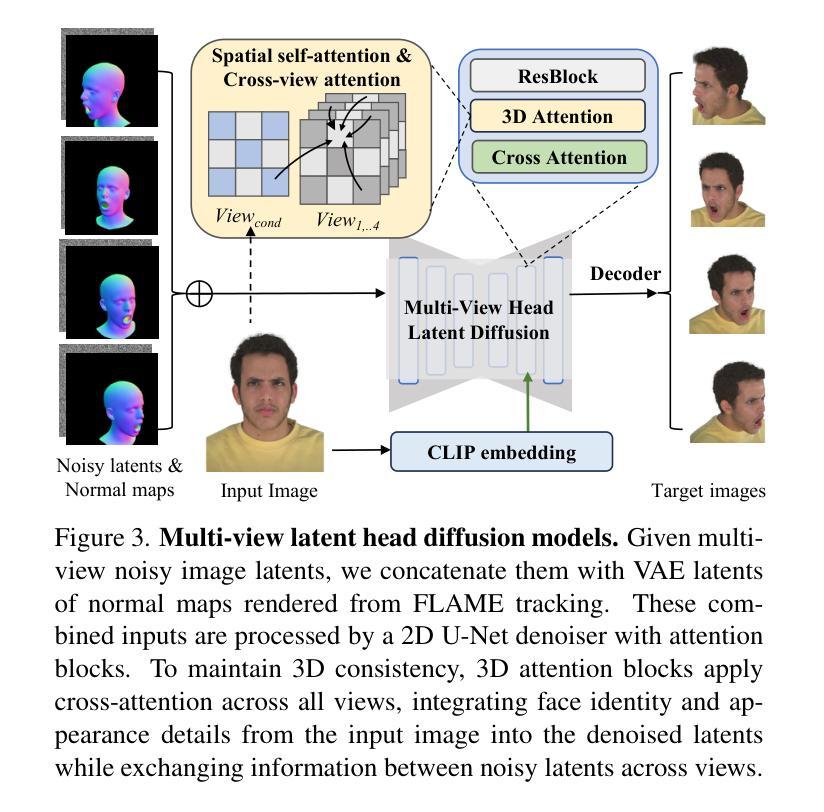
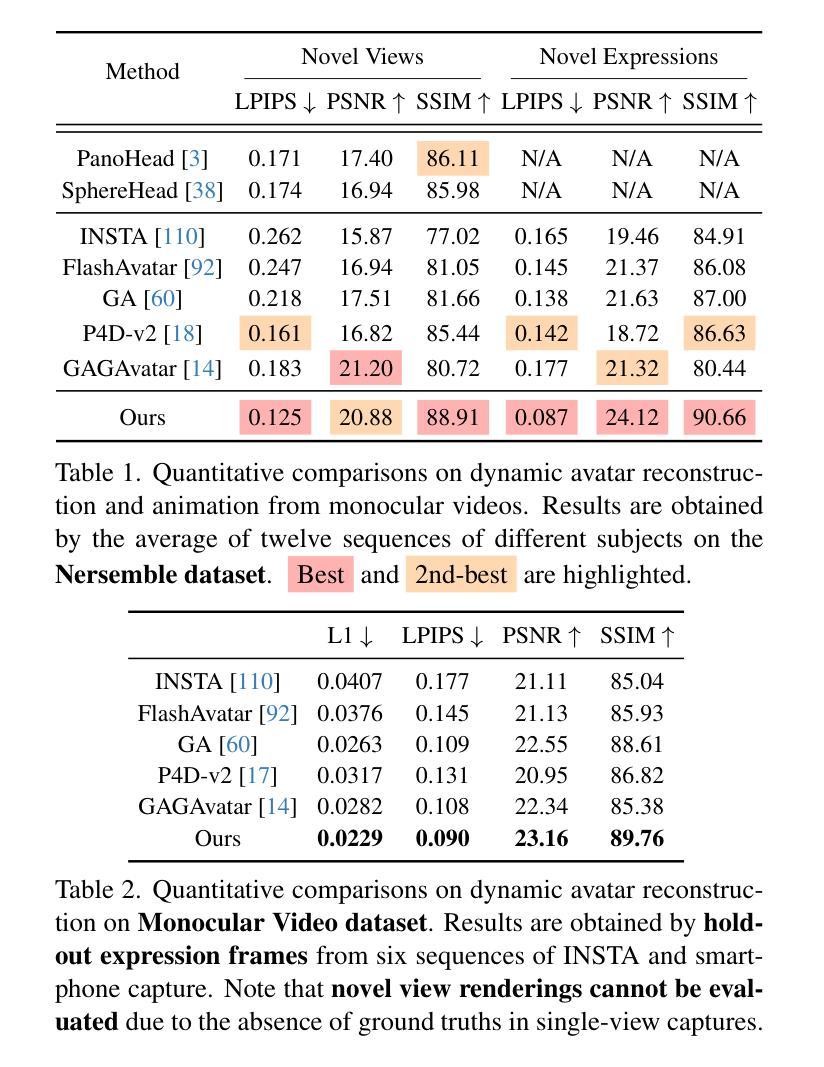
GAF: Gaussian Avatar Reconstruction from Monocular Videos via Multi-view Diffusion
Authors:Jiapeng Tang, Davide Davoli, Tobias Kirschstein, Liam Schoneveld, Matthias Niessner
We propose a novel approach for reconstructing animatable 3D Gaussian avatars from monocular videos captured by commodity devices like smartphones. Photorealistic 3D head avatar reconstruction from such recordings is challenging due to limited observations, which leaves unobserved regions under-constrained and can lead to artifacts in novel views. To address this problem, we introduce a multi-view head diffusion model, leveraging its priors to fill in missing regions and ensure view consistency in Gaussian splatting renderings. To enable precise viewpoint control, we use normal maps rendered from FLAME-based head reconstruction, which provides pixel-aligned inductive biases. We also condition the diffusion model on VAE features extracted from the input image to preserve facial identity and appearance details. For Gaussian avatar reconstruction, we distill multi-view diffusion priors by using iteratively denoised images as pseudo-ground truths, effectively mitigating over-saturation issues. To further improve photorealism, we apply latent upsampling priors to refine the denoised latent before decoding it into an image. We evaluate our method on the NeRSemble dataset, showing that GAF outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods in novel view synthesis. Furthermore, we demonstrate higher-fidelity avatar reconstructions from monocular videos captured on commodity devices.
我们提出了一种新的方法,可以从普通设备(如智能手机)拍摄的单目视频中重建可动画的3D高斯化身。从这种录制中重建逼真的3D头部化身是一个挑战,因为观察有限,这使得未观察到的区域约束不足,可能导致新视角出现伪影。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一种多视角头部扩散模型,利用先验知识来填充缺失区域,并确保在高斯平铺渲染中的视角一致性。为了实现精确的观点控制,我们使用基于FLAME的头部重建渲染的法线图,这提供了像素对齐的归纳偏见。我们还根据从输入图像中提取的VAE特征对扩散模型进行条件处理,以保留面部身份和外观细节。对于高斯化身重建,我们通过使用迭代去噪图像作为伪真实值来提炼多视角扩散先验,有效地减轻过饱和问题。为了进一步提高逼真度,我们应用潜在上采样先验来精细化去噪潜在码,然后再将其解码为图像。我们在NeRSemble数据集上评估了我们的方法,结果表明GAF在新型视角合成方面优于先前最先进的方法。此外,我们还展示了从普通设备拍摄的单目视频中进行的高保真化身重建。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper Video: https://youtu.be/QuIYTljvhyg Project Page: https://tangjiapeng.github.io/projects/GAF
Summary
本文提出了一种新颖的动画化三维高斯化身重建方法,可从单目视频重建逼真的三维头部化身。该方法利用多视角头部扩散模型填充缺失区域并优化渲染的视点和细节质量,提高了高质量合成的逼真度和效果。借助由基于FLAME的头部重建渲染得到的法线图,实现了精确的视点控制。此外,通过提取输入图像的VAE特征进行训练条件,以保证面部身份和外观细节的保留。在高斯化身重建中采用去噪图像迭代作为伪真实值,有效解决了过度饱和问题。通过潜在上采样先验对去噪潜在进行精炼,进一步提高了图像的光照质量和纹理细节。经过在NeRSemble数据集上的评估,证明了GAF在合成新视角下的性能优于先前最先进的重建方法。本文成功地实现了使用普通设备捕获的单目视频生成高保真度的三维头部化身。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新颖的动画化三维高斯化身重建方法。
- 通过引入多视角头部扩散模型,解决因缺乏观察而导致的不足和视觉缺陷问题。
- 利用FLAME生成的法线图进行视点控制,增强了视觉效果。
- 利用输入图像的VAE特征作为训练条件,保留了面部身份和外观细节。
- 通过迭代去噪图像作为伪真实值,解决了过度饱和问题。
- 通过潜在上采样先验提高图像的光照质量和纹理细节。
点此查看论文截图

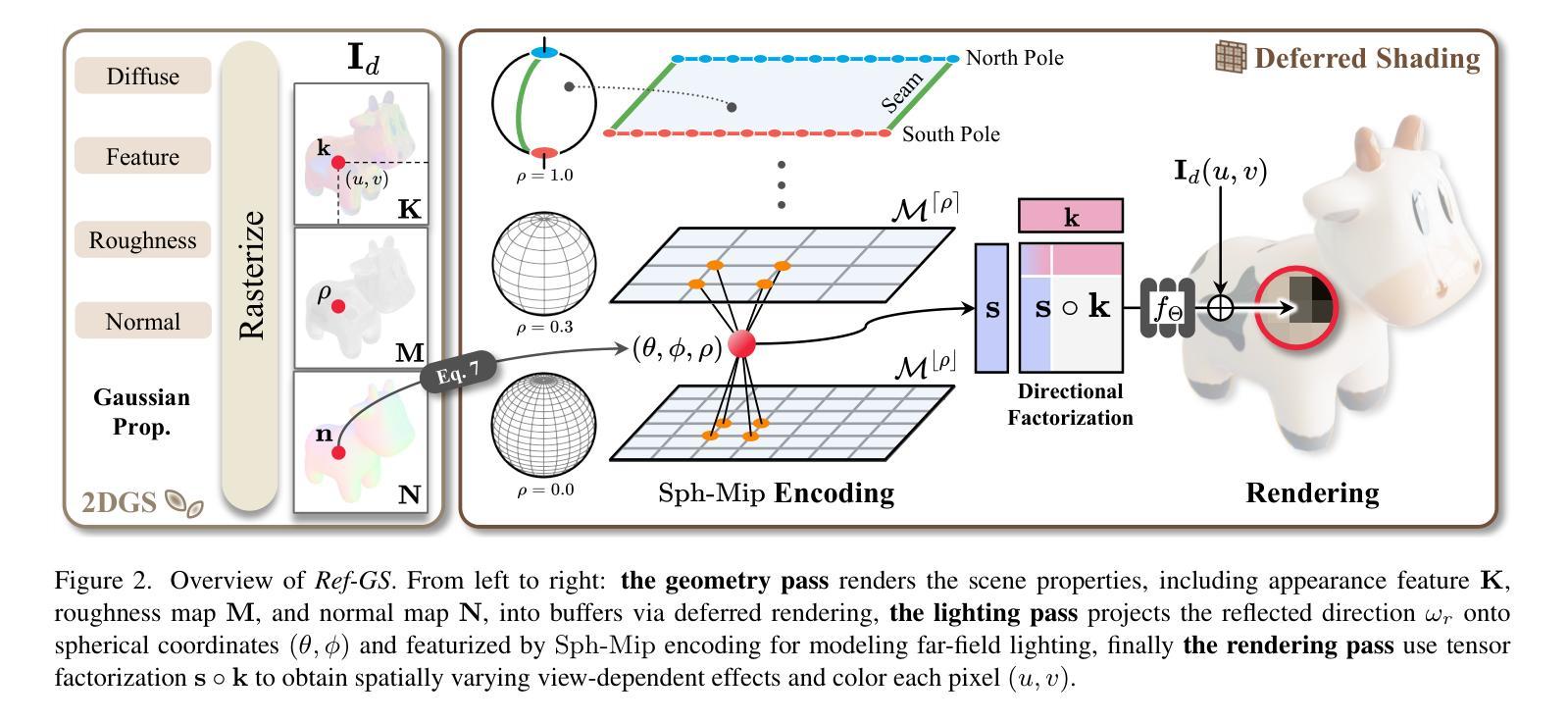
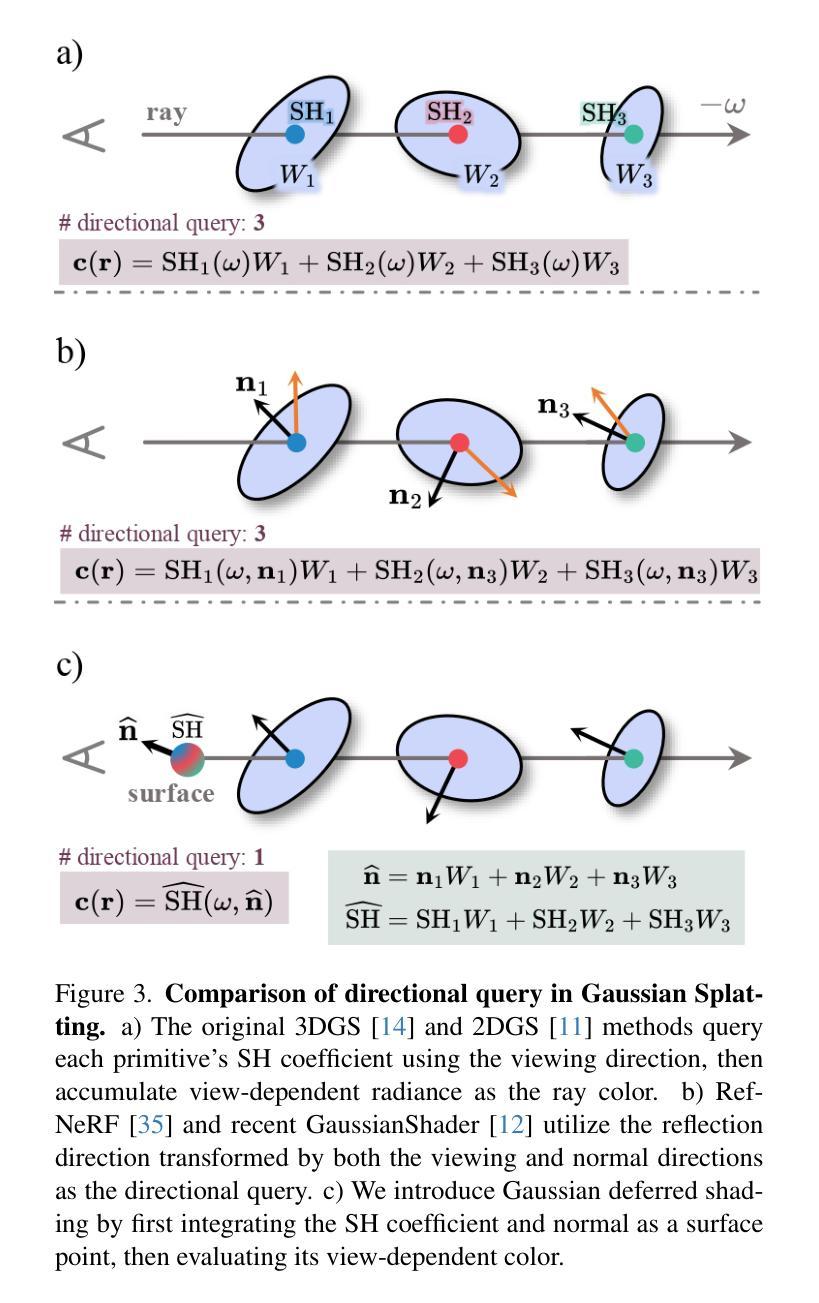
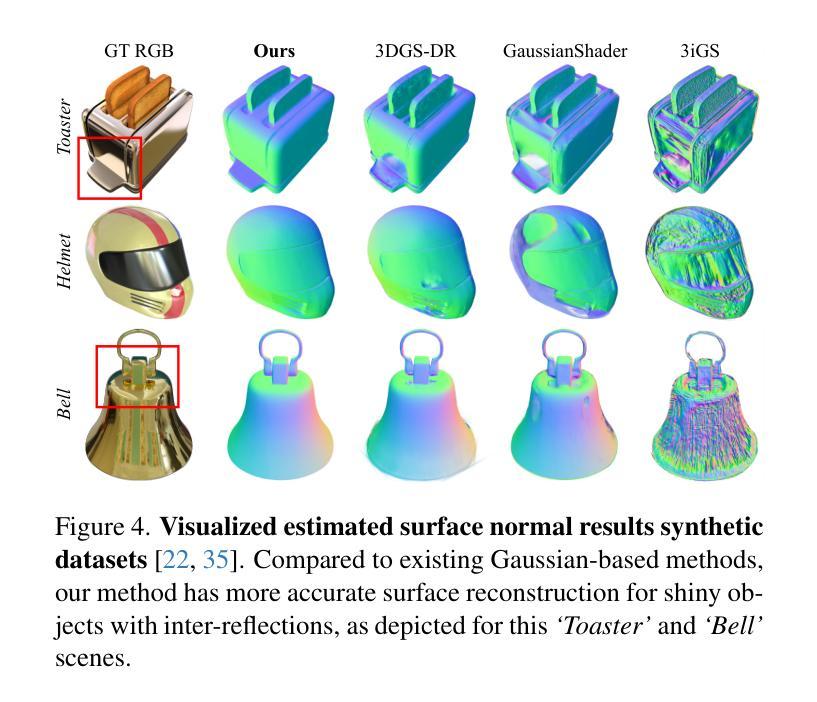
Ref-GS: Directional Factorization for 2D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Youjia Zhang, Anpei Chen, Yumin Wan, Zikai Song, Junqing Yu, Yawei Luo, Wei Yang
In this paper, we introduce Ref-GS, a novel approach for directional light factorization in 2D Gaussian splatting, which enables photorealistic view-dependent appearance rendering and precise geometry recovery. Ref-GS builds upon the deferred rendering of Gaussian splatting and applies directional encoding to the deferred-rendered surface, effectively reducing the ambiguity between orientation and viewing angle. Next, we introduce a spherical Mip-grid to capture varying levels of surface roughness, enabling roughness-aware Gaussian shading. Additionally, we propose a simple yet efficient geometry-lighting factorization that connects geometry and lighting via the vector outer product, significantly reducing renderer overhead when integrating volumetric attributes. Our method achieves superior photorealistic rendering for a range of open-world scenes while also accurately recovering geometry.
本文介绍了一种名为Ref-GS的新型方法,用于在二维高斯混染中进行方向性光照分解,从而实现与视图相关的逼真外观渲染和精确几何恢复。Ref-GS基于高斯混染的延迟渲染,对延迟渲染表面应用方向编码,有效减少了方向和视角之间的歧义。接下来,我们引入了一个球形Mip网格来捕捉不同级别的表面粗糙度,从而实现粗糙度感知的高斯着色。此外,我们提出了一种简单高效的地形-光照分解方法,通过向量外积将地形和光照连接起来,在集成体积属性时大大降低了渲染器开销。我们的方法在为一系列开放世界场景实现逼真的渲染的同时,还能准确地恢复地形。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project page: https://ref-gs.github.io/
Summary
本文提出了Ref-GS方法,这是一种用于二维高斯平铺中的方向光因子化的新方法,可实现与视图相关的逼真外观渲染和精确几何恢复。Ref-GS基于高斯平铺的延迟渲染,并将方向编码应用于延迟渲染的表面,有效地减少了方向和观看角度之间的歧义。此外,还引入了球形Mip网格来捕捉不同级别的表面粗糙度,实现了粗糙度感知的高斯着色。同时,提出了一种简单而高效的地形光照因子化方法,通过向量外积连接地形和光照,大大减少了集成体积属性时的渲染器开销。该方法为开放世界场景实现了逼真的渲染,并准确恢复了地形。
Key Takeaways
- Ref-GS方法是一种用于二维高斯平铺中的方向光因子化新技术。
- Ref-GS实现了与视图相关的逼真外观渲染和精确几何恢复。
- 该方法基于高斯平铺的延迟渲染,利用方向编码减少方向和观看角度的歧义。
- 引入了球形Mip网格来捕捉不同级别的表面粗糙度,实现粗糙度感知的高斯着色。
- 提出了一种简单而高效的地形光照因子化方法,连接地形和光照。
- 该方法大大减少了集成体积属性时的渲染器开销。
点此查看论文截图
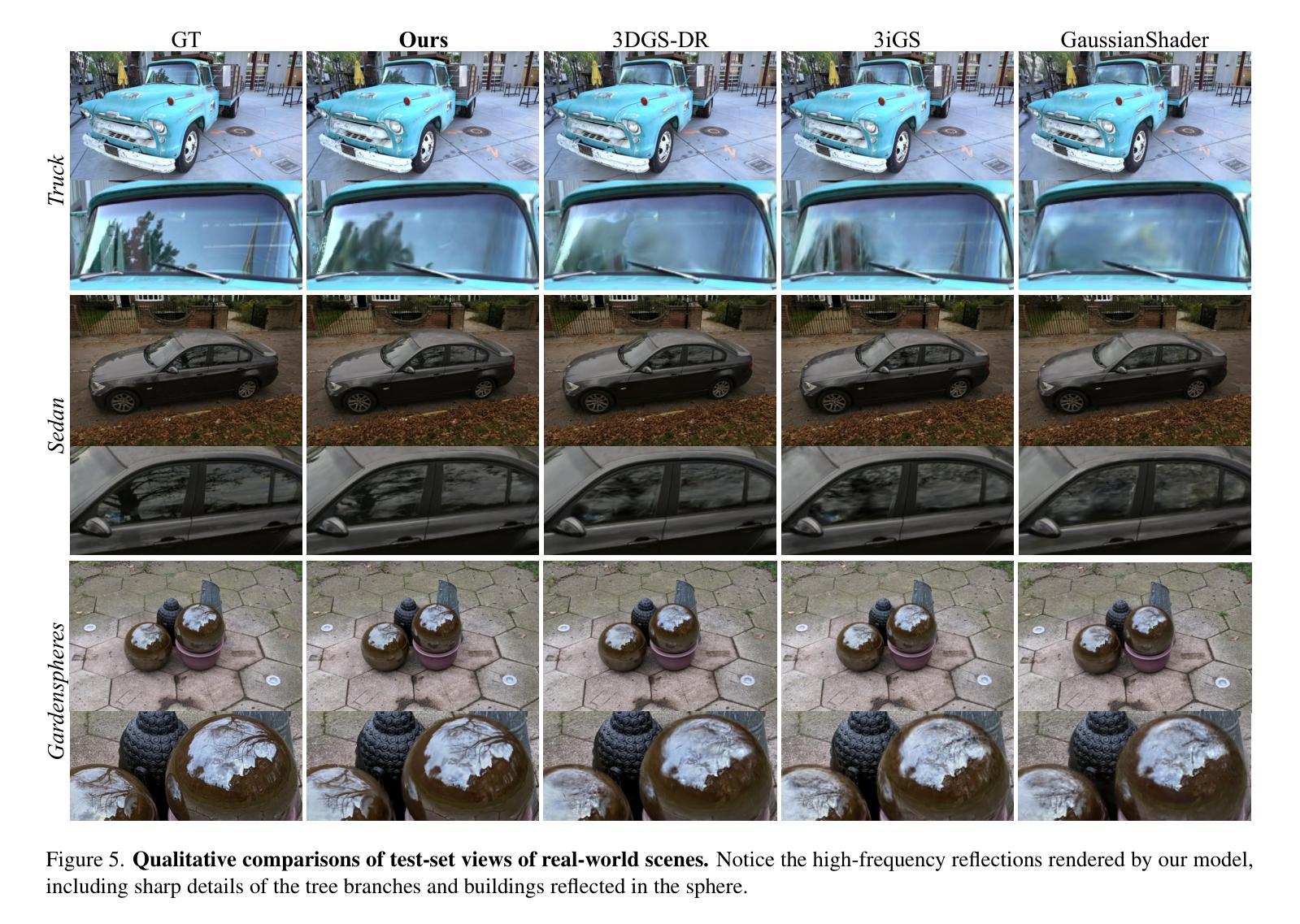


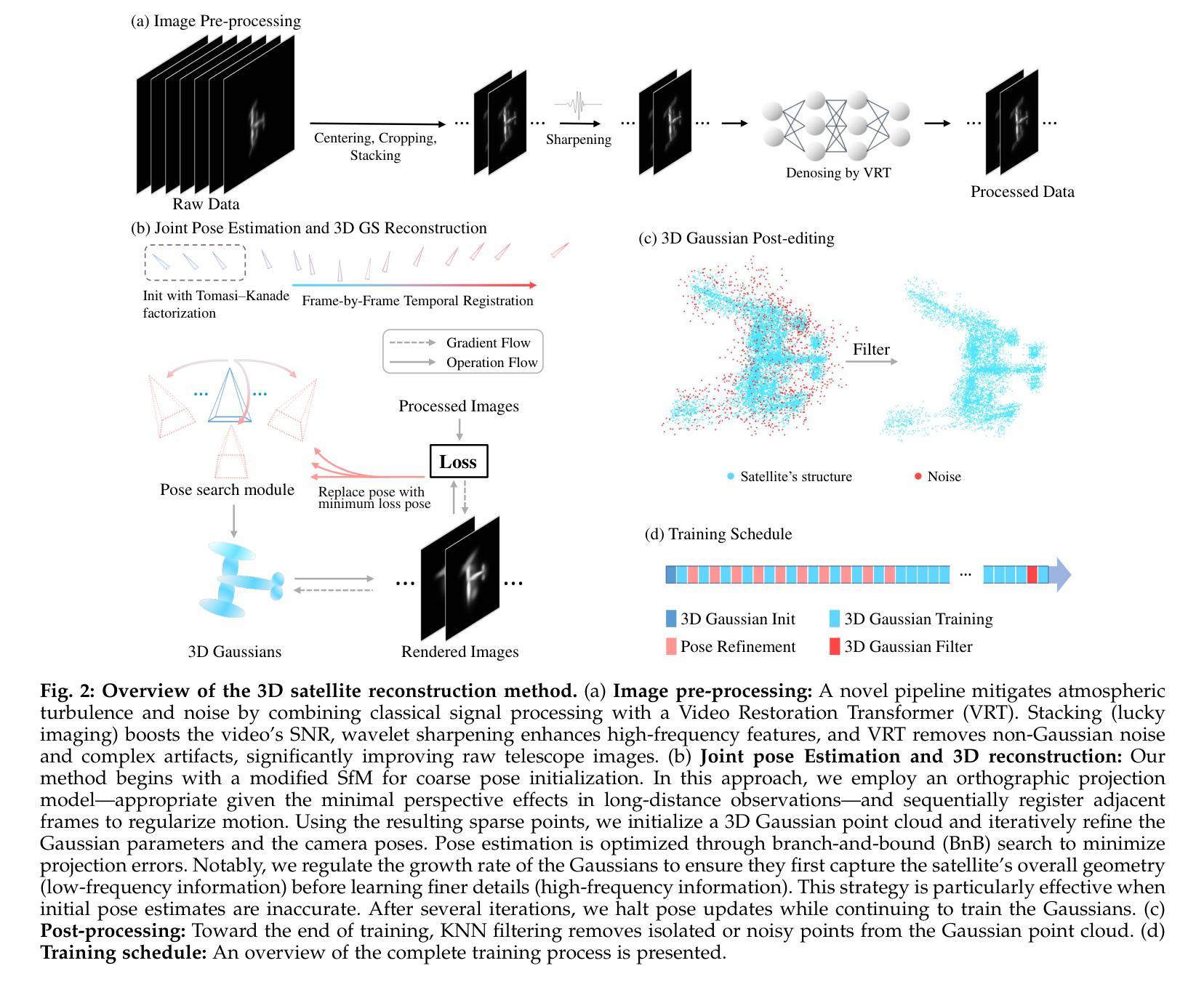
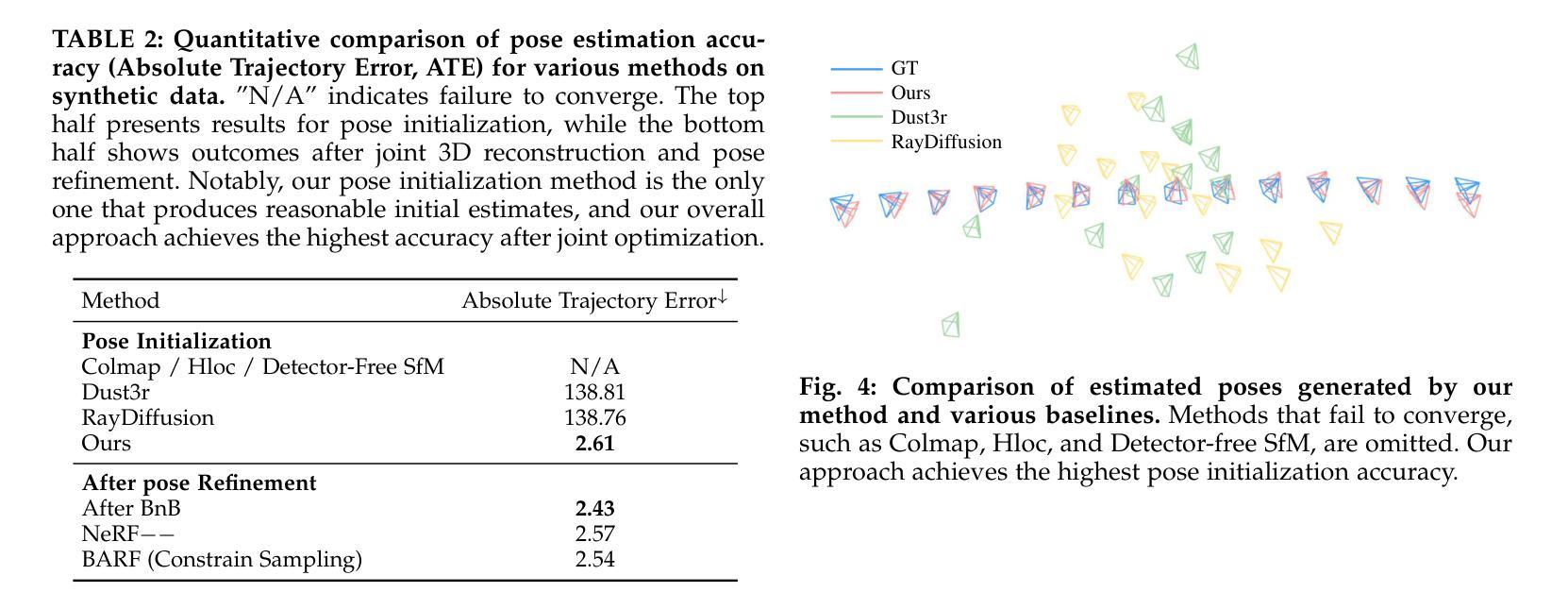
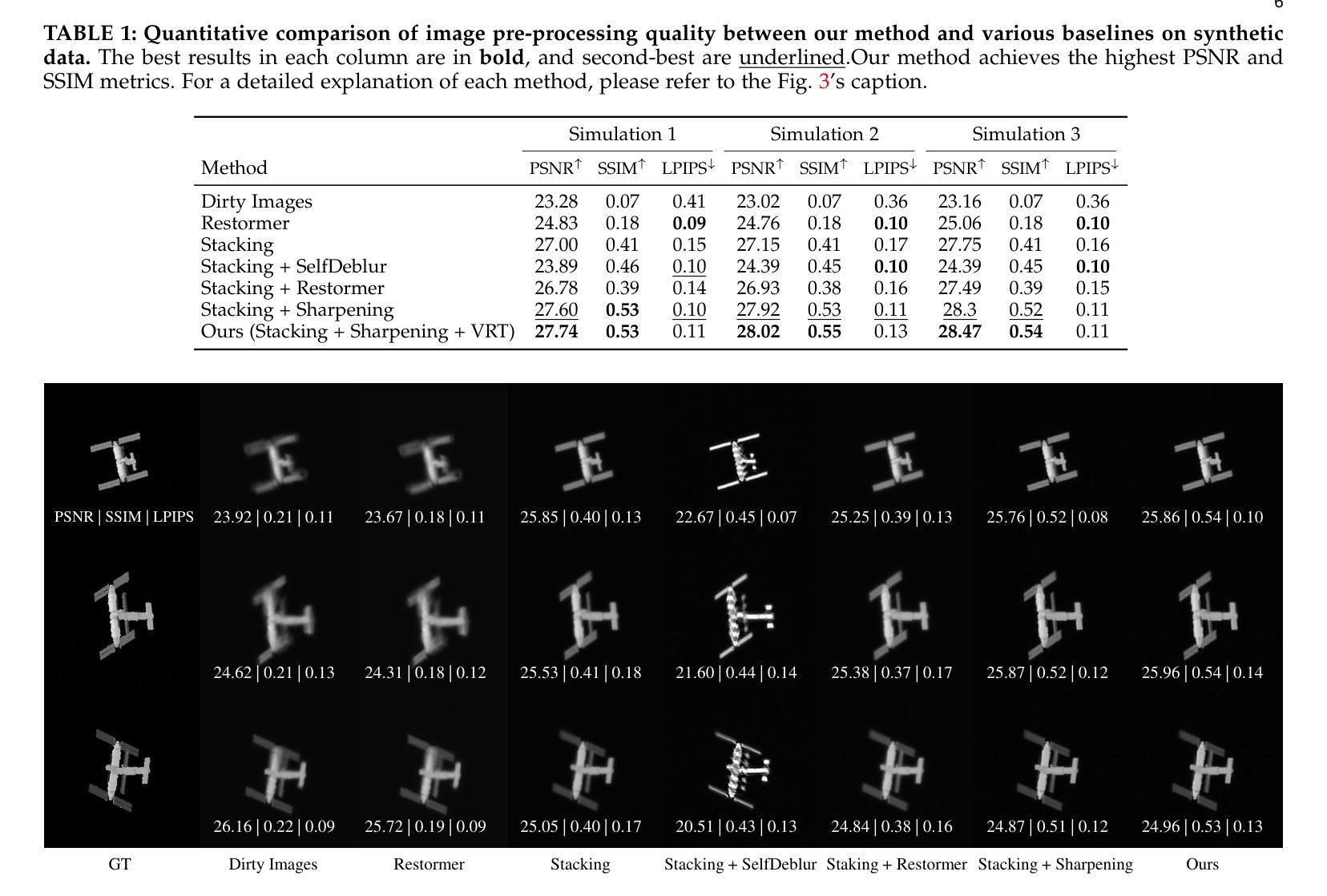
Reconstructing Satellites in 3D from Amateur Telescope Images
Authors:Zhiming Chang, Boyang Liu, Yifei Xia, Youming Guo, Boxin Shi, He Sun
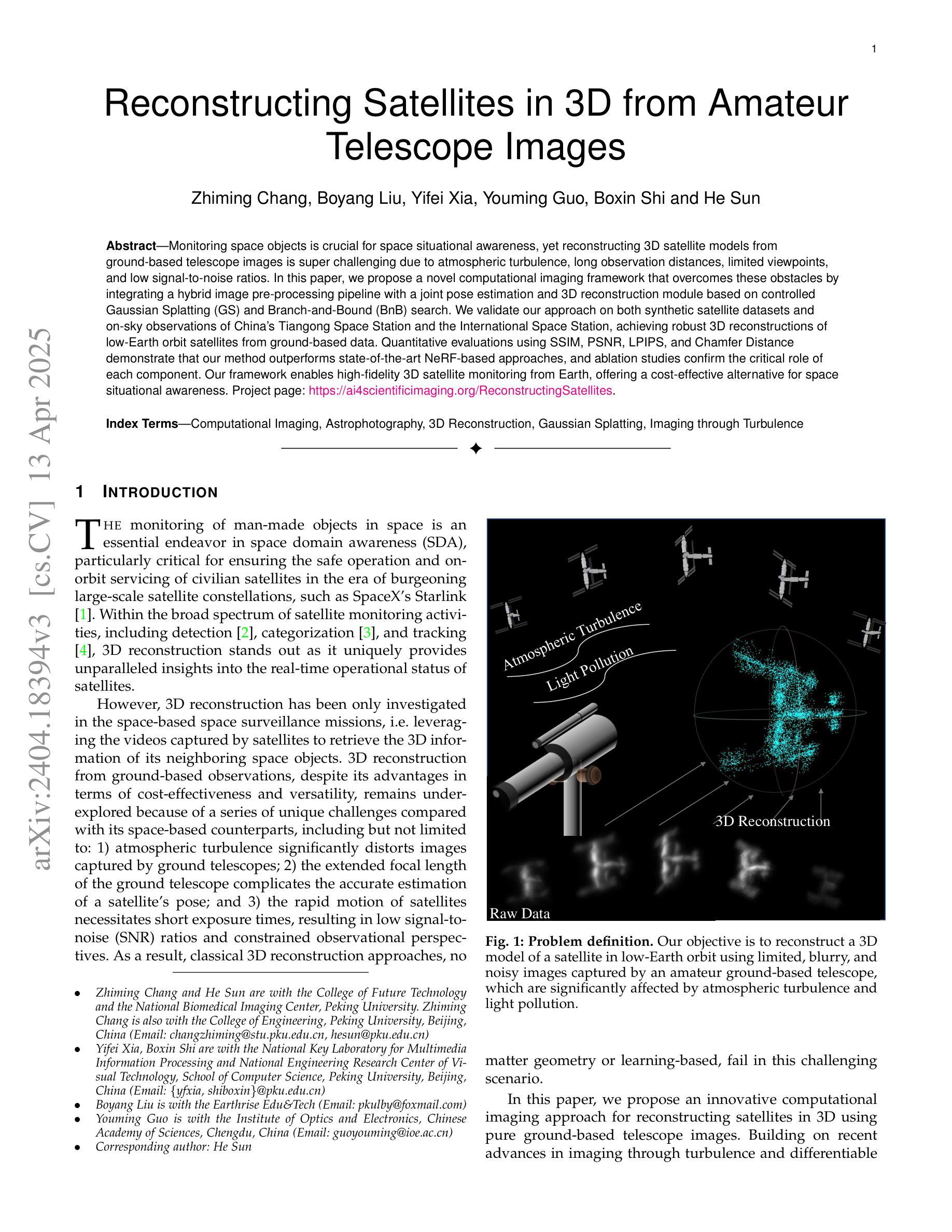
Monitoring space objects is crucial for space situational awareness, yet reconstructing 3D satellite models from ground-based telescope images is challenging due to atmospheric turbulence, long observation distances, limited viewpoints, and low signal-to-noise ratios. In this paper, we propose a novel computational imaging framework that overcomes these obstacles by integrating a hybrid image pre-processing pipeline with a joint pose estimation and 3D reconstruction module based on controlled Gaussian Splatting (GS) and Branch-and-Bound (BnB) search. We validate our approach on both synthetic satellite datasets and on-sky observations of China’s Tiangong Space Station and the International Space Station, achieving robust 3D reconstructions of low-Earth orbit satellites from ground-based data. Quantitative evaluations using SSIM, PSNR, LPIPS, and Chamfer Distance demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art NeRF-based approaches, and ablation studies confirm the critical role of each component. Our framework enables high-fidelity 3D satellite monitoring from Earth, offering a cost-effective alternative for space situational awareness. Project page: https://ai4scientificimaging.org/ReconstructingSatellites
对空间目标进行监测对于空间态势感知至关重要,然而,从地面望远镜图像重建3D卫星模型是一项具有挑战性的任务,面临着大气扰动、长观测距离、观测视角有限和信噪比低等问题。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的计算成像框架,通过融合混合图像预处理管道与基于受控的高斯涂斑(GS)和分形界定(BnB)搜索的联合姿态估计和3D重建模块,克服了这些障碍。我们通过对合成卫星数据集和中国天宫空间站以及国际空间站的天文观测进行了验证,实现了从地面数据对低地球轨道卫星的稳健3D重建。使用结构相似性度量(SSIM)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)、局部感知图像相似性(LPIPS)和Chamfer距离进行的定量评估表明,我们的方法优于最新的基于NeRF的方法,消融研究证实了每个组件的关键作用。我们的框架能够实现从地球进行的高保真3D卫星监测,为空间态势感知提供了经济高效的替代方案。项目页面:网站链接。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的计算成像框架,通过整合混合图像预处理管道与基于受控高斯Splatting和分支定界搜索的联合姿态估计和3D重建模块,克服了大气扰动、长观测距离、有限观测视角以及低信噪比等问题,实现了对低轨道卫星的稳健3D重建。该方法已在合成卫星数据集和中国天宫空间站及国际空间站的星空观测上得到验证,表现出优于现有NeRF方法的效果。此框架为从地球进行的高保真卫星监测提供了成本效益高的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 文中强调了监测太空物体对于太空态势感知的重要性。
- 重建3D卫星模型从地面望远镜图像是一个挑战,存在多个难点,如大气扰动、观测距离等。
- 提出了一种新型计算成像框架,整合了图像预处理管道和3D重建模块。
- 该框架利用受控高斯Splatting和分支定界搜索技术,实现了稳健的3D卫星重建。
- 在合成卫星数据集及实际星空观测中验证了该方法的有效性。
- 与现有NeRF方法相比,该方法表现出更好的效果。
点此查看论文截图
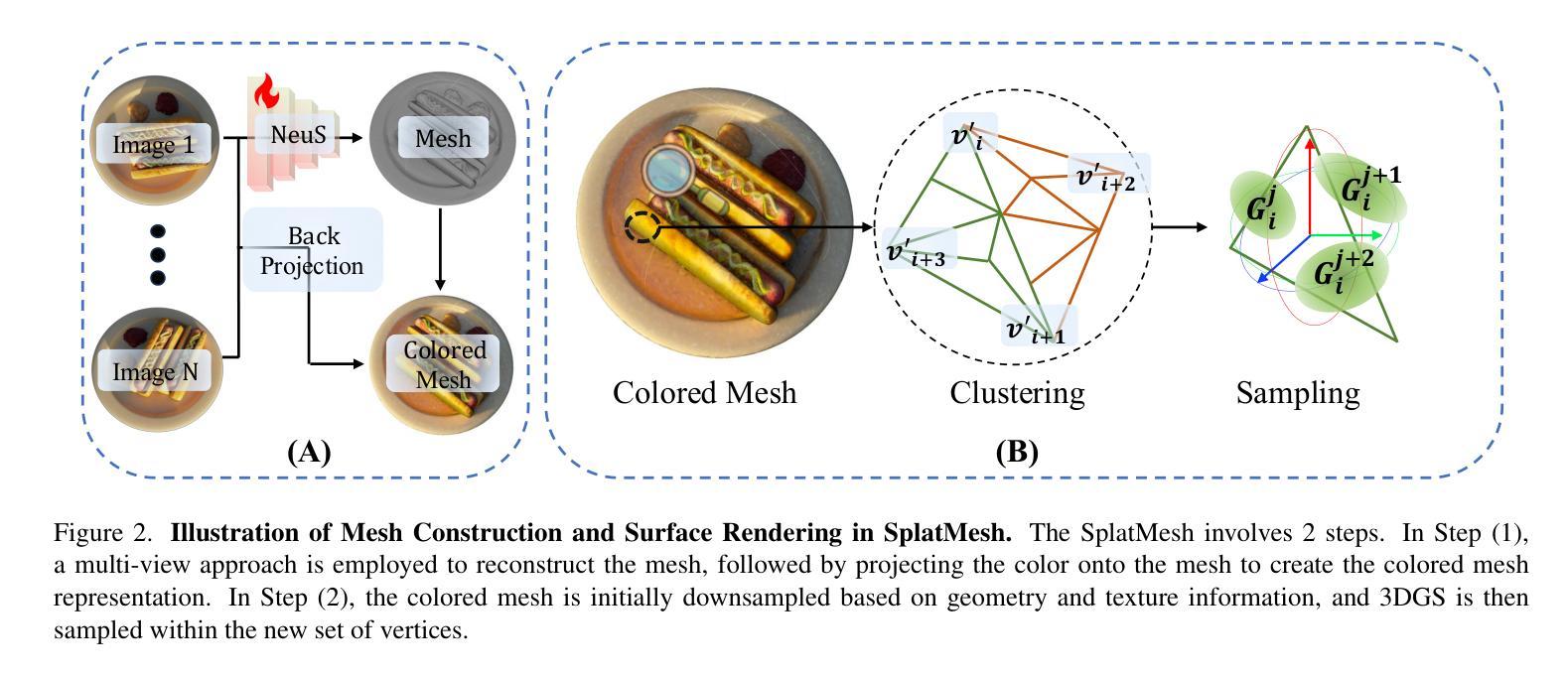
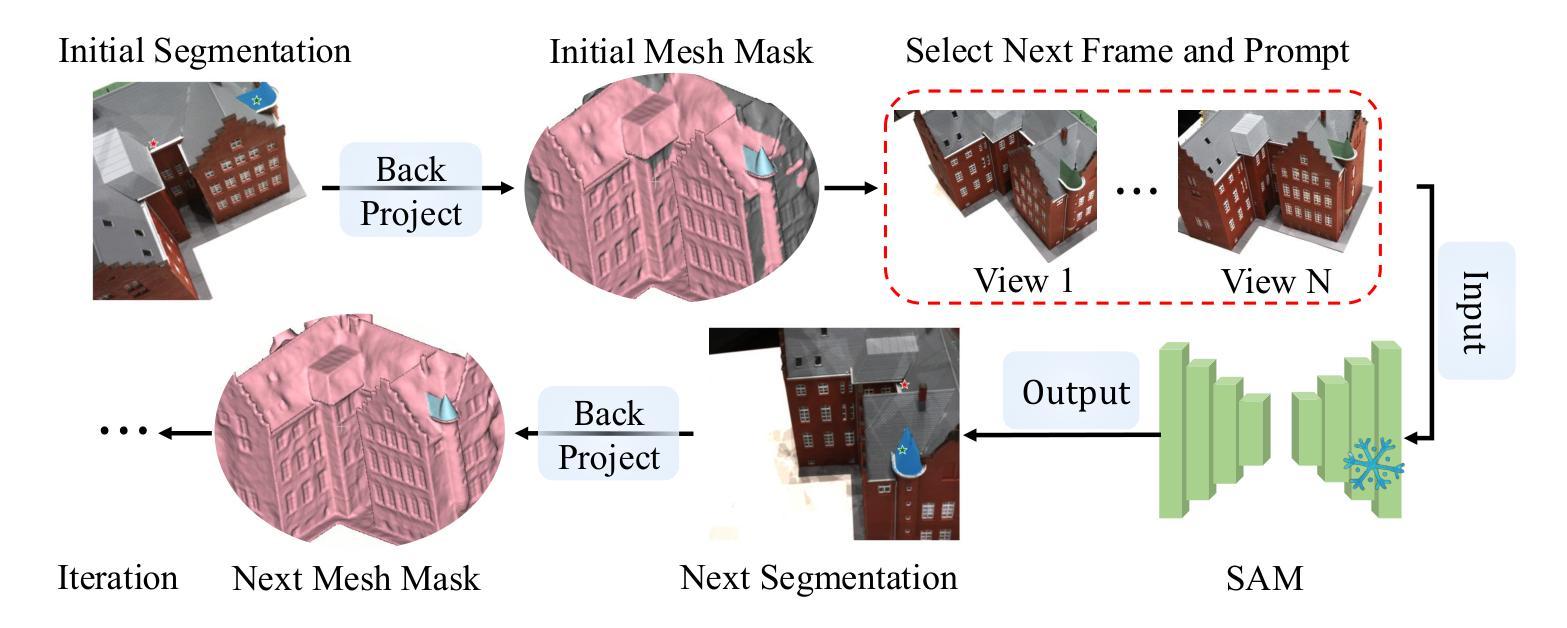
SplatMesh: Interactive 3D Segmentation and Editing Using Mesh-Based Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Kaichen Zhou, Lanqing Hong, Xinhai Chang, Yingji Zhong, Enze Xie, Hao Dong, Zhihao Li, Yongxin Yang, Zhenguo Li, Wei Zhang
A key challenge in fine-grained 3D-based interactive editing is the absence of an efficient representation that balances diverse modifications with high-quality view synthesis under a given memory constraint. While 3D meshes provide robustness for various modifications, they often yield lower-quality view synthesis compared to 3D Gaussian Splatting, which, in turn, suffers from instability during extensive editing. A straightforward combination of these two representations results in suboptimal performance and fails to meet memory constraints. In this paper, we introduce SplatMesh, a novel fine-grained interactive 3D segmentation and editing algorithm that integrates 3D Gaussian Splat with a precomputed mesh and could adjust the memory request based on the requirement. Specifically, given a mesh, \method simplifies it while considering both color and shape, ensuring it meets memory constraints. Then, SplatMesh aligns Gaussian splats with the simplified mesh by treating each triangle as a new reference point. By segmenting and editing the simplified mesh, we can effectively edit the Gaussian splats as well, which will lead to extensive experiments on real and synthetic datasets, coupled with illustrative visual examples, highlighting the superiority of our approach in terms of representation quality and editing performance. Code of our paper can be found here: https://github.com/kaichen-z/SplatMesh.
在基于精细粒度的3D交互式编辑中,主要挑战在于缺乏一种有效的表示方法,能够在给定的内存约束下平衡多种修改与高质量视图合成。虽然3D网格对各种修改提供了稳健性,但它们通常产生的视图合成质量较低,与3D高斯平铺相比尤其如此,而后者在大量编辑时又会出现不稳定。这两种表示的直接结合会导致性能不佳,无法满足内存约束。在本文中,我们介绍了SplatMesh,这是一种新颖的精细粒度交互式3D分割和编辑算法,它结合了3D高斯平铺和预计算网格,并可以根据需求调整内存请求。具体来说,给定一个网格,该方法在考虑颜色和形状的同时对其进行简化,确保其满足内存约束。然后,SplatMesh通过将每个三角形视为新的参考点,将高斯平铺与简化的网格对齐。通过分割和编辑简化的网格,我们可以有效地编辑高斯平铺,这将导致在真实和合成数据集上进行大量实验,同时配以说明性的视觉示例,突出我们在表示质量和编辑性能方面的方法的优越性。我们的论文代码可以在此找到:https://github.com/kaichen-z/SplatMesh。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了SplatMesh,一种新型的基于精细交互的3D分割和编辑算法。该算法结合了3D高斯Splat和预计算网格,能够在内存需求方面进行调整。SplatMesh通过简化网格并考虑颜色和形状,确保满足内存约束,然后通过将高斯splats与简化网格对齐,实现对网格的精细分割和编辑,从而达到高质量的表现。
Key Takeaways
- SplatMesh是一种新型的交互式3D分割和编辑算法,融合了3D高斯Splat和预计算网格技术。
- 该算法能够在内存需求方面进行调整,以适应不同的应用场景。
- SplatMesh通过简化网格并考虑颜色和形状,确保满足内存约束,实现高效的表示。
- 该算法通过将高斯splats与简化网格对齐,实现对网格的精细分割和编辑。
- SplatMesh算法在真实和合成数据集上进行了广泛的实验验证。
- 实验结果突出了SplatMesh在表示质量和编辑性能方面的优越性。
点此查看论文截图