⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-16 更新
Anchor Token Matching: Implicit Structure Locking for Training-free AR Image Editing
Authors:Taihang Hu, Linxuan Li, Kai Wang, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang, Ming-Ming Cheng
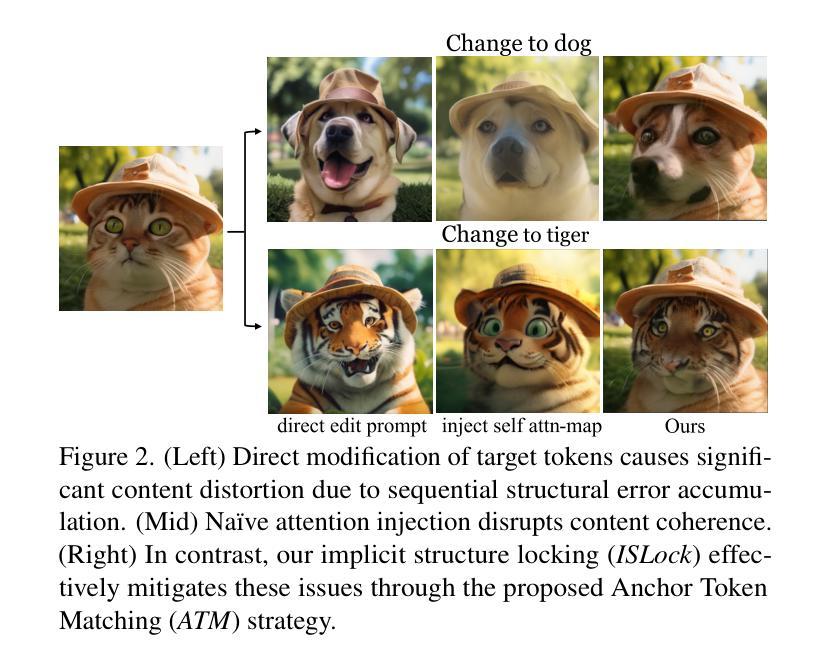
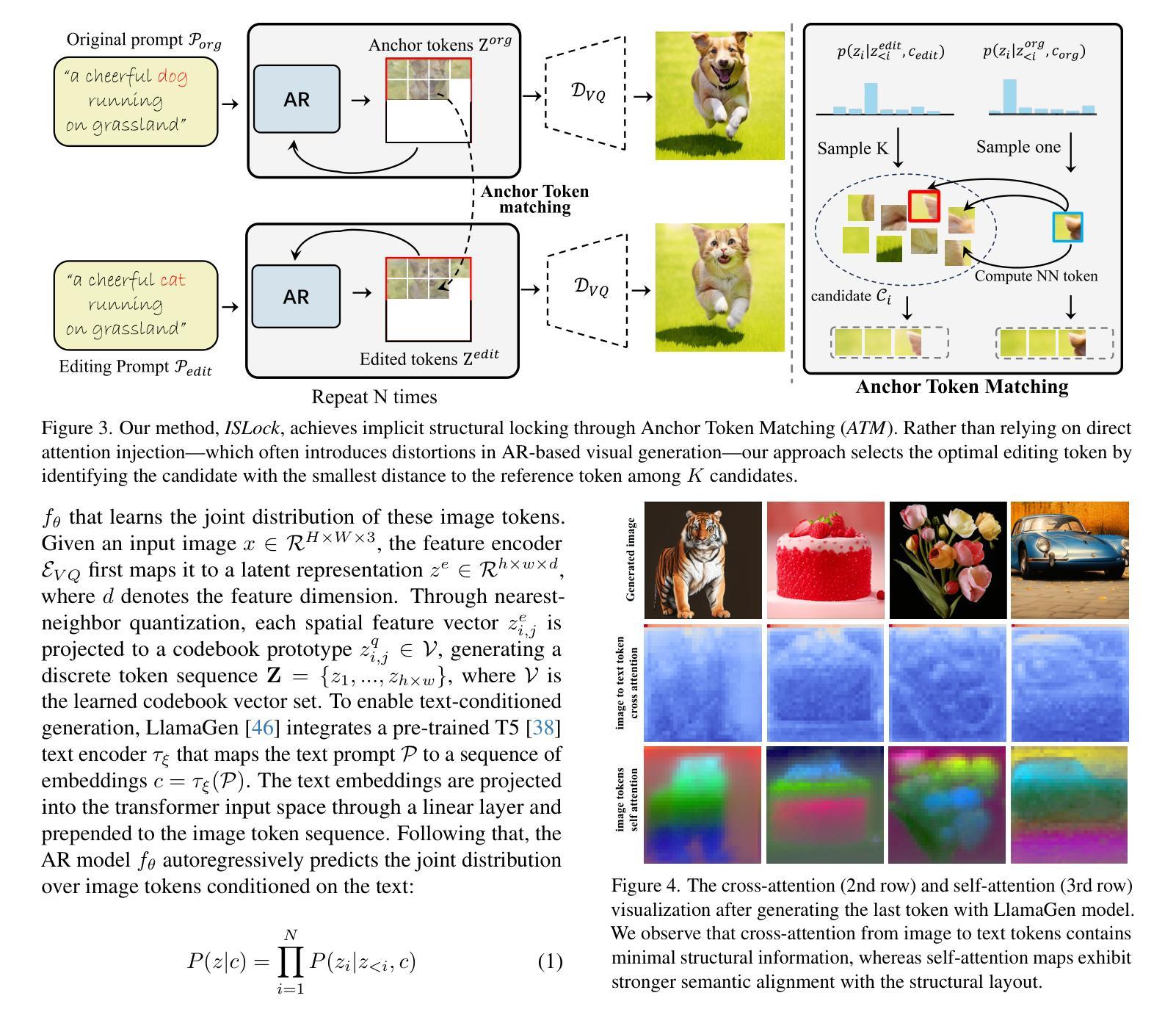
Text-to-image generation has seen groundbreaking advancements with diffusion models, enabling high-fidelity synthesis and precise image editing through cross-attention manipulation. Recently, autoregressive (AR) models have re-emerged as powerful alternatives, leveraging next-token generation to match diffusion models. However, existing editing techniques designed for diffusion models fail to translate directly to AR models due to fundamental differences in structural control. Specifically, AR models suffer from spatial poverty of attention maps and sequential accumulation of structural errors during image editing, which disrupt object layouts and global consistency. In this work, we introduce Implicit Structure Locking (ISLock), the first training-free editing strategy for AR visual models. Rather than relying on explicit attention manipulation or fine-tuning, ISLock preserves structural blueprints by dynamically aligning self-attention patterns with reference images through the Anchor Token Matching (ATM) protocol. By implicitly enforcing structural consistency in latent space, our method ISLock enables structure-aware editing while maintaining generative autonomy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ISLock achieves high-quality, structure-consistent edits without additional training and is superior or comparable to conventional editing techniques. Our findings pioneer the way for efficient and flexible AR-based image editing, further bridging the performance gap between diffusion and autoregressive generative models. The code will be publicly available at https://github.com/hutaiHang/ATM
文本到图像生成领域在扩散模型(Diffusion Models)的推动下取得了突破性进展,通过跨注意力操纵(cross-attention manipulation)实现了高保真合成和精确图像编辑。近期,自回归(AR)模型作为强大的替代方案重新崭露头角,它利用下一个标记生成(next-token generation)技术匹配扩散模型。然而,针对扩散模型设计的现有编辑技术无法直接应用于AR模型,因为它们在结构控制上存在根本差异。具体来说,AR模型在图像编辑时存在注意力图的空间贫困(spatial poverty of attention maps)和结构性错误顺序累积的问题,这会破坏对象布局和全局一致性。在这项工作中,我们介绍了隐式结构锁定(ISLock)——这是一种针对AR视觉模型的首个无需训练即可进行编辑的策略。ISLock不依赖于显式注意力操纵或微调,而是通过锚标记匹配(ATM)协议动态地将自我注意力模式与参考图像对齐,从而保留结构蓝图。通过在潜在空间中隐式强制执行结构一致性,我们的ISLock方法能够在保持生成自主性的同时进行结构感知编辑。大量实验表明,ISLock无需额外训练即可实现高质量、结构一致性的编辑,并且其性能优于或可与传统编辑技术相提并论。我们的发现开辟了基于自回归(AR)的高效灵活图像编辑的道路,进一步缩小了扩散模型和自回归生成模型之间的性能差距。代码将在https://github.com/hutaiHang/ATM公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在文本转图像生成领域取得了突破性进展,近期自回归(AR)模型作为强有力的替代方案崭露头角。然而,针对扩散模型设计的编辑技术无法直接应用于AR模型,因为两者在结构控制上存在根本差异。针对AR模型的空间注意力图贫困和图像编辑中的结构错误累积问题,本文提出了无需训练的编辑策略——隐式结构锁定(ISLock)。通过动态对齐参考图像的自我关注模式,ISLock能够保留结构蓝图。实验表明,ISLock能够在无需额外训练的情况下实现高质量、结构一致性的编辑,并优于或相当于传统编辑技术。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本转图像生成领域取得重大进展,自回归(AR)模型成为有力替代。
- 现有编辑技术无法直接应用于AR模型,因为结构控制上的根本差异。
- AR模型面临空间注意力图贫困和图像编辑中的结构错误累积问题。
- ISLock是首个针对AR视觉模型的无需训练的编辑策略。
- ISLock通过动态对齐自我关注模式与参考图像,保留结构蓝图。
- ISLock实现了高质量、结构一致性的编辑,无需额外训练。
- ISLock优于或相当于传统编辑技术,为AR模型基于图像编辑开辟了新途径。
点此查看论文截图

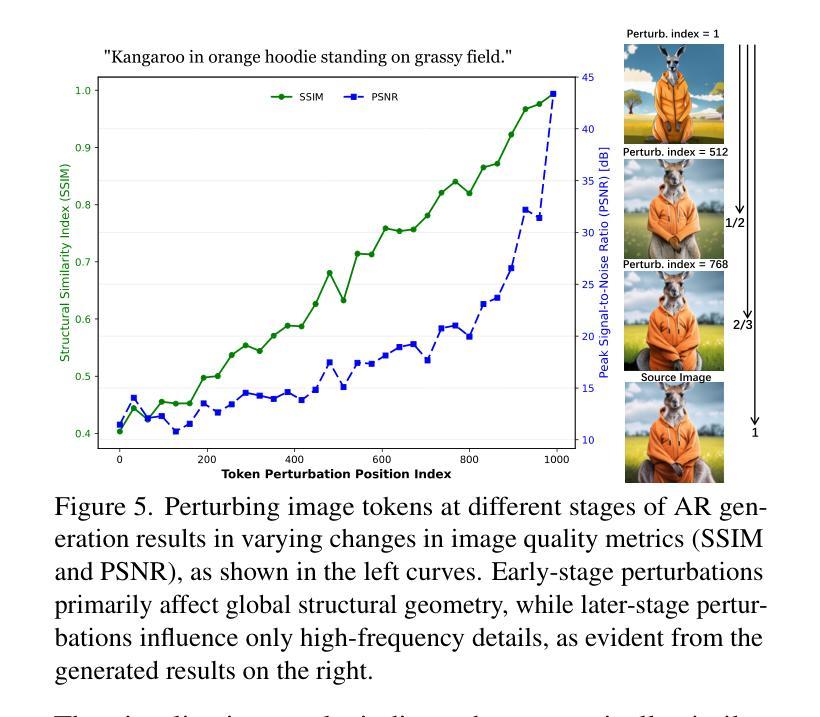
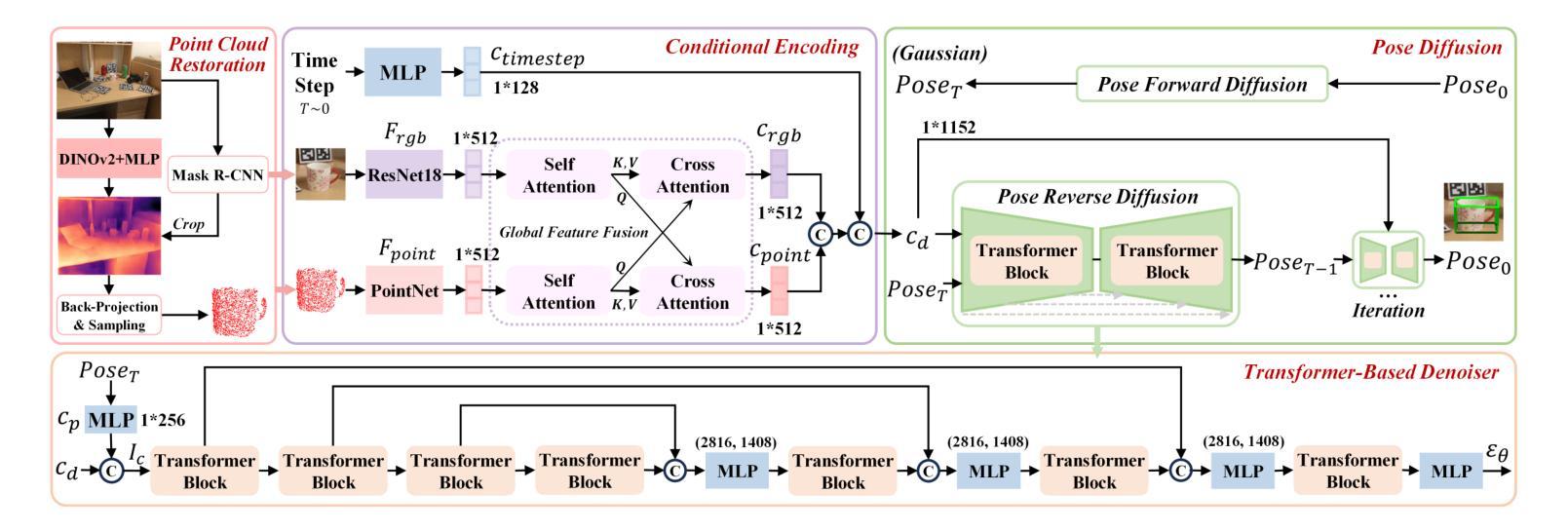
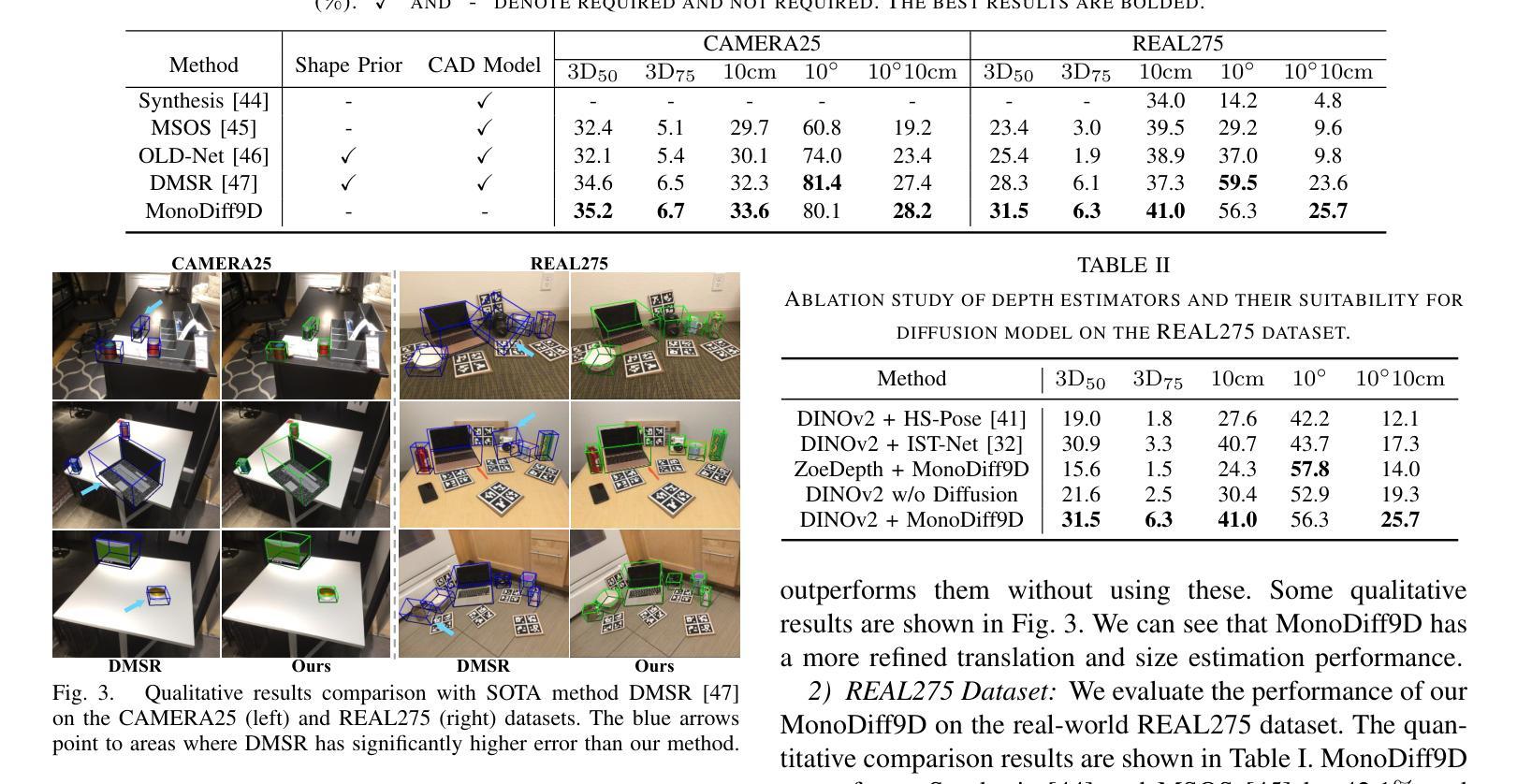
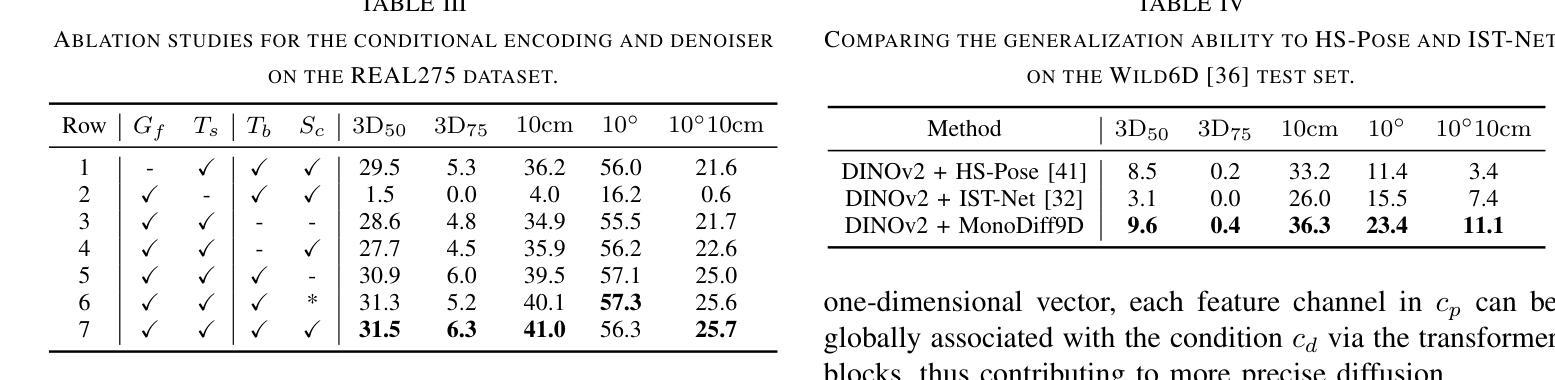
MonoDiff9D: Monocular Category-Level 9D Object Pose Estimation via Diffusion Model
Authors:Jian Liu, Wei Sun, Hui Yang, Jin Zheng, Zichen Geng, Hossein Rahmani, Ajmal Mian
Object pose estimation is a core means for robots to understand and interact with their environment. For this task, monocular category-level methods are attractive as they require only a single RGB camera. However, current methods rely on shape priors or CAD models of the intra-class known objects. We propose a diffusion-based monocular category-level 9D object pose generation method, MonoDiff9D. Our motivation is to leverage the probabilistic nature of diffusion models to alleviate the need for shape priors, CAD models, or depth sensors for intra-class unknown object pose estimation. We first estimate coarse depth via DINOv2 from the monocular image in a zero-shot manner and convert it into a point cloud. We then fuse the global features of the point cloud with the input image and use the fused features along with the encoded time step to condition MonoDiff9D. Finally, we design a transformer-based denoiser to recover the object pose from Gaussian noise. Extensive experiments on two popular benchmark datasets show that MonoDiff9D achieves state-of-the-art monocular category-level 9D object pose estimation accuracy without the need for shape priors or CAD models at any stage. Our code will be made public at https://github.com/CNJianLiu/MonoDiff9D.
对象姿态估计是机器人理解和与其环境交互的核心手段。对于此任务,单目类别级方法很有吸引力,因为它们仅需要单个RGB相机。然而,当前的方法依赖于形状先验或已知对象的类内CAD模型。我们提出了一种基于扩散的单目类别级9D对象姿态生成方法,称为MonoDiff9D。我们的动机是利用扩散模型的概率性质,减轻对形状先验、CAD模型或深度传感器的需求,用于类内未知对象姿态估计。我们首先通过DINOv2以零样本方式从单目图像估计粗略深度并将其转换为点云。然后,我们将点云的全局特征与输入图像融合,并使用融合的特征以及编码的时间步长来调节MonoDiff9D。最后,我们设计了一个基于变压器的去噪器,从高斯噪声中恢复对象姿态。在两个流行的基准数据集上的大量实验表明,MonoDiff9D在不使用形状先验或任何阶段的CAD模型的情况下,实现了最先进的单目类别级9D对象姿态估计精度。我们的代码将在https://github.com/CNJianLiu/MonoDiff9D公开。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICRA’25
Summary
本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的单目类别级9D物体姿态生成方法,名为MonoDiff9D。该方法利用扩散模型的概率性质,无需形状先验、CAD模型或深度传感器即可实现同类未知物体的姿态估计。通过单目图像进行粗略深度估计,转换为点云,并与输入图像融合特征。设计基于变压器的去噪器,从高斯噪声中恢复物体姿态。在主流数据集上的实验表明,MonoDiff9D在无需形状先验或CAD模型的条件下,实现了最先进的单目类别级9D物体姿态估计精度。
Key Takeaways
- 对象姿态估计是机器人理解和与其环境交互的核心手段。
- 当前方法需要形状先验或已知对象的CAD模型。
- 提出了一种基于扩散模型的MonoDiff9D方法,用于单目类别级9D对象姿态生成。
- MonoDiff9D利用扩散模型的概率性质,无需形状先验、CAD模型或深度传感器。
- 通过单目图像估计粗略深度并转换为点云,与输入图像融合特征。
- 设计基于变压器的去噪器,从高斯噪声中恢复物体姿态。
- 在主流数据集上的实验表明,MonoDiff9D实现了最先进的估计精度。
点此查看论文截图

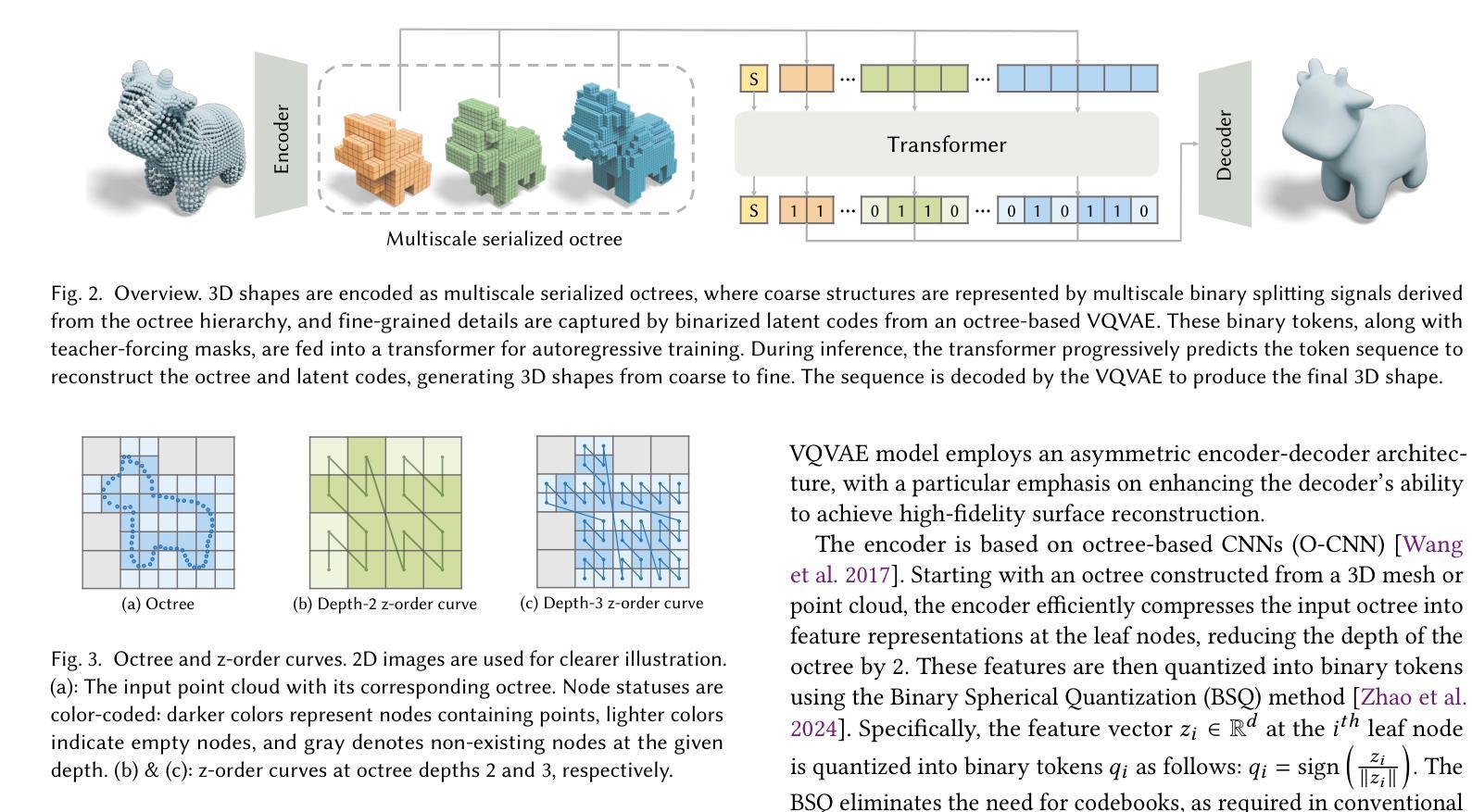
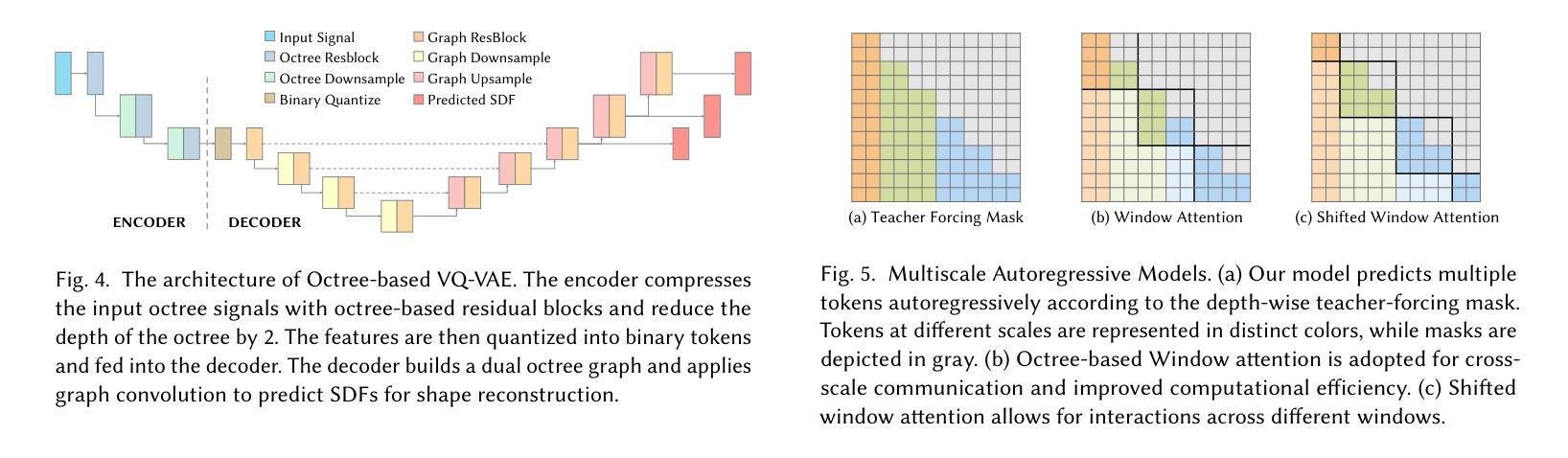
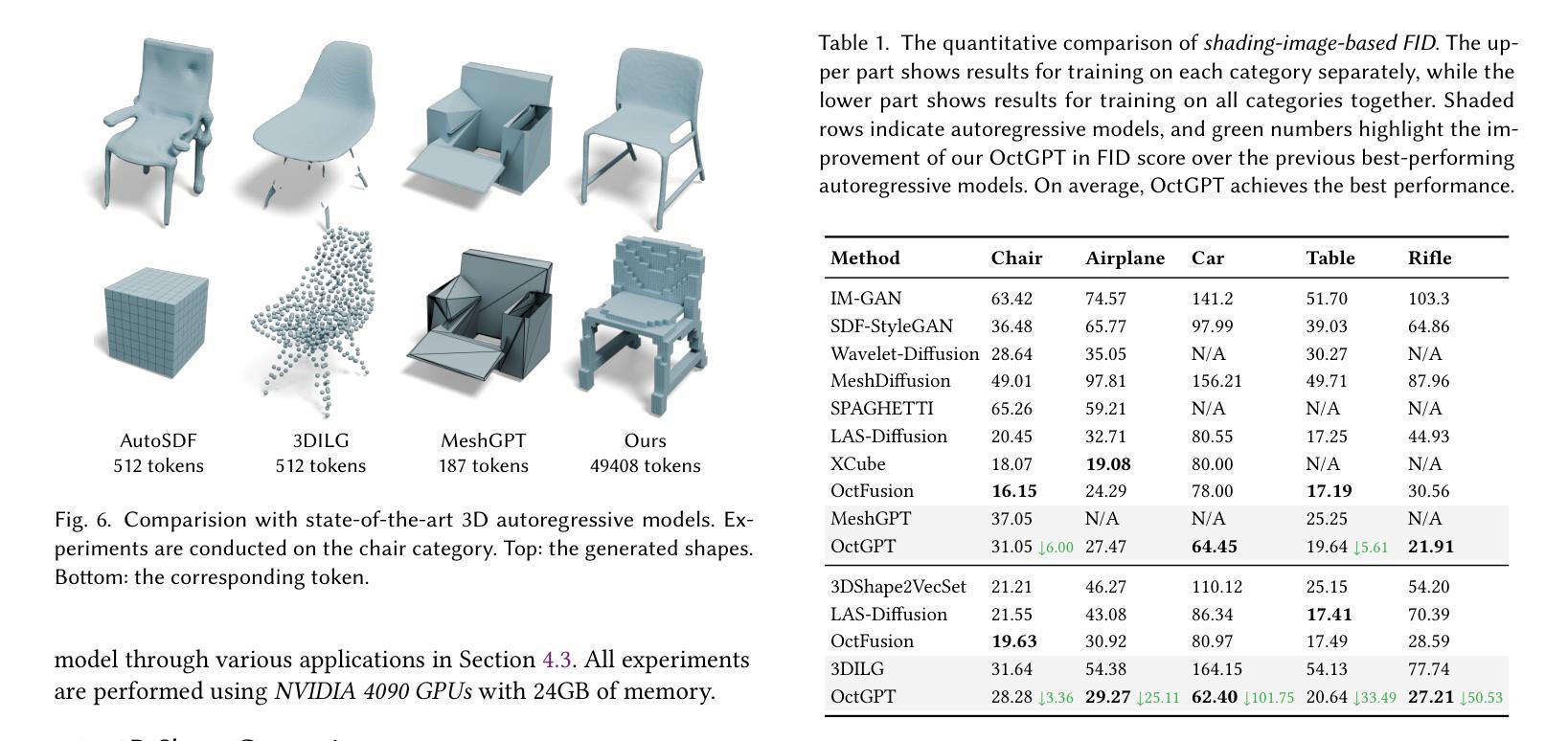
OctGPT: Octree-based Multiscale Autoregressive Models for 3D Shape Generation
Authors:Si-Tong Wei, Rui-Huan Wang, Chuan-Zhi Zhou, Baoquan Chen, Peng-Shuai Wang
Autoregressive models have achieved remarkable success across various domains, yet their performance in 3D shape generation lags significantly behind that of diffusion models. In this paper, we introduce OctGPT, a novel multiscale autoregressive model for 3D shape generation that dramatically improves the efficiency and performance of prior 3D autoregressive approaches, while rivaling or surpassing state-of-the-art diffusion models. Our method employs a serialized octree representation to efficiently capture the hierarchical and spatial structures of 3D shapes. Coarse geometry is encoded via octree structures, while fine-grained details are represented by binary tokens generated using a vector quantized variational autoencoder (VQVAE), transforming 3D shapes into compact \emph{multiscale binary sequences} suitable for autoregressive prediction. To address the computational challenges of handling long sequences, we incorporate octree-based transformers enhanced with 3D rotary positional encodings, scale-specific embeddings, and token-parallel generation schemes. These innovations reduce training time by 13 folds and generation time by 69 folds, enabling the efficient training of high-resolution 3D shapes, e.g.,$1024^3$, on just four NVIDIA 4090 GPUs only within days. OctGPT showcases exceptional versatility across various tasks, including text-, sketch-, and image-conditioned generation, as well as scene-level synthesis involving multiple objects. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OctGPT accelerates convergence and improves generation quality over prior autoregressive methods, offering a new paradigm for high-quality, scalable 3D content creation.
自回归模型已经在各个领域取得了显著的成果,但在3D形状生成方面,其性能远远落后于扩散模型。在本文中,我们介绍了OctGPT,这是一种用于3D形状生成的新型多尺度自回归模型,它显著提高了之前3D自回归方法的效率和性能,同时与最先进的扩散模型相抗衡甚至超越。我们的方法采用序列化八叉树表示法,有效地捕捉3D形状的层次结构和空间结构。粗糙几何结构通过八叉树结构进行编码,而细粒度细节则由使用向量量化变分自动编码器(VQVAE)生成的二进制令牌表示,将3D形状转换为适合自回归预测的多尺度二进制序列。为了解决处理长序列的计算挑战,我们结合了基于八叉树的变压器,并增强了3D旋转位置编码、尺度特定嵌入和令牌并行生成方案。这些创新将训练时间缩短了13倍,生成时间缩短了69倍,使得在仅四台NVIDIA 4090 GPU上在几天内就能有效地训练高分辨率的3D形状,例如$1024^3$。OctGPT在各种任务中展示了出色的通用性,包括文本、草图和图像条件下的生成,以及涉及多个对象的场景级别合成。大量实验表明,OctGPT加速了收敛,提高了生成质量,为高质量、可扩展的3D内容创建提供了新的范式。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH 2025
Summary
本文介绍了OctGPT,这是一种用于3D形状生成的新型多尺度自回归模型。它通过采用序列化八叉树表示法,有效地捕捉3D形状的层次结构和空间结构,提高了先前3D自回归方法的效率和性能,同时与或超越了最先进的扩散模型。通过采用基于八叉树的变压器、3D旋转位置编码、尺度特定嵌入和令牌并行生成方案等创新技术,减少了训练和生成时间。OctGPT在不同任务中表现出卓越的多功能性,包括文本、草图和图像条件生成,以及涉及多个对象的场景级别合成。
Key Takeaways
- OctGPT是一个用于3D形状生成的多尺度自回归模型,显著提高了自回归模型的效率和性能。
- OctGPT采用了序列化八叉树表示法,有效捕捉3D形状的层次结构和空间结构。
- OctGPT通过与扩散模型的竞争,展现了强大的性能。
- 通过采用基于八叉树的变压器和其他创新技术,OctGPT减少了训练和生成时间。
- OctGPT具有出色的多功能性,支持文本、草图和图像条件生成,以及场景级别合成。
- OctGPT可以在不同任务中生成高质量、可伸缩的3D内容。
点此查看论文截图

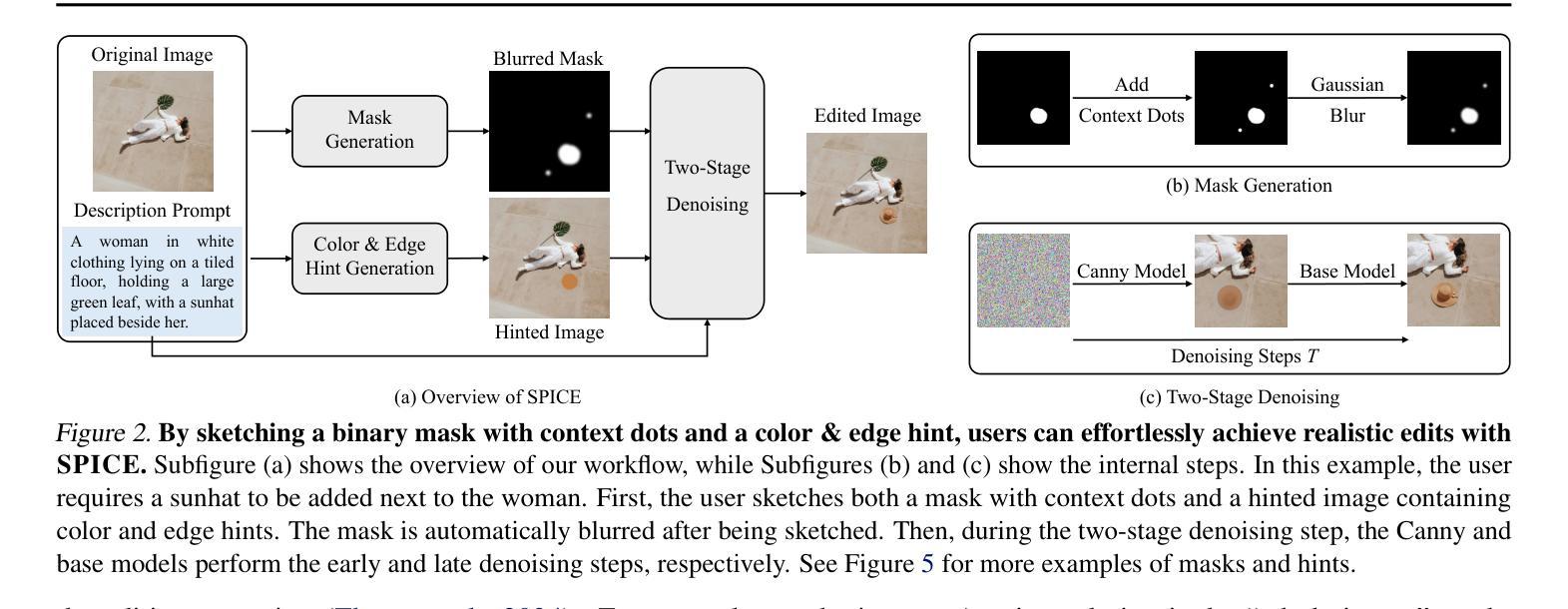
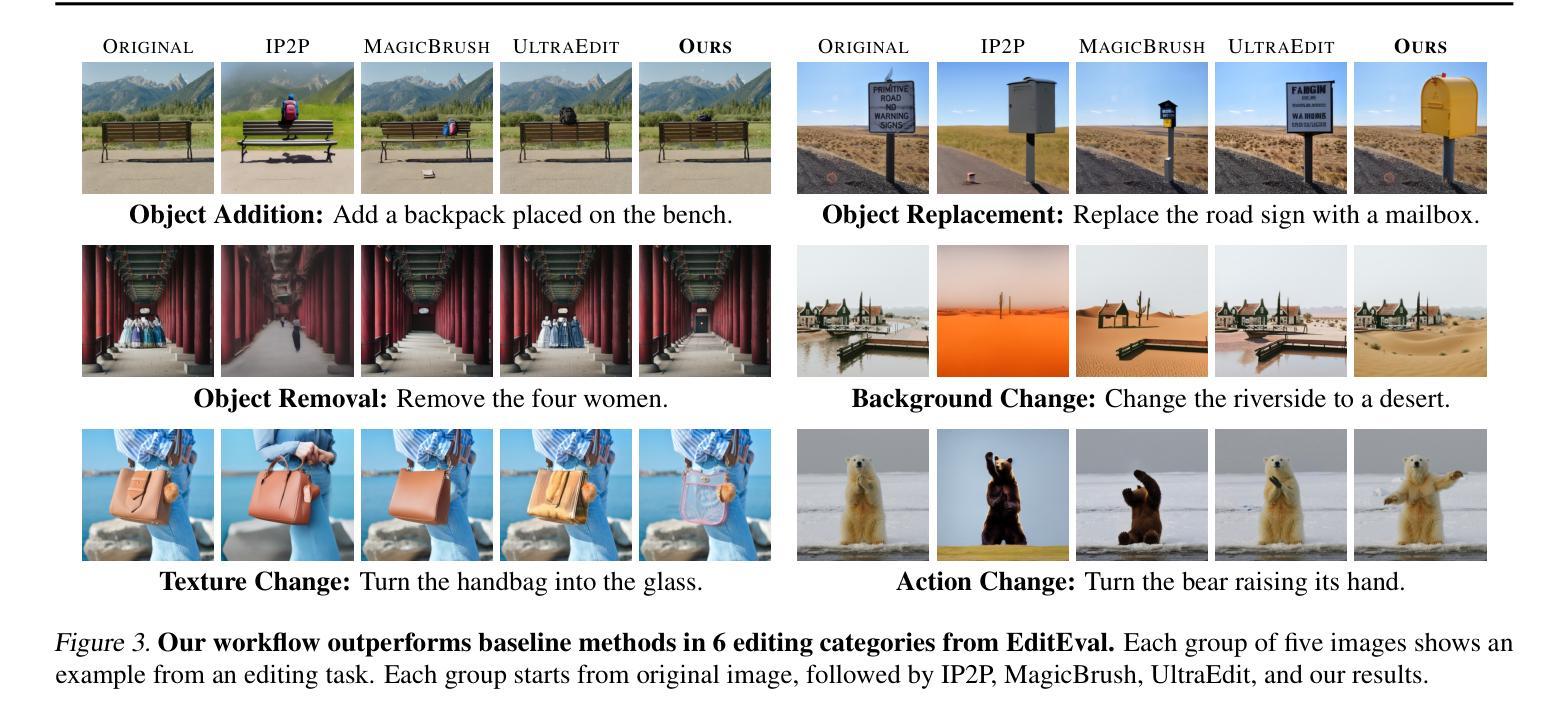
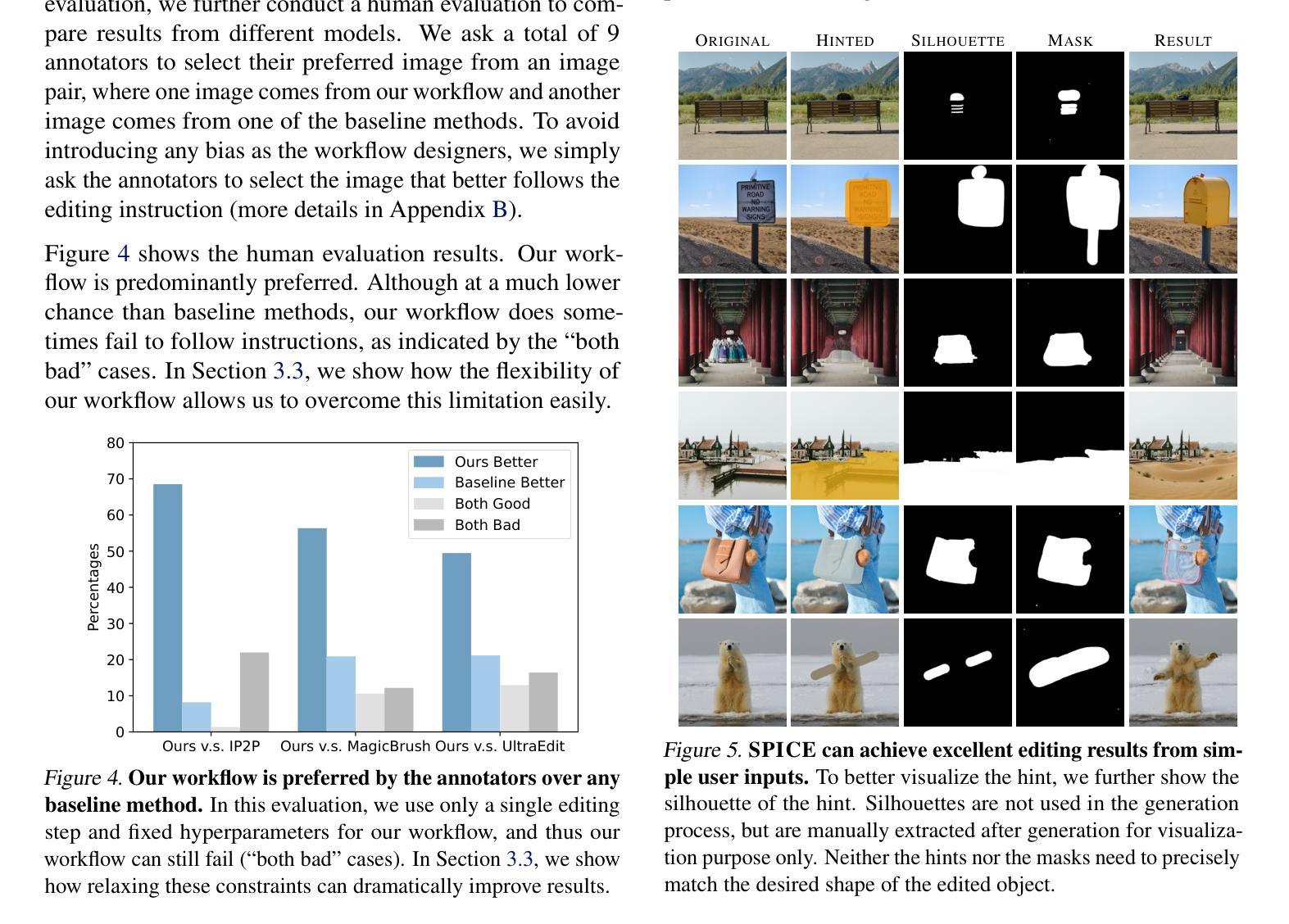
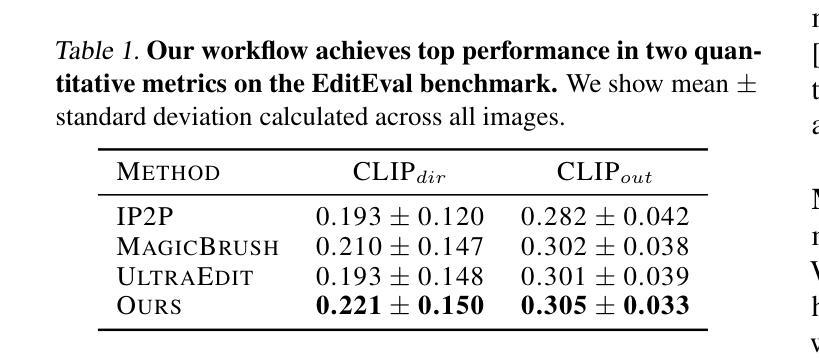
SPICE: A Synergistic, Precise, Iterative, and Customizable Image Editing Workflow
Authors:Kenan Tang, Yanhong Li, Yao Qin
Recent prompt-based image editing models have demonstrated impressive prompt-following capability at structural editing tasks. However, existing models still fail to perform local edits, follow detailed editing prompts, or maintain global image quality beyond a single editing step. To address these challenges, we introduce SPICE, a training-free workflow that accepts arbitrary resolutions and aspect ratios, accurately follows user requirements, and improves image quality consistently during more than 100 editing steps. By synergizing the strengths of a base diffusion model and a Canny edge ControlNet model, SPICE robustly handles free-form editing instructions from the user. SPICE outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on a challenging realistic image-editing dataset consisting of semantic editing (object addition, removal, replacement, and background change), stylistic editing (texture changes), and structural editing (action change) tasks. Not only does SPICE achieve the highest quantitative performance according to standard evaluation metrics, but it is also consistently preferred by users over existing image-editing methods. We release the workflow implementation for popular diffusion model Web UIs to support further research and artistic exploration.
近期基于提示的图像编辑模型在结构编辑任务中展现出了令人印象深刻的遵循提示能力。然而,现有模型仍然无法执行局部编辑、遵循详细的编辑提示或在单步编辑之外保持全局图像质量。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了SPICE,这是一种无需训练的工作流程,可接受任意分辨率和长宽比,能准确地遵循用户需求,并在超过100步编辑过程中持续提高图像质量。SPICE通过结合基础扩散模型和Canny边缘ControlNet模型的优点,稳健地处理用户的自由形式编辑指令。在包含语义编辑(对象添加、删除、替换和背景更改)、风格编辑(纹理更改)和结构编辑(动作更改)任务的挑战性现实图像编辑数据集上,SPICE超越了最新基线。根据标准评估指标,SPICE不仅达到了最高的量化性能,而且相较于现有图像编辑方法,用户也始终更偏爱使用SPICE。我们为流行的扩散模型Web界面发布了工作流程实现,以支持进一步的研究和艺术探索。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 21 figures. Figure 9(b) has been accepted by CVPR AI Art Gallery 2025
Summary
现有基于prompt的图像编辑模型在处理结构编辑任务时具有良好的表现,但在进行局部编辑、遵循详细编辑提示和维持图像全局质量方面存在不足。为解决这些问题,我们提出了SPICE训练无流程模型,该模型支持任意分辨率和比例,能够准确遵循用户需求,并在超过100步的编辑过程中持续提高图像质量。通过结合基础扩散模型和Canny边缘ControlNet模型的优点,SPICE能够稳健地处理用户的自由形式编辑指令。SPICE在包含语义编辑、风格编辑和结构编辑任务的挑战性真实图像编辑数据集上优于最新基线技术。它不仅在标准评估指标上取得了最高的定量性能,而且相较于现有图像编辑方法更受用户青睐。我们为流行的扩散模型Web UI发布了工作流程实现,以支持进一步的研究和艺术探索。
Key Takeaways
- SPICE是一个训练无流程的模型,用于解决现有图像编辑模型在局部编辑、遵循详细编辑提示和维持全局图像质量方面的不足。
- SPICE支持任意分辨率和比例,能够准确遵循用户的自由形式编辑指令。
- SPICE结合了基础扩散模型和Canny边缘ControlNet模型的优点,以处理复杂的图像编辑任务。
- SPICE在包含语义编辑、风格编辑和结构编辑任务的图像编辑数据集上表现优异。
- SPICE不仅在标准评估指标上取得最高定量性能,还获得了用户的青睐。
- SPICE模型对于进一步的科研和艺术探索具有很高的支持性。
点此查看论文截图


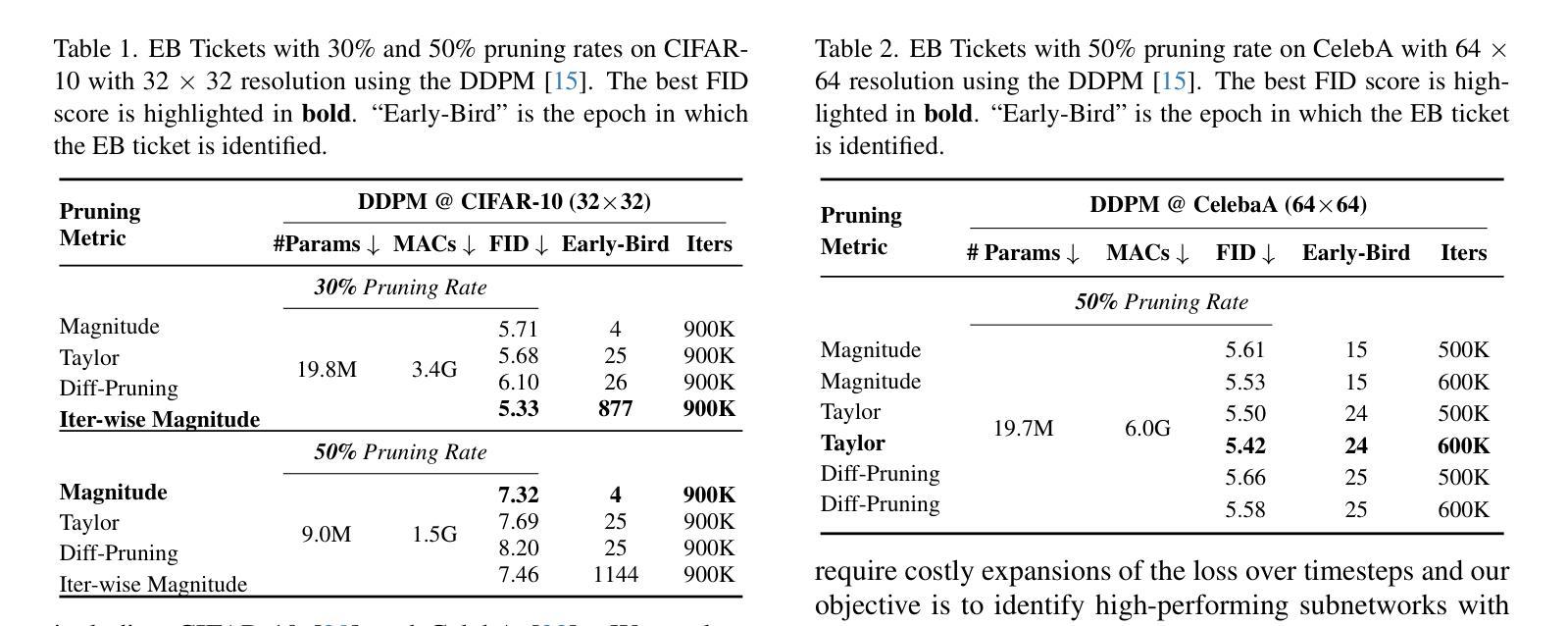
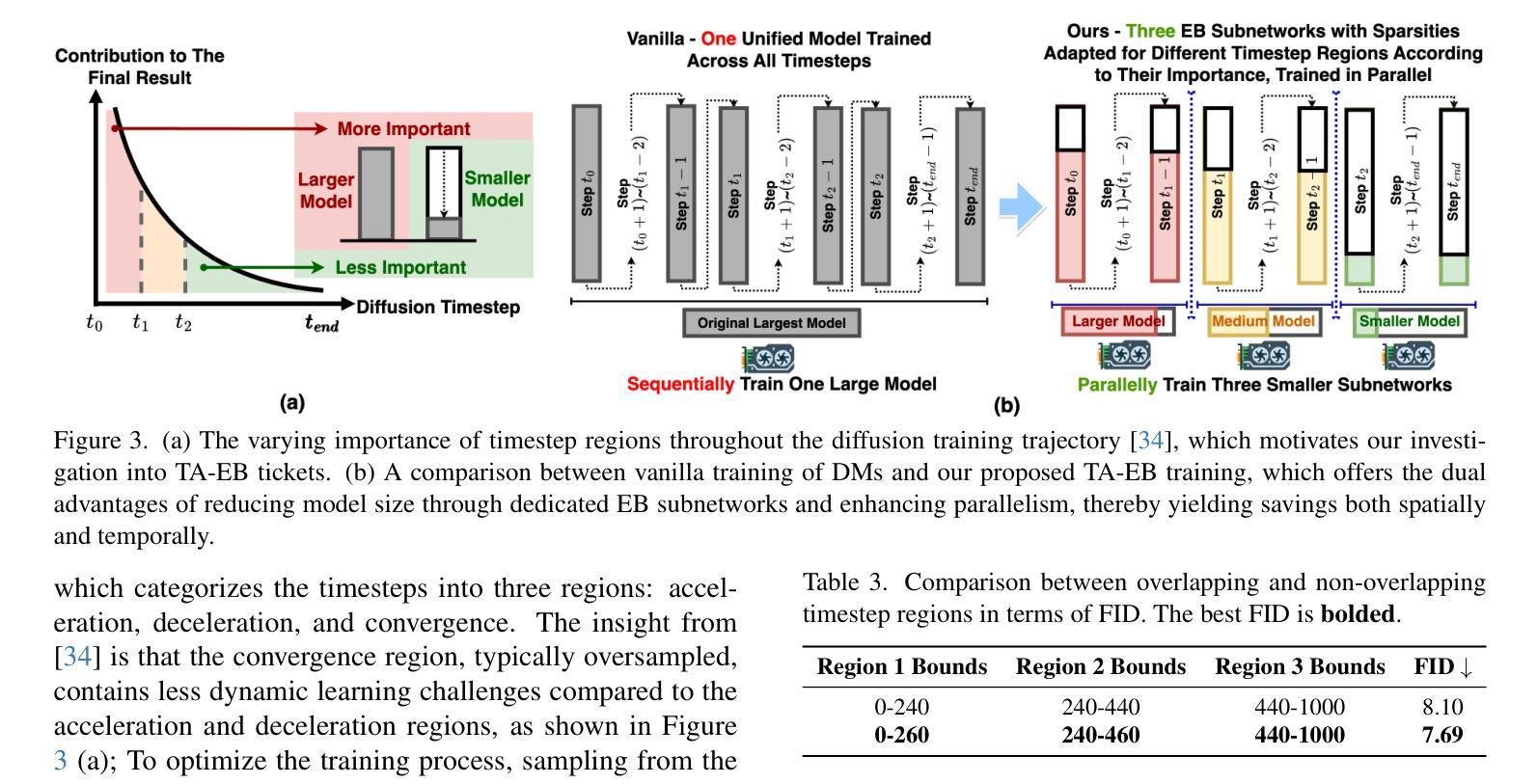
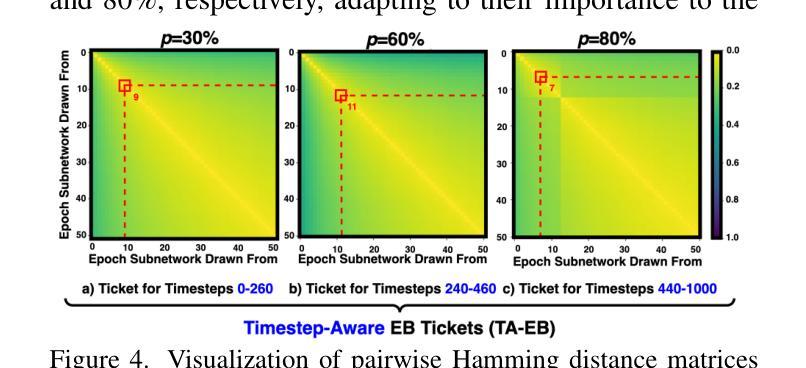
Early-Bird Diffusion: Investigating and Leveraging Timestep-Aware Early-Bird Tickets in Diffusion Models for Efficient Training
Authors:Lexington Whalen, Zhenbang Du, Haoran You, Chaojian Li, Sixu Li, Yingyan, Lin
Training diffusion models (DMs) requires substantial computational resources due to multiple forward and backward passes across numerous timesteps, motivating research into efficient training techniques. In this paper, we propose EB-Diff-Train, a new efficient DM training approach that is orthogonal to other methods of accelerating DM training, by investigating and leveraging Early-Bird (EB) tickets – sparse subnetworks that manifest early in the training process and maintain high generation quality. We first investigate the existence of traditional EB tickets in DMs, enabling competitive generation quality without fully training a dense model. Then, we delve into the concept of diffusion-dedicated EB tickets, drawing on insights from varying importance of different timestep regions. These tickets adapt their sparsity levels according to the importance of corresponding timestep regions, allowing for aggressive sparsity during non-critical regions while conserving computational resources for crucial timestep regions. Building on this, we develop an efficient DM training technique that derives timestep-aware EB tickets, trains them in parallel, and combines them during inference for image generation. Extensive experiments validate the existence of both traditional and timestep-aware EB tickets, as well as the effectiveness of our proposed EB-Diff-Train method. This approach can significantly reduce training time both spatially and temporally – achieving 2.9$\times$ to 5.8$\times$ speedups over training unpruned dense models, and up to 10.3$\times$ faster training compared to standard train-prune-finetune pipelines – without compromising generative quality. Our code is available at https://github.com/GATECH-EIC/Early-Bird-Diffusion.
训练扩散模型(DMs)需要大量的计算资源,因为需要在多个时间步上进行多次正向和反向传递,这促使人们研究高效的训练技术。在本文中,我们提出了EB-Diff-Train,这是一种新的高效DM训练方法,它与其他加速DM训练的方法正交,通过研究和利用早期鸟(EB)门票——稀疏子网络,这些子网络在训练过程中早期出现并保持良好的生成质量。首先,我们研究了DM中传统EB门票的存在,能够在不全面训练密集模型的情况下实现有竞争力的生成质量。然后,我们深入研究了扩散专用EB门票的概念,从不同时间步区域的重要性中汲取见解。这些门票根据相应时间步区域的重要性调整其稀疏度,在非关键区域实现大胆的稀疏性,同时保留计算资源用于关键时间步区域。在此基础上,我们开发了一种高效的DM训练技术,该技术派生出时间感知EB门票,并行训练它们,并在图像生成时进行组合推理。大量实验验证了传统和时间感知EB门票的存在以及我们提出的EB-Diff-Train方法的有效性。这种方法可以在空间和时间上显著减少训练时间——相对于未修剪的密集模型实现2.9至5.8倍的速度提升,与标准的训练-修剪-微调管道相比,训练速度最快可提高10.3倍——且不影响生成质量。我们的代码可在https://github.com/GATECH-EIC/Early-Bird-Diffusion找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures. Accepted to the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2025
摘要
本文提出一种高效的扩散模型(DM)训练新方法EB-Diff-Train。该方法通过探究和利用早期鸟(EB)票,即训练过程中早期出现的稀疏子网络并保持高生成质量,来提高DM的训练效率。研究内容包括:探究DM中传统EB票的存在,使在不完全训练密集模型的情况下也能实现竞争的生成质量;深入研究扩散专用的EB票,根据不同时间步区域的重要性调整其稀疏水平,实现非关键区域的激进稀疏,同时保留关键时间步区域的计算资源。在此基础上,开发了一种高效的DM训练技术,该技术产生时间步感知的EB票,并行训练,并在图像生成时进行推理组合。实验验证了传统和时间步感知的EB票的存在以及EB-Diff-Train方法的有效性。该方法可在时间和空间上显著减少训练时间,与未修剪的密集模型相比,最高可达5.8倍的速度提升,与标准的训练-修剪-微调管道相比,最高可达10.3倍的训练速度提升,同时不损害生成质量。
关键见解
- 扩散模型(DMs)的训练需要大量计算资源,由于其在多个时间步长上的前向和反向传递。
- EB-Diff-Train是一种新的高效DM训练方法,通过利用早期鸟(EB)票来提高训练效率。
- 研究确认了传统EB票在DM中的存在,即使在不完全训练的情况下也能实现高质量的生成。
- 引入了扩散专用的EB票概念,根据时间步区域的重要性调整稀疏性。
- 方法实现了在关键和非关键时间步区域的资源优化分配,允许在非关键区域进行更大的稀疏性。
- EB-Diff-Train方法显著提高了DM的训练效率,与未修剪的密集模型相比,最高可提高5.8倍的速度。
- 该方法在不损害生成质量的情况下实现了快速训练,代码已公开发布。
点此查看论文截图



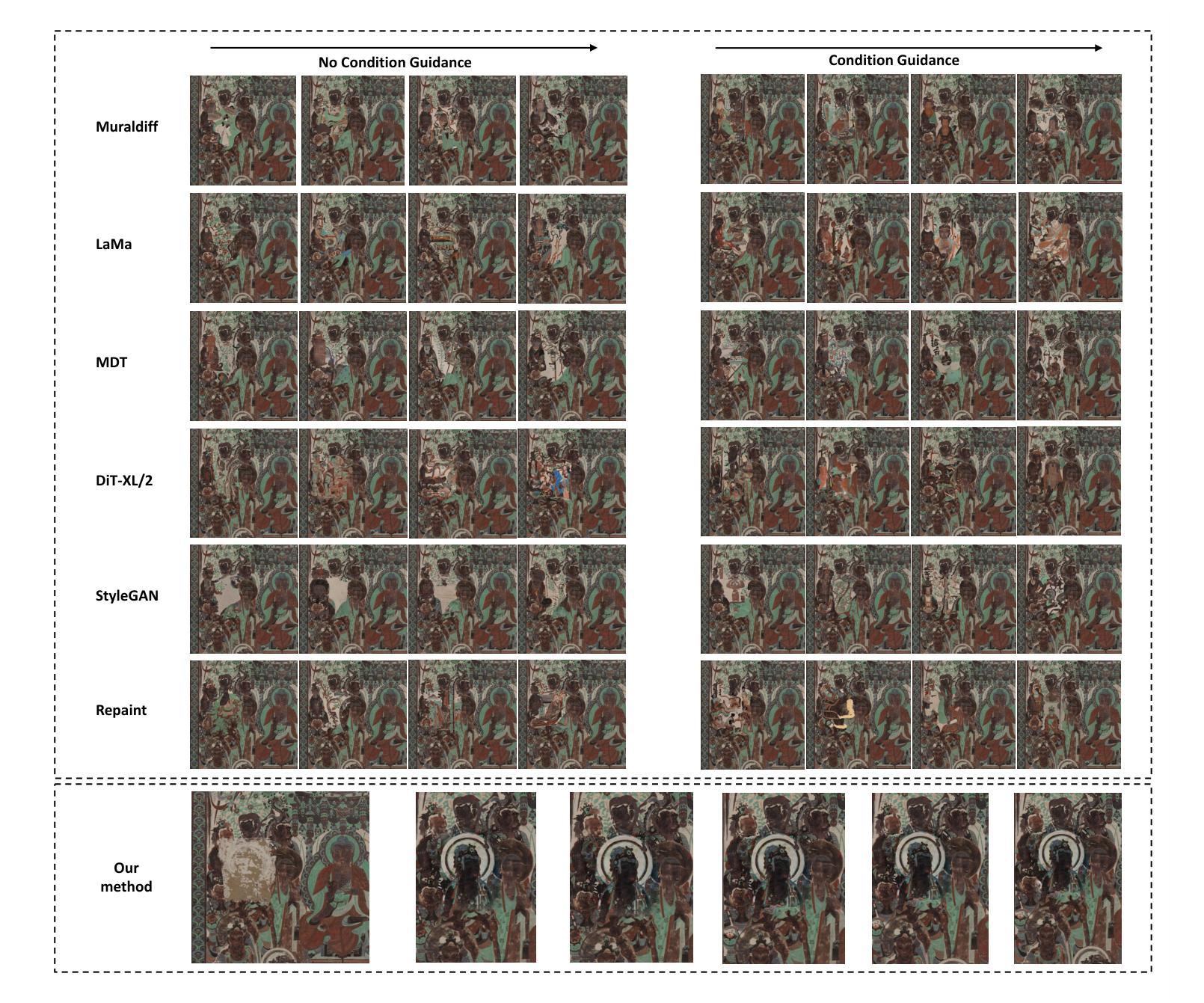
DiffuMural: Restoring Dunhuang Murals with Multi-scale Diffusion
Authors:Puyu Han, Jiaju Kang, Yuhang Pan, Erting Pan, Zeyu Zhang, Qunchao Jin, Juntao Jiang, Zhichen Liu, Luqi Gong
Large-scale pre-trained diffusion models have produced excellent results in the field of conditional image generation. However, restoration of ancient murals, as an important downstream task in this field, poses significant challenges to diffusion model-based restoration methods due to its large defective area and scarce training samples. Conditional restoration tasks are more concerned with whether the restored part meets the aesthetic standards of mural restoration in terms of overall style and seam detail, and such metrics for evaluating heuristic image complements are lacking in current research. We therefore propose DiffuMural, a combined Multi-scale convergence and Collaborative Diffusion mechanism with ControlNet and cyclic consistency loss to optimise the matching between the generated images and the conditional control. DiffuMural demonstrates outstanding capabilities in mural restoration, leveraging training data from 23 large-scale Dunhuang murals that exhibit consistent visual aesthetics. The model excels in restoring intricate details, achieving a coherent overall appearance, and addressing the unique challenges posed by incomplete murals lacking factual grounding. Our evaluation framework incorporates four key metrics to quantitatively assess incomplete murals: factual accuracy, textural detail, contextual semantics, and holistic visual coherence. Furthermore, we integrate humanistic value assessments to ensure the restored murals retain their cultural and artistic significance. Extensive experiments validate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) approaches in both qualitative and quantitative metrics.
大规模预训练扩散模型在条件图像生成领域取得了优异的结果。然而,古壁画修复作为该领域的一个重要下游任务,由于缺陷面积大、训练样本稀少,对基于扩散模型的修复方法构成了重大挑战。条件修复任务更关心修复部分是否符合壁画修复的审美标准,涉及整体风格和细节接缝等方面,而当前研究中缺乏评估启发式图像补充的指标。因此,我们提出了DiffuMural,它是一种结合多尺度收敛和协作扩散机制的方法,通过ControlNet和循环一致性损失来优化生成图像与条件控制之间的匹配。DiffuMural在壁画修复方面表现出卓越的能力,利用来自23幅大型敦煌壁画的一致视觉美学训练数据。该模型在恢复细节、实现整体外观连贯性,以及解决因缺乏事实依据而不完整的壁画所带来的独特挑战方面表现出色。我们的评估框架包含了四个关键指标来定量评估不完整的壁画:事实准确性、纹理细节、上下文语义和整体视觉连贯性。此外,我们融入了人文价值评估,以确保修复的壁画保留其文化和艺术意义。大量实验证明,我们的方法在定性和定量指标上均优于当前先进技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型预训练扩散模型的优秀表现,本研究提出针对古壁画修复的任务,构建了一种多尺度收敛与协同扩散机制的扩散模型DiffuMural。结合ControlNet和循环一致性损失优化生成图像与条件控制的匹配。在壁画修复领域展现卓越能力,利用来自敦煌的大型壁画训练数据,实现细节恢复、整体外观连贯性和对缺乏事实依据的不完整壁画的独特挑战。评价框架包括四项关键指标和人类价值评估,以确保修复的壁画保留其文化和艺术意义。本研究的方法在定性和定量指标上均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 大型预训练扩散模型在条件图像生成领域表现出色。
- 古壁画修复是扩散模型面临的重要下游任务,存在大面积缺陷和稀缺训练样本的挑战。
- DiffuMural模型结合了多尺度收敛和协同扩散机制,优化生成图像与条件控制的匹配。
- DiffuMural在壁画修复领域展现卓越能力,利用来自敦煌的大型壁画训练数据。
- 评估框架包括四项关键指标:事实准确性、纹理细节、上下文语义和整体视觉连贯性。
- 引入人文价值评估确保修复的壁画保留文化和艺术意义。
点此查看论文截图





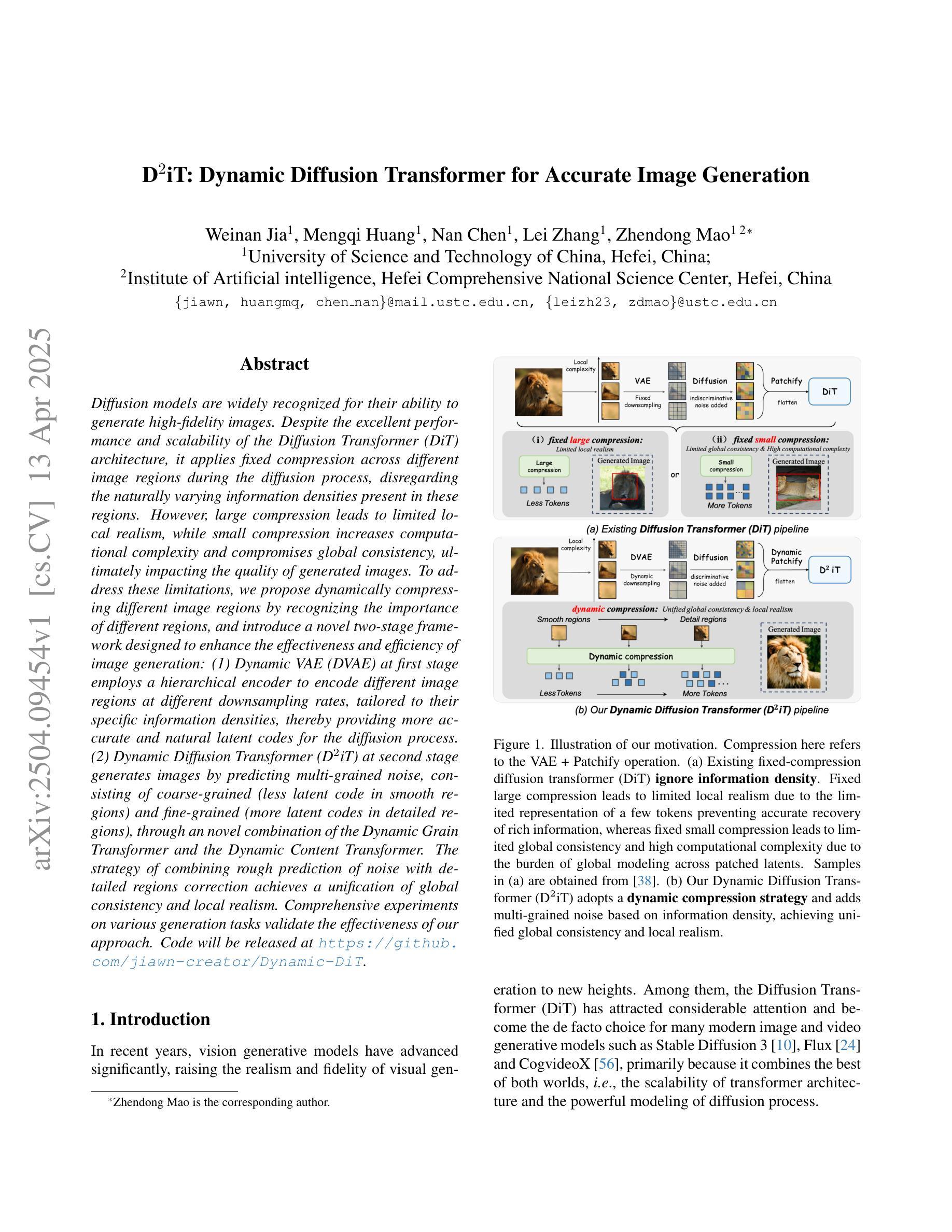
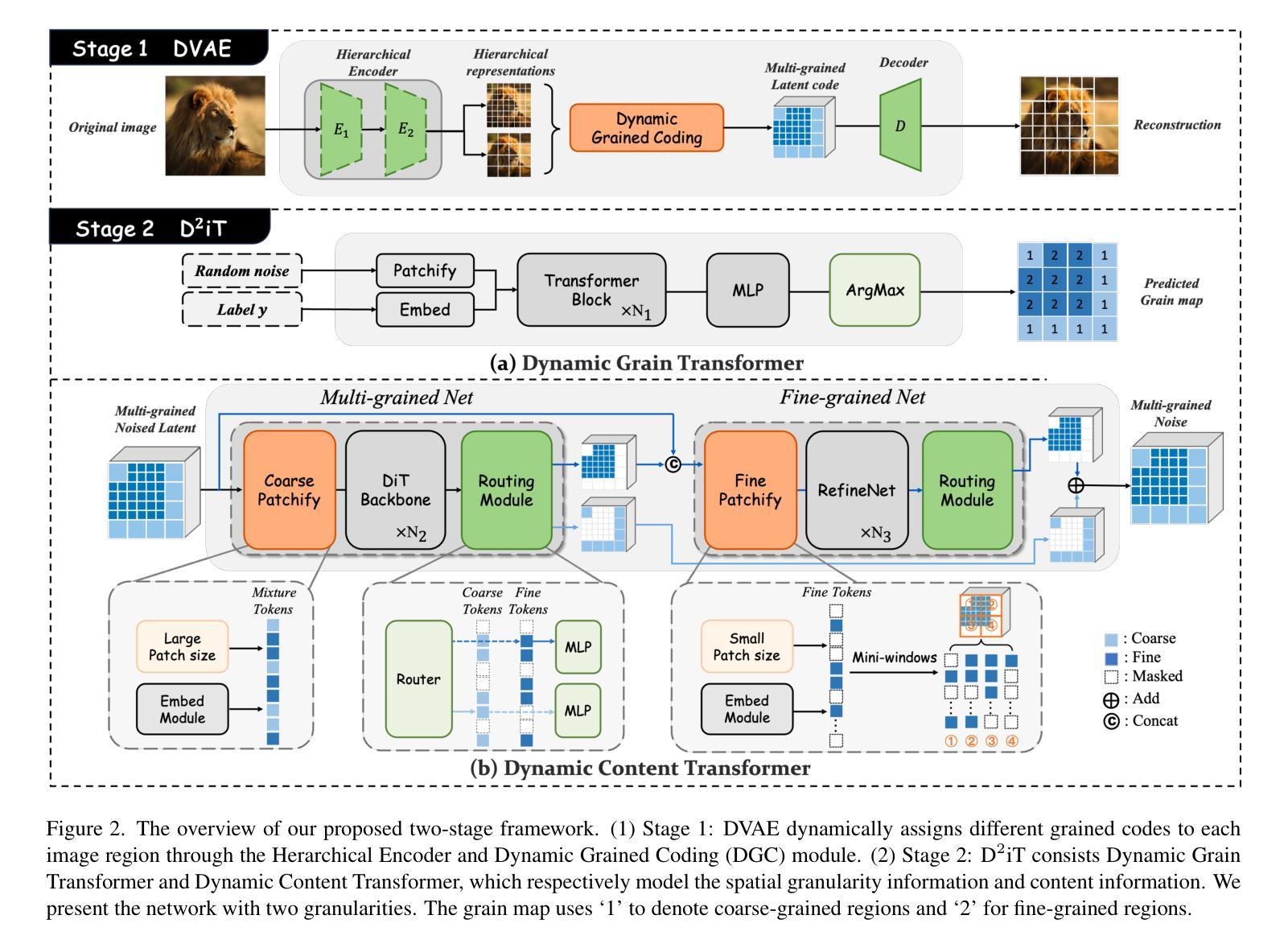
D$^2$iT: Dynamic Diffusion Transformer for Accurate Image Generation
Authors:Weinan Jia, Mengqi Huang, Nan Chen, Lei Zhang, Zhendong Mao
Diffusion models are widely recognized for their ability to generate high-fidelity images. Despite the excellent performance and scalability of the Diffusion Transformer (DiT) architecture, it applies fixed compression across different image regions during the diffusion process, disregarding the naturally varying information densities present in these regions. However, large compression leads to limited local realism, while small compression increases computational complexity and compromises global consistency, ultimately impacting the quality of generated images. To address these limitations, we propose dynamically compressing different image regions by recognizing the importance of different regions, and introduce a novel two-stage framework designed to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of image generation: (1) Dynamic VAE (DVAE) at first stage employs a hierarchical encoder to encode different image regions at different downsampling rates, tailored to their specific information densities, thereby providing more accurate and natural latent codes for the diffusion process. (2) Dynamic Diffusion Transformer (D$^2$iT) at second stage generates images by predicting multi-grained noise, consisting of coarse-grained (less latent code in smooth regions) and fine-grained (more latent codes in detailed regions), through an novel combination of the Dynamic Grain Transformer and the Dynamic Content Transformer. The strategy of combining rough prediction of noise with detailed regions correction achieves a unification of global consistency and local realism. Comprehensive experiments on various generation tasks validate the effectiveness of our approach. Code will be released at https://github.com/jiawn-creator/Dynamic-DiT.
扩散模型因其生成高保真图像的能力而受到广泛认可。尽管扩散变压器(DiT)架构具有出色的性能和可扩展性,但在扩散过程中,它在不同的图像区域应用固定压缩,而忽略了这些区域中存在的天然信息密度差异。然而,大压缩会导致局部真实感有限,而小压缩会增加计算复杂性并损害全局一致性,最终影响生成的图像质量。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了动态压缩不同图像区域的策略,通过识别不同区域的重要性,并引入了一种新的两阶段框架,旨在提高图像生成的有效性和效率:(1)第一阶段采用动态变分自编码器(DVAE),使用分层编码器以不同的下采样率编码不同的图像区域,以适应其特定的信息密度,从而为扩散过程提供更准确、更自然的潜在代码。(2)第二阶段采用动态扩散变压器(D^2iT),通过预测多粒度噪声生成图像,包括粗粒度(平滑区域中较少的潜在代码)和细粒度(详细区域中更多的潜在代码),这通过动态粒度和动态内容的变压器的组合来实现。结合噪声的粗略预测和详细区域的校正策略实现了全局一致性和局部真实感的统一。在各种生成任务上的综合实验验证了我们的方法的有效性。代码将在https://github.com/jiawn-creator/Dynamic-DiT上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了针对Diffusion Transformer(DiT)模型的改进方案,解决了其在图像生成过程中对不同区域进行固定压缩的问题。通过动态识别图像区域的重要性,实现区域动态压缩,并引入两阶段框架,包括动态VAE(DVAE)和动态扩散变压器(D^2iT)。DVAE通过分层编码器按不同下采样率编码图像区域,D^2iT则通过预测多粒度噪声实现全局一致性和局部现实性的统一。实验验证该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion models can generate high-fidelity images but face challenges in balancing local realism and global consistency.
- DiT模型在扩散过程中对不同图像区域应用固定压缩,忽略了自然信息密度的差异。
- 大压缩会导致局部现实感有限,小压缩则增加计算复杂性并影响全局一致性。
- 本文提出了动态压缩不同图像区域的方法,以识别各区域的重要性。
- 引入两阶段框架,包括DVAE和D^2iT,增强图像生成的有效性和效率。
- DVAE使用分层编码器,按图像区域的信息密度进行下采样编码。
点此查看论文截图

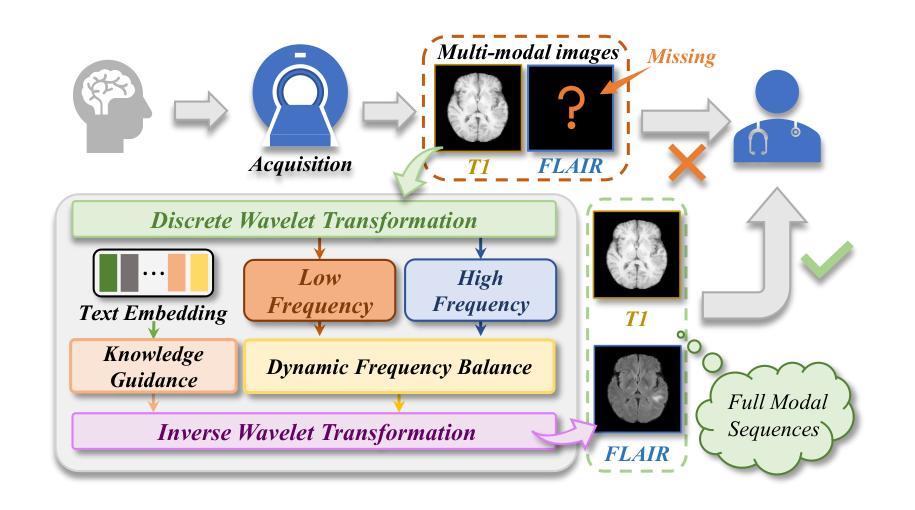
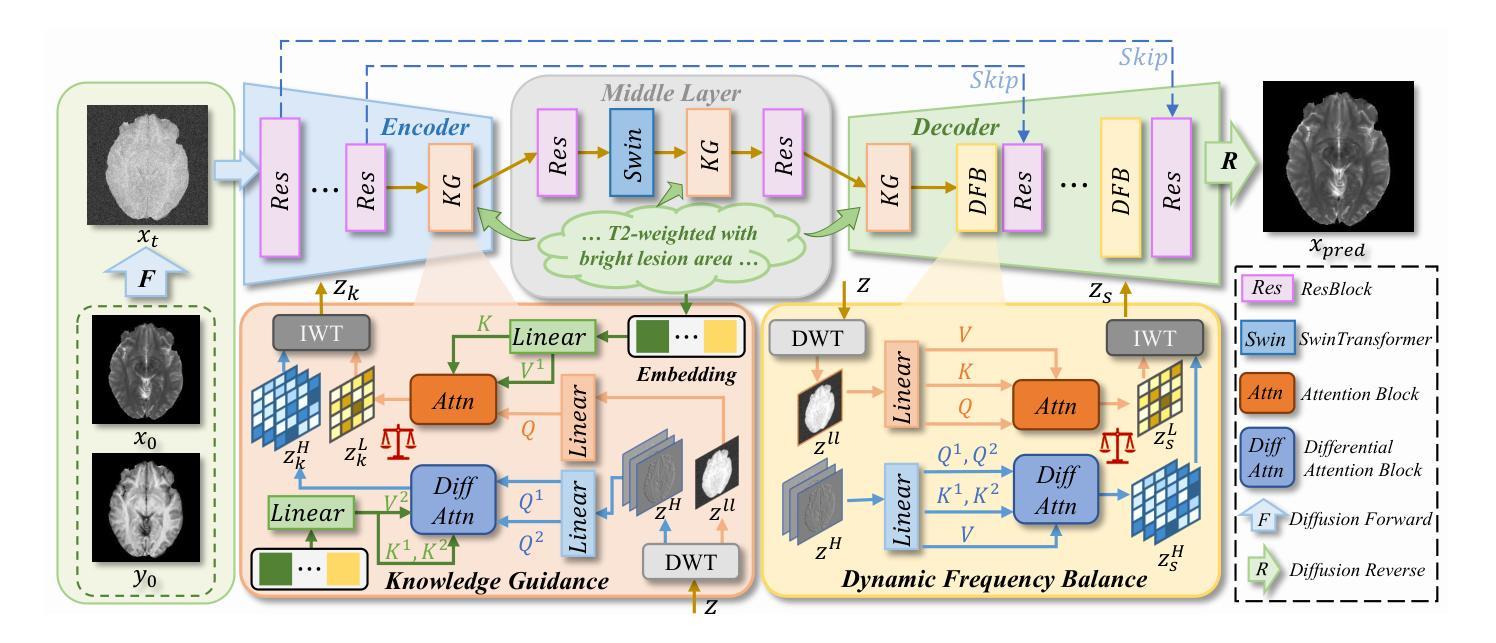
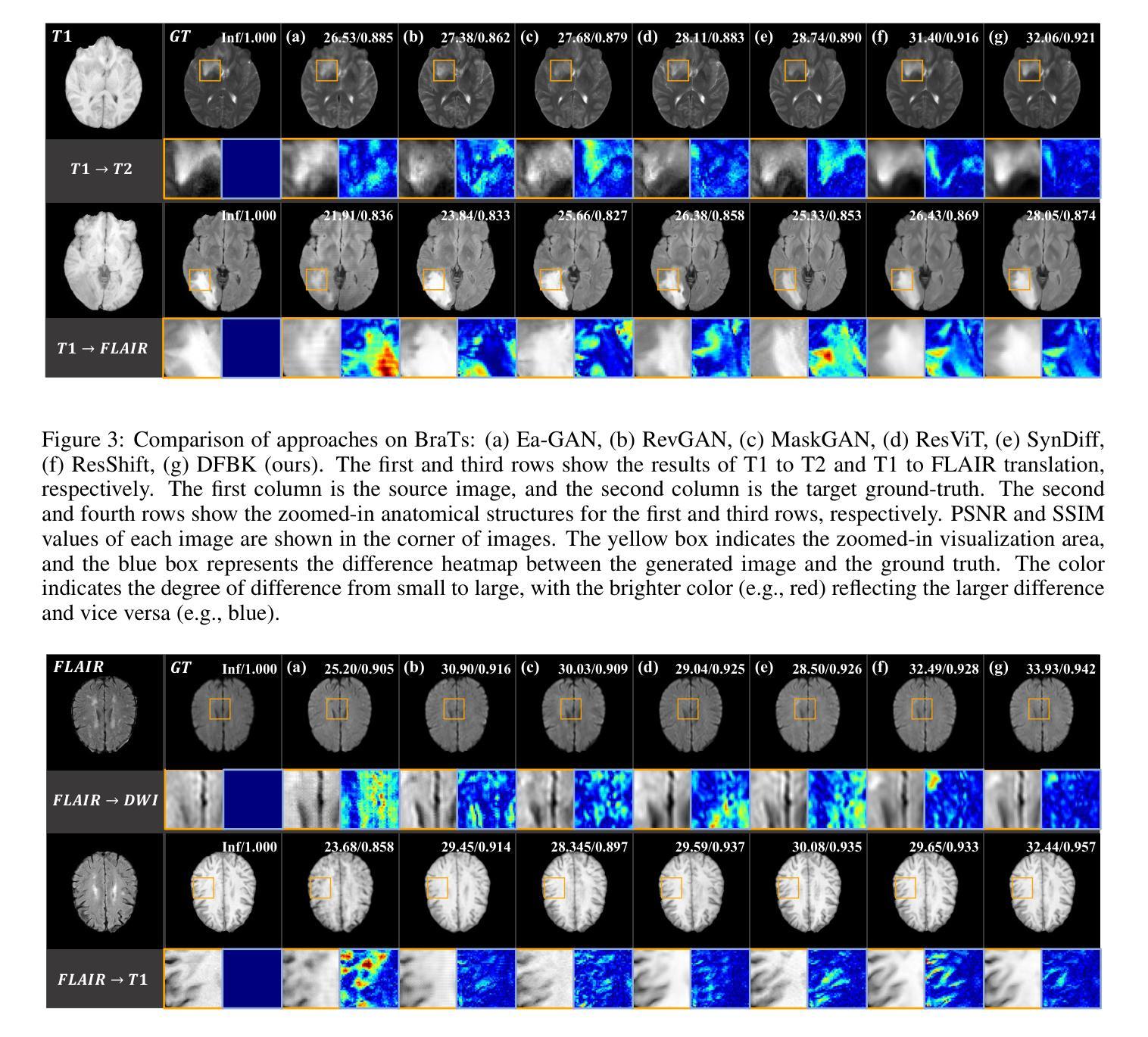
Structure-Accurate Medical Image Translation based on Dynamic Frequency Balance and Knowledge Guidance
Authors:Jiahua Xu, Dawei Zhou, Lei Hu, Zaiyi Liu, Nannan Wang, Xinbo Gao
Multimodal medical images play a crucial role in the precise and comprehensive clinical diagnosis. Diffusion model is a powerful strategy to synthesize the required medical images. However, existing approaches still suffer from the problem of anatomical structure distortion due to the overfitting of high-frequency information and the weakening of low-frequency information. Thus, we propose a novel method based on dynamic frequency balance and knowledge guidance. Specifically, we first extract the low-frequency and high-frequency components by decomposing the critical features of the model using wavelet transform. Then, a dynamic frequency balance module is designed to adaptively adjust frequency for enhancing global low-frequency features and effective high-frequency details as well as suppressing high-frequency noise. To further overcome the challenges posed by the large differences between different medical modalities, we construct a knowledge-guided mechanism that fuses the prior clinical knowledge from a visual language model with visual features, to facilitate the generation of accurate anatomical structures. Experimental evaluations on multiple datasets show the proposed method achieves significant improvements in qualitative and quantitative assessments, verifying its effectiveness and superiority.
多模态医学图像在精确和全面的临床诊断和治疗中发挥着至关重要的作用。扩散模型是合成所需医学图像的一种强大策略。然而,现有方法仍存在因高频信息过度拟合而导致解剖结构扭曲的问题,以及低频信息减弱的问题。因此,我们提出了一种基于动态频率平衡和知识指导的新型方法。具体来说,我们首先通过小波变换分解模型的关键特征,提取低频和高频成分。然后,设计了一个动态频率平衡模块,以自适应地调整频率,增强全局低频特征和有效的高频细节,同时抑制高频噪声。为了克服不同医学模态之间差异巨大所带来的挑战,我们构建了一个知识引导机制,该机制融合了视觉语言模型的先验临床知识与视觉特征,以促进准确解剖结构的生成。在多个数据集上的实验评估表明,该方法在定性和定量评估方面取得了显著的改进,验证了其有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Medical image translation, Diffusion model, 16 pages
Summary
基于动态频率平衡和知识指导的医学图像合成方法,解决了现有扩散模型在医学图像合成中因高频信息过拟合和低频信息减弱导致的解剖结构失真问题。通过小波变换提取图像的低频和高频成分,设计动态频率平衡模块自适应调整频率,增强全局低频特征和有效高频细节,同时抑制高频噪声。此外,构建知识引导机制,融合视觉语言模型的先验临床知识,促进生成准确的解剖结构。实验评估显示,该方法在多个数据集上实现了显著的改进,验证了其有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态医学图像在临床诊断中具有重要作用,扩散模型是合成医学图像的有效策略。
- 现有方法存在解剖结构失真问题,主要由于高频信息过拟合和低频信息减弱。
- 引入动态频率平衡模块,自适应调整频率,增强低频和有效高频细节,抑制高频噪声。
- 提出知识引导机制,融合先验临床知识,促进准确解剖结构的生成。
- 方法在多个数据集上进行实验评估,实现显著改进。
- 方法的优点在于解决了现有问题,提高了医学图像合成的准确性和质量。
点此查看论文截图


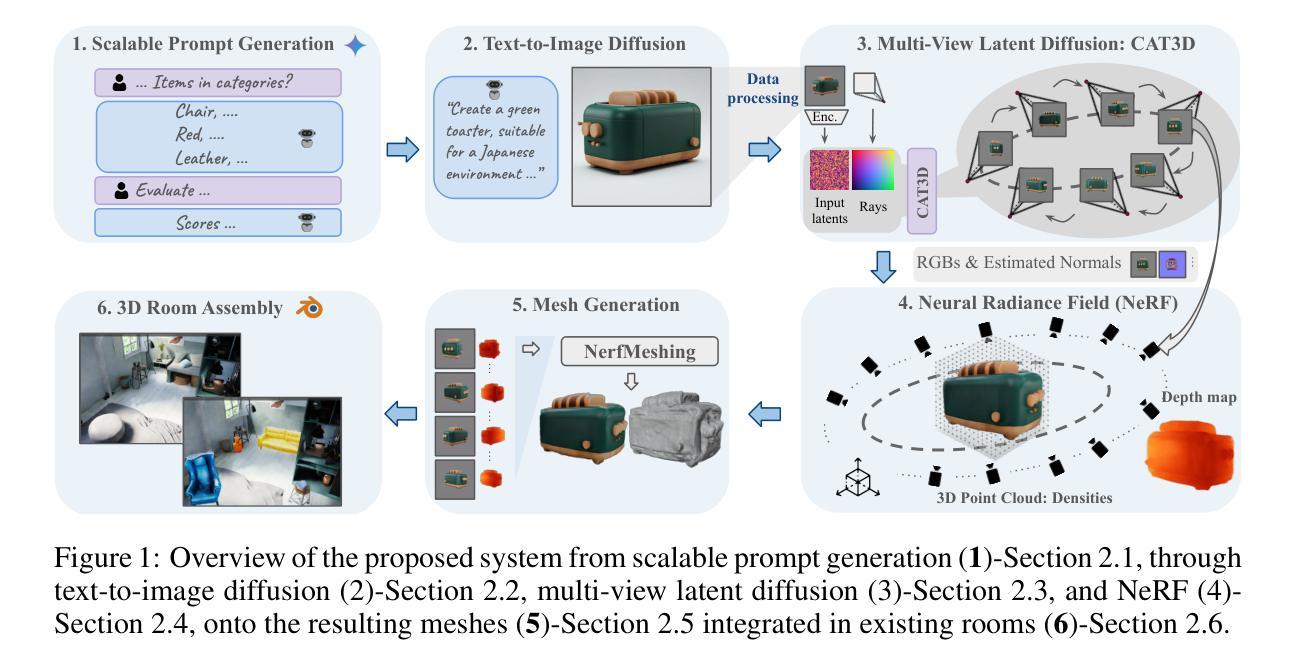
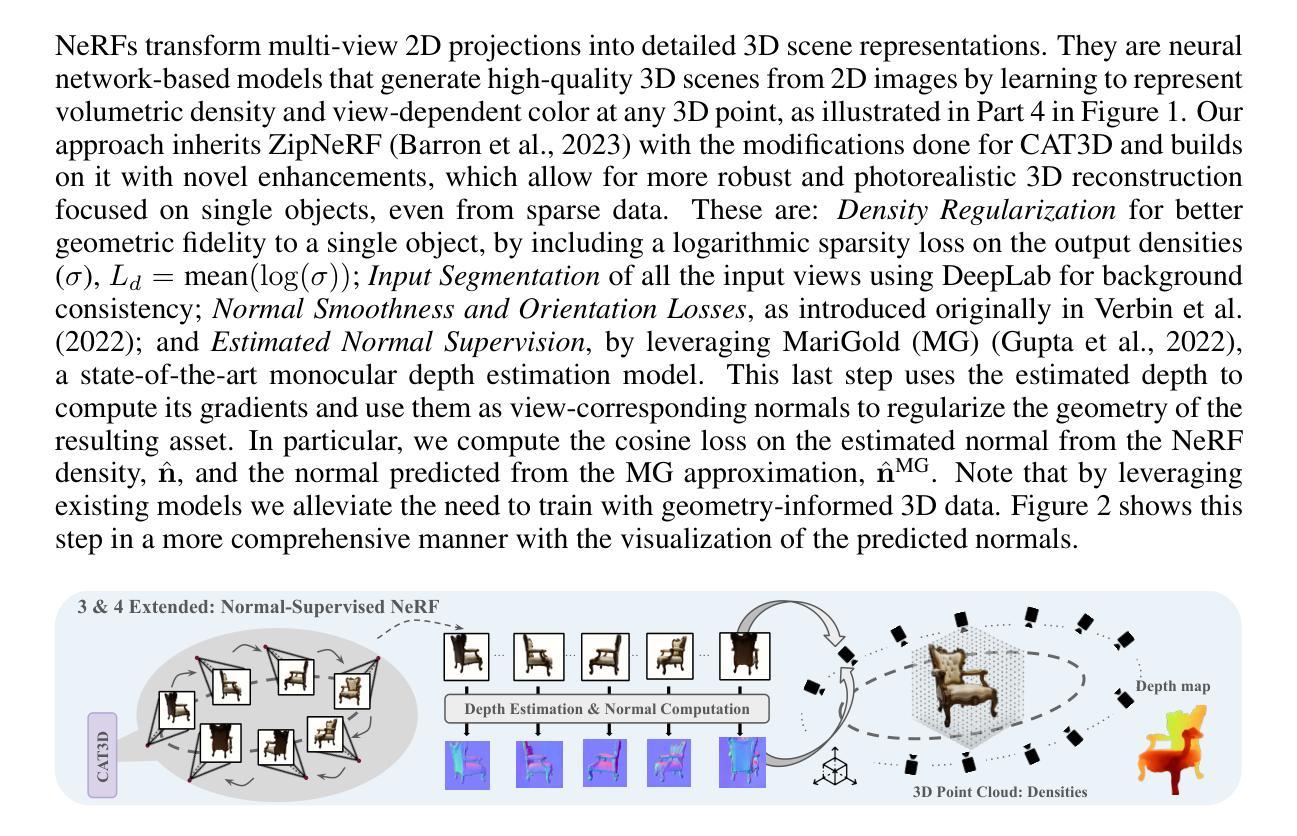
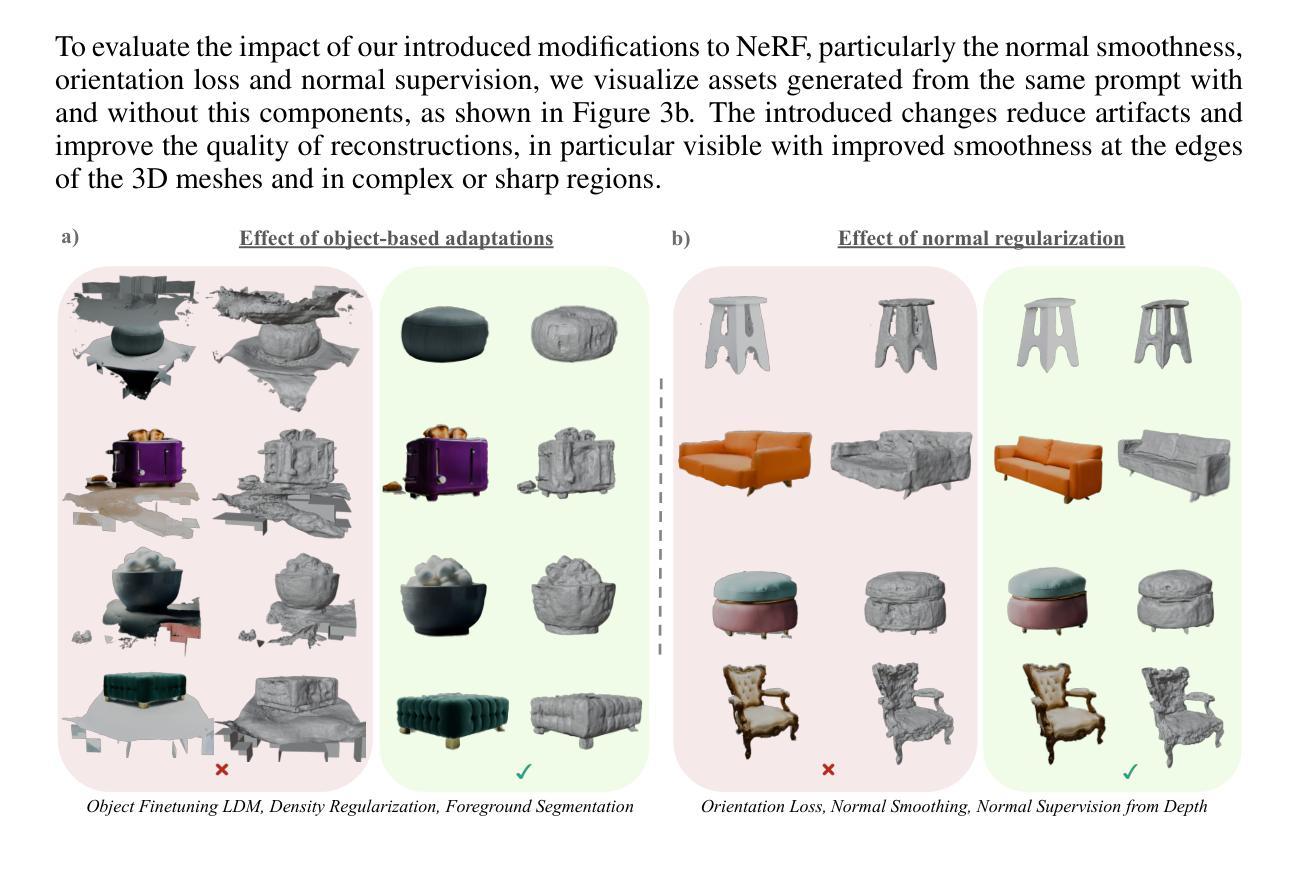
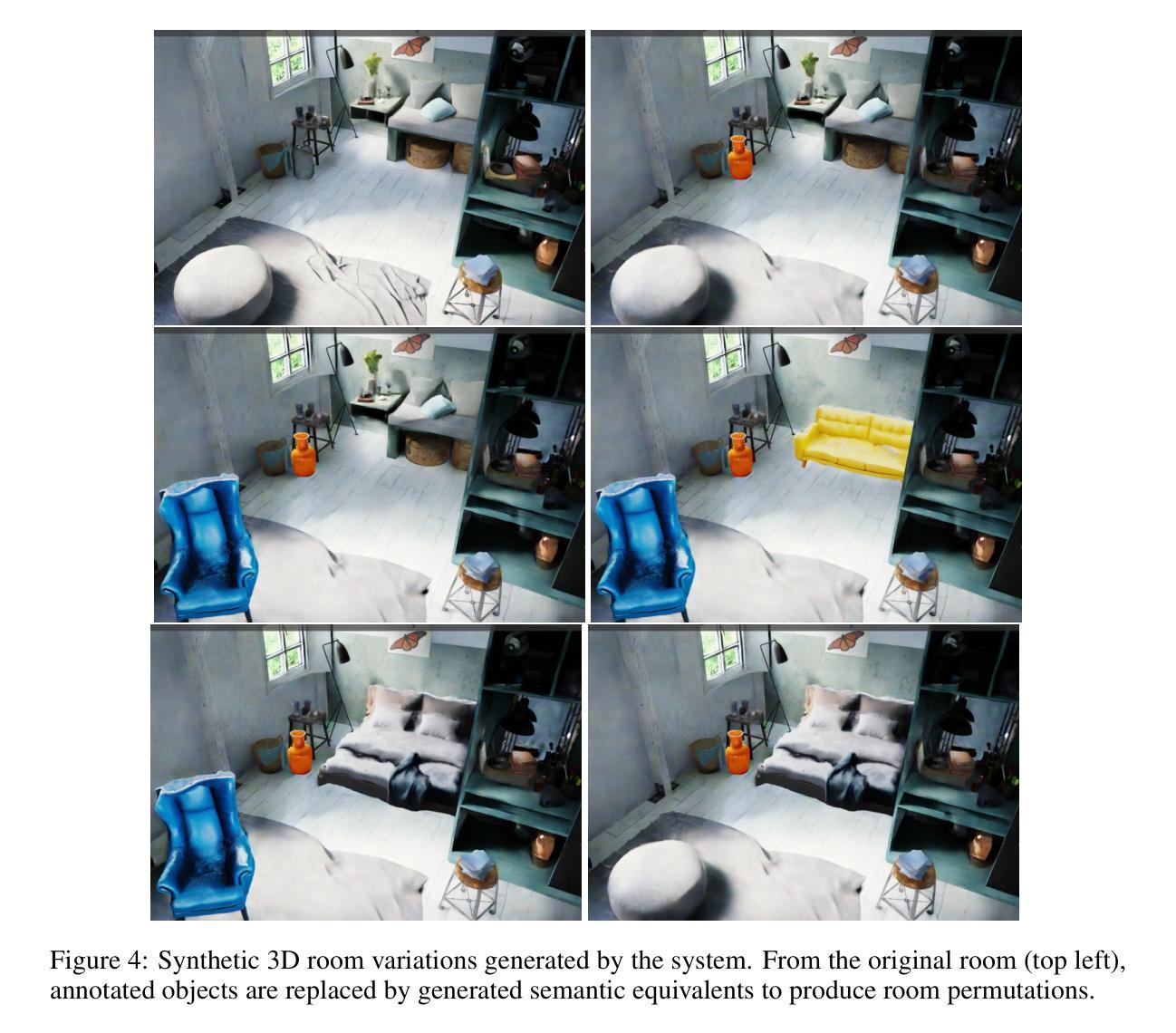
Text To 3D Object Generation For Scalable Room Assembly
Authors:Sonia Laguna, Alberto Garcia-Garcia, Marie-Julie Rakotosaona, Stylianos Moschoglou, Leonhard Helminger, Sergio Orts-Escolano
Modern machine learning models for scene understanding, such as depth estimation and object tracking, rely on large, high-quality datasets that mimic real-world deployment scenarios. To address data scarcity, we propose an end-to-end system for synthetic data generation for scalable, high-quality, and customizable 3D indoor scenes. By integrating and adapting text-to-image and multi-view diffusion models with Neural Radiance Field-based meshing, this system generates highfidelity 3D object assets from text prompts and incorporates them into pre-defined floor plans using a rendering tool. By introducing novel loss functions and training strategies into existing methods, the system supports on-demand scene generation, aiming to alleviate the scarcity of current available data, generally manually crafted by artists. This system advances the role of synthetic data in addressing machine learning training limitations, enabling more robust and generalizable models for real-world applications.
现代用于场景理解的机器学习模型,如深度估计和对象跟踪,依赖于模仿真实世界部署场景的大规模、高质量数据集。为了解决数据稀缺的问题,我们提出了一种用于生成可扩展、高质量和可定制的3D室内场景的合成数据端到端系统。该系统通过整合和适应文本到图像和多视角扩散模型,以及基于神经辐射场的网格化技术,从文本提示生成高保真3D对象资产,并使用渲染工具将其融入到预先定义的平面布局中。通过引入新颖的损失函数和培训策略到现有方法中,该系统支持按需场景生成,旨在缓解当前可用数据的稀缺性,这些现有数据通常需要艺术家手动制作。此系统推动了合成数据在解决机器学习训练限制方面的作用,为真实世界应用启用了更稳健和可推广的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at the ICLR 2025 Workshop on Synthetic Data
Summary
本文提出一种端到端的合成数据生成系统,用于生成可扩展、高质量、可定制的3D室内场景。该系统结合了文本到图像和多视角扩散模型与基于神经辐射场的网格化技术,通过文本提示生成高保真度的3D对象资产,并将其融入预定义的平面布局中。引入新颖的损失函数和培训策略,该系统支持按需生成场景,旨在解决当前可用数据的稀缺问题,通常这些数据是由艺术家手工制作的。此系统推动了合成数据在解决机器学习训练限制方面的作用,为真实世界应用提供了更稳健和可推广的模型。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种端到端的合成数据生成系统,用于生成3D室内场景。
- 系统结合了文本到图像和多视角扩散模型技术。
- 利用神经辐射场基于网格化的技术生成高保真度的3D对象资产。
- 系统支持将生成的3D对象资产融入预定义的平面布局中。
- 通过引入新颖的损失函数和培训策略,支持按需生成场景。
- 该系统旨在解决当前机器学习训练数据的稀缺问题。
点此查看论文截图

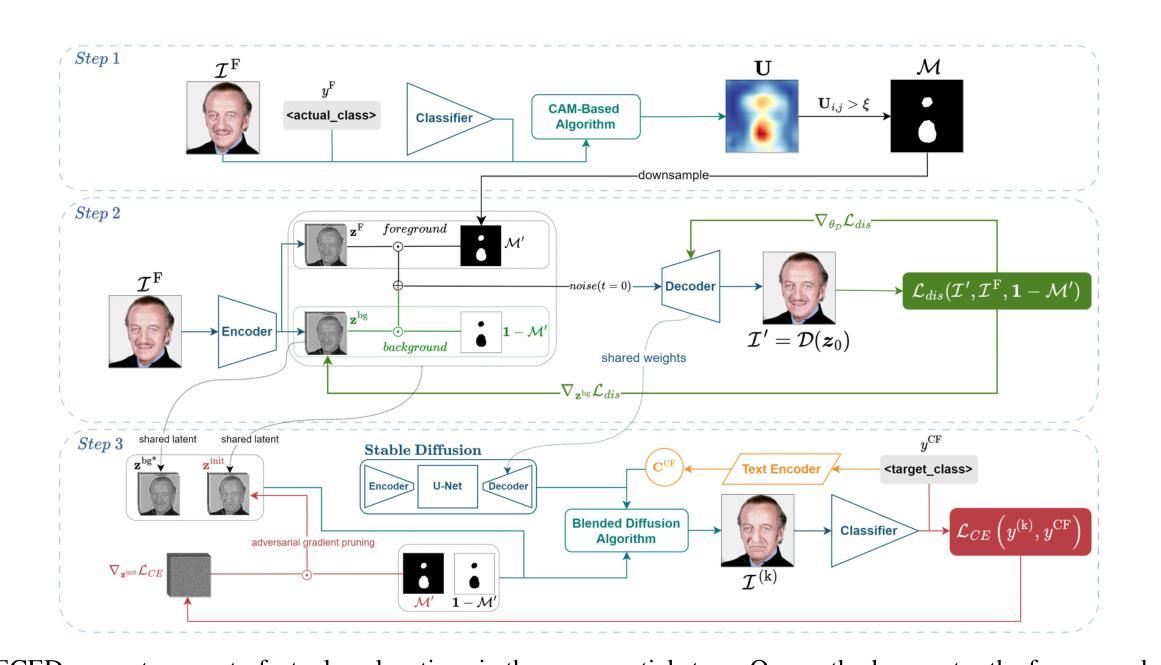
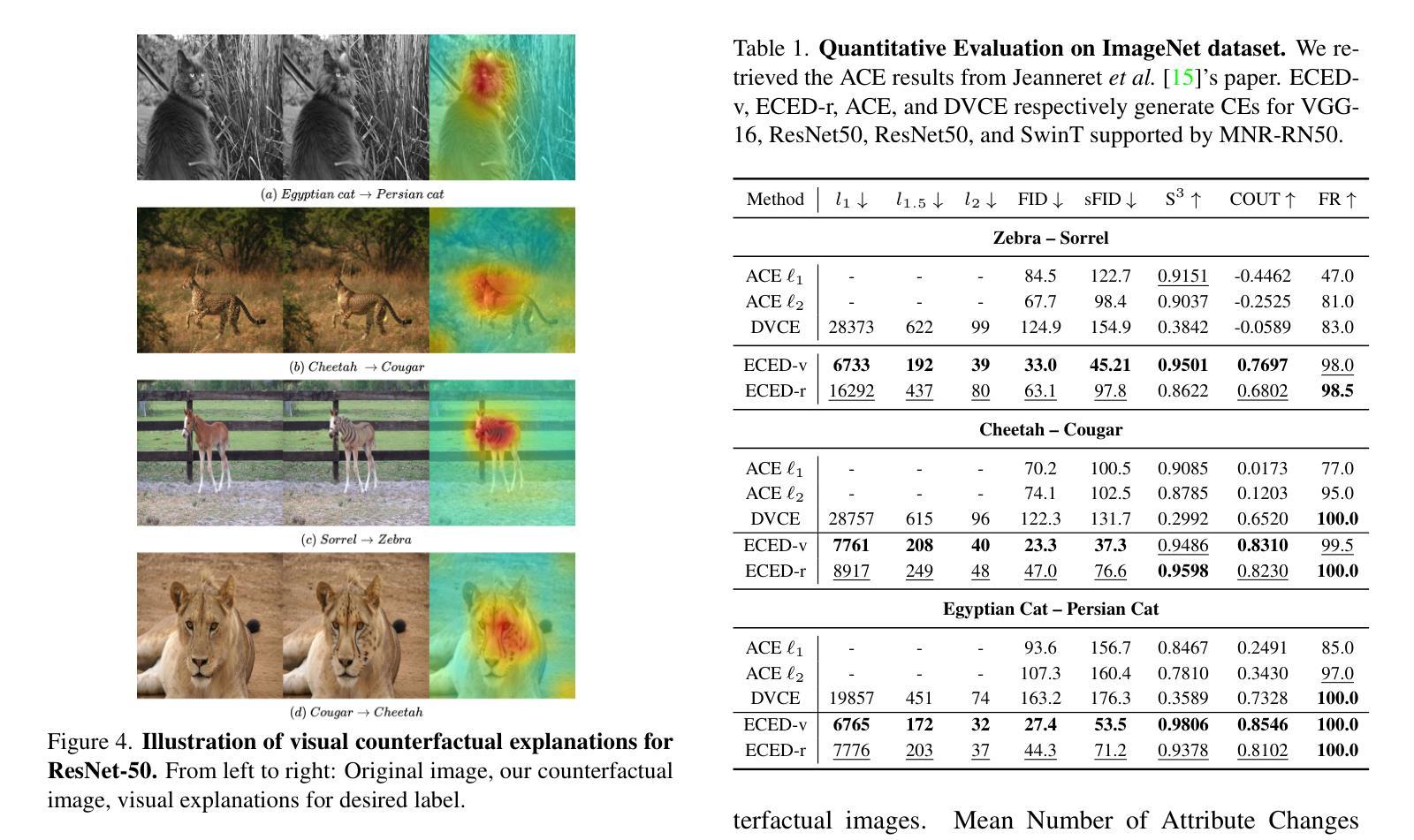
From Visual Explanations to Counterfactual Explanations with Latent Diffusion
Authors:Tung Luu, Nam Le, Duc Le, Bac Le
Visual counterfactual explanations are ideal hypothetical images that change the decision-making of the classifier with high confidence toward the desired class while remaining visually plausible and close to the initial image. In this paper, we propose a new approach to tackle two key challenges in recent prominent works: i) determining which specific counterfactual features are crucial for distinguishing the “concept” of the target class from the original class, and ii) supplying valuable explanations for the non-robust classifier without relying on the support of an adversarially robust model. Our method identifies the essential region for modification through algorithms that provide visual explanations, and then our framework generates realistic counterfactual explanations by combining adversarial attacks based on pruning the adversarial gradient of the target classifier and the latent diffusion model. The proposed method outperforms previous state-of-the-art results on various evaluation criteria on ImageNet and CelebA-HQ datasets. In general, our method can be applied to arbitrary classifiers, highlight the strong association between visual and counterfactual explanations, make semantically meaningful changes from the target classifier, and provide observers with subtle counterfactual images.
视觉反事实解释是一种理想的假设图像,它能够以高信心改变分类器的决策,使决策转向目标类别,同时保持视觉上的合理性和接近原始图像。在本文中,我们提出了一种新方法来解决最近热门工作中的两个关键挑战:一)确定哪些特定的反事实特征对于区分目标类别的“概念”与原始类别至关重要;二)在不依赖对抗性稳健模型的支持下,为不稳健的分类器提供有价值的解释。我们的方法通过提供视觉解释的算法来确定需要修改的关键区域,然后我们的框架通过结合对抗性攻击和基于目标分类器的对抗性梯度的修剪以及潜在扩散模型,生成现实的反事实解释。该方法在ImageNet和CelebA-HQ数据集上的各种评价标准上均优于以前的最先进结果。总的来说,我们的方法可以应用于任意分类器,突出了视觉和反事实解释之间的强烈关联,使目标分类器能够进行语义上有意义的变化,并为观察者提供微妙的反事实图像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2025 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV)
Summary
本文提出了视觉反事实解释的新方法,旨在解决两个关键问题:确定目标类“概念”与原始类之间的关键反事实特征,以及为非稳健分类器提供有价值的解释而不依赖于对抗稳健模型的支持。该方法通过提供视觉解释的算法确定修改的关键区域,然后通过结合对抗性攻击和潜在扩散模型生成逼真的反事实解释。在ImageNet和CelebA-HQ数据集上,该方法优于现有技术,可应用于任意分类器,强调视觉与反事实解释之间的强烈关联,为观察者提供微妙的反事实图像。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉反事实解释是通过生成理想假设图像来改变分类器的决策,使决策更有信心地朝向目标类别,同时保持视觉上的合理性和接近原始图像。
- 该方法解决了两个关键挑战:确定目标类别与原始类别之间的关键反事实特征,以及为非稳健分类器提供解释而不依赖对抗稳健模型。
- 方法通过提供视觉解释的算法来确定修改的关键区域。
- 结合对抗性攻击和潜在扩散模型生成逼真的反事实解释。
- 该方法在多个评估标准上优于现有技术,适用于各种图像数据集。
- 方法可应用于任意分类器,强调视觉与反事实解释之间的强烈关联。
点此查看论文截图


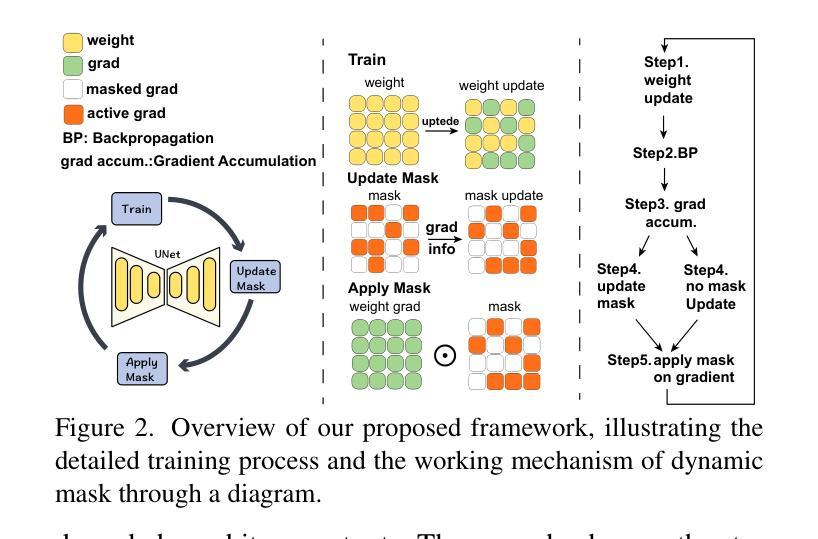
Sculpting Memory: Multi-Concept Forgetting in Diffusion Models via Dynamic Mask and Concept-Aware Optimization
Authors:Gen Li, Yang Xiao, Jie Ji, Kaiyuan Deng, Bo Hui, Linke Guo, Xiaolong Ma
Text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in generating high-quality images from textual prompts. However, their ability to store vast amounts of knowledge raises concerns in scenarios where selective forgetting is necessary, such as removing copyrighted content, reducing biases, or eliminating harmful concepts. While existing unlearning methods can remove certain concepts, they struggle with multi-concept forgetting due to instability, residual knowledge persistence, and generation quality degradation. To address these challenges, we propose \textbf{Dynamic Mask coupled with Concept-Aware Loss}, a novel unlearning framework designed for multi-concept forgetting in diffusion models. Our \textbf{Dynamic Mask} mechanism adaptively updates gradient masks based on current optimization states, allowing selective weight modifications that prevent interference with unrelated knowledge. Additionally, our \textbf{Concept-Aware Loss} explicitly guides the unlearning process by enforcing semantic consistency through superclass alignment, while a regularization loss based on knowledge distillation ensures that previously unlearned concepts remain forgotten during sequential unlearning. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate our approach. Results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing unlearning techniques in forgetting effectiveness, output fidelity, and semantic coherence, particularly in multi-concept scenarios. Our work provides a principled and flexible framework for stable and high-fidelity unlearning in generative models. The code will be released publicly.
文本到图像(T2I)的扩散模型已经从文本提示生成高质量图像方面取得了显著的成就。然而,它们存储大量知识的能力在一些需要选择性遗忘的场景中引发了关注,例如去除版权内容、减少偏见或消除有害概念。现有的遗忘方法虽然能移除某些概念,但由于不稳定、残留知识持续存在以及生成质量下降,它们在多概念遗忘方面遇到了困难。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了名为“动态掩码与概念感知损失”的新型遗忘框架,旨在处理扩散模型中的多概念遗忘问题。我们的“动态掩码”机制能基于当前优化状态自适应地更新梯度掩码,允许选择性地修改权重以避免干扰无关知识。此外,我们的“概念感知损失”通过超类对齐明确指导遗忘过程,同时通过基于知识蒸馏的正则化损失确保先前未学习的概念在连续遗忘过程中保持遗忘。我们进行了大量实验来评估我们的方法。结果表明,我们的方法在遗忘有效性、输出保真度和语义连贯性方面优于现有遗忘技术,特别是在多概念场景中。我们的工作为生成模型中的稳定和高保真遗忘提供了一个有原则和灵活性的框架。代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)的扩散模型在根据文本提示生成高质量图像方面取得了显著的成功。然而,其存储大量知识的能力在某些需要选择性遗忘的场景中引发了担忧,如去除版权内容、减少偏见或消除有害概念。为了应对挑战,我们提出了一个名为“动态掩膜与概念感知损失”的新型遗忘框架,用于处理扩散模型中的多概念遗忘问题。我们的动态掩膜机制能够根据当前的优化状态自适应地更新梯度掩膜,实现选择性权重修改,避免干扰无关知识。同时,我们的概念感知损失通过超类对齐方式明确指导遗忘过程,保证语义一致性。通过大量实验评估,我们的方法展现出优异的遗忘效果、输出保真度和语义连贯性,尤其在多概念场景中表现尤为突出。我们的研究为生成模型中的稳定和高保真遗忘提供了一个有原则和灵活性的框架。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像的扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面取得了显著成功。
- 在需要选择性遗忘的场景中(如去除版权内容、减少偏见等),这些模型的挑战在于如何实现多概念遗忘。
- 现有遗忘方法在处理多概念遗忘时面临稳定性、残留知识持久性和生成质量下降的问题。
- 提出的“动态掩膜与概念感知损失”框架旨在解决这些挑战。
- 动态掩膜机制能够自适应更新梯度掩膜,实现选择性权重修改,避免干扰无关知识。
- 概念感知损失通过超类对齐明确指导遗忘过程,确保语义一致性。
点此查看论文截图


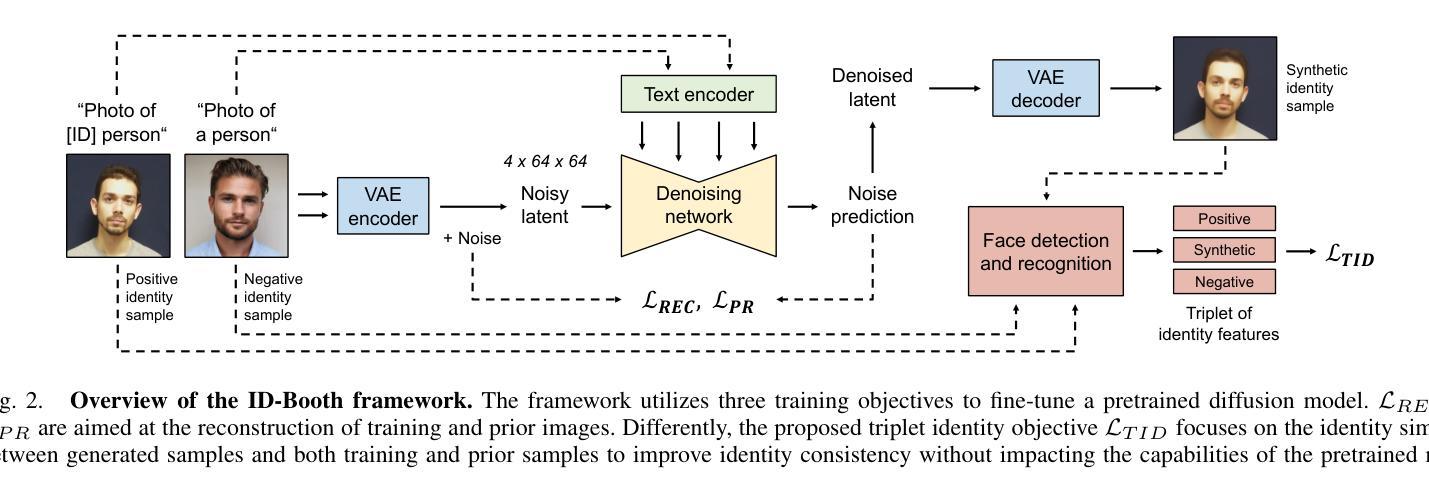
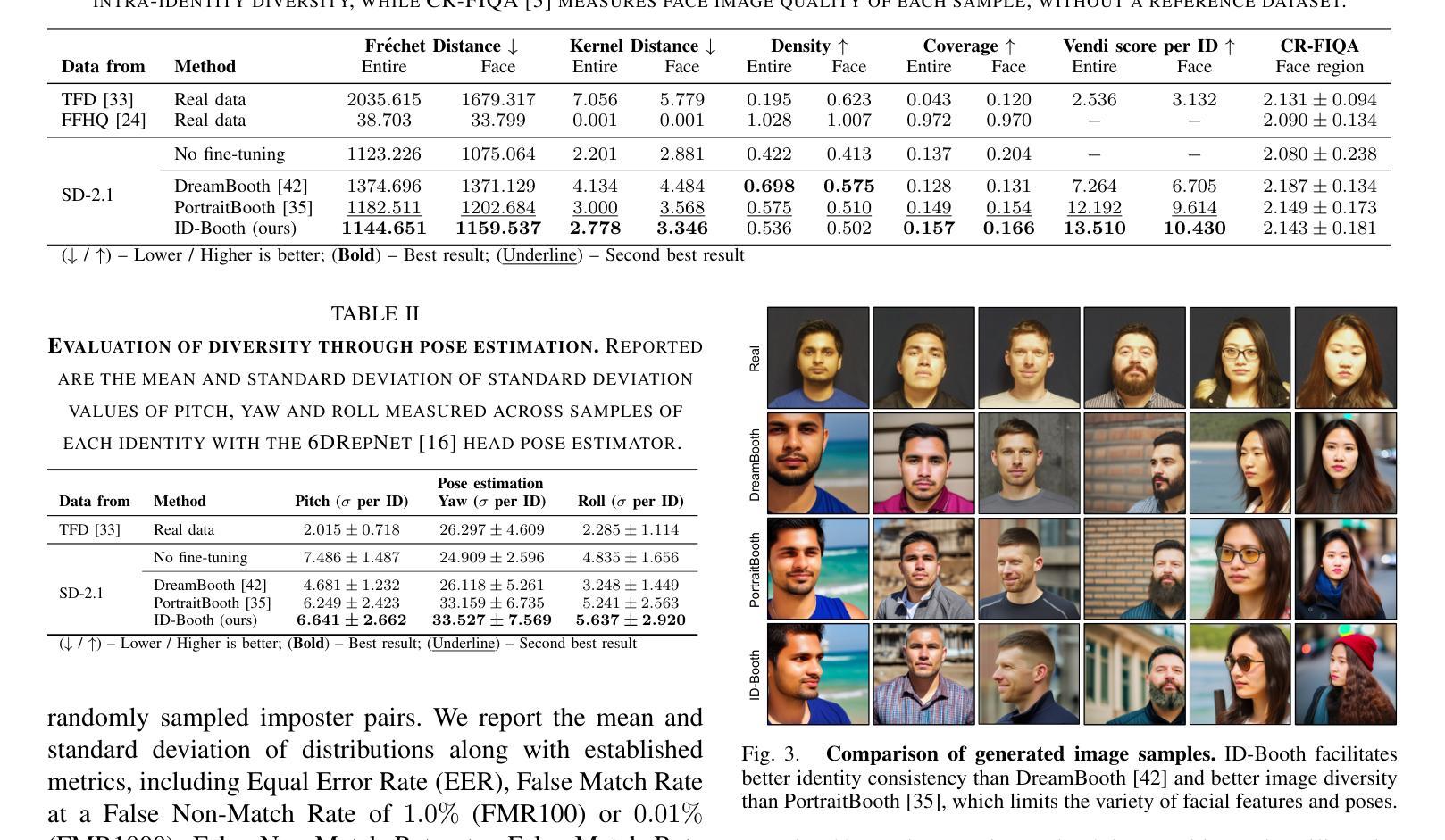
ID-Booth: Identity-consistent Face Generation with Diffusion Models
Authors:Darian Tomašević, Fadi Boutros, Chenhao Lin, Naser Damer, Vitomir Štruc, Peter Peer
Recent advances in generative modeling have enabled the generation of high-quality synthetic data that is applicable in a variety of domains, including face recognition. Here, state-of-the-art generative models typically rely on conditioning and fine-tuning of powerful pretrained diffusion models to facilitate the synthesis of realistic images of a desired identity. Yet, these models often do not consider the identity of subjects during training, leading to poor consistency between generated and intended identities. In contrast, methods that employ identity-based training objectives tend to overfit on various aspects of the identity, and in turn, lower the diversity of images that can be generated. To address these issues, we present in this paper a novel generative diffusion-based framework, called ID-Booth. ID-Booth consists of a denoising network responsible for data generation, a variational auto-encoder for mapping images to and from a lower-dimensional latent space and a text encoder that allows for prompt-based control over the generation procedure. The framework utilizes a novel triplet identity training objective and enables identity-consistent image generation while retaining the synthesis capabilities of pretrained diffusion models. Experiments with a state-of-the-art latent diffusion model and diverse prompts reveal that our method facilitates better intra-identity consistency and inter-identity separability than competing methods, while achieving higher image diversity. In turn, the produced data allows for effective augmentation of small-scale datasets and training of better-performing recognition models in a privacy-preserving manner. The source code for the ID-Booth framework is publicly available at https://github.com/dariant/ID-Booth.
近期生成建模技术的进步使得能够生成适用于多种领域的高质量合成数据,其中包括人脸识别。在这里,最先进的生成模型通常依赖于强大预训练扩散模型的条件和微调,以促进合成具有所需身份的逼真图像。然而,这些模型在训练过程中往往不考虑主体的身份,导致生成身份与预期身份之间的一致性较差。相比之下,采用基于身份的训练目标的方法往往会在身份的各个方面出现过拟合现象,进而降低了可生成图像的多样性。为了解决这些问题,我们在本文中提出了一种基于扩散的新型生成框架,称为ID-Booth。ID-Booth由一个负责数据生成的降噪网络、一个用于将图像映射到低维潜在空间及其反向映射的变分自动编码器和一个文本编码器组成,该文本编码器可实现基于提示对生成过程的控制。该框架利用了一种新型的三重身份训练目标,能够在保持预训练扩散模型的合成能力的同时,实现身份一致的图像生成。使用最先进的潜在扩散模型和多种提示进行的实验表明,我们的方法在身份内部一致性和身份间可分性方面优于其他方法,同时实现了更高的图像多样性。此外,生成的数据能够有效增强小规模数据集,以隐私保护的方式训练性能更好的识别模型。ID-Booth框架的源代码可在https://github.com/dariant/ID-Booth公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG) 2025, 14 pages
摘要
本文介绍了一种基于扩散的新型生成模型ID-Booth,该模型结合了去噪网络、变分自编码器和文本编码器,能够在生成图像时实现基于身份的提示控制。ID-Booth采用新颖的三重身份训练目标,能够在保留预训练扩散模型的合成能力的同时,实现身份一致的图像生成。实验证明,与其他方法相比,ID-Booth在身份内一致性和身份间可分性方面表现更佳,同时保持了较高的图像多样性。这为小型数据集的有效扩充和性能更佳的隐私保护识别模型的训练提供了可能。
关键见解
- 先进的生成模型通常依赖于预训练的扩散模型的调整和微调,以合成具有所需身份的逼真图像。
- 当前模型在训练期间很少考虑身份因素,导致生成身份与预期身份之间的一致性较差。
- 基于身份的训练目标方法往往过分关注身份的各个方面,从而降低了可生成图像的多样性。
- ID-Booth通过结合去噪网络、变分自编码器和文本编码器,解决了上述问题。
- ID-Booth采用新颖的三重身份训练目标,实现了身份一致的图像生成,同时保留了预训练扩散模型的合成能力。
- 实验表明,ID-Booth在保持图像多样性的同时,提高了身份内的一致性和身份间的可分性。
- ID-Booth产生的数据可用于有效地扩充小型数据集,并以隐私保护的方式训练性能更佳的识别模型。
点此查看论文截图

Solving Inverse Problems using Diffusion with Iterative Colored Renoising
Authors:Matt C. Bendel, Saurav K. Shastri, Rizwan Ahmad, Philip Schniter
Imaging inverse problems can be solved in an unsupervised manner using pre-trained diffusion models, but doing so requires approximating the gradient of the measurement-conditional score function in the diffusion reverse process. We show that the approximations produced by existing methods are relatively poor, especially early in the reverse process, and so we propose a new approach that iteratively reestimates and “renoises” the estimate several times per diffusion step. This iterative approach, which we call Fast Iterative REnoising (FIRE), injects colored noise that is shaped to ensure that the pre-trained diffusion model always sees white noise, in accordance with how it was trained. We then embed FIRE into the DDIM reverse process and show that the resulting “DDfire” offers state-of-the-art accuracy and runtime on several linear inverse problems, as well as phase retrieval. Our implementation is at https://github.com/matt-bendel/DDfire
使用预训练的扩散模型以无监督的方式解决成像反问题,需要在扩散反向过程中近似测量条件得分函数的梯度。我们显示现有方法产生的近似值相对较差,尤其是在反向过程的早期,因此,我们提出了一种新方法,该方法在每个扩散步骤中多次重新估计和“增加噪声”。我们称这种迭代方法为快速迭代重噪声化(FIRE),它注入有色噪声,以确保预训练的扩散模型始终看到白噪声,这与它的训练方式相符。然后,我们将FIRE嵌入到DDIM反向过程中,并证明由此产生的DDfire在多个线性反问题以及相位检索方面提供了最先进的准确性和运行时性能。我们的实现位于https://github.com/matt-bendel/DDfire。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
利用预训练的扩散模型以无监督的方式解决成像逆问题,需要在扩散逆过程中近似测量条件分数函数的梯度。现有方法产生的近似值较差,特别是在逆过程的早期,因此提出了一种新的方法——快速迭代重噪声法(FIRE),该方法在每个扩散步骤中多次重新估计和“加入噪声”。我们将FIRE嵌入到DDIM逆过程中,并证明“DDfire”在多个线性逆问题和相位检索方面提供了最先进的准确性和运行时效率。
Key Takeaways:
- 扩散模型可以无监督地解决成像逆问题。
- 需要近似测量条件分数函数的梯度在扩散逆过程中。
- 现有方法的近似值在扩散逆过程早期表现较差。
- 提出了一种新的方法——快速迭代重噪声法(FIRE),该方法在扩散过程的每个步骤中多次重新估计和加入噪声。
- FIRE方法通过注入有色噪声,确保预训练的扩散模型始终看到白噪声,与其训练方式一致。
- 将FIRE嵌入到DDIM逆过程中,形成了“DDfire”方法。
- “DDfire”在多个线性逆问题和相位检索方面表现出最先进的准确性和运行时效率。
点此查看论文截图



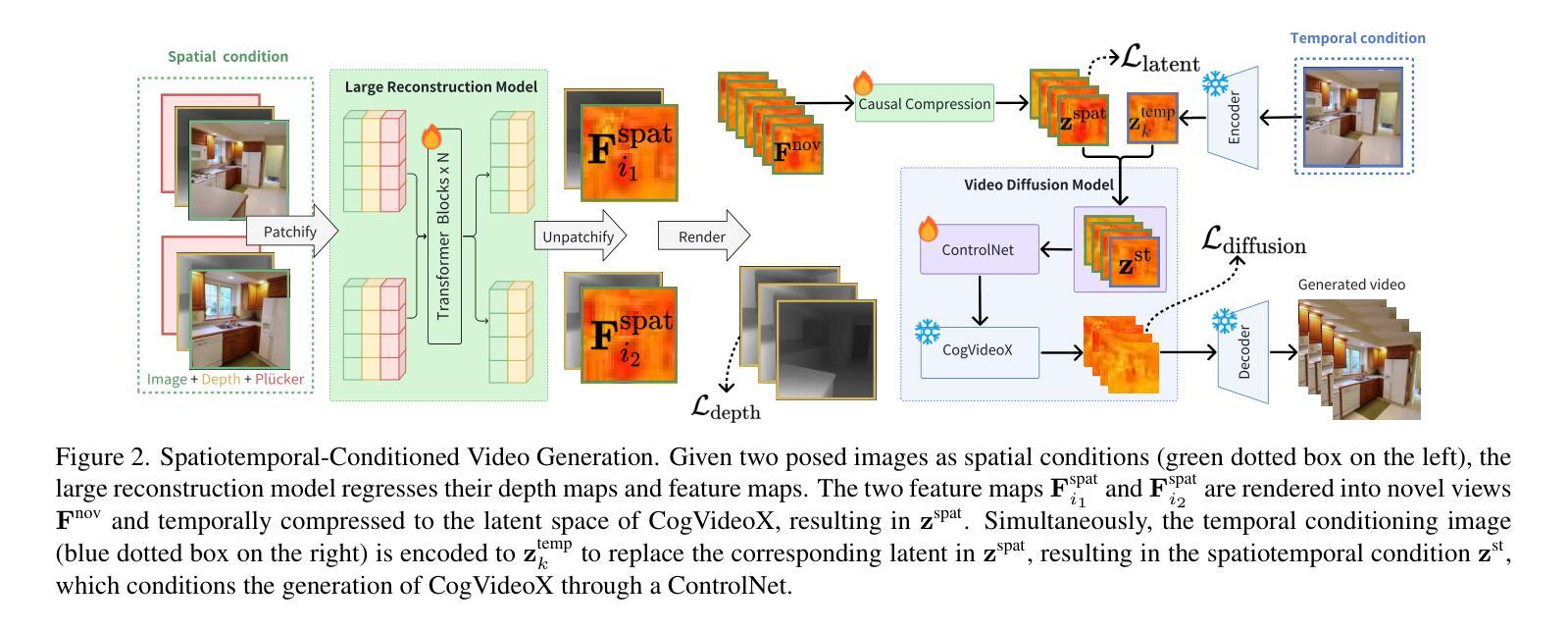
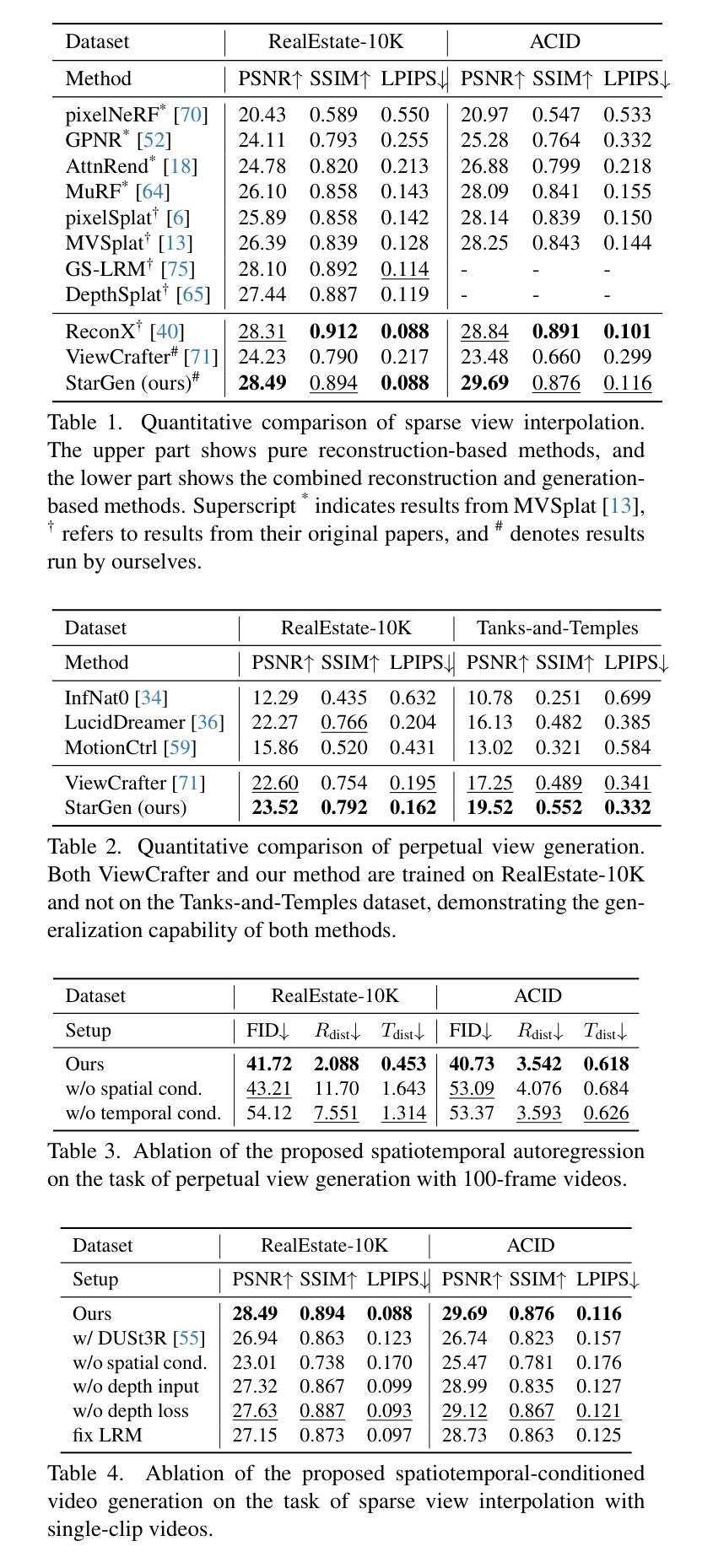
StarGen: A Spatiotemporal Autoregression Framework with Video Diffusion Model for Scalable and Controllable Scene Generation
Authors:Shangjin Zhai, Zhichao Ye, Jialin Liu, Weijian Xie, Jiaqi Hu, Zhen Peng, Hua Xue, Danpeng Chen, Xiaomeng Wang, Lei Yang, Nan Wang, Haomin Liu, Guofeng Zhang
Recent advances in large reconstruction and generative models have significantly improved scene reconstruction and novel view generation. However, due to compute limitations, each inference with these large models is confined to a small area, making long-range consistent scene generation challenging. To address this, we propose StarGen, a novel framework that employs a pre-trained video diffusion model in an autoregressive manner for long-range scene generation. The generation of each video clip is conditioned on the 3D warping of spatially adjacent images and the temporally overlapping image from previously generated clips, improving spatiotemporal consistency in long-range scene generation with precise pose control. The spatiotemporal condition is compatible with various input conditions, facilitating diverse tasks, including sparse view interpolation, perpetual view generation, and layout-conditioned city generation. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate StarGen’s superior scalability, fidelity, and pose accuracy compared to state-of-the-art methods. Project page: https://zju3dv.github.io/StarGen.
近期重建和生成模型方面的进展极大地推动了场景重建和新颖视角生成的技术。然而,由于计算资源的限制,这些大型模型的每次推断都局限于一个小范围,使得大范围一致的场景生成面临挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了StarGen,这是一个采用预训练视频扩散模型的新型框架,以自回归的方式进行大范围场景生成。每个视频片段的生成都基于空间相邻图像的3D变形和之前生成的片段的时间重叠图像,这提高了大范围场景生成中的时空一致性,并实现了精确的姿态控制。这种时空条件与各种输入条件兼容,能够促进多种任务,包括稀疏视图插值、永久视图生成和布局控制的城市生成。定量和定性评估表明,StarGen在可扩展性、保真度和姿态准确性方面优于最先进的方法。项目页面:https://zju3dv.github.io/StarGen。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型重建和生成模型的最新进展极大地改进了场景重建和新颖视角生成。然而,由于计算限制,这些大型模型的每次推断都局限于小范围,使得长距离一致场景生成面临挑战。为解决这个问题,我们提出了StarGen框架,它采用预训练的视频扩散模型进行自回归长距离场景生成。每个视频剪辑的生成基于空间相邻图像的3D变形和先前生成的剪辑中时间上重叠的图像,提高了长距离场景生成的时空一致性,并实现了精确的姿态控制。这种时空条件适用于各种输入条件,可以促进包括稀疏视图插值、永久视图生成和布局控制城市生成在内的各种任务。
Key Takeaways
- 大型重建和生成模型的最新进展推动了场景重建和新颖视角生成的进步。
- 由于计算限制,现有模型在长距离场景生成方面面临挑战。
- StarGen框架采用预训练的视频扩散模型进行自回归长距离场景生成。
- StarGen利用空间相邻图像的3D变形和先前生成的剪辑中的重叠图像,提高时空一致性。
- StarGen具备精确的姿态控制能力。
- 框架支持多种任务,包括稀疏视图插值、永久视图生成和布局控制城市生成等。
点此查看论文截图


Navigating Image Restoration with VAR’s Distribution Alignment Prior
Authors:Siyang Wang, Feng Zhao
Generative models trained on extensive high-quality datasets effectively capture the structural and statistical properties of clean images, rendering them powerful priors for transforming degraded features into clean ones in image restoration. VAR, a novel image generative paradigm, surpasses diffusion models in generation quality by applying a next-scale prediction approach. It progressively captures both global structures and fine-grained details through the autoregressive process, consistent with the multi-scale restoration principle widely acknowledged in the restoration community. Furthermore, we observe that during the image reconstruction process utilizing VAR, scale predictions automatically modulate the input, facilitating the alignment of representations at subsequent scales with the distribution of clean images. To harness VAR’s adaptive distribution alignment capability in image restoration tasks, we formulate the multi-scale latent representations within VAR as the restoration prior, thus advancing our delicately designed VarFormer framework. The strategic application of these priors enables our VarFormer to achieve remarkable generalization on unseen tasks while also reducing training computational costs. Extensive experiments underscores that our VarFormer outperforms existing multi-task image restoration methods across various restoration tasks.
生成模型经过大量高质量数据集的训练,能够有效捕捉清洁图像的结构和统计特性,使其在图像恢复中将退化特征转换为清洁特征方面具有强大的先验能力。VAR作为一种新型图像生成范式,通过应用下一尺度预测方法,在生成质量上超越了扩散模型。它通过自回归过程逐步捕捉全局结构和精细细节,这与恢复社区广泛认可的多尺度恢复原则相一致。此外,我们在使用VAR进行图像重建过程时观察到,尺度预测会自动调制输入,便于后续尺度的表示与清洁图像分布的对齐。为了利用VAR在图像恢复任务中的自适应分布对齐能力,我们将VAR内的多尺度潜在表示作为恢复先验,从而推进了我们精心设计的VarFormer框架。这些先验的战略应用使我们的VarFormer在未见过任务上实现了显著泛化,同时降低了训练计算成本。大量实验证明,我们的VarFormer在各种恢复任务上优于现有的多任务图像恢复方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大规模高质量数据集训练的生成模型能有效捕捉清晰图像的结构和统计特性,可作为图像修复中将退化特征转化为清晰特征的强大先验。VAR作为一种新型图像生成范式,通过尺度预测方法,在生成质量上超越了扩散模型。VAR遵循广泛认可的图像修复多尺度恢复原则,逐步捕捉全局结构和精细细节。在利用VAR进行图像重建时,尺度预测会自动调整输入,促进后续尺度表示与干净图像分布的对齐。我们将VAR中的多尺度潜在表示作为修复先验,构建了精心设计的VarFormer框架,利用其自适应分布对齐能力。VarFormer在未见任务上实现了卓越泛化能力,同时降低了训练计算成本。实验表明,VarFormer在多种修复任务上优于现有多任务图像修复方法。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型基于大规模高质量数据集可有效捕捉图像结构和统计特性。
- VAR成为新的图像生成范式,通过尺度预测提升生成质量。
- VAR遵循多尺度恢复原则,能逐步捕捉全局结构和精细细节。
- 在图像重建过程中,VAR的尺度预测能自动调整输入,促进后续尺度与干净图像分布对齐。
- VarFormer利用VAR中的多尺度潜在表示作为修复先验。
- VarFormer实现卓越泛化能力并降低训练计算成本。
点此查看论文截图

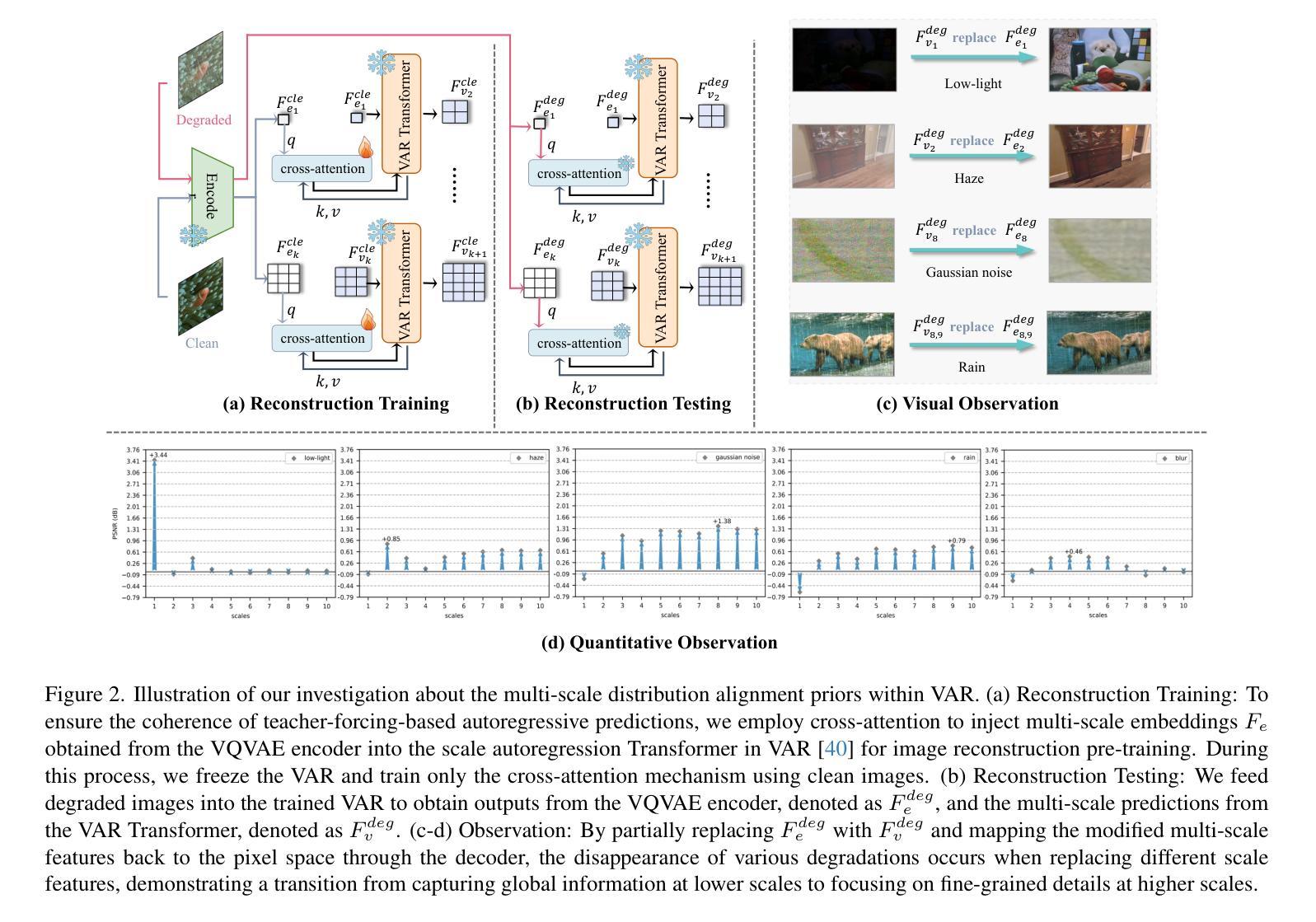

Nearly Zero-Cost Protection Against Mimicry by Personalized Diffusion Models
Authors:Namhyuk Ahn, KiYoon Yoo, Wonhyuk Ahn, Daesik Kim, Seung-Hun Nam
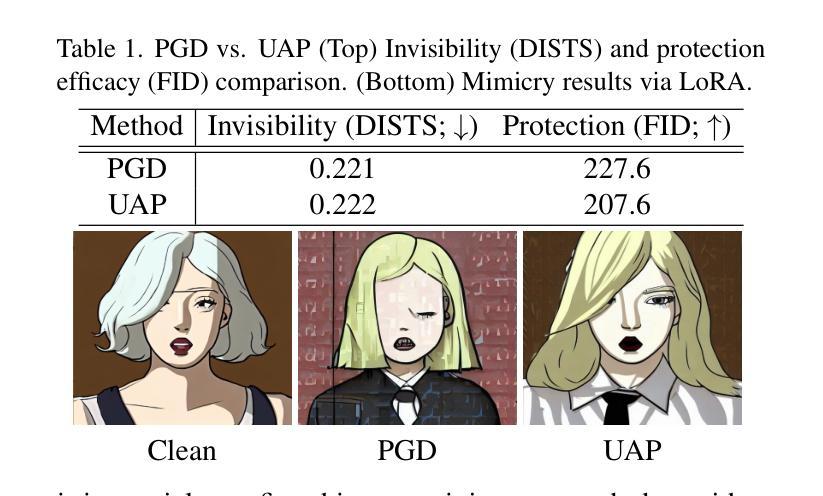
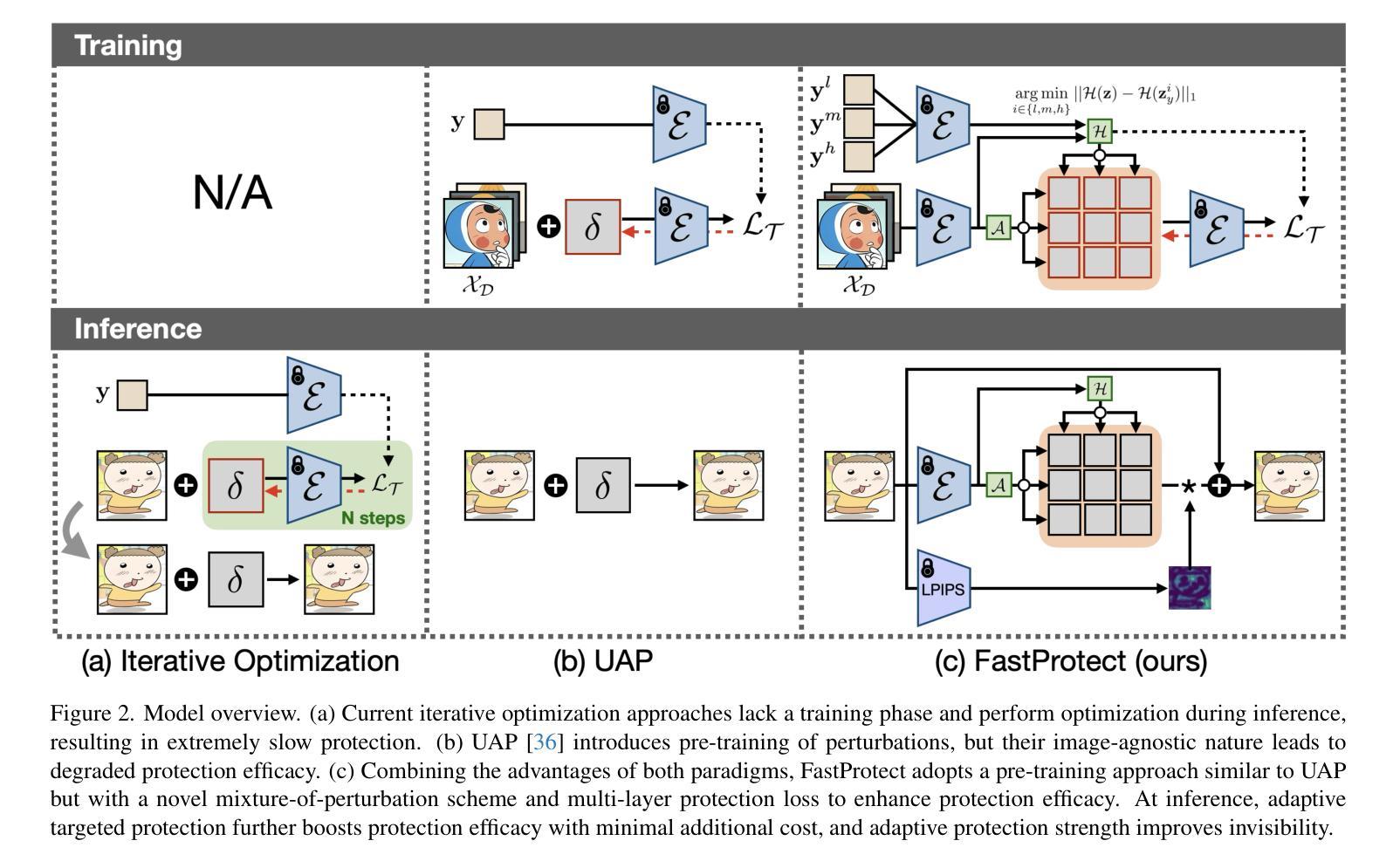
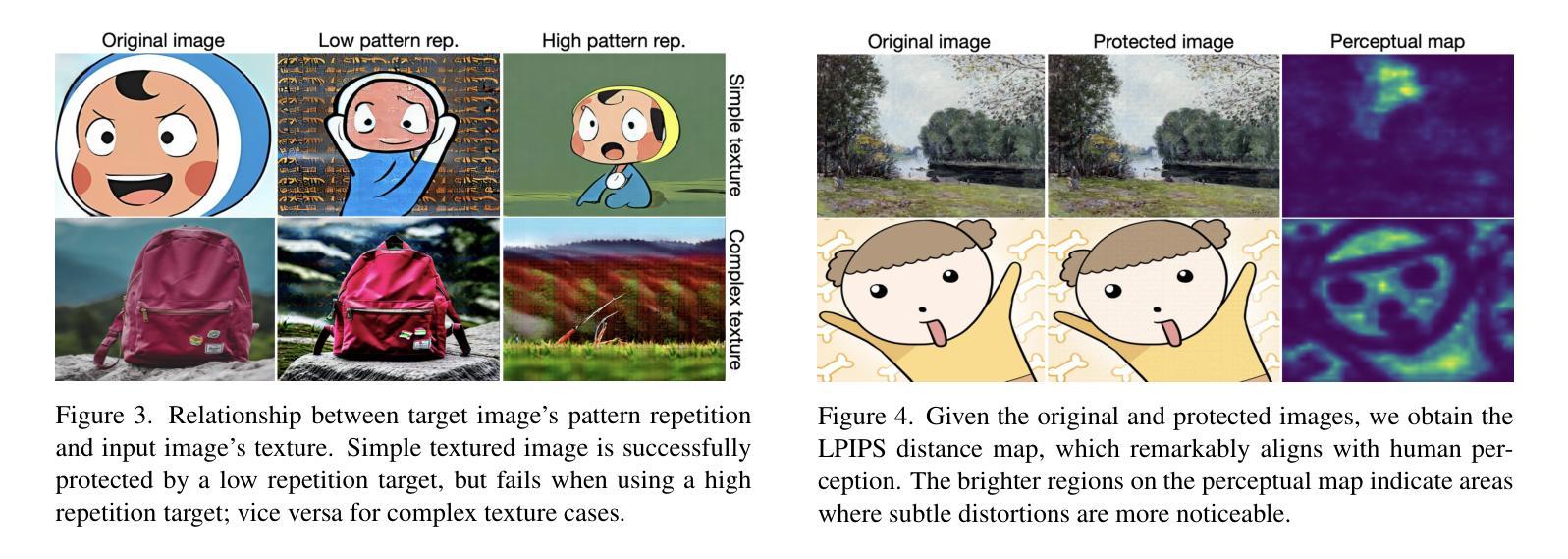
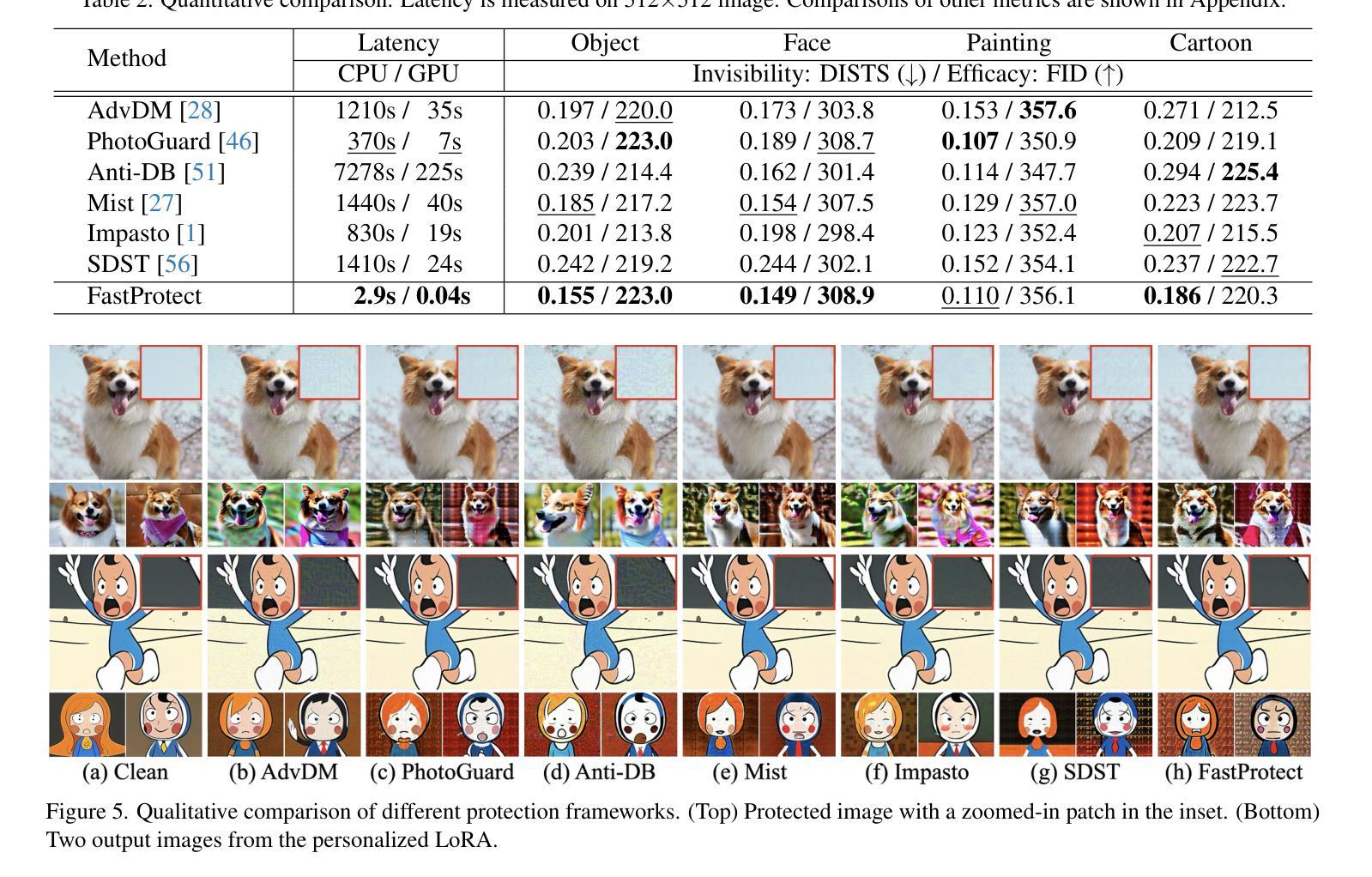
Recent advancements in diffusion models revolutionize image generation but pose risks of misuse, such as replicating artworks or generating deepfakes. Existing image protection methods, though effective, struggle to balance protection efficacy, invisibility, and latency, thus limiting practical use. We introduce perturbation pre-training to reduce latency and propose a mixture-of-perturbations approach that dynamically adapts to input images to minimize performance degradation. Our novel training strategy computes protection loss across multiple VAE feature spaces, while adaptive targeted protection at inference enhances robustness and invisibility. Experiments show comparable protection performance with improved invisibility and drastically reduced inference time. The code and demo are available at https://webtoon.github.io/impasto
最近扩散模型的进展虽然为图像生成带来了革命性的变化,但也带来了滥用风险,比如复制艺术品或生成深度伪造图像。虽然现有图像保护方法有效,但在保护效果、隐形性和延迟之间难以平衡,从而限制了实际应用。我们引入扰动预训练以减少延迟,并提出一种混合扰动方法,该方法可动态适应输入图像,以最小化性能下降。我们新颖的训练策略计算了多个VAE特征空间中的保护损失,同时推理阶段的自适应目标保护增强了稳健性和隐形性。实验表明,保护性能相当,隐形性有所提高,推理时间大大减少。代码和演示可在https://webtoon.github.io/impasto查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
近期扩散模型在图像生成方面的进步推动了艺术创新,但同时也带来了滥用风险,如复制艺术品或生成深度伪造图像。现有图像保护方法在保护效果、隐形性和延迟之间难以平衡,限制了实际应用。我们引入扰动预训练以降低延迟,并提出混合扰动方法,动态适应输入图像以最小化性能下降。我们的新训练策略计算多个VAE特征空间中的保护损失,同时在推理时进行自适应靶向保护,以增强稳健性和隐形性。实验表明,保护性能相当,隐形性提高,推理时间大幅降低。相关代码和演示可在webtoon.github.io/impasto上查看。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的最新进展推动了图像生成的发展,但存在滥用风险。
- 现有图像保护方法在平衡保护效果、隐形性和延迟方面存在困难。
- 引入扰动预训练以降低延迟和提高性能。
- 提出混合扰动方法,动态适应输入图像。
- 新训练策略计算多个VAE特征空间中的保护损失。
- 自适应靶向保护增强稳健性和隐形性。
- 实验显示保护性能相当,隐形性提高,推理时间减少。
点此查看论文截图
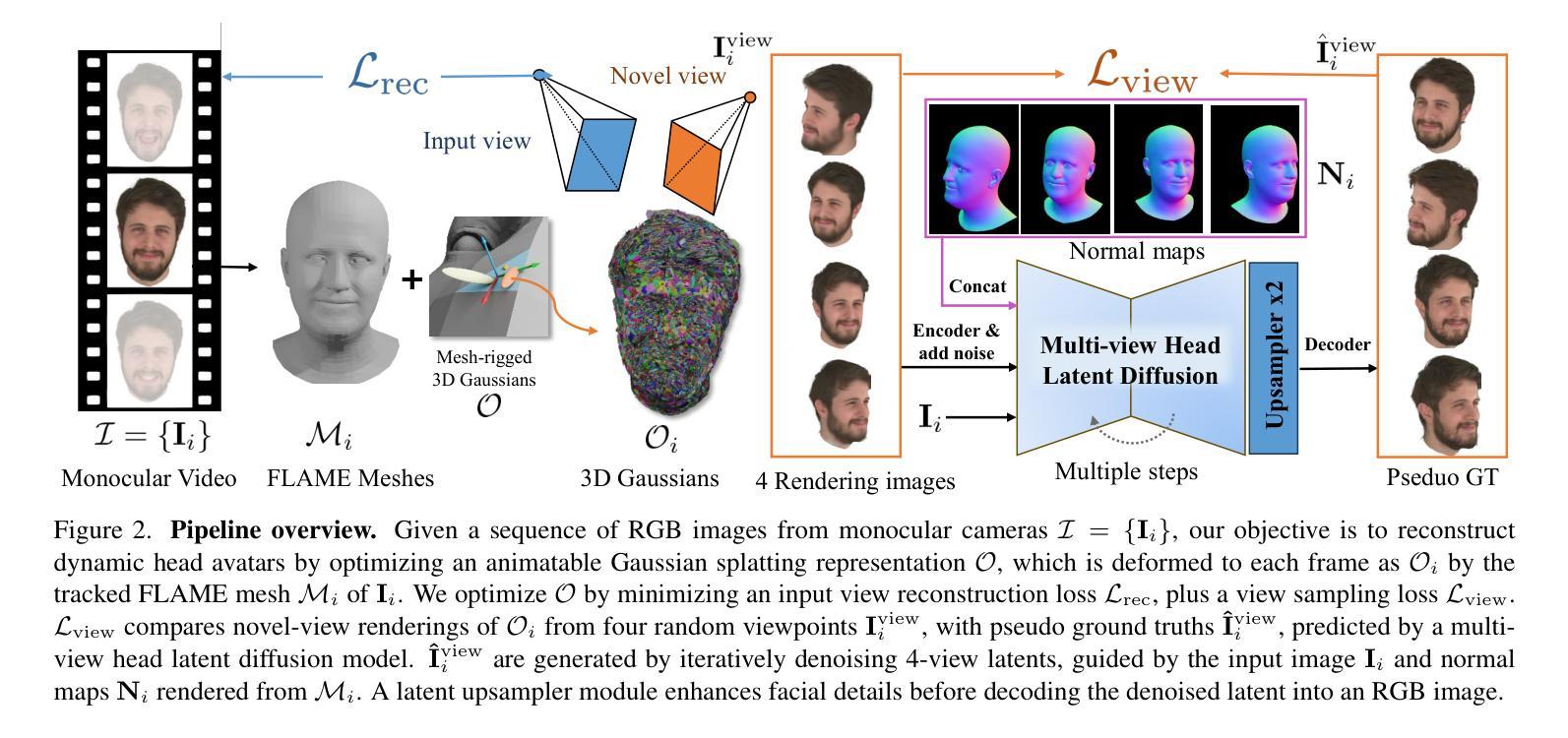
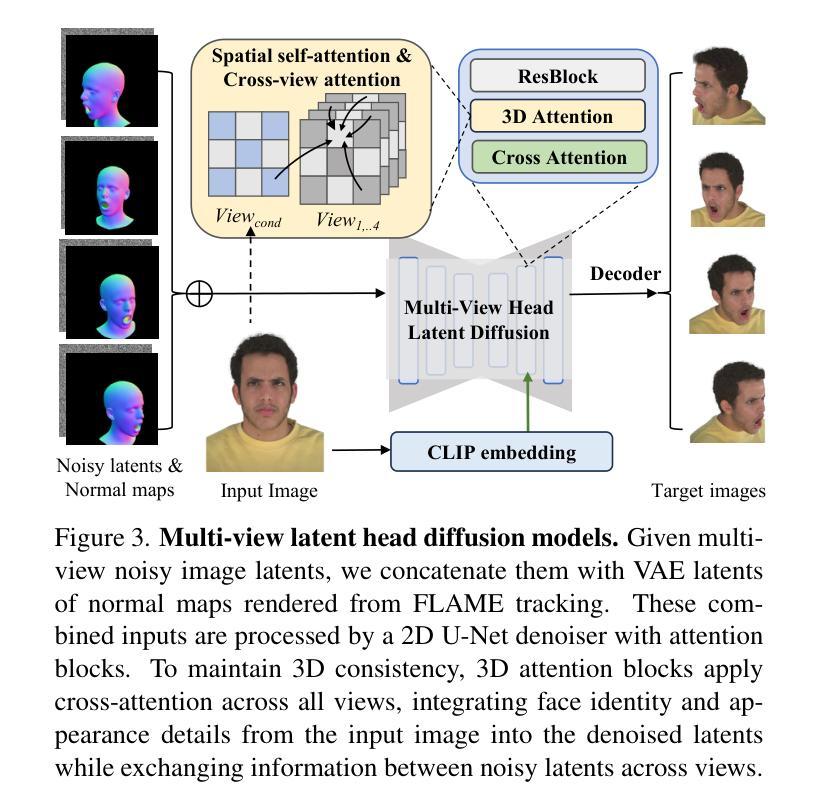
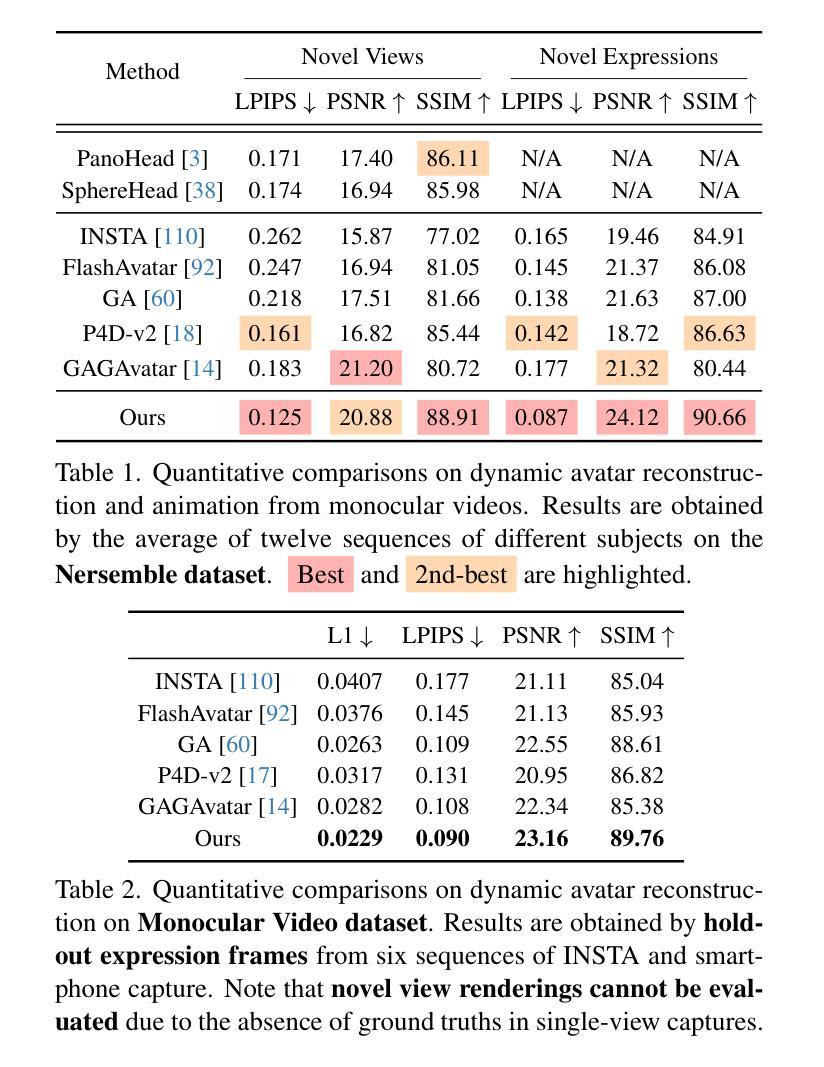
GAF: Gaussian Avatar Reconstruction from Monocular Videos via Multi-view Diffusion
Authors:Jiapeng Tang, Davide Davoli, Tobias Kirschstein, Liam Schoneveld, Matthias Niessner
We propose a novel approach for reconstructing animatable 3D Gaussian avatars from monocular videos captured by commodity devices like smartphones. Photorealistic 3D head avatar reconstruction from such recordings is challenging due to limited observations, which leaves unobserved regions under-constrained and can lead to artifacts in novel views. To address this problem, we introduce a multi-view head diffusion model, leveraging its priors to fill in missing regions and ensure view consistency in Gaussian splatting renderings. To enable precise viewpoint control, we use normal maps rendered from FLAME-based head reconstruction, which provides pixel-aligned inductive biases. We also condition the diffusion model on VAE features extracted from the input image to preserve facial identity and appearance details. For Gaussian avatar reconstruction, we distill multi-view diffusion priors by using iteratively denoised images as pseudo-ground truths, effectively mitigating over-saturation issues. To further improve photorealism, we apply latent upsampling priors to refine the denoised latent before decoding it into an image. We evaluate our method on the NeRSemble dataset, showing that GAF outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods in novel view synthesis. Furthermore, we demonstrate higher-fidelity avatar reconstructions from monocular videos captured on commodity devices.
我们提出了一种从单目视频重建可动画的3D高斯化身的新方法,这些视频是由智能手机等商品设备捕捉的。从这种记录中进行逼真的3D头部化身重建是一个挑战,因为观察有限,导致未观测区域约束不足,并在新视角中产生伪影。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一个多视角头部扩散模型,利用其先验知识来填充缺失区域并确保高斯平铺渲染中的视角一致性。为了实现精确的观点控制,我们使用基于FLAME的头部重建渲染的法线图,这提供了像素对齐的归纳偏见。我们还根据输入图像提取的VAE特征对扩散模型进行条件处理,以保留面部身份和外观细节。对于高斯化身重建,我们通过使用迭代去噪图像作为伪真实值来提炼多视角扩散先验知识,有效地减轻过饱和问题。为了提高逼真度,我们应用潜在上采样先验知识来精细化去噪潜在代码,然后将其解码为图像。我们在NeRSemble数据集上评估了我们的方法,结果表明GAF在新型视角合成方面优于先前最先进的方法。此外,我们还展示了从单目视频捕捉的商品设备上的更高保真度化身重建。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper Video: https://youtu.be/QuIYTljvhyg Project Page: https://tangjiapeng.github.io/projects/GAF
Summary
本文提出了一种新的方法,利用单目视频和商品设备(如智能手机)来重建可动画的3D高斯头像。由于有限的观察角度带来的未观测区域约束不足的问题,传统的从单目视频进行真实感的3D头像重建会有很大的挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种多视角头部扩散模型,通过其先验知识填充缺失区域并确保高斯贴图渲染中的视角一致性。为了精确控制视角,我们采用基于FLAME的头部重建渲染法向量图,提供像素对齐的诱导偏差。此外,我们将扩散模型的条件设定为输入图像的VAE特征,以保留面部身份和外观细节。对于高斯头像重建,我们通过使用去噪图像作为伪真实值来提炼多视角扩散先验知识,有效缓解过度饱和问题。为进一步提高真实感,我们应用潜在上采样先验知识来细化去噪潜在编码,然后将其解码为图像。我们在NeRSemble数据集上评估了我们的方法,结果表明GAF在新型视角合成方面优于之前的最先进方法。此外,我们还展示了从单目视频捕获的商品设备中生成更高保真度的头像重建。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种利用单目视频和商品设备(智能手机)重建可动画的3D高斯头像的新方法。
- 通过引入多视角头部扩散模型解决了有限的观察角度带来的问题,填充缺失区域并确保视角一致性。
- 利用基于FLAME的头部重建渲染法向量图实现精确视角控制。
- 使用输入图像的VAE特征作为扩散模型的条件以保留面部身份和外观细节。
- 通过使用迭代去噪图像作为伪真实值提炼多视角扩散先验知识来缓解过度饱和问题。
- 应用潜在上采样先验知识提高重建头像的真实感。
点此查看论文截图

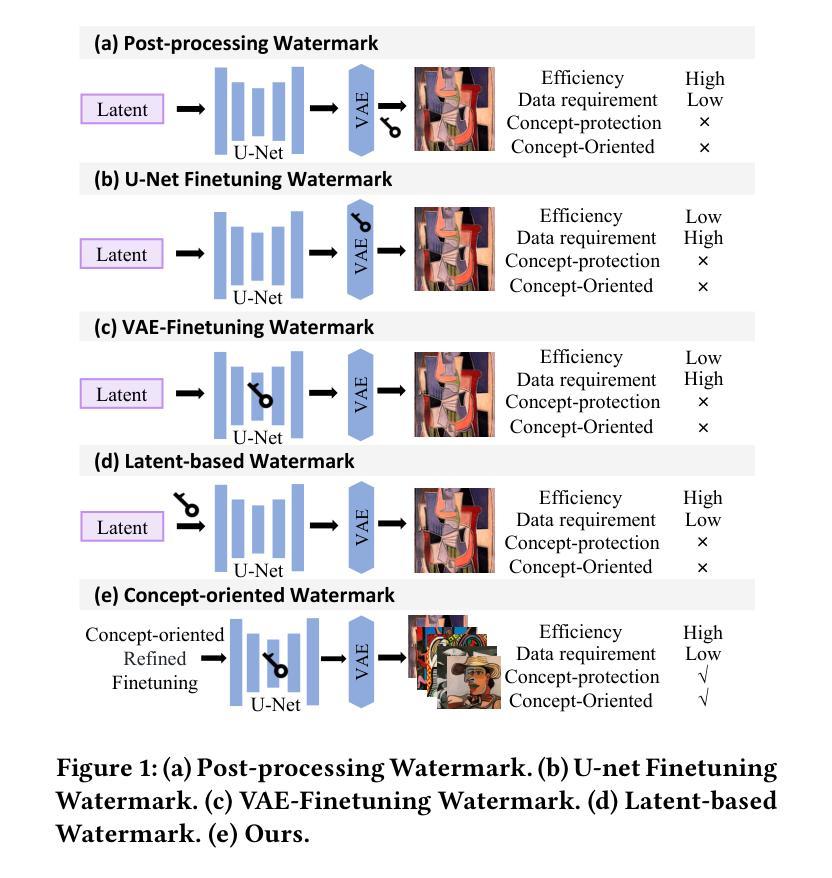
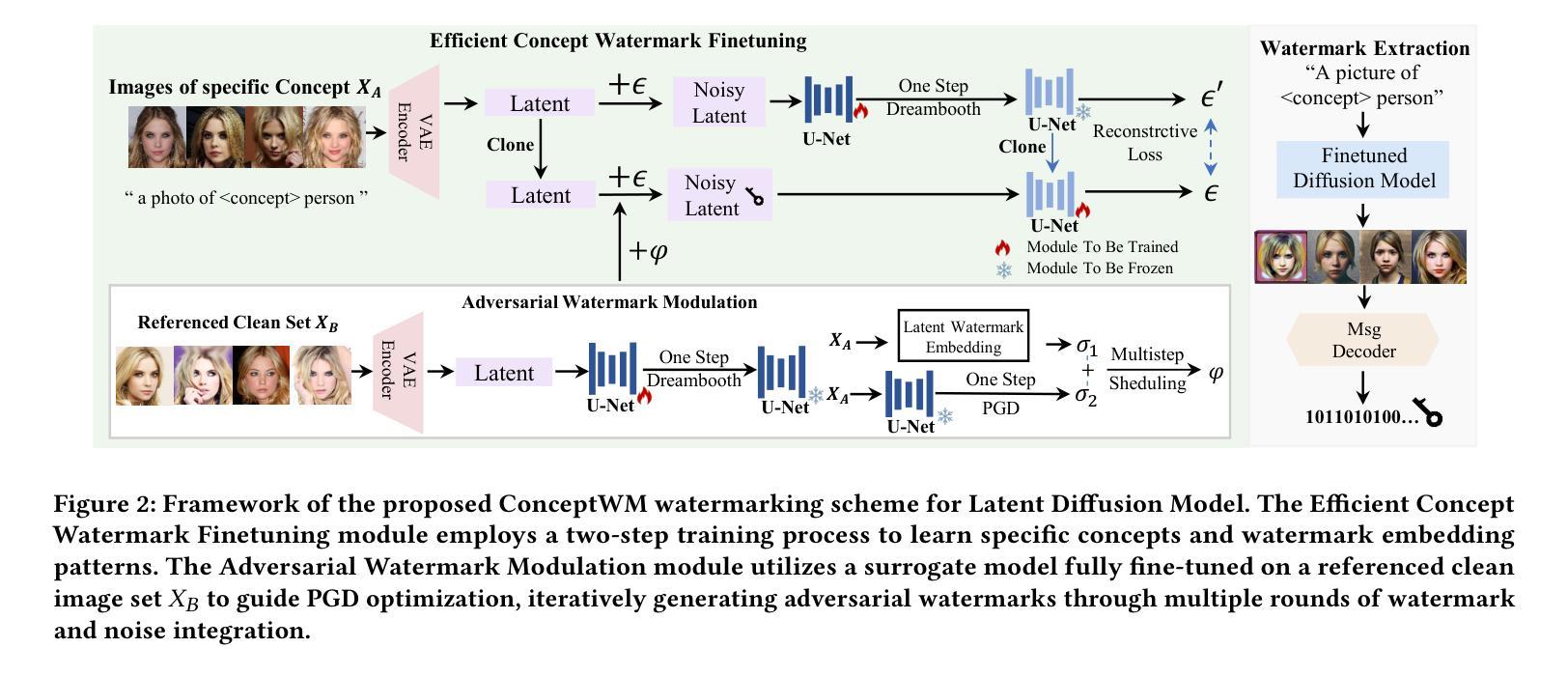
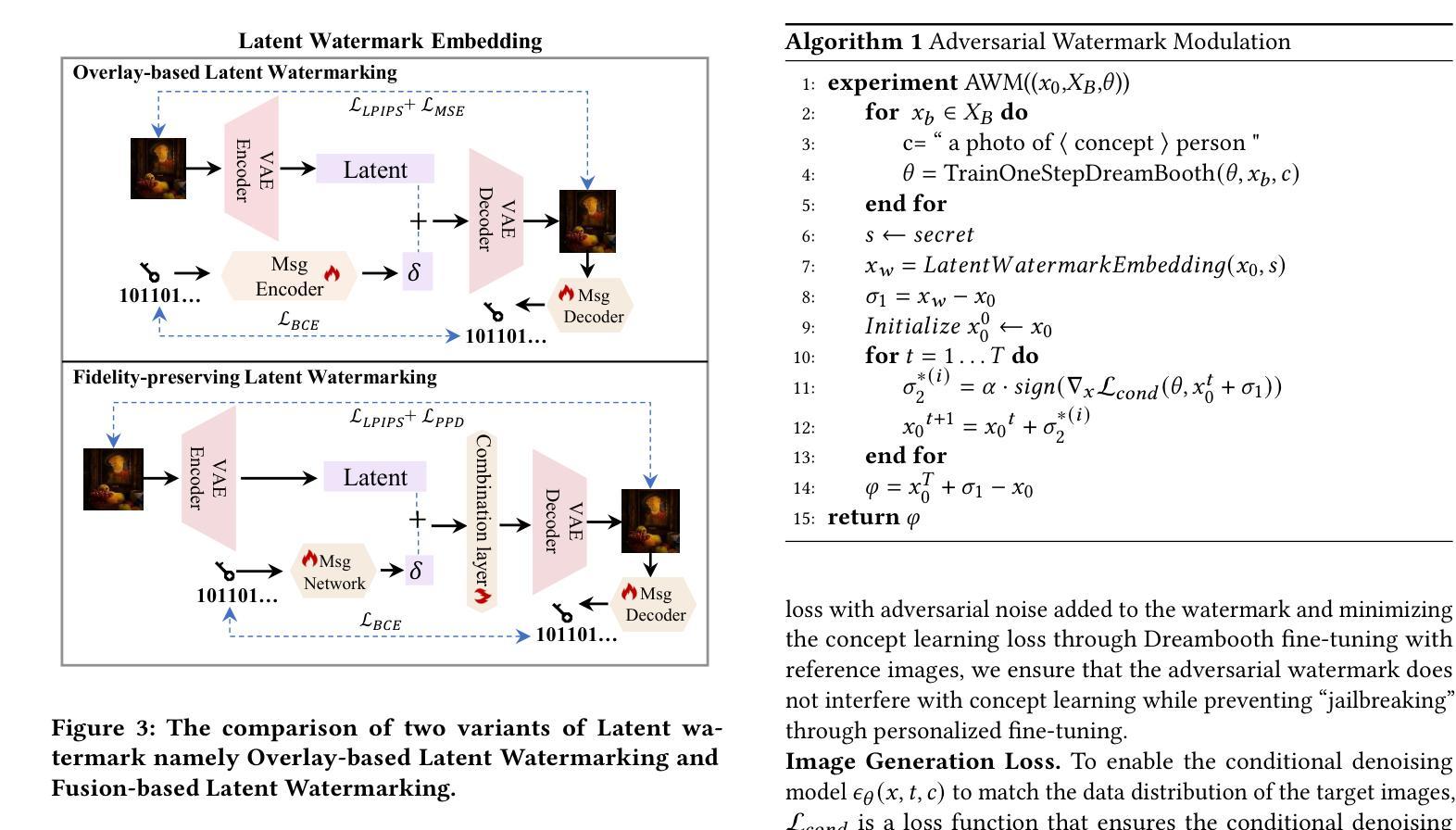
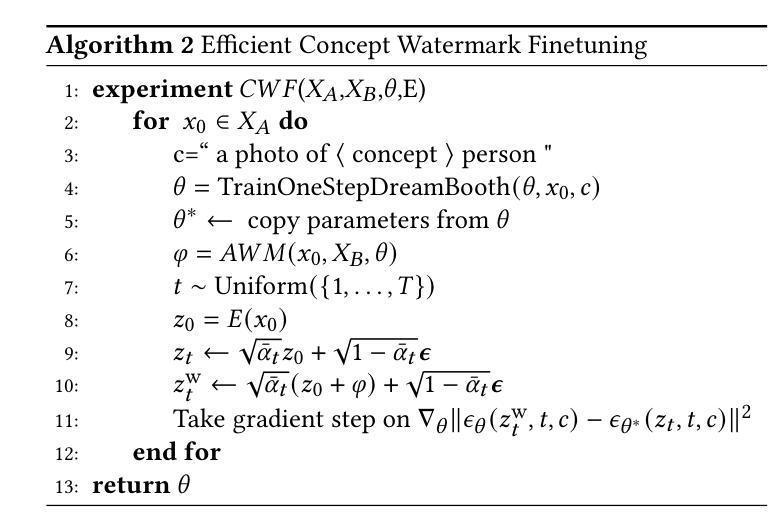
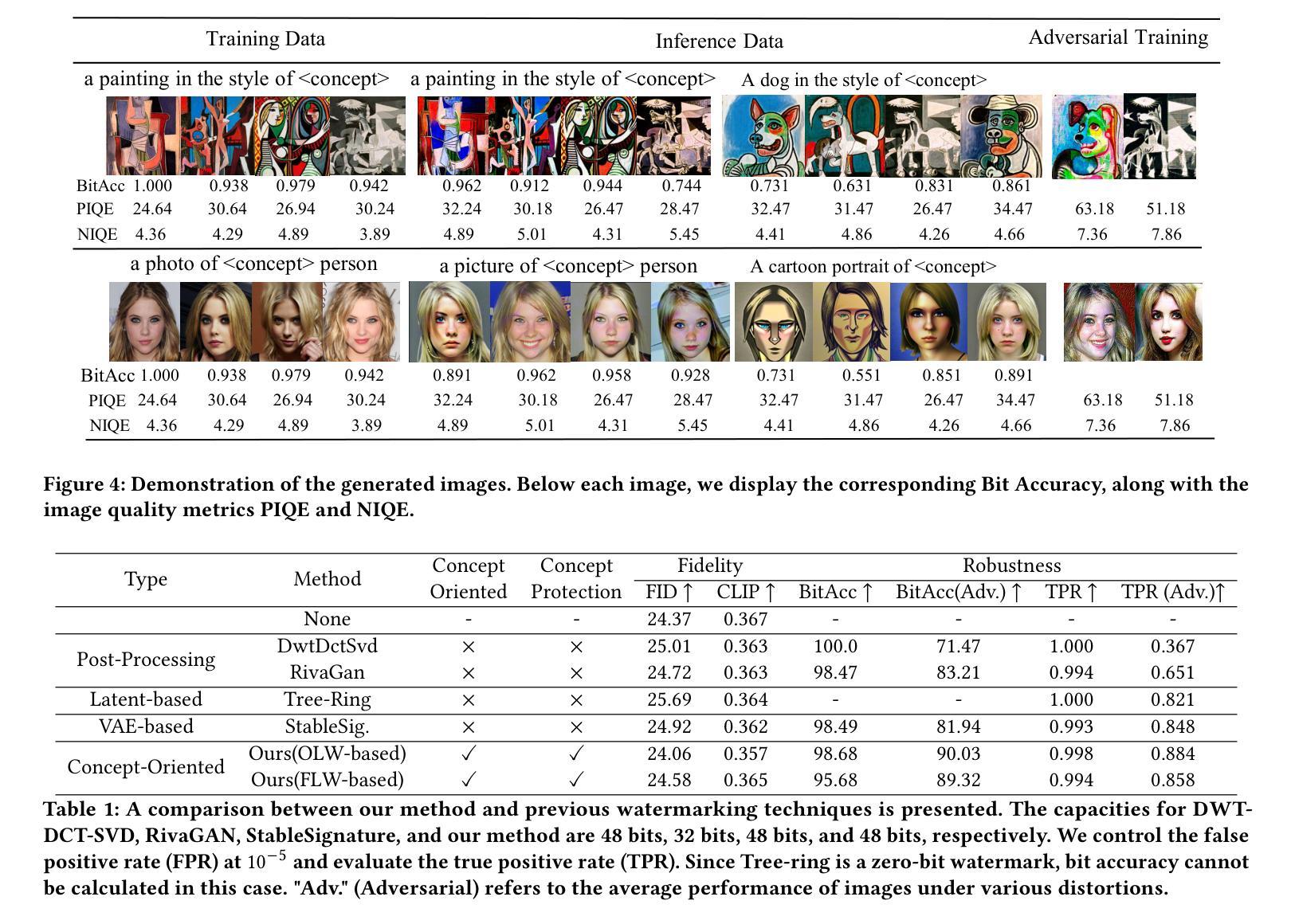
Conceptwm: A Diffusion Model Watermark for Concept Protection
Authors:Liangqi Lei, Keke Gai, Jing Yu, Liehuang Zhu, Qi Wu
The personalization techniques of diffusion models succeed in generating specific concepts but also pose threats to copyright protection and illegal use. Model Watermarking is an effective method to prevent the unauthorized use of subject-driven or style-driven image generation, safeguarding concept copyrights. However, under the goal of concept-oriented protection, current watermarking schemes typically add watermarks to all images rather than applying them in a refined manner targeted at specific concepts. Additionally, the personalization techniques of diffusion models can easily remove watermarks. Existing watermarking methods struggle to achieve fine-grained watermark embedding with a few images of specific concept and prevent removal of watermarks through personalized fine-tuning. Therefore, we introduce a novel concept-oriented watermarking framework that seamlessly embeds imperceptible watermarks into the concept of diffusion models. We introduce Fidelity-preserving Latent Watermarking (FLW) to generate latent watermarks based on image characteristics and the Adversarial Watermarking Modulation module to prevent “jailbreaking” via personalized finetuning. To enhance U-Net’s efficiency in learning watermark patterns with limited samples, we propose Efficient Concept Watermark Finetuning, which alternates optimization of model parameters for both watermark embedding and concept learning. We conduct extensive experiments and ablation studies to verify our framework. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Conceptwm-4EB3/.
个性化扩散模型的生成技术虽然能够成功生成特定概念,但也对版权保护和非法使用构成了威胁。模型水印是一种防止主题驱动或风格驱动图像生成未经授权使用的有效方法,保护概念版权。然而,在面向概念保护的目标下,当前的水印方案通常对所有图像都添加水印,而不是以精细的方式针对特定概念进行应用。此外,扩散模型的个性化技术很容易去除水印。现有的水印方法难以实现针对少数具有特定概念图像进行精细粒度水印嵌入,并防止通过个性化微调去除水印。因此,我们引入了一种新型的概念导向水印框架,无缝地将不可见水印嵌入到扩散模型的概念中。我们提出了基于图像特性的保真性保持潜在水印(FLW)生成潜在水印,并引入对抗性水印调制模块,以防止通过个性化微调进行“越狱”。为了提高U-Net在有限样本中学习水印模式的效率,我们提出了高效概念水印微调方法,该方法交替优化用于水印嵌入和概念学习的模型参数。我们进行了大量实验和消融研究来验证我们的框架。我们的代码可通过以下链接获取:https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Conceptwm-4EB3/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型的个性化技术在生成特定概念的同时,也对版权保护和非法使用构成了威胁。模型水印是一种防止滥用主题驱动或风格驱动图像生成的有效方法,保护概念版权。然而,在概念导向的保护目标下,当前的水印方案通常对所有图像都添加水印,而非针对特定概念进行精细应用。此外,扩散模型的个性化技术可以轻松去除水印。现有的水印方法难以实现少数具有特定概念图像的水印嵌入,并防止通过个性化微调去除水印。因此,我们引入了一种新的概念导向水印框架,无缝地将不可察觉的水印嵌入扩散模型的概念中。我们提出基于图像特性的保真性保留潜在水印(FLW)和对抗性水印调制模块,以防止个性化微调导致的“越狱”。为提高U-Net在学习水印模式时的效率并减少样本量限制,我们提出了高效概念水印微调方法,该方法交替优化水印嵌入和概念学习的模型参数。我们进行了大量实验和消融研究来验证我们的框架。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的个人化技术在生成特定概念方面具有优势,但也带来版权保护和非法使用的风险。
- 模型水印是保护概念版权的有效方法,但现有方案在针对特定概念的精细保护上存在不足。
- 当前的水印容易被扩散模型的个性化技术去除。
- 提出一种新的概念导向水印框架,能够无缝嵌入不可察觉的水印在扩散模型的概念中。
- 引入保真性保留潜在水印(FLW)和对抗性水印调制模块来增强水印的稳固性和安全性。
- 提出高效概念水印微调方法以提高U-Net在学习水印模式时的效率。
点此查看论文截图

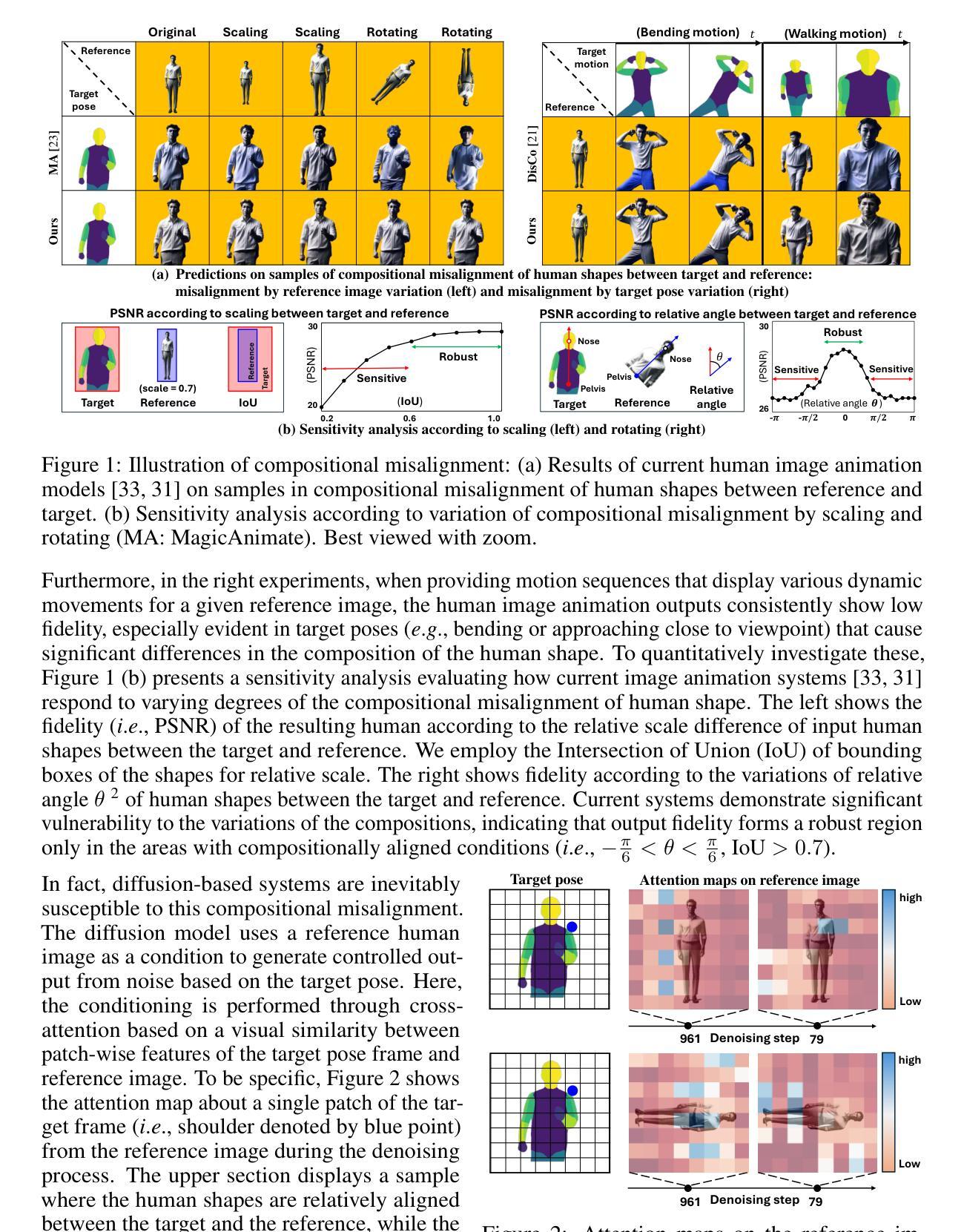
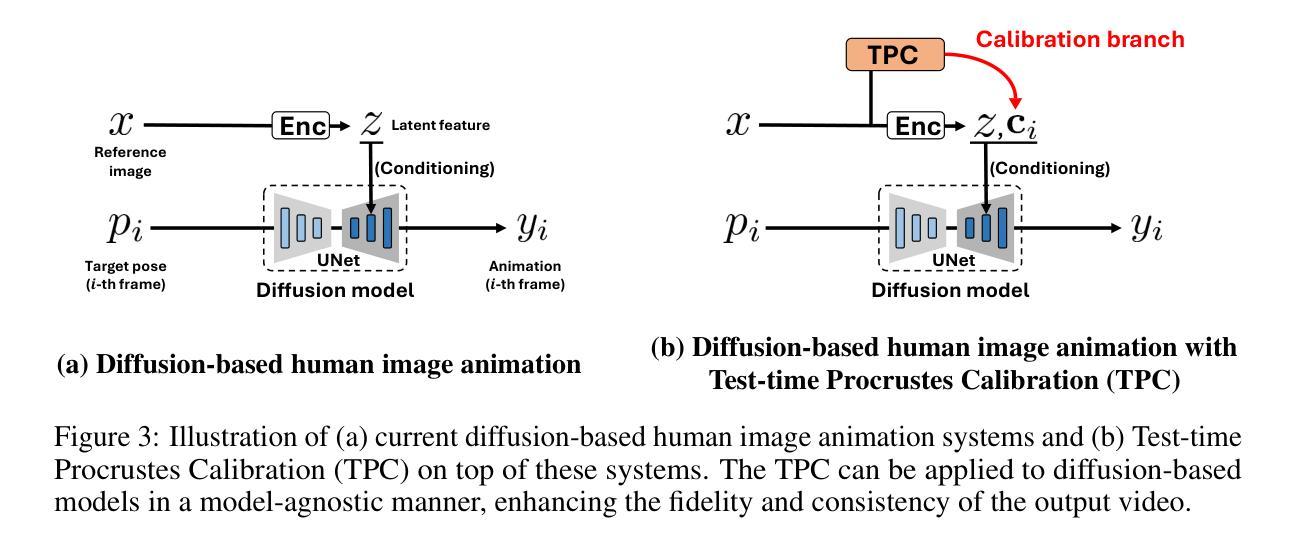
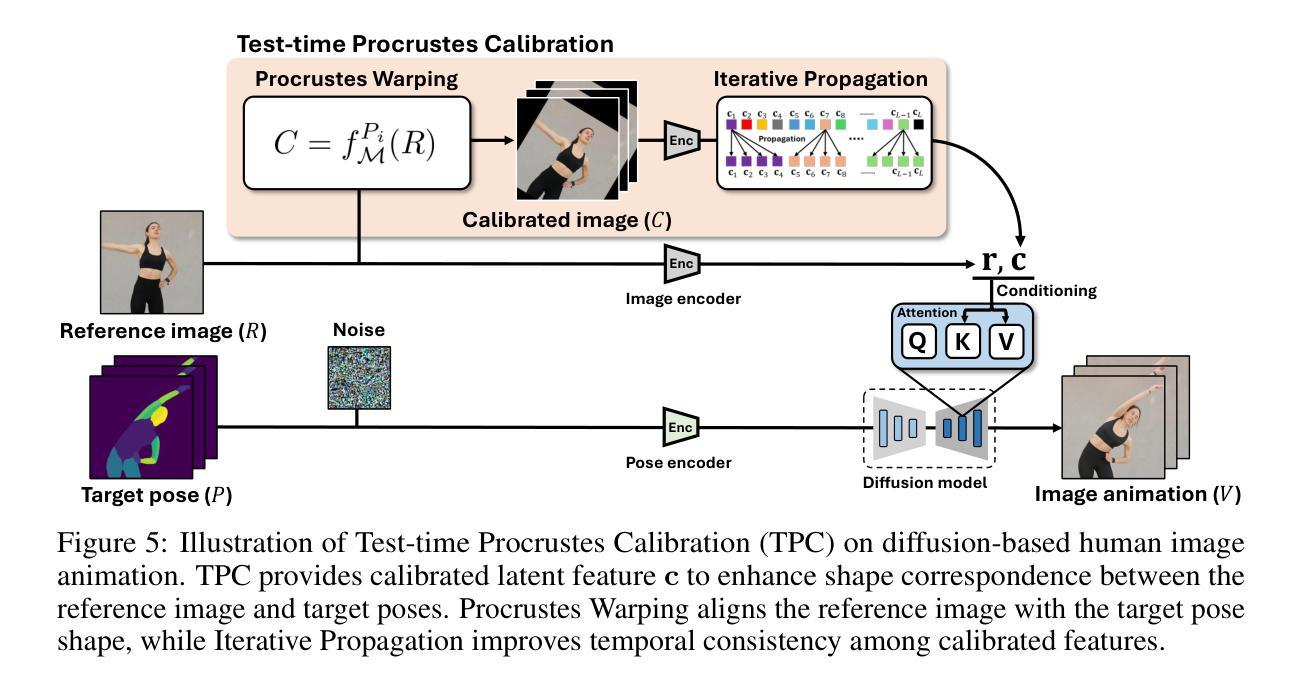
TPC: Test-time Procrustes Calibration for Diffusion-based Human Image Animation
Authors:Sunjae Yoon, Gwanhyeong Koo, Younghwan Lee, Chang D. Yoo
Human image animation aims to generate a human motion video from the inputs of a reference human image and a target motion video. Current diffusion-based image animation systems exhibit high precision in transferring human identity into targeted motion, yet they still exhibit irregular quality in their outputs. Their optimal precision is achieved only when the physical compositions (i.e., scale and rotation) of the human shapes in the reference image and target pose frame are aligned. In the absence of such alignment, there is a noticeable decline in fidelity and consistency. Especially, in real-world environments, this compositional misalignment commonly occurs, posing significant challenges to the practical usage of current systems. To this end, we propose Test-time Procrustes Calibration (TPC), which enhances the robustness of diffusion-based image animation systems by maintaining optimal performance even when faced with compositional misalignment, effectively addressing real-world scenarios. The TPC provides a calibrated reference image for the diffusion model, enhancing its capability to understand the correspondence between human shapes in the reference and target images. Our method is simple and can be applied to any diffusion-based image animation system in a model-agnostic manner, improving the effectiveness at test time without additional training.
人类图像动画旨在从参考人类图像和目标运动视频输入生成人类运动视频。当前的基于扩散的图像动画系统在人像转移到目标动作时表现出高精确度,但它们的输出质量仍存在不规则现象。它们的最佳精度只有在参考图像和目标姿势框架中的人类形状的物理组成(即比例和旋转)对齐时才能实现。在缺少这种对齐的情况下,保真度和一致性会明显下降。特别是在现实环境中,这种组成上的不对齐是常见的,给当前系统的实际应用带来了重大挑战。为此,我们提出了测试时校准(TPC),它通过保持最佳性能,即使面对组成上的不对齐,也增强了基于扩散的图像动画系统的稳健性,有效地解决了现实世界场景中的问题。TPC为扩散模型提供了一个校准后的参考图像,增强了其对参考图像和目标图像之间人类形状对应关系的理解。我们的方法简单,可以应用于任何基于扩散的图像动画系统,以模型无关的方式提高测试时的有效性,而无需额外的训练。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 16 figures, NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文讨论的是基于扩散模型的人体图像动画技术面临的挑战。由于参考图像和目标运动视频中的身体姿态组成(如尺度和旋转)未对齐时,现有系统的精度和一致性会明显下降。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种名为Test-time Procrustes Calibration(TPC)的方法,增强了扩散模型在人体图像动画中的稳健性,确保在面临组成不匹配时仍能保持最佳性能。TPC通过为扩散模型提供校准后的参考图像,提高了其对参考图像和目标图像之间形状对应的理解。此方法简单且可应用于任何扩散模型的人体图像动画系统,无需额外训练即可提高测试效果。
Key Takeaways
- 人体图像动画旨在从参考图像和目标运动视频生成人体运动视频。
- 当前扩散模型在人体图像动画中虽具有高精度,但在输出质量方面仍存在不规则性。
- 扩散模型在参考图像和目标姿态帧的物理组成(如尺度和旋转)对齐时才能达到最佳精度。
- 在现实世界环境中,组成不匹配是常见的,给现有系统实用带来了挑战。
- TPC方法提高了扩散模型在人体图像动画中的稳健性,以应对组成不匹配的问题。
- TPC通过提供校准后的参考图像,增强了扩散模型对参考图像和目标图像之间形状对应的理解。
点此查看论文截图

On the Wasserstein Convergence and Straightness of Rectified Flow
Authors:Vansh Bansal, Saptarshi Roy, Purnamrita Sarkar, Alessandro Rinaldo
Diffusion models have emerged as a powerful tool for image generation and denoising. Typically, generative models learn a trajectory between the starting noise distribution and the target data distribution. Recently Liu et al. (2023b) proposed Rectified Flow (RF), a generative model that aims to learn straight flow trajectories from noise to data using a sequence of convex optimization problems with close ties to optimal transport. If the trajectory is curved, one must use many Euler discretization steps or novel strategies, such as exponential integrators, to achieve a satisfactory generation quality. In contrast, RF has been shown to theoretically straighten the trajectory through successive rectifications, reducing the number of function evaluations (NFEs) while sampling. It has also been shown empirically that RF may improve the straightness in two rectifications if one can solve the underlying optimization problem within a sufficiently small error. In this paper, we make two contributions. First, we provide a theoretical analysis of the Wasserstein distance between the sampling distribution of RF and the target distribution. Our error rate is characterized by the number of discretization steps and a novel formulation of straightness stronger than that in the original work. Secondly, we present general conditions guaranteeing uniqueness and straightness of 1-RF, which is in line with previous empirical findings. As a byproduct of our analysis, we show that, in one dimension, RF started at the standard Gaussian distribution yields the Monge map. Additionally, we also present empirical results on both simulated and real datasets to validate our theoretical findings. The code is available at https://github.com/bansal-vansh/rectified-flow.
扩散模型已经成为图像生成和去噪的强大工具。通常,生成模型学习从初始噪声分布到目标数据分布之间的轨迹。最近,Liu等人(2023b)提出了Rectified Flow(RF)这一生成模型,旨在通过一系列与最佳传输紧密相关的凸优化问题来学习从噪声到数据的直线轨迹。如果轨迹是弯曲的,必须使用许多欧拉离散化步骤或新型策略(如指数积分器)来实现令人满意的生成质量。相比之下,RF理论上有能力通过连续校正来使轨迹直线化,从而在采样时减少函数评估次数(NFEs)。此外,经验证据表明,如果在足够小的误差范围内解决底层优化问题,RF可能在两次校正中提高直线度。本文我们做出了两项贡献。首先,我们对RF采样分布与目标分布之间的Wasserstein距离进行了理论分析。我们的误差率由离散化步骤的数量以及比原始工作中更强的直线性新型公式所决定。其次,我们提出了保证1-RF唯一性和直线性的通用条件,这与之前的经验发现相一致。作为分析的一个副产品,我们表明,在一维空间中,从标准高斯分布开始的RF会产生Monge地图。此外,我们还展示了模拟数据集和真实数据集上的实验结果,以验证我们的理论发现。代码可在https://github.com/bansal-vansh/rectified-flow上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 38 pages
Summary
扩散模型已成为图像生成和去噪的强大工具。近期Liu等人提出的Rectified Flow模型旨在通过一系列凸优化问题来学习从噪声到数据的直线轨迹,与最优传输紧密相关。该模型可简化采样过程中的轨迹,提高生成质量。本文分析了Rectified Flow采样分布与目标分布之间的Wasserstein距离,并提供了独特性和直线性的通用条件保证。此外,本文还在一维条件下进行了实证分析。相关代码可在github.com/bansal-ansh查找。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型用于图像生成和去噪。
- Rectified Flow模型通过学习直线轨迹从噪声到数据来提高生成质量。
- Rectified Flow通过凸优化问题和最优传输实现轨迹直线化。
- 理论分析了Rectified Flow采样分布与目标分布之间的Wasserstein距离。
- 分析了轨迹直线性的独特性和通用条件保证。
- 在一维条件下进行了实证分析。
点此查看论文截图