⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-16 更新
Siamese Network with Dual Attention for EEG-Driven Social Learning: Bridging the Human-Robot Gap in Long-Tail Autonomous Driving
Authors:Xiaoshan Zhou, Carol C. Menassa, Vineet R. Kamat
Robots with wheeled, quadrupedal, or humanoid forms are increasingly integrated into built environments. However, unlike human social learning, they lack a critical pathway for intrinsic cognitive development, namely, learning from human feedback during interaction. To understand human ubiquitous observation, supervision, and shared control in dynamic and uncertain environments, this study presents a brain-computer interface (BCI) framework that enables classification of Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals to detect cognitively demanding and safety-critical events. As a timely and motivating co-robotic engineering application, we simulate a human-in-the-loop scenario to flag risky events in semi-autonomous robotic driving-representative of long-tail cases that pose persistent bottlenecks to the safety performance of smart mobility systems and robotic vehicles. Drawing on recent advances in few-shot learning, we propose a dual-attention Siamese convolutional network paired with Dynamic Time Warping Barycenter Averaging approach to generate robust EEG-encoded signal representations. Inverse source localization reveals activation in Broadman areas 4 and 9, indicating perception-action coupling during task-relevant mental imagery. The model achieves 80% classification accuracy under data-scarce conditions and exhibits a nearly 100% increase in the utility of salient features compared to state-of-the-art methods, as measured through integrated gradient attribution. Beyond performance, this study contributes to our understanding of the cognitive architecture required for BCI agents-particularly the role of attention and memory mechanisms-in categorizing diverse mental states and supporting both inter- and intra-subject adaptation. Overall, this research advances the development of cognitive robotics and socially guided learning for service robots in complex built environments.
带有轮子、四足或人形形式的机器人越来越多地被集成到建筑环境中。然而,与人类的社会学习不同,它们在内在认知发展的关键途径上有所缺失,即在与人类互动过程中从人类反馈中学习。为了理解人类在动态和不确定环境中的普遍观察、监督以及共享控制,本研究提出了一个脑机接口(BCI)框架,该框架能够对脑电图(EEG)信号进行分类,以检测认知需求和安全关键事件。作为一个及时且鼓舞人心的协同机器人工程应用,我们模拟了一个有人类参与的闭环场景来标记半自主机器人驾驶中的危险事件——这代表了智能移动系统和机器人车辆安全性能中持久的瓶颈的长期尾部案例。基于最近的小样本学习进展,我们提出了一种双注意力孪生卷积网络,结合动态时间规整质心平均法,生成稳健的EEG编码信号表示。逆向源定位显示Broadman 4区和9区的激活,这表明在任务相关的心理意象过程中感知-行动耦合。该模型在数据稀缺的条件下实现了80%的分类精度,与最先进的方法相比,显著特征的实用性增加了近100%,这是通过集成梯度归属度来衡量的。除了性能之外,该研究还有助于我们理解脑机接口代理所需的认知架构——特别是注意力和记忆机制在分类不同心理状态和支持主体间和主体内适应中的作用。总体而言,这项研究推动了认知机器人以及在复杂建筑环境中服务机器人的社会指导学习的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 50 pages, 18 figures
摘要
本研究提出了一种基于脑机接口(BCI)的框架,通过采集和分析脑电图(EEG)信号,以实现对人类在动态和不确定环境中普遍的观察、监督和共享控制的理解。该研究利用先进的少样本学习技术,通过双注意力Siamese卷积网络和动态时间规整重心平均法生成稳健的EEG信号表示。逆源定位揭示了Broadman 4区和9区的激活,表明在任务相关心理图像中的感知动作耦合。在数据稀缺条件下,该模型实现了80%的分类精度,与现有方法相比,显著特征效用提高了近100%。本研究不仅提高了性能,而且加深了对BCI代理所需认知架构的理解,特别是注意力和记忆机制在分类各种心理状态和支持跨主体和主体内适应中的作用。这项研究推动了认知机器人和复杂建筑环境中服务机器人的社会指导学习的发展。
关键见解
- 研究提出了基于脑机接口(BCI)的框架,旨在理解人类在与机器人交互中的观察、监督和共享控制。
- 结合少样本学习技术,通过双注意力Siamese卷积网络和Dynamic Time Warping Barycenter Averaging方法处理EEG信号。
- 研究通过逆源定位发现了与任务相关心理图像感知动作耦合的脑部激活区域。
- 模型在数据稀缺条件下达到了80%的分类精度。
- 与现有方法相比,该模型的显著特征效用提升了近100%。
- 研究结果不仅关注性能提升,还深入探讨了BCI所需的认知架构。
- 研究推动了认知机器人在复杂建筑环境中的发展,特别是在服务机器人领域的社会指导学习。
点此查看论文截图

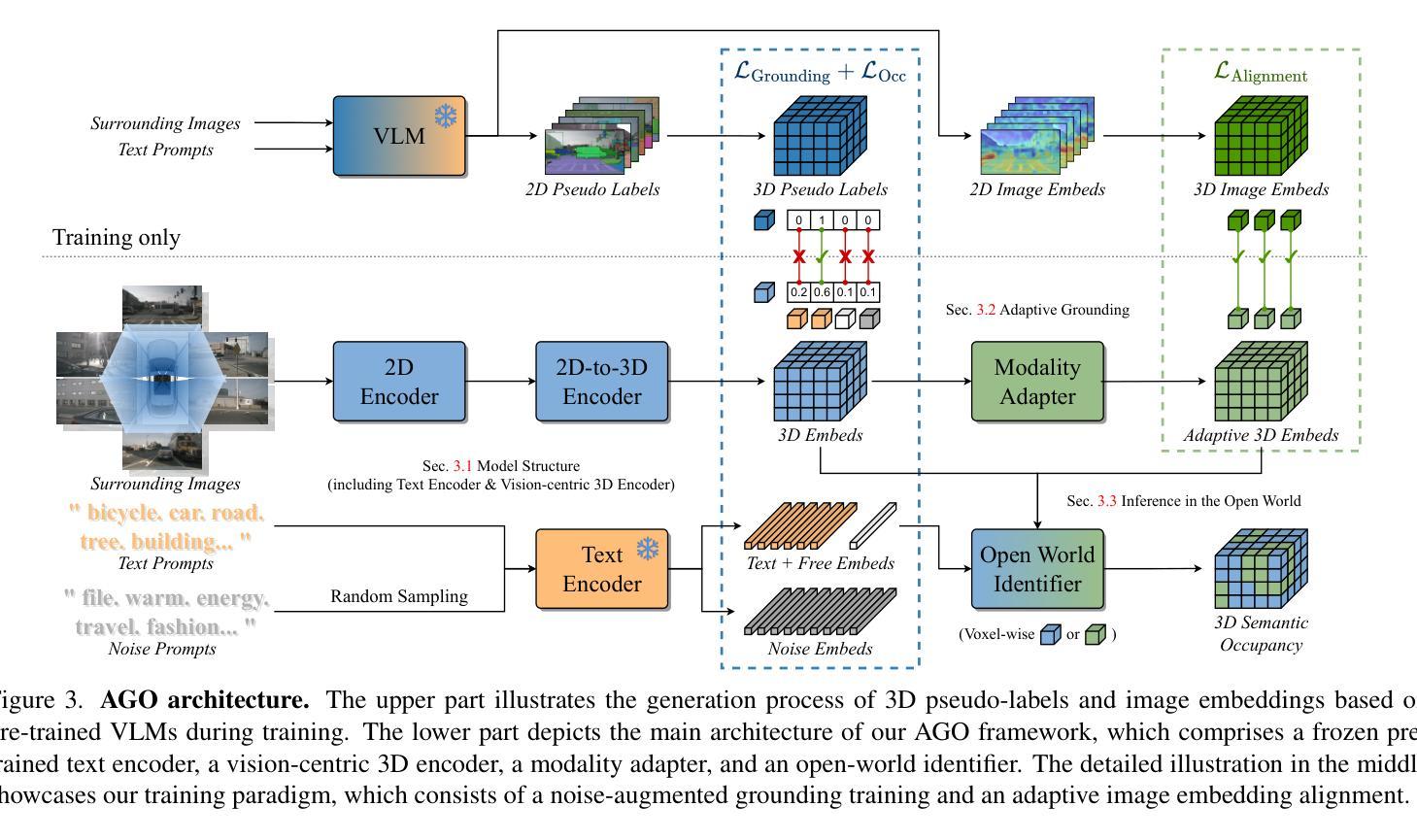
AGO: Adaptive Grounding for Open World 3D Occupancy Prediction
Authors:Peizheng Li, Shuxiao Ding, You Zhou, Qingwen Zhang, Onat Inak, Larissa Triess, Niklas Hanselmann, Marius Cordts, Andreas Zell
Open-world 3D semantic occupancy prediction aims to generate a voxelized 3D representation from sensor inputs while recognizing both known and unknown objects. Transferring open-vocabulary knowledge from vision-language models (VLMs) offers a promising direction but remains challenging. However, methods based on VLM-derived 2D pseudo-labels with traditional supervision are limited by a predefined label space and lack general prediction capabilities. Direct alignment with pretrained image embeddings, on the other hand, fails to achieve reliable performance due to often inconsistent image and text representations in VLMs. To address these challenges, we propose AGO, a novel 3D occupancy prediction framework with adaptive grounding to handle diverse open-world scenarios. AGO first encodes surrounding images and class prompts into 3D and text embeddings, respectively, leveraging similarity-based grounding training with 3D pseudo-labels. Additionally, a modality adapter maps 3D embeddings into a space aligned with VLM-derived image embeddings, reducing modality gaps. Experiments on Occ3D-nuScenes show that AGO improves unknown object prediction in zero-shot and few-shot transfer while achieving state-of-the-art closed-world self-supervised performance, surpassing prior methods by 4.09 mIoU.
开放世界3D语义占用预测旨在从传感器输入生成体素化3D表示,同时识别已知和未知对象。从视觉语言模型(VLM)转移开放词汇知识提供了一个有前途的方向,但仍然具有挑战性。然而,基于VLM衍生的具有传统监督的2D伪标签的方法受限于预定义的标签空间,并且缺乏通用的预测能力。另一方面,与预训练图像嵌入的直接对齐由于VLM中图像和文本表示经常不一致,无法实现可靠性能。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了AGO,这是一种具有自适应定位功能的新型3D占用预测框架,用于处理各种开放世界场景。AGO首先编码周围图像和类别提示为3D和文本嵌入,分别利用基于相似性的定位训练和3D伪标签。此外,模态适配器将3D嵌入映射到与VLM衍生的图像嵌入对齐的空间,减少模态间隙。在Occ3D-nuScenes上的实验表明,AGO在零样本和少样本转移中改进了未知对象的预测,同时在封闭世界自监督情况下达到最先进的性能,比先前的方法高出4.09 mIoU。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了开放世界下的三维语义占用预测技术,该技术旨在从传感器输入生成体素化的三维表示,并识别已知和未知物体。文章指出,从视觉语言模型(VLMs)转移开放词汇知识是一个有前途的方向,但面临挑战。现有方法如基于VLM衍生的二维伪标签和传统监督方法受限于预定义的标签空间,缺乏通用预测能力。直接对齐预训练图像嵌入则由于VLMs中图像和文本表示的不一致性而无法实现可靠性能。为应对这些挑战,本文提出了一种名为AGO的新型三维占用预测框架,具有自适应定位功能,以处理多样化的开放世界场景。AGO通过编码周围图像和类别提示到三维和文本嵌入,利用基于相似性的定位训练和三维伪标签。此外,模态适配器将三维嵌入映射到与VLM衍生的图像嵌入对齐的空间,减少模态差距。在Occ3D-nuScenes的实验显示,AGO在零样本和少样本转移中改进了未知物体的预测,同时实现了最先进的封闭世界自监督性能,超出之前的方法4.09 mIoU。
Key Takeaways
- 开放世界下的三维语义占用预测旨在从传感器输入生成体素化的三维表示,并识别已知和未知物体。
- 从视觉语言模型转移开放词汇知识在这一领域具有潜力,但面临诸多挑战。
- 现有方法受限于预定义的标签空间,缺乏通用预测能力。
- 直接对齐预训练图像嵌入由于表示不一致性而无法实现可靠性能。
- AGO框架通过编码周围图像和类别提示到三维和文本嵌入来解决这些问题。
- AGO利用基于相似性的定位训练和三维伪标签。
点此查看论文截图

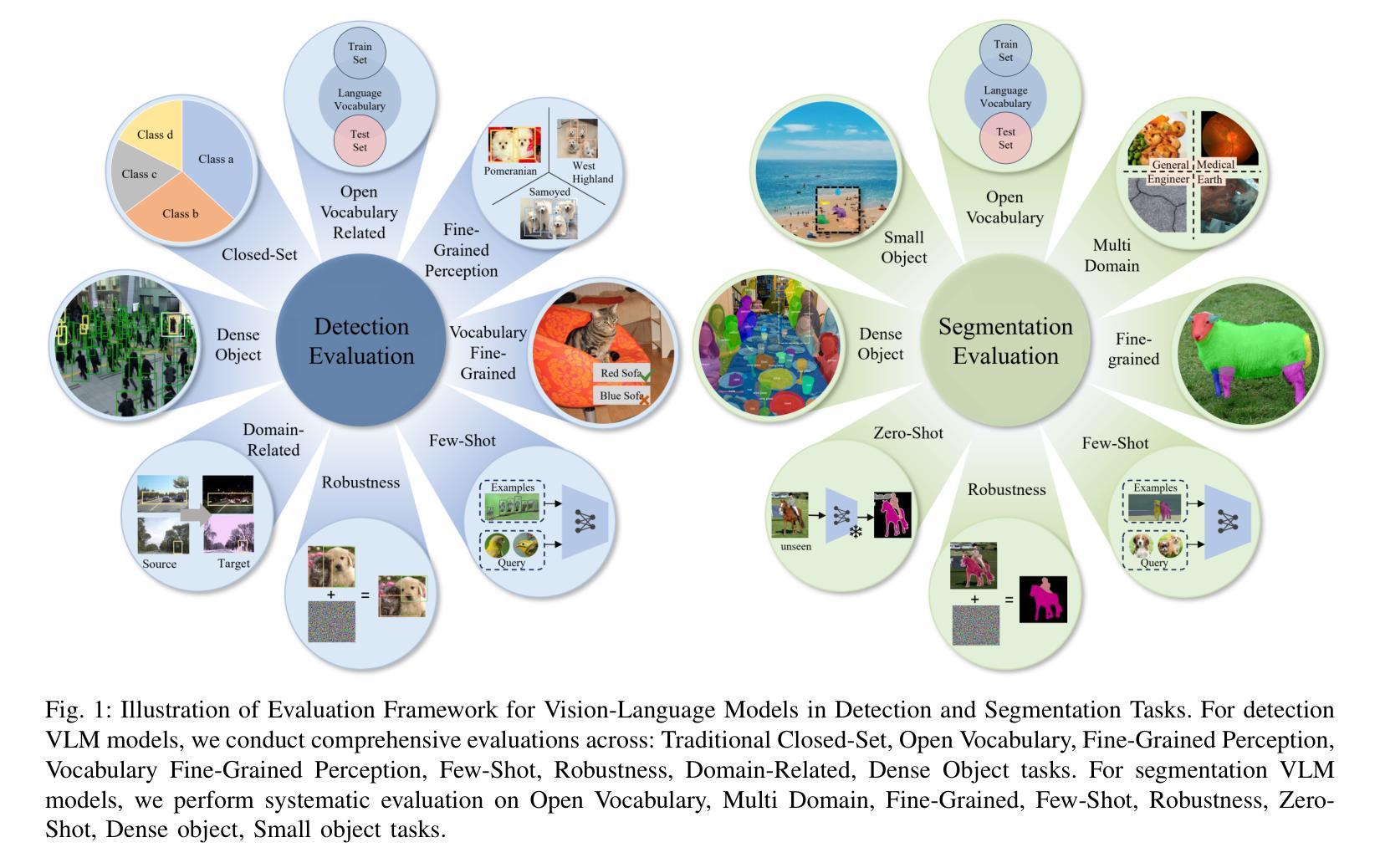
Hierarchical Relation-augmented Representation Generalization for Few-shot Action Recognition
Authors:Hongyu Qu, Ling Xing, Rui Yan, Yazhou Yao, Guo-Sen Xie, Xiangbo Shu
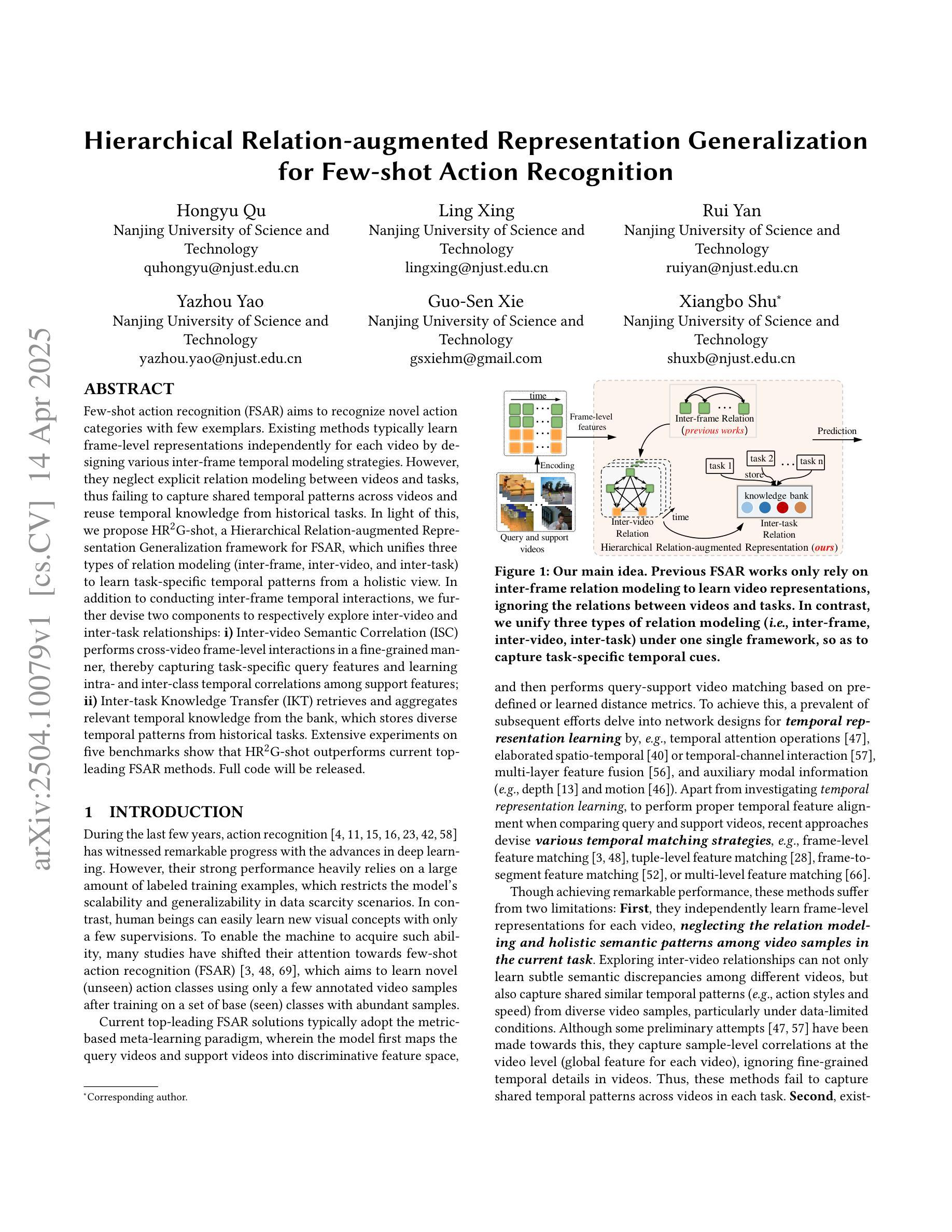
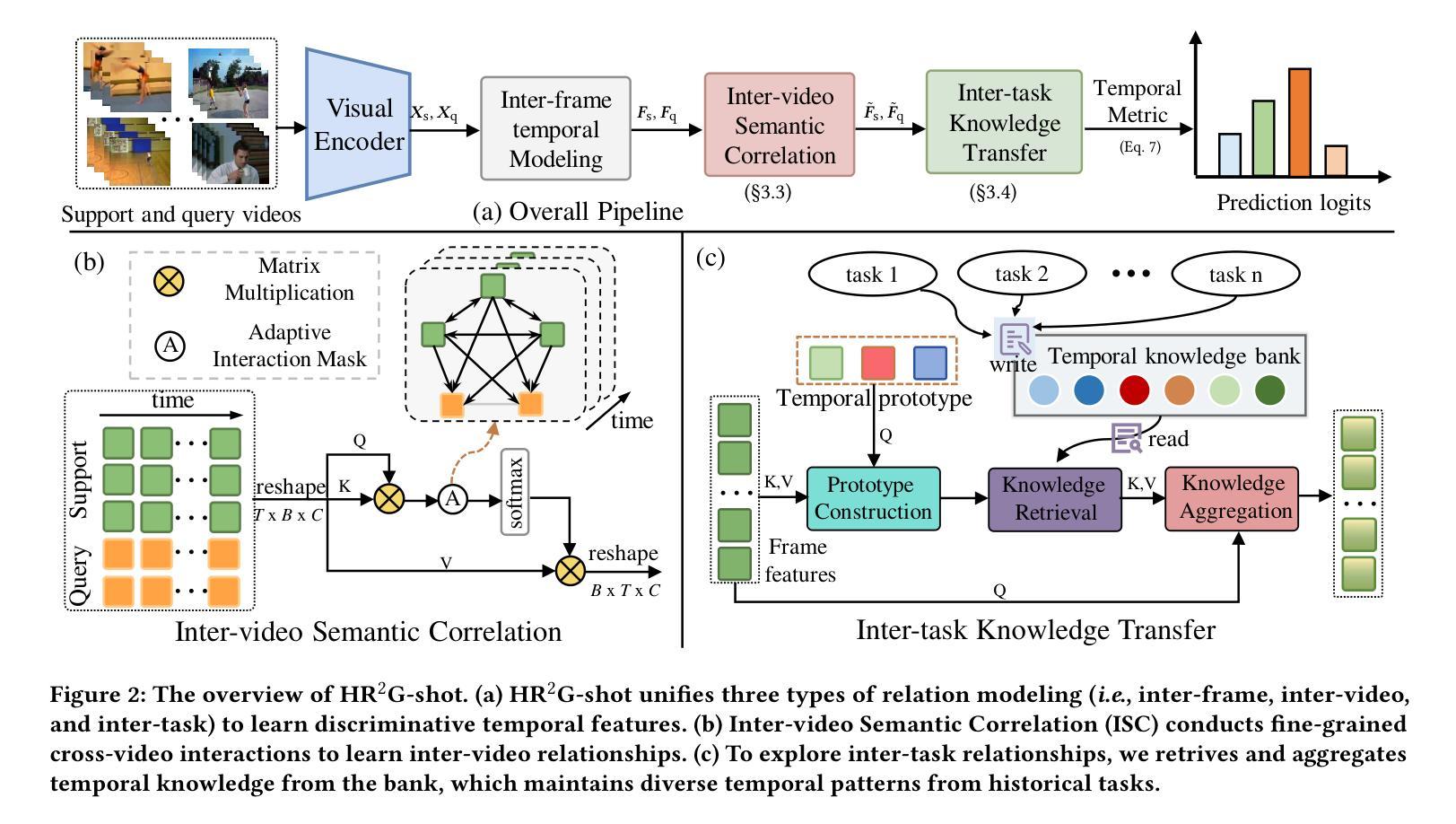
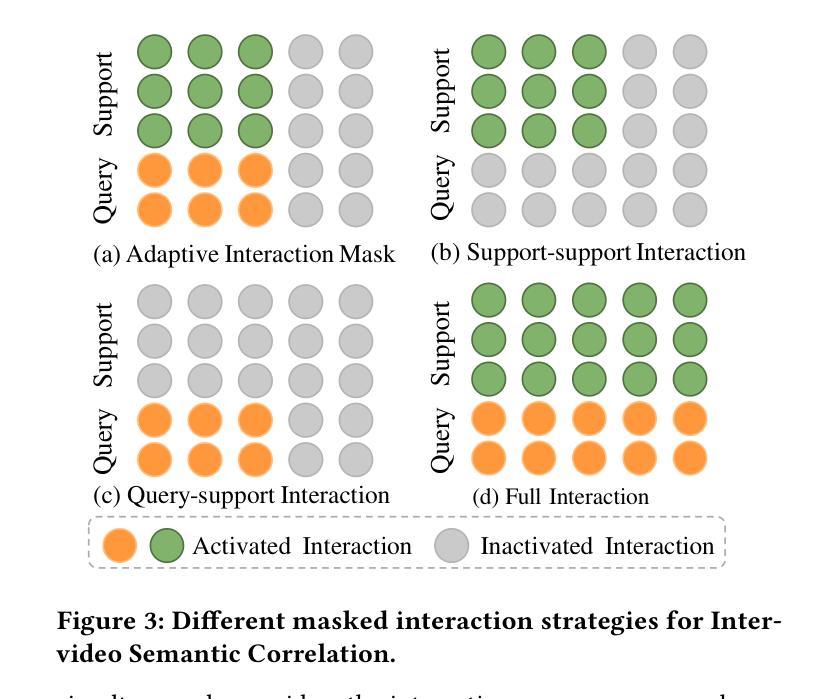
Few-shot action recognition (FSAR) aims to recognize novel action categories with few exemplars. Existing methods typically learn frame-level representations independently for each video by designing various inter-frame temporal modeling strategies. However, they neglect explicit relation modeling between videos and tasks, thus failing to capture shared temporal patterns across videos and reuse temporal knowledge from historical tasks. In light of this, we propose HR2G-shot, a Hierarchical Relation-augmented Representation Generalization framework for FSAR, which unifies three types of relation modeling (inter-frame, inter-video, and inter-task) to learn task-specific temporal patterns from a holistic view. In addition to conducting inter-frame temporal interactions, we further devise two components to respectively explore inter-video and inter-task relationships: i) Inter-video Semantic Correlation (ISC) performs cross-video frame-level interactions in a fine-grained manner, thereby capturing task-specific query features and learning intra- and inter-class temporal correlations among support features; ii) Inter-task Knowledge Transfer (IKT) retrieves and aggregates relevant temporal knowledge from the bank, which stores diverse temporal patterns from historical tasks. Extensive experiments on five benchmarks show that HR2G-shot outperforms current top-leading FSAR methods.
小样动作识别(FSAR)旨在通过少量的样本识别新的动作类别。现有的方法通常通过设计各种帧间时序建模策略,为每个视频独立地学习帧级表示。然而,他们忽略了视频与任务之间的显式关系建模,因此无法捕获跨视频的共享时序模式,也无法重用来自历史任务的时间知识。鉴于此,我们提出了HR2G-shot,这是一个用于FSAR的分层关系增强表示泛化框架,它统一了三种关系建模(帧间、视频间和任务间),以从整体视角学习特定任务的时序模式。除了进行帧间时序交互外,我们还进一步设计了两个组件来分别探索视频间和任务间的关系:一、视频间语义相关性(ISC)以精细的方式执行跨视频帧级交互,从而捕获特定任务的查询特征,并学习支持特征内部和跨类的时序相关性;二、任务间知识转移(IKT)从知识库中检索并聚合相关的时序知识,该知识库存储了来自历史任务的各种时序模式。在五个基准测试上的广泛实验表明,HR2G-shot的性能优于当前领先的FSAR方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
少量样本动作识别(FSAR)旨在通过少量样本识别新型动作类别。现有方法主要通过设计各种帧间时序建模策略独立学习每个视频帧级别的表示,但忽略了视频与任务之间的关系建模,因此无法捕获跨视频的共享时序模式并无法利用历史任务中的时序知识。因此,我们提出HR2G-shot,一个用于FSAR的层次关系增强表示泛化框架,它统一了三种关系建模(帧间、视频间和任务间),从整体上学习特定任务的时序模式。除了进行帧间时序交互外,我们还分别设计了两个组件来探索视频间和任务间的关系:一是跨视频语义相关性(ISC),以精细的方式执行跨视频帧级别的交互,从而捕获特定任务的查询特征,并学习支持特征中的类内和类间时序相关性;二是任务间知识转移(IKT),从知识库中检索和聚合相关的时序知识,该知识库存储了来自历史任务的各种时序模式。在五个基准测试上的广泛实验表明,HR2G-shot优于当前领先的FSAR方法。
Key Takeaways
- Few-shot action recognition (FSAR) 旨在通过少量样本识别新型动作类别。
- 现有方法主要关注帧级别的独立表示学习,忽略了视频与任务之间的关系建模。
- HR2G-shot框架集成了三种关系建模(帧间、视频间和任务间),以全面学习特定任务的时序模式。
- HR2G-shot通过跨视频语义相关性(ISC)和任务间知识转移(IKT)两个组件来探索视频间和任务间的关系。
- ISC执行精细的跨视频帧级别交互,捕获特定任务的查询特征并学习类内和类间的时序相关性。
- IKT从知识库中检索和聚合相关时序知识,该知识库包含历史任务中的多样时序模式。
点此查看论文截图
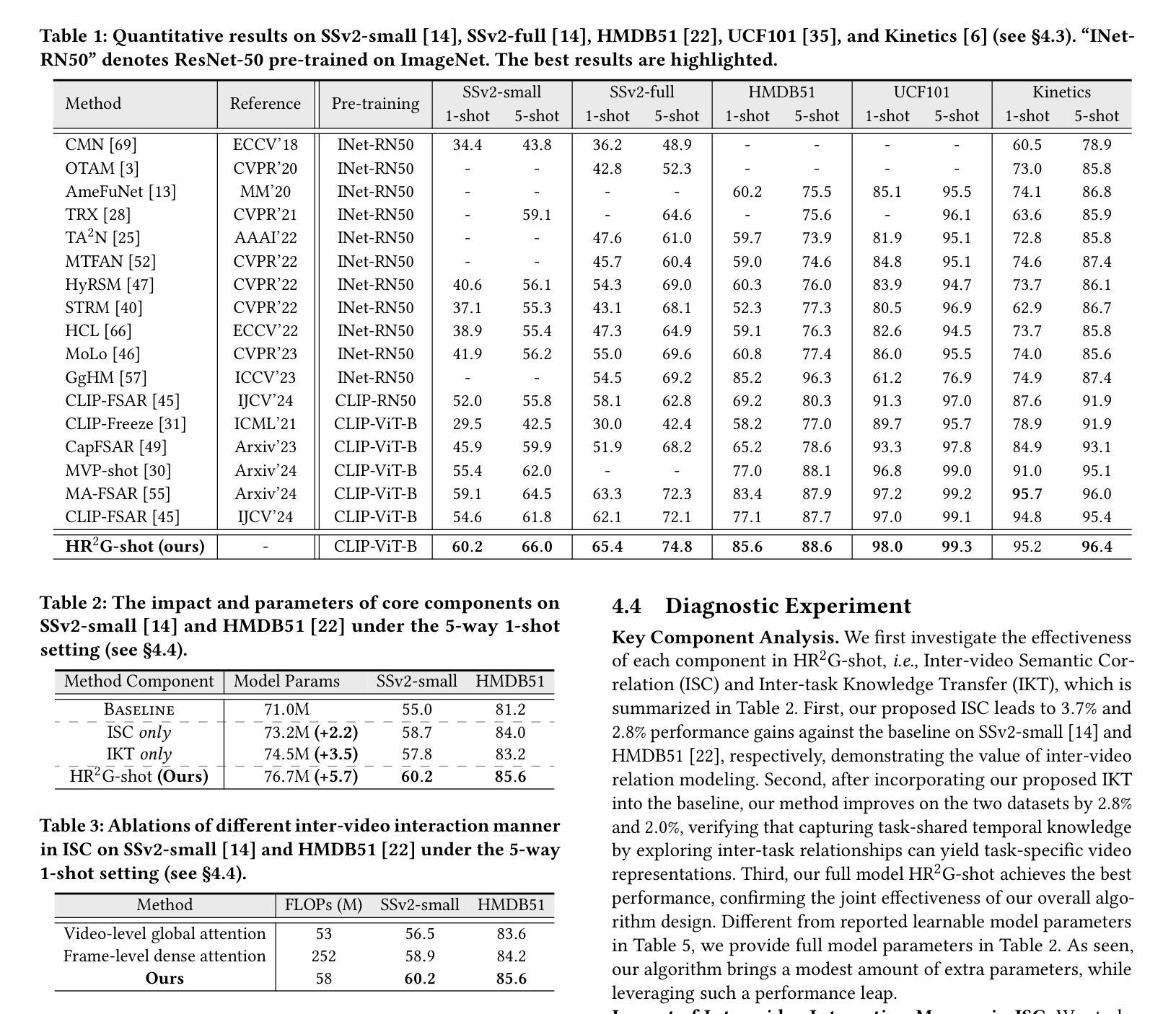
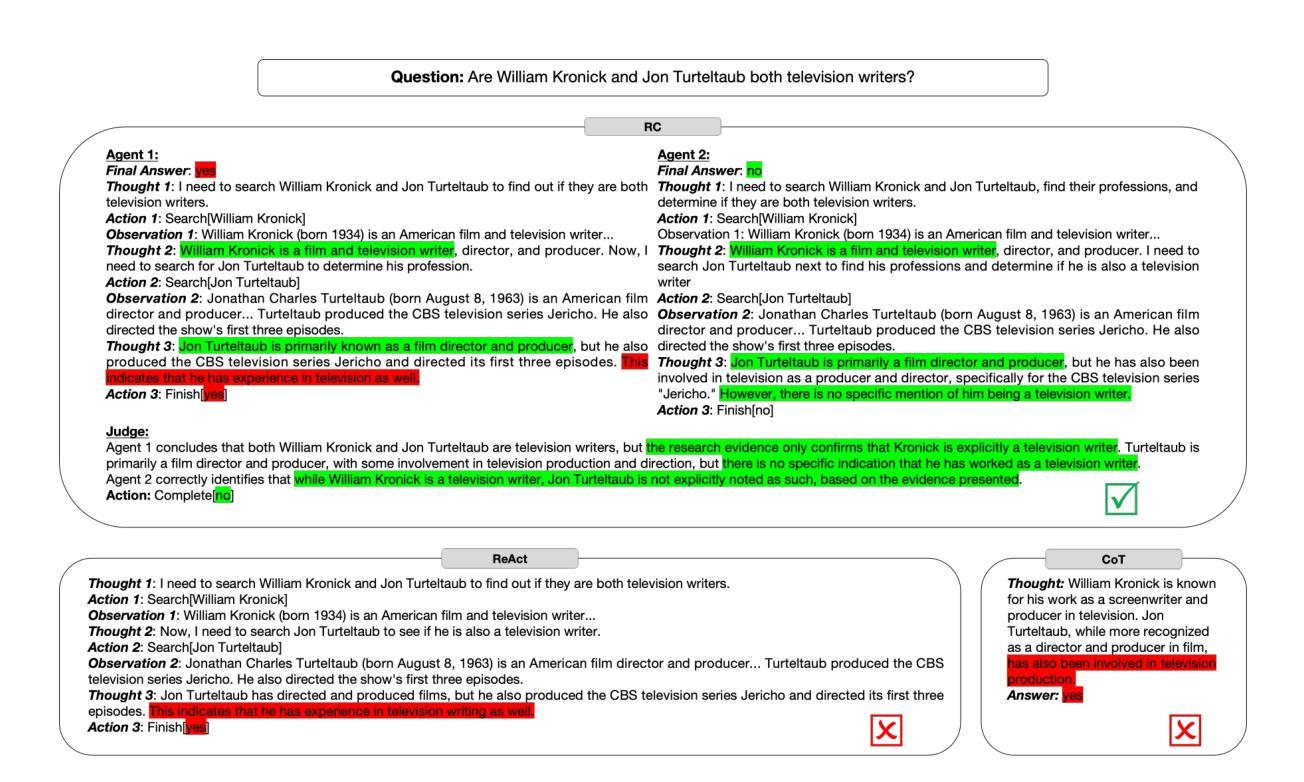
Reasoning Court: Combining Reasoning, Action, and Judgment for Multi-Hop Reasoning
Authors:Jingtian Wu, Claire Cardie
While large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong capabilities in tasks like question answering and fact verification, they continue to suffer from hallucinations and reasoning errors, especially in multi-hop tasks that require integration of multiple information sources. Current methods address these issues through retrieval-based techniques (grounding reasoning in external evidence), reasoning-based approaches (enhancing coherence via improved prompting), or hybrid strategies combining both elements. One prominent hybrid method, ReAct, has outperformed purely retrieval-based or reasoning-based approaches; however, it lacks internal verification of intermediate reasoning steps, allowing potential errors to propagate through complex reasoning tasks. In this paper, we introduce Reasoning Court (RC), a novel framework that extends iterative reasoning-and-retrieval methods, such as ReAct, with a dedicated LLM judge. Unlike ReAct, RC employs this judge to independently evaluate multiple candidate answers and their associated reasoning generated by separate LLM agents. The judge is asked to select the answer that it considers the most factually grounded and logically coherent based on the presented reasoning and evidence, or synthesizes a new answer using available evidence and its pre-trained knowledge if all candidates are inadequate, flawed, or invalid. Evaluations on multi-hop benchmarks (HotpotQA, MuSiQue) and fact-verification (FEVER) demonstrate that RC consistently outperforms state-of-the-art few-shot prompting methods without task-specific fine-tuning.
大型语言模型(LLM)在问答和事实核查等任务中表现出了强大的能力,但它们仍然存在着幻想和推理错误的问题,特别是在需要整合多个信息源的多跳任务中。当前的方法通过基于检索的技术(以外部证据为推理基础)、基于推理的方法(通过改进提示来提高连贯性)或结合两者的混合策略来解决这些问题。一种突出的混合方法ReAct已经超越了纯粹的检索或基于推理的方法;然而,它缺乏对中间推理步骤的内部验证,使得潜在错误可能通过复杂的推理任务而传播。在本文中,我们引入了Reasoning Court(RC),这是一个新的框架,它将迭代推理和检索方法(如ReAct)与专用的LLM法官相结合。不同于ReAct,RC使用法官独立评估多个候选答案及其相关的推理,这些答案和推理由单独的LLM代理生成。法官被要求选择它认为最基于事实、逻辑上连贯的答案,该答案基于提供的推理和证据,或者当所有候选答案都不足、有缺陷或无效时,利用可用证据和其预训练知识合成新的答案。在Multi-hop基准测试(HotpotQA、MuSiQue)和事实核查(FEVER)上的评估表明,RC始终优于最新的少提示提示方法,且无需针对特定任务进行微调。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Reasoning Court(RC)的新框架,它扩展了迭代推理和检索方法(如ReAct),并引入了一个独立的LLM法官来评估多个候选答案及其相关推理。RC的法官能够基于提供的推理和证据,选择它认为最符合事实和逻辑连贯性的答案,或者在所有候选答案都不足、有缺陷或无效时,利用可用证据和预训练知识合成新的答案。在多跳基准测试(HotpotQA、MuSiQue)和事实验证(FEVER)上的评估表明,RC在无需特定任务微调的情况下,始终优于最新的少样本提示方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型(LLMs)在问答和事实验证等任务中表现出强大的能力,但在需要整合多个信息源的多跳任务中仍存在幻觉和推理错误。
- 当前方法通过检索、推理或混合策略来解决这些问题,但存在误差传播风险。
- ReAct等迭代推理和检索方法得到了扩展,引入了一个新的框架Reasoning Court(RC)。
- RC的关键特性是引入了一个独立的LLM法官,用于评估多个候选答案及其相关推理,选择最符合事实和逻辑连贯性的答案。
- 如果所有候选答案都不足、有缺陷或无效,RC的法官能够利用可用证据和预训练知识合成新的答案。
- 在多跳基准测试和事实验证上的评估表明,RC在无需任务特定微调的情况下表现优异。
- RC框架为改进LLMs在处理复杂推理任务时的性能提供了新的方向。
点此查看论文截图

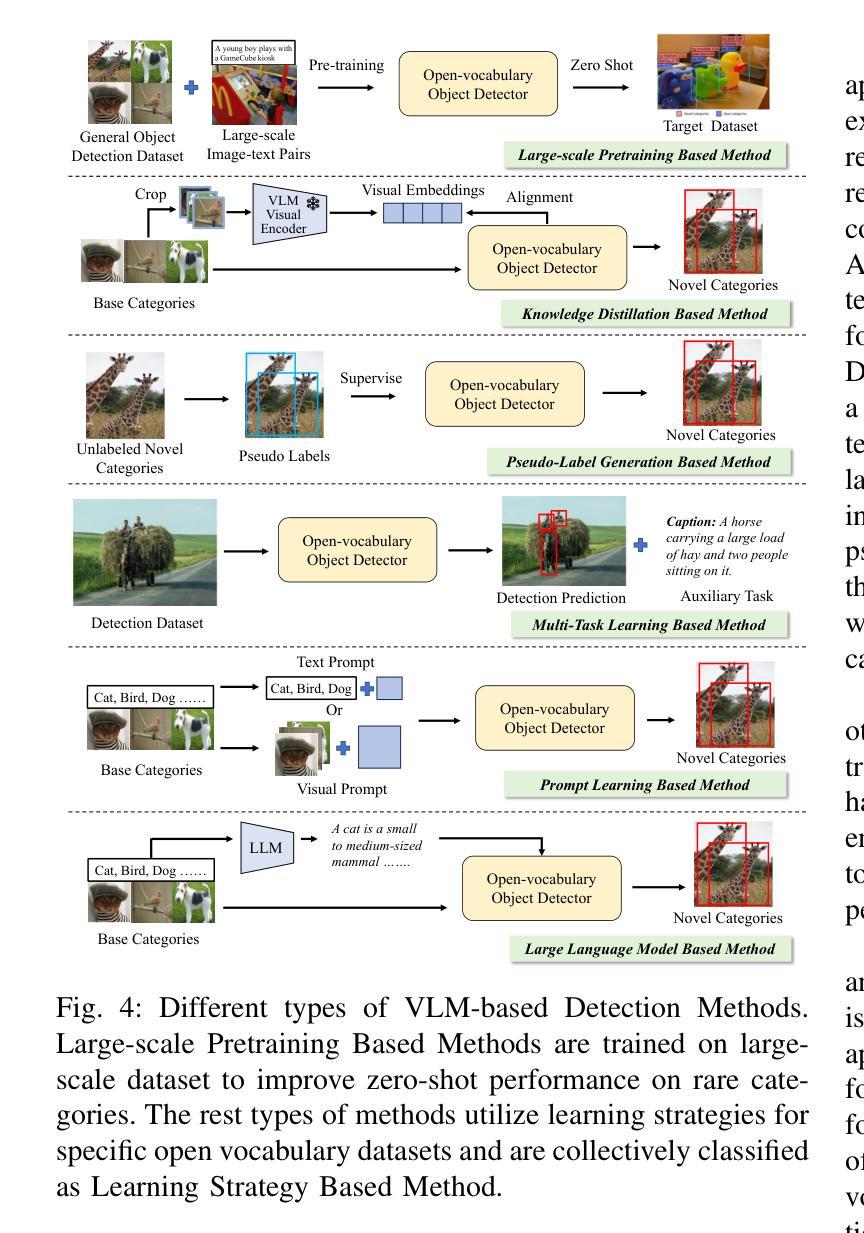
Vision-Language Model for Object Detection and Segmentation: A Review and Evaluation
Authors:Yongchao Feng, Yajie Liu, Shuai Yang, Wenrui Cai, Jinqing Zhang, Qiqi Zhan, Ziyue Huang, Hongxi Yan, Qiao Wan, Chenguang Liu, Junzhe Wang, Jiahui Lv, Ziqi Liu, Tengyuan Shi, Qingjie Liu, Yunhong Wang
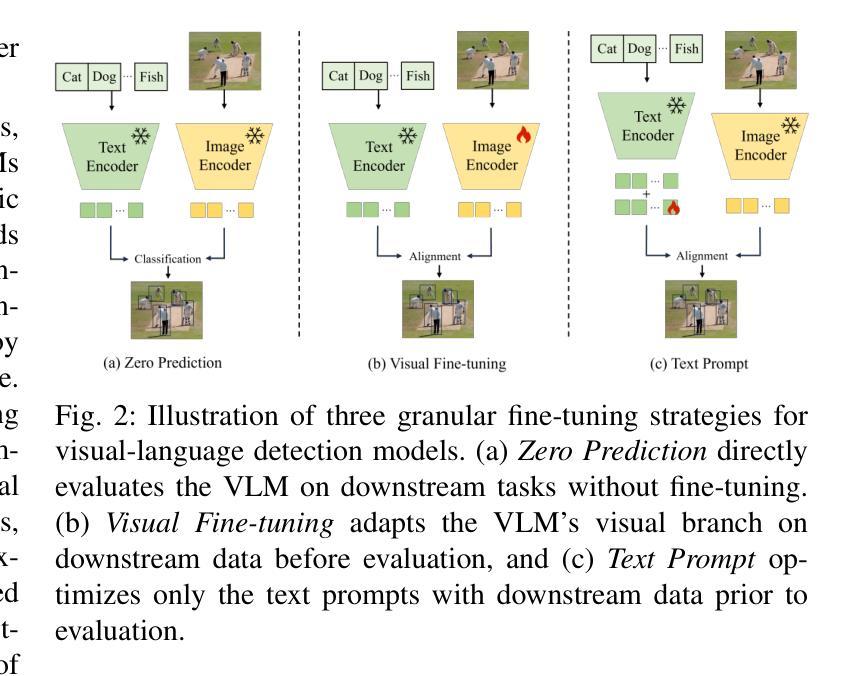
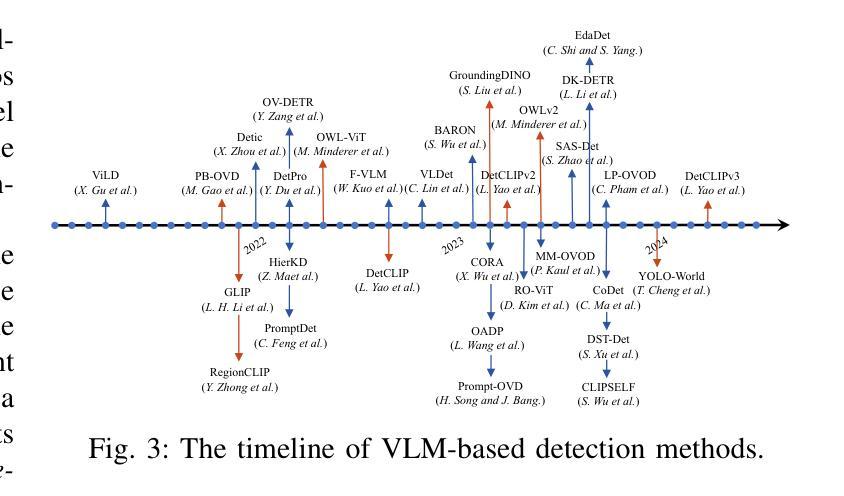
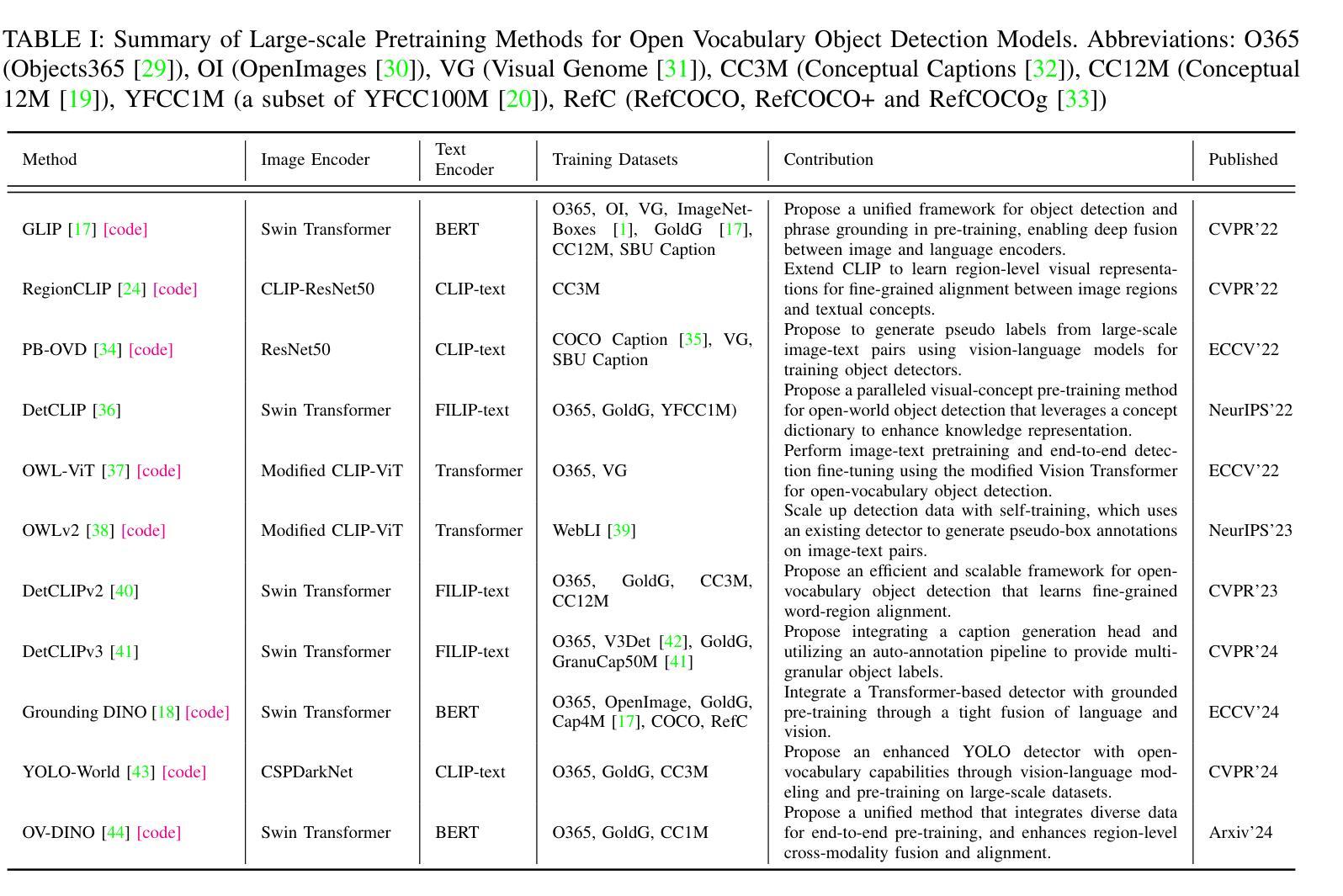
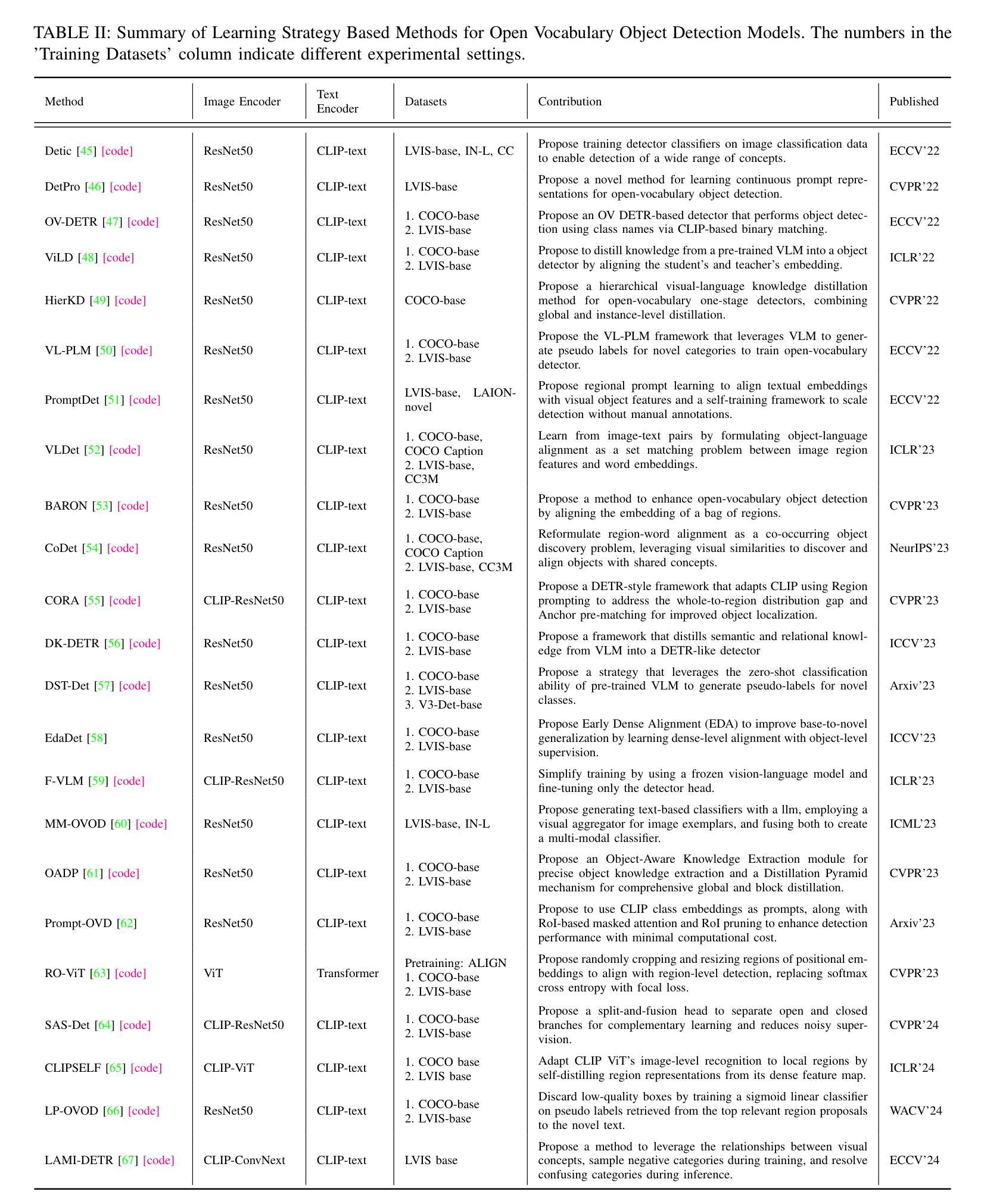
Vision-Language Model (VLM) have gained widespread adoption in Open-Vocabulary (OV) object detection and segmentation tasks. Despite they have shown promise on OV-related tasks, their effectiveness in conventional vision tasks has thus far been unevaluated. In this work, we present the systematic review of VLM-based detection and segmentation, view VLM as the foundational model and conduct comprehensive evaluations across multiple downstream tasks for the first time: 1) The evaluation spans eight detection scenarios (closed-set detection, domain adaptation, crowded objects, etc.) and eight segmentation scenarios (few-shot, open-world, small object, etc.), revealing distinct performance advantages and limitations of various VLM architectures across tasks. 2) As for detection tasks, we evaluate VLMs under three finetuning granularities: \textit{zero prediction}, \textit{visual fine-tuning}, and \textit{text prompt}, and further analyze how different finetuning strategies impact performance under varied task. 3) Based on empirical findings, we provide in-depth analysis of the correlations between task characteristics, model architectures, and training methodologies, offering insights for future VLM design. 4) We believe that this work shall be valuable to the pattern recognition experts working in the fields of computer vision, multimodal learning, and vision foundation models by introducing them to the problem, and familiarizing them with the current status of the progress while providing promising directions for future research. A project associated with this review and evaluation has been created at https://github.com/better-chao/perceptual_abilities_evaluation.
视觉语言模型(VLM)在开放词汇(OV)目标检测和分割任务中得到了广泛应用。尽管它们在OV相关任务上显示出潜力,但它们在传统视觉任务中的有效性迄今为止尚未得到评估。在这项工作中,我们对基于VLM的检测和分割进行了系统综述,将VLM视为基础模型,首次对多个下游任务进行了全面评估:1)评估涵盖八种检测场景(封闭集检测、域适应、拥挤目标等)和八种分割场景(小样本、开放世界、小目标等),揭示了各种VLM架构在不同任务之间的不同性能优势和局限性。2)对于检测任务,我们在三种微调粒度下评估VLM:\emph{零预测}、\emph{视觉微调}和\emph{文本提示},并进一步分析不同微调策略在不同任务下对性能的影响。3)基于实证发现,我们对任务特性、模型架构和训练方法之间的关联性进行了深入分析,为未来的VLM设计提供了见解。4)我们相信,这项工作对于计算机视觉、多模态学习和视觉基础模型领域的模式识别专家来说将具有很高的价值,通过引入问题,让他们熟悉当前的研究进展,并为未来的研究提供有前景的方向。与此次审查和评估相关的项目已在https://github.com/better-chao/perceptual_abilities_evaluation创建。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF A Review and Evaluation about Vision-Language Model for Object Detection and Segmentation
Summary
本文系统评述了基于Vision-Language Model(VLM)的检测和分割技术。研究对VLM在多个下游任务上的表现进行了全面评估,包括封闭集检测、域适应、拥挤对象等八个检测场景,以及少样本、开放世界、小物体等八个分割场景。此外,还探讨了不同微调策略对性能的影响,并为未来VLM设计提供了深入的分析和见解。
Key Takeaways
- VLM在Open-Vocabulary(OV)物体检测和分割任务中得到广泛应用,但在传统视觉任务中的效果尚未评估。
- 首次对VLM基础的检测和分割进行全面评价,涵盖多个下游任务。
- 在检测任务中,评估了VLM在零预测、视觉微调、文本提示三种微调粒度下的性能。
- 发现不同微调策略对性能的影响,并提供任务特性、模型架构、训练方法的深度分析。
点此查看论文截图

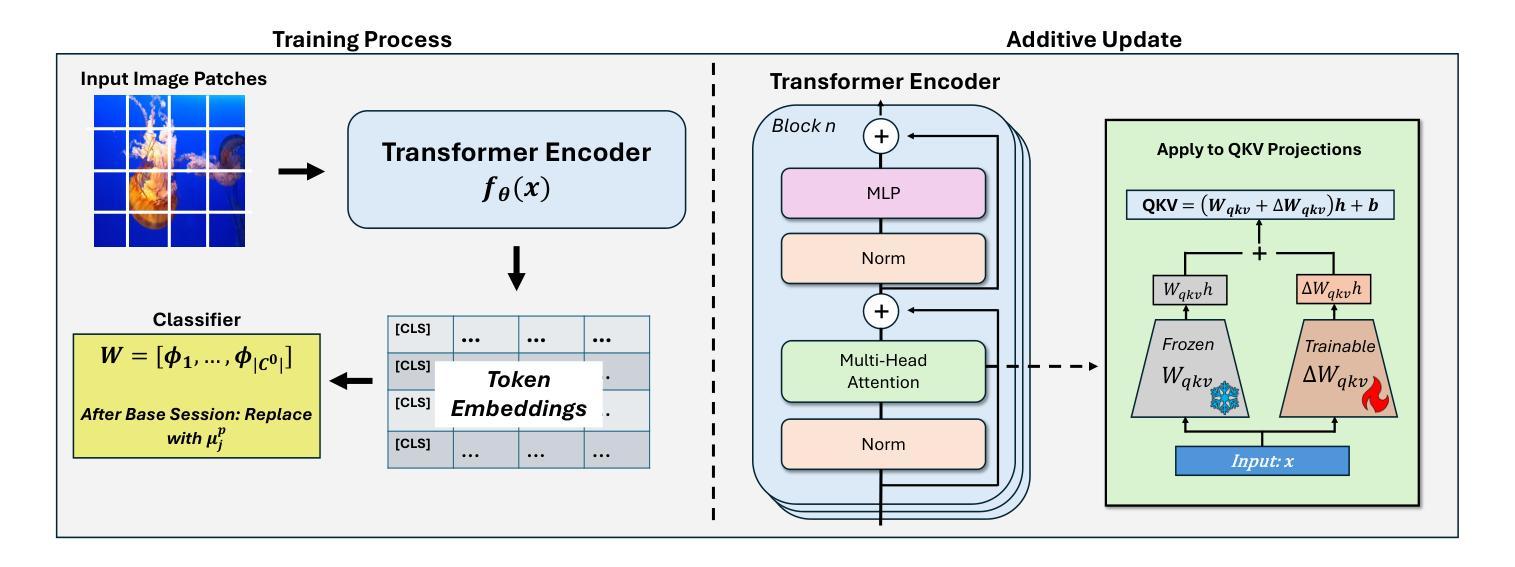
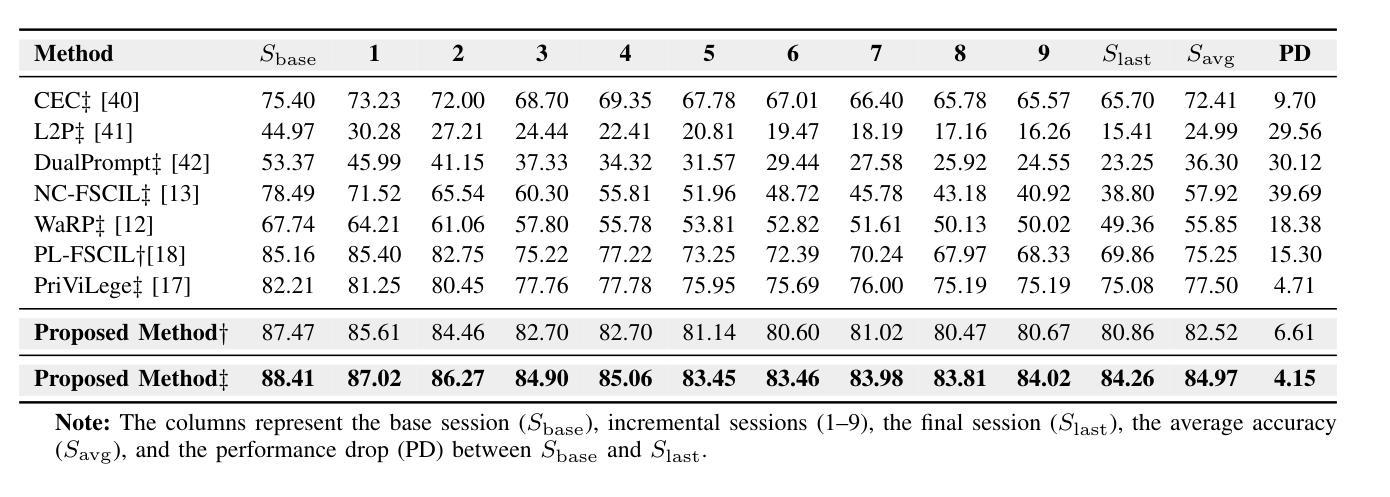
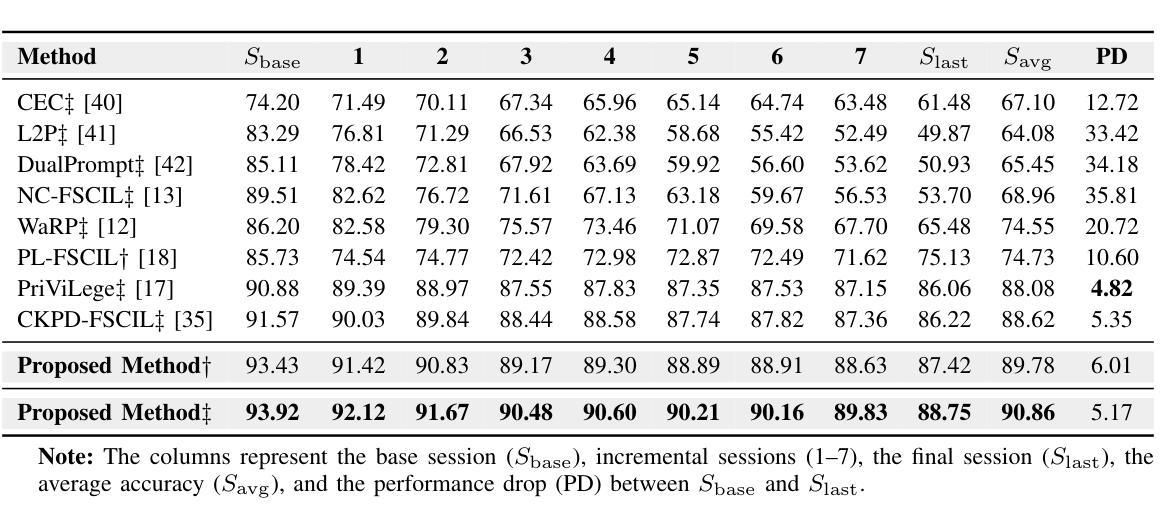
Adaptive Additive Parameter Updates of Vision Transformers for Few-Shot Continual Learning
Authors:Kyle Stein, Andrew Arash Mahyari, Guillermo Francia III, Eman El-Sheikh
Integrating new class information without losing previously acquired knowledge remains a central challenge in artificial intelligence, often referred to as catastrophic forgetting. Few-shot class incremental learning (FSCIL) addresses this by first training a model on a robust dataset of base classes and then incrementally adapting it in successive sessions using only a few labeled examples per novel class. However, this approach is prone to overfitting on the limited new data, which can compromise overall performance and exacerbate forgetting. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective novel FSCIL framework that leverages a frozen Vision Transformer (ViT) backbone augmented with parameter-efficient additive updates. Our approach freezes the pre-trained ViT parameters and selectively injects trainable weights into the self-attention modules via an additive update mechanism. This design updates only a small subset of parameters to accommodate new classes without sacrificing the representations learned during the base session. By fine-tuning a limited number of parameters, our method preserves the generalizable features in the frozen ViT while reducing the risk of overfitting. Furthermore, as most parameters remain fixed, the model avoids overwriting previously learned knowledge when small novel data batches are introduced. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach yields state-of-the-art performance compared to baseline FSCIL methods.
将新类别信息集成到模型中而不丢失先前获取的知识仍然是人工智能领域的一个核心挑战,通常被称为灾难性遗忘。少样本类别增量学习(FSCIL)通过首先使用基础类别的稳健数据集训练模型,然后逐步仅使用每个新类别的少量标记样本对其进行适应来解决这个问题。然而,这种方法对新数据的过度拟合倾向较高,可能会损害整体性能并加剧遗忘问题。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种简单有效的FSCIL新框架,该框架利用冻结的Vision Transformer(ViT)主干并辅以高效的参数添加更新。我们的方法冻结了预训练的ViT参数,并通过添加更新机制有选择地将可训练权重注入自注意力模块。这种设计只更新一小部分参数以适应新类别,同时不牺牲基础会话期间学习的表示。通过微调有限数量的参数,我们的方法在保留冻结ViT的通用特征的同时降低了过度拟合的风险。此外,由于大多数参数保持不变,当引入少量新数据批次时,模型避免了覆盖先前学习的知识。在基准数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法与基线FSCIL方法相比达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的少样本类增量学习(FSCIL)框架,该框架利用冻结的Vision Transformer(ViT)主干网,并通过参数有效的添加更新进行增强。该方法在预训练的ViT参数冻结的基础上,通过添加更新机制有选择地将可训练权重注入自注意力模块。该设计仅更新一小部分参数以适应新类别,同时保留基础会话期间学习的表示。通过微调有限数量的参数,该方法保留了冻结ViT的通用特征,并降低了过度拟合的风险。此外,由于大部分参数保持不变,当引入少量新数据批次时,模型避免了覆盖先前学习的知识。在基准数据集上的实验表明,该方法与基线FSCIL方法相比具有最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 少样本类增量学习(FSCIL)是人工智能领域的一个重要挑战,旨在整合新类别信息而不会丢失先前获得的知识。
- 本文提出了一种新的FSCIL框架,利用冻结的Vision Transformer(ViT)主干网,通过参数有效的添加更新进行增强。
- 该方法通过冻结预训练的ViT参数并仅更新一小部分参数以适应新类别,同时保留基础会话期间学习的表示。
- 通过微调有限数量的参数,该方法在保留通用特征的同时降低了过度拟合的风险。
- 大部分参数保持不变,使得模型在引入少量新数据批次时避免覆盖先前学习的知识。
- 基准数据集上的实验表明,该方法具有最佳性能,优于其他FSCIL方法。
点此查看论文截图

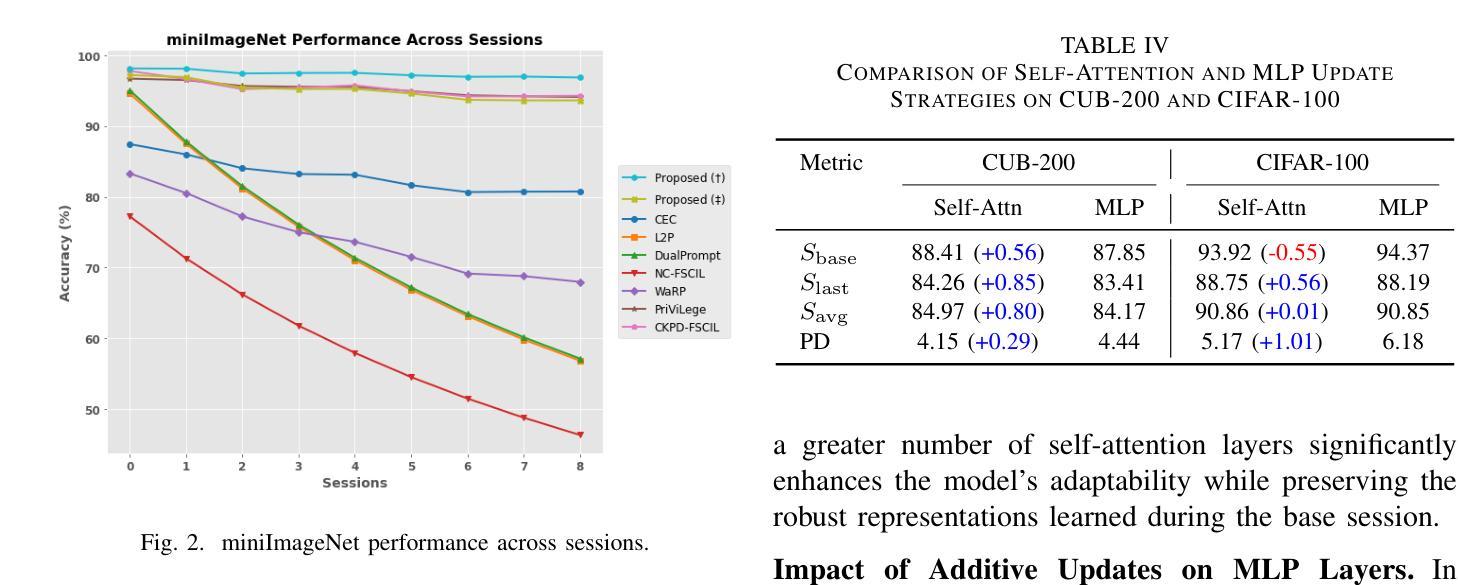
Rethinking Few-Shot Fusion: Granular Ball Priors Enable General-Purpose Deep Image Fusion
Authors:Minjie Deng, Yan Wei, Hao Zhai, An Wu, Yuncan Ouyang, Qianyao Peng
In image fusion tasks, due to the lack of real fused images as priors, most deep learning-based fusion methods obtain global weight features from original images in large-scale data pairs to generate images that approximate real fused images. However, unlike previous studies, this paper utilizes Granular Ball adaptation to extract features in the brightness space as priors for deep networks, enabling the fusion network to converge quickly and complete the fusion task. This leads to few-shot training for a general image fusion network, and based on this, we propose the GBFF fusion method. According to the information expression division of pixel pairs in the original fused image, we classify pixel pairs with significant performance as the positive domain and non-significant pixel pairs as the boundary domain. We perform split inference in the brightness space using Granular Ball adaptation to compute weights for pixels that express information to varying degrees, generating approximate supervision images that provide priors for the neural network in the structural brightness space. Additionally, the extracted global saliency features also adaptively provide priors for setting the loss function weights of each image in the network, guiding the network to converge quickly at both global and pixel levels alongside the supervised images, thereby enhancing the expressiveness of the fused images. Each modality only used 10 pairs of images as the training set, completing the fusion task with a limited number of iterations. Experiments validate the effectiveness of the algorithm and theory, and qualitative and quantitative comparisons with SOTA methods show that this approach is highly competitive in terms of fusion time and image expressiveness.
在图像融合任务中,由于缺乏真实的融合图像作为先验知识,大多数基于深度学习的方法都是从大规模数据对的原始图像中提取全局权重特征,以生成近似真实的融合图像。然而,不同于以往的研究,本文利用粒球适应法提取亮度空间中的特征作为深度网络的先验知识,使融合网络能够快速收敛并完成融合任务。这导致了对通用图像融合网络进行小样本训练,并基于此我们提出了GBFF融合方法。根据原始融合图像中像素对的信息表达划分,我们将表现显著的像素对分类为正向域,将非显著的像素对分类为边界域。我们在亮度空间中使用粒球适应法进行分割推理,计算不同程度表达信息的像素权重,生成近似监督图像,为神经网络在结构亮度空间中提供先验知识。此外,提取的全局显著性特征也自适应地为设置网络中每张图像的损失函数权重提供先验知识,引导网络在全局和像素级别上快速收敛,同时结合监督图像,从而提高融合图像的表达性。每种模态仅使用10对图像作为训练集,在有限的迭代次数中完成融合任务。实验验证了算法和理论的有效性,与最先进方法的定性和定量比较表明,该方法在融合时间和图像表达方面具有很强的竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于Granular Ball适应性的图像融合方法,通过提取亮度空间特征作为深度网络的先验信息,实现快速融合任务。利用像素对的信息表达分类,将具有显著性能的像素对归为正域,非显著像素对归为边界域。通过分割推理计算不同表达程度的像素权重,生成近似监督图像,为网络提供结构亮度空间的先验信息。同时,提取的全局显著性特征自适应地为设置网络中的每个图像损失函数权重提供先验知识,从而在全局和像素级别快速引导网络收敛。仅使用少量图像对即可完成融合任务。实验验证了算法和理论的有效性,与最新方法的定性和定量比较表明,该方法在融合时间和图像表现力方面表现出高度竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 利用Granular Ball适应性提取亮度空间特征作为深度网络的先验信息。
- 通过分类像素对实现快速融合任务,显著性能像素对归为正域,非显著像素对归为边界域。
- 通过分割推理计算像素权重,生成近似监督图像,为网络提供结构亮度空间的先验。
- 提取的全局显著性特征自适应地设置网络中的损失函数权重。
- 仅需少量图像对即可完成融合任务,提高了效率。
- 实验验证了算法和理论的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

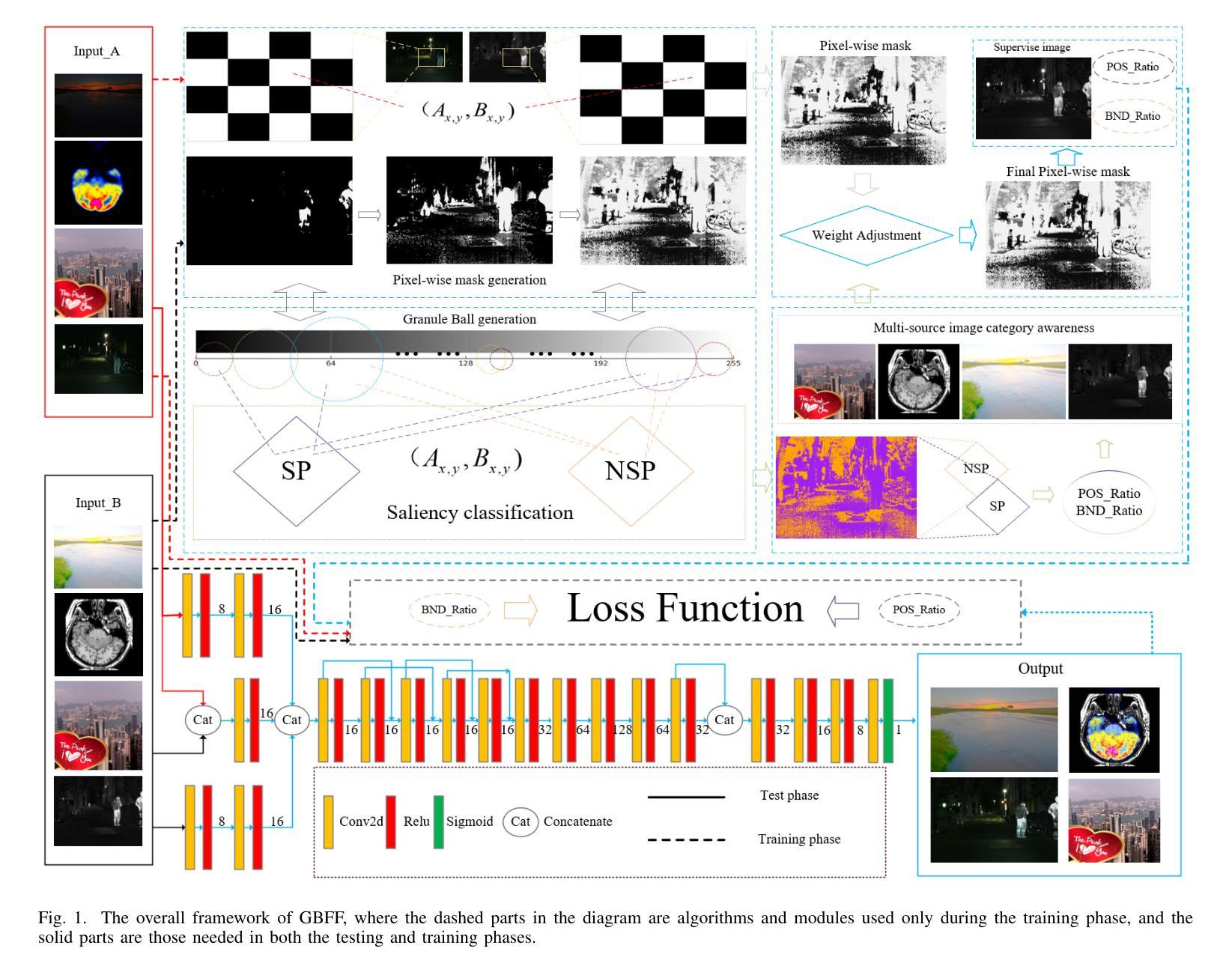


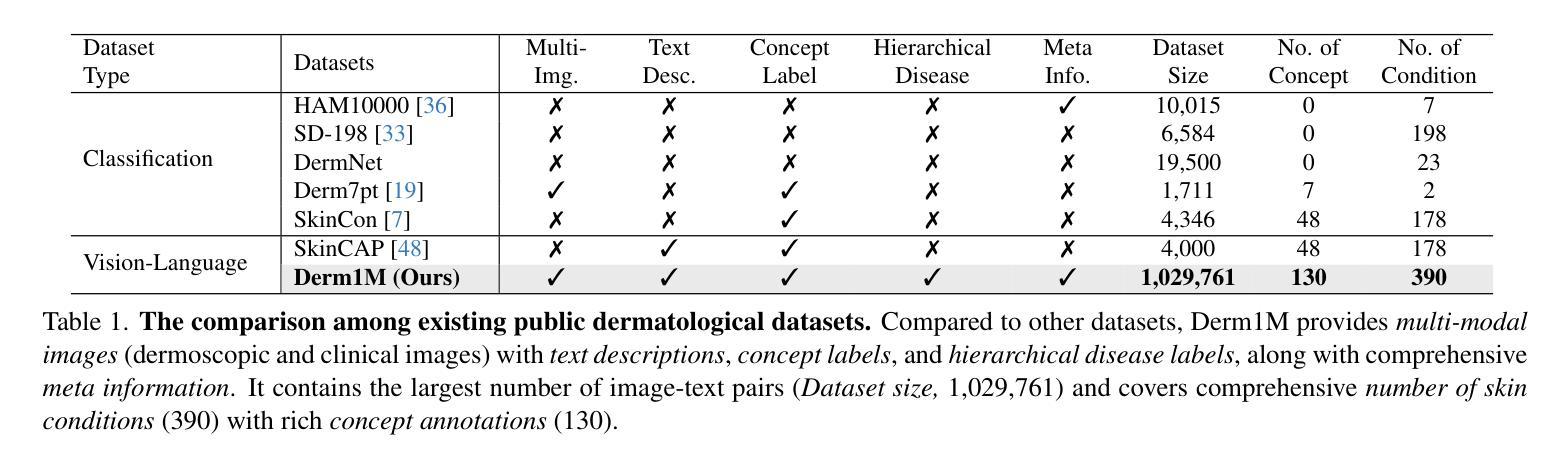
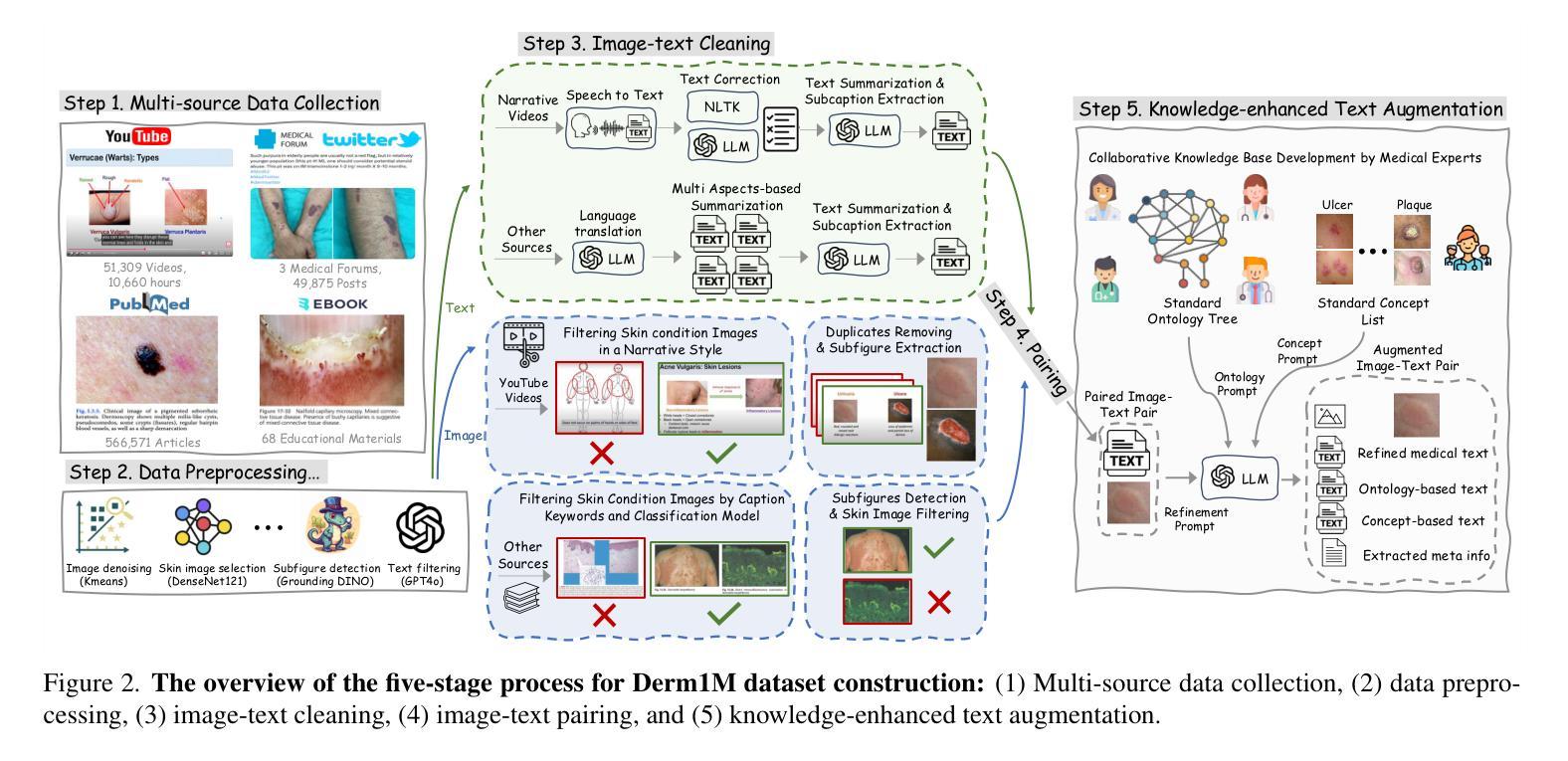
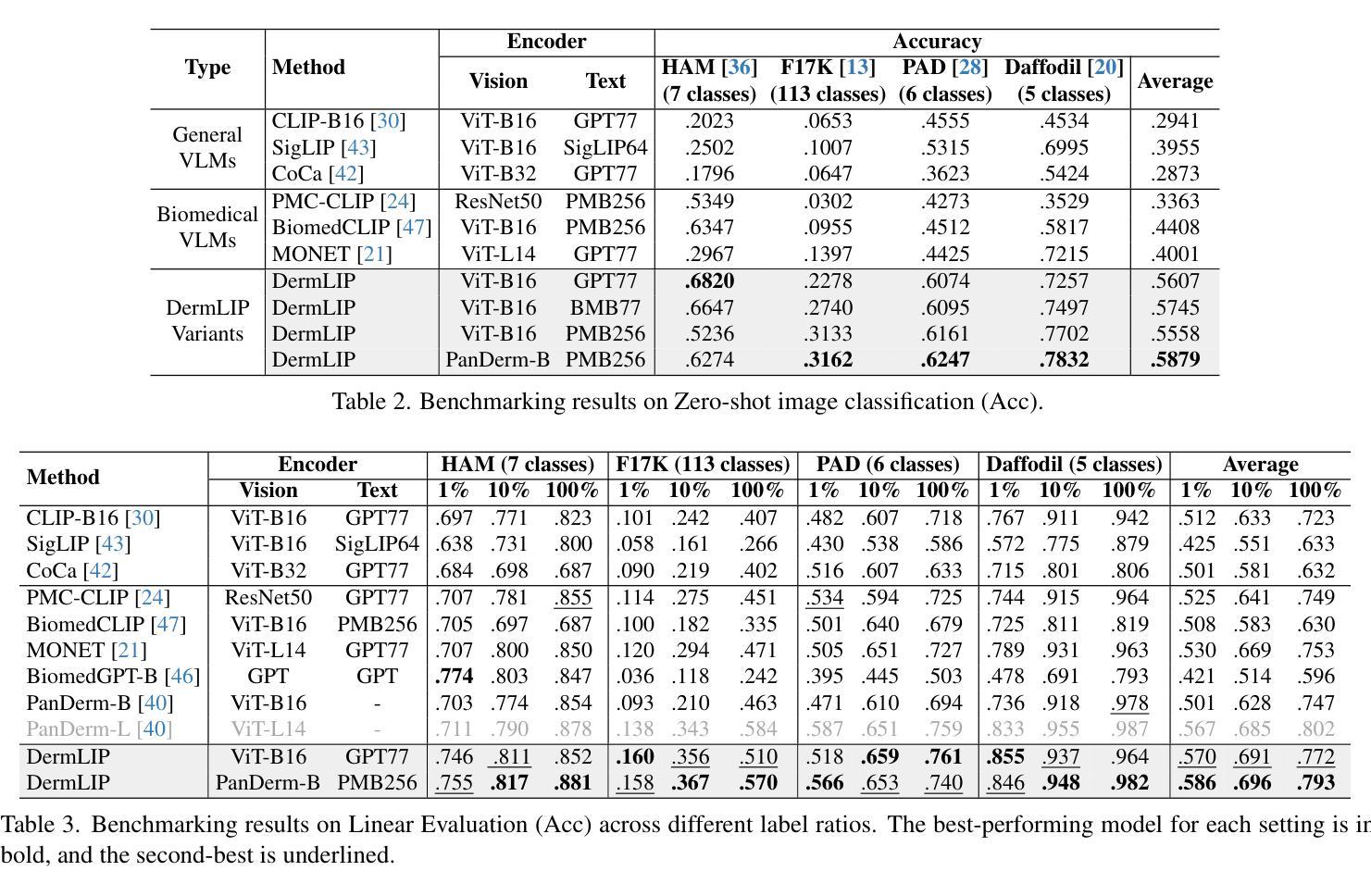
Derm1M: A Million-scale Vision-Language Dataset Aligned with Clinical Ontology Knowledge for Dermatology
Authors:Siyuan Yan, Ming Hu, Yiwen Jiang, Xieji Li, Hao Fei, Philipp Tschandl, Harald Kittler, Zongyuan Ge
The emergence of vision-language models has transformed medical AI, enabling unprecedented advances in diagnostic capability and clinical applications. However, progress in dermatology has lagged behind other medical domains due to the lack of standard image-text pairs. Existing dermatological datasets are limited in both scale and depth, offering only single-label annotations across a narrow range of diseases instead of rich textual descriptions, and lacking the crucial clinical context needed for real-world applications. To address these limitations, we present Derm1M, the first large-scale vision-language dataset for dermatology, comprising 1,029,761 image-text pairs. Built from diverse educational resources and structured around a standard ontology collaboratively developed by experts, Derm1M provides comprehensive coverage for over 390 skin conditions across four hierarchical levels and 130 clinical concepts with rich contextual information such as medical history, symptoms, and skin tone. To demonstrate Derm1M potential in advancing both AI research and clinical application, we pretrained a series of CLIP-like models, collectively called DermLIP, on this dataset. The DermLIP family significantly outperforms state-of-the-art foundation models on eight diverse datasets across multiple tasks, including zero-shot skin disease classification, clinical and artifacts concept identification, few-shot/full-shot learning, and cross-modal retrieval. Our dataset and code will be publicly available at https://github.com/SiyuanYan1/Derm1M upon acceptance.
视觉语言模型的涌现已经推动了医疗人工智能的进步,使得诊断能力和临床应用方面取得了前所未有的进展。然而,皮肤病学方面的进展由于缺少标准图像文本配对而落后于其他医学领域。现有的皮肤病数据集在规模和深度上均有限,只提供狭窄疾病范围内的单一标签注释,缺乏丰富的文本描述和现实世界应用所需的关键临床背景。为了解决这些局限性,我们推出了Derm1M,这是皮肤病学领域第一个大规模视觉语言数据集,包含1,029,761个图像文本对。Derm1M由多样化的教育资源构建而成,围绕专家共同开发的标准本体结构构建,对超过390种皮肤状况进行了全面覆盖,涉及四个层次和130个临床概念,并提供了丰富的上下文信息,如病史、症状和肤色等。为了证明Derm1M在推动人工智能研究和临床应用方面的潜力,我们在该数据集上预训练了一系列类似于CLIP的模型,统称为DermLIP系列。DermLIP家族在多个任务的八个不同数据集上显著优于最新的基础模型,包括零样本皮肤疾病分类、临床和文物概念识别、小样本/全样本学习和跨模态检索。我们的数据集和代码将在论文被接受后公开于https://github.com/SiyuanYan1/Derm1M。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our dataset and code will be publicly available at https://github.com/SiyuanYan1/Derm1M
Summary
本文介绍了新兴的视觉语言模型在医疗AI领域的变革性作用,特别是在诊断能力和临床应用方面的突破。然而,皮肤病学领域的进展因缺乏标准图像文本配对而滞后。为解决此问题,本文提出了首个大规模皮肤病学视觉语言数据集Derm1M,包含1,029,761个图像文本对。该数据集涵盖了超过390种皮肤疾病,提供了丰富的上下文信息,如病史、症状和肤色等。为展示Derm1M在推进AI研究和临床应用方面的潜力,本文预训练了一系列名为DermLIP的CLIP类模型。DermLIP家族在多个任务上的表现显著优于现有最先进的模型,包括零样本皮肤疾病分类、临床和伪概念识别、少样本/全样本学习以及跨模态检索。数据集和相关代码将在论文被接受后公开提供。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型的出现在医疗AI领域带来了革命性的进步,特别是在诊断和临床应用方面。
- 皮肤病学领域在AI应用方面的进展相对滞后,主要由于缺乏标准的图像文本配对数据集。
- Derm1M是首个针对皮肤病学的大规模视觉语言数据集,包含大量的图像文本对,覆盖了多种皮肤疾病和丰富的上下文信息。
- DermLIP系列模型在多个任务上表现出卓越性能,包括零样本分类、临床和伪概念识别等。
- Derm1M数据集对AI研究和临床应用具有巨大潜力。
- Derm1M数据集和相关代码将在论文被接受后公开提供,便于其他研究者使用。
点此查看论文截图
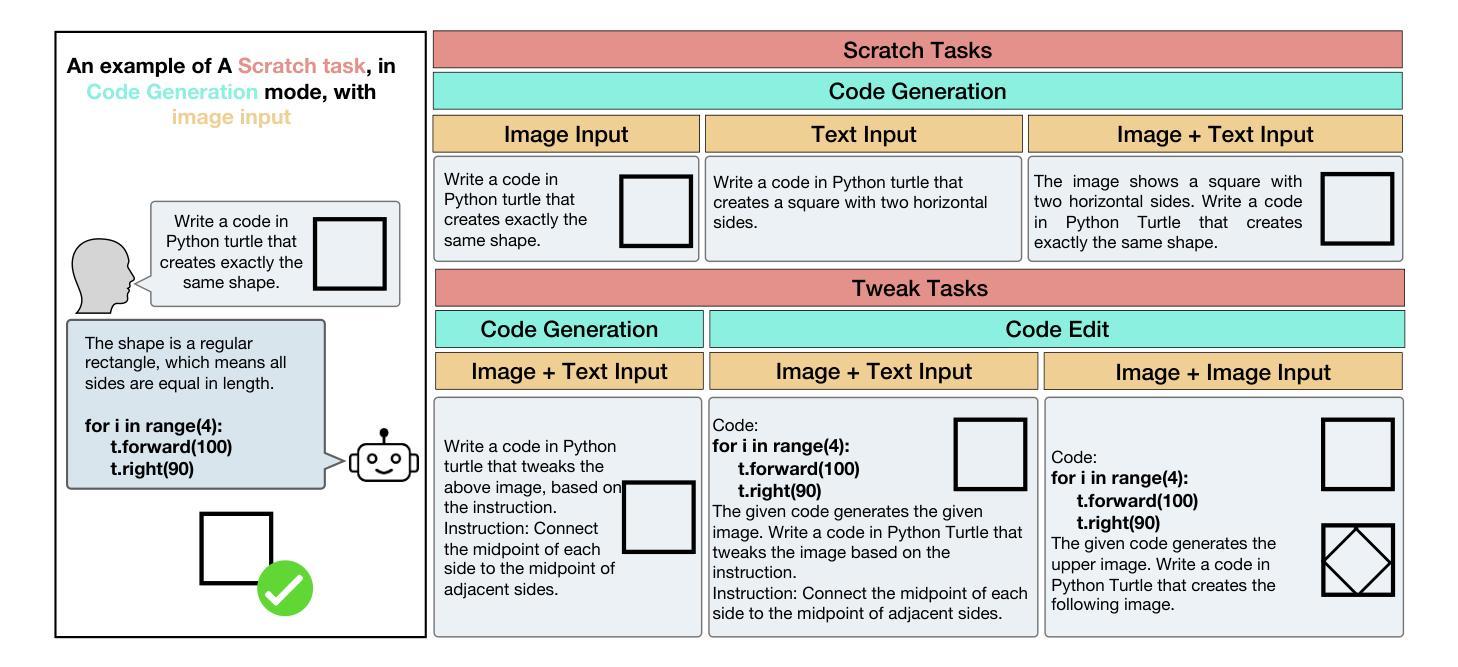
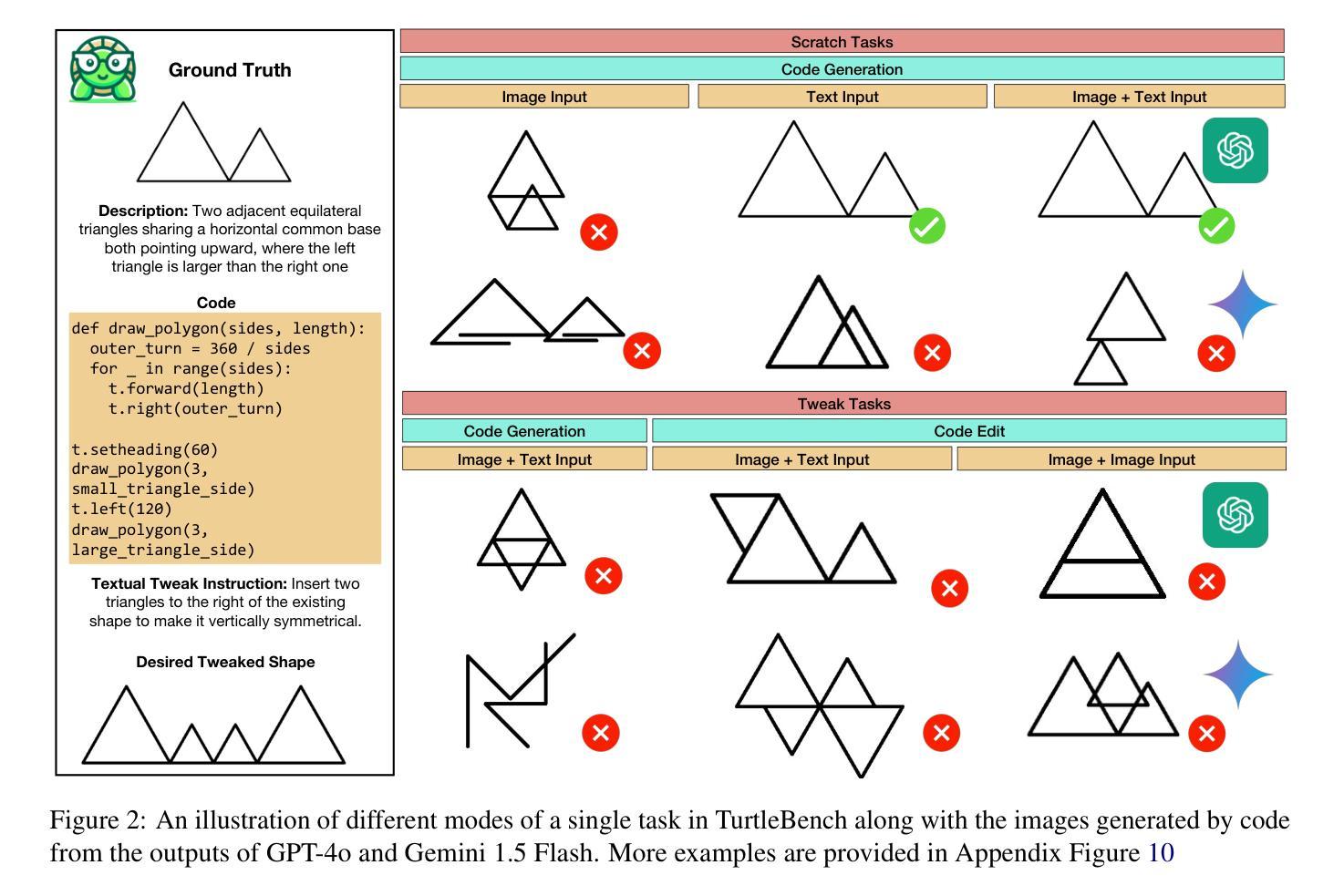
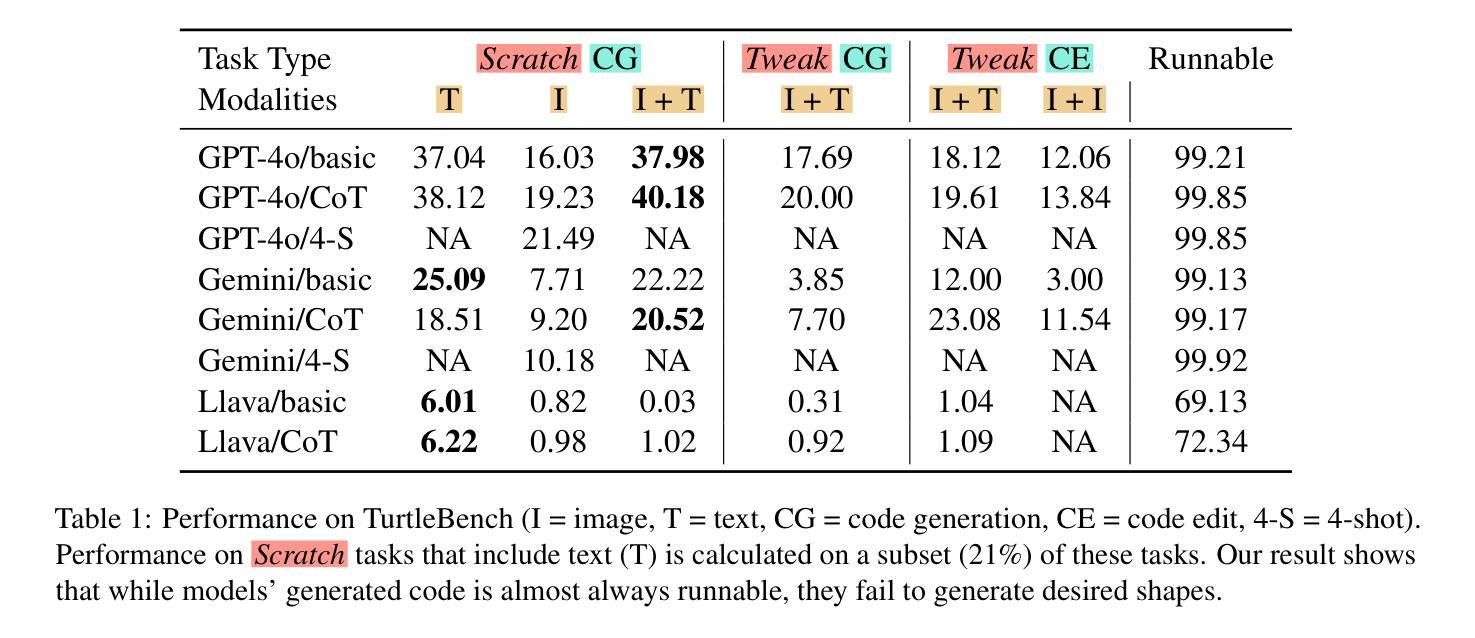
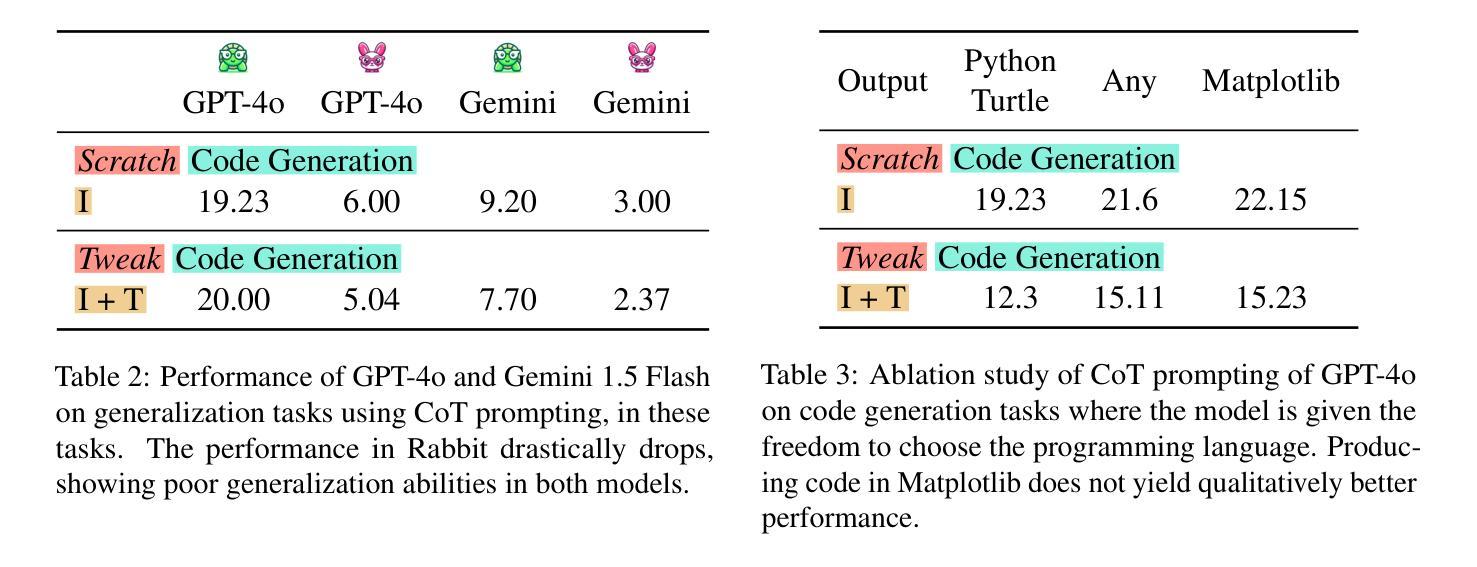
TurtleBench: A Visual Programming Benchmark in Turtle Geometry
Authors:Sina Rismanchian, Yasaman Razeghi, Sameer Singh, Shayan Doroudi
Humans have the ability to reason about geometric patterns in images and scenes from a young age. However, developing large multimodal models (LMMs) capable of similar reasoning remains a challenge, highlighting the need for robust evaluation methods to assess these capabilities. We introduce \Turtle, a benchmark designed to evaluate LMMs’ capacity to interpret geometric patterns – given visual examples, textual instructions, or both – and generate precise code outputs. Inspired by turtle geometry, a notion used to teach children foundational coding and geometric concepts, TurtleBench features tasks with patterned shapes that have underlying algorithmic logic. Our evaluation reveals that leading LMMs struggle significantly with these tasks, with GPT-4o achieving only 19% accuracy on the simplest tasks and few-shot prompting only marginally improves their performance ($<2%$). \Turtle highlights the gap between human and AI performance in intuitive and visual geometrical understanding, setting the stage for future research in this area. \Turtle stands as one of the few benchmarks to evaluate the integration of visual understanding and code generation capabilities in LMMs, setting the stage for future research. Code and Dataset for this paper is provided here: \href{https://github.com/sinaris76/TurtleBench}{https://github.com/sinaris76/TurtleBench}
人类从小就具备理解和分析图像和场景中的几何模式的能力。然而,开发具有类似推理能力的大型多模式模型(LMM)仍然是一个挑战,这突显了需要可靠的评估方法来评估这些能力。我们推出了TurtleBench,一个旨在评估LMM解释几何模式的能力的基准测试。给定视觉示例、文本指令或两者兼有,并生成精确的代码输出。TurtleBench以海龟几何学为灵感,这是一种用于教授儿童基础编码和几何概念的概念,其特征是具有潜在算法逻辑的模式形状任务。我们的评估发现,领先的LMM在这些任务上面临巨大挑战,GPT-4在最简单任务上的准确率仅为19%,而且few-shot提示只略微提高了其性能(小于2%)。Turtle突出了人类在直观和视觉几何理解方面与人工智能的性能差距,为这一领域的未来研究奠定了基础。Turtle是少数几个能够评估LMM中视觉理解与代码生成能力融合的基准测试之一,为未来的研究奠定了基础。本文的代码和数据集请参见:https://github.com/sinaris76/TurtleBench。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个名为Turtle的基准测试平台,旨在评估多模态模型对图像和场景中的几何模式进行解读的能力。该基准测试通过视觉示例、文本指令或两者的组合来评估模型生成精确代码输出的能力。研究表明,领先的大型多模态模型在这些任务上表现挣扎,GPT-4的准确率仅为19%,且少样本提示仅略微改善其表现。Turtle凸显了人类与人工智能在直观和视觉几何理解方面的差距,为未来研究奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- Turtle是一个用于评估大型多模态模型(LMMs)解读几何模式能力的基准测试平台。
- 平台涵盖的任务包括解读图案形状背后的算法逻辑。
- 现有领先的大型多模态模型在Turtle的任务上表现不佳,GPT-4的准确率仅为19%。
- 少样本提示对模型的性能提升有限。
- Turtle揭示了人类与人工智能在直观和视觉几何理解方面的差距。
- Turtle是少数能够评估多模态模型中视觉理解与代码生成能力整合的基准测试之一。
点此查看论文截图

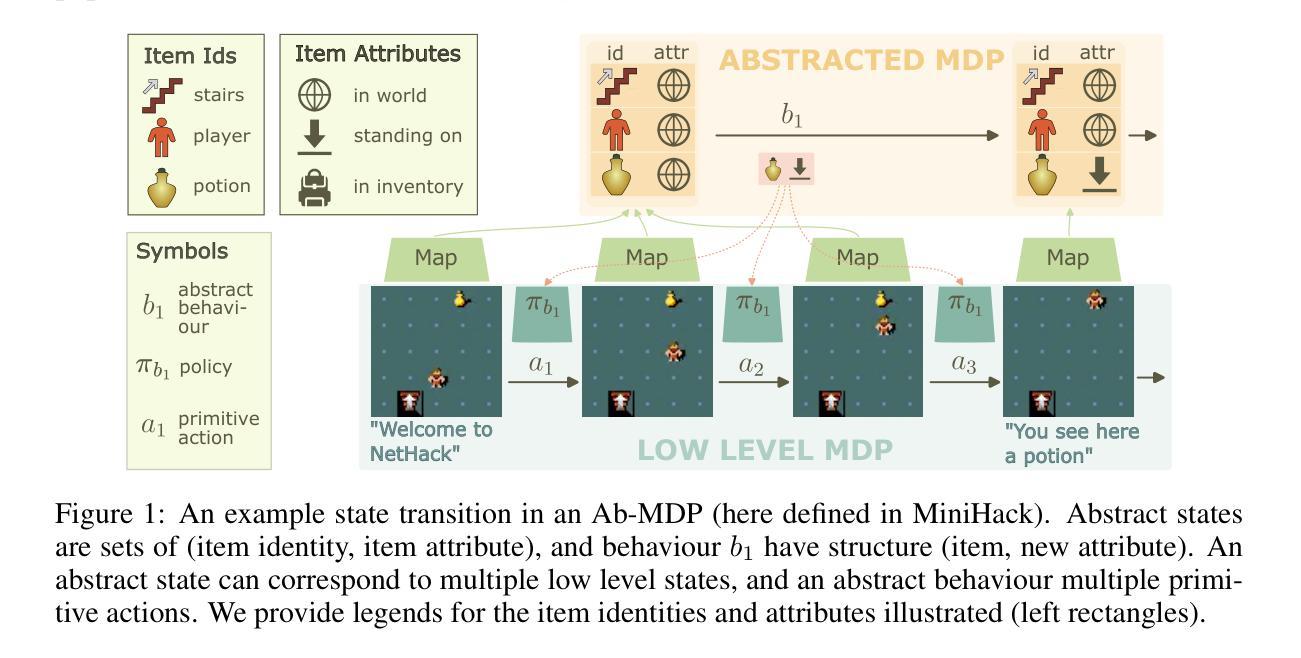
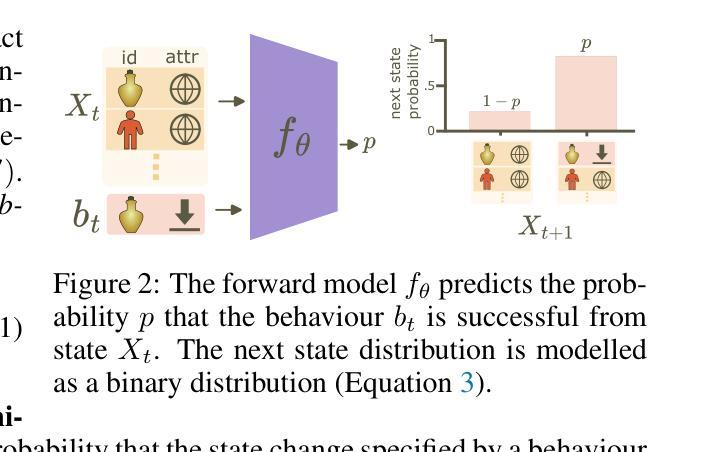
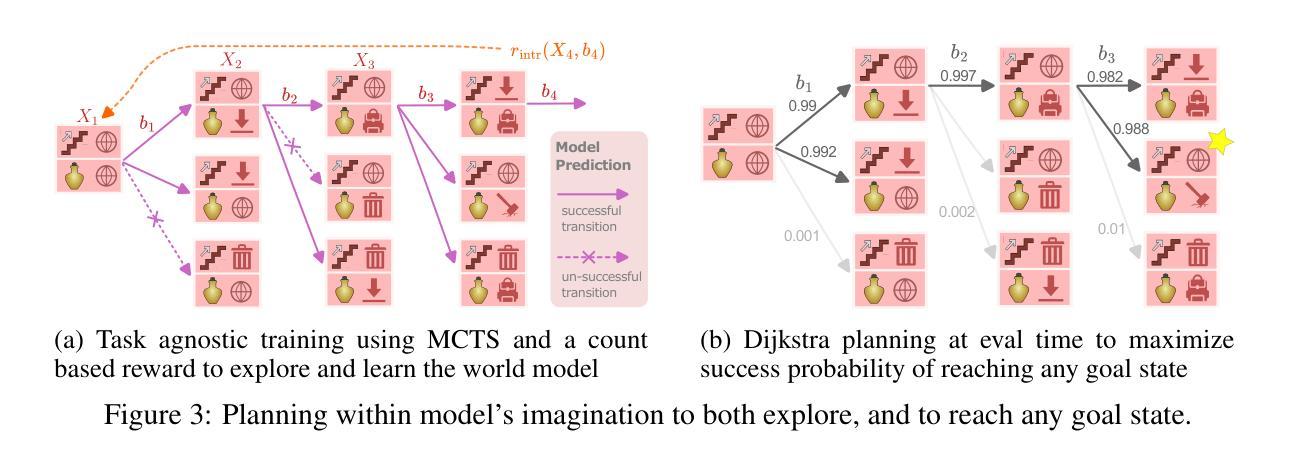
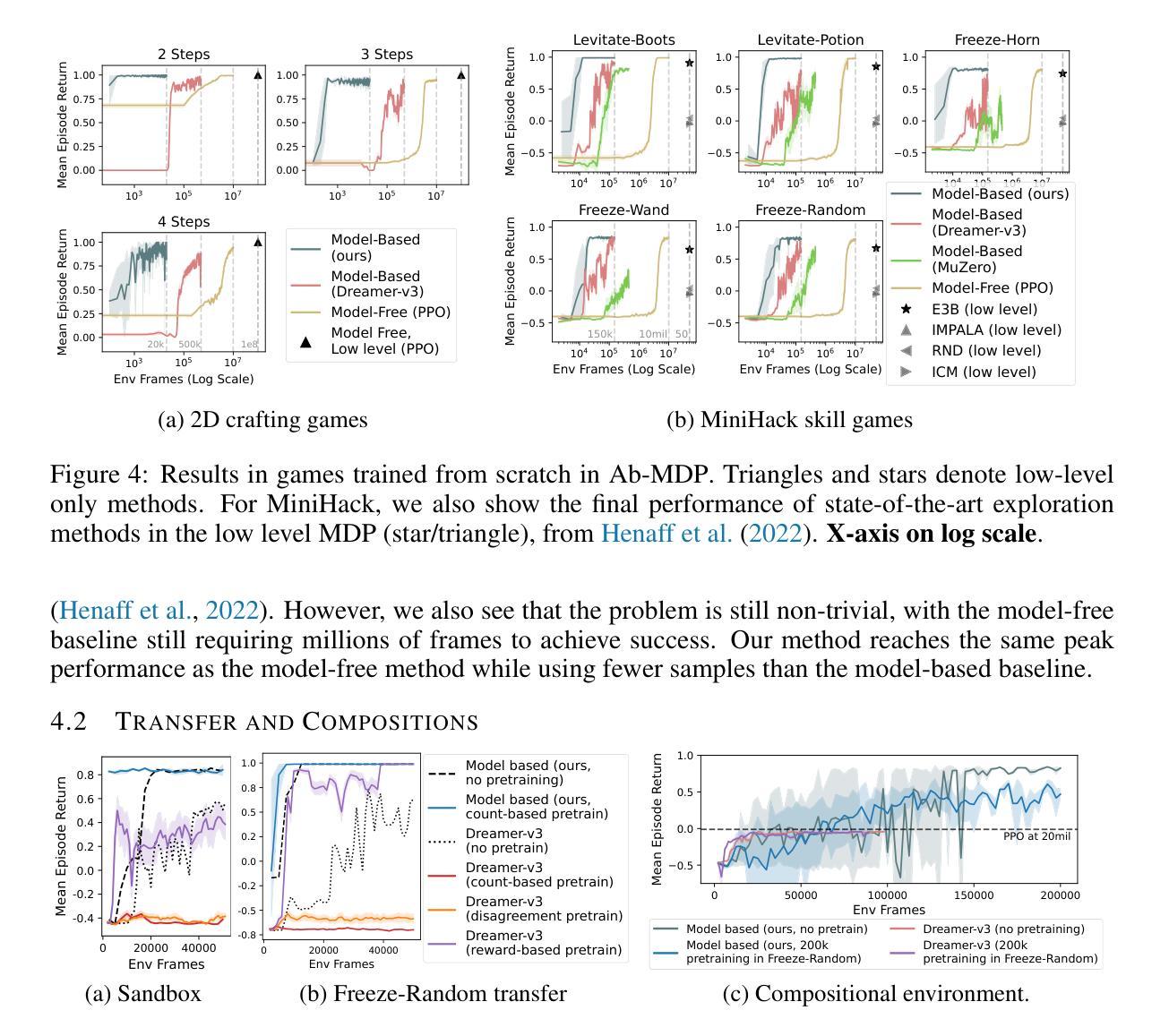
Efficient Exploration and Discriminative World Model Learning with an Object-Centric Abstraction
Authors:Anthony GX-Chen, Kenneth Marino, Rob Fergus
In the face of difficult exploration problems in reinforcement learning, we study whether giving an agent an object-centric mapping (describing a set of items and their attributes) allow for more efficient learning. We found this problem is best solved hierarchically by modelling items at a higher level of state abstraction to pixels, and attribute change at a higher level of temporal abstraction to primitive actions. This abstraction simplifies the transition dynamic by making specific future states easier to predict. We make use of this to propose a fully model-based algorithm that learns a discriminative world model, plans to explore efficiently with only a count-based intrinsic reward, and can subsequently plan to reach any discovered (abstract) states. We demonstrate the model’s ability to (i) efficiently solve single tasks, (ii) transfer zero-shot and few-shot across item types and environments, and (iii) plan across long horizons. Across a suite of 2D crafting and MiniHack environments, we empirically show our model significantly out-performs state-of-the-art low-level methods (without abstraction), as well as performant model-free and model-based methods using the same abstraction. Finally, we show how to learn low level object-perturbing policies via reinforcement learning, and the object mapping itself by supervised learning.
面对强化学习中的困难探索问题,我们研究了给智能体一个以物体为中心的映射(描述一组物品及其属性)是否能够更有效地进行学习。我们发现这个问题最好通过分层建模来解决,将物品建模为更高层次的状态抽象,像素为更低层次的细节;将属性变化建模为更高层次的临时抽象,基本行动为更低层次的细节。这种抽象通过使特定未来状态更容易预测来简化转移动态。我们利用这一点提出了一种完全基于模型的算法,该算法学习具有区分性的世界模型,仅使用基于计数的内在奖励来有效地进行探索,并且可以随后达到任何发现的(抽象)状态。我们证明了该模型能够(i)有效地解决单一任务,(ii)在不同物品类型和环境中实现零启动和少量启动迁移,(iii)进行长期规划。在一系列2D工艺和MiniHack环境中,我们通过实证研究证明,我们的模型显著优于最新的低层次方法(没有抽象),以及使用相同抽象的高性能无模型模型和基于模型的模型方法。最后,我们展示了如何通过强化学习来学习低层次的对象扰动策略,以及通过监督学习来学习对象映射本身。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
强化学习在解决困难探索问题时,通过使用对象为中心的映射(描述一系列物品及其属性)可以提高学习效率。研究发现,通过层级建模,将物品置于状态抽象的高层,将属性变化置于时间抽象的高层(原始动作),可以更好地解决此问题。这种抽象简化了状态转移的动态过程,使特定未来状态更容易预测。在此基础上,提出了一种全模型算法,该算法可以学习判别世界模型,仅通过基于计数的内在奖励进行高效探索规划,并可以规划到达任何发现的(抽象)状态。模型能够在(i)解决单一任务,(ii)在不同物品类型和环境中实现零起点和少量起点转移,(iii)进行长期规划方面表现出色。在多个二维制作和MiniHack环境中进行的实证研究表明,该模型显著优于最先进的低层次方法(无抽象),以及使用相同抽象的模型自由和基于模型的方法。最后,展示了如何通过强化学习学习低层次的对象扰动策略以及通过监督学习学习对象映射本身。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习中面对困难探索问题时,使用对象为中心的映射能提高学习效率。
- 层级建模是解决此问题的最佳途径,将物品和属性变化置于不同的抽象层级。
- 该模型通过简化状态转移动态,使预测未来状态更为容易。
- 提出了一种全模型算法,能学习判别世界模型并高效探索规划。
- 模型在解决单一任务、跨物品和环境转移以及长期规划方面表现出色。
- 该模型在多个环境中显著优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图