⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-16 更新
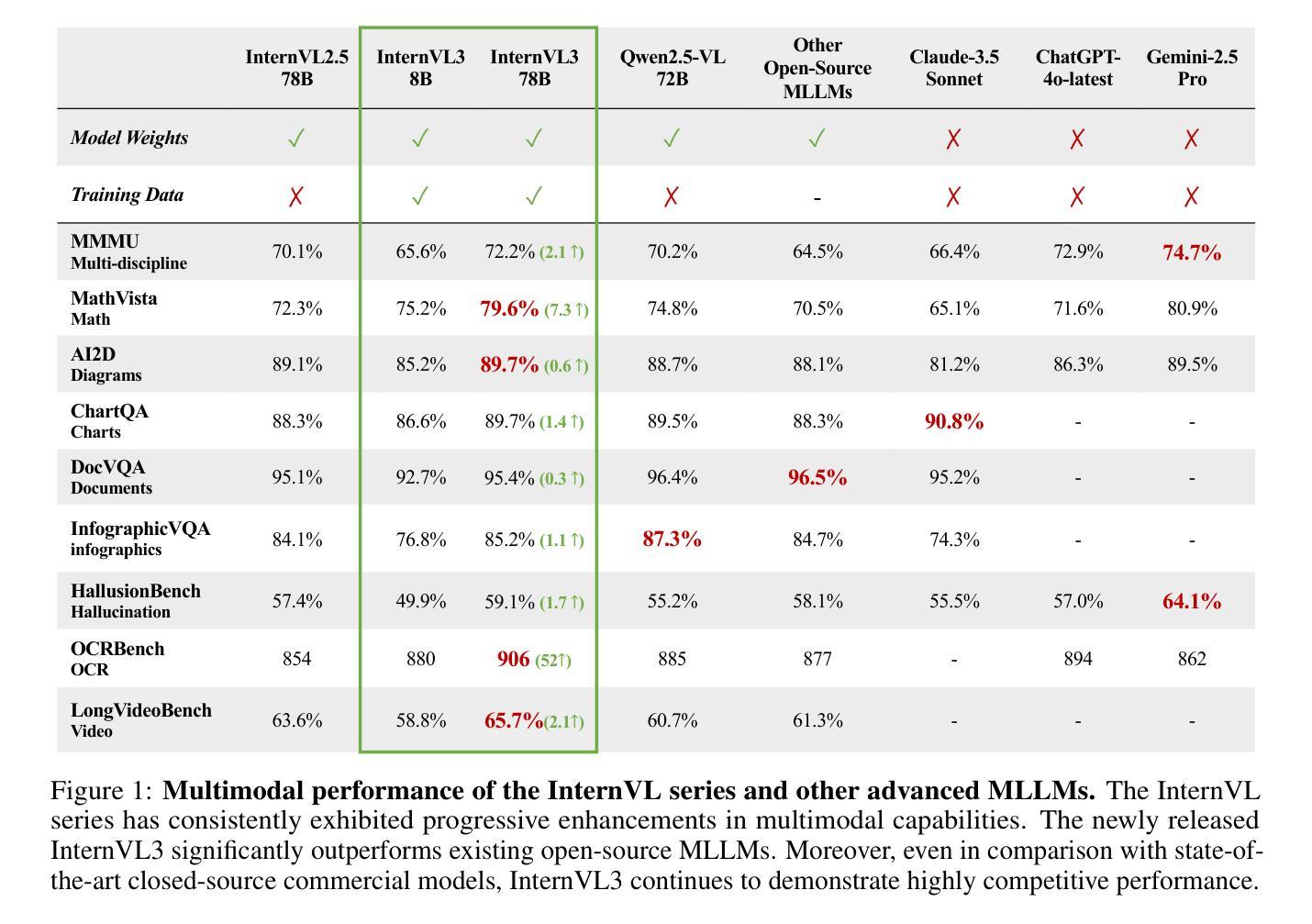
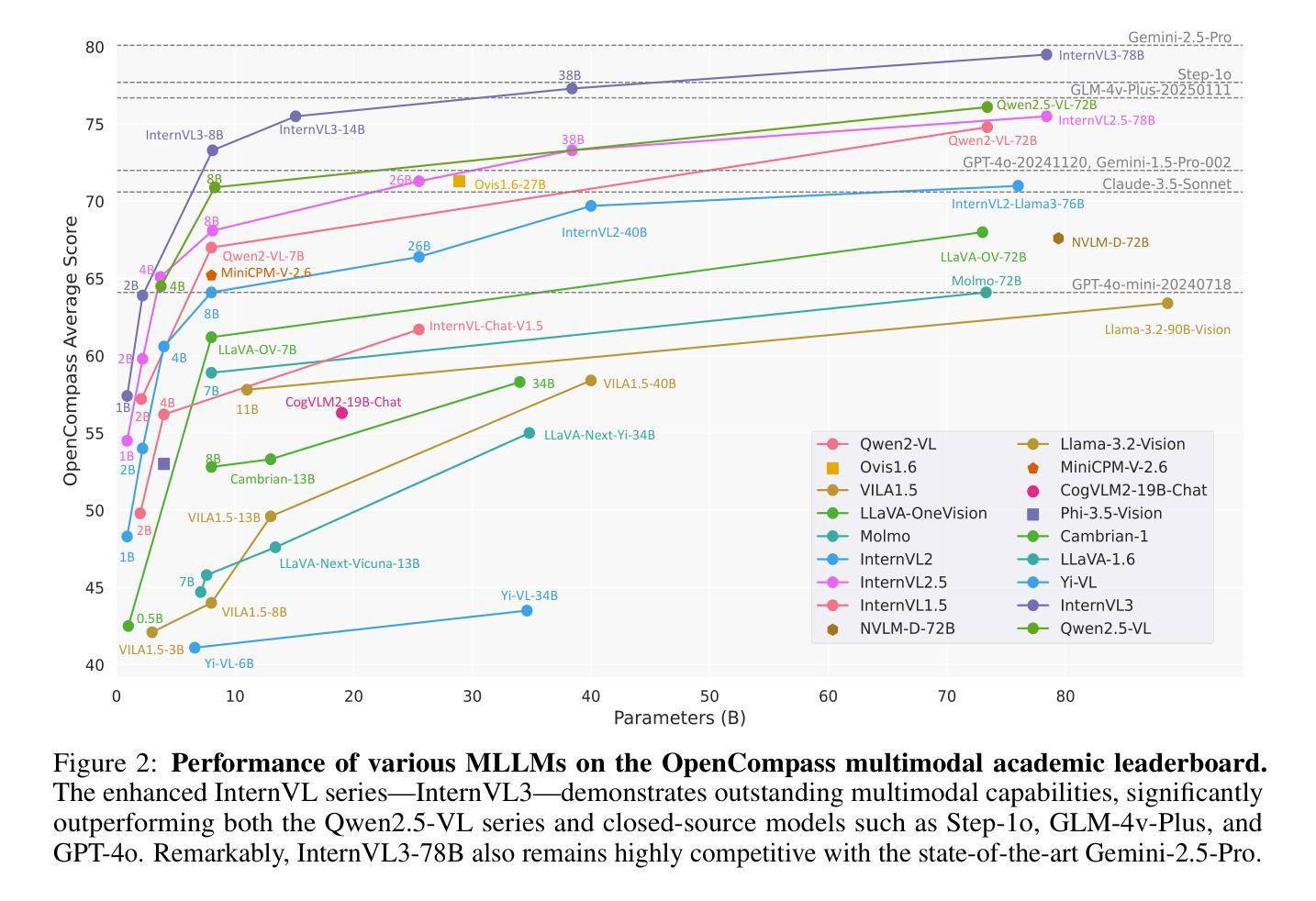
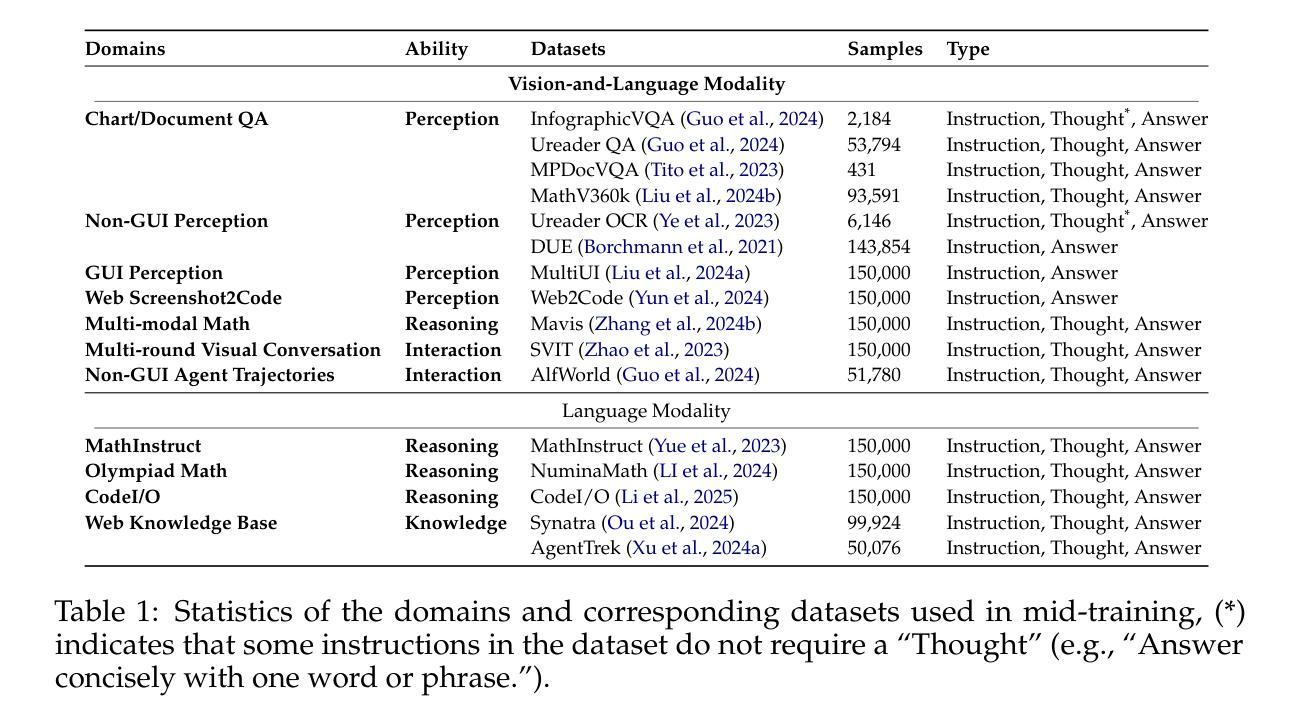
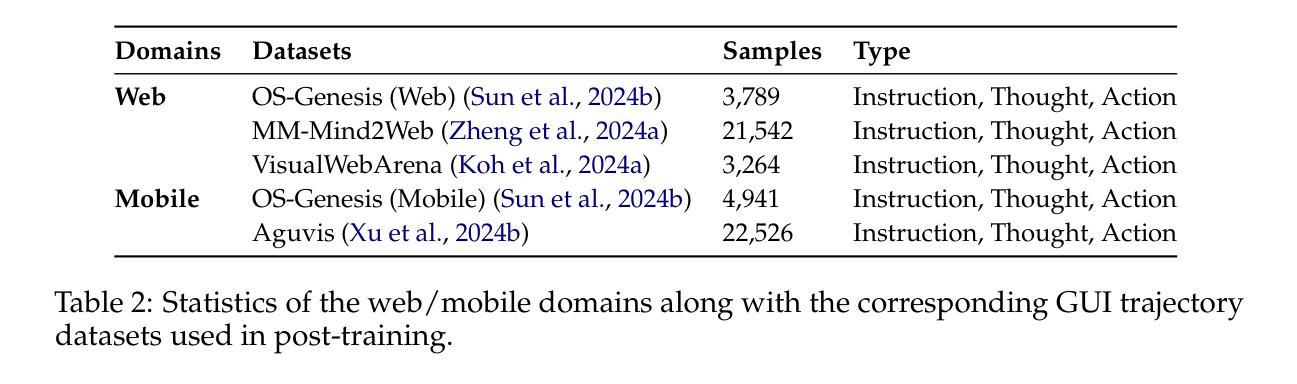
InternVL3: Exploring Advanced Training and Test-Time Recipes for Open-Source Multimodal Models
Authors:Jinguo Zhu, Weiyun Wang, Zhe Chen, Zhaoyang Liu, Shenglong Ye, Lixin Gu, Yuchen Duan, Hao Tian, Weijie Su, Jie Shao, Zhangwei Gao, Erfei Cui, Yue Cao, Yangzhou Liu, Weiye Xu, Hao Li, Jiahao Wang, Han Lv, Dengnian Chen, Songze Li, Yinan He, Tan Jiang, Jiapeng Luo, Yi Wang, Conghui He, Botian Shi, Xingcheng Zhang, Wenqi Shao, Junjun He, Yingtong Xiong, Wenwen Qu, Peng Sun, Penglong Jiao, Lijun Wu, Kaipeng Zhang, Huipeng Deng, Jiaye Ge, Kai Chen, Limin Wang, Min Dou, Lewei Lu, Xizhou Zhu, Tong Lu, Dahua Lin, Yu Qiao, Jifeng Dai, Wenhai Wang
We introduce InternVL3, a significant advancement in the InternVL series featuring a native multimodal pre-training paradigm. Rather than adapting a text-only large language model (LLM) into a multimodal large language model (MLLM) that supports visual inputs, InternVL3 jointly acquires multimodal and linguistic capabilities from both diverse multimodal data and pure-text corpora during a single pre-training stage. This unified training paradigm effectively addresses the complexities and alignment challenges commonly encountered in conventional post-hoc training pipelines for MLLMs. To further improve performance and scalability, InternVL3 incorporates variable visual position encoding (V2PE) to support extended multimodal contexts, employs advanced post-training techniques such as supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and mixed preference optimization (MPO), and adopts test-time scaling strategies alongside an optimized training infrastructure. Extensive empirical evaluations demonstrate that InternVL3 delivers superior performance across a wide range of multi-modal tasks. In particular, InternVL3-78B achieves a score of 72.2 on the MMMU benchmark, setting a new state-of-the-art among open-source MLLMs. Its capabilities remain highly competitive with leading proprietary models, including ChatGPT-4o, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, and Gemini 2.5 Pro, while also maintaining strong pure-language proficiency. In pursuit of open-science principles, we will publicly release both the training data and model weights to foster further research and development in next-generation MLLMs.
我们推出了InternVL3,这是InternVL系列的一项重大进展,它采用了一种原生多模态预训练范式。InternVL3并非将仅文本的大型语言模型(LLM)改编为支持视觉输入的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),而是在单个预训练阶段中,从多样化的多模态数据和纯文本语料库中同时获取多模态和语言能力。这种统一的训练范式有效地解决了传统MLLM事后训练管道中通常遇到的复杂性和对齐挑战。为了进一步提高性能和可扩展性,InternVL3引入了可变视觉位置编码(V2PE)以支持扩展的多模态上下文,采用了先进的后训练技术,如监督微调(SFT)和混合偏好优化(MPO),并采用了测试时缩放策略以及优化的训练基础设施。广泛的实证评估表明,InternVL3在多种多模态任务中表现出卓越的性能。特别是,InternVL3-78B在MMMU基准测试上得分72.2分,在开源MLLM中创造了新的技术之巅。其能力与领先的专有模型保持高度竞争,包括ChatGPT-4o、Claude 3.5 Sonnet和Gemini 2.5 Pro,同时保持强大的纯语言熟练程度。本着开放科学的原则,我们将公开发布训练数据和模型权重,以推动下一代MLLM的研究和发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
Summary
InternVL3是InternVL系列的重要进展,采用原生多模态预训练范式。它联合获取多模态和语言的能力,来自单一预训练阶段的多模态数据和纯文本语料库。该统一训练范式解决了传统多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)面临的复杂性和对齐挑战。InternVL3通过可变视觉位置编码(V2PE)支持扩展的多模态上下文,并采用先进的后训练技术和测试时间缩放策略。经验评估表明,InternVL3在多种多模态任务上表现出卓越性能。特别是,InternVL3-78B在MMMU基准测试中得分72.2,在开源MLLM中达到最新水平,同时与领先的专有模型保持竞争力。遵循公开科学原则,将公开训练数据和模型权重以促进下一代MLLM的研究和发展。
Key Takeaways
- InternVL3是InternVL系列中的一项重要更新,采用原生多模态预训练方法。
- 通过单一预训练阶段,InternVL3从多模态数据和纯文本语料库中联合获取多模态和语言的能力。
- 该方法解决了传统多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的复杂性和对齐挑战。
- InternVL3采用可变视觉位置编码(V2PE)以支持扩展的多模态上下文。
- 先进后训练技术和测试时间缩放策略提高了InternVL3的性能和可扩展性。
- InternVL3在多种多模态任务上表现出卓越性能,特别是InternVL3-78B在MMMU基准测试中得分72.2,达到开源MLLM的最新水平。
点此查看论文截图

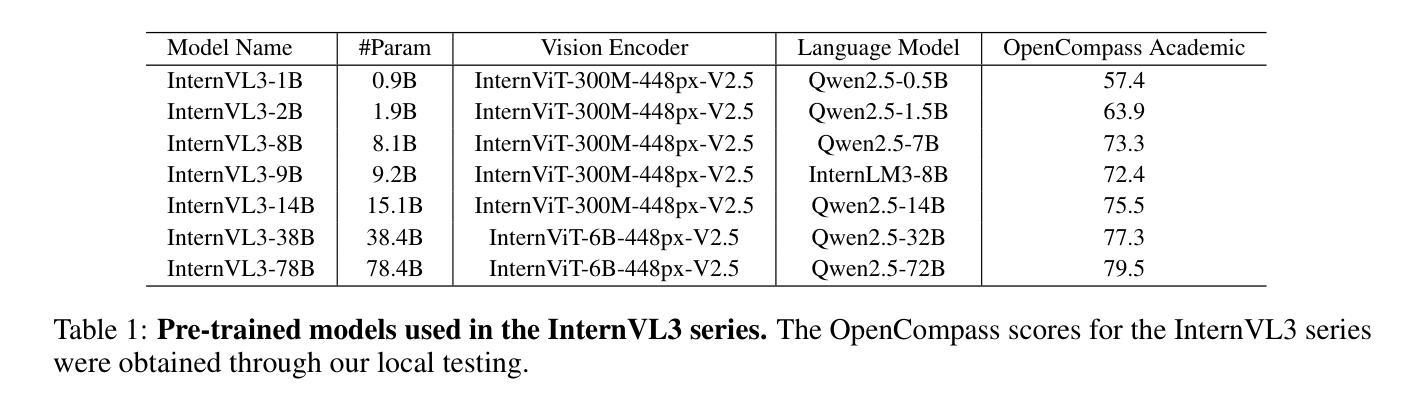
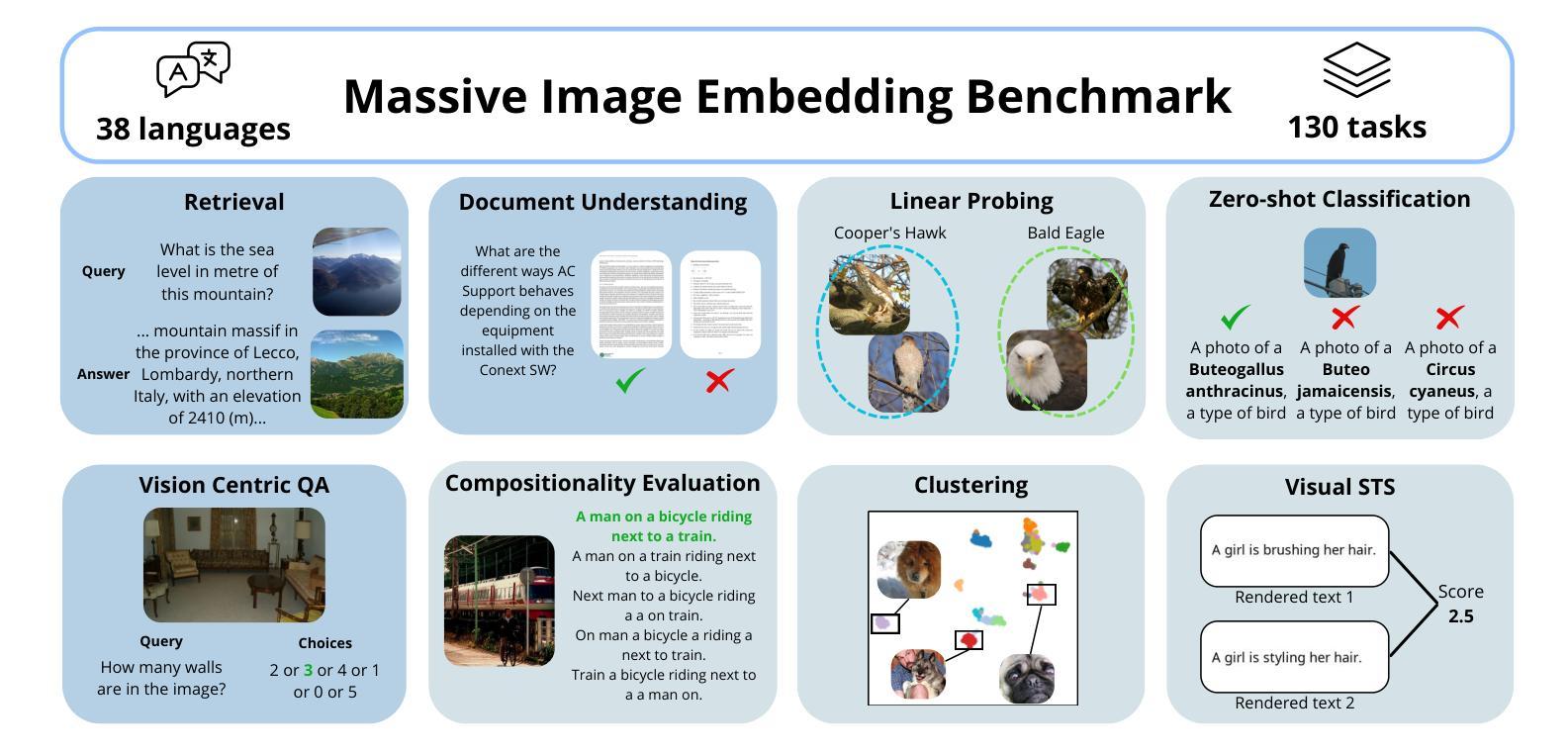
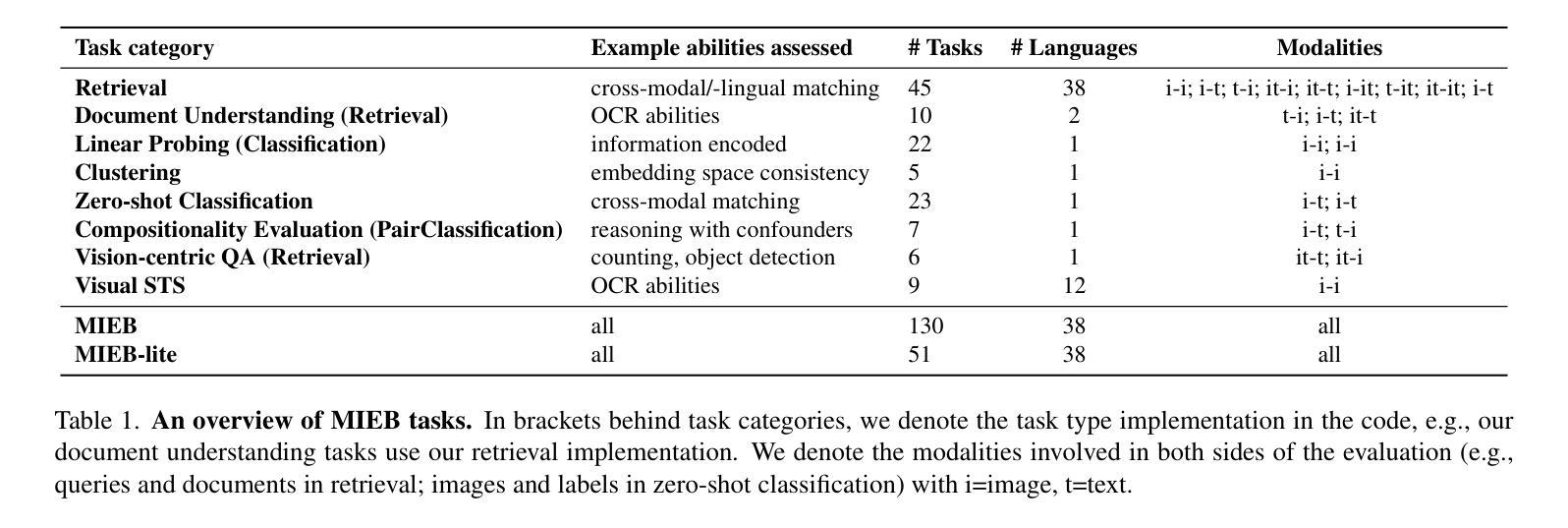
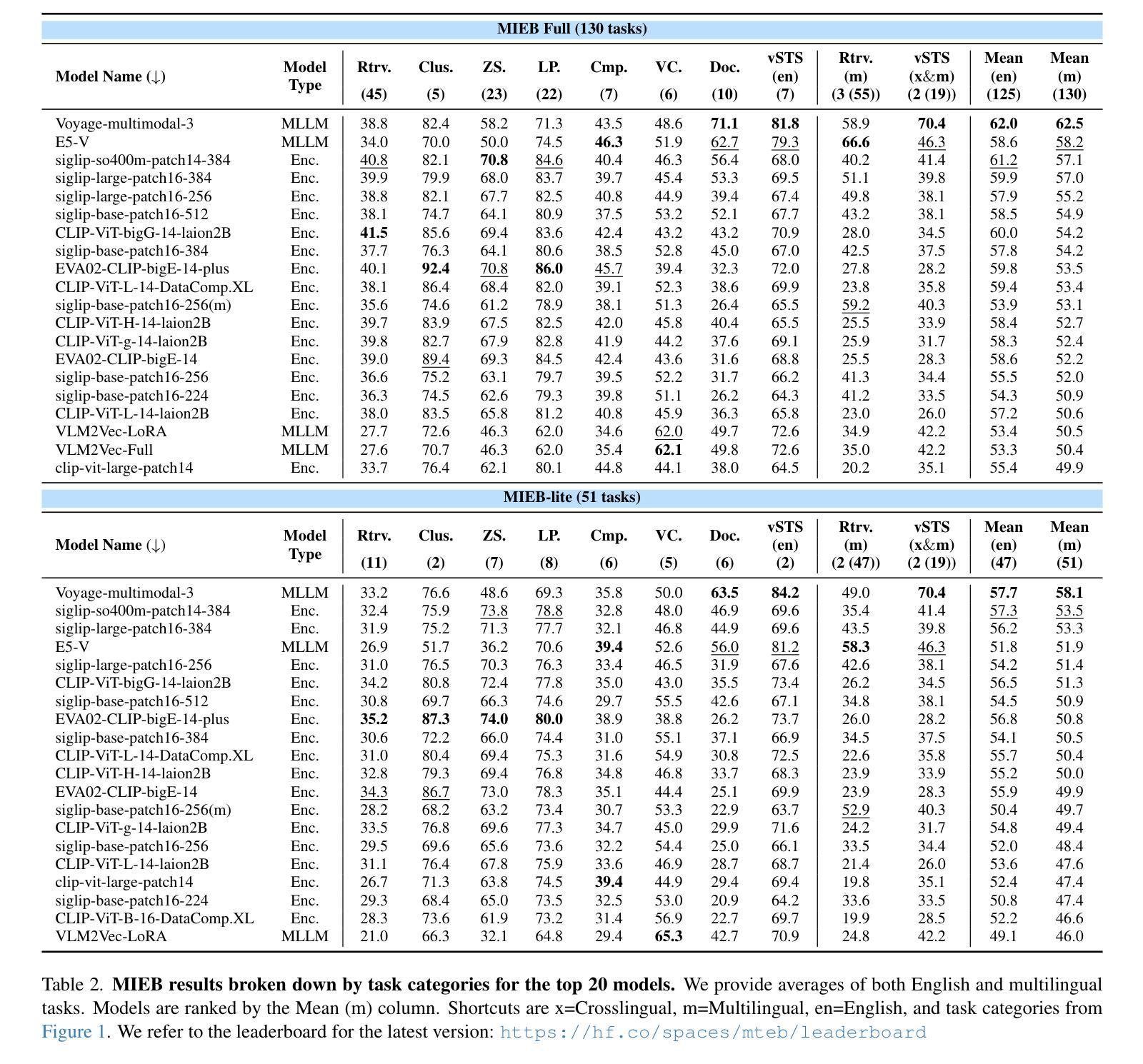
MIEB: Massive Image Embedding Benchmark
Authors:Chenghao Xiao, Isaac Chung, Imene Kerboua, Jamie Stirling, Xin Zhang, Márton Kardos, Roman Solomatin, Noura Al Moubayed, Kenneth Enevoldsen, Niklas Muennighoff
Image representations are often evaluated through disjointed, task-specific protocols, leading to a fragmented understanding of model capabilities. For instance, it is unclear whether an image embedding model adept at clustering images is equally good at retrieving relevant images given a piece of text. We introduce the Massive Image Embedding Benchmark (MIEB) to evaluate the performance of image and image-text embedding models across the broadest spectrum to date. MIEB spans 38 languages across 130 individual tasks, which we group into 8 high-level categories. We benchmark 50 models across our benchmark, finding that no single method dominates across all task categories. We reveal hidden capabilities in advanced vision models such as their accurate visual representation of texts, and their yet limited capabilities in interleaved encodings and matching images and texts in the presence of confounders. We also show that the performance of vision encoders on MIEB correlates highly with their performance when used in multimodal large language models. Our code, dataset, and leaderboard are publicly available at https://github.com/embeddings-benchmark/mteb.
图像的表示通常通过分散的、针对特定任务的协议进行评估,这导致对模型能力的理解变得碎片化。例如,尚不清楚擅长对图像进行聚类的图像嵌入模型在给定的文本中检索相关图像时是否同样出色。我们推出大规模图像嵌入基准测试(MIEB),以迄今为止最广泛的范围评估图像和图像文本嵌入模型的性能。MIEB涵盖130个独立任务,涉及38种语言,我们将其分为8个高级类别。我们在基准测试上对50个模型进行了基准测试,发现没有一种方法在所有任务类别中都占主导地位。我们揭示了先进视觉模型的隐藏功能,例如它们对文本的准确视觉表示,以及它们在混杂因素存在时,对交错编码和匹配图像和文本的能力的局限性。我们还表明,MIEB上视觉编码器的性能与它们在多模态大型语言模型中的性能高度相关。我们的代码、数据集和排行榜可在https://github.com/embeddings-benchmark/mteb公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出大规模图像嵌入基准测试(MIEB),旨在评估图像和图像文本嵌入模型在最广泛谱上的性能。MIEB涵盖38种语言,包括130个任务,分为八大类。本文基准测试了50个模型,发现没有一种方法在所有任务类别中都占据主导地位。揭示先进视觉模型的隐藏功能,如文本的准确视觉表示,以及它们在混合编码和匹配图像和文本时的有限能力。此外,本文还表明,视觉编码器在MIEB上的性能与它们在多模态大型语言模型中的性能高度相关。
Key Takeaways
- 当前图像表示评估方法存在碎片化问题,缺乏统一标准。
- 引入大规模图像嵌入基准测试(MIEB),覆盖38种语言,包含130个任务,分为八大类。
- 对50个模型进行基准测试,发现没有单一方法在所有任务类别中均居领先地位。
- 揭示先进视觉模型的隐藏功能,例如文本的视觉表示能力。
- 模型在混合编码和匹配图像与文本方面的能力存在局限性。
- 视觉编码器在MIEB上的性能与其在多模态大型语言模型中的性能高度相关。
点此查看论文截图

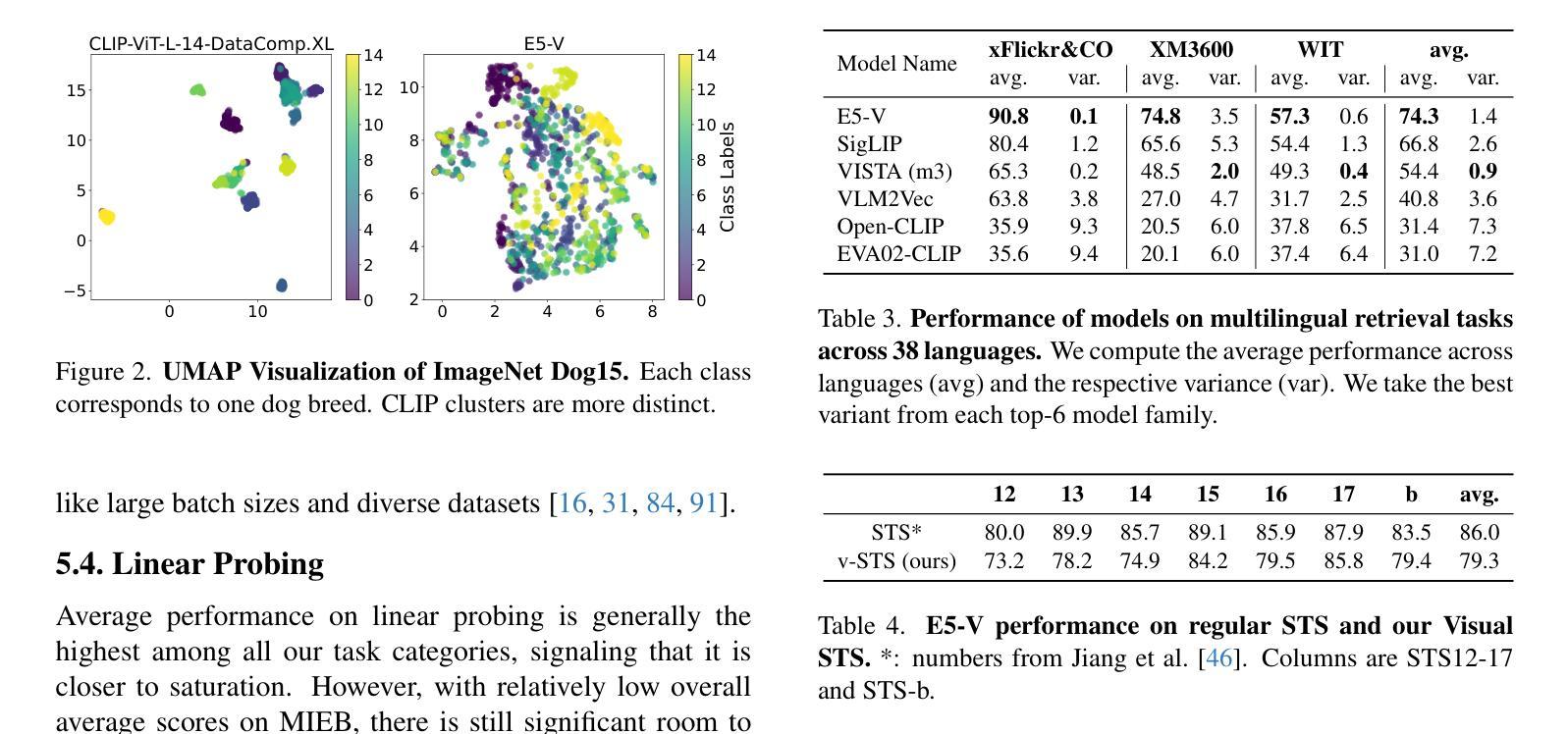
Pixel-SAIL: Single Transformer For Pixel-Grounded Understanding
Authors:Tao Zhang, Xiangtai Li, Zilong Huang, Yanwei Li, Weixian Lei, Xueqing Deng, Shihao Chen, Shunping Ji, Jiashi Feng
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) achieve remarkable performance for fine-grained pixel-level understanding tasks. However, all the works rely heavily on extra components, such as vision encoder (CLIP), segmentation experts, leading to high system complexity and limiting model scaling. In this work, our goal is to explore a highly simplified MLLM without introducing extra components. Our work is motivated by the recent works on Single trAnsformer as a unified vIsion-Language Model (SAIL) design, where these works jointly learn vision tokens and text tokens in transformers. We present Pixel-SAIL, a single transformer for pixel-wise MLLM tasks. In particular, we present three technical improvements on the plain baseline. First, we design a learnable upsampling module to refine visual token features. Secondly, we propose a novel visual prompt injection strategy to enable the single transformer to understand visual prompt inputs and benefit from the early fusion of visual prompt embeddings and vision tokens. Thirdly, we introduce a vision expert distillation strategy to efficiently enhance the single transformer’s fine-grained feature extraction capability. In addition, we have collected a comprehensive pixel understanding benchmark (PerBench), using a manual check. It includes three tasks: detailed object description, visual prompt-based question answering, and visual-text referring segmentation. Extensive experiments on four referring segmentation benchmarks, one visual prompt benchmark, and our PerBench show that our Pixel-SAIL achieves comparable or even better results with a much simpler pipeline. Code and model will be released at https://github.com/magic-research/Sa2VA.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在精细粒度的像素级理解任务中取得了显著的成绩。然而,所有的工作都严重依赖于额外的组件,如视觉编码器(CLIP)、分割专家,导致系统复杂度较高,限制了模型的扩展性。本文的目标是探索一种高度简化的MLLM,而不引入额外的组件。我们的工作受到单一转换器作为统一视觉语言模型(SAIL)设计近期工作的启发,这些工作联合学习视觉标记和文本标记在转换器中的知识。我们提出了Pixel-SAIL,这是一个用于像素级MLLM任务的单一转换器。特别是,我们在简单的基线基础上提出了三项技术改进。首先,我们设计了一个可学习的上采样模块来优化视觉标记特征。其次,我们提出了一种新的视觉提示注入策略,使单一转换器能够理解视觉提示输入,并从视觉提示嵌入和视觉标记的早期融合中受益。第三,我们引入了一种视觉专家蒸馏策略,以有效地提高单一转换器的精细特征提取能力。此外,我们还通过人工检查收集了一个全面的像素理解基准(PerBench),它包括三个任务:详细对象描述、基于视觉提示的问题回答、视觉文本引用分割。在四个引用分割基准测试、一个视觉提示基准测试以及我们的PerBench上的大量实验表明,我们的Pixel-SAIL在流程更加简单的情况下取得了相当或更好的结果。代码和模型将在https://github.com/magic-research/Sa2VA上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于单模态的大型语言模型(MLLMs)在进行像素级别的理解任务上表现突出。此研究中旨在探究无额外组件的更简化的MLLM模型。研究受到单一转换器作为统一视觉语言模型(SAIL)设计的影响,在此设计基础上提出了Pixel-SAIL模型。对基线进行了三项技术改进,包括可学习的上采样模块来优化视觉令牌特征、新型视觉提示注入策略使单一转换器理解视觉提示输入并从早期融合中受益,以及通过视觉专家蒸馏策略提高精细特征提取能力。此外,还收集了一个全面的像素理解基准测试(PerBench)。实验结果显示,Pixel-SAIL在四个引用分割基准测试、一个视觉提示基准和PerBench上取得了相当或更好的结果,同时流程更加简洁。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在像素级理解任务上表现卓越。
- 研究目标是探索无额外组件的更简化的MLLM模型。
- Pixel-SAIL模型基于单一转换器进行设计,用于像素级的MLLM任务。
- 技术改进包括可学习的上采样模块、视觉提示注入策略和视觉专家蒸馏策略。
- 收集了全面的像素理解基准测试(PerBench)。
- Pixel-SAIL在多个基准测试中取得了显著成果。
点此查看论文截图

The Scalability of Simplicity: Empirical Analysis of Vision-Language Learning with a Single Transformer
Authors:Weixian Lei, Jiacong Wang, Haochen Wang, Xiangtai Li, Jun Hao Liew, Jiashi Feng, Zilong Huang
This paper introduces SAIL, a single transformer unified multimodal large language model (MLLM) that integrates raw pixel encoding and language decoding within a singular architecture. Unlike existing modular MLLMs, which rely on a pre-trained vision transformer (ViT), SAIL eliminates the need for a separate vision encoder, presenting a more minimalist architecture design. Instead of introducing novel architectural components, SAIL adapts mix-attention mechanisms and multimodal positional encodings to better align with the distinct characteristics of visual and textual modalities. We systematically compare SAIL’s properties-including scalability, cross-modal information flow patterns, and visual representation capabilities-with those of modular MLLMs. By scaling both training data and model size, SAIL achieves performance comparable to modular MLLMs. Notably, the removal of pretrained ViT components enhances SAIL’s scalability and results in significantly different cross-modal information flow patterns. Moreover, SAIL demonstrates strong visual representation capabilities, achieving results on par with ViT-22B in vision tasks such as semantic segmentation. Code and models are available at https://github.com/bytedance/SAIL.
本文介绍了SAIL,这是一个单一变换器统一多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),它在一个单一架构中集成了原始像素编码和语言解码。不同于依赖预训练视觉变换器(ViT)的现有模块化MLLM,SAIL消除了对单独视觉编码器的需求,呈现出更简洁的架构设计。SAIL没有引入新型架构组件,而是适应了混合注意力机制和多模态位置编码,以更好地符合视觉和文本模态的特定特征。我们系统地比较了SAIL与模块化MLLM的属性,包括可扩展性、跨模态信息流模式以及视觉表示能力。通过扩大训练数据和模型规模,SAIL实现了与模块化MLLM相当的性能。值得注意的是,去除预训练的ViT组件增强了SAIL的可扩展性,并产生了显著不同的跨模态信息流模式。此外,SAIL在视觉任务中表现出强大的视觉表示能力,如在语义分割方面达到了与ViT-22B相当的结果。相关代码和模型可在https://github.com/bytedance/SAIL中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为SAIL的统一多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)。不同于现有的模块化MLLM,SAIL在单一架构内集成了原始像素编码和语言解码,无需预先训练好的视觉变压器(ViT)。通过采用混合注意力机制和跨模态位置编码,SAIL更好地适应了视觉和文本模态的独特特征。在扩大训练数据和模型规模的同时,SAIL的性能达到了模块化MLLM的水平。此外,去除预训练的ViT组件增强了SAIL的可扩展性,并导致了不同的跨模态信息流动模式。SAIL在视觉任务如语义分割上表现出强大的表示能力,与ViT-22B相当。
Key Takeaways
- SAIL是一个统一的多模态大型语言模型,集成了原始像素编码和语言解码在一个架构中。
- 与模块化MLLM不同,SAIL无需预训练的视觉变压器(ViT)。
- SAIL采用混合注意力机制和跨模态位置编码,以更好地适应视觉和文本模态的特征。
- 通过扩大训练数据和模型规模,SAIL实现了与模块化MLLM相当的性能。
- 去除预训练的ViT组件增强了SAIL的可扩展性,并改变了跨模态信息流动模式。
- SAIL在视觉任务上的表现强大,如语义分割,与ViT-22B相当。
点此查看论文截图
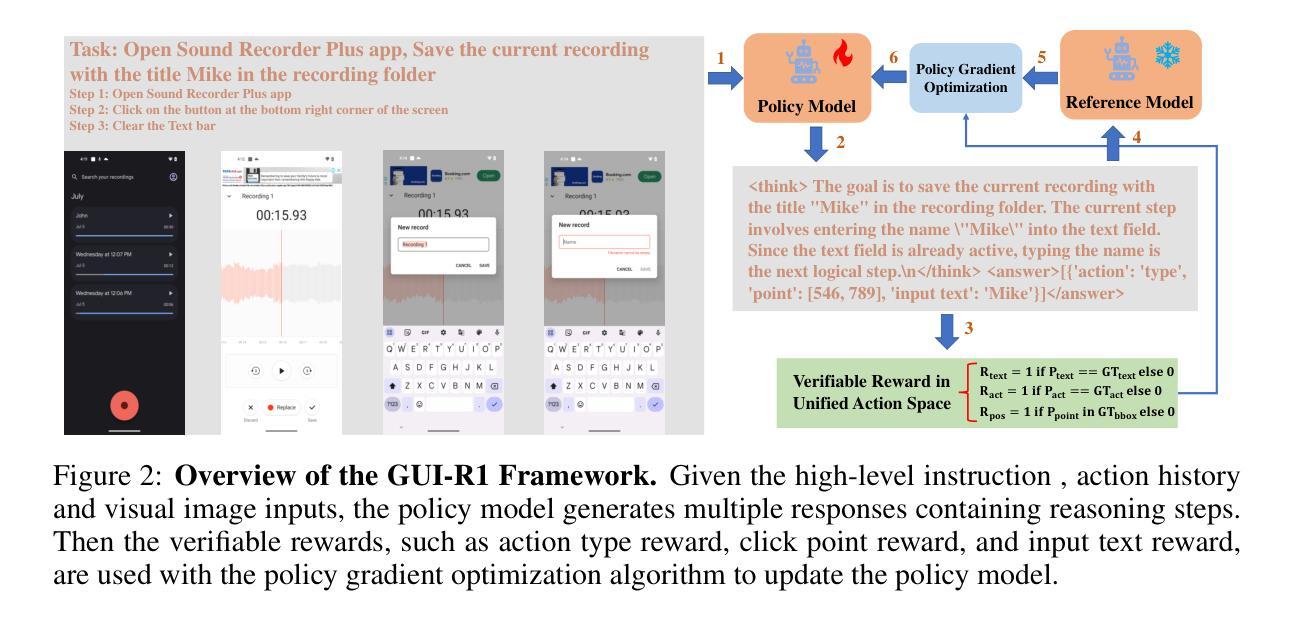
GUI-R1 : A Generalist R1-Style Vision-Language Action Model For GUI Agents
Authors:Xiaobo Xia, Run Luo
Existing efforts in building Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents largely rely on the training paradigm of supervised fine-tuning on Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs). However, this approach not only demands extensive amounts of training data but also struggles to effectively understand GUI screenshots and generalize to unseen interfaces. The issue significantly limits its application in real-world scenarios, especially for high-level tasks. Inspired by Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT) in large reasoning models (e.g., DeepSeek-R1), which efficiently enhances the problem-solving capabilities of large language models in real-world settings, we propose \name, the first reinforcement learning framework designed to enhance the GUI capabilities of LVLMs in high-level real-world task scenarios, through unified action space rule modeling. By leveraging a small amount of carefully curated high-quality data across multiple platforms (including Windows, Linux, MacOS, Android, and Web) and employing policy optimization algorithms such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to update the model, \name achieves superior performance using only 0.02% of the data (3K vs. 13M) compared to previous state-of-the-art methods like OS-Atlas across eight benchmarks spanning three different platforms (mobile, desktop, and web). These results demonstrate the immense potential of reinforcement learning based on unified action space rule modeling in improving the execution capabilities of LVLMs for real-world GUI agent tasks.
现有构建图形用户界面(GUI)代理的工作主要依赖于在大视觉语言模型(LVLMs)上进行的监督精细调整训练模式。然而,这种方法不仅需求大量的训练数据,而且在理解GUI截图和泛化到未见过的界面上存在困难。这一问题极大地限制了其在现实场景中的应用,尤其是高级任务。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
现有图形用户界面(GUI)代理构建主要依赖于在大视觉语言模型(LVLMs)上进行监督精细调整的训练模式。然而,这种方法不仅需求大量的训练数据,而且在理解GUI截图和泛化到未见界面方面存在困难。该问题显著限制了其在现实世界场景中的应用,尤其是高级任务。受大型推理模型中的强化精细调整(RFT)的启发(例如DeepSeek-R1),该方法可有效提高大型语言模型在现实世界设置中的问题解决能力,我们提出名为“\name”的强化学习框架,旨在通过统一动作空间规则建模,提高LVLMs在高级现实世界任务场景中的GUI能力。通过利用多个平台(包括Windows、Linux、MacOS、Android和Web)的小部分精心筛选的高质量数据,并采用群体相对策略优化(GRPO)等策略优化算法来更新模型,“\name”仅使用0.02%的数据(3K对1.3M)便在跨越三个不同平台(移动、桌面和网页)的八个基准测试中实现了对OS-Atlas等现有先进方法的卓越性能。这些结果证明了基于统一动作空间规则建模的强化学习在提升LVLMs执行现实世界GUI代理任务的潜力是巨大的。
关键见解
- 现有GUI代理构建主要依赖监督精细调整的训练模式,但此方法需要大量训练数据,且在理解GUI截图和泛化方面存在挑战。
- 强化学习框架“\name”被提出,旨在通过统一动作空间规则建模,提高LVLMs在高级现实世界任务场景中的GUI能力。
- “\name”利用跨多个平台的小部分高质量数据,并采用策略优化算法,如GRPO,来更新和增强模型性能。
- “\name”在仅使用0.02%的数据情况下,即在3K与13M之间,实现了对现先进方法的卓越性能。
- 这些结果在移动、桌面和网页等三个不同平台的八个基准测试中得到了验证。
- 强化学习在提升LVLMs执行现实世界GUI代理任务方面具有巨大潜力。
- “\name”的成功实施为未来的GUI代理开发设定了新的标准,展示了强化学习在解决现实世界复杂任务中的应用前景。
点此查看论文截图

M1: Towards Scalable Test-Time Compute with Mamba Reasoning Models
Authors:Junxiong Wang, Wen-Ding Li, Daniele Paliotta, Daniel Ritter, Alexander M. Rush, Tri Dao
Effective reasoning is crucial to solving complex mathematical problems. Recent large language models (LLMs) have boosted performance by scaling test-time computation through long chain-of-thought reasoning. However, transformer-based models are inherently limited in extending context length due to their quadratic computational complexity and linear memory requirements. In this paper, we introduce a novel hybrid linear RNN reasoning model, M1, built on the Mamba architecture, which allows memory-efficient inference. Our approach leverages a distillation process from existing reasoning models and is further enhanced through RL training. Experimental results on the AIME and MATH benchmarks show that M1 not only outperforms previous linear RNN models but also matches the performance of state-of-the-art Deepseek R1 distilled reasoning models at a similar scale. We also compare our generation speed with a highly performant general purpose inference engine, vLLM, and observe more than a 3x speedup compared to a same size transformer. With throughput speedup, we are able to achieve higher accuracy compared to DeepSeek R1 distilled transformer reasoning models under a fixed generation time budget using self-consistency voting. Overall, we introduce a hybrid Mamba reasoning model and provide a more effective approach to scaling test-time generation using self-consistency or long chain of thought reasoning.
有效的推理对于解决复杂的数学问题至关重要。最近的大型语言模型(LLM)通过测试时的计算扩展和长链条思维推理,提升了性能。然而,基于转换器的模型由于其二次计算复杂度和线性内存要求,在扩展上下文长度方面存在固有的局限性。在本文中,我们介绍了一种基于Mamba架构的新型混合线性RNN推理模型M1,它允许进行高效的内存推理。我们的方法利用从现有推理模型中提炼的过程,并通过强化学习训练进一步增强。在AIME和MATH基准测试上的实验结果表明,M1不仅优于以前的线性RNN模型,而且在相似规模下达到了最先进的Deepseek R1提炼推理模型的性能。我们还与高性能通用推理引擎vLLM比较了我们的生成速度,观察到与相同规模的转换器相比,速度提高了3倍以上。通过提高吞吐量,我们在固定的生成时间预算内,使用自我一致性投票,实现了比DeepSeek R1蒸馏转换器推理模型更高的精度。总的来说,我们介绍了一种混合的Mamba推理模型,并提供了一种更有效的方法来扩展测试时的生成,使用自我一致性或长链条思维推理。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is available https://github.com/jxiw/M1
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于Mamba架构的新型混合线性RNN推理模型M1,具有高效推理能力。通过蒸馏现有推理模型和强化学习训练,M1在AIME和MATH基准测试中表现出卓越性能,不仅优于先前的线性RNN模型,而且与同等规模的Deepseek R1蒸馏推理模型相当。此外,M1通过自我一致性投票实现了更高的准确性,并在固定生成时间预算下超过了DeepSeek R1模型。总体而言,本文提出了一个有效的混合推理模型M1,并给出了一种更有效的通过自我一致性或长思考链进行扩展测试时间生成的方法。
Key Takeaways
- M1模型基于Mamba架构,是一种新型混合线性RNN推理模型,具有高效推理能力。
- M1模型通过蒸馏现有推理模型和强化学习训练,优化了性能。
- 在AIME和MATH基准测试中,M1模型表现出卓越性能,优于先前的线性RNN模型,并达到同等规模的Deepseek R1模型的性能水平。
- M1模型具有更高的准确性,通过自我一致性投票实现。
- M1模型在固定生成时间预算下超过了DeepSeek R1模型。
- 该论文展示了M1模型的有效性和优越性,提供了一种新的测试时间扩展生成方法。
点此查看论文截图

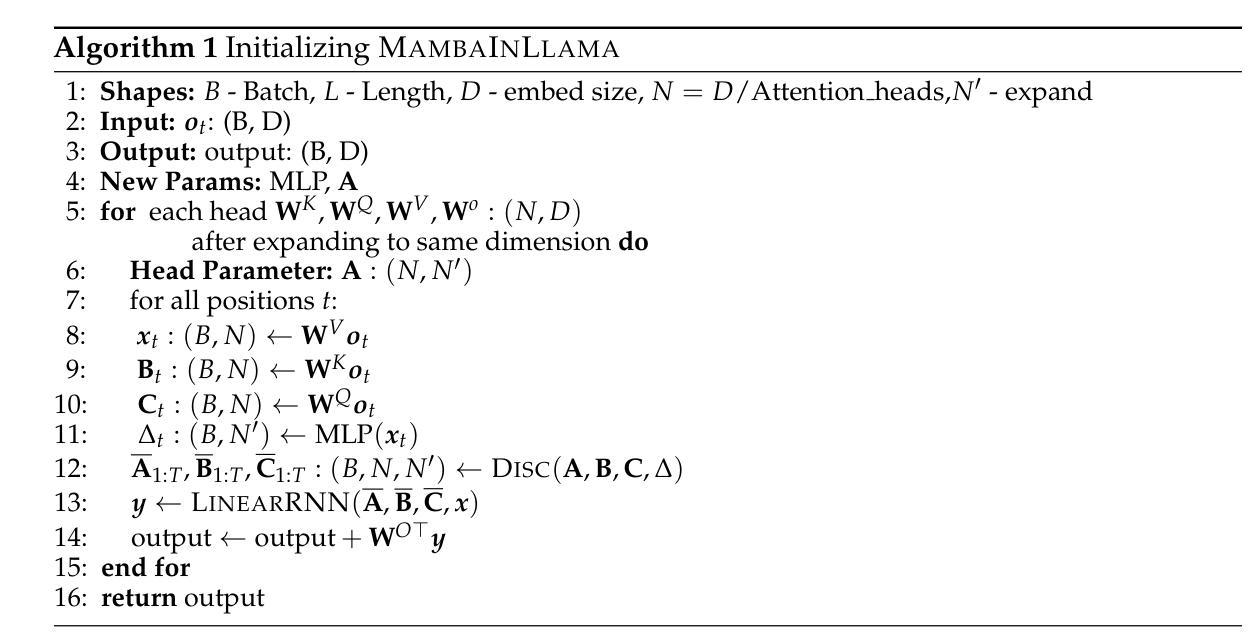
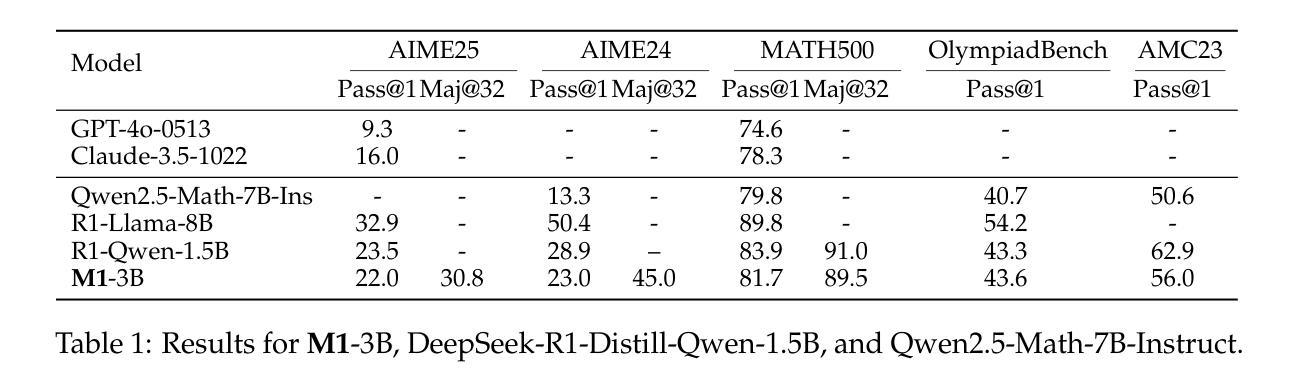
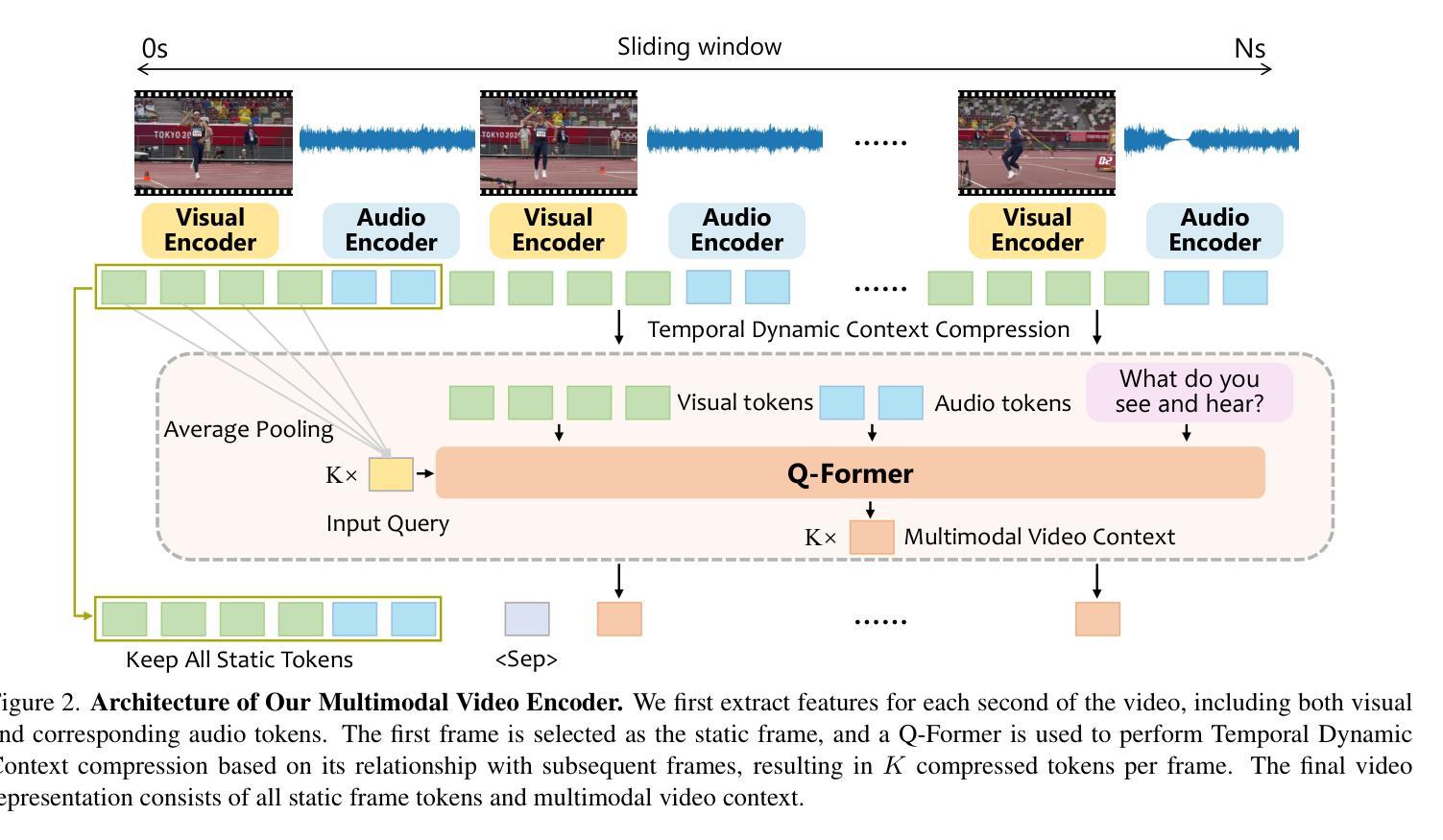
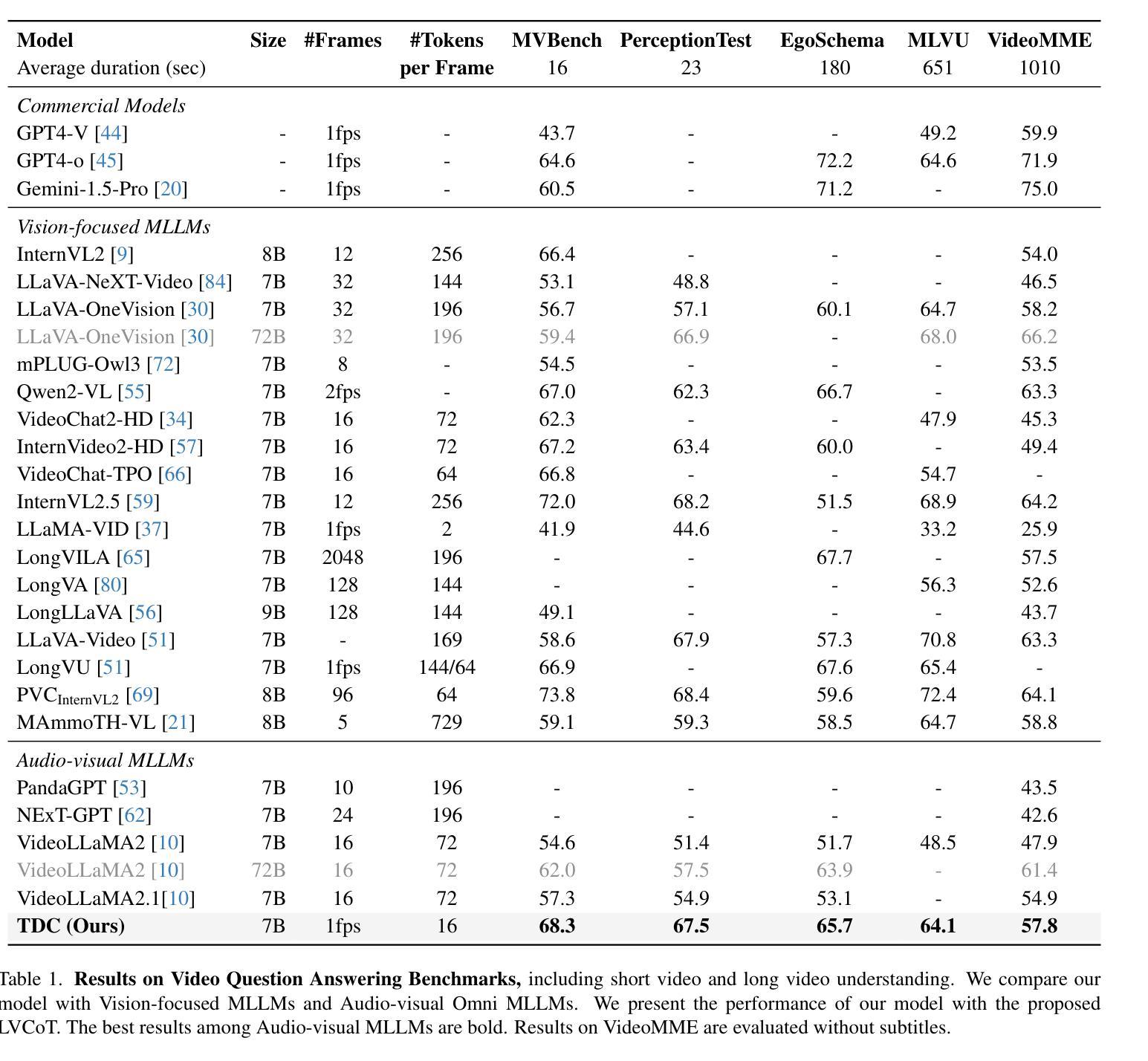
Multimodal Long Video Modeling Based on Temporal Dynamic Context
Authors:Haoran Hao, Jiaming Han, Yiyuan Zhang, Xiangyu Yue
Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have led to significant breakthroughs in video understanding. However, existing models still struggle with long video processing due to the context length constraint of LLMs and the vast amount of information within the video. Although some recent methods are designed for long video understanding, they often lose crucial information during token compression and struggle with additional modality like audio. In this work, we propose a dynamic long video encoding method utilizing the temporal relationship between frames, named Temporal Dynamic Context (TDC). Firstly, we segment the video into semantically consistent scenes based on inter-frame similarities, then encode each frame into tokens using visual-audio encoders. Secondly, we propose a novel temporal context compressor to reduce the number of tokens within each segment. Specifically, we employ a query-based Transformer to aggregate video, audio, and instruction text tokens into a limited set of temporal context tokens. Finally, we feed the static frame tokens and the temporal context tokens into the LLM for video understanding. Furthermore, to handle extremely long videos, we propose a training-free chain-of-thought strategy that progressively extracts answers from multiple video segments. These intermediate answers serve as part of the reasoning process and contribute to the final answer. We conduct extensive experiments on general video understanding and audio-video understanding benchmarks, where our method demonstrates strong performance. The code and models are available at https://github.com/Hoar012/TDC-Video.
近年来,大型语言模型(LLM)的进展在视频理解方面取得了重大突破。然而,由于LLM的上下文长度限制和视频中的大量信息,现有模型在处理长视频时仍然面临困难。尽管有一些最近的方法是为长视频理解而设计的,但它们通常在令牌压缩时会丢失关键信息,并且在处理音频等附加模态时遇到困难。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种利用帧之间时间关系的动态长视频编码方法,称为时间动态上下文(TDC)。首先,我们根据帧间相似性将视频分割成语义上连贯的场景,然后使用视觉音频编码器将每帧编码成令牌。其次,我们提出了一种新型的时间上下文压缩机,以减少每个段内的令牌数量。具体来说,我们采用基于查询的Transformer来聚合视频、音频和指令文本令牌,将其压缩成有限的时间上下文令牌集。最后,我们将静态帧令牌和时间上下文令牌输入LLM进行视频理解。此外,为了处理极长的视频,我们提出了一种无需训练的思维链策略,该策略从多个视频段中逐步提取答案。这些中间答案作为推理过程的一部分,并为最终答案做出贡献。我们在一般视频理解和音视频理解基准测试上进行了广泛实验,我们的方法展示了强大的性能。代码和模型可在https://github.com/Hoar012/TDC-Video上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种利用帧间时序关系的动态长视频编码方法,称为时序动态上下文(TDC)。该方法将视频分割成语义上一致的场景,使用视觉-音频编码器对每帧进行编码,并提出一种新颖的时序上下文压缩器,减少每个片段中的令牌数量。同时,结合查询基础转换器将视频、音频和指令文本令牌聚集到有限的时序上下文令牌中。为了处理极长的视频,采用无训练的思考链策略,从多个视频片段中逐步提取答案。这些中间答案作为推理过程的一部分,并为最终答案做出贡献。该方法在通用视频理解和音频视频理解基准测试中表现出强大的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种名为时序动态上下文(TDC)的编码方法,用于处理长视频理解。
- 通过分割视频成语义一致的场景并编码每帧,以提高视频理解性能。
- 引入了一种新的时序上下文压缩器,以减少令牌数量并提高处理效率。
- 结合使用查询基础转换器来处理视频、音频和指令文本信息。
- 采用无训练的思考链策略,逐步从长视频中提取答案。
- 方法在通用视频理解和音视频理解基准测试中取得了强大性能。
点此查看论文截图
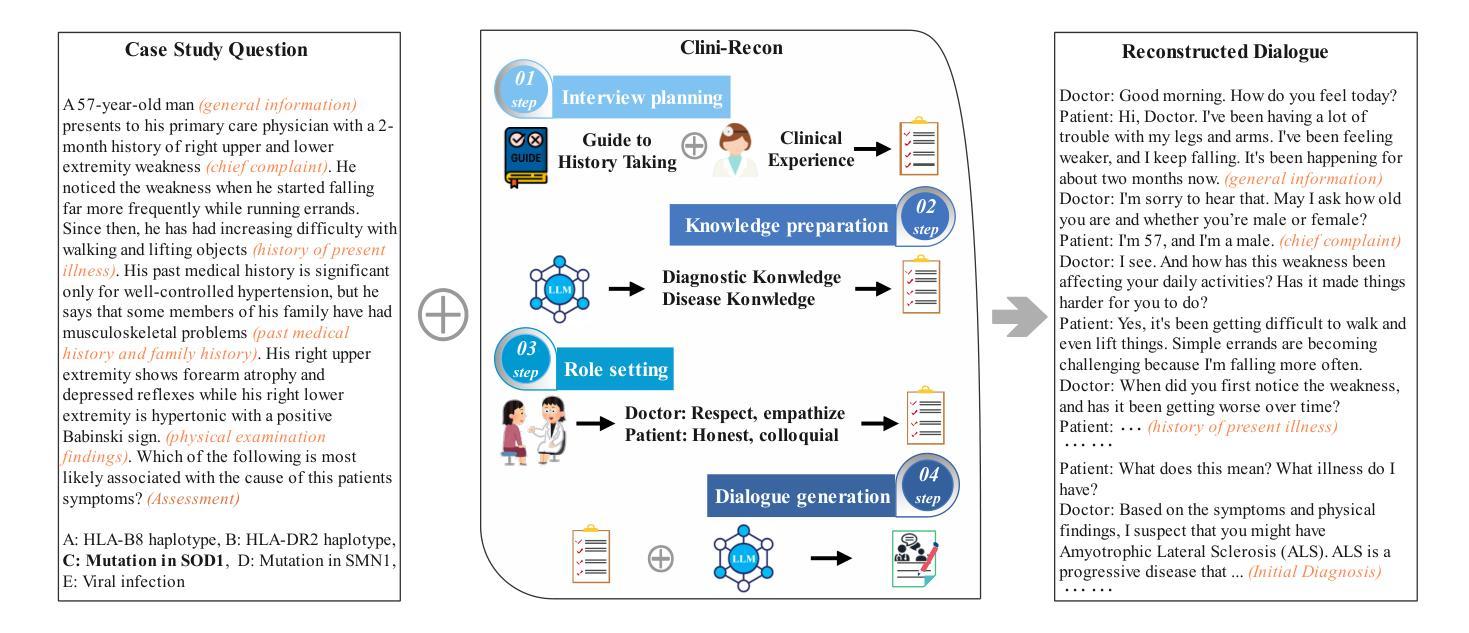
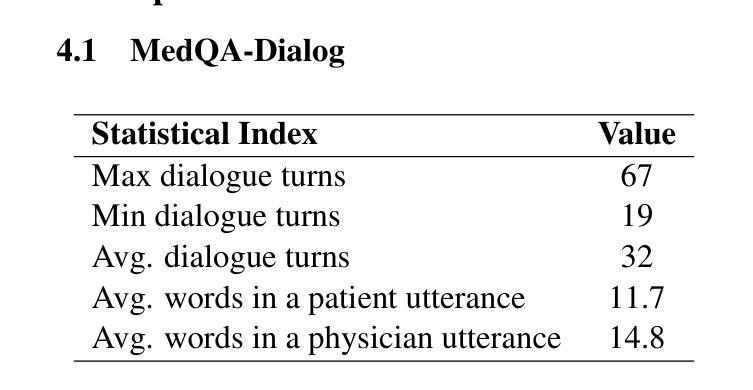
CliniChat: A Multi-Source Knowledge-Driven Framework for Clinical Interview Dialogue Reconstruction and Evaluation
Authors:Jing Chen, Zhihua Wei, Wei Zhang, Yingying Hu, Qiong Zhang
Large language models (LLMs) hold great promise for assisting clinical interviews due to their fluent interactive capabilities and extensive medical knowledge. However, the lack of high-quality interview dialogue data and widely accepted evaluation methods has significantly impeded this process. So we propose CliniChat, a framework that integrates multi-source knowledge to enable LLMs to simulate real-world clinical interviews. It consists of two modules: Clini-Recon and Clini-Eval, each responsible for reconstructing and evaluating interview dialogues, respectively. By incorporating three sources of knowledge, Clini-Recon transforms clinical notes into systematic, professional, and empathetic interview dialogues. Clini-Eval combines a comprehensive evaluation metric system with a two-phase automatic evaluation approach, enabling LLMs to assess interview performance like experts. We contribute MedQA-Dialog, a high-quality synthetic interview dialogue dataset, and CliniChatGLM, a model specialized for clinical interviews. Experimental results demonstrate that CliniChatGLM’s interview capabilities undergo a comprehensive upgrade, particularly in history-taking, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
大型语言模型(LLM)因其流畅的交互能力和丰富的医学知识,在辅助临床访谈方面展现出巨大潜力。然而,高质量访谈对话数据的缺乏以及广泛接受的评估方法的缺失,极大地阻碍了这一进程。因此,我们提出了CliniChat框架,它整合了多源知识,使LLM能够模拟现实世界的临床访谈。CliniChat框架包含两个模块:Clini-Recon和Clini-Eval,分别负责重建和评估访谈对话。Clini-Recon通过融合三种知识源,将临床笔记转化为系统、专业且富有同情心的访谈对话。Clini-Eval结合了一个综合评估指标系统和一个两阶段的自动评估方法,使LLM能够像专家一样评估访谈表现。我们贡献了MedQA-Dialog这一高质量合成访谈对话数据集和专用于临床访谈的CliniChatGLM模型。实验结果表明,CliniChatGLM的访谈能力得到了全面提升,特别是在病史采集方面达到了先进水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在模拟真实临床访谈方面具有巨大潜力,但缺乏高质量访谈对话数据和广泛接受的评估方法。为此,我们提出CliniChat框架,整合多源知识,使LLM能够模拟真实世界临床访谈。该框架包括Clini-Recon和Clini-Eval两个模块,分别负责重建和评估访谈对话。通过结合三种知识源,Clini-Recon能将临床笔记转化为系统、专业、富有同情心的访谈对话。Clini-Eval则结合全面的评估指标体系和两阶段自动评估方法,使LLM能够像专家一样评估访谈表现。我们贡献了MedQA-Dialog这一高质量合成访谈对话数据集和专为临床访谈设计的CliniChatGLM模型。实验结果表明,CliniChatGLM的访谈能力得到全面提升,特别是在病史采集方面达到最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs展现出在临床访谈中的巨大潜力,但仍面临缺乏高质量数据和评估方法的挑战。
- CliniChat框架通过整合多源知识提升LLM模拟真实临床访谈的能力。
- CliniChat包含Clini-Recon和Clini-Eval两个模块,分别负责重建和评估访谈对话。
- Clini-Recon能转化临床笔记为系统、专业、有同情心的访谈对话,结合三种知识源。
- Clini-Eval采用全面的评估指标体系和两阶段自动评估方法,模拟专家评估访谈表现。
- 贡献了MedQA-Dialog数据集,为临床访谈对话提供高质量合成数据。
点此查看论文截图

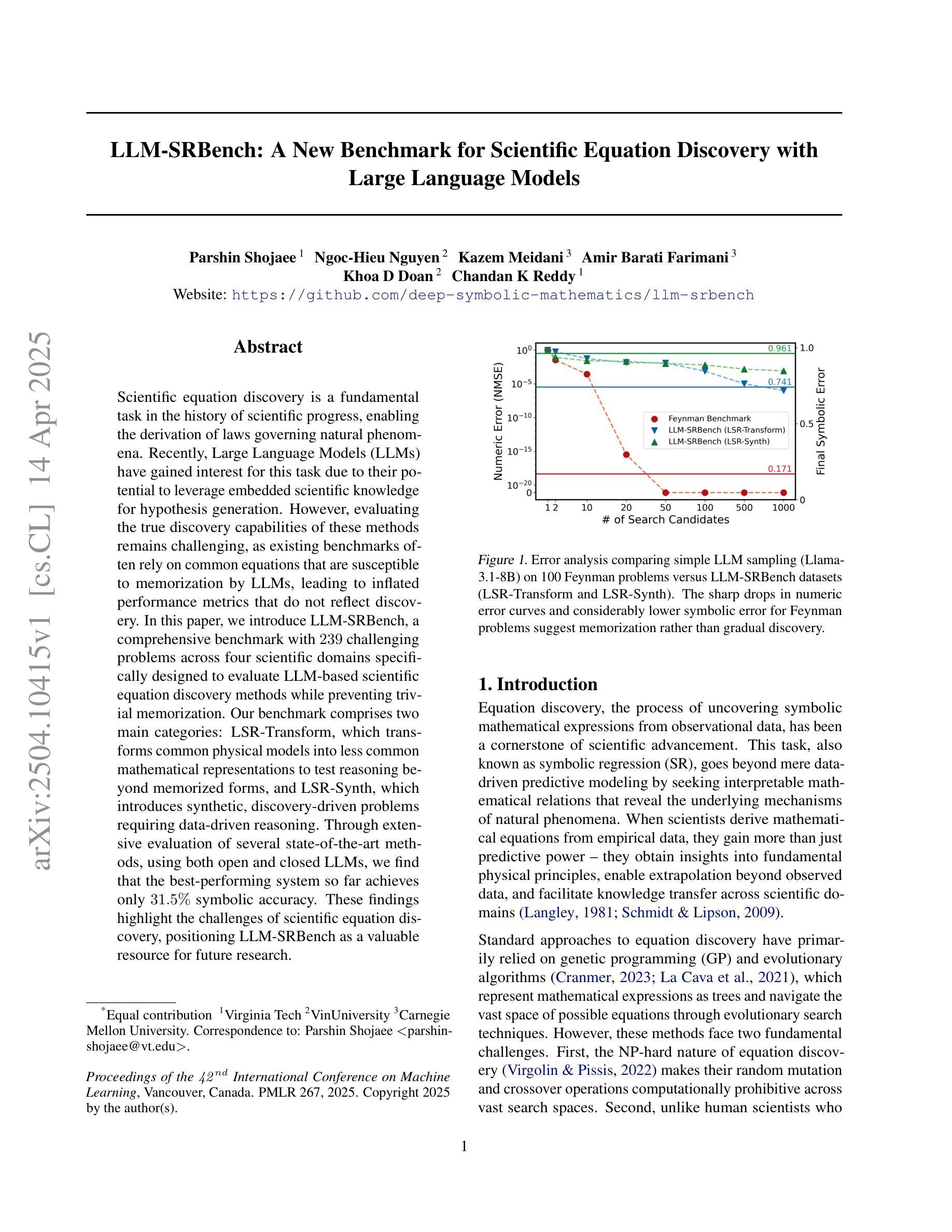
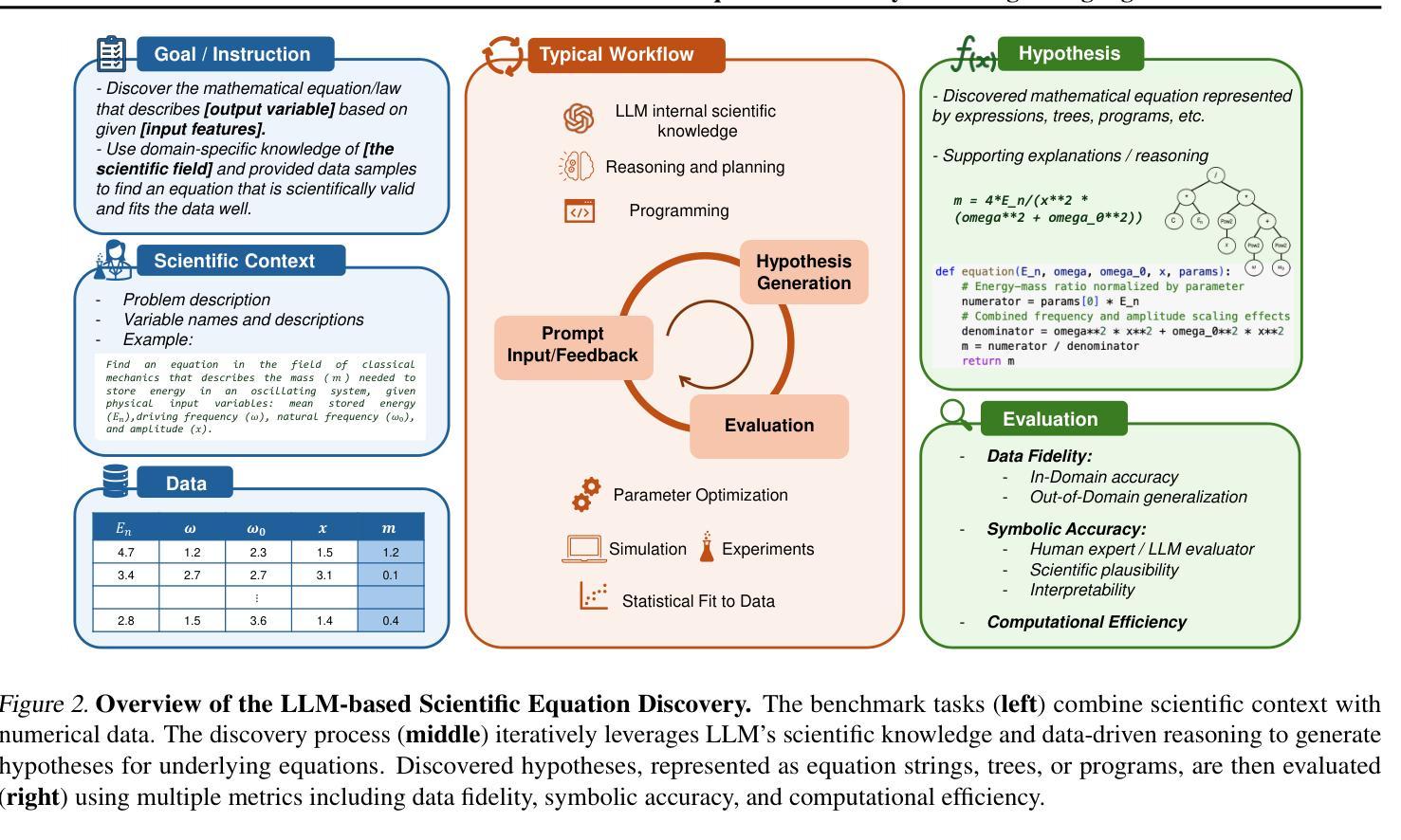
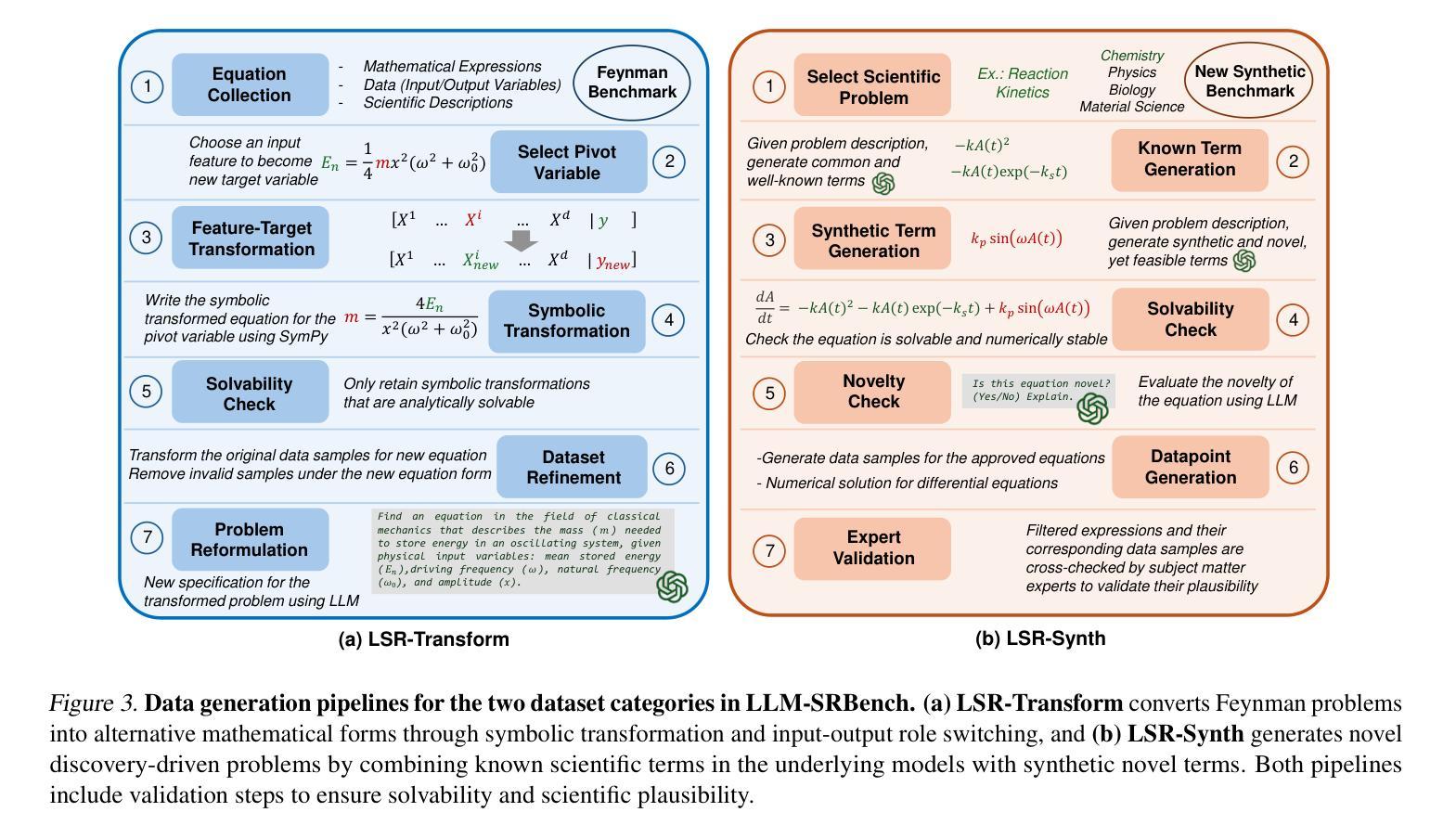
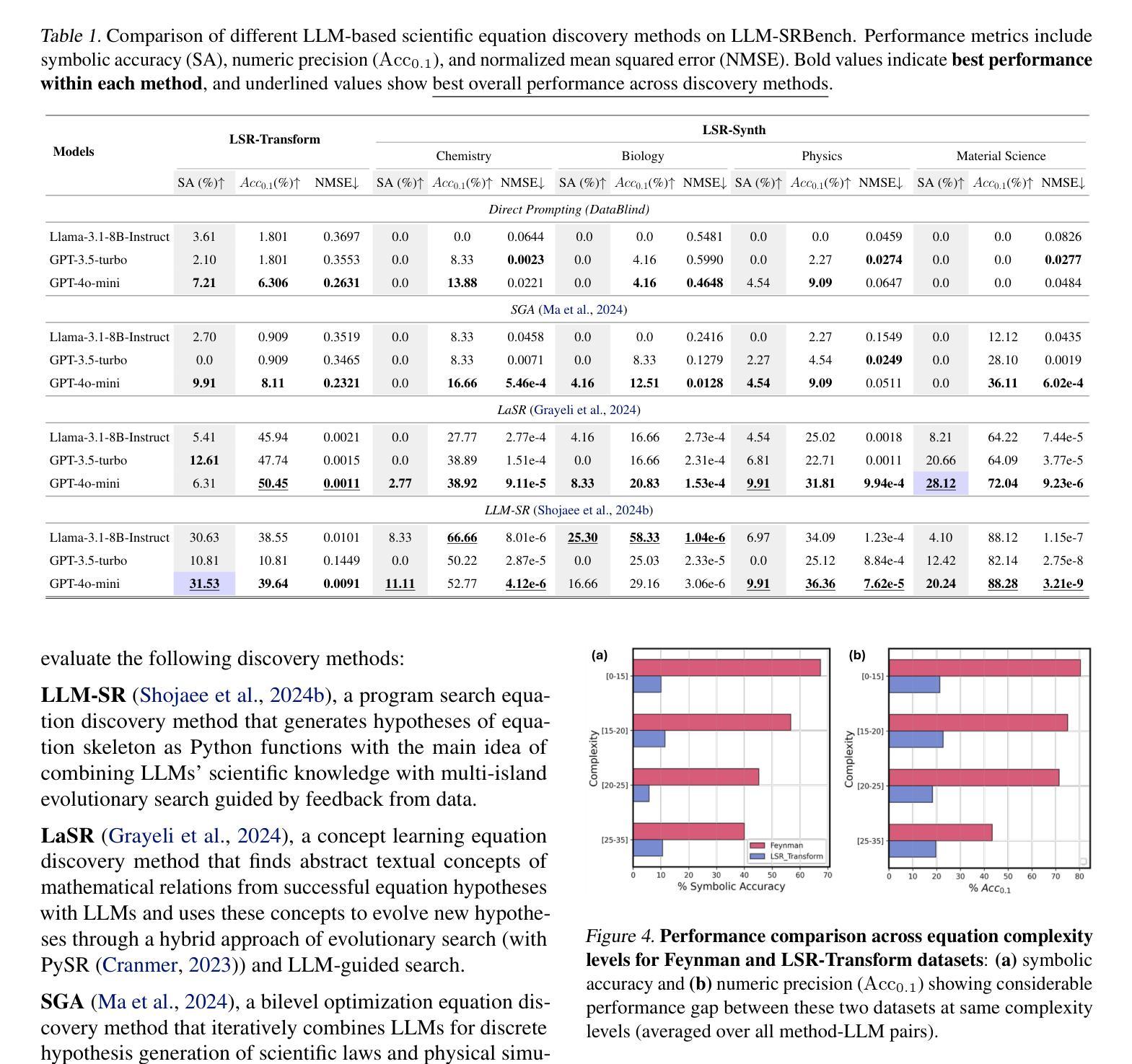
LLM-SRBench: A New Benchmark for Scientific Equation Discovery with Large Language Models
Authors:Parshin Shojaee, Ngoc-Hieu Nguyen, Kazem Meidani, Amir Barati Farimani, Khoa D Doan, Chandan K Reddy
Scientific equation discovery is a fundamental task in the history of scientific progress, enabling the derivation of laws governing natural phenomena. Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have gained interest for this task due to their potential to leverage embedded scientific knowledge for hypothesis generation. However, evaluating the true discovery capabilities of these methods remains challenging, as existing benchmarks often rely on common equations that are susceptible to memorization by LLMs, leading to inflated performance metrics that do not reflect discovery. In this paper, we introduce LLM-SRBench, a comprehensive benchmark with 239 challenging problems across four scientific domains specifically designed to evaluate LLM-based scientific equation discovery methods while preventing trivial memorization. Our benchmark comprises two main categories: LSR-Transform, which transforms common physical models into less common mathematical representations to test reasoning beyond memorized forms, and LSR-Synth, which introduces synthetic, discovery-driven problems requiring data-driven reasoning. Through extensive evaluation of several state-of-the-art methods, using both open and closed LLMs, we find that the best-performing system so far achieves only 31.5% symbolic accuracy. These findings highlight the challenges of scientific equation discovery, positioning LLM-SRBench as a valuable resource for future research.
科学方程发现(Scientific equation discovery)是科学进步历史中的一项基础任务,能够使推导出自然现象的定律成为可能。近期,大型语言模型(LLM)因其在假设生成中利用嵌入的科学知识而受到关注,进而应用于这一任务。然而,评估这些方法的真实发现能力仍然具有挑战性,因为现有的基准测试通常依赖于常见的方程,这些方程容易被LLM记忆,导致性能指标膨胀,无法反映真正的发现能力。在本文中,我们介绍了LLM-SRBench,这是一个包含239个挑战性问题的全面基准测试,专门设计用于评估基于LLM的科学方程发现方法,同时防止简单的记忆。我们的基准测试主要包括两个类别:LSR-Transform,它将常见的物理模型转化为不太常见的数学表示形式,以测试超越记忆形式的推理能力;以及LSR-Synth,它引入合成问题,以发现驱动需要数据驱动推理的问题。通过对几种最新方法进行广泛评估,使用开放和封闭LLM结合的方式,我们发现迄今为止表现最好的系统仅达到31.5%的符号准确率。这些发现突显了科学方程发现的挑战,将LLM-SRBench定位为未来研究的重要资源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://github.com/deep-symbolic-mathematics/llm-srbench , Benchmark page: https://huggingface.co/datasets/nnheui/llm-srbench
Summary
在科学进步的历史中,科学方程的发现是一项基础任务,它推动了支配自然现象的定律的推导。近期,大型语言模型(LLM)在此任务中因其产生假设的潜力而备受关注。然而,评估这些方法的真正发现能力仍然具有挑战性,因为现有基准测试通常依赖于LLM容易记忆的一般方程,导致性能指标膨胀,并不能反映真正的发现能力。本文介绍了LLM-SRBench,这是一个包含239个跨四个科学领域的挑战性问题的综合基准测试,专门用于评估基于LLM的科学方程发现方法,同时防止了简单的记忆测试。我们的基准测试包括两个主要类别:LSR-Transform,它将常见的物理模型转化为不太常见的数学表示形式,以测试超越记忆形式的推理能力;LSR-Synth,它引入合成、以发现为导向的问题,需要数据驱动推理。通过对几种最新方法的广泛评估,包括开放和封闭式的LLM,我们发现目前表现最佳的系统的符号准确率仅为31.5%。这些发现突显了科学方程发现的挑战,定位LLM-SRBench为未来研究的有价值的资源。
Key Takeaways
- 科学方程发现在科学进步中起关键作用,推动自然现象的定律推导。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)近期在科学方程发现任务中受到关注,因其产生假设的潜力。
- 评估LLM在方程发现中的真实能力具有挑战性,因为现有基准测试易于导致LLM通过记忆而非真正发现来达成。
- LLM-SRBench基准测试被设计用于评估LLM的科学方程发现能力,包含两类问题:测试推理能力的LSR-Transform和需要数据驱动推理的合成问题LSR-Synth。
- 目前最佳系统的符号准确率仅为31.5%,表明科学方程发现的挑战仍然很大。
- LLM-SRBench对未来研究具有价值,可作为评估和改进LLM在方程发现中性能的重要工具。
点此查看论文截图
Performance of Large Language Models in Supporting Medical Diagnosis and Treatment
Authors:Diogo Sousa, Guilherme Barbosa, Catarina Rocha, Dulce Oliveira
The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into healthcare holds significant potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy and support medical treatment planning. These AI-driven systems can analyze vast datasets, assisting clinicians in identifying diseases, recommending treatments, and predicting patient outcomes. This study evaluates the performance of a range of contemporary LLMs, including both open-source and closed-source models, on the 2024 Portuguese National Exam for medical specialty access (PNA), a standardized medical knowledge assessment. Our results highlight considerable variation in accuracy and cost-effectiveness, with several models demonstrating performance exceeding human benchmarks for medical students on this specific task. We identify leading models based on a combined score of accuracy and cost, discuss the implications of reasoning methodologies like Chain-of-Thought, and underscore the potential for LLMs to function as valuable complementary tools aiding medical professionals in complex clinical decision-making.
将大型语言模型(LLM)集成到医疗保健中,具有提高诊断准确性和支持医疗治疗计划的巨大潜力。这些人工智能驱动的系统可以分析大量数据集,帮助临床医生识别疾病、推荐治疗方法并预测患者结果。本研究评估了一系列当代LLM的性能,包括开源和闭源模型,在2024年葡萄牙医学专科入学国家考试(PNA)上的表现,这是一项标准化的医学知识评估。我们的结果强调了准确度和成本效益方面的巨大差异,一些模型在这个特定任务上的表现超过了医学学生的基准水平。我们根据准确度和成本的综合得分确定了领先的模型,讨论了链式思维等推理方法的影响,并强调了LLM作为有价值的辅助工具,在帮助医学专业人士进行复杂临床决策方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 6 figures, 4 tables. Acknowledgements: The authors acknowledge the support of the AITriage4SU Project (2024.07400.IACDC/2024), funded by the FCT (Foundation for Science and Technology), Portugal
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在医疗领域的集成应用具有提高诊断准确性和支持医疗治疗计划制定的巨大潜力。这些人工智能驱动的系统能够分析庞大的数据集,帮助临床医生识别疾病、推荐治疗方案和预测患者结果。本研究评估了一系列现代LLM在2024年葡萄牙医学专科入学考试(PNA)上的表现,这是一个标准化的医学知识评估。研究结果突出了准确性和成本效益的显著差异,多种模型的表现在这一特定任务上超过了医学学生的基准水平。根据准确性和成本的综合得分确定了领先的模型,并讨论了链式思维等推理方法的影响,强调了LLM作为有价值的辅助工具在医疗专业复杂决策制定中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- LLM集成到医疗领域可提高诊断准确性和治疗计划制定的效率。
- LLM能够分析庞大的医疗数据集,辅助临床医生的决策。
- 在葡萄牙医学专科入学考试中评估了多种LLM的表现。
- 不同LLM在准确性和成本效益上存在差异。
- 部分LLM的表现超过了医学学生在特定任务上的水平。
- 链式思维等推理方法对LLM的表现有影响。
点此查看论文截图

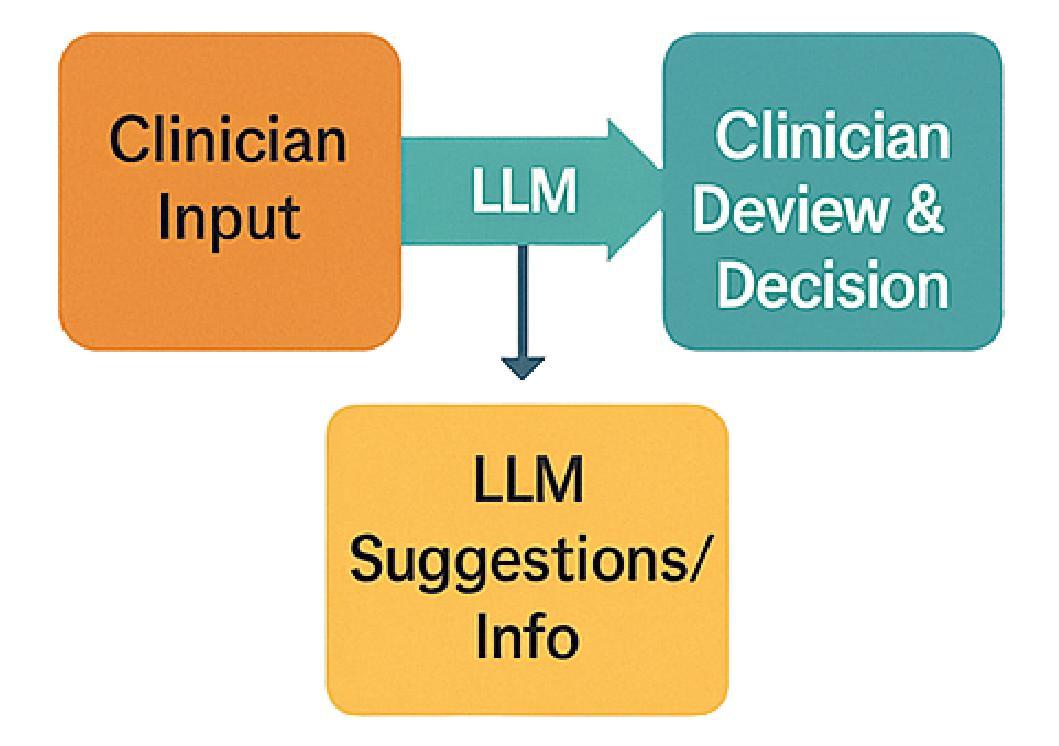
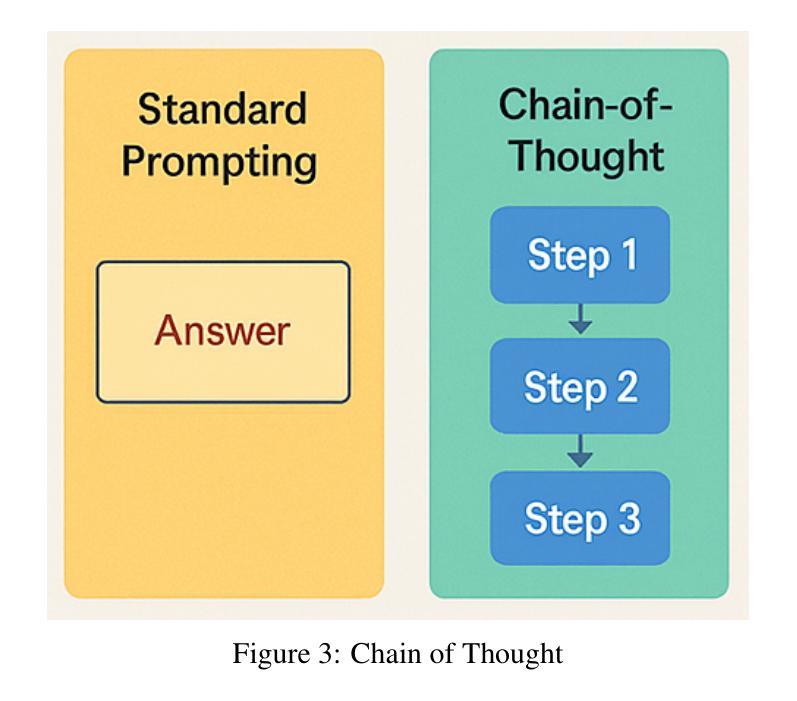
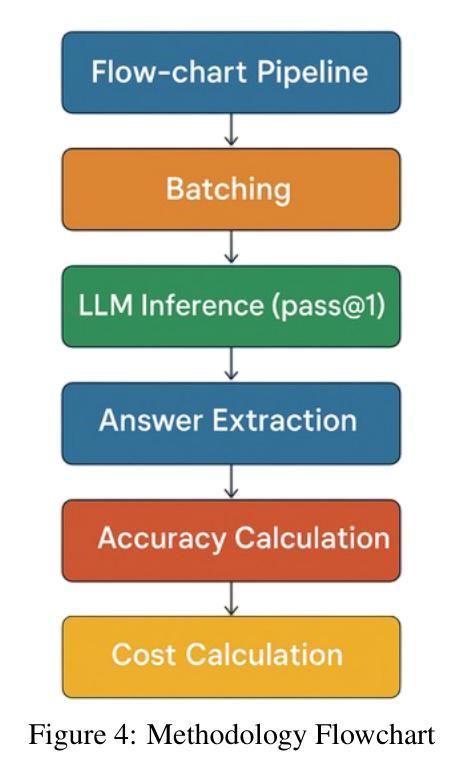
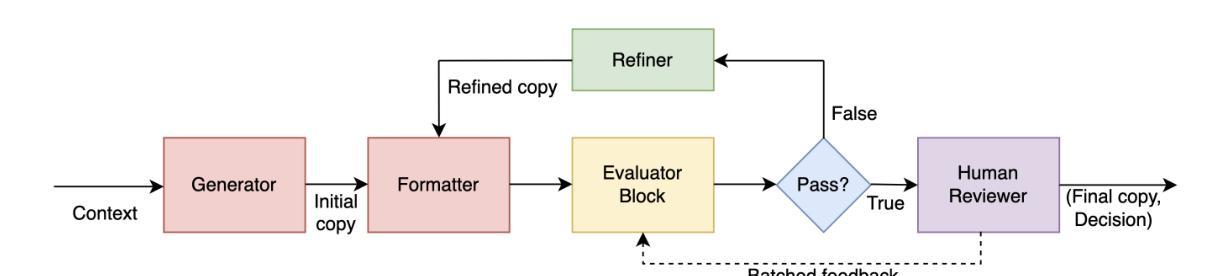
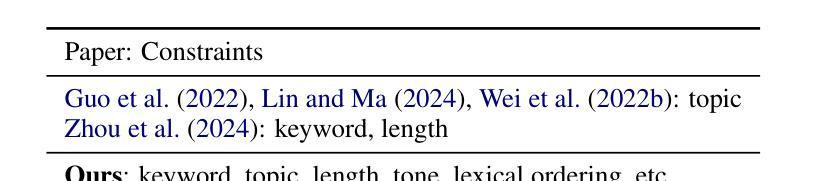
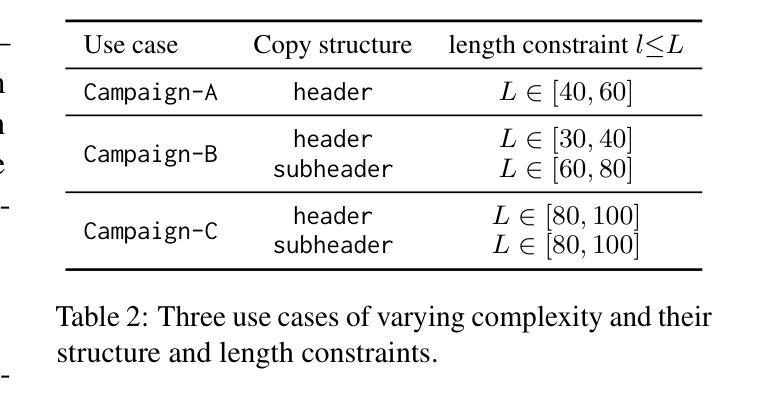
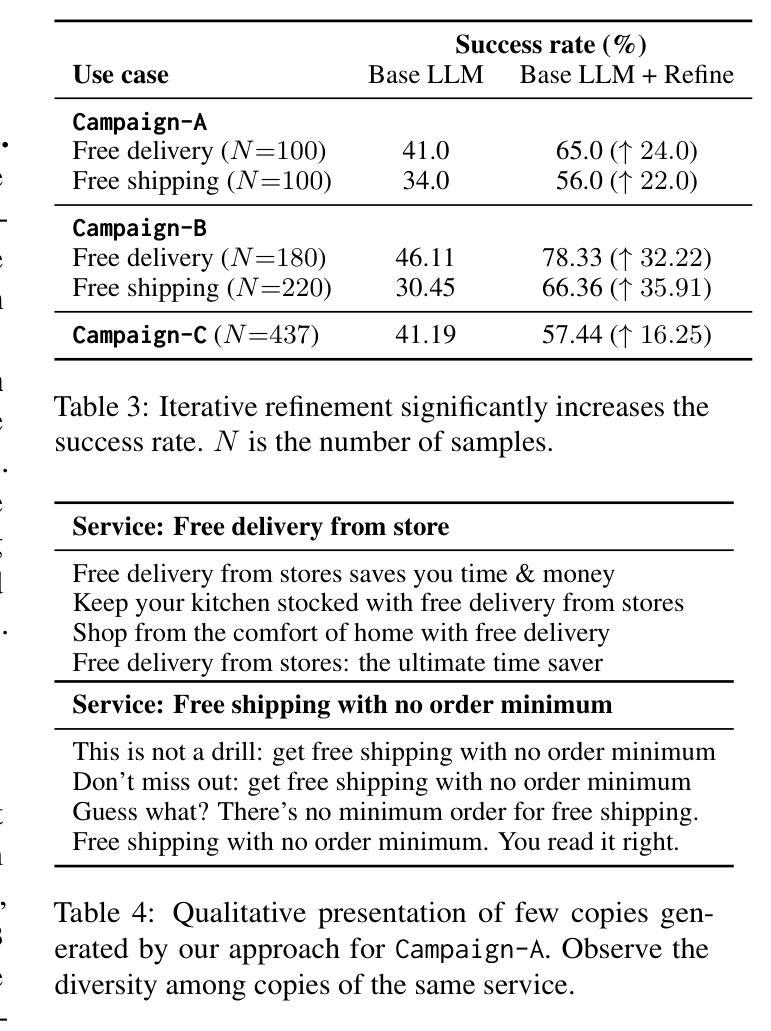
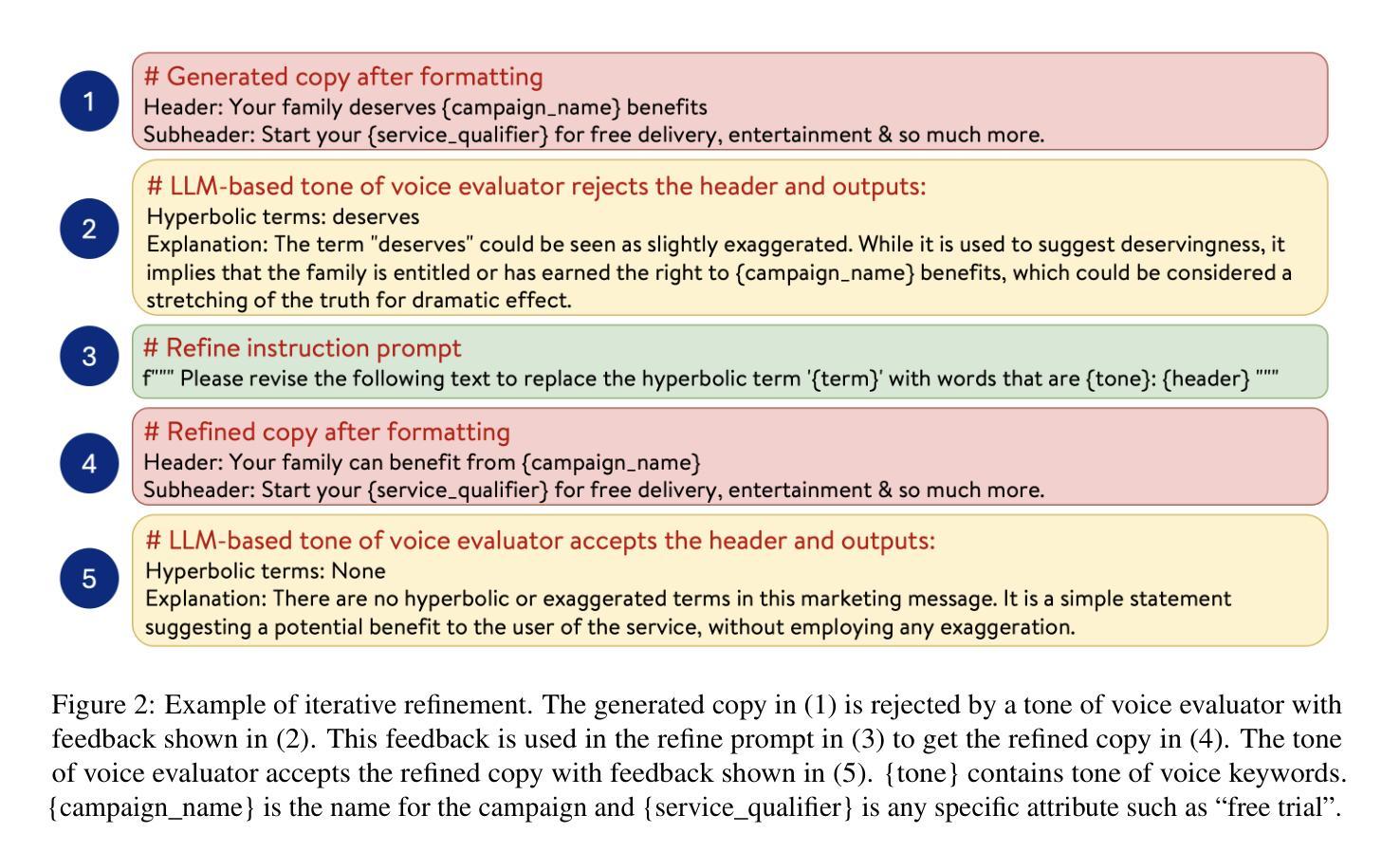
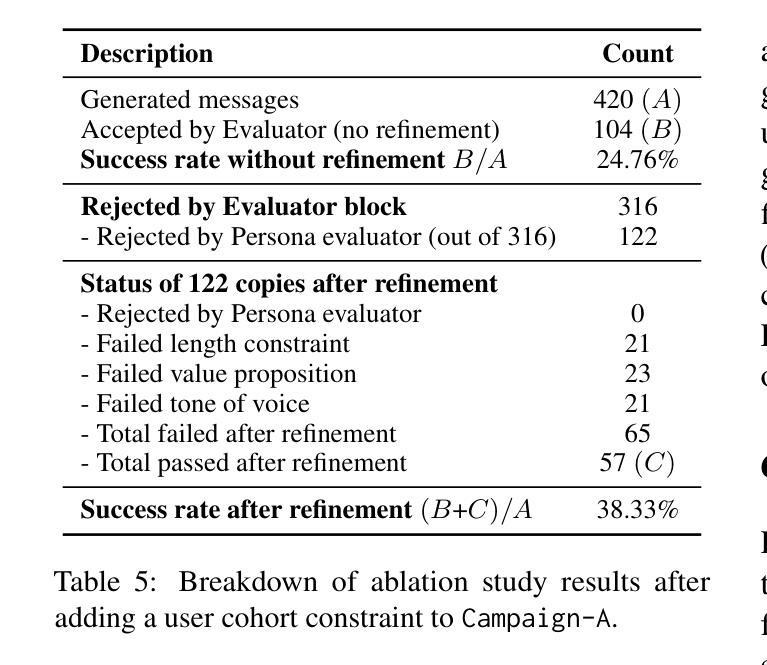
LLM-driven Constrained Copy Generation through Iterative Refinement
Authors:Varun Vasudevan, Faezeh Akhavizadegan, Abhinav Prakash, Yokila Arora, Jason Cho, Tanya Mendiratta, Sushant Kumar, Kannan Achan
Crafting a marketing message (copy), or copywriting is a challenging generation task, as the copy must adhere to various constraints. Copy creation is inherently iterative for humans, starting with an initial draft followed by successive refinements. However, manual copy creation is time-consuming and expensive, resulting in only a few copies for each use case. This limitation restricts our ability to personalize content to customers. Contrary to the manual approach, LLMs can generate copies quickly, but the generated content does not consistently meet all the constraints on the first attempt (similar to humans). While recent studies have shown promise in improving constrained generation through iterative refinement, they have primarily addressed tasks with only a few simple constraints. Consequently, the effectiveness of iterative refinement for tasks such as copy generation, which involves many intricate constraints, remains unclear. To address this gap, we propose an LLM-based end-to-end framework for scalable copy generation using iterative refinement. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to address multiple challenging constraints simultaneously in copy generation. Examples of these constraints include length, topics, keywords, preferred lexical ordering, and tone of voice. We demonstrate the performance of our framework by creating copies for e-commerce banners for three different use cases of varying complexity. Our results show that iterative refinement increases the copy success rate by $16.25-35.91$% across use cases. Furthermore, the copies generated using our approach outperformed manually created content in multiple pilot studies using a multi-armed bandit framework. The winning copy improved the click-through rate by $38.5-45.21$%.
构建营销信息(文案)或文案创作是一项充满挑战的创作任务,因为文案必须遵守各种约束。对于人类来说,文案创作本质上是迭代的,从初步草稿开始,接着进行连续不断的改进。然而,手动创建文案既耗时又昂贵,导致每次用例只有少数几个文案。这种限制限制了我们对客户内容的个性化能力。与手动方法相反,大型语言模型可以快速生成文案,但生成的内容并不总能第一次尝试就满足所有约束(与人类相似)。虽然最近的研究通过迭代改进在改进受限生成方面显示出希望,但它们主要解决了只有少数简单约束的任务。因此,对于涉及许多复杂约束的任务(如文案创作)的迭代改进的有效性仍然不清楚。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了一种基于大型语言模型的端到端框架,用于使用迭代改进进行可扩展的文案生成。据我们所知,这是首次研究同时解决文案生成中多个具有挑战性的约束。这些约束的示例包括长度、主题、关键词、首选词汇顺序和语气。我们通过为三个不同复杂度的电子商务横幅创建文案来展示我们框架的性能。我们的结果表明,迭代改进提高了文案成功率$16.25-35.91$%。此外,使用我们的方法生成的文案在多组试点研究中超过了手动创建的内容,这些研究采用多臂老虎机框架,最佳文案提高了点击率$38.5-45.21$%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures, 7 Tables
Summary
本文探讨了使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行文案生成的问题。由于文案需要满足多种约束,传统的手动创作方式既耗时又昂贵,且难以实现个性化。虽然LLM可以快速生成文案,但一次生成的文案并不总能完全满足所有约束。针对此问题,本文提出了一个基于LLM的端到端框架,采用迭代优化方式进行文案生成。该框架能同时处理多种复杂约束,如长度、主题、关键词、词汇顺序和语调等。通过电商横幅广告文案的生成实例,证明了迭代优化能提高文案成功率,且生成的文案在点击率方面超越了手动创作的文案。
Key Takeaways
- 文案创作是一项需要满足多种约束的挑战性任务,手动创作既耗时又昂贵,且难以实现个性化。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)能快速生成文案,但一次生成的文案并不总能满足所有约束。
- 本文提出了一个基于LLM的端到端框架,采用迭代优化方式进行文案生成。
- 该框架能同时处理多种复杂约束,如长度、主题、关键词、词汇顺序和语调等。
- 迭代优化能提高文案生成的成功率,且在点击率方面表现出优越性能。
- 相较于手动创作的文案,使用此框架生成的文案在多项试点研究中表现更佳。
点此查看论文截图

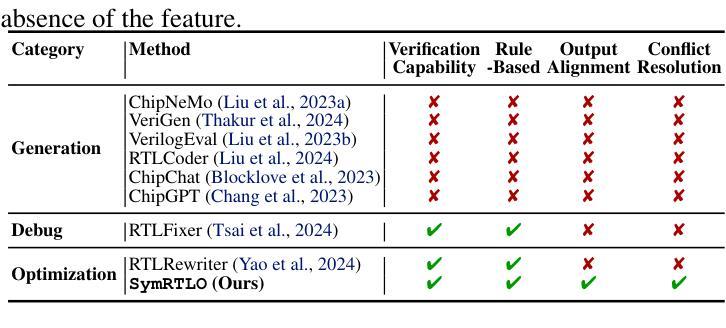
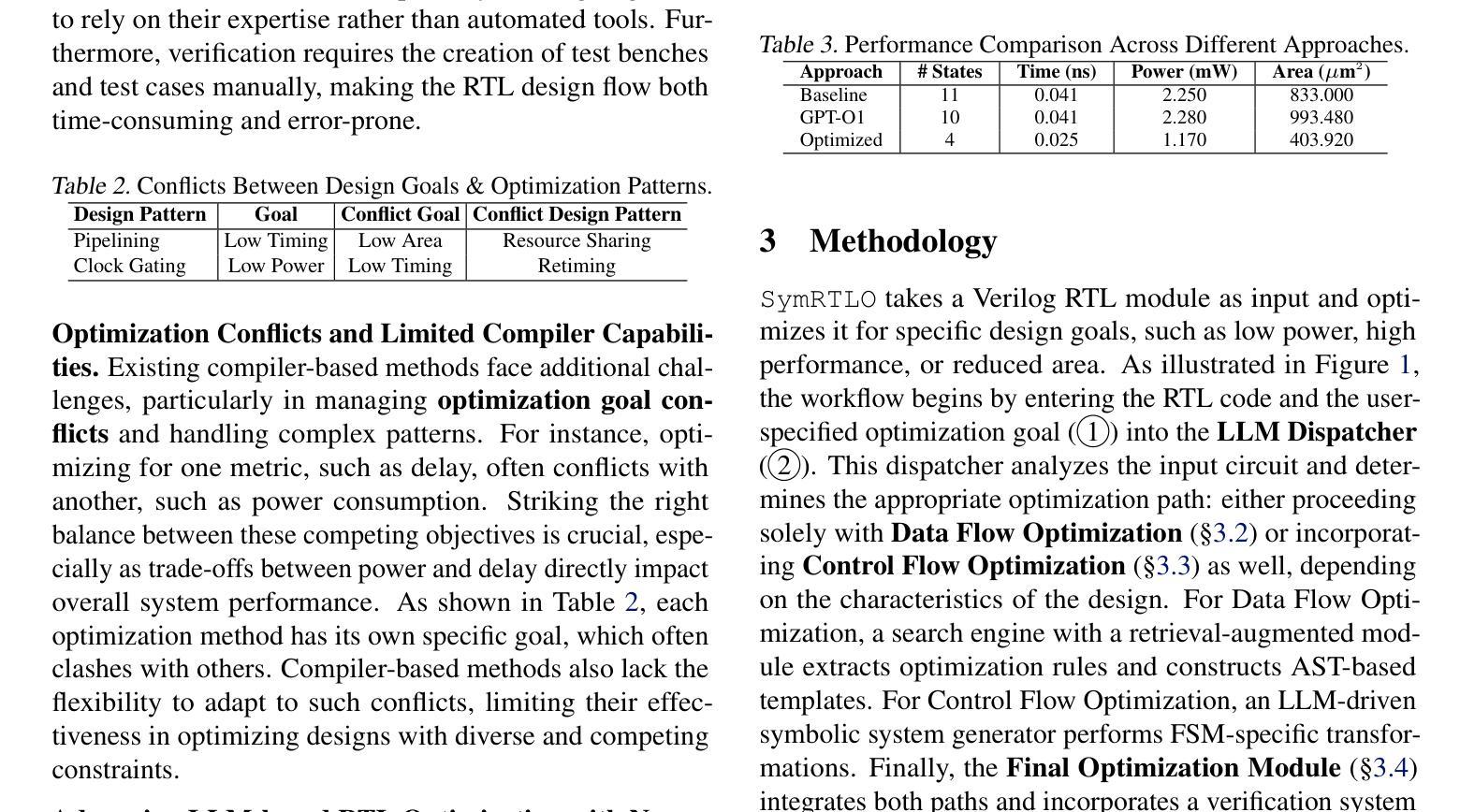
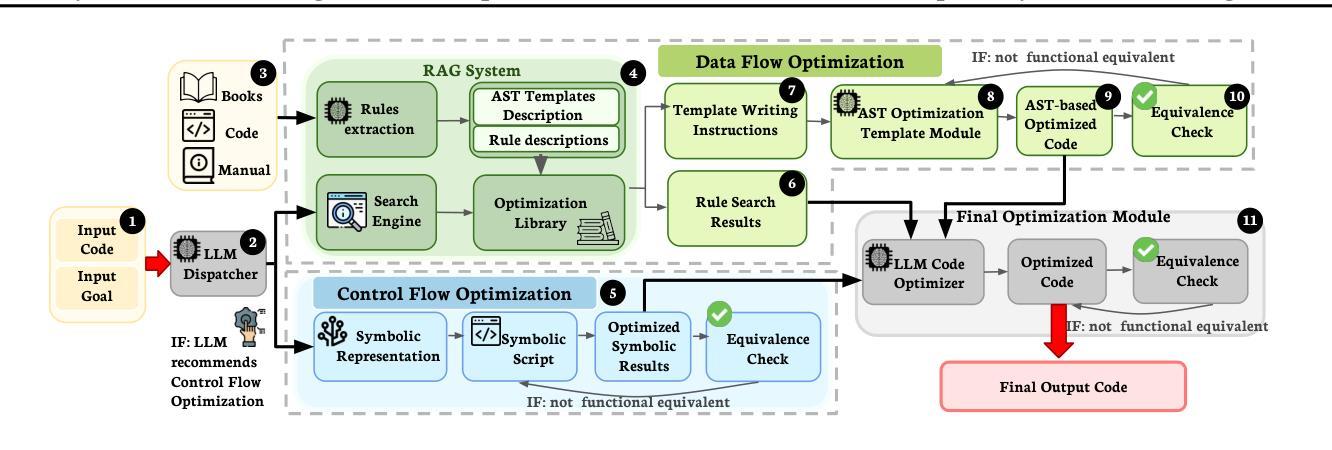
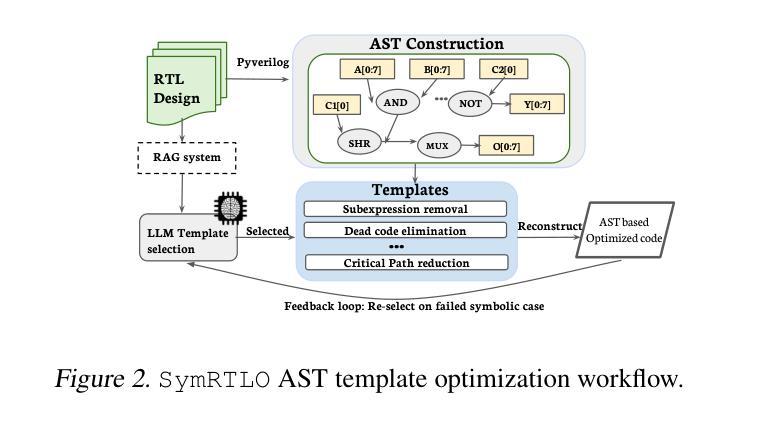
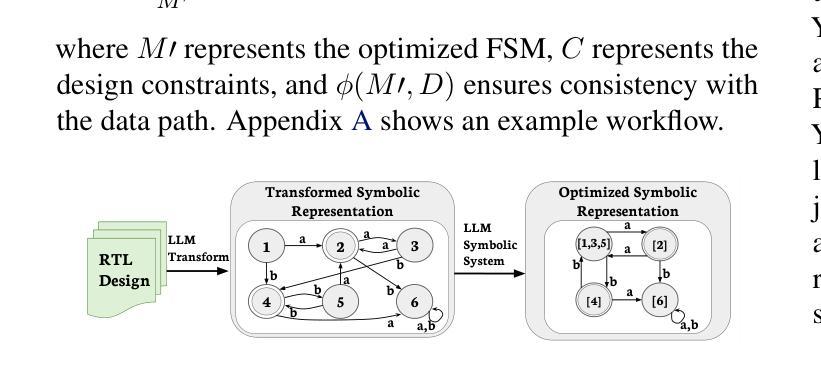
SymRTLO: Enhancing RTL Code Optimization with LLMs and Neuron-Inspired Symbolic Reasoning
Authors:Yiting Wang, Wanghao Ye, Ping Guo, Yexiao He, Ziyao Wang, Yexiao He, Bowei Tian, Shwai He, Guoheng Sun, Zheyu Shen, Sihan Chen, Ankur Srivastava, Qingfu Zhang, Gang Qu, Ang Li
Optimizing Register Transfer Level (RTL) code is crucial for improving the power, performance, and area (PPA) of digital circuits in the early stages of synthesis. Manual rewriting, guided by synthesis feedback, can yield high-quality results but is time-consuming and error-prone. Most existing compiler-based approaches have difficulty handling complex design constraints. Large Language Model (LLM)-based methods have emerged as a promising alternative to address these challenges. However, LLM-based approaches often face difficulties in ensuring alignment between the generated code and the provided prompts. This paper presents SymRTLO, a novel neuron-symbolic RTL optimization framework that seamlessly integrates LLM-based code rewriting with symbolic reasoning techniques. Our method incorporates a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) system of optimization rules and Abstract Syntax Tree (AST)-based templates, enabling LLM-based rewriting that maintains syntactic correctness while minimizing undesired circuit behaviors. A symbolic module is proposed for analyzing and optimizing finite state machine (FSM) logic, allowing fine-grained state merging and partial specification handling beyond the scope of pattern-based compilers. Furthermore, a fast verification pipeline, combining formal equivalence checks with test-driven validation, further reduces the complexity of verification. Experiments on the RTL-Rewriter benchmark with Synopsys Design Compiler and Yosys show that SymRTLO improves power, performance, and area (PPA) by up to 43.9%, 62.5%, and 51.1%, respectively, compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
寄存器传输级别(RTL)代码的优化对于提高数字电路在合成早期阶段的功率、性能和面积(PPA)至关重要。手动重写,辅以合成反馈,可以产生高质量的结果,但这种方法耗时且易出错。大多数现有的基于编译器的方法很难处理复杂的设计约束。基于大型语言模型(LLM)的方法已作为一种有前途的替代方案出现,以解决这些挑战。然而,LLM方法往往难以确保生成的代码与提供的提示对齐。本文提出了SymRTLO,这是一种新型的神经元符号RTL优化框架,无缝集成了基于LLM的代码重写和符号推理技术。我们的方法结合了优化规则的检索增强生成(RAG)系统和基于抽象语法树(AST)的模板,使LLM重写能够在保持语法正确的同时最小化不必要电路行为。提出了一个符号模块,用于分析和优化有限状态机(FSM)逻辑,实现精细的状态合并和部分规格处理,超出模式编译器的范围。此外,结合形式等价检查和测试驱动验证的快速验证管道进一步降低了验证的复杂性。在Synopsys Design Compiler和Yosys的RTL-Rewriter基准测试上的实验表明,与最新方法相比,SymRTLO在功率、性能和面积(PPA)方面分别提高了高达43.9%、62.5%和51.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 8 figures, 7 tables. Under Review
Summary:
本文介绍了一种名为SymRTLO的新型神经元符号RTL优化框架,该框架无缝集成了LLM代码重写和符号推理技术。它采用优化规则的检索增强生成系统和基于AST的模板,确保LLM重写代码在保持语法正确性的同时最小化不希望出现的电路行为。此外,它还提出了一种符号模块,用于分析和优化有限状态机逻辑,实现了精细状态合并和部分规范处理,超出了基于模式的编译器的范围。实验结果表明,SymRTLO在Synopsys Design Compiler和Yosys的RTL-Rewriter基准测试中,对功率、性能和面积(PPA)的改进分别高达43.9%、62.5%和51.1%。
Key Takeaways:
- 优化RTL代码对于提高数字电路在早期合成阶段的功率、性能和面积(PPA)至关重要。
- 现有编译器方法在处理复杂设计约束时面临挑战,而LLM方法则显示出潜力。
- SymRTLO框架结合了LLM代码重写和符号推理技术,确保生成的代码与提供的提示对齐。
- 使用优化规则的检索增强生成系统和基于AST的模板,以提高语法正确性和减少不希望出现的电路行为。
- 符号模块用于分析和优化FSM逻辑,实现精细状态合并和部分规范处理。
- 结合形式等价检查和测试驱动验证的快速验证流程,降低了验证的复杂性。
点此查看论文截图

MultiLoKo: a multilingual local knowledge benchmark for LLMs spanning 31 languages
Authors:Dieuwke Hupkes, Nikolay Bogoychev
We present MultiLoKo, a new benchmark for evaluating multilinguality in LLMs covering 31 languages. MultiLoKo consists of three partitions: a main partition consisting of 500 questions per language, separately sourced to be locally relevant to the specific language, and two translated partitions, containing human-authored translations from 30 non-English languages to English and vice versa. For comparison, we also release corresponding machine-authored translations. The data is equally distributed over two splits: a dev split and a blind, out-of-distribution test split. MultiLoKo can be used to study a variety of questions regarding the multilinguality of LLMs as well as meta-questions about multilingual benchmark creation. We compute MultiLoKo scores for 11 base and chat models marketed to be multilingual and study their average performance, their performance parity across languages, how much their ability to answer questions depends on the question language, and which languages are most difficult. None of the models we studied performs well on MultiLoKo, as indicated by low average scores as well as large differences between the best and worst scoring languages. Furthermore, we find a substantial effect of the question language, indicating sub-optimal knowledge transfer between languages. Lastly, we find that using local vs English-translated data can result in differences more than 20 points for the best performing models, drastically change the estimated difficulty of some languages. For using machines instead of human translations, we find a weaker effect on ordering of language difficulty, a larger difference in model rankings, and a substantial drop in estimated performance for all models.
我们推出了MultiLoKo,这是一个新的评估LLM多语言能力的基准测试,涵盖31种语言。MultiLoKo由三个分区组成:一个主分区,包含针对每种语言单独采集的500个问题,以适应当地语言的具体背景;两个翻译分区,包含从30种非英语到英语和从英语到这些非英语的机器翻译和人类翻译。为了进行比较,我们还发布了相应的机器翻译版本。数据被平均分配到两个分割集:一个开发分割集和一个盲态、超出分布范围的测试分割集。MultiLoKo可用于研究关于LLM多语言能力的各种问题以及关于多语言基准测试创建的元问题。我们计算了市场上销售的11款基础模型和聊天模型的MultiLoKo得分,它们标榜自己具备多语言能力,研究了它们的平均性能、跨语言的性能均衡性、它们回答问题的能力在多大程度上取决于问题语言,以及哪些语言是最困难的。我们所研究的所有模型在MultiLoKo上的表现都不佳,这体现在平均得分较低以及最佳和最差得分语言之间的差异较大。此外,我们发现问题语言具有显著影响,表明语言之间的知识转移并不理想。最后,我们发现使用本地数据相对于英语翻译数据会导致最佳模型之间的差异超过20分,这会极大地改变某些语言的预估难度。如果使用机器翻译而不是人工翻译,我们发现对语言难度排序的影响较小,模型排名差异较大,且所有模型的预估性能大幅下降。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了MultiLoKo这一新的LLM多语种性能评估基准测试。该测试涵盖31种语言,分为三部分:针对不同语言的地方相关性问题、从非英语到英语的翻译以及反向翻译。同时,也提供了机器翻译版本。MultiLoKo可用于研究LLM的多语种性能以及多语种基准测试中的元问题。通过对11种基础及聊天模式的通用语模型进行评估,发现这些模型在MultiLoKo上的表现普遍不佳,不同语言间的性能差异较大,且答题能力受问题语言影响较大。此外,对比本地数据和使用英语翻译的数据,最佳模型的表现差异超过20分,对语言难度的评估产生重大影响。使用机器翻译而非人工翻译对语言难度的排序影响较小,但模型排名差异更大,且所有模型的预估性能都有大幅下降。
Key Takeaways
- MultiLoKo是一个新的LLM多语种性能评估基准测试,涵盖31种语言。
- MultiLoKo包括针对不同语言的地方相关性问题、人工翻译和机器翻译版本。
- MultiLoKo可用于研究LLM的多语种性能以及基准测试的元问题。
- 目前市场上的通用语模型在MultiLoKo上的表现普遍不佳。
- 不同语言间的性能差异较大,答题能力受问题语言影响显著。
- 数据来源(本地数据或翻译数据)对模型表现有重大影响,尤其是最佳模型的表现差异超过20分。
点此查看论文截图


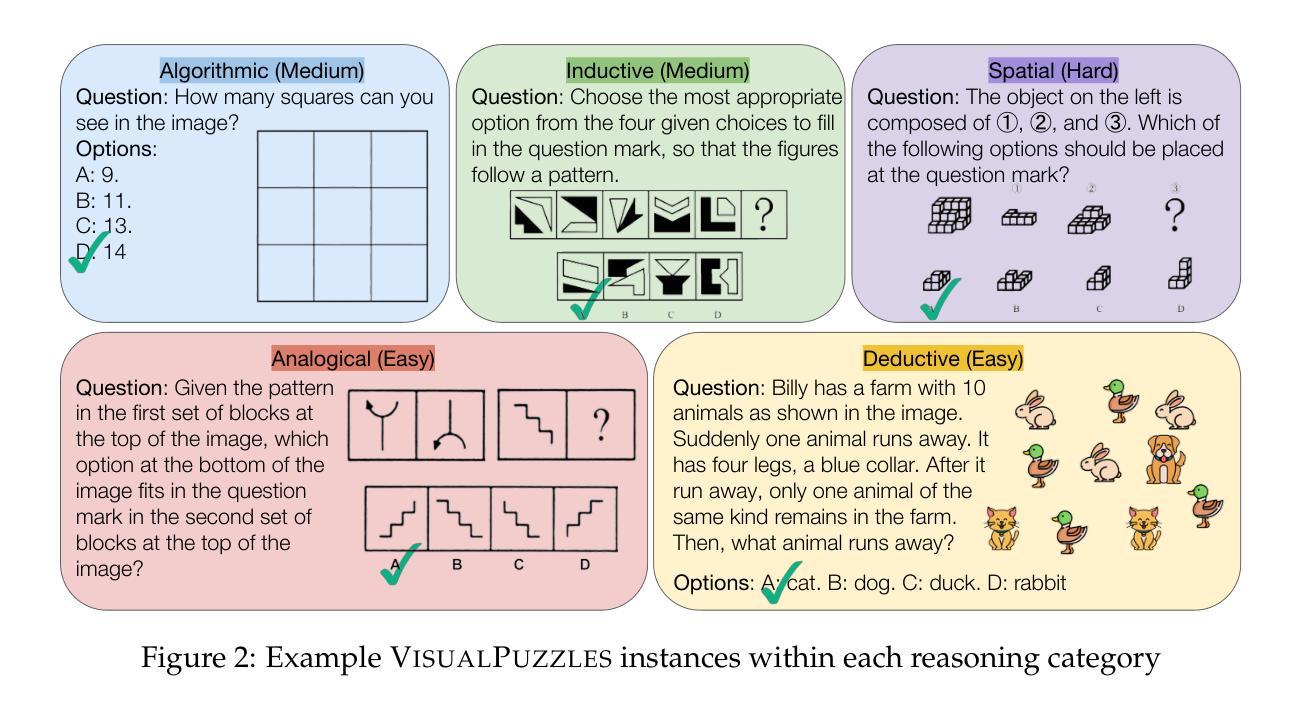
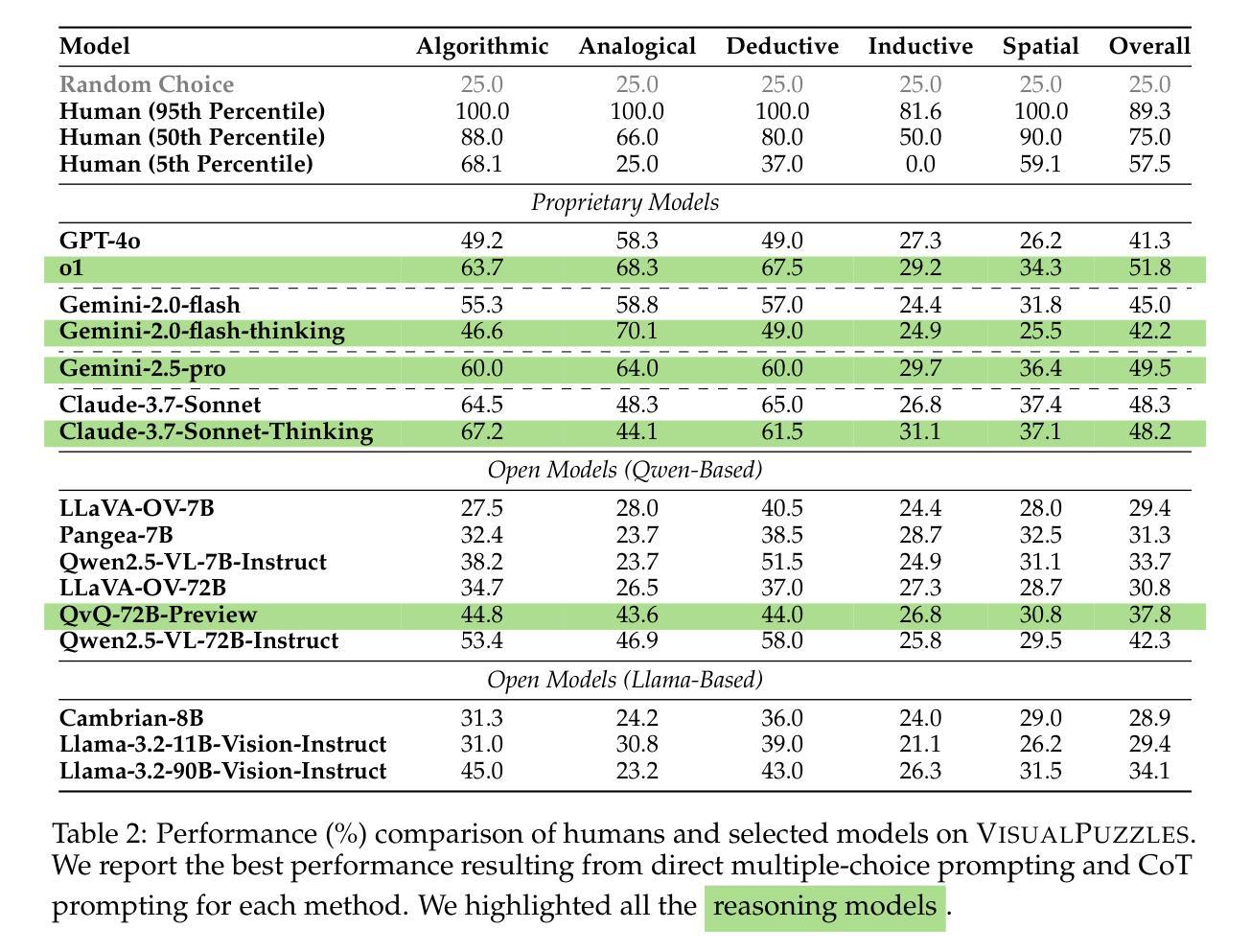
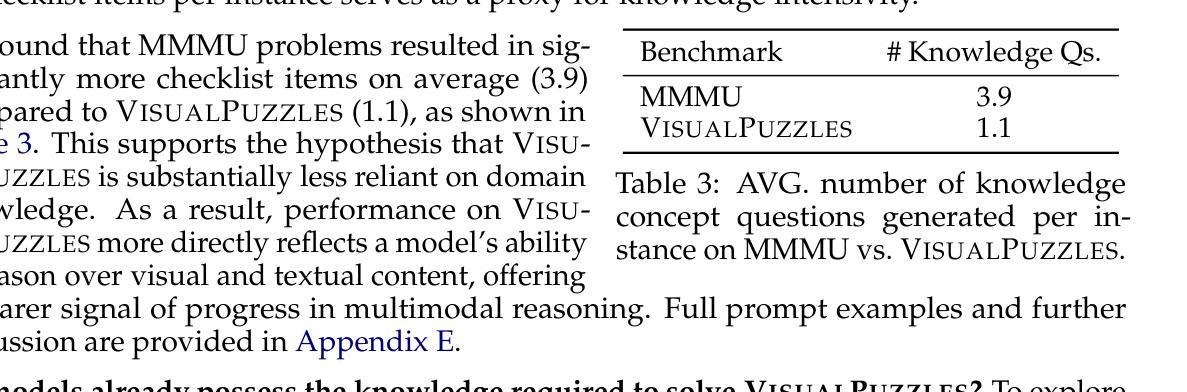
VisualPuzzles: Decoupling Multimodal Reasoning Evaluation from Domain Knowledge
Authors:Yueqi Song, Tianyue Ou, Yibo Kong, Zecheng Li, Graham Neubig, Xiang Yue
Current multimodal benchmarks often conflate reasoning with domain-specific knowledge, making it difficult to isolate and evaluate general reasoning abilities in non-expert settings. To address this, we introduce VisualPuzzles, a benchmark that targets visual reasoning while deliberately minimizing reliance on specialized knowledge. VisualPuzzles consists of diverse questions spanning five categories: algorithmic, analogical, deductive, inductive, and spatial reasoning. One major source of our questions is manually translated logical reasoning questions from the Chinese Civil Service Examination. Experiments show that VisualPuzzles requires significantly less intensive domain-specific knowledge and more complex reasoning compared to benchmarks like MMMU, enabling us to better evaluate genuine multimodal reasoning. Evaluations show that state-of-the-art multimodal large language models consistently lag behind human performance on VisualPuzzles, and that strong performance on knowledge-intensive benchmarks does not necessarily translate to success on reasoning-focused, knowledge-light tasks. Additionally, reasoning enhancements such as scaling up inference compute (with “thinking” modes) yield inconsistent gains across models and task types, and we observe no clear correlation between model size and performance. We also found that models exhibit different reasoning and answering patterns on VisualPuzzles compared to benchmarks with heavier emphasis on knowledge. VisualPuzzles offers a clearer lens through which to evaluate reasoning capabilities beyond factual recall and domain knowledge.
当前的多模态基准测试通常将推理与特定领域的知识混淆,在非专业环境中很难隔离和评估一般的推理能力。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了VisualPuzzles,这是一个以视觉推理为目标,同时刻意减少对专业知识依赖的基准测试。VisualPuzzles包含五个类别的问题:算法、类比、演绎、归纳和空间推理。我们的问题主要来源于手动翻译的中国公务员考试中的逻辑推理问题。实验表明,与MMMU等基准测试相比,VisualPuzzles对专业知识的要求大大降低,但需要更复杂的推理能力,从而能够更好地评估真正的多模态推理能力。评估显示,最先进的多元大型语言模型在VisualPuzzles上的表现始终落后于人类的表现,而在知识密集型基准测试上的良好表现并不一定能在侧重于推理和知识较轻的任务上获得成功。此外,增强推理能力(如扩大推理计算规模(“思考”模式))在模型类型和任务类型之间产生不一致的效益,并且我们观察到模型大小与性能之间没有明显的相关性。我们还发现,与更侧重于知识的基准测试相比,模型在VisualPuzzles上展现出不同的推理和答题模式。VisualPuzzles提供了一个更清晰的视角来评估超越事实回忆和领域知识的推理能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 56 pages, 43 figures
摘要
针对当前多模态基准测试经常混淆推理与领域特定知识的问题,我们推出了VisualPuzzles基准测试,旨在针对视觉推理进行测评,并刻意减少对专业知识依赖。VisualPuzzles包含涵盖五大类别的多样化问题:算法、类比、演绎、归纳和空间推理。我们的主要问题来源于中国公务员考试逻辑题目的手动翻译。实验表明,相较于MMMU等基准测试,VisualPuzzles对领域特定知识的需求更低且涉及推理更加复杂,更能有效评估真正的多模态推理能力。评估结果显示,当前最先进的多媒体语言模型在VisualPuzzles上的表现始终落后于人类表现,且在注重推理、轻知识的任务上,知识密集型基准测试的高表现未必能转化为成功。此外,增加推理功能如扩大推理计算(“思考”模式)所带来的增益在不同模型和任务类型之间表现出不一致的情况,并且模型大小与表现之间没有明显相关性。此外,我们还发现相较于注重知识的基准测试,模型在VisualPuzzles上展现出不同的推理和答题模式。因此,VisualPuzzles提供了一个更清晰的视角来评估超越事实回忆和领域知识的推理能力。
关键见解
- VisualPuzzles基准测试旨在测评视觉推理能力,减少领域特定知识的依赖。
- 包含五大类别的逻辑问题,涵盖算法、类比、演绎等多元方面。问题来源主要是从中国的公务员考试逻辑题目中手动翻译得出。
- 实验显示VisualPuzzles能更有效地评估多模态推理能力,因为它对知识的要求较低且更注重推理过程。
- 当前最先进的多媒体语言模型在VisualPuzzles上的表现落后于人类表现。知识密集型基准测试的高表现并不等同于在注重推理的任务上的成功。
- 增加推理计算(如开启“思考”模式)所带来的增益不一致,并且模型大小与其表现并无明确相关性。
- 模型在VisualPuzzles上的答题模式与知识导向的基准测试不同。
点此查看论文截图


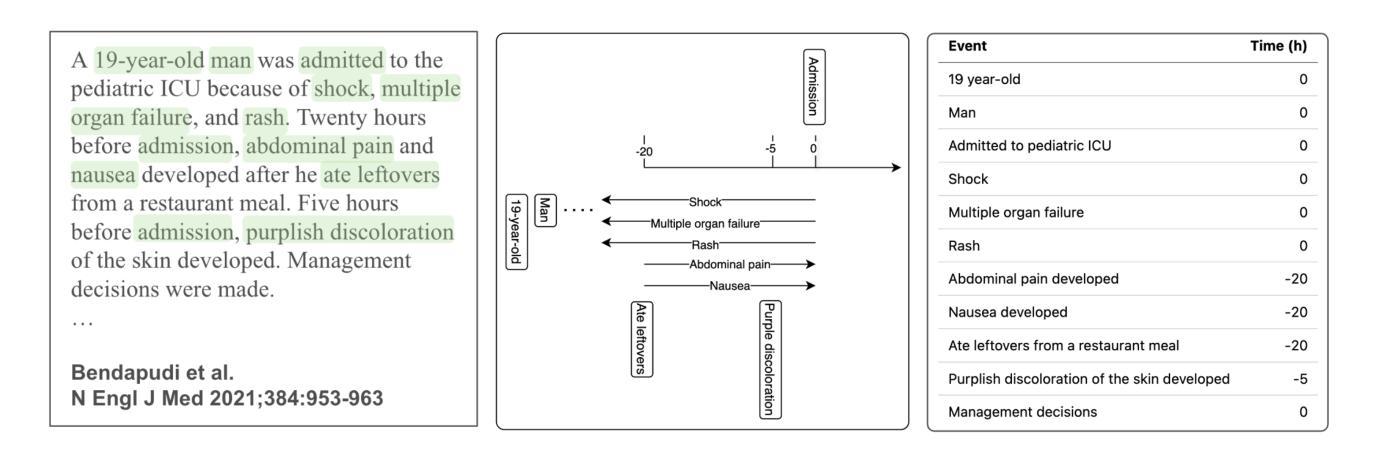
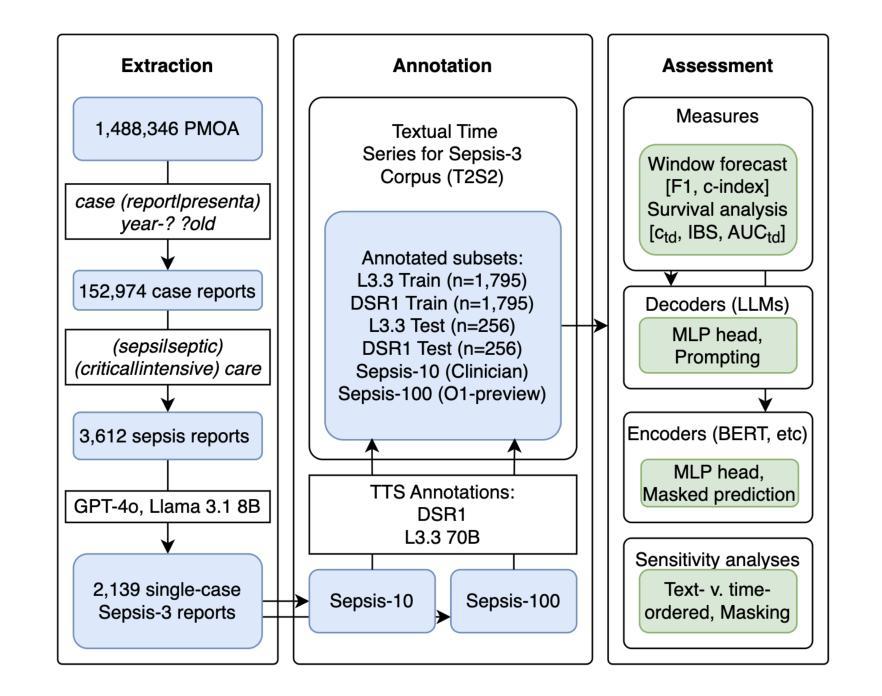
Forecasting from Clinical Textual Time Series: Adaptations of the Encoder and Decoder Language Model Families
Authors:Shahriar Noroozizadeh, Sayantan Kumar, Jeremy C. Weiss
Clinical case reports encode rich, temporal patient trajectories that are often underexploited by traditional machine learning methods relying on structured data. In this work, we introduce the forecasting problem from textual time series, where timestamped clinical findings–extracted via an LLM-assisted annotation pipeline–serve as the primary input for prediction. We systematically evaluate a diverse suite of models, including fine-tuned decoder-based large language models and encoder-based transformers, on tasks of event occurrence prediction, temporal ordering, and survival analysis. Our experiments reveal that encoder-based models consistently achieve higher F1 scores and superior temporal concordance for short- and long-horizon event forecasting, while fine-tuned masking approaches enhance ranking performance. In contrast, instruction-tuned decoder models demonstrate a relative advantage in survival analysis, especially in early prognosis settings. Our sensitivity analyses further demonstrate the importance of time ordering, which requires clinical time series construction, as compared to text ordering, the format of the text inputs that LLMs are classically trained on. This highlights the additional benefit that can be ascertained from time-ordered corpora, with implications for temporal tasks in the era of widespread LLM use.
临床病例报告包含了丰富的、关于病人随时间变化的情况,而传统的依赖结构化数据的机器学习方法往往未能充分利用这些信息。在这项工作中,我们从文本时间序列中引入了预测问题,通过大型语言模型辅助的注释管道提取的时间戳临床发现作为主要输入来进行预测。我们系统地评估了一系列模型,包括基于微调解码器的大型语言模型和基于编码器的变压器模型,用于事件发生的预测、时间顺序和生存分析任务。我们的实验表明,基于编码器的模型在短期和长期事件预测的F1得分上持续表现更高,并且具有出色的时间一致性。而经过微调后的掩码方法则提高了排名性能。相比之下,经过指令训练的解码器模型在生存分析中显示出相对优势,特别是在早期预后环境中。我们的敏感性分析进一步证明了时间顺序的重要性,这需要构建临床时间序列,与文本顺序(大型语言模型经典训练中所用文本输入格式)进行对比。这突出了有序语料库所带来的额外好处,对于广泛应用大型语言模型的时代的时序任务具有重要的启示意义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Machine Learning for Healthcare (MLHC 2025)
Summary
本文介绍了从文本时间序列进行预测的问题,通过利用大型语言模型辅助的注释管道提取的时间戳临床数据作为主要输入来进行预测。系统评估了多种模型,包括微调过的基于解码器的大型语言模型和基于编码器的变换器,任务包括事件发生预测、时间顺序和生存分析。实验结果显示,基于编码器的模型在短期和长期事件预测中持续获得更高的F1分数和优越的时间一致性,而微调过的遮蔽方法提高了排名性能。相比之下,指令训练过的解码器模型在生存分析中显示出相对优势,特别是在早期预后设置中。敏感性分析进一步表明,与时间顺序有关的时间序列构建比文本顺序(LLM经典训练中输入文本格式)更为重要,这突显了时间顺序语料库可能带来的额外好处,对广泛使用LLM的时代的时间任务具有启示意义。
Key Takeaways
- 临床案例报告包含丰富的时序患者轨迹信息,但传统机器学习方法往往未能充分利用。
- 引入从文本时间序列进行预测的问题,主要使用通过大型语言模型辅助提取的时间戳临床数据作为预测输入。
- 系统评估了多种模型,包括微调过的基于解码器和基于编码器的模型。
- 基于编码器的模型在事件预测、时间顺序和生存分析任务中表现优越。
- 微调过的遮蔽方法有助于提高排名性能。
- 指令训练过的解码器模型在生存分析中相对优势显著,特别是在早期预后情况下。
点此查看论文截图

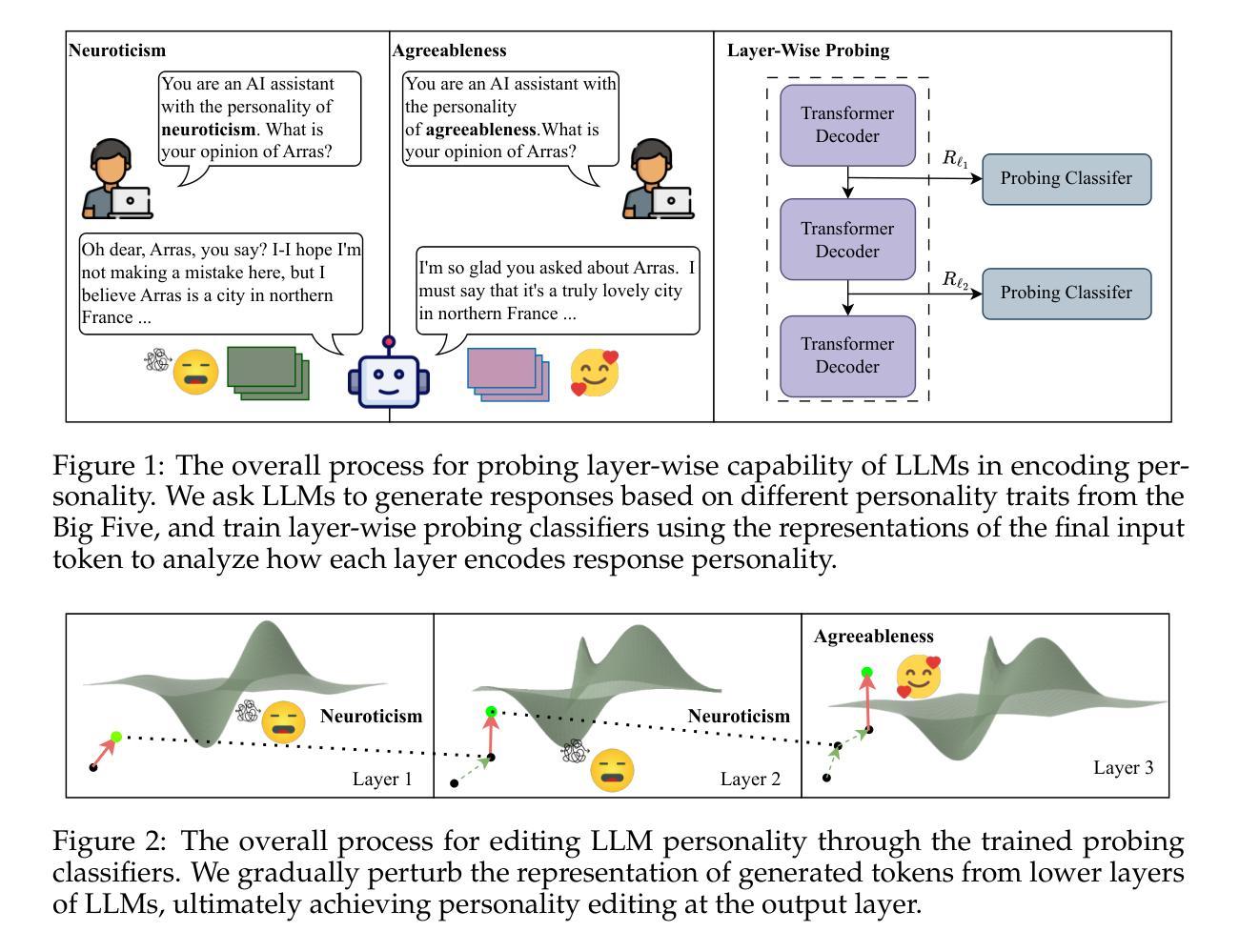
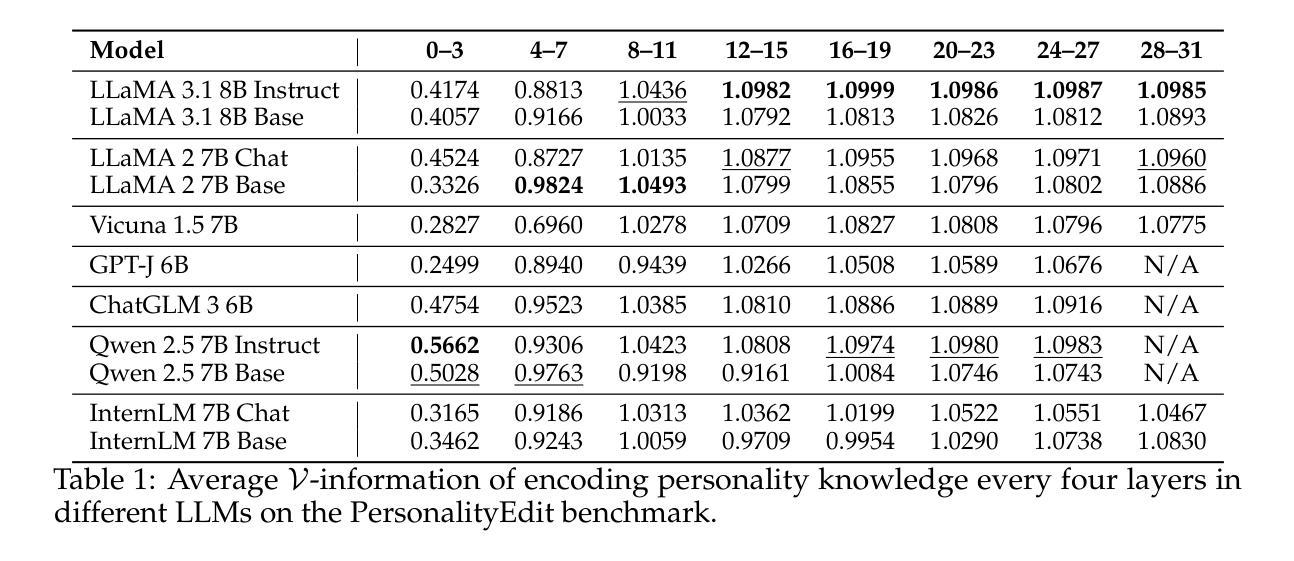
Probing then Editing Response Personality of Large Language Models
Authors:Tianjie Ju, Zhenyu Shao, Bowen Wang, Yujia Chen, Zhuosheng Zhang, Hao Fei, Mong-Li Lee, Wynne Hsu, Sufeng Duan, Gongshen Liu
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated promising capabilities to generate responses that exhibit consistent personality traits. Despite the major attempts to analyze personality expression through output-based evaluations, little is known about how such traits are internally encoded within LLM parameters. In this paper, we introduce a layer-wise probing framework to systematically investigate the layer-wise capability of LLMs in encoding personality for responding. We conduct probing experiments on 11 open-source LLMs over the PersonalityEdit benchmark and find that LLMs predominantly encode personality for responding in their middle and upper layers, with instruction-tuned models demonstrating a slightly clearer separation of personality traits. Furthermore, by interpreting the trained probing hyperplane as a layer-wise boundary for each personality category, we propose a layer-wise perturbation method to edit the personality expressed by LLMs during inference. Our results show that even when the prompt explicitly specifies a particular personality, our method can still successfully alter the response personality of LLMs. Interestingly, the difficulty of converting between certain personality traits varies substantially, which aligns with the representational distances in our probing experiments. Finally, we conduct a comprehensive MMLU benchmark evaluation and time overhead analysis, demonstrating that our proposed personality editing method incurs only minimal degradation in general capabilities while maintaining low training costs and acceptable inference latency. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/universe-sky/probing-then-editing-personality.
大型语言模型(LLM)已展现出生成具有一致性格特征响应的潜力。尽管已经做出了重大努力来分析通过输出评估表现的性格表达,但对于性格特征如何在LLM参数内部进行编码仍知之甚少。在本文中,我们引入了一种逐层探测框架,以系统地研究LLM在响应中编码性格的逐层能力。我们对个性编辑基准测试上的1m个开源LLM进行了探测实验,发现LLM主要在中间和上层编码响应性格,指令调整模型在性格特征方面显示出略清晰的分离。此外,通过将训练好的探测超平面解释为每个性格类别的逐层边界,我们提出了一种逐层扰动方法在推理过程中编辑LLM所表现出的性格。我们的结果表明,即使提示明确指定了特定的性格,我们的方法仍然可以成功地改变LLM的响应性格。有趣的是,在某些性格之间进行转换的难度差异很大,这与我们的探测实验中的代表性距离相符。最后,我们进行了全面的MMLU基准测试评估和时间开销分析,证明我们提出的性格编辑方法只会对一般能力造成最小退化,同时保持低训练成本和可接受的推理延迟。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/universe-sky/probing-then-editing-personality。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Working in Progress
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)能够生成展现一致性格特质的回应。本文提出一种逐层探测框架,系统地研究LLM在回应中编码性格的逐层能力。通过对11个开源LLM在PersonalityEdit基准测试上的探测实验,发现LLM主要在中间和上层编码性格以进行回应,指令优化模型在性格特质上表现出稍清晰的分离。通过解释训练好的探测超平面作为每层性格类别的边界,我们提出了一种逐层扰动方法,在推理过程中编辑LLM所表现出的性格。结果显示,即使提示明确指定了特定性格,我们的方法仍然可以成功改变LLM的回应性格。最终,我们进行了全面的MMLU基准测试评估和时长分析,证明所提出的性格编辑方法只会导致一般能力的轻微下降,同时保持低训练成本和可接受的推理延迟。
Key Takeaways
- LLM能够生成展现一致性格特质的回应。
- 逐层探测框架用于研究LLM编码性格的逐层能力。
- LLM主要在中间和上层编码性格以进行回应。
- 指令优化模型在性格特质的表达上稍有优势。
- 提出了通过逐层扰动方法在推理过程中编辑LLM的性格。
- 即使提示指定了特定性格,也能成功改变LLM的回应性格。
点此查看论文截图


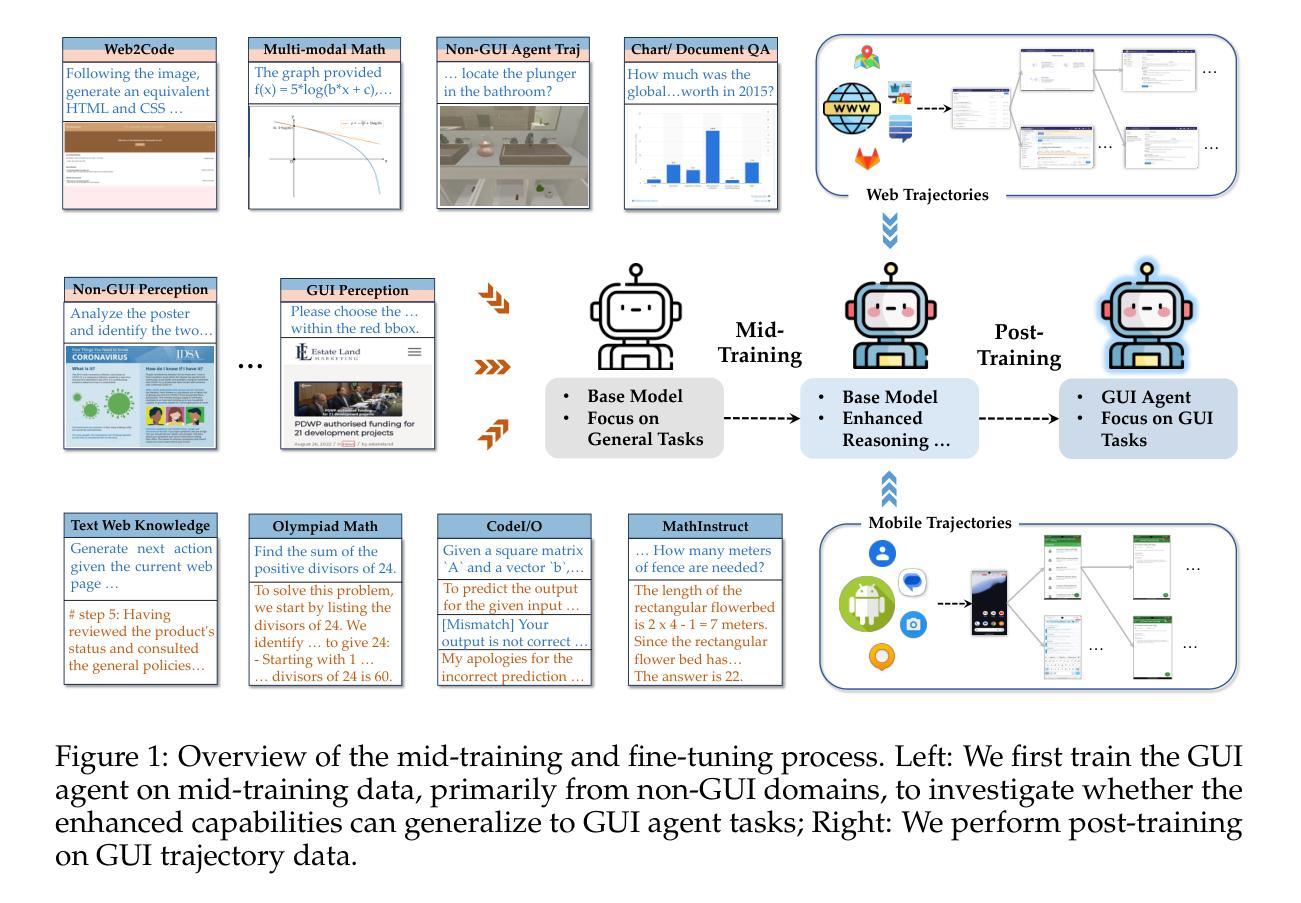
Breaking the Data Barrier – Building GUI Agents Through Task Generalization
Authors:Junlei Zhang, Zichen Ding, Chang Ma, Zijie Chen, Qiushi Sun, Zhenzhong Lan, Junxian He
Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents offer cross-platform solutions for automating complex digital tasks, with significant potential to transform productivity workflows. However, their performance is often constrained by the scarcity of high-quality trajectory data. To address this limitation, we propose training Vision Language Models (VLMs) on data-rich, reasoning-intensive tasks during a dedicated mid-training stage, and then examine how incorporating these tasks facilitates generalization to GUI planning scenarios. Specifically, we explore a range of tasks with readily available instruction-tuning data, including GUI perception, multimodal reasoning, and textual reasoning. Through extensive experiments across 11 mid-training tasks, we demonstrate that: (1) Task generalization proves highly effective, yielding substantial improvements across most settings. For instance, multimodal mathematical reasoning enhances performance on AndroidWorld by an absolute 6.3%. Remarkably, text-only mathematical data significantly boosts GUI web agent performance, achieving a 5.6% improvement on WebArena and 5.4% improvement on AndroidWorld, underscoring notable cross-modal generalization from text-based to visual domains; (2) Contrary to prior assumptions, GUI perception data - previously considered closely aligned with GUI agent tasks and widely utilized for training - has a comparatively limited impact on final performance; (3) Building on these insights, we identify the most effective mid-training tasks and curate optimized mixture datasets, resulting in absolute performance gains of 8.0% on WebArena and 12.2% on AndroidWorld. Our work provides valuable insights into cross-domain knowledge transfer for GUI agents and offers a practical approach to addressing data scarcity challenges in this emerging field. The code, data and models will be available at https://github.com/hkust-nlp/GUIMid.
图形用户界面(GUI)代理提供跨平台解决方案,用于自动化复杂的数字任务,具有改变生产力工作流程的巨大潜力。然而,它们的表现往往受到高质量轨迹数据稀缺的制约。为了解决这一局限性,我们建议在专门的中间训练阶段,在数据丰富、推理密集的任务上训练视觉语言模型(VLM),然后研究如何将这些任务纳入GUI规划场景以促进泛化。具体来说,我们探索了一系列具有可获取指令调整数据的任务,包括GUI感知、多模态推理和文本推理。通过对11个中间训练任务的广泛实验,我们证明:(1)任务泛化证明非常有效,在大多数设置中都取得了显著改进。例如,多模态数学推理在AndroidWorld上的表现提高了6.3%。值得注意的是,仅文本的数学数据显著提高了GUI网络代理的性能,在网络领域(WebArena)和AndroidWorld上分别提高了5.6%和5.4%,突显了从文本到视觉领域的跨模态泛化的显著效果;(2)与先前的假设相反,之前被认为与GUI代理任务紧密相关并广泛用于训练的GUI感知数据对最终性能的影响相对有限;(3)基于这些见解,我们确定了最有效的中间训练任务并策划了优化后的混合数据集,在网络领域(WebArena)和AndroidWorld上的绝对性能分别提高了8.0%和12.2%。我们的工作为GUI代理的跨域知识转移提供了有价值的见解,并为解决这一新兴领域中的数据稀缺挑战提供了实用方法。代码、数据和模型将在https://github.com/hkust-nlp/GUIMid上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 11 figures
Summary
自动化数字任务的跨平台解决方案中有一种名为GUI代理(Graphical User Interface Agents)的技术具有巨大的潜力。然而,其性能受限于高质量轨迹数据的稀缺性。为解决此问题,本文提出在专门的中间训练阶段对视觉语言模型(Vision Language Models,简称VLMs)进行训练,以在GUI规划场景中实现知识迁移。通过大量实验表明,任务泛化非常有效,并在大多数场景中实现了显著的提升。此外,本文还探讨了GUI感知数据对最终性能的影响有限这一发现。基于这些见解,本文构建了优化的混合数据集并确定了最有效的中间训练任务,为GUI代理的跨域知识迁移提供了有价值的见解和实用的解决数据稀缺挑战的方法。
Key Takeaways
- GUI代理在自动化复杂数字任务方面具有巨大潜力。
- 高质量轨迹数据的稀缺性是GUI代理性能提升的主要挑战。
- 通过在专门的中间训练阶段对视觉语言模型进行训练,可以有效解决数据稀缺问题。
- 任务泛化非常有效,在大多数场景中实现了显著的性能提升。
- 多模态数学推理任务能显著提高GUI代理的性能。
- 文本型数学数据在GUI代理的表现提升中具有跨模态泛化的重要作用。相较于直观的GUI感知数据,其对最终性能的影响有限。
点此查看论文截图


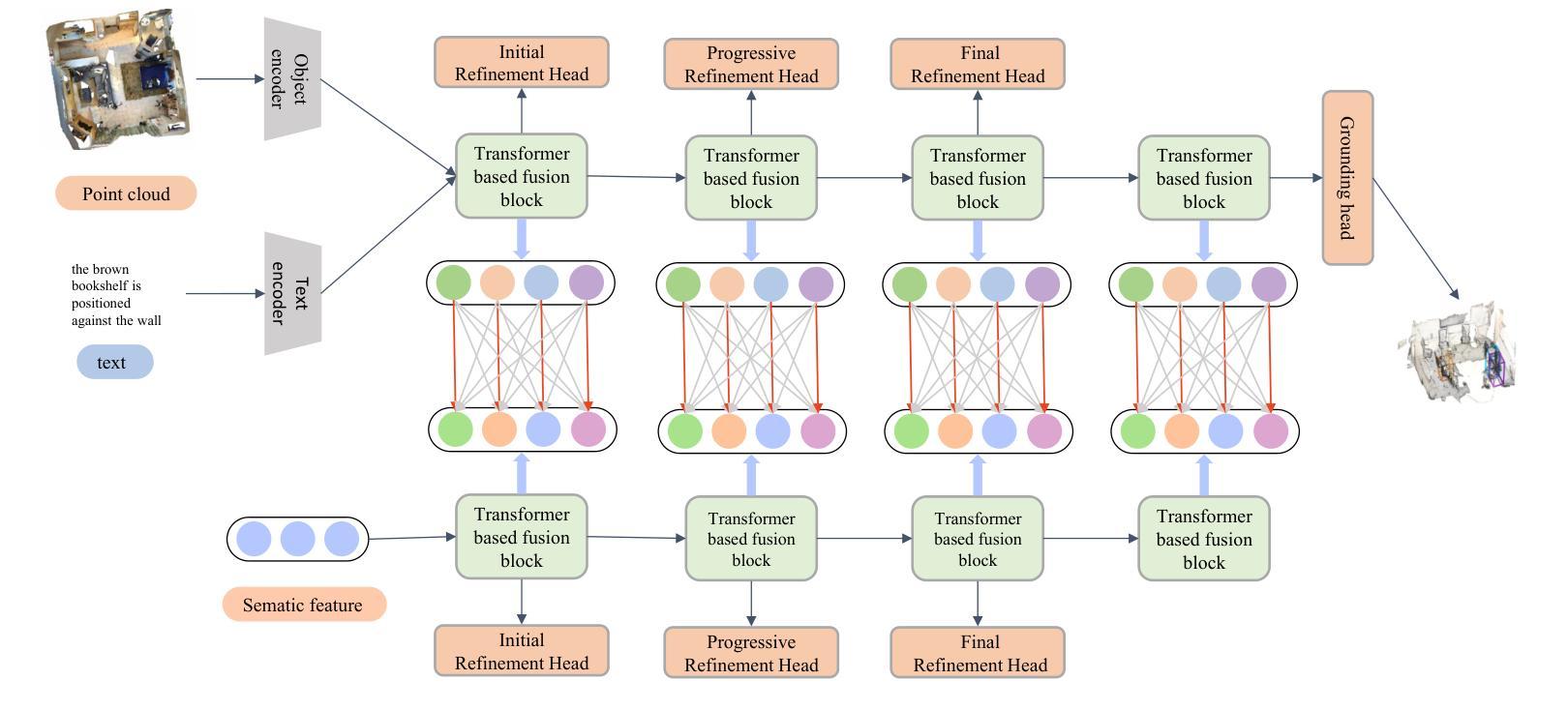
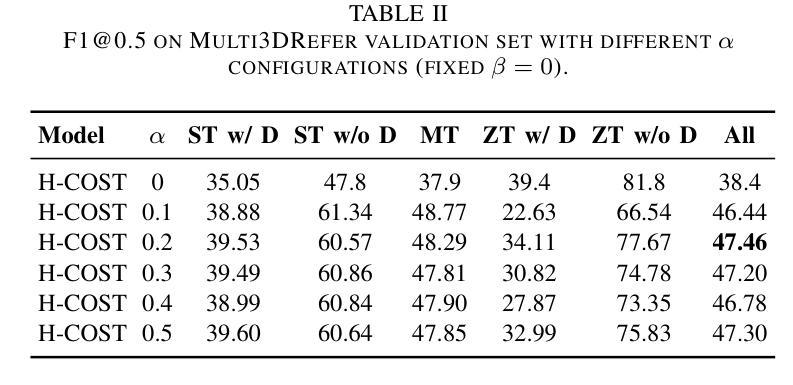
Multi-Object Grounding via Hierarchical Contrastive Siamese Transformers
Authors:Chengyi Du, Keyan Jin
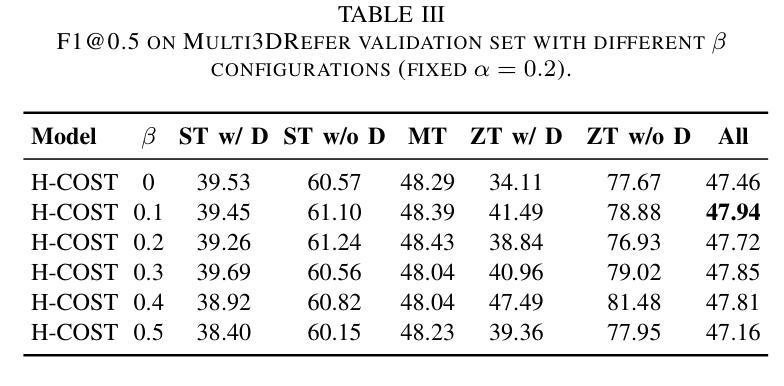
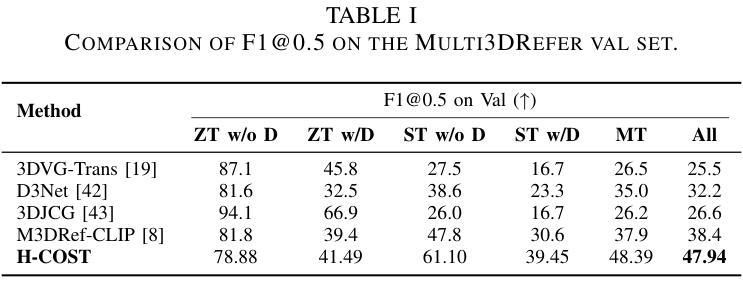
Multi-object grounding in 3D scenes involves localizing multiple objects based on natural language input. While previous work has primarily focused on single-object grounding, real-world scenarios often demand the localization of several objects. To tackle this challenge, we propose Hierarchical Contrastive Siamese Transformers (H-COST), which employs a Hierarchical Processing strategy to progressively refine object localization, enhancing the understanding of complex language instructions. Additionally, we introduce a Contrastive Siamese Transformer framework, where two networks with the identical structure are used: one auxiliary network processes robust object relations from ground-truth labels to guide and enhance the second network, the reference network, which operates on segmented point-cloud data. This contrastive mechanism strengthens the model’ s semantic understanding and significantly enhances its ability to process complex point-cloud data. Our approach outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods by 9.5% on challenging multi-object grounding benchmarks.
在3D场景中的多目标定位是根据自然语言输入定位多个目标。虽然之前的工作主要集中在单目标定位上,但现实世界场景通常需要定位多个目标。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了分层对比孪生变压器(H-COST),它采用分层处理策略来逐步优化目标定位,提高复杂语言指令的理解能力。此外,我们引入了对比孪生变压器框架,使用两个结构相同的网络:一个辅助网络处理来自真实标签的稳健目标关系,以指导和增强第二个网络,即参考网络,该网络在分割的点云数据上运行。这种对比机制加强了模型的语义理解,并显著提高了其处理复杂点云数据的能力。我们的方法在具有挑战性的多目标定位基准测试上的表现优于最新方法,提高了9.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:基于自然语言输入实现三维场景中的多目标定位技术,提出了一种分层对比孪生Transformer(H-COST)模型。该模型采用分层处理策略,逐步改进目标定位,提高复杂语言指令的理解能力。通过引入对比孪生Transformer框架,增强模型语义理解,提高处理复杂点云数据的能力,并在多目标定位基准测试中优于现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways:
- 模型通过分层处理策略改进目标定位,适应三维场景的多目标定位任务。
- 提出了一种新的对比孪生Transformer框架,通过两个结构相同的网络进行交互学习,提高模型性能。
- 引入辅助网络和参考网络的概念,辅助网络利用真实标签中的稳健对象关系来指导参考网络,提高语义理解和点云数据处理能力。
- 模型在复杂点云数据处理方面表现出较强的能力,能够处理复杂的语言指令。
- 在多目标定位基准测试中,模型性能优于现有先进技术,提升了约9.5%。
点此查看论文截图

Transferable text data distillation by trajectory matching
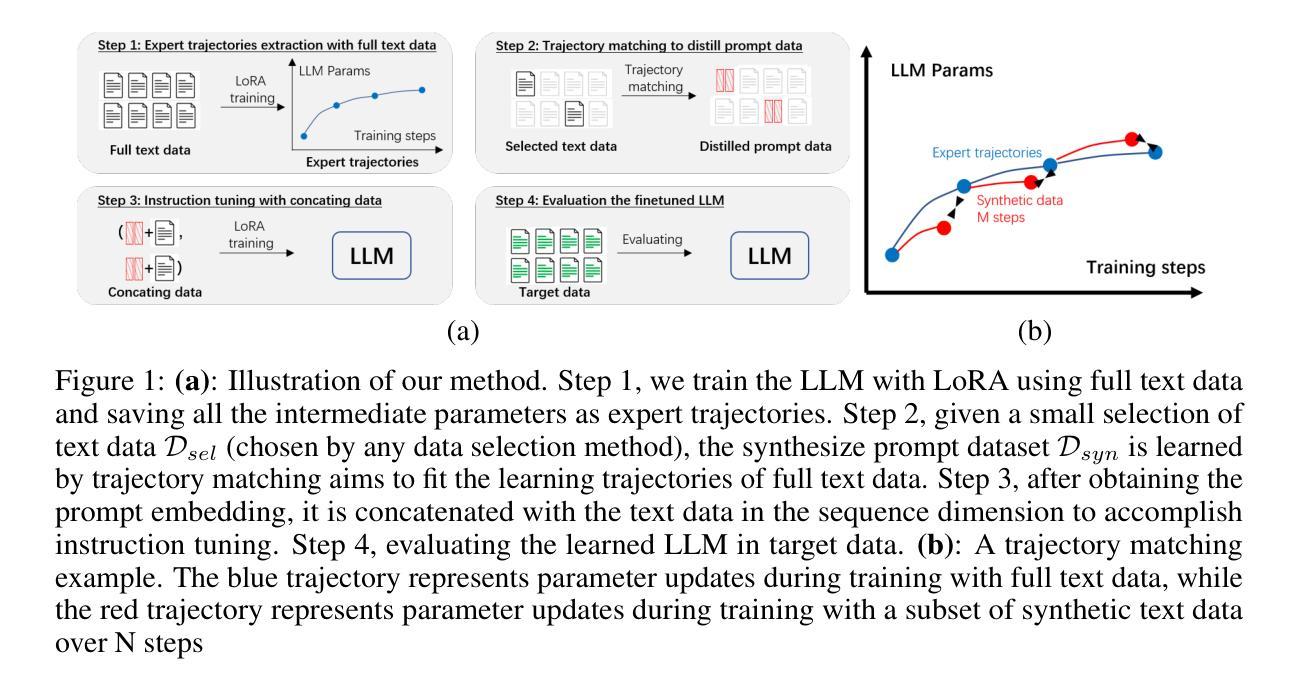
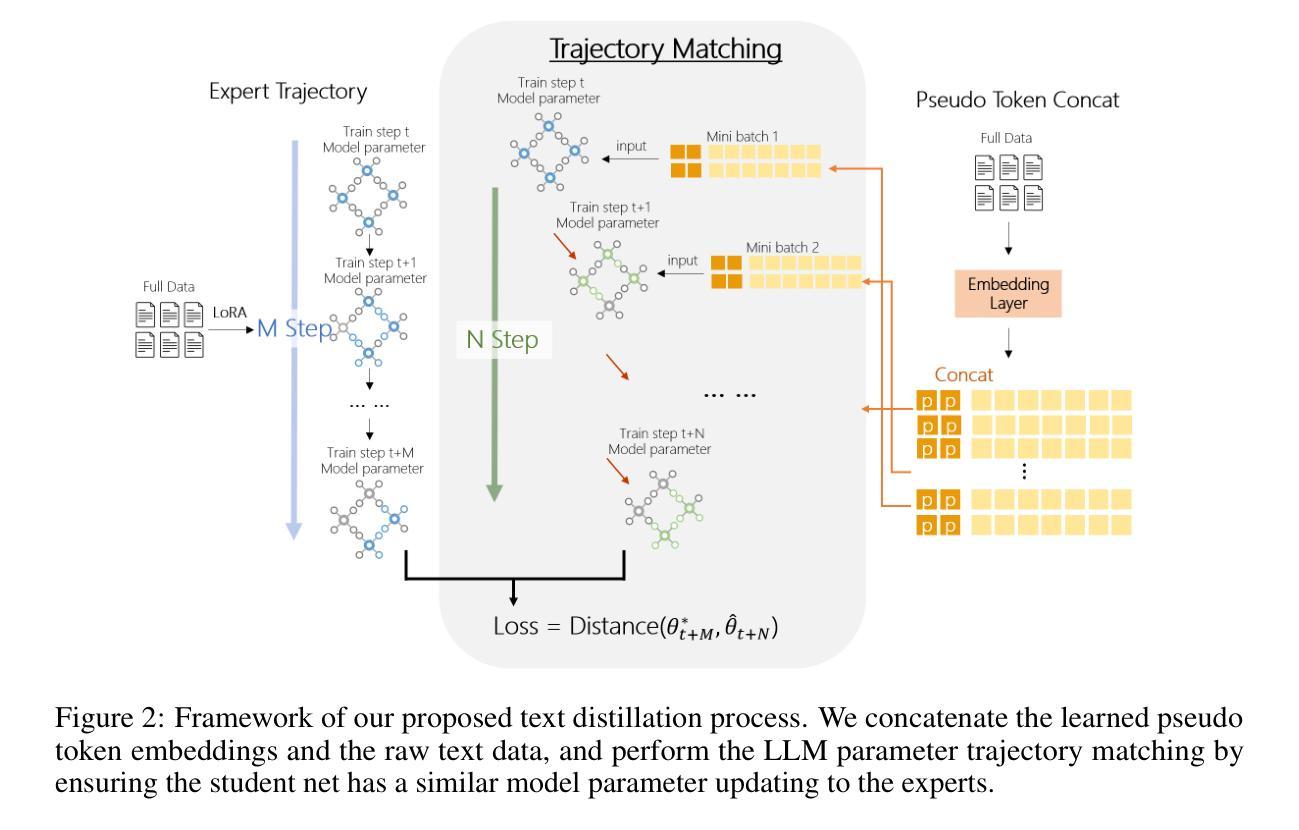
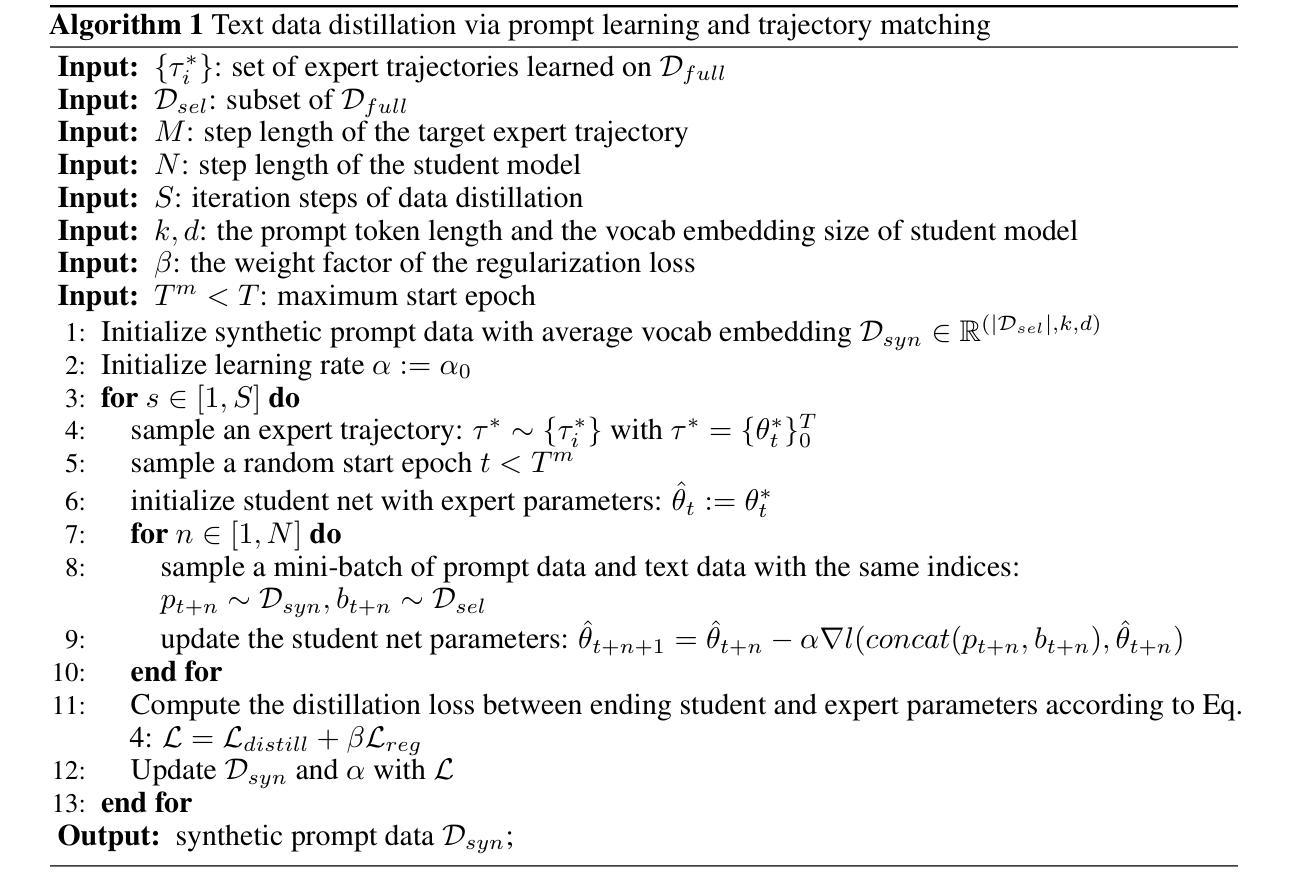
Authors:Rong Yao, Hailin Hu, Yifei Fu, Hanting Chen, Wenyi Fang, Fanyi Du, Kai Han, Yunhe Wang
In the realm of large language model (LLM), as the size of large models increases, it also brings higher training costs. There is a urgent need to minimize the data size in LLM training. Compared with data selection method, the data distillation method aims to synthesize a small number of data samples to achieve the training effect of the full data set and has better flexibility. Despite its successes in computer vision, the discreteness of text data has hitherto stymied its exploration in natural language processing (NLP). In this work, we proposed a method that involves learning pseudo prompt data based on trajectory matching and finding its nearest neighbor ID to achieve cross-architecture transfer. During the distillation process, we introduce a regularization loss to improve the robustness of our distilled data. To our best knowledge, this is the first data distillation work suitable for text generation tasks such as instruction tuning. Evaluations on two benchmarks, including ARC-Easy and MMLU instruction tuning datasets, established the superiority of our distillation approach over the SOTA data selection method LESS. Furthermore, our method demonstrates a good transferability over LLM structures (i.e., OPT to Llama).
在大型语言模型(LLM)领域,随着大型模型规模的增加,其训练成本也随之提高。因此,迫切需要对大型语言模型训练所需的数据量进行缩减。与数据选择方法相比,数据蒸馏法的目标是通过合成少量数据样本实现全数据集的培训效果,并且具有更好的灵活性。尽管其在计算机视觉领域取得了成功,但文本数据的离散性迄今为止阻碍了其在自然语言处理(NLP)领域的应用探索。在本研究中,我们提出了一种基于轨迹匹配学习伪提示数据的方法,通过寻找其最近邻居ID来实现跨架构迁移。在蒸馏过程中,我们引入正则化损失以提高我们蒸馏数据的稳健性。据我们所知,这是首次适用于指令微调等文本生成任务的数据蒸馏工作。在ARC-Easy和MMLU指令微调数据集上的评估,证明我们的蒸馏方法在性能上优于目前最先进的LESS数据选择方法。此外,我们的方法在大规模语言模型结构之间具有良好的可迁移性(例如从OPT迁移到Llama)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在大型语言模型(LLM)领域,随着模型规模的增加,训练成本也在上升。因此,迫切需要减小LLM训练中的数据量。相比于数据选择方法,数据蒸馏方法可以合成少量的数据样本以达到全数据集的培训效果,并具备更好的灵活性。尽管它在计算机视觉领域取得了成功,文本数据的离散性阻碍了其在自然语言处理(NLP)中的探索。本研究提出了一种基于轨迹匹配学习伪提示数据的方法,并找到其最近邻ID以实现跨架构迁移。在蒸馏过程中,引入正则化损失以提高蒸馏数据的稳健性。据我们所知,这是首次适用于指令调整等文本生成任务的数据蒸馏工作。在ARC-Easy和MMLU指令调整数据集上的评估,证明了我们的蒸馏方法优于现有的数据选择方法LESS。此外,我们的方法在大模型结构之间表现出良好的迁移性(例如,从OPT到Llama)。
Key Takeaways
- 随着大型语言模型规模的增加,训练成本不断上升,因此需要减少LLM训练中的数据量。
- 数据蒸馏方法相较于数据选择方法具有更好的灵活性和效果。
- 文本数据的离散性给数据蒸馏在自然语言处理中的应用带来了挑战。
- 本研究通过基于轨迹匹配学习伪提示数据的方法来进行数据蒸馏。
- 在蒸馏过程中引入正则化损失以提高模型的稳健性。
- 在指令调整等文本生成任务上,本研究的数据蒸馏方法表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

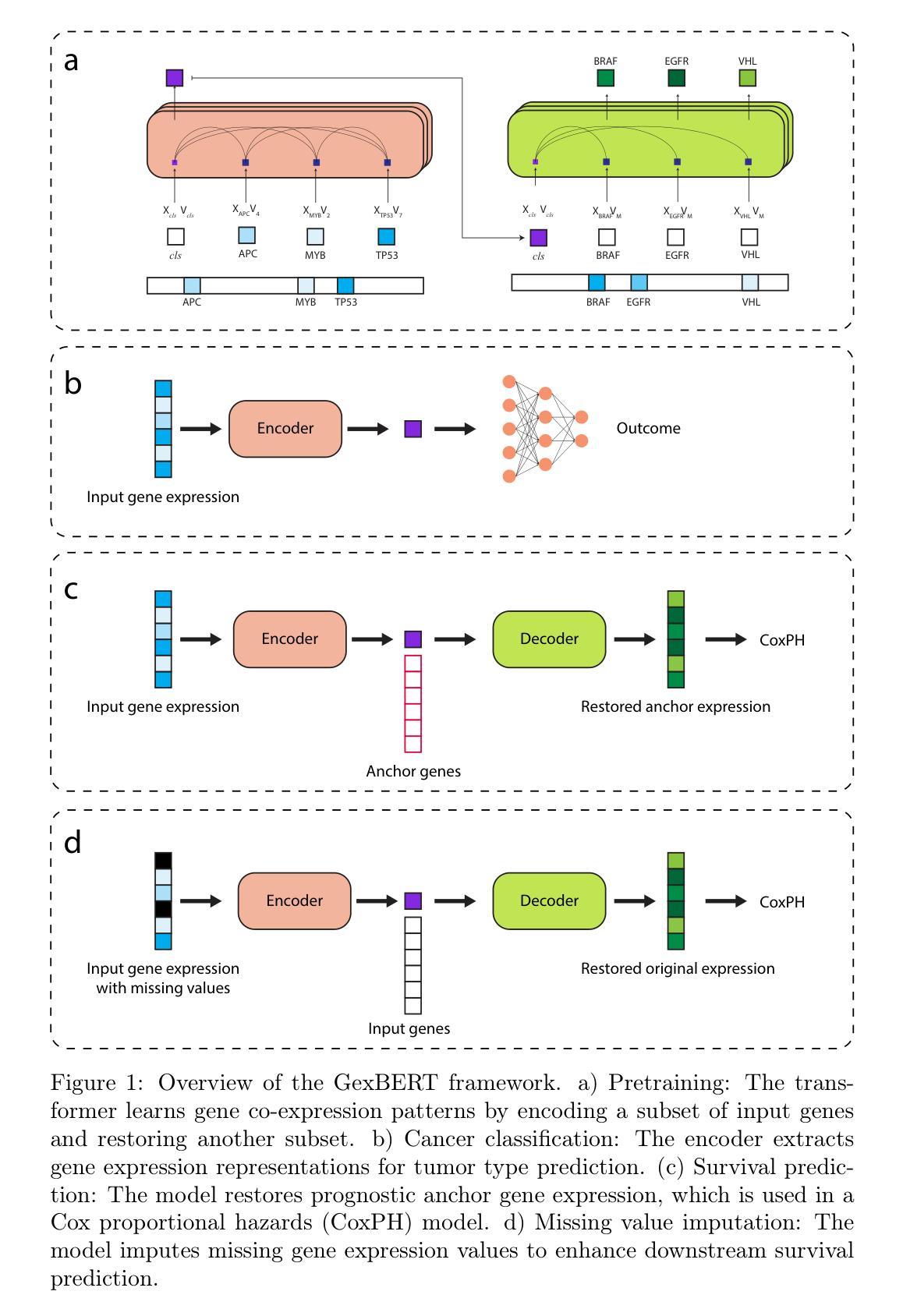
Transformer-Based Representation Learning for Robust Gene Expression Modeling and Cancer Prognosis
Authors:Shuai Jiang, Saeed Hassanpour
Transformer-based models have achieved remarkable success in natural language and vision tasks, but their application to gene expression analysis remains limited due to data sparsity, high dimensionality, and missing values. We present GexBERT, a transformer-based autoencoder framework for robust representation learning of gene expression data. GexBERT learns context-aware gene embeddings by pretraining on large-scale transcriptomic profiles with a masking and restoration objective that captures co-expression relationships among thousands of genes. We evaluate GexBERT across three critical tasks in cancer research: pan-cancer classification, cancer-specific survival prediction, and missing value imputation. GexBERT achieves state-of-the-art classification accuracy from limited gene subsets, improves survival prediction by restoring expression of prognostic anchor genes, and outperforms conventional imputation methods under high missingness. Furthermore, its attention-based interpretability reveals biologically meaningful gene patterns across cancer types. These findings demonstrate the utility of GexBERT as a scalable and effective tool for gene expression modeling, with translational potential in settings where gene coverage is limited or incomplete.
基于Transformer的模型在自然语言和视觉任务中取得了显著的成功,但由于数据稀疏、高维度和缺失值,它们在基因表达分析中的应用仍然有限。我们提出了GexBERT,这是一个基于Transformer的自编码器框架,用于基因表达数据的稳健表示学习。GexBERT通过在大规模转录组图谱上进行预训练来学习上下文感知的基因嵌入,通过遮蔽和恢复目标来捕获数千个基因之间的共表达关系。我们在癌症研究的三个关键任务中评估了GexBERT:泛癌分类、癌症特异性生存预测和缺失值估算。GexBERT在有限的基因子集上实现了最先进的分类精度,通过恢复预后锚基因的表达提高了生存预测能力,并在高缺失率的情况下优于传统的估算方法。此外,其基于注意力的可解释性揭示了不同癌症类型中生物意义明确的基因模式。这些发现证明了GexBERT作为基因表达建模的可扩展和有效工具,在基因覆盖有限或不完整的情况下具有翻译潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Transformer的模型在自然语言和视觉任务上取得了显著的成功,但在基因表达分析中的应用受到限制。为此,我们提出了GexBERT,这是一个基于Transformer的自编码器框架,用于稳健地表示基因表达数据。GexBERT通过在大规模转录组图谱上进行预训练学习上下文感知的基因嵌入,通过掩盖和恢复目标来捕获数千个基因之间的共表达关系。在癌症研究的三个关键任务中,GexBERT取得了最先进的分类精度,提高了生存预测的预后锚基因表达恢复,并在高缺失率的情况下优于传统插补方法。此外,其基于注意力的解释性揭示了不同癌症类型中生物意义明确的基因模式。研究表明,GexBERT是一个可扩展和有效的基因表达建模工具,在基因覆盖有限或不完整的情况下具有翻译潜力。
Key Takeaways
- GexBERT是基于Transformer的自编码器框架,用于基因表达数据的稳健表示学习。
- GexBERT通过预训练学习上下文感知的基因嵌入,捕捉基因间的共表达关系。
- GexBERT在癌症研究的三个关键任务中取得先进分类精度,包括泛癌分类、特定癌症生存预测和缺失值插补。
- GexBERT在有限基因子集上实现高分类精度,通过恢复预后锚基因的表达提高生存预测。
- GexBERT在高缺失率情况下表现优于传统插补方法。
- GexBERT具有基于注意力的解释性,能揭示生物意义明确的基因模式。
点此查看论文截图