⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-16 更新
Masked Autoencoder Self Pre-Training for Defect Detection in Microelectronics
Authors:Nikolai Röhrich, Alwin Hoffmann, Richard Nordsieck, Emilio Zarbali, Alireza Javanmardi
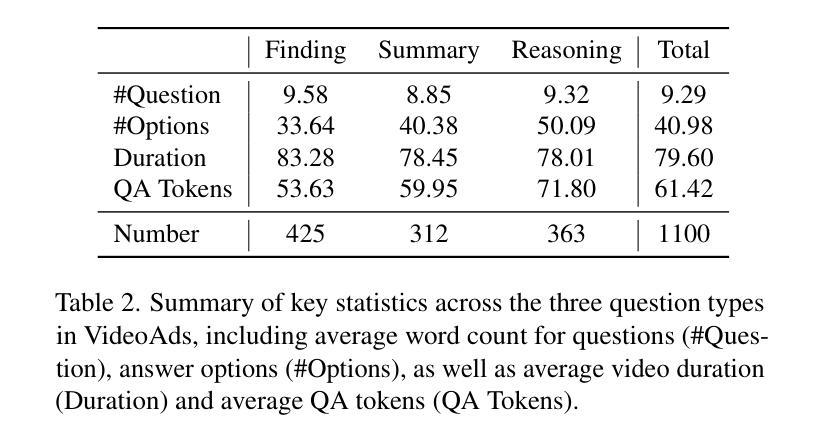
Whereas in general computer vision, transformer-based architectures have quickly become the gold standard, microelectronics defect detection still heavily relies on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). We hypothesize that this is due to the fact that a) transformers have an increased need for data and b) labelled image generation procedures for microelectronics are costly, and labelled data is therefore sparse. Whereas in other domains, pre-training on large natural image datasets can mitigate this problem, in microelectronics transfer learning is hindered due to the dissimilarity of domain data and natural images. Therefore, we evaluate self pre-training, where models are pre-trained on the target dataset, rather than another dataset. We propose a vision transformer (ViT) pre-training framework for defect detection in microelectronics based on masked autoencoders (MAE). In MAE, a large share of image patches is masked and reconstructed by the model during pre-training. We perform pre-training and defect detection using a dataset of less than 10.000 scanning acoustic microscopy (SAM) images labelled using transient thermal analysis (TTA). Our experimental results show that our approach leads to substantial performance gains compared to a) supervised ViT, b) ViT pre-trained on natural image datasets, and c) state-of-the-art CNN-based defect detection models used in the literature. Additionally, interpretability analysis reveals that our self pre-trained models, in comparison to ViT baselines, correctly focus on defect-relevant features such as cracks in the solder material. This demonstrates that our approach yields fault-specific feature representations, making our self pre-trained models viable for real-world defect detection in microelectronics.
在通用计算机视觉领域,基于变压器的架构已经迅速成为金标准,但微电子缺陷检测仍然严重依赖于卷积神经网络(CNN)。我们假设这是因为a) 变压器对数据的需求增加,以及b) 微电子的标签图像生成程序成本高昂,因此标签数据很稀疏。在其他领域,通过在大规模自然图像数据集上进行预训练可以缓解这个问题,但在微电子领域,由于领域数据与自然图像的差异性,迁移学习受到阻碍。因此,我们评估了自我预训练,即模型在目标数据集上进行预训练,而不是在其他数据集上进行。我们提出了一种基于掩码自编码器(MAE)的用于微电子缺陷检测的视觉变压器(ViT)预训练框架。在MAE中,大部分图像补丁在预训练阶段被掩盖,并由模型重建。我们使用小于10,000张通过瞬态热分析(TTA)标记的扫描声学显微镜(SAM)图像进行预训练和缺陷检测。我们的实验结果表明,与a) 监督ViT、b) 在自然图像数据集上预训练的ViT以及c) 文献中使用的最先进的CNN缺陷检测模型相比,我们的方法带来了巨大的性能提升。此外,解释性分析表明,与基线ViT相比,我们的自训练模型正确地关注缺陷相关特征,如焊料中的裂缝。这证明我们的方法产生了特定的故障特征表示,使得我们的自训练模型在微电子领域的真实世界缺陷检测中切实可行。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文研究了在微电子缺陷检测中应用Vision Transformer(ViT)的情况。由于微电子设备缺陷检测的数据稀缺且标注成本高,直接应用通用的Vision Transformer模型受到限制。因此,本文提出了基于Masked Autoencoder(MAE)的ViT自训练框架,用于在少量标注的扫描声学显微镜(SAM)图像上进行预训练和缺陷检测。实验结果表明,该方法相较于其他方法性能有明显提升,并且模型能够关注到缺陷相关的特征,如焊料中的裂缝。
Key Takeaways
- 在微电子缺陷检测领域,由于数据稀缺和标注成本高,虽然通用计算机视觉领域Transformer架构成为金标准,但卷积神经网络(CNN)仍占据主导地位。
- 提出了一种基于Masked Autoencoder(MAE)的Vision Transformer(ViT)自训练框架用于微电子缺陷检测。
- 自训练策略在少量标注扫描声学显微镜(SAM)图像上的表现优于监督学习的ViT、在自然图像数据集上预训练的ViT以及现有的CNN缺陷检测模型。
- 实验结果显示自训练模型能正确关注缺陷相关特征,如焊料中的裂缝。
- 自训练模型具有实际应用价值,可用于微电子领域的真实缺陷检测。
- 该方法不仅提高了检测性能,而且提高了模型的解释性,有助于理解模型如何识别和处理缺陷。
点此查看论文截图


Correlative and Discriminative Label Grouping for Multi-Label Visual Prompt Tuning
Authors:LeiLei Ma, Shuo Xu, MingKun Xie, Lei Wang, Dengdi Sun, Haifeng Zhao
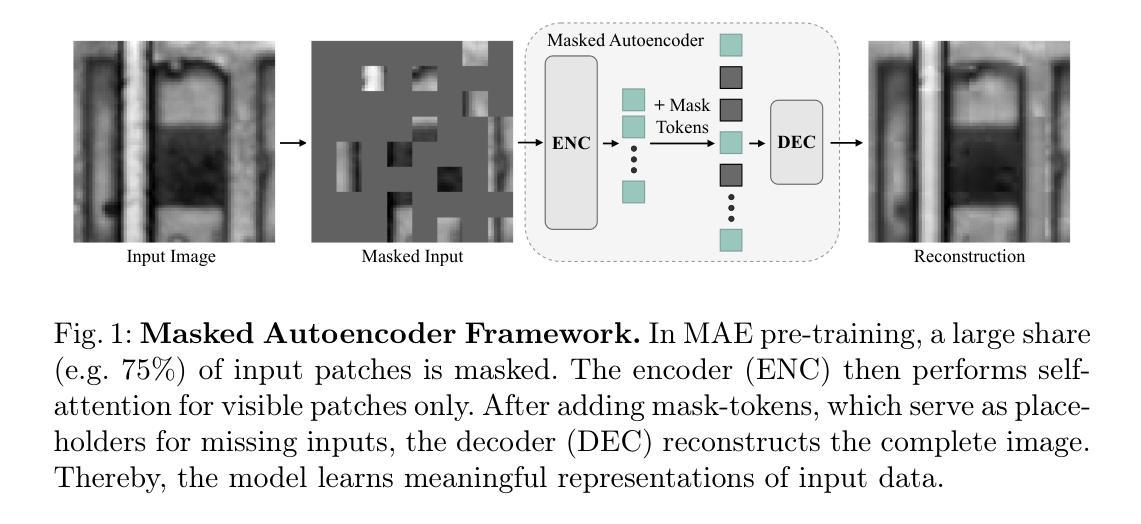
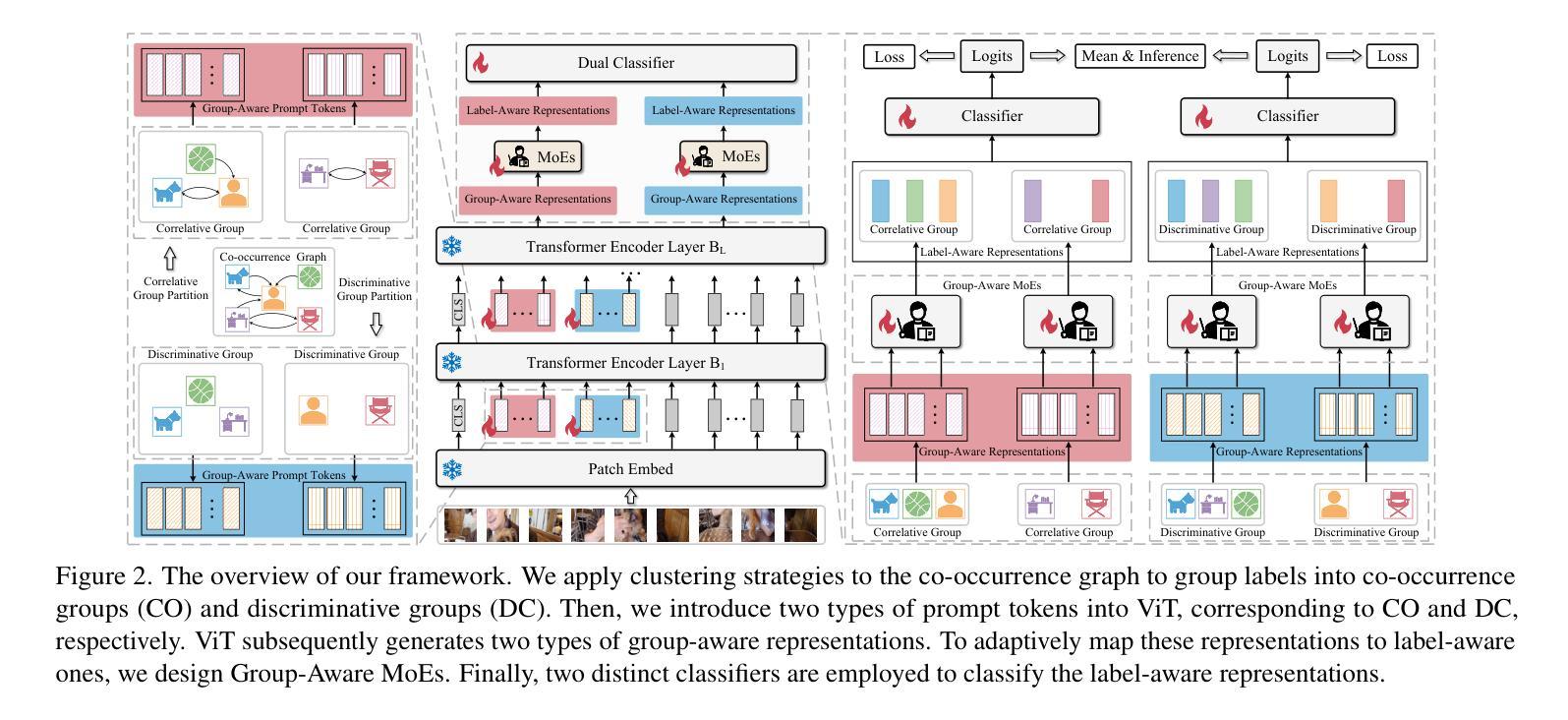
Modeling label correlations has always played a pivotal role in multi-label image classification (MLC), attracting significant attention from researchers. However, recent studies have overemphasized co-occurrence relationships among labels, which can lead to overfitting risk on this overemphasis, resulting in suboptimal models. To tackle this problem, we advocate for balancing correlative and discriminative relationships among labels to mitigate the risk of overfitting and enhance model performance. To this end, we propose the Multi-Label Visual Prompt Tuning framework, a novel and parameter-efficient method that groups classes into multiple class subsets according to label co-occurrence and mutual exclusivity relationships, and then models them respectively to balance the two relationships. In this work, since each group contains multiple classes, multiple prompt tokens are adopted within Vision Transformer (ViT) to capture the correlation or discriminative label relationship within each group, and effectively learn correlation or discriminative representations for class subsets. On the other hand, each group contains multiple group-aware visual representations that may correspond to multiple classes, and the mixture of experts (MoE) model can cleverly assign them from the group-aware to the label-aware, adaptively obtaining label-aware representation, which is more conducive to classification. Experiments on multiple benchmark datasets show that our proposed approach achieves competitive results and outperforms SOTA methods on multiple pre-trained models.
在多元标签图像分类(MLC)中,建模标签相关性始终发挥着至关重要的作用,吸引了研究人员的广泛关注。然而,最近的研究过分强调了标签之间的共现关系,这可能导致对这种过分强调的过度拟合,从而产生次优模型。为了解决这个问题,我们主张平衡标签之间的相关性和判别性关系,以降低过度拟合的风险并增强模型性能。为此,我们提出了多标签视觉提示调整框架,这是一种新颖且参数高效的方法,根据标签的共现和相互排斥关系将类别分为多个类别子集,然后分别进行建模,以平衡这两种关系。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2025
Summary
多标签图像分类中标签关联建模至关重要,但过度强调标签间的共现关系可能导致模型过拟合。为解决这个问题,我们平衡标签间的关联性和判别性关系,提出多标签视觉提示调整框架。该框架根据标签共现和互斥关系将类别分组,并采用Vision Transformer中的多个提示标记来捕捉每个分组内的标签关系,学习类别子集的相关性或判别性表示。此外,采用混合专家模型将组感知视觉表示适应性地转化为标签感知表示,有利于分类。实验证明,该方法在多个基准数据集上表现优异,超越现有预训练模型。
Key Takeaways
- 多标签图像分类中标签关联建模是关键,但需平衡关联性和判别性关系,以避免模型过拟合。
- 提出多标签视觉提示调整框架,根据标签共现和互斥关系对类别进行分组。
- 采用Vision Transformer中的多个提示标记来捕捉每个分组内的标签相关性。
- 学习类别子集的相关性和判别性表示,提高模型性能。
- 采用混合专家模型将组感知视觉表示转化为标签感知表示,增强分类效果。
- 框架在多个基准数据集上表现优异,具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

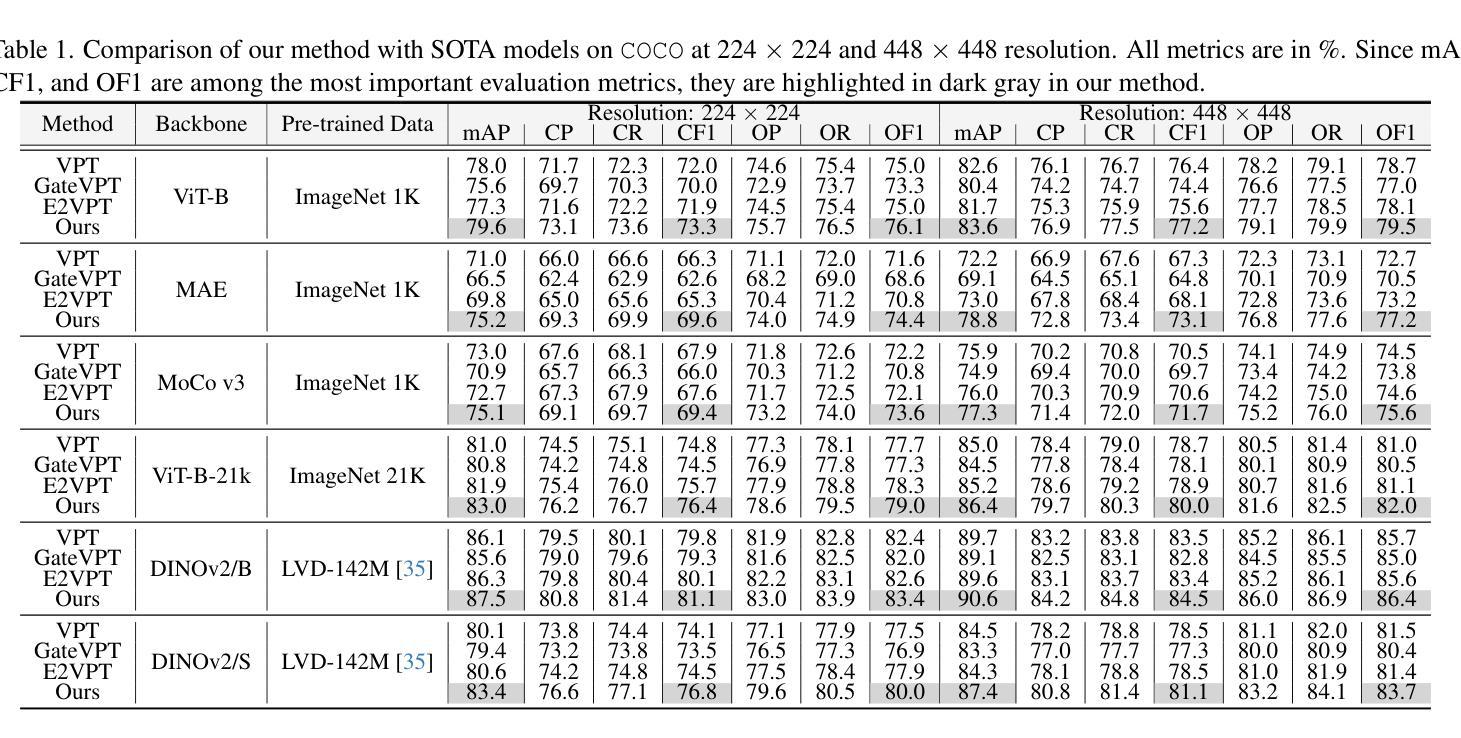
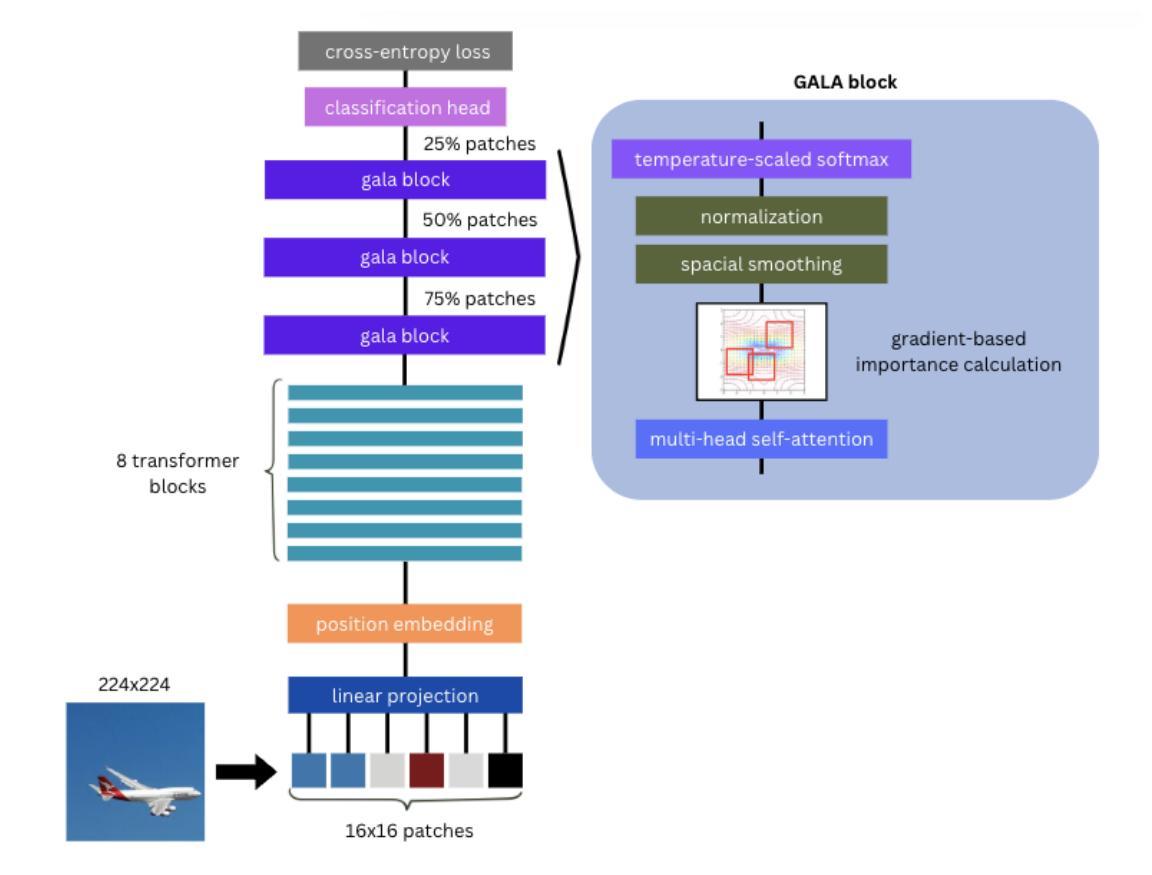
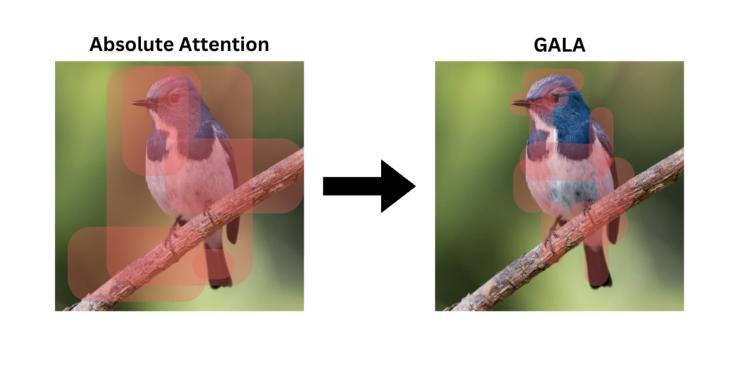
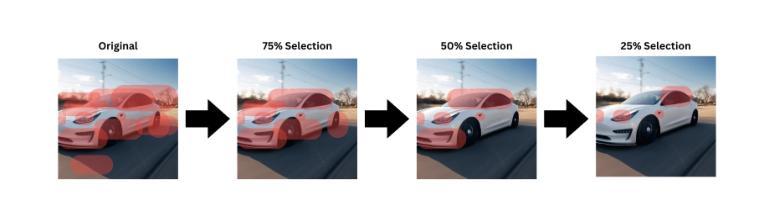
GFT: Gradient Focal Transformer
Authors:Boris Kriuk, Simranjit Kaur Gill, Shoaib Aslam, Amir Fakhrutdinov
Fine-Grained Image Classification (FGIC) remains a complex task in computer vision, as it requires models to distinguish between categories with subtle localized visual differences. Well-studied CNN-based models, while strong in local feature extraction, often fail to capture the global context required for fine-grained recognition, while more recent ViT-backboned models address FGIC with attention-driven mechanisms but lack the ability to adaptively focus on truly discriminative regions. TransFG and other ViT-based extensions introduced part-aware token selection to enhance attention localization, yet they still struggle with computational efficiency, attention region selection flexibility, and detail-focus narrative in complex environments. This paper introduces GFT (Gradient Focal Transformer), a new ViT-derived framework created for FGIC tasks. GFT integrates the Gradient Attention Learning Alignment (GALA) mechanism to dynamically prioritize class-discriminative features by analyzing attention gradient flow. Coupled with a Progressive Patch Selection (PPS) strategy, the model progressively filters out less informative regions, reducing computational overhead while enhancing sensitivity to fine details. GFT achieves SOTA accuracy on FGVC Aircraft, Food-101, and COCO datasets with 93M parameters, outperforming ViT-based advanced FGIC models in efficiency. By bridging global context and localized detail extraction, GFT sets a new benchmark in fine-grained recognition, offering interpretable solutions for real-world deployment scenarios.
细粒度图像分类(FGIC)仍是计算机视觉中的一项复杂任务,因为它要求模型能够区分具有细微局部视觉差异的分类。基于CNN的模型虽然在局部特征提取方面表现出色,但往往无法捕获细粒度识别所需的全局上下文。而最新的基于ViT的模型采用注意力驱动机制来解决FGIC问题,但缺乏自适应关注真正判别区域的能力。TransFG和其他基于ViT的扩展通过引入部分感知令牌选择来增强注意力定位,但在计算效率、注意力区域选择的灵活性和复杂环境中的细节关注叙述方面仍存在挑战。本文介绍了GFT(梯度聚焦转换器),这是一种为FGIC任务而设计的新ViT衍生框架。GFT集成了梯度注意力学习对齐(GALA)机制,通过分析注意力梯度流来动态优先处理类判别特征。结合渐进式补丁选择(PPS)策略,该模型逐步过滤掉信息较少的区域,在提高计算效率的同时提高对细微细节的敏感性。GFT在FGVC飞机、食品101和COCO数据集上实现了最先进的准确性,具有93M参数,在效率上超越了基于ViT的高级FGIC模型。通过桥接全局上下文和局部细节提取,GFT在细粒度识别方面树立了新的基准,为现实世界部署场景提供了可解释的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 tables, 5 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的细粒度图像分类(FGIC)模型——GFT(Gradient Focal Transformer)。该模型通过集成梯度注意力学习对齐(GALA)机制和渐进性补丁选择(PPS)策略,能够动态捕捉类判别特征并优化计算效率。在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,GFT在细粒度识别任务上实现了最先进的准确性,为真实世界应用场景提供了可解释的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- GFT是一种新型的ViT衍生框架,专为细粒度图像分类(FGIC)任务设计。
- GFT通过集成GALA机制和PPS策略,提高了模型的注意力和计算效率。
- GFT能够动态捕捉类判别特征,并优化对细微差别的敏感性。
- GFT在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能,包括FGVC Aircraft、Food-101和COCO数据集。
- GFT通过结合全局上下文和局部细节提取,为细粒度识别设定了新的基准。
- GFT提供了一种可解释的解决方案,适用于真实世界的部署场景。
点此查看论文截图

RAC3: Retrieval-Augmented Corner Case Comprehension for Autonomous Driving with Vision-Language Models
Authors:Yujin Wang, Quanfeng Liu, Jiaqi Fan, Jinlong Hong, Hongqing Chu, Mengjian Tian, Bingzhao Gao, Hong Chen
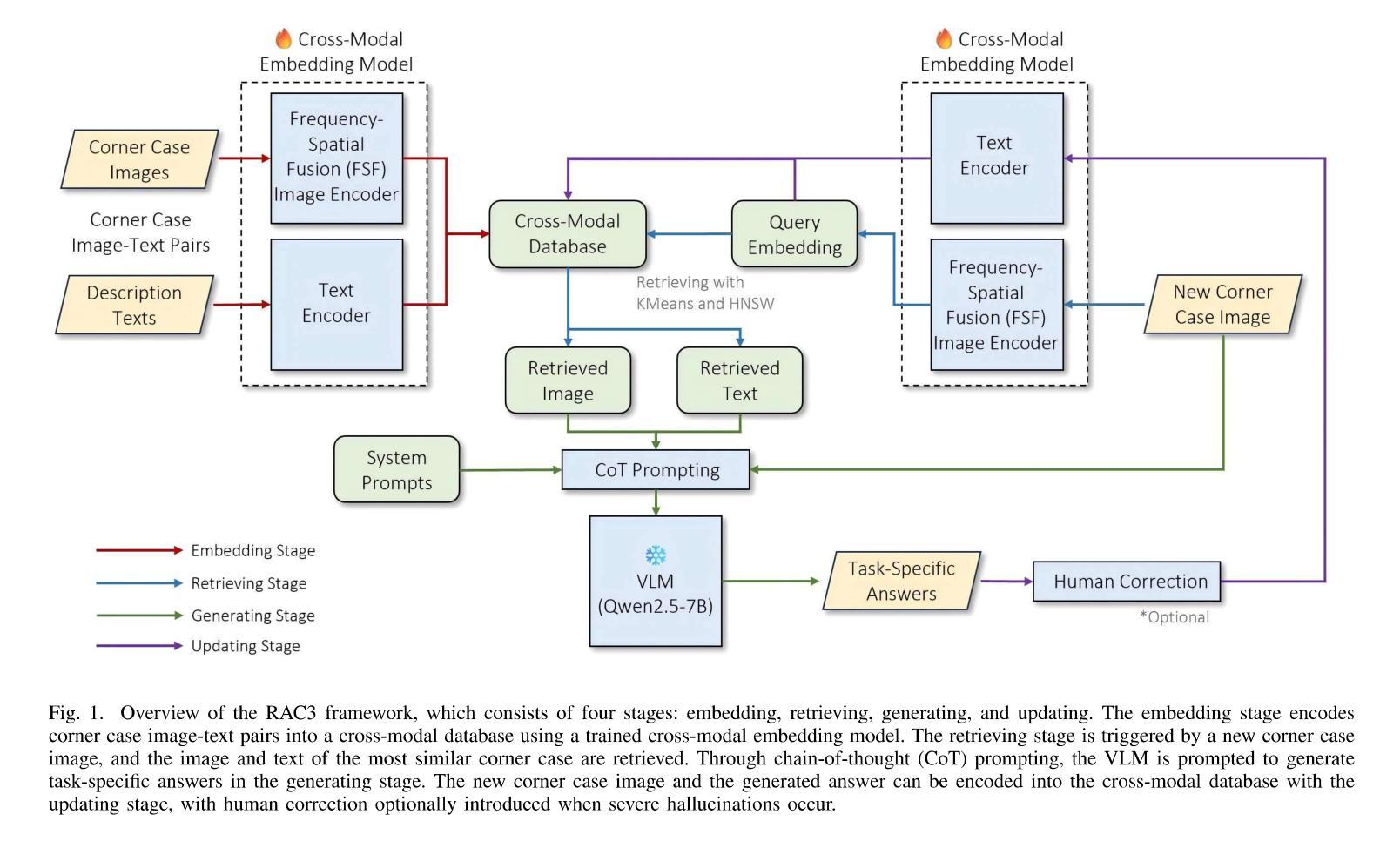
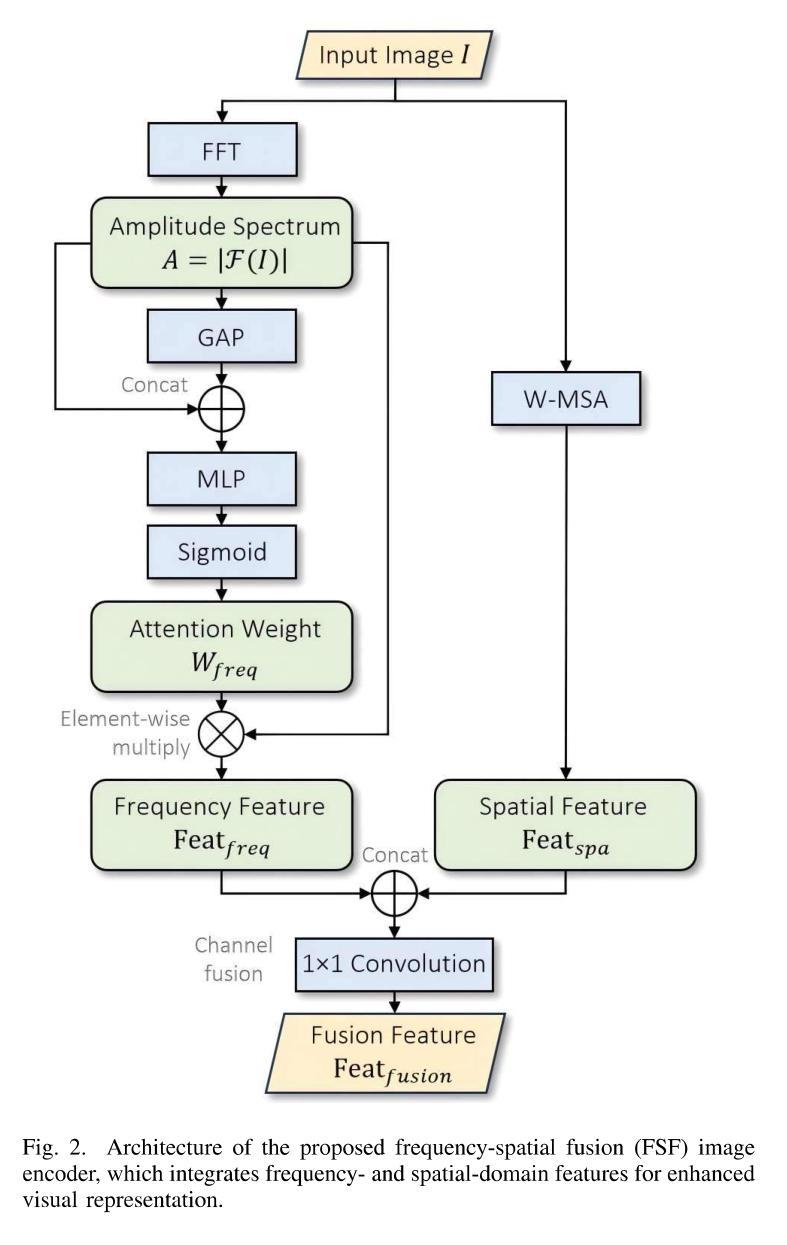
Understanding and addressing corner cases is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of autonomous driving systems. Vision-language models (VLMs) play a crucial role in enhancing scenario comprehension, yet they face significant challenges, such as hallucination and insufficient real-world grounding, which compromise their performance in critical driving scenarios. In this work, RAC3, a novel framework designed to enhance the performance of VLMs in corner case comprehension, is proposed. RAC3 integrates a frequency-spatial fusion (FSF) image encoder, cross-modal alignment fine-tuning with hard and semi-hard negative mining, and a fast querying pipeline based on KMeans clustering and hierarchical navigable small world (HNSW) indexing. A multimodal chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting strategy to guide analogical reasoning and reduce hallucinations during inference is introduced. Moreover, an update mechanism is integrated into RAC3 to ensure continual learning within the framework. Extensive experiments on the CODA and NuScenes datasets demonstrate that RAC3 significantly improves corner case comprehension across multiple downstream tasks. Compared to prior state-of-the-art methods, RAC3 achieves the highest final score of 74.46 on the CODA-LM benchmark and shows consistent performance gains when integrated with end-to-end frameworks like DriveLM. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of retrieval-augmented strategies and cross-modal alignment for safer and more interpretable autonomous driving.
理解和处理极端情况对于确保自动驾驶系统的安全和可靠性至关重要。视觉语言模型(VLM)在提高场景理解方面起着关键作用,但它们面临着重大挑战,如幻象和现实世界基础不足,这损害了它们在关键驾驶场景中的性能。针对这些问题,本文提出了RAC3框架,旨在提高VLM在极端情况理解方面的性能。RAC3集成了频率空间融合(FSF)图像编码器、带有硬和半硬负挖掘的跨模态对齐微调、基于KMeans聚类和分层可导航小世界(HNSW)索引的快速查询管道。还引入了一种多模态思维链(CoT)提示策略,以引导类比推理并减少推理过程中的幻象。此外,RAC3还集成了更新机制,以确保框架内的持续学习。在CODA和NuScenes数据集上的大量实验表明,RAC3在多个下游任务中显著提高了极端情况的理解能力。与之前的最新方法相比,RAC3在CODA-LM基准测试中取得了最高分74.46分,在与端到端框架(如DriveLM)集成时表现出持续的性能提升。这些结果证明了检索增强策略和跨模态对齐对于更安全、更可解释的自动驾驶的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 7 figures
Summary
该文本介绍了一种名为RAC3的新型框架,旨在提高视觉语言模型在自动驾驶系统的关键场景理解性能。RAC3集成了频率空间融合图像编码器、跨模态对齐微调与硬和半硬负样本挖掘等技术,同时引入了基于KMeans聚类和层次可导航小世界索引的快速查询管道。此外,RAC3还采用了一种多模态思维链引导策略,以引导类比推理并减少推理过程中的幻觉。在CODA和NuScenes数据集上的实验表明,RAC3在多个下游任务中显著提高关键场景的理解能力。与现有最先进的相比,RAC3在CODA-LM基准测试中取得了最高分74.46分,并且当与端到端框架(如DriveLM)集成时,显示出持续的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶系统中理解和处理关键场景至关重要,涉及安全性和可靠性。
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在提高场景理解方面扮演重要角色,但面临挑战如幻觉和缺乏真实世界基础。
- RAC3框架旨在提高VLMs在关键场景理解方面的性能。
- RAC3集成了频率空间融合图像编码器以改善视觉处理。
- 跨模态对齐微调与硬和半硬负样本挖掘被用于提高模型的准确性和泛化能力。
- 快速查询管道基于KMeans聚类和HNSW索引,提高了模型效率。
点此查看论文截图
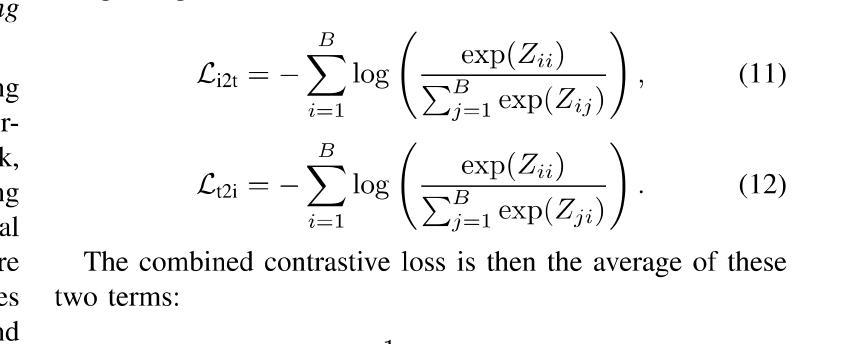
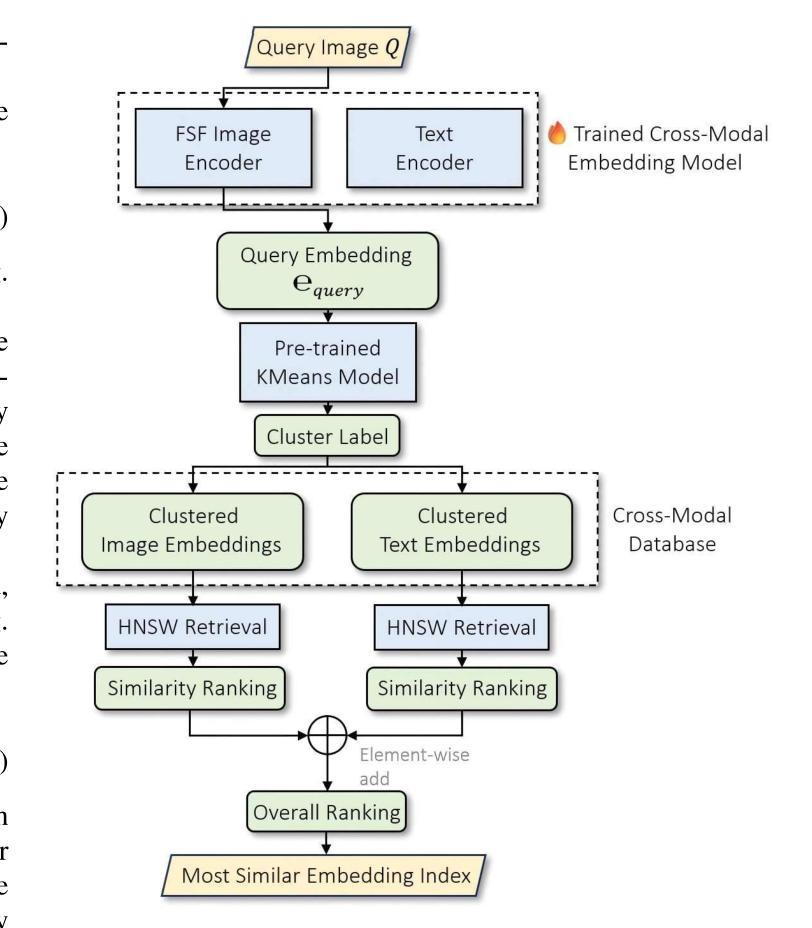
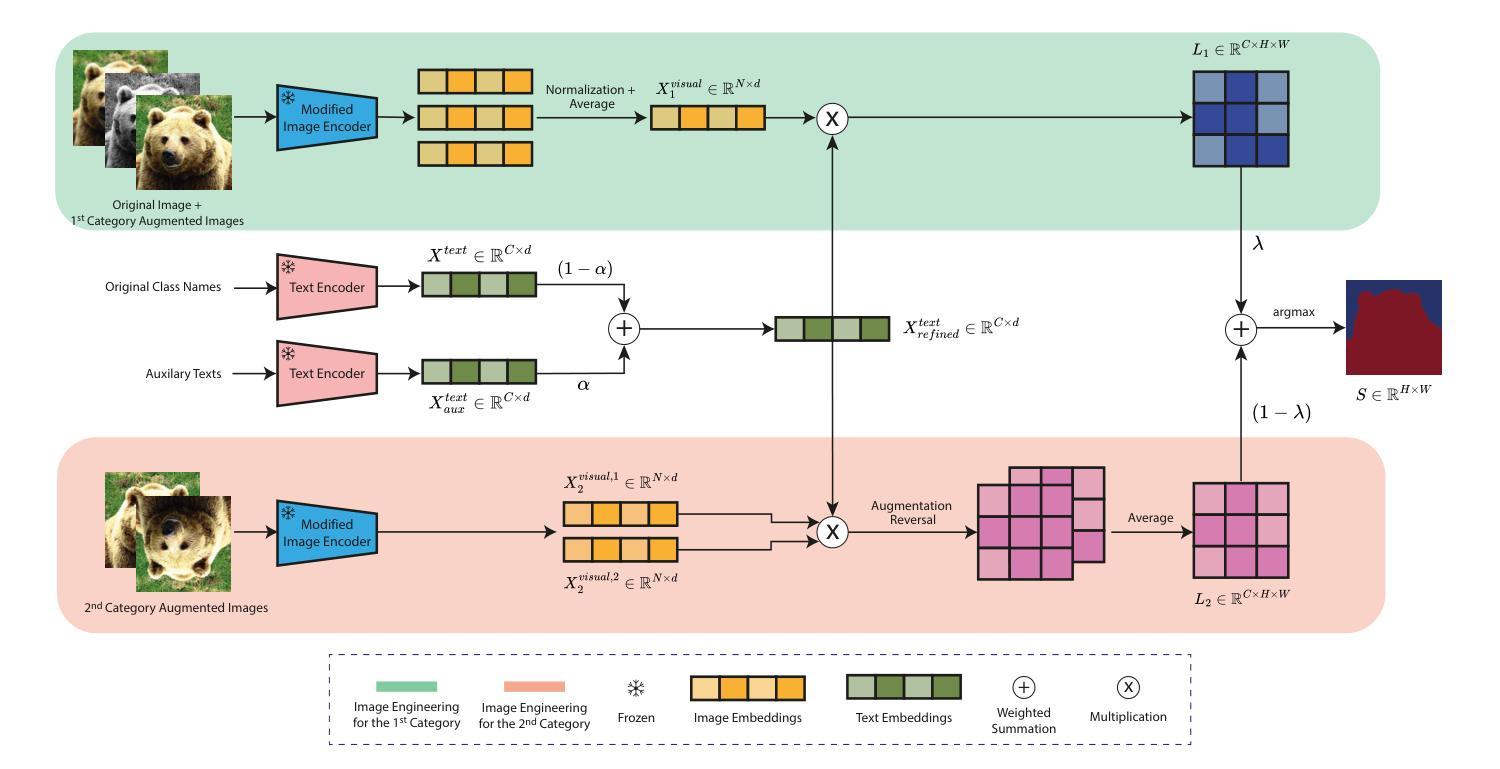
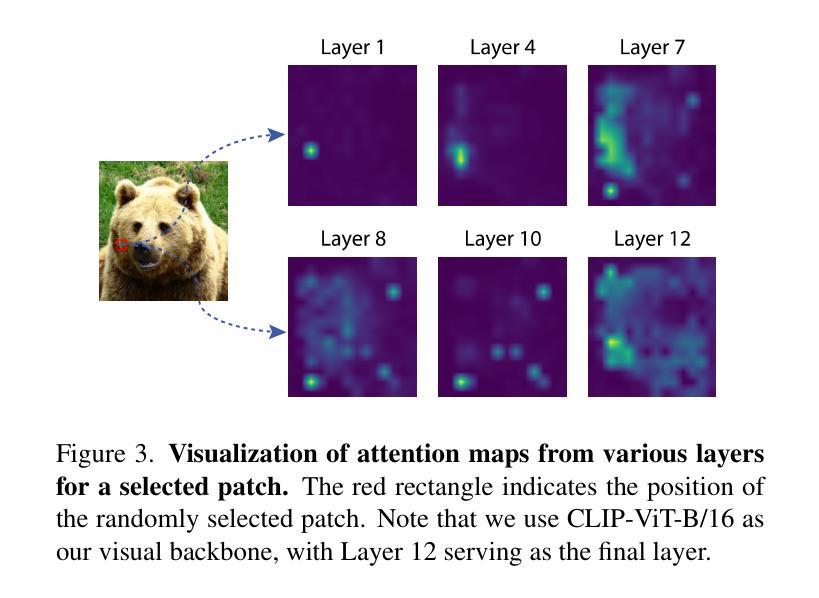
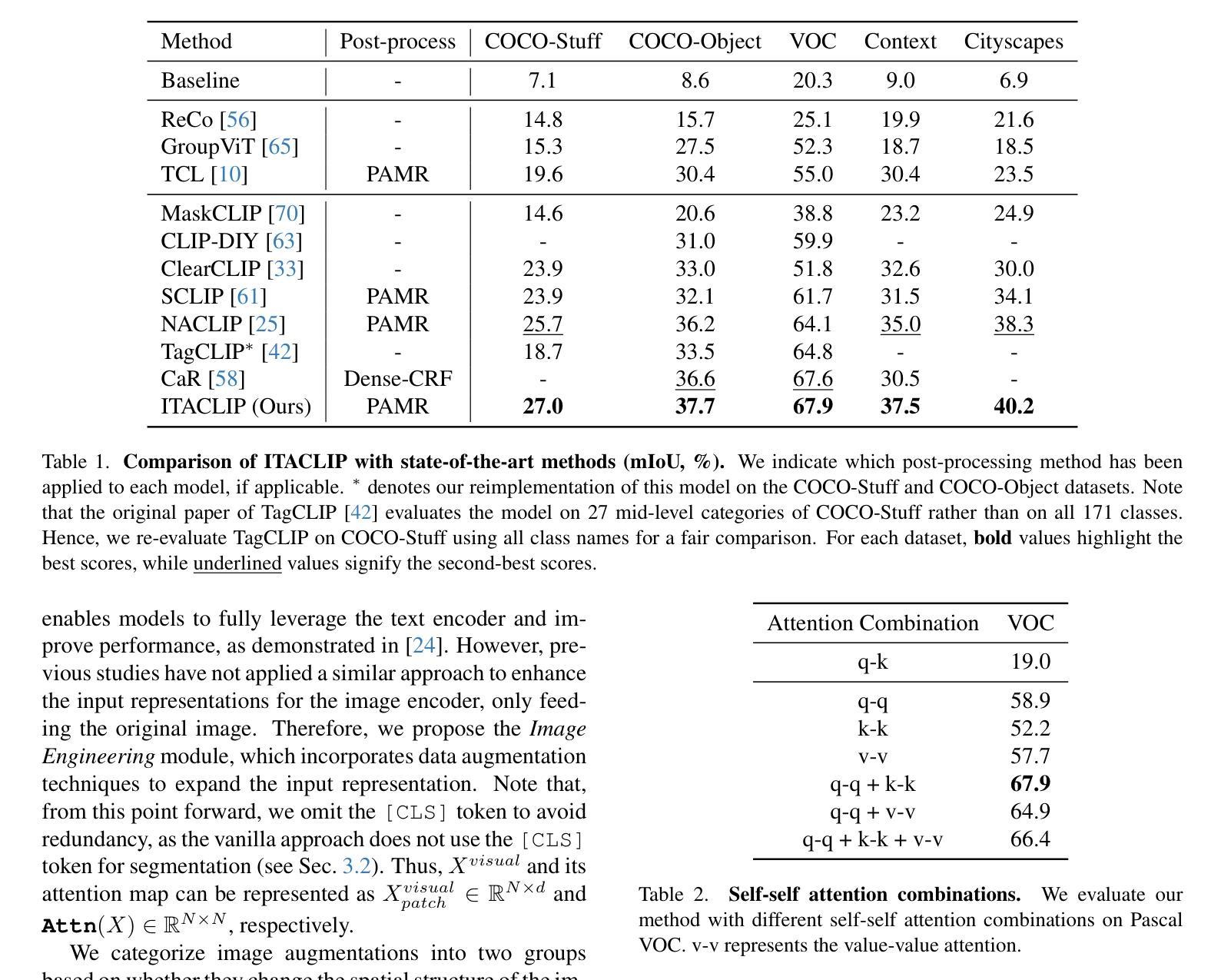
ITACLIP: Boosting Training-Free Semantic Segmentation with Image, Text, and Architectural Enhancements
Authors:M. Arda Aydın, Efe Mert Çırpar, Elvin Abdinli, Gozde Unal, Yusuf H. Sahin
Recent advances in foundational Vision Language Models (VLMs) have reshaped the evaluation paradigm in computer vision tasks. These foundational models, especially CLIP, have accelerated research in open-vocabulary computer vision tasks, including Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation (OVSS). Although the initial results are promising, the dense prediction capabilities of VLMs still require further improvement. In this study, we enhance the semantic segmentation performance of CLIP by introducing new modules and modifications: 1) architectural changes in the last layer of ViT and the incorporation of attention maps from the middle layers with the last layer, 2) Image Engineering: applying data augmentations to enrich input image representations, and 3) using Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate definitions and synonyms for each class name to leverage CLIP’s open-vocabulary capabilities. Our training-free method, ITACLIP, outperforms current state-of-the-art approaches on segmentation benchmarks such as COCO-Stuff, COCO-Object, Pascal Context, and Pascal VOC. Our code is available at https://github.com/m-arda-aydn/ITACLIP.
最新的视觉语言模型(VLMs)进展已经改变了计算机视觉任务的评估范式。尤其是CLIP等基础性模型,已经加速了开放词汇计算机视觉任务的研究,包括开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)。尽管初步结果令人鼓舞,但VLMs的密集预测能力仍需进一步改进。在本研究中,我们通过引入新模块和修改来提高CLIP的语义分割性能:1)对ViT最后一层进行架构更改,并将中间层的注意力图与最后一层相结合;2)图像工程:应用数据增强来丰富输入图像表示;3)使用大型语言模型(LLMs)为每一类名称生成定义和同义词,以利用CLIP的开放词汇能力。我们的无训练方法ITACLIP在COCO-Stuff、COCO-Object、Pascal Context和Pascal VOC等分割基准测试上优于当前最先进的方法。我们的代码可在https://github.com/m-arda-aydn/ITACLIP上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了近期基础视觉语言模型(VLMs)的进展改变了计算机视觉任务的评估模式。研究团队通过引入新的模块和改进,提升了CLIP在开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)任务中的性能。他们进行了架构变更,结合了中间层的注意力图与最后一层的信息;通过图像工程丰富输入图像表征;并利用大型语言模型(LLMs)为每类生成定义和同义词,以利用CLIP的开放词汇能力。其无训练的方法ITACLIP在COCO-Stuff、COCO-Object、Pascal Context和Pascal VOC等分割基准测试中优于当前最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 基础视觉语言模型(VLMs)的发展已经改变了计算机视觉任务的评估模式。
- CLIP等模型加速了开放词汇计算机视觉任务的研究。
- 研究团队通过引入新模块和改进提升了CLIP在语义分割中的性能。
- 架构变更结合了中间层的注意力图与最后一层的信息。
- 图像工程通过数据增强丰富了输入图像表征。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLMs)为每类生成定义和同义词,以增强CLIP的开放词汇能力。
- ITACLIP方法在多个分割基准测试中表现优于当前最先进的方法。
点此查看论文截图

AMBER – Advanced SegFormer for Multi-Band Image Segmentation: an application to Hyperspectral Imaging
Authors:Andrea Dosi, Massimo Brescia, Stefano Cavuoti, Mariarca D’Aniello, Michele Delli Veneri, Carlo Donadio, Adriano Ettari, Giuseppe Longo, Alvi Rownok, Luca Sannino, Maria Zampella
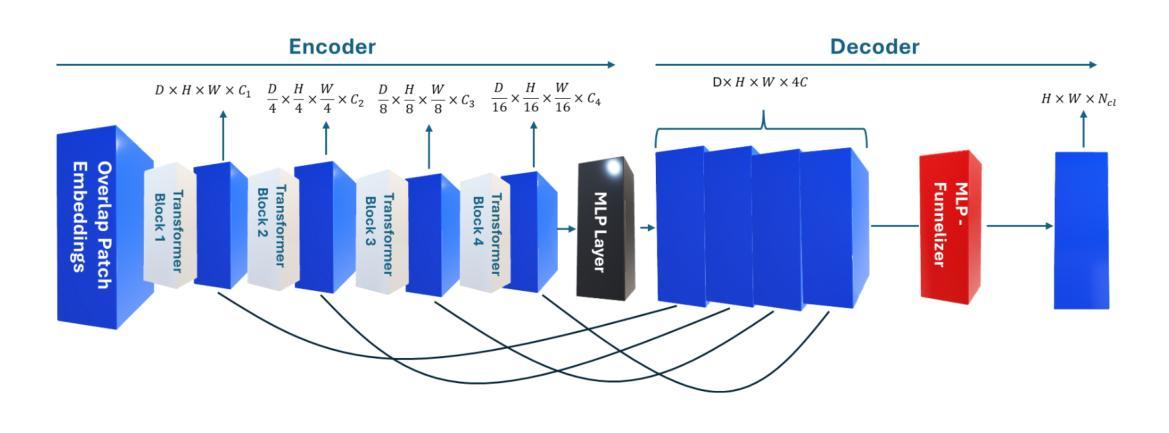
Deep learning has revolutionized the field of hyperspectral image (HSI) analysis, enabling the extraction of complex spectral and spatial features. While convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been the backbone of HSI classification, their limitations in capturing global contextual features have led to the exploration of Vision Transformers (ViTs). This paper introduces AMBER, an advanced SegFormer specifically designed for multi-band image segmentation. AMBER enhances the original SegFormer by incorporating three-dimensional convolutions, custom kernel sizes, and a Funnelizer layer. This architecture enables processing hyperspectral data directly, without requiring spectral dimensionality reduction during preprocessing. Our experiments, conducted on three benchmark datasets (Salinas, Indian Pines, and Pavia University) and on a dataset from the PRISMA satellite, show that AMBER outperforms traditional CNN-based methods in terms of Overall Accuracy, Kappa coefficient, and Average Accuracy on the first three datasets, and achieves state-of-the-art performance on the PRISMA dataset. These findings highlight AMBER’s robustness, adaptability to both airborne and spaceborne data, and its potential as a powerful solution for remote sensing and other domains requiring advanced analysis of high-dimensional data.
深度学习已经彻底改变了高光谱图像(HSI)分析领域,能够提取复杂的光谱和空间特征。虽然卷积神经网络(CNN)已成为HSI分类的支柱,但在捕捉全局上下文特征方面的局限性促使人们探索视觉变压器(ViT)。本文介绍了AMBER,这是一种专为多波段图像分割设计的先进SegFormer。AMBER通过引入三维卷积、自定义内核大小和漏斗层,增强了原始的SegFormer。该架构能够直接处理高光谱数据,无需在预处理期间降低光谱维度。我们在三个基准数据集(Salinas、Indian Pines和Pavia University)以及PRISMA卫星数据集上进行的实验表明,AMBER在总体精度、Kappa系数和平均精度方面优于传统的基于CNN的方法,在PRISMA数据集上达到了最新技术水平。这些发现突出了AMBER的稳健性、对机载和星载数据的适应性,以及其作为遥感和其他需要高级高维数据分析领域的潜在强大解决方案的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF submitted to Neural Computing & Applications (Springer). Accepted with minor revisions
Summary
深度学习在光谱图像分析领域引发革命,卷积神经网络在光谱图像分类中占据主导地位,但其捕捉全局上下文特征的局限性促使了对视觉Transformer的探索。本文介绍了一种用于多波段图像分割的高级SegFormer——AMBER。AMBER通过引入三维卷积、自定义内核大小和Funnelizer层,增强了原始SegFormer的性能,可直接处理光谱数据,无需预处理中的光谱维度降低。实验表明,AMBER在三个基准数据集上优于传统CNN方法,并在PRISMA数据集上达到最新性能水平。这表明AMBER具有稳健性和对航空和太空数据的适应性,以及在遥感和其他需要高级高维数据分析领域的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在光谱图像分析领域具有显著优势,推动了该领域的发展。
- 卷积神经网络在HSI分类中占据主导地位,但存在捕捉全局上下文特征的局限性。
- Vision Transformers(ViTs)的探索是为了解决CNN的局限性。
- AMBER是一种先进的SegFormer,专为多波段图像分割设计。
- AMBER通过引入三维卷积、自定义内核和Funnelizer层增强了SegFormer的性能。
- AMBER可直接处理光谱数据,无需预处理中的光谱维度降低。
点此查看论文截图

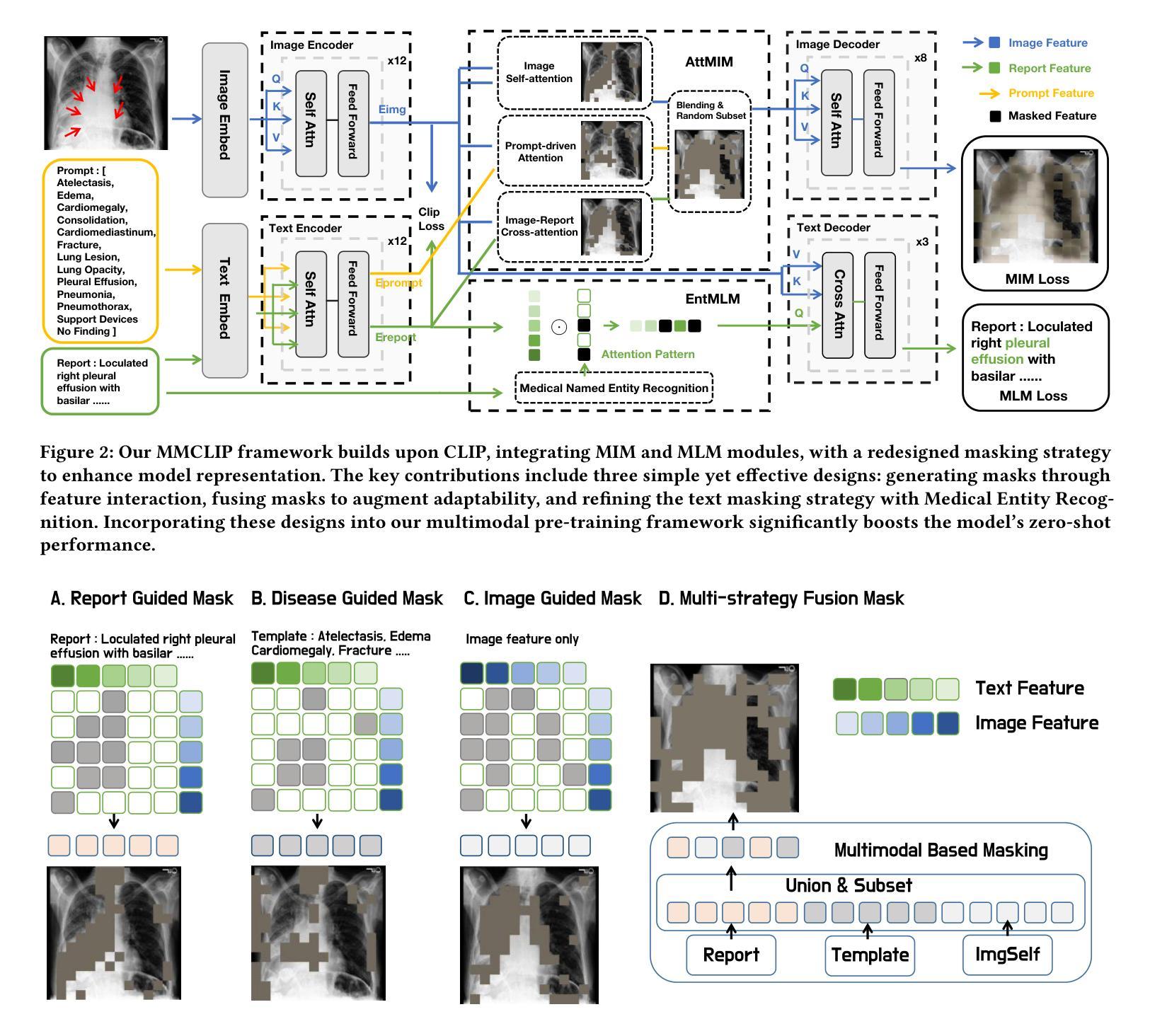
MMCLIP: Cross-modal Attention Masked Modelling for Medical Language-Image Pre-Training
Authors:Biao Wu, Yutong Xie, Zeyu Zhang, Minh Hieu Phan, Qi Chen, Ling Chen, Qi Wu
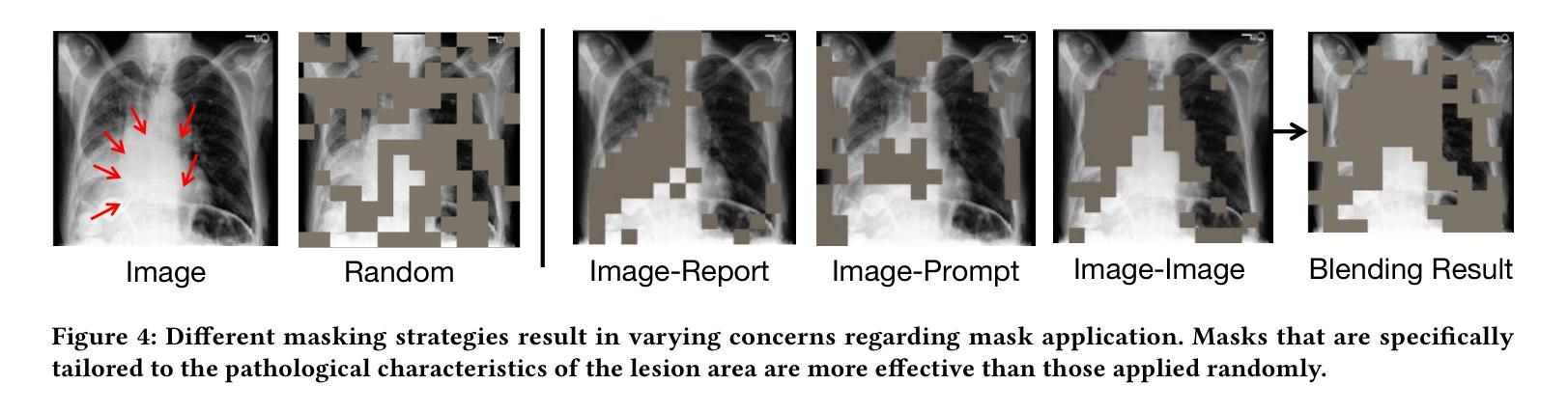
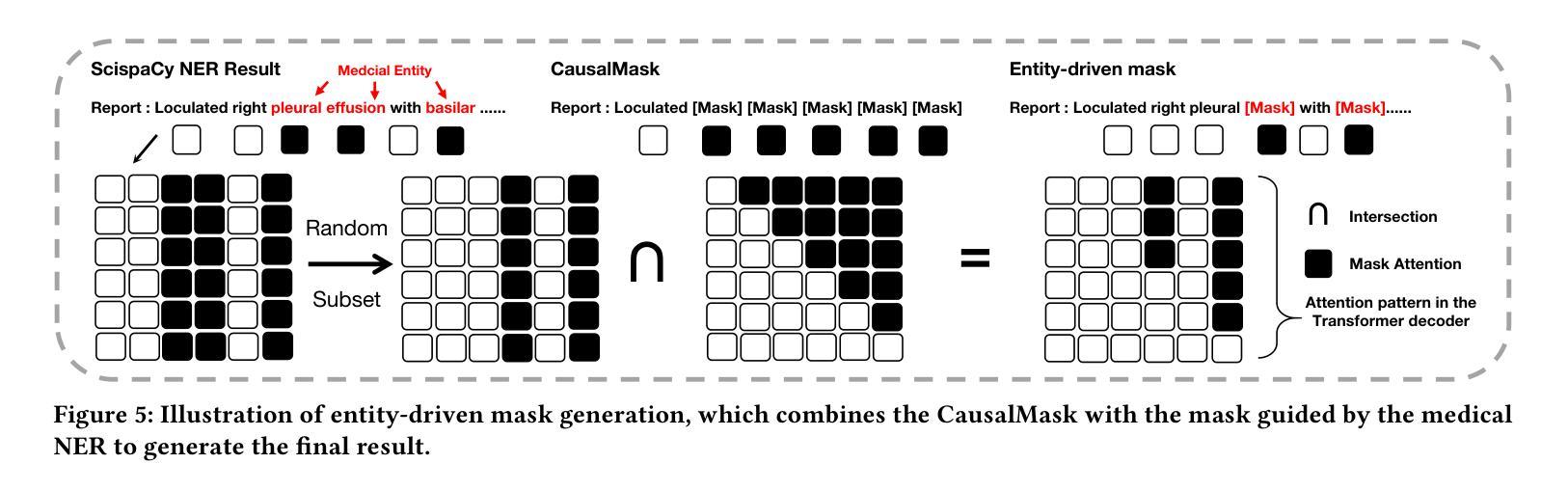
Vision-and-language pretraining (VLP) in the medical field utilizes contrastive learning on image-text pairs to achieve effective transfer across tasks. Yet, current VLP approaches with the masked modeling strategy face two challenges when applied to the medical domain. First, current models struggle to accurately reconstruct key pathological features due to the scarcity of medical data. Second, most methods only adopt either paired image-text or image-only data, failing to exploit the combination of both paired and unpaired data. To this end, this paper proposes the MMCLIP (Masked Medical Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training) framework to enhance pathological learning and feature learning via unpaired data. First, we introduce the attention-masked image modeling (AttMIM) and entity-driven masked language modeling module (EntMLM), which learns to reconstruct pathological visual and textual tokens via multi-modal feature interaction, thus improving medical-enhanced features. The AttMIM module masks a portion of the image features that are highly responsive to textual features. This allows MMCLIP to improve the reconstruction of highly similar image data in medicine efficiency. Second, our MMCLIP capitalizes unpaired data to enhance multimodal learning by introducing disease-kind prompts. The experimental results show that MMCLIP achieves SOTA for zero-shot and fine-tuning classification performance on five datasets. Our code will be available at https://github.com/White65534/MMCLIP.
在医学领域的视觉和语言预训练(VLP)通过对图像文本对进行对比学习,实现了跨任务的有效迁移。然而,当前采用掩模建模策略的VLP方法在应用到医学领域时面临两个挑战。首先,由于医疗数据的稀缺,当前模型难以准确重建关键病理特征。其次,大多数方法只采用配对图像文本或仅图像数据,未能充分利用配对和未配对数据的组合。鉴于此,本文提出了MMCLIP(基于掩膜医学对比语言图像预训练)框架,通过未配对数据增强病理学习和特征学习。首先,我们引入了注意力掩膜图像建模(AttMIM)和实体驱动掩膜语言建模模块(EntMLM),通过多模态特征交互学习重建病理视觉和文本标记,从而提高医学增强的特征。AttMIM模块会掩去与文本特征高度响应的图像特征的一部分。这使得MMCLIP能够在医学效率上提高高度相似图像数据的重建。其次,我们的MMCLIP利用未配对的数据,通过引入疾病提示来增强多模态学习。实验结果表明,MMCLIP在五个数据集上实现了零样本和微调分类性能的最新技术表现。我们的代码将在https://github.com/White65534/MMCLIP上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对医疗领域的视觉与语言预训练(VLP)技术。由于医疗数据的稀缺性,当前采用掩盖建模策略的VLP方法面临两大挑战:一是难以准确重建关键病理特征,二是仅采用配对图像文本或仅采用图像数据,未能充分利用配对和未配对数据的结合。为此,本文提出了MMCLIP(Masked Medical Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training)框架,通过未配对数据增强病理学习和特征学习。该框架引入了注意力掩盖图像建模(AttMIM)和实体驱动掩盖语言建模模块(EntMLM),通过多模态特征交互学习重建病理视觉和文本符号,从而改进医学增强特征。实验结果表明,MMCLIP在五个数据集上实现了零样本和微调分类性能的最好水平。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗领域的视觉与语言预训练(VLP)利用对比学习在图像文本对上实现任务间的有效迁移。
- 当前VLP方法在应用至医疗领域时面临数据稀缺和未能充分利用配对与未配对数据的挑战。
- MMCLIP框架通过引入AttMIM和EntMLM模块,学习重建病理视觉和文本符号,改进医学增强特征。
- MMCLIP利用未配对数据增强多模态学习,并通过疾病类型提示来提高效果。
- MMCLIP在五个数据集上实现了零样本和微调分类性能的最佳水平。
- MMCLIP代码将公开在https://github.com/White65534/MMCLIP。
点此查看论文截图