⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-17 更新
Aligning Generative Denoising with Discriminative Objectives Unleashes Diffusion for Visual Perception
Authors:Ziqi Pang, Xin Xu, Yu-Xiong Wang
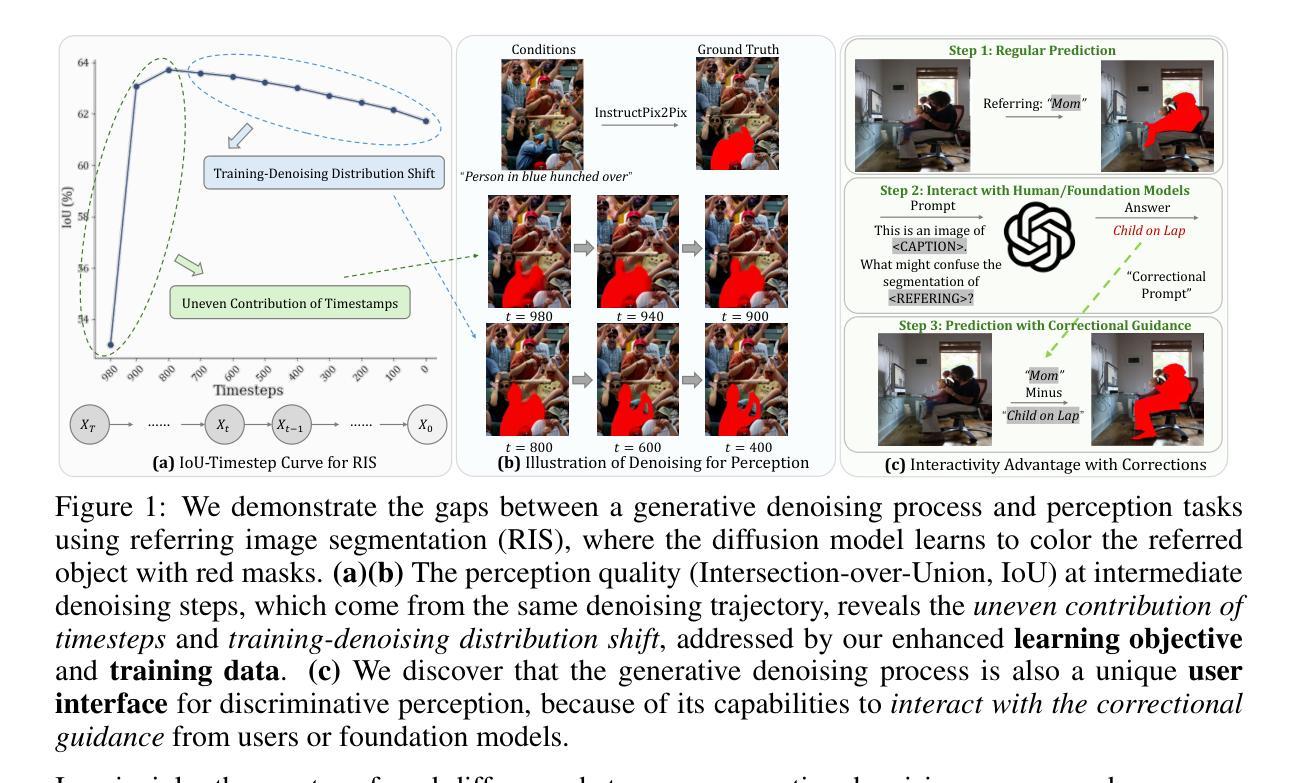
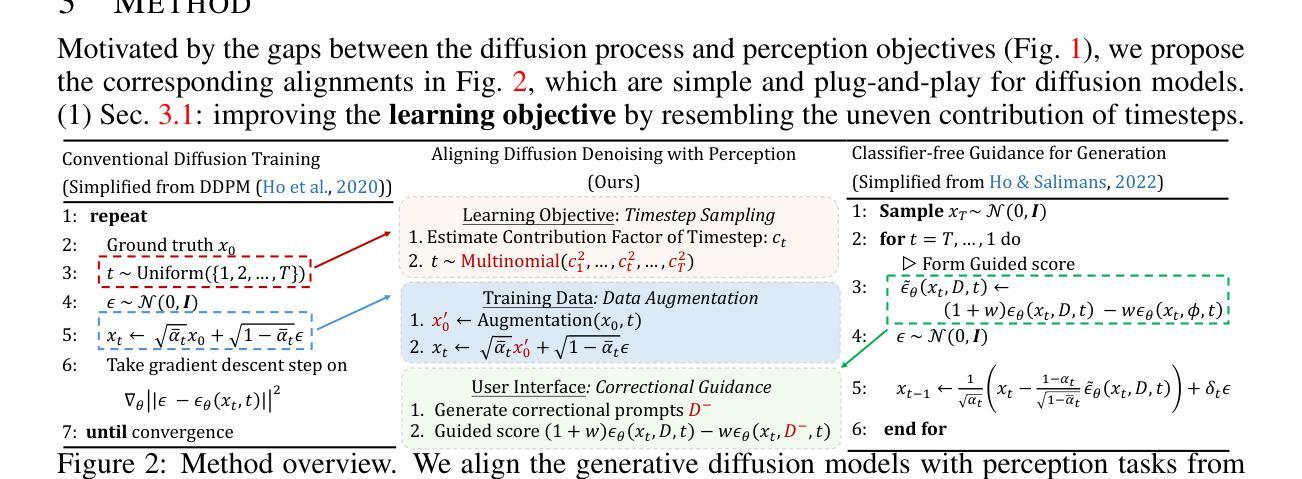
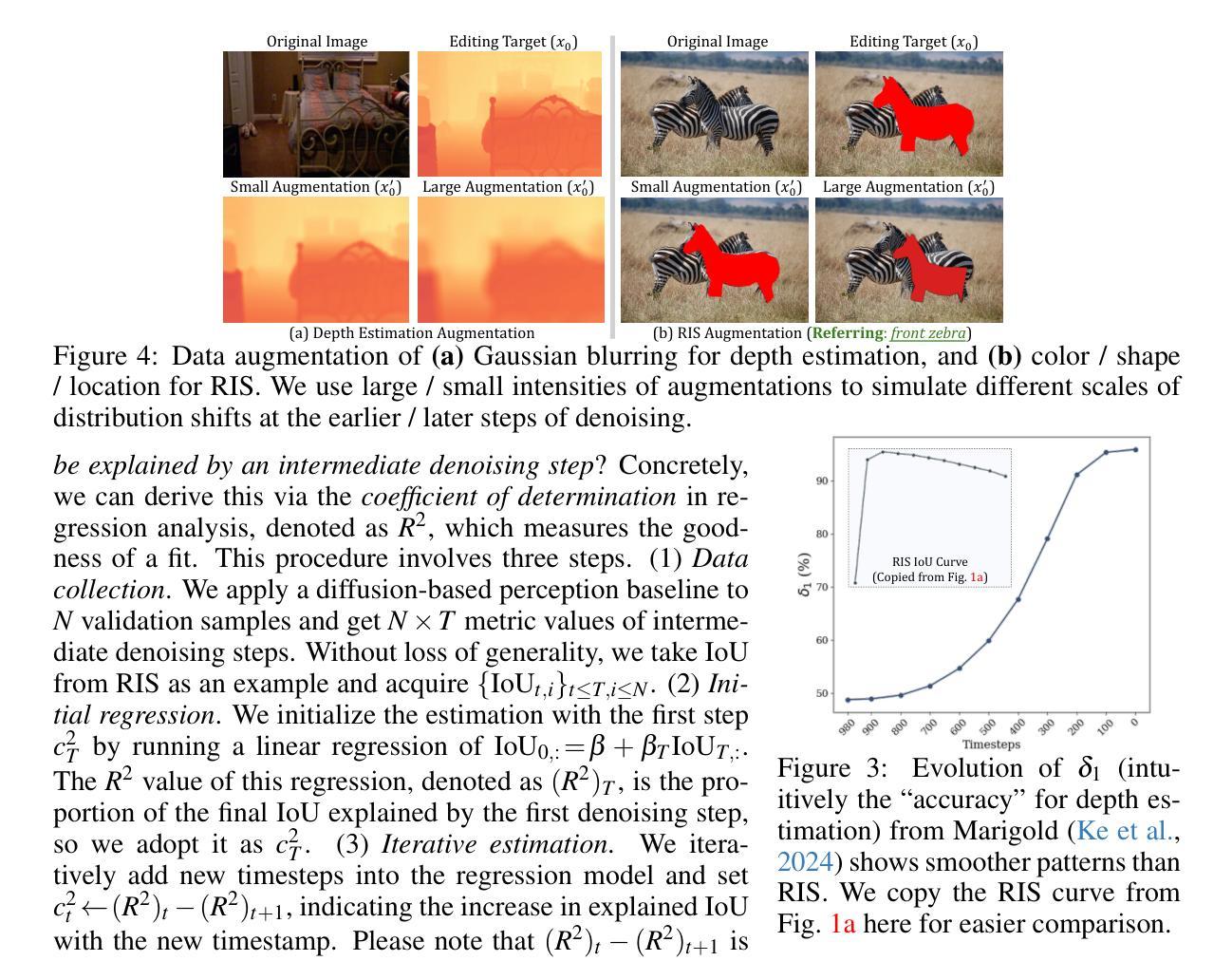
With the success of image generation, generative diffusion models are increasingly adopted for discriminative tasks, as pixel generation provides a unified perception interface. However, directly repurposing the generative denoising process for discriminative objectives reveals critical gaps rarely addressed previously. Generative models tolerate intermediate sampling errors if the final distribution remains plausible, but discriminative tasks require rigorous accuracy throughout, as evidenced in challenging multi-modal tasks like referring image segmentation. Motivated by this gap, we analyze and enhance alignment between generative diffusion processes and perception tasks, focusing on how perception quality evolves during denoising. We find: (1) earlier denoising steps contribute disproportionately to perception quality, prompting us to propose tailored learning objectives reflecting varying timestep contributions; (2) later denoising steps show unexpected perception degradation, highlighting sensitivity to training-denoising distribution shifts, addressed by our diffusion-tailored data augmentation; and (3) generative processes uniquely enable interactivity, serving as controllable user interfaces adaptable to correctional prompts in multi-round interactions. Our insights significantly improve diffusion-based perception models without architectural changes, achieving state-of-the-art performance on depth estimation, referring image segmentation, and generalist perception tasks. Code available at https://github.com/ziqipang/ADDP.
随着图像生成的成功,生成性扩散模型(Generative Diffusion Models)在判别任务中的应用越来越广泛,因为像素生成提供了一个统一的感知接口。然而,直接将生成去噪过程应用于判别目标却暴露出之前很少解决的关键差距。生成模型如果最终分布仍然可行,可以容忍中间采样过程中的错误,但判别任务需要在整个过程中严格保持准确性,就像在图像引用分割等多模式任务中所显示的那样。为了填补这一差距,我们对生成扩散过程和感知任务之间的对齐进行了分析和改进,重点研究去噪过程中感知质量如何演变。我们发现:(1)早期的去噪步骤对感知质量的贡献不成比例,促使我们提出反映不同时间步贡献的学习目标;(2)在较后的去噪步骤中出现了意外的感知质量下降,这突显了对训练去噪分布变化的敏感性,我们的扩散定制数据增强解决了这一问题;(3)生成过程具有独特的交互性,可作为可控的用户界面,适应多轮交互中的校正提示。我们的见解在不改变架构的情况下显著改进了基于扩散的感知模型,在深度估计、图像引用分割和通用感知任务上实现了最先进的性能。代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/ziqipang/ADDP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
基于图像生成的成功,生成性扩散模型在判别任务中的应用日益广泛,像素生成提供了统一的感知接口。本文分析了将生成性去噪过程直接应用于判别任务时存在的关键差距,提出了一系列针对扩散过程和感知任务之间对齐性的改进策略。研究发现早期去噪步骤对感知质量的贡献较大,提出了反映不同时间步贡献的学习目标;后期去噪步骤会出现感知退化,通过扩散定制的数据增强解决训练去噪分布偏移问题;生成过程具有独特的交互性,可作为多轮交互中的可校正提示。这些见解在不改变架构的情况下显著提高了基于扩散的感知模型性能,在深度估计、引用图像分割和通用感知任务上达到了最新性能水平。
Key Takeaways
- 生成性扩散模型在判别任务中的应用逐渐普及,但仍存在关键差距。
- 早期去噪步骤对感知质量的贡献较大,需要针对性地设计学习目标。
- 后期去噪步骤存在感知退化问题,训练去噪分布偏移是主要原因,可通过数据增强解决。
- 生成过程具有交互性优势,可作为多轮交互中的可校正提示。
- 针对以上发现,提出的策略在不改变模型架构的情况下显著提高了感知性能。
- 在深度估计、引用图像分割和通用感知任务上取得了最新性能水平。
点此查看论文截图

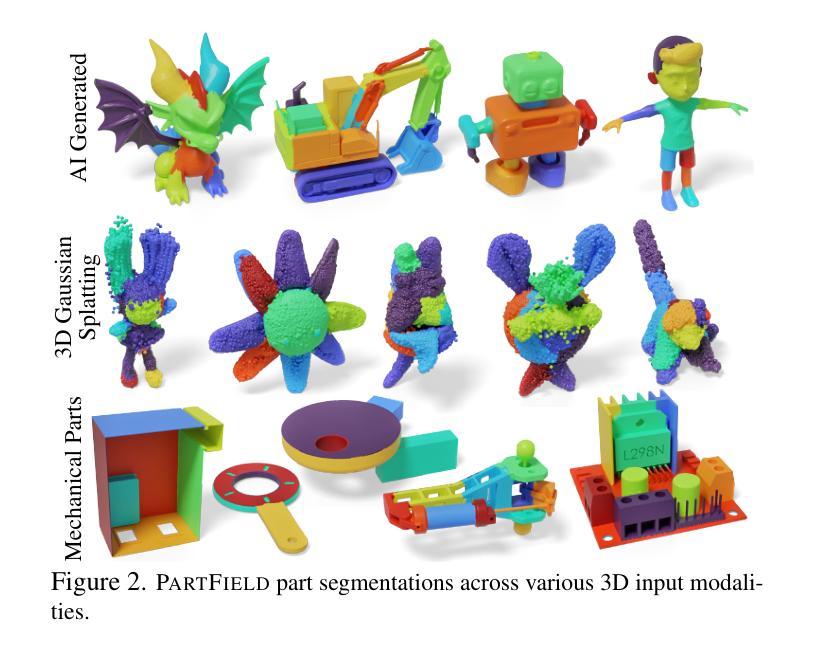
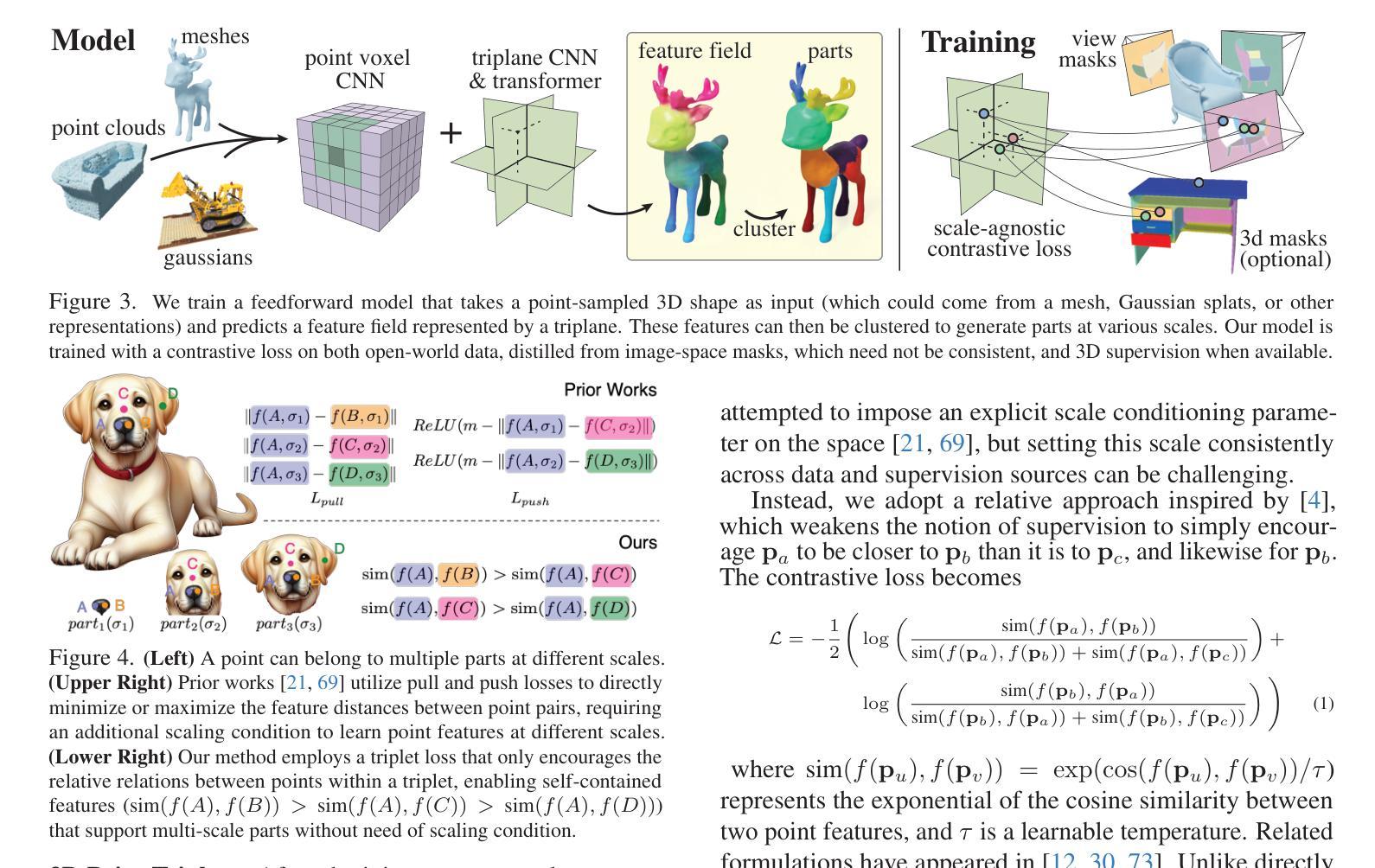
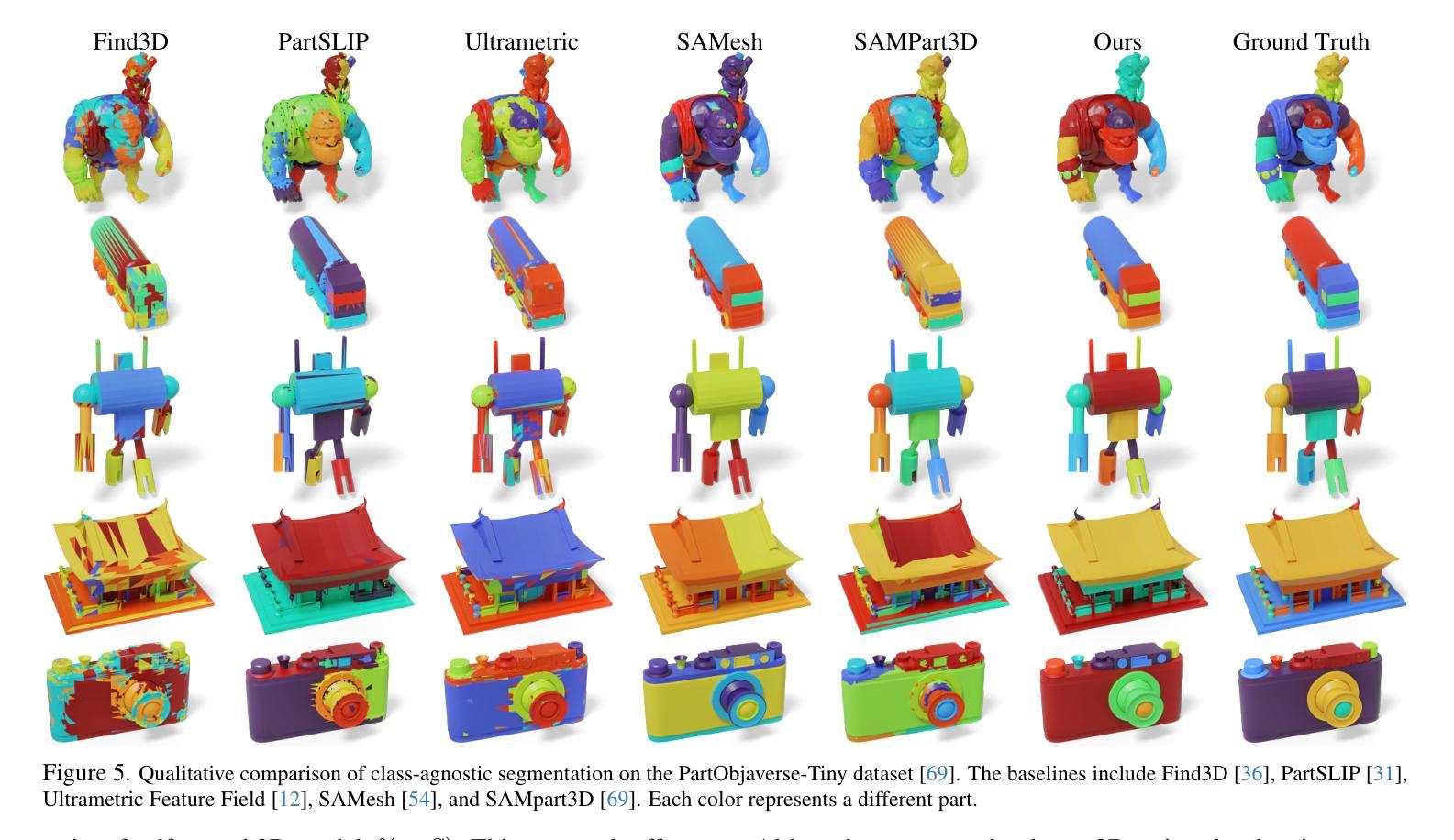
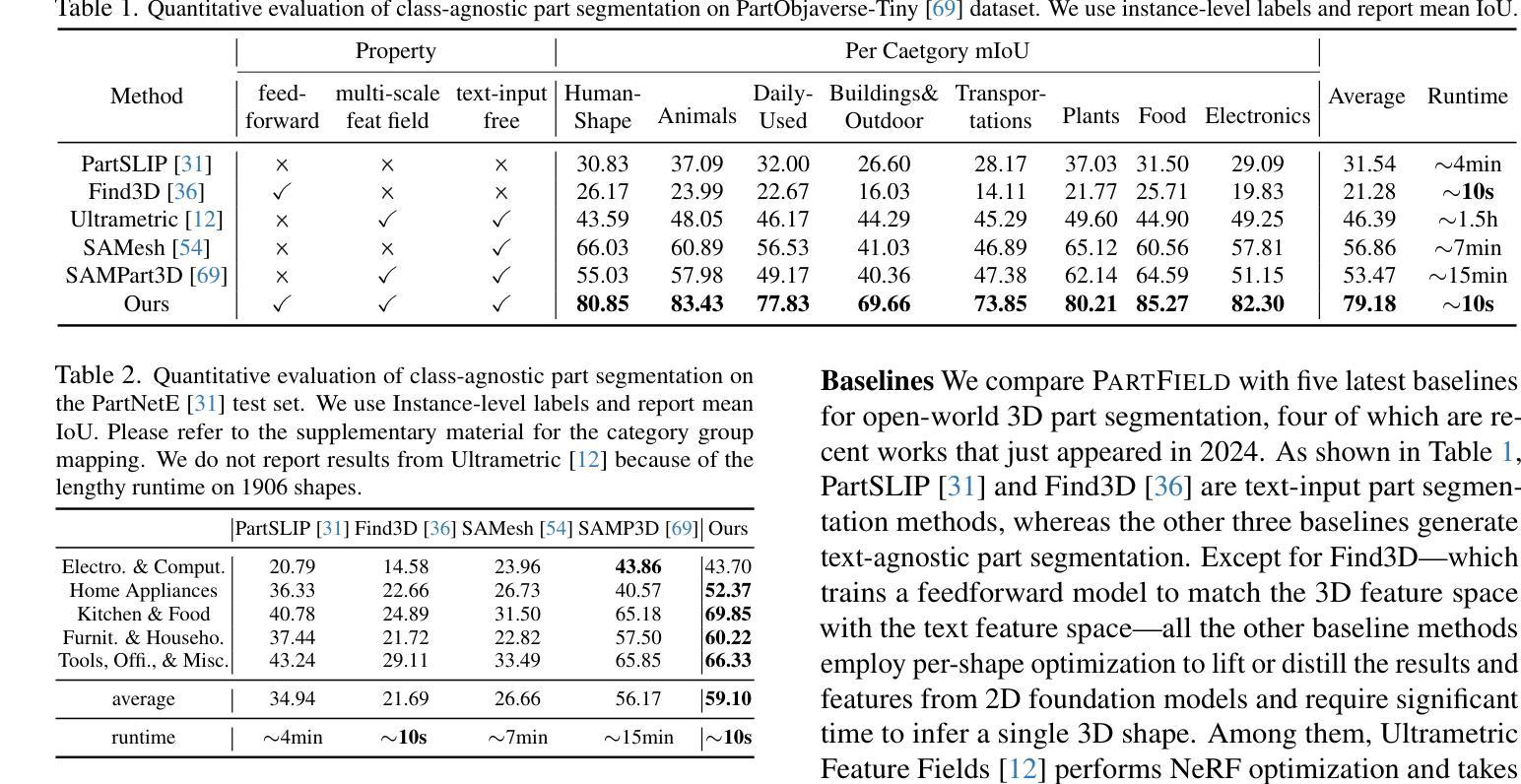
PARTFIELD: Learning 3D Feature Fields for Part Segmentation and Beyond
Authors:Minghua Liu, Mikaela Angelina Uy, Donglai Xiang, Hao Su, Sanja Fidler, Nicholas Sharp, Jun Gao
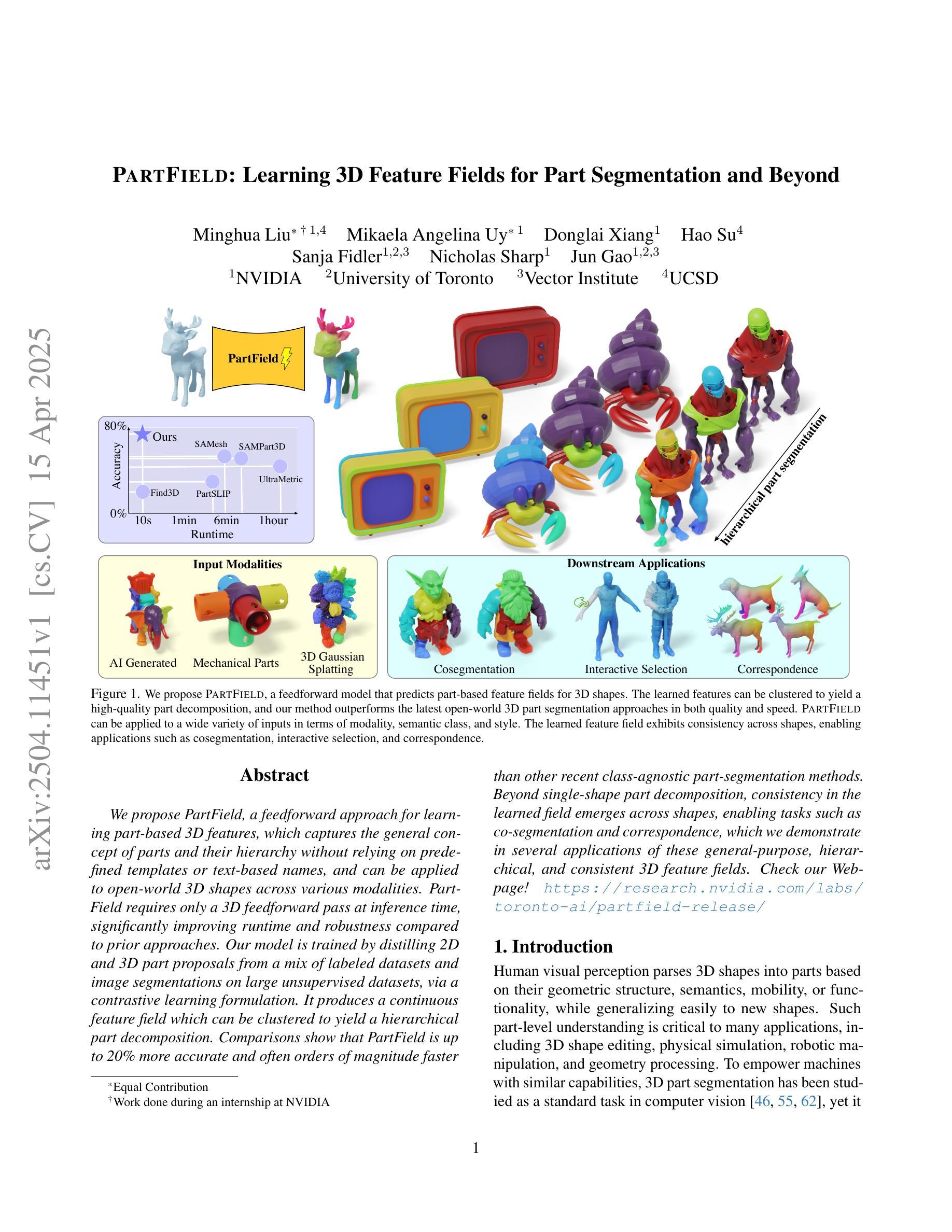
We propose PartField, a feedforward approach for learning part-based 3D features, which captures the general concept of parts and their hierarchy without relying on predefined templates or text-based names, and can be applied to open-world 3D shapes across various modalities. PartField requires only a 3D feedforward pass at inference time, significantly improving runtime and robustness compared to prior approaches. Our model is trained by distilling 2D and 3D part proposals from a mix of labeled datasets and image segmentations on large unsupervised datasets, via a contrastive learning formulation. It produces a continuous feature field which can be clustered to yield a hierarchical part decomposition. Comparisons show that PartField is up to 20% more accurate and often orders of magnitude faster than other recent class-agnostic part-segmentation methods. Beyond single-shape part decomposition, consistency in the learned field emerges across shapes, enabling tasks such as co-segmentation and correspondence, which we demonstrate in several applications of these general-purpose, hierarchical, and consistent 3D feature fields. Check our Webpage! https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/partfield-release/
我们提出了PartField,这是一种基于前馈的学习局部三维特征的方法。PartField捕捉了部件的一般概念和它们的层次结构,而无需依赖预先定义的模板或基于文本的名称,并可应用于各种模态的开放世界三维形状。PartField在推理时间只需要进行三维前馈传递,与先前的方法相比,显著提高了运行时间和稳健性。我们的模型通过从混合标记数据集和大型无监督数据集上的图像分割中蒸馏二维和三维部件提议,通过对比学习公式进行训练。它产生了一个连续的特征场,可以对其进行聚类以产生层次化的部件分解。比较显示,PartField的准确度高达其他最近的类别无关部件分割方法的20%,并且通常快几个数量级。除了单个形状的部件分解之外,学习字段之间的一致性还体现在各种形状之间,使共分割和对应关系等任务成为可能,我们在这些通用、层次化和一致的三维特征字段的多个应用中展示了这一点。请访问我们的网页了解详情!https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/partfield-release/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/partfield-release/
Summary
本文提出了PartField方法,这是一种基于前馈的学习部分三维特征的方法。该方法能够捕捉部分的一般概念和它们的层次结构,无需依赖预先定义的模板或基于文本的名称,并可应用于各种模态的开放世界三维形状。PartField在推理时间仅需进行三维前馈传递,与先前的方法相比,显著提高了运行时间和稳健性。该模型通过蒸馏来自混合标记数据集和图像分割的大型无监督数据集的二维和三维部分建议,通过对比学习公式进行训练。它产生了一个连续的特征场,可以对其进行聚类以获得层次化的部分分解。与其他最新的类无关的部分分割方法相比,PartField的准确度高达20%,并且在许多情况下,速度比其他方法快几个数量级。此外,学习到的场的一致性超越了单一形状的部分分解,使我们能够在形状之间进行共同分割和对应,我们在几个应用中都证明了这一点。
Key Takeaways
- PartField是一种基于前馈的学习方法,用于学习部分三维特征。
- 它能够捕捉部分的一般概念和层次结构,无需依赖预先定义的模板或基于文本的名称。
- PartField适用于各种模态的开放世界三维形状。
- PartField在推理时间仅需进行三维前馈传递,提高了运行时间和稳健性。
- PartField通过混合标记数据集和图像分割的大型无监督数据集进行训练。
- 它产生了一个连续的特征场,可以对其进行聚类以获得层次化的部分分解。
点此查看论文截图
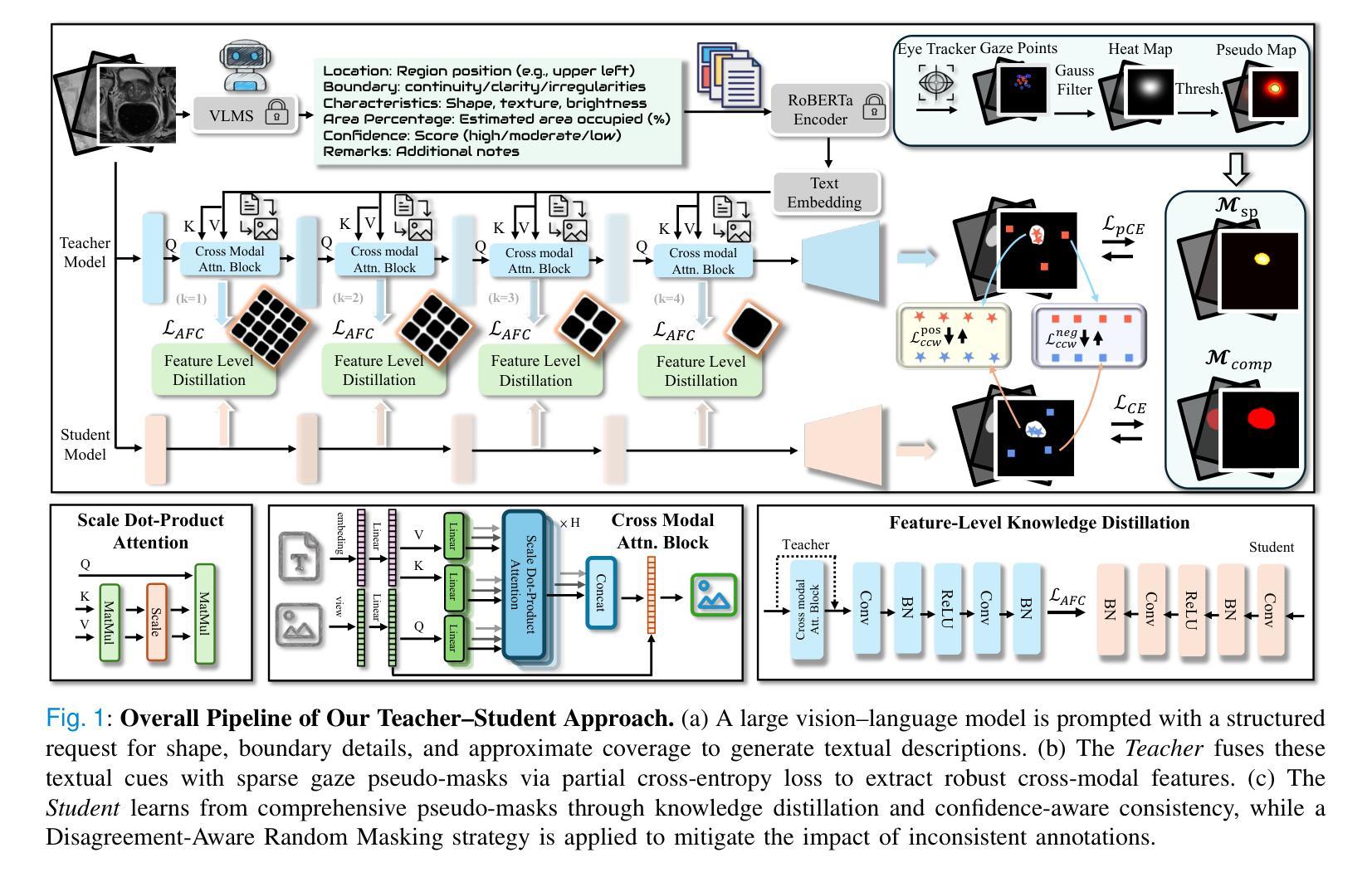
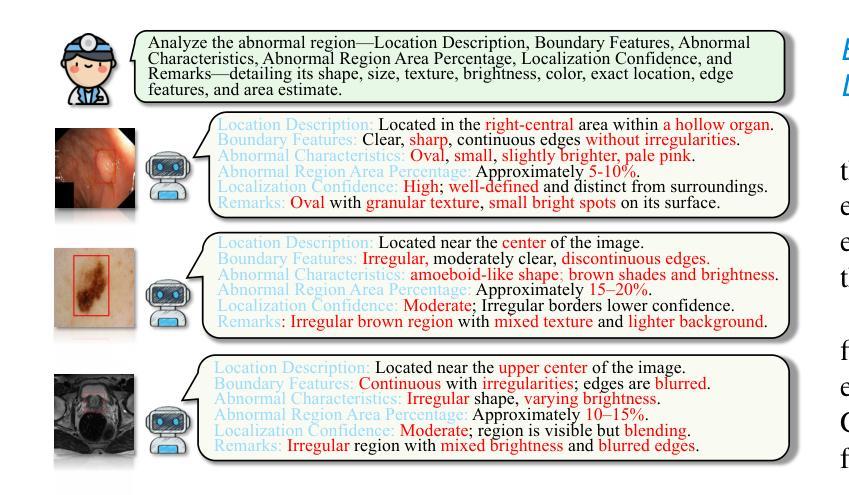
From Gaze to Insight: Bridging Human Visual Attention and Vision Language Model Explanation for Weakly-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jingkun Chen, Haoran Duan, Xiao Zhang, Boyan Gao, Tao Tan, Vicente Grau, Jungong Han
Medical image segmentation remains challenging due to the high cost of pixel-level annotations for training. In the context of weak supervision, clinician gaze data captures regions of diagnostic interest; however, its sparsity limits its use for segmentation. In contrast, vision-language models (VLMs) provide semantic context through textual descriptions but lack the explanation precision required. Recognizing that neither source alone suffices, we propose a teacher-student framework that integrates both gaze and language supervision, leveraging their complementary strengths. Our key insight is that gaze data indicates where clinicians focus during diagnosis, while VLMs explain why those regions are significant. To implement this, the teacher model first learns from gaze points enhanced by VLM-generated descriptions of lesion morphology, establishing a foundation for guiding the student model. The teacher then directs the student through three strategies: (1) Multi-scale feature alignment to fuse visual cues with textual semantics; (2) Confidence-weighted consistency constraints to focus on reliable predictions; (3) Adaptive masking to limit error propagation in uncertain areas. Experiments on the Kvasir-SEG, NCI-ISBI, and ISIC datasets show that our method achieves Dice scores of 80.78%, 80.53%, and 84.22%, respectively-improving 3-5% over gaze baselines without increasing the annotation burden. By preserving correlations among predictions, gaze data, and lesion descriptions, our framework also maintains clinical interpretability. This work illustrates how integrating human visual attention with AI-generated semantic context can effectively overcome the limitations of individual weak supervision signals, thereby advancing the development of deployable, annotation-efficient medical AI systems. Code is available at: https://github.com/jingkunchen/FGI.git.
医学图像分割仍然是一个挑战,因为像素级标注的训练成本很高。在弱监督的背景下,医生视线数据能够捕捉诊断时的感兴趣区域,但其稀疏性限制了其在分割中的应用。相比之下,视觉语言模型(VLM)通过文本描述提供语义上下文,但缺乏必要的解释精度。我们认识到,单一来源的信息不足以满足需求,因此提出了一种融合视线和语言监督的教师-学生框架,以发挥二者的互补优势。我们的关键见解是,视线数据可以指示医生在诊断时的关注焦点,而VLM则解释这些区域的重要性。为了实现这一点,教师模型首先从由VLM生成的病变形态描述增强的视线点中学习,为引导学生模型奠定基础。然后,教师通过三种策略引导学生:(1)多尺度特征对齐,融合视觉线索和文本语义;(2)基于置信度的一致性约束,专注于可靠预测;(3)自适应掩码,以限制不确定区域的误差传播。在Kvasir-SEG、NCI-ISBI和ISIC数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法分别实现了80.78%、80.53%和84.22%的Dice得分,在不需要增加标注负担的情况下比基于视线的基线提高了3-5%。通过保持预测、视线数据和病变描述之间的相关性,我们的框架还保持了临床可解释性。这项工作说明了如何将人类视觉注意力与AI生成的语义上下文相结合,从而有效克服单个弱监督信号的局限性,推动可部署、标注效率高的医疗AI系统的发展。代码可用在:https://github.com/jingkunchen/FGI.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures
摘要
本文探讨医学图像分割面临的挑战,主要由于训练时的像素级标注成本高。研究提出一种融合医师注视数据和语言监督的教与学框架,旨在解决弱监督下注视数据的稀疏性和语言模型的解释精度不足的问题。通过结合注视数据反映医师诊断时的关注点,以及语言模型提供的语义上下文,提高医学图像分割的精度和临床可解释性。实验结果表明,该方法在Kvasir-SEG、NCI-ISBI和ISIC数据集上分别实现了80.78%、80.53%和84.22%的Dice得分,较仅使用注视数据的方法提高了3-5%,且未增加标注负担。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割面临高成本标注的挑战,弱监督下注视数据和语言模型的互补性成为研究焦点。
- 医师注视数据反映诊断关注点,但稀疏性限制了其在分割中的应用。
- 语言模型提供语义上下文,但缺乏解释精确度。
- 提出结合注视数据和语言监督的教与学框架,整合两者优势。
- 教师模型通过融合注视点和由语言模型生成的病变形态描述来学习,为学生模型提供指导。
- 实施多尺度特征对齐、置信度加权一致性约束和自适应掩码等策略,提高分割精度和临床可解释性。
- 在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法实现了较高的Dice得分,并保持了临床可解释性,为部署高效的医学人工智能系统提供了方向。
点此查看论文截图

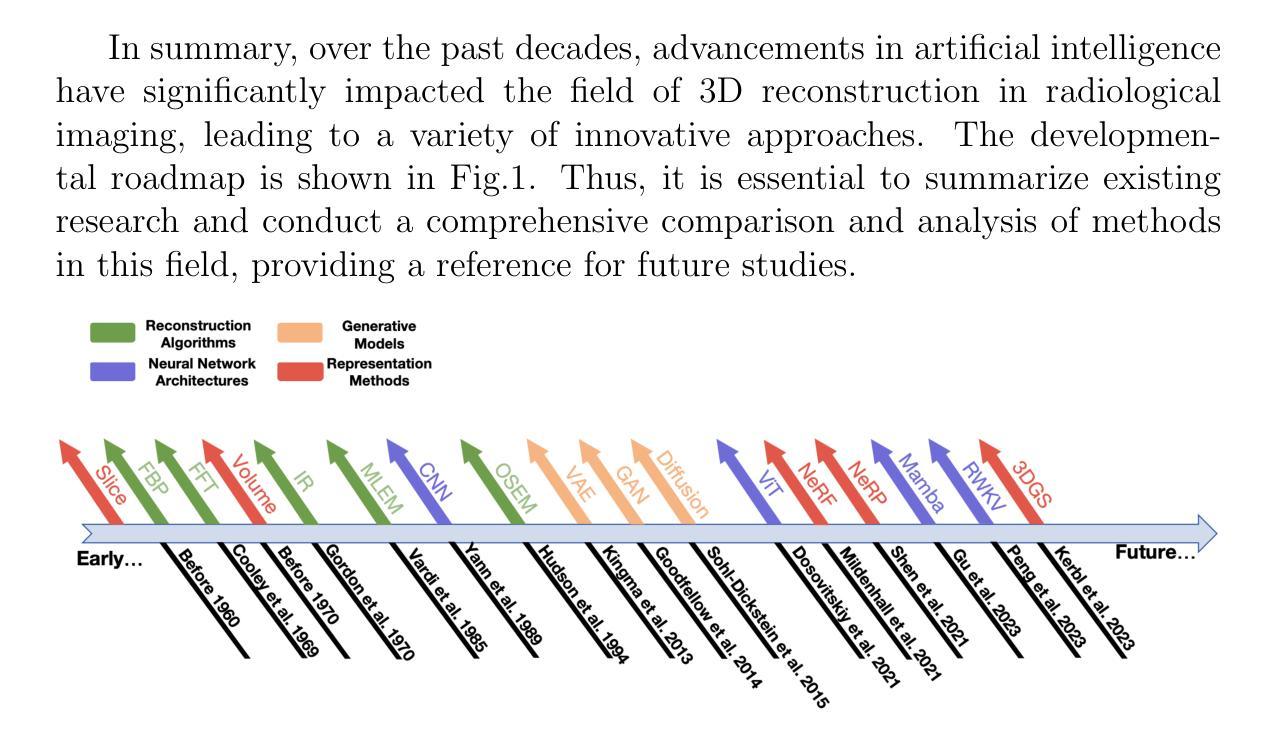
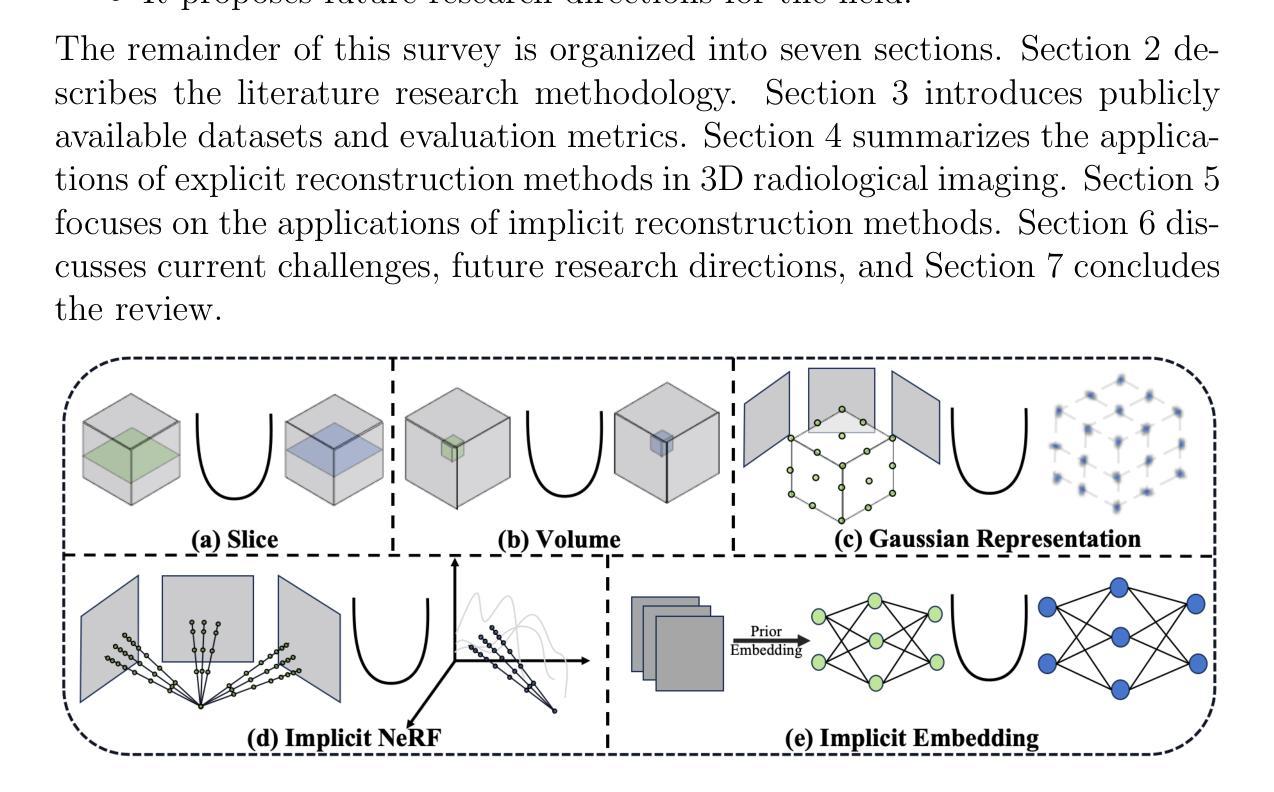
Explicit and Implicit Representations in AI-based 3D Reconstruction for Radiology: A systematic literature review
Authors:Yuezhe Yang, Boyu Yang, Yaqian Wang, Yang He, Xingbo Dong, Zhe Jin
The demand for high-quality medical imaging in clinical practice and assisted diagnosis has made 3D reconstruction in radiological imaging a key research focus. Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a promising approach to enhancing reconstruction accuracy while reducing acquisition and processing time, thereby minimizing patient radiation exposure and discomfort and ultimately benefiting clinical diagnosis. This review explores state-of-the-art AI-based 3D reconstruction algorithms in radiological imaging, categorizing them into explicit and implicit approaches based on their underlying principles. Explicit methods include point-based, volume-based, and Gaussian representations, while implicit methods encompass implicit prior embedding and neural radiance fields. Additionally, we examine commonly used evaluation metrics and benchmark datasets. Finally, we discuss the current state of development, key challenges, and future research directions in this evolving field. Our project available on: https://github.com/Bean-Young/AI4Med.
在临床实践和辅助诊断中对高质量医学成像的需求使得放射学成像中的3D重建成为关键的研究焦点。人工智能(AI)已成为一种有前途的方法,可以提高重建精度,同时减少采集和处理时间,从而最小化患者的辐射暴露和不适感,并最终有益于临床诊断。本文综述了基于人工智能的放射学成像中3D重建算法的最新进展,根据它们的基本原理将它们分为显式方法和隐式方法。显式方法包括点基、体积基和高斯表示法,而隐式方法包括隐式先验嵌入和神经辐射场。此外,我们还介绍了常用的评估指标和基准数据集。最后,我们讨论了该领域的当前发展状态、关键挑战和未来研究方向。我们的项目可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/Bean-Young/AI4Med
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 43 pages, 5 figures, submit to Medical Image Analysis
Summary
人工智能在医学影像学三维重建中的应用前景广阔。通过提高重建精度、缩短采集和处理时间,AI能够减少患者辐射暴露和不适感,为临床诊断带来好处。本文综述了最新的AI三维重建算法,分为显式方法和隐式方法两大类,并探讨了常用的评估指标和基准数据集。
Key Takeaways
- 医学影像学中对高质量三维重建的需求促使AI在该领域的研究成为重点。
- AI能够提高三维重建的精度,同时缩短采集和处理时间。
- AI在医学影像学三维重建中的应用能够减少患者的辐射暴露和不适感。
- 当前的AI三维重建算法可分为显式方法和隐式方法,其中显式方法包括点基、体积基和高斯表示法,隐式方法包括隐式先验嵌入和神经辐射场。
- 在评估AI三维重建算法时,常用的评估指标和基准数据集也很重要。
- 当前,AI在医学影像学三维重建领域仍面临一些挑战。
点此查看论文截图

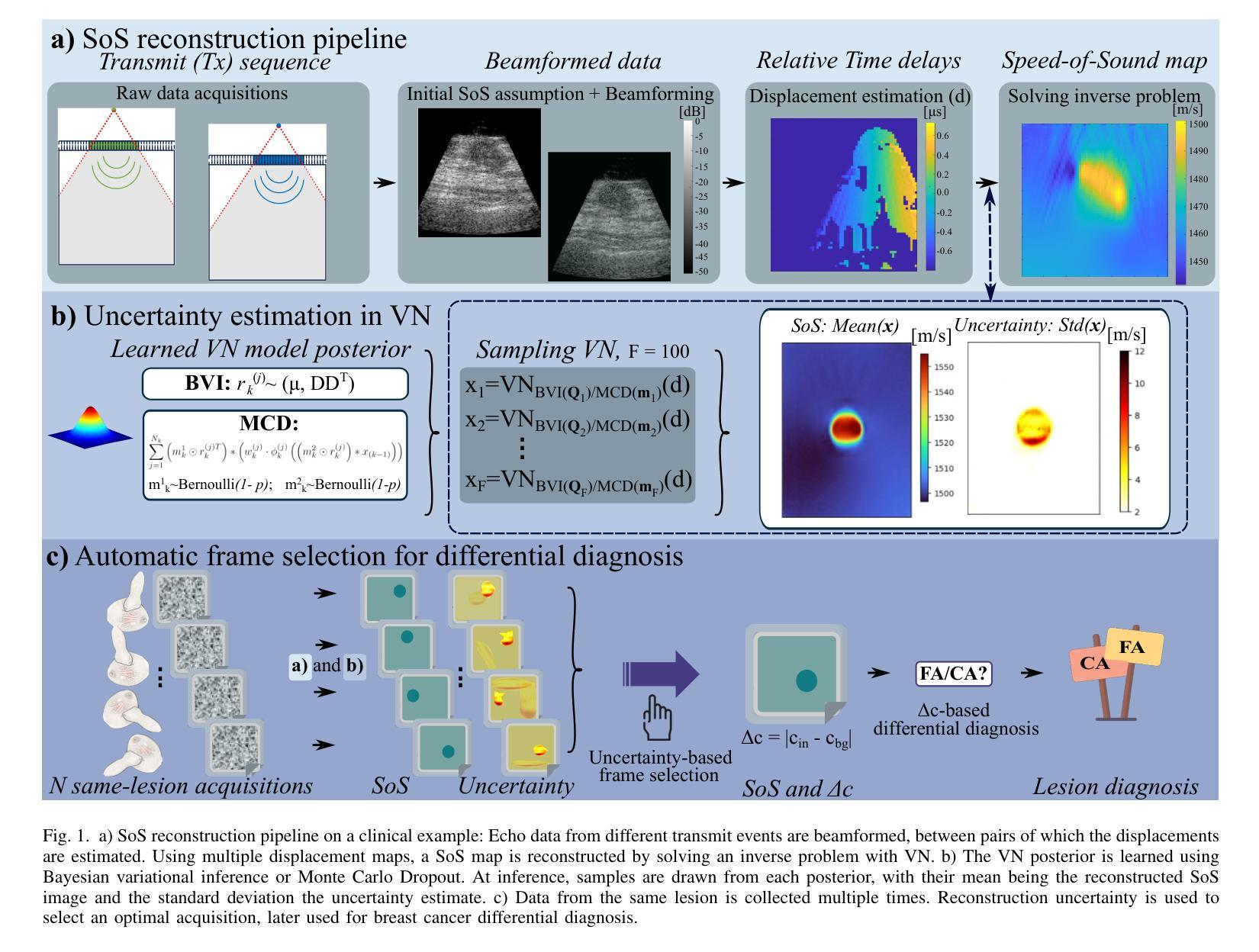
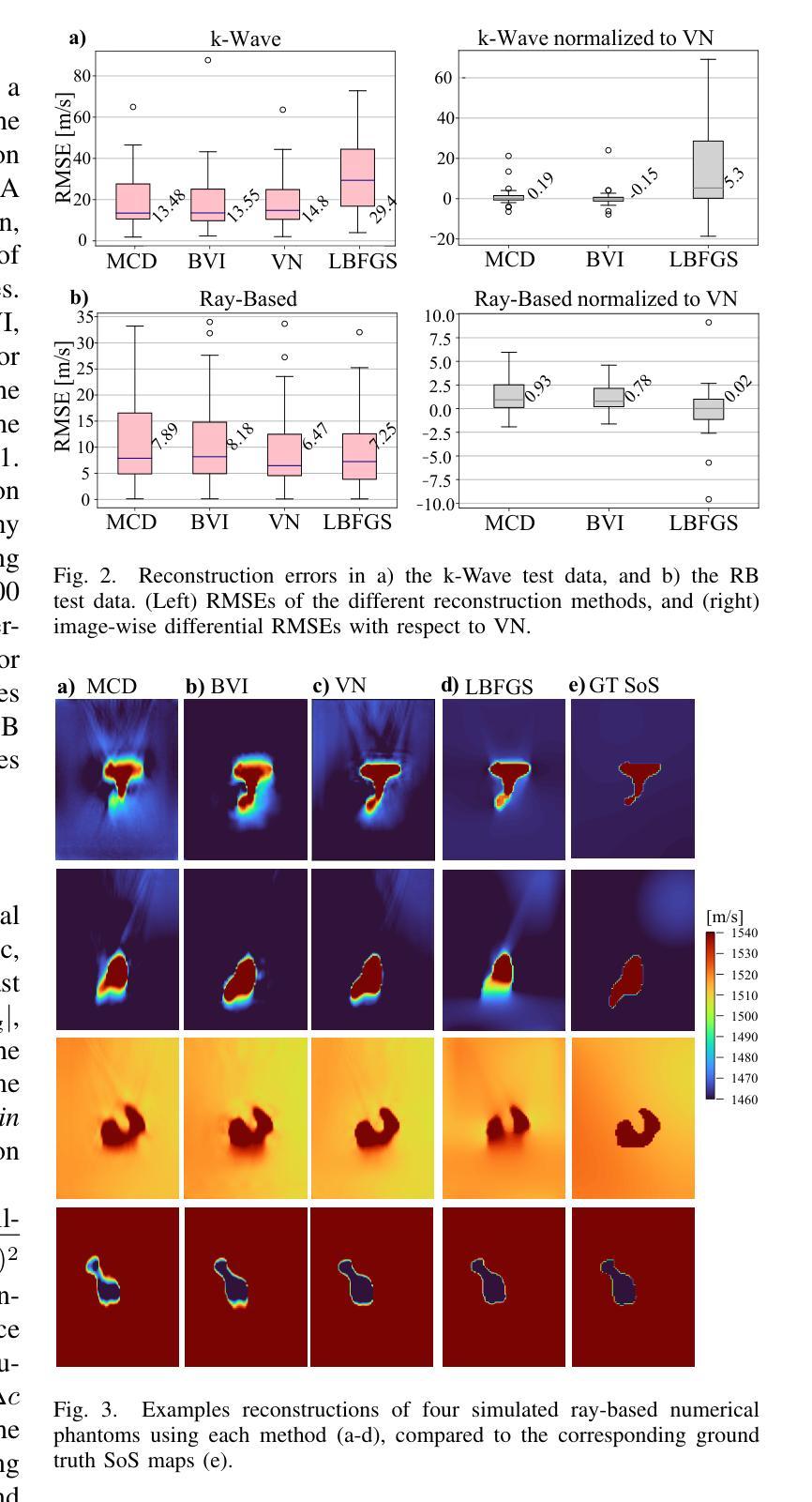
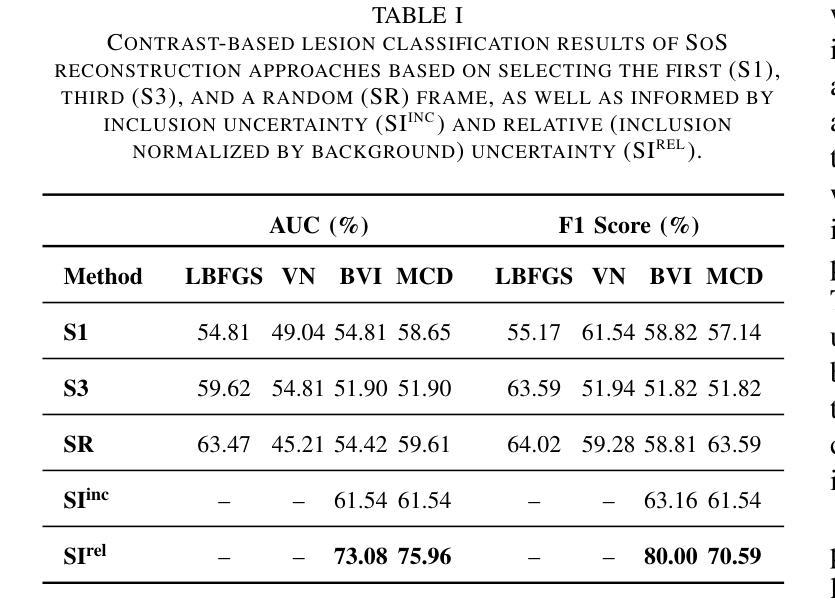
Uncertainty Estimation for Trust Attribution to Speed-of-Sound Reconstruction with Variational Networks
Authors:Sonia Laguna, Lin Zhang, Can Deniz Bezek, Monika Farkas, Dieter Schweizer, Rahel A. Kubik-Huch, Orcun Goksel
Speed-of-sound (SoS) is a biomechanical characteristic of tissue, and its imaging can provide a promising biomarker for diagnosis. Reconstructing SoS images from ultrasound acquisitions can be cast as a limited-angle computed-tomography problem, with Variational Networks being a promising model-based deep learning solution. Some acquired data frames may, however, get corrupted by noise due to, e.g., motion, lack of contact, and acoustic shadows, which in turn negatively affects the resulting SoS reconstructions. We propose to use the uncertainty in SoS reconstructions to attribute trust to each individual acquired frame. Given multiple acquisitions, we then use an uncertainty based automatic selection among these retrospectively, to improve diagnostic decisions. We investigate uncertainty estimation based on Monte Carlo Dropout and Bayesian Variational Inference. We assess our automatic frame selection method for differential diagnosis of breast cancer, distinguishing between benign fibroadenoma and malignant carcinoma. We evaluate 21 lesions classified as BI-RADS~4, which represents suspicious cases for probable malignancy. The most trustworthy frame among four acquisitions of each lesion was identified using uncertainty based criteria. Selecting a frame informed by uncertainty achieved an area under curve of 76% and 80% for Monte Carlo Dropout and Bayesian Variational Inference, respectively, superior to any uncertainty-uninformed baselines with the best one achieving 64%. A novel use of uncertainty estimation is proposed for selecting one of multiple data acquisitions for further processing and decision making.
声速(SoS)是组织的生物力学特征,其成像为诊断提供了一个有前景的生物标志物。从超声采集重建声速图像可以看作是一个有限角度的计算机断层扫描问题,基于模型的深度学习方法变分网络是一个有前途的解决方案。然而,由于运动、接触不良和声音阴影等原因,某些获取的数据帧可能会被噪声损坏,这反过来又会对所得的声速重建结果产生负面影响。我们提议利用声速重建中的不确定性来给每个单独获取的数据帧赋予信任度。在多次采集的情况下,我们利用基于不确定性的自动选择方法,对它们进行回顾性选择,以改进诊断决策。我们研究了基于蒙特卡洛删除和贝叶斯变分推断的不确定性估计。我们评估了我们的自动数据帧选择方法,用于乳腺癌的鉴别诊断,区分良性纤维腺瘤和恶性癌。我们评估了21个被分类为BI-RADS 4的病变,这代表可疑的恶性病例。利用不确定性标准确定了每个病变四个采集数据中最可信赖的一帧。基于不确定性的帧选择达到了蒙特卡洛删除和贝叶斯变分推断的曲线下面积分别为76%和80%,优于任何不考虑不确定性的基线,其中表现最好的基线达到64%。不确定性估计的新应用被提出用于从多次数据采集中选择一帧进行进一步处理和决策。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at the International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery. Presented at the 16th International Conference on Information Processing in Computer-Assisted Interventions 2025
Summary
超声成像中的声速(SoS)成像作为一种有前景的生物标志物诊断方法,能够从超声波数据中重建SoS图像。然而,由于噪声干扰、运动、接触不良和声影等原因,获取的数据帧可能会受到破坏,影响SoS重建结果。本研究利用SoS重建中的不确定性来评估每个获取的数据帧的可信度,并基于不确定性对多次采集的数据进行自动筛选,以提高诊断决策的可靠性。本研究采用蒙特卡洛Dropout和贝叶斯变分推断进行不确定性评估,并对乳腺病变进行鉴别诊断。评估结果显示,基于不确定性的自动筛选能够有效区分良性纤维腺瘤和恶性癌。在BI-RADS4分类的疑似恶性病变中,通过不确定性标准筛选最可靠的数据帧,使用蒙特卡洛Dropout和贝叶斯变分推断的AUC分别达到了76%和80%,优于未考虑不确定性的基线方法。本研究提出一种新型的不确定性评估方法,用于从多次数据采集中选择一个用于进一步处理和决策。
Key Takeaways
- 声速(SoS)成像作为诊断的生物标志物具有潜力。
- 数据帧可能因噪声、运动等因素而受破坏,影响SoS重建。
- 利用不确定性评估数据帧可信度,对多次采集的数据进行自动筛选。
- 采用蒙特卡洛Dropout和贝叶斯变分推断进行不确定性评估。
- 在乳腺病变鉴别诊断中,基于不确定性的自动筛选效果良好。
- 最佳方法实现较高AUC,优于不考虑不确定性的基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

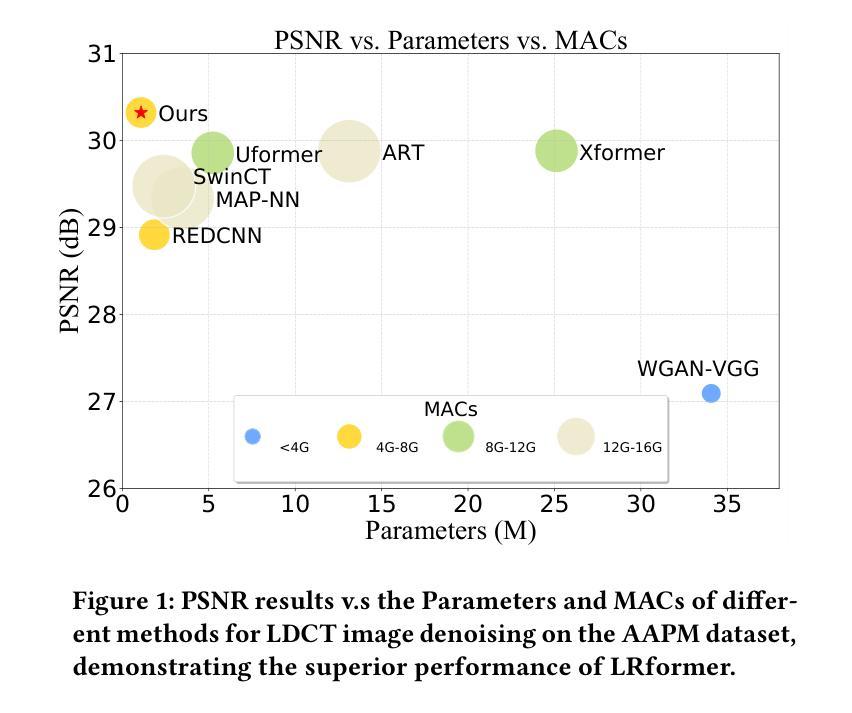
Efficient Medical Image Restoration via Reliability Guided Learning in Frequency Domain
Authors:Pengcheng Zheng, Kecheng Chen, Jiaxin Huang, Bohao Chen, Ju Liu, Yazhou Ren, Xiaorong Pu
Medical image restoration tasks aim to recover high-quality images from degraded observations, exhibiting emergent desires in many clinical scenarios, such as low-dose CT image denoising, MRI super-resolution, and MRI artifact removal. Despite the success achieved by existing deep learning-based restoration methods with sophisticated modules, they struggle with rendering computationally-efficient reconstruction results. Moreover, they usually ignore the reliability of the restoration results, which is much more urgent in medical systems. To alleviate these issues, we present LRformer, a Lightweight Transformer-based method via Reliability-guided learning in the frequency domain. Specifically, inspired by the uncertainty quantification in Bayesian neural networks (BNNs), we develop a Reliable Lesion-Semantic Prior Producer (RLPP). RLPP leverages Monte Carlo (MC) estimators with stochastic sampling operations to generate sufficiently-reliable priors by performing multiple inferences on the foundational medical image segmentation model, MedSAM. Additionally, instead of directly incorporating the priors in the spatial domain, we decompose the cross-attention (CA) mechanism into real symmetric and imaginary anti-symmetric parts via fast Fourier transform (FFT), resulting in the design of the Guided Frequency Cross-Attention (GFCA) solver. By leveraging the conjugated symmetric property of FFT, GFCA reduces the computational complexity of naive CA by nearly half. Extensive experimental results in various tasks demonstrate the superiority of the proposed LRformer in both effectiveness and efficiency.
医学图像恢复任务旨在从退化的观察中恢复高质量图像,这在许多临床场景中表现出了迫切的需求,例如低剂量CT图像去噪、MRI超分辨率和MRI伪影去除。尽管现有的基于深度学习的恢复方法使用复杂的模块取得了成功,但它们难以生成计算效率高的重建结果。此外,它们通常忽略了医疗系统中恢复结果的可靠性,这一点更加迫切。为了缓解这些问题,我们提出了LRformer,这是一种基于轻量级Transformer的可靠性引导频率域学习方法。具体来说,受到贝叶斯神经网络(BNNs)中的不确定性量化的启发,我们开发了一种可靠的病灶语义先验生产者(RLPP)。RLPP利用蒙特卡洛(MC)估计器和随机采样操作,通过对基础医学图像分割模型MedSAM进行多次推理,生成足够可靠的先验。此外,我们没有直接在空间域中融入这些先验知识,而是通过快速傅里叶变换(FFT)将交叉注意力(CA)机制分解为实对称和虚反对称两部分,从而设计出导向频率交叉注意力(GFCA)求解器。利用FFT的共轭对称属性,GFCA将原始CA的计算复杂度降低了近一半。在多个任务上的大量实验结果证明了LRformer在有效性和效率方面的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了针对医学图像恢复任务的一种新型方法——LRformer。该方法结合了轻量级Transformer、可靠性指导学习和频域技术来解决医学图像恢复问题,并在多个任务中展示了其高效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像恢复任务旨在从退化的观察中恢复高质量图像,在许多临床场景中具有重要作用。
- 现有深度学习恢复方法在复杂模块上取得了成功,但在计算效率方面存在问题,且忽视了恢复结果的可靠性。
- LRformer是一种基于轻量级Transformer的方法,通过可靠性指导学习来解决这些问题。
- LRformer受到贝叶斯神经网络不确定性的启发,开发了可靠的病灶语义先验生成器(RLPP)。
- RLPP利用蒙特卡洛估计器和随机采样操作生成可靠的先验,通过对基础医学图像分割模型MedSAM进行多次推断来实现。
- LRformer通过快速傅里叶变换(FFT)将交叉注意机制分解为实对称和虚反对称部分,设计出导向频率交叉注意(GFCA)求解器。
点此查看论文截图

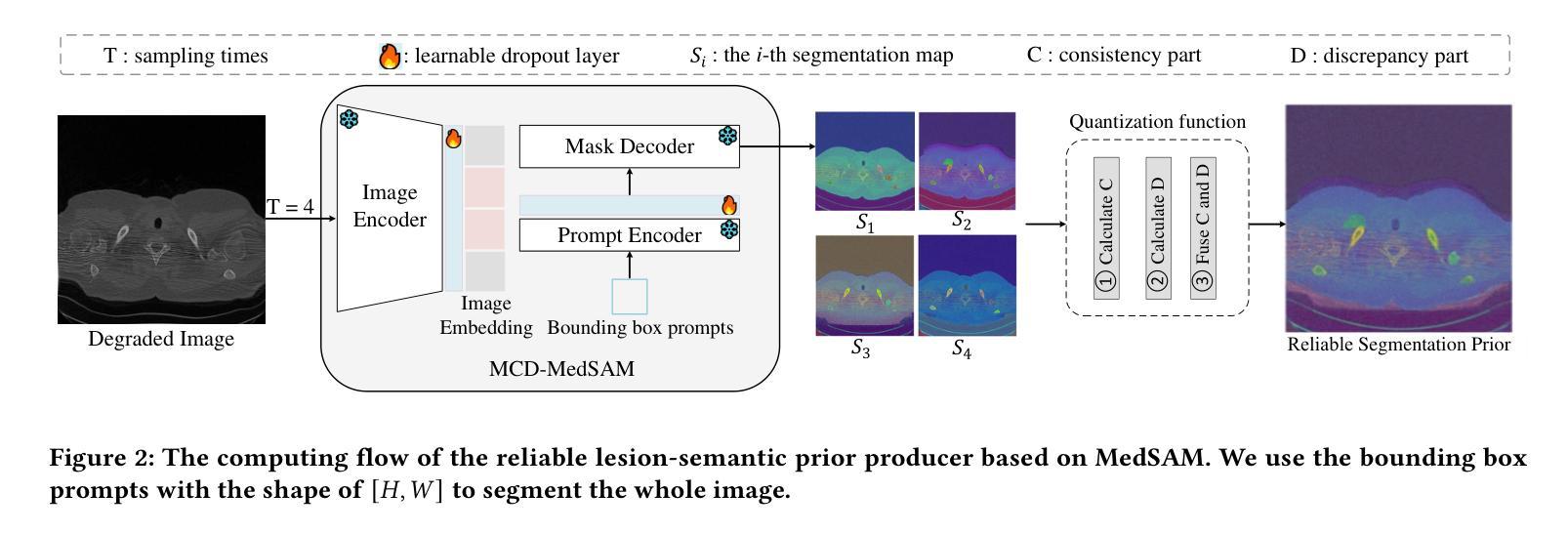
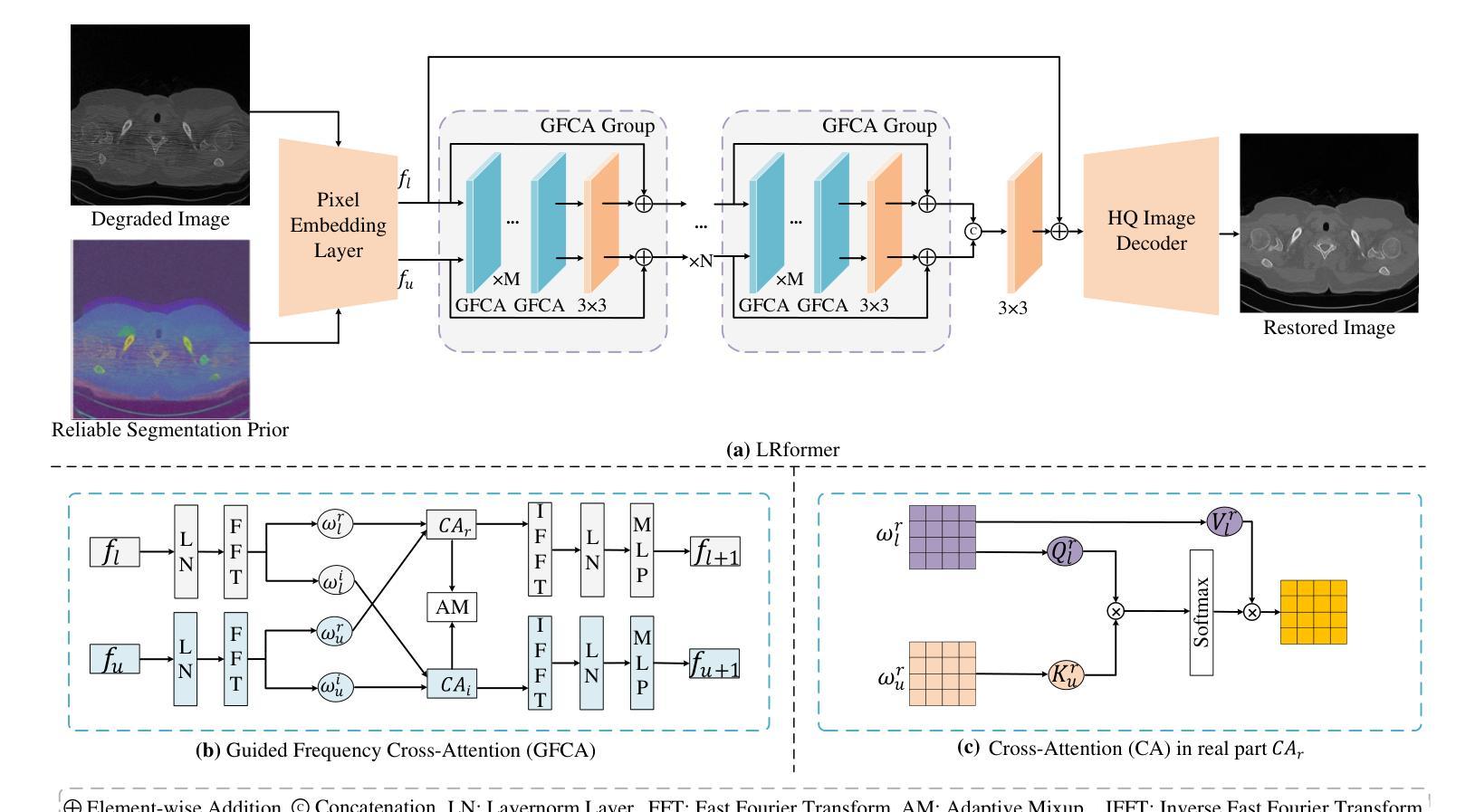
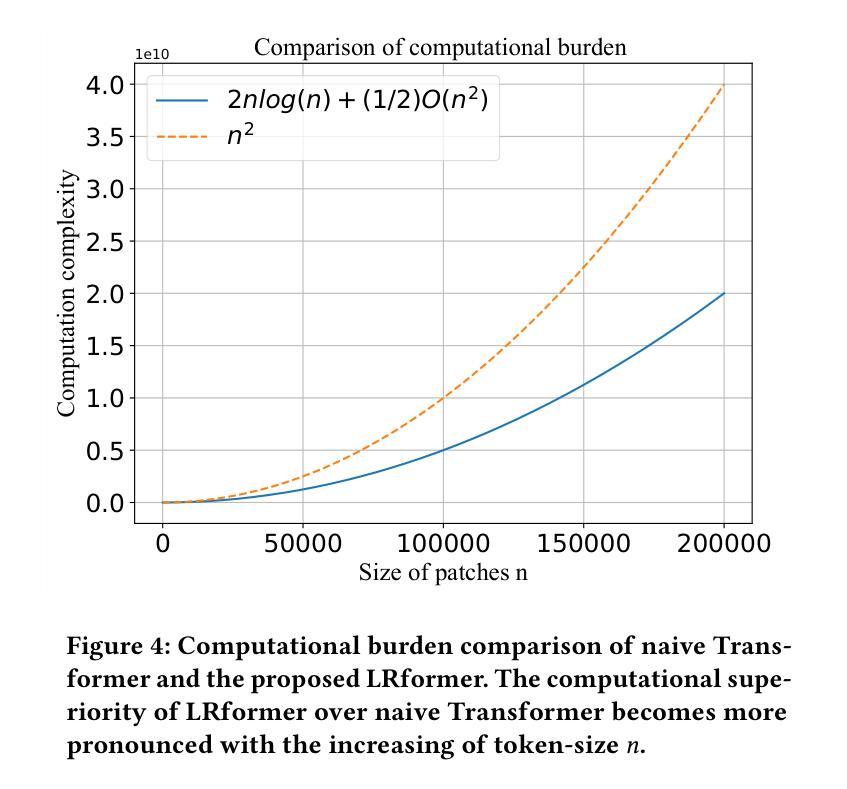
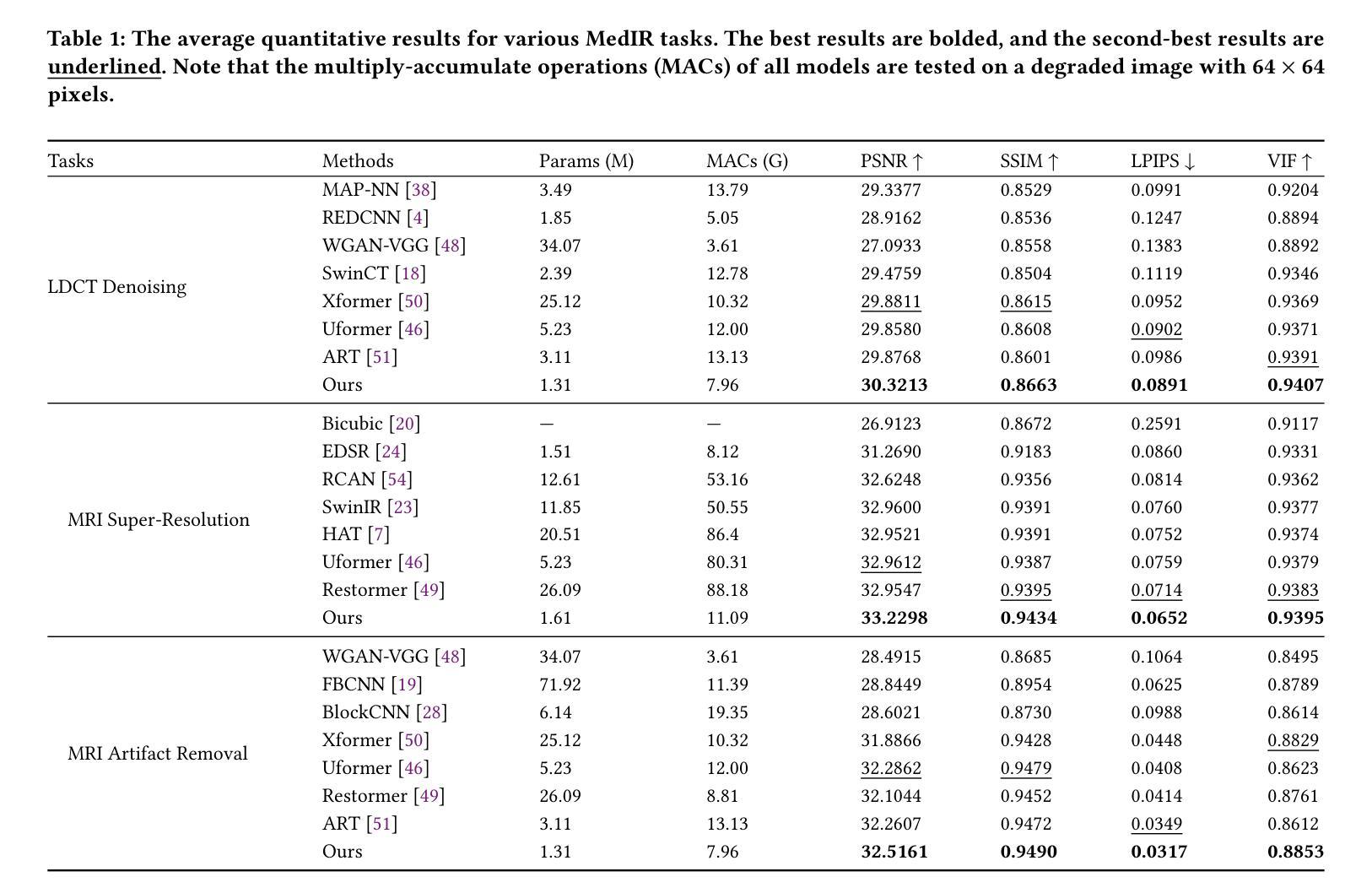
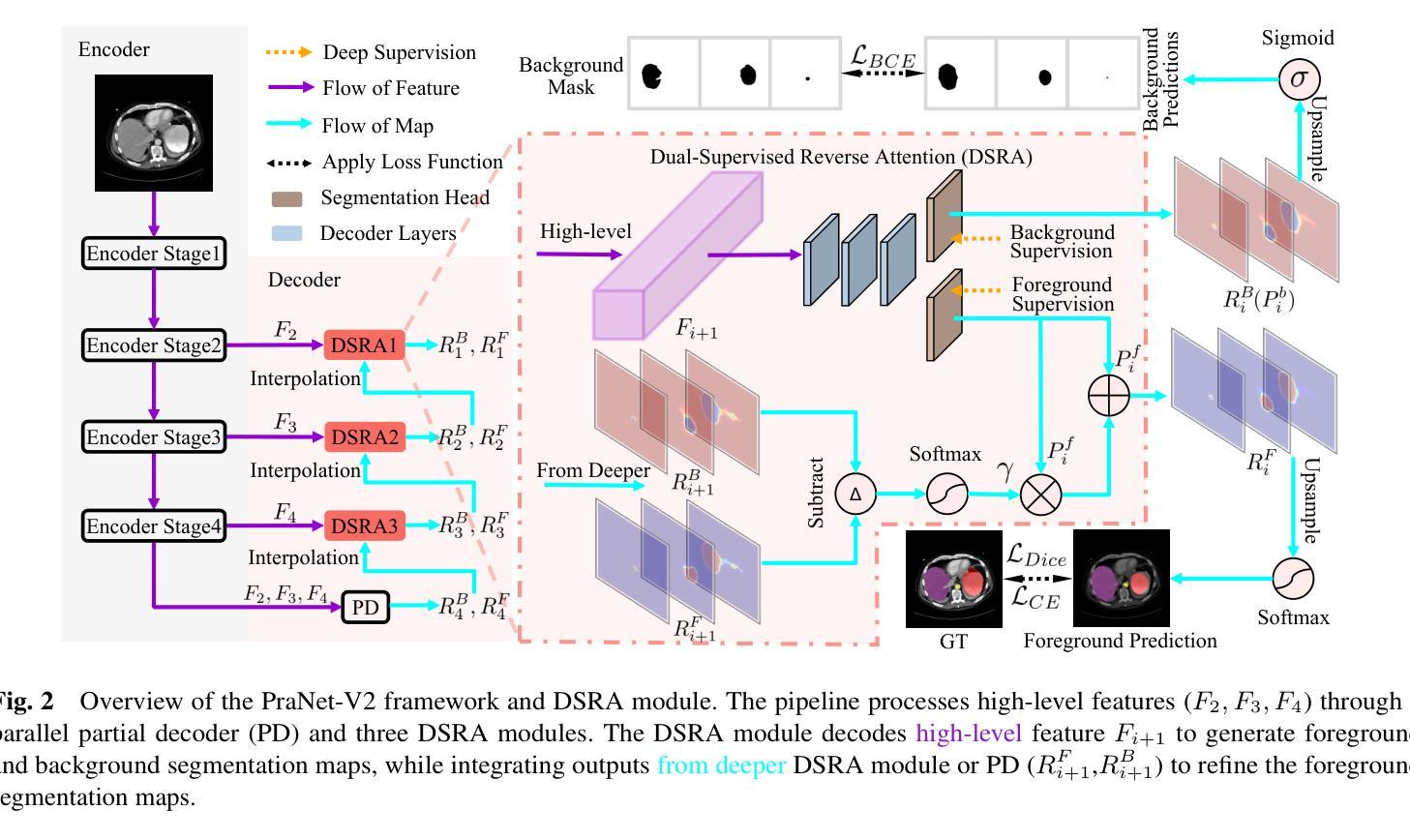
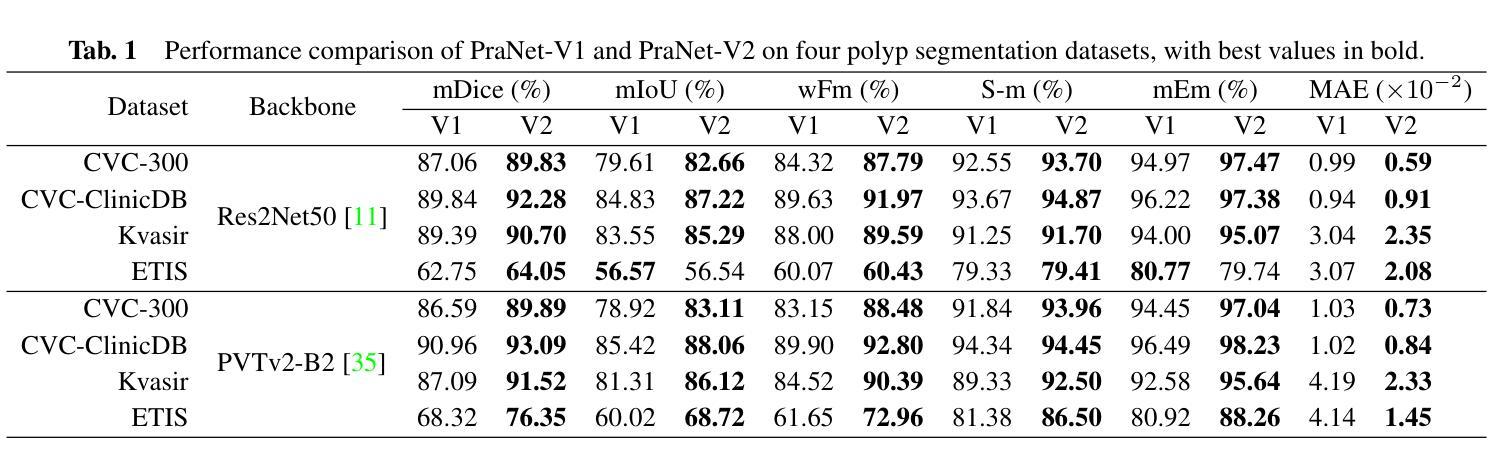
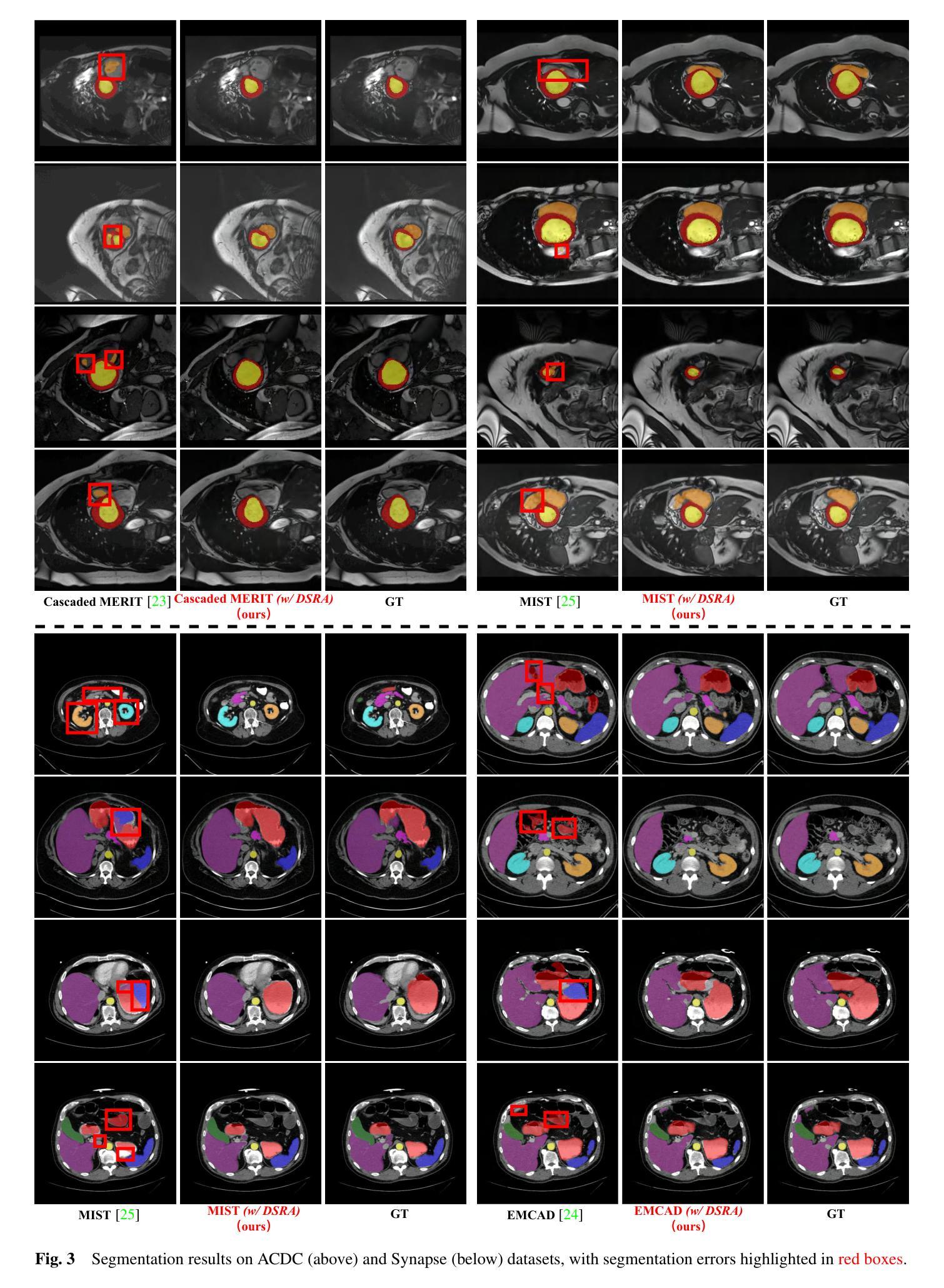
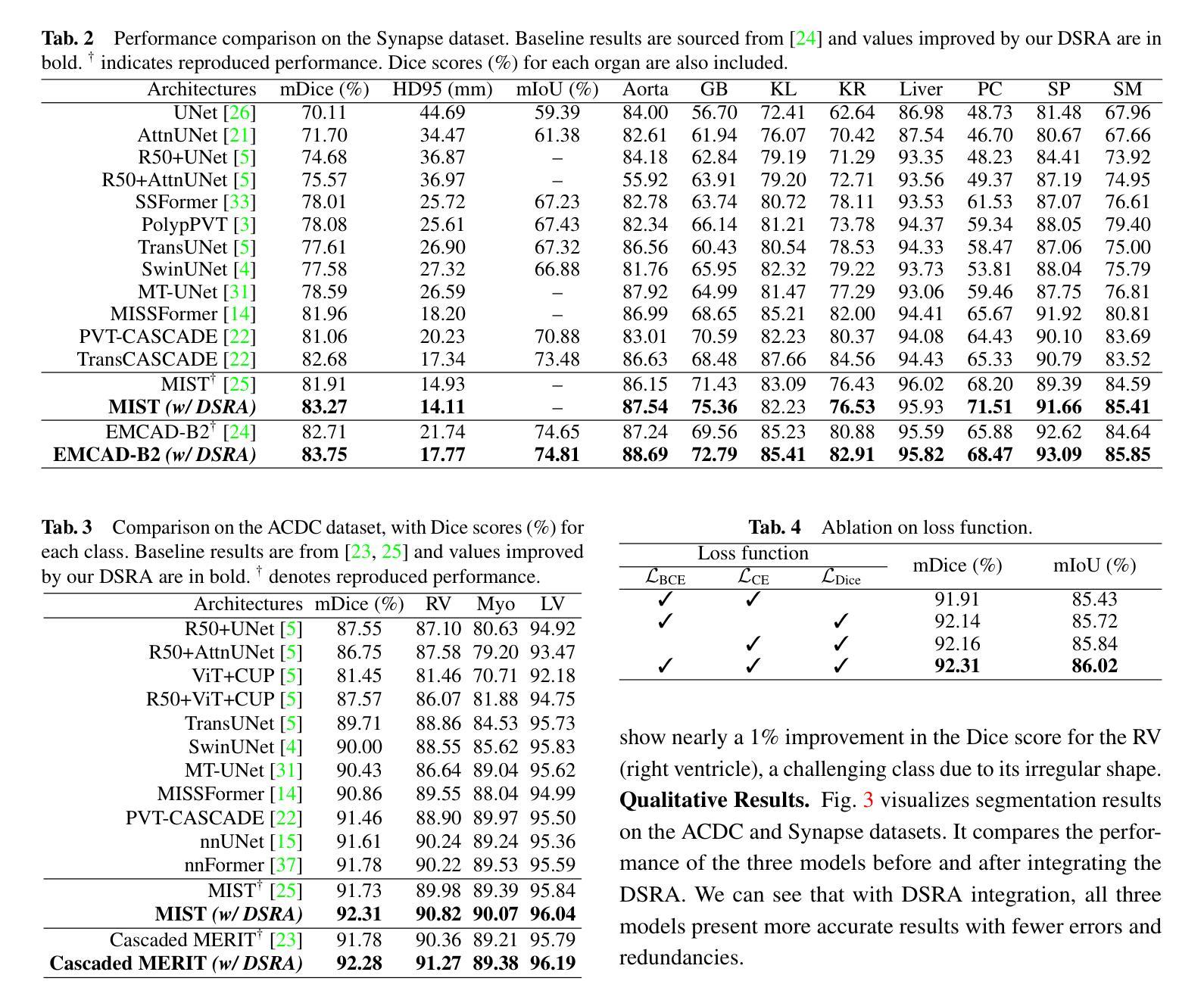
PraNet-V2: Dual-Supervised Reverse Attention for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Bo-Cheng Hu, Ge-Peng Ji, Dian Shao, Deng-Ping Fan
Accurate medical image segmentation is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment. Previously, PraNet-V1 was proposed to enhance polyp segmentation by introducing a reverse attention (RA) module that utilizes background information. However, PraNet-V1 struggles with multi-class segmentation tasks. To address this limitation, we propose PraNet-V2, which, compared to PraNet-V1, effectively performs a broader range of tasks including multi-class segmentation. At the core of PraNet-V2 is the Dual-Supervised Reverse Attention (DSRA) module, which incorporates explicit background supervision, independent background modeling, and semantically enriched attention fusion. Our PraNet-V2 framework demonstrates strong performance on four polyp segmentation datasets. Additionally, by integrating DSRA to iteratively enhance foreground segmentation results in three state-of-the-art semantic segmentation models, we achieve up to a 1.36% improvement in mean Dice score. Code is available at: https://github.com/ai4colonoscopy/PraNet-V2/tree/main/binary_seg/jittor.
准确的医学图像分割对于有效的诊断和治疗至关重要。此前,提出了PraNet-V1,通过引入反向注意(RA)模块利用背景信息来增强息肉分割。然而,PraNet-V1在多类别分割任务方面存在困难。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了PraNet-V2。与PraNet-V1相比,PraNet-V2更有效地执行更广泛的任务,包括多类别分割。PraNet-V2的核心是双重监督反向注意(DSRA)模块,它结合了明确的背景监督、独立的背景建模和语义丰富的注意力融合。我们的PraNet-V2框架在四个息肉分割数据集上表现出强大的性能。此外,通过将DSRA集成到三个最先进的语义分割模型中,以迭代方式提高前景分割结果,我们实现了平均Dice得分高达1.36%的改进。代码可在:https://github.com/ai4colonoscopy/PraNet-V2/tree/main/binary_seg/jittor。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report (4 tables 3 figures 8 pages)
Summary
医学图像准确分割对于有效诊断和治疗至关重要。针对PraNet-V1在多类别分割任务上的局限性,我们提出了PraNet-V2。该模型引入双重监督反向注意力(DSRA)模块,实现更广泛的任务范围,包括多类别分割。通过结合DSRA模块迭代增强前景分割结果,PraNet-V2在四个息肉分割数据集上表现优异,且在三种主流语义分割模型中实现了平均Dice得分的提升。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割对于诊断和治疗的准确性至关重要。
- PraNet-V2是对PraNet-V1的改进,能够处理多类别分割任务。
- DSRA模块是PraNet-V2的核心,它通过明确的背景监督、独立背景建模和语义丰富的注意力融合来实现有效分割。
- PraNet-V2在四个息肉分割数据集上表现出强大的性能。
- 通过结合DSRA模块迭代增强前景分割结果,在三种语义分割模型中实现了性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

Embedding Radiomics into Vision Transformers for Multimodal Medical Image Classification
Authors:Zhenyu Yang, Haiming Zhu, Rihui Zhang, Haipeng Zhang, Jianliang Wang, Chunhao Wang, Minbin Chen, Fang-Fang Yin
Background: Deep learning has significantly advanced medical image analysis, with Vision Transformers (ViTs) offering a powerful alternative to convolutional models by modeling long-range dependencies through self-attention. However, ViTs are inherently data-intensive and lack domain-specific inductive biases, limiting their applicability in medical imaging. In contrast, radiomics provides interpretable, handcrafted descriptors of tissue heterogeneity but suffers from limited scalability and integration into end-to-end learning frameworks. In this work, we propose the Radiomics-Embedded Vision Transformer (RE-ViT) that combines radiomic features with data-driven visual embeddings within a ViT backbone. Purpose: To develop a hybrid RE-ViT framework that integrates radiomics and patch-wise ViT embeddings through early fusion, enhancing robustness and performance in medical image classification. Methods: Following the standard ViT pipeline, images were divided into patches. For each patch, handcrafted radiomic features were extracted and fused with linearly projected pixel embeddings. The fused representations were normalized, positionally encoded, and passed to the ViT encoder. A learnable [CLS] token aggregated patch-level information for classification. We evaluated RE-ViT on three public datasets (including BUSI, ChestXray2017, and Retinal OCT) using accuracy, macro AUC, sensitivity, and specificity. RE-ViT was benchmarked against CNN-based (VGG-16, ResNet) and hybrid (TransMed) models. Results: RE-ViT achieved state-of-the-art results: on BUSI, AUC=0.950+/-0.011; on ChestXray2017, AUC=0.989+/-0.004; on Retinal OCT, AUC=0.986+/-0.001, which outperforms other comparison models. Conclusions: The RE-ViT framework effectively integrates radiomics with ViT architectures, demonstrating improved performance and generalizability across multimodal medical image classification tasks.
背景:深度学习在医学图像分析方面取得了显著进展,而Vision Transformers(ViTs)通过自注意力机制建模长距离依赖关系,为卷积模型提供了一种强大的替代方案。然而,ViTs本质上需要大量的数据,并且缺乏特定领域的归纳偏见,这限制了其在医学成像中的应用。相比之下,放射组学提供了组织异质性的可解释、手工描述符,但受限于可扩展性和整合到端到端学习框架的能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了Radiomics-Embedded Vision Transformer(RE-ViT),它将放射组学特征与数据驱动的视觉嵌入相结合,在一个ViT主干中。目的:开发一个混合RE-ViT框架,通过早期融合整合放射组学和补丁级ViT嵌入,提高医学图像分类的稳健性和性能。方法:遵循标准的ViT管道,将图像分成补丁。对于每个补丁,提取手工制作的放射组学特征,并与线性投影的像素嵌入融合。融合后的表示形式经过归一化、位置编码后,传递给ViT编码器。一个可学习的[CLS]标记聚合补丁级别的信息用于分类。我们在三个公共数据集(包括BUSI、ChestXray2017和Retinal OCT)上评估了RE-ViT的性能,使用了准确度、宏AUC、灵敏度和特异度。RE-ViT与基于CNN(VGG-16、ResNet)和混合(TransMed)模型进行了比较。结果:RE-ViT达到了最新水平的结果:在BUSI上,AUC=0.950+/-0.011;在ChestXray2017上,AUC=0.989+/-0.004;在视网膜OCT上,AUC=0.986+/-0.001,优于其他对比模型。结论:RE-ViT框架有效地将放射组学与ViT架构相结合,显示出在多模态医学图像分类任务上的改进性能和泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文提出一种融合放射组学与Vision Transformer(ViT)的混合框架RE-ViT,通过早期融合放射组学特征和数据驱动视觉嵌入,提高在医学图像分类任务中的稳健性和性能。在三个公共数据集上的实验结果显示,RE-ViT达到了先进水平,并优于其他对比模型。
Key Takeaways
- RE-ViT结合了放射组学特征和Vision Transformer(ViT)的优势,形成了一种混合框架用于医学图像分析。
- 通过早期融合放射组学特征和ViT嵌入,RE-ViT提高了医学图像分类的稳健性和性能。
- RE-ViT在三个公共数据集上的表现达到了先进水平,证明了其有效性和优越性。
- 与其他模型相比,RE-ViT展现出更强的性能。
- RE-ViT框架具有良好的通用性,可应用于多种模态的医学图像分类任务。
- 融合表示经过归一化、位置编码后传递给ViT编码器进行处理。
点此查看论文截图

Bringing together invertible UNets with invertible attention modules for memory-efficient diffusion models
Authors:Karan Jain, Mohammad Nayeem Teli
Diffusion models have recently gained state of the art performance on many image generation tasks. However, most models require significant computational resources to achieve this. This becomes apparent in the application of medical image synthesis due to the 3D nature of medical datasets like CT-scans, MRIs, electron microscope, etc. In this paper we propose a novel architecture for a single GPU memory-efficient training for diffusion models for high dimensional medical datasets. The proposed model is built by using an invertible UNet architecture with invertible attention modules. This leads to the following two contributions: 1. denoising diffusion models and thus enabling memory usage to be independent of the dimensionality of the dataset, and 2. reducing the energy usage during training. While this new model can be applied to a multitude of image generation tasks, we showcase its memory-efficiency on the 3D BraTS2020 dataset leading to up to 15% decrease in peak memory consumption during training with comparable results to SOTA while maintaining the image quality.
扩散模型最近在许多图像生成任务上达到了最先进的性能。然而,大多数模型为了实现这一点需要大量的计算资源。这在医学图像合成的应用中变得尤为明显,因为医学数据集如CT扫描、MRI、电子显微镜等具有3D特性。在本文中,我们提出了一种针对高维医学数据集扩散模型的单GPU内存高效训练的新型架构。该模型采用可逆UNet架构和可逆注意力模块构建。这带来了以下两个贡献:1. 降噪扩散模型,从而使内存使用与数据集维度无关,并降低了训练过程中的能耗。虽然这个新模型可以应用于多种图像生成任务,但我们在3D BraTS2020数据集上展示了其内存效率,在保持图像质量的同时,训练期间的峰值内存使用量减少了高达15%,同时获得了与最新技术相当的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文提出了一种用于扩散模型的新型架构,该架构适用于高维医学数据集的单GPU内存高效训练。该模型采用可逆UNet架构和可逆注意力模块,能够实现去噪扩散模型,使内存使用与数据集维度无关,并减少训练过程中的能耗。在3D BraTS2020数据集上,新模型表现出较高的内存效率,训练时的峰值内存使用量减少了高达15%,同时保持图像质量与最新技术相当。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成任务上达到最新技术水平,但大多数模型需要巨大的计算资源。
- 医学图像合成应用中,由于医学数据集(如CT扫描、MRI、电子显微镜等)的3D特性,计算资源需求尤为显著。
- 论文提出了一种新型架构,适用于高维医学数据集的扩散模型的单个GPU内存高效训练。
- 新模型采用可逆UNet架构和可逆注意力模块,实现了去噪扩散模型。
- 该模型使内存使用与数据集维度无关,并降低了训练过程中的能耗。
- 在3D BraTS2020数据集上,新模型展示了较高的内存效率,训练时的峰值内存使用量减少了高达15%。
点此查看论文截图

The origin of X-ray intra-day variability in HBL PKS 2155-304
Authors:W. Hu, J. L. Kang, J. X. Wang, G. C. Xiao, G. W. Ren
The origin and physics of X-ray intra-day variability (IDV) in blazars, which is a long-standing issue, is studied by modelling the broad-band X-ray spectrum, the light curves (LCs), and the Fourier time lags. We present the timing analysis of three archived XMM-Newton observations with a total exposure of $>80$ ks of PKS 2155-304, which is one of the brightest and most studied HBLs in the X-ray band. For each observation, we constructed averaged X-ray spectra in 0.5-10 keV band, as well as 100 s binned LCs in various sub-bands. We performed the Bayesian power spectral density (PSD) analysis and Fourier time-lag analyses of the variable LCs. The results are carefully modelled in the context of a multi-zone jet model. PSD analysis reveals that the X-ray variability can be characterised by red noise. The lag-frequency spectra measured in two observations show only the soft or negative lags, with the magnitude of the lags increasing as the frequency decreases. For another observation, the lag-frequency spectra are characterised by small positive or zero time lags at the lowest frequencies, which drops to negative values at higher frequencies. The magnitude of the soft lags ranges from $\sim5$ to $\sim40$ minutes, and increases with the energy difference of two compared LCs. The observed X-ray spectra and lag-frequency spectra can both be successfully described by our proposed two-zone model, with the physical parameters constrained in a fully acceptable space. Moreover, the LC profiles at different energy bands can be satisfactorily reproduced by only varying the injection rate of the energetic electrons. The IDV of PKS 2155-304 should be caused by the injection of energetic electrons, and accelerated by shocks formed in a weakly magnetised jet.
对于闪烁源中的X射线日间变化(IDV)的起源和物理性质,一直是一个长期存在的问题。通过宽带X射线光谱、光变曲线(LCs)和傅里叶时间延迟进行建模研究。我们展示了PKS 2155-304的三次存档XMM-Newton观测的时序分析,总曝光时间超过80ks,这是X射线波段中最明亮、研究最多的HBL之一。对于每次观测,我们在0.5-10keV波段构建了平均X射线光谱,以及各种子波段中的每100秒分箱光变曲线。我们对可变光变曲线进行了贝叶斯功率谱密度(PSD)分析和傅里叶时间延迟分析。结合多区喷射模型,我们对结果进行了仔细建模。PSD分析表明,X射线变化可以用红噪声来表征。两次观测测得的滞后频率光谱仅显示软滞后或负滞后,滞后的幅度随着频率的降低而增加。对于另一次观测,滞后频率光谱在最低频率下表现为较小的正时滞或零时滞,然后在更高频率时降为负数。软滞后的幅度范围从约5分钟到约40分钟,并随着两个比较光变曲线的能量差而增加。所提出的两区模型能够成功描述观测到的X射线光谱和滞后频率光谱,物理参数在完全可接受的范围内受到限制。此外,通过仅改变高能电子的注入率,可以令人满意地再现不同能带的光变曲线轮廓。PKS 2155-304的IDV应由高能电子的注入引起,并在弱磁化喷射流中形成的冲击波的推动下加速。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in A&A, 13pages, 11 figures
Summary
PKS 2155-304的X射线内日变化(IDV)的源头和物理机制通过对其宽带X射线谱、光变曲线和傅里叶时间滞后进行建模研究。采用贝叶斯功率谱密度分析和傅里叶时间滞后分析等方法,对其观测数据进行时序分析。结果显示,X射线变率可由红色噪声特征描述;时间滞后随频率降低而增加,或在高频率时为零或转为负值。这些现象可通过提出的两区模型成功描述,其中物理参数在一定的可接受空间内受到限制。光变曲线不同能带的轮廓可以通过仅改变高能电子的注入率来复制。因此,PKS 2155-304的IDV可能由高能电子的注入引起,并在弱磁化喷流中的激波作用下加速。
Key Takeaways
- 对PKS 2155-304进行了长期观察的X射线内日变化(IDV)研究。
- 通过分析光变曲线和傅里叶时间滞后,揭示了X射线变率的特征。
- 贝叶斯功率谱密度分析显示X射线变率具有红色噪声特征。
- 时间滞后随频率变化的现象可通过两区模型成功描述。
- 光变曲线不同能带的轮廓差异可以通过高能电子注入率的变化来解释。
- IDV可能由高能电子在弱磁化喷流中的注入和激波加速引起。
点此查看论文截图

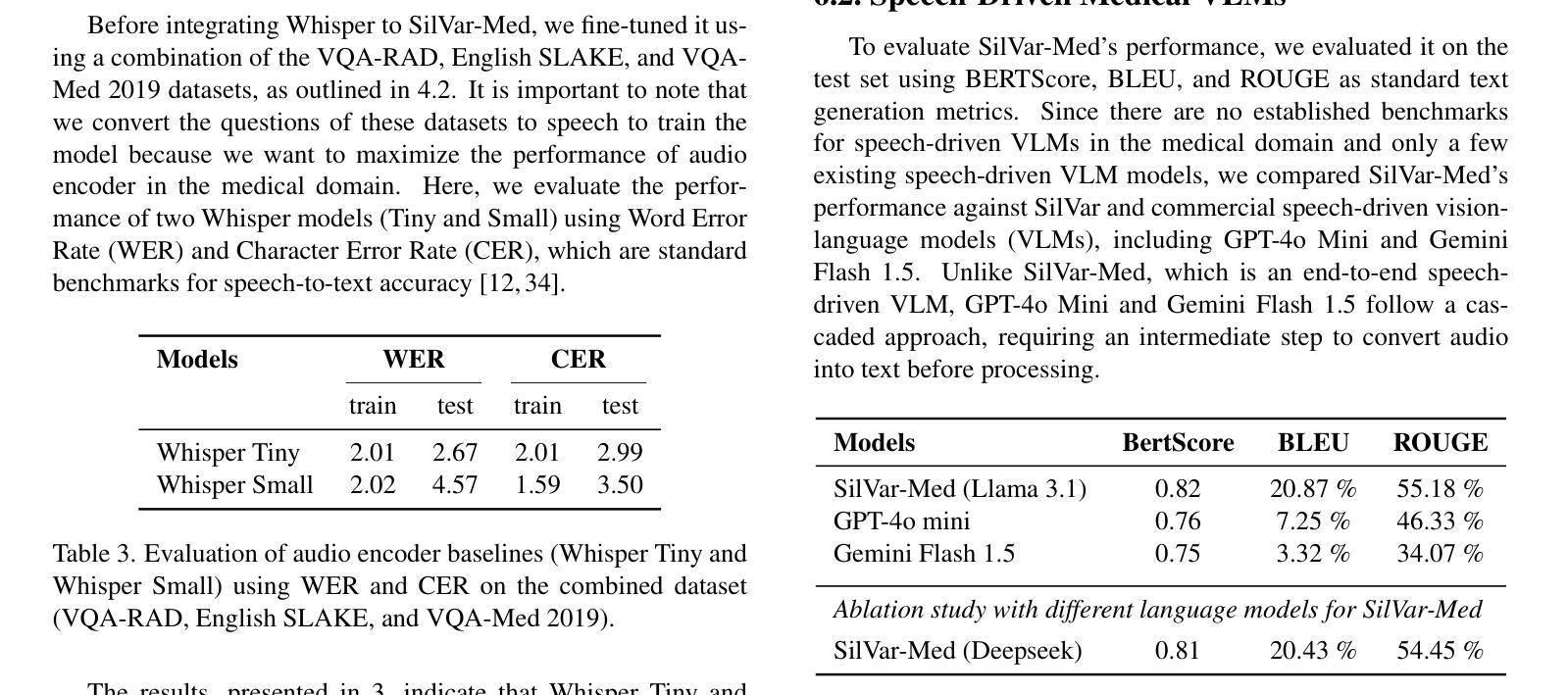
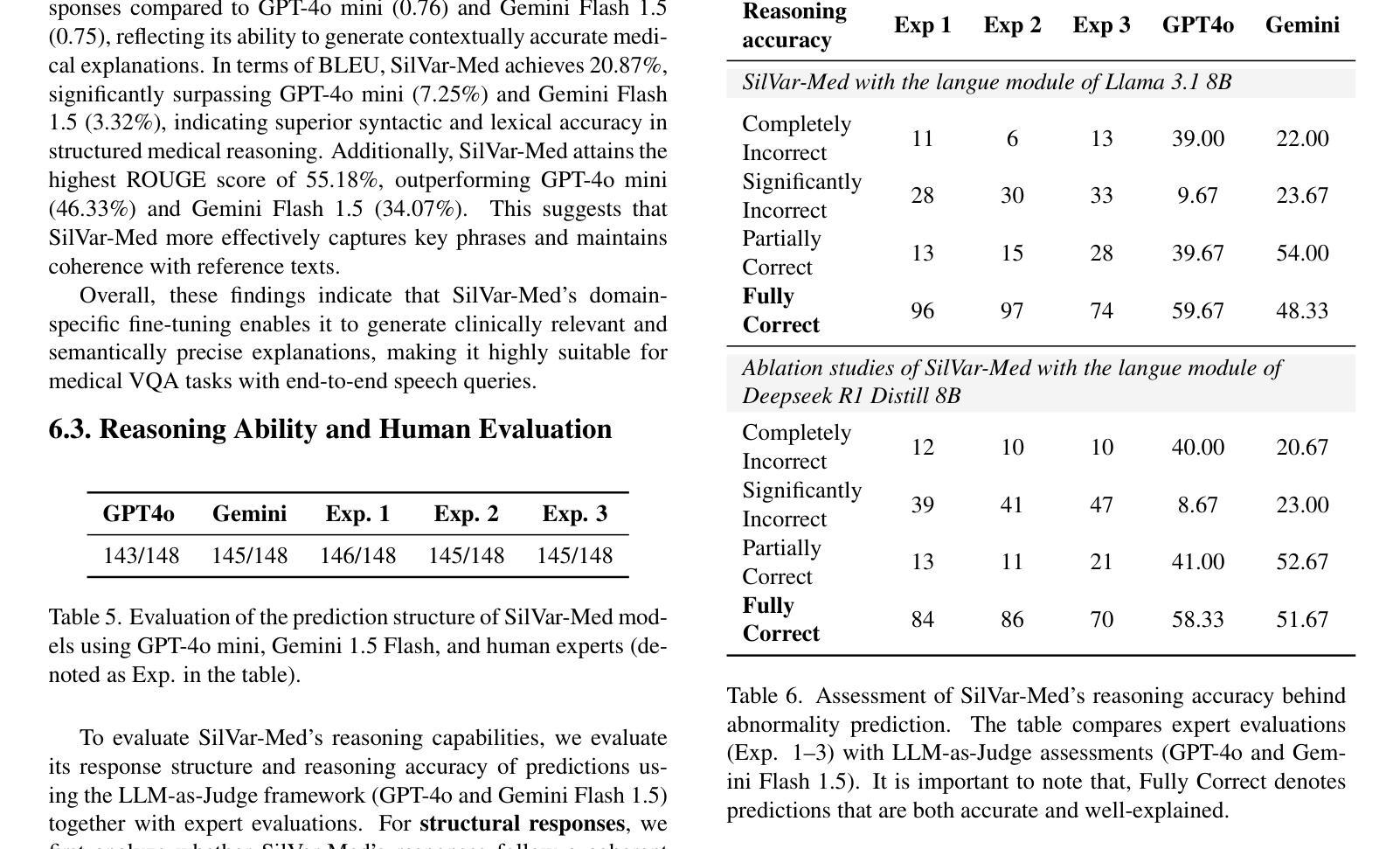
SilVar-Med: A Speech-Driven Visual Language Model for Explainable Abnormality Detection in Medical Imaging
Authors:Tan-Hanh Pham, Chris Ngo, Trong-Duong Bui, Minh Luu Quang, Tan-Huong Pham, Truong-Son Hy
Medical Visual Language Models have shown great potential in various healthcare applications, including medical image captioning and diagnostic assistance. However, most existing models rely on text-based instructions, limiting their usability in real-world clinical environments especially in scenarios such as surgery, text-based interaction is often impractical for physicians. In addition, current medical image analysis models typically lack comprehensive reasoning behind their predictions, which reduces their reliability for clinical decision-making. Given that medical diagnosis errors can have life-changing consequences, there is a critical need for interpretable and rational medical assistance. To address these challenges, we introduce an end-to-end speech-driven medical VLM, SilVar-Med, a multimodal medical image assistant that integrates speech interaction with VLMs, pioneering the task of voice-based communication for medical image analysis. In addition, we focus on the interpretation of the reasoning behind each prediction of medical abnormalities with a proposed reasoning dataset. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate a proof-of-concept study for reasoning-driven medical image interpretation with end-to-end speech interaction. We believe this work will advance the field of medical AI by fostering more transparent, interactive, and clinically viable diagnostic support systems. Our code and dataset are publicly available at SiVar-Med.
医疗视觉语言模型在各种医疗健康应用中显示出巨大潜力,包括医学图像描述和诊断辅助。然而,大多数现有模型依赖于文本指令,限制了它们在真实世界临床环境中的实用性,尤其是在手术等场景中,基于文本的交互对医生来说通常不切实际。此外,当前的医学图像分析模型通常缺乏预测背后的综合推理,这降低了它们在临床决策中的可靠性。鉴于医疗诊断错误可能会带来改变生命的后果,因此需要可解释和合理的医疗辅助。针对这些挑战,我们引入了一种端到端的语音驱动医疗视觉语言模型(SilVar-Med),这是一种多模式医学图像助理,它将语音交互与视觉语言模型集成在一起,率先完成基于语音的医学图像分析通信任务。此外,我们着重于通过提出的推理数据集解释医学异常预测背后的推理。通过广泛的实验,我们展示了端到端语音交互驱动的推理驱动医学图像解释的概念验证研究。我们相信这项工作将通过促进更透明、互动和临床可行的诊断支持系统来推动医疗人工智能领域的发展。我们的代码和数据集可在SiVar-Med上公开获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR Multimodal Algorithmic Reasoning Workshop 2025 - SilVarMed
摘要
医疗视觉语言模型在医疗应用的各个领域展现出了巨大的潜力,包括医学图像描述和诊断辅助。然而,大多数现有模型依赖于文本指令,这在现实世界的临床环境中尤其不实用,如在手术等场景中,基于文本的交互对医生来说并不方便。此外,当前的医学图像分析模型通常缺乏对其预测的全面理解,这降低了它们在临床决策中的可靠性。考虑到医疗诊断错误可能会带来改变生命的后果,迫切需要可解释和合理的医疗辅助。针对这些挑战,我们提出了一种端到端的语音驱动医疗视觉语言模型SilVar-Med,这是一种将语音交互与视觉语言模型相结合的多模式医学图像辅助工具,率先实现了基于语音的医学图像分析通信任务。此外,我们重点关注每个医学异常预测背后的解释,并推出了一个解释性数据集。通过大量实验,我们展示了以解释为导向的医学图像解读与端到端语音交互的概念验证研究。我们相信这项工作将通过促进更透明、互动和临床可行的诊断支持系统来推动医疗人工智能领域的发展。我们的代码和数据集已在SiVar-Med上公开可用。
关键见解
- 医疗视觉语言模型在医疗应用中具有巨大潜力,包括医学图像描述和诊断辅助。
- 现有模型主要依赖于文本指令,这在现实临床环境中存在局限性。
- 医学图像分析模型缺乏全面的预测理解,影响临床决策的可靠性。
- 语音驱动的医疗视觉语言模型(如SilVar-Med)通过语音交互提供多模式医学图像辅助。
- SilVar-Med率先实现基于语音的医学图像分析通信任务,强调预测背后的解释性。
- 通过推出解释性数据集,加强对医学异常预测背后理由的关注。
- 概念验证研究表明,以解释为导向的医学图像解读与端到端语音交互相结合的方法具有可行性。
点此查看论文截图

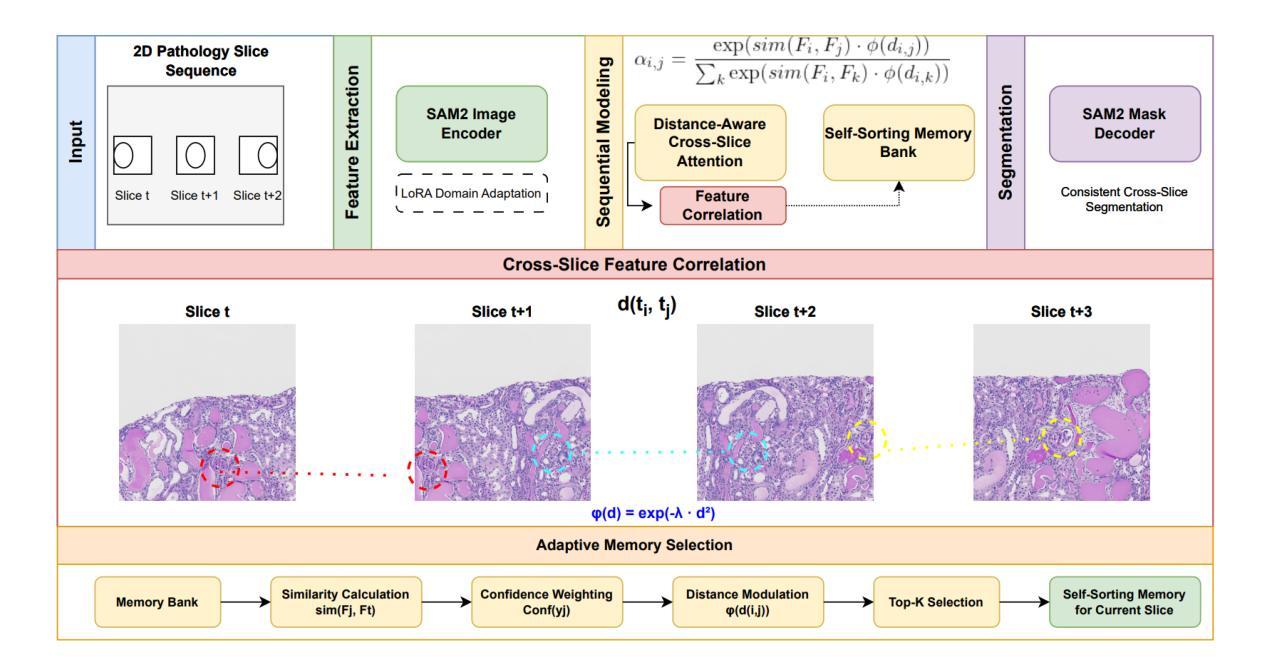
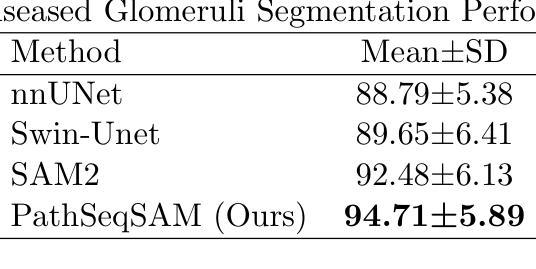
PathSeqSAM: Sequential Modeling for Pathology Image Segmentation with SAM2
Authors:Mingyang Zhu, Yinting Liu, Mingyu Li, Jiacheng Wang
Current methods for pathology image segmentation typically treat 2D slices independently, ignoring valuable cross-slice information. We present PathSeqSAM, a novel approach that treats 2D pathology slices as sequential video frames using SAM2’s memory mechanisms. Our method introduces a distance-aware attention mechanism that accounts for variable physical distances between slices and employs LoRA for domain adaptation. Evaluated on the KPI Challenge 2024 dataset for glomeruli segmentation, PathSeqSAM demonstrates improved segmentation quality, particularly in challenging cases that benefit from cross-slice context. We have publicly released our code at https://github.com/JackyyyWang/PathSeqSAM.
现有的病理学图像分割方法通常独立处理2D切片,忽略了有价值的跨切片信息。我们提出了PathSeqSAM,这是一种新方法,利用SAM2的记忆机制将2D病理学切片视为连续的视频帧。我们的方法引入了一种距离感知注意力机制,该机制考虑了切片之间的物理距离变化,并采用了LoRA进行域自适应。在肾小球分割的KPI Challenge 2024数据集上评估的PathSeqSAM,显示出分割质量的提升,特别是在受益于跨切片上下文的挑战性案例中。我们的代码已公开发布在https://github.com/JackyyyWang/PathSeqSAM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割当前方法多忽略跨切片信息,独立处理2D切片。本文提出PathSeqSAM新方法,利用SAM2的记忆机制将2D病理切片视作连续视频帧处理。该方法引入距离感知注意力机制,考虑切片间不同物理距离,并采用LoRA进行领域适配。在KPI Challenge 2024肾小球分割数据集上评估,PathSeqSAM提高了分割质量,特别是在受益于跨切片上下文的挑战案例中。代码已公开于https://github.com/JackyyyWang/PathSeqSAM。
Key Takeaways
- 当前医学图像分割方法多忽略跨切片信息。
- PathSeqSAM方法将2D病理切片视作连续视频帧处理。
- PathSeqSAM利用SAM2的记忆机制。
- PathSeqSAM引入距离感知注意力机制。
- PathSeqSAM考虑切片间的物理距离。
- PathSeqSAM采用LoRA进行领域适配。
点此查看论文截图

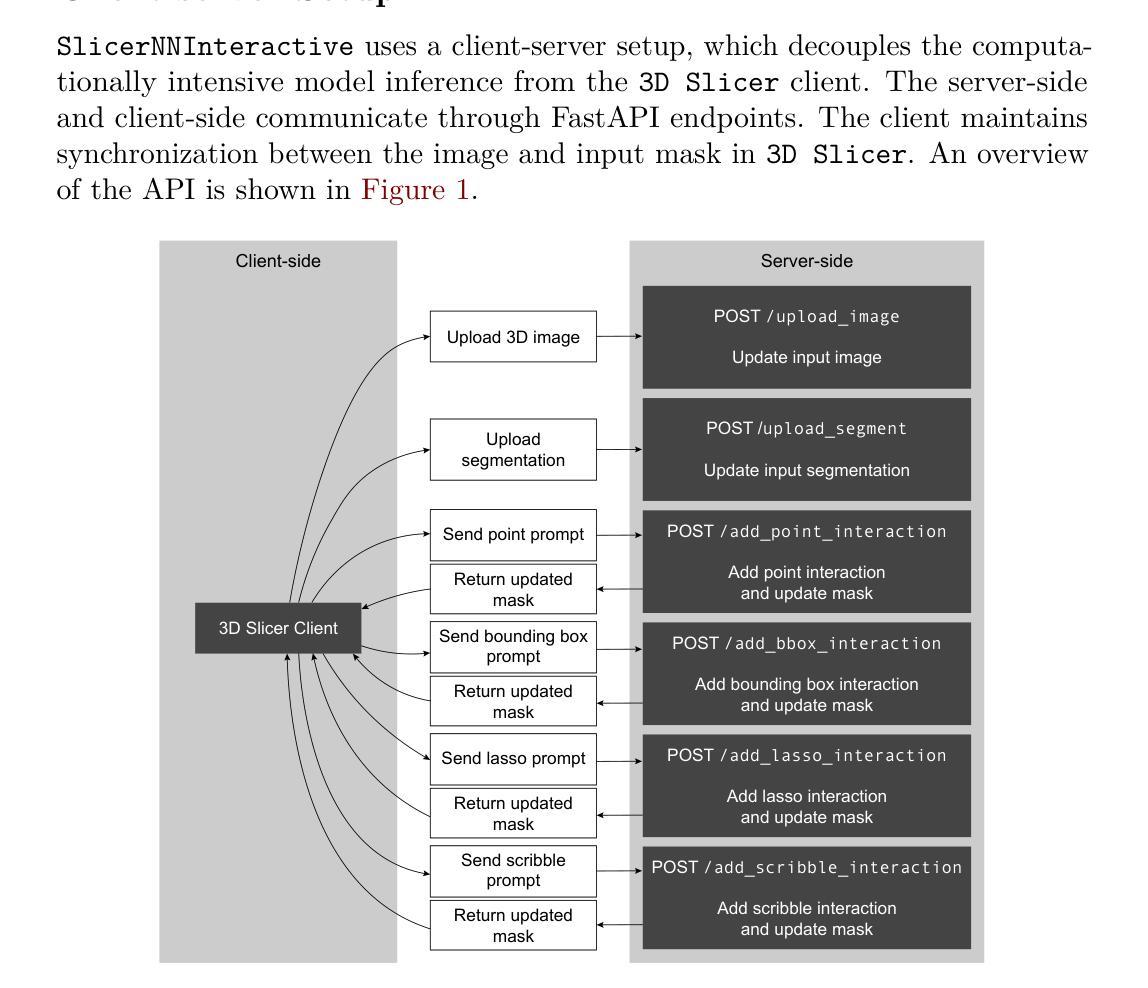
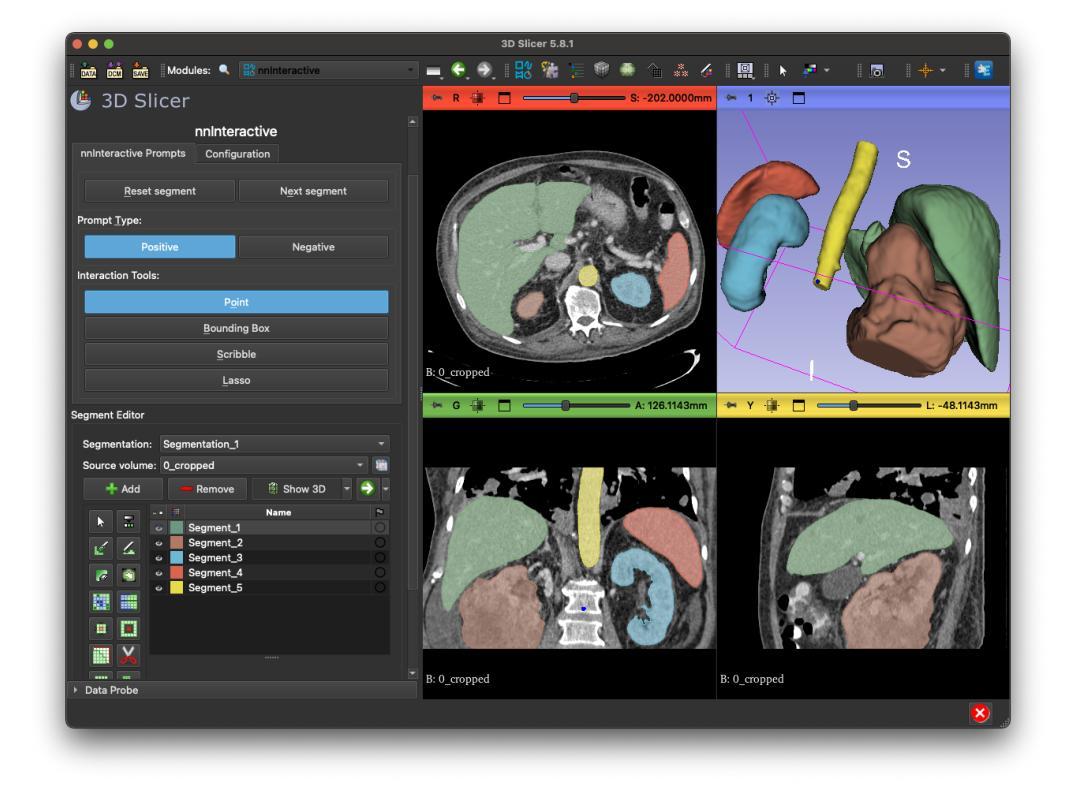
SlicerNNInteractive: A 3D Slicer extension for nnInteractive
Authors:Coen de Vente, Kiran Vaidhya Venkadesh, Bram van Ginneken, Clara I. Sánchez
SlicerNNInteractive integrates nnInteractive, a state-of-the-art promptable deep learning-based framework for 3D image segmentation, into the widely used 3D Slicer platform. Our extension implements a client-server architecture that decouples computationally intensive model inference from the client-side interface. Therefore, SlicerNNInteractive eliminates heavy hardware constraints on the client-side and enables better operating system compatibility than existing plugins for nnInteractive. Running both the client and server-side on a single machine is also possible, offering flexibility across different deployment scenarios. The extension provides an intuitive user interface with all interaction types available in the original framework (point, bounding box, scribble, and lasso prompts), while including a comprehensive set of keyboard shortcuts for efficient workflow.
SlicerNNInteractive将nnInteractive(一种用于3D图像分割的先进提示式深度学习框架)集成到广泛使用的3D Slicer平台中。我们的扩展实现了一种客户端-服务器架构,该架构将计算密集型的模型推理与客户端界面解耦。因此,SlicerNNInteractive消除了客户端端的繁重硬件约束,并且与现有的nnInteractive插件相比,具有更好的操作系统兼容性。在单机上同时运行客户端和服务器端也是可能的,为不同的部署场景提供了灵活性。该扩展提供了一个直观的用户界面,拥有原始框架中所有可用的交互类型(点、边界框、涂鸦和套索提示),同时包括一组全面的键盘快捷键,以提高工作效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 2 figures
Summary
SlicerNNInteractive将nnInteractive这一先进的可提示的深度学习三维图像分割框架集成到广泛使用的3D Slicer平台中。它通过客户端-服务器架构实现模型推理与客户端界面之间的解耦,消除了客户端硬件的繁重约束,提高了操作系统的兼容性。同时,该扩展提供了直观的用户界面和丰富的交互类型,包括键盘快捷键,以提高工作效率。
Key Takeaways
- SlicerNNInteractive集成了nnInteractive框架到3D Slicer平台。
- 采用客户端-服务器架构,实现模型推理与客户端界面的解耦。
- 消除了客户端硬件的繁重约束,提高了操作系统兼容性。
- 扩展了直观的用户界面和丰富的交互类型。
- 键盘快捷键提高了工作效率。
- 支持在单机上同时运行客户端和服务器端,适应不同部署场景。
点此查看论文截图

Core-Excited States of Linear and Bent Uranyl Complexes: Insights from High-Energy Resolution X-ray Spectroscopy and Relativistic Quantum Chemistry
Authors:Wilken Aldair Misael, Lucia Amidani, Juliane März, Elena F. Bazarkina, Kristina O. Kvashnina, Valérie Vallet, André Severo Pereira Gomes
Advanced X-ray spectroscopic techniques are widely recognized as state-of-the-art tools for probing the electronic structure, bonding, and chemical environments of the heaviest elements in the periodic table. In this study, we employ X-ray absorption near-edge structure measurements in high-energy resolution fluorescence detection (HERFD-XANES) mode to investigate the core states arising from excitations out of the U 3d${_{3/2}}$ (M$_4$ edge) levels for molecular complexes in which the uranyl moiety deviates from linearity to varying degrees, and in particular systems containing the UO$_2$Cl$_2$ group such as UO$_2$Cl$_2$.n(H$_2$O) and UO$_2$Cl$_2$(phen)$_2$, which in the latter case exhibits a pronounced O-U-O bending angle. These U M$_4$ edge HERFD-XANES spectra are compared to those of other linear (Cs$_2$UO$_2$Cl$_4$) or pseudo-linear ([UO$_2$(NO$_3$)$_2$.n(H$_2$O)]) uranyl complexes. This evaluation is complemented by ab initio relativistic quantum chemistry simulations using 2-component Time-Dependent Density Functional Theory (TD-DFT) with the CAM-B3LYP functional, employing the Tamm-Dancoff approximation (2c-TDA). Our 2c-TDA simulations show modest deviations from the HERFD-XANES data, with peak splittings differing by less than 1 eV from experimental values. These core-excited states were further characterized by Natural Transition Orbital (NTO) analysis. Overall, our results highlight the influence of equatorial ligands on the spectroscopic signatures, particularly pronounced in UO$_2$Cl$_2$(phen)$2$, where the U 3d${{3/2}} \rightarrow$ $5f$ $\sigma{_u}^{*}$ satellite transition appears at lower energies compared to the other systems studied.
高级X射线光谱技术被公认为是探索周期表中重元素的电子结构、键合和化学环境的最新工具。在这项研究中,我们采用高能量分辨率荧光检测(HERFD)模式下的X射线吸收近边缘结构测量技术,研究偏离线性的铀酰分子复合物的核心状态,特别是含有UO2Cl2基团的系统,如UO2Cl2.n(H2O)和UO2Cl2(phen)2。在后一种情况下,表现出明显的O-U-O弯曲角。我们将这些UM4边缘的HERFD-XANES光谱与线性铀酰配合物(如Cs2UO2Cl4)或伪线性配合物(如UO2(NO3)2.n(H2O))的光谱进行比较。这一评估辅以基于时间的从头计算相对论量子化学模拟,采用含时密度泛函理论(TD-DFT)的CAM-B3LYP功能,采用Tamm-Dancoff近似(2c-TDA)。我们的2c-TDA模拟与HERFD-XANES数据略有偏差,峰值分裂与实验值相差不到1电子伏特。这些核心激发态进一步通过自然跃迁轨道(NTO)分析表征。总体而言,我们的结果突出了赤道配体对光谱特征的影响,特别是在UO2Cl2(phen)2中尤为明显,其中U 3d 3/2 → 5f σu*卫星过渡出现在比其他系统更低的能量处。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 9 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本研究采用高能量分辨率荧光检测(HERFD-XANES)模式的X射线吸收近边结构测量技术,对不同程度偏离线性的铀酰分子复合物的核心状态进行研究,特别是对含有UO2Cl2基团的系统,如UO2Cl2·n(H2O)和UO2Cl2(phen)2。通过与其他线性或伪线性铀酰复合物的比较,并结合基于时间的密度泛函理论(TD-DFT)进行模拟分析,揭示了赤道配体对光谱特征的影响,特别是在UO2Cl2(phen)2中表现尤为突出。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究使用HERFD-XANES技术对铀酰分子复合物的电子结构、键合和化学环境进行了研究。
- 研究对象包括不同程度偏离线性的铀酰分子复合物,特别是含有UO2Cl2基团的系统。
- 通过与其他线性或伪线性铀酰复合物的比较,对光谱特征进行了深入分析。
- 使用基于时间的密度泛函理论(TD-DFT)进行模拟分析,揭示了核心状态的一些特征。
- 模拟结果中赤道配体的影响尤为突出,特别是在UO2Cl2(phen)2系统中。
- U 3d_{3/2}至$5f$ $\sigma{_u}^{*}$卫星跃迁的能量较低,与其他系统相比具有显著特征。
点此查看论文截图

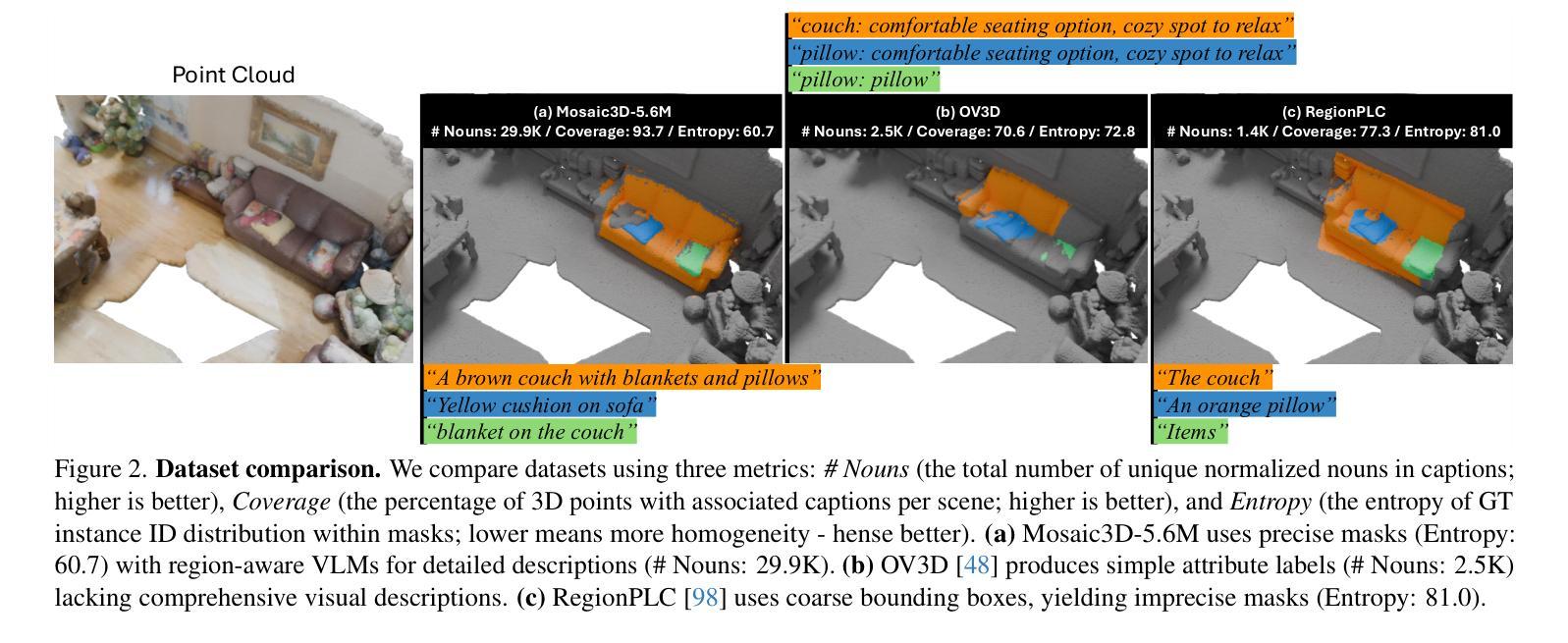
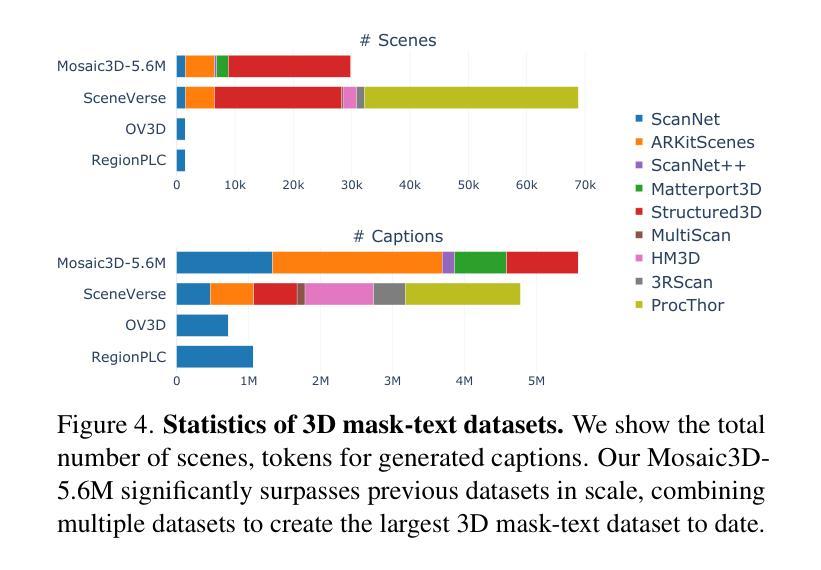
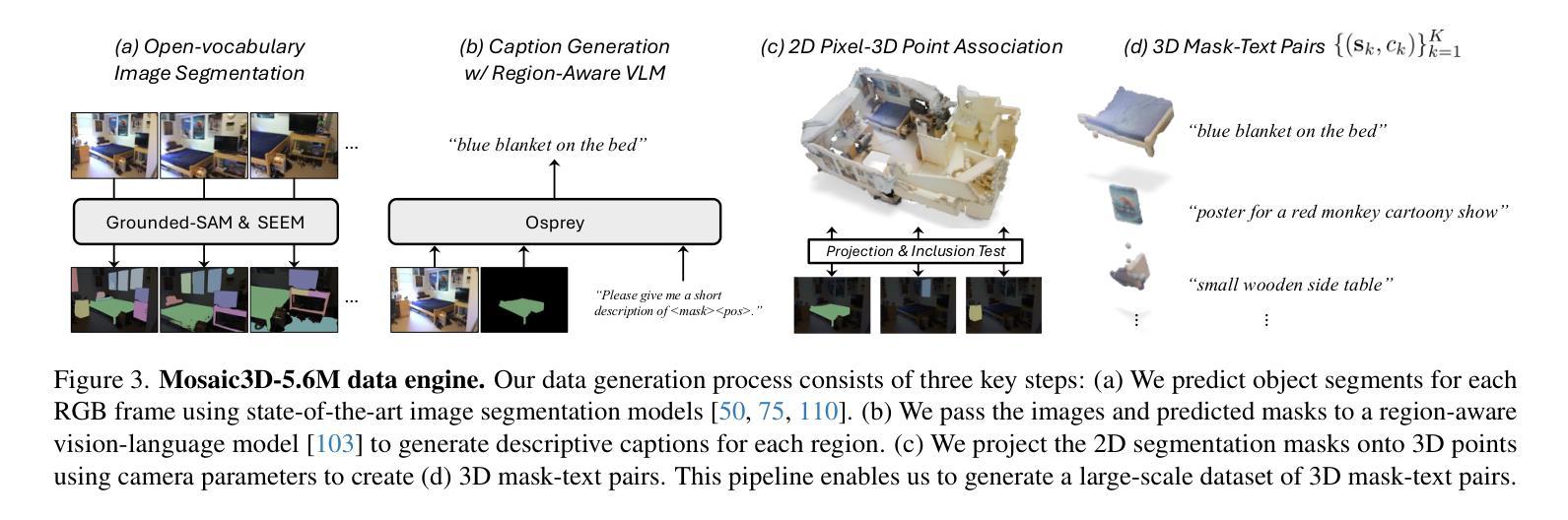
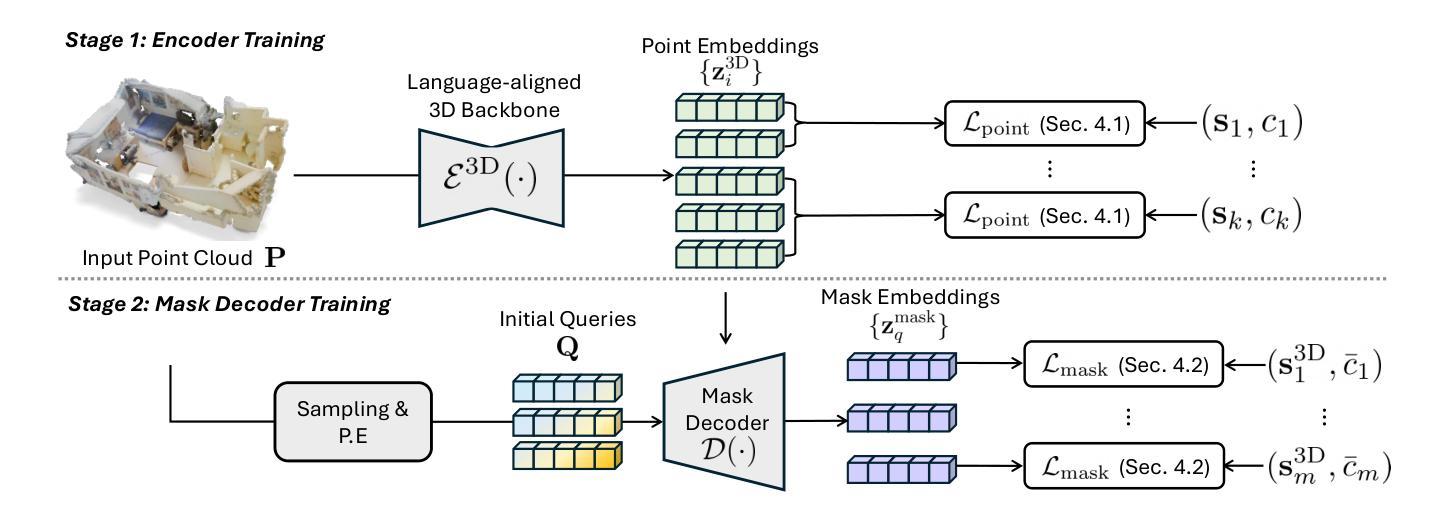
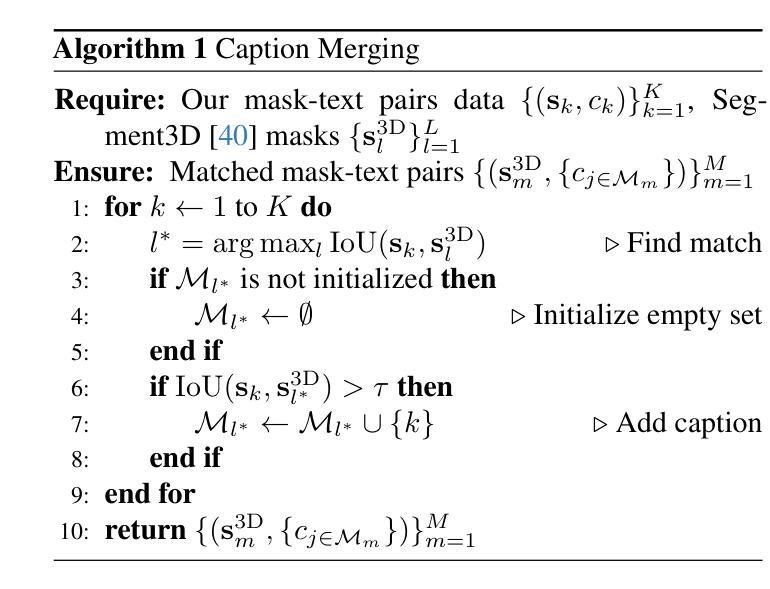
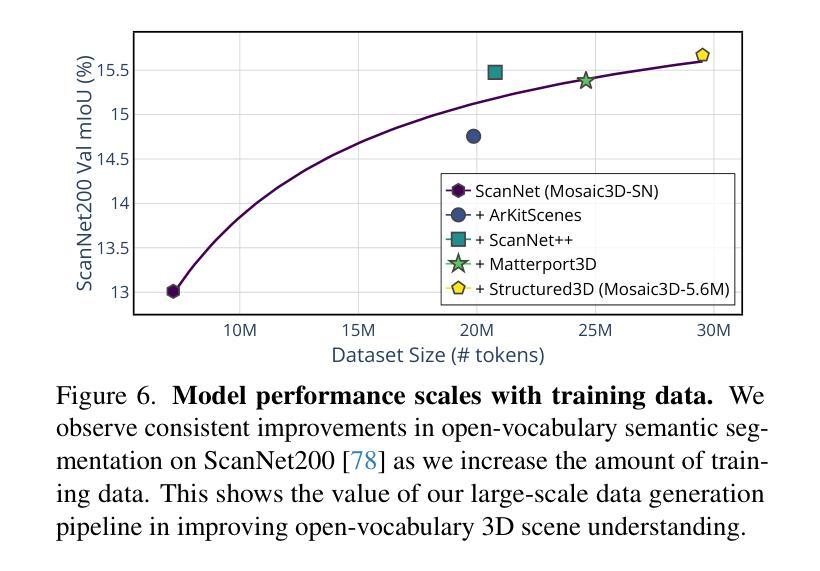
Mosaic3D: Foundation Dataset and Model for Open-Vocabulary 3D Segmentation
Authors:Junha Lee, Chunghyun Park, Jaesung Choe, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang, Jan Kautz, Minsu Cho, Chris Choy
We tackle open-vocabulary 3D scene understanding by introducing a novel data generation pipeline and training framework. Our method addresses three critical requirements for effective training: precise 3D region segmentation, comprehensive textual descriptions, and sufficient dataset scale. By leveraging state-of-the-art open-vocabulary image segmentation models and region-aware Vision-Language Models, we develop an automatic pipeline that generates high-quality 3D mask-text pairs. Applying this pipeline to multiple 3D scene datasets, we create Mosaic3D-5.6M, a dataset of over 30K annotated scenes with 5.6M mask-text pairs, significantly larger than existing datasets. Building upon this data, we propose Mosaic3D, a foundation model combining a 3D encoder trained with contrastive learning and a lightweight mask decoder for open-vocabulary 3D semantic and instance segmentation. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on open-vocabulary 3D semantic and instance segmentation tasks including ScanNet200, Matterport3D, and ScanNet++, with ablation studies validating the effectiveness of our large-scale training data.
我们通过引入新型数据生成流程和训练框架来解决开放式词汇表中的三维场景理解问题。我们的方法满足了有效训练的三个关键需求:精确的3D区域分割、全面的文本描述和足够的数据集规模。我们借助最新先进开放式词汇表的图像分割模型和区域感知视觉语言模型,开发了一个自动管道,生成高质量的三维掩膜-文本对。将此管道应用于多个三维场景数据集,我们创建了Mosaic3D-5.6M数据集,包含超过3万个注释场景和560万个掩膜-文本对,显著大于现有数据集。在此基础上,我们提出了Mosaic3D模型,这是一个结合了通过对比学习训练的3D编码器和用于开放式词汇表的三维语义和实例分割的轻量级掩膜解码器的基础模型。我们的方法在开放式词汇表的三维语义和实例分割任务上达到了最新结果,包括ScanNet200、Matterport3D和ScanNet++等数据集,并进行了效果验证的大规模训练数据消融研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF project page: https://nvlabs.github.io/Mosaic3D/
Summary
新一代数据生成管道和训练框架解决了开放词汇表的三维场景理解问题。通过精确的三维区域分割、全面的文本描述和足够的数据集规模,生成高质量的三维掩膜-文本对。创建了Mosaic3D-5.6M数据集,包含超过3万标注场景和560万掩膜-文本对。在此基础上,提出了Mosaic3D模型,结合三维编码器对比学习和轻量级掩膜解码器,实现开放词汇表的三维语义和实例分割的最佳结果。
Key Takeaways
- 引入新型数据生成管道和训练框架,解决开放词汇表的三维场景理解难题。
- 方法满足三个关键训练要求:精确三维区域分割、全面文本描述和足够的数据集规模。
- 利用先进开放词汇表的图像分割模型和区域感知视觉语言模型,自动生成高质量的三维掩膜-文本对。
- 创建了Mosaic3D-5.6M数据集,包含大量标注场景和掩膜-文本对,显著大于现有数据集。
- 提出Mosaic3D模型,结合三维编码器和掩膜解码器,用于开放词汇表的三维语义和实例分割。
- 模型在多个数据集上达到开放词汇表的三维语义和实例分割的最佳结果。
点此查看论文截图


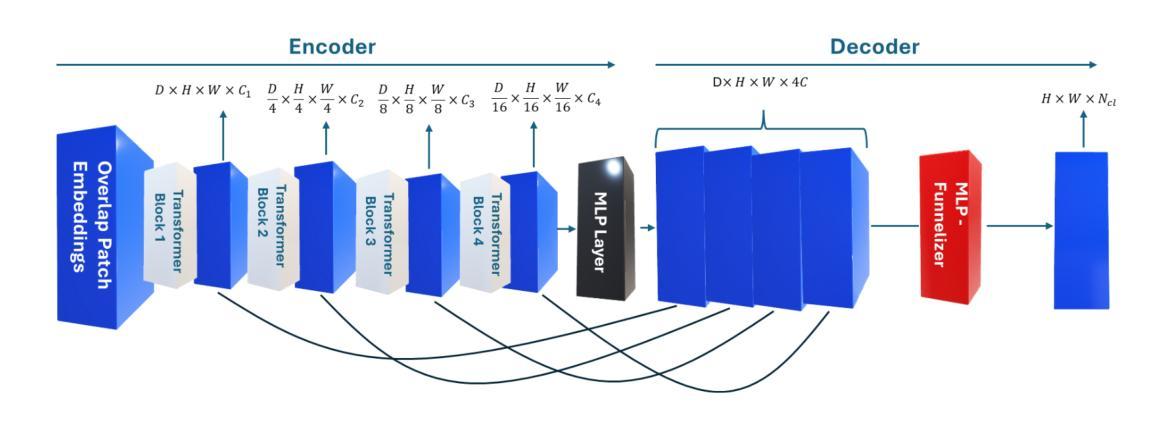
AMBER – Advanced SegFormer for Multi-Band Image Segmentation: an application to Hyperspectral Imaging
Authors:Andrea Dosi, Massimo Brescia, Stefano Cavuoti, Mariarca D’Aniello, Michele Delli Veneri, Carlo Donadio, Adriano Ettari, Giuseppe Longo, Alvi Rownok, Luca Sannino, Maria Zampella
Deep learning has revolutionized the field of hyperspectral image (HSI) analysis, enabling the extraction of complex spectral and spatial features. While convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been the backbone of HSI classification, their limitations in capturing global contextual features have led to the exploration of Vision Transformers (ViTs). This paper introduces AMBER, an advanced SegFormer specifically designed for multi-band image segmentation. AMBER enhances the original SegFormer by incorporating three-dimensional convolutions, custom kernel sizes, and a Funnelizer layer. This architecture enables processing hyperspectral data directly, without requiring spectral dimensionality reduction during preprocessing. Our experiments, conducted on three benchmark datasets (Salinas, Indian Pines, and Pavia University) and on a dataset from the PRISMA satellite, show that AMBER outperforms traditional CNN-based methods in terms of Overall Accuracy, Kappa coefficient, and Average Accuracy on the first three datasets, and achieves state-of-the-art performance on the PRISMA dataset. These findings highlight AMBER’s robustness, adaptability to both airborne and spaceborne data, and its potential as a powerful solution for remote sensing and other domains requiring advanced analysis of high-dimensional data.
深度学习已经彻底改变了高光谱图像(HSI)分析领域,能够实现复杂光谱和空间特征的提取。虽然卷积神经网络(CNN)已成为HSI分类的支柱,但在捕捉全局上下文特征方面的局限性促使人们探索视觉转换器(ViTs)。本文介绍了AMBER,这是一个专为多波段图像分割设计的先进SegFormer。AMBER通过引入三维卷积、自定义内核大小和漏斗层增强了原始SegFormer。该架构能够直接处理高光谱数据,无需在预处理阶段进行光谱维度缩减。我们在三个基准数据集(Salinas、Indian Pines和Pavia University)以及PRISMA卫星数据集上进行的实验表明,AMBER在总体精度、Kappa系数和平均精度方面优于传统的CNN方法,在PRISMA数据集上达到了最先进的性能。这些发现突出了AMBER的稳健性,以及对空中和太空数据的适应性,以及其在遥感和其他需要高级分析高维数据的领域中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF submitted to Neural Computing & Applications (Springer). Accepted with minor revisions
Summary
深度学习在超光谱图像(HSI)分析领域引起了革命性的变革,使复杂光谱和空间特征的提取成为可能。虽然卷积神经网络(CNN)是HSI分类的基石,但在捕捉全局上下文特征方面的局限性促使了对视觉转换器(ViTs)的探索。本文介绍了AMBER,这是一种专为多波段图像分割设计的先进SegFormer。AMBER通过引入三维卷积、自定义内核大小和漏斗层(Funnelizer layer)增强了原始SegFormer。该架构能够直接处理超光谱数据,无需在预处理阶段降低光谱维度。实验表明,AMBER在三个基准数据集(Salinas、Indian Pines和Pavia University)和PRISMA卫星数据集上的表现优于传统基于CNN的方法,整体精度、Kappa系数和平均精度均有显著提高,展现了其稳健性、适应空中和太空数据的能力,以及作为遥感和其他需要高级高维数据分析领域的强大解决方案的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在超光谱图像分析中具有革命性作用,能够提取复杂的光谱和空间特征。
- 虽然卷积神经网络在HSI分类中是基石,但它们存在捕捉全局上下文特征的局限性。
- Vision Transformers(ViTs)被探索用于解决CNN的局限性。
- 论文介绍了AMBER,一个基于SegFormer的高级模型,具有直接处理超光谱数据的能力。
- AMBER通过引入三维卷积、自定义内核大小和漏斗层增强了性能。
- AMBER在多个基准数据集上的表现优于传统CNN方法,显示出其强大的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Real-Time Image Analysis Software Suitable for Resource-Constrained Computing
Authors:Alexandre Matov
Methods: We have developed a software suite (DataSet Tracker) for real-time analysis designed to run on computers, smartphones, and smart glasses hardware and suitable for resource-constrained, on-the-fly computing in microscopes without internet connectivity; a demo is available for viewing at datasetanalysis.com. Our objective is to present the community with an integrated, easy to use by all, tool for resolving the complex dynamics of the cytoskeletal meshworks, intracytoplasmic membranous networks, and vesicle trafficking. Our software is optimized for resource-constrained computing and can be installed even on microscopes without internet connectivity. Results: Our computational platform can provide high-content analyses and functional secondary screening of novel compounds that are in the process of approval, or at a pre-clinical stage of development, and putative combination therapies based on FDA-approved drugs. Importantly, dissecting the mechanisms of drug action with quantitative detail will allow the design of drugs that impede relapse and optimal dose regimens with minimal harmful side effects by carefully exploiting disease-specific aberrations. Conclusions: DataSet Tracker, the real-time optical flow feature tracking software presented in this contribution, can serve as the base module of an integrated platform of existing and future algorithms for real-time cellular analysis. The computational assay we propose could successfully be applied to evaluate treatment strategies for any human organ. It is our goal to have this integrated tool approved for use in the clinical practice.
方法:我们开发了一套名为DataSet Tracker的实时分析软件套件,旨在在计算机、智能手机和智能眼镜等硬件上运行,适用于无网络连接显微镜下的资源受限、即时计算。可以在datasetanalysis.com上查看演示版本。我们的目标是向研究群体提供一个集成工具,解决细胞骨架网格、细胞内膜网络和囊泡运输的复杂动态问题,该工具易于所有人使用。我们的软件针对资源受限计算进行了优化,甚至可以在没有网络连接的显微镜上安装使用。
结果:我们的计算平台可以提供高内涵分析以及新药在获批过程中或处于预临床研究阶段的功能二次筛选,以及基于FDA批准药物的潜在联合疗法。重要的是,以定量细节分析药物作用机制,可设计阻止复发药物和最佳剂量方案,通过精心利用疾病特异性异常达到将有害副作用降至最低的目的。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于实时分析的软件套件(DataSet Tracker),可在计算机、智能手机和智能眼镜上运行,适用于资源受限、无需互联网连接的显微镜环境下的移动计算。该软件的目的是为社区提供一个集成工具,解决细胞骨架网格、胞质内膜网络和囊泡运输的复杂动态问题。该软件可优化资源受限的计算环境,即使在无互联网连接的显微镜下也能安装使用。计算平台可以提供高内容分析和功能二级筛选,基于FDA批准的药物进行新型化合物的预先临床阶段开发以及潜在联合疗法。该软件能够详细定量地剖析药物作用机制,以便设计能够阻碍复发、最佳剂量方案的药物,并通过利用疾病特异性异常来减少有害的副作用。DataSet Tracker可以作为现有和未来算法的集成平台的基础模块,用于实时细胞分析。所提出的计算测定法可成功应用于评估任何人类器官的治疗策略,目标是在临床实践中获得批准使用。
Key Takeaways
- 开发了一种实时分析软件DataSet Tracker,可在多种设备上运行,包括计算机、智能手机和智能眼镜。
- 适合资源受限环境,可在无互联网连接的显微镜环境下使用。
- 旨在解决细胞骨架网格、胞质内膜网络和囊泡运输等复杂动态问题。
- 可进行高内容分析和功能二级筛选,适用于新药开发过程中的药物组合疗法评估。
- 能够详细定量地剖析药物作用机制,为设计减少复发和优化剂量方案的药物提供依据。
- DataSet Tracker可作为集成平台的基础模块,用于实时细胞分析的未来算法。
点此查看论文截图

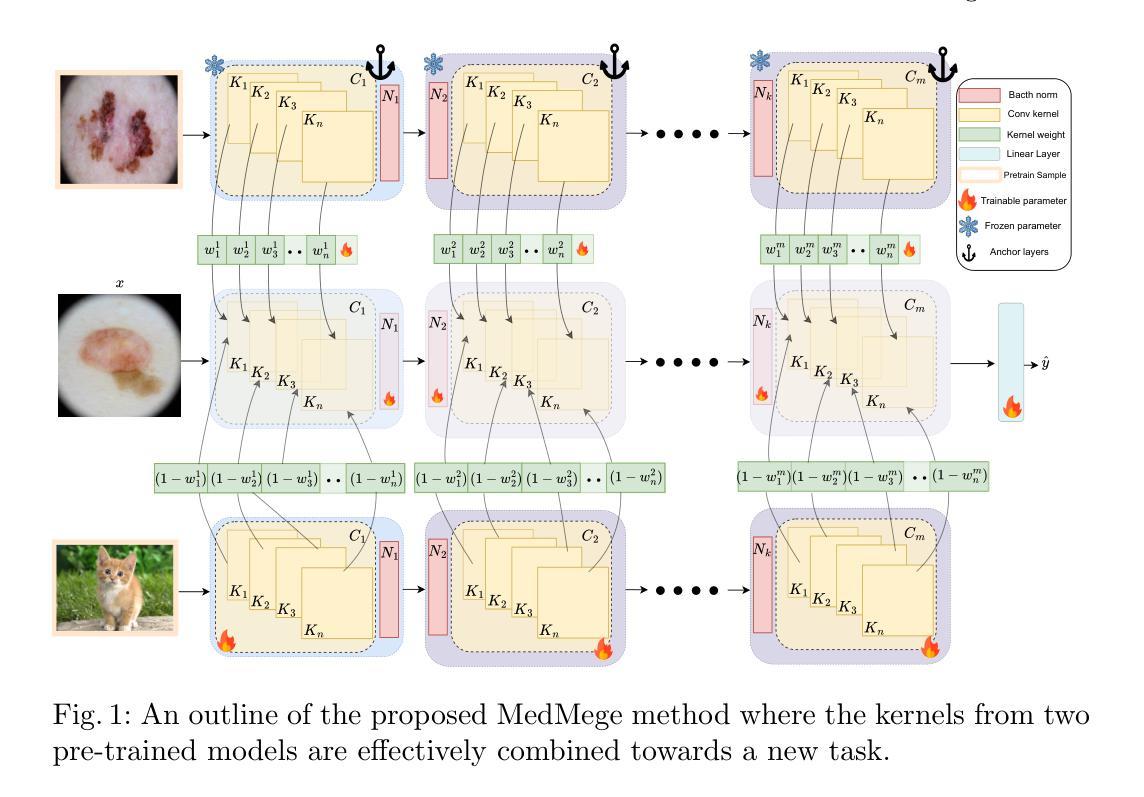
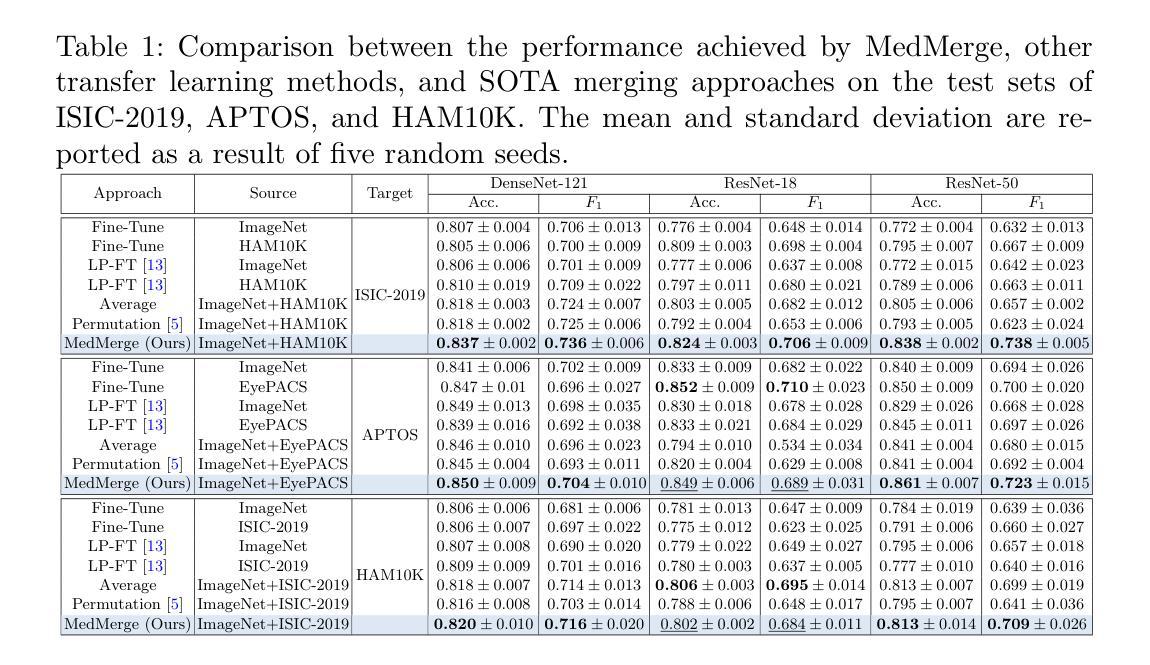
MedMerge: Merging Models for Effective Transfer Learning to Medical Imaging Tasks
Authors:Ibrahim Almakky, Santosh Sanjeev, Anees Ur Rehman Hashmi, Mohammad Areeb Qazi, Hu Wang, Mohammad Yaqub
Transfer learning has become a powerful tool to initialize deep learning models to achieve faster convergence and higher performance. This is especially useful in the medical imaging analysis domain, where data scarcity limits possible performance gains for deep learning models. Some advancements have been made in boosting the transfer learning performance gain by merging models starting from the same initialization. However, in the medical imaging analysis domain, there is an opportunity to merge models starting from different initializations, thus combining the features learned from different tasks. In this work, we propose MedMerge, a method whereby the weights of different models can be merged, and their features can be effectively utilized to boost performance on a new task. With MedMerge, we learn kernel-level weights that can later be used to merge the models into a single model, even when starting from different initializations. Testing on various medical imaging analysis tasks, we show that our merged model can achieve significant performance gains, with up to 7% improvement on the F1 score. The code implementation of this work is available at github.com/BioMedIA-MBZUAI/MedMerge.
迁移学习已经成为初始化深度学习模型以更快收敛和提高性能的强大工具。这在医学成像分析领域尤其有用,因为数据稀缺限制了深度学习模型的性能提升。一些进步是通过合并从同一初始化开始的模型来提高迁移学习性能增益而实现的。然而,在医学成像分析领域,存在合并从不同初始化开始的模型的机会,从而结合从不同任务中学到的特征。在这项工作中,我们提出了MedMerge方法,通过该方法可以合并不同模型的权重,并有效利用其特征来提高新任务的性能。通过MedMerge,我们学习内核级别的权重,这些权重以后可用于将模型合并为一个单独的模型,即使从初始状态有所不同也可以进行合并。通过对各种医学成像分析任务的测试,我们证明合并后的模型能够实现显著的性能提升,在F1分数上最多可提高7%。该工作的代码实现可在github.com/BioMedIA-MBZUAI/MedMerge找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分析中,迁移学习成为初始化深度学习模型的有力工具,能加快收敛速度并提高性能。本文提出MedMerge方法,通过合并不同初始化模型的权重,有效结合不同任务学习的特征,提升新任务上的性能。通过内核级别的权重学习,实现模型的合并。实验表明,合并模型在多种医学图像分析任务上取得了显著的性能提升,F1分数最多可提高7%。代码实现已发布在github.com/BioMedIA-MBZUAI/MedMerge。
Key Takeaways
- 迁移学习在医学图像分析中展现出巨大潜力,有助于提升深度学习模型的性能。
- MedMerge方法通过合并不同初始化模型的权重,实现性能提升。
- MedMerge可以合并不同任务学习的特征,增强模型在新任务上的表现。
- 通过内核级别的权重学习,实现模型的合并,即使模型从不同的初始化开始。
- MedMerge在多种医学图像分析任务上取得了显著的性能提升。
- 合并模型的表现优于单一模型,F1分数最多可提高7%。
点此查看论文截图