⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-17 更新
Uncertainty Estimation for Trust Attribution to Speed-of-Sound Reconstruction with Variational Networks
Authors:Sonia Laguna, Lin Zhang, Can Deniz Bezek, Monika Farkas, Dieter Schweizer, Rahel A. Kubik-Huch, Orcun Goksel
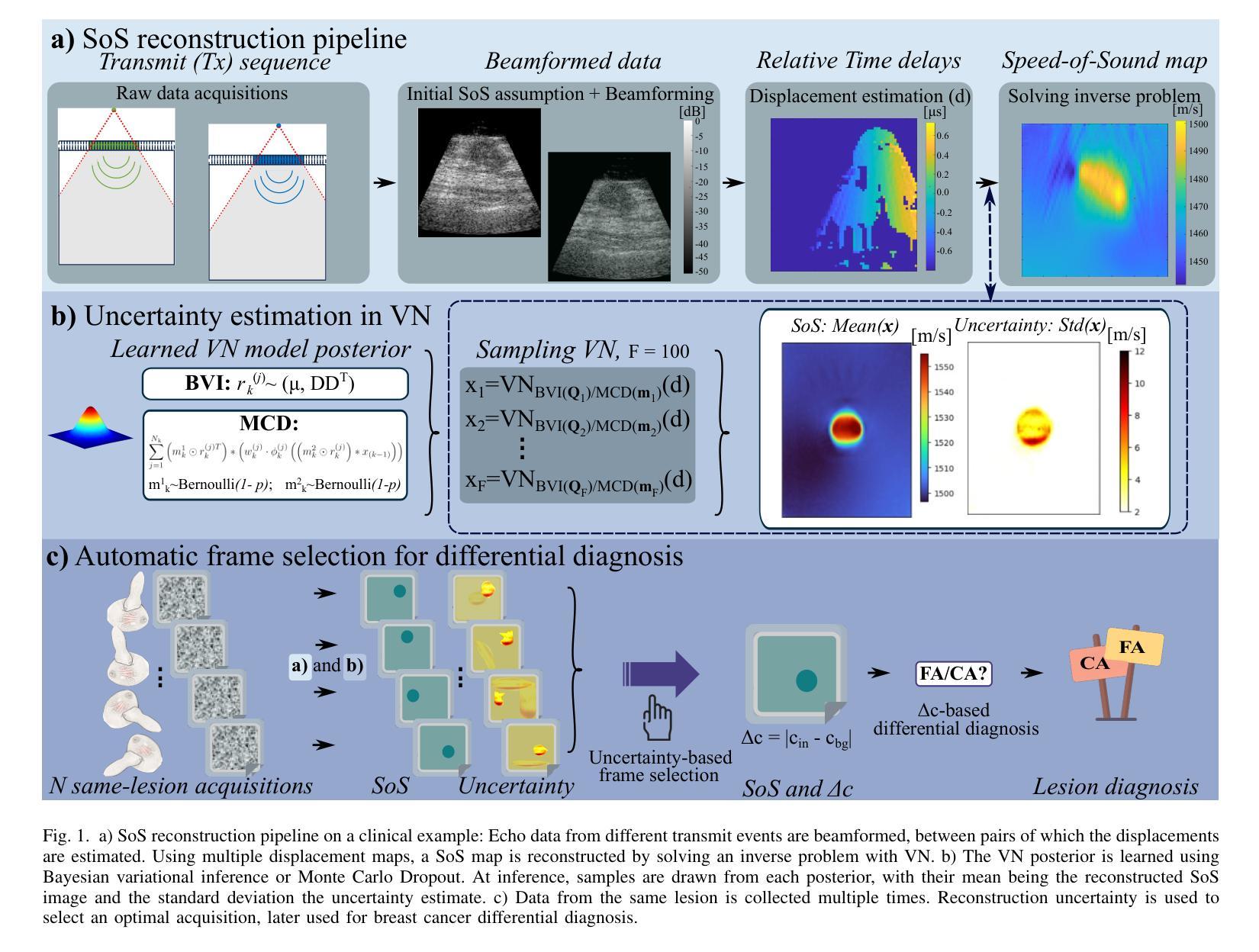
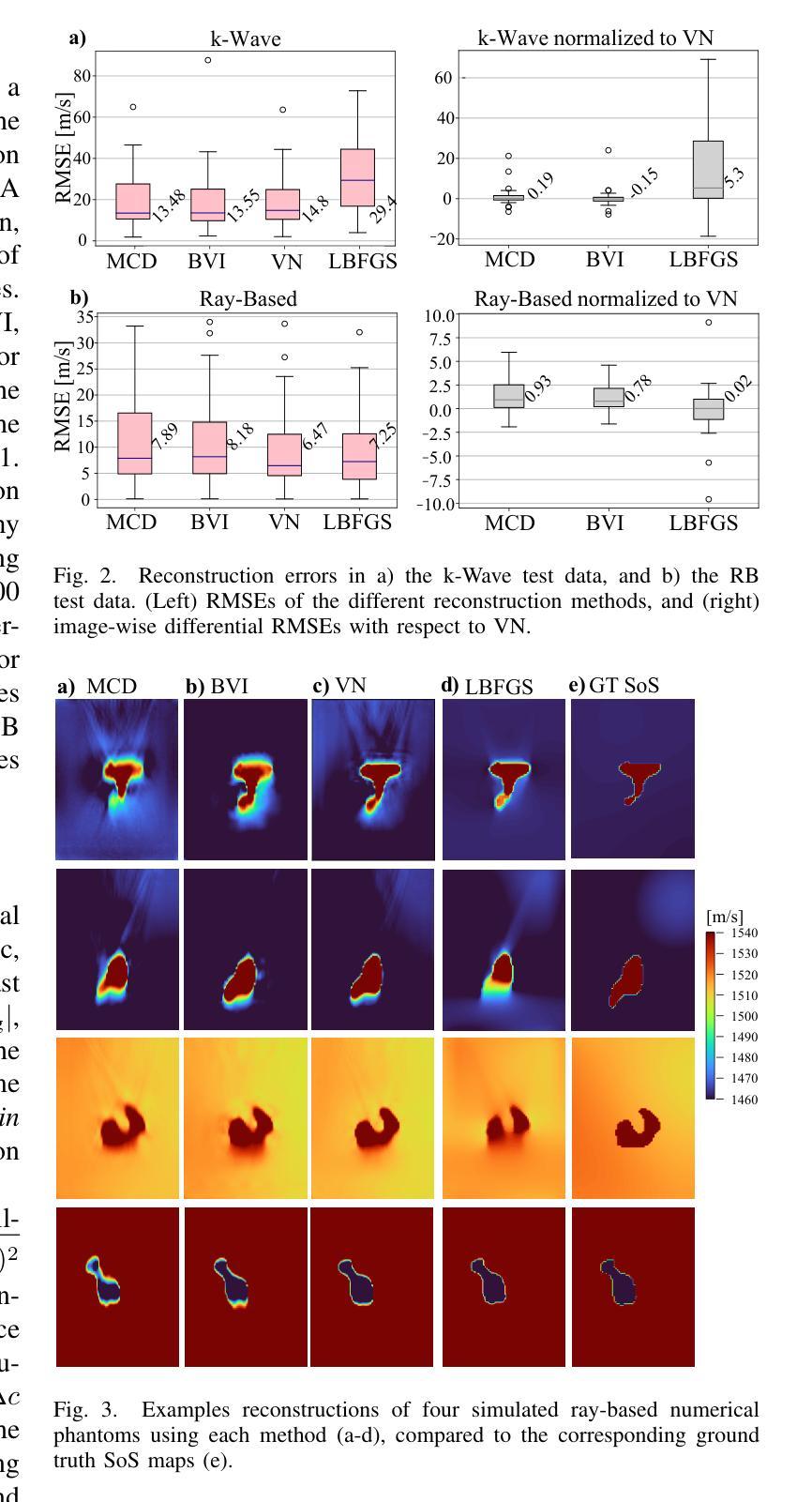
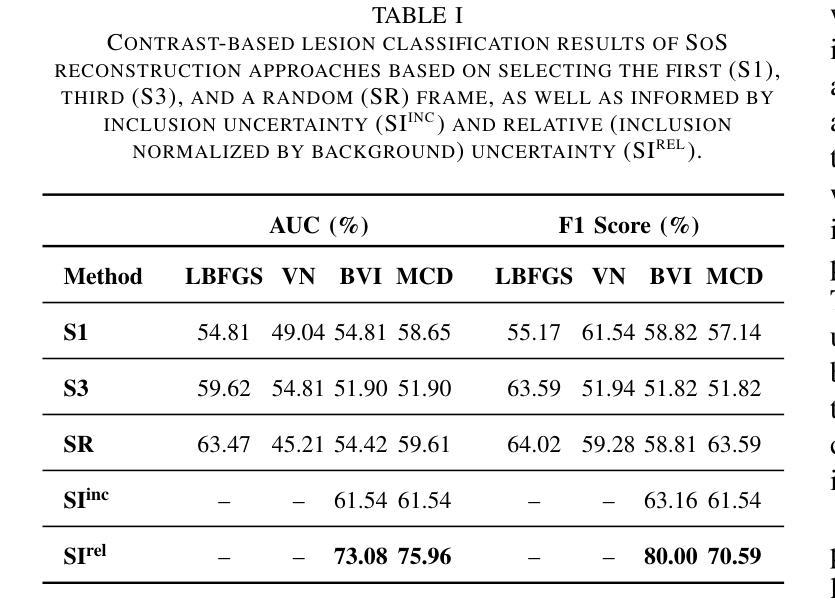
Speed-of-sound (SoS) is a biomechanical characteristic of tissue, and its imaging can provide a promising biomarker for diagnosis. Reconstructing SoS images from ultrasound acquisitions can be cast as a limited-angle computed-tomography problem, with Variational Networks being a promising model-based deep learning solution. Some acquired data frames may, however, get corrupted by noise due to, e.g., motion, lack of contact, and acoustic shadows, which in turn negatively affects the resulting SoS reconstructions. We propose to use the uncertainty in SoS reconstructions to attribute trust to each individual acquired frame. Given multiple acquisitions, we then use an uncertainty based automatic selection among these retrospectively, to improve diagnostic decisions. We investigate uncertainty estimation based on Monte Carlo Dropout and Bayesian Variational Inference. We assess our automatic frame selection method for differential diagnosis of breast cancer, distinguishing between benign fibroadenoma and malignant carcinoma. We evaluate 21 lesions classified as BI-RADS~4, which represents suspicious cases for probable malignancy. The most trustworthy frame among four acquisitions of each lesion was identified using uncertainty based criteria. Selecting a frame informed by uncertainty achieved an area under curve of 76% and 80% for Monte Carlo Dropout and Bayesian Variational Inference, respectively, superior to any uncertainty-uninformed baselines with the best one achieving 64%. A novel use of uncertainty estimation is proposed for selecting one of multiple data acquisitions for further processing and decision making.
声波速度(SoS)是组织的生物力学特征,其成像可以为诊断提供有前景的生物标志物。从超声采集重建SoS图像可以看作是一个有限角度计算机断层扫描问题,基于变分网络的模型深度学习方法是一个有前途的解决方案。然而,由于运动、接触不良和声影等原因,某些获取的数据帧可能会被噪声破坏,这反过来又会对最终的SoS重建结果产生负面影响。我们提议利用SoS重建中的不确定性来为每一个单独获取的数据帧赋予信任度。给定多次采集的数据,我们基于不确定性的自动选择方法对这些数据进行回顾性筛选,以提高诊断决策的准确性。我们研究了基于蒙特卡罗Dropout和贝叶斯变分推断的不确定性估计。我们评估了我们的自动数据帧选择方法,用于乳腺癌的鉴别诊断,区分良性纤维腺瘤和恶性癌。我们评估了21个被分类为BI-RADS 4的病变,这代表可疑的恶性肿瘤病例。使用不确定性标准在四个采集的病变中确定了最可靠的数据帧。基于不确定性的数据帧选择取得了蒙特卡罗Dropout和贝叶斯变分推断的曲线下面积分别为76%和80%,优于所有未受不确定性影响的基础线,其中最佳基础线达到64%。提出了一种新型的不确定性估计方法,用于从多次数据采集中选择一个进行进一步的处理和决策。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at the International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery. Presented at the 16th International Conference on Information Processing in Computer-Assisted Interventions 2025
摘要
声波成像为诊断提供了一个有前景的生物标志物。从超声成像重建声波图像可视为一个有限角度的计算机断层扫描问题,变分网络是一种基于模型的深度学习解决方案。然而,由于运动、接触不良和声音阴影等原因,获取的一些数据帧可能会被噪声破坏,从而影响声波重建的结果。本研究提出利用声波重建中的不确定性为每次采集的数据帧分配信任度,并在多次采集的基础上,利用基于不确定性的自动选择方法,以提高诊断决策的准确性。本研究探讨了基于蒙特卡洛dropout和贝叶斯变分推断的不确定性估计。在区分乳腺良性纤维腺瘤和恶性癌的乳腺癌鉴别诊断中,评估了本研究的自动帧选择方法。在BI-RADS 4分类的疑似恶性病变中,使用不确定性标准确定了每个病变四个采集中最可靠的帧。基于不确定性的帧选择达到了Monte Carlo dropout的曲线下面积为76%,以及Bayesian Variational Inference的80%,优于所有未使用不确定性的基线,其中最佳基线达到64%。本研究提出了不确定性估计的新用途,用于从多次数据采集中选择一个用于进一步处理和决策制定。
关键见解
- 声波(SoS)成像可作为诊断的生物标志物。
- 变分网络在有限角度的计算机断层扫描问题中表现良好,适用于声波图像的重建。
- 数据帧可能会被噪声破坏,影响声波重建结果。
- 利用不确定性为每次采集的数据帧分配信任度,可以提高诊断的准确性。
- 研究了基于蒙特卡洛dropout和贝叶斯变分推断的不确定性估计方法。
- 在区分乳腺良性纤维腺瘤和恶性癌的鉴别诊断中评估了自动帧选择方法。
点此查看论文截图