⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-17 更新
3DAffordSplat: Efficient Affordance Reasoning with 3D Gaussians
Authors:Zeming wei, Junyi Lin, Yang Liu, Weixing Chen, Jingzhou Luo, Guanbin Li, Liang Lin
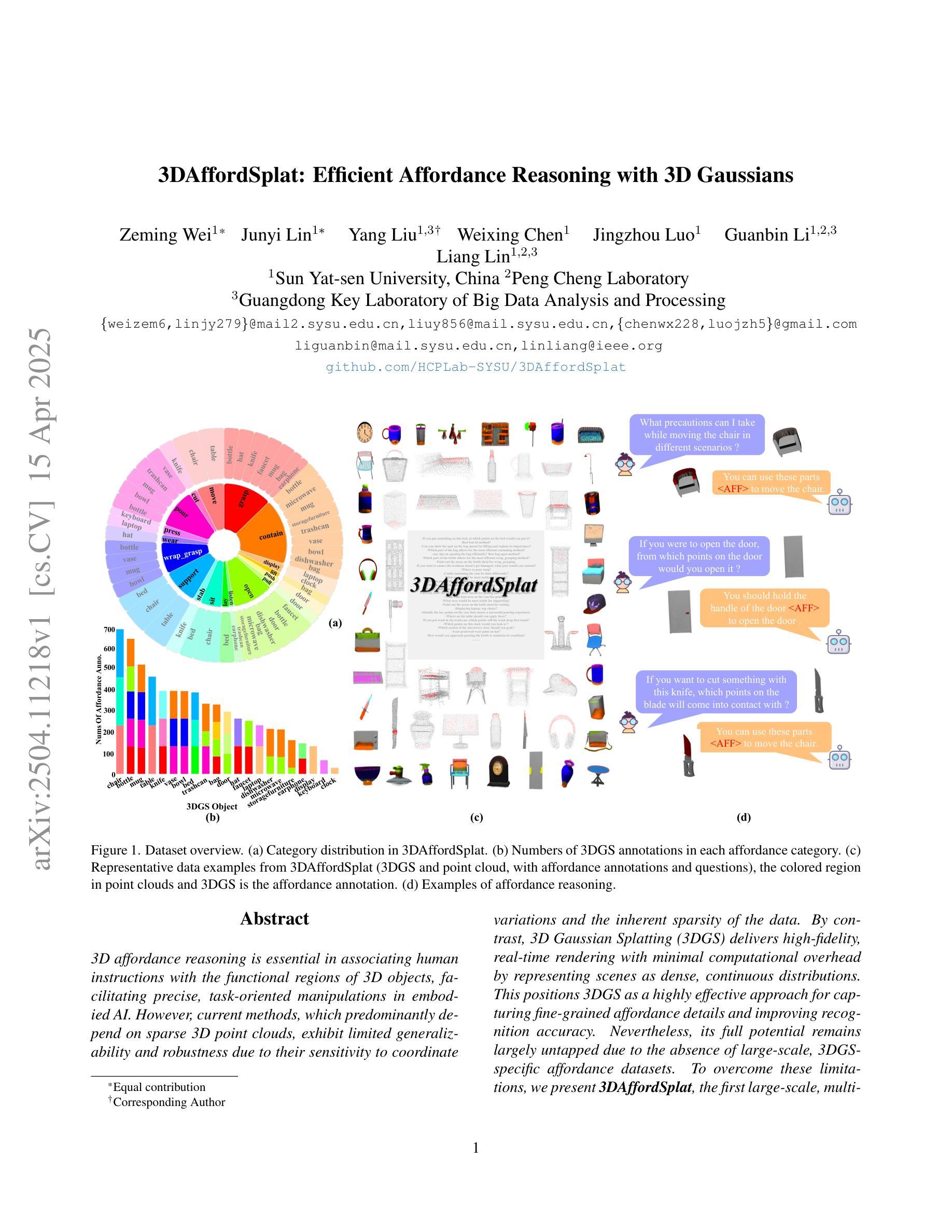
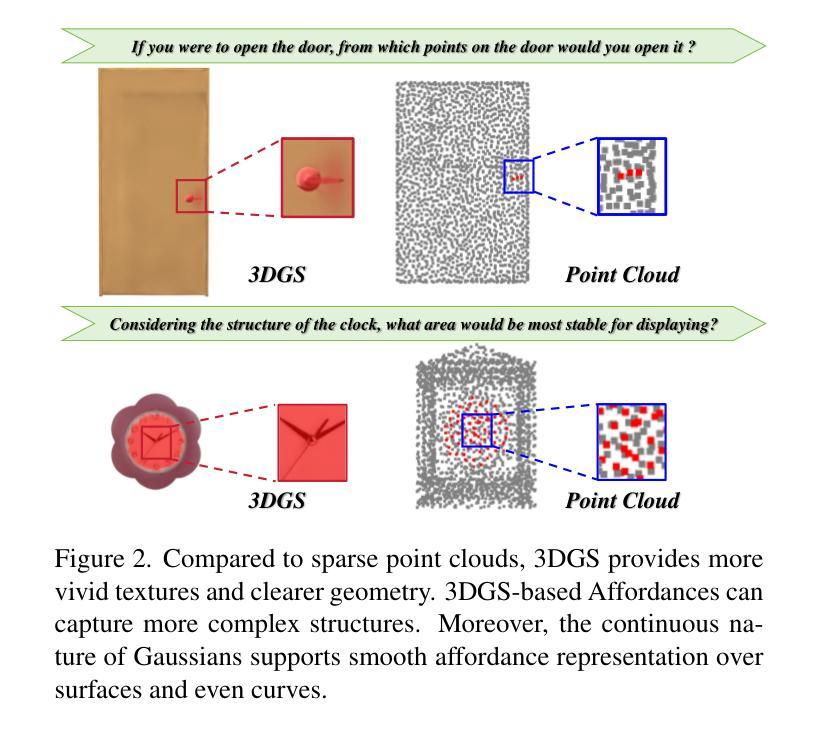
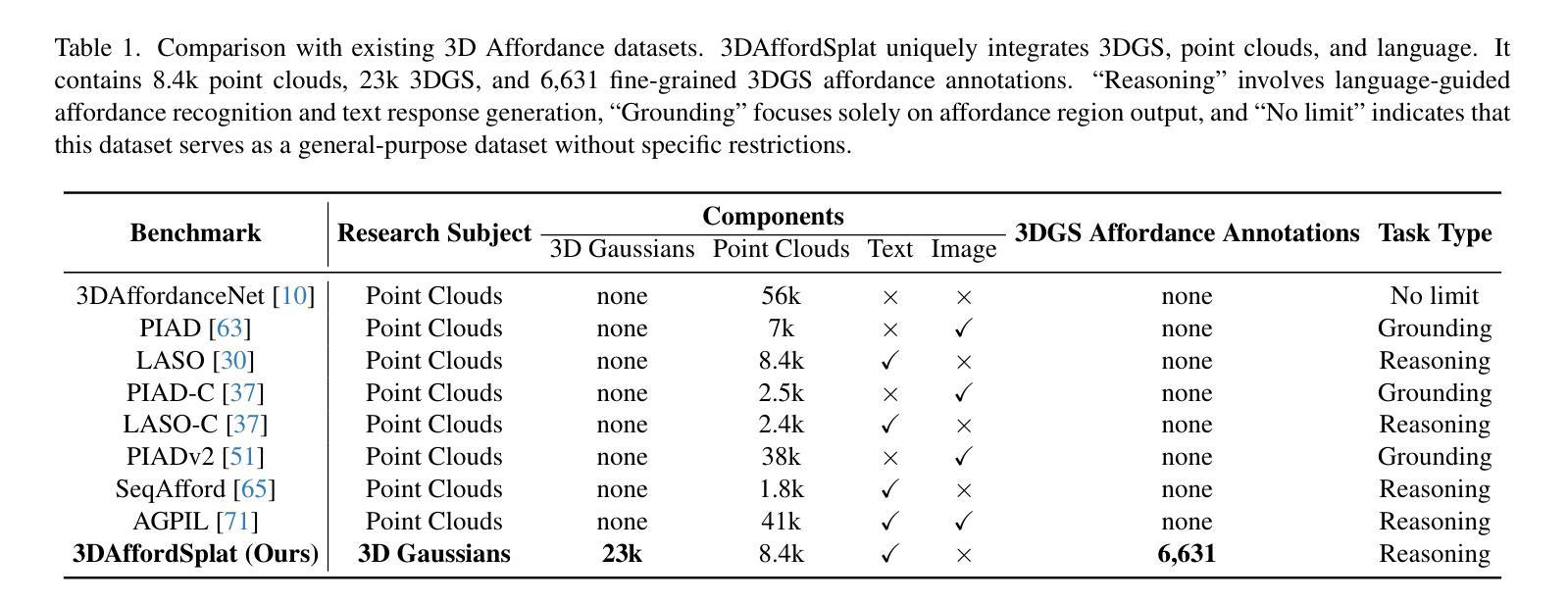
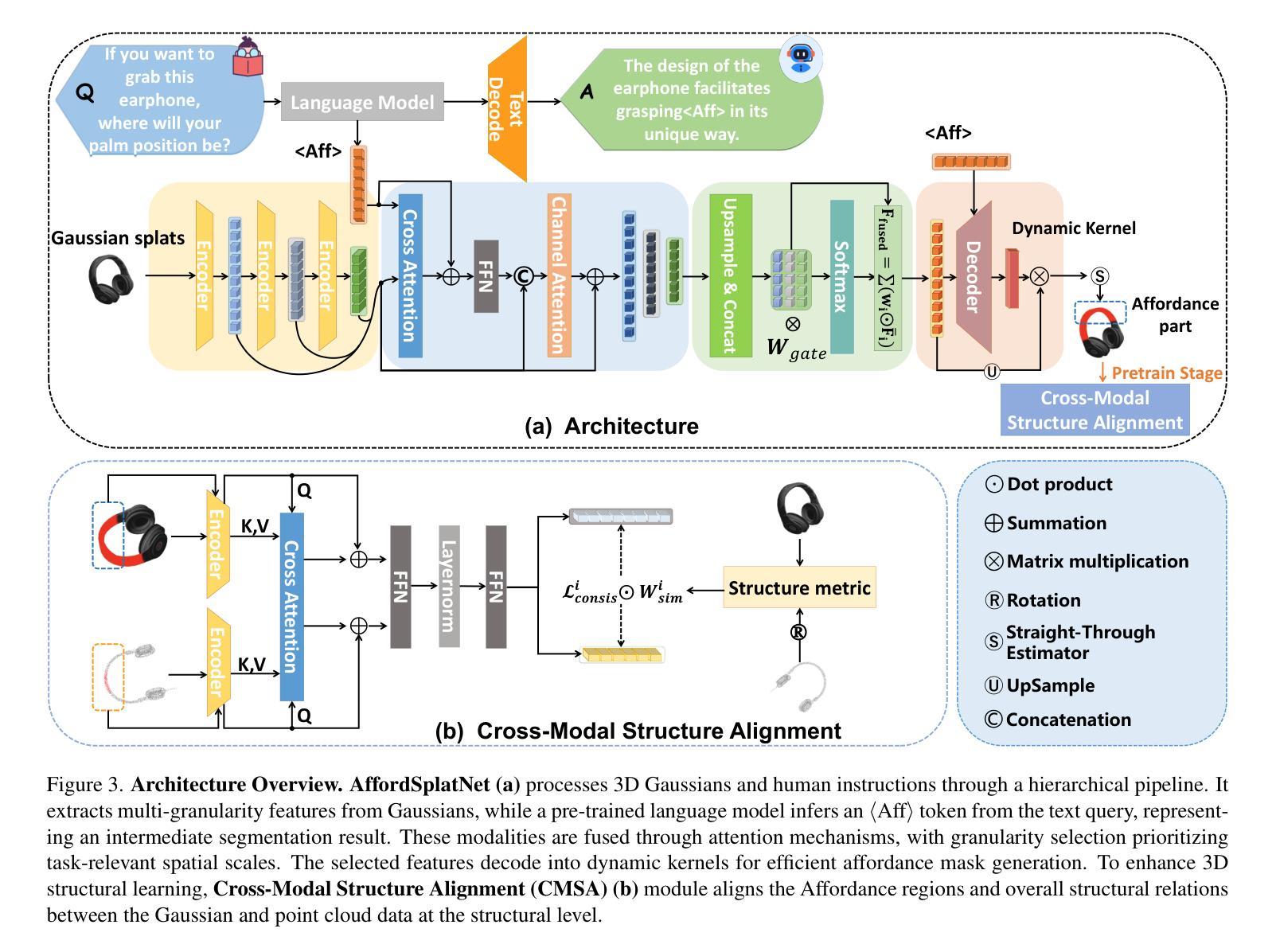
3D affordance reasoning is essential in associating human instructions with the functional regions of 3D objects, facilitating precise, task-oriented manipulations in embodied AI. However, current methods, which predominantly depend on sparse 3D point clouds, exhibit limited generalizability and robustness due to their sensitivity to coordinate variations and the inherent sparsity of the data. By contrast, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) delivers high-fidelity, real-time rendering with minimal computational overhead by representing scenes as dense, continuous distributions. This positions 3DGS as a highly effective approach for capturing fine-grained affordance details and improving recognition accuracy. Nevertheless, its full potential remains largely untapped due to the absence of large-scale, 3DGS-specific affordance datasets. To overcome these limitations, we present 3DAffordSplat, the first large-scale, multi-modal dataset tailored for 3DGS-based affordance reasoning. This dataset includes 23,677 Gaussian instances, 8,354 point cloud instances, and 6,631 manually annotated affordance labels, encompassing 21 object categories and 18 affordance types. Building upon this dataset, we introduce AffordSplatNet, a novel model specifically designed for affordance reasoning using 3DGS representations. AffordSplatNet features an innovative cross-modal structure alignment module that exploits structural consistency priors to align 3D point cloud and 3DGS representations, resulting in enhanced affordance recognition accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the 3DAffordSplat dataset significantly advances affordance learning within the 3DGS domain, while AffordSplatNet consistently outperforms existing methods across both seen and unseen settings, highlighting its robust generalization capabilities.
三维智能管理研究是人类指令与三维对象功能区相结合的关键技术,在嵌入式人工智能中实现精确的任务导向操控。然而,当前主要依赖于稀疏的三维点云的方法,由于其对坐标变化的敏感性和数据的固有稀疏性,其通用性和稳健性受到限制。相比之下,三维高斯贴图技术(3DGS)通过高密度连续分布来表示场景,以最小的计算开销实现高保真实时渲染,成为捕获精细智能管理细节、提高识别精度的有效方法。然而,由于缺乏大规模、专门针对三维高斯贴图技术的智能管理数据集,其潜力尚未得到充分发掘。为了克服这些局限性,我们推出了首个大规模多模态数据集——三维智能管理贴图(3DAffordSplat),专门用于基于三维高斯贴图技术的智能管理推理。该数据集包含23677个高斯实例、8354个点云实例和6631个手动标注的智能管理标签,涵盖21个对象类别和18种智能管理类型。在此基础上,我们引入了专为智能管理推理设计的全新模型——AffordSplatNet。AffordSplatNet具有创新性的跨模态结构对齐模块,利用结构一致性先验知识来对齐三维点云和三维高斯贴图表示,提高了智能管理的识别精度。大量实验表明,三维智能管理贴图数据集显著推动了三维高斯贴图领域的智能管理学习,而AffordSplatNet在可见和不可见环境中均表现出优于现有方法的性能,凸显了其稳健的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first large-scale 3D Gaussians Affordance Reasoning Benchmark
Summary
3DGS在三维物体功能区域与人类指令的关联中起到关键作用,有助于实现精确的任务导向型操作。然而,当前方法主要依赖稀疏的三维点云,存在泛化能力和鲁棒性受限的问题。为此,我们推出首个针对3DGS的规模化多模态数据集3DAffordSplat,并构建基于此数据集的AffordSplatNet模型。该模型利用结构一致性先验,实现对点云和3DGS表示的跨模态结构对齐,提高3DGS领域的操作能力识别精度。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS能够呈现高保真、实时的渲染效果,在计算开销上较小,可以表示密集的连续分布场景。
- 当前基于点云的方法在泛化能力和鲁棒性上有限制,难以满足精细化的需求。
- 推出首个针对3DGS的大规模多模态数据集3DAffordSplat,包括高斯分布的实例、点云实例以及手动的可操作性标签等。
- AffordSplatNet模型设计专门用于利用3DGS进行可操作性推理,包括创新的跨模态结构对齐模块。
- 该对齐模块利用结构一致性先验进行点云和3DGS表示的对齐,提高了可操作性识别的准确性。
点此查看论文截图
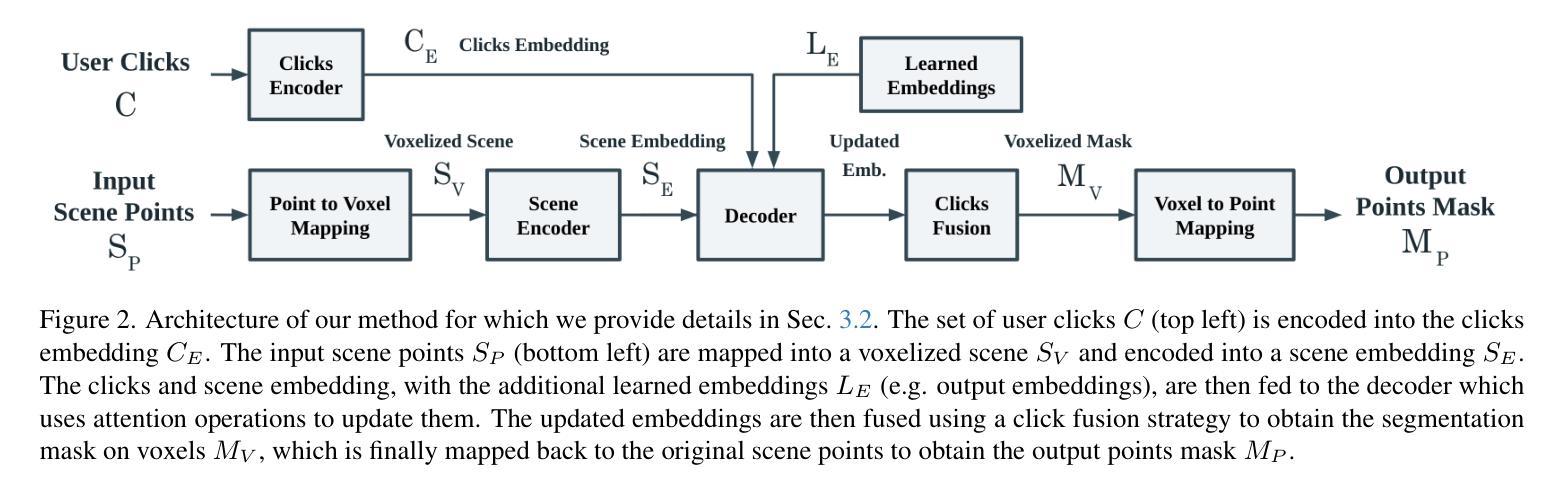
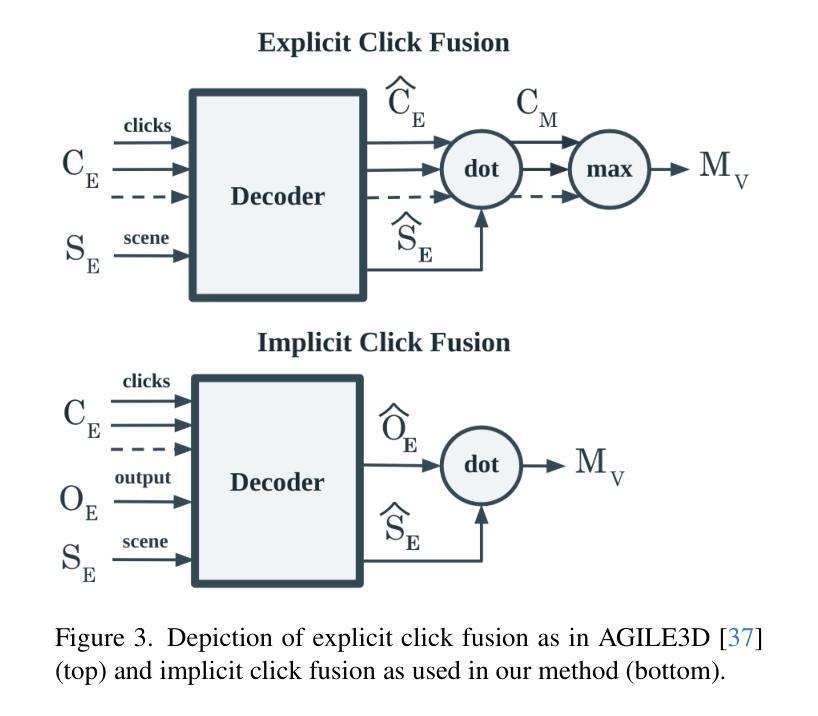
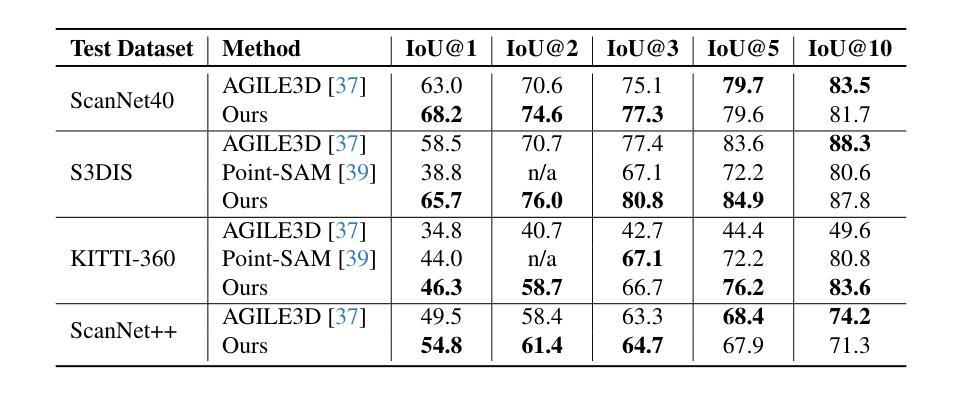
Easy3D: A Simple Yet Effective Method for 3D Interactive Segmentation
Authors:Andrea Simonelli, Norman Müller, Peter Kontschieder
The increasing availability of digital 3D environments, whether through image-based 3D reconstruction, generation, or scans obtained by robots, is driving innovation across various applications. These come with a significant demand for 3D interaction, such as 3D Interactive Segmentation, which is useful for tasks like object selection and manipulation. Additionally, there is a persistent need for solutions that are efficient, precise, and performing well across diverse settings, particularly in unseen environments and with unfamiliar objects. In this work, we introduce a 3D interactive segmentation method that consistently surpasses previous state-of-the-art techniques on both in-domain and out-of-domain datasets. Our simple approach integrates a voxel-based sparse encoder with a lightweight transformer-based decoder that implements implicit click fusion, achieving superior performance and maximizing efficiency. Our method demonstrates substantial improvements on benchmark datasets, including ScanNet, ScanNet++, S3DIS, and KITTI-360, and also on unseen geometric distributions such as the ones obtained by Gaussian Splatting. The project web-page is available at https://simonelli-andrea.github.io/easy3d.
随着基于图像的三维重建、生成或机器人扫描获得的三维数字环境日益普及,正在推动各种应用领域的创新。这引发了大量的三维交互需求,如三维交互分割,这对对象选择和操作等任务非常有用。此外,在多种环境中表现良好且对未知环境和未知对象都能有效处理的解决方案有着持续的需求。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种三维交互分割方法,无论是在领域内还是领域外的数据集上,该方法都始终超越了最新的技术。我们的简单方法结合了基于体素的稀疏编码器和基于轻量级转换器的解码器,实现了隐式点击融合,既保证了高性能又确保了高效率。我们的方法在基准数据集上都表现出了实质性的改进,包括ScanNet、ScanNet++、S3DIS和KITTI-360,以及对高斯飞溅等未见过的几何分布也表现出了改进。项目网页可通过以下链接访问:https://simonelli-andrea.github.io/easy3d。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着数字3D环境的普及,对3D交互的需求不断增长,包括3D交互分割等应用。本文介绍了一种新型的3D交互分割方法,该方法结合了基于体素的稀疏编码器和基于轻量级变压器的解码器,实现了隐式点击融合,在域内和域外数据集上均超越了现有技术。此方法在标准数据集上实现了显著的性能改进,并能在未见过的几何分布上表现良好。
Key Takeaways
- 数字3D环境的普及推动了3D交互的需求。
- 3D交互分割是一个重要应用,用于对象选择和操作。
- 提出的3D交互分割方法结合了基于体素的稀疏编码器和基于轻量级变压器的解码器。
- 该方法实现了隐式点击融合,提高了性能和效率。
- 该方法在多个标准数据集上表现优异,包括ScanNet, ScanNet++, S3DIS和KITTI-360。
- 该方法在未见的几何分布上也能表现良好。
点此查看论文截图

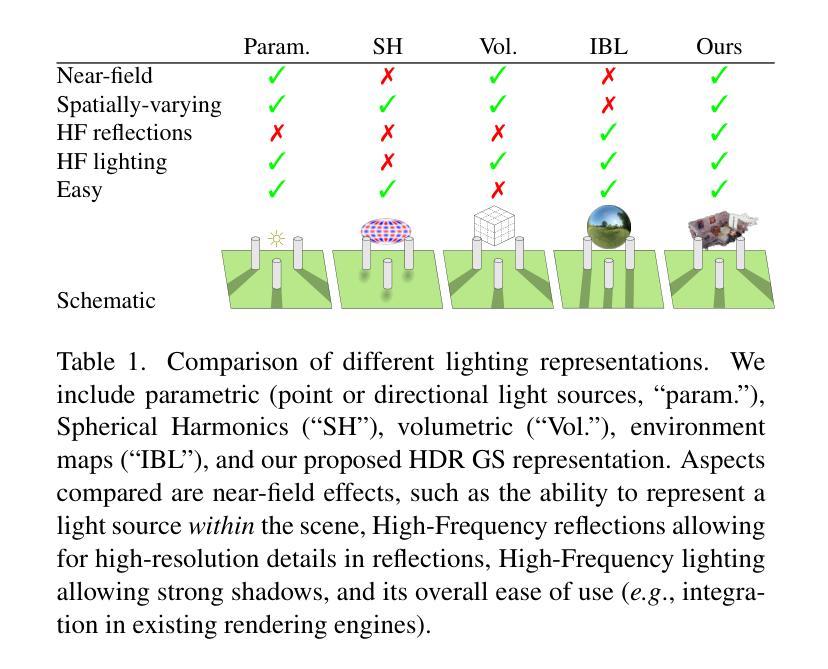
GaSLight: Gaussian Splats for Spatially-Varying Lighting in HDR
Authors:Christophe Bolduc, Yannick Hold-Geoffroy, Zhixin Shu, Jean-François Lalonde
We present GaSLight, a method that generates spatially-varying lighting from regular images. Our method proposes using HDR Gaussian Splats as light source representation, marking the first time regular images can serve as light sources in a 3D renderer. Our two-stage process first enhances the dynamic range of images plausibly and accurately by leveraging the priors embedded in diffusion models. Next, we employ Gaussian Splats to model 3D lighting, achieving spatially variant lighting. Our approach yields state-of-the-art results on HDR estimations and their applications in illuminating virtual objects and scenes. To facilitate the benchmarking of images as light sources, we introduce a novel dataset of calibrated and unsaturated HDR to evaluate images as light sources. We assess our method using a combination of this novel dataset and an existing dataset from the literature. The code to reproduce our method will be available upon acceptance.
我们提出了GaSLight方法,该方法可以从常规图像生成空间变化的光照。我们的方法建议使用HDR高斯斑块作为光源表示,这是首次实现常规图像可以作为3D渲染中的光源。我们的两阶段过程首先利用扩散模型中的先验知识,以合理且准确的方式增强图像的动态范围。接下来,我们使用高斯斑块对3D照明进行建模,实现空间变化的光照。我们的方法在HDR估算及其应用于照明虚拟对象和场景方面产生了最先进的成果。为了将图像作为基准光源进行衡量,我们引入了一个新型的校准且不饱和HDR数据集来评估图像作为光源的能力。我们结合了这种新型数据集和文献中的现有数据集来评估我们的方法。该方法复现的代码将在接受后提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了名为GaSLight的方法,它能从常规图像生成空间变化的光照。该方法首次实现了利用普通图像作为三维渲染的光源。其分为两个阶段,首先利用扩散模型的先验知识来增强图像的动态范围;接着采用高斯斯帕塔模型对三维光照进行建模,实现空间变化的光照效果。该方法在HDR估计及其应用于虚拟对象和场景的照明方面取得了最新成果。同时引入新型数据集评估图像作为光源的性能表现。总体而言,该方法为提高图像渲染的真实感和动态范围提供了新的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- GaSLight方法可从常规图像生成空间变化的光照效果。
- HDR高斯斯帕塔作为光源表示方法,实现了普通图像在三维渲染中的首次应用。
- 方法分为两个阶段:增强图像动态范围和采用高斯斯帕塔模型建模三维光照。
- 该方法在HDR估计和虚拟场景照明方面具有最先进的成果表现。
- 引入新型数据集以评估图像作为光源的效果性能。
- 该方法可以提升图像渲染的真实感和动态范围。
点此查看论文截图

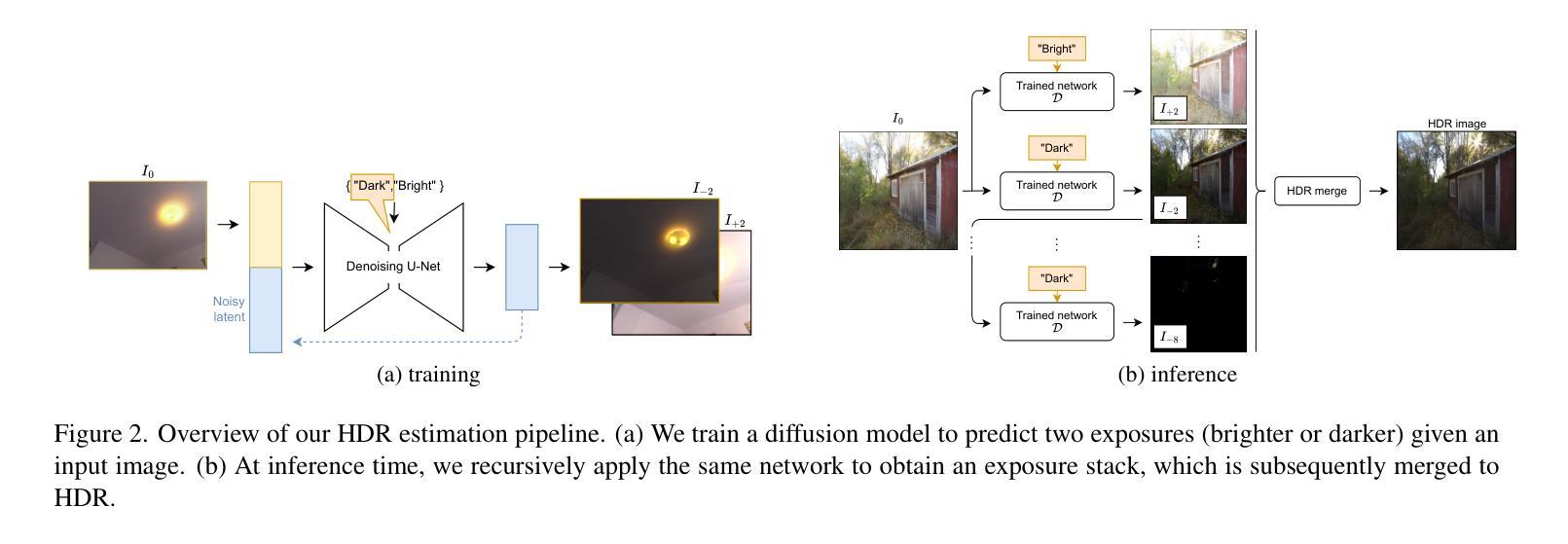
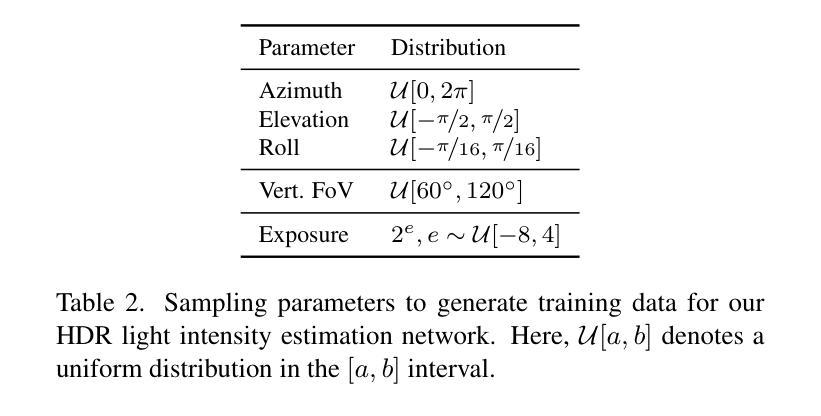
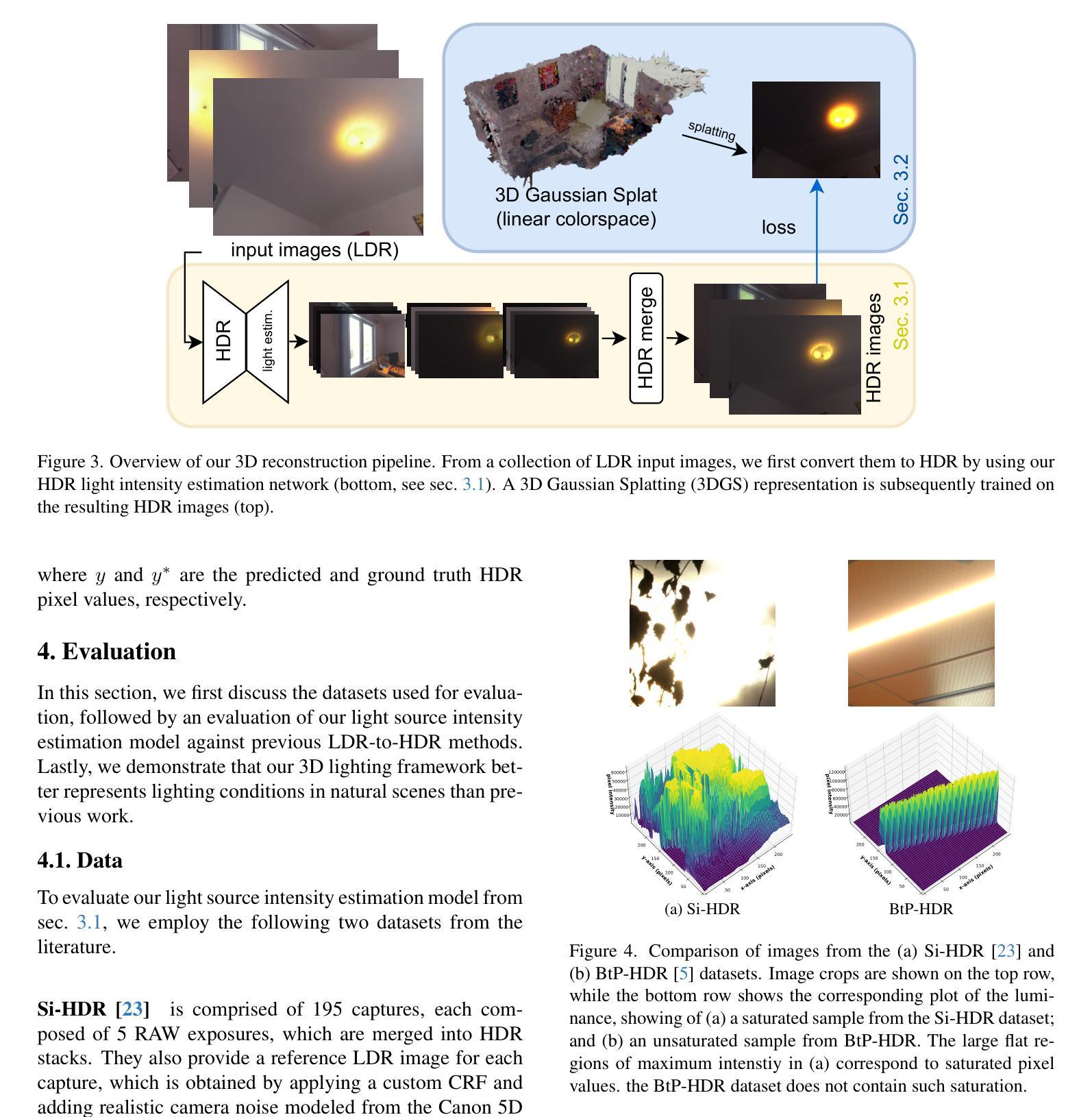
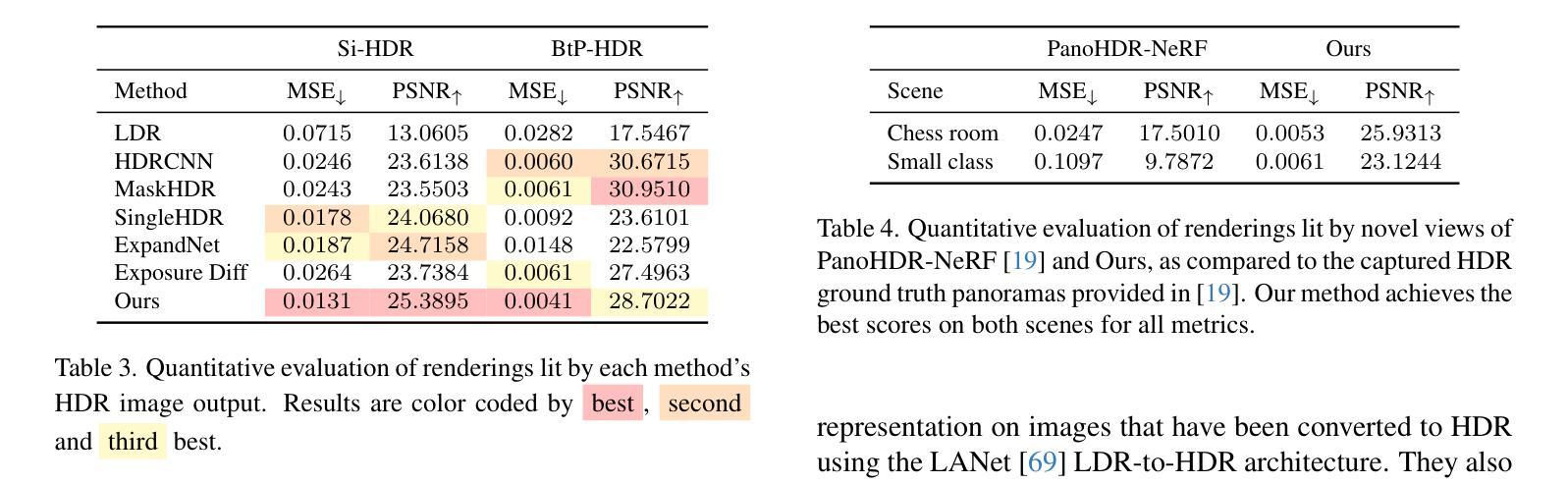
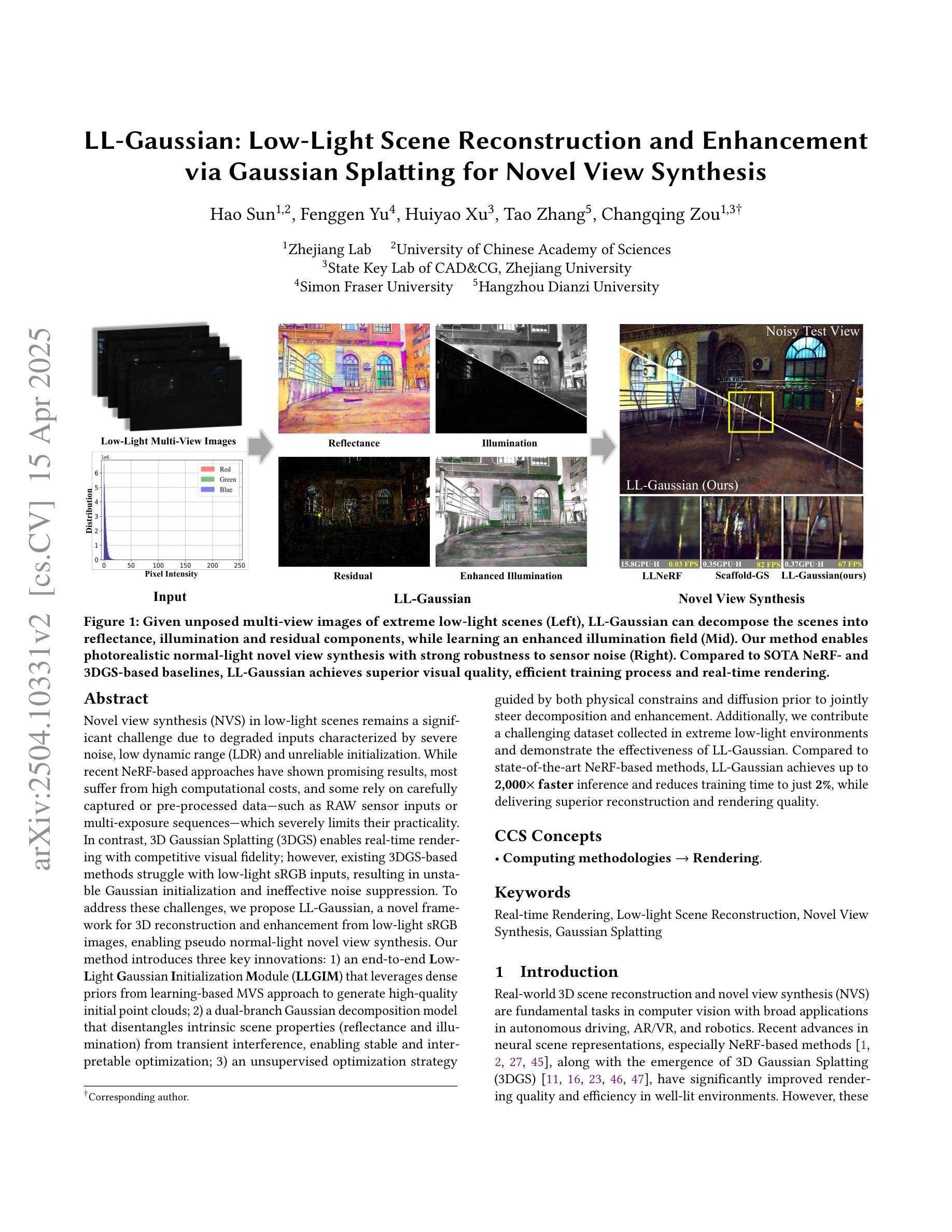
LL-Gaussian: Low-Light Scene Reconstruction and Enhancement via Gaussian Splatting for Novel View Synthesis
Authors:Hao Sun, Fenggen Yu, Huiyao Xu, Tao Zhang, Changqing Zou
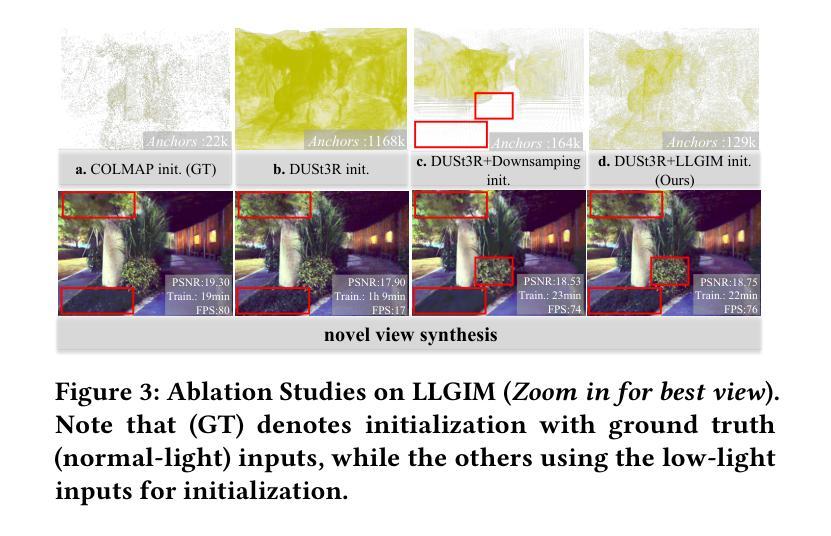
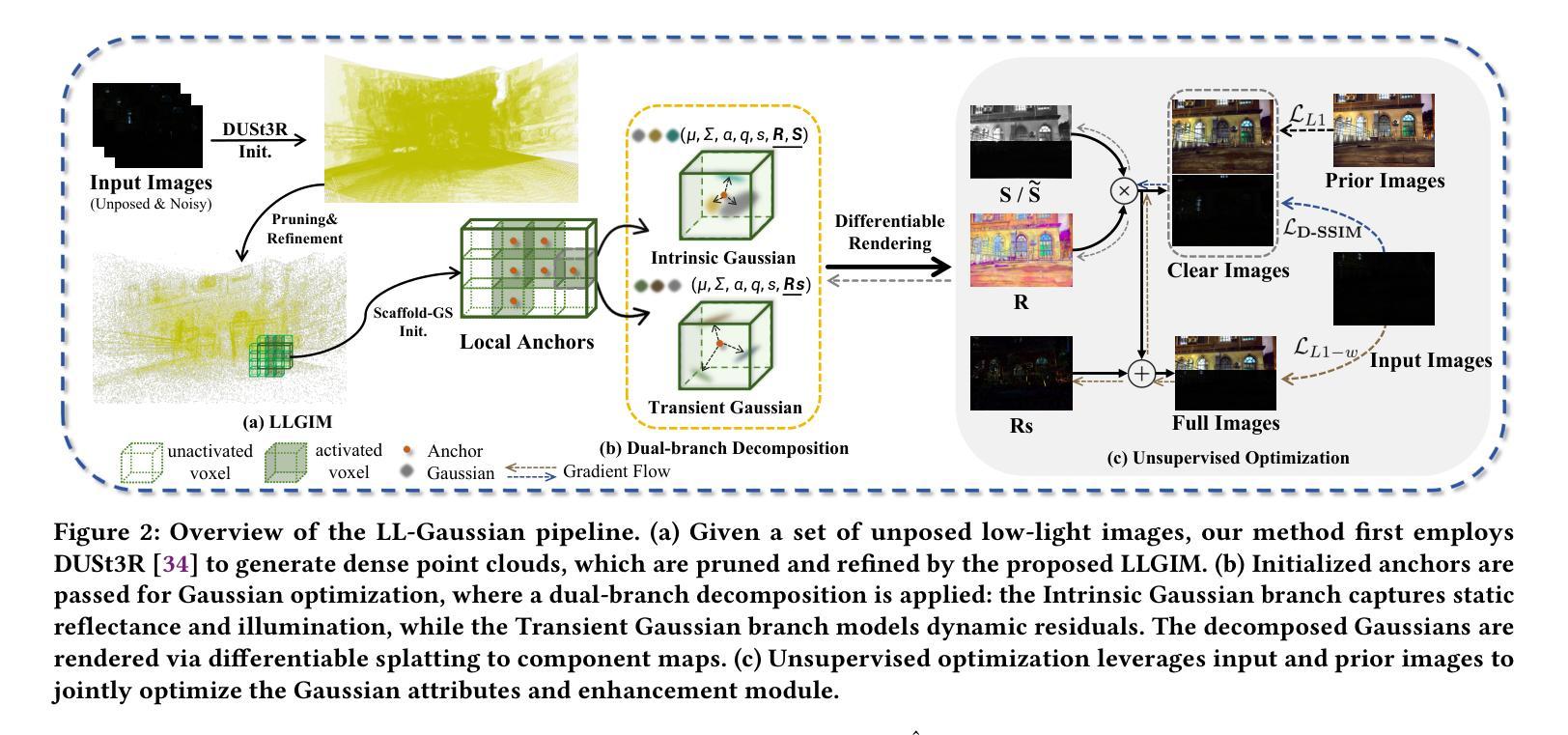
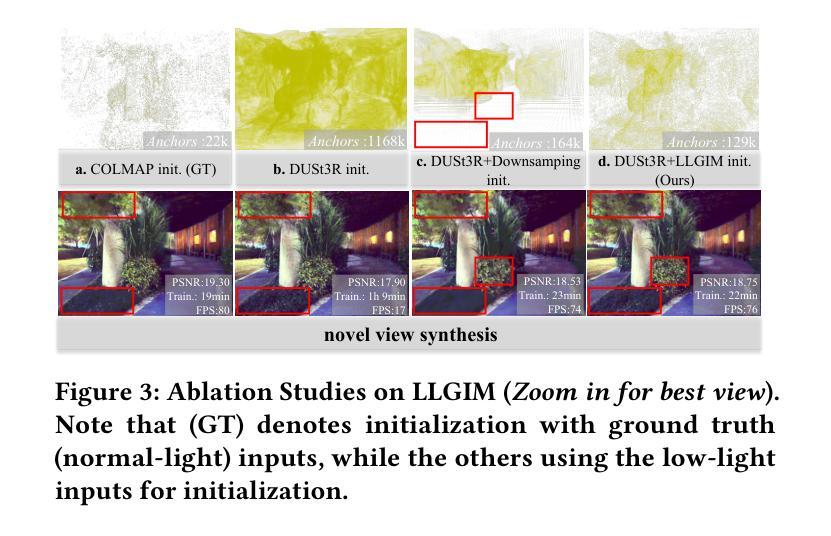
Novel view synthesis (NVS) in low-light scenes remains a significant challenge due to degraded inputs characterized by severe noise, low dynamic range (LDR) and unreliable initialization. While recent NeRF-based approaches have shown promising results, most suffer from high computational costs, and some rely on carefully captured or pre-processed data–such as RAW sensor inputs or multi-exposure sequences–which severely limits their practicality. In contrast, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) enables real-time rendering with competitive visual fidelity; however, existing 3DGS-based methods struggle with low-light sRGB inputs, resulting in unstable Gaussian initialization and ineffective noise suppression. To address these challenges, we propose LL-Gaussian, a novel framework for 3D reconstruction and enhancement from low-light sRGB images, enabling pseudo normal-light novel view synthesis. Our method introduces three key innovations: 1) an end-to-end Low-Light Gaussian Initialization Module (LLGIM) that leverages dense priors from learning-based MVS approach to generate high-quality initial point clouds; 2) a dual-branch Gaussian decomposition model that disentangles intrinsic scene properties (reflectance and illumination) from transient interference, enabling stable and interpretable optimization; 3) an unsupervised optimization strategy guided by both physical constrains and diffusion prior to jointly steer decomposition and enhancement. Additionally, we contribute a challenging dataset collected in extreme low-light environments and demonstrate the effectiveness of LL-Gaussian. Compared to state-of-the-art NeRF-based methods, LL-Gaussian achieves up to 2,000 times faster inference and reduces training time to just 2%, while delivering superior reconstruction and rendering quality.
低光场景中的新颖视图合成(NVS)仍然是一个重大挑战,因为输入退化,表现为严重噪声、低动态范围(LDR)和不可靠的初始化。虽然最近的基于NeRF的方法已经显示出有希望的结果,但大多数方法的计算成本很高,有些方法依赖于精心捕获或预处理的数据,如RAW传感器输入或多曝光序列,这严重限制了其实用性。相比之下,3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)能够实现具有竞争力的视觉保真度的实时渲染;然而,现有的基于3DGS的方法在处理低光sRGB输入时遇到困难,导致高斯初始化不稳定和噪声抑制无效。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了LL-Gaussian,这是一个从低光sRGB图像进行3D重建和增强的新型框架,能够实现伪正常光新颖视图合成。我们的方法引入了三个关键创新点:1)端到端的低光高斯初始化模块(LLGIM),它利用基于学习的MVS方法的密集先验来生成高质量初始点云;2)双分支高斯分解模型,将场景的内在属性(反射和照明)从瞬态干扰中分离出来,实现稳定和可解释的优化;3)由物理约束和扩散先验引导的无监督优化策略,共同引导分解和增强。此外,我们贡献了一个在极端低光环境中收集的挑战性数据集,并展示了LL-Gaussian的有效性。与最先进的基于NeRF的方法相比,LL-Gaussian实现了高达2000倍更快的推理速度,并将训练时间减少到仅2%,同时提供卓越的重建和渲染质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一种针对低光场景的新型视图合成方法LL-Gaussian。该方法基于3D高斯拼贴(3DGS),解决了现有方法在低光sRGB输入下的不稳定高斯初始化和噪声抑制问题。LL-Gaussian通过三个关键创新点实现高效、稳定的低光场景三维重建和增强,包括低光高斯初始化模块(LLGIM)、双分支高斯分解模型和受物理约束和扩散先验引导的无监督优化策略。此外,还贡献了在极端低光环境中收集的具有挑战性的数据集,并展示了LL-Gaussian的有效性。与传统的NeRF方法相比,LL-Gaussian推理速度提高了高达2000倍,训练时间仅减少至2%,同时提供卓越的重构和渲染质量。
Key Takeaways
- LL-Gaussian解决了在低光场景中新型视图合成(NVS)的挑战,包括输入降质、噪声严重、动态范围低和初始化不稳定等问题。
- LL-Gaussian基于3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)实现实时渲染,并保持较高的视觉保真度。
- 该方法引入了三个关键创新点:低光高斯初始化模块(LLGIM)、双分支高斯分解模型和受物理约束和扩散先验引导的无监督优化策略。
- LL-Gaussian能够生成高质量初始点云,通过密集先验信息提高合成的稳定性。
- 双分支高斯分解模型能够将场景的内在属性(反射和照明)与瞬时干扰分离,实现稳定和可解释的优化。
- LL-Gaussian在保证高效性的同时,也大大缩短了训练时间,与传统NeRF方法相比,推理速度更快。
点此查看论文截图

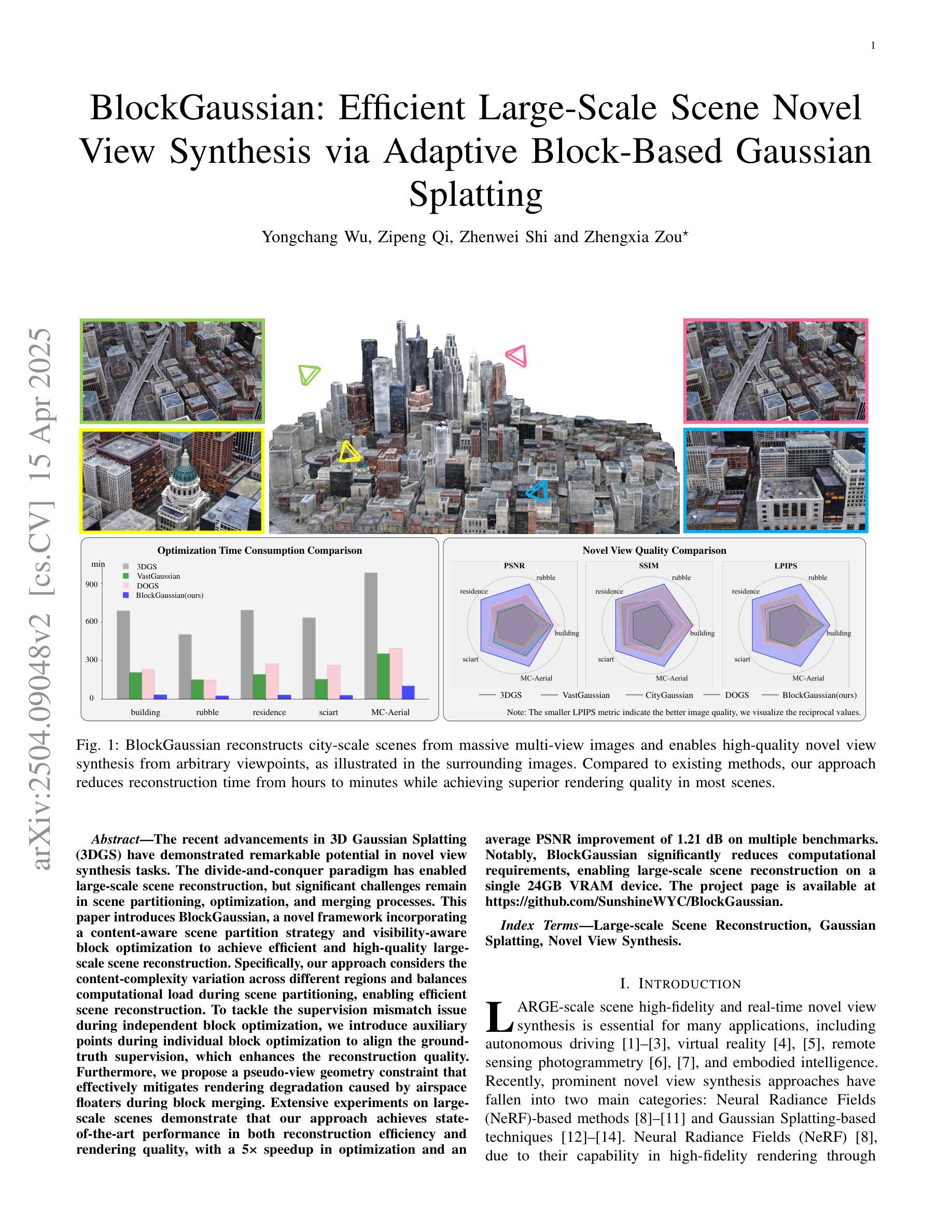
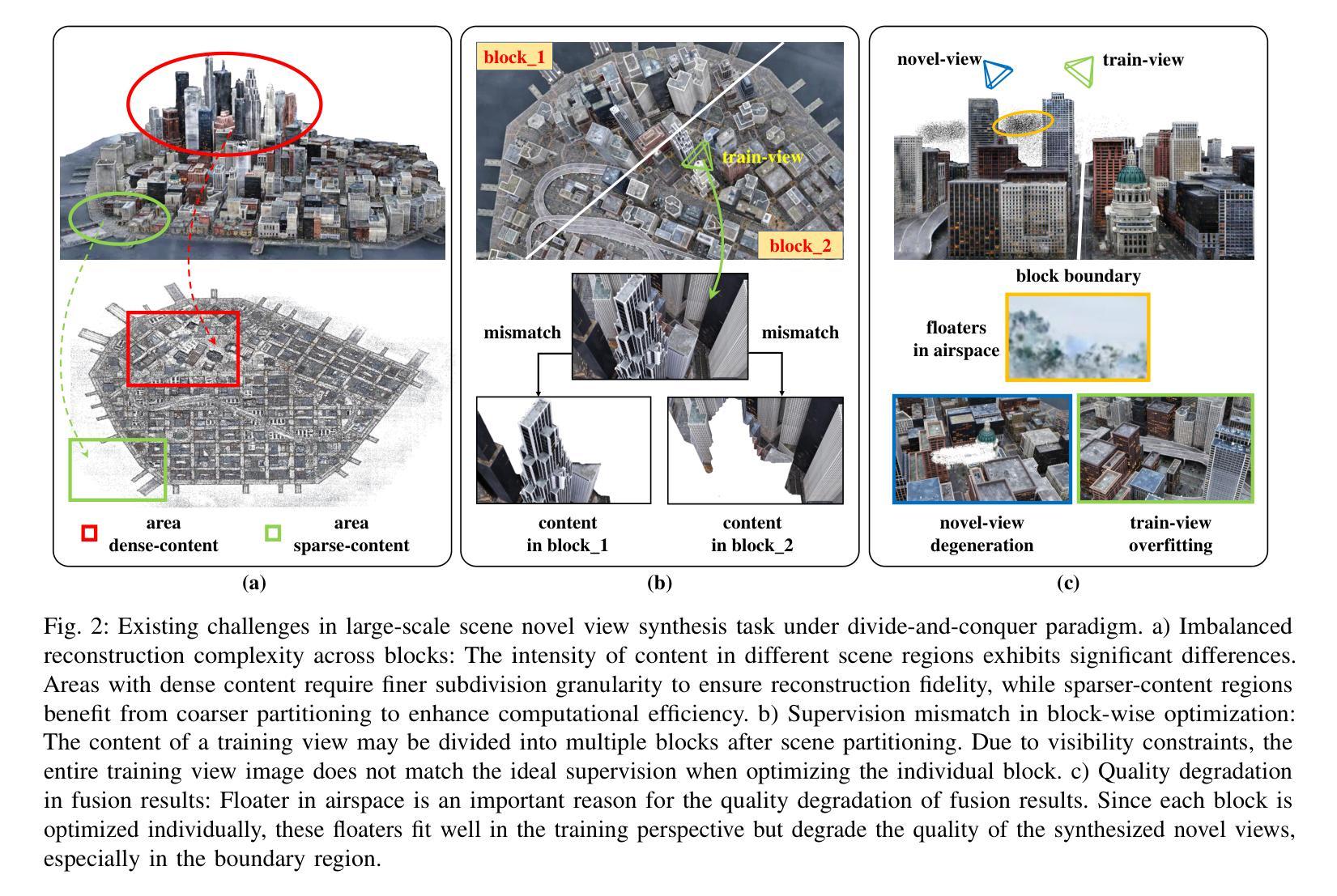
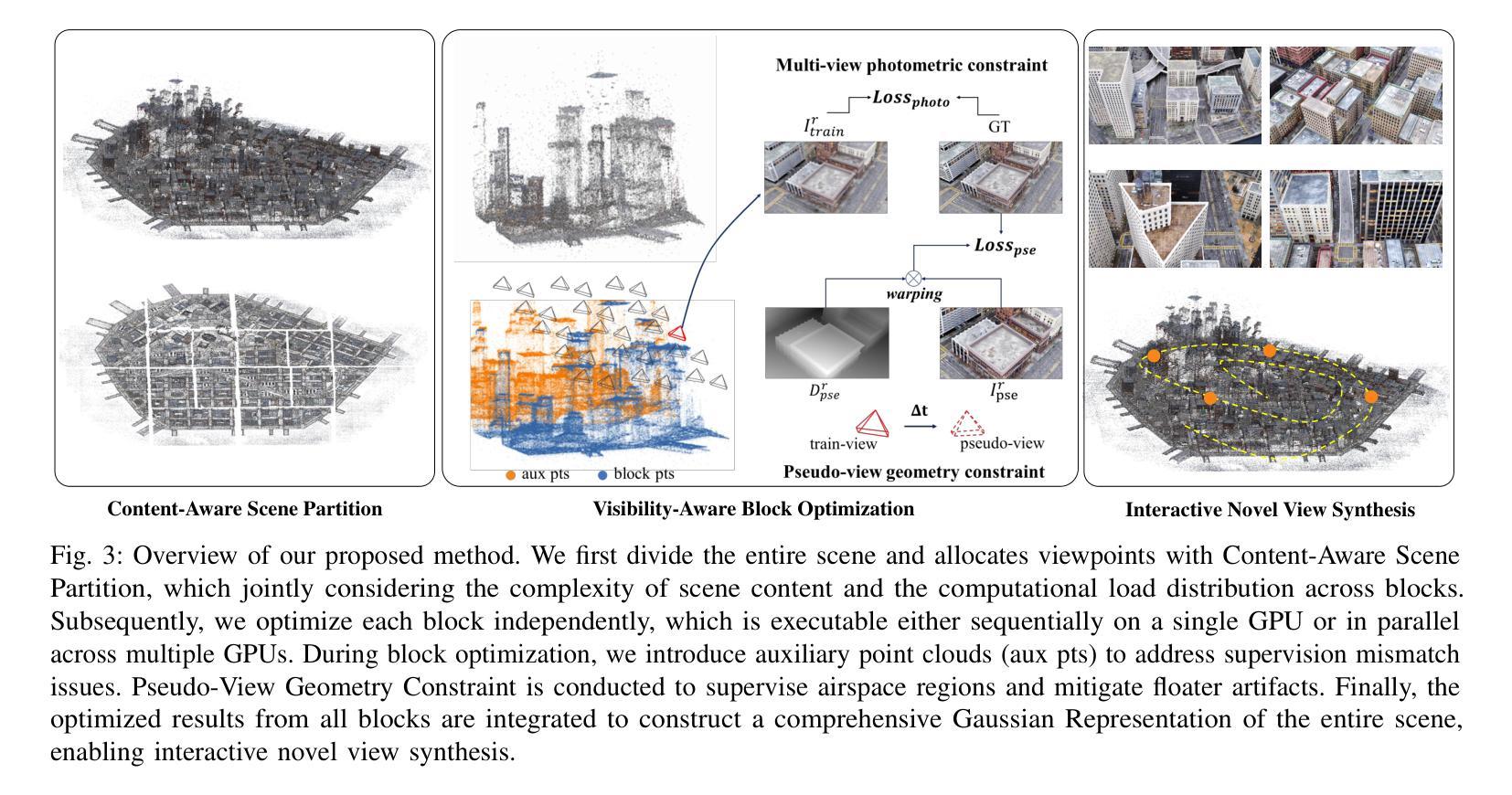
BlockGaussian: Efficient Large-Scale Scene Novel View Synthesis via Adaptive Block-Based Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yongchang Wu, Zipeng Qi, Zhenwei Shi, Zhengxia Zou
The recent advancements in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have demonstrated remarkable potential in novel view synthesis tasks. The divide-and-conquer paradigm has enabled large-scale scene reconstruction, but significant challenges remain in scene partitioning, optimization, and merging processes. This paper introduces BlockGaussian, a novel framework incorporating a content-aware scene partition strategy and visibility-aware block optimization to achieve efficient and high-quality large-scale scene reconstruction. Specifically, our approach considers the content-complexity variation across different regions and balances computational load during scene partitioning, enabling efficient scene reconstruction. To tackle the supervision mismatch issue during independent block optimization, we introduce auxiliary points during individual block optimization to align the ground-truth supervision, which enhances the reconstruction quality. Furthermore, we propose a pseudo-view geometry constraint that effectively mitigates rendering degradation caused by airspace floaters during block merging. Extensive experiments on large-scale scenes demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in both reconstruction efficiency and rendering quality, with a 5x speedup in optimization and an average PSNR improvement of 1.21 dB on multiple benchmarks. Notably, BlockGaussian significantly reduces computational requirements, enabling large-scale scene reconstruction on a single 24GB VRAM device. The project page is available at https://github.com/SunshineWYC/BlockGaussian
近年来,3D高斯扩展(3DGS)的最新进展在新型视图合成任务中显示出显著潜力。分而治之的方法已经实现了大规模场景重建,但在场景分割、优化和合并过程中仍存在重大挑战。本文介绍了BlockGaussian,这是一个结合内容感知场景分割策略和可见性感知块优化的新型框架,以实现高效高质量的大规模场景重建。具体来说,我们的方法考虑到不同区域的内容复杂性变化,并在场景分割过程中平衡计算负载,以实现高效的场景重建。为了解决独立块优化过程中的监督不匹配问题,我们在单个块优化过程中引入辅助点以对齐地面真实监督,从而提高重建质量。此外,我们提出了一种伪视图几何约束,有效减轻了块合并过程中因空中漂浮物造成的渲染质量下降。大规模场景上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在重建效率和渲染质量方面达到了最新性能水平,优化速度提高了5倍,多个基准测试的平均峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高了1.21分贝。值得注意的是,BlockGaussian显著降低了计算要求,能够在单个2
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/SunshineWYC/BlockGaussian
Summary
3DGS技术的新进展在新型视图合成任务中展现出巨大潜力。BlockGaussian框架采用分而治之的策略,引入内容感知的场景分割策略和可见性感知的块优化,实现了高效且高质量的大规模场景重建。它通过考虑内容复杂性的区域变化,平衡计算负载,解决了监督不匹配的问题,并引入伪视图几何约束,有效减轻了渲染退化。该框架显著提高了重建效率和渲染质量,优化速度提升5倍,平均PSNR值在多个基准测试上提高1.21 dB。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术在新型视图合成任务中有显著进展。
- BlockGaussian框架通过分而治之的策略实现大规模场景重建。
- 内容感知的场景分割策略和可见性感知的块优化被引入。
- 考虑内容复杂性的区域变化以平衡计算负载。
- 通过引入辅助点解决独立块优化中的监督不匹配问题。
- 伪视图几何约束有效减轻渲染退化问题。
点此查看论文截图
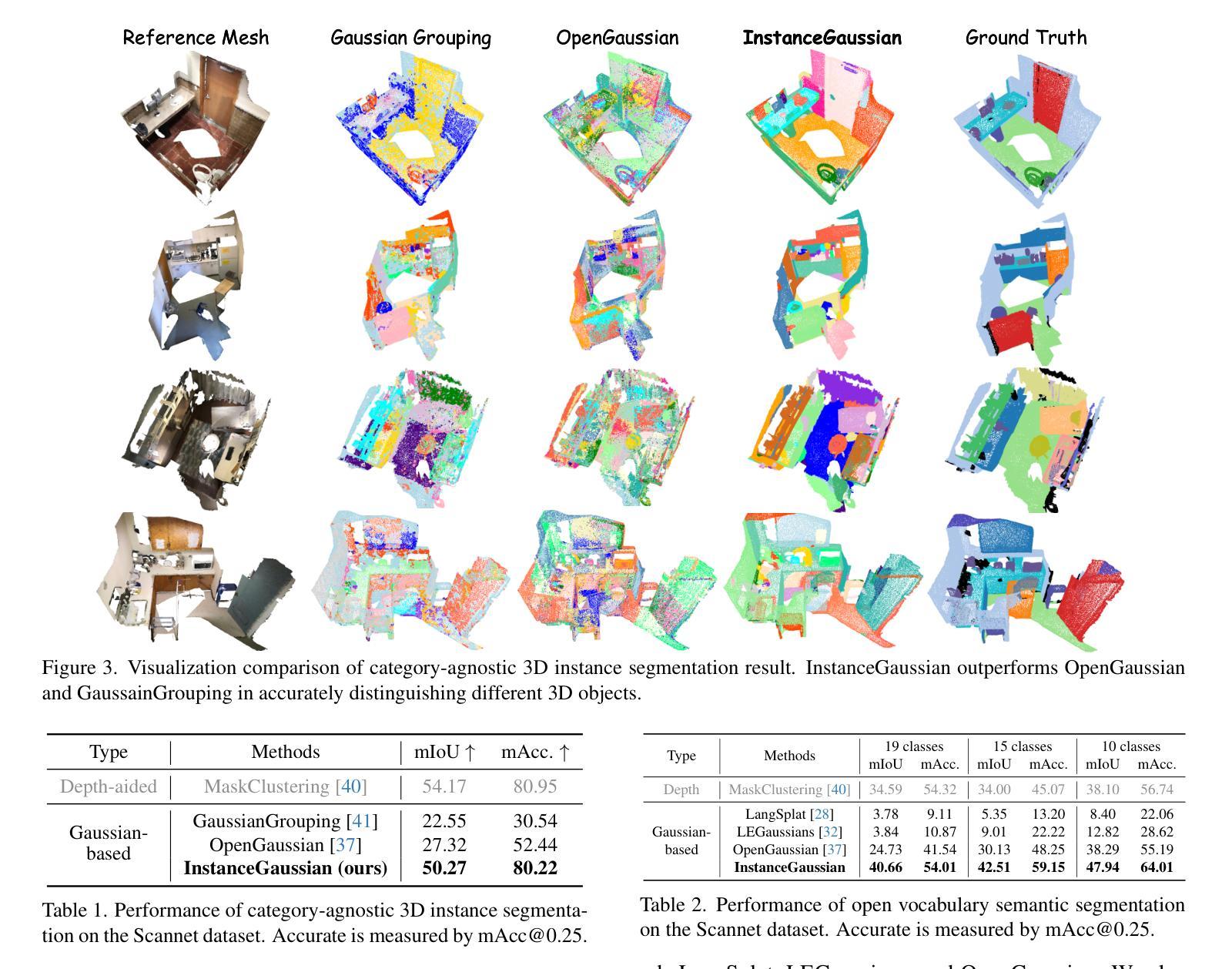
InstanceGaussian: Appearance-Semantic Joint Gaussian Representation for 3D Instance-Level Perception
Authors:Haijie Li, Yanmin Wu, Jiarui Meng, Qiankun Gao, Zhiyao Zhang, Ronggang Wang, Jian Zhang
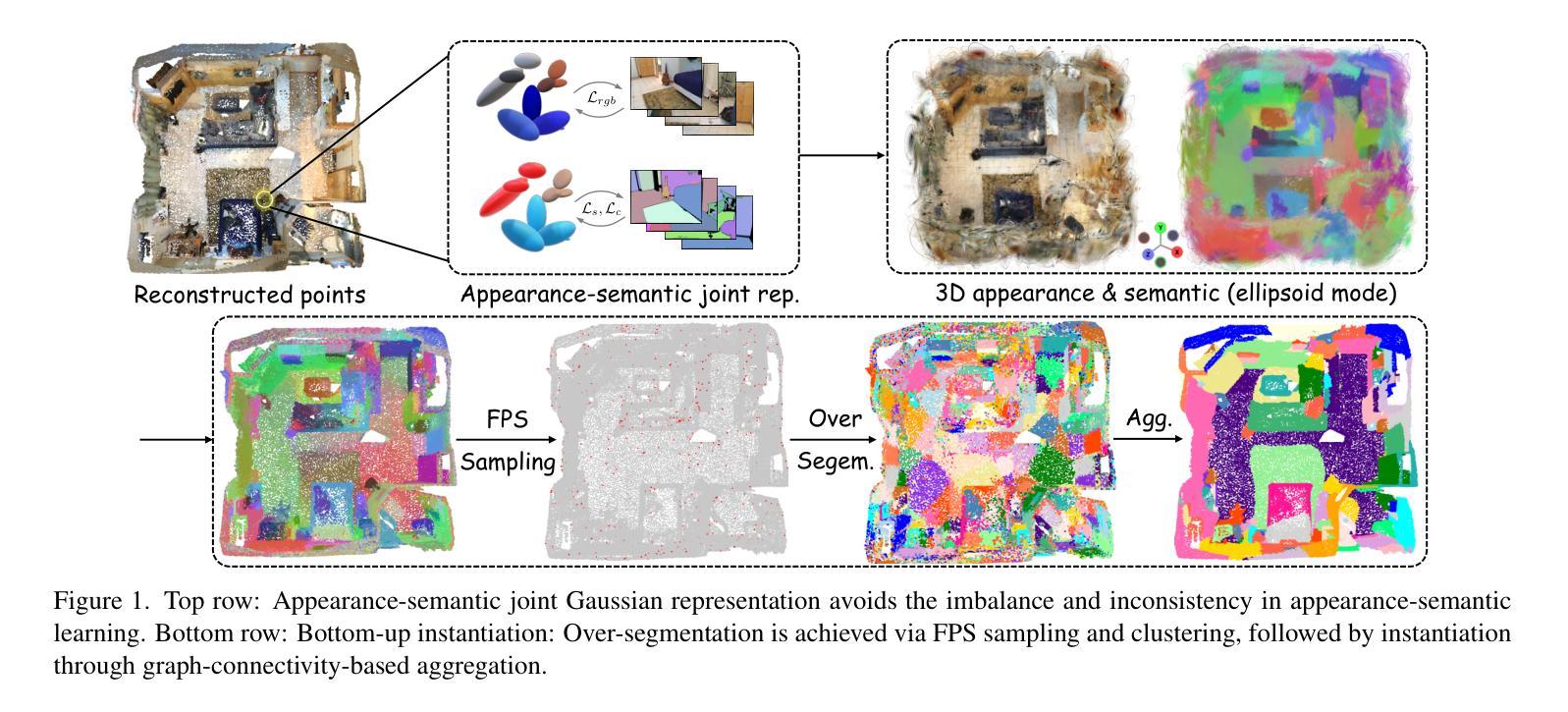
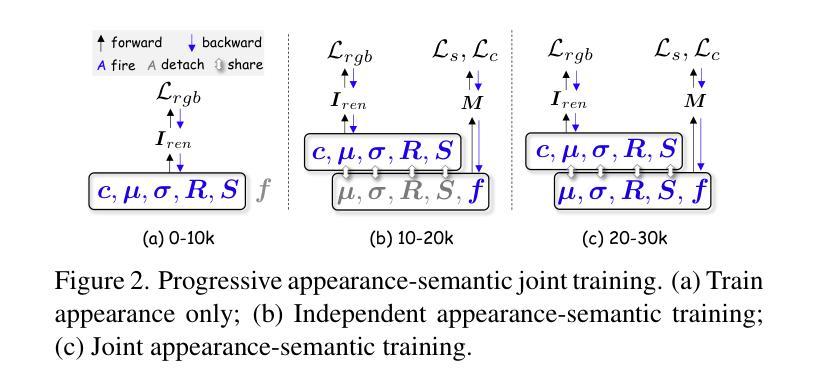
3D scene understanding has become an essential area of research with applications in autonomous driving, robotics, and augmented reality. Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a powerful approach, combining explicit modeling with neural adaptability to provide efficient and detailed scene representations. However, three major challenges remain in leveraging 3DGS for scene understanding: 1) an imbalance between appearance and semantics, where dense Gaussian usage for fine-grained texture modeling does not align with the minimal requirements for semantic attributes; 2) inconsistencies between appearance and semantics, as purely appearance-based Gaussians often misrepresent object boundaries; and 3) reliance on top-down instance segmentation methods, which struggle with uneven category distributions, leading to over- or under-segmentation. In this work, we propose InstanceGaussian, a method that jointly learns appearance and semantic features while adaptively aggregating instances. Our contributions include: i) a novel Semantic-Scaffold-GS representation balancing appearance and semantics to improve feature representations and boundary delineation; ii) a progressive appearance-semantic joint training strategy to enhance stability and segmentation accuracy; and iii) a bottom-up, category-agnostic instance aggregation approach that addresses segmentation challenges through farthest point sampling and connected component analysis. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in category-agnostic, open-vocabulary 3D point-level segmentation, highlighting the effectiveness of the proposed representation and training strategies. Project page: https://lhj-git.github.io/InstanceGaussian/
三维场景理解已成为一个具有重要应用价值的研究领域,广泛应用于自动驾驶、机器人技术和增强现实。最近,三维高斯溅出(3DGS)作为一种强大的方法已经出现,它将显式建模与神经适应性相结合,提供高效且详细的场景表示。然而,在利用3DGS进行场景理解时,仍存在三大挑战:1)外观和语义之间的不平衡,密集的高斯用于精细纹理建模与语义属性所需的最少要求不一致;2)外观和语义之间不一致,仅基于外观的高斯常常会误代表对象边界;3)对自上而下实例分割方法的依赖,这些方法在处理不均匀的类别分布时遇到困难,导致过度分割或分割不足。在这项工作中,我们提出了InstanceGaussian方法,该方法能够联合学习外观和语义特征,同时自适应地聚合实例。我们的贡献包括:i)一种新型Semantic-Scaffold-GS表示,平衡外观和语义,以改进特征表示和边界描绘;ii)一种渐进的外观-语义联合训练策略,以提高稳定性和分割精度;iii)一种自下而上的、与类别无关的实例聚合方法,通过最远点采样和连通组件分析来解决分割挑战。我们的方法在类别无关、开放词汇表的三维点级分割中实现了最先进的性能,凸显了所提出的表示和训练策略的有效性。项目页面:[https://lhj-git.github.io/InstanceGaussian/]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, accepted by CVPR 2025 as poster
Summary
本文介绍了三维场景理解的重要性以及在该领域的新兴技术——3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)。虽然3DGS具有强大的潜力,但在实际应用中仍面临三大挑战。为应对这些挑战,本文提出了一种名为InstanceGaussian的新方法,该方法能够联合学习外观和语义特征,并自适应地聚合实例。该方法通过平衡外观和语义、采用渐进的联合训练策略以及类别无关的实例聚合方法,有效提高了特征表示、边界描绘和分割准确性。该方法的性能在类别无关、开放词汇表的3D点级分割方面达到了领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 3D场景理解是当前的热门研究领域,具有广泛的应用前景。
- 3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)是一种新兴技术,结合了显式建模和神经适应性,为场景表示提供了高效和详细的方法。
- 在利用3DGS进行场景理解时,存在三大挑战:外观与语义的不平衡、外观与语义的不一致以及依赖自上而下的实例分割方法的问题。
- InstanceGaussian方法通过联合学习外观和语义特征、自适应地聚合实例来应对这些挑战。
- InstanceGaussian的贡献包括:提出平衡的语义支架高斯表示、渐进的联合训练策略以及类别无关的实例聚合方法。
点此查看论文截图


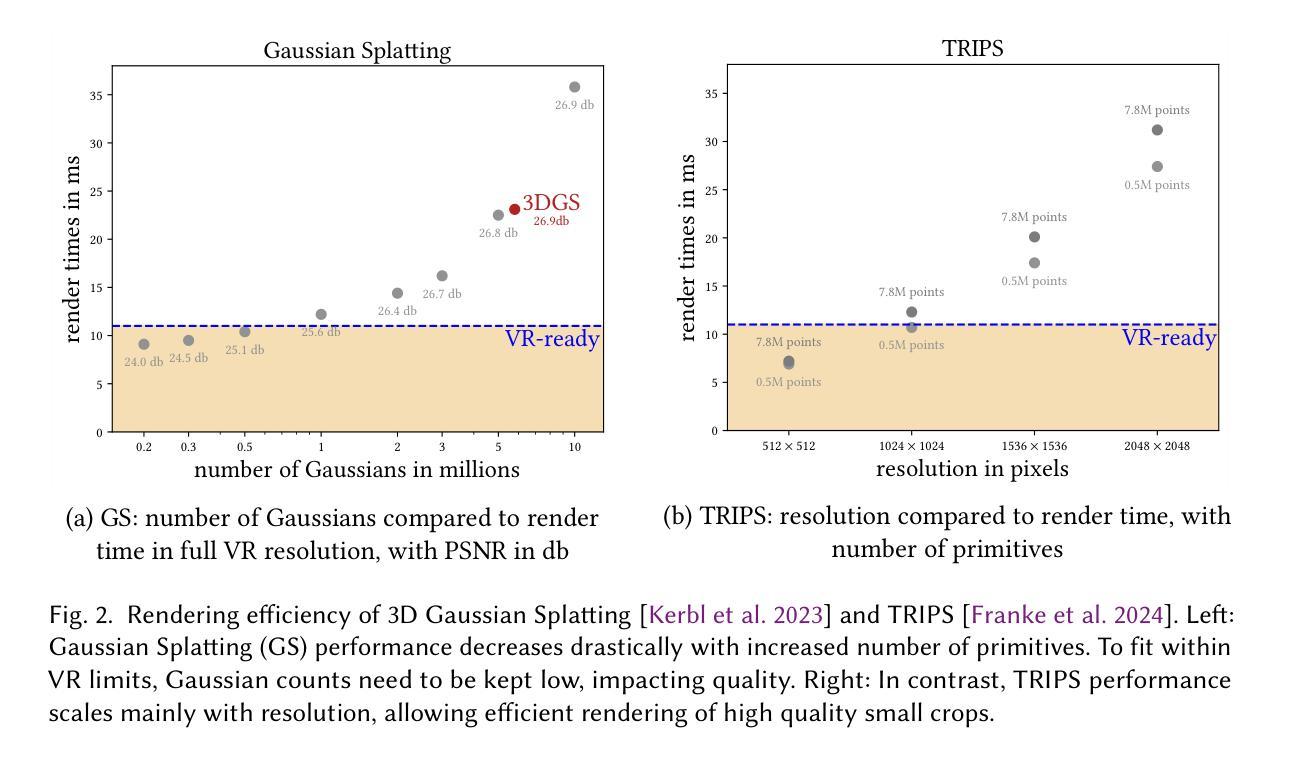
VR-Splatting: Foveated Radiance Field Rendering via 3D Gaussian Splatting and Neural Points
Authors:Linus Franke, Laura Fink, Marc Stamminger
Recent advances in novel view synthesis have demonstrated impressive results in fast photorealistic scene rendering through differentiable point rendering, either via Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) [Kerbl and Kopanas et al. 2023] or neural point rendering [Aliev et al. 2020]. Unfortunately, these directions require either a large number of small Gaussians or expensive per-pixel post-processing for reconstructing fine details, which negatively impacts rendering performance. To meet the high performance demands of virtual reality (VR) systems, primitive or pixel counts therefore must be kept low, affecting visual quality. In this paper, we propose a novel hybrid approach based on foveated rendering as a promising solution that combines the strengths of both point rendering directions regarding performance sweet spots. Analyzing the compatibility with the human visual system, we find that using a low-detailed, few primitive smooth Gaussian representation for the periphery is cheap to compute and meets the perceptual demands of peripheral vision. For the fovea only, we use neural points with a convolutional neural network for the small pixel footprint, which provides sharp, detailed output within the rendering budget. This combination also allows for synergistic method accelerations with point occlusion culling and reducing the demands on the neural network. Our evaluation confirms that our approach increases sharpness and details compared to a standard VR-ready 3DGS configuration, and participants of a user study overwhelmingly preferred our method. Our system meets the necessary performance requirements for real-time VR interactions, ultimately enhancing the user’s immersive experience. The project page can be found at: https://lfranke.github.io/vr_splatting
近期,新型视图合成领域的进展通过可微点渲染展现了令人印象深刻的结果,无论是通过高斯展布(3DGS)[Kerbl和Kopanas等人,2023年]还是神经点渲染[Aliev等人,2020年],在快速的光照逼真的场景渲染中都取得了显著成果。然而,这些方向需要大量的小高斯或昂贵的逐像素后处理来重建细节,这会对渲染性能产生负面影响。为了满足虚拟现实(VR)系统的高性能需求,因此必须保持低元或像素计数,从而影响视觉质量。
在本文中,我们提出了一种基于注视点渲染的新型混合方法,作为一种有前途的解决方案,结合了这两种点渲染方向在性能优势方面的优点。通过分析与人类视觉系统的兼容性,我们发现使用低细节、少量平滑高斯表示周边区域计算成本低,并符合周边视觉的感知要求。对于中心视力区域,我们使用带有卷积神经网络的神视点进行小像素足迹处理,从而在渲染预算内提供清晰、详细的输出。这种结合还允许通过点遮挡剔除进行协同方法加速,减少对神经网络的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出了一种基于凝视渲染的混合方法,该方法结合了点渲染方向的优势,针对虚拟现实(VR)系统的高性能需求,采用低细节、少原始平滑高斯表示周边视觉,仅在凝视区使用神经网络点进行精细渲染。此方法提高了渲染性能,增强了用户的沉浸式体验。
Key Takeaways
- 研究背景:介绍了近期在新型视图合成方面的进展,特别是通过可微分的点渲染技术(包括高斯贴图和神经点渲染)在快速逼真场景渲染方面取得的成果。
- 面临的挑战:现有的方法需要大量的小高斯或昂贵的逐像素后处理来重建细节,这对渲染性能产生负面影响。在VR系统中,为了性能需求,原始或像素计数必须保持较低水平,从而影响视觉质量。
- 解决方案:提出了一种基于凝视渲染的混合方法,结合点渲染的优势,对于周边视觉采用低细节、少原始平滑高斯表示,仅在凝视区使用神经网络点进行精细渲染。这种方法的计算成本低,并满足周边视觉的感知要求。
- 方法优势:该混合方法允许协同方法加速,如点遮挡剔除,并降低对神经网络的需求。
- 实验结果:与标准VR准备的3DGS配置相比,该方法提高了清晰度和细节。用户研究的结果也支持该方法的优越性。
- 性能表现:该方法满足实时VR交互所需的性能要求,增强了用户的沉浸式体验。
点此查看论文截图


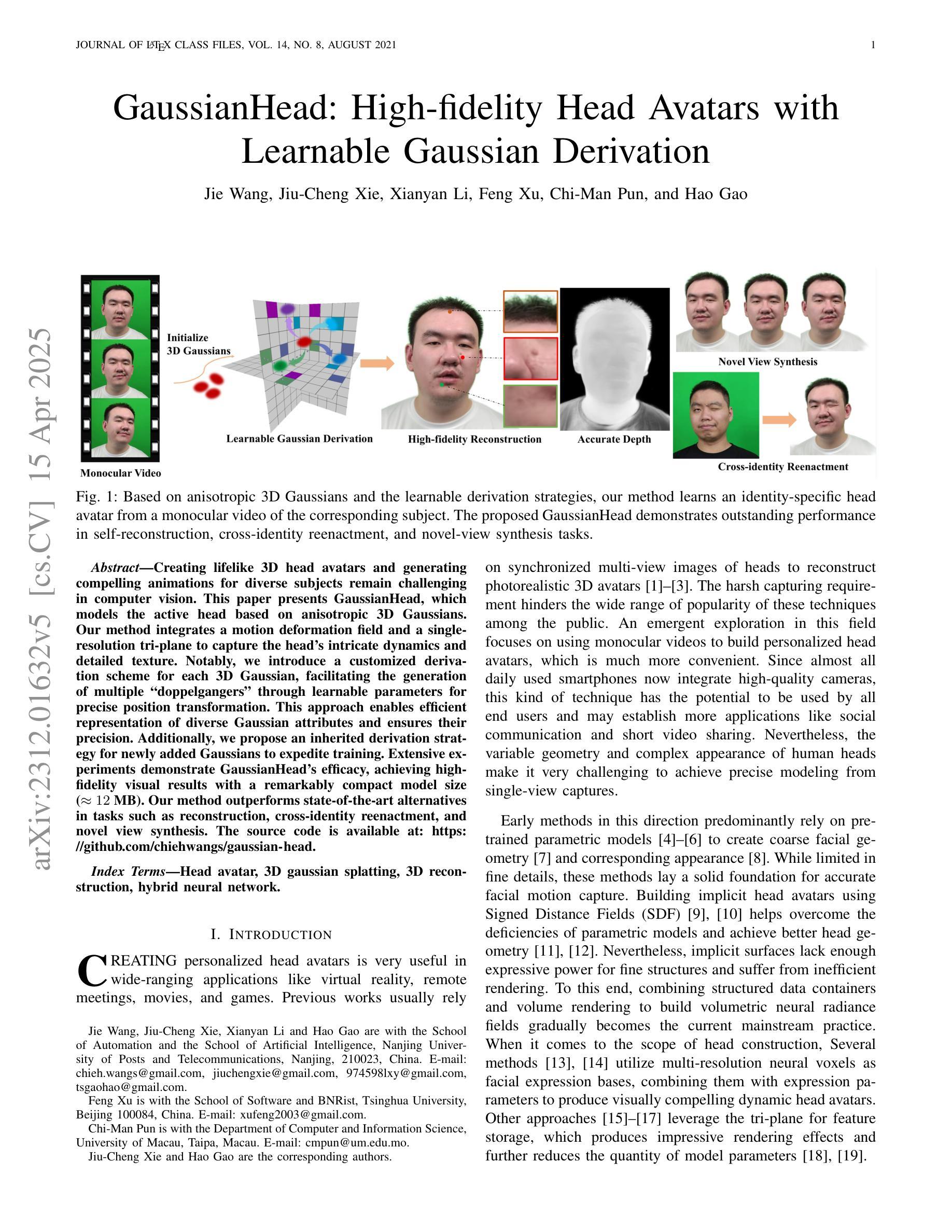
GaussianHead: High-fidelity Head Avatars with Learnable Gaussian Derivation
Authors:Jie Wang, Jiu-Cheng Xie, Xianyan Li, Feng Xu, Chi-Man Pun, Hao Gao
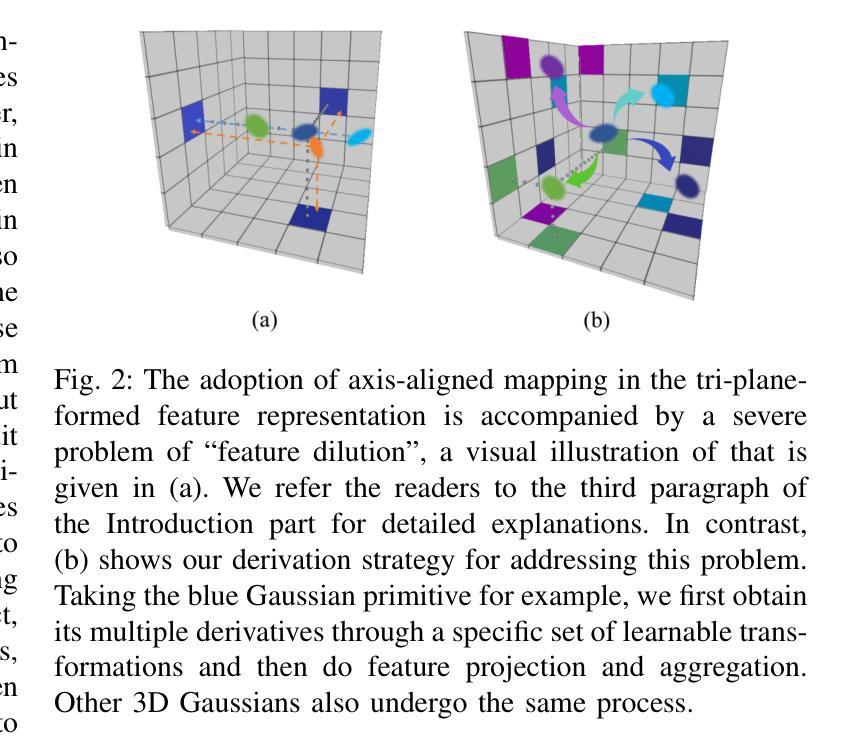
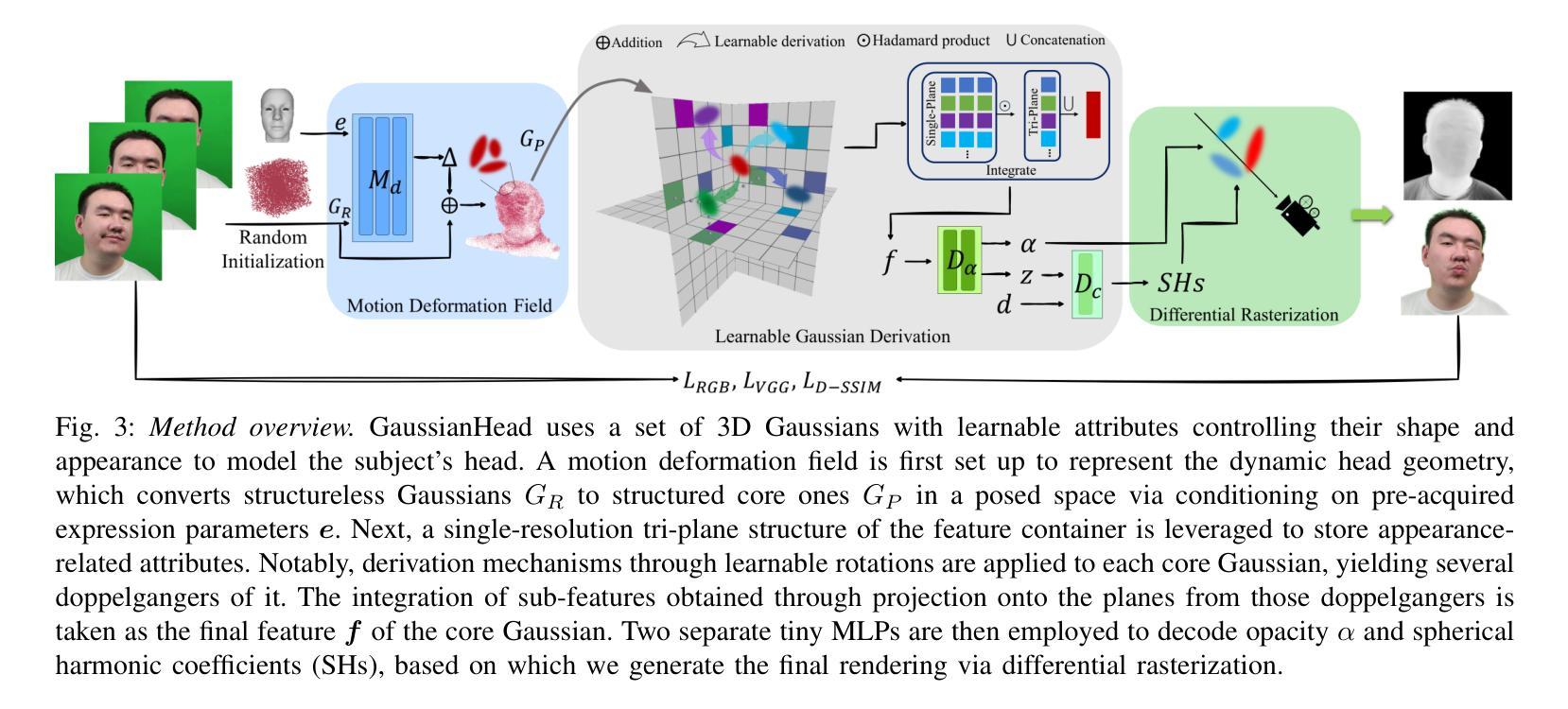
Constructing vivid 3D head avatars for given subjects and realizing a series of animations on them is valuable yet challenging. This paper presents GaussianHead, which models the actional human head with anisotropic 3D Gaussians. In our framework, a motion deformation field and multi-resolution tri-plane are constructed respectively to deal with the head’s dynamic geometry and complex texture. Notably, we impose an exclusive derivation scheme on each Gaussian, which generates its multiple doppelgangers through a set of learnable parameters for position transformation. With this design, we can compactly and accurately encode the appearance information of Gaussians, even those fitting the head’s particular components with sophisticated structures. In addition, an inherited derivation strategy for newly added Gaussians is adopted to facilitate training acceleration. Extensive experiments show that our method can produce high-fidelity renderings, outperforming state-of-the-art approaches in reconstruction, cross-identity reenactment, and novel view synthesis tasks. Our code is available at: https://github.com/chiehwangs/gaussian-head.
构建生动逼真的三维头像并对其进行动画制作具有重要的价值且极具挑战性。本文提出了GaussianHead,它使用各向异性三维高斯模型对动作人头进行建模。在我们的框架中,分别构建了运动变形场和多分辨率tri-plane,用于处理头部动态的几何形状和复杂的纹理。值得注意的是,我们对每个高斯施加了一种独特的推导方案,通过一组可学习的参数生成其多个分身,用于位置变换。通过这种设计,我们可以紧凑且准确地编码高斯的外貌信息,甚至可以很好地适应头部具有复杂结构的特定部位。此外,对于新添加的高斯,我们还采用了一种继承的推导策略,以加快训练速度。大量实验表明,我们的方法可以生成高保真度的渲染效果,在重建、跨身份重建和新颖视图合成任务方面优于最先进的方法。我们的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/chiehwangs/gaussian-head。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 14 figures, published to TVCG
Summary
本文介绍了GaussianHead方法,该方法使用各向异性3D高斯建模动态人类头部。通过构建运动变形场和多分辨率平面,该方法能够处理头部的动态几何和复杂纹理。设计了一种独特的推导方案,通过一组可学习参数生成高斯分布的多个复制品,实现位置转换。此外,采用继承推导策略加速新高斯分布的训练。实验表明,该方法可以生成高保真渲染,在重建、跨身份重建和新颖视角合成任务上优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- GaussianHead使用各向异性3D高斯对动态人类头部进行建模。
- 通过构建运动变形场和多分辨率平面,处理头部的动态几何和复杂纹理。
- 设计了一种独特的推导方案,通过可学习参数生成高斯分布的复制品,实现位置转换。
- 采用继承推导策略加速新高斯分布的训练过程。
- 该方法可以生成高保真渲染。
- GaussianHead在重建、跨身份重建任务上表现出优越性能。
点此查看论文截图