⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-17 更新
Aligning Generative Denoising with Discriminative Objectives Unleashes Diffusion for Visual Perception
Authors:Ziqi Pang, Xin Xu, Yu-Xiong Wang
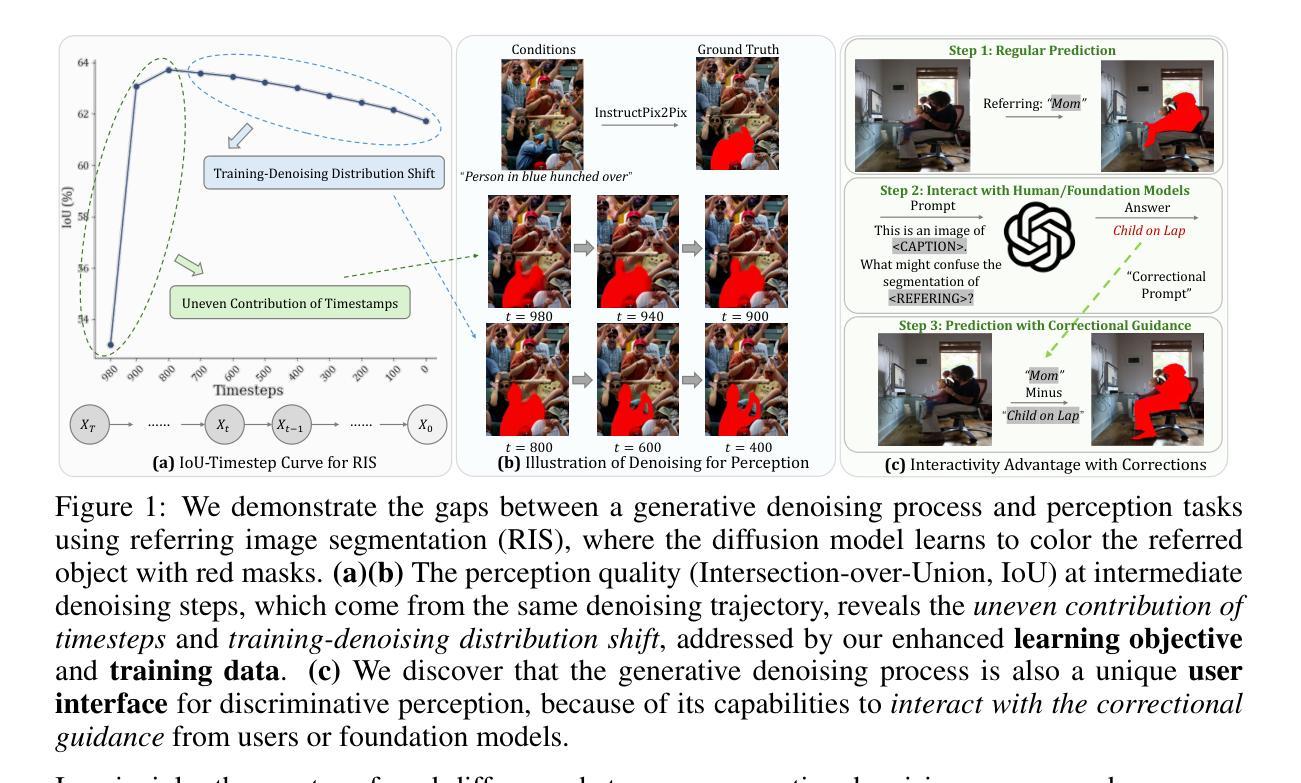
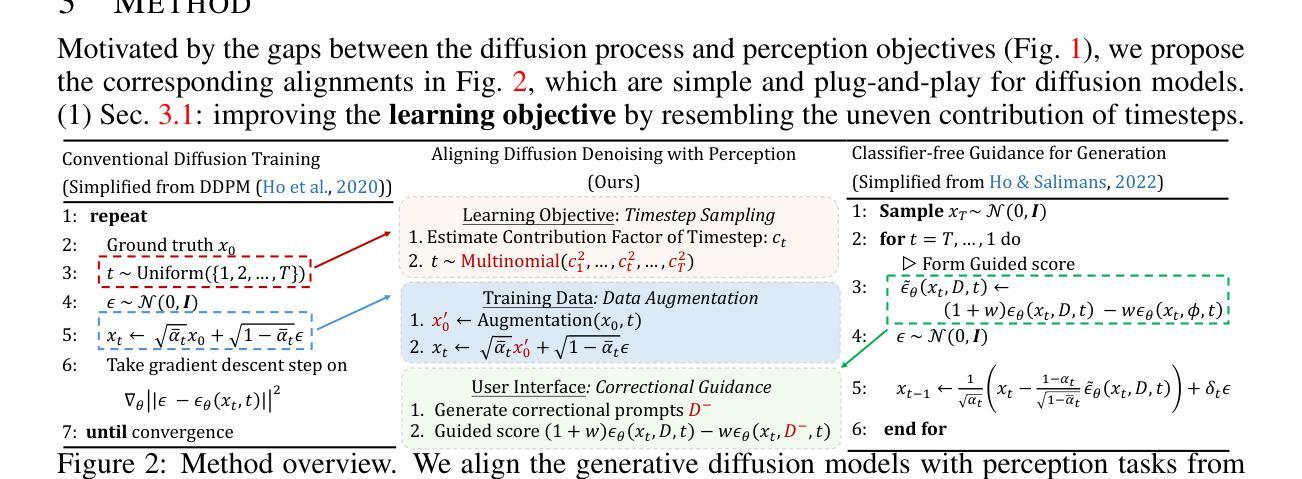
With the success of image generation, generative diffusion models are increasingly adopted for discriminative tasks, as pixel generation provides a unified perception interface. However, directly repurposing the generative denoising process for discriminative objectives reveals critical gaps rarely addressed previously. Generative models tolerate intermediate sampling errors if the final distribution remains plausible, but discriminative tasks require rigorous accuracy throughout, as evidenced in challenging multi-modal tasks like referring image segmentation. Motivated by this gap, we analyze and enhance alignment between generative diffusion processes and perception tasks, focusing on how perception quality evolves during denoising. We find: (1) earlier denoising steps contribute disproportionately to perception quality, prompting us to propose tailored learning objectives reflecting varying timestep contributions; (2) later denoising steps show unexpected perception degradation, highlighting sensitivity to training-denoising distribution shifts, addressed by our diffusion-tailored data augmentation; and (3) generative processes uniquely enable interactivity, serving as controllable user interfaces adaptable to correctional prompts in multi-round interactions. Our insights significantly improve diffusion-based perception models without architectural changes, achieving state-of-the-art performance on depth estimation, referring image segmentation, and generalist perception tasks. Code available at https://github.com/ziqipang/ADDP.
随着图像生成的成功,生成扩散模型越来越多地被用于判别任务,因为像素生成提供了一个统一的感知接口。然而,直接将生成去噪过程用于判别目标会暴露出之前很少解决的关键差距。生成模型如果最终分布仍然可行的话,可以容忍中间采样错误,但判别任务需要始终严格的准确性,如指代图像分割等具有挑战性的多模式任务所证明。受此差距的驱动,我们分析和提高了生成扩散过程和感知任务之间的对齐性,重点关注去噪过程中感知质量如何发展。我们发现:(1)早期的去噪步骤对感知质量的贡献不成比例,促使我们提出反映不同时间步长贡献的定制学习目标;(2)后期的去噪步骤显示出意外的感知退化,突出显示对训练-去噪分布变化的敏感性,这可以通过我们针对扩散定制的数据增强来解决;(3)生成过程具有独特的交互性,可作为可控制的用户界面,适应多轮交互中的纠正提示。我们的见解在不需要架构更改的情况下,显著改进了基于扩散的感知模型,在深度估计、指代图像分割和通用感知任务上实现了最先进的性能。代码可访问 https://github.com/ziqipang/ADDP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
本文探讨了生成性扩散模型在判别任务中的应用,分析了将生成性去噪过程直接应用于判别目标时存在的问题。针对这些问题,本文重点研究了生成扩散过程与感知任务之间的对齐问题,并发现早期去噪步骤对感知质量的贡献不均等,提出了反映不同时间步长贡献的学习目标。此外,还发现后期去噪步骤会出现意外的感知退化问题,对此本文通过扩散定制的数据增强方法来解决。最后,本文还探讨了生成过程的交互性特点,实现了多轮交互中的纠正提示功能。这些发现有助于提高扩散模型的感知性能,在深度估计、引用图像分割和通用感知任务上实现了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 生成性扩散模型在判别任务中的应用逐渐增多,但直接将生成性去噪过程用于判别任务存在关键差距。
- 早期去噪步骤对感知质量的贡献较大,提出需反映不同时间步长贡献的学习目标。
- 后期去噪步骤可能出现意外的感知退化,这主要是由于训练与去噪分布之间的变化,需要通过扩散定制的数据增强来解决。
- 生成过程具有交互性特点,适用于多轮交互中的纠正提示。
- 这些发现显著提高扩散模型的感知性能,实现深度估计、引用图像分割和通用感知任务的先进性能。
- 相关工作代码已公开在GitHub上共享。
点此查看论文截图

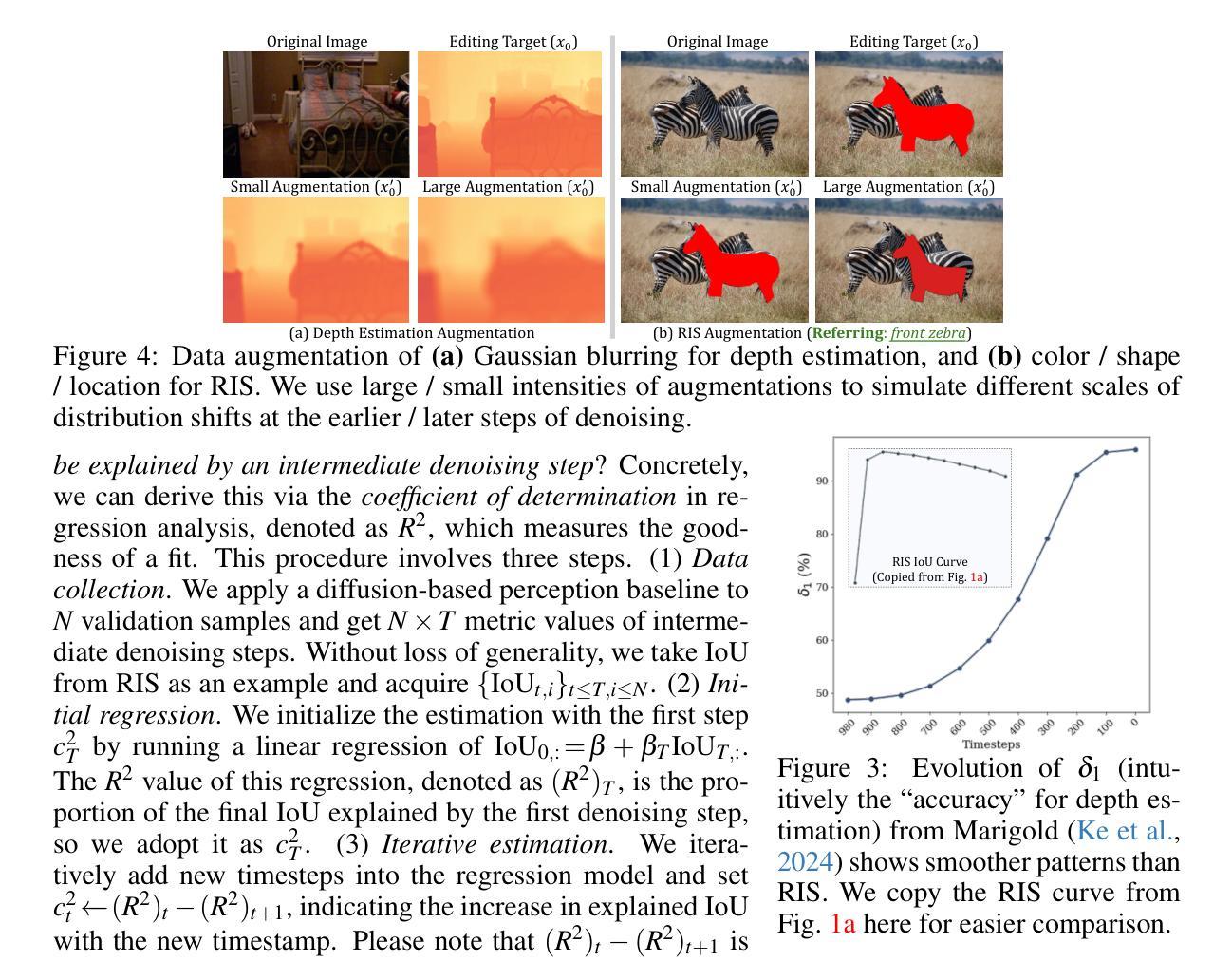
ADT: Tuning Diffusion Models with Adversarial Supervision
Authors:Dazhong Shen, Guanglu Song, Yi Zhang, Bingqi Ma, Lujundong Li, Dongzhi Jiang, Zhuofan Zong, Yu Liu
Diffusion models have achieved outstanding image generation by reversing a forward noising process to approximate true data distributions. During training, these models predict diffusion scores from noised versions of true samples in a single forward pass, while inference requires iterative denoising starting from white noise. This training-inference divergences hinder the alignment between inference and training data distributions, due to potential prediction biases and cumulative error accumulation. To address this problem, we propose an intuitive but effective fine-tuning framework, called Adversarial Diffusion Tuning (ADT), by stimulating the inference process during optimization and aligning the final outputs with training data by adversarial supervision. Specifically, to achieve robust adversarial training, ADT features a siamese-network discriminator with a fixed pre-trained backbone and lightweight trainable parameters, incorporates an image-to-image sampling strategy to smooth discriminative difficulties, and preserves the original diffusion loss to prevent discriminator hacking. In addition, we carefully constrain the backward-flowing path for back-propagating gradients along the inference path without incurring memory overload or gradient explosion. Finally, extensive experiments on Stable Diffusion models (v1.5, XL, and v3), demonstrate that ADT significantly improves both distribution alignment and image quality.
扩散模型通过逆转正向噪声过程来近似真实数据分布,从而实现了出色的图像生成。在训练过程中,这些模型在一次前向传递中从真实样本的噪声版本预测扩散分数,而推理则需要从白噪声开始进行迭代去噪。由于潜在的预测偏差和累积误差的累积,这种训练与推理之间的差异阻碍了推理和训练数据分布之间的对齐。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种直观而有效的微调框架,称为对抗性扩散调整(ADT),通过优化过程中刺激推理过程,并通过对抗性监督使最终输出与训练数据对齐。具体而言,为了进行稳健的对抗性训练,ADT使用一个带有固定预训练主干和轻量级可训练参数的Siamese网络鉴别器,采用图像到图像的采样策略来平滑鉴别难度,并保留原始扩散损失以防止鉴别器被攻击。此外,我们小心地约束反向传播路径,以便在推理路径上反向传播梯度,而不会导致内存过载或梯度爆炸。最后,对Stable Diffusion模型(v1.5、XL和v3)的大量实验表明,ADT显著提高了分布对齐和图像质量。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
扩散模型通过反转前向噪声过程来近似真实数据分布,实现了出色的图像生成。训练过程中,模型从真实样本的噪声版本预测扩散分数,推理则需要从白噪声开始进行迭代去噪。这种训练与推理的偏差可能导致预测偏差和累积误差的累积,进而影响推理与训练数据分布的对齐。为解决这一问题,我们提出了名为“对抗性扩散调整”(ADT)的微调框架,通过优化过程中刺激推理过程并实现最终输出与训练数据的对齐。ADT采用具有固定预训练主干和轻量级可训练参数的孪生网络鉴别器,采用图像到图像的采样策略来解决鉴别困难,并保留原始扩散损失以防止鉴别器黑客攻击。此外,我们仔细约束反向传播梯度在推理路径上的向后流动路径,避免内存过载或梯度爆炸。在Stable Diffusion模型上的实验表明,ADT显著提高了分布对齐和图像质量。
关键见解
- 扩散模型通过反转前向噪声过程来生成图像。
- 训练过程中模型预测扩散分数,而推理需要从白噪声迭代去噪。
- 这种训练与推理的偏差可能影响数据分布的对齐。
- 提出的ADT框架通过对抗性监督来优化推理与训练数据对齐。
- ADT采用孪生网络鉴别器,具有固定预训练主干和轻量级可训练参数。
- ADT采用图像到图像的采样策略来解决鉴别困难,并保留原始扩散损失。
- 实验表明,ADT提高了分布对齐和图像质量。
点此查看论文截图

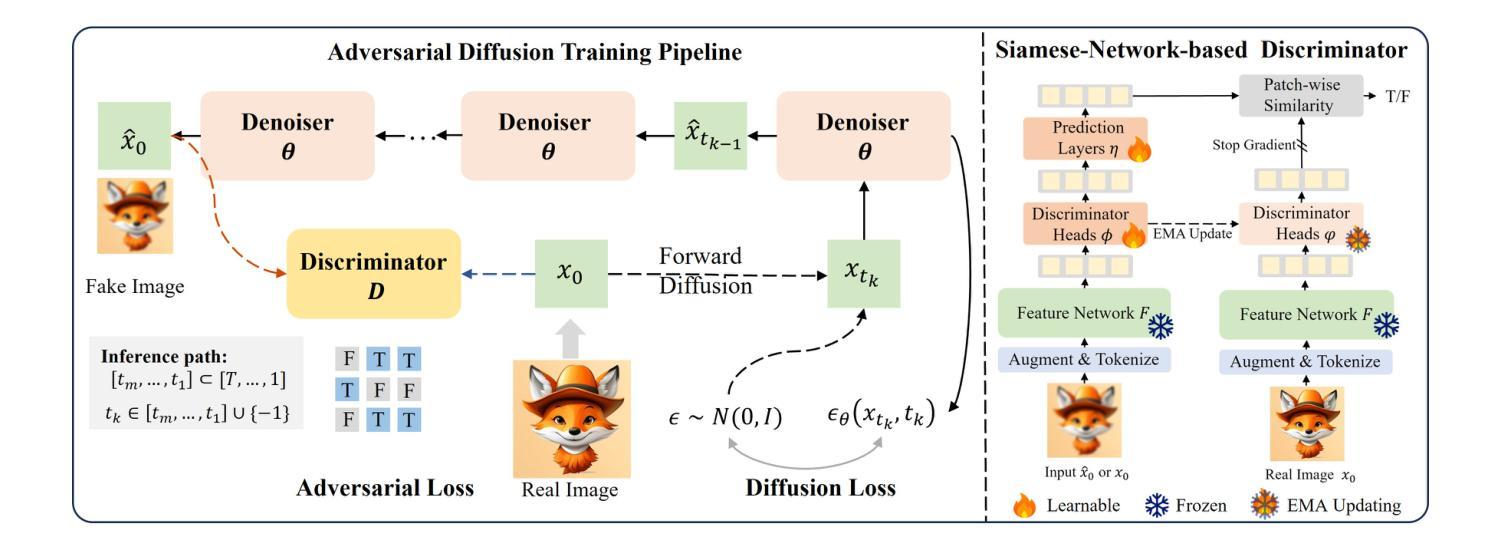

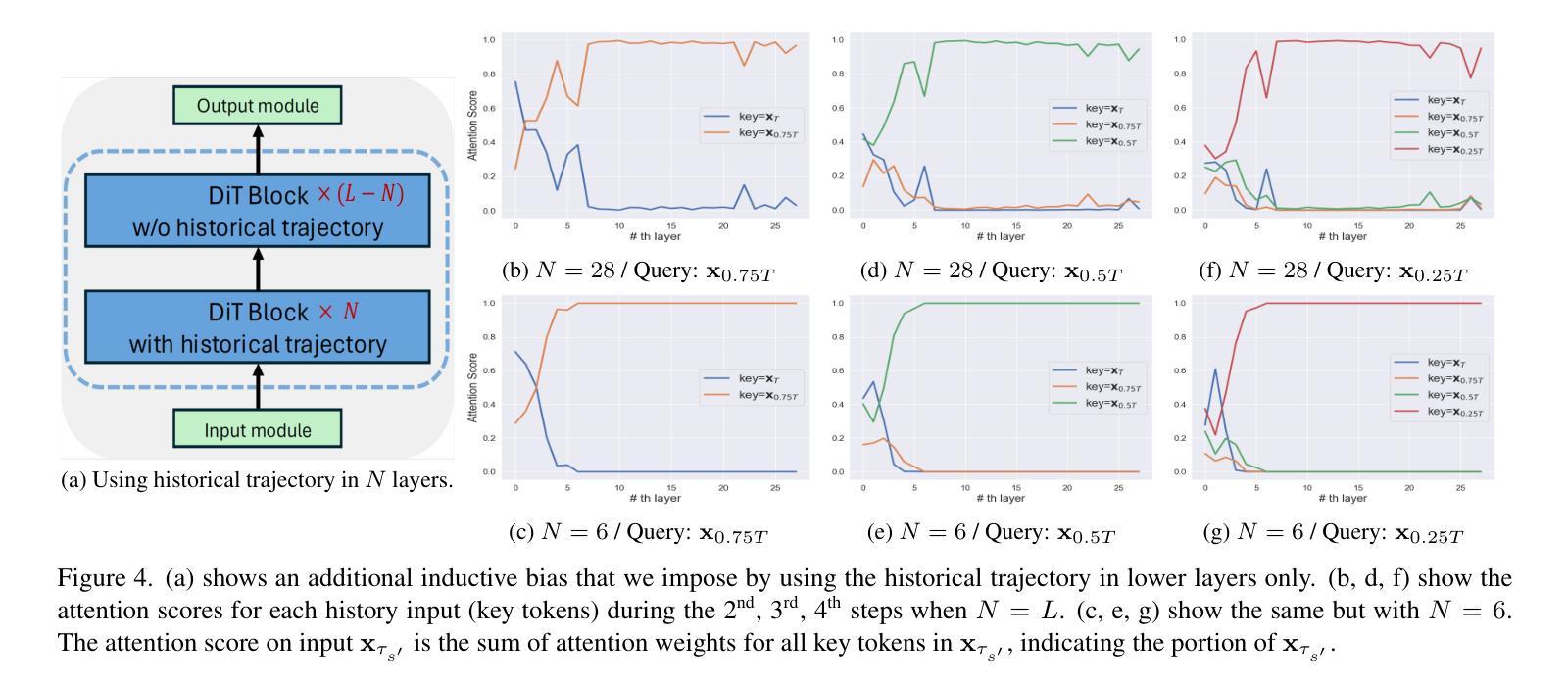
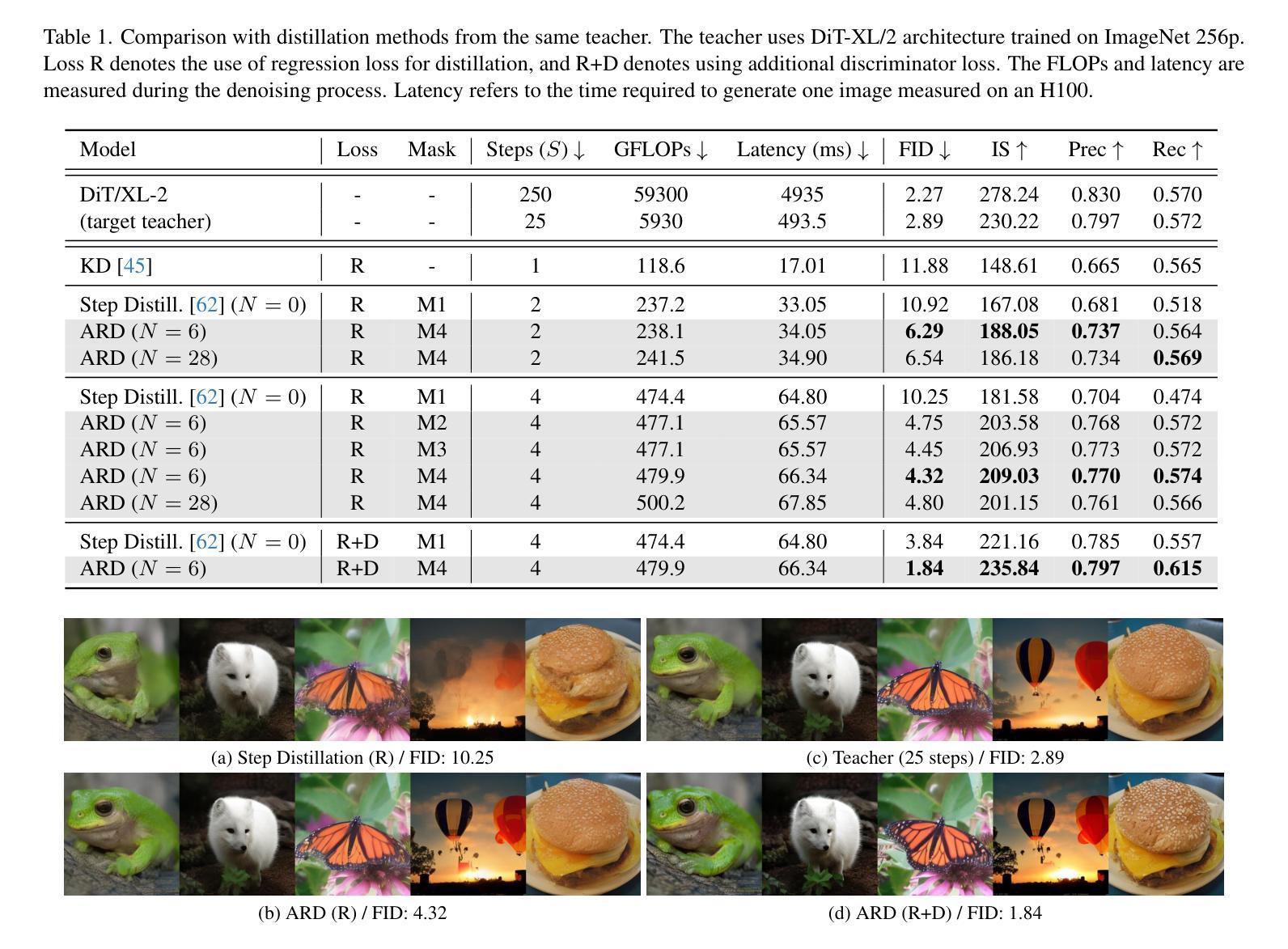
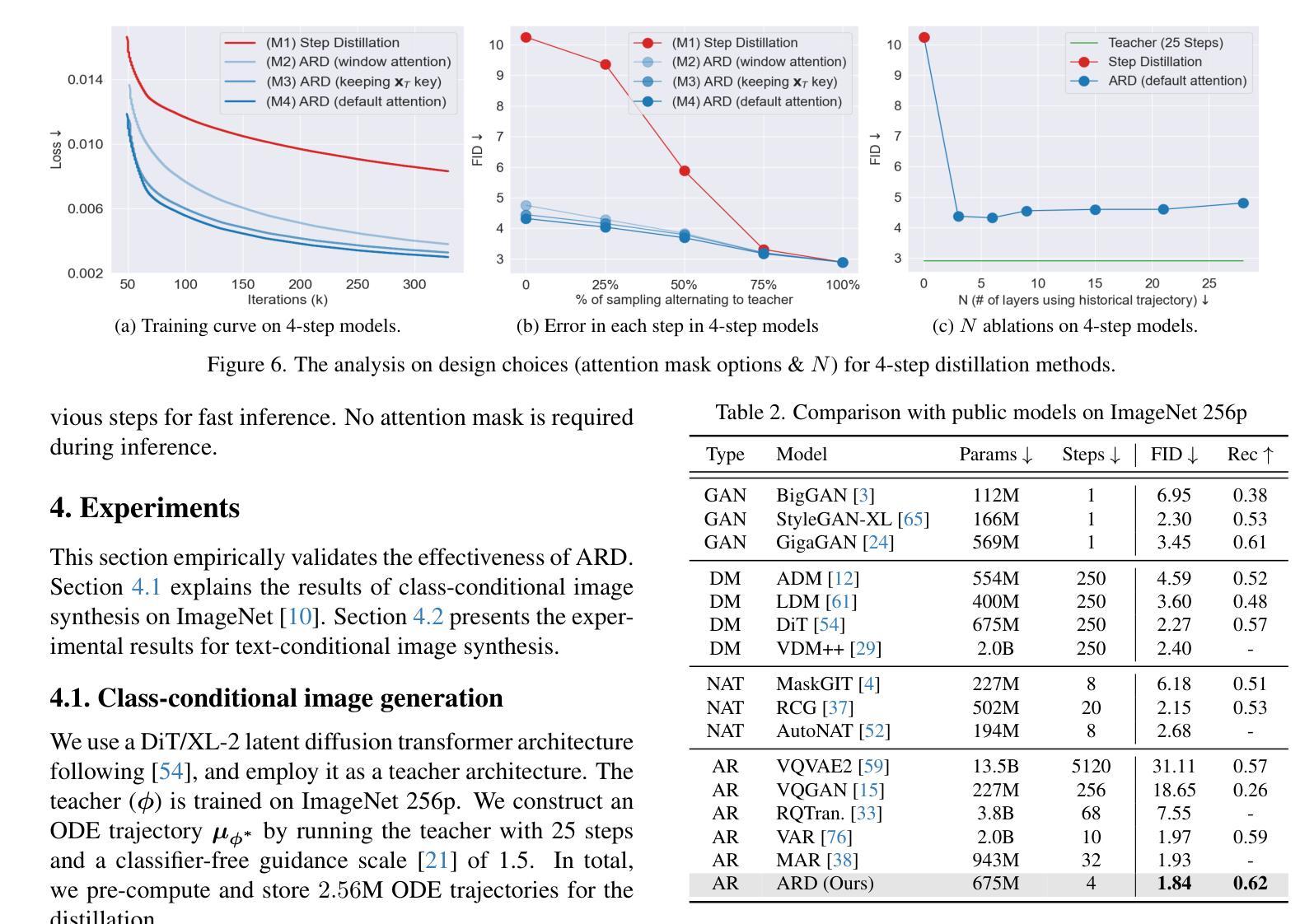
Autoregressive Distillation of Diffusion Transformers
Authors:Yeongmin Kim, Sotiris Anagnostidis, Yuming Du, Edgar Schönfeld, Jonas Kohler, Markos Georgopoulos, Albert Pumarola, Ali Thabet, Artsiom Sanakoyeu
Diffusion models with transformer architectures have demonstrated promising capabilities in generating high-fidelity images and scalability for high resolution. However, iterative sampling process required for synthesis is very resource-intensive. A line of work has focused on distilling solutions to probability flow ODEs into few-step student models. Nevertheless, existing methods have been limited by their reliance on the most recent denoised samples as input, rendering them susceptible to exposure bias. To address this limitation, we propose AutoRegressive Distillation (ARD), a novel approach that leverages the historical trajectory of the ODE to predict future steps. ARD offers two key benefits: 1) it mitigates exposure bias by utilizing a predicted historical trajectory that is less susceptible to accumulated errors, and 2) it leverages the previous history of the ODE trajectory as a more effective source of coarse-grained information. ARD modifies the teacher transformer architecture by adding token-wise time embedding to mark each input from the trajectory history and employs a block-wise causal attention mask for training. Furthermore, incorporating historical inputs only in lower transformer layers enhances performance and efficiency. We validate the effectiveness of ARD in a class-conditioned generation on ImageNet and T2I synthesis. Our model achieves a $5\times$ reduction in FID degradation compared to the baseline methods while requiring only 1.1% extra FLOPs on ImageNet-256. Moreover, ARD reaches FID of 1.84 on ImageNet-256 in merely 4 steps and outperforms the publicly available 1024p text-to-image distilled models in prompt adherence score with a minimal drop in FID compared to the teacher. Project page: https://github.com/alsdudrla10/ARD.
基于Transformer架构的扩散模型在生成高保真图像和高分辨率方面表现出有前景的能力。然而,合成所需的迭代采样过程非常耗费资源。一系列研究专注于将概率流常微分方程(ODEs)的解决方案蒸馏成少数步骤的学生模型。然而,现有方法受限于它们对最新去噪样本的依赖,使其容易受到暴露偏差的影响。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了AutoRegressive Distillation(ARD)这一新方法,它利用ODE的历史轨迹来预测未来步骤。ARD有两个主要优点:1)它通过利用预测的历史轨迹(不太容易受累积误差影响)来缓解暴露偏差;2)它利用ODE轨迹的先前历史作为更有效的粗粒度信息来源。ARD通过添加标记每个输入来自轨迹历史的token级时间嵌入来修改教师transformer架构,并采用块级因果注意力掩码进行训练。此外,仅在较低层的transformer中纳入历史输入可提高性能和效率。我们在ImageNet上的类别条件生成和T2I合成上验证了ARD的有效性。与基准方法相比,我们的模型在FID退化方面实现了5倍的减少,同时在ImageNet-256上仅需要额外的1.1% FLOPs。此外,ARD在ImageNet-256上仅需4步即可达到FID为1.84,并且在提示遵循得分方面优于公开可用的1024p文本到图像蒸馏模型,同时与教师的FID相比几乎没有下降。项目页面:https://github.com/alsdudrla10/ARD。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 Oral
摘要
基于扩散模型的自回归蒸馏(ARD)方法通过利用ODE历史轨迹来预测未来步骤,解决了迭代采样过程中的资源密集型和暴露偏差问题。ARD通过添加时间嵌入和块级因果注意力掩码来修改教师转换器架构,并将历史输入仅纳入较低层转换器中以提高性能和效率。在ImageNet和T2I合成上的类条件生成验证表明,ARD在减少FID降解方面比基线方法提高了5倍,同时在ImageNet-256上仅需要额外1.1%的浮点运算。此外,ARD在仅有四步的情况下达到了ImageNet-256的FID为1.84,并在提示遵循得分方面超越了公开的1024p文本到图像蒸馏模型。
关键见解
- 扩散模型具有生成高保真图像和良好扩展性的潜力。
- 迭代采样过程对于图像合成非常资源密集。
- 当前方法依赖于最近的去噪样本作为输入,容易受到暴露偏差的影响。
- 提出了一种新的自回归蒸馏(ARD)方法,利用ODE的历史轨迹来预测未来步骤。
- ARD通过添加时间嵌入和块级因果注意力掩码修改教师转换器架构。
- ARD通过结合历史输入在下层转换器中实现高性能和效率。
- ARD在ImageNet和T2I合成上的表现优于基线方法,显著减少了FID降解,并在提示遵循得分方面表现出色。
点此查看论文截图

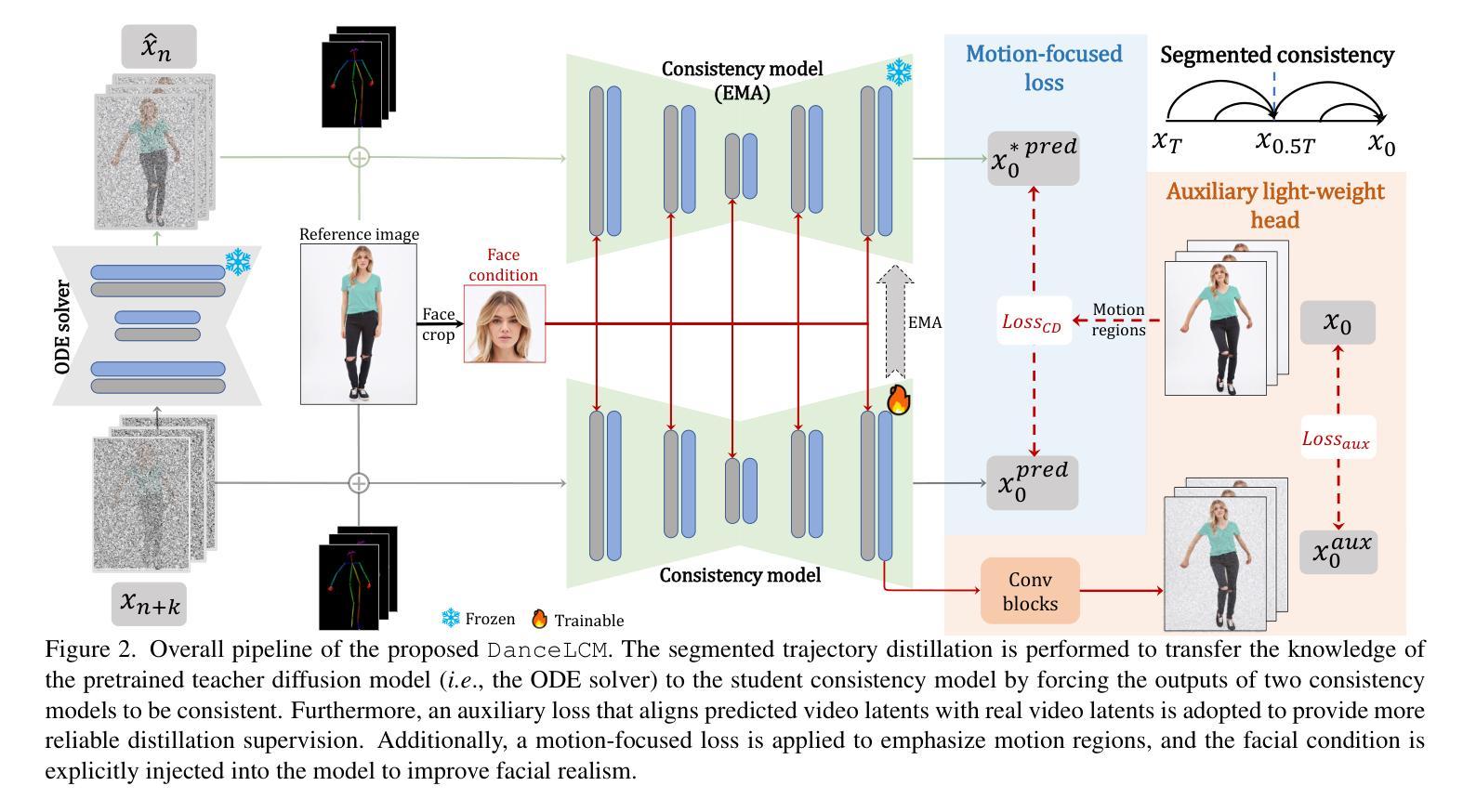
Taming Consistency Distillation for Accelerated Human Image Animation
Authors:Xiang Wang, Shiwei Zhang, Hangjie Yuan, Yujie Wei, Yingya Zhang, Changxin Gao, Yuehuan Wang, Nong Sang
Recent advancements in human image animation have been propelled by video diffusion models, yet their reliance on numerous iterative denoising steps results in high inference costs and slow speeds. An intuitive solution involves adopting consistency models, which serve as an effective acceleration paradigm through consistency distillation. However, simply employing this strategy in human image animation often leads to quality decline, including visual blurring, motion degradation, and facial distortion, particularly in dynamic regions. In this paper, we propose the DanceLCM approach complemented by several enhancements to improve visual quality and motion continuity at low-step regime: (1) segmented consistency distillation with an auxiliary light-weight head to incorporate supervision from real video latents, mitigating cumulative errors resulting from single full-trajectory generation; (2) a motion-focused loss to centre on motion regions, and explicit injection of facial fidelity features to improve face authenticity. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that DanceLCM achieves results comparable to state-of-the-art video diffusion models with a mere 2-4 inference steps, significantly reducing the inference burden without compromising video quality. The code and models will be made publicly available.
近期人类图像动画技术的进展得益于视频扩散模型。然而,它们依赖于大量的迭代去噪步骤,导致推理成本高昂和速度缓慢。一种直观的解决方案是采用一致性模型,通过一致性蒸馏成为一种有效的加速范式。然而,仅仅在人类图像动画中采用这种策略往往会导致质量下降,包括视觉模糊、运动退化以及面部失真,特别是在动态区域。在本文中,我们提出了DanceLCM方法,并辅以几项增强功能,以在低步骤制度下提高视觉质量和运动连续性:(1)分段一致性蒸馏,辅以辅助的轻量级头,以融入真实视频潜变量的监督信息,缓解由单一全轨迹生成导致的累积误差;(2)以运动为中心的损失函数,专注于运动区域,并显式注入面部保真特征以提高面部真实性。大量的定性和定量实验表明,DanceLCM在仅使用2-4个推理步骤的情况下,就能达到与最先进的视频扩散模型相当的结果,显著减少了推理负担,同时不妥协视频质量。代码和模型将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视频扩散模型推动了人像动画的最新发展,但其依赖于大量的迭代去噪步骤导致推理成本高、速度慢。采用一致性模型作为有效的加速范式可以通过一致性蒸馏来解决这个问题,但简单应用于人像动画往往会导致质量下降,包括视觉模糊、运动退化以及面部失真,特别是在动态区域。本文提出了结合多种改进的DanceLCM方法,在低步状态下提高视觉质量和运动连续性:(1)通过辅助的轻量级头进行分段一致性蒸馏,以融入真实视频潜变量的监督信息,缓解单一全轨迹生成导致的累积误差;(2)以运动为中心的损失聚焦于运动区域,并显式注入面部保真特征以提高面部真实性。大量定性和定量实验表明,DanceLCM仅需2-4步推理即可获得与最先进的视频扩散模型相当的结果,显著降低了推理负担,且不损害视频质量。
Key Takeaways
- 视频扩散模型在人像动画领域取得最新进展,但存在推理成本高和速度慢的问题。
- 一致性模型能有效加速视频扩散模型的推理过程。
- 单纯采用一致性模型会导致质量下降,包括视觉模糊、运动退化以及面部失真。
- DanceLCM方法通过分段一致性蒸馏和面部保真特征的注入来提高视觉质量和运动连续性。
- DanceLCM方法在低步状态下实现高速推理,仅需2-4步即可获得与先进模型相当的结果。
- DanceLCM方法显著降低了推理负担,同时保持视频质量不损失。
点此查看论文截图

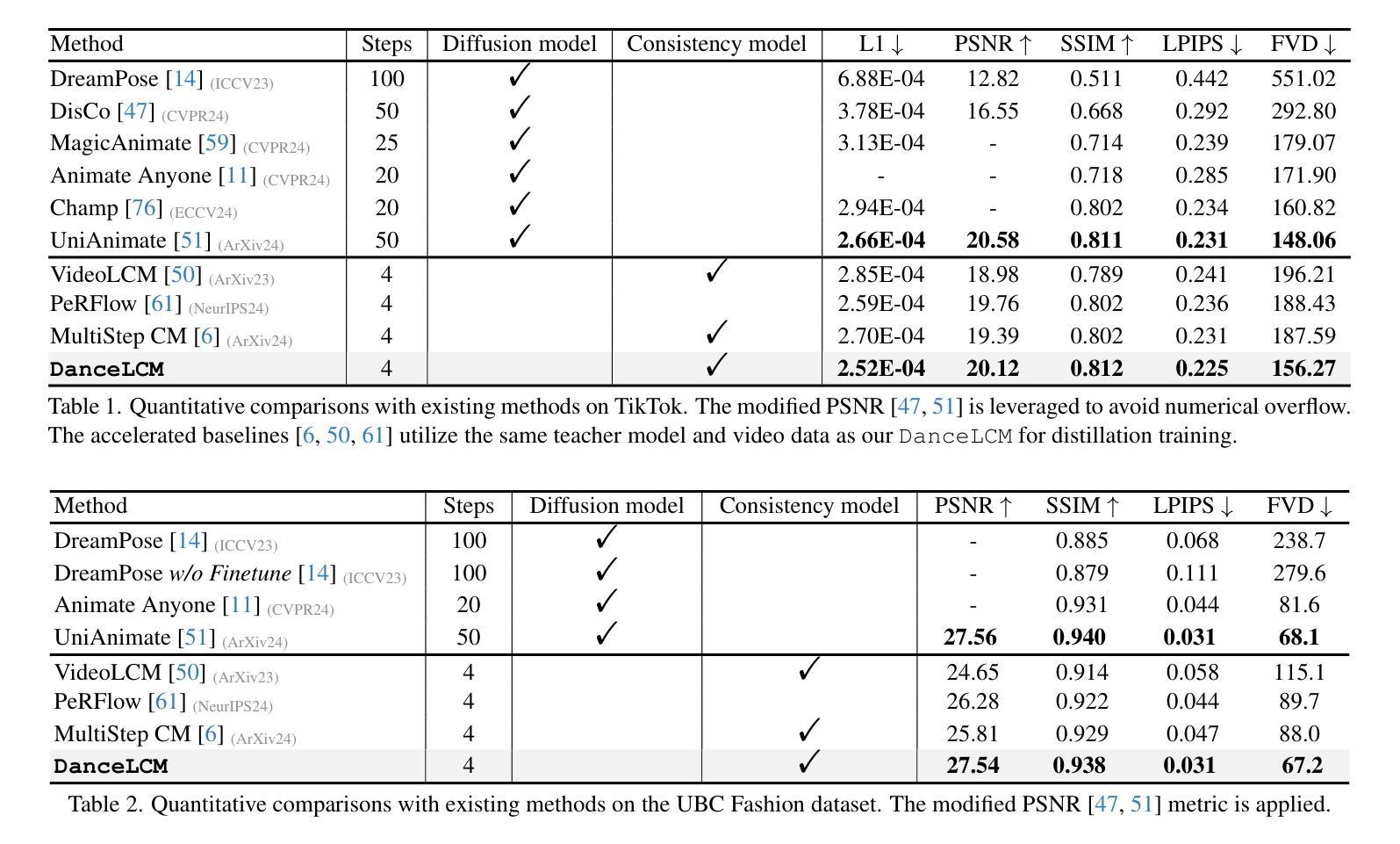

AnimeDL-2M: Million-Scale AI-Generated Anime Image Detection and Localization in Diffusion Era
Authors:Chenyang Zhu, Xing Zhang, Yuyang Sun, Ching-Chun Chang, Isao Echizen
Recent advances in image generation, particularly diffusion models, have significantly lowered the barrier for creating sophisticated forgeries, making image manipulation detection and localization (IMDL) increasingly challenging. While prior work in IMDL has focused largely on natural images, the anime domain remains underexplored-despite its growing vulnerability to AI-generated forgeries. Misrepresentations of AI-generated images as hand-drawn artwork, copyright violations, and inappropriate content modifications pose serious threats to the anime community and industry. To address this gap, we propose AnimeDL-2M, the first large-scale benchmark for anime IMDL with comprehensive annotations. It comprises over two million images including real, partially manipulated, and fully AI-generated samples. Experiments indicate that models trained on existing IMDL datasets of natural images perform poorly when applied to anime images, highlighting a clear domain gap between anime and natural images. To better handle IMDL tasks in anime domain, we further propose AniXplore, a novel model tailored to the visual characteristics of anime imagery. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that AniXplore achieves superior performance compared to existing methods. Dataset and code can be found in https://flytweety.github.io/AnimeDL2M/.
图像生成领域的最新进展,尤其是扩散模型,极大地降低了创建复杂伪造作品的门槛,使得图像操纵检测与定位(IMDL)越来越具有挑战性。尽管先前在IMDL方面的工作主要集中在自然图像上,但动漫领域仍然被忽视,尽管它越来越容易受到AI生成的伪造作品的威胁。将AI生成的图像误表示为手绘艺术品、版权侵犯和不适当的内容修改对动漫社区和行业构成严重威胁。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了AnimeDL-2M,这是首个用于动漫IMDL的大规模基准测试,包含全面注释。它包含超过两百万张图像,包括真实、部分操纵和完全AI生成的样本。实验表明,在自然人图像IMDL数据集上训练的模型在应用于动漫图像时表现不佳,这突出了动漫和自然人图像之间的明显领域差距。为了更好地处理动漫领域的IMDL任务,我们进一步提出了AniXplore,这是一个针对动漫图像视觉特征量身定制的新模型。大量评估表明,与现有方法相比,AniXplore实现了卓越的性能。数据集和代码可在https://flytweety.github.io/AnimeDL2M/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期图像生成技术,特别是扩散模型的发展,使得创建高级伪造作品的门槛大幅降低,使得图像操作检测与定位(IMDL)面临越来越大的挑战。以往的研究主要关注自然图像领域,但动漫领域却被忽略。虽然动漫的虚假AI生成图像易被用作手绘作品诈骗等违法行为,对动漫界和产业构成严重威胁。针对这一问题,推出首个大型动漫IMDL基准测试数据集AnimeDL-2M,含有超过两百万图片样本。研究结果显示,在动漫图像上训练的模型表现不佳,显示动漫与自然图像领域间的明显差距。为此推出针对动漫视觉特性的新模型AniXplore,评估显示其表现优越于现有方法。更多信息可通过链接获取。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型降低了创建高级伪造作品的难度,使图像操作检测与定位(IMDL)更具挑战性。
- 动漫领域的IMDL研究相对缺乏,存在巨大的研究空间。
- 动漫的虚假AI生成图像存在误当作手绘作品的法律风险。
- 推出首个大型动漫IMDL数据集AnimeDL-2M,含有超过两百万图片样本。
- 在动漫图像上训练的模型表现欠佳,表明动漫与常规自然图像领域的差距。
- 提出针对动漫视觉特性的新模型AniXplore。
- AniXplore模型相较于现有方法表现优越。
点此查看论文截图


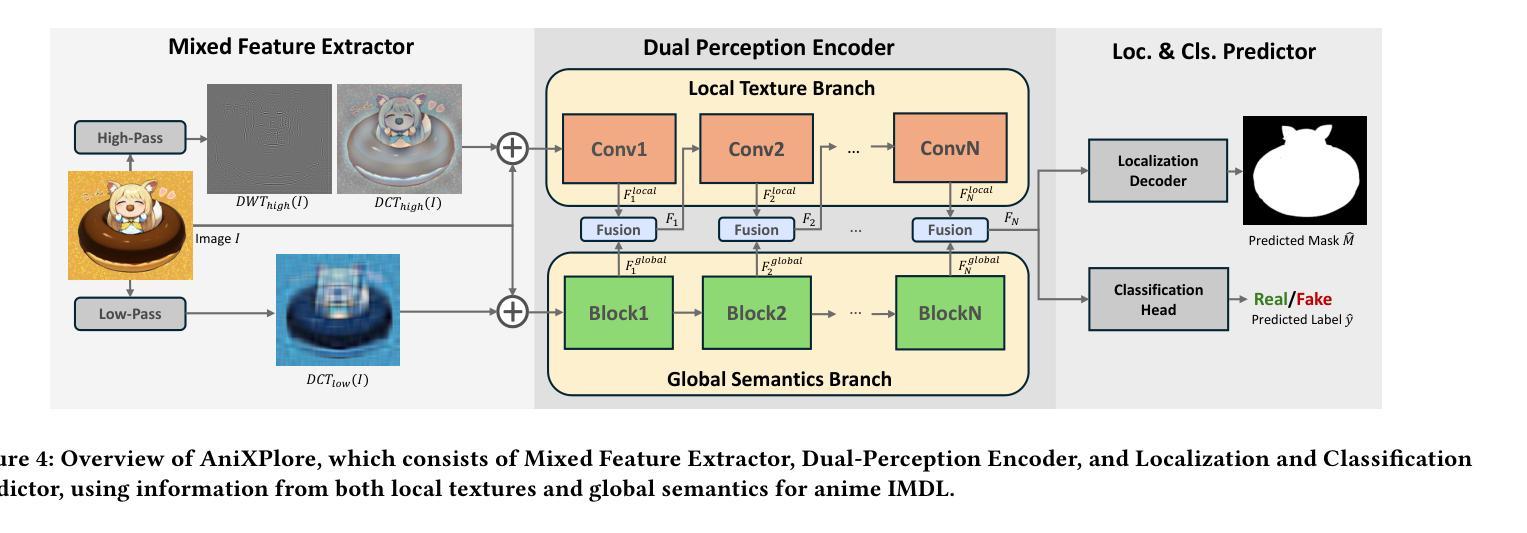
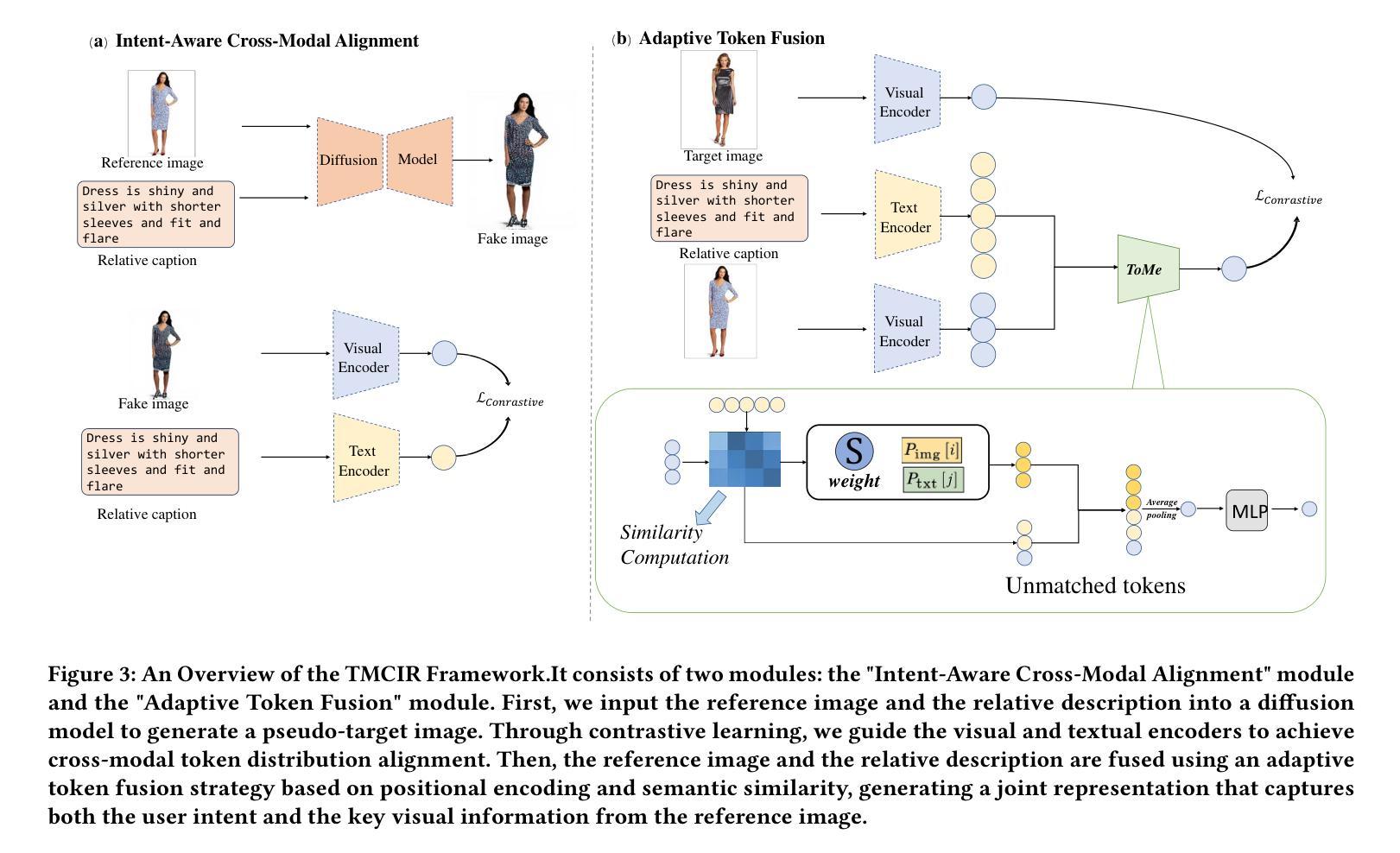
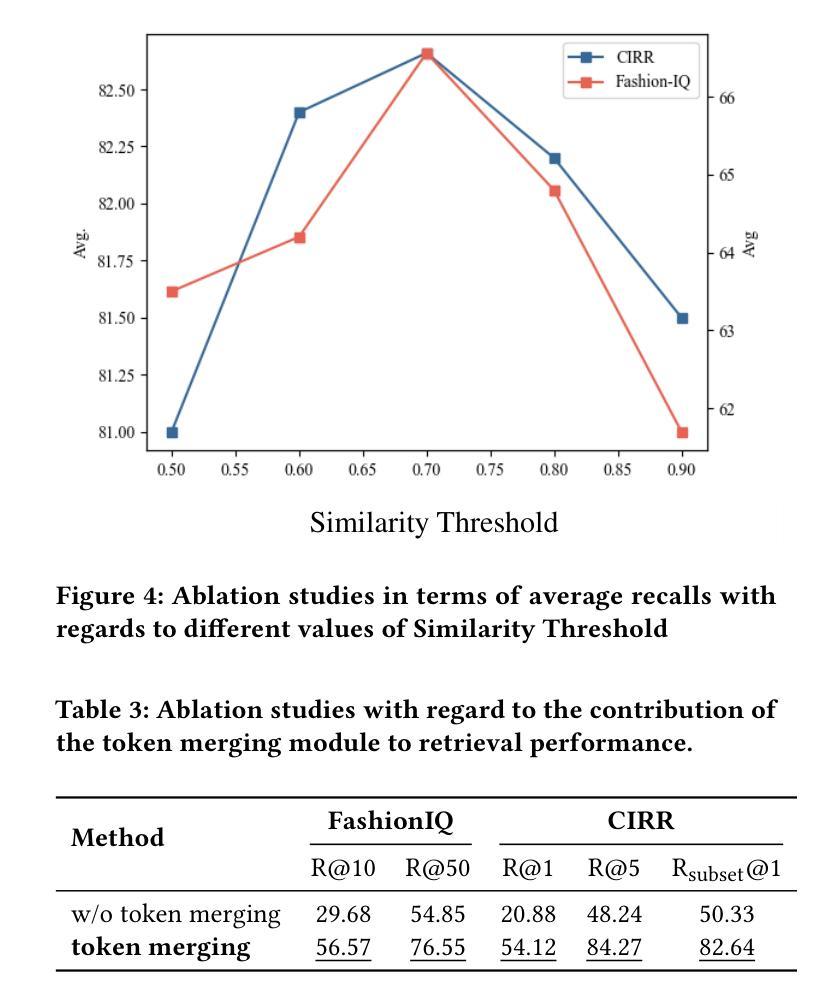
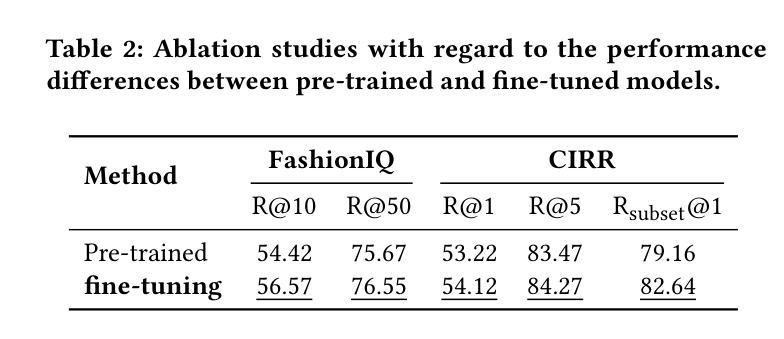
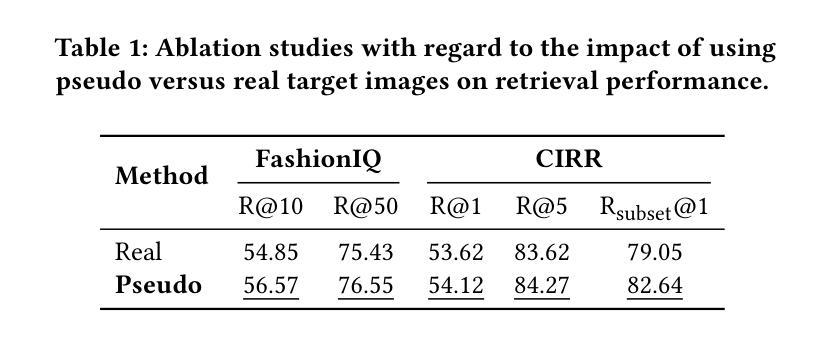
TMCIR: Token Merge Benefits Composed Image Retrieval
Authors:Chaoyang Wang, Zeyu Zhang, Long Teng, Zijun Li, Shichao Kan
Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) retrieves target images using a multi-modal query that combines a reference image with text describing desired modifications. The primary challenge is effectively fusing this visual and textual information. Current cross-modal feature fusion approaches for CIR exhibit an inherent bias in intention interpretation. These methods tend to disproportionately emphasize either the reference image features (visual-dominant fusion) or the textual modification intent (text-dominant fusion through image-to-text conversion). Such an imbalanced representation often fails to accurately capture and reflect the actual search intent of the user in the retrieval results. To address this challenge, we propose TMCIR, a novel framework that advances composed image retrieval through two key innovations: 1) Intent-Aware Cross-Modal Alignment. We first fine-tune CLIP encoders contrastively using intent-reflecting pseudo-target images, synthesized from reference images and textual descriptions via a diffusion model. This step enhances the encoder ability of text to capture nuanced intents in textual descriptions. 2) Adaptive Token Fusion. We further fine-tune all encoders contrastively by comparing adaptive token-fusion features with the target image. This mechanism dynamically balances visual and textual representations within the contrastive learning pipeline, optimizing the composed feature for retrieval. Extensive experiments on Fashion-IQ and CIRR datasets demonstrate that TMCIR significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, particularly in capturing nuanced user intent.
图像组合检索(CIR)使用多模态查询检索目标图像,该查询将参考图像与描述所需修改的文本相结合。主要挑战是如何有效地融合这种视觉和文本信息。当前用于CIR的跨模态特征融合方法表现出意图解释的固有偏见。这些方法往往过分强调参考图像特征(视觉主导融合)或文本修改意图(通过图像到文本的转换实现文本主导融合)。这种不平衡的表示通常在检索结果中无法准确捕获和反映用户的实际搜索意图。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2310.05473 by other authors
Summary
一种融合文本与图像信息的跨模态检索方法。目前CIR存在视觉和文本信息融合的问题,通常会出现过度偏向参考图像或文本描述的偏向性问题,难以准确捕捉用户意图。本文提出的TMCIR框架通过两种关键创新方法解决这一问题:一是意图感知的跨模态对齐,利用扩散模型合成反映意图的伪目标图像对CLIP编码器进行微调;二是自适应令牌融合,通过对比自适应令牌融合特征与目标图像对编码器进行进一步微调。实验证明,TMCIR显著优于当前的主流方法,尤其在于捕捉用户细微意图的能力上。
Key Takeaways
- CIR利用多模态查询(结合参考图像和描述文本)检索目标图像。
- 当前CIR方法的挑战在于如何有效融合视觉和文本信息。
- 存在的方法倾向于偏向参考图像或文本描述,导致无法准确捕捉用户意图。
- TMCIR框架通过两种创新方法解决这一问题:意图感知的跨模态对齐和自适应令牌融合。
- 意图感知的跨模态对齐通过合成反映意图的伪目标图像对CLIP编码器进行微调。
- 自适应令牌融合通过对比特征与目标图像对编码器进行微调,实现视觉和文本信息的动态平衡。
- 实验证明,TMCIR在捕捉用户细微意图和检索性能上显著优于当前的主流方法。
- TMCIR框架在Fashion-IQ和CIRR数据集上的实验表现优异。
点此查看论文截图


Bringing together invertible UNets with invertible attention modules for memory-efficient diffusion models
Authors:Karan Jain, Mohammad Nayeem Teli
Diffusion models have recently gained state of the art performance on many image generation tasks. However, most models require significant computational resources to achieve this. This becomes apparent in the application of medical image synthesis due to the 3D nature of medical datasets like CT-scans, MRIs, electron microscope, etc. In this paper we propose a novel architecture for a single GPU memory-efficient training for diffusion models for high dimensional medical datasets. The proposed model is built by using an invertible UNet architecture with invertible attention modules. This leads to the following two contributions: 1. denoising diffusion models and thus enabling memory usage to be independent of the dimensionality of the dataset, and 2. reducing the energy usage during training. While this new model can be applied to a multitude of image generation tasks, we showcase its memory-efficiency on the 3D BraTS2020 dataset leading to up to 15% decrease in peak memory consumption during training with comparable results to SOTA while maintaining the image quality.
扩散模型最近在许多图像生成任务上达到了最先进的性能。然而,大多数模型为了实现这一点需要大量的计算资源。这在医学图像合成的应用中变得尤为明显,因为医学数据集如CT扫描、MRI、电子显微镜等的三维性质。在本文中,我们提出了一种针对高维医学数据集扩散模型的单GPU内存高效训练的新型架构。该模型采用可逆UNet架构和可逆注意力模块构建。这带来了以下两个贡献:1.降噪扩散模型,从而使内存使用量与数据集维度的无关性成为可能;2.减少训练过程中的能耗。虽然这种新型模型可以应用于多种图像生成任务,但我们展示了其在3D BraTS2020数据集上的内存效率,在训练过程中峰值内存使用率降低了高达15%,同时保持与最新技术相当的结果和图像质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在图像生成任务上取得了最新性能表现,但其需要巨大的计算资源。对于医疗图像合成应用而言,由于其涉及高维医学数据集如CT扫描、MRI等,这一问题尤为突出。本文提出了一种针对扩散模型的新型单GPU内存高效训练架构,采用可逆UNet架构和可逆注意力模块,为医疗数据集提供了去噪扩散模型。此模型可应用于多种图像生成任务,展示了其在BraTS数据集上的内存效率,减少了训练过程中的峰值内存使用量,同时在维持图像质量的情况下达到了一流的性能表现。其降低了训练和计算时的能源成本以及改善了可复用性成为关键的两个优势。我们相信扩散模型的轻量级计算解决方案不仅将使现代神经退行性疾病的三维动态成像成为可能,还将为医学研究和诊断带来重大突破。这一突破将为医学领域带来深远的影响。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在高维医疗数据集上表现出卓越性能。针对图像生成任务特别突出。对于高维医学数据集如CT扫描和MRI等,其性能表现尤为显著。
点此查看论文截图

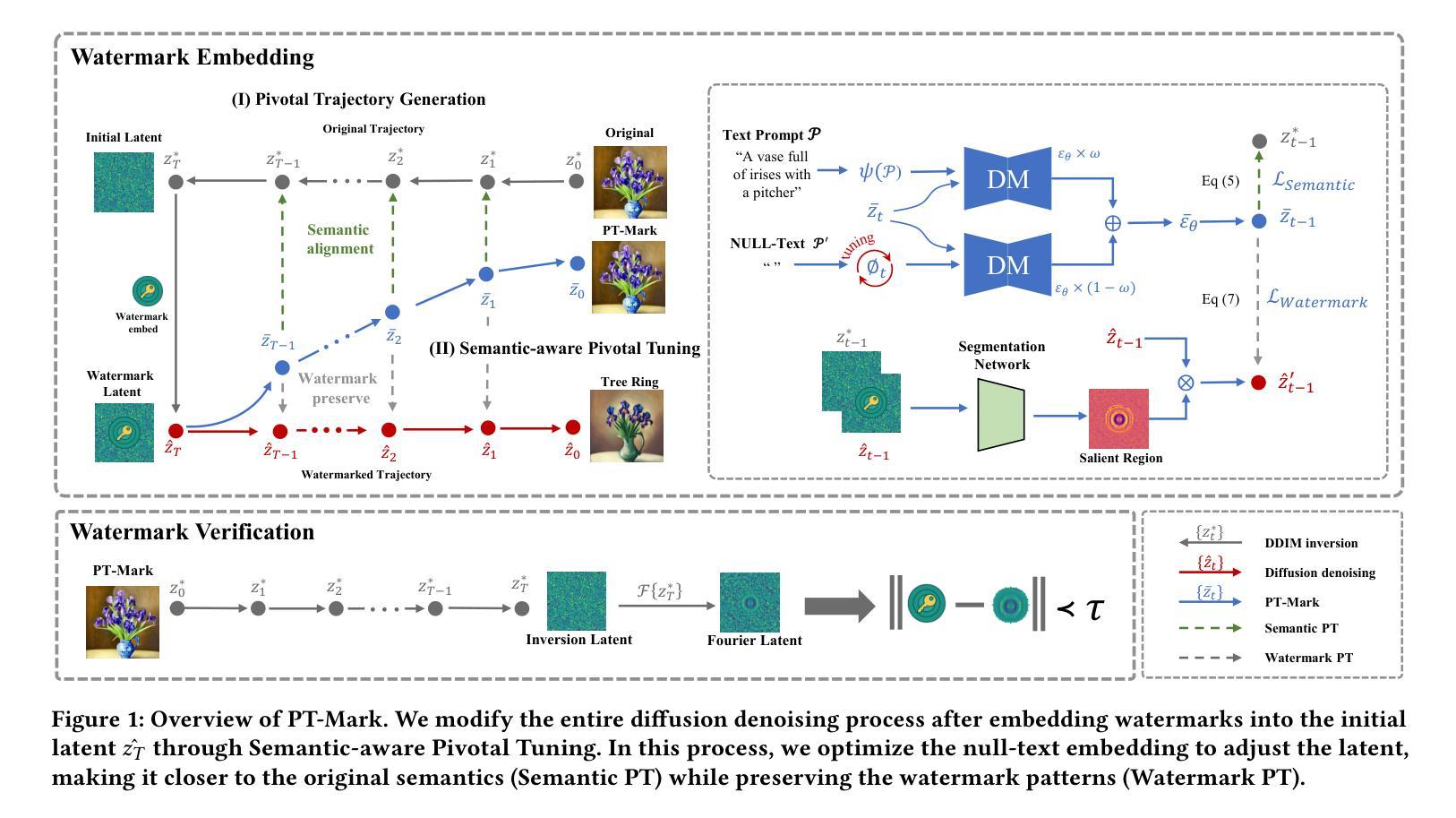
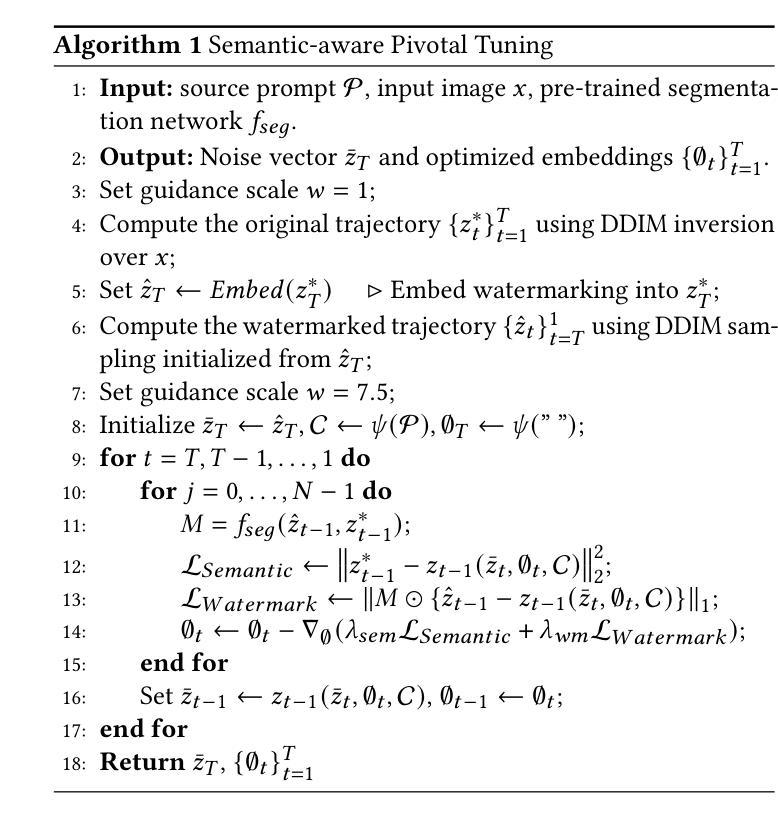
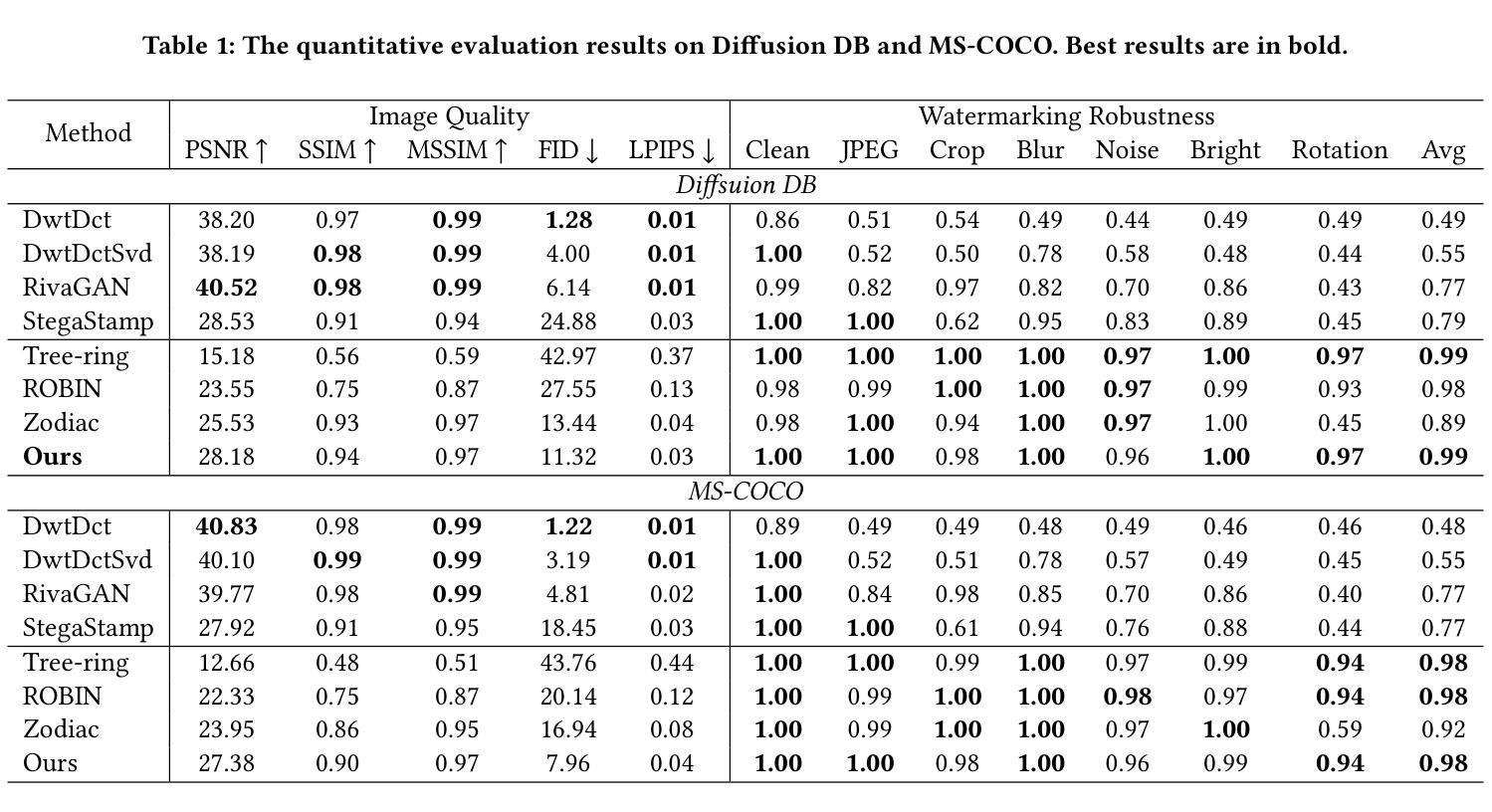
PT-Mark: Invisible Watermarking for Text-to-image Diffusion Models via Semantic-aware Pivotal Tuning
Authors:Yaopeng Wang, Huiyu Xu, Zhibo Wang, Jiacheng Du, Zhichao Li, Yiming Li, Qiu Wang, Kui Ren
Watermarking for diffusion images has drawn considerable attention due to the widespread use of text-to-image diffusion models and the increasing need for their copyright protection. Recently, advanced watermarking techniques, such as Tree Ring, integrate watermarks by embedding traceable patterns (e.g., Rings) into the latent distribution during the diffusion process. Such methods disrupt the original semantics of the generated images due to the inevitable distribution shift caused by the watermarks, thereby limiting their practicality, particularly in digital art creation. In this work, we present Semantic-aware Pivotal Tuning Watermarks (PT-Mark), a novel invisible watermarking method that preserves both the semantics of diffusion images and the traceability of the watermark. PT-Mark preserves the original semantics of the watermarked image by gradually aligning the generation trajectory with the original (pivotal) trajectory while maintaining the traceable watermarks during whole diffusion denoising process. To achieve this, we first compute the salient regions of the watermark at each diffusion denoising step as a spatial prior to identify areas that can be aligned without disrupting the watermark pattern. Guided by the region, we then introduce an additional pivotal tuning branch that optimizes the text embedding to align the semantics while preserving the watermarks. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that PT-Mark can preserve the original semantics of the diffusion images while integrating robust watermarks. It achieves a 10% improvement in the performance of semantic preservation (i.e., SSIM, PSNR, and LPIPS) compared to state-of-the-art watermarking methods, while also showing comparable robustness against real-world perturbations and four times greater efficiency.
针对扩散图像的水印技术得到了广泛关注,这主要是由于文本到图像的扩散模型的广泛应用和对版权保护的不断增长的需求。最近,先进的水印技术,如Tree Ring,通过在扩散过程中将可追踪的模式(例如圆环)嵌入潜在分布来集成水印。这些方法由于水印引起的不可避免的分布偏移而破坏了生成图像的原语意,从而限制了它们的实用性,特别是在数字艺术创作中。在这项工作中,我们提出了语义感知的枢轴调整水印(PT-Mark),这是一种新的不可见水印方法,能够同时保留扩散图像语义和水印的可追踪性。PT-Mark通过在整个扩散去噪过程中保持可追踪的水印,同时逐步调整生成轨迹与原始(枢轴)轨迹对齐,从而保留水印图像的原语意。为了实现这一点,我们首先在每个扩散去噪步骤中计算水印的显著区域作为空间先验,以识别可以不对齐而不会影响水印模式的区域。在该区域的指导下,然后我们引入了一个额外的枢轴调整分支,优化文本嵌入以对齐语义同时保留水印。广泛评估表明,PT-Mark能够在集成稳健水印的同时保留扩散图像的原语意。与最先进的水印方法相比,它在语义保留性能(即结构相似性度量、峰值信噪比和结构相似性度量指数)上提高了10%,同时显示出对现实世界扰动的相当鲁棒性并提高四倍效率。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
扩散图像水印因其广泛应用于文本到图像的扩散模型及版权保护需求而受到关注。最新的水印技术,如Tree Ring,通过嵌入可追溯模式(例如环形)到扩散过程的潜在分布中进行集成。但这种方法会破坏生成图像的原语义,限制了其实用性。在此,我们提出一种新型不可见水印方法——语义感知关键调整水印(PT-Mark),它既能保留扩散图像语义,又能追溯水印。PT-Mark通过逐步调整生成轨迹与原始(关键)轨迹对齐,同时在整个扩散去噪过程中保持可追溯的水印,从而保留水印图像的原语义。为实现这一目标,我们首先在每个扩散去噪步骤中计算水印的显著区域作为空间先验,以识别可对齐的区域而不干扰水印图案。在该区域的引导下,我们引入了一个额外的关键调整分支,优化文本嵌入以对齐语义同时保留水印。评估表明,PT-Mark在保留扩散图像原语义的同时集成了稳健的水印,在语义保留性能上较现有水印方法提高了10%,同时显示了对现实世界扰动的可比性鲁棒性和四倍效率。
关键见解
- 扩散图像水印因文本-图像扩散模型广泛应用和版权保护需求而受到关注。
- 现有方法如Tree Ring会破坏生成图像的原语义,限制其实用性。
- PT-Mark是一种新型不可见水印方法,能同时保留扩散图像的语义和追溯水印。
- PT-Mark通过逐步对齐生成轨迹与原始轨迹,同时保持整个扩散去噪过程中的水印来实现语义保留。
- PT-Mark引入空间先验和关键调整分支以提高语义保留和水印的稳健性。
- 评估显示PT-Mark在语义保留性能上较现有方法有所提升,同时效率更高。
点此查看论文截图

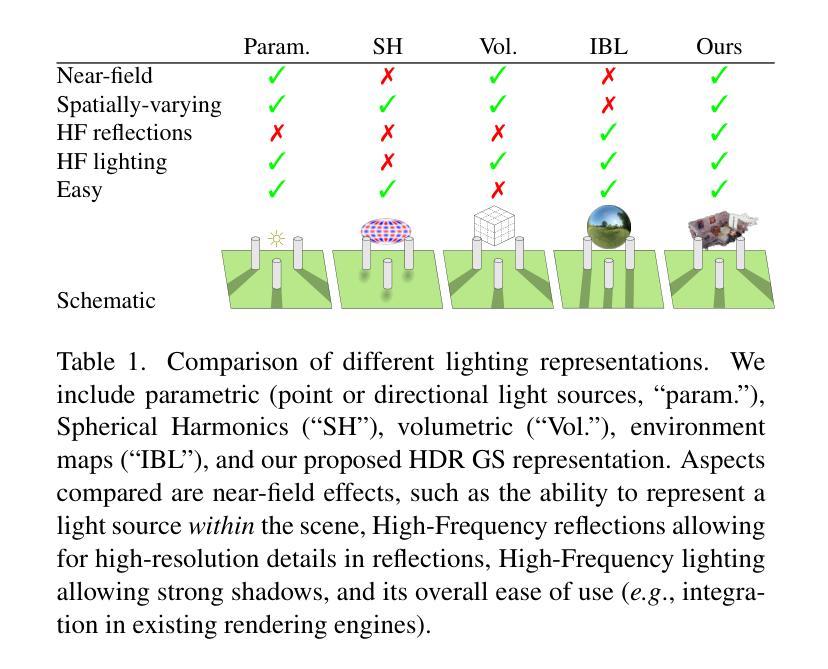
GaSLight: Gaussian Splats for Spatially-Varying Lighting in HDR
Authors:Christophe Bolduc, Yannick Hold-Geoffroy, Zhixin Shu, Jean-François Lalonde
We present GaSLight, a method that generates spatially-varying lighting from regular images. Our method proposes using HDR Gaussian Splats as light source representation, marking the first time regular images can serve as light sources in a 3D renderer. Our two-stage process first enhances the dynamic range of images plausibly and accurately by leveraging the priors embedded in diffusion models. Next, we employ Gaussian Splats to model 3D lighting, achieving spatially variant lighting. Our approach yields state-of-the-art results on HDR estimations and their applications in illuminating virtual objects and scenes. To facilitate the benchmarking of images as light sources, we introduce a novel dataset of calibrated and unsaturated HDR to evaluate images as light sources. We assess our method using a combination of this novel dataset and an existing dataset from the literature. The code to reproduce our method will be available upon acceptance.
我们提出了GaSLight方法,该方法可以从常规图像生成空间变化的光照。我们的方法建议使用HDR高斯Splats作为光源表示,这是首次将常规图像作为3D渲染器的光源。我们的两阶段过程首先利用扩散模型中嵌入的先验知识,以合理且准确的方式增强图像的动态范围。接下来,我们采用高斯Splats对3D照明进行建模,实现空间变化的光照。我们的方法在HDR估计及其用于照明虚拟对象和场景的应用方面产生了最先进的成果。为了对图像作为光源进行基准测试,我们引入了一个新型校准和不饱和HDR数据集来评估图像作为光源。我们使用这个新型数据集和文献中的现有数据集来评估我们的方法。接受后将提供复制我们方法的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
我们提出了一种名为GaSLight的方法,该方法可以从常规图像生成空间变化的光照。我们使用HDR高斯Splats作为光源表示,这是首次将常规图像作为光源用于三维渲染。我们的两步过程首先利用扩散模型中的先验知识,以合理且准确的方式增强图像的动态范围。然后,我们使用高斯Splats对三维照明进行建模,实现空间变化的光照。我们的方法在HDR估计及其用于照明虚拟对象和场景方面的应用方面达到了最新水平。为了方便图像作为光源的基准测试,我们引入了一个新型的校准和不饱和HDR数据集来评估图像作为光源。我们使用这个新数据集和文献中的现有数据集来评估我们的方法。
Key Takeaways
- GaSLight方法能从常规图像生成空间变化的光照。
- HDR高斯Splats首次被用作光源表示,用于三维渲染。
- 该方法采用两步过程,首先增强图像动态范围,然后利用高斯Splats进行三维照明建模。
- 方法在HDR估计及其应用于虚拟对象和场景的照明方面达到了最新水平。
- 为了评估图像作为光源的效果,引入了一个新型的校准和不饱和HDR数据集。
- 该方法结合了新数据集和现有数据集进行评估。
- 方法代码在接受后将公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

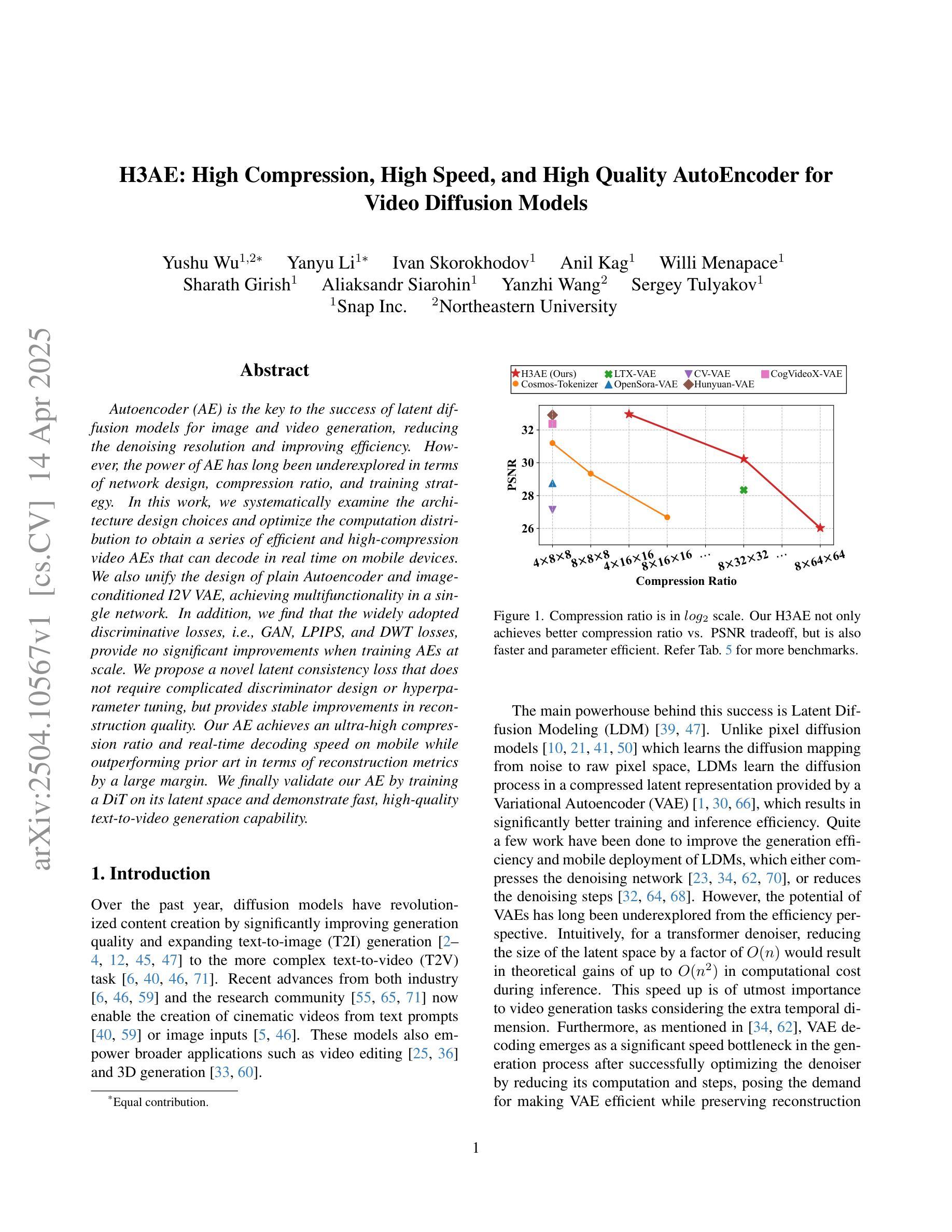
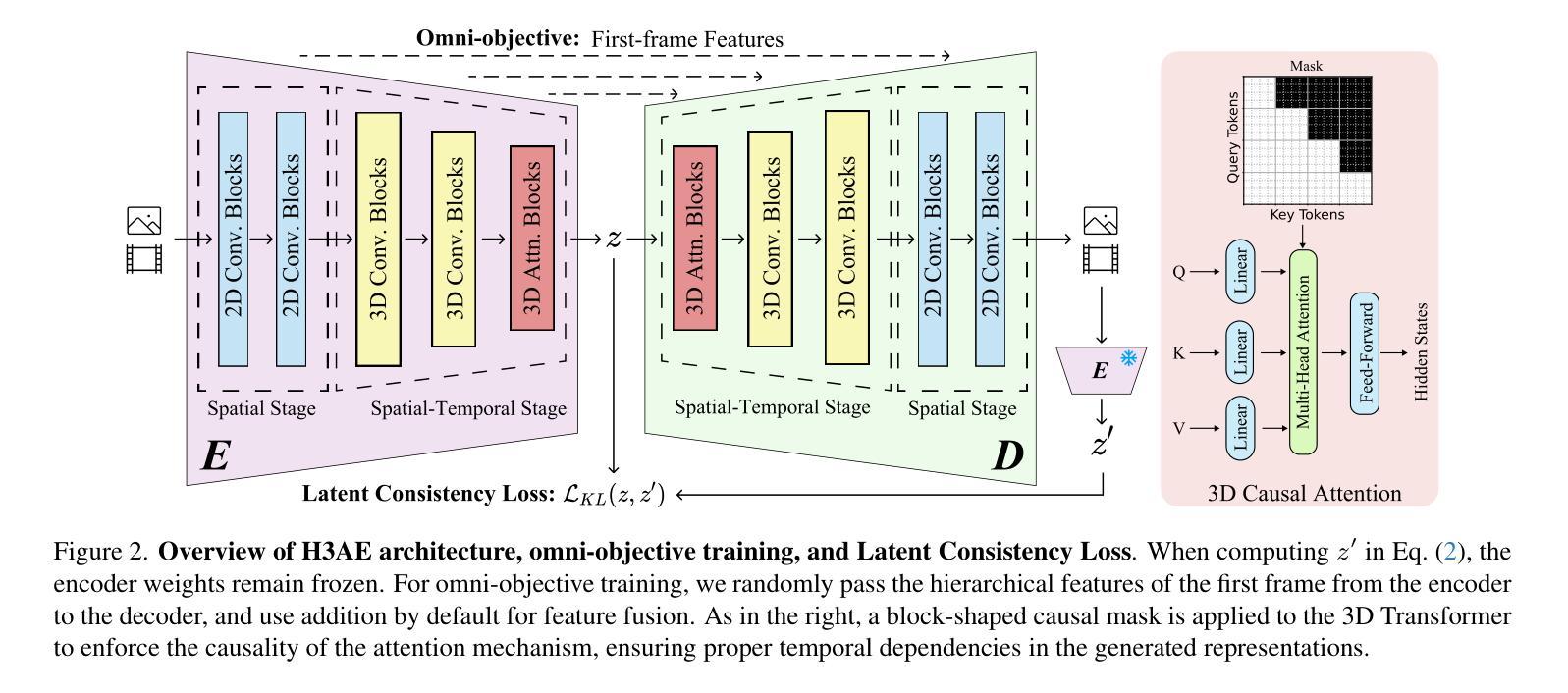
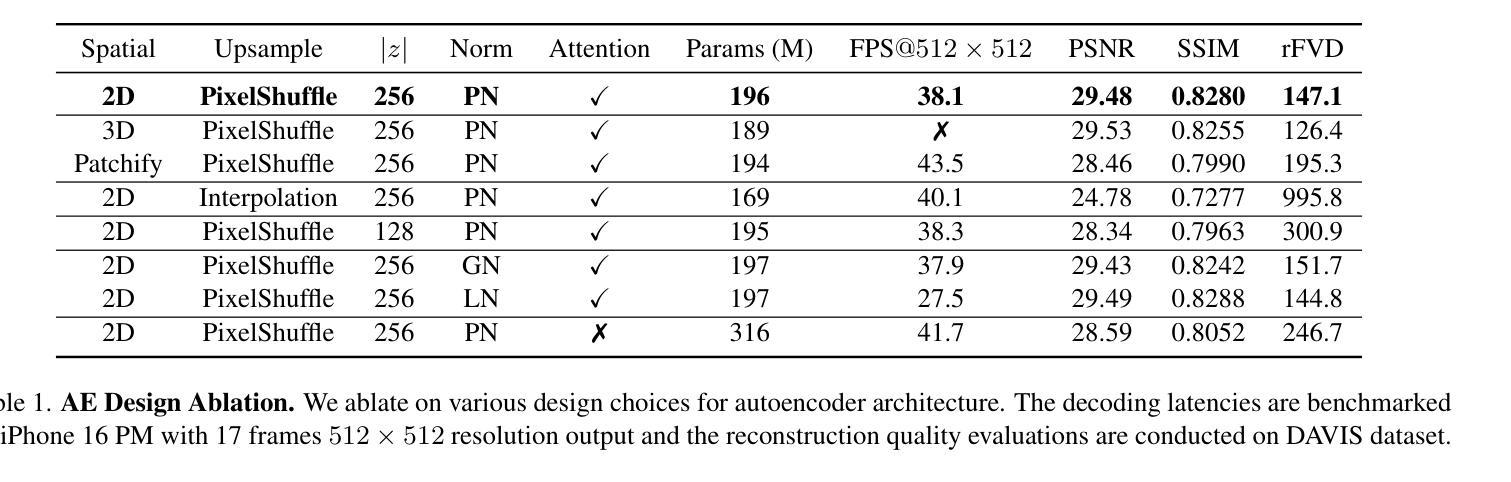
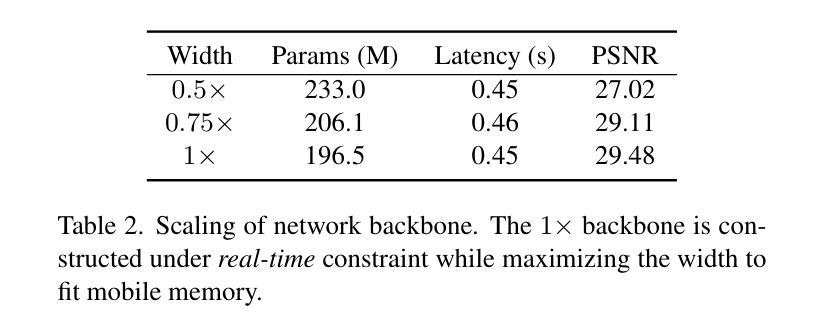
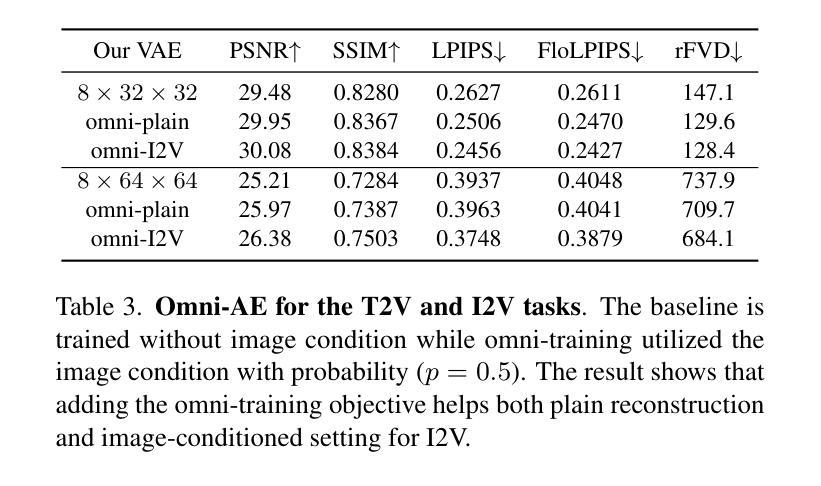
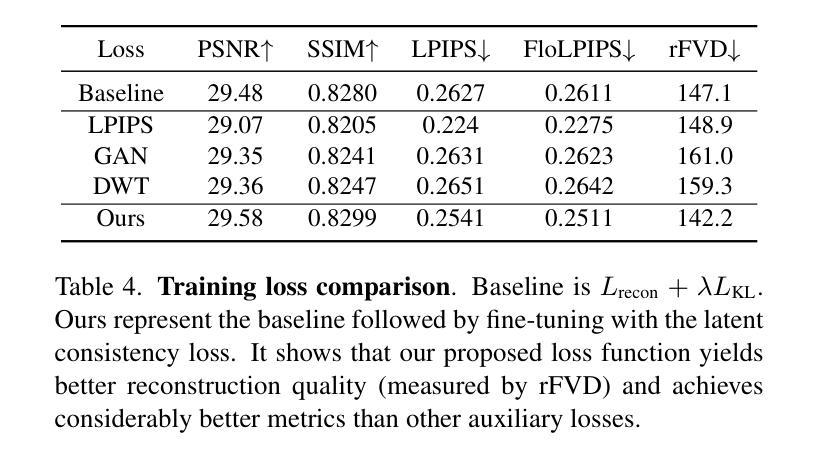
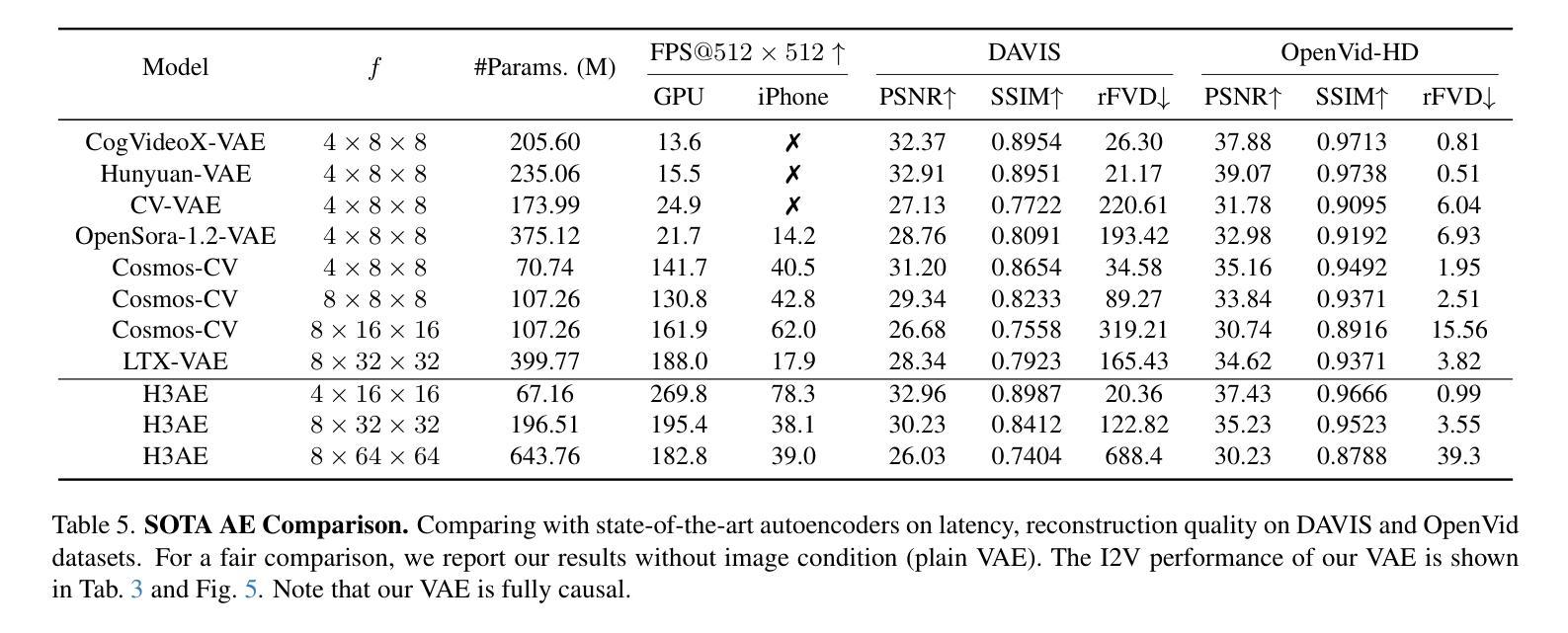
H3AE: High Compression, High Speed, and High Quality AutoEncoder for Video Diffusion Models
Authors:Yushu Wu, Yanyu Li, Ivan Skorokhodov, Anil Kag, Willi Menapace, Sharath Girish, Aliaksandr Siarohin, Yanzhi Wang, Sergey Tulyakov
Autoencoder (AE) is the key to the success of latent diffusion models for image and video generation, reducing the denoising resolution and improving efficiency. However, the power of AE has long been underexplored in terms of network design, compression ratio, and training strategy. In this work, we systematically examine the architecture design choices and optimize the computation distribution to obtain a series of efficient and high-compression video AEs that can decode in real time on mobile devices. We also unify the design of plain Autoencoder and image-conditioned I2V VAE, achieving multifunctionality in a single network. In addition, we find that the widely adopted discriminative losses, i.e., GAN, LPIPS, and DWT losses, provide no significant improvements when training AEs at scale. We propose a novel latent consistency loss that does not require complicated discriminator design or hyperparameter tuning, but provides stable improvements in reconstruction quality. Our AE achieves an ultra-high compression ratio and real-time decoding speed on mobile while outperforming prior art in terms of reconstruction metrics by a large margin. We finally validate our AE by training a DiT on its latent space and demonstrate fast, high-quality text-to-video generation capability.
自动编码器(AE)是潜扩散模型在图像和视频生成方面成功的关键,可以降低降噪分辨率并提高效率。然而,关于自动编码器的网络设计、压缩比和训练策略等方面的潜力一直被低估。在这项工作中,我们系统地研究了架构设计选择,优化了计算分配,获得了一系列高效的高压缩视频自动编码器,能够在移动设备上实时解码。我们还统一了普通自动编码器和图像条件I2V VAE的设计,在单个网络中实现了多功能性。此外,我们发现广泛采用的判别损失,即GAN、LPIPS和DWT损失,在训练大规模AE时并没有提供显著的改进。我们提出了一种新的潜在一致性损失,它不需要复杂的鉴别器设计或超参数调整,但在重建质量方面提供了稳定的改进。我们的自动编码器在移动设备上实现了超高的压缩比和实时解码速度,同时在重建指标方面大大超越了先前的技术。最后,我们通过在其潜在空间上训练DiT来验证我们的自动编码器,并展示了快速、高质量的文字到视频生成能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 4 figures, 6 tables
Summary
自动编码器(AE)是潜在扩散模型在图像和视频生成中成功的关键,它通过降低去噪分辨率并提高效率来实现这一点。然而,关于自动编码器的网络设计、压缩比和训练策略等方面的潜力一直被忽视。在这项工作中,我们系统地研究了架构设计的选择,优化了计算分布,获得了一系列高效且高压缩的视频自动编码器,能够在移动设备上实时解码。我们还统一了普通自动编码器和图像条件I2V VAE的设计,实现单一网络的多功能性。此外,我们发现广泛采用的判别损失(如GAN、LPIPS和DWT损失)在训练大规模AE时并未提供显著改进。我们提出了一种新型潜在一致性损失,该损失不需要复杂的鉴别器设计或超参数调整,但在重建质量上提供了稳定的改进。我们的自动编码器在具有超高压缩比和实时解码速度的同时,在重建指标上大幅度超越了先前技术。最后,我们通过在其潜在空间上训练DiT来验证我们的自动编码器,并展示了快速、高质量的文字到视频生成能力。
Key Takeaways
- 自动编码器(AE)是潜在扩散模型成功的关键,尤其在图像和视频生成领域。
- 通过优化网络设计、压缩比和训练策略,提高了视频自动编码器的效率和性能。
- 实现了一种实时解码的移动设备上的高效、高压缩视频自动编码器。
- 融合了普通自动编码器和图像条件I2V VAE的设计,增强了单一网络的多功能性。
- 传统的判别损失在训练大规模AE时效果有限。
- 提出了一种新型潜在一致性损失,能有效提升自动编码器的重建质量。
点此查看论文截图
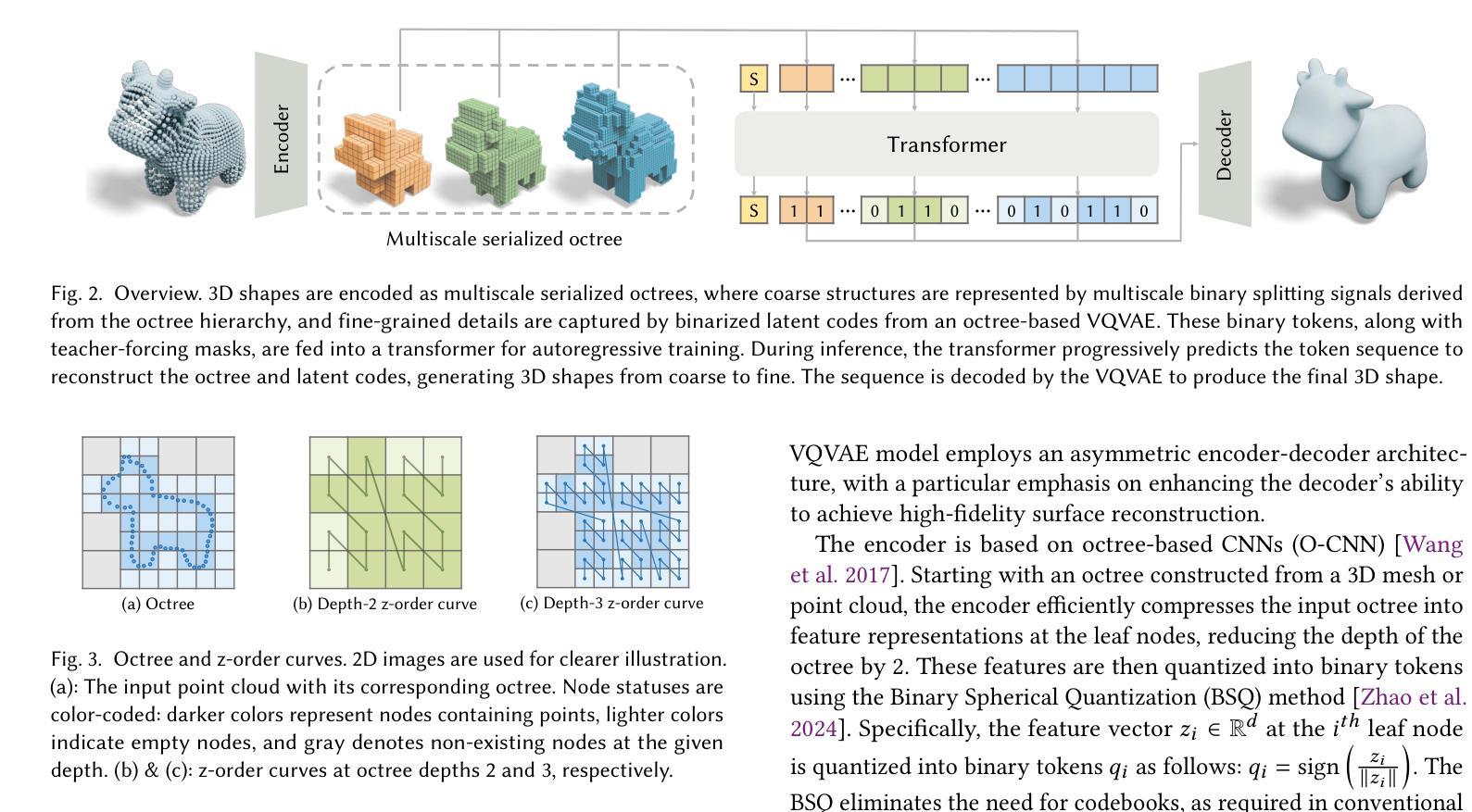
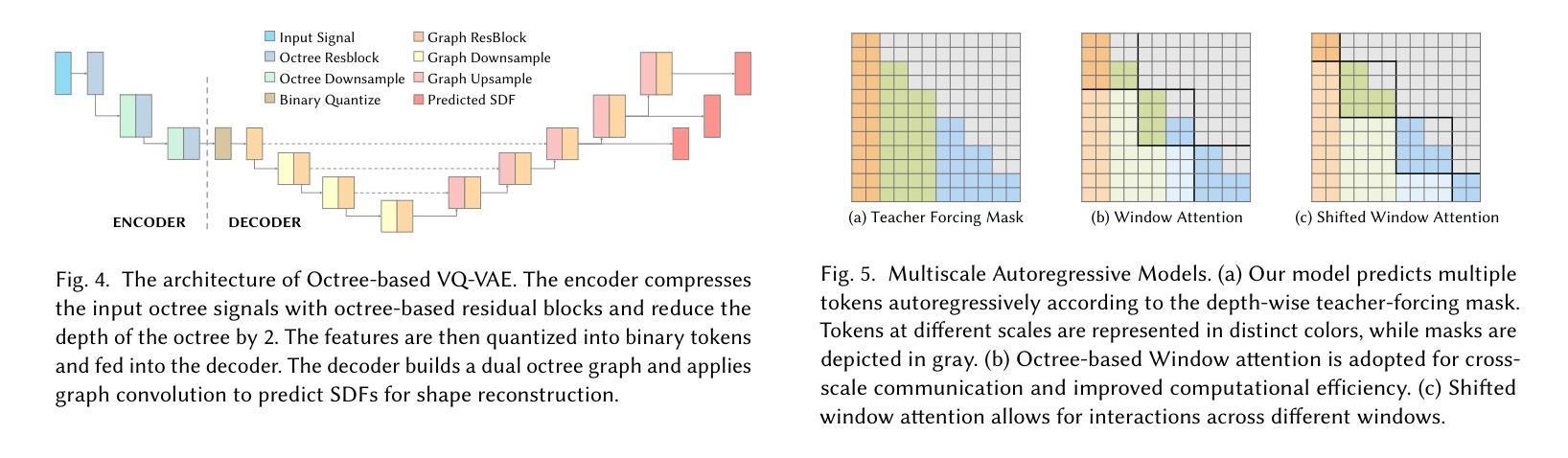
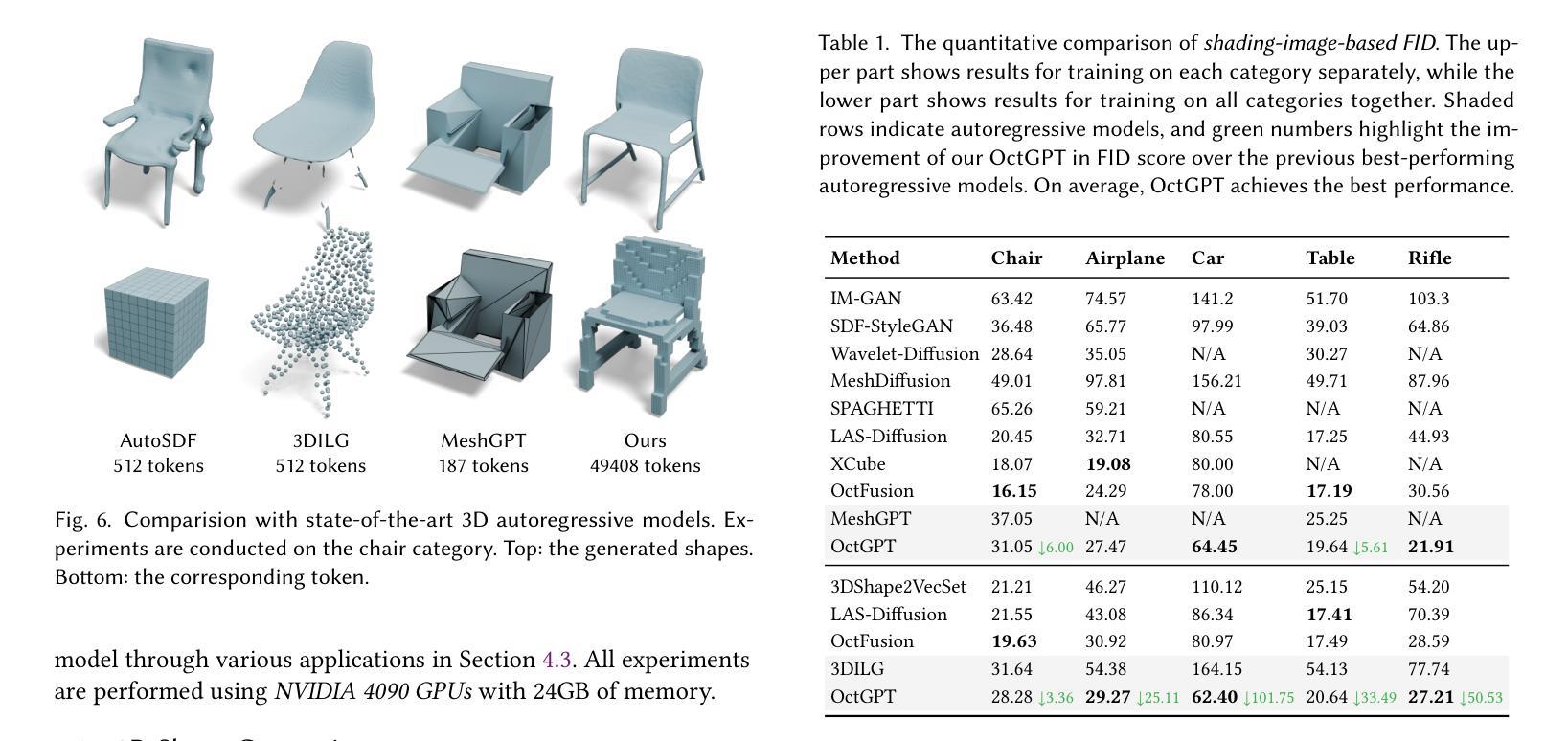
OctGPT: Octree-based Multiscale Autoregressive Models for 3D Shape Generation
Authors:Si-Tong Wei, Rui-Huan Wang, Chuan-Zhi Zhou, Baoquan Chen, Peng-Shuai Wang
Autoregressive models have achieved remarkable success across various domains, yet their performance in 3D shape generation lags significantly behind that of diffusion models. In this paper, we introduce OctGPT, a novel multiscale autoregressive model for 3D shape generation that dramatically improves the efficiency and performance of prior 3D autoregressive approaches, while rivaling or surpassing state-of-the-art diffusion models. Our method employs a serialized octree representation to efficiently capture the hierarchical and spatial structures of 3D shapes. Coarse geometry is encoded via octree structures, while fine-grained details are represented by binary tokens generated using a vector quantized variational autoencoder (VQVAE), transforming 3D shapes into compact multiscale binary sequences suitable for autoregressive prediction. To address the computational challenges of handling long sequences, we incorporate octree-based transformers enhanced with 3D rotary positional encodings, scale-specific embeddings, and token-parallel generation schemes. These innovations reduce training time by 13 folds and generation time by 69 folds, enabling the efficient training of high-resolution 3D shapes, e.g.,$1024^3$, on just four NVIDIA 4090 GPUs only within days. OctGPT showcases exceptional versatility across various tasks, including text-, sketch-, and image-conditioned generation, as well as scene-level synthesis involving multiple objects. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OctGPT accelerates convergence and improves generation quality over prior autoregressive methods, offering a new paradigm for high-quality, scalable 3D content creation. Our code and trained models are available at https://github.com/octree-nn/octgpt.
自回归模型已经在多个领域取得了显著的成功,但在3D形状生成方面的性能却远远落后于扩散模型。在本文中,我们介绍了OctGPT,这是一种用于3D形状生成的新型多尺度自回归模型,它大大提高了先前3D自回归方法的效率和性能,同时与最先进的扩散模型相匹敌甚至超越。我们的方法采用序列化八叉树表示形式,以有效地捕获3D形状的层次结构和空间结构。粗几何结构通过八叉树结构进行编码,而精细细节则由使用向量量化变分自动编码器(VQVAE)生成的二进制令牌表示,将3D形状转换为适合自回归预测的多尺度二进制序列。为了解决处理长序列的计算挑战,我们结合了基于八叉树的变压器,并增强了3D旋转位置编码、尺度特定嵌入和令牌并行生成方案。这些创新将训练时间缩短了13倍,生成时间缩短了69倍,使得在仅四台NVIDIA 4090 GPU上在几天内对高分辨率3D形状(例如1024^3)进行有效训练成为可能。OctGPT在各种任务中展示了出色的通用性,包括文本、草图和图像条件下的生成,以及涉及多个对象的场景级别合成。大量实验表明,OctGPT加速了收敛,提高了生成质量,为高质量、可扩展的3D内容创建提供了新的范式。我们的代码和训练好的模型可在https://github.com/octree-nn/octgpt上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH 2025
Summary
本文介绍了OctGPT模型,这是一种用于三维形状生成的新型多尺度自回归模型。该模型通过采用序列化八叉树表示法,有效捕捉三维形状的层次和空间结构,改进了先前的三维自回归方法的效率和性能,同时与最先进的扩散模型相抗衡或更胜一筹。OctGPT具有出色的多任务适应性,包括文本、草图、图像条件生成以及涉及多个对象的场景级别合成。它通过创新的技术手段,如基于八叉树的变压器、三维旋转位置编码、尺度特定嵌入和令牌并行生成方案,解决了处理长序列的计算挑战。该模型为高质量、可伸缩的三维内容创建提供了新的范例。
Key Takeaways
- OctGPT是一个用于3D形状生成的多尺度自回归模型,显著提高了先前自回归方法的效率和性能。
- OctGPT采用了序列化八叉树表示法,有效捕捉了3D形状的层次和空间结构。
- OctGPT可与最先进的扩散模型相抗衡或表现更佳。
- OctGPT具有出色的多任务适应性,包括文本、草图、图像条件生成和场景级别合成。
- 通过采用基于八叉树的变压器等创新技术,解决了处理长序列的计算挑战。
- OctGPT实现了高效的训练,能够在仅四天内在四台NVIDIA 4090 GPU上训练高分辨率(例如1024^3)的3D形状。
点此查看论文截图

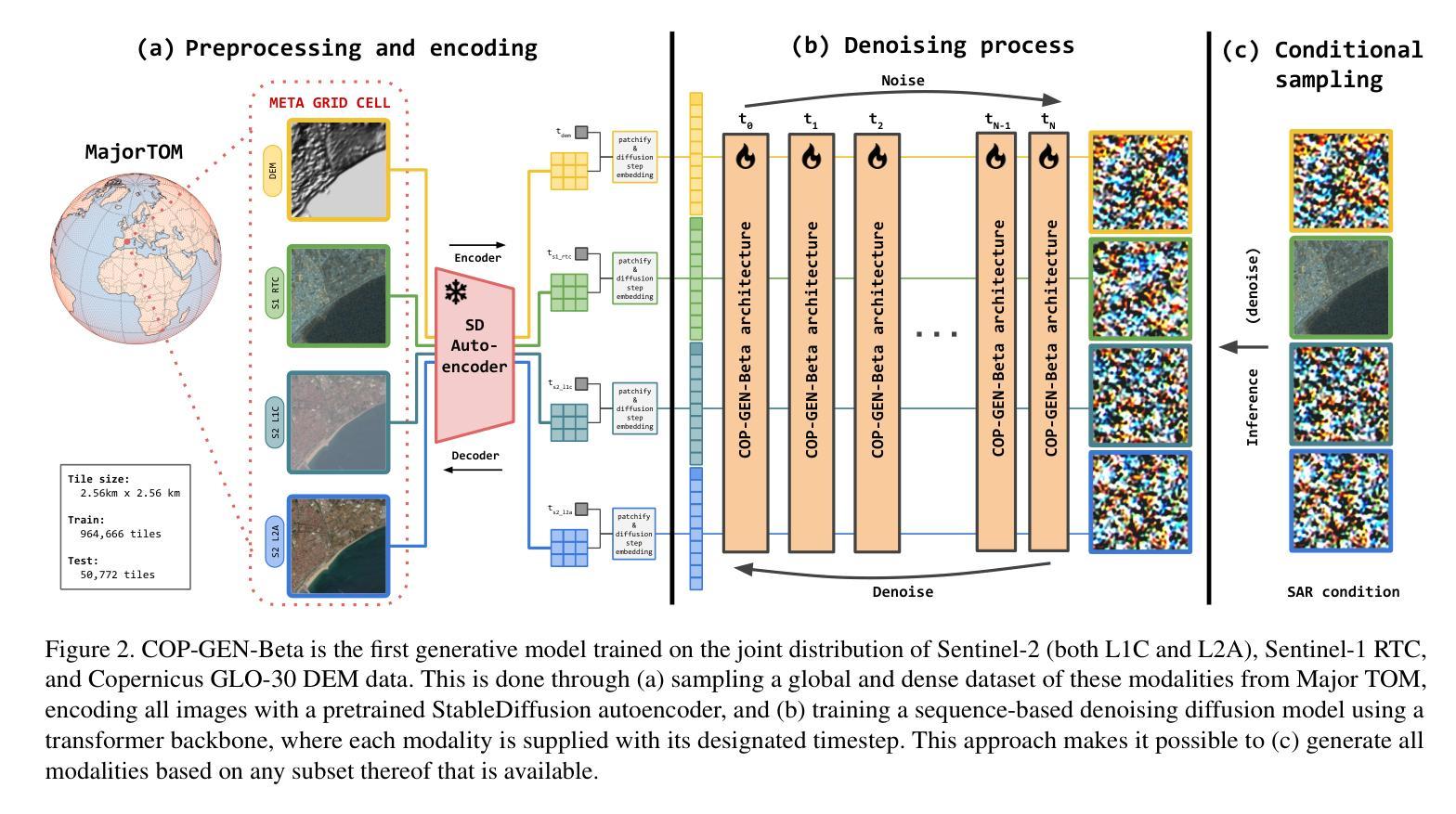
COP-GEN-Beta: Unified Generative Modelling of COPernicus Imagery Thumbnails
Authors:Miguel Espinosa, Valerio Marsocci, Yuru Jia, Elliot J. Crowley, Mikolaj Czerkawski
In remote sensing, multi-modal data from various sensors capturing the same scene offers rich opportunities, but learning a unified representation across these modalities remains a significant challenge. Traditional methods have often been limited to single or dual-modality approaches. In this paper, we introduce COP-GEN-Beta, a generative diffusion model trained on optical, radar, and elevation data from the Major TOM dataset. What sets COP-GEN-Beta apart is its ability to map any subset of modalities to any other, enabling zero-shot modality translation after training. This is achieved through a sequence-based diffusion transformer, where each modality is controlled by its own timestep embedding. We extensively evaluate COP-GEN-Beta on thumbnail images from the Major TOM dataset, demonstrating its effectiveness in generating high-quality samples. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations validate the model’s performance, highlighting its potential as a powerful pre-trained model for future remote sensing tasks.
在遥感领域,从不同传感器捕捉同一场景的多模态数据提供了丰富的机会,但在这些模态上学习统一表征仍是一个巨大的挑战。传统方法通常局限于单一或双模态方法。在本文中,我们介绍了COP-GEN-Beta,这是一个在Major TOM数据集的光学、雷达和海拔数据上训练的生成型扩散模型。COP-GEN-Beta的特殊之处在于,它能够将任何模态子集映射到其他模态,实现训练后的零样本模态转换。这是通过基于序列的扩散变压器实现的,其中每个模态由自己的时间步长嵌入控制。我们在Major TOM数据集的缩略图图像上对COP-GEN-Beta进行了广泛评估,证明了它在生成高质量样本方面的有效性。定性和定量评估验证了该模型的性能,突显了其在未来遥感任务中作为强大预训练模型的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025 Workshop MORSE
Summary
多模态数据在遥感领域提供了丰富的机会,但学习跨模态的统一表示仍然是一个挑战。本文介绍了一种名为COP-GEN-Beta的生成型扩散模型,该模型能够在Major TOM数据集的光学、雷达和地形数据上进行训练。COP-GEN-Beta的突出特点是能够实现任意模态子集之间的映射,训练后能够实现零样本模态转换。这通过基于序列的扩散变换器实现,每个模态由自己的时间步长嵌入控制。在Major TOM数据集缩略图上的广泛评估证明了COP-GEN-Beta生成高质量样本的有效性。该模型表现出色,有望成为未来遥感任务的强大预训练模型。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态数据在遥感中具有丰富机会,但跨模态统一表示学习具有挑战性。
- COP-GEN-Beta是一种生成型扩散模型,能在多种模态数据上进行训练。
- COP-GEN-Beta能够实现任意模态子集之间的映射,实现零样本模态转换。
- 通过序列扩散变换器实现模型,每个模态具有自己的时间步长嵌入控制。
- 在Major TOM数据集缩略图上的评估证明了COP-GEN-Beta生成高质量样本的能力。
- 模型的性能通过定性和定量评估得到验证。
点此查看论文截图


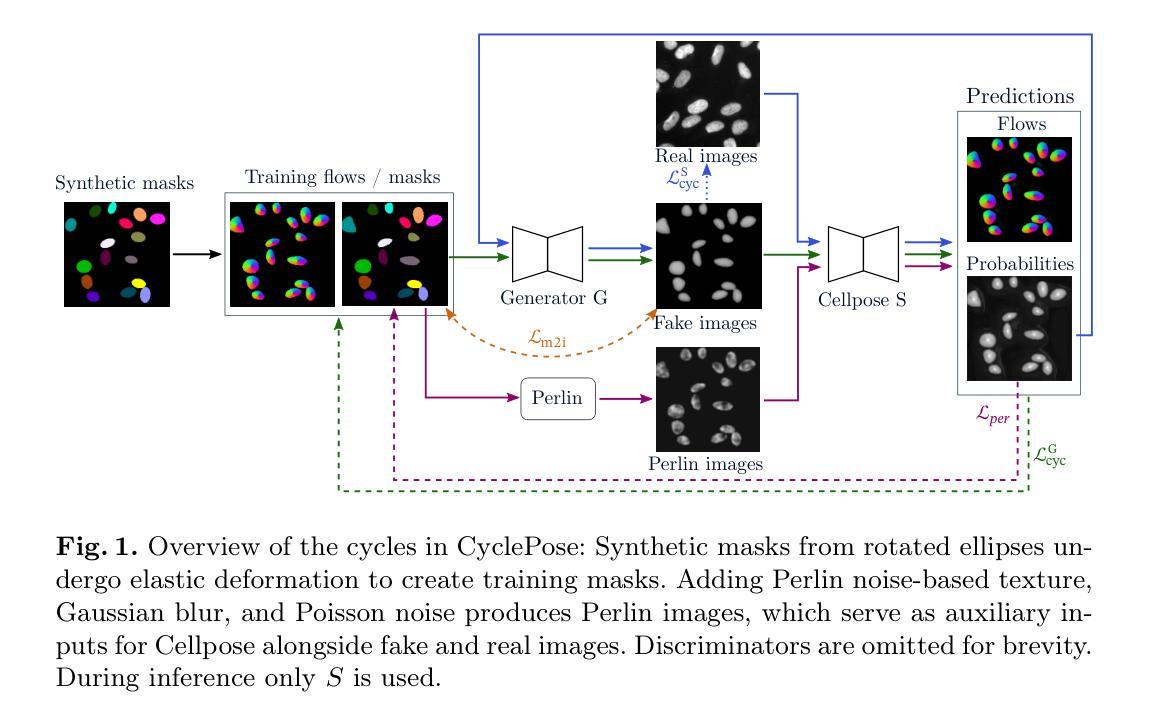
CyclePose – Leveraging Cycle-Consistency for Annotation-Free Nuclei Segmentation in Fluorescence Microscopy
Authors:Jonas Utz, Stefan Vocht, Anne Tjorven Buessen, Dennis Possart, Fabian Wagner, Mareike Thies, Mingxuan Gu, Stefan Uderhardt, Katharina Breininger
In recent years, numerous neural network architectures specifically designed for the instance segmentation of nuclei in microscopic images have been released. These models embed nuclei-specific priors to outperform generic architectures like U-Nets; however, they require large annotated datasets, which are often not available. Generative models (GANs, diffusion models) have been used to compensate for this by synthesizing training data. These two-stage approaches are computationally expensive, as first a generative model and then a segmentation model has to be trained. We propose CyclePose, a hybrid framework integrating synthetic data generation and segmentation training. CyclePose builds on a CycleGAN architecture, which allows unpaired translation between microscopy images and segmentation masks. We embed a segmentation model into CycleGAN and leverage a cycle consistency loss for self-supervision. Without annotated data, CyclePose outperforms other weakly or unsupervised methods on two public datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/jonasutz/CyclePose
近年来,专为显微图像中的细胞核实例分割设计的神经网络架构已经陆续发布。这些模型会嵌入特定的细胞核先验知识,以超越U-Net等通用架构的性能;然而,它们需要大量标注数据集,而这些数据通常并不可用。生成模型(GANs、扩散模型)已被用来通过合成训练数据来弥补这一缺陷。这些两阶段的方法计算成本高昂,因为首先需要训练一个生成模型,然后训练一个分割模型。我们提出了CyclePose,这是一个集成合成数据生成和分割训练于一体的混合框架。CyclePose基于CycleGAN架构,允许显微图像和分割掩膜之间的无配对转换。我们将分割模型嵌入到CycleGAN中,并利用循环一致性损失进行自监督。无需标注数据,CyclePose在两个公共数据集上的表现优于其他弱监督或无监督方法。相关代码可通过https://github.com/jonasutz/CyclePose获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review for MICCAI 2025
摘要
近期发布多种专为微观图像核实例分割设计的神经网络架构,这些模型通过嵌入核特异性先验知识,性能优于通用架构(如U-Net),但它们需要大量标注数据集,而这通常难以获取。生成模型(GANs,扩散模型)已用于合成训练数据以弥补这一缺陷。这些两阶段方法计算成本高昂,需先训练生成模型,再训练分割模型。我们提出CyclePose,一个集成合成数据生成和分割训练的混合框架。CyclePose基于CycleGAN架构,实现显微镜图像和分割掩膜之间的无配对转换。我们在CycleGAN中嵌入分割模型,并利用循环一致性损失实现自监督。无需标注数据,CyclePose在公开数据集上的表现优于其他弱监督或无监督方法。相关代码已发布至https://github.com/jonasutz/CyclePose。
关键见解
- 近年出现多种专为微观图像核实例分割设计的神经网络架构,但需求大量标注数据。
- 生成模型(如GANs和扩散模型)已被用于合成训练数据以克服数据缺乏的问题。
- 当前方法多为两阶段,计算成本高昂,需分别训练生成模型和分割模型。
- 提出CyclePose混合框架,整合合成数据生成和分割训练。
- CyclePose基于CycleGAN架构,实现图像和分割掩膜之间的无配对转换。
- CyclePose在无需标注数据的情况下,公开数据集上的表现优于其他弱监督或无监督方法。
- CyclePose的相关代码已发布至GitHub供公众访问。
点此查看论文截图

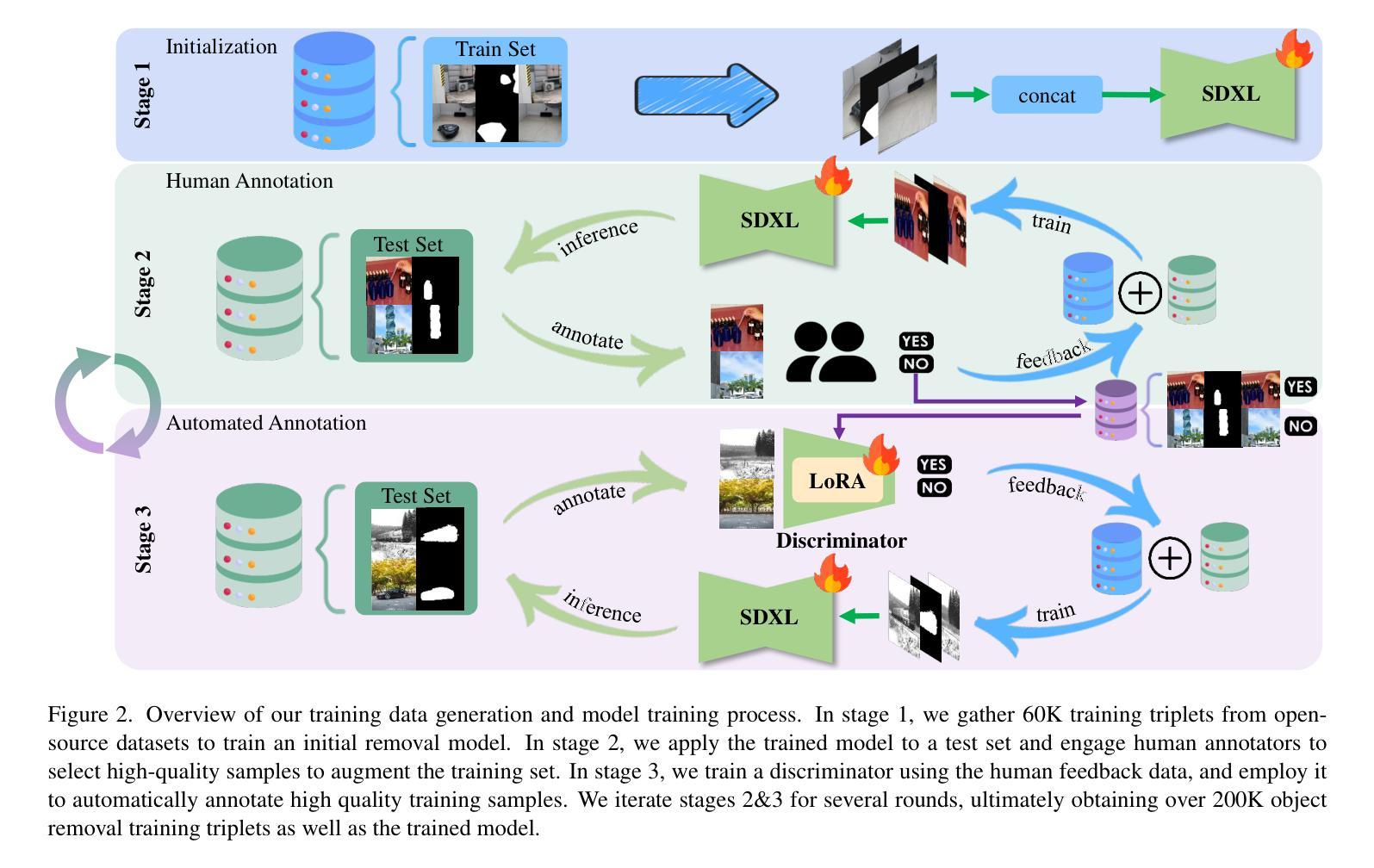
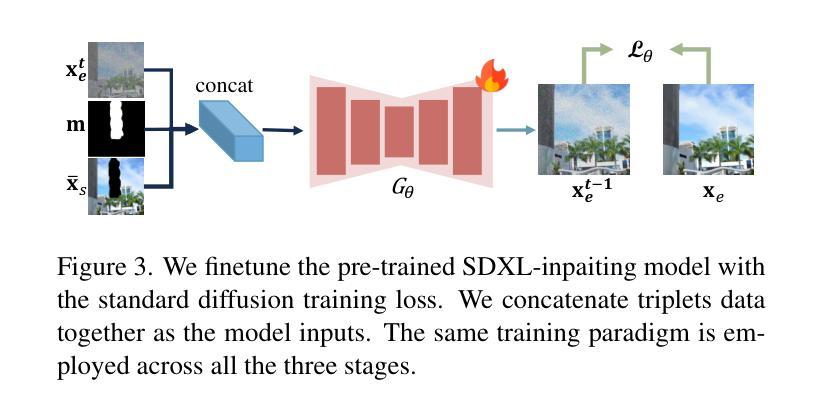
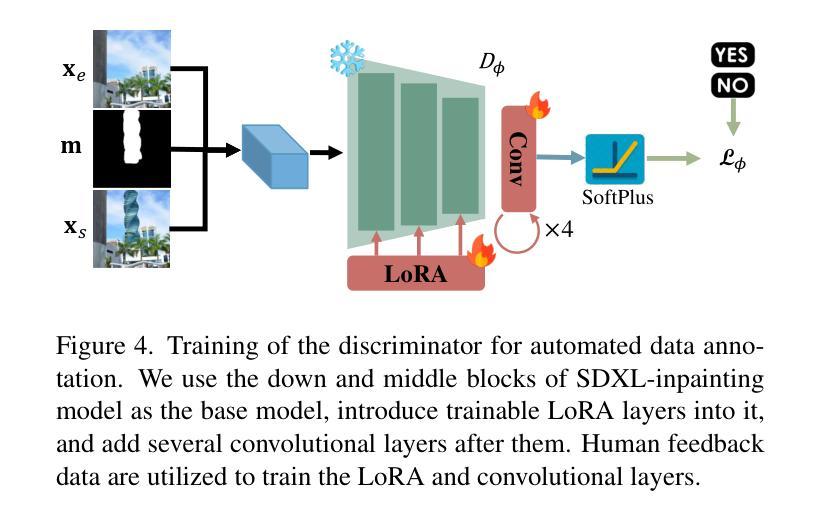
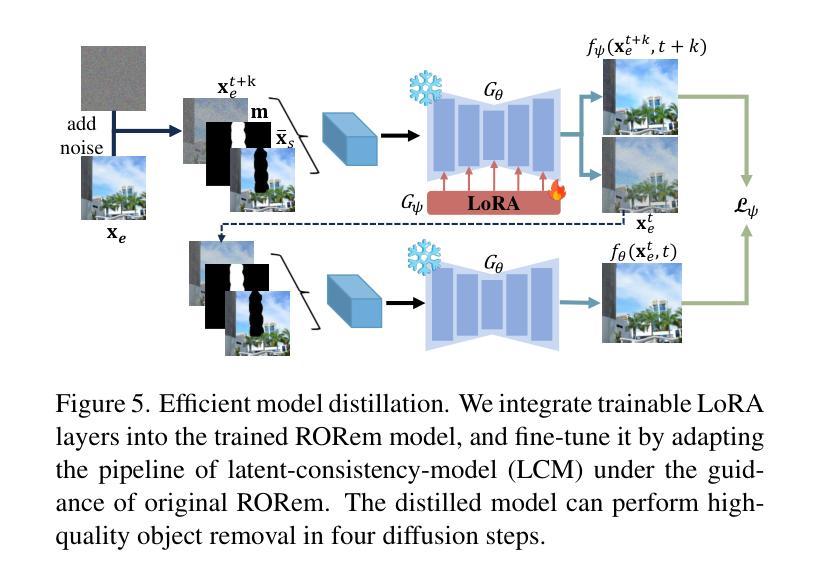
RORem: Training a Robust Object Remover with Human-in-the-Loop
Authors:Ruibin Li, Tao Yang, Song Guo, Lei Zhang
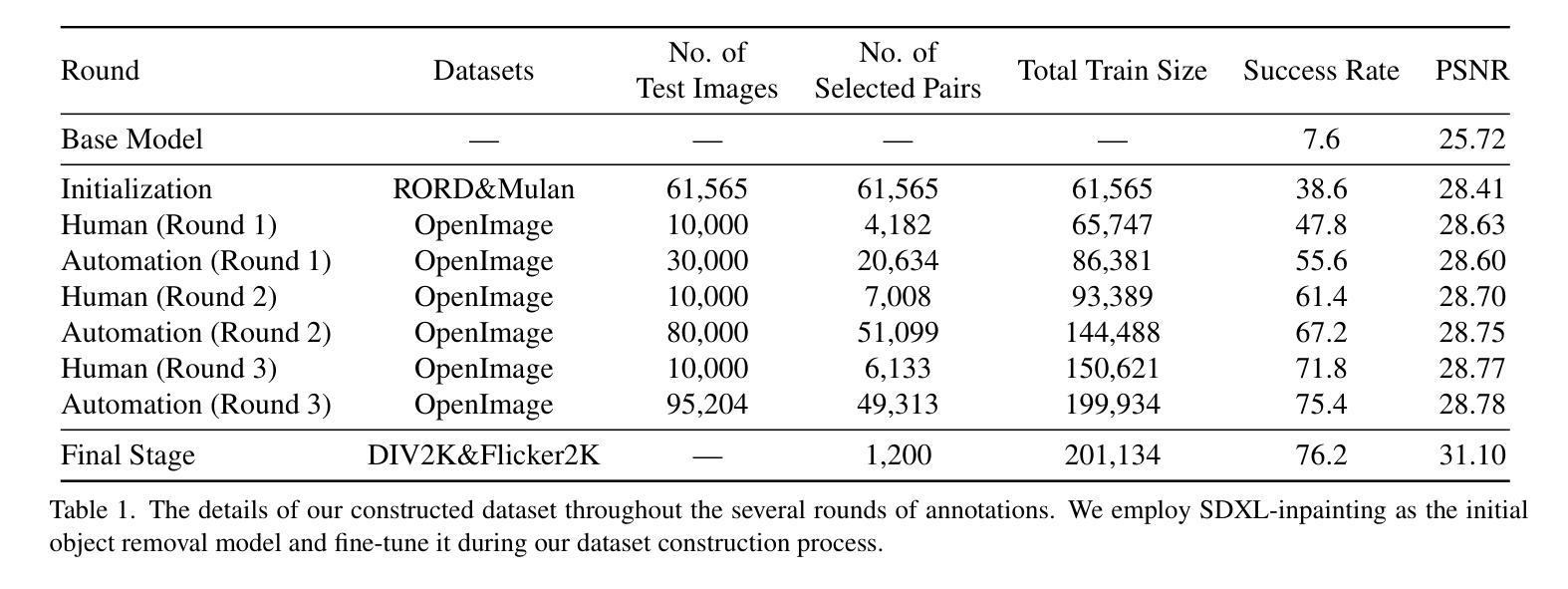
Despite the significant advancements, existing object removal methods struggle with incomplete removal, incorrect content synthesis and blurry synthesized regions, resulting in low success rates. Such issues are mainly caused by the lack of high-quality paired training data, as well as the self-supervised training paradigm adopted in these methods, which forces the model to in-paint the masked regions, leading to ambiguity between synthesizing the masked objects and restoring the background. To address these issues, we propose a semi-supervised learning strategy with human-in-the-loop to create high-quality paired training data, aiming to train a Robust Object Remover (RORem). We first collect 60K training pairs from open-source datasets to train an initial object removal model for generating removal samples, and then utilize human feedback to select a set of high-quality object removal pairs, with which we train a discriminator to automate the following training data generation process. By iterating this process for several rounds, we finally obtain a substantial object removal dataset with over 200K pairs. Fine-tuning the pre-trained stable diffusion model with this dataset, we obtain our RORem, which demonstrates state-of-the-art object removal performance in terms of both reliability and image quality. Particularly, RORem improves the object removal success rate over previous methods by more than 18%. The dataset, source code and trained model are available at https://github.com/leeruibin/RORem.
尽管取得了重大进展,现有的物体移除方法仍存在困扰,例如去除不完全、内容合成不正确以及合成区域模糊,导致成功率较低。这些问题主要是由于缺乏高质量配对训练数据以及这些方法所采用的自监督训练范式导致的。自监督训练范式迫使模型对遮罩区域进行填充,导致合成遮罩物体和恢复背景之间产生模糊。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种半监督学习策略,并引入人类参与来创建高质量配对训练数据,旨在训练一个稳健物体移除器(RORem)。我们首先从公开数据源收集6万组训练配对数据,用于训练初始物体移除模型以生成移除样本,然后利用人类反馈选择一组高质量的物体移除配对数据,并使用这些数据训练一个鉴别器,以自动化后续的训练数据生成过程。经过几轮迭代后,我们最终获得了一个包含超过20万组配对数据的物体移除数据集。使用此数据集对预训练的稳定扩散模型进行微调,我们得到了RORem,它在可靠性和图像质量方面实现了最先进的物体移除性能。特别地,RORem将物体移除成功率提高了超过18%。数据集、源代码和训练好的模型均可在https://github.com/leeruibin/RORem上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种半监督学习策略,结合人工参与,创建高质量配对训练数据,旨在训练一个稳健的对象移除器(RORem)。通过迭代收集训练样本和人类反馈选择高质量的数据对,训练判别器自动化后续的训练数据生成过程。使用此数据集微调预训练的稳定扩散模型,获得具有先进性能的RORem,在可靠性和图像质量方面均表现优异,对象移除成功率较之前的方法提高了18%以上。
Key Takeaways
- 现有对象移除方法存在不完整移除、内容合成不正确和合成区域模糊等问题,导致成功率低。
- 问题主要源于缺乏高质量配对训练数据和自监督训练范式。
- 提出一种半监督学习策略,结合人工参与创建高质量配对训练数据,以训练稳健的对象移除器(RORem)。
- 通过迭代收集训练样本和人类反馈选择数据对,训练判别器自动化后续数据生成。
- RORem在可靠性和图像质量方面表现优异,对象移除成功率较之前的方法提高18%以上。
- RORem模型、数据集和源代码均可在指定GitHub仓库中找到。
点此查看论文截图

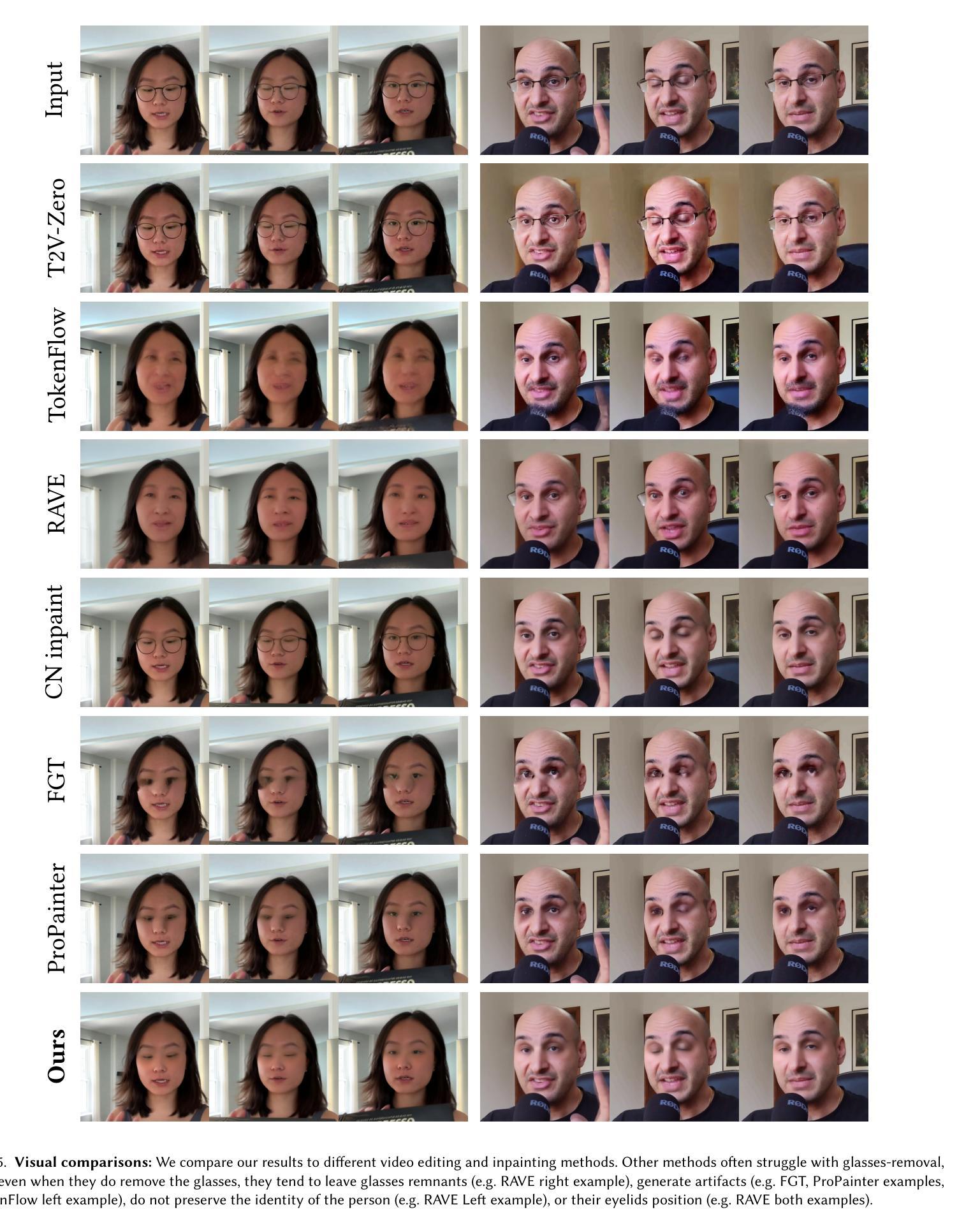
V-LASIK: Consistent Glasses-Removal from Videos Using Synthetic Data
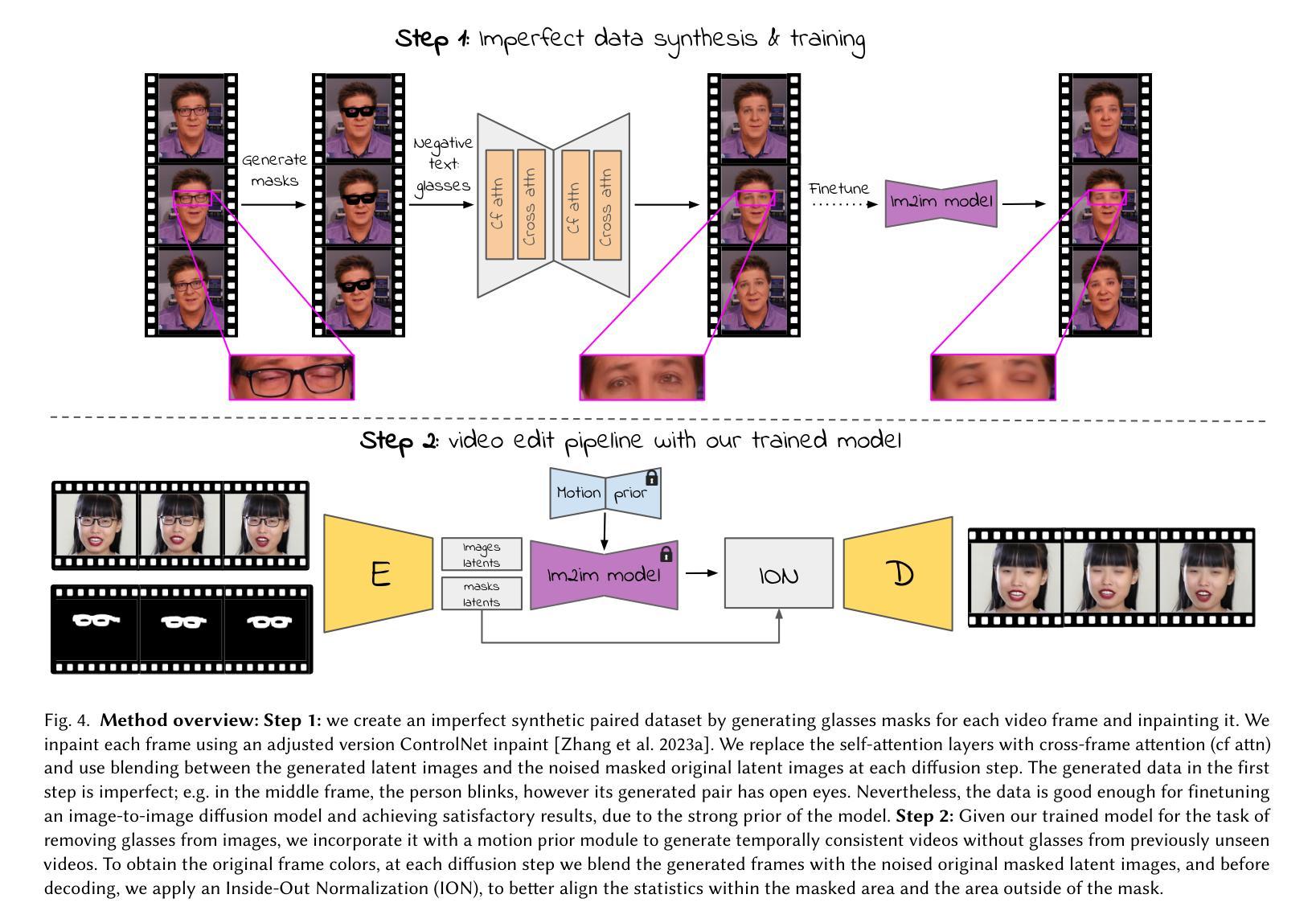
Authors:Rotem Shalev-Arkushin, Aharon Azulay, Tavi Halperin, Eitan Richardson, Amit H. Bermano, Ohad Fried
Diffusion-based generative models have recently shown remarkable image and video editing capabilities. However, local video editing, particularly removal of small attributes like glasses, remains a challenge. Existing methods either alter the videos excessively, generate unrealistic artifacts, or fail to perform the requested edit consistently throughout the video. In this work, we focus on consistent and identity-preserving removal of glasses in videos, using it as a case study for consistent local attribute removal in videos. Due to the lack of paired data, we adopt a weakly supervised approach and generate synthetic imperfect data, using an adjusted pretrained diffusion model. We show that despite data imperfection, by learning from our generated data and leveraging the prior of pretrained diffusion models, our model is able to perform the desired edit consistently while preserving the original video content. Furthermore, we exemplify the generalization ability of our method to other local video editing tasks by applying it successfully to facial sticker-removal. Our approach demonstrates significant improvement over existing methods, showcasing the potential of leveraging synthetic data and strong video priors for local video editing tasks.
基于扩散的生成模型最近在图像和视频编辑功能方面表现出了显著的实力。然而,局部视频编辑,特别是去除像眼镜这样的小属性,仍然是一个挑战。现有方法要么过度修改视频,产生不真实的伪影,要么无法在视频中持续执行所需的编辑。在这项工作中,我们专注于在视频中一致且保持身份地去除眼镜,将其作为视频中一致局部属性去除的个案研究。由于缺乏配对数据,我们采用弱监督方法并生成合成的不完美数据,使用调整过的预训练扩散模型。我们表明,尽管数据存在不完美之处,但通过从生成的数据中学习并利用预训练扩散模型的先验知识,我们的模型能够一致地执行所需的编辑操作同时保留原始视频内容。此外,我们通过成功将其应用于面部贴纸去除,展示了该方法在其他局部视频编辑任务上的泛化能力。我们的方法相较于现有方法有明显的改进,展示了利用合成数据和强大的视频先验信息在局部视频编辑任务中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于扩散模型的视频编辑技术,特别是在处理局部视频编辑方面的挑战,如眼镜去除等。研究团队针对这一问题,采用弱监督方法,利用调整后的预训练扩散模型生成合成不完美数据。即使数据存在缺陷,模型也能从生成的数据中学习,并利用预训练扩散模型的先验知识,实现对视频的连续眼镜去除,同时保留视频内容的原始性。此外,该研究还展示了该方法在其他局部视频编辑任务中的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像和视频编辑中显示出强大的能力。
- 局部视频编辑(如眼镜去除)仍然存在挑战。
- 现有方法往往会导致视频内容过度修改、生成不真实伪影或无法持续执行编辑请求。
- 研究提出了一种弱监督方法,利用调整后的预训练扩散模型生成合成不完美数据来解决眼镜去除问题。
- 即使数据存在缺陷,模型也能学习并成功执行眼镜去除操作,同时保持视频内容的连贯性和真实性。
- 该方法具有泛化到其他局部视频编辑任务的能力。
点此查看论文截图




Financial Models in Generative Art: Black-Scholes-Inspired Concept Blending in Text-to-Image Diffusion
Authors:Divya Kothandaraman, Ming Lin, Dinesh Manocha
We introduce a novel approach for concept blending in pretrained text-to-image diffusion models, aiming to generate images at the intersection of multiple text prompts. At each time step during diffusion denoising, our algorithm forecasts predictions w.r.t. the generated image and makes informed text conditioning decisions. Central to our method is the unique analogy between diffusion models, which are rooted in non-equilibrium thermodynamics, and the Black-Scholes model for financial option pricing. By drawing parallels between key variables in both domains, we derive a robust algorithm for concept blending that capitalizes on the Markovian dynamics of the Black-Scholes framework. Our text-based concept blending algorithm is data-efficient, meaning it does not need additional training. Furthermore, it operates without human intervention or hyperparameter tuning. We highlight the benefits of our approach by comparing it qualitatively and quantitatively to other text based concept blending techniques, including linear interpolation, alternating prompts, step-wise prompt switching, and CLIP-guided prompt selection across various scenarios such as single object per text prompt, multiple objects per text prompt and objects against backgrounds. Our work shows that financially inspired techniques can enhance text-to-image concept blending in generative AI, paving the way for broader innovation. Code is available at https://github.com/divyakraman/BlackScholesDiffusion2024.
我们介绍了一种在预训练文本到图像扩散模型中进行概念融合的新方法,旨在生成多个文本提示的交叉点的图像。在扩散去噪的每个时间步长中,我们的算法预测生成的图像并做出明智的文本条件决策。我们的方法的核心在于扩散模型与非平衡热力学的独特类比,以及与金融期权定价的Black-Scholes模型之间的关联。通过比较两个领域中的关键变量,我们推导出了一个稳健的概念融合算法,该算法充分利用了Black-Scholes框架的马尔可夫动力学。我们的基于文本的概念融合算法具有数据效率,意味着它不需要额外的训练。此外,它可以在没有人工干预或超参数调整的情况下运行。我们通过与其他基于文本的概念融合技术进行比较,突出了我们方法的好处,包括线性插值、交替提示、逐步提示切换以及CLIP引导的提示选择等。比较场景包括每个文本提示单个对象、每个文本提示多个对象以及对象与背景。我们的研究表明,金融启发技术可以增强生成人工智能中的文本到图像概念融合,为更广泛的创新铺平道路。代码可在https://github.com/divyakraman/BlackScholesDiffusion2024找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种在预训练文本到图像扩散模型中进行概念融合的新方法,旨在生成多个文本提示的交叉点的图像。在扩散去噪的每个时间步长中,我们的算法预测生成的图像并做出明智的文本条件决策。我们的方法的核心在于扩散模型与非平衡态热力学之间的独特类比,以及与金融期权定价的Black-Scholes模型之间的类比。通过比较两个领域的关键变量,我们推导出一种概念融合算法,该算法利用Black-Scholes框架的马尔可夫动力学。我们的基于文本的概融算法非常注重数据效率,无需额外的训练。此外,它无需人工干预或超参数调整。我们通过与其他基于文本的概融合技术(包括线性插值、交替提示、逐步提示切换和CLIP引导提示选择等)在各种场景下的定性和定量比较,突出了我们方法的优势。本文展示了金融启发技术可以增强生成人工智能中的文本到图像概念融合,为更广泛的创新铺平了道路。相关代码已公开发布于https://github.com/divyakraman/BlackScholesDiffusion2024。
关键见解
- 提出了一种新颖的文本到图像扩散模型中的概念融合方法,旨在生成多个文本提示交叉点的图像。
- 通过将扩散模型与Black-Scholes金融期权定价模型进行类比,提出了一种稳健的概念融合算法。
- 该算法在数据效率方面表现出色,无需额外的训练,而且不需要人工干预或超参数调整。
- 在各种场景下与现有的文本概念融合技术进行了比较,证明了其优势。
- 展示了金融启发技术在生成人工智能中的文本到图像概念融合的潜力。
- 为更广泛的创新和进一步的研发提供了新的视角和思路。
点此查看论文截图