⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-17 更新
TerraMind: Large-Scale Generative Multimodality for Earth Observation
Authors:Johannes Jakubik, Felix Yang, Benedikt Blumenstiel, Erik Scheurer, Rocco Sedona, Stefano Maurogiovanni, Jente Bosmans, Nikolaos Dionelis, Valerio Marsocci, Niklas Kopp, Rahul Ramachandran, Paolo Fraccaro, Thomas Brunschwiler, Gabriele Cavallaro, Juan Bernabe-Moreno, Nicolas Longépé
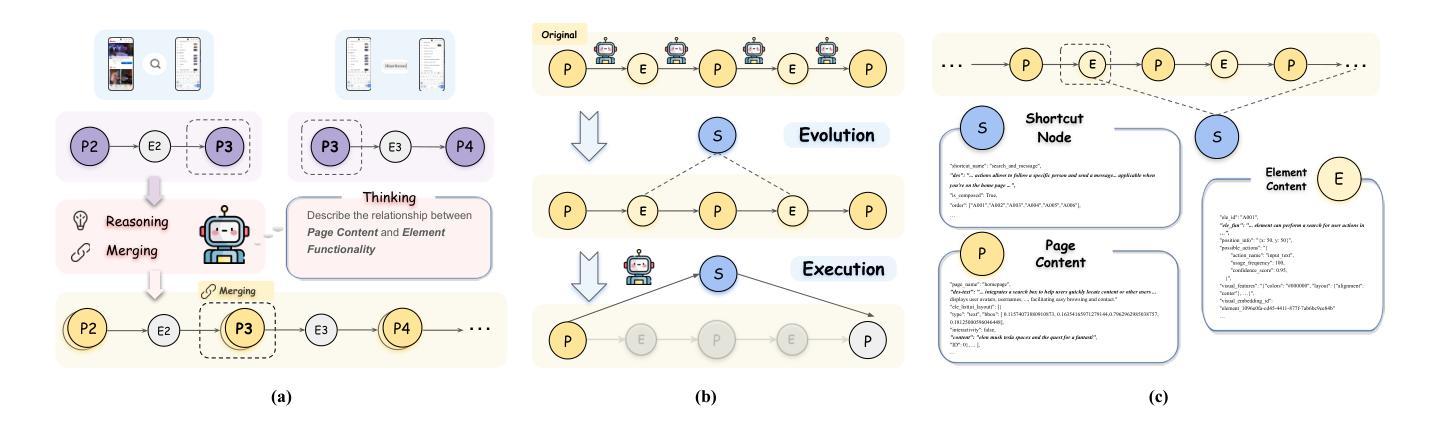
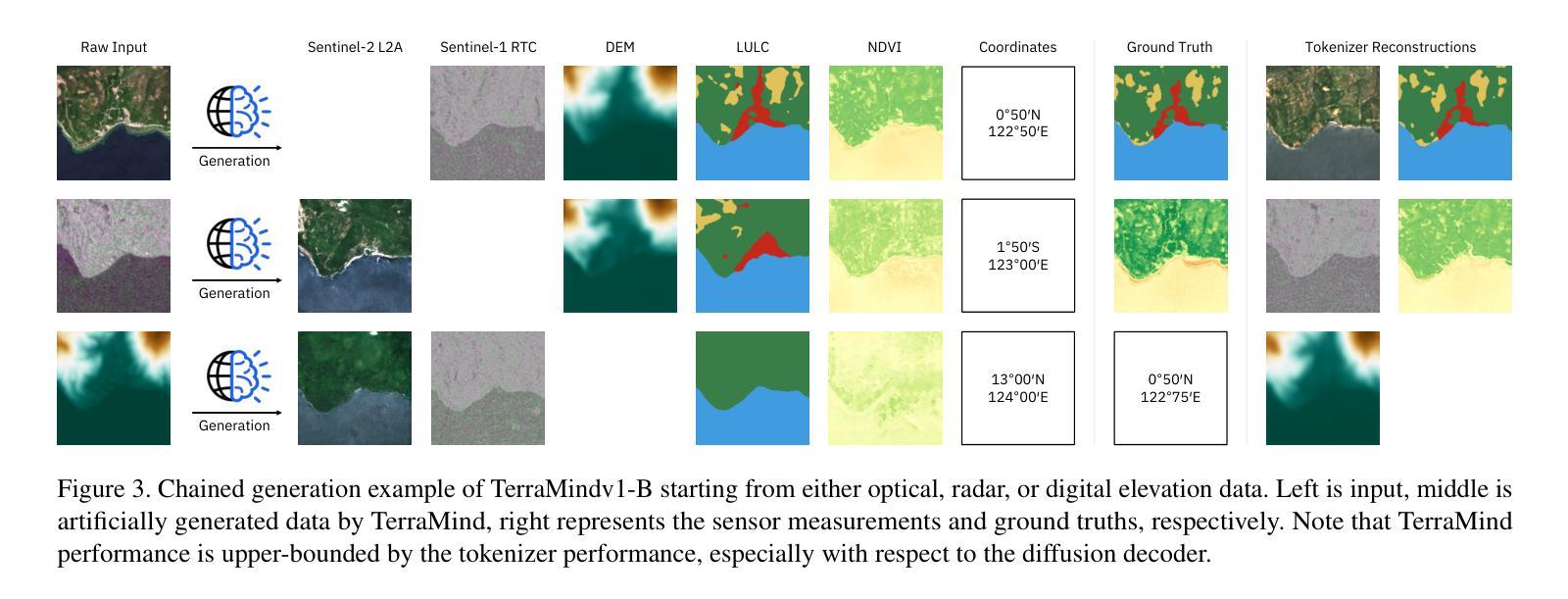
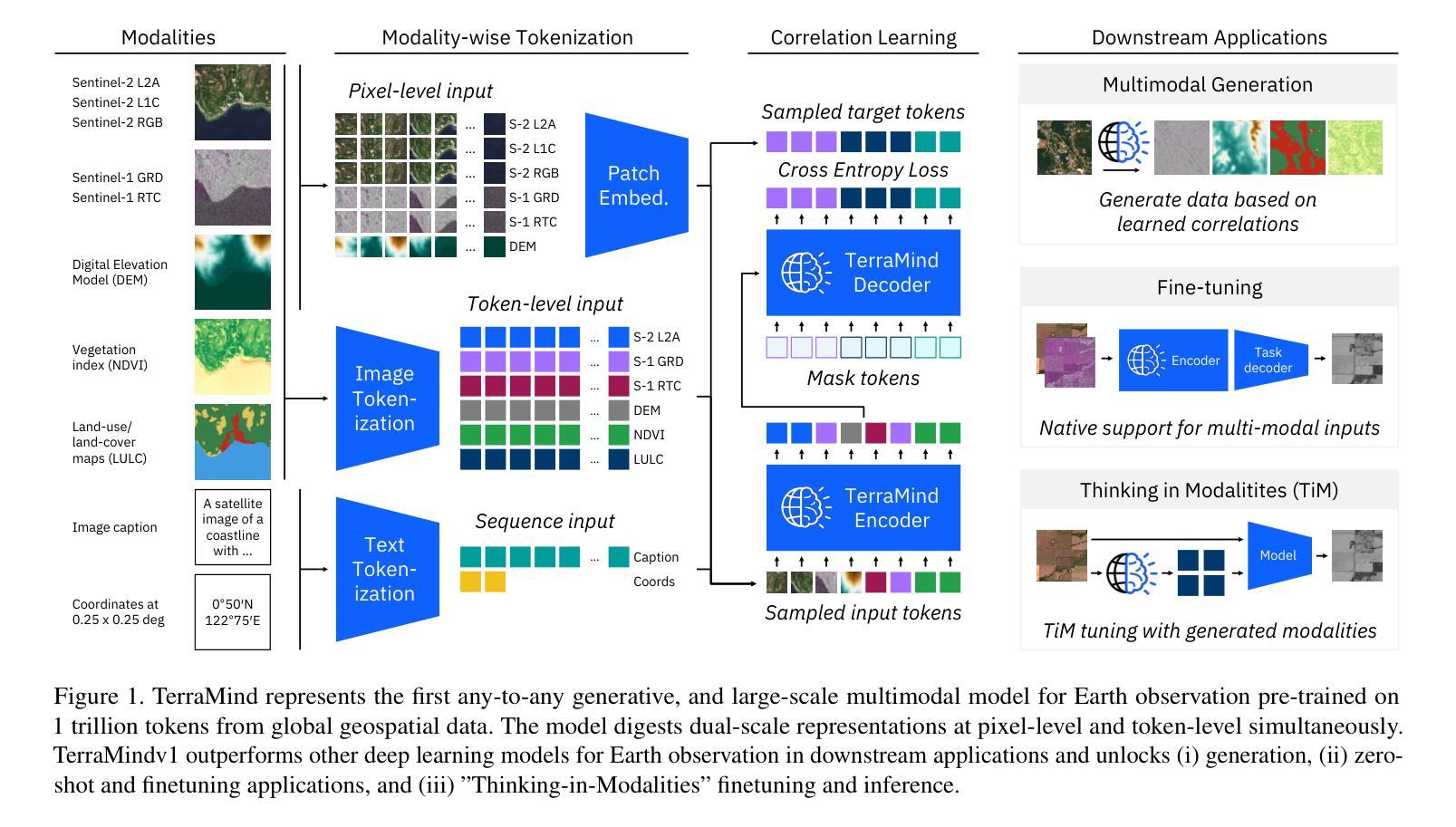
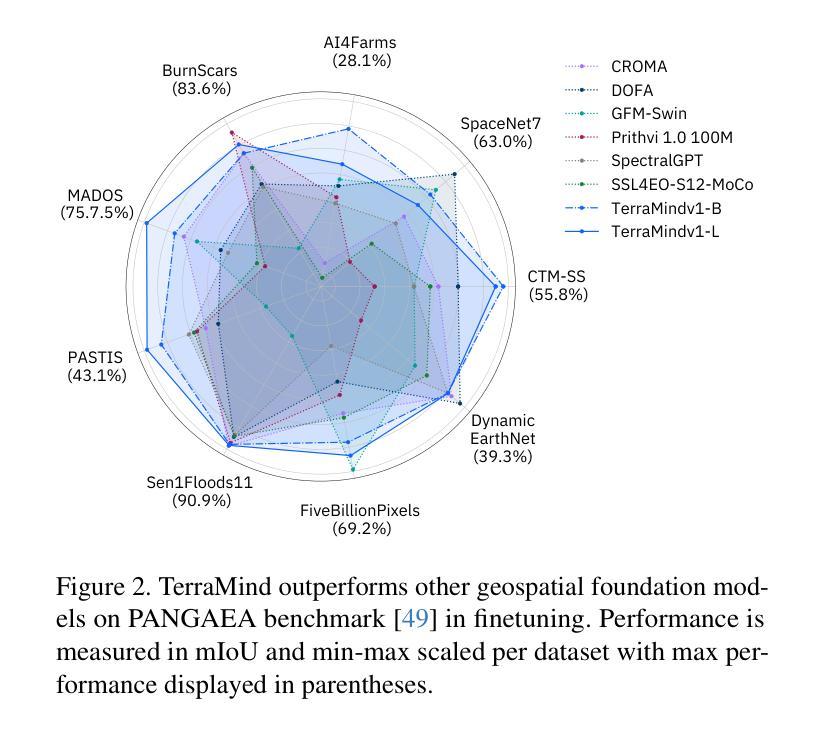
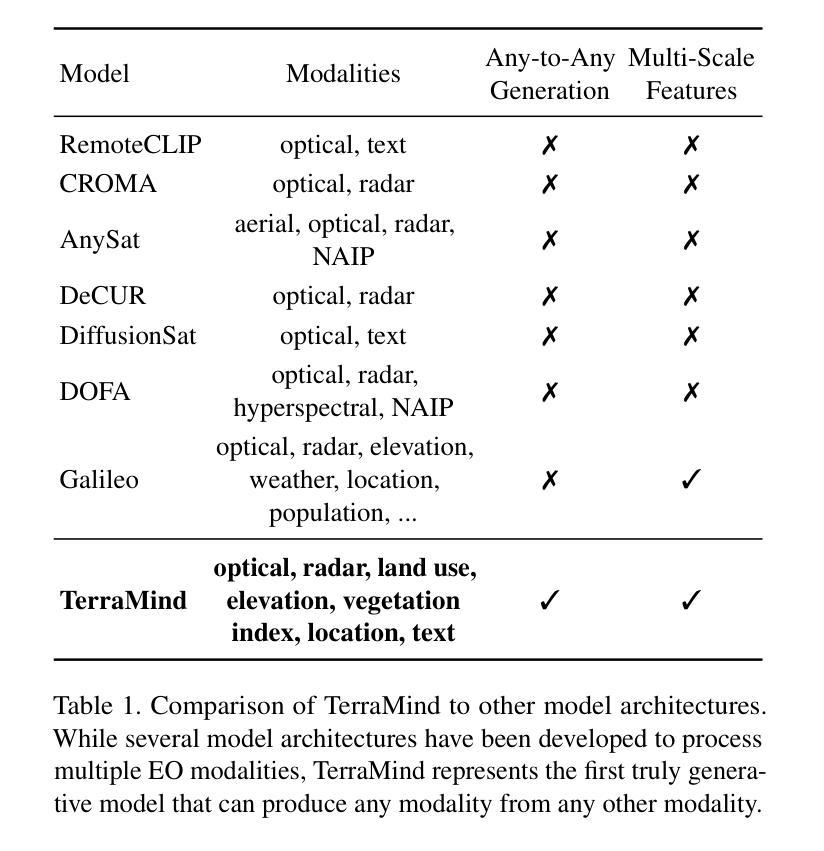
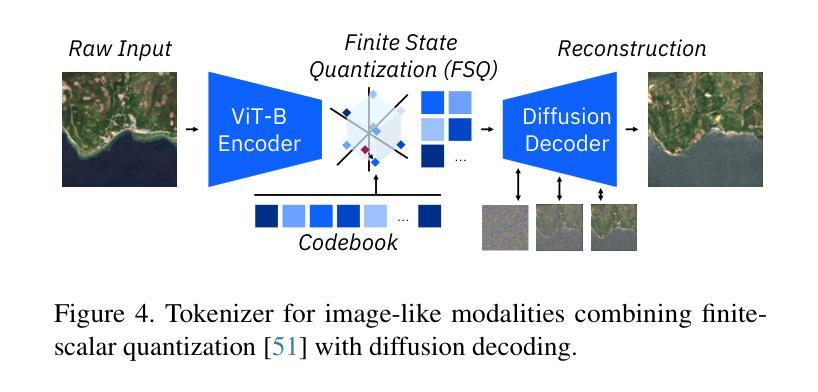
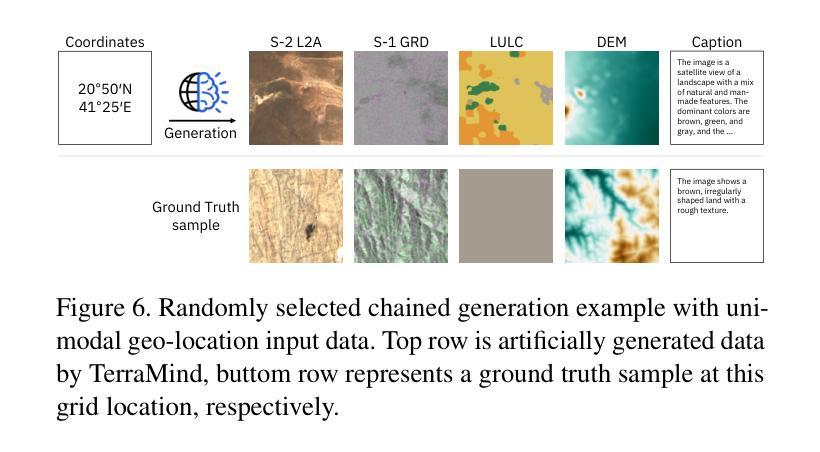
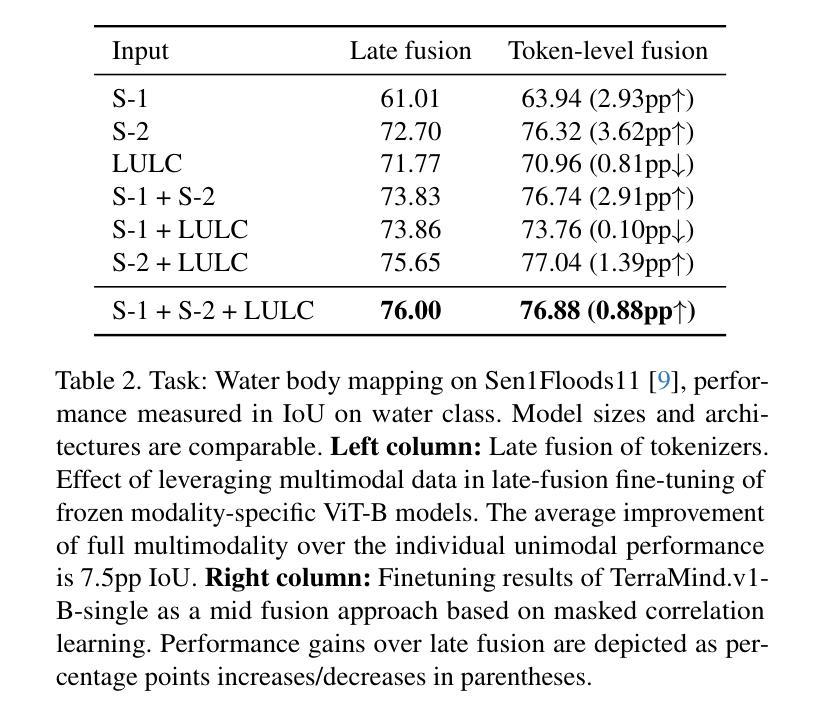
We present TerraMind, the first any-to-any generative, multimodal foundation model for Earth observation (EO). Unlike other multimodal models, TerraMind is pretrained on dual-scale representations combining both token-level and pixel-level data across modalities. On a token level, TerraMind encodes high-level contextual information to learn cross-modal relationships, while on a pixel level, TerraMind leverages fine-grained representations to capture critical spatial nuances. We pretrained TerraMind on nine geospatial modalities of a global, large-scale dataset. In this paper, we demonstrate that (i) TerraMind’s dual-scale early fusion approach unlocks a range of zero-shot and few-shot applications for Earth observation, (ii) TerraMind introduces “Thinking-in-Modalities” (TiM) – the capability of generating additional artificial data during finetuning and inference to improve the model output – and (iii) TerraMind achieves beyond state-of-the-art performance in community-standard benchmarks for EO like PANGAEA. The pretraining dataset, the model weights, and our code is open-sourced under a permissive license.
我们推出TerraMind,这是首个面向地球观测(EO)的任意到任意生成、多模式基础模型。与其他多模式模型不同,TerraMind是在双尺度表示上预训练的,结合了跨模式的令牌级别和像素级别的数据。在令牌级别上,TerraMind编码高级上下文信息来学习跨模式关系,而在像素级别上,TerraMind利用精细表示来捕捉关键的空间细微差别。我们在全球大规模数据的九个地理空间模式上预训练了TerraMind。在本文中,我们证明(i)TerraMind的双尺度早期融合方法解锁了一系列零样本和少样本的地球观测应用,(ii)TerraMind引入了“思考模式”(Thinking-in-Modalities)的能力——在微调过程中和推理期间生成额外的合成数据,以改善模型输出——以及(iii)TerraMind在像PANGAEA这样的地球观测社区标准基准测试中达到了超越现有技术的性能。预训练数据集、模型权重和我们的代码都是在许可下开源的。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
TerraMind是首个针对地球观测的任意输入-任意生成、多模态基础模型。它采用双尺度表示法,结合标记级别和像素级别的数据跨模态进行预训练。TerraMind的预训练数据集包含全球大规模数据的九种地理空间模态。本文展示了TerraMind的多种零样本和少样本应用、其特有的“模态思考”(TiM)能力以及其在地球观测社区标准基准测试中的卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- TerraMind是首个地球观测的多模态基础模型,支持任意输入和生成。
- TerraMind采用独特的双尺度预训练方法,结合标记和像素级别的数据。
- 模型能在标记级别编码高级上下文信息,学习跨模态关系。
- 在像素级别,TerraMind利用精细表示来捕捉关键的空间细微差别。
- TerraMind的“模态思考”(TiM)能力可在微调及推理过程中生成额外的人工数据,改善模型输出。
- TerraMind在地球观测的社区标准基准测试中实现了超越现有技术水平的性能。
- TerraMind的预训练数据集、模型权重和代码已开源。
点此查看论文截图



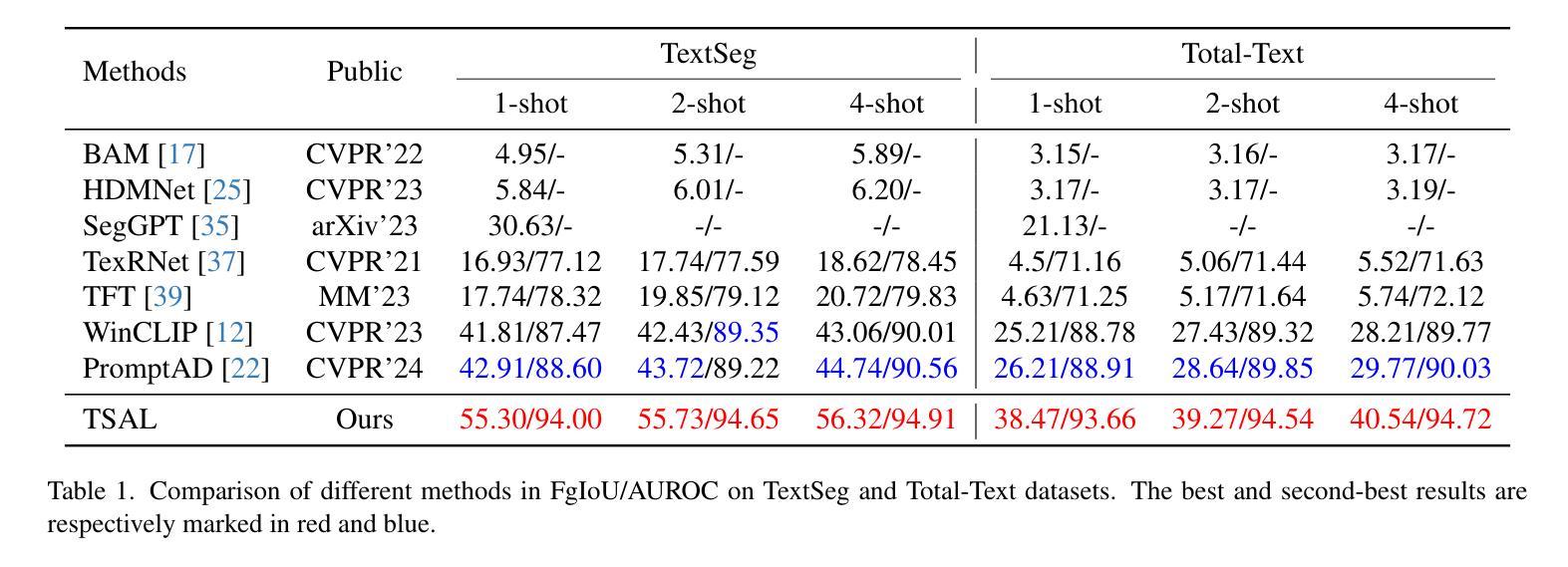
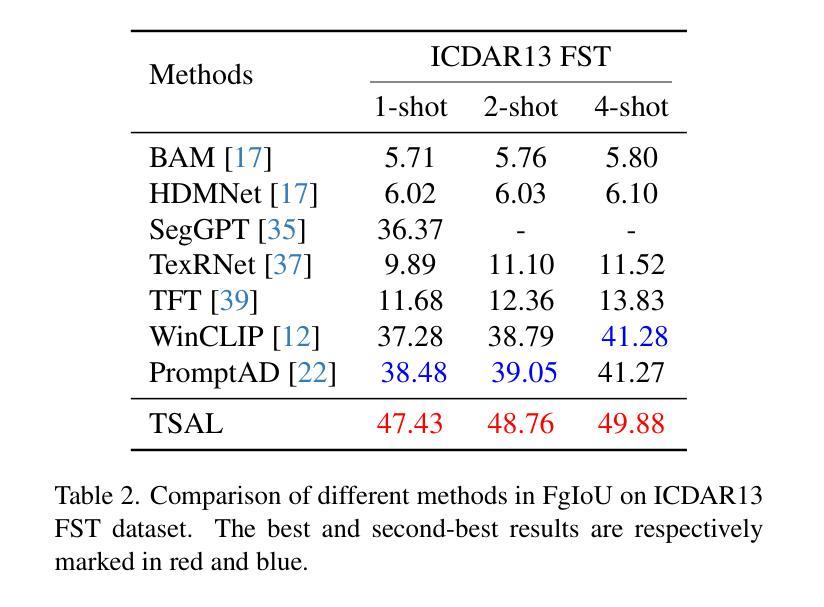
TSAL: Few-shot Text Segmentation Based on Attribute Learning
Authors:Chenming Li, Chengxu Liu, Yuanting Fan, Xiao Jin, Xingsong Hou, Xueming Qian
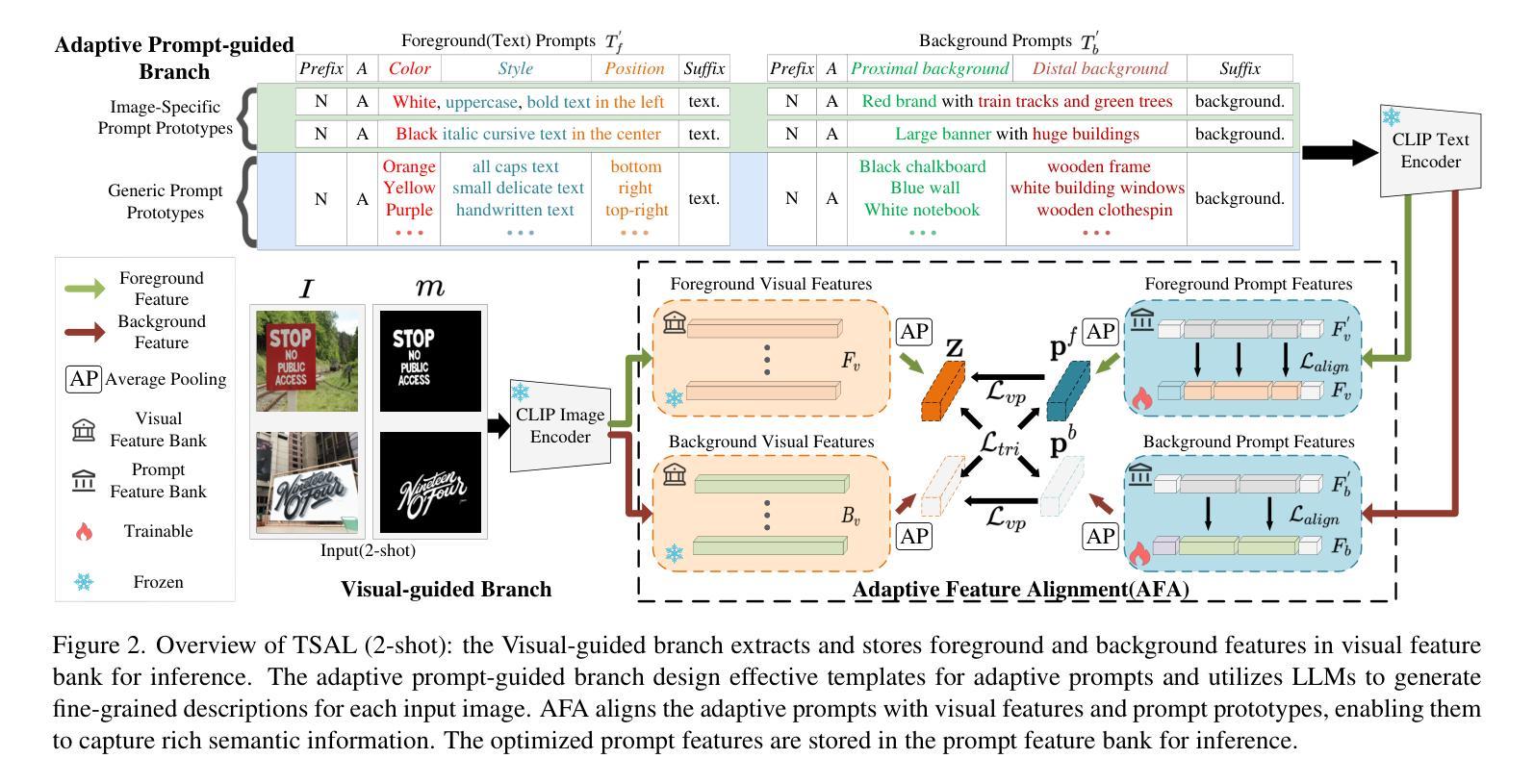
Recently supervised learning rapidly develops in scene text segmentation. However, the lack of high-quality datasets and the high cost of pixel annotation greatly limit the development of them. Considering the well-performed few-shot learning methods for downstream tasks, we investigate the application of the few-shot learning method to scene text segmentation. We propose TSAL, which leverages CLIP’s prior knowledge to learn text attributes for segmentation. To fully utilize the semantic and texture information in the image, a visual-guided branch is proposed to separately extract text and background features. To reduce data dependency and improve text detection accuracy, the adaptive prompt-guided branch employs effective adaptive prompt templates to capture various text attributes. To enable adaptive prompts capture distinctive text features and complex background distribution, we propose Adaptive Feature Alignment module(AFA). By aligning learnable tokens of different attributes with visual features and prompt prototypes, AFA enables adaptive prompts to capture both general and distinctive attribute information. TSAL can capture the unique attributes of text and achieve precise segmentation using only few images. Experiments demonstrate that our method achieves SOTA performance on multiple text segmentation datasets under few-shot settings and show great potential in text-related domains.
近期,有监督学习在场景文本分割领域得到了快速发展。然而,高质量数据集的缺乏以及像素注释的高成本极大地限制了其发展。考虑到下游任务中表现良好的小样本学习方法,我们研究了小样本学习方法在场景文本分割中的应用。我们提出TSAL,它利用CLIP的先验知识来学习文本属性进行分割。为了充分利用图像中的语义和纹理信息,我们提出了视觉引导分支来分别提取文本和背景特征。为了减少数据依赖并提高文本检测精度,自适应提示引导分支采用有效的自适应提示模板来捕获各种文本属性。为了使自适应提示能够捕捉独特的文本特征和复杂的背景分布,我们提出了自适应特征对齐模块(AFA)。通过将对不同属性的可学习标记与视觉特征和提示原型进行对齐,AFA使自适应提示能够捕获一般和独特的属性信息。TSAL可以捕捉文本的独特属性,并使用仅少量的图像实现精确分割。实验表明,我们的方法在多个文本分割数据集的小样本设置下达到了最先进的性能,并在文本相关领域具有巨大的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期监督学习在场景文本分割领域快速发展,但缺乏高质量数据集和像素标注的高成本限制了其发展。研究将少样本学习方法应用于场景文本分割,提出TSAL方法,利用CLIP的先验知识学习文本属性进行分割。为充分利用图像中的语义和纹理信息,提出视觉引导分支以分别提取文本和背景特征。为降低数据依赖并提高文本检测精度,采用自适应提示引导分支,使用有效的自适应提示模板捕获各种文本属性。为使自适应提示捕捉独特的文本特征和复杂的背景分布,提出Adaptive Feature Alignment模块(AFA)。通过对齐不同属性的学习标记和视觉特征以及提示原型,AFA使自适应提示能够捕捉通用和独特的属性信息。TSAL仅使用少量图像即可捕捉文本的独特属性,并实现精确分割。实验表明,该方法在多个文本分割数据集上实现了SOTA性能,并在文本相关领域具有巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 监督学习在场景文本分割中发展快速,受限因素包括高质量数据集缺乏和像素标注的高成本。
- 研究将少样本学习方法应用于场景文本分割,提出TSAL方法。
- TSAL利用CLIP的先验知识学习文本属性进行分割。
- 为充分利用图像中的语义和纹理信息,提出视觉引导分支。
- 自适应提示引导分支用于降低数据依赖并提高文本检测精度。
- 引入Adaptive Feature Alignment模块(AFA),帮助自适应提示捕捉独特的文本特征和复杂的背景分布。
点此查看论文截图

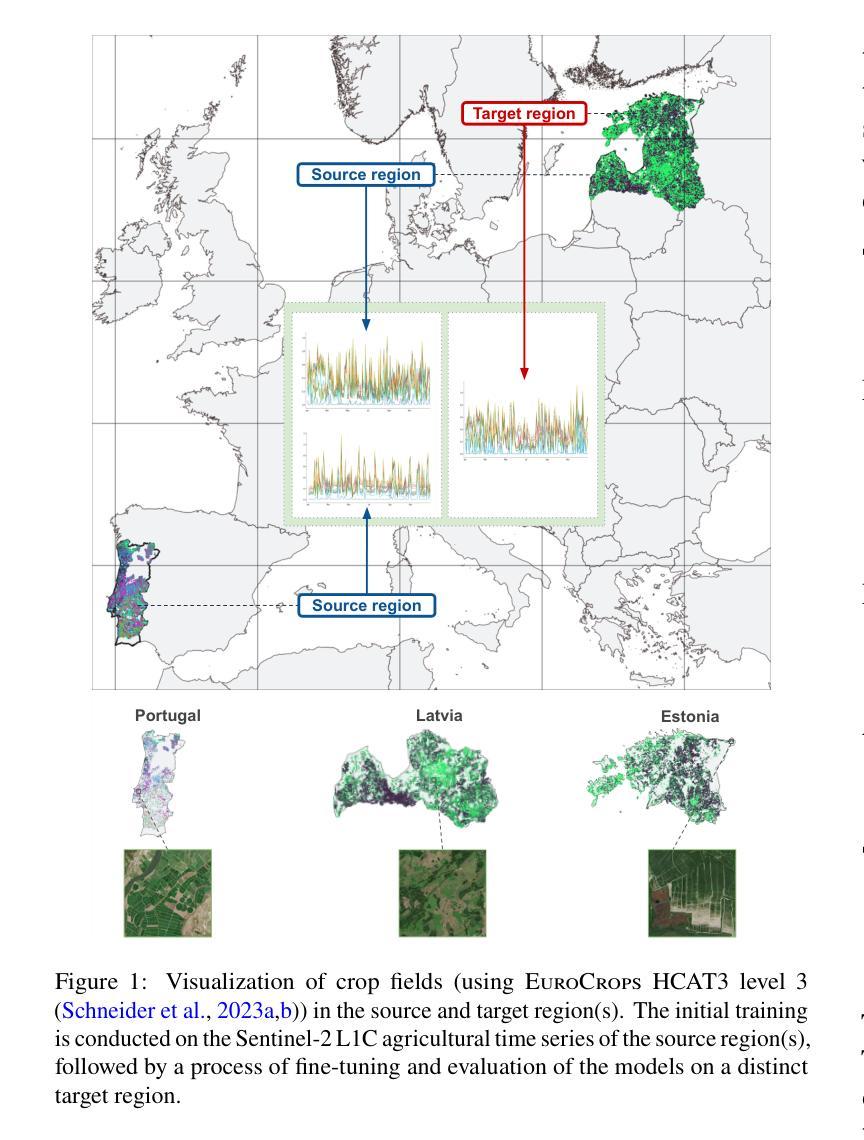
Meta-learning For Few-Shot Time Series Crop Type Classification: A Benchmark On The EuroCropsML Dataset
Authors:Joana Reuss, Jan Macdonald, Simon Becker, Konrad Schultka, Lorenz Richter, Marco Körner
Spatial imbalances in crop type data pose significant challenges for accurate classification in remote sensing applications. Algorithms aiming at transferring knowledge from data-rich to data-scarce tasks have thus surged in popularity. However, despite their effectiveness in previous evaluations, their performance in challenging real-world applications is unclear and needs to be evaluated. This study benchmarks transfer learning and several meta-learning algorithms, including (First-Order) Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning ((FO)-MAML), Almost No Inner Loop (ANIL), and Task-Informed Meta-Learning (TIML), on the real-world EuroCropsML time series dataset, which combines farmer-reported crop data with Sentinel-2 satellite observations from Estonia, Latvia, and Portugal. Our findings indicate that MAML-based meta-learning algorithms achieve slightly higher accuracy compared to simpler transfer learning methods when applied to crop type classification tasks in Estonia after pre-training on data from Latvia. However, this improvement comes at the cost of increased computational demands and training time. Moreover, we find that the transfer of knowledge between geographically disparate regions, such as Estonia and Portugal, poses significant challenges to all investigated algorithms. These insights underscore the trade-offs between accuracy and computational resource requirements in selecting machine learning methods for real-world crop type classification tasks and highlight the difficulties of transferring knowledge between different regions of the Earth. To facilitate future research in this domain, we present the first comprehensive benchmark for evaluating transfer and meta-learning methods for crop type classification under real-world conditions. The corresponding code is publicly available at https://github.com/dida-do/eurocrops-meta-learning.
农作物类型数据在空间上的不平衡给遥感应用中的准确分类带来了重大挑战。因此,旨在从数据丰富任务向数据稀缺任务转移知识的算法变得非常受欢迎。然而,尽管这些算法在之前的评估中非常有效,它们在具有挑战性的现实世界应用中的表现尚不清楚,需要进行评估。本研究对迁移学习和几种元学习算法进行了基准测试,包括(一阶)模型无关元学习(FO-MAML)、几乎无内环(ANIL)和任务信息元学习(TIML),基准测试是在现实世界的EuroCropsML时间序列数据集上进行的,该数据集结合了农民报告的作物数据与来自爱沙尼亚、拉脱维亚和葡萄牙的Sentinel-2卫星观测数据。我们的研究发现,基于MAML的元学习算法在爱沙尼亚的作物类型分类任务上,与较简单的迁移学习方法相比,取得了略高的精度,这些算法是在拉脱维亚的数据上进行预训练之后应用的。然而,这一改进是以增加计算需求和训练时间为代价的。此外,我们发现,在地理上相距较远的地区之间转移知识,如爱沙尼亚和葡萄牙,给所有调查过的算法都带来了重大挑战。这些见解强调了选择机器学习方法进行现实世界作物类型分类任务时在准确性和计算资源需求之间的权衡,并突出了在不同地区之间转移知识的困难。为了促进该领域未来的研究,我们提供了第一个全面的基准测试,以评估现实世界条件下作物类型分类的迁移和元学习方法。相应的代码可在https://github.com/dida-do/eurocrops-meta-learning公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 7 figures, 12 tables
Summary
该文本研究了作物类型数据中的空间不平衡现象对遥感应用中的准确分类带来的挑战。为了应对这一问题,采用基于知识转移的算法变得越来越流行。本文在真实的EuroCropsML时间序列数据集上评估了迁移学习和几种元学习算法的性能,该数据集结合了农民报告的作物数据与Sentinel-2卫星观测数据,来自爱沙尼亚、拉脱维亚和葡萄牙。研究发现,基于MAML的元学习算法在爱沙尼亚的作物类型分类任务上略优于简单的迁移学习方法,但这需要更高的计算需求和更长的训练时间。此外,不同地理区域间的知识转移存在挑战。这些见解强调了选择机器学习方法进行实际作物类型分类时在准确性和计算资源要求之间的权衡,并突出了在地球不同地区转移知识的困难。
Key Takeaways
- 空间不平衡的作物类型数据对遥感应用的准确分类构成挑战。
- 知识转移算法在处理数据稀缺任务时受到欢迎。
- 在真实的EuroCropsML数据集上评估了迁移学习和多种元学习算法。
- 基于MAML的元学习算法在爱沙尼亚的作物分类任务上表现出较高的准确性,但计算需求较高。
- 地理区域间的知识转移存在挑战。
- 在选择机器学习方法进行实际作物类型分类时,需要权衡准确性和计算资源要求。
点此查看论文截图

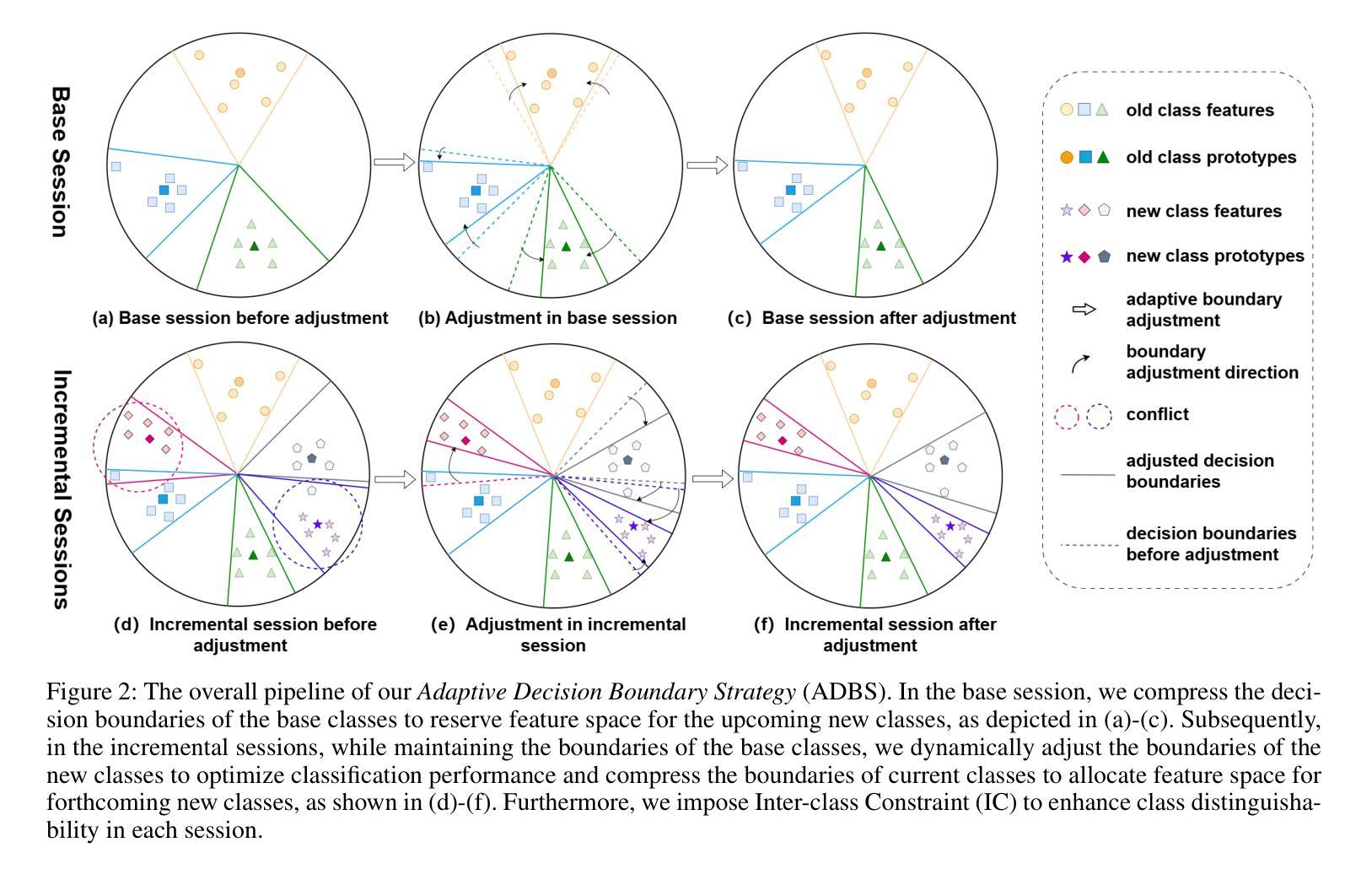
Adaptive Decision Boundary for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Authors:Linhao Li, Yongzhang Tan, Siyuan Yang, Hao Cheng, Yongfeng Dong, Liang Yang
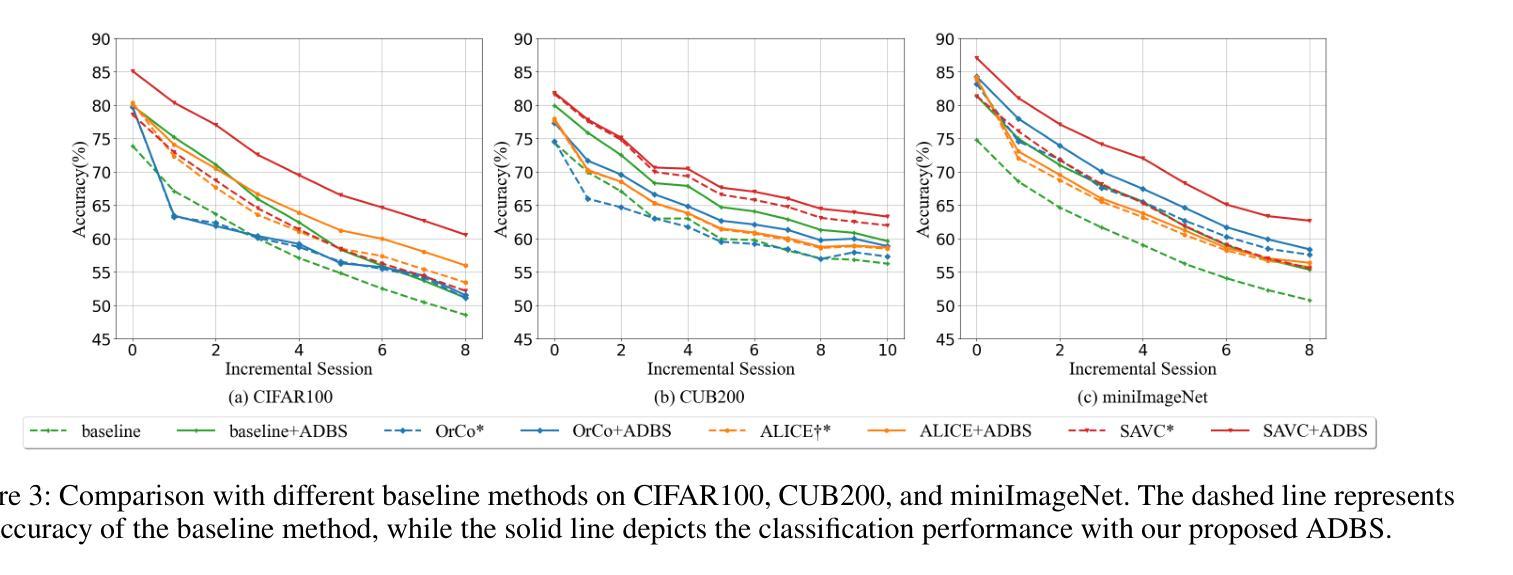
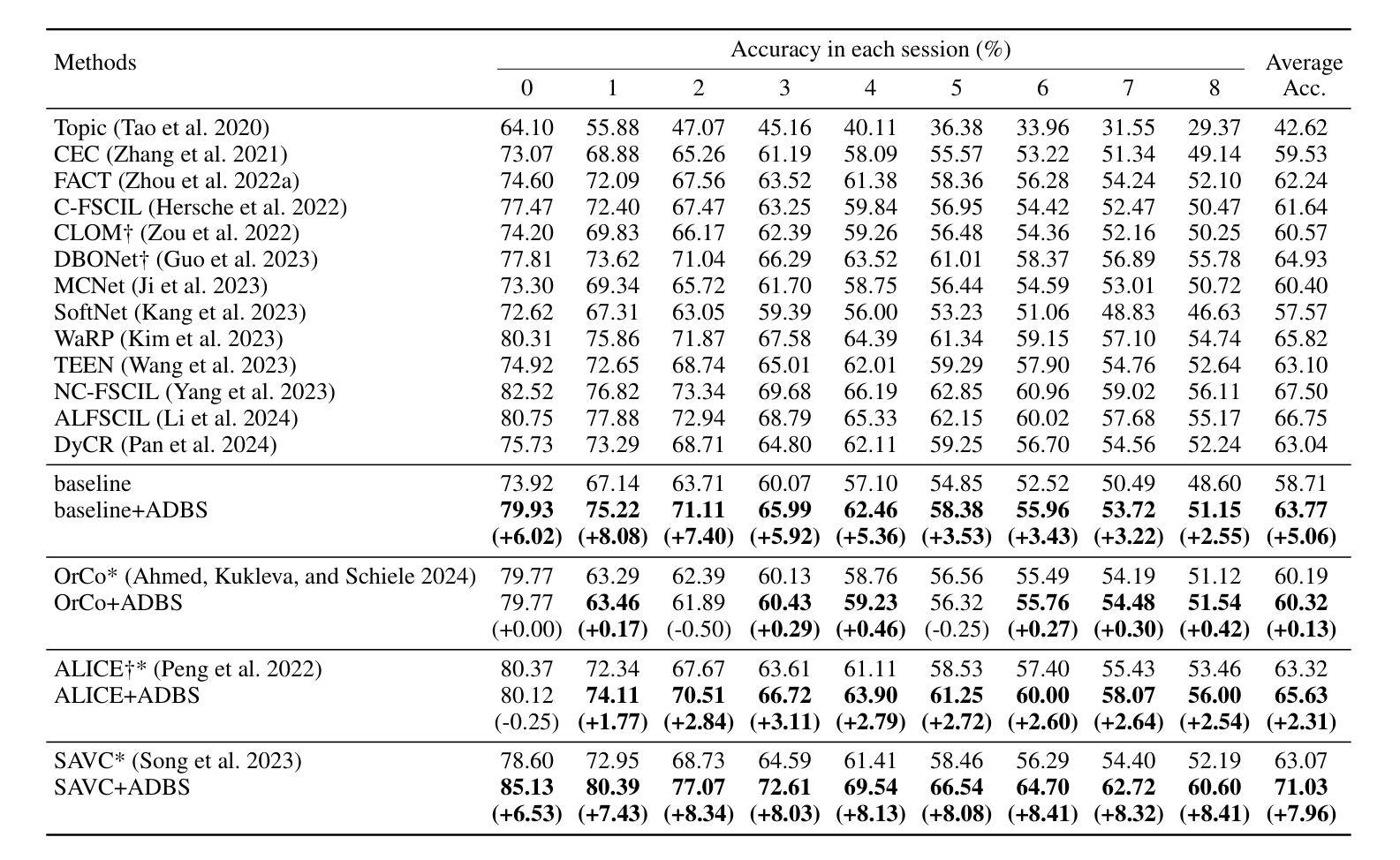
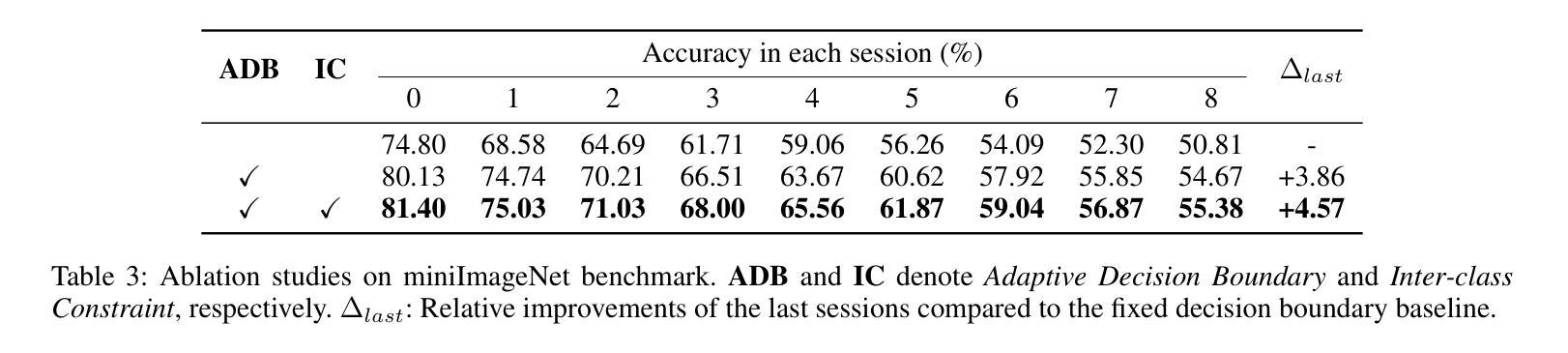
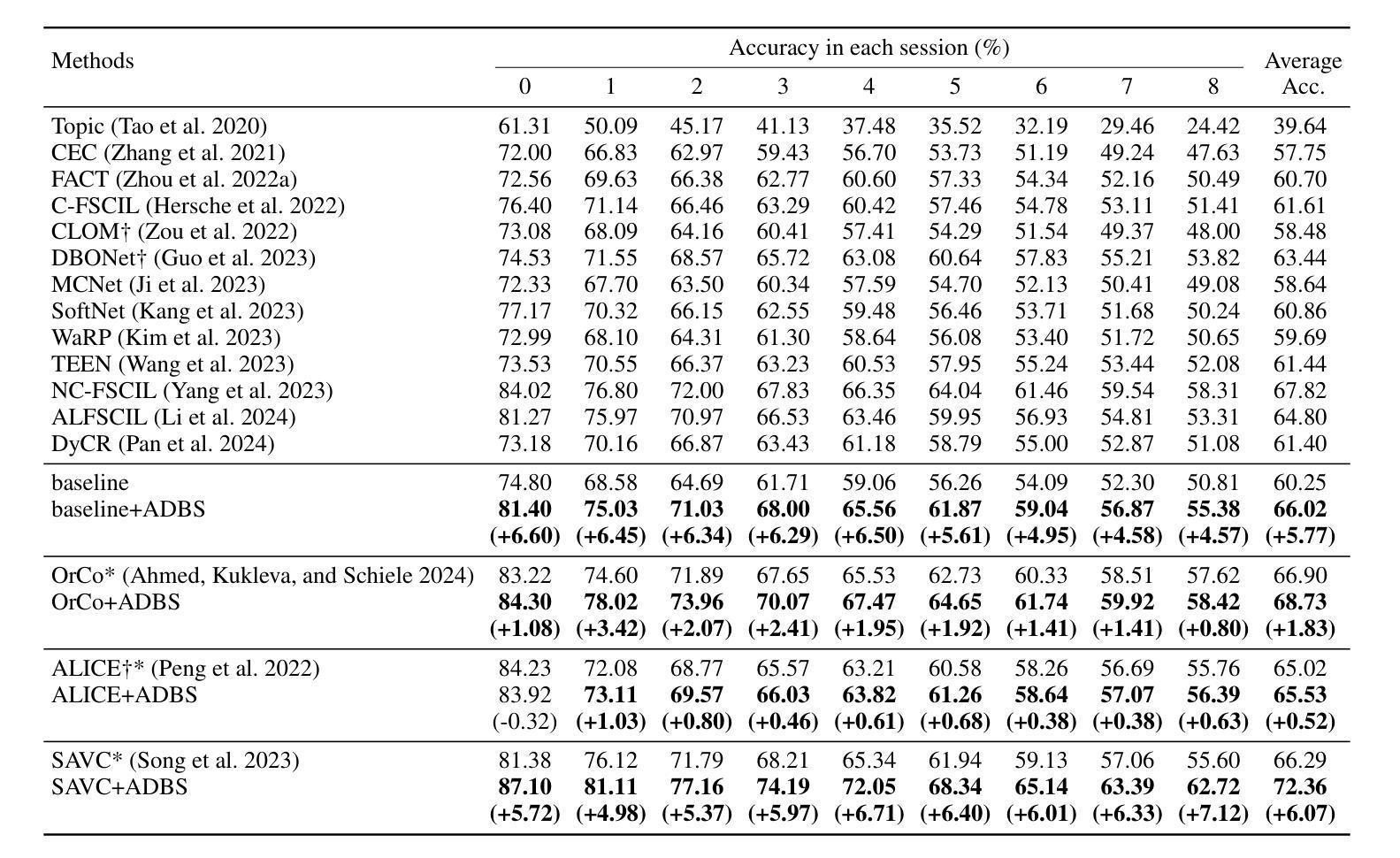
Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) aims to continuously learn new classes from a limited set of training samples without forgetting knowledge of previously learned classes. Conventional FSCIL methods typically build a robust feature extractor during the base training session with abundant training samples and subsequently freeze this extractor, only fine-tuning the classifier in subsequent incremental phases. However, current strategies primarily focus on preventing catastrophic forgetting, considering only the relationship between novel and base classes, without paying attention to the specific decision spaces of each class. To address this challenge, we propose a plug-and-play Adaptive Decision Boundary Strategy (ADBS), which is compatible with most FSCIL methods. Specifically, we assign a specific decision boundary to each class and adaptively adjust these boundaries during training to optimally refine the decision spaces for the classes in each session. Furthermore, to amplify the distinctiveness between classes, we employ a novel inter-class constraint loss that optimizes the decision boundaries and prototypes for each class. Extensive experiments on three benchmarks, namely CIFAR100, miniImageNet, and CUB200, demonstrate that incorporating our ADBS method with existing FSCIL techniques significantly improves performance, achieving overall state-of-the-art results.
少量类别增量学习(FSCIL)旨在从有限的训练样本中持续学习新类别,同时不遗忘已学类别的知识。传统的FSCIL方法通常在基础训练会话中利用丰富的训练样本构建强大的特征提取器,随后冻结该提取器,仅在后续的增量阶段微调分类器。然而,当前策略主要集中在防止灾难性遗忘上,只考虑新类别与基础类别之间的关系,而没有关注每个类别的特定决策空间。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种即插即用的自适应决策边界策略(ADBS),它与大多数FSCIL方法兼容。具体来说,我们为每个类别分配一个特定的决策边界,并在训练过程中自适应地调整这些边界,以最优方式细化每个会话中类别的决策空间。此外,为了放大类别之间的差异性,我们采用了一种新型类间约束损失,该损失优化了决策边界和每个类的原型。在CIFAR100、miniImageNet和CUB200三个基准测试上的大量实验表明,将我们的ADBS方法与现有的FSCIL技术相结合,可以显著提高性能,达到最新最先进的水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了Few-Shot类增量学习(FSCIL)的目标和现有方法的问题。文中指出FSCIL旨在从有限的训练样本中持续学习新类别,同时不遗忘已学类别的知识。传统FSCIL方法通常会在基础训练阶段构建强大的特征提取器,并在后续增量阶段仅微调分类器。然而,当前策略主要关注防止灾难性遗忘,考虑新类别与基础类别之间的关系,而忽视了每个类别的特定决策空间。为解决这一问题,提出了兼容大多数FSCIL方法的即插即用自适应决策边界策略(ADBS)。通过为每个类别分配特定的决策边界,并在训练过程中自适应地调整这些边界,以优化每个会话中的类别决策空间。此外,还采用了一种新型的类间约束损失,以优化每个类别的决策边界和原型,放大类之间的差异性。在CIFAR100、miniImageNet和CUB200三个基准测试上的实验表明,将ADBS方法与现有FSCIL技术相结合,可显著提高性能,达到最新状态。
Key Takeaways
- Few-Shot类增量学习(FSCIL)的目标是持续学习新类别,从有限的训练样本中,同时保持对旧知识的记忆。
- 传统FSCIL方法主要关注防止灾难性遗忘,忽视了每个类别的特定决策空间。
- 提出的Adaptive Decision Boundary Strategy(ADBS)策略为每个类别分配特定的决策边界,并在训练过程中自适应调整这些边界。
- ADBS策略通过优化决策边界和原型,提高了类之间的区分度。
- ADBS策略与大多数FSCIL方法兼容,可以显著提高性能。
- 在多个基准测试上,结合ADBS方法和现有FSCIL技术的性能达到了最新状态。
点此查看论文截图

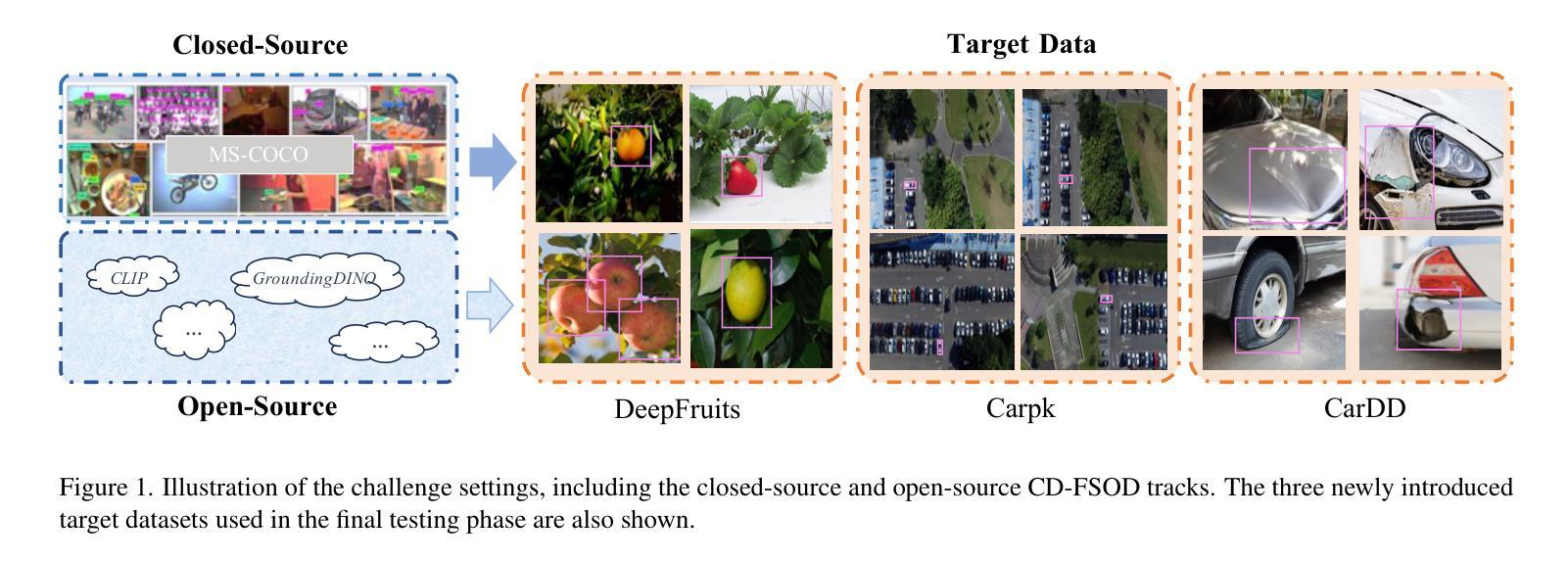
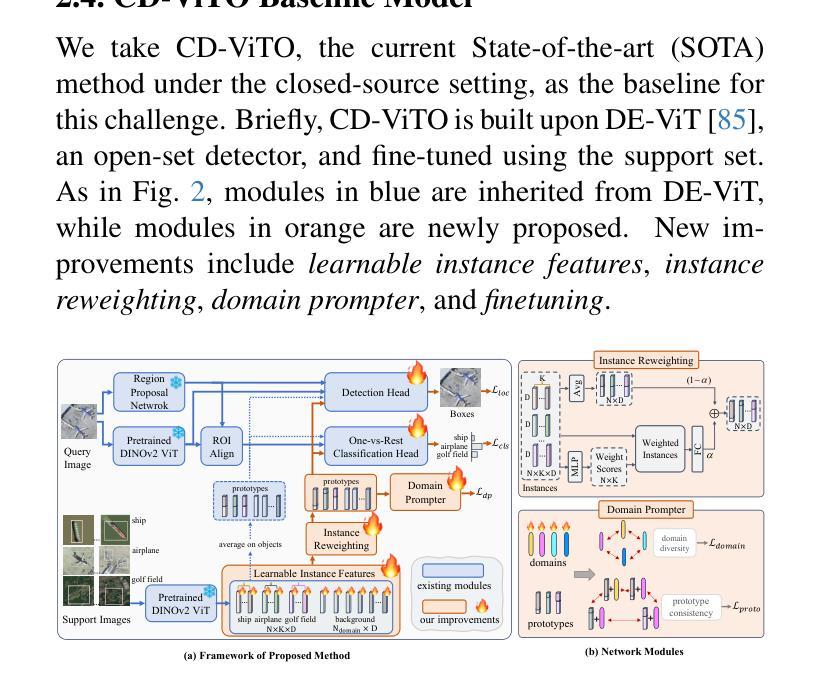
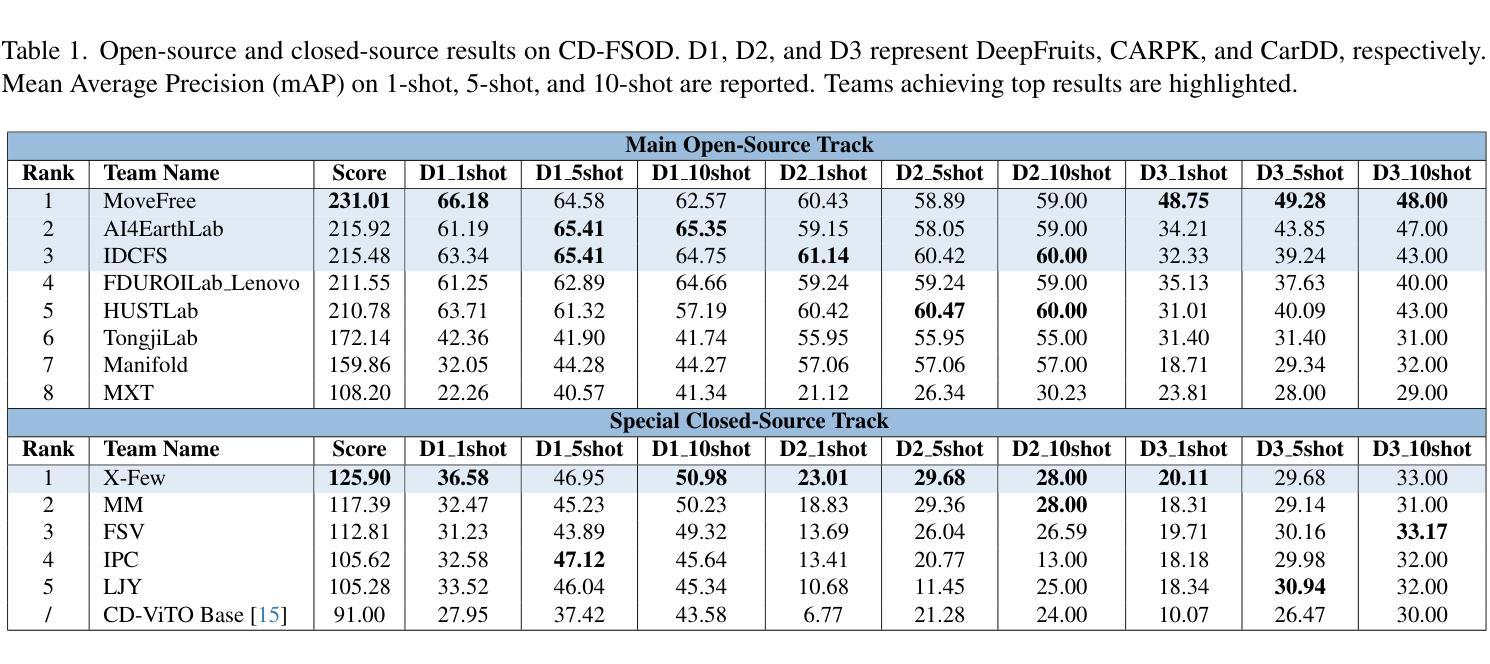
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection: Methods and Results
Authors:Yuqian Fu, Xingyu Qiu, Bin Ren, Yanwei Fu, Radu Timofte, Nicu Sebe, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Luc Van Gool, Kaijin Zhang, Qingpeng Nong, Xiugang Dong, Hong Gao, Xiangsheng Zhou, Jiancheng Pan, Yanxing Liu, Xiao He, Jiahao Li, Yuze Sun, Xiaomeng Huang, Zhenyu Zhang, Ran Ma, Yuhan Liu, Zijian Zhuang, Shuai Yi, Yixiong Zou, Lingyi Hong, Mingxi Chen, Runze Li, Xingdong Sheng, Wenqiang Zhang, Weisen Chen, Yongxin Yan, Xinguo Chen, Yuanjie Shao, Zhengrong Zuo, Nong Sang, Hao Wu, Haoran Sun, Shuming Hu, Yan Zhang, Zhiguang Shi, Yu Zhang, Chao Chen, Tao Wang, Da Feng, Linhai Zhuo, Ziming Lin, Yali Huang, Jie Me, Yiming Yang, Mi Guo, Mingyuan Jiu, Mingliang Xu, Maomao Xiong, Qunshu Zhang, Xinyu Cao, Yuqing Yang, Dianmo Sheng, Xuanpu Zhao, Zhiyu Li, Xuyang Ding, Wenqian Li
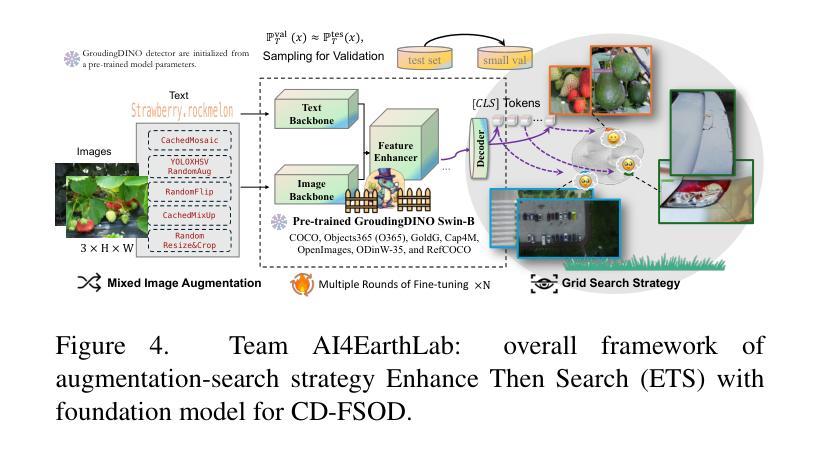
Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection (CD-FSOD) poses significant challenges to existing object detection and few-shot detection models when applied across domains. In conjunction with NTIRE 2025, we organized the 1st CD-FSOD Challenge, aiming to advance the performance of current object detectors on entirely novel target domains with only limited labeled data. The challenge attracted 152 registered participants, received submissions from 42 teams, and concluded with 13 teams making valid final submissions. Participants approached the task from diverse perspectives, proposing novel models that achieved new state-of-the-art (SOTA) results under both open-source and closed-source settings. In this report, we present an overview of the 1st NTIRE 2025 CD-FSOD Challenge, highlighting the proposed solutions and summarizing the results submitted by the participants.
跨域小样本目标检测(CD-FSOD)给现有的目标检测和少样本检测模型带来了重大挑战,尤其是在跨域应用时。结合NTIRE 2025,我们组织了首届CD-FSOD挑战赛,旨在提高当前目标检测器在仅有少量标注数据的新目标域上的性能。该挑战赛吸引了152名注册参赛者,收到42个团队的提交,最终有13个团队提交了有效的最终作品。参赛者从不同角度入手,提出新型模型,在开源和闭源环境下均取得了最新的最新结果。本报告将概述NTIRE 2025首届CD-FSOD挑战赛,重点介绍提出的解决方案,并总结参赛者提交的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by CVPRW 25 @ NTIRE
Summary
面向跨域小样本目标检测(CD-FSOD)的挑战性问题,NTIRE 2025首次举办了CD-FSOD挑战赛,旨在提高当前目标检测器在全新目标域有限标签数据下的性能。吸引了大量参与者提交新型模型和方法,部分模型在开放源代码和封闭源代码环境中都达到了最新的技术水平。本报告详细介绍了此次挑战赛的参与者提交的方案及结果。
Key Takeaways
- CD-FSOD挑战赛旨在解决跨域小样本目标检测的难题。
- 挑战赛吸引了大量参与者提交新型模型和方法。
- 部分模型在开放源代码和封闭源代码环境中都达到了最新的技术水平。
- 参赛者从不同的角度采用了多元化的策略来应对挑战。
- 比赛结果显示了在有限的标签数据下实现高准确率的可能性。
点此查看论文截图

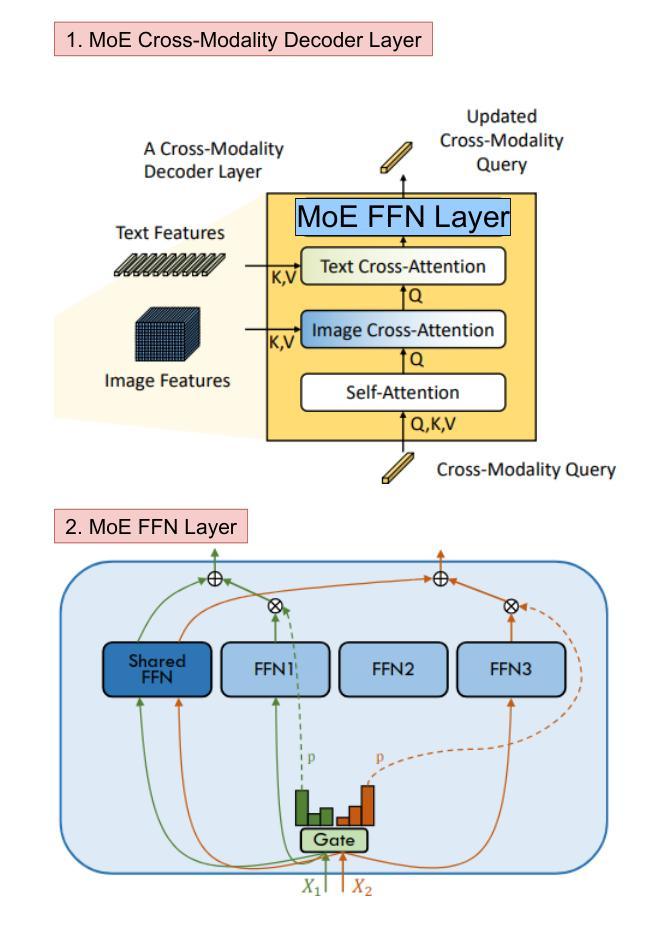
Improving In-Context Learning with Reasoning Distillation
Authors:Nafis Sadeq, Xin Xu, Zhouhang Xie, Julian McAuley, Byungkyu Kang, Prarit Lamba, Xiang Gao
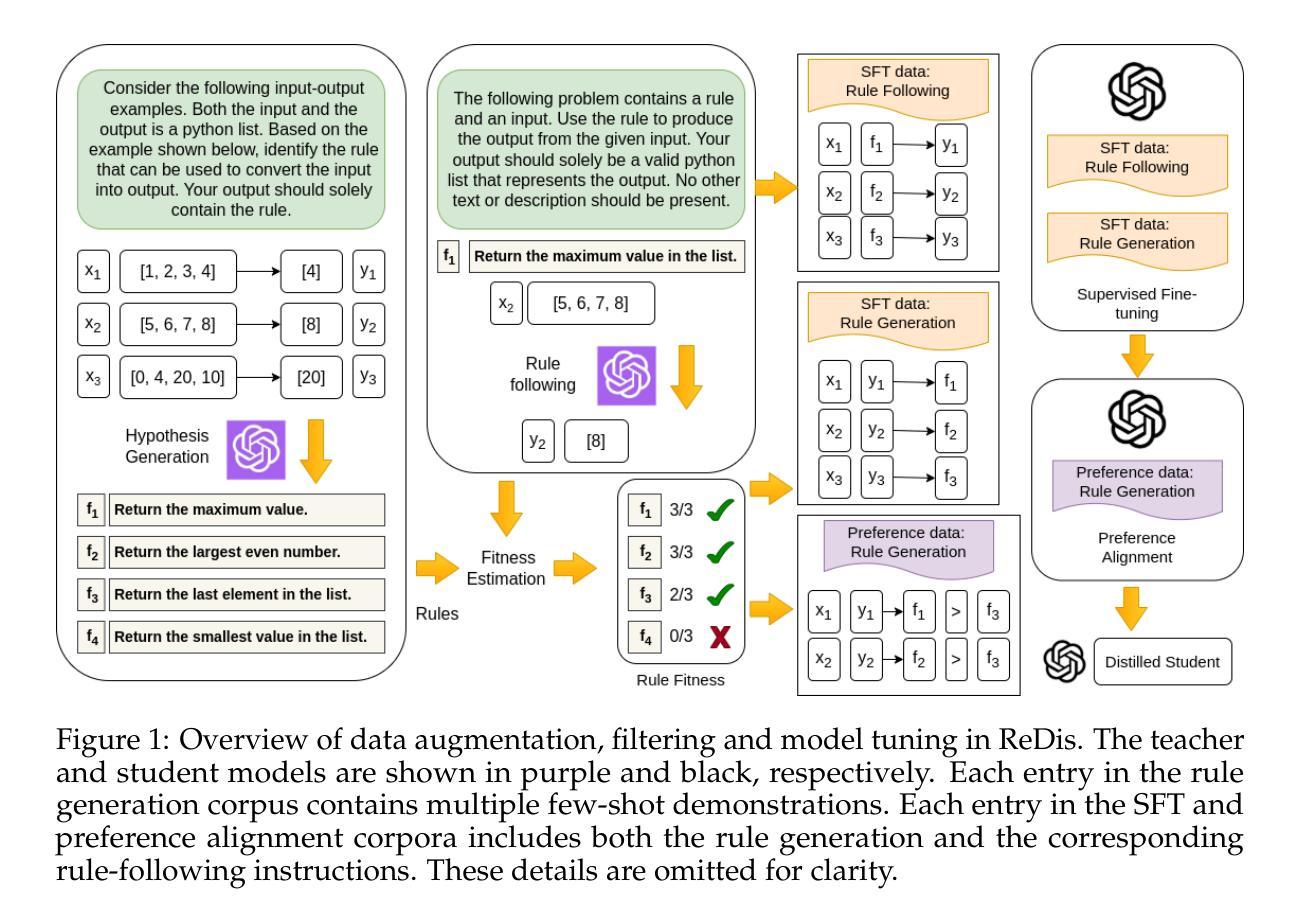
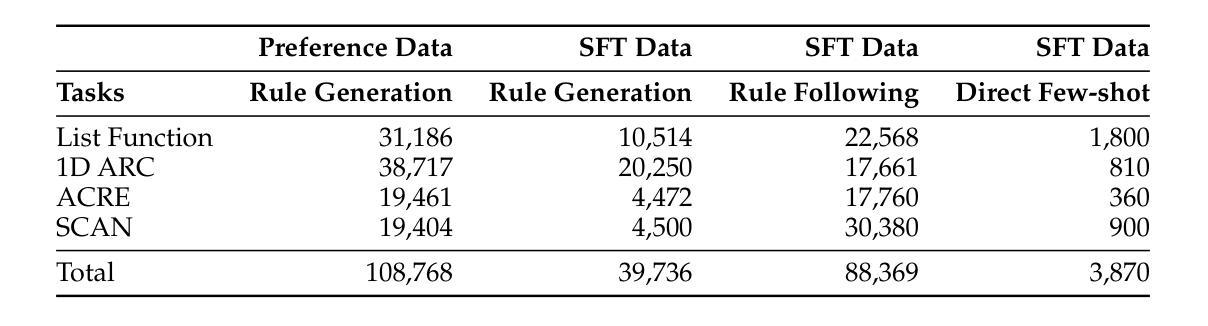
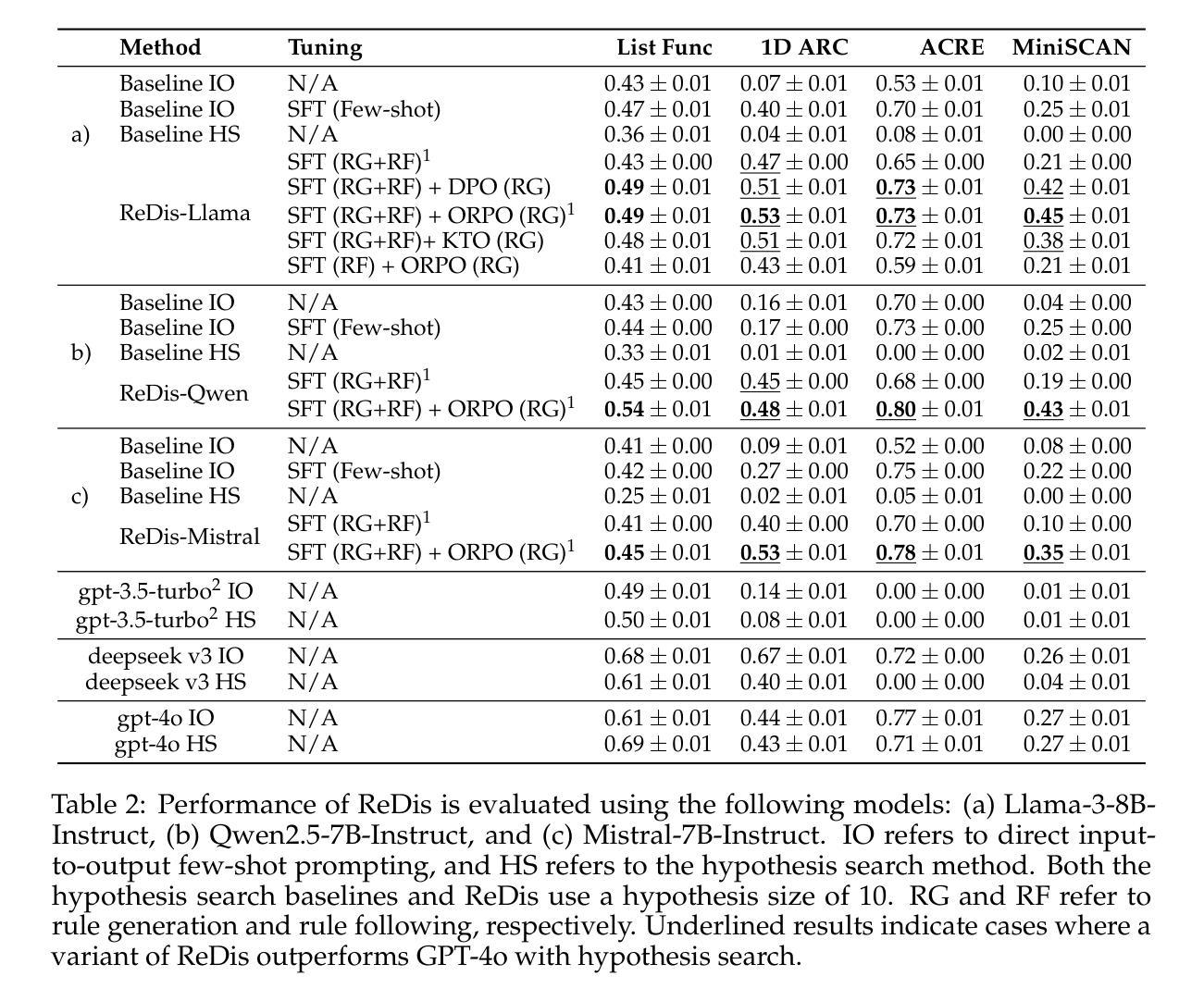
Language models rely on semantic priors to perform in-context learning, which leads to poor performance on tasks involving inductive reasoning. Instruction-tuning methods based on imitation learning can superficially enhance the in-context learning performance of language models, but they often fail to improve the model’s understanding of the underlying rules that connect inputs and outputs in few-shot demonstrations. We propose ReDis, a reasoning distillation technique designed to improve the inductive reasoning capabilities of language models. Through a careful combination of data augmentation, filtering, supervised fine-tuning, and alignment, ReDis achieves significant performance improvements across a diverse range of tasks, including 1D-ARC, List Function, ACRE, and MiniSCAN. Experiments on three language model backbones show that ReDis outperforms equivalent few-shot prompting baselines across all tasks and even surpasses the teacher model, GPT-4o, in some cases. ReDis, based on the LLaMA-3 backbone, achieves relative improvements of 23.2%, 2.8%, and 66.6% over GPT-4o on 1D-ARC, ACRE, and MiniSCAN, respectively, within a similar hypothesis search space. The code, dataset, and model checkpoints will be made available at https://github.com/NafisSadeq/reasoning-distillation.git.
语言模型依赖语义先验来进行上下文学习,这导致在处理涉及归纳推理的任务时表现不佳。基于模仿学习的指令调整方法表面上看似增强了语言模型的上下文学习能力,但它们往往未能改善模型对少量演示中输入和输出之间基本规则的理解。我们提出了ReDis,这是一种推理蒸馏技术,旨在提高语言模型的归纳推理能力。通过数据增强、过滤、监督微调和对齐的精心结合,ReDis在多种任务上实现了显著的性能提升,包括1D-ARC、List Function、ACRE和MiniSCAN。在三个语言模型主干上的实验表明,ReDis在所有任务上的表现都超过了等效的少量提示基线,甚至在某些情况下超越了教师模型GPT-4o。基于LLaMA-3主干的ReDis在类似假设搜索空间内相对于GPT-4o在1D-ARC、ACRE和MiniSCAN上分别实现了23.2%、2.8%和66.6%的相对改进。代码、数据集和模型检查点将在https://github.com/NafisSadeq/reasoning-distillation.git上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了语言模型在涉及归纳推理任务时的性能问题。为解决这一问题,提出了一种名为ReDis的推理蒸馏技术。该技术通过数据增强、过滤、监督微调和对齐等步骤,显著提高了语言模型在多种任务上的归纳推理能力。实验表明,ReDis在多个任务上超越了少样本提示基线,甚至在某些情况下超越了教师模型GPT-4o。
Key Takeaways
- 语言模型依赖语义先验进行上下文学习,这在涉及归纳推理的任务上表现不佳。
- 指令调整方法虽然能提升语言模型的上下文学习性能,但难以提高模型对少数演示中输入输出规则的理解。
- 提出了ReDis推理蒸馏技术,旨在提高语言模型的归纳推理能力。
- ReDis通过数据增强、过滤、监督微调和对齐等步骤实现性能提升。
- ReDis在多种任务上表现出显著性能改进,包括1D-ARC、List Function、ACRE和MiniSCAN。
- 实验表明,ReDis在三个不同的语言模型骨架上均超越了少样本提示基线,并在某些情况下超越了教师模型GPT-4o。
点此查看论文截图

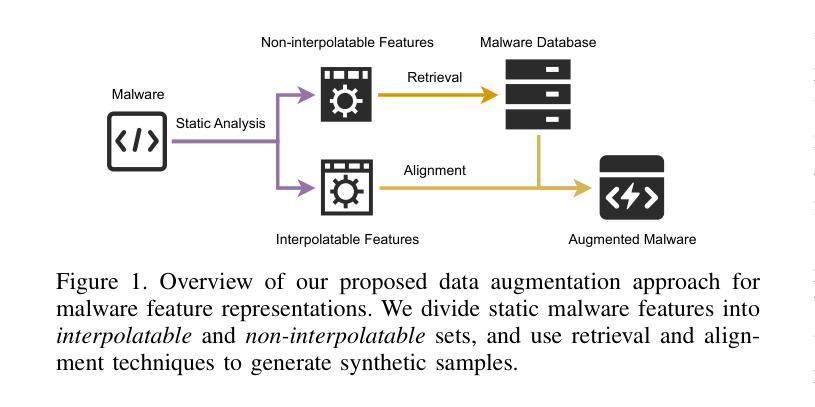
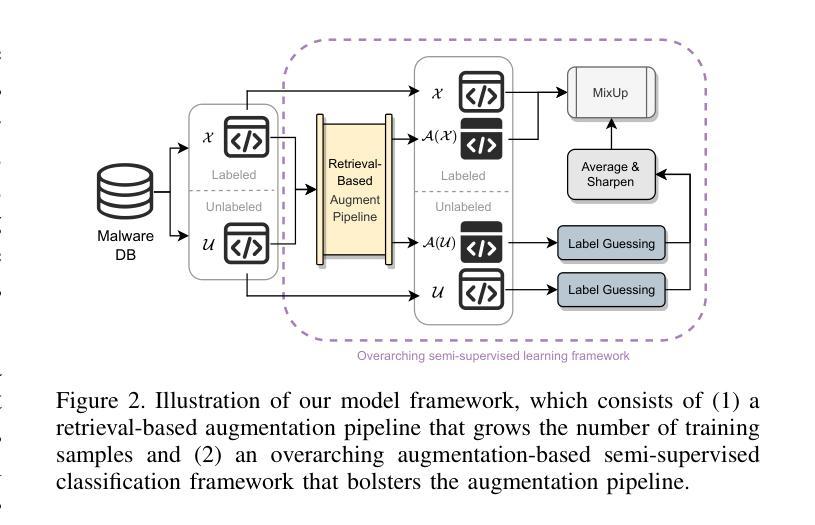
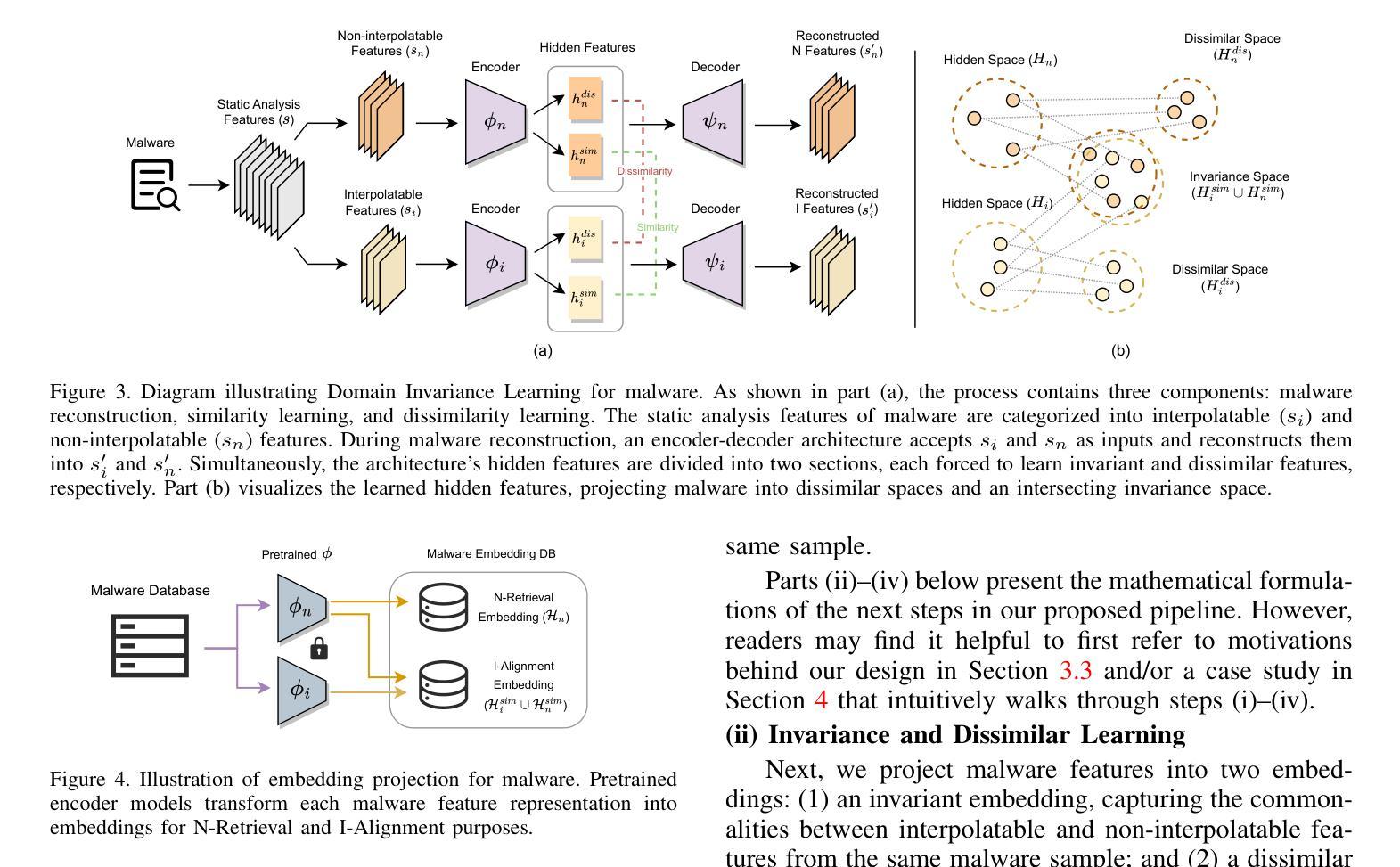
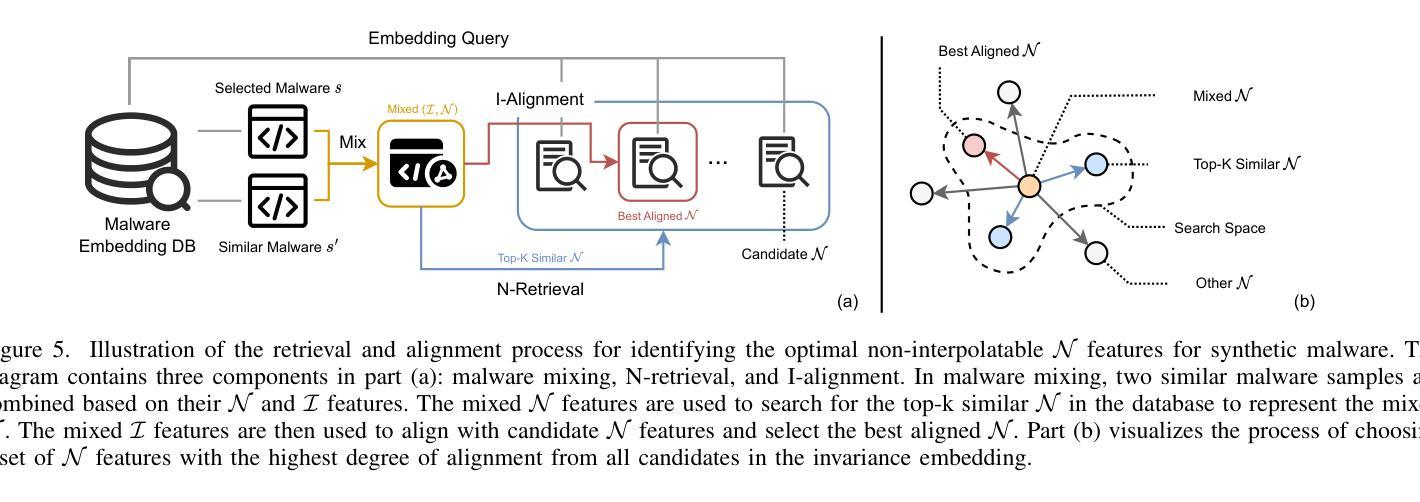
MalMixer: Few-Shot Malware Classification with Retrieval-Augmented Semi-Supervised Learning
Authors:Jiliang Li, Yifan Zhang, Yu Huang, Kevin Leach
Recent growth and proliferation of malware has tested practitioners’ ability to promptly classify new samples according to malware families. In contrast to labor-intensive reverse engineering efforts, machine learning approaches have demonstrated increased speed and accuracy. However, most existing deep-learning malware family classifiers must be calibrated using a large number of samples that are painstakingly manually analyzed before training. Furthermore, as novel malware samples arise that are beyond the scope of the training set, additional reverse engineering effort must be employed to update the training set. The sheer volume of new samples found in the wild creates substantial pressure on practitioners’ ability to reverse engineer enough malware to adequately train modern classifiers. In this paper, we present MalMixer, a malware family classifier using semi-supervised learning that achieves high accuracy with sparse training data. We present a novel domain-knowledge-aware technique for augmenting malware feature representations, enhancing few-shot performance of semi-supervised malware family classification. We show that MalMixer achieves state-of-the-art performance in few-shot malware family classification settings. Our research confirms the feasibility and effectiveness of lightweight, domain-knowledge-aware feature augmentation methods and highlights the capabilities of similar semi-supervised classifiers in addressing malware classification issues.
最近恶意软件的增长和扩散考验了从业人员根据恶意软件家族及时对新样本进行分类的能力。与劳动密集型的逆向工程努力相比,机器学习的方法已经显示出更高的速度和准确性。然而,大多数现有的深度学习的恶意软件家族分类器需要使用大量样本进行校准,这些样本在训练之前需要进行繁琐的手动分析。此外,随着超出训练集范围的新的恶意软件样本的出现,必须采用更多的逆向工程工作来更新训练集。野外发现的新样本的数量给从业人员带来了巨大的压力,他们必须逆向工程足够多的恶意软件以充分训练现代分类器。在本文中,我们提出了使用半监督学习的恶意软件家族分类器MalMixer,它在稀疏的训练数据下就能实现较高的准确性。我们提出了一种新颖的基于领域知识的增强技术,用于增强恶意软件特征表示,提高了半监督恶意软件家族分类的小样本性能。我们证明了MalMixer在少量恶意软件家族分类场景中达到了最先进的性能。我们的研究证实了轻量级、基于领域知识的特征增强方法的可行性和有效性,并突出了类似的半监督分类器在解决恶意软件分类问题方面的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文介绍了MalMixer,一种使用半监督学习的高效的恶意软件家族分类器。它能够在训练数据稀疏的情况下实现高准确率。通过采用一种新颖的域知识感知技术增强恶意软件特征表示,提高半监督恶意软件家族的小样本分类性能。研究证实了轻量级、域知识感知的特征增强方法在实际应用中的可行性和有效性,并突出了类似半监督分类器在解决恶意软件分类问题方面的能力。
Key Takeaways
- MalMixer是一种高效的恶意软件家族分类器,采用半监督学习方法,可在训练数据稀疏的情况下实现高准确率。
- 提出了新颖的域知识感知技术,用于增强恶意软件特征表示,提高小样本分类性能。
- 研究证实了轻量级特征增强方法在处理恶意软件分类问题时的有效性。
- MalMixer在少样本恶意软件家族分类设置中达到最先进的性能。
- 域知识感知技术在恶意软件分类中的应用展现了巨大的潜力。
- 半监督学习在解决恶意软件分类问题方面具有优势。
点此查看论文截图