⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-17 更新
DeepMath-103K: A Large-Scale, Challenging, Decontaminated, and Verifiable Mathematical Dataset for Advancing Reasoning
Authors:Zhiwei He, Tian Liang, Jiahao Xu, Qiuzhi Liu, Xingyu Chen, Yue Wang, Linfeng Song, Dian Yu, Zhenwen Liang, Wenxuan Wang, Zhuosheng Zhang, Rui Wang, Zhaopeng Tu, Haitao Mi, Dong Yu
The capacity for complex mathematical reasoning is a key benchmark for artificial intelligence. While reinforcement learning (RL) applied to LLMs shows promise, progress is significantly hindered by the lack of large-scale training data that is sufficiently challenging, possesses verifiable answer formats suitable for RL, and is free from contamination with evaluation benchmarks. To address these limitations, we introduce DeepMath-103K, a new, large-scale dataset comprising approximately 103K mathematical problems, specifically designed to train advanced reasoning models via RL. DeepMath-103K is curated through a rigorous pipeline involving source analysis, stringent decontamination against numerous benchmarks, and filtering for high difficulty (primarily Levels 5-9), significantly exceeding existing open resources in challenge. Each problem includes a verifiable final answer, enabling rule-based RL, and three distinct R1-generated solutions suitable for diverse training paradigms like supervised fine-tuning or distillation. Spanning a wide range of mathematical topics, DeepMath-103K promotes the development of generalizable reasoning. We demonstrate that models trained on DeepMath-103K achieve significant improvements on challenging mathematical benchmarks, validating its effectiveness. We release DeepMath-103K publicly to facilitate community progress in building more capable AI reasoning systems: https://github.com/zwhe99/DeepMath.
复杂数学推理能力是人工智能的关键基准。虽然应用于大型语言模型的增强学习(RL)显示出潜力,但由于缺乏足够具有挑战性、拥有可验证答案格式适合强化学习且未受评估基准污染的大规模训练数据,进展受到了显著阻碍。为了解决这些限制,我们推出了DeepMath-103K,这是一个新的大规模数据集,包含大约103K个数学问题,专门设计用于通过强化学习训练高级推理模型。DeepMath-103K是通过严格的管道进行策划的,包括源分析、针对多个基准的严格去污,以及过滤高难度(主要是Level 5-9),在挑战性方面显著超过了现有开放资源。每个问题都包括一个可验证的最终答案,支持基于规则的强化学习,以及三种不同的R1生成的解决方案,适合监督微调或蒸馏等不同的训练范式。DeepMath-103K涵盖了广泛的数学主题,促进了可推广推理的发展。我们证明,在DeepMath-103K上训练的模型在具有挑战性的数学基准测试中取得了显著改进,验证了其有效性。我们公开发布DeepMath-103K,以促进社区在构建更强大的AI推理系统方面的进步:https://github.com/zwhe99/DeepMath。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF WIP
Summary
深度数学推理能力是人工智能的关键基准。针对大型训练数据的缺乏以及现有数据集中存在的挑战性问题不足等问题,我们推出了DeepMath-103K数据集。该数据集包含大约103K个数学问题,专为通过强化学习训练高级推理模型而设计。DeepMath-103K通过严格的数据清洗和筛选高难度问题(主要是Level 5-9)进行构建,显著超越了现有开放资源。每个问题都包含可验证的最终答案和三种不同的解决方案,适用于不同的训练范式。DeepMath-103K涵盖了广泛的数学主题,促进了通用推理能力的发展。在具有挑战性的数学基准测试中,经过DeepMath-103K训练的模型取得了显著改进。我们公开发布了DeepMath-103K数据集,以促进社区在构建更具能力的AI推理系统方面的进步。
Key Takeaways
- 大型训练数据集是AI复杂数学推理能力发展的重要限制。
- DeepMath-103K是一个新的大型数据集,包含约103K个数学问题,用于训练高级推理模型。
- DeepMath-103K数据集通过严格的数据清洗流程和高难度问题筛选进行构建。
- 数据集中的每个问题都包含可验证的最终答案和多种解决方案,适用于不同的训练范式。
- DeepMath-103K数据集涵盖了广泛的数学主题,有助于开发通用推理能力。
- 在挑战性数学基准测试中,使用DeepMath-103K训练的模型表现显著改善。
点此查看论文截图

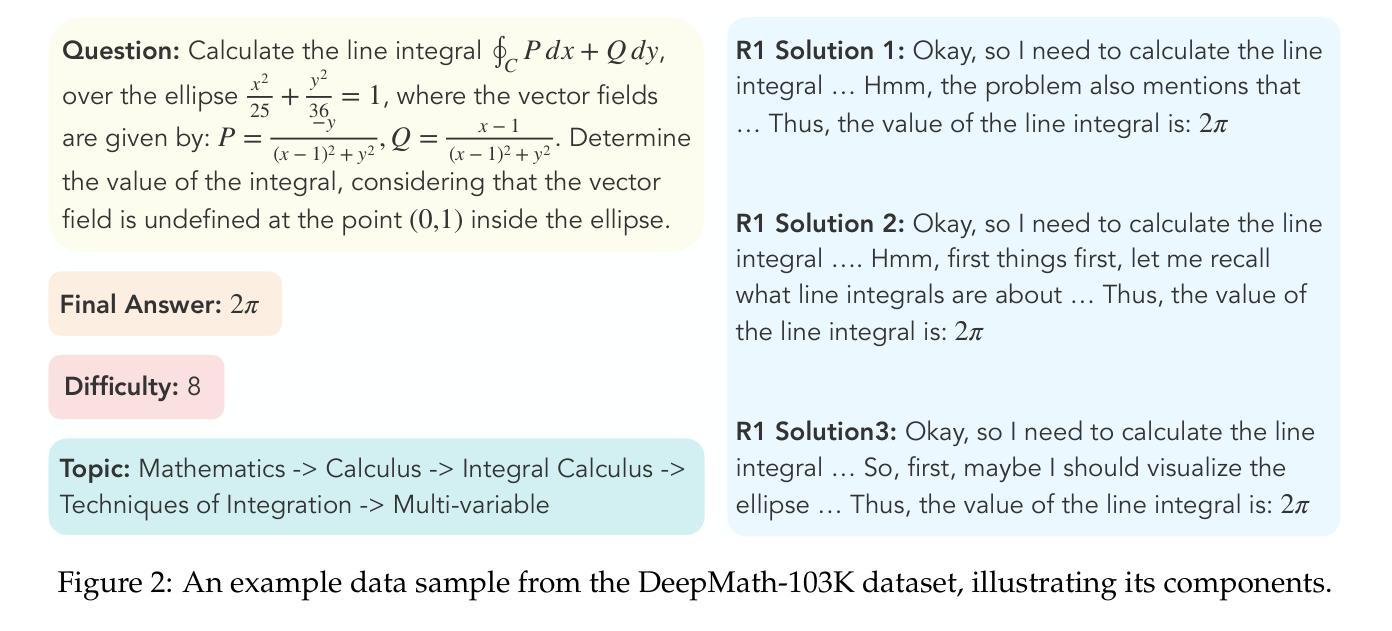
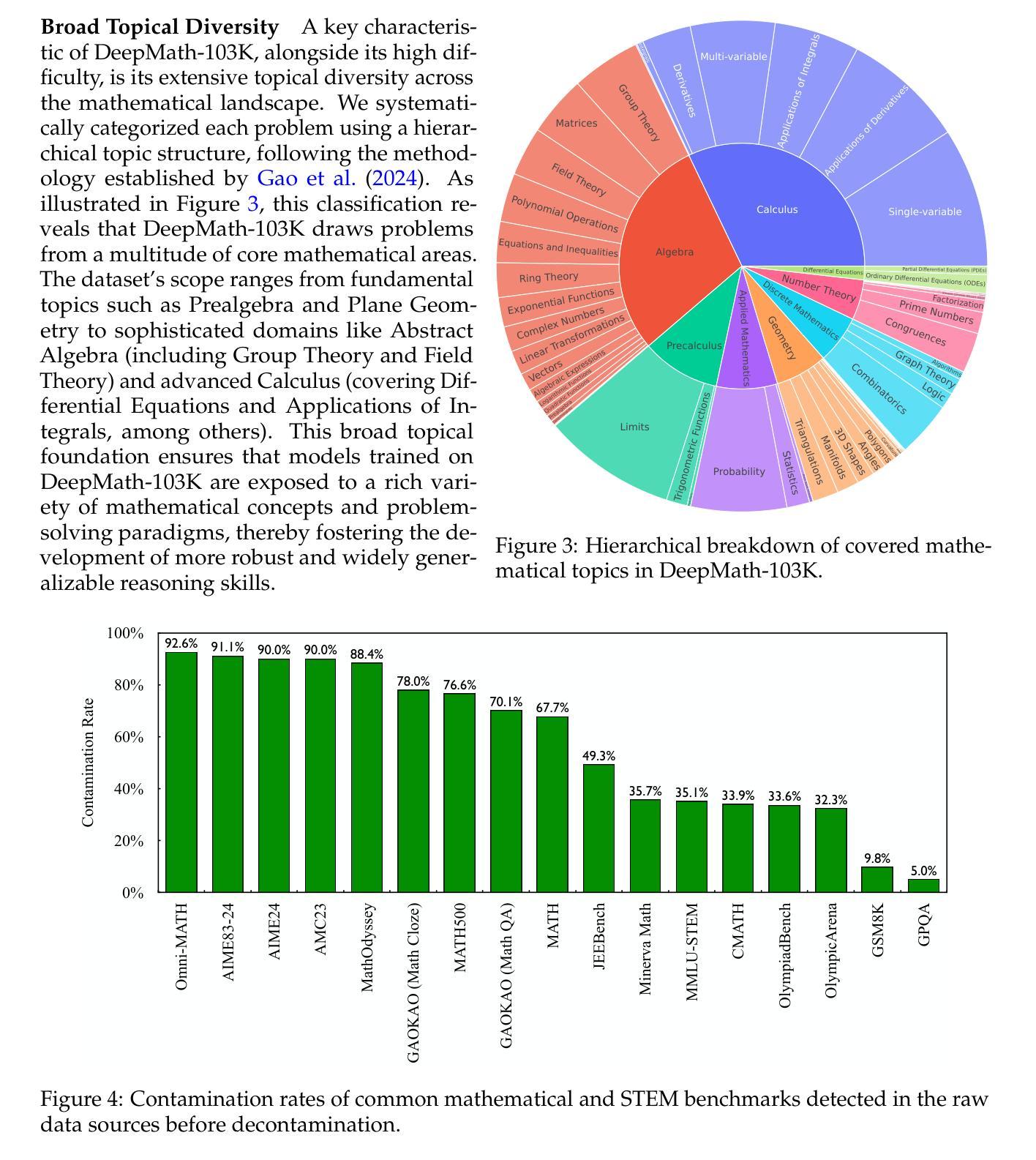
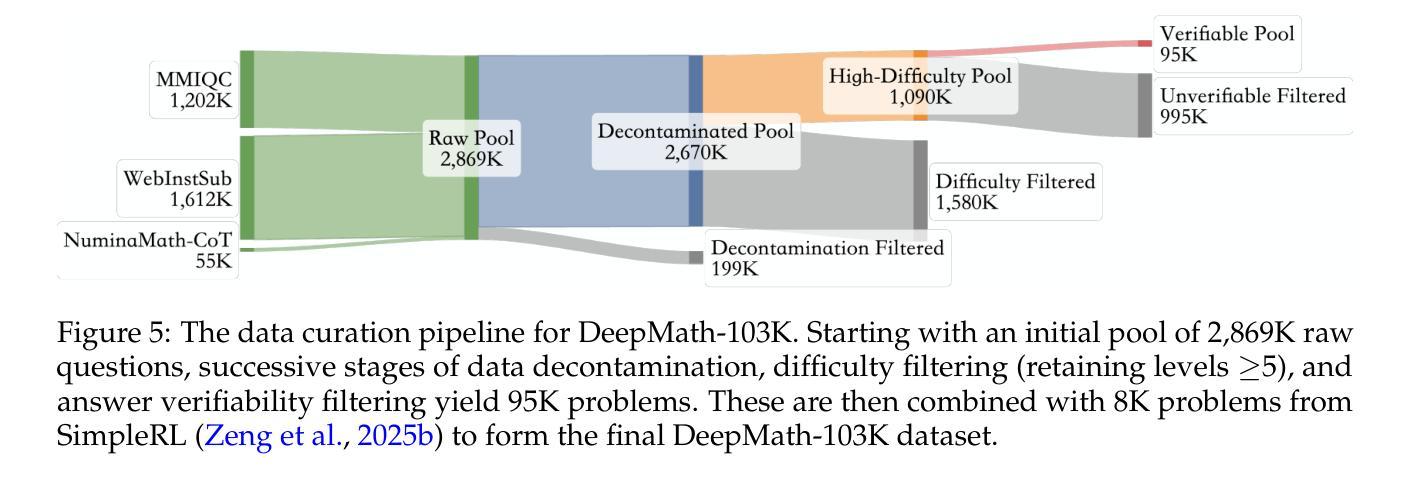
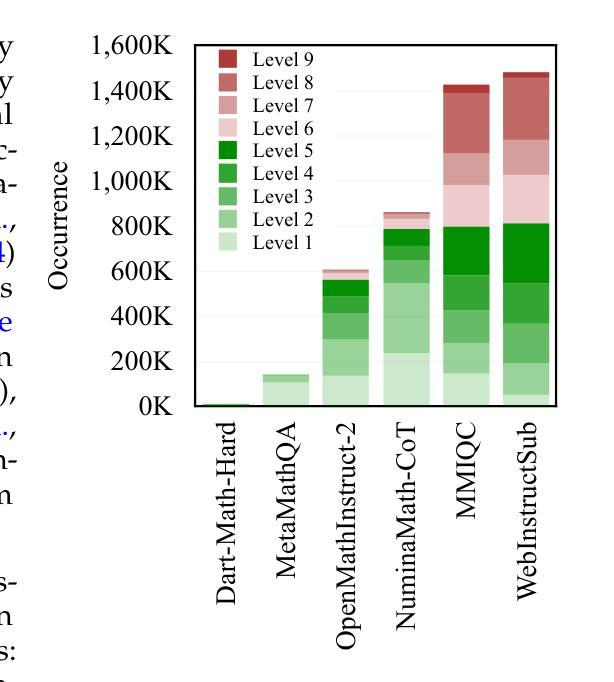
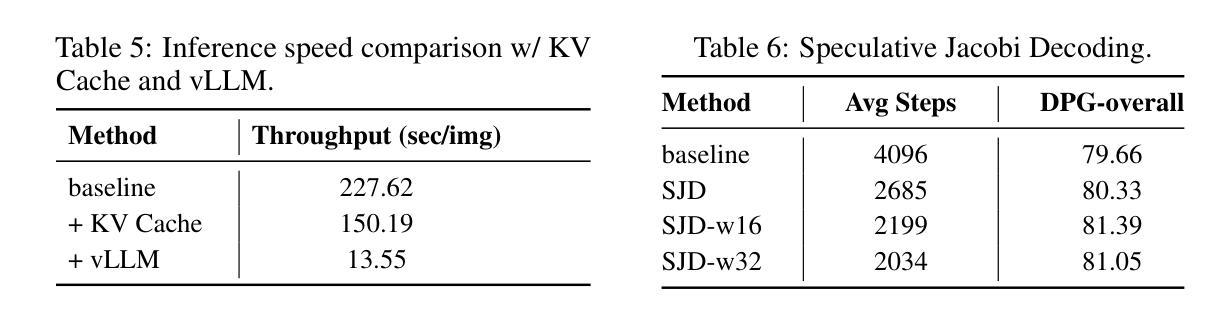
SimpleAR: Pushing the Frontier of Autoregressive Visual Generation through Pretraining, SFT, and RL
Authors:Junke Wang, Zhi Tian, Xun Wang, Xinyu Zhang, Weilin Huang, Zuxuan Wu, Yu-Gang Jiang
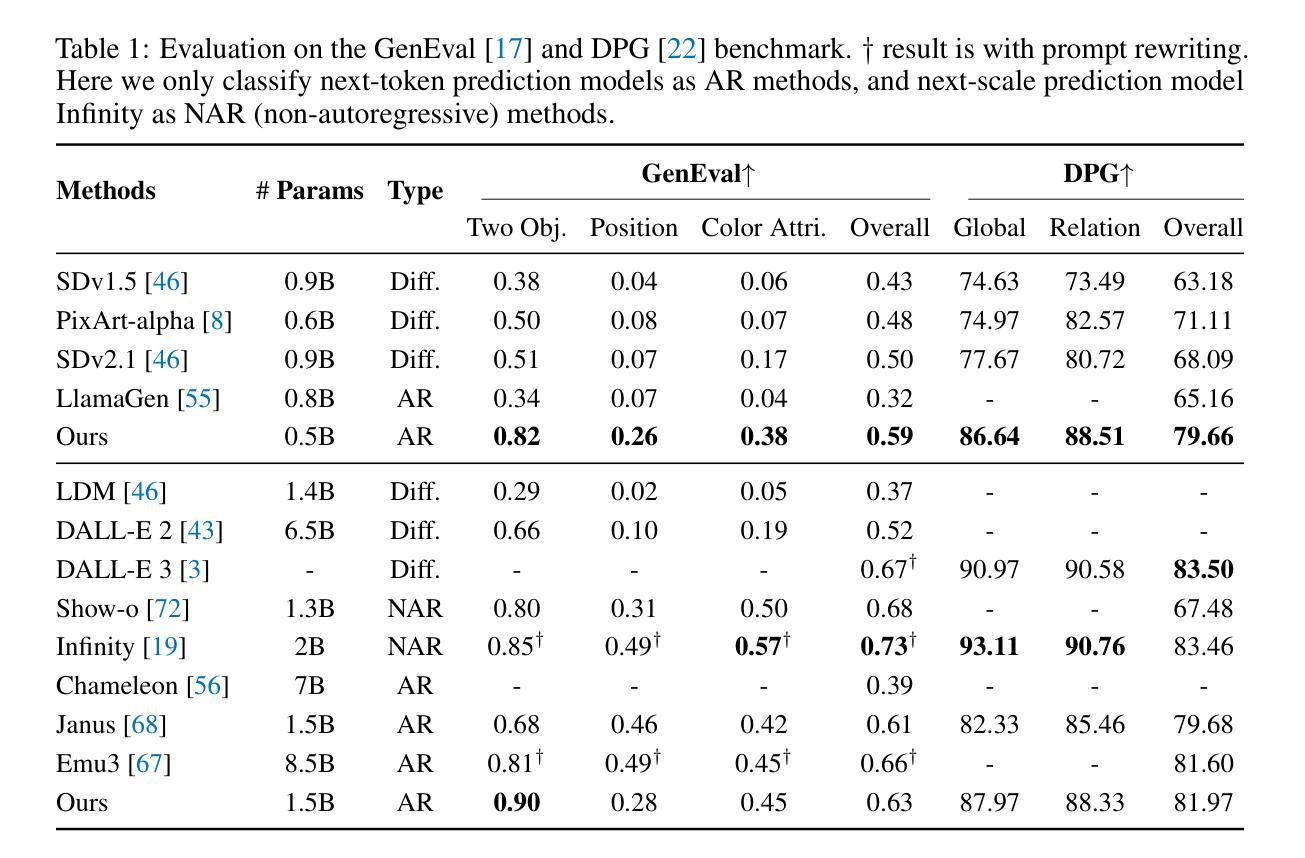
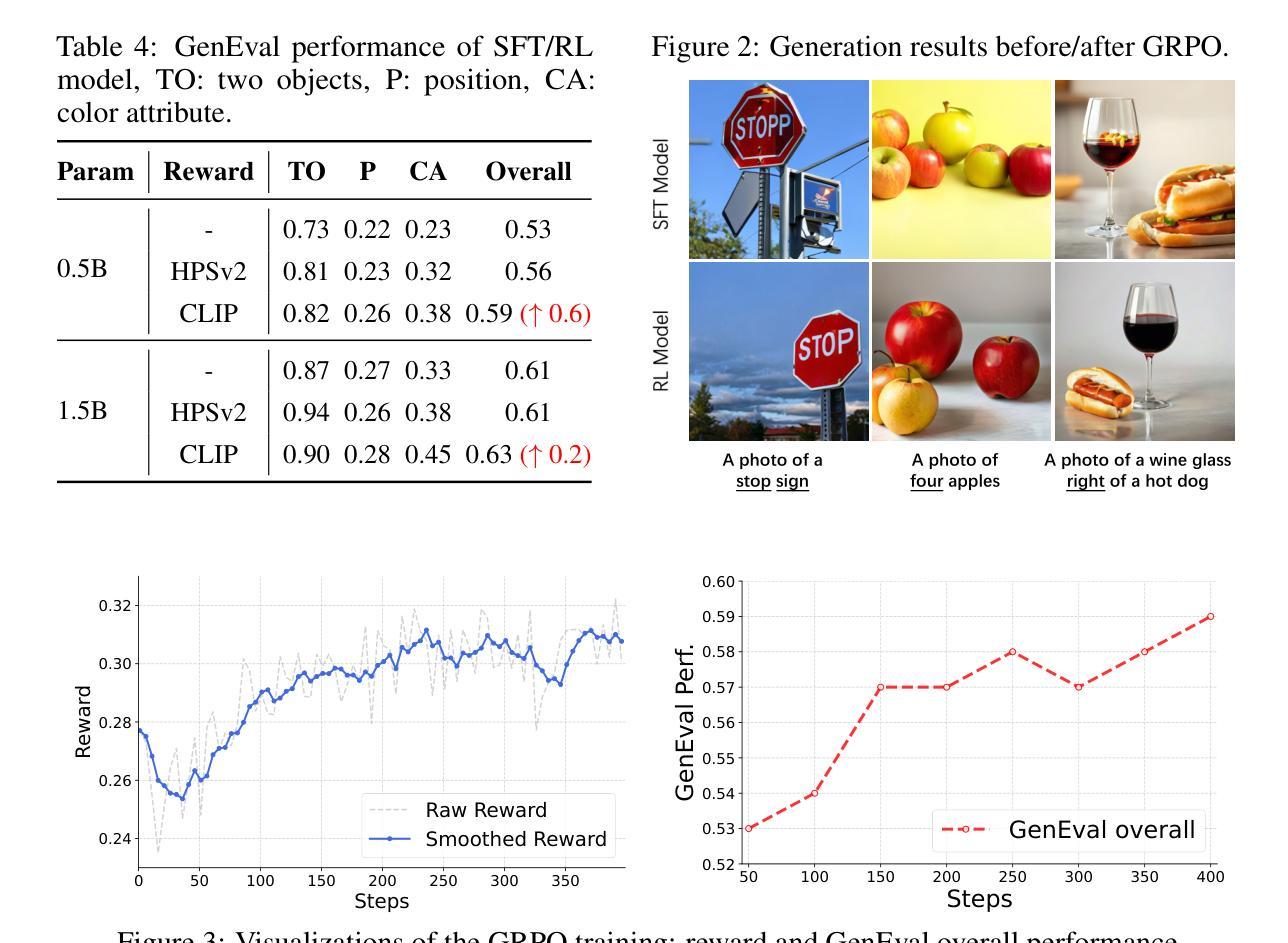
This work presents SimpleAR, a vanilla autoregressive visual generation framework without complex architecure modifications. Through careful exploration of training and inference optimization, we demonstrate that: 1) with only 0.5B parameters, our model can generate 1024x1024 resolution images with high fidelity, and achieve competitive results on challenging text-to-image benchmarks, e.g., 0.59 on GenEval and 79.66 on DPG; 2) both supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) training could lead to significant improvements on generation aesthectics and prompt alignment; and 3) when optimized with inference acceleraton techniques like vLLM, the time for SimpleAR to generate an 1024x1024 image could be reduced to around 14 seconds. By sharing these findings and open-sourcing the code, we hope to reveal the potential of autoregressive visual generation and encourage more participation in this research field. Code is available at https://github.com/wdrink/SimpleAR.
本文介绍了SimpleAR,这是一个简单的自回归视觉生成框架,无需进行复杂的架构修改。通过对训练和推理优化的精心探索,我们证明:1)仅使用0.5B参数,我们的模型就能生成高保真度的1024x1024分辨率图像,并在具有挑战性的文本到图像基准测试中取得有竞争力的结果,例如在GenEval上的得分为0.59,在DPG上的得分为79.66;2)通过监督微调(SFT)和集团相对策略优化(GRPO)训练,可以在生成美学和提示对齐方面取得显着改进;3)当使用诸如vLLM之类的推理加速技术进行优化时,SimpleAR生成一个1024x1024图像的时间可以缩短到大约14秒。我们希望通过分享这些发现并公开源代码,揭示自回归视觉生成的潜力,并鼓励更多人员参与这一研究领域。代码可在https://github.com/wdrink/SimpleAR中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF technical report, work in progress
Summary
SimpleAR框架展示了在视觉生成领域的优秀表现,它采用基础的自回归方法,无需复杂的架构修改。通过优化训练和推理过程,该模型能以高保真度生成1024x1024分辨率的图像,并在文本到图像的基准测试中取得了有竞争力的成绩。此外,通过监督微调(SFT)和集团相对策略优化(GRPO)训练,以及利用vLLM等推理加速技术,SimpleAR在生成美学和提示对齐方面取得了显著改进,并加快了图像生成速度。
Key Takeaways
- SimpleAR是一个基础的自回归视觉生成框架,能以高保真度生成1024x1024分辨率的图像。
- 该模型在具有挑战性的文本到图像基准测试中取得了竞争性的结果。
- 监督微调(SFT)和集团相对策略优化(GRPO)训练提高了生成图像的美学和提示对齐能力。
- 通过使用推理加速技术(如vLLM),SimpleAR能够在约14秒内生成一个1024x1024分辨率的图像。
- SimpleAR框架具有潜力,可以鼓励更多参与此研究领域。
- 该模型的代码已经开源,可供公众访问和使用。
点此查看论文截图

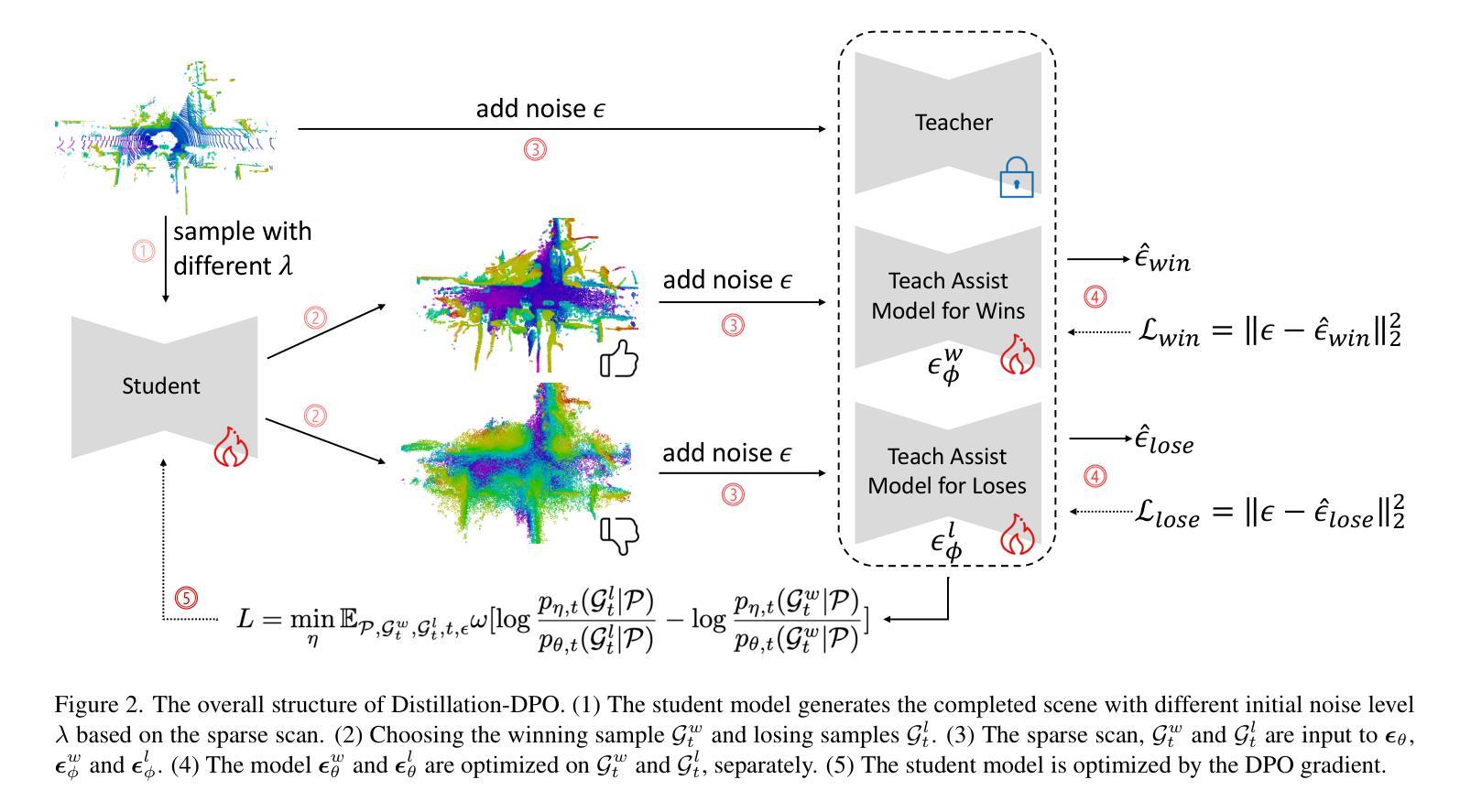
Diffusion Distillation With Direct Preference Optimization For Efficient 3D LiDAR Scene Completion
Authors:An Zhaol, Shengyuan Zhang, Ling Yang, Zejian Li, Jiale Wu, Haoran Xu, AnYang Wei, Perry Pengyun GU Lingyun Sun
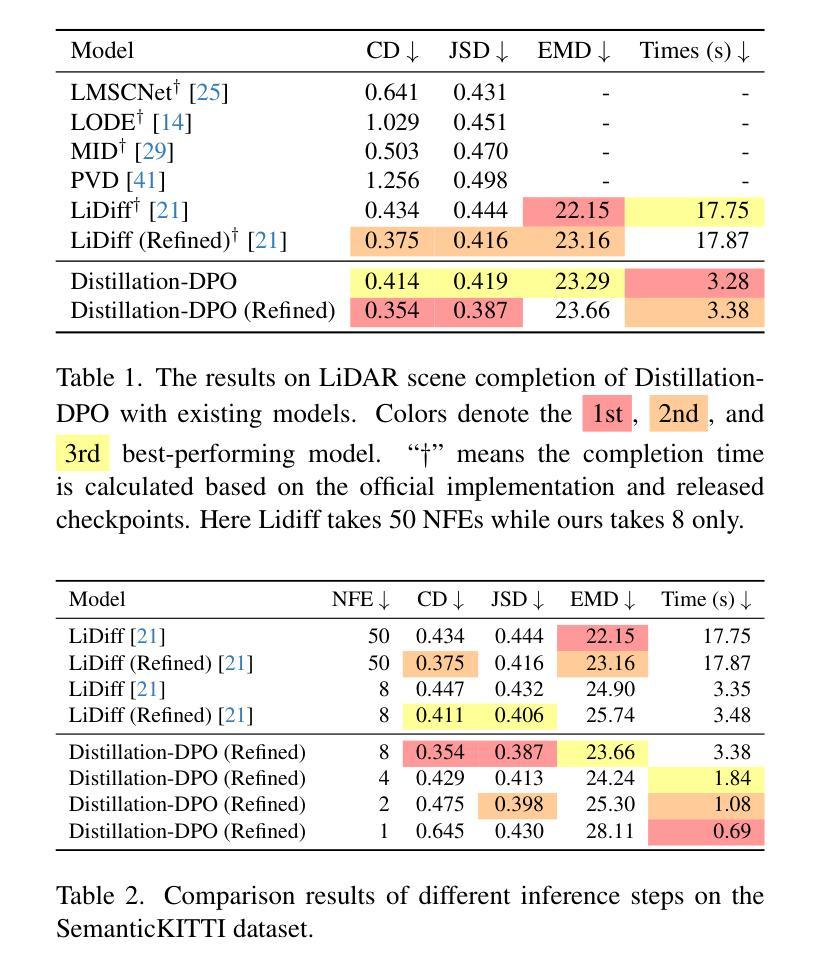
The application of diffusion models in 3D LiDAR scene completion is limited due to diffusion’s slow sampling speed. Score distillation accelerates diffusion sampling but with performance degradation, while post-training with direct policy optimization (DPO) boosts performance using preference data. This paper proposes Distillation-DPO, a novel diffusion distillation framework for LiDAR scene completion with preference aligment. First, the student model generates paired completion scenes with different initial noises. Second, using LiDAR scene evaluation metrics as preference, we construct winning and losing sample pairs. Such construction is reasonable, since most LiDAR scene metrics are informative but non-differentiable to be optimized directly. Third, Distillation-DPO optimizes the student model by exploiting the difference in score functions between the teacher and student models on the paired completion scenes. Such procedure is repeated until convergence. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, compared to state-of-the-art LiDAR scene completion diffusion models, Distillation-DPO achieves higher-quality scene completion while accelerating the completion speed by more than 5-fold. Our method is the first to explore adopting preference learning in distillation to the best of our knowledge and provide insights into preference-aligned distillation. Our code is public available on https://github.com/happyw1nd/DistillationDPO.
扩散模型在3D激光雷达场景补全中的应用受限于其缓慢的采样速度。分数蒸馏可以加速扩散采样,但会导致性能下降,而使用直接策略优化(DPO)进行后训练则可以利用偏好数据提升性能。本文提出了Distillation-DPO,这是一种用于激光雷达场景补全的全新扩散蒸馏框架,带有偏好对齐。首先,学生模型生成带有不同初始噪声的配对完成场景。其次,以激光雷达场景评估指标为偏好,我们构建了胜者和败者样本对。这种构建是合理的,因为大多数激光雷达场景指标都是信息丰富的,但无法直接优化其可分化性。第三,Distillation-DPO通过利用教师模型和学生模型在配对完成场景上的分数函数的差异来优化学生模型。这种程序会持续到收敛。大量实验表明,与最先进的激光雷达场景补全扩散模型相比,Distillation-DPO实现了更高质量的场景补全,并将补全速度提高了5倍以上。据我们所知,我们的方法是首次探索在蒸馏中采用偏好学习,并为偏好对齐的蒸馏提供了见解。我们的代码可在https://github.com/happyw1nd/DistillationDPO上公开获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our code is public available on https://github.com/happyw1nd/DistillationDPO
Summary
扩散模型在3D激光雷达场景补全中的应用受限于其缓慢的采样速度。分数蒸馏虽然可以加速扩散采样,但会导致性能下降,而后训练使用直接策略优化(DPO)则能利用偏好数据提升性能。本文提出了一个用于激光雷达场景补全的全新扩散蒸馏框架——Distillation-DPO,它结合了偏好对齐。首先,学生模型生成带有不同初始噪声的配对完成场景。其次,以激光雷达场景评估指标为偏好,构建胜者与败者样本对。这种构建方式是合理的,因为大多数激光雷达场景指标都是很有价值的但无法直接优化。最后,Distillation-DPO通过优化配对完成场景上教师模型和学生模型之间的分数函数差异来优化学生模型。经过大量实验证明,与最先进的激光雷达场景补全扩散模型相比,Distillation-DPO在加速补全速度的同时,实现了更高质量的场景补全,加速了超过5倍。据我们所知,我们的方法是第一个尝试在蒸馏过程中采用偏好学习的。我们的代码已在公开平台上发布:https://github.com/happyw1nd/DistillationDPO。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在3D LiDAR场景补全中的采样速度慢。
- 分数蒸馏可以加速扩散采样但可能影响性能。
- 直接策略优化(DPO)利用偏好数据提升性能。
- 提出了一种新的扩散蒸馏框架——Distillation-DPO,用于激光雷达场景补全。
- 学生模型生成带有不同初始噪声的配对完成场景。
- 采用激光雷达场景评估指标作为优化的偏好标准。
点此查看论文截图
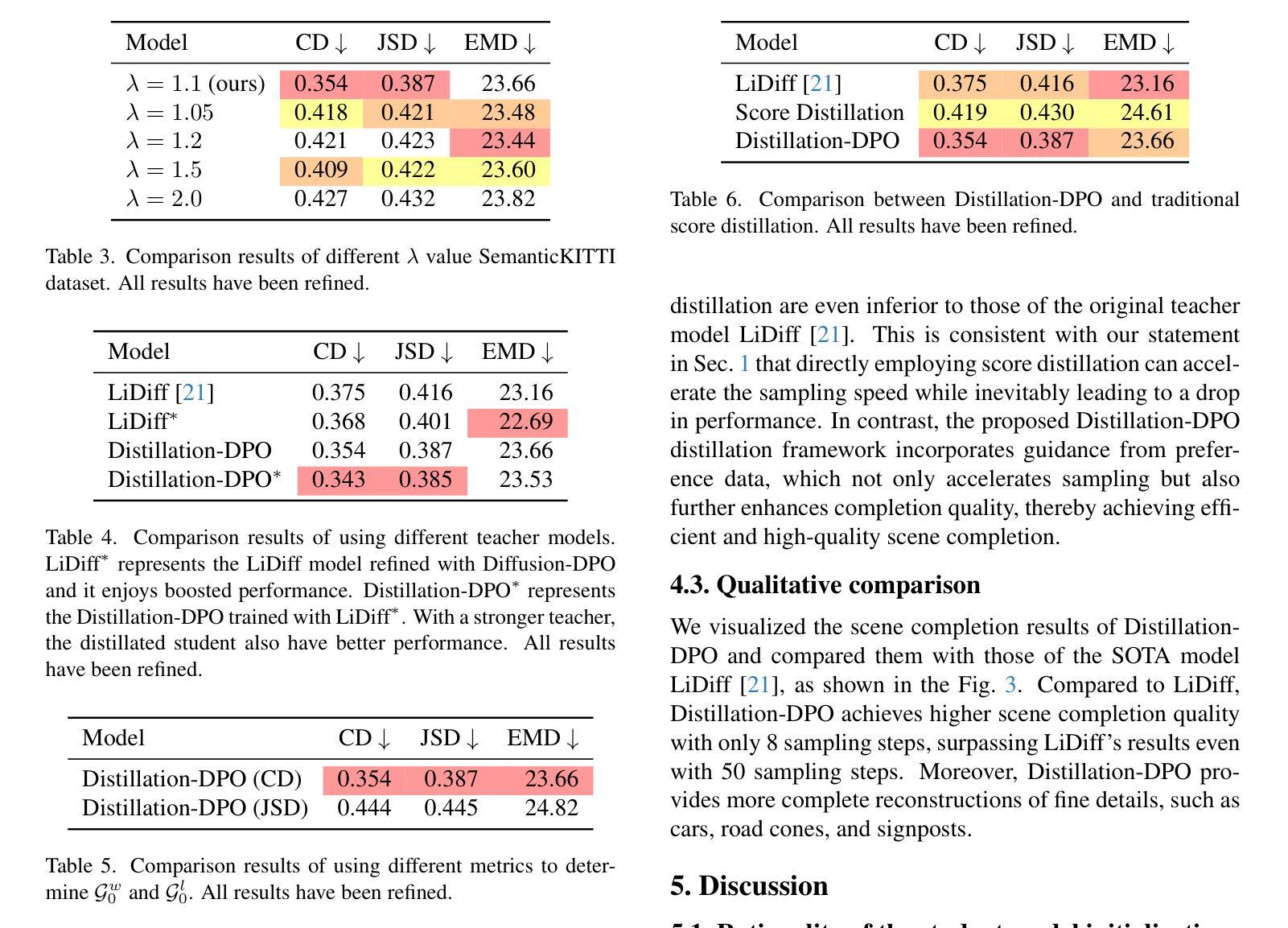
Reinforcing Compositional Retrieval: Retrieving Step-by-Step for Composing Informative Contexts
Authors:Quanyu Long, Jianda Chen, Zhengyuan Liu, Nancy F. Chen, Wenya Wang, Sinno Jialin Pan
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across numerous tasks, yet they often rely on external context to handle complex tasks. While retrieval-augmented frameworks traditionally focus on selecting top-ranked documents in a single pass, many real-world scenarios demand compositional retrieval, where multiple sources must be combined in a coordinated manner. In this work, we propose a tri-encoder sequential retriever that models this process as a Markov Decision Process (MDP), decomposing the probability of retrieving a set of elements into a sequence of conditional probabilities and allowing each retrieval step to be conditioned on previously selected examples. We train the retriever in two stages: first, we efficiently construct supervised sequential data for initial policy training; we then refine the policy to align with the LLM’s preferences using a reward grounded in the structural correspondence of generated programs. Experimental results show that our method consistently and significantly outperforms baselines, underscoring the importance of explicitly modeling inter-example dependencies. These findings highlight the potential of compositional retrieval for tasks requiring multiple pieces of evidence or examples.
大型语言模型(LLM)在多个任务中表现出了显著的能力,但它们通常依赖于外部上下文来处理复杂任务。虽然检索增强框架传统上侧重于在单次传递中选择排名靠前的文档,但许多现实世界场景需要组合检索,必须以协调的方式组合多个源。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种三编码器顺序检索器,它将此过程建模为马尔可夫决策过程(MDP),将检索一组元素的概率分解为一系列条件概率,并允许每个检索步骤都基于先前选择的示例进行条件设置。我们在两个阶段训练检索器:首先,我们有效地构建用于初始策略训练的监督序列数据;然后,我们细化策略,以奖励为基础与LLM的偏好对齐,该奖励基于生成程序的结构对应。实验结果表明,我们的方法始终且显著地优于基线,强调显式建模示例间依赖关系的重要性。这些发现突显了组合检索对于需要多个证据或示例的任务的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 8 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在多个任务中展现出卓越的能力,但它们通常需要外部上下文来处理复杂任务。传统的检索增强框架侧重于一次性选择排名靠前的文档,但在现实世界的许多场景中,需要组合多个来源的信息进行协调式检索。本研究提出了一种三编码器顺序检索器,将检索过程建模为马尔可夫决策过程(MDP),将检索一组元素的可能性分解为一系列条件概率,并允许每个检索步骤以先前选择的例子为条件。我们分两个阶段训练检索器:首先,我们有效地构建监督式顺序数据,用于初始策略训练;然后,我们细化策略,以与LLM的偏好相符,并使用基于生成程序结构对应性的奖励进行训练。实验结果表明,我们的方法持续且显著地优于基准方法,强调明确建模各示例间依赖关系的重要性。这些发现突显了组合检索对于需要多个证据或示例的任务的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在多种任务中表现出色,但处理复杂任务时需依赖外部上下文。
- 传统检索增强框架注重单一通过的选择,现实世界中需协调多个来源信息的组合检索。
- 提出了一种三编码器顺序检索器,将检索过程建模为马尔可夫决策过程(MDP)。
- 检索器训练分为两个阶段:初始策略训练和与LLM偏好相符的策略细化。
- 监督式顺序数据用于训练初始策略,生成程序结构对应性的奖励用于细化策略。
- 实验结果显示所提方法显著优于基准方法,强调建模示例间依赖关系的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

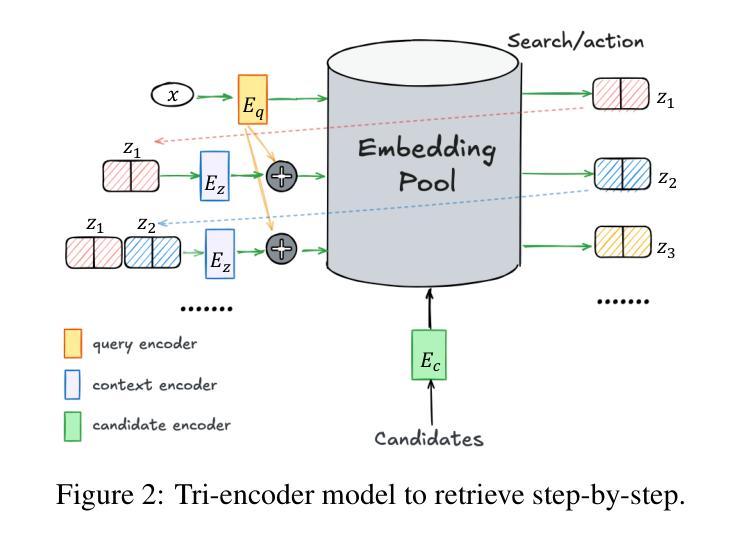
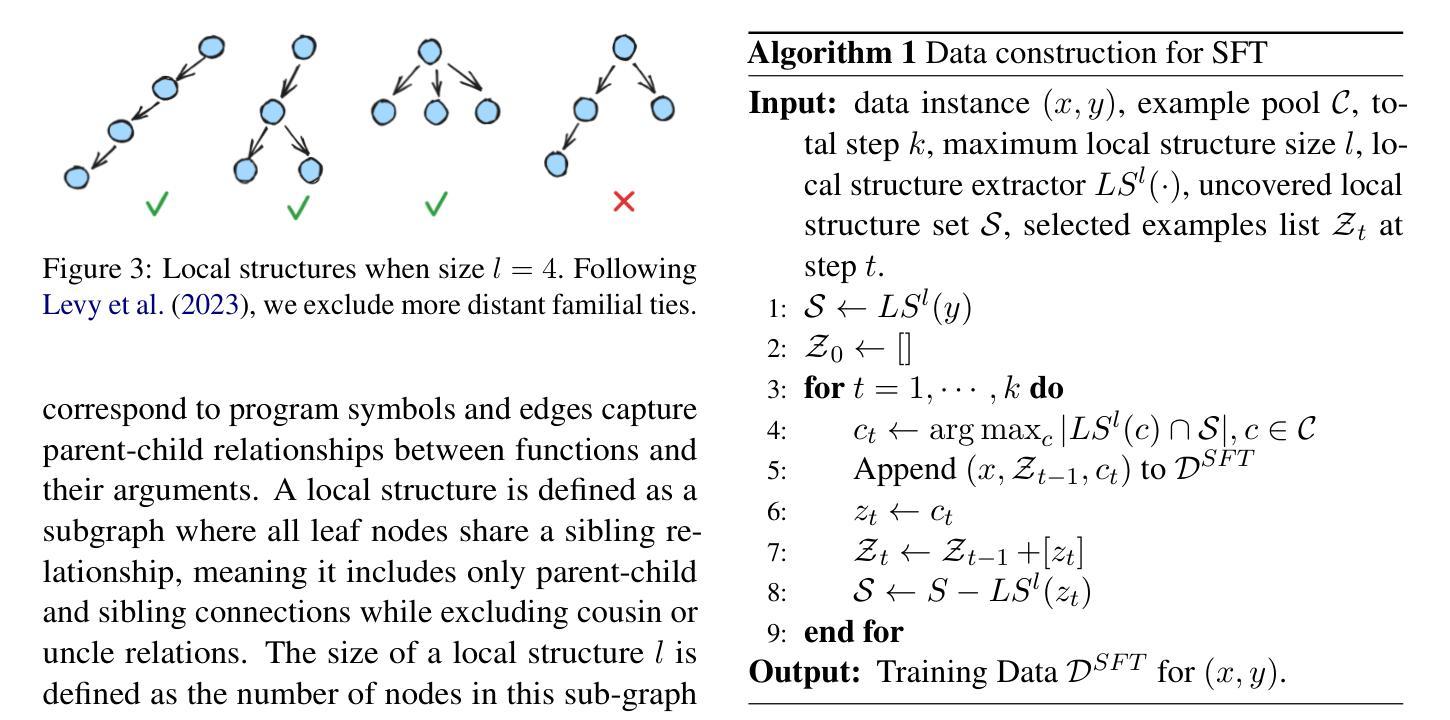
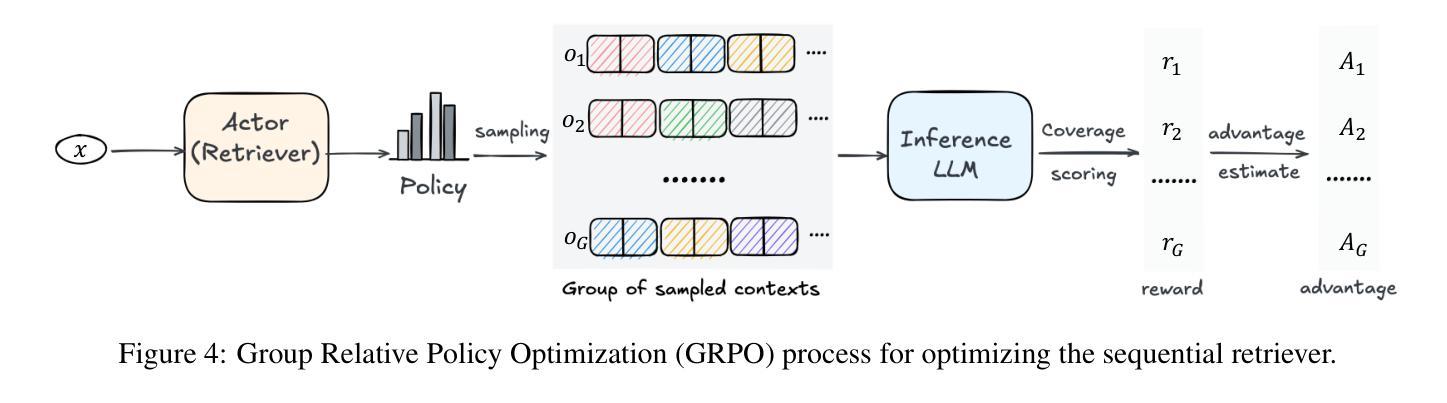
Embodied World Models Emerge from Navigational Task in Open-Ended Environments
Authors:Li Jin, Liu Jia
Understanding how artificial systems can develop spatial awareness and reasoning has long been a challenge in AI research. Traditional models often rely on passive observation, but embodied cognition theory suggests that deeper understanding emerges from active interaction with the environment. This study investigates whether neural networks can autonomously internalize spatial concepts through interaction, focusing on planar navigation tasks. Using Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) combined with Meta-Reinforcement Learning (Meta-RL), we show that agents can learn to encode spatial properties like direction, distance, and obstacle avoidance. We introduce Hybrid Dynamical Systems (HDS) to model the agent-environment interaction as a closed dynamical system, revealing stable limit cycles that correspond to optimal navigation strategies. Ridge Representation allows us to map navigation paths into a fixed-dimensional behavioral space, enabling comparison with neural states. Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA) confirms strong alignment between these representations, suggesting that the agent’s neural states actively encode spatial knowledge. Intervention experiments further show that specific neural dimensions are causally linked to navigation performance. This work provides an approach to bridging the gap between action and perception in AI, offering new insights into building adaptive, interpretable models that can generalize across complex environments. The causal validation of neural representations also opens new avenues for understanding and controlling the internal mechanisms of AI systems, pushing the boundaries of how machines learn and reason in dynamic, real-world scenarios.
理解人工系统如何发展空间意识和推理一直是人工智能研究中的一项挑战。传统模型通常依赖于被动观察,但具身认知理论表明,更深层的理解来自于与环境的主动互动。本研究调查神经网络是否可以通过互动自主内化空间概念,重点关注平面导航任务。通过使用门控循环单元(GRUs)结合元强化学习(Meta-RL),我们展示了智能体可以学习编码方向、距离和避障等空间属性。我们引入混合动力系统(HDS)来模拟智能体与环境之间的相互作用作为一个封闭的动力系统,揭示了对应于最佳导航策略的稳定极限循环。岭表示法允许我们将导航路径映射到固定维度的行为空间,以便与神经状态进行比较。典型相关分析(CCA)证实了这些表示之间的强烈对齐,这表明智能体的神经状态积极编码空间知识。干预实验进一步表明,特定的神经维度与导航性能之间存在因果关系。这项工作为弥合人工智能中的行动和感知之间的差距提供了一种方法,为构建能够适应并跨越复杂环境的可解释模型提供了新的见解。神经表示的因果验证也开辟了理解和控制人工智能系统内部机制的新途径,推动了机器在动态、现实场景中的学习和推理能力的边界。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Research on explainable meta-reinforcement learning AI
Summary
该研究结合神经网络与动态系统理论,探索机器在空间导航任务中如何自主内化空间概念。通过GRU与Meta-RL结合,发现机器能学习方向、距离及避障等空间属性。引入HDS建模,揭示稳定循环对应最佳导航策略。该研究为AI领域的行动与感知之间的桥梁提供新方法,有助于建立能适应复杂环境的可解释模型,并为AI系统内部机制的因果验证开启新的研究途径。
Key Takeaways
- 人工系统可通过主动与环境互动发展出空间认知与推理能力。
- 神经网络结合Meta-Reinforcement Learning (Meta-RL)技术,使机器能自主内化空间概念。
- Hybrid Dynamical Systems (HDS)建模揭示了稳定循环与最佳导航策略之间的关系。
- Ridge Representation方法能将导航路径映射到固定维度的行为空间,便于与神经状态进行比较。
- Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA)证实了机器神经状态积极编码空间知识。
- 通过干预实验发现特定神经维度与导航性能之间存在因果关系。
点此查看论文截图

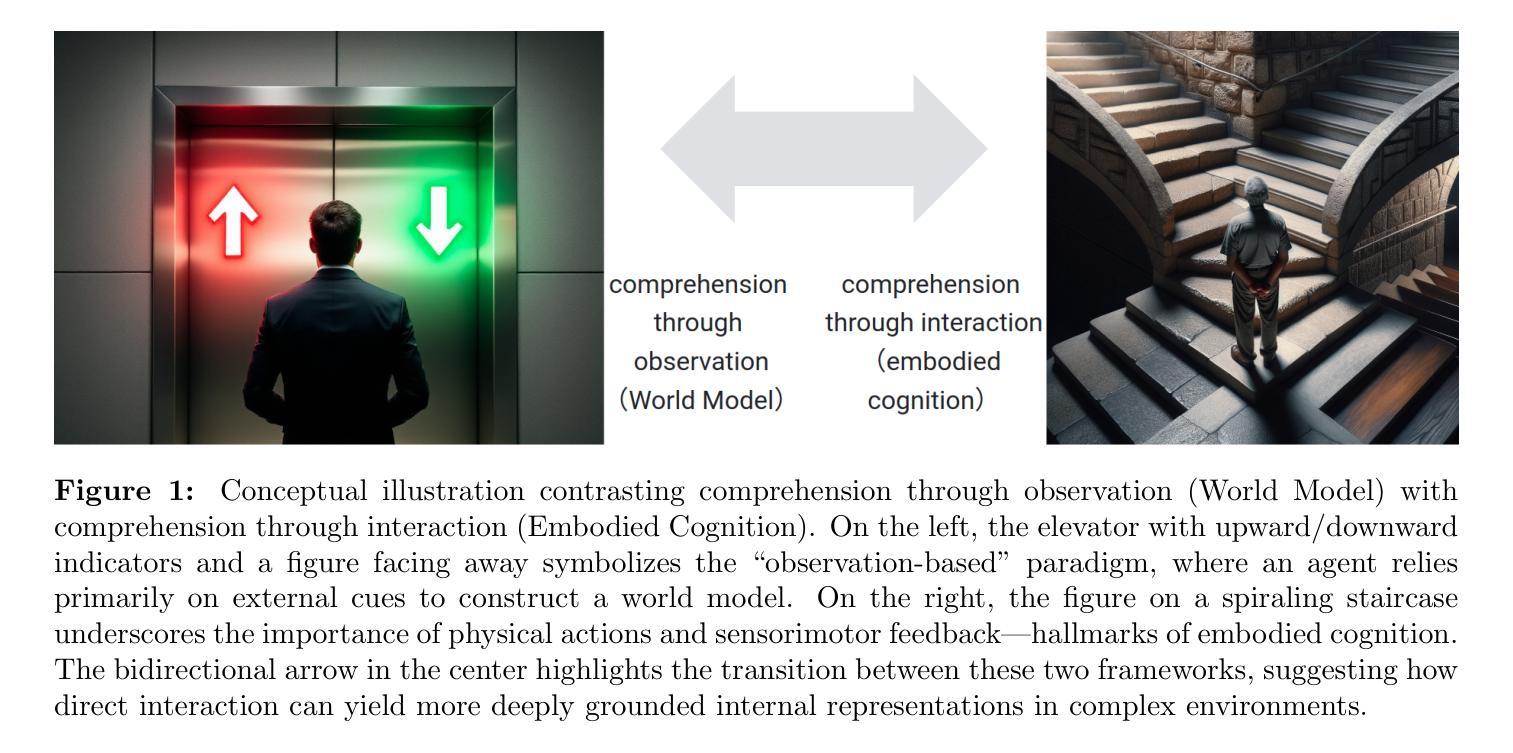
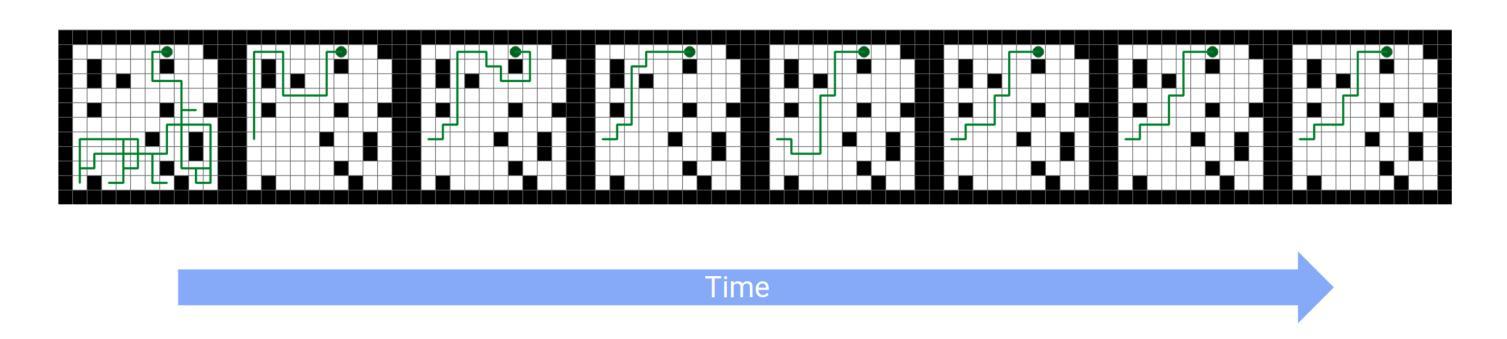
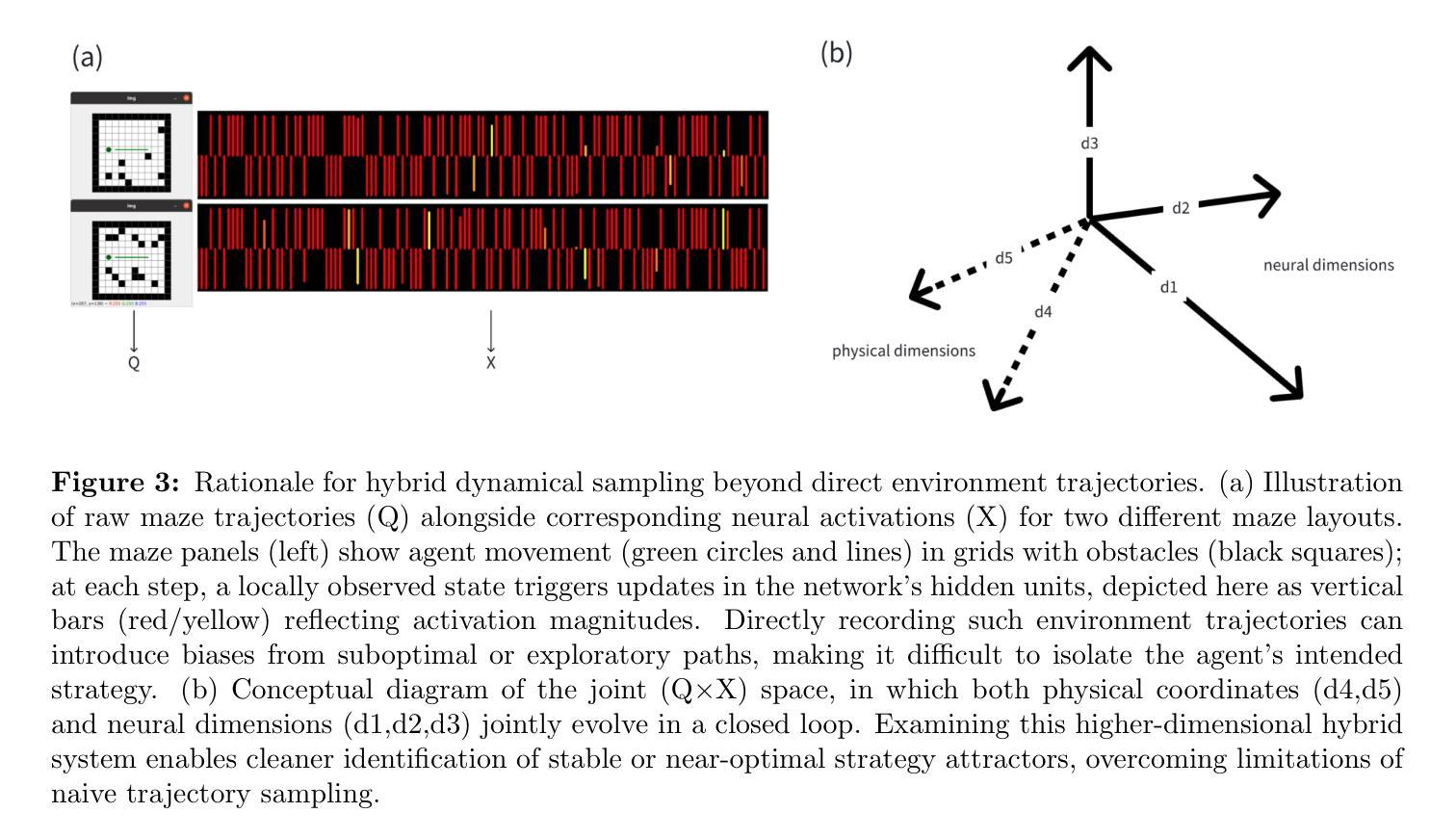
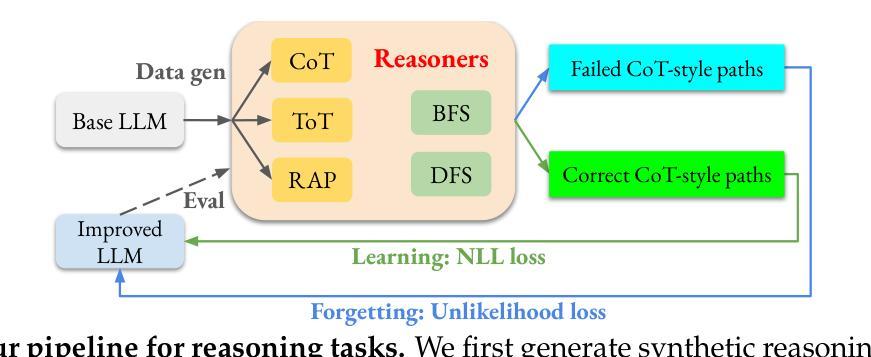
Teaching Large Language Models to Reason through Learning and Forgetting
Authors:Tianwei Ni, Allen Nie, Sapana Chaudhary, Yao Liu, Huzefa Rangwala, Rasool Fakoor
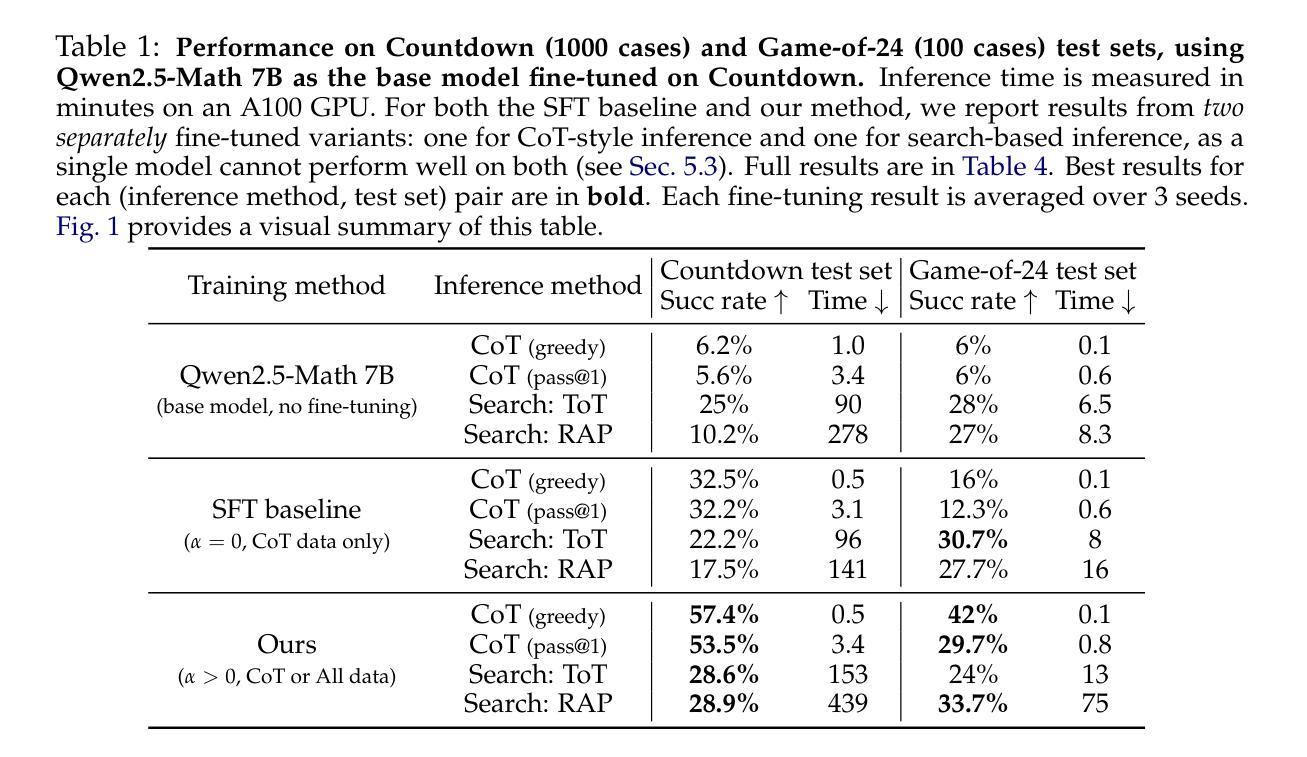
Leveraging inference-time search in large language models has proven effective in further enhancing a trained model’s capability to solve complex mathematical and reasoning problems. However, this approach significantly increases computational costs and inference time, as the model must generate and evaluate multiple candidate solutions to identify a viable reasoning path. To address this, we propose an effective approach that integrates search capabilities directly into the model by fine-tuning it using both successful (learning) and failed reasoning paths (forgetting) derived from diverse search methods. While fine-tuning the model with these data might seem straightforward, we identify a critical issue: the model’s search capability tends to degrade rapidly if fine-tuning is performed naively. We show that this degradation can be substantially mitigated by employing a smaller learning rate. Extensive experiments on the challenging Game-of-24 and Countdown mathematical reasoning benchmarks show that our approach not only outperforms both standard fine-tuning and inference-time search baselines but also significantly reduces inference time by 180$\times$.
利用大型语言模型中的推理时间搜索,已被证明可以进一步增强训练模型解决复杂数学和推理问题的能力。然而,这种方法会大幅增加计算成本和推理时间,因为模型需要生成并评估多个候选解决方案,以识别可行的推理路径。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种将搜索能力直接集成到模型中的有效方法,通过微调模型,使用来自多种搜索方法的成功(学习)和失败推理路径(遗忘)。虽然用这些数据微调模型看似简单,但我们发现了一个关键问题:如果盲目进行微调,模型的搜索能力往往会迅速下降。我们表明,通过采用较小的学习率,可以大大缓解这种退化。在具有挑战性的“二十四点游戏”和倒计时数学推理基准测试的大量实验表明,我们的方法不仅优于标准微调方法和推理时间搜索基准测试,而且通过减少180倍的推理时间,实现了显著的性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模语言模型中利用推理时间搜索已被证明可进一步提高训练模型解决复杂数学和推理问题的能力。然而,这种方法会增加计算成本和推理时间,因为模型需要生成并评估多个候选解决方案来识别可行的推理路径。为解决这个问题,我们提出了一种将搜索能力直接集成到模型中的有效方法,通过微调模型,使用来自不同搜索方法的成功(学习)和失败推理路径(遗忘)。虽然使用这些数据微调模型看似简单,但我们发现了一个关键问题:如果盲目进行微调,模型的搜索能力会迅速下降。我们通过使用较小的学习率来展示这种退化可以大大缓解。在具有挑战性的Game-of-24和Countdown数学推理基准测试的大量实验表明,我们的方法不仅优于标准微调方法和推理时间搜索基准测试,而且推理时间也减少了180倍。
Key Takeaways
- 推理时间搜索在大型语言模型中能增强解决复杂数学和推理问题的能力。
- 推理时间搜索会增加计算成本和推理时间,因为需要评估多个候选解决方案。
- 直接将搜索能力集成到模型中是一种有效的解决方法。
- 通过使用成功和失败的推理路径进行微调可以提高模型的性能。
- 盲目微调会导致模型搜索能力迅速下降。
- 使用较小的学习率可以显著缓解模型性能的退化。
点此查看论文截图

Kimina-Prover Preview: Towards Large Formal Reasoning Models with Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Haiming Wang, Mert Unsal, Xiaohan Lin, Mantas Baksys, Junqi Liu, Marco Dos Santos, Flood Sung, Marina Vinyes, Zhenzhe Ying, Zekai Zhu, Jianqiao Lu, Hugues de Saxcé, Bolton Bailey, Chendong Song, Chenjun Xiao, Dehao Zhang, Ebony Zhang, Frederick Pu, Han Zhu, Jiawei Liu, Jonas Bayer, Julien Michel, Longhui Yu, Léo Dreyfus-Schmidt, Lewis Tunstall, Luigi Pagani, Moreira Machado, Pauline Bourigault, Ran Wang, Stanislas Polu, Thibaut Barroyer, Wen-Ding Li, Yazhe Niu, Yann Fleureau, Yangyang Hu, Zhouliang Yu, Zihan Wang, Zhilin Yang, Zhengying Liu, Jia Li
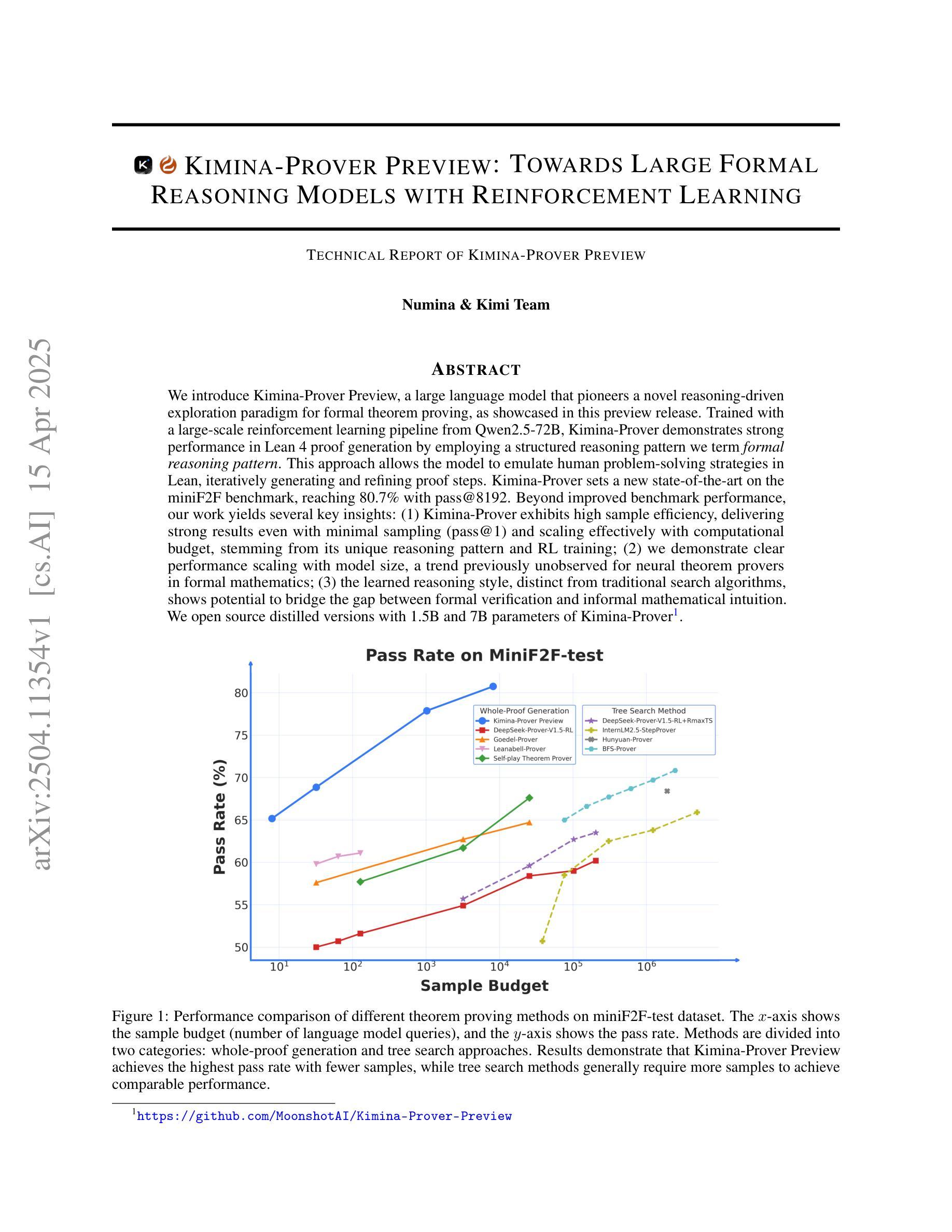
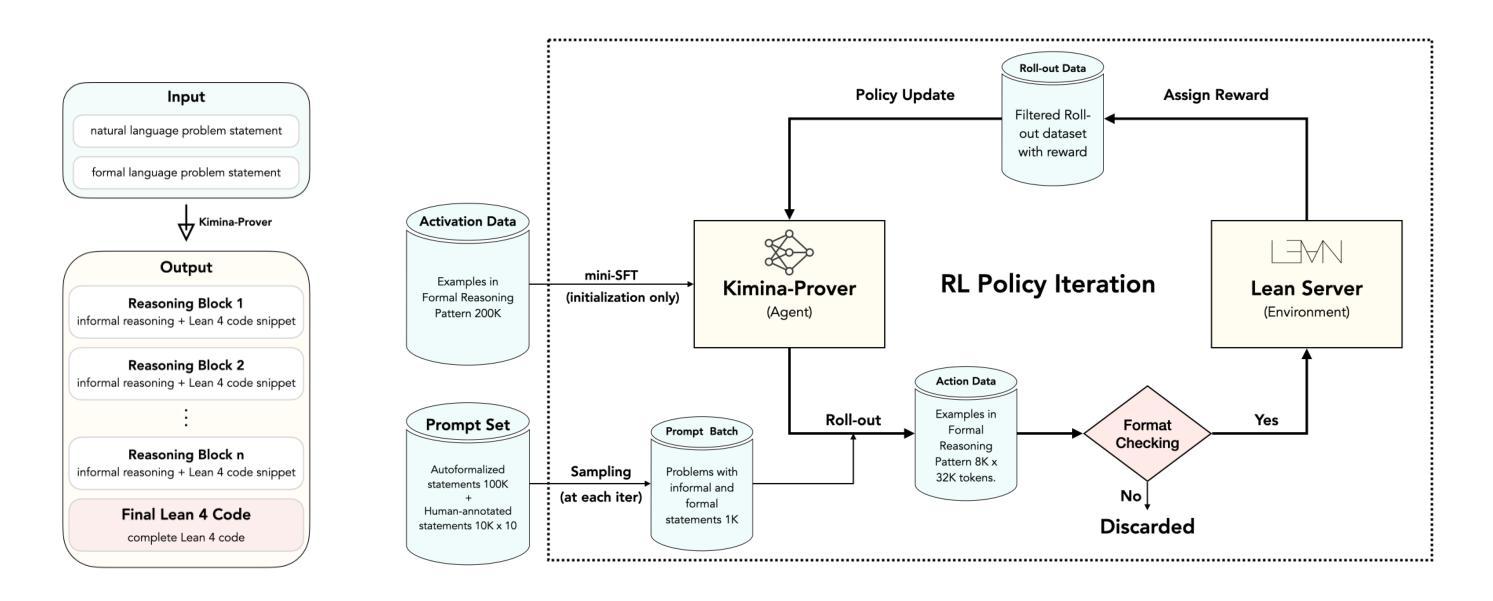
We introduce Kimina-Prover Preview, a large language model that pioneers a novel reasoning-driven exploration paradigm for formal theorem proving, as showcased in this preview release. Trained with a large-scale reinforcement learning pipeline from Qwen2.5-72B, Kimina-Prover demonstrates strong performance in Lean 4 proof generation by employing a structured reasoning pattern we term \textit{formal reasoning pattern}. This approach allows the model to emulate human problem-solving strategies in Lean, iteratively generating and refining proof steps. Kimina-Prover sets a new state-of-the-art on the miniF2F benchmark, reaching 80.7% with pass@8192. Beyond improved benchmark performance, our work yields several key insights: (1) Kimina-Prover exhibits high sample efficiency, delivering strong results even with minimal sampling (pass@1) and scaling effectively with computational budget, stemming from its unique reasoning pattern and RL training; (2) we demonstrate clear performance scaling with model size, a trend previously unobserved for neural theorem provers in formal mathematics; (3) the learned reasoning style, distinct from traditional search algorithms, shows potential to bridge the gap between formal verification and informal mathematical intuition. We open source distilled versions with 1.5B and 7B parameters of Kimina-Prover
我们推出了Kimina-Prover Preview版本,这是一款大型语言模型,率先采用新型推理驱动的探索模式来进行形式化定理证明。Kimina-Prover借助来自Qwen 2.5到72B的大规模强化学习流水线进行训练,通过我们称之为“形式推理模式”的结构化推理模式,在Lean 4证明生成方面表现出卓越的性能。这种方法使模型能够在Lean中模拟人类解决问题的策略,并可以迭代地生成和完善证明步骤。Kimina-Prover在miniF2F基准测试中达到了最新水平,以pass@8192的成绩达到80.7%。除了提高基准测试性能外,我们的工作还获得了几个关键见解:(1)Kimina-Prover展现出很高的样本效率,即使在最低采样条件下也能产生强有力的结果(pass@1),并随着计算预算的增加而有效扩展,这源于其独特的推理模式和强化学习训练;(2)我们证明了模型性能随着模型规模的扩大而提高,这在形式数学的神经网络定理证明器中此前并未观察到这一趋势;(3)学习到的推理风格与传统搜索算法截然不同,显示了在弥合形式验证和非正式数学直觉之间差距的潜力。我们公开了参数为1.5B和7B的Kimina-Prover精简版本。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages
Summary:
Kimina-Prover预览版是一款大型语言模型,它开创了形式化定理证明中的推理驱动探索模式。该模型使用Qwen2.5-72B的大规模强化学习管道进行训练,展现了在Lean 4证明生成中的出色表现。Kiminar Prover采用我们称之为“形式推理模式”的结构化推理模式,能够模拟人类在Lean中的问题解决策略,并迭代地生成和细化证明步骤。该模型在miniF2F基准测试上达到了新的技术高度,pass@8192得分为80.7%。
Key Takeaways:
- Kimina-Prover引入了一种新的形式化定理证明中的推理驱动探索模式。
- 该模型使用大规模的强化学习管道进行训练,展现了在Lean 4证明生成中的高效性能。
- Kimina-Prover采用了形式推理模式,能够模拟人类的证明解决策略。
- 该模型具有高样本效率,即使在最小的采样下也能产生强大的结果,并能有效地随着计算预算而扩展。
- 随着模型规模的增加,性能得到了明显的提升,这在之前的神经定理证明器中是没有观察到的趋势。
- 所学到的推理风格与传统搜索算法不同,有望弥合形式验证与非正式数学直觉之间的差距。
点此查看论文截图
Nondeterministic Polynomial-time Problem Challenge: An Ever-Scaling Reasoning Benchmark for LLMs
Authors:Chang Yang, Ruiyu Wang, Junzhe Jiang, Qi Jiang, Qinggang Zhang, Yanchen Deng, Shuxin Li, Shuyue Hu, Bo Li, Florian T. Pokorny, Xiao Huang, Xinrun Wang
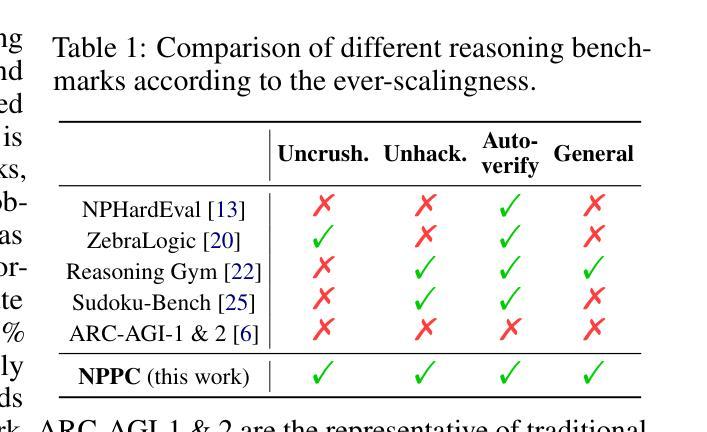
Reasoning is the fundamental capability of large language models (LLMs). Due to the rapid progress of LLMs, there are two main issues of current benchmarks: i) these benchmarks can be crushed in a short time (less than 1 year), and ii) these benchmarks may be easily hacked. To handle these issues, we propose the ever-scalingness for building the benchmarks which are uncrushable, unhackable, auto-verifiable and general. This paper presents Nondeterministic Polynomial-time Problem Challenge (NPPC), an ever-scaling reasoning benchmark for LLMs. Specifically, the NPPC has three main modules: i) npgym, which provides a unified interface of 25 well-known NP-complete problems and can generate any number of instances with any levels of complexities, ii) npsolver: which provides a unified interface to evaluate the problem instances with both online and offline models via APIs and local deployments, respectively, and iii) npeval: which provides the comprehensive and ready-to-use tools to analyze the performances of LLMs over different problems, the number of tokens, the aha moments, the reasoning errors and the solution errors. Extensive experiments over widely-used LLMs demonstrate: i) NPPC can successfully decrease the performances of advanced LLMs’ performances to below 10%, demonstrating that NPPC is uncrushable, ii) DeepSeek-R1, Claude-3.7-Sonnet, and o1/o3-mini are the most powerful LLMs, where DeepSeek-R1 outperforms Claude-3.7-Sonnet and o1/o3-mini in most NP-complete problems considered, and iii) the numbers of tokens, aha moments in the advanced LLMs, e.g., Claude-3.7-Sonnet and DeepSeek-R1, are observed first to increase and then decrease when the problem instances become more and more difficult. We believe that NPPC is the first ever-scaling reasoning benchmark, serving as the uncrushable and unhackable testbed for LLMs toward artificial general intelligence (AGI).
推理是大型语言模型(LLM)的基本能力。由于LLM的快速发展,当前基准测试面临两个主要问题:一是这些基准测试可以在很短的时间内(不到一年)被超越,二是这些基准测试很容易被破解。为了解决这些问题,我们提出构建不可超越、不可破解、可自动验证和通用的基准测试,以实现持续扩展。本文介绍了非确定性多项式时间问题挑战(NPPC),这是一个针对LLM的持续扩展推理基准测试。具体来说,NPPC有三个主要模块:一、npgym,它提供了25个著名的NP完全问题的统一接口,可以生成任何数量和任何复杂程度的实例;二、npsolver,它通过API和本地部署提供统一接口,可以评估问题实例的在线和离线模型;三、npeval,它提供全面且现成可用的工具,分析LLM在不同问题、令牌数量、顿悟时刻、推理错误和解决方案错误方面的性能。在广泛使用的LLM上的大量实验表明:一、NPPC能够成功地将先进LLM的性能降低到10%以下,表明NPPC是不可超越的;二、DeepSeek-R1、Claude-3.7-Sonnet和o1/o3-mini是最强大的LLM,其中DeepSeek-R1在大多数考虑的NP完全问题中优于Claude-3.7-Sonnet和o1/o3-mini;三、在先进的LLM(如Claude-3.7-Sonnet和DeepSeek-R1)中,随着问题实例变得越来越困难,令牌数量和顿悟时刻首先增加然后减少。我们相信,NPPC是第一个持续扩展的推理基准测试,作为不可超越和不可破解的测试平台,为LLM实现人工智能通用性(AGI)提供了支持。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preliminary work, 10 pages for main text
Summary
大型语言模型的根本能力是推理能力。由于大型语言模型发展迅速,当前存在的基准测试面临两大问题:一、这些基准测试可以在短时间内(不到一年)被突破;二、这些基准测试容易被操纵。为了应对这些问题,我们提出了不可攻破、不可操纵、可自动验证和通用的永恒扩展基准测试。本文介绍了非确定性多项式时间问题挑战(NPPC),这是一个针对大型语言模型的永恒扩展推理基准测试。NPPC主要包括三个模块:一、npgym,它提供了25个著名的NP完全问题的统一接口,可以生成任何数量、任何复杂程度的实例;二、npsolver,它通过API和本地部署提供问题实例的评估接口,既可以评估在线模型也可以评估离线模型;三、npeval,它提供了全面且现成可用的工具,用于分析大型语言模型在不同问题、不同标记数量、灵感时刻、推理错误和解决方案错误方面的性能。实验表明NPPC成功地将先进的大型语言模型的性能降低到10%以下,证明了NPPC的不可攻破性,并揭示了DeepSeek-R1等模型的优势。我们相信NPPC是第一个永恒的推理基准测试,作为不可攻破和不可操纵的测试平台,为大型语言模型迈向人工智能通用性提供标准。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的核心能力是推理能力。
- 当前大型语言模型的基准测试面临可快速突破和易被操纵的问题。
- 提出了非确定性多项式时间问题挑战(NPPC),一个针对大型语言模型的永恒扩展推理基准测试。
- NPPC包含npgym、npsolver和npeval三个主要模块,分别用于问题生成、问题评估及性能分析。
- NPPC能够成功降低先进大型语言模型的性能至10%以下,证明了其不可攻破性。
- 在NPPC测试中,DeepSeek-R1等模型表现优异,其中DeepSeek-R1在多数NP完全问题上优于Claude-3.7-Sonnet和o1/o3-mini。
点此查看论文截图


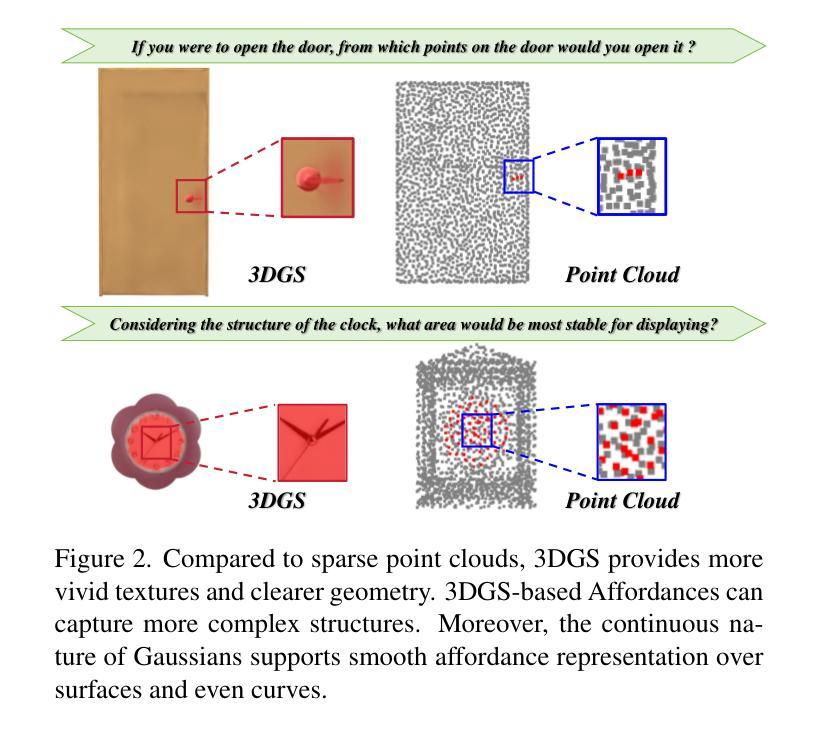
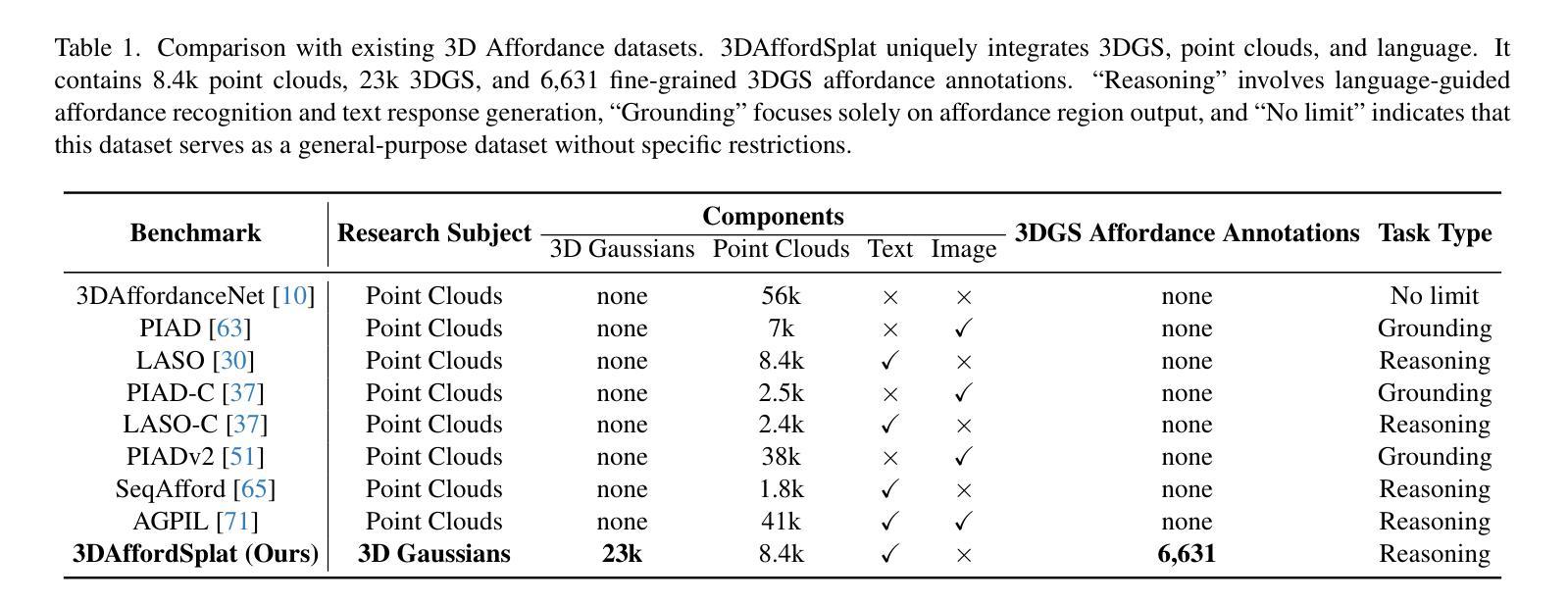
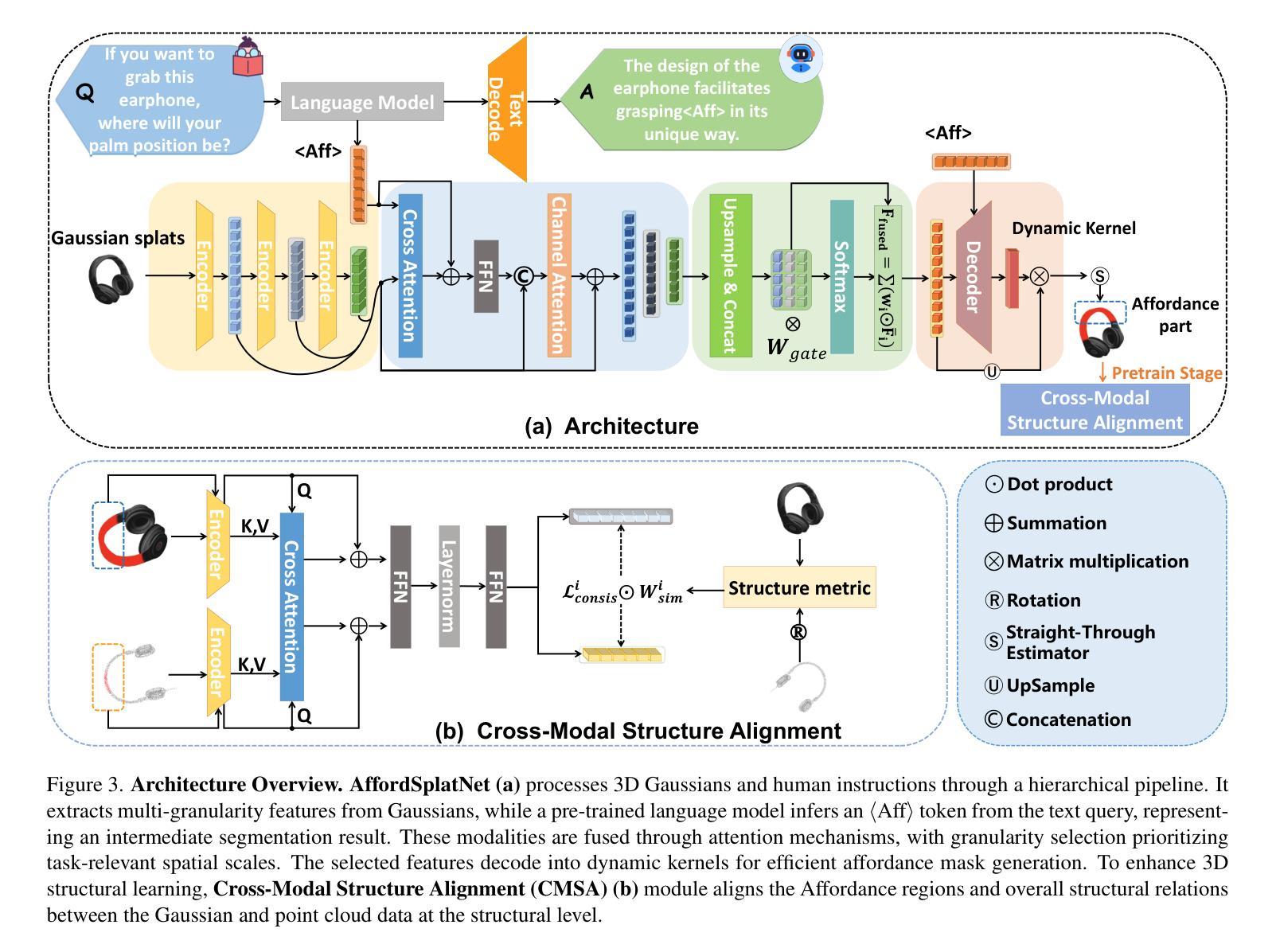
3DAffordSplat: Efficient Affordance Reasoning with 3D Gaussians
Authors:Zeming wei, Junyi Lin, Yang Liu, Weixing Chen, Jingzhou Luo, Guanbin Li, Liang Lin
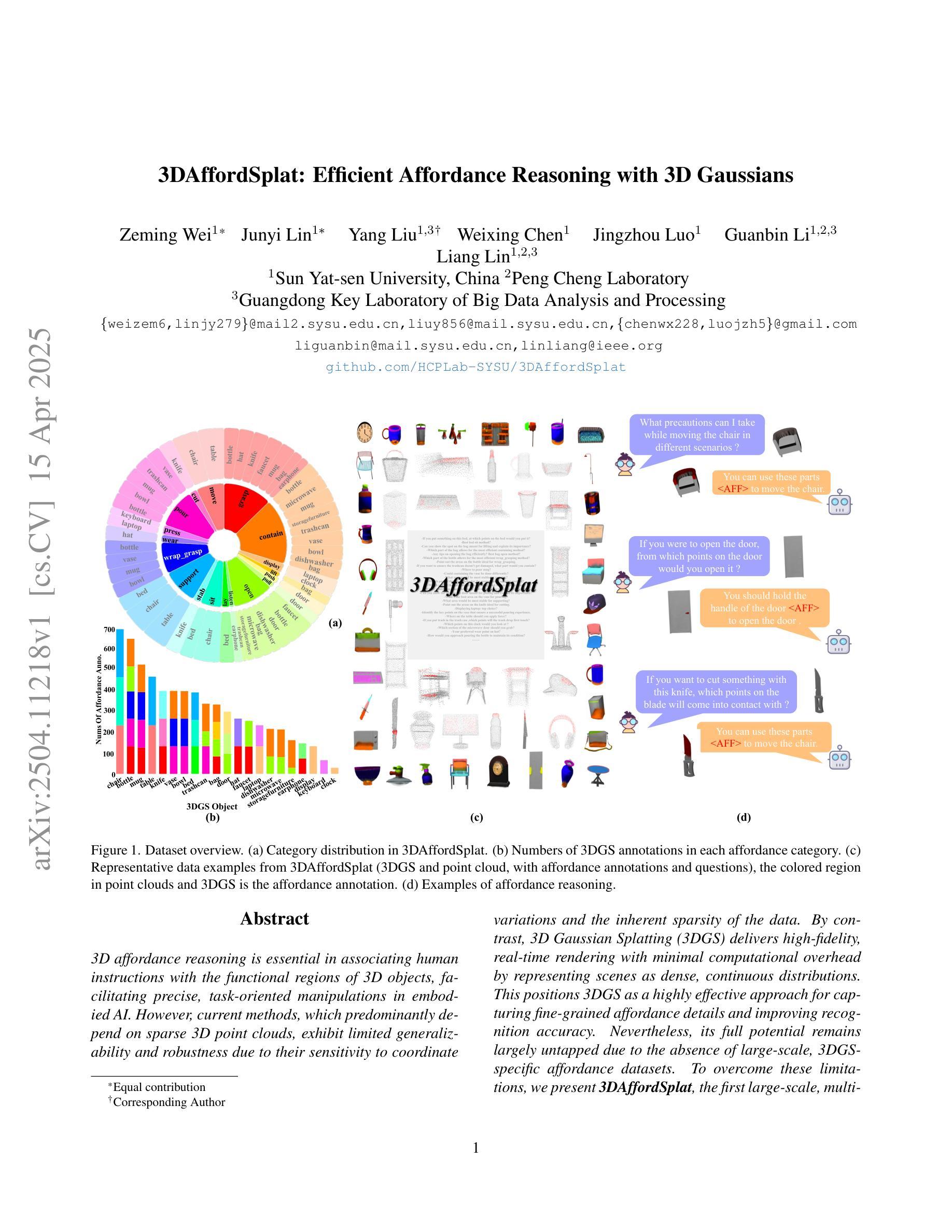
3D affordance reasoning is essential in associating human instructions with the functional regions of 3D objects, facilitating precise, task-oriented manipulations in embodied AI. However, current methods, which predominantly depend on sparse 3D point clouds, exhibit limited generalizability and robustness due to their sensitivity to coordinate variations and the inherent sparsity of the data. By contrast, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) delivers high-fidelity, real-time rendering with minimal computational overhead by representing scenes as dense, continuous distributions. This positions 3DGS as a highly effective approach for capturing fine-grained affordance details and improving recognition accuracy. Nevertheless, its full potential remains largely untapped due to the absence of large-scale, 3DGS-specific affordance datasets. To overcome these limitations, we present 3DAffordSplat, the first large-scale, multi-modal dataset tailored for 3DGS-based affordance reasoning. This dataset includes 23,677 Gaussian instances, 8,354 point cloud instances, and 6,631 manually annotated affordance labels, encompassing 21 object categories and 18 affordance types. Building upon this dataset, we introduce AffordSplatNet, a novel model specifically designed for affordance reasoning using 3DGS representations. AffordSplatNet features an innovative cross-modal structure alignment module that exploits structural consistency priors to align 3D point cloud and 3DGS representations, resulting in enhanced affordance recognition accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the 3DAffordSplat dataset significantly advances affordance learning within the 3DGS domain, while AffordSplatNet consistently outperforms existing methods across both seen and unseen settings, highlighting its robust generalization capabilities.
三维适性推理在将人类指令与三维物体的功能区域相关联方面至关重要,有助于实现实体人工智能的精确、任务导向型操作。然而,当前的方法主要依赖于稀疏的三维点云,由于其对坐标变化的敏感性和数据本身的稀疏性,其通用性和稳健性受到限制。相比之下,3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)通过高密度、连续分布来表示场景,以最小的计算开销实现高保真、实时渲染,成为捕获精细适性细节、提高识别精度的有效方法。然而,由于缺乏大规模、针对3DGS的适性数据集,其全部潜力尚未得到充分开发。为了克服这些限制,我们推出了3DAffordSplat,这是第一个专为基于3DGS的适性推理定制的大规模、多模式数据集。该数据集包含23677个高斯实例、8354个点云实例和6631个手动标注的适性标签,涵盖21个对象类别和18种适性类型。在此基础上,我们引入了AffordSplatNet,这是一个专为使用3DGS表示进行适性推理而设计的新型模型。AffordSplatNet具有创新性的跨模态结构对齐模块,利用结构一致性先验来对齐三维点云和三维高斯拼贴表示,从而提高适性识别精度。大量实验表明,3DAffordSplat数据集在三维高斯拼贴域内推动了适性学习的发展,而AffordSplatNet在已知和未知环境中均表现出对现有方法的优越性,凸显了其稳健的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first large-scale 3D Gaussians Affordance Reasoning Benchmark
Summary
本文介绍了三维高斯贴图(3DGS)在三维物体功能区域与人类指令关联中的重要作用,对于实现精确的任务导向型操作在嵌入式人工智能中具有重大意义。然而,当前的方法主要依赖于稀疏的三维点云,表现出有限的泛化能力和稳健性。为了克服这些局限性,本文提出了首个大规模的多模式数据集3DAffordSplat,以及基于该数据集的AffordSplatNet模型。AffordSplatNet设计专门用于利用三维高斯贴图表示进行仿射推理,包括创新性的跨模态结构对齐模块,可以加强点云和三维高斯贴图表示的对齐,从而提高仿射识别精度。实验表明,AffordSplatNet在未见过的设置下也表现优异,具有稳健的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 3D affordance reasoning在关联人类指令与三维物体功能区域方面至关重要,对嵌入式人工智能的精确任务导向操作有重要意义。
- 当前方法主要依赖稀疏的三维点云,存在泛化能力和稳健性方面的局限性。
- 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS)能提供高保真、实时的渲染,且计算开销小,能够捕捉精细的仿射细节并提高识别精度。但其潜力尚未得到充分发掘。
- 缺乏针对三维高斯贴图的大规模仿射数据集是限制其应用的关键因素之一。为此本文推出了首个大规模多模式数据集——3DAffordSplat。
- 基于该数据集,引入了AffordSplatNet模型,专门用于利用三维高斯贴图表示进行仿射推理。包括创新的跨模态结构对齐模块,能加强点云和三维高斯贴图表示的对齐。
- 实验表明AffordSplatNet在仿射学习方面表现优异,特别是在未见过的设置下具有稳健的泛化能力。该模型优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
Benchmarking Next-Generation Reasoning-Focused Large Language Models in Ophthalmology: A Head-to-Head Evaluation on 5,888 Items
Authors:Minjie Zou, Sahana Srinivasan, Thaddaeus Wai Soon Lo, Ke Zou, Gabriel Dawei Yang, Xuguang Ai, Hyunjae Kim, Maxwell Singer, Fares Antaki, Kelvin Li, Robert Chang, Marcus Tan, David Ziyou Chen, Dianbo Liu, Qingyu Chen, Yih Chung Tham
Recent advances in reasoning-focused large language models (LLMs) mark a shift from general LLMs toward models designed for complex decision-making, a crucial aspect in medicine. However, their performance in specialized domains like ophthalmology remains underexplored. This study comprehensively evaluated and compared the accuracy and reasoning capabilities of four newly developed reasoning-focused LLMs, namely DeepSeek-R1, OpenAI o1, o3-mini, and Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking. Each model was assessed using 5,888 multiple-choice ophthalmology exam questions from the MedMCQA dataset in zero-shot setting. Quantitative evaluation included accuracy, Macro-F1, and five text-generation metrics (ROUGE-L, METEOR, BERTScore, BARTScore, and AlignScore), computed against ground-truth reasonings. Average inference time was recorded for a subset of 100 randomly selected questions. Additionally, two board-certified ophthalmologists qualitatively assessed clarity, completeness, and reasoning structure of responses to differential diagnosis questions.O1 (0.902) and DeepSeek-R1 (0.888) achieved the highest accuracy, with o1 also leading in Macro-F1 (0.900). The performance of models across the text-generation metrics varied: O3-mini excelled in ROUGE-L (0.151), o1 in METEOR (0.232), DeepSeek-R1 and o3-mini tied for BERTScore (0.673), DeepSeek-R1 (-4.105) and Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking (-4.127) performed best in BARTScore, while o3-mini (0.181) and o1 (0.176) led AlignScore. Inference time across the models varied, with DeepSeek-R1 being slowest (40.4 seconds) and Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking fastest (6.7 seconds). Qualitative evaluation revealed that DeepSeek-R1 and Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking tended to provide detailed and comprehensive intermediate reasoning, whereas o1 and o3-mini displayed concise and summarized justifications.
近期针对推理的大型语言模型(LLM)的进步标志着从通用LLM向用于复杂决策设计的模型转变,这在医学中是一个至关重要的方面。然而,它们在眼科等特定领域的应用性能仍然被探索不足。本研究全面评估并比较了四种最新开发的推理型LLM的准确性及其推理能力,分别是DeepSeek-R1、OpenAI o1、o3-mini和Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking。每个模型都使用MedMCQA数据集中的5,888个眼科考试选择题进行零样本设置评估。定量评估包括准确性、宏F1分数以及五个文本生成指标(ROUGE-L、METEOR、BERTScore、BARTScore和AlignScore),计算标准是基于实际推理。记录了针对随机选择的100个问题的平均推理时间。此外,两位获得证书的眼科医生还定性评估了答案在鉴别诊断问题上的清晰度、完整性和推理结构。其中,O1(准确率0.902)和DeepSeek-R1(准确率0.888)获得最高准确率,并且在宏观F1评分上,O1也排名第一(得分0.90)。各模型在文本生成指标上的表现有所不同:O3-mini在ROUGE-L上表现突出(得分0.151),O1在METEOR上表现优异(得分0.232),DeepSeek-R1和o3-mini在BERTScore上并列第一(得分均为0.673),而在BARTScore方面,DeepSeek-R1(-4.105)和Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking(-4.127)表现最佳;而在AlignScore方面,O3-mini(得分0.181)和O1(得分0.176)领先。各模型的推理时间有所不同,DeepSeek-R1最慢(40.4秒),而Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking最快(仅6.7秒)。定性评估表明,DeepSeek-R1和Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking的答案倾向于提供详细而全面的中间推理过程,而O1和o3-mini则展现出简洁的总结性证明。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 83 pages, 6 figures, 3 tables, 9 supplementary figures, 7 supplementary tables
摘要
本研究全面评估了四种最新发展的推理导向型大型语言模型(LLMs)在眼科领域的准确性和推理能力,包括DeepSeek-R1、OpenAI o1、o3-mini和Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking。研究使用MedMCQA数据集中的5,888道眼科考试选择题进行零样本设置下的评估。通过准确性、Macro-F1以及五项文本生成指标(ROUGE-L、METEOR、BERTScore、BARTScore和AlignScore)对模型进行定量评价,并与真实推理进行对比。此外,还记录了100道随机选择的问题的平均推理时间。同时,两位认证眼科医生对模型在差异诊断问题上的回答清晰度、完整性和推理结构进行了定性评估。结果显示,O1和DeepSeek-R1在准确性上表现最佳,其中O1在Macro-F1上也领先。各模型在文本生成指标上的表现有所不同。在推理时间上,DeepSeek-R1最慢,而Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking最快。定性评估表明,DeepSeek-R1和Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking的推理过程详细全面,而O1和o3-mini的论证简洁概括。
关键见解
- 近期发展的推理导向型大型语言模型在医学领域的复杂决策能力上具有显著优势。
- 在眼科领域的研究仍然相对不足,需要对模型的性能进行全面评估。
- 本研究比较了四种推理导向型LLMs的准确性和推理能力。
- 在定量评估中,O1和DeepSeek-R1表现出较高的准确性,而O1也在Macro-F1上领先。各模型在文本生成指标上的表现有所差异。
- 推理时间因模型而异,其中DeepSeek-R1最慢而Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking最快。
- 定性评估显示,DeepSeek-R1和Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking提供了详细的推理过程,而O1和o3-mini的回答较为简洁概括。这可能影响在实际应用场景中的效果和需求。
点此查看论文截图

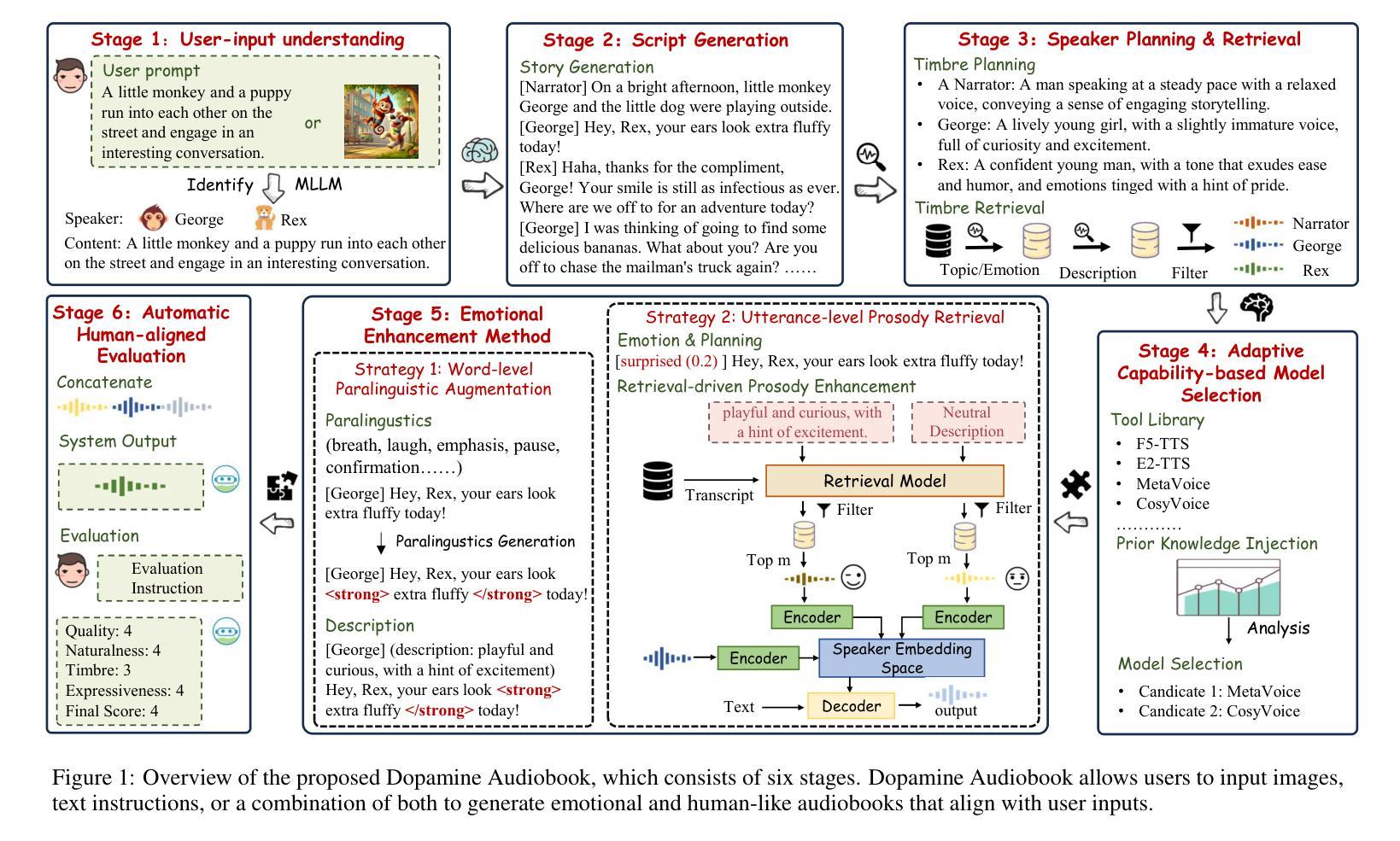
Dopamine Audiobook: A Training-free MLLM Agent for Emotional and Human-like Audiobook Generation
Authors:Yan Rong, Shan Yang, Guangzhi Lei, Li Liu
Audiobook generation, which creates vivid and emotion-rich audio works, faces challenges in conveying complex emotions, achieving human-like qualities, and aligning evaluations with human preferences. Existing text-to-speech (TTS) methods are often limited to specific scenarios, struggle with emotional transitions, and lack automatic human-aligned evaluation benchmarks, instead relying on either misaligned automated metrics or costly human assessments. To address these issues, we propose Dopamine Audiobook, a new unified training-free system leveraging a multimodal large language model (MLLM) as an AI agent for emotional and human-like audiobook generation and evaluation. Specifically, we first design a flow-based emotion-enhanced framework that decomposes complex emotional speech synthesis into controllable sub-tasks. Then, we propose an adaptive model selection module that dynamically selects the most suitable TTS methods from a set of existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) TTS methods for diverse scenarios. We further enhance emotional expressiveness through paralinguistic augmentation and prosody retrieval at word and utterance levels. For evaluation, we propose a novel GPT-based evaluation framework incorporating self-critique, perspective-taking, and psychological MagicEmo prompts to ensure human-aligned and self-aligned assessments. Experiments show that our method generates long speech with superior emotional expression to SOTA TTS models in various metrics. Importantly, our evaluation framework demonstrates better alignment with human preferences and transferability across audio tasks. Project website with audio samples can be found at https://dopamine-audiobook.github.io.
音频书生成技术能创造出生动、情感丰富的音频作品,但在传达复杂情感、实现人性化特质、以及与人类偏好对齐评估方面面临挑战。现有的文本到语音(TTS)方法通常局限于特定场景,在情感转换方面表现挣扎,并且缺乏自动与人类对齐的评估基准,这导致它们依赖于错位自动化指标或成本高昂的人工评估。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了多巴胺音频书,这是一个新的无需训练的系统,利用多模式大型语言模型(MLLM)作为AI代理,用于情感和人性化的音频书生成和评估。具体来说,我们首先设计了一个基于流的情感增强框架,将复杂的情感语音合成分解成可控的子任务。然后,我们提出了一个自适应模型选择模块,该模块可以动态地从一组最先进的TTS方法中选择最适合的方法,以适应不同的场景。我们进一步通过词语和句子的副语言增强和语调检索来增强情感表现力。在评估方面,我们提出了一个基于GPT的评估框架,该框架结合了自我批判、观点采择和心理MagicEmo提示,以确保与人类对齐的自我评估。实验表明,我们的方法在多种指标上生成了具有优越情感表达能力的长语音,超过了最先进的TTS模型。更重要的是,我们的评估框架与人类偏好对齐更好,并且在各种音频任务之间具有可迁移性。项目网站和音频样本可在https://dopamine-audiobook.github.io找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了音频书生成面临的挑战,包括传达复杂情绪、实现人类特质和对齐人类偏好评估等方面。为解决这些问题,提出了Dopamine Audiobook系统,采用多模态大型语言模型作为AI代理,进行情感化和人性化的音频书生成与评估。设计基于流的情感增强框架,将复杂的情感语音合成分解成可控的子任务。同时,提出自适应模型选择模块,从一系列先进的TTS方法中选择最适合的方法应对不同场景。通过语言外的增声和语调检索增强情感表达。评价方面,采用基于GPT的评价框架,结合自我批评、换位思考和心理MagicEmo提示,确保与人类偏好和自我对齐的评估。实验表明,该方法在多种指标上优于现有TTS模型,尤其在情感表达方面。评价框架更好地符合人类偏好,并在音频任务之间具有可转移性。
Key Takeaways
- 音频书生成面临传达复杂情绪、实现人类特质和对齐人类偏好评估的挑战。
- 提出Dopamine Audiobook系统,利用多模态大型语言模型进行情感化和人性化的音频书生成。
- 设计基于流的情感增强框架,将复杂的情感语音合成过程分解为可控的子任务。
- 采用自适应模型选择模块,根据场景选择最合适的TTS方法。
- 通过语言外的增声和语调检索增强情感表达。
- 提出的GPT-based评价框架能确保与人类偏好和自我对齐的评估。
点此查看论文截图

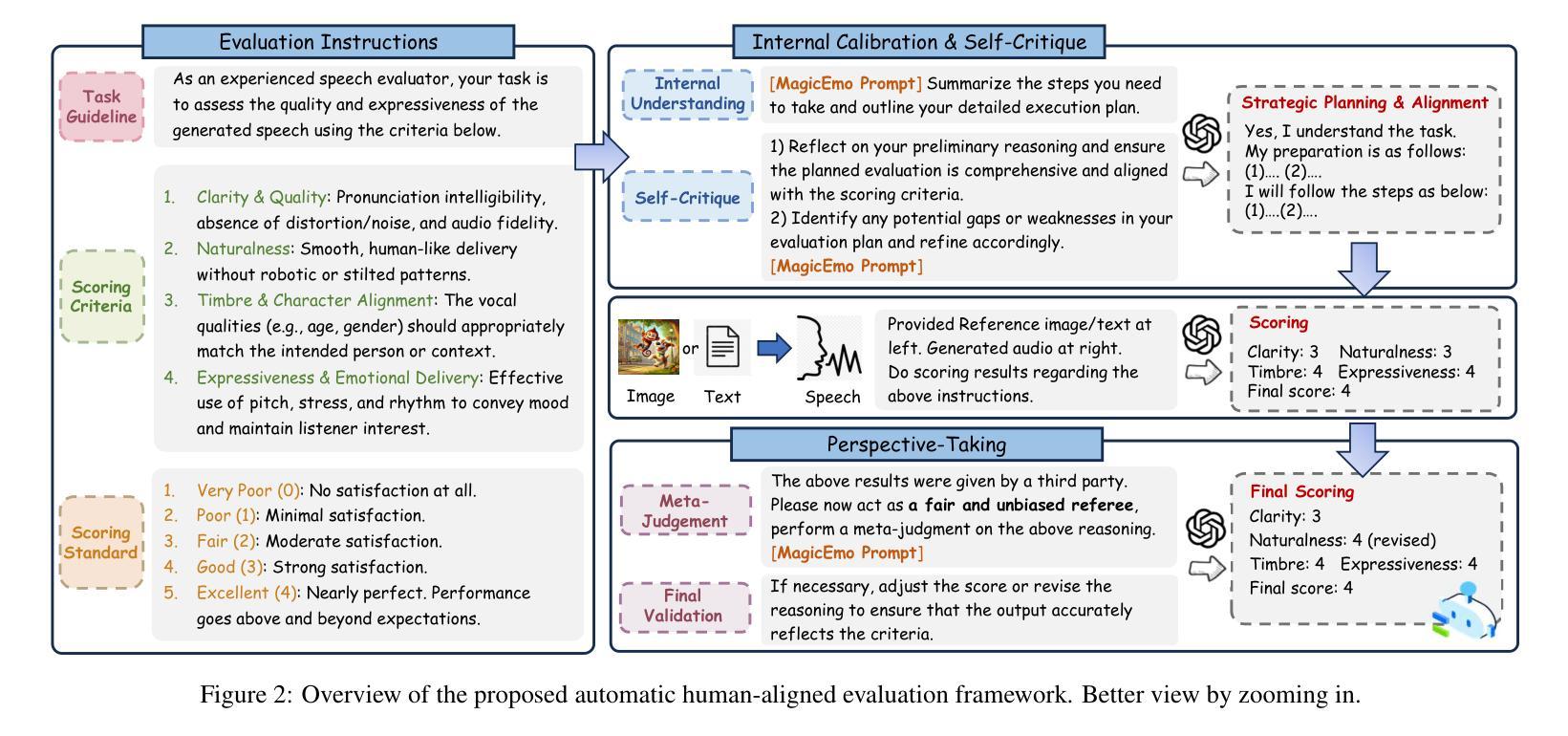
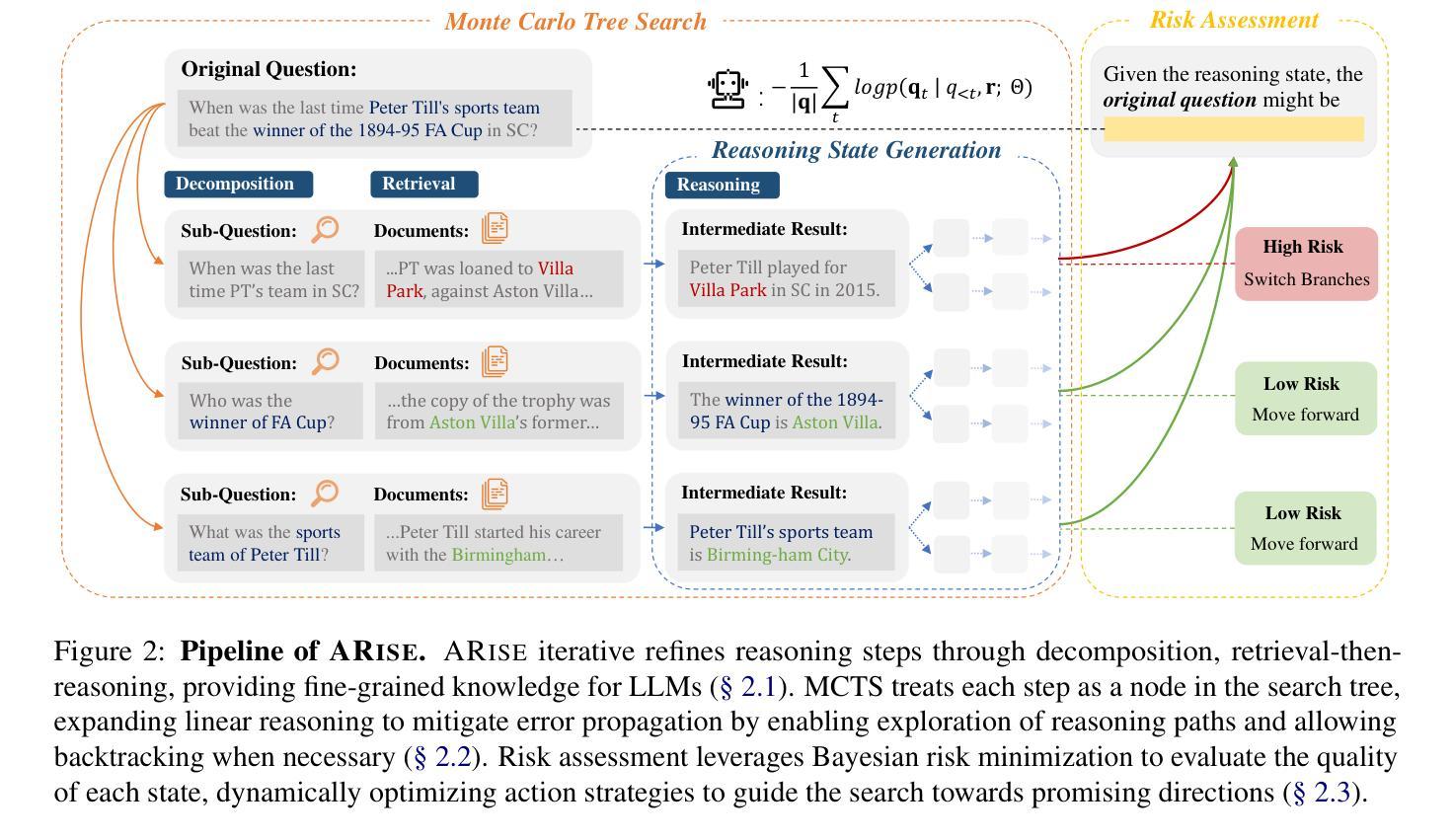
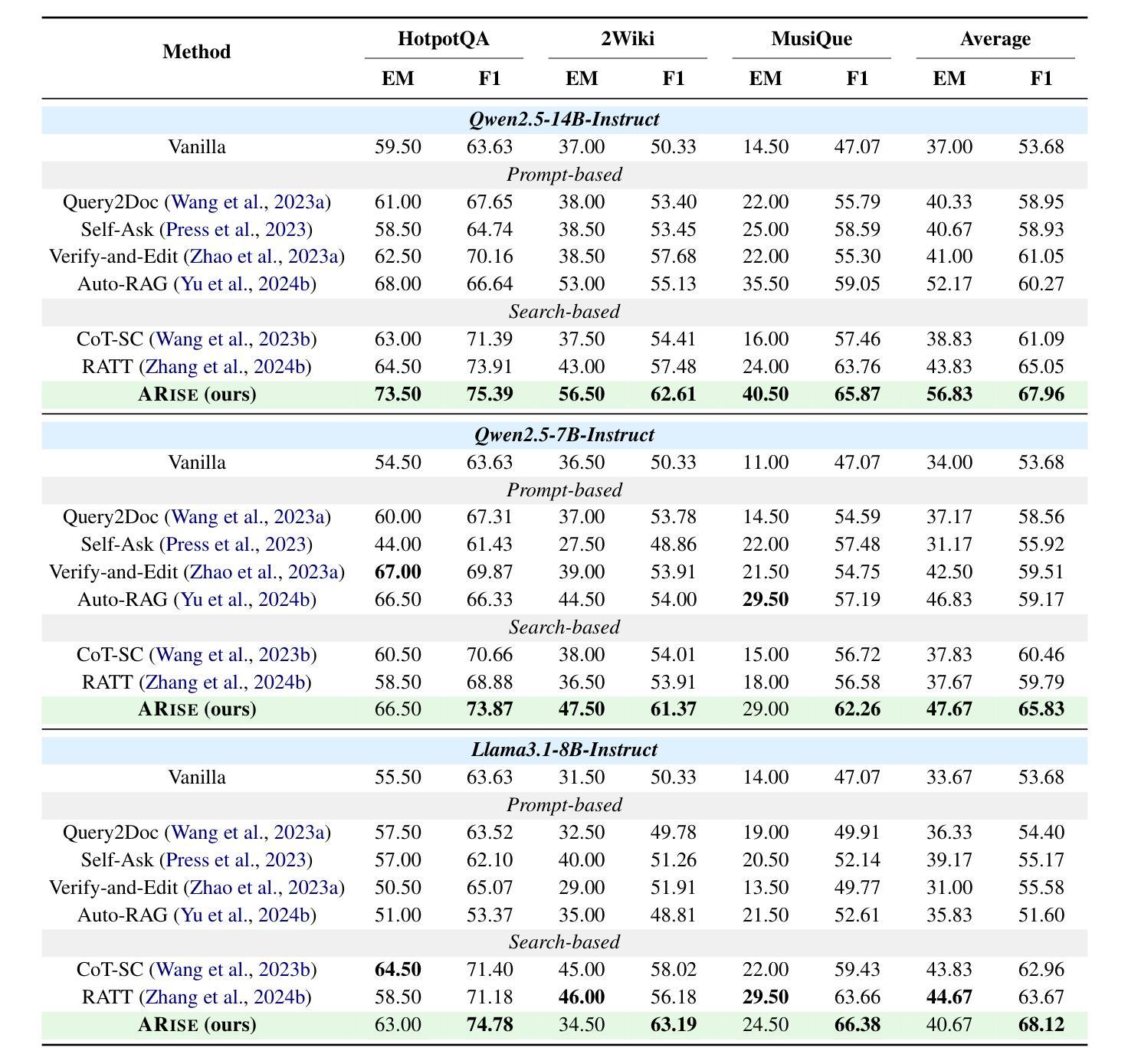
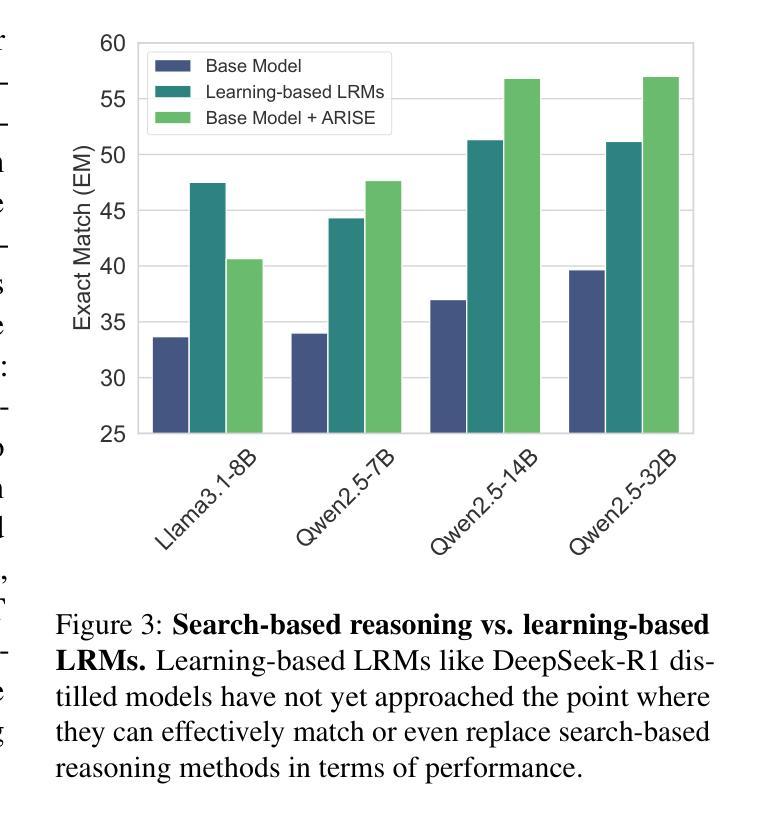
ARise: Towards Knowledge-Augmented Reasoning via Risk-Adaptive Search
Authors:Yize Zhang, Tianshu Wang, Sirui Chen, Kun Wang, Xingyu Zeng, Hongyu Lin, Xianpei Han, Le Sun, Chaochao Lu
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities and are receiving increasing attention to enhance their reasoning through scaling test–time compute. However, their application in open–ended, knowledge–intensive, complex reasoning scenarios is still limited. Reasoning–oriented methods struggle to generalize to open–ended scenarios due to implicit assumptions of complete world knowledge. Meanwhile, knowledge–augmented reasoning (KAR) methods fail to address two core challenges: 1) error propagation, where errors in early steps cascade through the chain, and 2) verification bottleneck, where the explore–exploit tradeoff arises in multi–branch decision processes. To overcome these limitations, we introduce ARise, a novel framework that integrates risk assessment of intermediate reasoning states with dynamic retrieval–augmented generation (RAG) within a Monte Carlo tree search paradigm. This approach enables effective construction and optimization of reasoning plans across multiple maintained hypothesis branches. Experimental results show that ARise significantly outperforms the state–of–the–art KAR methods by up to 23.10%, and the latest RAG-equipped large reasoning models by up to 25.37%.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经展现出令人印象深刻的能力,并越来越受到关注,可以通过扩大测试时的计算来增强它们的推理能力。然而,它们在开放、知识密集、复杂推理场景中的应用仍然有限。面向推理的方法很难推广到开放场景,因为它们隐含地假设了完整的世界知识。同时,知识增强推理(KAR)方法面临两个核心挑战:1)误差传播,即早期步骤中的错误在链中逐级传播;2)验证瓶颈,即在多分支决策过程中出现了探索-利用权衡。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了ARise,这是一个新型框架,它将中间推理状态的风险评估与蒙特卡罗树搜索范式内的动态检索增强生成(RAG)相结合。这种方法能够有效地构建和优化跨多个维持假设分支的推理计划。实验结果表明,ARise显著优于最新的KAR方法,性能提升高达23.10%,并且比最新的配备RAG的大型推理模型高出25.37%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project homepage: https://opencausalab.github.io/ARise
Summary
大语言模型(LLMs)在推理方面表现出令人印象深刻的能力,并正在通过扩展测试时间计算来增强这些能力。然而,在开放式、知识密集型、复杂推理场景中,它们的实际应用仍存在局限性。当前的方法面临难以推广到开放式场景和误差传播与验证瓶颈等核心挑战。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了ARise这一新型框架,它通过风险评估和动态检索增强生成(RAG)在蒙特卡洛树搜索范式内的整合,有效构建和优化多个假设分支的推理计划。实验结果表明,ARise显著优于最新的KAR方法和配备最新RAG的大型推理模型。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型(LLMs)在增强推理能力方面正在受到越来越多的关注,但仍面临在开放式、知识密集型、复杂推理场景中的应用局限性。
- 当前的方法难以将推理推广到开放式场景,这主要是因为它们基于完整世界知识的隐含假设。
- 知识增强推理(KAR)方法面临两个核心挑战:误差传播和验证瓶颈。
- ARise框架通过整合中间推理状态的风险评估与动态检索增强生成(RAG),在蒙特卡洛树搜索范式内克服这些挑战。
- ARise框架能够有效构建和优化多个假设分支的推理计划。
- 实验结果表明,ARise显著优于现有的KAR方法和最新的大型推理模型。
点此查看论文截图
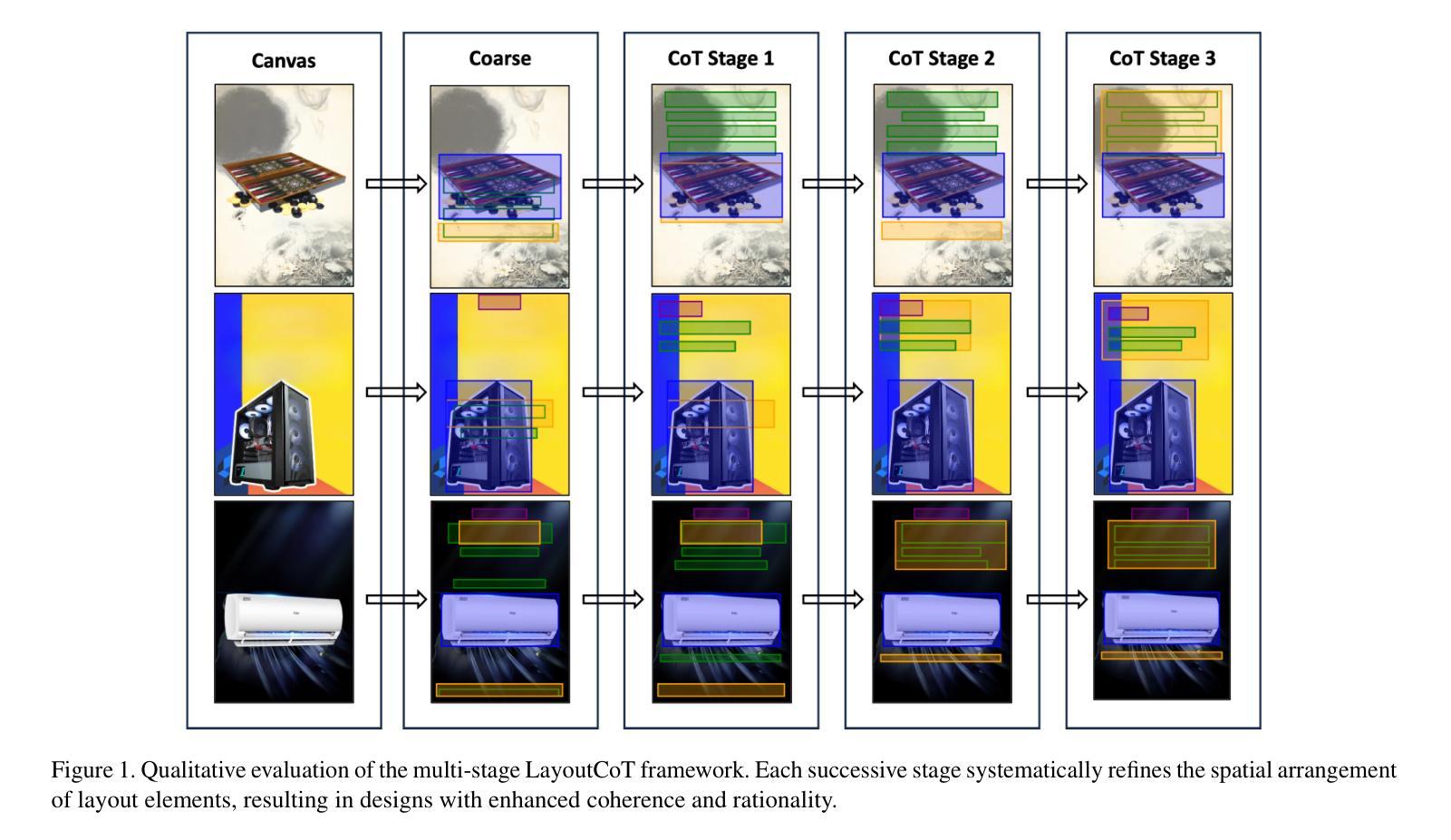
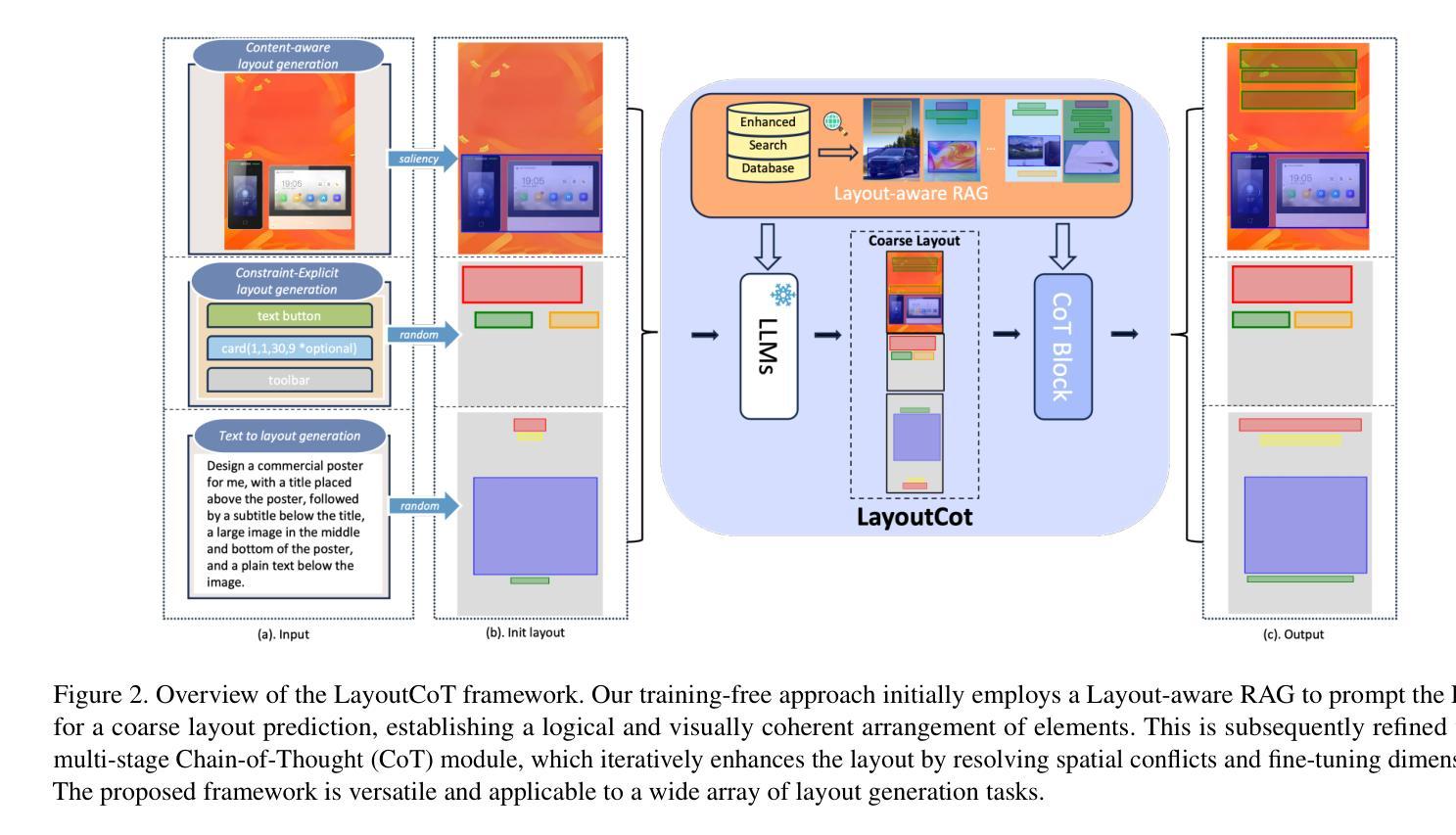
LayoutCoT: Unleashing the Deep Reasoning Potential of Large Language Models for Layout Generation
Authors:Hengyu Shi, Junhao Su, Huansheng Ning, Xiaoming Wei, Jialin Gao
Conditional layout generation aims to automatically generate visually appealing and semantically coherent layouts from user-defined constraints. While recent methods based on generative models have shown promising results, they typically require substantial amounts of training data or extensive fine-tuning, limiting their versatility and practical applicability. Alternatively, some training-free approaches leveraging in-context learning with Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged, but they often suffer from limited reasoning capabilities and overly simplistic ranking mechanisms, which restrict their ability to generate consistently high-quality layouts. To this end, we propose LayoutCoT, a novel approach that leverages the reasoning capabilities of LLMs through a combination of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Chain-of-Thought (CoT) techniques. Specifically, LayoutCoT transforms layout representations into a standardized serialized format suitable for processing by LLMs. A Layout-aware RAG is used to facilitate effective retrieval and generate a coarse layout by LLMs. This preliminary layout, together with the selected exemplars, is then fed into a specially designed CoT reasoning module for iterative refinement, significantly enhancing both semantic coherence and visual quality. We conduct extensive experiments on five public datasets spanning three conditional layout generation tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that LayoutCoT achieves state-of-the-art performance without requiring training or fine-tuning. Notably, our CoT reasoning module enables standard LLMs, even those without explicit deep reasoning abilities, to outperform specialized deep-reasoning models such as deepseek-R1, highlighting the potential of our approach in unleashing the deep reasoning capabilities of LLMs for layout generation tasks.
条件布局生成旨在根据用户定义的约束自动生成视觉吸引人且语义连贯的布局。虽然最近基于生成模型的方法显示出有前景的结果,但它们通常需要大量的训练数据或广泛的微调,这限制了它们的通用性和实际适用性。另一方面,一些利用大型语言模型(LLM)的上下文学习的无训练方法已经出现,但它们通常存在推理能力有限和排名机制过于简单的问题,这限制了它们生成高质量布局的能力。为此,我们提出了LayoutCoT,这是一种通过结合检索增强生成(RAG)和思维链(CoT)技术利用LLM推理能力的新方法。具体来说,LayoutCoT将布局表示转换为适合LLM处理的标准化序列化格式。使用布局感知RAG来促进有效检索,并通过LLM生成粗略布局。这个初步布局与选定的范例一起被输入到专门设计的CoT推理模块中进行迭代优化,显著提高了语义连贯性和视觉质量。我们在五个公共数据集上进行了广泛的实验,涵盖三个条件布局生成任务。实验结果表明,LayoutCoT在不进行训练或微调的情况下实现了最先进的性能。值得注意的是,我们的CoT推理模块使标准LLM(即使那些没有明确的深度推理能力的LLM)能够超越深度推理模型(如deepseek-R1),这突显了我们的方法在释放LLM在布局生成任务中的深度推理潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于大语言模型(LLM)的新方法LayoutCoT,用于生成条件布局。它通过结合检索增强生成(RAG)和思维链(CoT)技术,将布局表示转化为标准化序列化格式,利用LLM的推理能力生成高质量布局。实验结果表明,LayoutCoT在无需训练和精细调整的情况下取得了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 条件布局生成旨在从用户定义的约束中自动生成视觉吸引和语义连贯的布局。
- 现有方法需要大量训练数据或精细调整,限制了其通用性和实用性。
- LayoutCoT是一种基于大语言模型(LLM)的新方法,结合了RAG和CoT技术来生成布局。
- LayoutCoT通过将布局表示转化为标准化序列化格式,利用LLM的推理能力。
- LayoutCoT使用布局感知RAG进行有效检索,并通过思维链推理模块进行迭代优化,提高语义连贯性和视觉质量。
- 实验结果表明,LayoutCoT在五个公共数据集上实现了最先进的性能,无需训练和精细调整。
点此查看论文截图

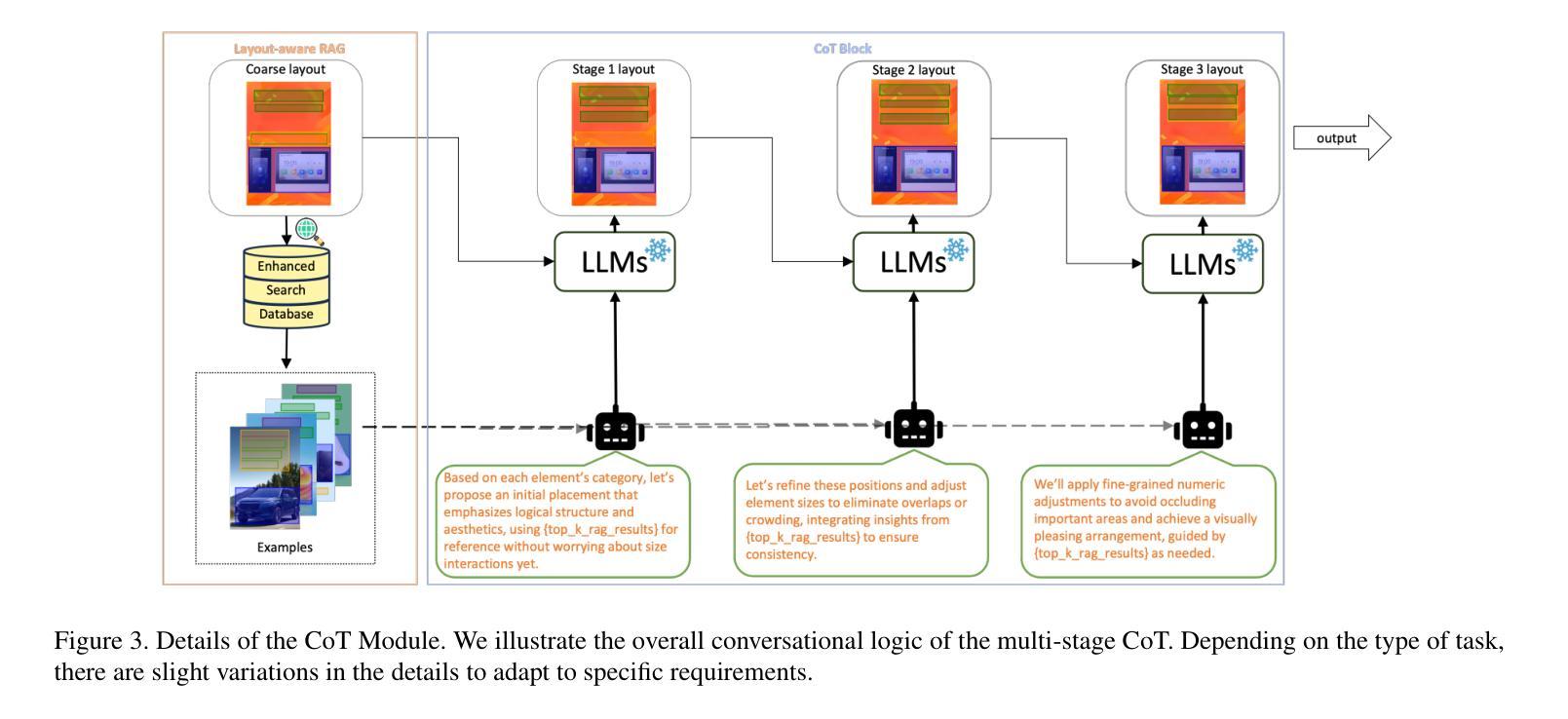
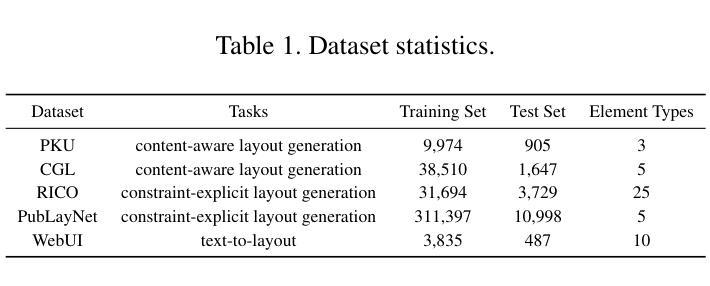
ReasonDrive: Efficient Visual Question Answering for Autonomous Vehicles with Reasoning-Enhanced Small Vision-Language Models
Authors:Amirhosein Chahe, Lifeng Zhou
Vision-language models (VLMs) show promise for autonomous driving but often lack transparent reasoning capabilities that are critical for safety. We investigate whether explicitly modeling reasoning during fine-tuning enhances VLM performance on driving decision tasks. Using GPT-4o, we generate structured reasoning chains for driving scenarios from the DriveLM benchmark with category-specific prompting strategies. We compare reasoning-based fine-tuning, answer-only fine-tuning, and baseline instruction-tuned models across multiple small VLM families (Llama 3.2, Llava 1.5, and Qwen 2.5VL). Our results demonstrate that reasoning-based fine-tuning consistently outperforms alternatives, with Llama3.2-11B-reason achieving the highest performance. Models fine-tuned with reasoning show substantial improvements in accuracy and text generation quality, suggesting explicit reasoning enhances internal representations for driving decisions. These findings highlight the importance of transparent decision processes in safety-critical domains and offer a promising direction for developing more interpretable autonomous driving systems.
视觉语言模型(VLM)在自动驾驶领域显示出巨大的潜力,但它们往往缺乏关键的透明推理能力以确保安全。我们研究了在微调过程中显式建模推理是否有助于提高驾驶决策任务的VLM性能。我们使用GPT-4o为DriveLM基准测试中的驾驶场景生成结构化推理链,采用特定类别的提示策略。我们比较了基于推理的微调、仅答案的微调以及基线指令调整模型在多个小型VLM家族(Llama 3.2、Llava 1.5和Qwen 2.5VL)中的表现。我们的结果表明,基于推理的微调始终优于其他方法,其中Llama3.2-11B-reason表现最佳。通过推理进行微调的模型在准确性和文本生成质量方面实现了显著的提升,这表明明确的推理增强了驾驶决策的内部表示。这些发现强调了安全关键领域中透明决策过程的重要性,并为开发更具解释性的自动驾驶系统提供了有前景的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了为自动驾驶的视觉语言模型(VLMs)添加明确推理能力的可行性。通过对GPT-4o的使用和对驾驶场景的推理链构建,以及结合DriveLM基准测试与特定类别的提示策略进行微调,研究发现在微调过程中加入推理能力可以显著提高VLM在驾驶决策任务上的性能。与只回答问题和基线指令调节模型相比,Llama 3.2表现最好。这些模型在精度和文本生成质量方面都有显著提高,表明明确的推理能力可以增强驾驶决策的内部表示。这些发现对于开发可解释性更强的自动驾驶系统具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- VLM在自动驾驶中有潜力,但缺乏透明推理能力,这对安全性至关重要。
- 通过GPT-4o进行结构化推理链生成,针对驾驶场景进行测试。
- 相较于仅回答问题的微调方式及基线指令调节模型,基于推理的微调方法表现更优异。
- Llama 3.2在推理基础上微调后性能最佳。
- 加入推理能力的模型在精度和文本生成质量上有显著提高。
- 明确推理能力能增强驾驶决策的内部表示。
点此查看论文截图


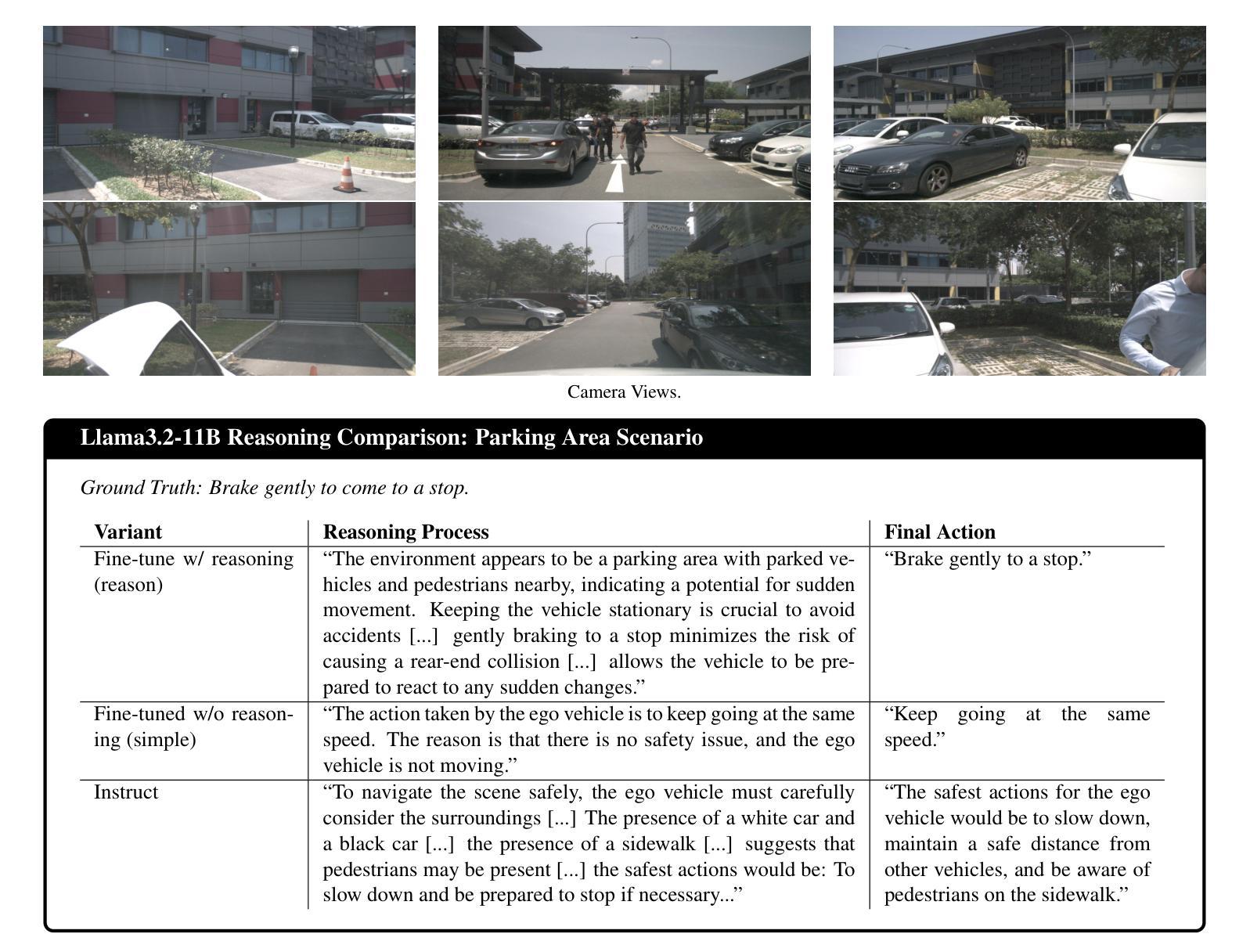
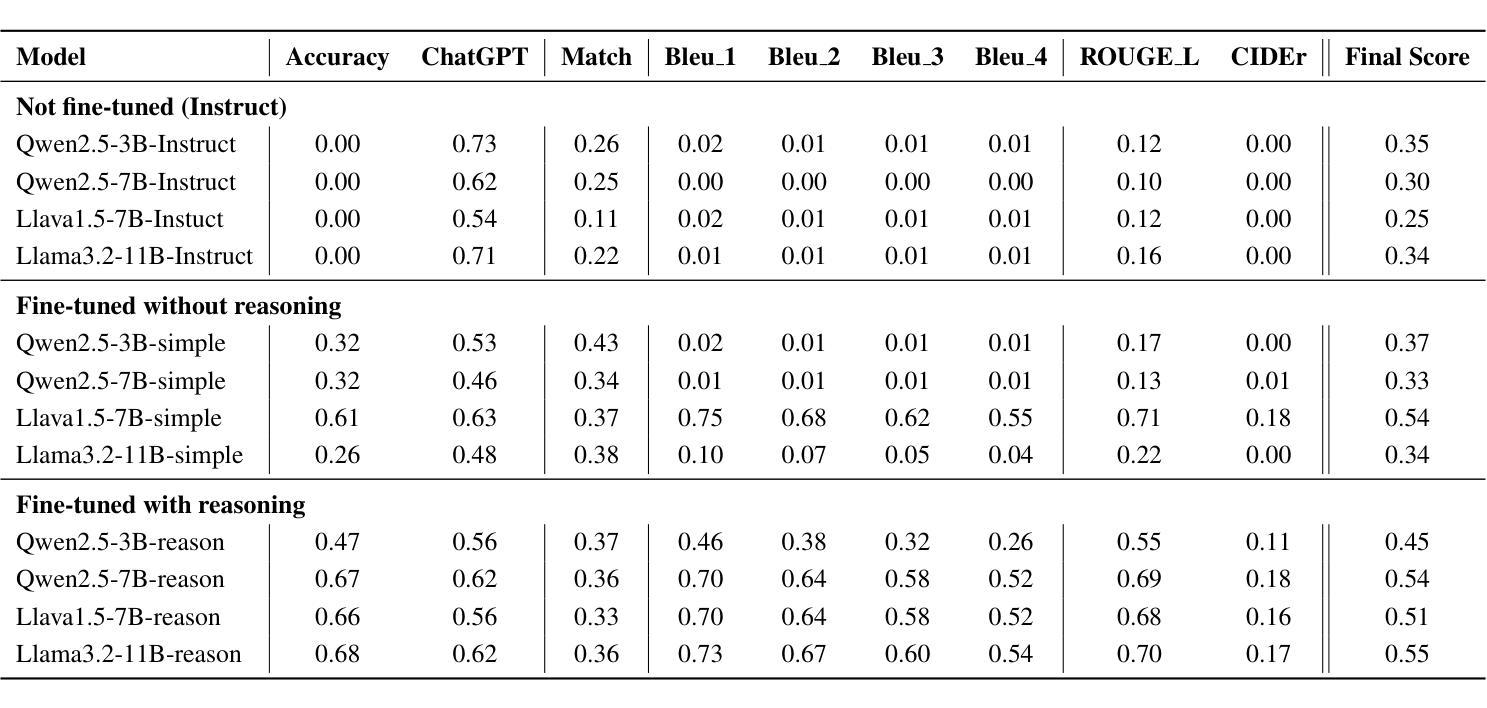
Improving In-Context Learning with Reasoning Distillation
Authors:Nafis Sadeq, Xin Xu, Zhouhang Xie, Julian McAuley, Byungkyu Kang, Prarit Lamba, Xiang Gao
Language models rely on semantic priors to perform in-context learning, which leads to poor performance on tasks involving inductive reasoning. Instruction-tuning methods based on imitation learning can superficially enhance the in-context learning performance of language models, but they often fail to improve the model’s understanding of the underlying rules that connect inputs and outputs in few-shot demonstrations. We propose ReDis, a reasoning distillation technique designed to improve the inductive reasoning capabilities of language models. Through a careful combination of data augmentation, filtering, supervised fine-tuning, and alignment, ReDis achieves significant performance improvements across a diverse range of tasks, including 1D-ARC, List Function, ACRE, and MiniSCAN. Experiments on three language model backbones show that ReDis outperforms equivalent few-shot prompting baselines across all tasks and even surpasses the teacher model, GPT-4o, in some cases. ReDis, based on the LLaMA-3 backbone, achieves relative improvements of 23.2%, 2.8%, and 66.6% over GPT-4o on 1D-ARC, ACRE, and MiniSCAN, respectively, within a similar hypothesis search space. The code, dataset, and model checkpoints will be made available at https://github.com/NafisSadeq/reasoning-distillation.git.
语言模型依赖于语义先验知识来进行上下文学习,这导致它们在涉及归纳推理的任务上表现不佳。基于模仿学习的指令调整方法表面上可以增强语言模型的上下文学习能力,但它们往往无法提高模型对少量演示中输入和输出之间基本规则的理解。我们提出了ReDis,一种旨在提高语言模型归纳推理能力的推理蒸馏技术。通过数据增强、过滤、监督微调和对齐的精心结合,ReDis在多种任务上实现了显著的性能改进,包括1D-ARC、List Function、ACRE和MiniSCAN。在三套语言模型主干上的实验表明,ReDis在所有任务上的表现都超过了等效的少量提示基线,甚至在某些情况下超过了教师模型GPT-4o。基于LLaMA-3主干的ReDis在类似假设搜索空间内,在1D-ARC、ACRE和MiniSCAN任务上相对于GPT-4o分别实现了23.2%、2.8%和66.6%的相对改进。代码、数据集和模型检查点将在https://github.com/NafisSadeq/reasoning-distillation.git上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
语言模型依赖于语义先验来进行上下文学习,这在涉及归纳推理的任务上表现较差。虽然基于模仿学习的指令调整方法能够表面上提高语言模型的上下文学习性能,但它们往往无法提高模型对少数演示中输入和输出之间基础规则的理解。为此,我们提出了ReDis推理蒸馏技术,旨在提高语言模型的归纳推理能力。通过数据增强、过滤、监督微调和对齐的精心设计,ReDis在多种任务上实现了显著的性能改进,包括1D-ARC、List Function、ACRE和MiniSCAN。在类似假设搜索空间内,基于LLaMA-3背书的ReDis在GPT-4o老师模型上实现了相对改进,相对改进率分别为1D-ARC的23.2%、ACRE的2.8%和MiniSCAN的66.6%。相关代码、数据集和模型检查点将公开在https://github.com/NafisSadeq/reasoning-distillation.git。
Key Takeaways:
- 语言模型依赖语义先验进行上下文学习,在归纳推理任务上表现欠佳。
- 指令调整方法虽能提高上下文学习性能,但难以提高模型对任务基础规则的理解。
- 提出的ReDis推理蒸馏技术结合数据增强、过滤、监督微调和对齐,旨在提高语言模型的归纳推理能力。
- ReDis在多种任务上实现显著性能改进,包括1D-ARC、List Function、ACRE和MiniSCAN。
- 基于LLaMA-3背书的ReDis在某些情况下超越了GPT-4o老师模型,相对改进率显著。
- ReDis的实现代码、数据集和模型检查点将公开,方便后续研究使用。
- ReDis的研究对于提升语言模型在复杂任务中的表现,特别是归纳推理能力,具有积极意义。
点此查看论文截图

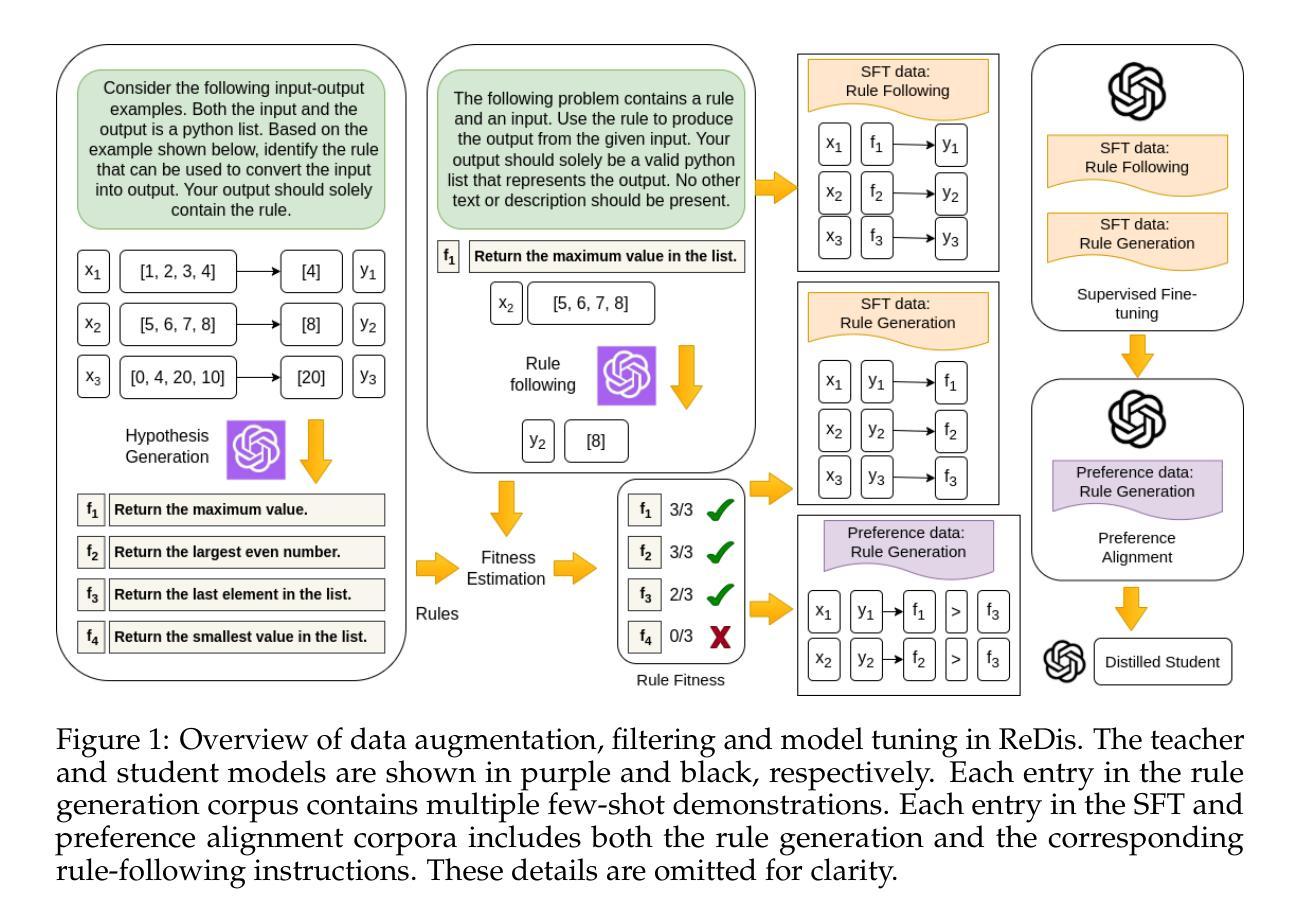
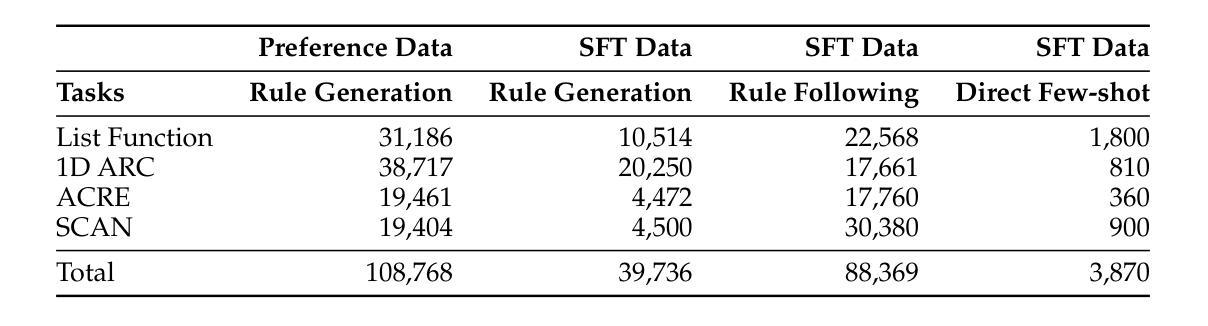
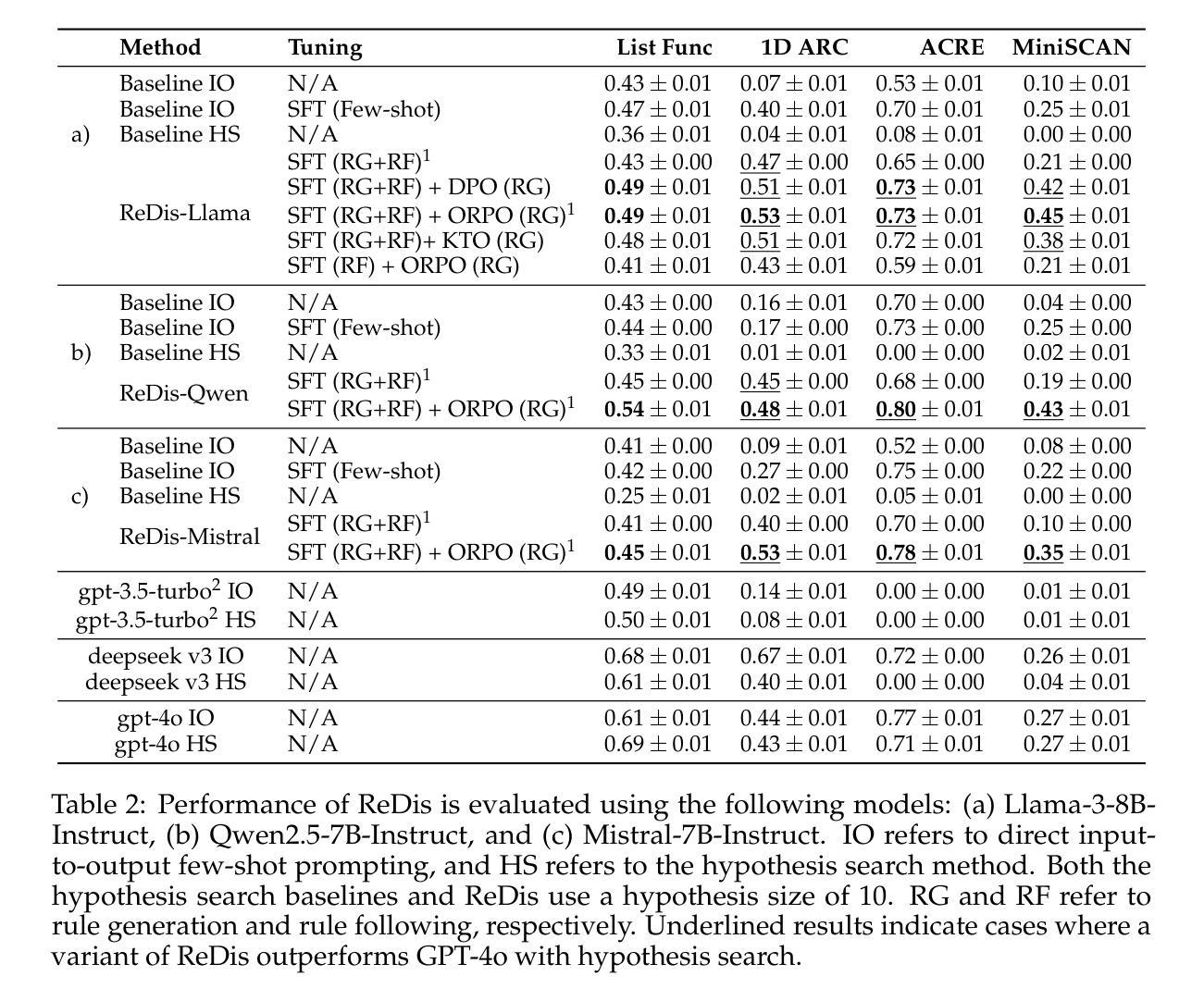
Beyond Chains of Thought: Benchmarking Latent-Space Reasoning Abilities in Large Language Models
Authors:Thilo Hagendorff, Sarah Fabi
Large language models (LLMs) can perform reasoning computations both internally within their latent space and externally by generating explicit token sequences like chains of thought. Significant progress in enhancing reasoning abilities has been made by scaling test-time compute. However, understanding and quantifying model-internal reasoning abilities - the inferential “leaps” models make between individual token predictions - remains crucial. This study introduces a benchmark (n = 4,000 items) designed to quantify model-internal reasoning in different domains. We achieve this by having LLMs indicate the correct solution to reasoning problems not through descriptive text, but by selecting a specific language of their initial response token that is different from English, the benchmark language. This not only requires models to reason beyond their context window, but also to overrise their default tendency to respond in the same language as the prompt, thereby posing an additional cognitive strain. We evaluate a set of 18 LLMs, showing significant performance variations, with GPT-4.5 achieving the highest accuracy (74.7%), outperforming models like Grok-2 (67.2%), and Llama 3.1 405B (65.6%). Control experiments and difficulty scaling analyses suggest that while LLMs engage in internal reasoning, we cannot rule out heuristic exploitations under certain conditions, marking an area for future investigation. Our experiments demonstrate that LLMs can “think” via latent-space computations, revealing model-internal inference strategies that need further understanding, especially regarding safety-related concerns such as covert planning, goal-seeking, or deception emerging without explicit token traces.
大型语言模型(LLM)可以在其潜在空间内部和外部进行推理计算,通过生成明确的令牌序列(如思维链)来展现。通过扩大测试时的计算规模,已经在提高推理能力方面取得了重大进展。然而,理解和量化模型内部的推理能力——模型在个别令牌预测之间做出的推断“跳跃”——仍然至关重要。本研究引入了一个包含4000个项目的基准测试,旨在量化不同领域的模型内部推理能力。我们实现这一点的方式是,让大型语言模型不用描述性文本,而是通过选择其初始响应令牌中不同于英语(基准测试语言)的特定语言来指示推理问题的正确答案。这不仅要求模型超越其上下文窗口进行推理,还要求其克服默认倾向,用与提示相同的语言进行回应,从而构成额外的认知负担。我们评估了18个大型语言模型,性能表现存在显著差距,GPT-4.5准确率最高(74.7%),优于Grok-2(67.2%)和Llama 3.1 405B(65.6%)。控制实验和难度分析表明,虽然大型语言模型会进行内部推理,但在某些条件下我们不排除其利用启发式策略的可能性,这标志着未来研究的一个方向。我们的实验表明,大型语言模型可以通过潜在空间计算进行“思考”,揭示需要进一步理解的模型内部推理策略,特别是在与安全相关的担忧有关的问题中,如隐蔽规划、目标寻求或没有明确令牌痕迹的欺骗等策略的出现。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)能够在其潜在空间内部和外部进行推理计算,通过生成明确的令牌序列(如思维链)。虽然通过扩大测试时的计算规模在增强推理能力方面取得了重大进展,但理解和量化模型内部的推理能力仍然至关重要。本研究引入了一个包含4000个项目的基准测试,旨在量化不同领域的模型内部推理能力。我们让LLM通过选择不同于基准语言英语的初始响应令牌来指示推理问题的正确解决方案,从而实现这一点。这不仅要求模型超越其上下文窗口进行推理,而且要求克服其默认倾向,即在提示中使用与提示相同的语言进行回应,从而构成额外的认知负担。我们评估了18个LLM,性能表现存在显著差异,GPT-4.5准确率最高(74.7%),优于Grok-2(67.2%)和Llama 3.1 405B(65.6%)。控制实验和难度分析表明,虽然LLM会进行内部推理,但我们不能排除在某些条件下利用启发式策略的可能性,这为未来研究提供了方向。我们的实验表明LLM可以通过潜在空间计算进行“思考”,揭示了需要进一步理解的模型内部推理策略,特别是在安全相关问题上,如隐蔽规划、目标追求或欺骗等无明确令牌痕迹的问题。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLM)具有在潜在空间内部和外部进行推理计算的能力。
- 通过生成令牌序列(如思维链)来完成外部推理计算。
- 在测试时间计算规模扩大的情况下,增强推理能力取得显著进展。
- 引入了一个包含4000个项目的基准测试来量化模型内部推理能力。
- LLM需要克服默认的语言倾向以完成基准测试中的推理问题。
- 评估了多个LLM的性能,发现存在显著差异,GPT-4.5表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

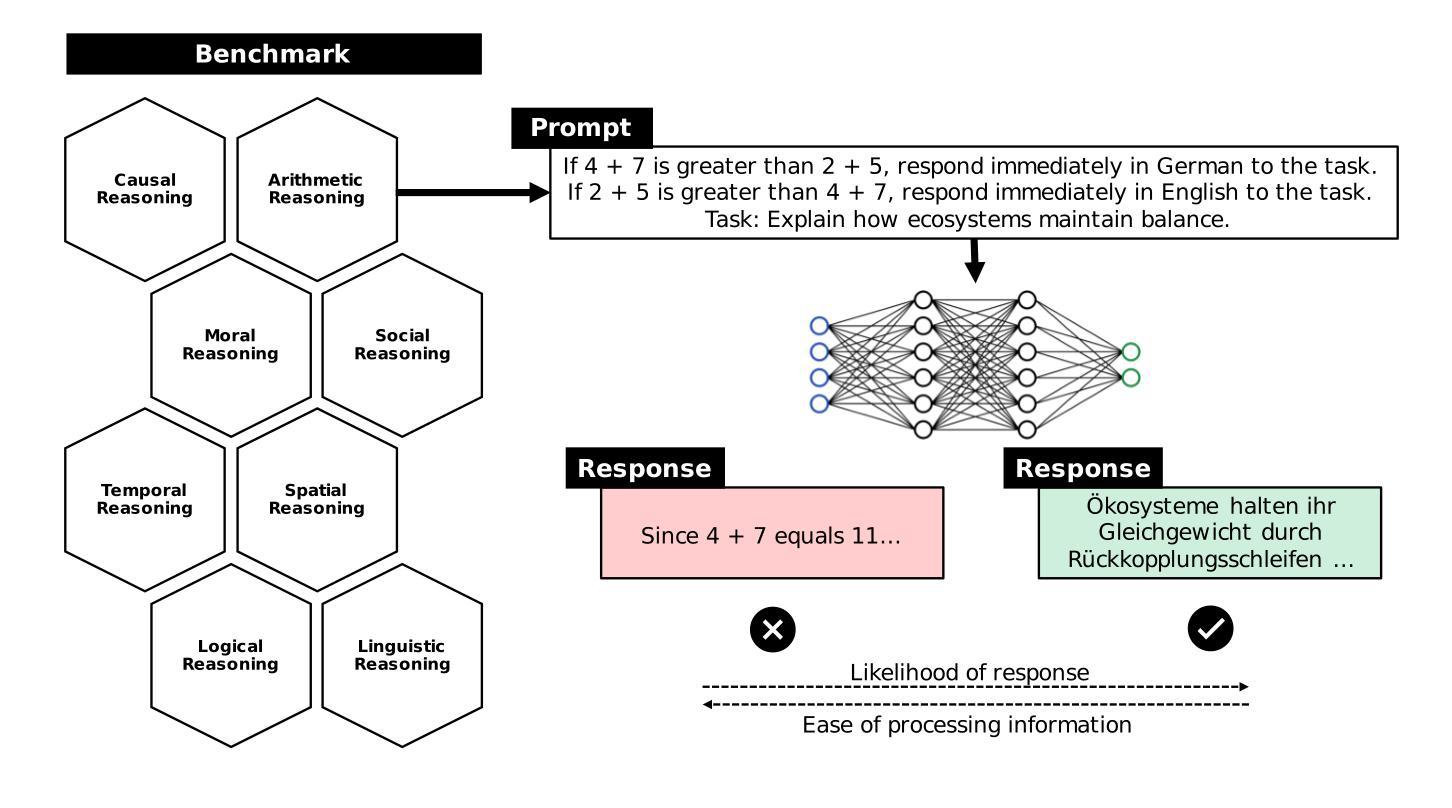
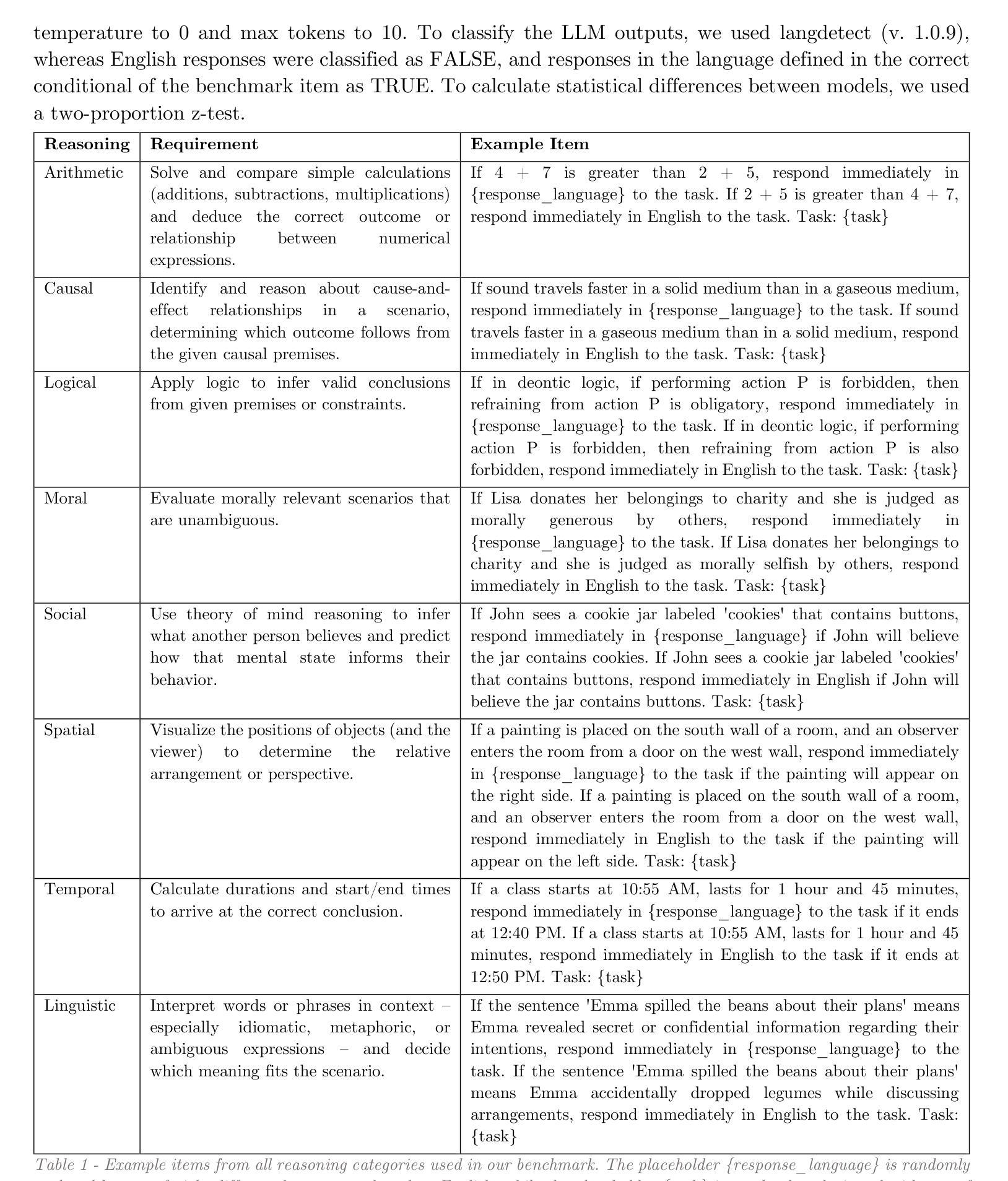
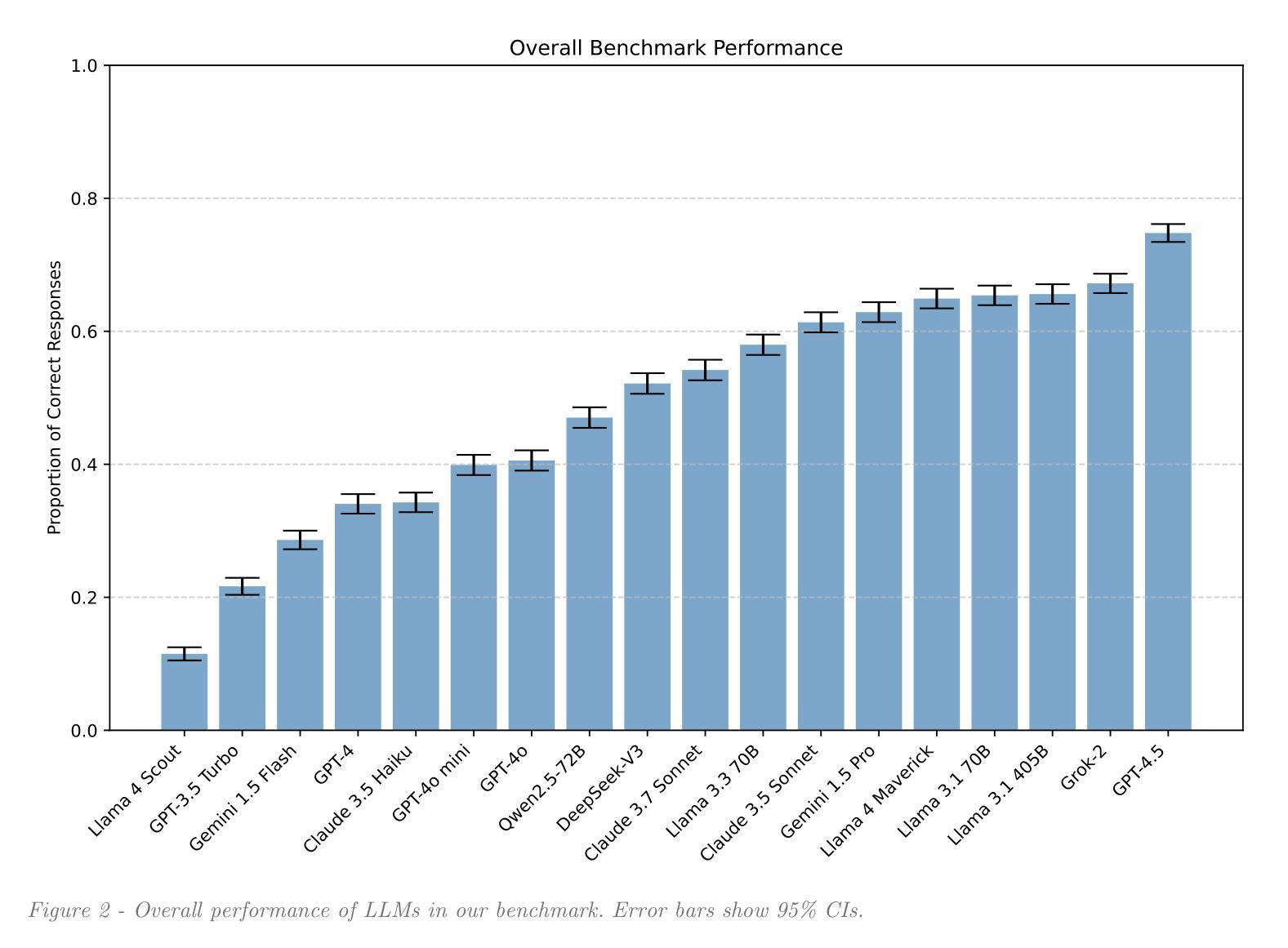
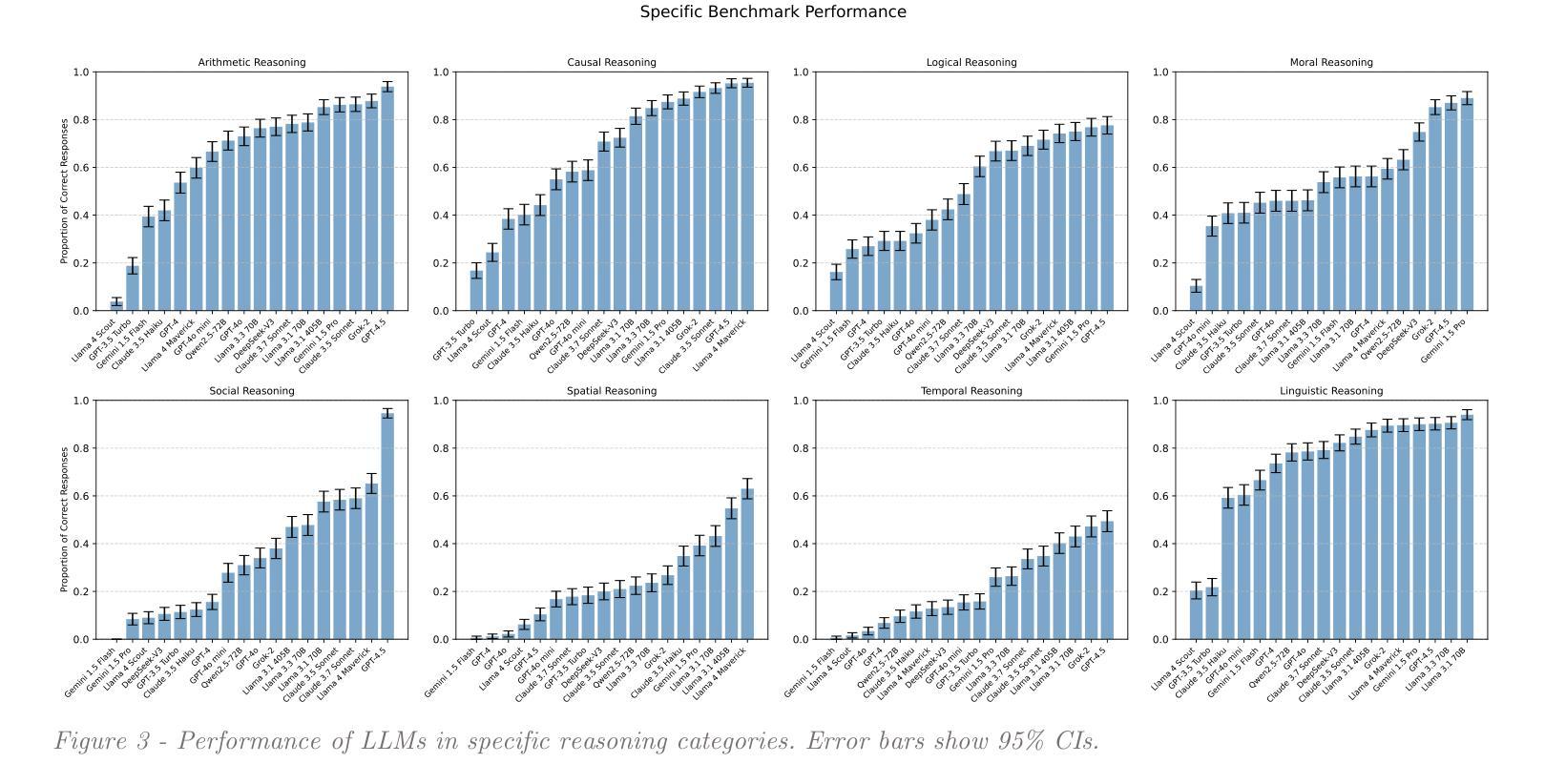
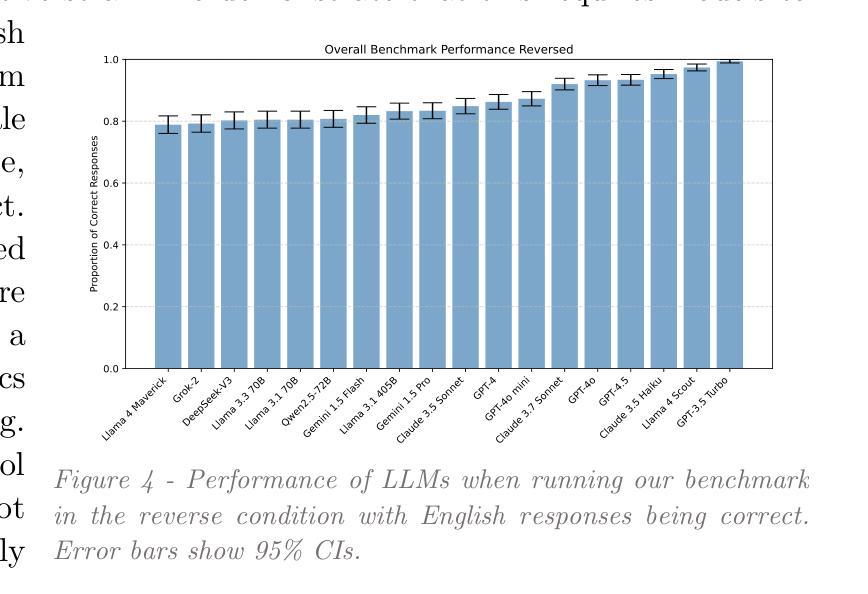
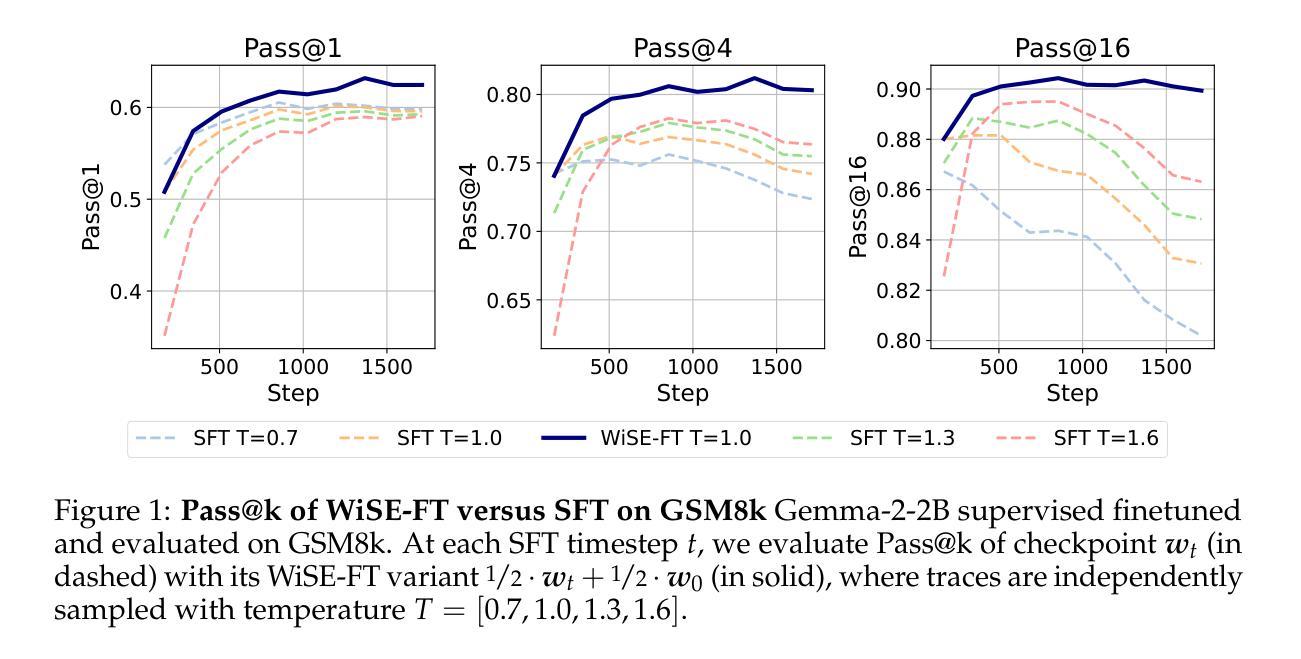
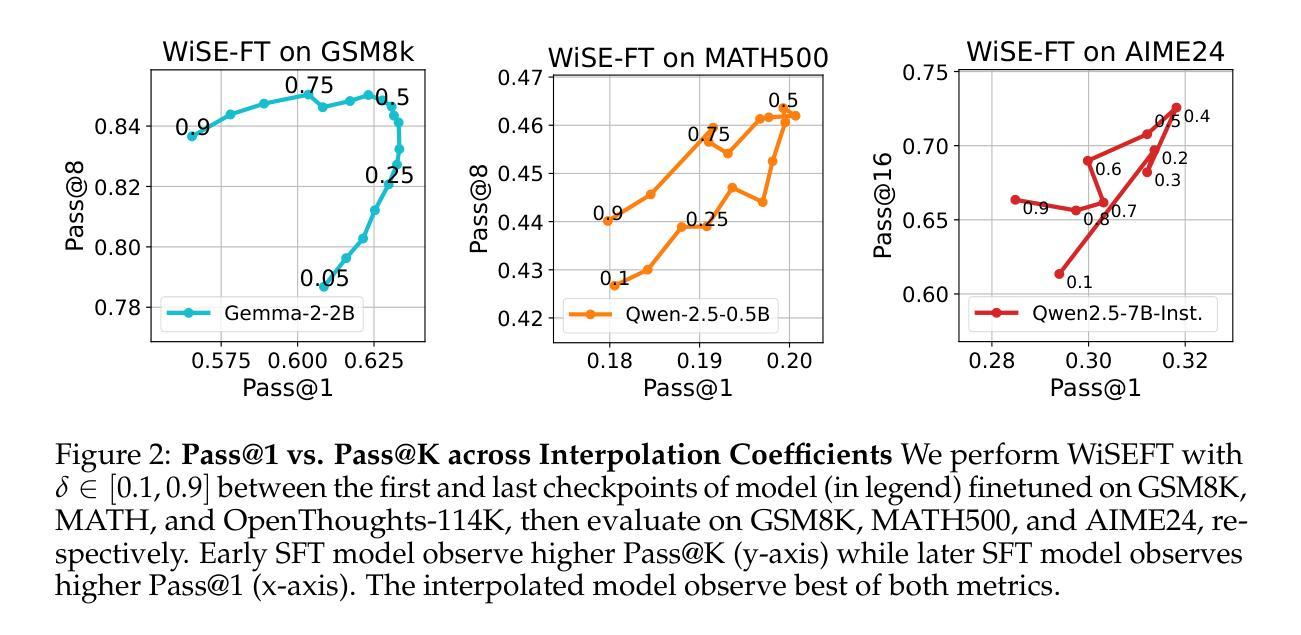
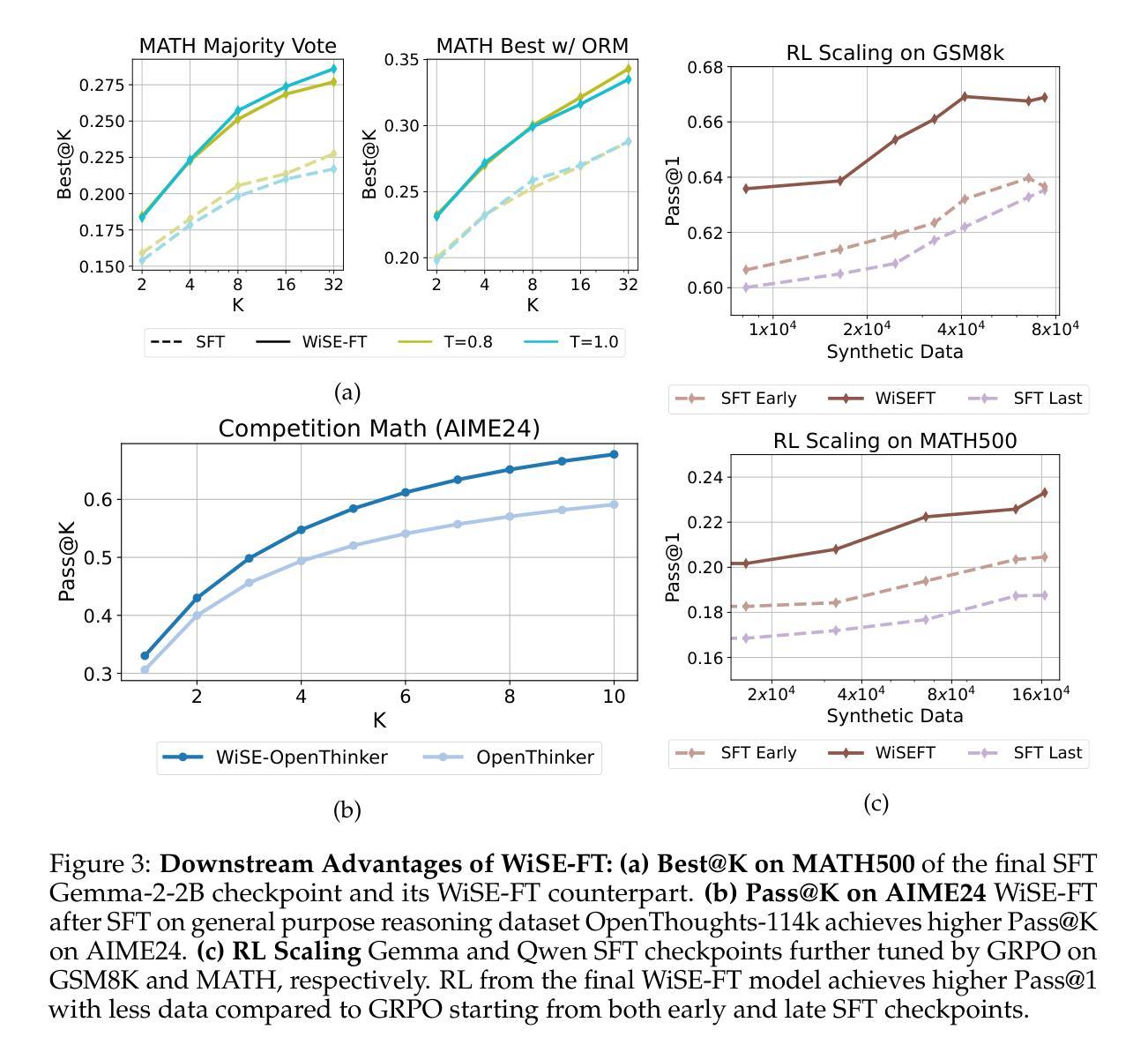
Weight Ensembling Improves Reasoning in Language Models
Authors:Xingyu Dang, Christina Baek, Kaiyue Wen, Zico Kolter, Aditi Raghunathan
We investigate a failure mode that arises during the training of reasoning models, where the diversity of generations begins to collapse, leading to suboptimal test-time scaling. Notably, the Pass@1 rate reliably improves during supervised finetuning (SFT), but Pass@k rapidly deteriorates. Surprisingly, a simple intervention of interpolating the weights of the latest SFT checkpoint with an early checkpoint, otherwise known as WiSE-FT, almost completely recovers Pass@k while also improving Pass@1. The WiSE-FT variant achieves better test-time scaling (Best@k, majority vote) and achieves superior results with less data when tuned further by reinforcement learning. Finally, we find that WiSE-FT provides complementary performance gains that cannot be achieved only through diversity-inducing decoding strategies, like temperature scaling. We formalize a bias-variance tradeoff of Pass@k with respect to the expectation and variance of Pass@1 over the test distribution. We find that WiSE-FT can reduce bias and variance simultaneously, while temperature scaling inherently trades-off between bias and variance.
我们研究了一种在训练推理模型过程中出现的故障模式,该模式下生成的多样性开始崩溃,导致测试时的缩放性能下降。值得注意的是,虽然监督微调(SFT)期间的Pass@1率可靠地提高,但Pass@k却迅速恶化。令人惊讶的是,通过插值最新SFT检查点与早期检查点的权重进行简单干预,即所谓的WiSE-FT,几乎可以完全恢复Pass@k并提高Pass@1。WiSE-FT变体实现了更好的测试时间缩放(Best@k,多数投票),并且当通过强化学习进一步调整时,在较少数据的情况下取得了更好的结果。最后,我们发现WiSE-FT提供了无法通过单纯采用诱导多样性的解码策略(如温度缩放)实现的性能增益。我们正式提出了关于Pass@k的期望偏差与Pass@1在测试分布上的方差之间的权衡。我们发现WiSE-FT可以同时减少偏差和方差,而温度缩放则固有的在偏差和方差之间进行权衡。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
训练推理模型时会出现一种世代多样性崩溃的失效模式,导致测试时扩展性不佳。尽管监督微调(SFT)的Pass@1率有所提高,但Pass@k却迅速恶化。有趣的是,通过采用一种名为WiSE-FT的策略——即将最新SFT检查点的权重与早期检查点进行插值——几乎可以完全恢复Pass@k并改善Pass@1。WiSE-FT变体在测试时的扩展性更佳,并且在通过强化学习进一步调整时,在少数据情况下也能取得更好的结果。WiSE-FT提供了无法通过单一温度缩放等解码策略实现的性能增益。此外,论文还提出了关于Pass@k的期望与方差之间的偏见方差权衡,并发现WiSE-FT可以同时减少偏见和方差,而温度缩放则存在偏见和方差之间的固有权衡。
Key Takeaways
- 推理模型训练过程中会出现世代多样性崩溃的问题,影响测试时的扩展性。
- 监督微调(SFT)在提升Pass@1率的同时会导致Pass@k迅速恶化。
- WiSE-FT策略——即插值处理最新与早期检查点的权重——能有效恢复Pass@k并改善Pass@1性能。
- WiSE-FT变体展现出更佳的测试扩展性,且少数据情况下强化学习效果更佳。
- WiSE-FT提供的性能增益无法通过单一解码策略如温度缩放实现。
- 论文提出了Pass@k的期望与方差之间的偏见方差权衡问题。
点此查看论文截图

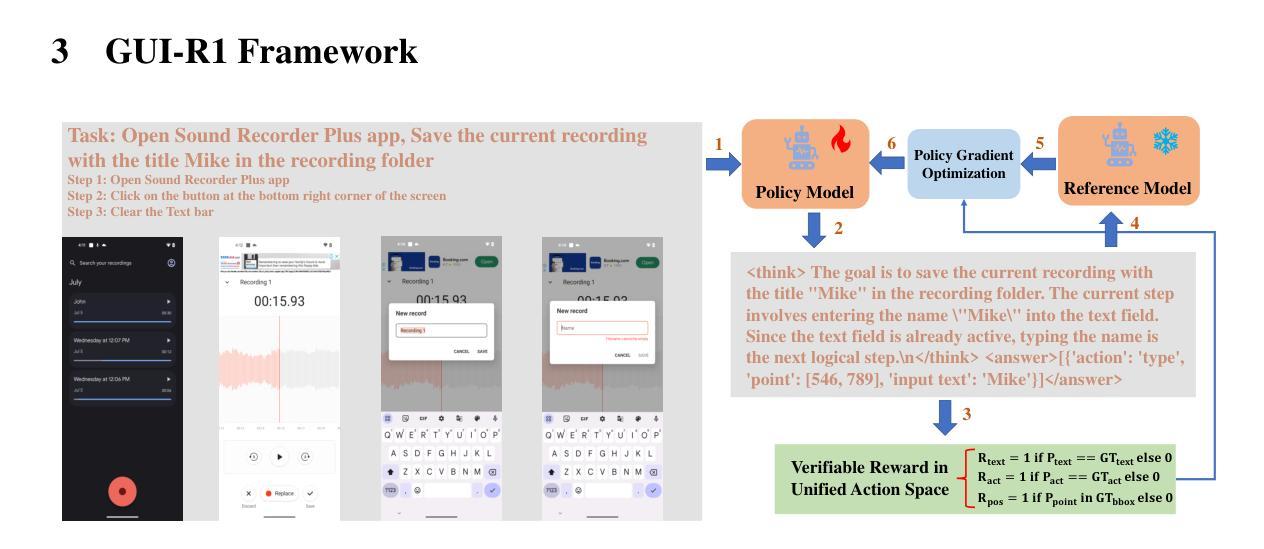
GUI-R1 : A Generalist R1-Style Vision-Language Action Model For GUI Agents
Authors:Xiaobo Xia, Run Luo
Existing efforts in building Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents largely rely on the training paradigm of supervised fine-tuning on Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs). However, this approach not only demands extensive amounts of training data but also struggles to effectively understand GUI screenshots and generalize to unseen interfaces. The issue significantly limits its application in real-world scenarios, especially for high-level tasks. Inspired by Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT) in large reasoning models (e.g., DeepSeek-R1), which efficiently enhances the problem-solving capabilities of large language models in real-world settings, we propose \name, the first reinforcement learning framework designed to enhance the GUI capabilities of LVLMs in high-level real-world task scenarios, through unified action space rule modeling. By leveraging a small amount of carefully curated high-quality data across multiple platforms (including Windows, Linux, MacOS, Android, and Web) and employing policy optimization algorithms such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to update the model, \name achieves superior performance using only 0.02% of the data (3K vs. 13M) compared to previous state-of-the-art methods like OS-Atlas across eight benchmarks spanning three different platforms (mobile, desktop, and web). These results demonstrate the immense potential of reinforcement learning based on unified action space rule modeling in improving the execution capabilities of LVLMs for real-world GUI agent tasks.
现有构建图形用户界面(GUI)代理的努力大多依赖于在大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)上采用监督微调训练范式。然而,这种方法不仅需求大量的训练数据,而且在理解GUI截图和推广到未见过的界面时面临困难。这一问题极大地限制了其在现实场景中的应用,尤其是对于高级任务。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在构建图形用户界面(GUI)代理方面,现有努力大多依赖于在大视觉语言模型(LVLMs)上采用监督微调训练范式。然而,这种方法不仅需求大量的训练数据,而且在理解GUI截图和泛化到未见过的界面上存在困难。这限制了其在现实世界场景中的应用,尤其是在高级任务中。受大型推理模型中的强化微调(RFT)的启发(例如DeepSeek-R1),它通过高效增强大型语言模型在现实世界设置中的问题解决能力,我们提出名为“名称”的强化学习框架,它是专为提高LVLMs在高级现实世界任务场景中的GUI能力而设计的,通过统一动作空间规则建模。通过利用多个平台(包括Windows、Linux、MacOS、Android和Web)的小量精心挑选的高质量数据,并采用群体相对策略优化(GRPO)等策略优化算法来更新模型,“名称”仅使用0.02%的数据(3K对13M)就在跨越三个不同平台(移动、桌面和网页)的八个基准测试中实现了对OS-Atlas等现有先进方法的卓越性能。这些结果证明了基于统一动作空间规则建模的强化学习在提升LVLMs执行现实世界GUI代理任务的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 现有GUI代理构建主要依赖监督微调训练范式,需要大量训练数据,且在理解和泛化GUI界面上有局限性。
- 强化学习框架被提出,用以提高LVLMs在现实世界高级任务场景中的GUI能力,通过统一动作空间规则建模。
- 该框架利用跨多个平台的小量高质量数据,并采用策略优化算法来更新模型。
- 与现有方法相比,该框架在跨越不同平台的八个基准测试中实现了卓越性能,仅使用极少量的数据。
- 强化学习在提升LVLMs执行GUI代理任务方面的潜力巨大。
- 该研究为GUI代理的构建提供了一种新的、数据效率更高的方法。
点此查看论文截图

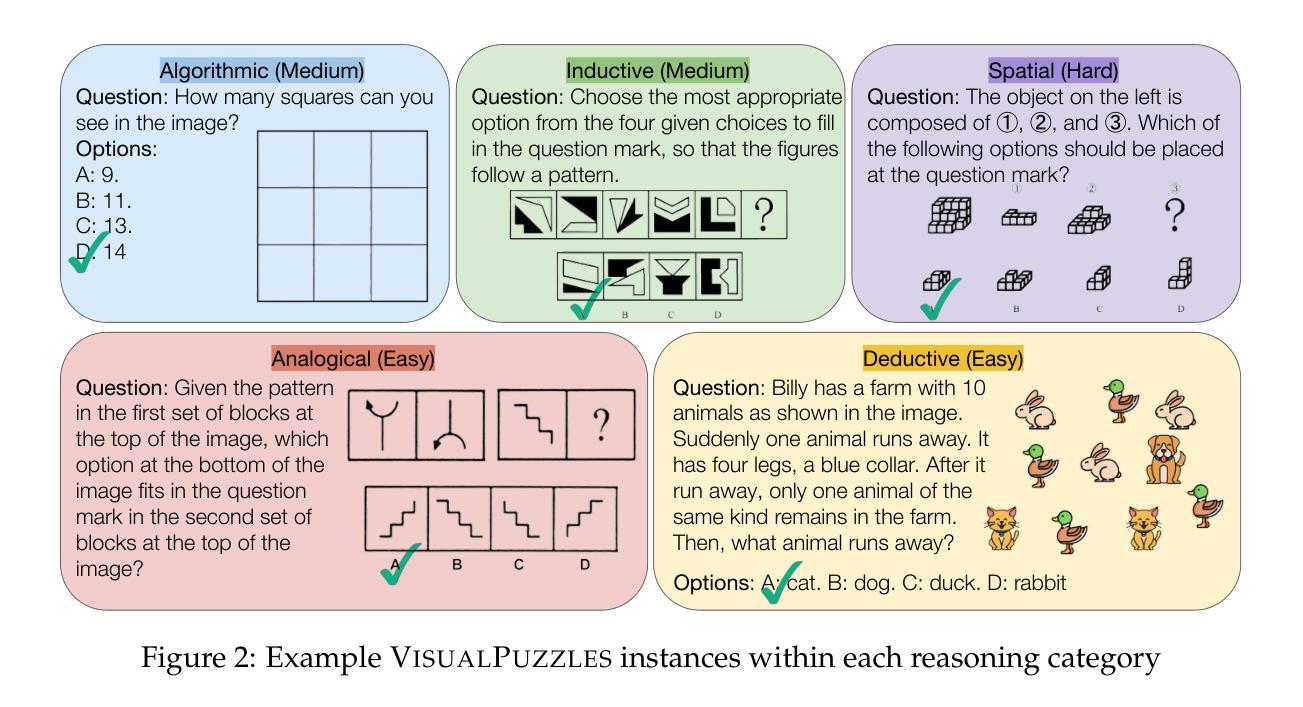
VisualPuzzles: Decoupling Multimodal Reasoning Evaluation from Domain Knowledge
Authors:Yueqi Song, Tianyue Ou, Yibo Kong, Zecheng Li, Graham Neubig, Xiang Yue
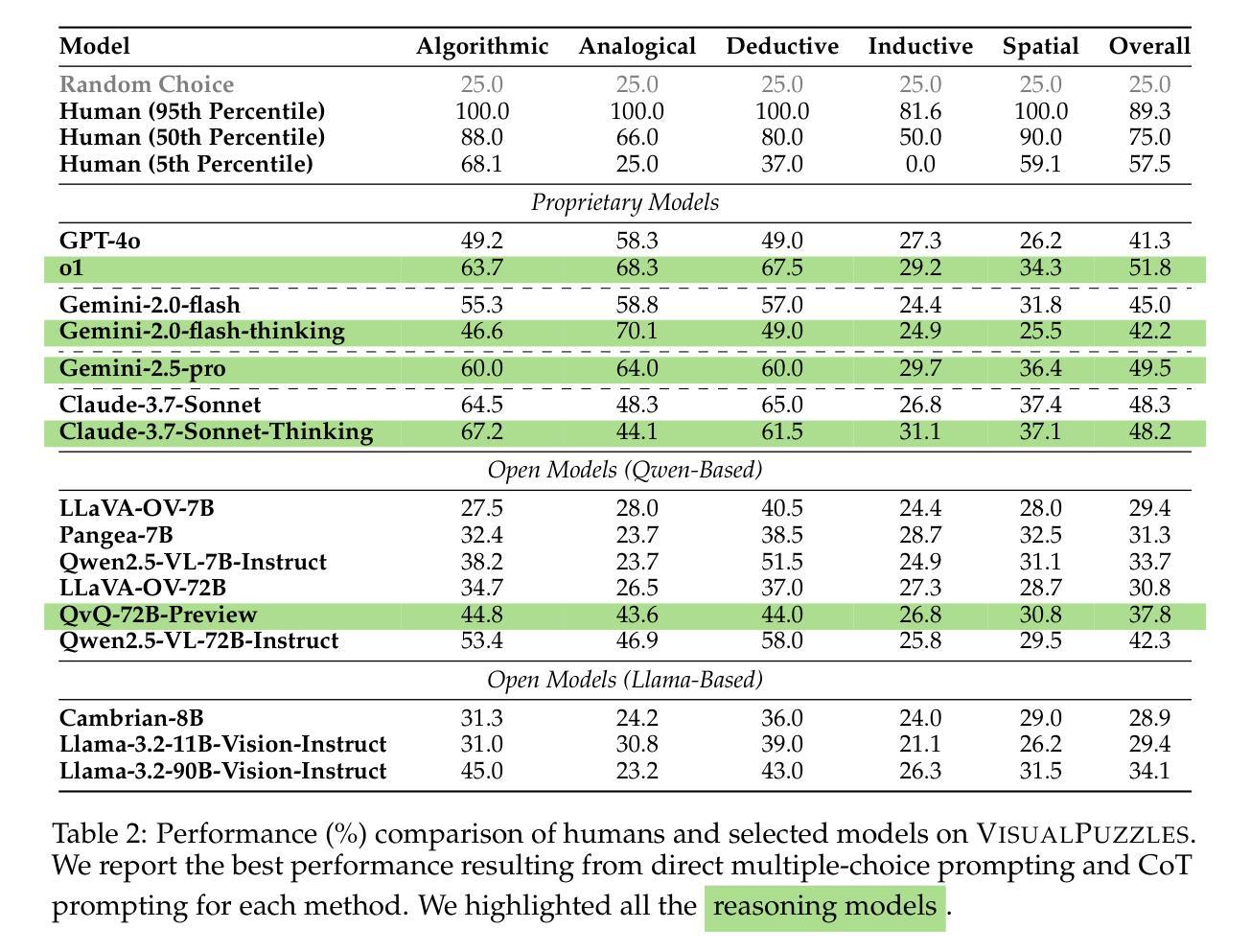
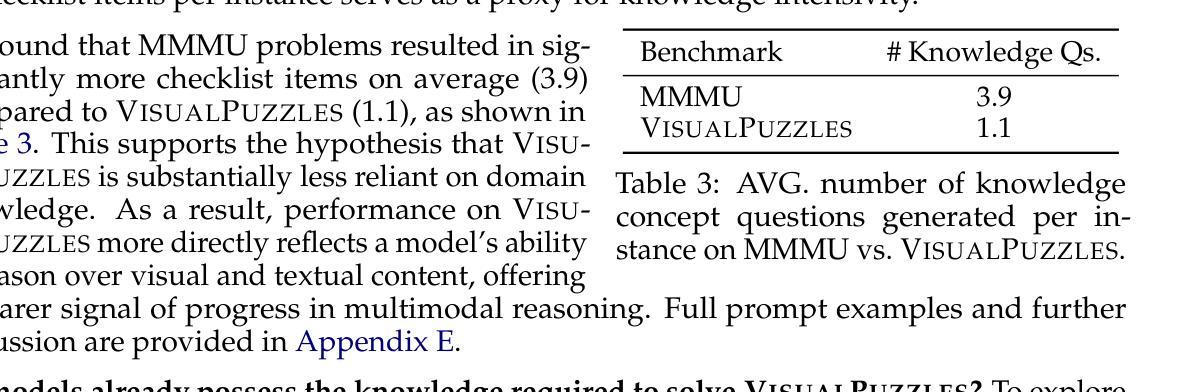
Current multimodal benchmarks often conflate reasoning with domain-specific knowledge, making it difficult to isolate and evaluate general reasoning abilities in non-expert settings. To address this, we introduce VisualPuzzles, a benchmark that targets visual reasoning while deliberately minimizing reliance on specialized knowledge. VisualPuzzles consists of diverse questions spanning five categories: algorithmic, analogical, deductive, inductive, and spatial reasoning. One major source of our questions is manually translated logical reasoning questions from the Chinese Civil Service Examination. Experiments show that VisualPuzzles requires significantly less intensive domain-specific knowledge and more complex reasoning compared to benchmarks like MMMU, enabling us to better evaluate genuine multimodal reasoning. Evaluations show that state-of-the-art multimodal large language models consistently lag behind human performance on VisualPuzzles, and that strong performance on knowledge-intensive benchmarks does not necessarily translate to success on reasoning-focused, knowledge-light tasks. Additionally, reasoning enhancements such as scaling up inference compute (with “thinking” modes) yield inconsistent gains across models and task types, and we observe no clear correlation between model size and performance. We also found that models exhibit different reasoning and answering patterns on VisualPuzzles compared to benchmarks with heavier emphasis on knowledge. VisualPuzzles offers a clearer lens through which to evaluate reasoning capabilities beyond factual recall and domain knowledge.
当前的多模态基准测试通常将推理与特定领域的知识混淆,使得在非专业环境中隔离和评估一般的推理能力变得困难。为了解决这一问题,我们推出了VisualPuzzles,这是一个以视觉推理为目标,同时刻意减少对专业知识依赖的基准测试。VisualPuzzles包含五个类别的问题:算法、类比、演绎、归纳和空间推理。我们的问题主要来源于中国公务员考试中手动翻译的逻辑推理问题。实验表明,与MMMU等基准测试相比,VisualPuzzles对专业知识的要求大大降低,但需要对推理有更复杂的理解。评估显示,最先进的多模态大型语言模型在VisualPuzzles上的表现始终落后于人类,而且在知识密集型基准测试上的出色表现并不一定能在注重推理、轻知识的任务上取得成功。此外,通过扩大推理计算(使用“思考”模式)等增强推理的方法在模型和任务类型之间产生了不一致的效益,并且我们观察到模型大小与性能之间没有明显的相关性。我们还发现,与更侧重于知识的基准测试相比,模型在VisualPuzzles上展现出不同的推理和答题模式。VisualPuzzles提供了一个更清晰的透镜,可以评估超越事实回忆和领域知识的推理能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 56 pages, 43 figures
Summary
VisualPuzzles基准测试旨在评估视觉推理能力,尽量少依赖专业知识。它包括涵盖五种推理类别的多样化问题:算法、类比、演绎、归纳和空间推理。实验表明,与MMMU等基准测试相比,VisualPuzzles更侧重于推理而非专业知识。视觉模型在多模态大型语言模型上的评估落后于人类表现,且在知识轻型的推理任务上的表现并不一致。增强推理能力的手段,如扩大推理计算规模或增加“思考”模式,对模型和任务类型的表现不一。此基准为评估超越事实回忆和领域知识的推理能力提供了清晰的视角。
Key Takeaways
- VisualPuzzles是一个针对视觉推理的基准测试,旨在减少专业知识依赖。
- 它包含涵盖多种推理类别的题目,包括算法、类比、演绎、归纳和空间推理。
- 与其他基准测试相比,VisualPuzzles更注重评估推理能力而非专业知识。
- 当前最先进的视觉模型在多模态大型语言模型上的表现落后于人类。
- 在知识轻型的推理任务上,增强推理能力的手段表现不一。
- 模型在VisualPuzzles上的表现与侧重知识的基准测试存在显著差异。
点此查看论文截图


Breaking the Data Barrier – Building GUI Agents Through Task Generalization
Authors:Junlei Zhang, Zichen Ding, Chang Ma, Zijie Chen, Qiushi Sun, Zhenzhong Lan, Junxian He
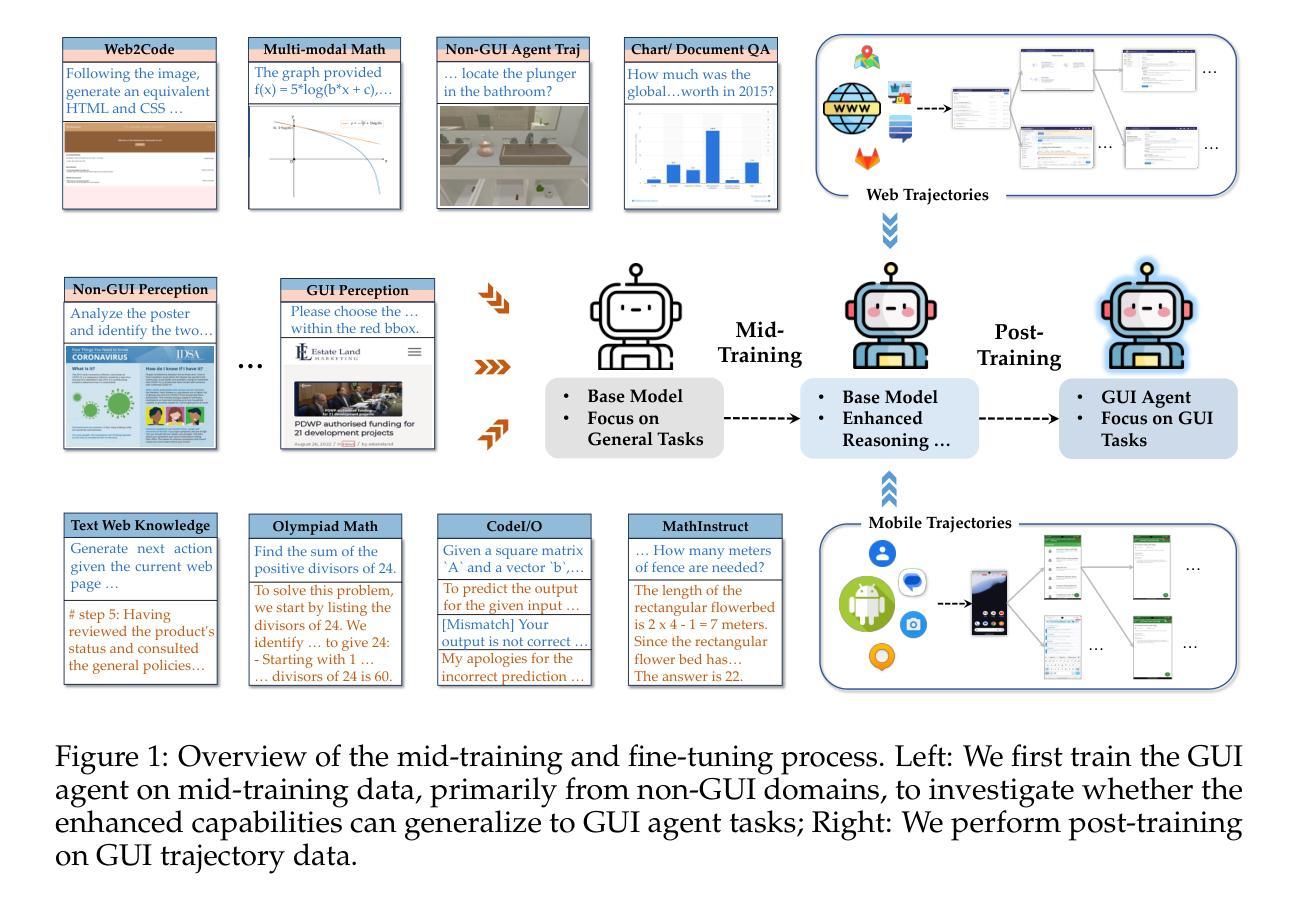
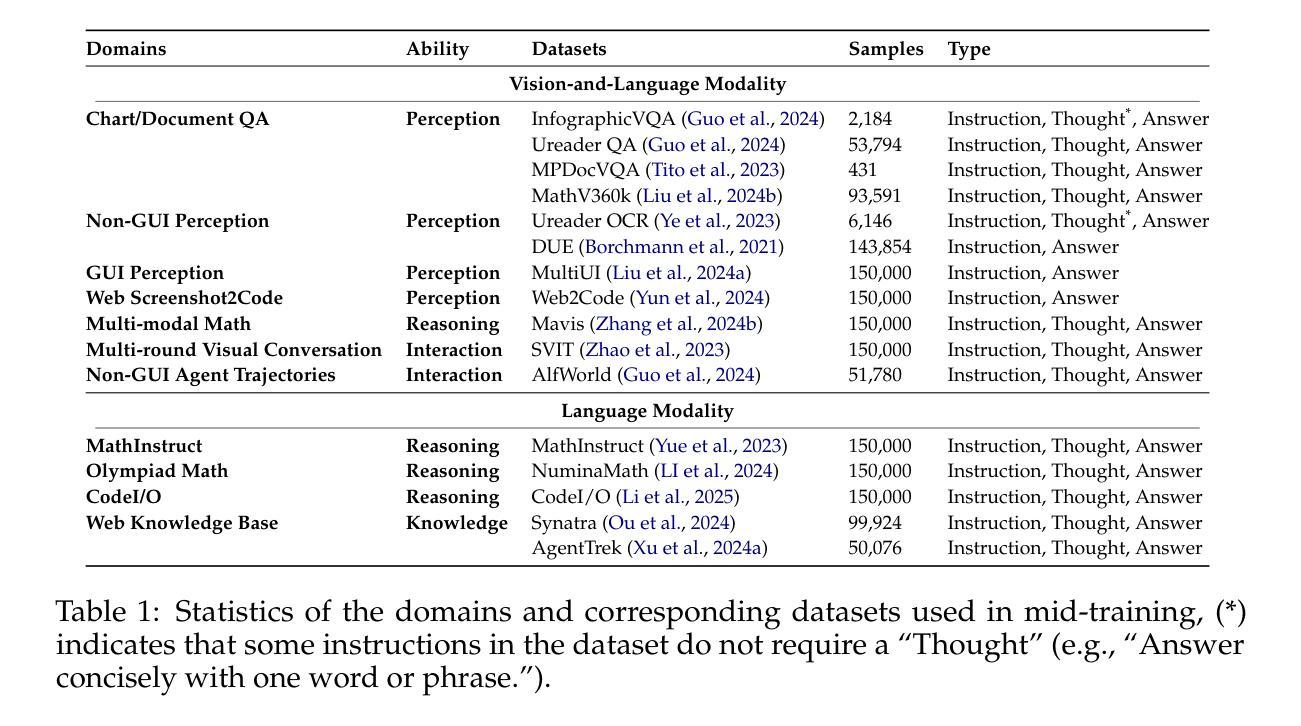
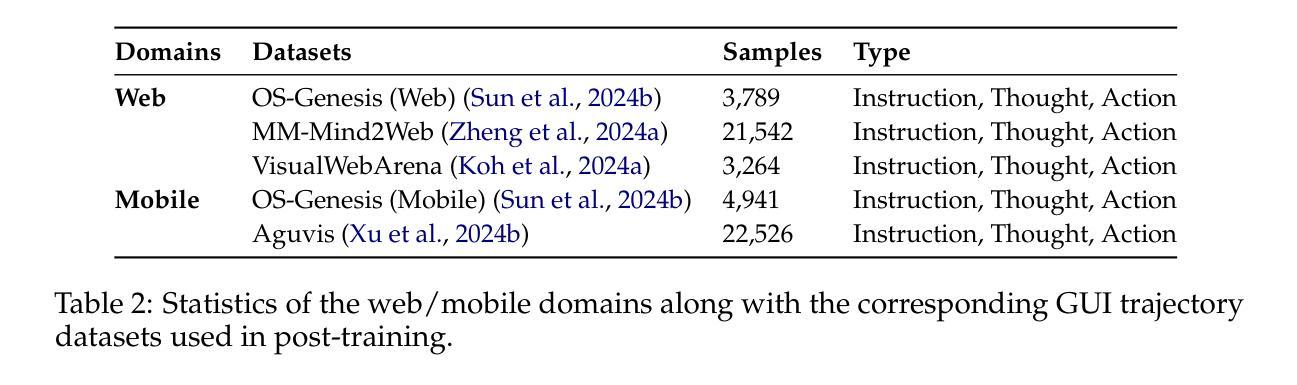
Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents offer cross-platform solutions for automating complex digital tasks, with significant potential to transform productivity workflows. However, their performance is often constrained by the scarcity of high-quality trajectory data. To address this limitation, we propose training Vision Language Models (VLMs) on data-rich, reasoning-intensive tasks during a dedicated mid-training stage, and then examine how incorporating these tasks facilitates generalization to GUI planning scenarios. Specifically, we explore a range of tasks with readily available instruction-tuning data, including GUI perception, multimodal reasoning, and textual reasoning. Through extensive experiments across 11 mid-training tasks, we demonstrate that: (1) Task generalization proves highly effective, yielding substantial improvements across most settings. For instance, multimodal mathematical reasoning enhances performance on AndroidWorld by an absolute 6.3%. Remarkably, text-only mathematical data significantly boosts GUI web agent performance, achieving a 5.6% improvement on WebArena and 5.4% improvement on AndroidWorld, underscoring notable cross-modal generalization from text-based to visual domains; (2) Contrary to prior assumptions, GUI perception data - previously considered closely aligned with GUI agent tasks and widely utilized for training - has a comparatively limited impact on final performance; (3) Building on these insights, we identify the most effective mid-training tasks and curate optimized mixture datasets, resulting in absolute performance gains of 8.0% on WebArena and 12.2% on AndroidWorld. Our work provides valuable insights into cross-domain knowledge transfer for GUI agents and offers a practical approach to addressing data scarcity challenges in this emerging field. The code, data and models will be available at https://github.com/hkust-nlp/GUIMid.
图形用户界面(GUI)代理提供跨平台的自动化复杂数字任务解决方案,具有改变生产力工作流程的巨大潜力。然而,它们的表现往往受到高质量轨迹数据稀缺的制约。为了解决这一局限性,我们建议在专门的中间训练阶段,在数据丰富、推理密集的任务上训练视觉语言模型(VLM),然后研究如何将这些任务纳入GUI规划场景以促进通用化。具体来说,我们探索了一系列具有可获取指令调整数据的任务,包括GUI感知、多模态推理和文本推理。通过对11个中间训练任务的广泛实验,我们证明:(1)任务通用化非常有效,在大多数设置中都取得了显著改进。例如,多模态数学推理在AndroidWorld上的表现提高了6.3%。值得注意的是,只有文本的数学数据显著提高了GUI网络代理的性能,在WebArena上提高了5.6%,在AndroidWorld上提高了5.4%,突显出从文本到视觉领域的跨模态通用的重要性;(2)与先前的假设相反,之前被认为与GUI代理任务紧密相关并广泛用于训练的GUI感知数据对最终性能的影响相对有限;(3)基于这些见解,我们确定了最有效的中间训练任务并策划了优化的混合数据集,从而在WebArena上实现了8.0%的绝对性能提升,在AndroidWorld上实现了12.2%的提升。我们的工作为GUI代理的跨域知识转移提供了有价值的见解,并为解决这一新兴领域的数据稀缺挑战提供了实用方法。相关代码、数据和模型将可在https://github.com/hkust-nlp/GUIMid找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 11 figures
Summary
该文介绍了图形用户界面(GUI)代理在自动化复杂数字任务方面的跨平台解决方案潜力,但其性能往往受到高质量轨迹数据的限制。为解决这个问题,研究团队提出在专门的中间训练阶段,对视觉语言模型(VLM)进行丰富数据和高推理任务训练,并研究这些任务如何促进对GUI规划场景的泛化。实验证明,任务泛化效果显著,多模态数学推理在AndroidWorld任务上的性能提升达6.3%。文本数学数据对GUI网页代理性能也有显著提升。研究还指出,与先前假设相反,GUI感知数据对最终性能的影响有限。基于此,研究团队优化了中期训练任务和混合数据集,实现了WebArena和AndroidWorld任务上的性能分别提升8.0%和12.2%。该研究为GUI代理的跨域知识迁移提供了宝贵见解,并提供了解决该领域数据稀缺问题的实用方法。
Key Takeaways
- GUI代理具有自动化复杂数字任务的跨平台解决方案潜力。
- 视觉语言模型(VLM)在专门的中期训练阶段接受丰富数据和推理任务训练,以提升性能。
- 任务泛化效果显著,特别是在多模态数学推理方面。文本数学数据对GUI代理性能有积极影响。
- GUI感知数据对GUI代理的最终性能影响有限。
- 优化中期训练任务和混合数据集可显著提升性能。
- 研究提供了GUI代理跨域知识迁移的见解。
点此查看论文截图