⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-17 更新
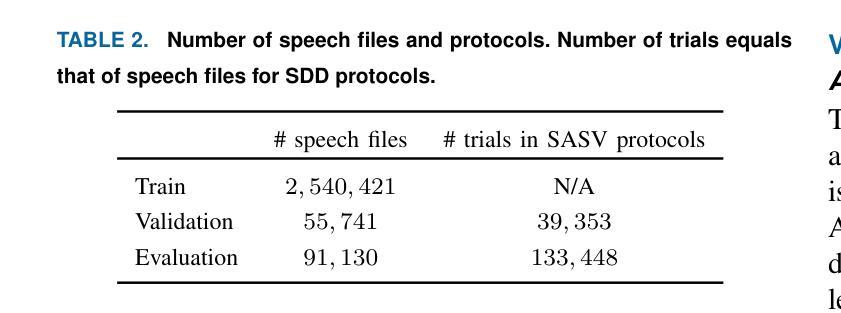
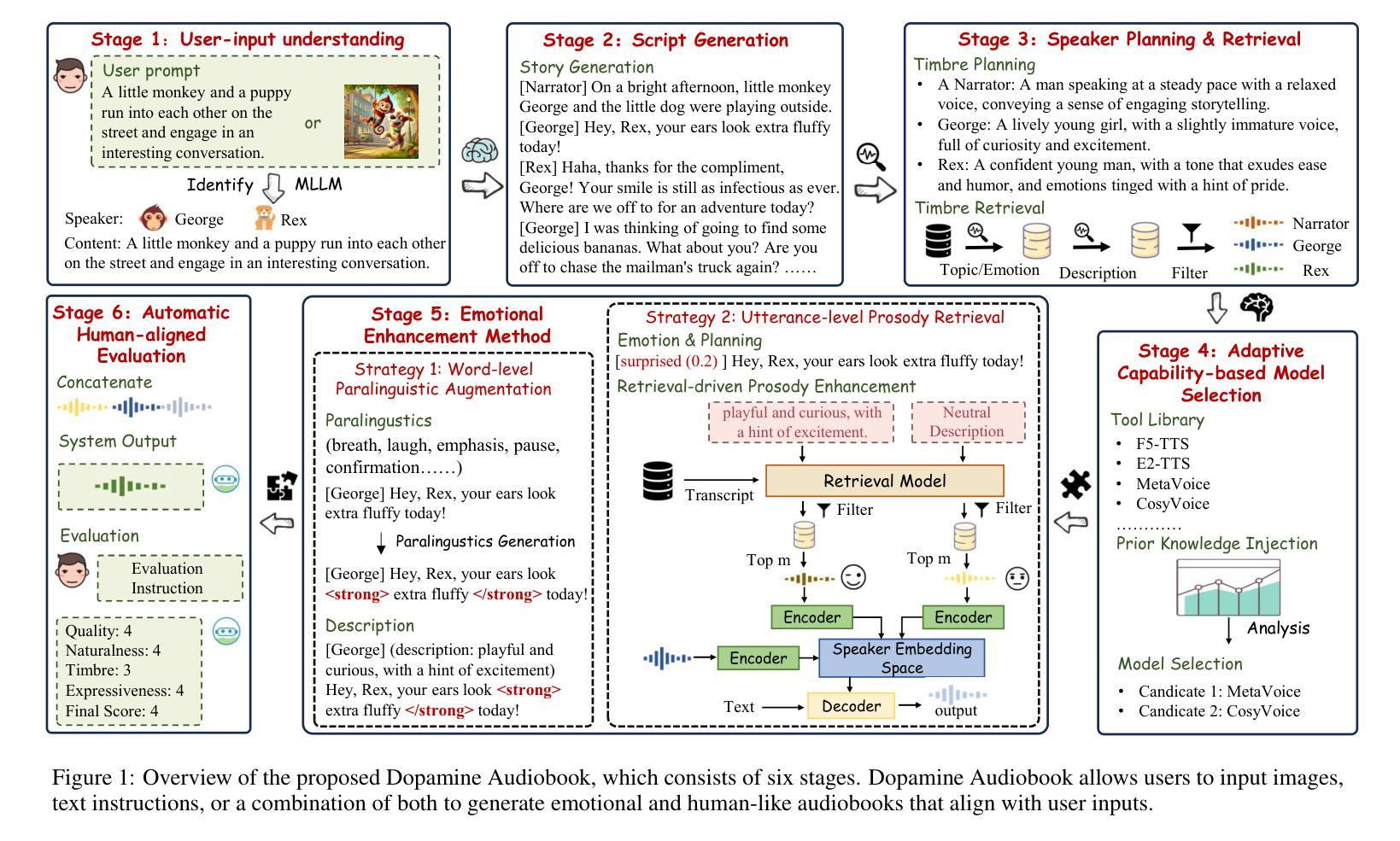
Dopamine Audiobook: A Training-free MLLM Agent for Emotional and Human-like Audiobook Generation
Authors:Yan Rong, Shan Yang, Guangzhi Lei, Li Liu
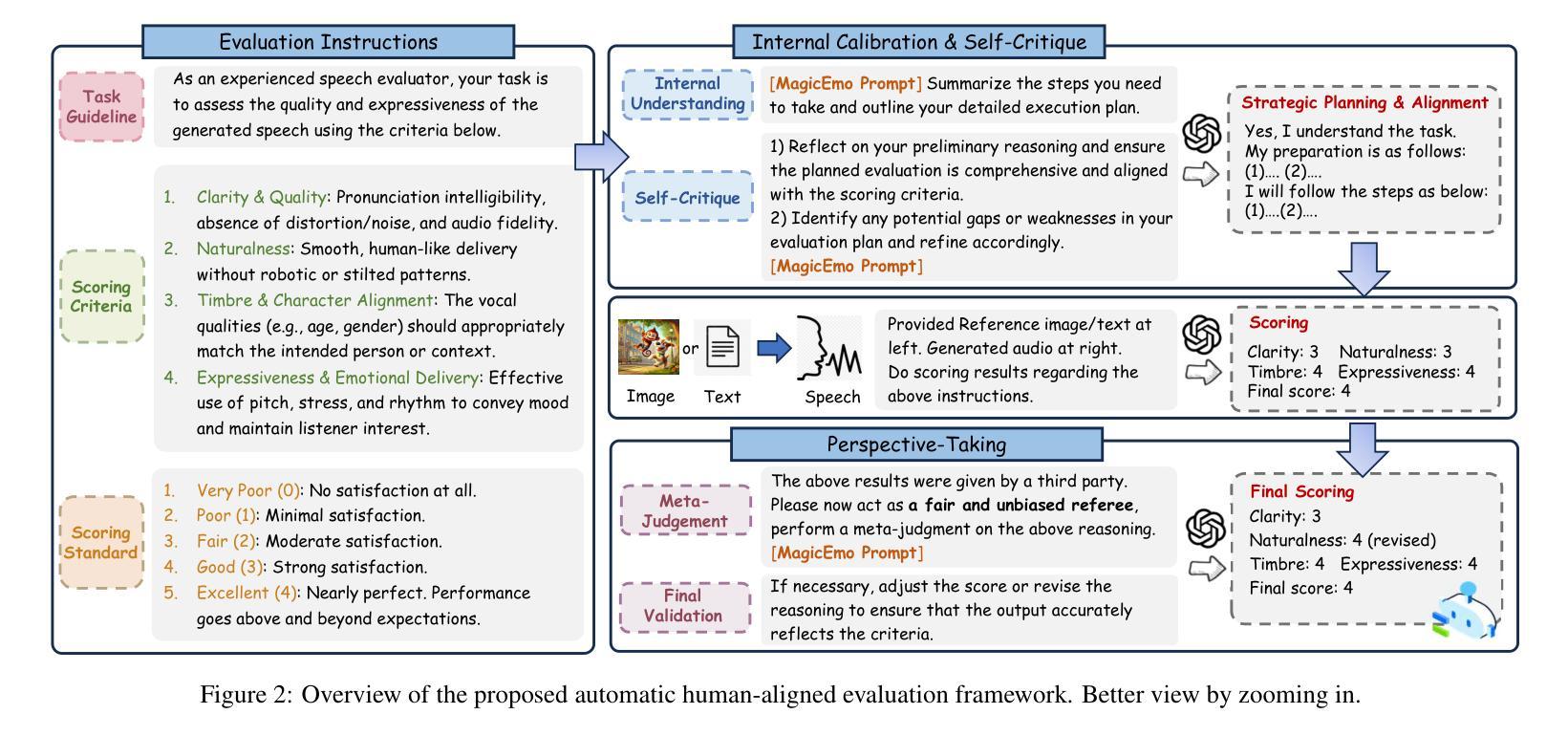
Audiobook generation, which creates vivid and emotion-rich audio works, faces challenges in conveying complex emotions, achieving human-like qualities, and aligning evaluations with human preferences. Existing text-to-speech (TTS) methods are often limited to specific scenarios, struggle with emotional transitions, and lack automatic human-aligned evaluation benchmarks, instead relying on either misaligned automated metrics or costly human assessments. To address these issues, we propose Dopamine Audiobook, a new unified training-free system leveraging a multimodal large language model (MLLM) as an AI agent for emotional and human-like audiobook generation and evaluation. Specifically, we first design a flow-based emotion-enhanced framework that decomposes complex emotional speech synthesis into controllable sub-tasks. Then, we propose an adaptive model selection module that dynamically selects the most suitable TTS methods from a set of existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) TTS methods for diverse scenarios. We further enhance emotional expressiveness through paralinguistic augmentation and prosody retrieval at word and utterance levels. For evaluation, we propose a novel GPT-based evaluation framework incorporating self-critique, perspective-taking, and psychological MagicEmo prompts to ensure human-aligned and self-aligned assessments. Experiments show that our method generates long speech with superior emotional expression to SOTA TTS models in various metrics. Importantly, our evaluation framework demonstrates better alignment with human preferences and transferability across audio tasks. Project website with audio samples can be found at https://dopamine-audiobook.github.io.
有声书生成能够创造出生动且情感丰富的音频作品,但面临着传达复杂情感、实现人性化特质以及评价与人类偏好对齐等挑战。现有的文本到语音(TTS)方法往往局限于特定场景,难以应对情感过渡,并且缺乏自动与人类对齐的评价基准,这依赖于错位自动化指标或昂贵的人类评估。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了多巴胺有声书,这是一个新的统一训练免费系统,利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)作为人工智能代理,用于情感和人性化的有声书生成与评价。具体来说,我们首先设计一个基于流的情感增强框架,将复杂的情感语音合成分解成可控的子任务。然后,我们提出了一个自适应模型选择模块,该模块可以从一组最先进的TTS方法中动态选择最适合的TTS方法,以适应不同的场景。我们进一步通过词语和句子的副语言增强和语调检索来增强情感表现力。在评价方面,我们提出了一个基于GPT的评价框架,该框架结合了自我批评、换位思考和心理MagicEmo提示,以确保与人类和自我评价对齐。实验表明,我们的方法在多种指标上生成了具有卓越情感表达的长语音,超过了最先进的TTS模型。重要的是,我们的评价框架与人类偏好对齐得更好,并且在音频任务之间具有可转移性。音频样本可在https://dopamine-audiobook.github.io项目网站上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代有声书生成技术面临表达复杂情感、实现人性化特质和对齐人类偏好评估等挑战。针对这些问题,提出了Dopamine有声书系统,该系统采用多模态大型语言模型作为AI代理,通过情绪增强框架和自适应模型选择模块实现情感化和人性化的有声书生成与评价。同时,通过语言外的增光和语调检索增强情感表达。评价方面,采用基于GPT的评价框架,确保与人类偏好和自我评估对齐。实验表明,该方法在多种指标上优于现有TTS模型,特别是在情感表达和人类偏好对齐方面。
Key Takeaways
- 有声书生成面临表达复杂情感、实现人性化特质和对齐人类偏好评估的挑战。
- 提出Dopamine有声书系统,采用多模态大型语言模型解决上述问题。
- 通过情绪增强框架和自适应模型选择模块实现情感化和人性化的有声书生成。
- 结合语言外的增光和语调检索增强情感表达。
- 采用基于GPT的评价框架,确保与人类偏好和自我评估对齐。
- 实验证明该方法在多种指标上优于现有TTS模型。
点此查看论文截图

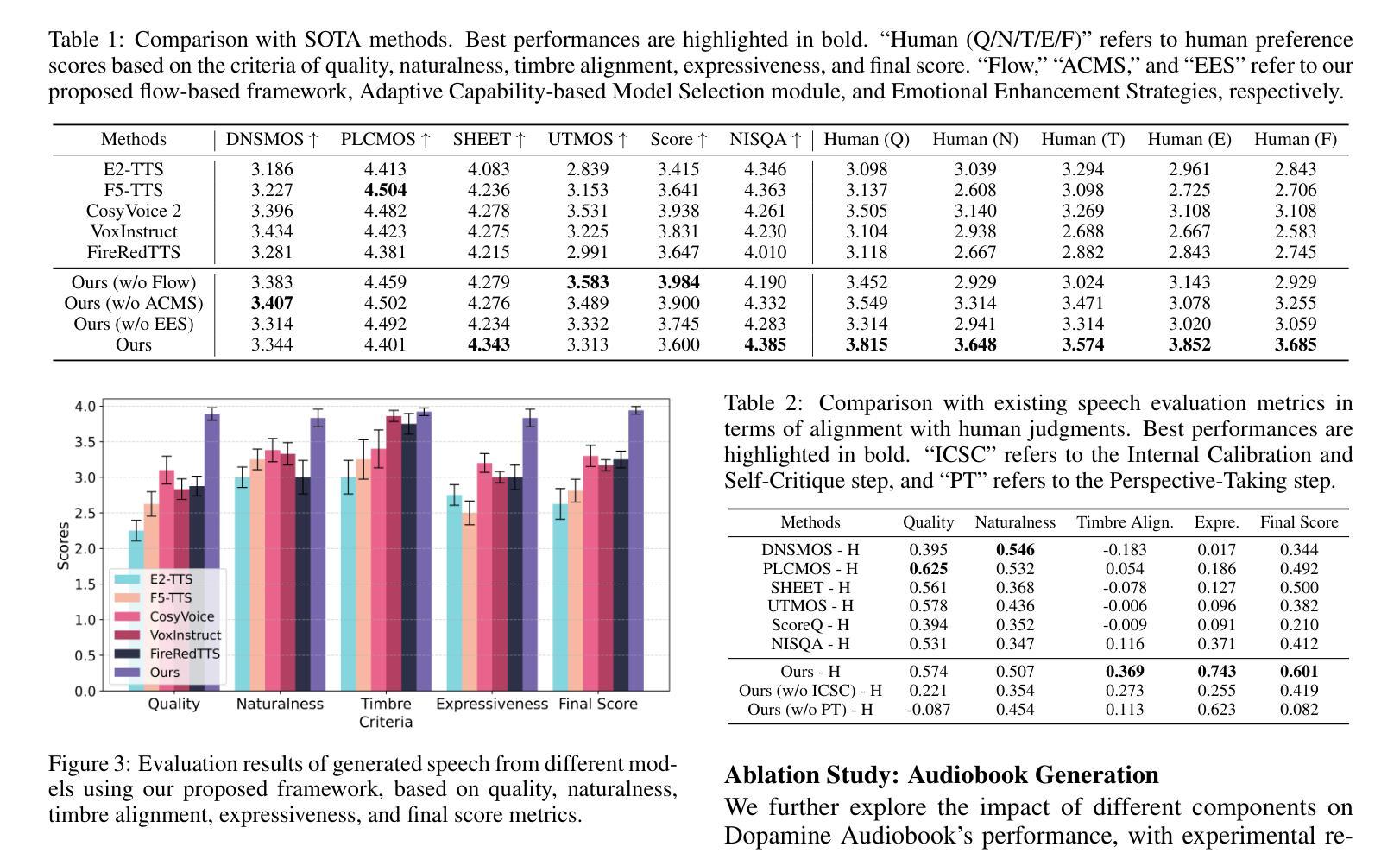
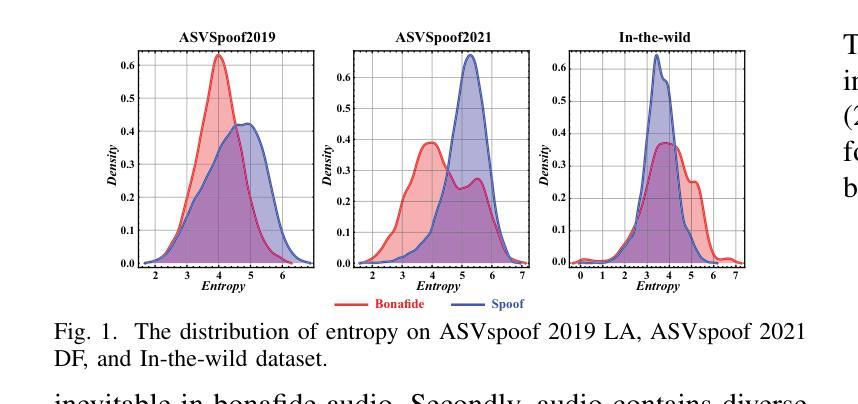
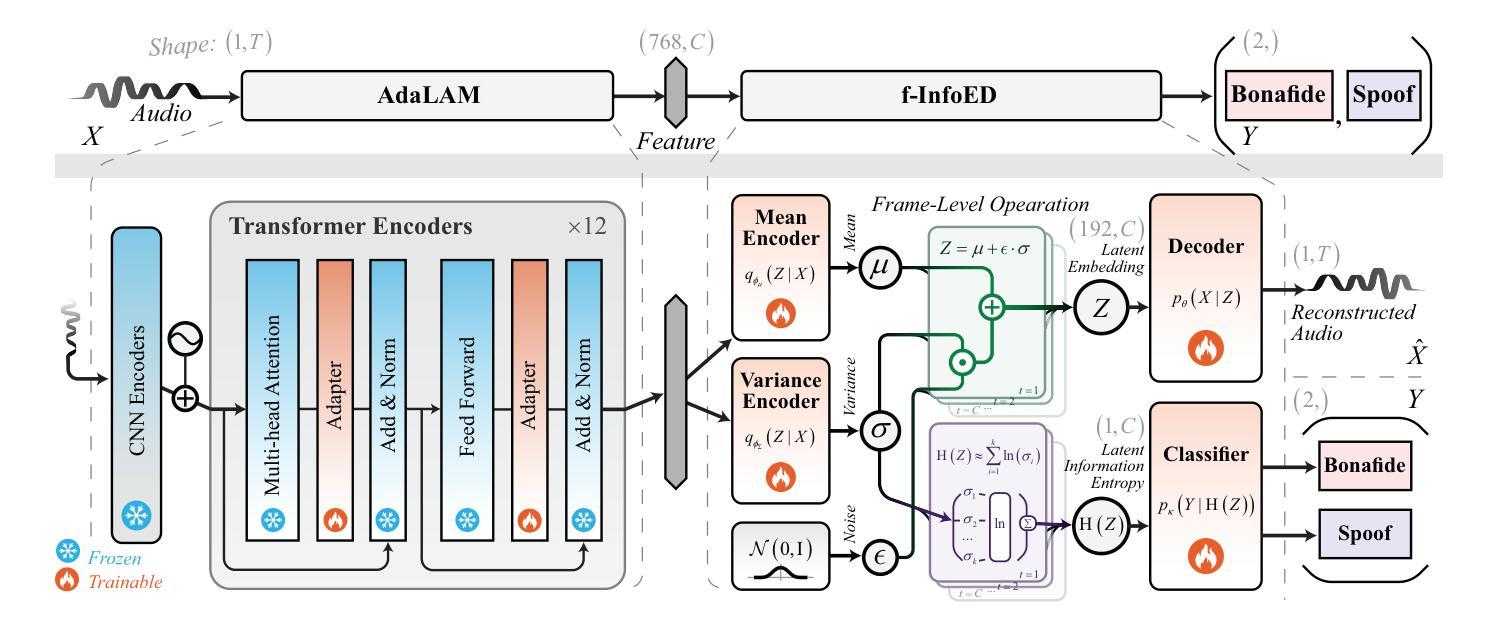
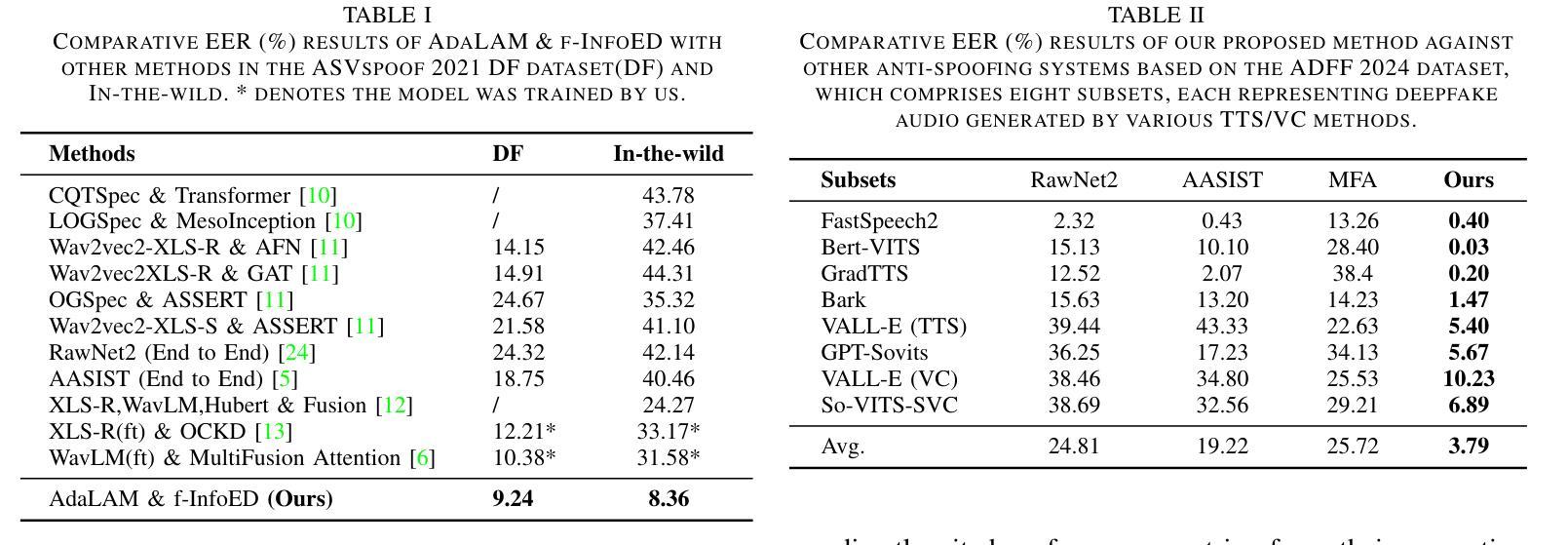
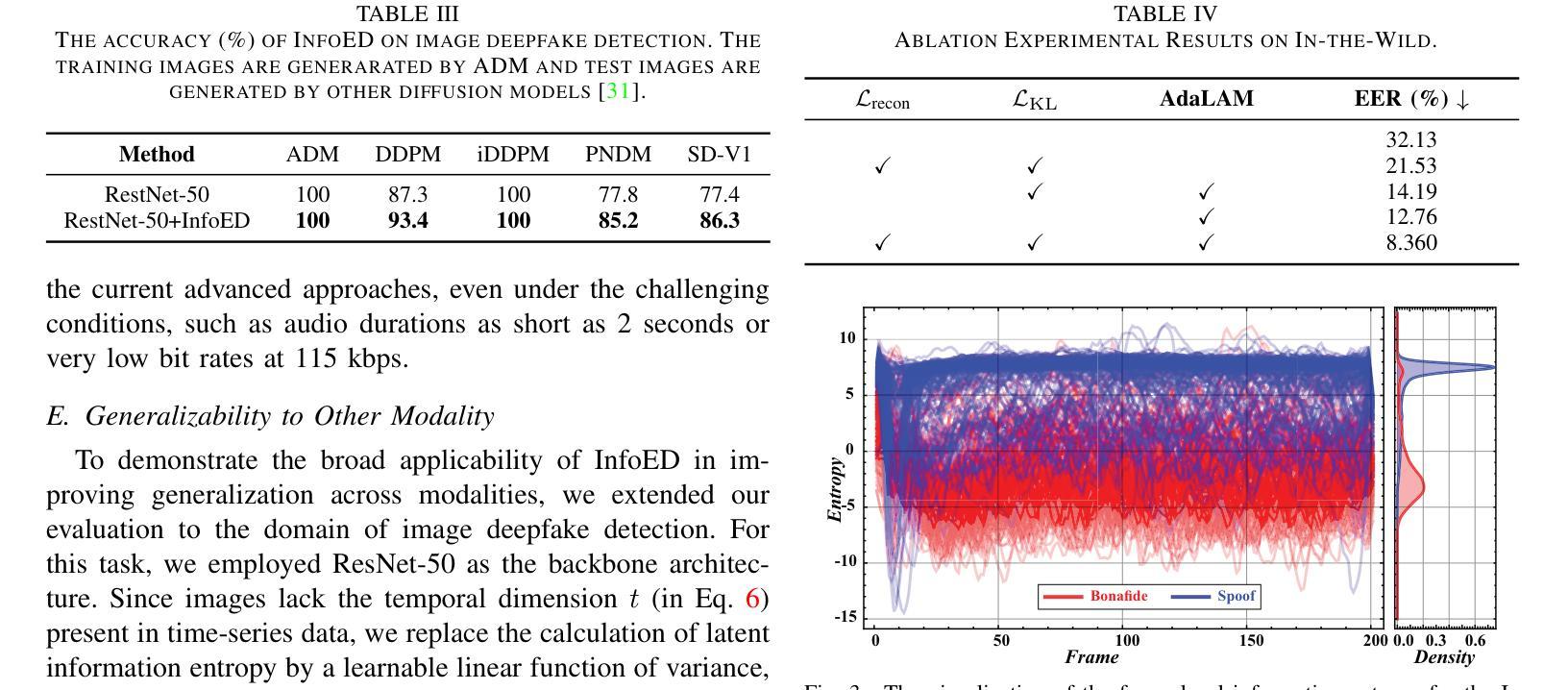
Generalized Audio Deepfake Detection Using Frame-level Latent Information Entropy
Authors:Botao Zhao, Zuheng Kang, Yayun He, Xiaoyang Qu, Junqing Peng, Jing Xiao, Jianzong Wang
Generalizability, the capacity of a robust model to perform effectively on unseen data, is crucial for audio deepfake detection due to the rapid evolution of text-to-speech (TTS) and voice conversion (VC) technologies. A promising approach to differentiate between bonafide and spoof samples lies in identifying intrinsic disparities to enhance model generalizability. From an information-theoretic perspective, we hypothesize the information content is one of the intrinsic differences: bonafide sample represents a dense, information-rich sampling of the real world, whereas spoof sample is typically derived from lower-dimensional, less informative representations. To implement this, we introduce frame-level latent information entropy detector(f-InfoED), a framework that extracts distinctive information entropy from latent representations at the frame level to identify audio deepfakes. Furthermore, we present AdaLAM, which extends large pre-trained audio models with trainable adapters for enhanced feature extraction. To facilitate comprehensive evaluation, the audio deepfake forensics 2024 (ADFF 2024) dataset was built by the latest TTS and VC methods. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance and exhibits remarkable generalization capabilities. Further analytical studies confirms the efficacy of AdaLAM in extracting discriminative audio features and f-InfoED in leveraging latent entropy information for more generalized deepfake detection.
通用性,即稳健模型在未见数据上有效执行的能力,由于文本到语音(TTS)和语音转换(VC)技术的快速发展,对于音频深度伪造检测至关重要。区分真实样本和欺骗样本的一种有前途的方法在于识别内在差异,以提高模型的通用性。从信息理论的角度来看,我们假设信息内容是内在差异之一:真实样本代表现实世界的信息丰富采样,而欺骗样本通常来源于低维度、信息较少的表示。为了实施这一点,我们引入了帧级潜在信息熵检测器(f-InfoED),这是一个框架,用于从帧级的潜在表示中提取独特的信息熵,以识别音频深度伪造。此外,我们推出了AdaLAM,它通过为大型预训练音频模型添加可训练的适配器,以进行增强的特征提取。为了促进全面评估,使用最新的TTS和VC方法构建了音频深度伪造取证2024(ADFF 2024)数据集。大量实验表明,我们提出的方法达到了最新技术性能,并显示出惊人的泛化能力。进一步的分析研究证实了AdaLAM在提取判别性音频特征和f-InfoED在利用潜在熵信息进行更通用的深度伪造检测中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accpeted by IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo 2025 (ICME 2025)
Summary
针对音频深度伪造检测,提出一种基于帧级潜在信息熵检测器(f-InfoED)的方法,能够从帧级别提取潜在表示中的独特信息熵来识别音频深度伪造。同时介绍AdaLAM,一种通过可训练适配器扩展大型预训练音频模型的方法,用于提高特征提取能力。实验表明,该方法具有最先进的性能和出色的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 音频深度伪造检测中,模型泛化能力至关重要,因为文本到语音(TTS)和语音转换(VC)技术发展迅速。
- 识别内在差异是提高模型泛化能力的关键,其中信息内容是重要的内在差异之一。
- 真实样本代表现实世界的信息丰富采样,而伪造样本通常来自低维度、信息较少的表示。
- 引入帧级潜在信息熵检测器(f-InfoED),通过提取潜在表示中的独特信息熵来识别音频深度伪造。
- 提出AdaLAM方法,通过可训练适配器扩展大型预训练音频模型,以提高特征提取能力。
- 音频深度伪造取证2024(ADFF 2024)数据集由最新的TTS和VC方法构建,为全面评估提供了便利。
点此查看论文截图

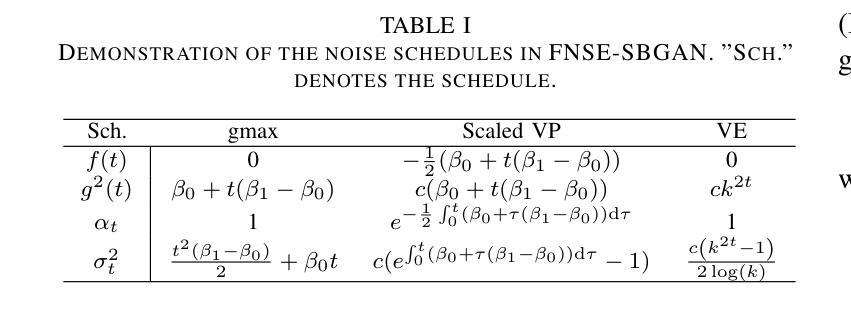
FNSE-SBGAN: Far-field Speech Enhancement with Schrodinger Bridge and Generative Adversarial Networks
Authors:Tong Lei, Qinwen Hu, Ziyao Lin, Andong Li, Rilin Chen, Meng Yu, Dong Yu, Jing Lu
The prevailing method for neural speech enhancement predominantly utilizes fully-supervised deep learning with simulated pairs of far-field noisy-reverberant speech and clean speech. Nonetheless, these models frequently demonstrate restricted generalizability to mixtures recorded in real-world conditions. To address this issue, this study investigates training enhancement models directly on real mixtures. Specifically, we revisit the single-channel far-field to near-field speech enhancement (FNSE) task, focusing on real-world data characterized by low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), high reverberation, and mid-to-high frequency attenuation. We propose FNSE-SBGAN, a framework that integrates a Schrodinger Bridge (SB)-based diffusion model with generative adversarial networks (GANs). Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across various metrics and subjective evaluations, significantly reducing the character error rate (CER) by up to 14.58% compared to far-field signals. Experimental results demonstrate that FNSE-SBGAN preserves superior subjective quality and establishes a new benchmark for real-world far-field speech enhancement. Additionally, we introduce an evaluation framework leveraging matrix rank analysis in the time-frequency domain, providing systematic insights into model performance and revealing the strengths and weaknesses of different generative methods.
当前神经网络语音增强的主流方法主要是利用模拟的远场带噪声和回响的语音与干净语音配对进行全监督深度学习。然而,这些模型对于真实世界条件下录制的混合语音的泛化能力往往有限。为了解决这一问题,本研究直接对真实混合语音进行增强模型训练。具体来说,我们重新审视单通道远场到近场语音增强(FNSE)任务,重点关注低信噪比、高回响以及中高频衰减等真实世界数据的特征。我们提出了FNSE-SBGAN框架,它结合了基于Schrodinger Bridge(SB)的扩散模型与生成对抗网络(GANs)。我们的方法在各种指标和主观评估上达到了最先进的性能,与远场信号相比,字符错误率(CER)降低了高达14.58%。实验结果表明,FNSE-SBGAN保持了较高的主观质量,为真实世界远场语音增强建立了新的基准。此外,我们还引入了一个利用时频域矩阵秩分析的评价框架,为模型性能提供了系统的见解,揭示了不同生成方法的优点和缺点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本研究针对神经网络语音增强方法在实际应用中的泛化能力受限的问题,提出了一种基于Schrodinger Bridge(SB)扩散模型与生成对抗网络(GANs)的FNSE-SBGAN框架,用于单通道远场到近场语音增强(FNSE)。该框架在真实世界的复杂噪声和回声环境下表现出卓越的性能,显著降低了字符错误率(CER),同时保持了高质量的主观评价,为远场语音增强设定了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- 研究重点:研究解决神经网络语音增强模型在实际环境中的泛化能力问题,特别是针对单通道远场到近场的语音增强(FNSE)。
- 数据挑战:关注真实世界数据,特点是低信噪比(SNR)、高回声、以及中高频衰减。
- 新方法:提出FNSE-SBGAN框架,结合Schrodinger Bridge(SB)扩散模型和生成对抗网络(GANs)。
- 性能提升:FNSE-SBGAN框架实现了业界最佳性能,相比远场信号降低了高达14.58%的字符错误率(CER)。
- 主观质量评价:实验结果表明,FNSE-SBGAN保持高质量的主观评价。
- 新的评估框架:引入基于矩阵秩分析的时间-频率域评估框架,为模型性能提供系统洞察,揭示不同生成方法的优势和劣势。
点此查看论文截图

SpoofCeleb: Speech Deepfake Detection and SASV In The Wild
Authors:Jee-weon Jung, Yihan Wu, Xin Wang, Ji-Hoon Kim, Soumi Maiti, Yuta Matsunaga, Hye-jin Shim, Jinchuan Tian, Nicholas Evans, Joon Son Chung, Wangyou Zhang, Seyun Um, Shinnosuke Takamichi, Shinji Watanabe
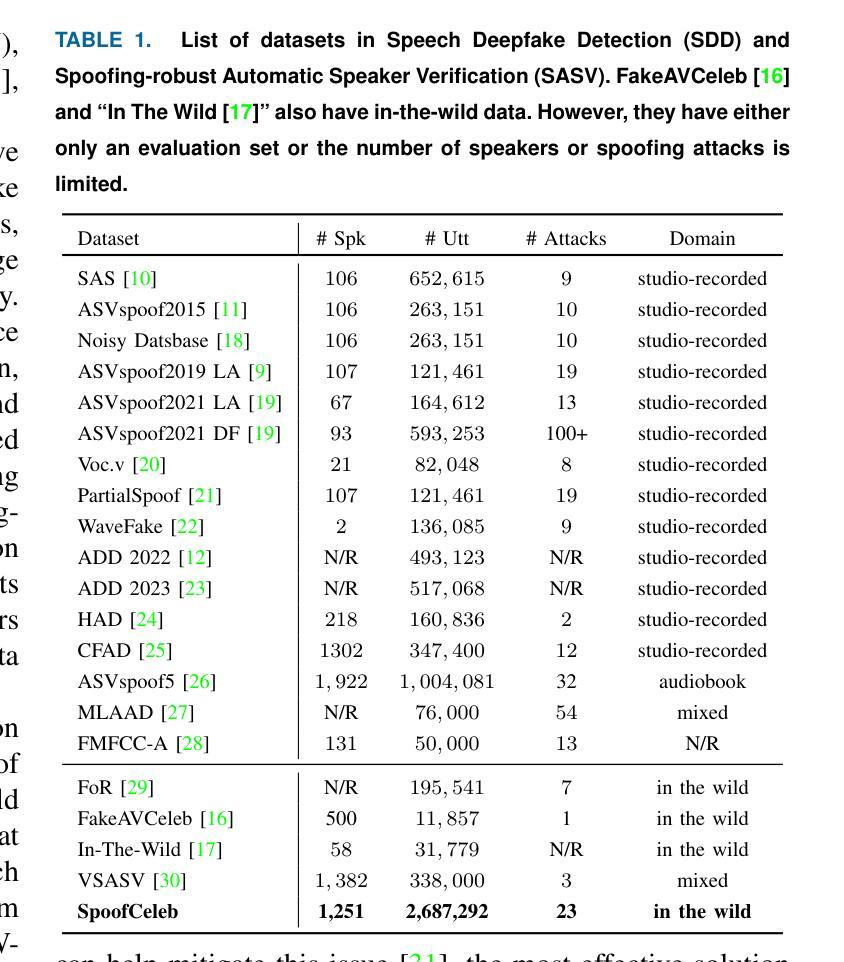
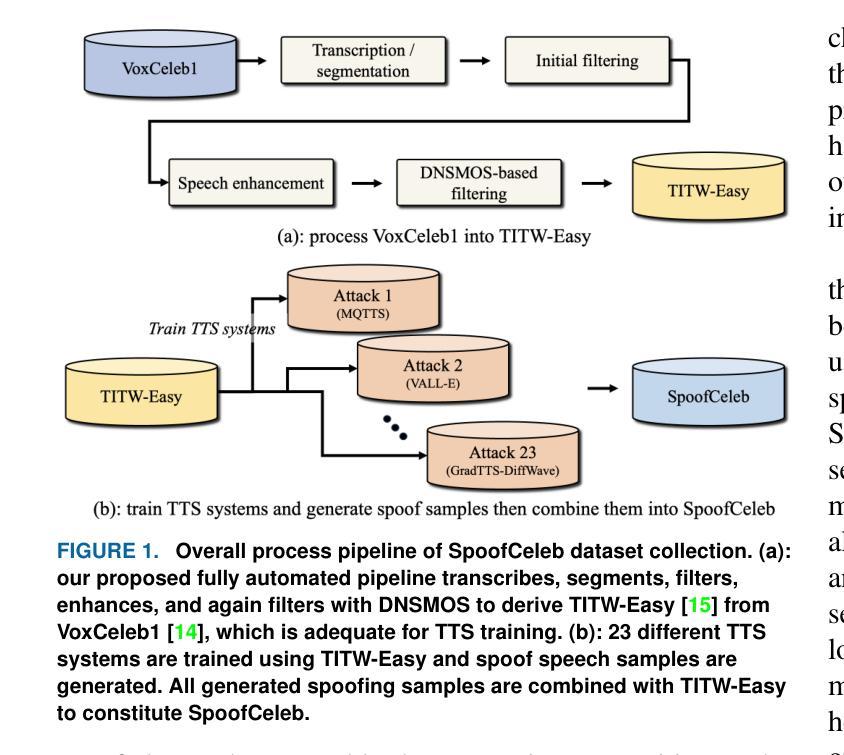
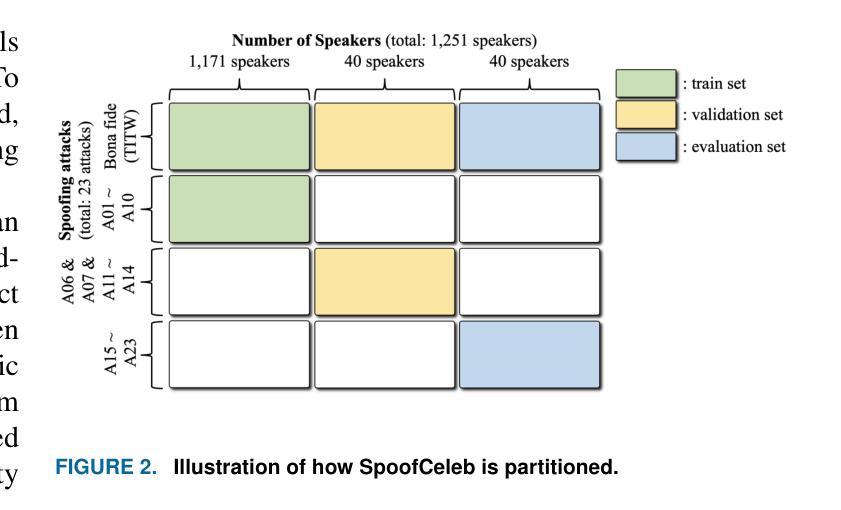
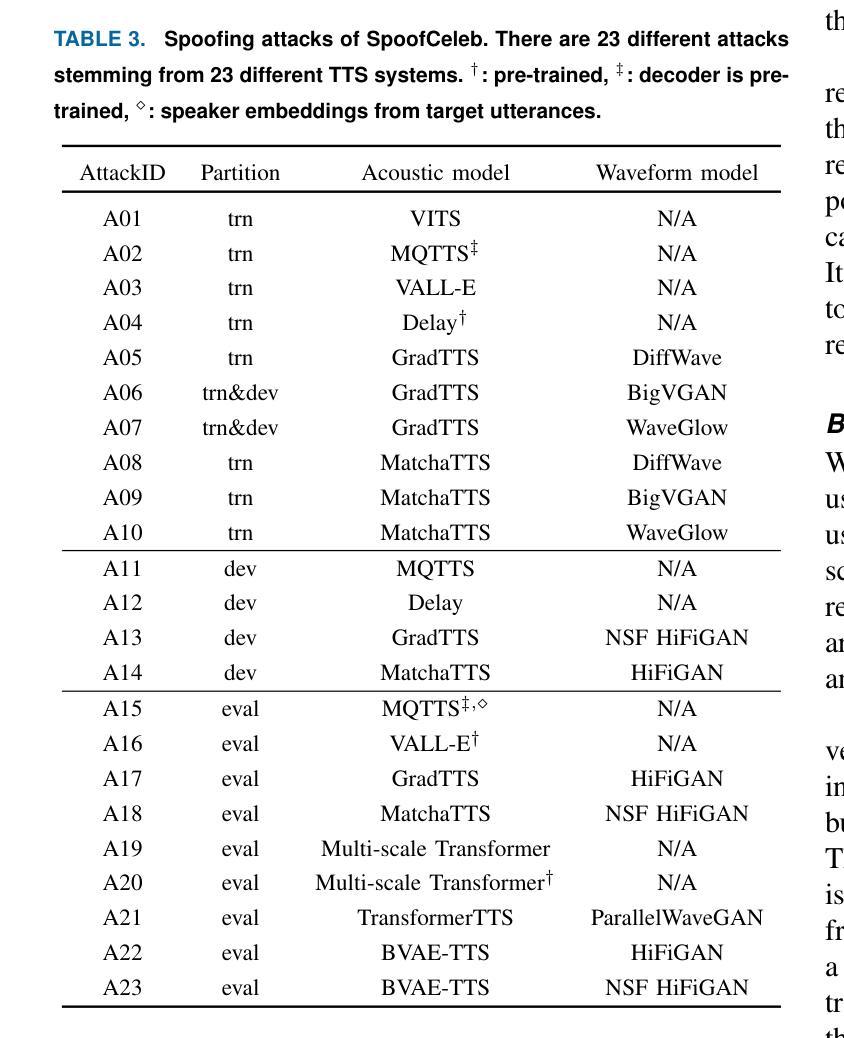
This paper introduces SpoofCeleb, a dataset designed for Speech Deepfake Detection (SDD) and Spoofing-robust Automatic Speaker Verification (SASV), utilizing source data from real-world conditions and spoofing attacks generated by Text-To-Speech (TTS) systems also trained on the same real-world data. Robust recognition systems require speech data recorded in varied acoustic environments with different levels of noise to be trained. However, current datasets typically include clean, high-quality recordings (bona fide data) due to the requirements for TTS training; studio-quality or well-recorded read speech is typically necessary to train TTS models. Current SDD datasets also have limited usefulness for training SASV models due to insufficient speaker diversity. SpoofCeleb leverages a fully automated pipeline we developed that processes the VoxCeleb1 dataset, transforming it into a suitable form for TTS training. We subsequently train 23 contemporary TTS systems. SpoofCeleb comprises over 2.5 million utterances from 1,251 unique speakers, collected under natural, real-world conditions. The dataset includes carefully partitioned training, validation, and evaluation sets with well-controlled experimental protocols. We present the baseline results for both SDD and SASV tasks. All data, protocols, and baselines are publicly available at https://jungjee.github.io/spoofceleb.
本文介绍了SpoofCeleb数据集,该数据集旨在用于语音深度伪造检测(SDD)和防欺骗自动说话人验证(SASV)。它利用来自真实世界条件的源数据以及由文本到语音(TTS)系统生成的欺骗攻击数据,这些TTS系统也在相同的真实世界数据上进行训练。鲁棒的识别系统需要记录在不同声学环境和不同噪声级别的语音数据进行训练。然而,由于文本到语音的训练要求,当前的数据集通常包含干净的高质量录音(真实数据);工作室质量或良好记录的朗读语音通常是训练TTS模型所必需的。当前的SDD数据集在训练SASV模型方面的用途有限,因为缺乏足够的说话人多样性。SpoofCeleb利用我们开发的完全自动化管道处理VoxCeleb1数据集,将其转化为适合TTS训练的形式。我们随后训练了23个当代的TTS系统。SpoofCeleb包含来自1251个不同说话人的超过250万条语音片段,这些语音片段是在自然、真实世界的条件下收集的。该数据集包括经过精心划分的训练集、验证集和评估集,并配有控制良好的实验协议。我们为SDD和SASV任务提供了基线结果。所有数据、协议和基线都在https://jungjee.github.io/spoofceleb上公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE OJSP. Official document lives at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=10839331
Summary:
本文介绍了SpoofCeleb数据集,该数据集专为语音深度伪造检测(SDD)和防篡改自动语音识别(SASV)设计。它利用真实世界条件下的源数据和由文本到语音(TTS)系统生成的欺骗攻击数据。SpoofCeleb使用全自动处理流程处理VoxCeleb数据集,并训练了多个TTS系统。该数据集包含超过250万条演讲记录,涉及数千个独特发言人的自然声音和自然条件录音,并对实验协议进行了严格控制。该数据集已在网络上公开发布并提供基线结果。
Key Takeaways:
- SpoofCeleb数据集专为语音深度伪造检测(SDD)和防篡改自动语音识别(SASV)设计。
- 数据集使用真实世界条件下的源数据和由文本到语音(TTS)系统生成的欺骗攻击数据。
- 当前数据集通常包括干净的高质量录音,但为了满足TTS训练的要求,需要训练语音识别系统以适应不同噪声级别的各种声学环境。
- 数据集包含了大量的发言人和多样的演讲内容,能够应对现有的语音数据集局限性,使得它非常适用于开发训练对攻击有强大鲁棒性的自动语音识别系统。
- SpoofCeleb采用了全自动处理流程来处理VoxCeleb数据集,并训练了多个TTS系统来生成欺骗语音数据。
- 数据集包含超过250万条演讲记录,涉及数千个独特发言人的自然声音和自然条件录音。
点此查看论文截图