⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-17 更新
Change State Space Models for Remote Sensing Change Detection
Authors:Elman Ghazaei, Erchan Aptoula
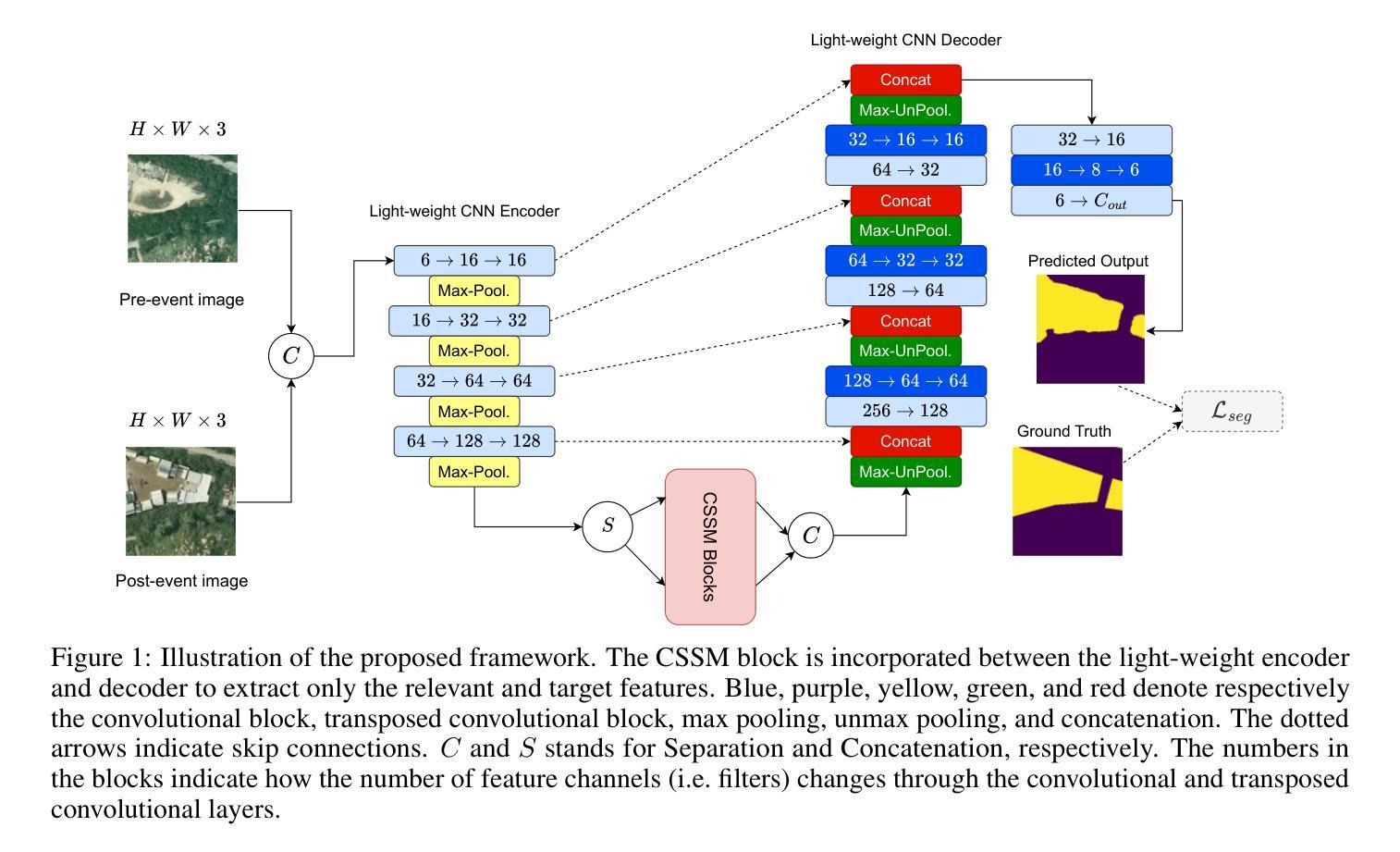
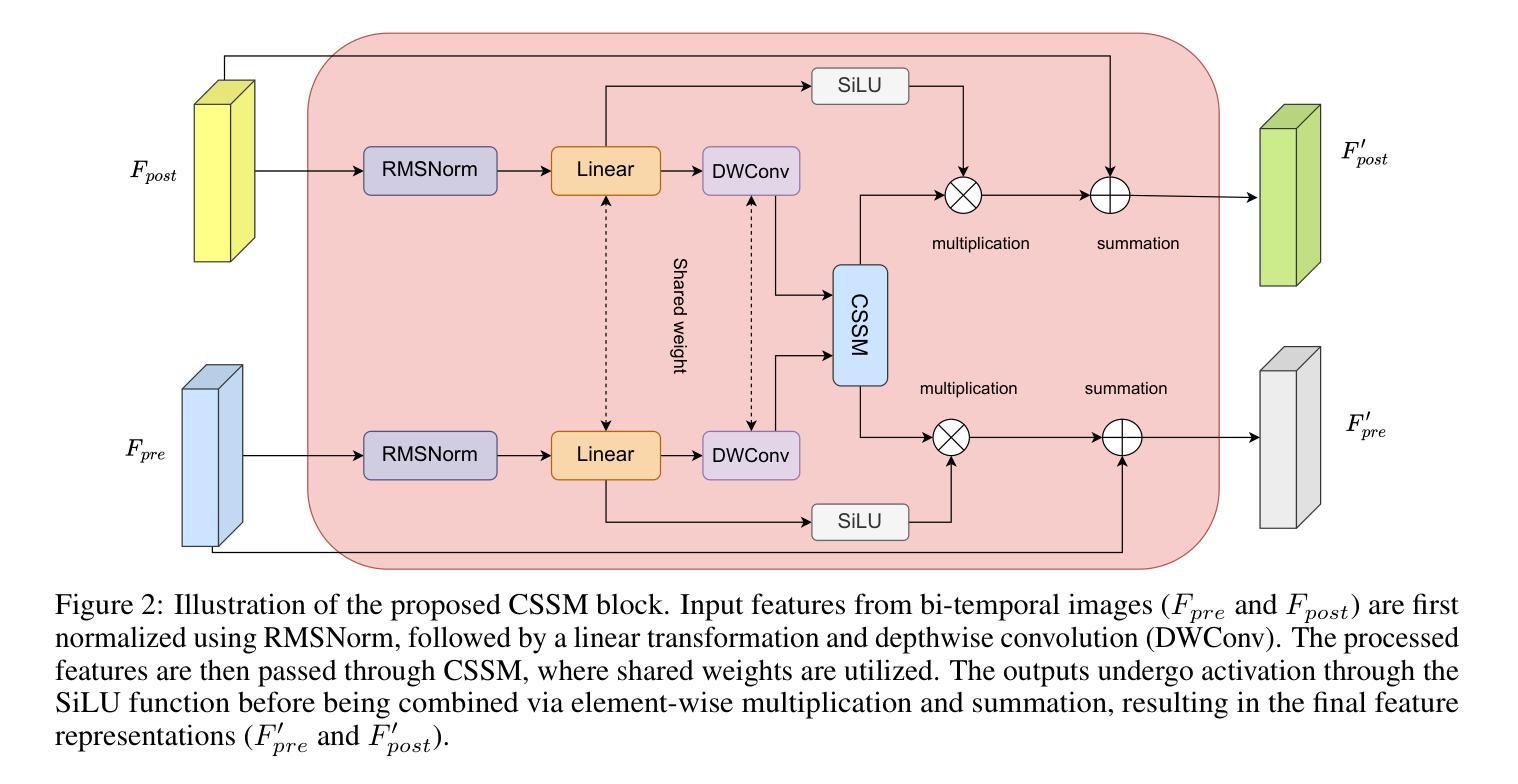
Despite their frequent use for change detection, both ConvNets and Vision transformers (ViT) exhibit well-known limitations, namely the former struggle to model long-range dependencies while the latter are computationally inefficient, rendering them challenging to train on large-scale datasets. Vision Mamba, an architecture based on State Space Models has emerged as an alternative addressing the aforementioned deficiencies and has been already applied to remote sensing change detection, though mostly as a feature extracting backbone. In this article the Change State Space Model is introduced, that has been specifically designed for change detection by focusing on the relevant changes between bi-temporal images, effectively filtering out irrelevant information. By concentrating solely on the changed features, the number of network parameters is reduced, enhancing significantly computational efficiency while maintaining high detection performance and robustness against input degradation. The proposed model has been evaluated via three benchmark datasets, where it outperformed ConvNets, ViTs, and Mamba-based counterparts at a fraction of their computational complexity. The implementation will be made available at https://github.com/Elman295/CSSM upon acceptance.
尽管卷积神经网络(ConvNets)和视觉转换器(ViT)经常用于变化检测,但它们都表现出了一些众所周知的局限性。具体来说,前者难以建模长距离依赖关系,而后者计算效率低下,难以在大型数据集上进行训练。基于状态空间模型的Vision Mamba架构作为替代方案应运而生,解决了上述缺陷,并已应用于遥感变化检测,但大多作为特征提取的骨干。本文介绍了专为变化检测而设计的变化状态空间模型(Change State Space Model)。该模型关注双时态图像之间的相关变化,有效地过滤了无关信息。通过专注于变化特征,减少了网络参数的数量,在保持高检测性能和对抗输入退化稳健性的同时,显著提高了计算效率。所提出的模型通过三个基准数据集进行了评估,在计算复杂度较低的情况下,其性能优于ConvNets、ViTs和基于Mamba的同类模型。代码实现将在https://github.com/Elman295/CSSM(接受后)提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对变化检测任务的新型视觉模型——变化状态空间模型(CSSM)。该模型基于状态空间模型设计,旨在解决卷积神经网络(ConvNets)和视觉转换器(ViT)在处理大规模数据集时的局限性。通过专注于双时态图像之间的相关变化,CSSM有效过滤掉无关信息,减少网络参数数量,显著提高计算效率,同时保持良好的检测性能和抗输入干扰的鲁棒性。在三个基准数据集上的评估显示,CSSM在性能上优于ConvNets、ViTs和基于Mamba的模型,同时计算复杂度大幅降低。
Key Takeaways
- 变化状态空间模型(CSSM)是一种针对变化检测任务的新型视觉模型。
- CSSM解决了卷积神经网络(ConvNets)和视觉转换器(ViT)在处理大规模数据集时的局限性。
- CSSM专注于双时态图像之间的相关变化,过滤掉无关信息。
- CSSM通过减少网络参数数量,显著提高了计算效率。
- CSSM在变化检测任务中表现出良好的性能和抗输入干扰的鲁棒性。
- 在三个基准数据集上的评估显示,CSSM优于其他模型,如ConvNets、ViTs和基于Mamba的模型。
点此查看论文截图


Embedding Radiomics into Vision Transformers for Multimodal Medical Image Classification
Authors:Zhenyu Yang, Haiming Zhu, Rihui Zhang, Haipeng Zhang, Jianliang Wang, Chunhao Wang, Minbin Chen, Fang-Fang Yin
Background: Deep learning has significantly advanced medical image analysis, with Vision Transformers (ViTs) offering a powerful alternative to convolutional models by modeling long-range dependencies through self-attention. However, ViTs are inherently data-intensive and lack domain-specific inductive biases, limiting their applicability in medical imaging. In contrast, radiomics provides interpretable, handcrafted descriptors of tissue heterogeneity but suffers from limited scalability and integration into end-to-end learning frameworks. In this work, we propose the Radiomics-Embedded Vision Transformer (RE-ViT) that combines radiomic features with data-driven visual embeddings within a ViT backbone. Purpose: To develop a hybrid RE-ViT framework that integrates radiomics and patch-wise ViT embeddings through early fusion, enhancing robustness and performance in medical image classification. Methods: Following the standard ViT pipeline, images were divided into patches. For each patch, handcrafted radiomic features were extracted and fused with linearly projected pixel embeddings. The fused representations were normalized, positionally encoded, and passed to the ViT encoder. A learnable [CLS] token aggregated patch-level information for classification. We evaluated RE-ViT on three public datasets (including BUSI, ChestXray2017, and Retinal OCT) using accuracy, macro AUC, sensitivity, and specificity. RE-ViT was benchmarked against CNN-based (VGG-16, ResNet) and hybrid (TransMed) models. Results: RE-ViT achieved state-of-the-art results: on BUSI, AUC=0.950+/-0.011; on ChestXray2017, AUC=0.989+/-0.004; on Retinal OCT, AUC=0.986+/-0.001, which outperforms other comparison models. Conclusions: The RE-ViT framework effectively integrates radiomics with ViT architectures, demonstrating improved performance and generalizability across multimodal medical image classification tasks.
背景:深度学习已经显著推进了医学图像分析的发展。通过自注意力进行长距离依赖建模,Vision Transformer(ViT)为卷积模型提供了强大的替代方案。然而,ViT本质上需要大量的数据,并且缺乏特定领域的归纳偏见,这在医学影像中限制了其适用性。相比之下,放射组学提供了可解释的组织异质性手工描述符,但受限于可扩展性和整合到端到端学习框架的能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了Radiomics-Embedded Vision Transformer(RE-ViT),它将放射组学特征与数据驱动的视觉嵌入相结合在一个ViT主干中。目的:为了开发一个混合RE-ViT框架,该框架通过早期融合整合放射组学和补丁式ViT嵌入,提高在医学图像分类中的稳健性和性能。方法:遵循标准的ViT管道,图像被分成补丁。对于每个补丁,手工提取放射组学特征并与线性投影的像素嵌入融合。融合后的表示被归一化、位置编码并传递给ViT编码器。一个可学习的[CLS]标记聚合了补丁级别的信息用于分类。我们在三个公共数据集(包括BUSI、ChestXray2017和Retinal OCT)上评估了RE-ViT,使用准确度、宏AUC、灵敏度和特异性。RE-ViT与基于CNN(VGG-16、ResNet)的模型和混合(TransMed)模型进行了比较。结果:RE-ViT达到了最先进的成果:在BUSI上,AUC=0.950±0.011;在ChestXray2017上,AUC=0.989±0.004;在视网膜OCT上,AUC=0.986±0.001,这超过了其他对比模型的表现。结论:RE-ViT框架有效地将放射组学与ViT架构相结合,显示出在多模态医学图像分类任务中改进的性能和通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文提出一种融合放射组学与Vision Transformer(ViT)的混合框架RE-ViT,旨在提高医疗图像分类的稳健性和性能。RE-ViT结合了放射组学特征和数据驱动的视觉嵌入,通过早期融合策略增强医疗图像分类的鲁棒性和性能。在三个公共数据集上的实验结果表明,RE-ViT达到了最先进的性能,并在不同医疗图像分类任务中展现出良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- RE-ViT结合了放射组学特征(手工艺品特征)与Vision Transformer(ViT)进行数据驱动的视觉嵌入,形成混合框架。
- RE-ViT通过早期融合策略,将放射组学特征与ViT嵌入结合,以提高医疗图像分类的稳健性和性能。
- 实验在三个公共数据集上进行,包括BUSI、ChestXray2017和Retinal OCT,使用准确性、宏观AUC、敏感性和特异性进行评估。
- RE-ViT达到了最先进的性能,表现出较高的分类准确性。
- RE-ViT框架具有良好的泛化能力,适用于多种医疗图像分类任务。
- 与CNN和混合模型相比,RE-ViT展现出更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

LPViT: Low-Power Semi-structured Pruning for Vision Transformers
Authors:Kaixin Xu, Zhe Wang, Chunyun Chen, Xue Geng, Jie Lin, Mohamed M. Sabry Aly, Xulei Yang, Min Wu, Xiaoli Li, Weisi Lin
Vision transformers have emerged as a promising alternative to convolutional neural networks for various image analysis tasks, offering comparable or superior performance. However, one significant drawback of ViTs is their resource-intensive nature, leading to increased memory footprint, computation complexity, and power consumption. To democratize this high-performance technology and make it more environmentally friendly, it is essential to compress ViT models, reducing their resource requirements while maintaining high performance. In this paper, we introduce a new block-structured pruning to address the resource-intensive issue for ViTs, offering a balanced trade-off between accuracy and hardware acceleration. Unlike unstructured pruning or channel-wise structured pruning, block pruning leverages the block-wise structure of linear layers, resulting in more efficient matrix multiplications. To optimize this pruning scheme, our paper proposes a novel hardware-aware learning objective that simultaneously maximizes speedup and minimizes power consumption during inference, tailored to the block sparsity structure. This objective eliminates the need for empirical look-up tables and focuses solely on reducing parametrized layer connections. Moreover, our paper provides a lightweight algorithm to achieve post-training pruning for ViTs, utilizing second-order Taylor approximation and empirical optimization to solve the proposed hardware-aware objective. Extensive experiments on ImageNet are conducted across various ViT architectures, including DeiT-B and DeiT-S, demonstrating competitive performance with other pruning methods and achieving a remarkable balance between accuracy preservation and power savings. Especially, we achieve 3.93x speedup on dedicated hardware and GPUs respectively for DeiT-B, and a power reduction by 1.4x on GPUs. Code released to https://github.com/Akimoto-Cris/LPViT.
视觉转换器(Vision Transformers)作为一种有前景的替代卷积神经网络(CNN)的方法,在各种图像分析任务中展现出相当或更优越的性能。然而,ViTs的一个重大缺点是它们资源密集型的特点,导致内存占用增加、计算复杂性和功耗增加。为了普及这种高性能技术并使其更加环保,压缩ViT模型至关重要,在保持高性能的同时减少其资源需求。在本文中,我们引入了一种新的块结构化剪枝来解决ViTs的资源密集问题,在准确度和硬件加速之间实现了平衡。与传统的非结构化剪枝或通道结构化剪枝不同,块剪枝利用线性层的块结构,从而实现更有效的矩阵乘法。为了优化这种剪枝方案,我们的论文提出了一个全新的硬件感知学习目标,同时最大化推理速度并最小化功耗,针对块稀疏结构进行定制。这一目标消除了对经验查找表的需求,并专注于减少参数化层连接。此外,我们的论文还提出了一种轻量级的算法来实现ViTs的训练后剪枝,利用二阶泰勒近似和实证优化来解决所提出的硬件感知目标。在ImageNet上进行了广泛的实验,涵盖了各种ViT架构,包括DeiT-B和DeiT-S,与现有剪枝方法相比展现出竞争力,并在保持准确度和节省功耗之间取得了显著平衡。特别是,我们在专用硬件和GPU上为DeiT-B实现了3.93倍的加速,并在GPU上实现了1.4倍的功耗降低。代码已发布至https://github.com/Akimoto-Cris/LPViT。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉转换器(Vision Transformer,ViT)已成为卷积神经网络在各种图像分析任务中的有前途的替代品,其性能相当或更优越。然而,ViT的一大缺点是资源密集,导致内存占用、计算复杂性和功耗增加。为了普及这种高性能技术并使其更加环保,压缩ViT模型至关重要,需要在减少资源需求的同时保持高性能。本文介绍了一种新的块结构剪枝来解决ViT的资源密集问题,在准确性和硬件加速之间提供了平衡。与无结构剪枝或通道结构化剪枝不同,块剪枝利用线性层的块结构,实现更有效的矩阵乘法。为了优化这种剪枝方案,本文提出了一个全新的硬件感知学习目标,旨在最大化速度并最小化推理过程中的功耗,针对块稀疏结构。此外,本文提供了一种轻量级的算法,用于在训练后对ViT进行剪枝,利用二阶泰勒近似和实证优化来解决所提出的硬件感知目标。在ImageNet上进行的大量实验表明,在各种ViT架构上,包括DeiT-B和DeiT-S,该方法在竞争激烈的剪枝方法中表现出竞争力,并在保持准确性和节省电力方面取得了显著平衡。代码已发布在https://github.com/Akimoto-Cris/LPViT。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉转换器(Vision Transformer, ViT)已成为图像分析任务中的有前途的CNN替代品。
- ViT存在资源密集的问题,导致内存占用、计算复杂性和功耗增加。
- 引入新的块结构剪枝方法来解决ViT的资源密集问题,实现准确性与硬件加速之间的平衡。
- 块剪枝利用线性层的块结构,不同于无结构剪枝或通道结构化剪枝,更加高效。
- 提出硬件感知学习目标,旨在最大化速度并最小化推理过程中的功耗。
- 提供了一种轻量级算法进行训练后剪枝,结合二阶泰勒近似和实证优化来解决硬件感知目标。
点此查看论文截图


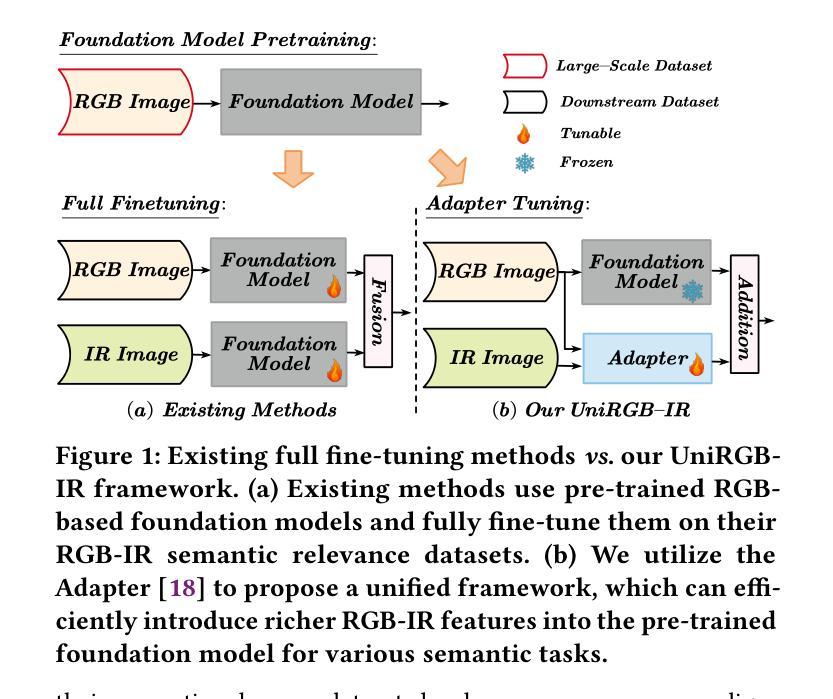
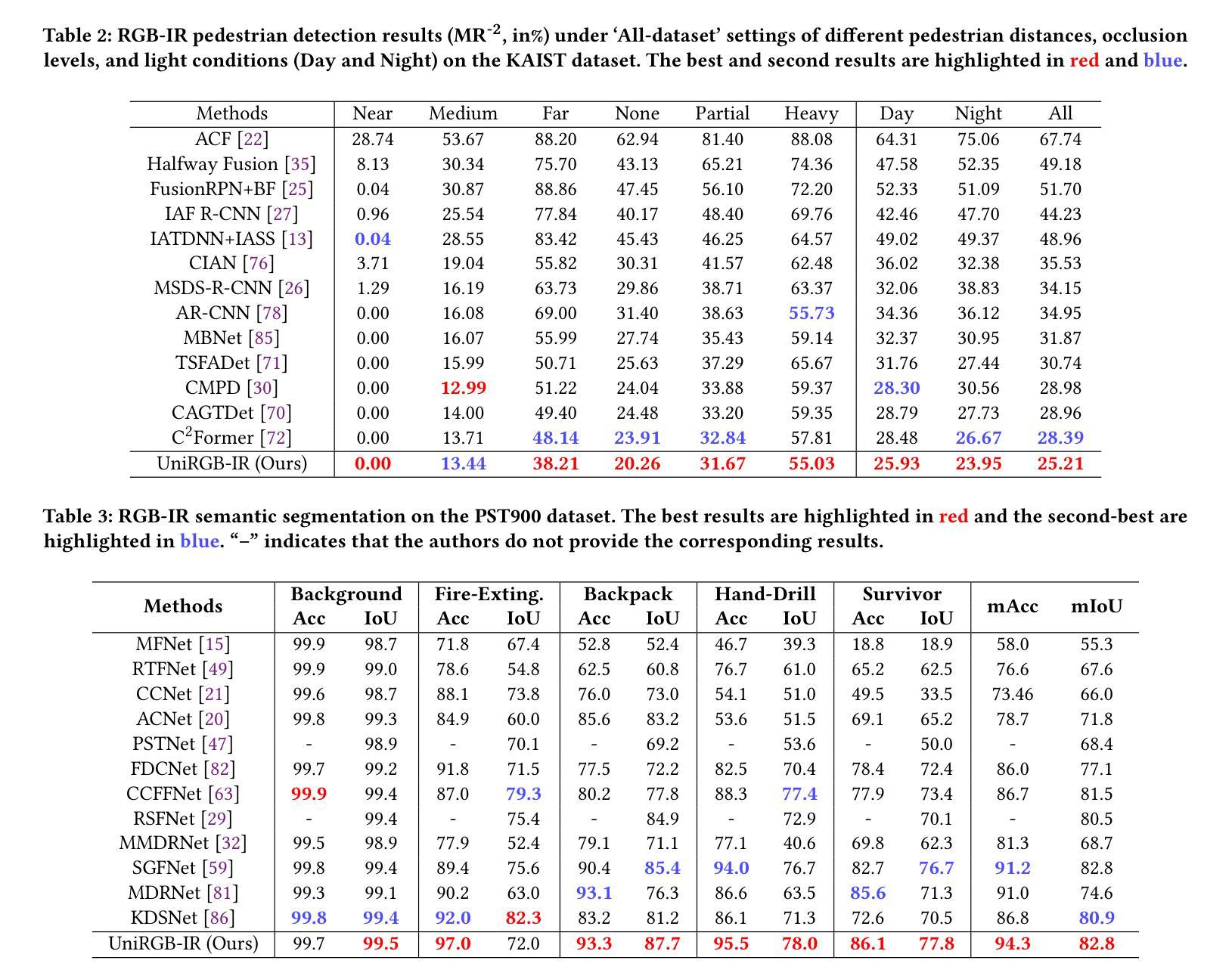
UniRGB-IR: A Unified Framework for Visible-Infrared Semantic Tasks via Adapter Tuning
Authors:Maoxun Yuan, Bo Cui, Tianyi Zhao, Jiayi Wang, Shan Fu, Xue Yang, Xingxing Wei
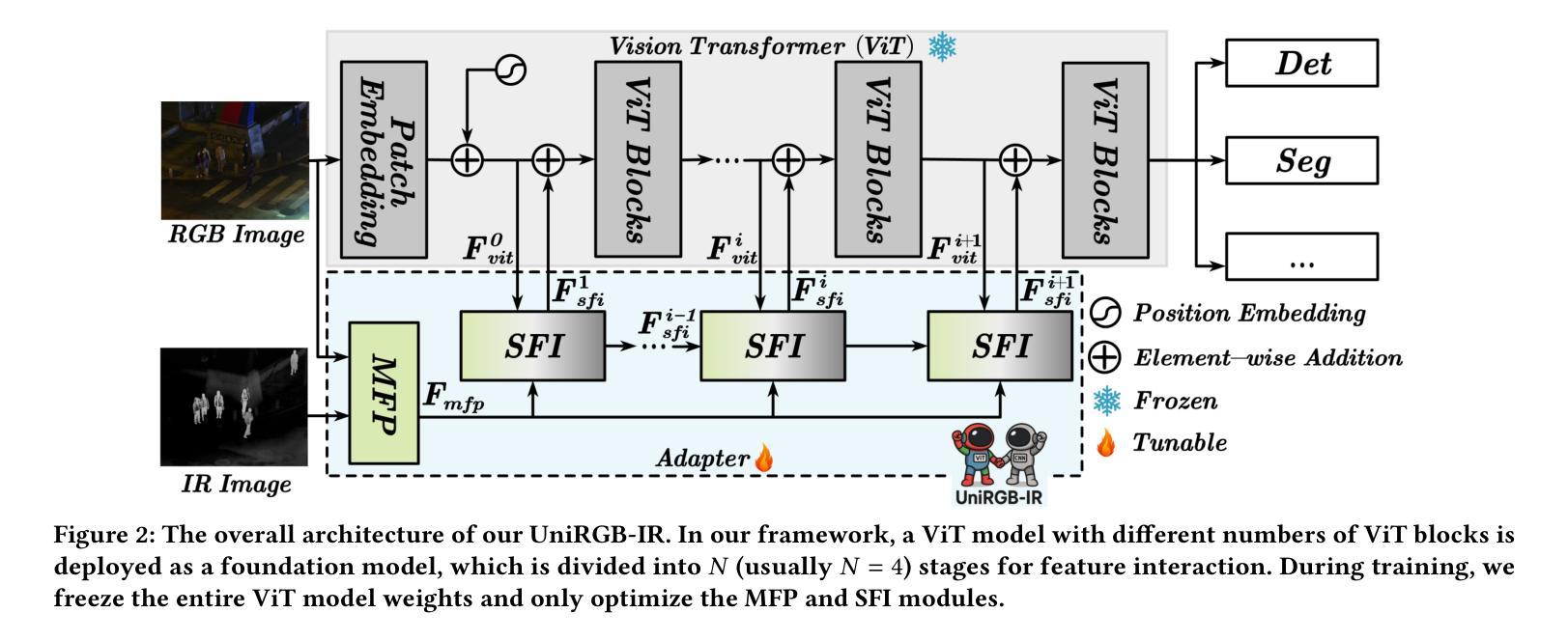
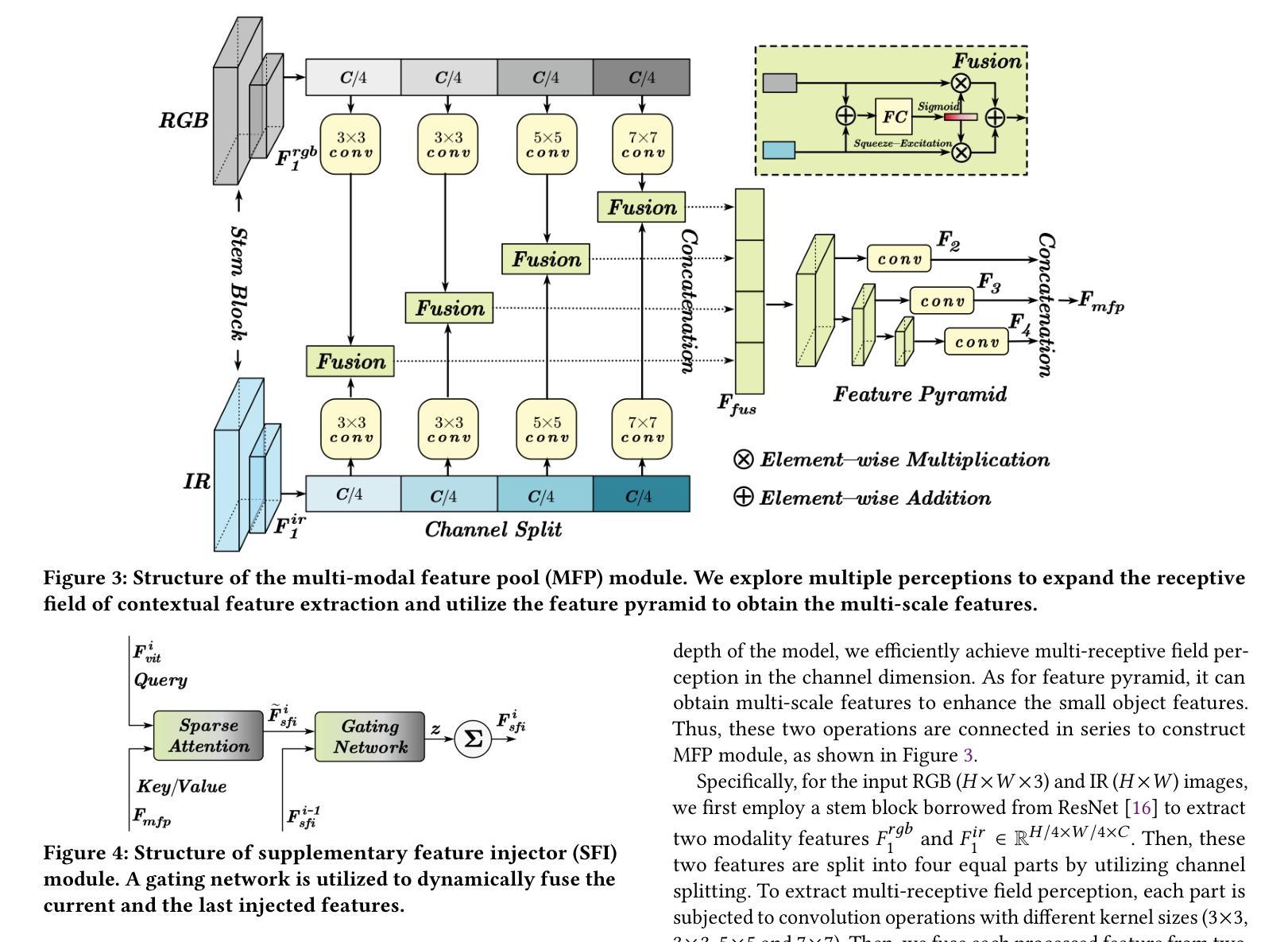
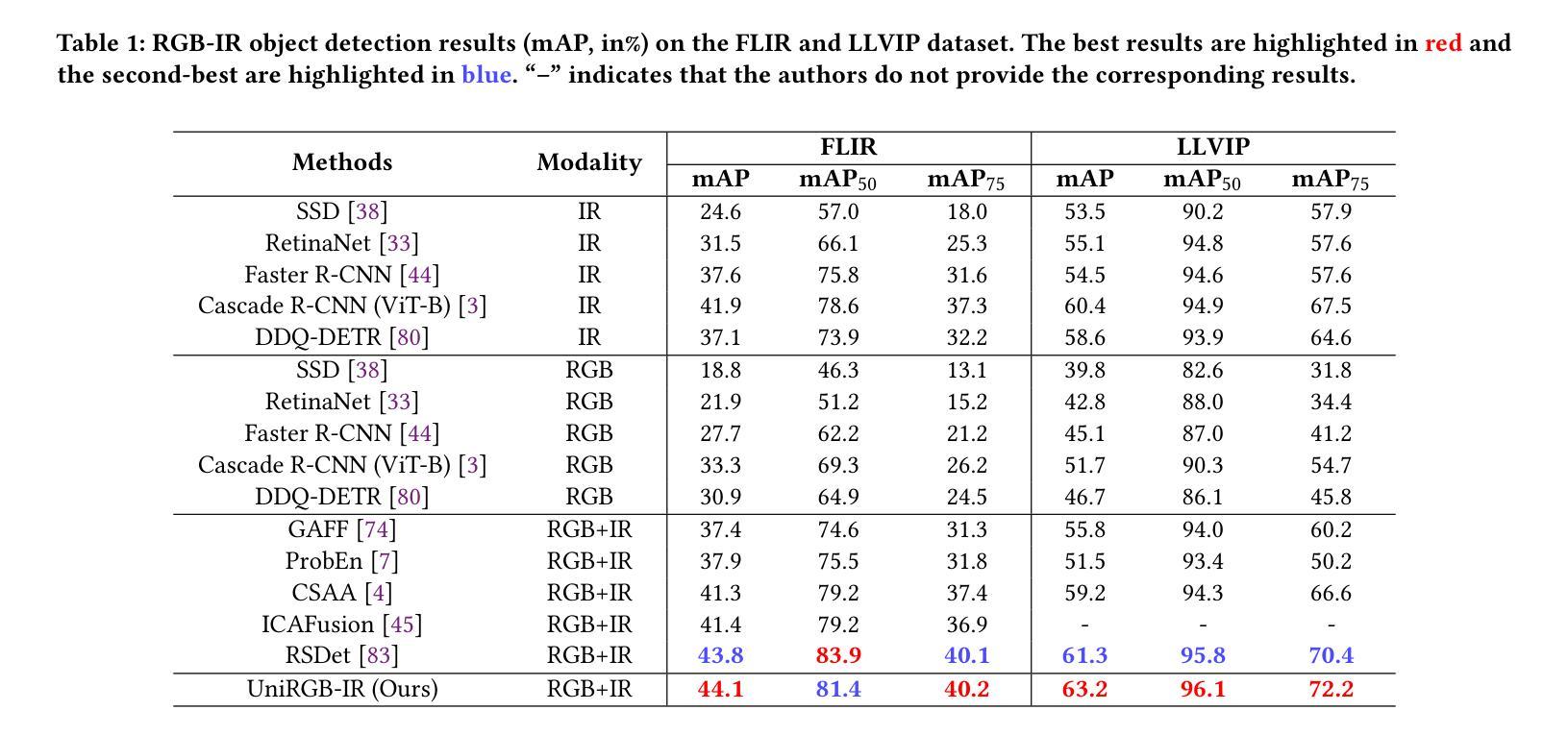
Semantic analysis on visible (RGB) and infrared (IR) images has gained significant attention due to their enhanced accuracy and robustness under challenging conditions including low-illumination and adverse weather. However, due to the lack of pre-trained foundation models on the large-scale infrared image datasets, existing methods prefer to design task-specific frameworks and directly fine-tune them with pre-trained foundation models on their RGB-IR semantic relevance datasets, which results in poor scalability and limited generalization. To address these limitations, we propose UniRGB-IR, a scalable and efficient framework for RGB-IR semantic tasks that introduces a novel adapter mechanism to effectively incorporate rich multi-modal features into pre-trained RGB-based foundation models. Our framework comprises three key components: a vision transformer (ViT) foundation model, a Multi-modal Feature Pool (MFP) module, and a Supplementary Feature Injector (SFI) module. The MFP and SFI modules cooperate with each other as an adpater to effectively complement the ViT features with the contextual multi-scale features. During training process, we freeze the entire foundation model to inherit prior knowledge and only optimize the MFP and SFI modules. Furthermore, to verify the effectiveness of our framework, we utilize the ViT-Base as the pre-trained foundation model to perform extensive experiments. Experimental results on various RGB-IR semantic tasks demonstrate that our method can achieve state-of-the-art performance. The source code and results are available at https://github.com/PoTsui99/UniRGB-IR.git.
针对可见光(RGB)和红外(IR)图像的语义分析因其能在低光照和恶劣天气等挑战性条件下提高准确性和稳健性而受到广泛关注。然而,由于缺乏大规模红外图像数据集上的预训练基础模型,现有方法更倾向于设计针对特定任务的框架,并使用预训练的RGB-IR语义相关性数据集对其进行微调,这导致了较差的可扩展性和有限的泛化能力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了UniRGB-IR,这是一个用于RGB-IR语义任务的可扩展且高效的框架,它引入了一种新的适配器机制,可以有效地将丰富的多模式特征融入到基于预训练RGB的基础模型中。我们的框架包括三个关键组件:视觉转换器(ViT)基础模型、多模式特征池(MFP)模块和补充特征注入器(SFI)模块。MFP和SFI模块相互协作,作为适配器,有效地将上下文多尺度特征与ViT特征相结合。在训练过程中,我们冻结整个基础模型以继承先验知识,并仅优化MFP和SFI模块。此外,为了验证我们框架的有效性,我们利用ViT-Base作为预训练基础模型进行了大量实验。在各种RGB-IR语义任务上的实验结果证明,我们的方法可以达到最先进的性能。源代码和结果可在https://github.com/PoTsui99/UniRGB-IR.git获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种针对RGB-IR语义任务的可扩展且高效的框架UniRGB-IR,通过引入新型适配器机制,有效整合多模态特征到预训练的RGB基础模型中。该框架包含三个关键组件:视觉转换器(ViT)基础模型、多模态特征池(MFP)模块和补充特征注入器(SFI)模块。通过冻结基础模型,仅优化MFP和SFI模块,实现知识的继承与多尺度特征的上下文补充。实验证明,该方法在多种RGB-IR语义任务上达到先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- UniRGB-IR是一个针对RGB-IR语义任务的新型框架,旨在解决现有方法在面对红外图像时的可扩展性和泛化能力问题。
- 该框架引入了一种新型适配器机制,通过多模态特征池(MFP)和补充特征注入器(SFI)模块,有效整合RGB和红外图像的多模态特征。
- UniRGB-IR采用预训练的RGB基础模型,如ViT-Base,并通过冻结基础模型,只优化MFP和SFI模块,实现知识的继承与优化。
- 实验证明,UniRGB-IR在多种RGB-IR语义任务上表现出卓越性能。
- 该框架的源代码和实验结果已公开,便于后续研究与应用。
- UniRGB-IR框架适用于低光照和恶劣天气等挑战条件下的图像语义分析。
点此查看论文截图

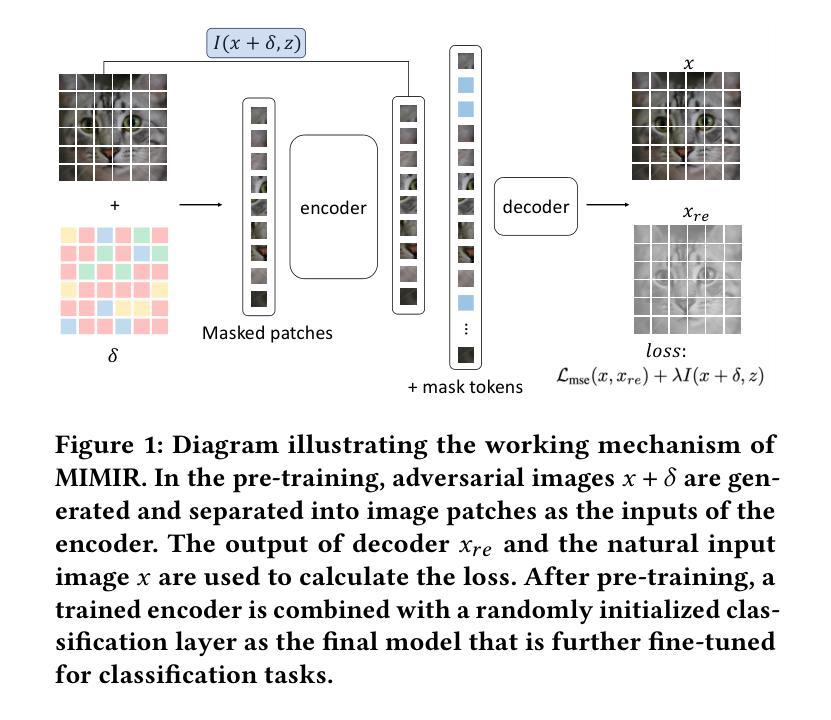
MIMIR: Masked Image Modeling for Mutual Information-based Adversarial Robustness
Authors:Xiaoyun Xu, Shujian Yu, Zhuoran Liu, Stjepan Picek
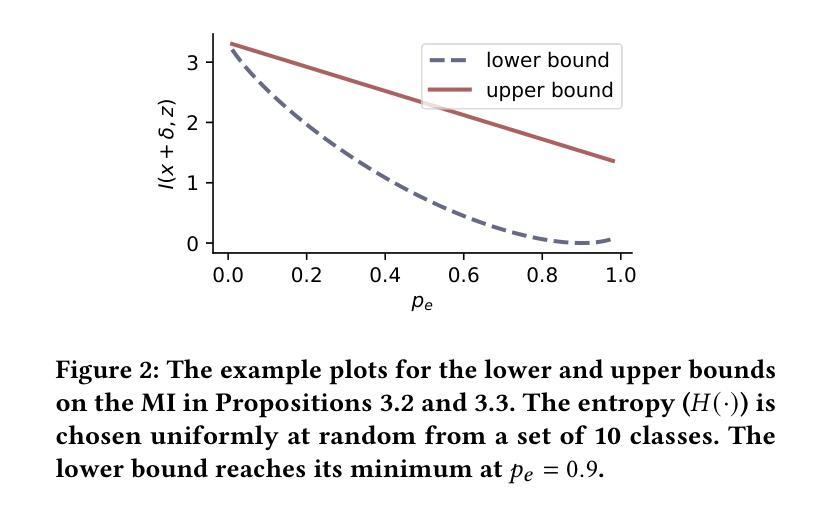
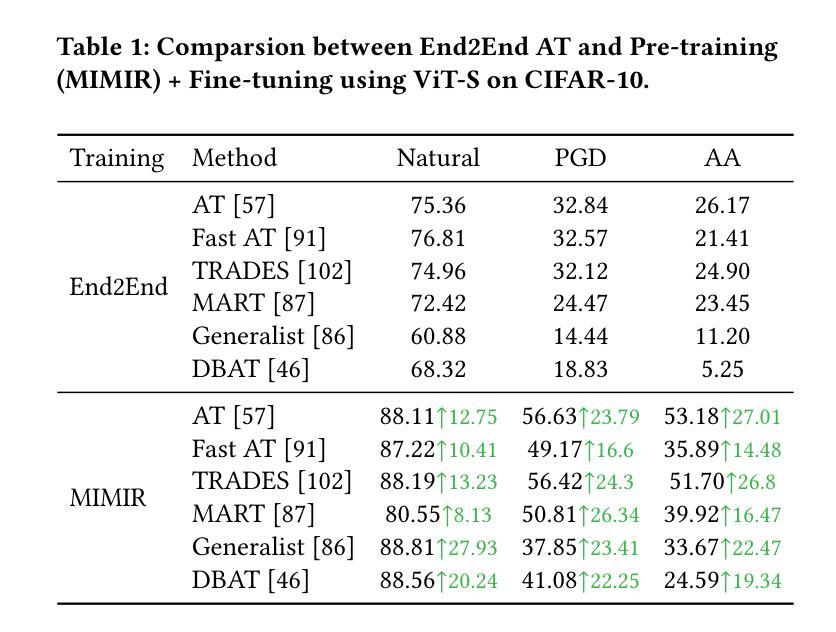
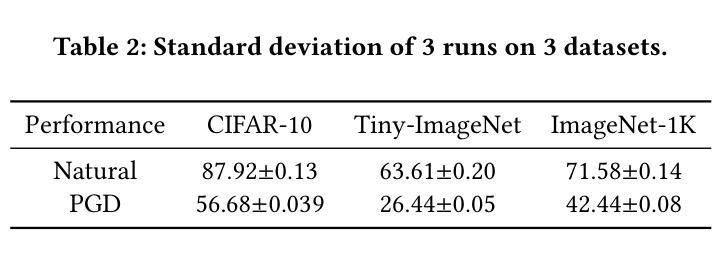
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have emerged as a fundamental architecture and serve as the backbone of modern vision-language models. Despite their impressive performance, ViTs exhibit notable vulnerability to evasion attacks, necessitating the development of specialized Adversarial Training (AT) strategies tailored to their unique architecture. While a direct solution might involve applying existing AT methods to ViTs, our analysis reveals significant incompatibilities, particularly with state-of-the-art (SOTA) approaches such as Generalist (CVPR 2023) and DBAT (USENIX Security 2024). This paper presents a systematic investigation of adversarial robustness in ViTs and provides a novel theoretical Mutual Information (MI) analysis in its autoencoder-based self-supervised pre-training. Specifically, we show that MI between the adversarial example and its latent representation in ViT-based autoencoders should be constrained via derived MI bounds. Building on this insight, we propose a self-supervised AT method, MIMIR, that employs an MI penalty to facilitate adversarial pre-training by masked image modeling with autoencoders. Extensive experiments on CIFAR-10, Tiny-ImageNet, and ImageNet-1K show that MIMIR can consistently provide improved natural and robust accuracy, where MIMIR outperforms SOTA AT results on ImageNet-1K. Notably, MIMIR demonstrates superior robustness against unforeseen attacks and common corruption data and can also withstand adaptive attacks where the adversary possesses full knowledge of the defense mechanism.
视觉转换器(ViTs)已经成为一种基本架构,并作为现代视觉语言模型的核心。尽管ViTs性能令人印象深刻,但它们对逃避攻击表现出明显的脆弱性,因此需要针对其独特架构开发专门的对抗性训练(AT)策略。虽然直接解决方案可能涉及将现有AT方法应用于ViTs,但我们的分析揭示了重大不兼容问题,尤其是与最新(SOTA)方法如Generalist(CVPR 2023)和DBAT(USENIX Security 2024)。本文系统地研究了ViTs中的对抗性稳健性,并在其基于自编码器的自监督预训练中提供了新型理论上的互信息(MI)分析。具体来说,我们表明,ViT基自编码器中的对抗样本与其潜在表示的互信息应通过推导的MI边界来约束。基于这一见解,我们提出了一种自监督AT方法MIMIR,该方法采用MI惩罚措施,通过带有自编码器的掩码图像建模来促进对抗性预训练。在CIFAR-10、Tiny-ImageNet和ImageNet-1K上的广泛实验表明,MIMIR可以持续提供改进的自然和稳健精度,并且在ImageNet-1K上MIMIR超越了SOTA AT的结果。值得注意的是,MIMIR在应对未曾预见到的攻击和常见腐败数据方面表现出卓越的稳健性,并且能够在对手完全了解防御机制的情况下抵御适应性攻击。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了Vision Transformers(ViTs)在面临对抗性攻击时的脆弱性,并提出了一种针对ViTs的自监督对抗训练(MIMIR)方法。该方法基于互信息(MI)理论,通过约束对抗样本与ViT自编码器潜表征之间的互信息,提高了模型的鲁棒性。实验表明,MIMIR在多个数据集上能显著提高自然和鲁棒精度,并对未知攻击和常见腐败数据具有优秀抗性。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 面临对抗性攻击的威胁,需要专门的对抗训练(AT)策略。
- 现有先进(SOTA)的AT方法在与ViTs结合时存在不兼容问题。
- 论文提出通过约束对抗样本与ViT自编码器潜表征之间的互信息(MI)来提高ViTs的鲁棒性。
- 基于此理论,论文提出了一种自监督的AT方法MIMIR。
- MIMIR在多个数据集上实验,表现优于SOTA的AT结果。
- MIMIR对未知攻击和常见腐败数据具有优秀抗性。
点此查看论文截图