⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-18 更新
Comparative Evaluation of Radiomics and Deep Learning Models for Disease Detection in Chest Radiography
Authors:Zhijin He, Alan B. McMillan
The application of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging has revolutionized diagnostic practices, enabling advanced analysis and interpretation of radiological data. This study presents a comprehensive evaluation of radiomics-based and deep learning-based approaches for disease detection in chest radiography, focusing on COVID-19, lung opacity, and viral pneumonia. While deep learning models, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs), learn directly from image data, radiomics-based models extract and analyze quantitative features, potentially providing advantages in data-limited scenarios. This study systematically compares the diagnostic accuracy and robustness of various AI models, including Decision Trees, Gradient Boosting, Random Forests, Support Vector Machines (SVM), and Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLP) for radiomics, against state-of-the-art computer vision deep learning architectures. Performance metrics across varying sample sizes reveal insights into each model’s efficacy, highlighting the contexts in which specific AI approaches may offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities. The results aim to inform the integration of AI-driven diagnostic tools in clinical practice, particularly in automated and high-throughput environments where timely, reliable diagnosis is critical. This comparative study addresses an essential gap, establishing guidance for the selection of AI models based on clinical and operational needs.
人工智能(AI)在医学成像领域的应用已经彻底改变了诊断实践,使放射学数据的先进分析和解释成为可能。本研究全面评估了基于放射学组和基于深度学习的方法在胸部放射摄影中检测疾病的性能,重点关注COVID-19、肺部不透光和病毒性肺炎。深度学习方法,特别是卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)直接从图像数据中学习,而基于放射学的模型则提取和分析定量特征,可能在数据有限的情况下具有潜在优势。本研究系统地比较了各种人工智能模型的诊断准确性和稳健性,包括用于放射学决策树、梯度提升、随机森林、支持向量机(SVM)和多层感知器(MLP)与最先进的计算机视觉深度学习架构之间的比较。不同样本量下的性能指标揭示了每种模型的有效性,并突出了特定人工智能方法可能在何种情况下提供增强的诊断能力。研究结果旨在为将AI驱动的诊断工具整合到临床实践提供信息,特别是在及时可靠的诊断至关重要的自动化和高通量环境中。这项比较研究解决了关键空白,根据临床和运营需求为选择AI模型提供了指导。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能在医学成像领域的应用已经彻底改变了诊断实践,使放射学数据的分析和解读更为先进。本研究全面评估了基于放射组学和基于深度学习的方法在胸部放射学中对疾病检测(特别是COVID-19、肺部不透明度和病毒性肺炎)的应用。研究系统地比较了各种AI模型的诊断准确性和稳健性,包括用于放射组学的决策树、梯度提升、随机森林、支持向量机(SVM)和多层感知器(MLP)以及先进的计算机视觉深度学习架构。研究结果为整合AI驱动的诊断工具于临床实践提供了信息,特别是在需要自动化和大规模处理的环境中,及时的可靠诊断至关重要。这项比较研究填补了重要空白,为基于临床和操作需求选择AI模型提供了指导。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在医学成像中的应用已经改变了诊断实践,使放射数据的分析和解读更为先进。
- 本研究比较了基于放射组学和基于深度学习的疾病检测方法,特别是在胸部放射学中针对COVID-19、肺部不透明和病毒性肺炎的应用。
- 深度学习模型,如卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉转换器(ViTs),可以直接从图像数据中学习。
- 放射组学模型通过提取和分析定量特征,可能在数据有限的情况下具有优势。
- 研究比较了不同AI模型的诊断准确性和稳健性,包括决策树、梯度提升、随机森林、SVM和MLP等,以及与先进的计算机视觉深度学习架构进行了对比。
- 研究结果提供了将AI驱动的诊断工具整合到临床实践中的信息,特别是在需要自动化和大规模处理的环境中。
点此查看论文截图

Remote sensing colour image semantic segmentation of trails created by large herbivorous Mammals
Authors:Jose Francisco Diez-Pastor, Francisco Javier Gonzalez-Moya, Pedro Latorre-Carmona, Francisco Javier Perez-Barbería, Ludmila I. Kuncheva, Antonio Canepa-Oneto, Alvar Arnaiz-González, Cesar Garcia-Osorio
Detection of spatial areas where biodiversity is at risk is of paramount importance for the conservation and monitoring of ecosystems. Large terrestrial mammalian herbivores are keystone species as their activity not only has deep effects on soils, plants, and animals, but also shapes landscapes, as large herbivores act as allogenic ecosystem engineers. One key landscape feature that indicates intense herbivore activity and potentially impacts biodiversity is the formation of grazing trails. Grazing trails are formed by the continuous trampling activity of large herbivores that can produce complex networks of tracks of bare soil. Here, we evaluated different algorithms based on machine learning techniques to identify grazing trails. Our goal is to automatically detect potential areas with intense herbivory activity, which might be beneficial for conservation and management plans. We have applied five semantic segmentation methods combined with fourteen encoders aimed at mapping grazing trails on aerial images. Our results indicate that in most cases the chosen methodology successfully mapped the trails, although there were a few instances where the actual trail structure was underestimated. The UNet architecture with the MambaOut encoder was the best architecture for mapping trails. The proposed approach could be applied to develop tools for mapping and monitoring temporal changes in these landscape structures to support habitat conservation and land management programs. This is the first time, to the best of our knowledge, that competitive image segmentation results are obtained for the detection and delineation of trails of large herbivorous mammals.
生物多样性易受影响的区域检测对于生态系统的保护和监测至关重要。大型陆地哺乳动物是旗舰物种,其活动不仅对土壤、植物和动物产生深远影响,还塑造地形地貌,因为大型草食动物充当着外来生态系统工程师的角色。一个关键地形特征是剧烈的草食动物活动,这可能影响生物多样性并造成牧场路径的形成。牧场路径是由大型草食动物持续践踏活动形成的,会产生裸露土壤的复杂轨迹网络。在这里,我们基于机器学习技术评估了不同的算法来识别牧场路径。我们的目标是自动检测可能存在强烈放牧活动的区域,这可能对保护和管理计划有益。我们采用了五种语义分割方法与十四种编码器相结合的方法,旨在将牧场路径映射到空中图像上。我们的结果表明,在大多数情况下,所选方法成功地绘制了路径,尽管在某些情况下实际路径结构被低估了。使用MambaOut编码器的UNet架构是绘制路径的最佳架构。所提出的方法可应用于开发工具和监测这些地形结构的临时变化,以支持栖息地保护和土地管理计划。据我们所知,这是首次成功获得大型草食动物的路径检测和划界的竞争性图像分割结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 6 figures. Submitted to Computers and Geosciences
Summary
本文利用机器学习算法对大型草食动物活动形成的放牧小径进行自动检测。研究评价了五种语义分割方法与十四种编码器在航空图像上绘制放牧小径的效果。结果显示,所选方法在多数情况下能成功绘制小径,但部分小径结构可能被低估。以UNet架构结合MambaOut编码器的效果最佳。该方法可用于开发工具,以监测这些景观结构的时空变化,支持栖息地保护和土地管理计划。这是首次成功利用图像分割技术检测与描绘大型草食动物的放牧小径。
Key Takeaways
- 检测生物多样性和生态系统健康的关键因素之一,是检测大规模陆生草食哺乳动物放牧区域。
- 研究中采用机器学习方法检测放牧小径(动物经常活动的路线),为后续研究和保护措施提供支持。
- 对比研究了五种语义分割方法与十四种编码器的性能表现。大部分方法在评估中被认为成功检测到放牧小径的存在,只有小部分情况下小径结构被低估。
- UNet架构结合MambaOut编码器是最佳的检测方法组合。
- 方法的运用前景包括为长期跟踪植被与生态系统健康建立相关工具和程序提供便利手段,通过监测放牧小径的时空变化来支持土地管理和保护计划。
- 这是首次成功利用图像分割技术来检测大型草食动物的放牧小径。此技术的突破可能对生态系统保护具有深远影响。
点此查看论文截图

A Diffusion-Based Framework for Terrain-Aware Remote Sensing Image Reconstruction
Authors:Zhenyu Yu, Mohd Yamani Inda Idris, Pei Wang
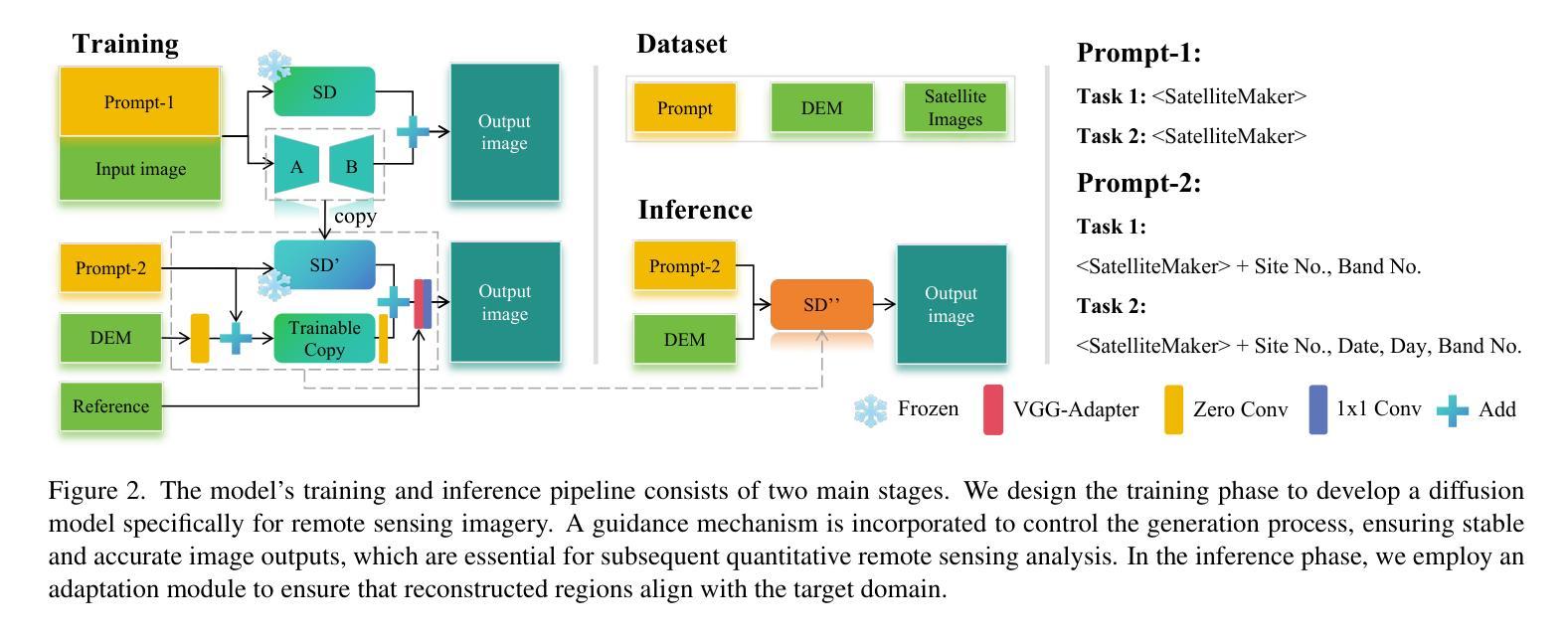
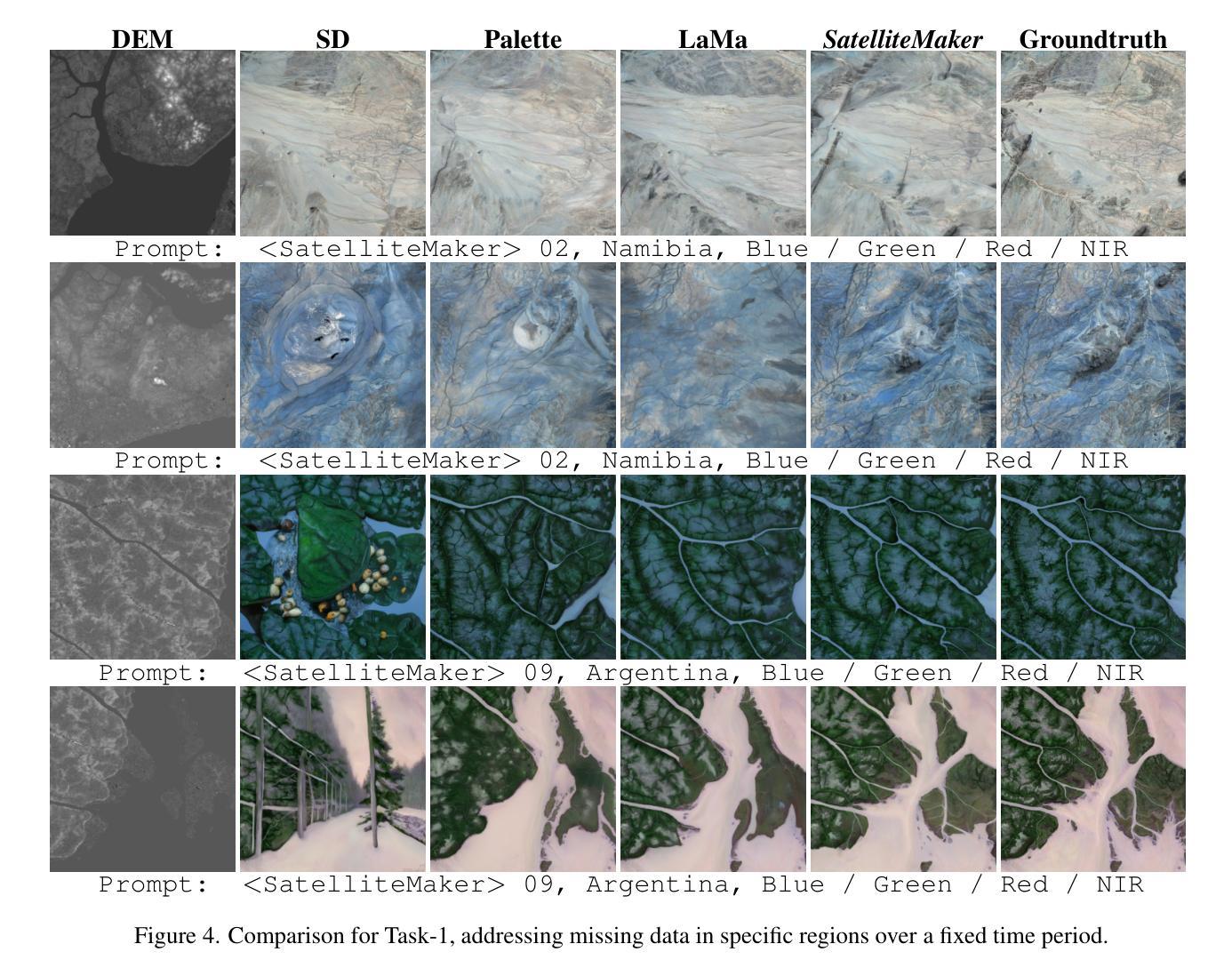
Remote sensing imagery is essential for environmental monitoring, agricultural management, and disaster response. However, data loss due to cloud cover, sensor failures, or incomplete acquisition-especially in high-resolution and high-frequency tasks-severely limits satellite imagery’s effectiveness. Traditional interpolation methods struggle with large missing areas and complex structures. Remote sensing imagery consists of multiple bands, each with distinct meanings, and ensuring consistency across bands is critical to avoid anomalies in the combined images. This paper proposes SatelliteMaker, a diffusion-based method that reconstructs missing data across varying levels of data loss while maintaining spatial, spectral, and temporal consistency. We also propose Digital Elevation Model (DEM) as a conditioning input and use tailored prompts to generate realistic images, making diffusion models applicable to quantitative remote sensing tasks. Additionally, we propose a VGG-Adapter module based on Distribution Loss, which reduces distribution discrepancy and ensures style consistency. Extensive experiments show that SatelliteMaker achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple tasks.
遥感影像在环境监测、农业管理和灾害应对方面发挥着重要作用。然而,由于云层覆盖、传感器故障或采集不完全等原因导致的数据丢失,特别是在高分辨率和高频率的任务中,严重限制了卫星影像的有效性。传统插值方法在处理大面积缺失和复杂结构时遇到了困难。遥感影像由多个波段组成,每个波段都有独特的含义,确保各波段之间的一致性对于避免合成图像中的异常至关重要。本文提出了SatelliteMaker,这是一种基于扩散的方法,能够在不同级别的数据丢失情况下重建缺失数据,同时保持空间、光谱和时间的一致性。我们还提出了数字高程模型(DEM)作为条件输入,并使用定制提示来生成逼真的图像,使扩散模型适用于定量遥感任务。此外,我们提出了基于分布损失的VGG适配器模块,它减少了分布差异并确保风格一致性。大量实验表明,SatelliteMaker在多个任务上达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
遥感影像在环境监测、农业管理和灾害响应中至关重要。然而,因云层覆盖、传感器故障或采集不完全等原因导致的数据丢失,特别是在高分辨和高频率的任务中,严重限制了卫星影像的有效性。传统插值方法在处理大面积缺失和复杂结构时面临挑战。本文提出一种基于扩散的SatelliteMaker方法,能够在不同级别的数据丢失情况下重建数据,同时保持空间、光谱和时间的一致性。此外,还提出使用数字高程模型(DEM)作为条件输入,并使用定制提示生成真实图像,使扩散模型适用于定量遥感任务。基于分布损失的VGG-Adapter模块减少了分布差异,确保了风格的一致性。大量实验表明,SatelliteMaker在多个任务上达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感影像在多个领域具有应用价值,但数据丢失限制了其有效性。
- 传统插值方法在处理大面积缺失和复杂结构时存在挑战。
- SatelliteMaker方法基于扩散,能够在不同级别的数据丢失情况下重建数据。
- SatelliteMaker方法保持空间、光谱和时间的一致性。
- 数字高程模型(DEM)被用作条件输入,结合定制提示,使扩散模型适用于遥感任务。
- VGG-Adapter模块基于分布损失,确保风格一致性。
点此查看论文截图



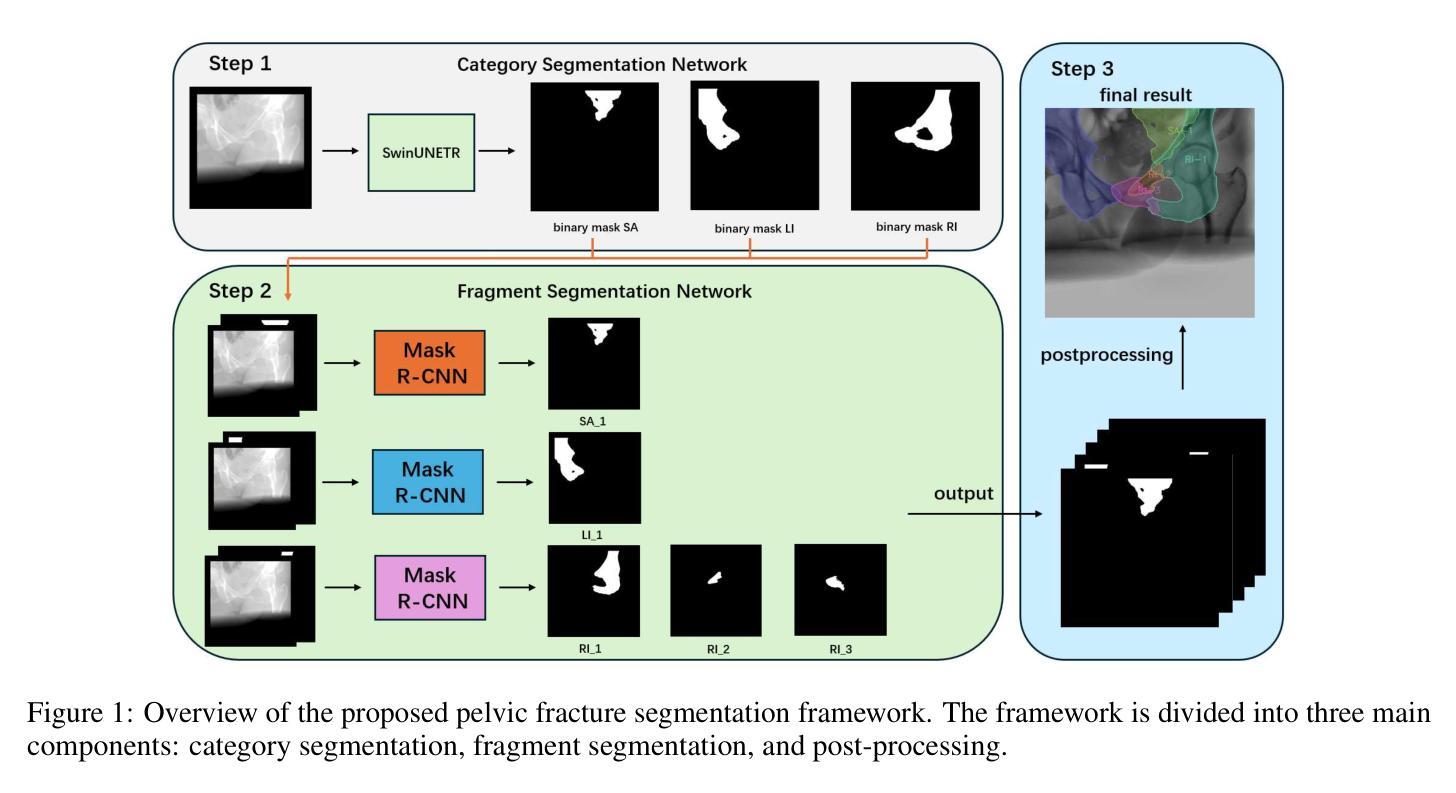
A Category-Fragment Segmentation Framework for Pelvic Fracture Segmentation in X-ray Images
Authors:Daiqi Liu, Fuxin Fan, Andreas Maier
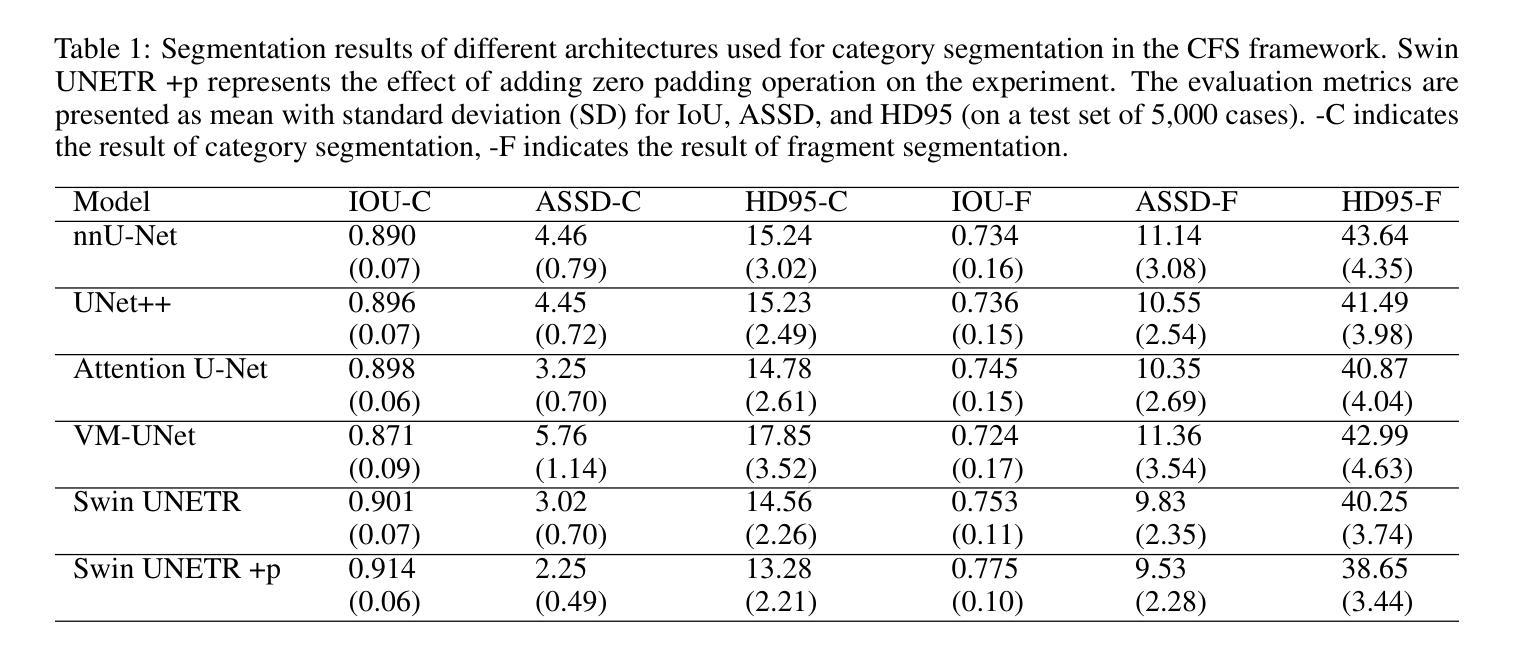
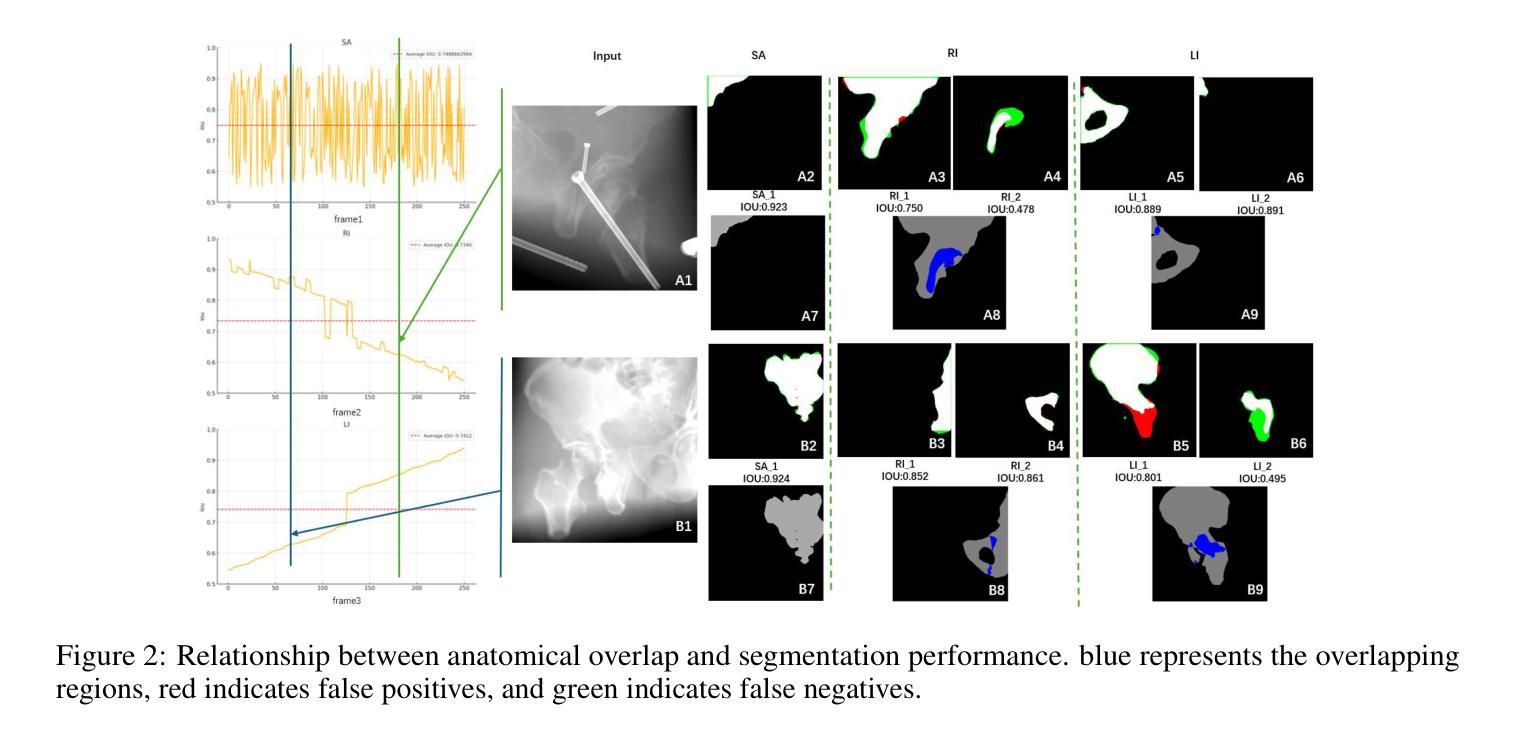
Pelvic fractures, often caused by high-impact trauma, frequently require surgical intervention. Imaging techniques such as CT and 2D X-ray imaging are used to transfer the surgical plan to the operating room through image registration, enabling quick intraoperative adjustments. Specifically, segmenting pelvic fractures from 2D X-ray imaging can assist in accurately positioning bone fragments and guiding the placement of screws or metal plates. In this study, we propose a novel deep learning-based category and fragment segmentation (CFS) framework for the automatic segmentation of pelvic bone fragments in 2D X-ray images. The framework consists of three consecutive steps: category segmentation, fragment segmentation, and post-processing. Our best model achieves an IoU of 0.91 for anatomical structures and 0.78 for fracture segmentation. Results demonstrate that the CFS framework is effective and accurate.
骨盆骨折通常是由高冲击力创伤引起的,经常需要手术干预。为了通过图像配准将手术计划转移到手术室,我们采用了CT和二维X射线成像等成像技术,从而实现术中快速调整。具体来说,通过二维X射线成像对骨盆骨折进行分割,有助于准确定位骨碎片并指导螺钉或金属板的放置。本研究提出了一种基于深度学习的类别和片段分割(CFS)框架,用于自动分割二维X射线图像中的骨盆骨碎片。该框架包括三个连续步骤:类别分割、片段分割和后处理。我们的最佳模型在解剖结构方面实现了0.91的IoU值,在骨折分割方面实现了0.78的IoU值。结果表明CFS框架是有效且准确的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 2 figures, 1 table
Summary
本研究利用深度学习技术,提出一种新型的基于二维X射线影像的骨盆骨折类别和片段分割(CFS)框架,可自动分割骨盆骨片段。该研究分为三个阶段:类别分割、片段分割和后处理。最佳模型的IoU达到解剖结构0.91和骨折分割0.78,证明CFS框架有效且准确。
Key Takeaways
- 骨盆骨折通常由高冲击性创伤引起,常需手术治疗。
- 影像技术如CT和2D X射线影像可用于通过图像配准将手术计划传输到手术室,实现术中快速调整。
- 在二维X射线影像中分割骨盆骨折可帮助准确定位骨碎片,指导螺钉或金属板的放置。
- 本研究提出了一种基于深度学习的自动分割骨盆骨片段的CFS框架。
- 该框架包括类别分割、片段分割和后处理三个步骤。
- 最佳模型的IoU值显示,该框架在解剖结构和骨折分割方面表现出高准确性和有效性。
点此查看论文截图

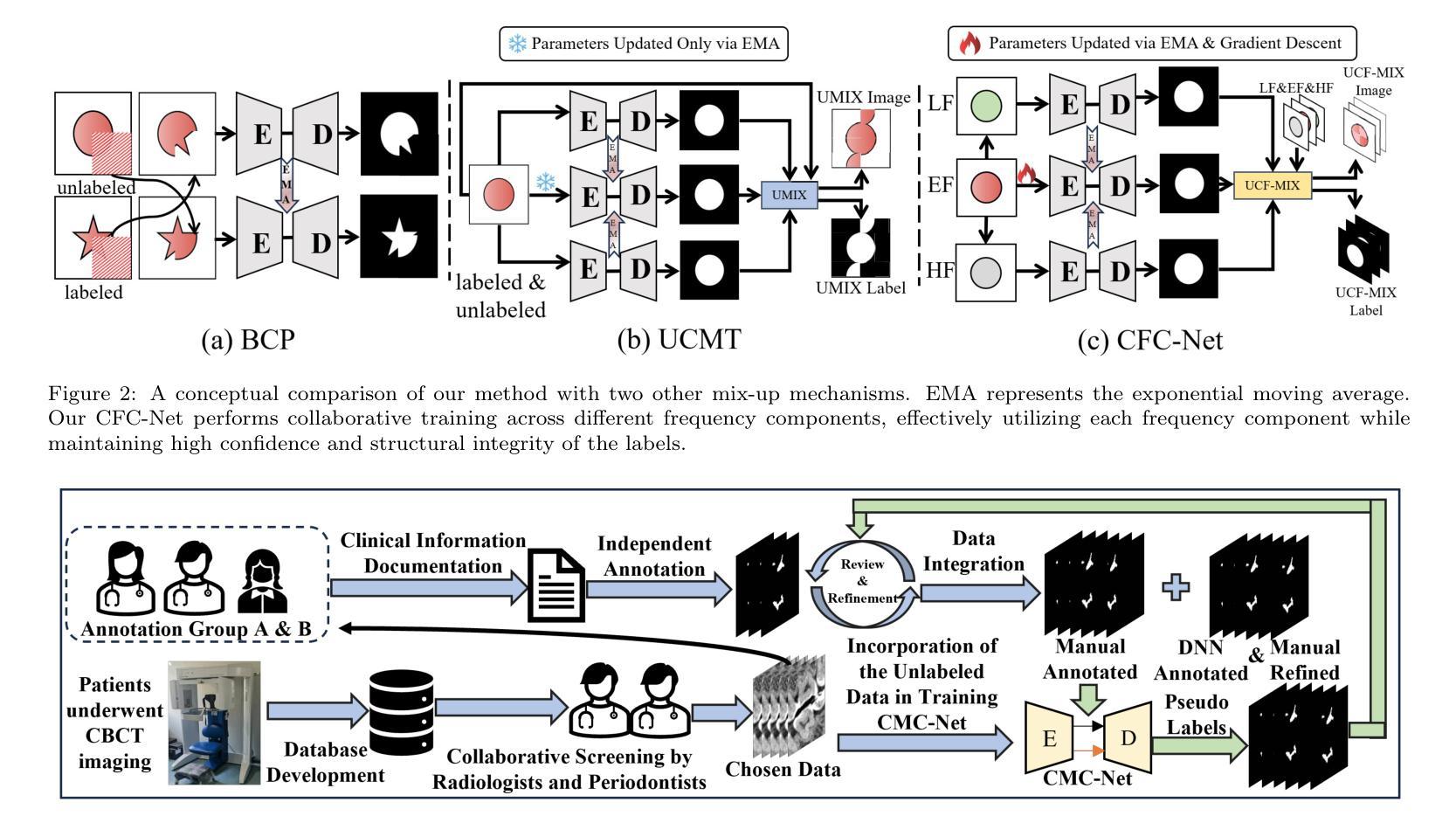
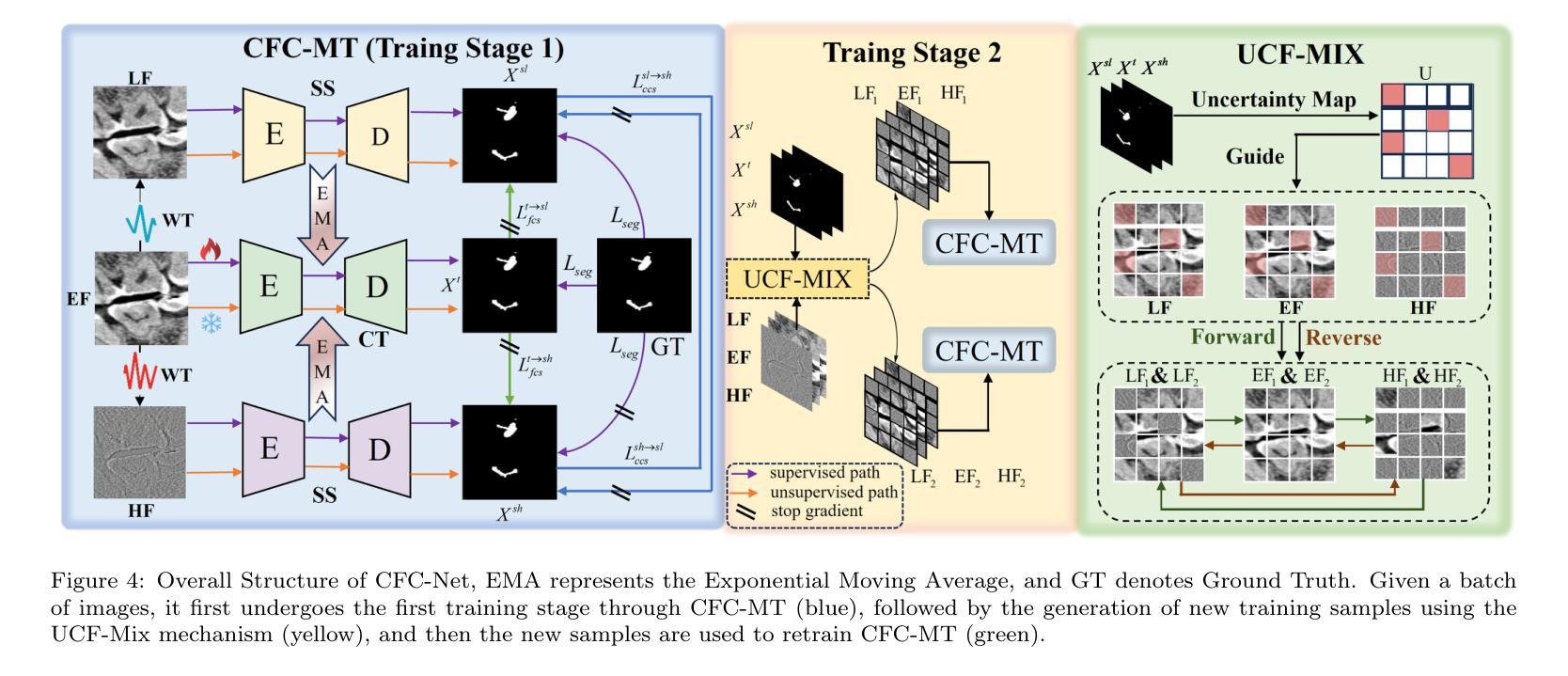
Cross-Frequency Collaborative Training Network and Dataset for Semi-supervised First Molar Root Canal Segmentation
Authors:Zhenhuan Zhou, Yuchen Zhang, Along He, Peng Wang, Xueshuo Xie, Tao Li
Root canal (RC) treatment is a highly delicate and technically complex procedure in clinical practice, heavily influenced by the clinicians’ experience and subjective judgment. Deep learning has made significant advancements in the field of computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) because it can provide more objective and accurate diagnostic results. However, its application in RC treatment is still relatively rare, mainly due to the lack of public datasets in this field. To address this issue, in this paper, we established a First Molar Root Canal segmentation dataset called FMRC-2025. Additionally, to alleviate the workload of manual annotation for dentists and fully leverage the unlabeled data, we designed a Cross-Frequency Collaborative training semi-supervised learning (SSL) Network called CFC-Net. It consists of two components: (1) Cross-Frequency Collaborative Mean Teacher (CFC-MT), which introduces two specialized students (SS) and one comprehensive teacher (CT) for collaborative multi-frequency training. The CT and SS are trained on different frequency components while fully integrating multi-frequency knowledge through cross and full frequency consistency supervisions. (2) Uncertainty-guided Cross-Frequency Mix (UCF-Mix) mechanism enables the network to generate high-confidence pseudo-labels while learning to integrate multi-frequency information and maintaining the structural integrity of the targets. Extensive experiments on FMRC-2025 and three public dental datasets demonstrate that CFC-MT is effective for RC segmentation and can also exhibit strong generalizability on other dental segmentation tasks, outperforming state-of-the-art SSL medical image segmentation methods. Codes and dataset will be released.
根管治疗(RC)是一种在临床实践中非常精细且技术复杂的程序,深受临床医生经验和主观判断的影响。深度学习在计算机辅助诊断(CAD)领域取得了显著进展,因为它可以提供更客观和准确的诊断结果。然而,其在根管治疗中的应用仍然相对罕见,主要是由于该领域缺乏公共数据集。为解决此问题,本文建立了一个名为FMRC-2025的第一磨牙根管 canal 分割数据集。此外,为了减轻牙医手动标注的工作量并充分利用未标记的数据,我们设计了一种跨频率协同训练半监督学习(SSL)网络,称为CFC-Net。它包含两个组件:(1)跨频率协同均值教师(CFC-MT),它引入两个特殊学生(SS)和一个综合教师(CT)进行协同多频率训练。CT和SS在不同的频率分量上进行训练,同时通过跨频率和完全频率一致性监督来完全整合多频率知识。(2)不确定性引导的跨频率混合(UCF-Mix)机制使网络能够生成高置信度的伪标签,同时学习整合多频率信息并保持目标的结构完整性。在FMRC-2025和三个公共牙科数据集上的大量实验表明,CFC-MT对于根管治疗分割是有效的,并且在其他牙科分割任务上也表现出强大的泛化能力,超越了最先进的SSL医学图像分割方法。代码和数据集将发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, Initial submission time 25 December 2024, Now Under Review
Summary
本研究建立了首个磨牙根管(First Molar Root Canal)分割数据集FMRC-2025,并提出了一种基于跨频协同训练半监督学习网络的FCM模型,该模型能够缓解牙医手动标注的工作量,充分利用无标签数据,在磨牙根管治疗图像分割上取得了优异表现。研究证明FCM模型能够有效提升分割精度和泛化能力。数据集和代码将公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 研究建立了首个磨牙根管分割数据集FMRC-2025,以解决缺乏公共数据集的问题。
- 提出了一种名为CFC-Net的跨频协同训练半监督学习网络,包括CFC-MT和UCF-Mix两个关键组件。
- CFC-MT通过引入两名专业学生和一名综合教师实现跨频协同训练,提高模型性能和多频知识整合能力。
- UCF-Mix机制使网络能够生成高置信度的伪标签,同时学习整合多频信息并保持目标的结构完整性。
- 实验证明,CFC-MT在FMRC-2025和其他公共牙科数据集上表现出强大的性能,优于现有的医学图像分割SSL方法。
点此查看论文截图

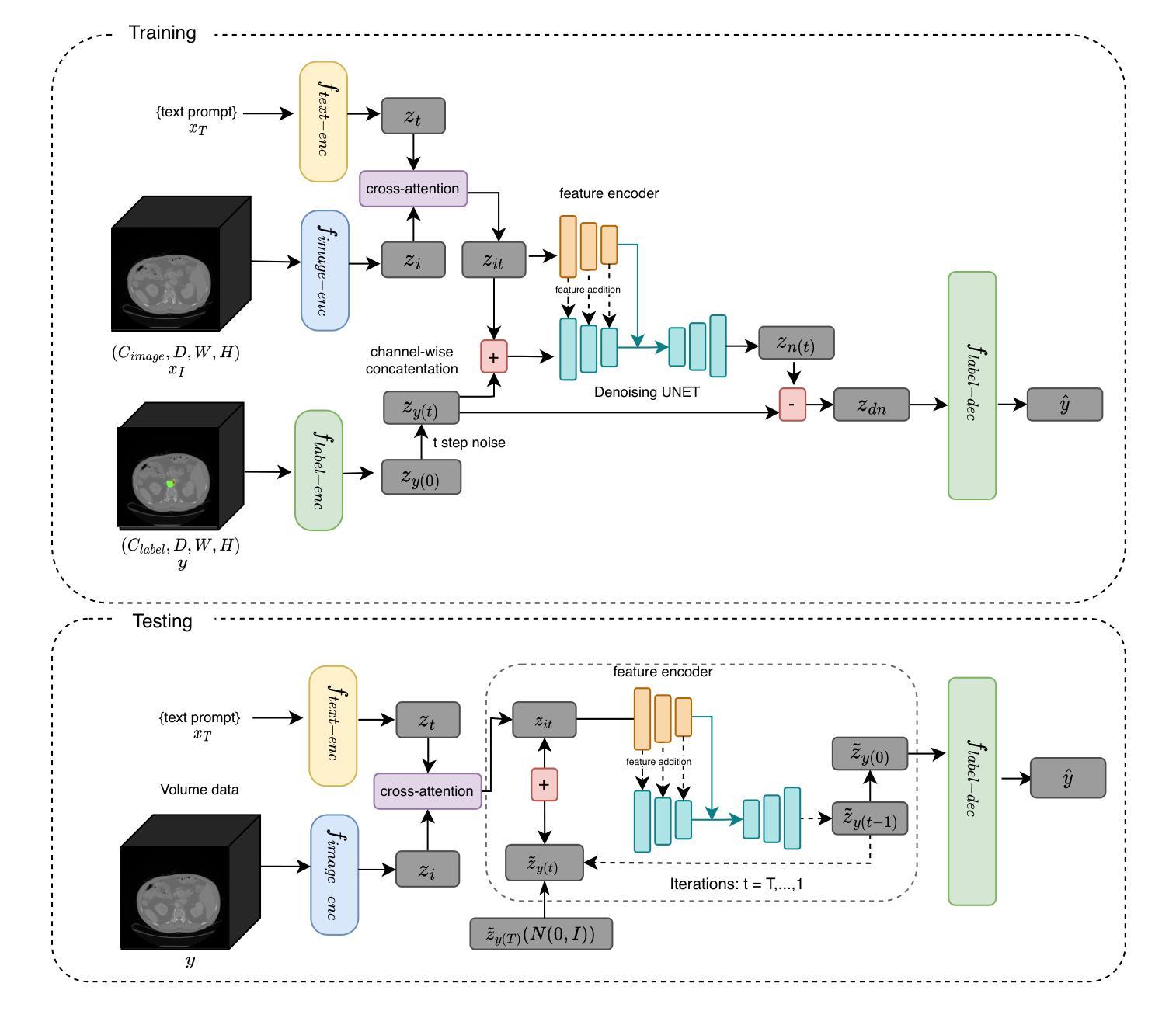
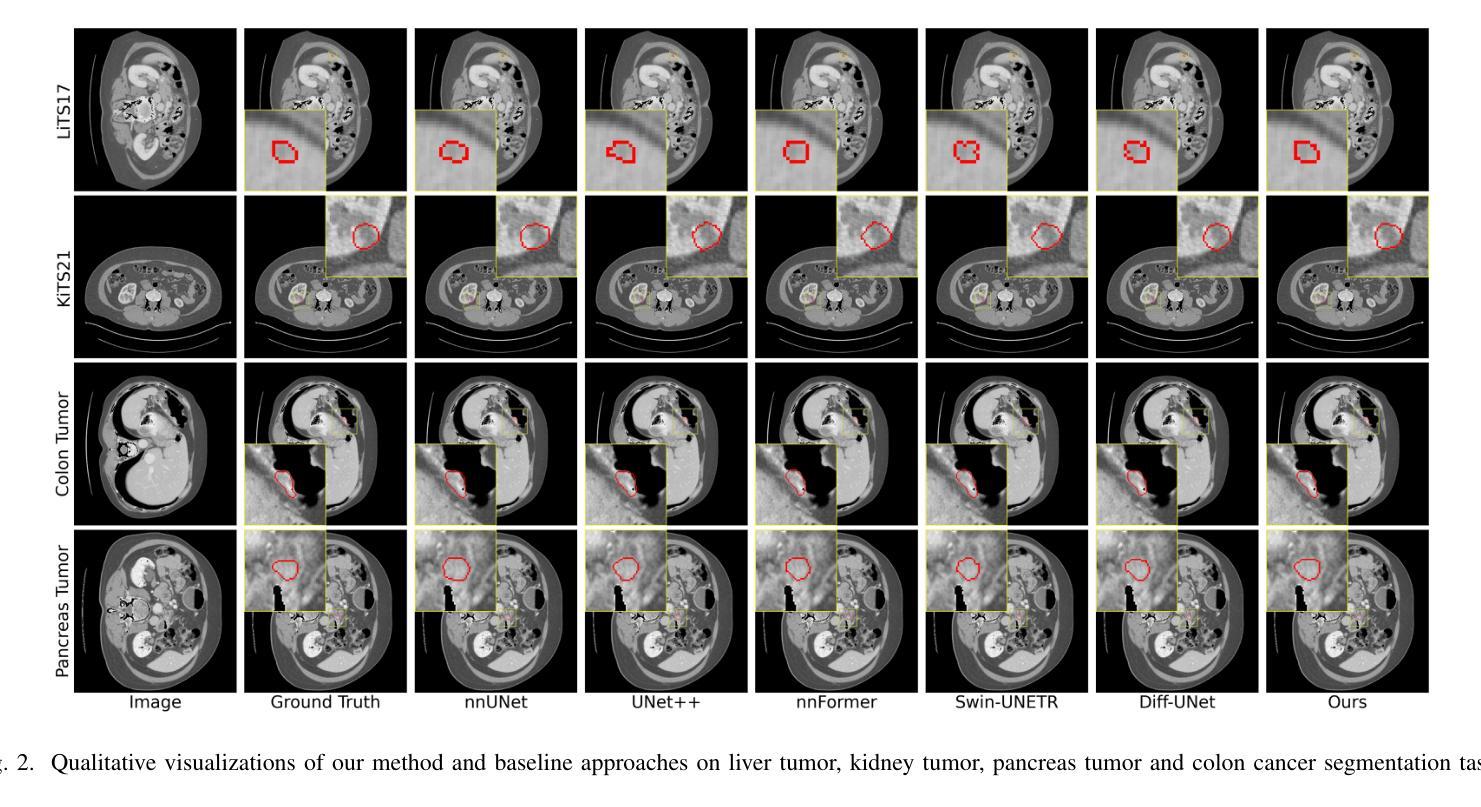
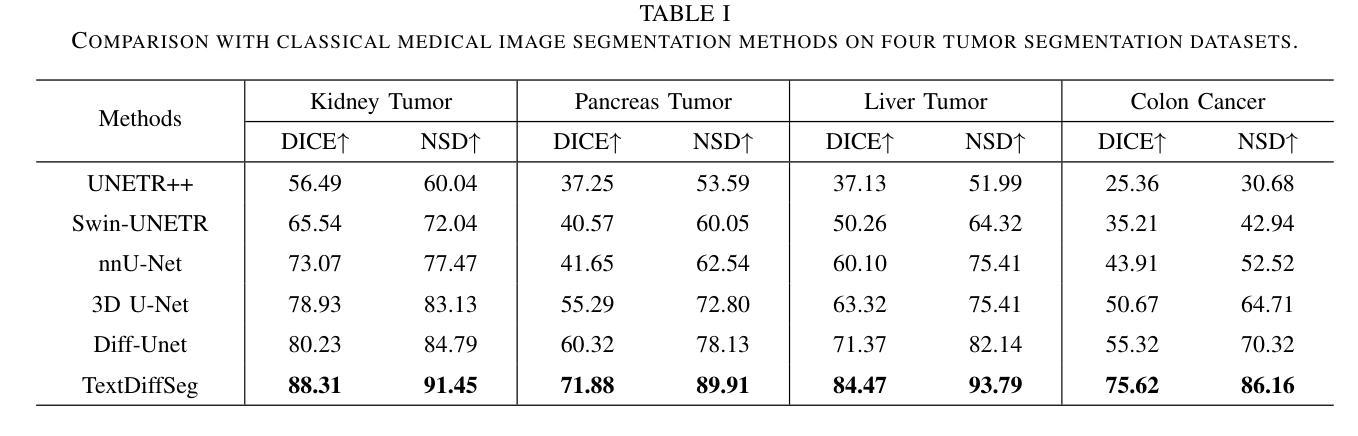
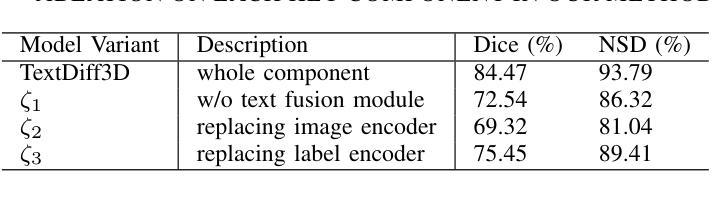
TextDiffSeg: Text-guided Latent Diffusion Model for 3d Medical Images Segmentation
Authors:Kangbo Ma
Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DPMs) have demonstrated significant potential in 3D medical image segmentation tasks. However, their high computational cost and inability to fully capture global 3D contextual information limit their practical applications. To address these challenges, we propose a novel text-guided diffusion model framework, TextDiffSeg. This method leverages a conditional diffusion framework that integrates 3D volumetric data with natural language descriptions, enabling cross-modal embedding and establishing a shared semantic space between visual and textual modalities. By enhancing the model’s ability to recognize complex anatomical structures, TextDiffSeg incorporates innovative label embedding techniques and cross-modal attention mechanisms, effectively reducing computational complexity while preserving global 3D contextual integrity. Experimental results demonstrate that TextDiffSeg consistently outperforms existing methods in segmentation tasks involving kidney and pancreas tumors, as well as multi-organ segmentation scenarios. Ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of key components, highlighting the synergistic interaction between text fusion, image feature extractor, and label encoder. TextDiffSeg provides an efficient and accurate solution for 3D medical image segmentation, showcasing its broad applicability in clinical diagnosis and treatment planning.
扩散概率模型(DPMs)在3D医学图像分割任务中显示出巨大潜力。然而,其较高的计算成本和无法完全捕获全局3D上下文信息,限制了其实际应用。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型的文本引导扩散模型框架,名为TextDiffSeg。该方法利用条件扩散框架,将3D体积数据与自然语言描述相结合,实现跨模态嵌入,建立视觉和文本模态之间的共享语义空间。通过增强模型对复杂解剖结构的识别能力,TextDiffSeg结合了创新的标签嵌入技术和跨模态注意力机制,在降低计算复杂性的同时,保持了全局3D上下文完整性。实验结果表明,TextDiffSeg在涉及肾脏和胰腺肿瘤的分割任务以及多器官分割场景中始终优于现有方法。消融研究进一步验证了关键组件的有效性,突出了文本融合、图像特征提取器和标签编码器之间的协同交互。TextDiffSeg为3D医学图像分割提供了高效准确的解决方案,展示了其在临床诊断和治疗计划中的广泛应用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
DPMs在3D医学图像分割任务中展现出巨大潜力,但其高计算成本和无法完全捕捉全局3D上下文信息限制了实际应用。为此,我们提出一种新型文本引导扩散模型框架TextDiffSeg。该方法结合3D体积数据与自然语言描述,建立跨模态嵌入和视觉与文本模态之间的共享语义空间,提高模型识别复杂解剖结构的能力。TextDiffSeg融入标签嵌入技术和跨模态注意力机制,在降低计算复杂度的同时保持全局3D上下文完整性。实验结果显示,TextDiffSeg在肾脏、胰腺肿瘤分割任务以及多器官分割场景中均表现出优异性能。
Key Takeaways
- DPMs在3D医学图像分割中潜力巨大,但存在计算成本高和3D上下文信息捕捉不足的问题。
- TextDiffSeg是一种新型的文本引导扩散模型框架,结合了3D体积数据和自然语言描述。
- TextDiffSeg通过跨模态嵌入建立视觉和文本模态之间的共享语义空间。
- TextDiffSeg提高了模型识别复杂解剖结构的能力,并融入了标签嵌入技术和跨模态注意力机制。
- TextDiffSeg在肾脏、胰腺肿瘤分割任务以及多器官分割场景中表现优异。
- 消融研究验证了TextDiffSeg关键组件的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

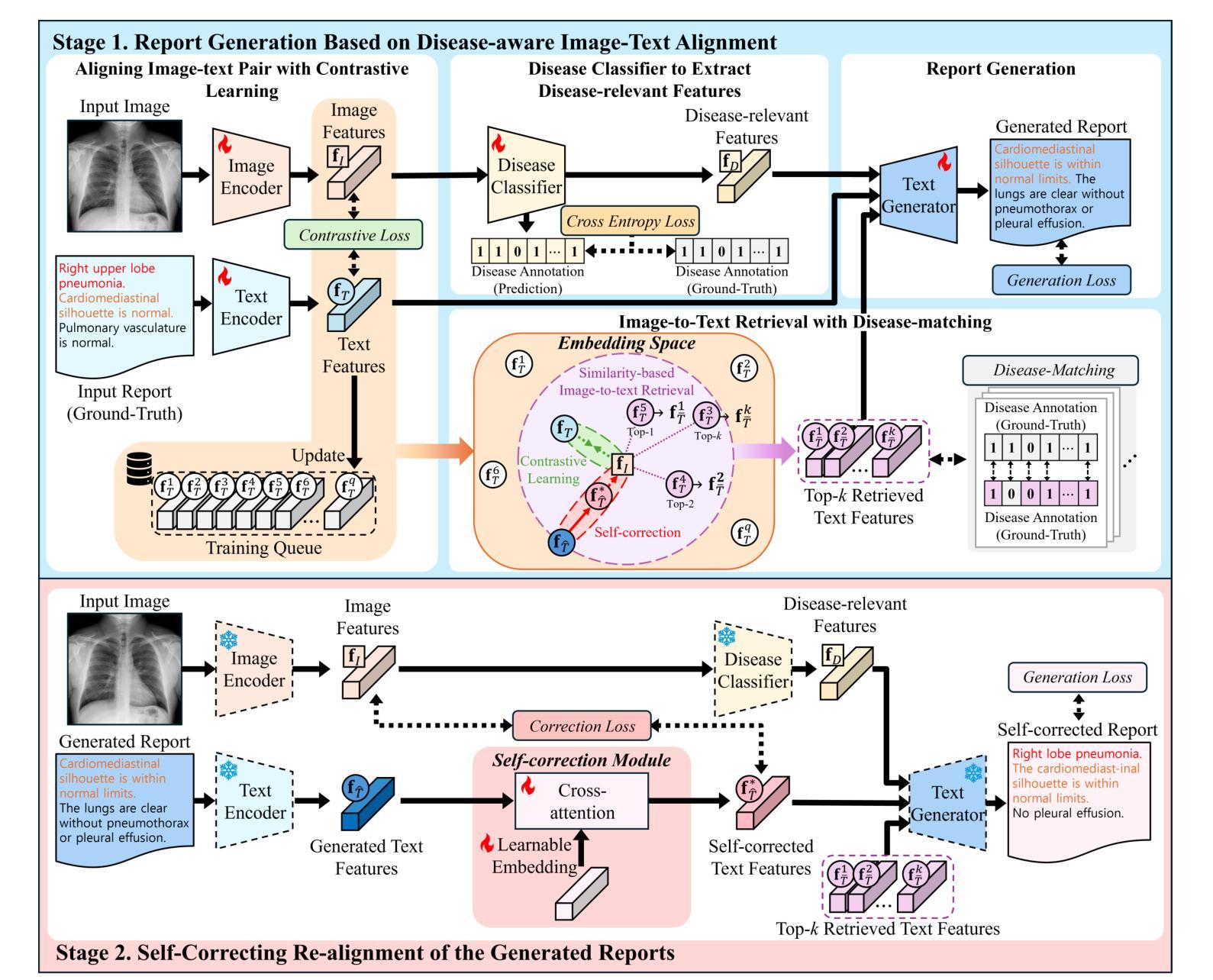
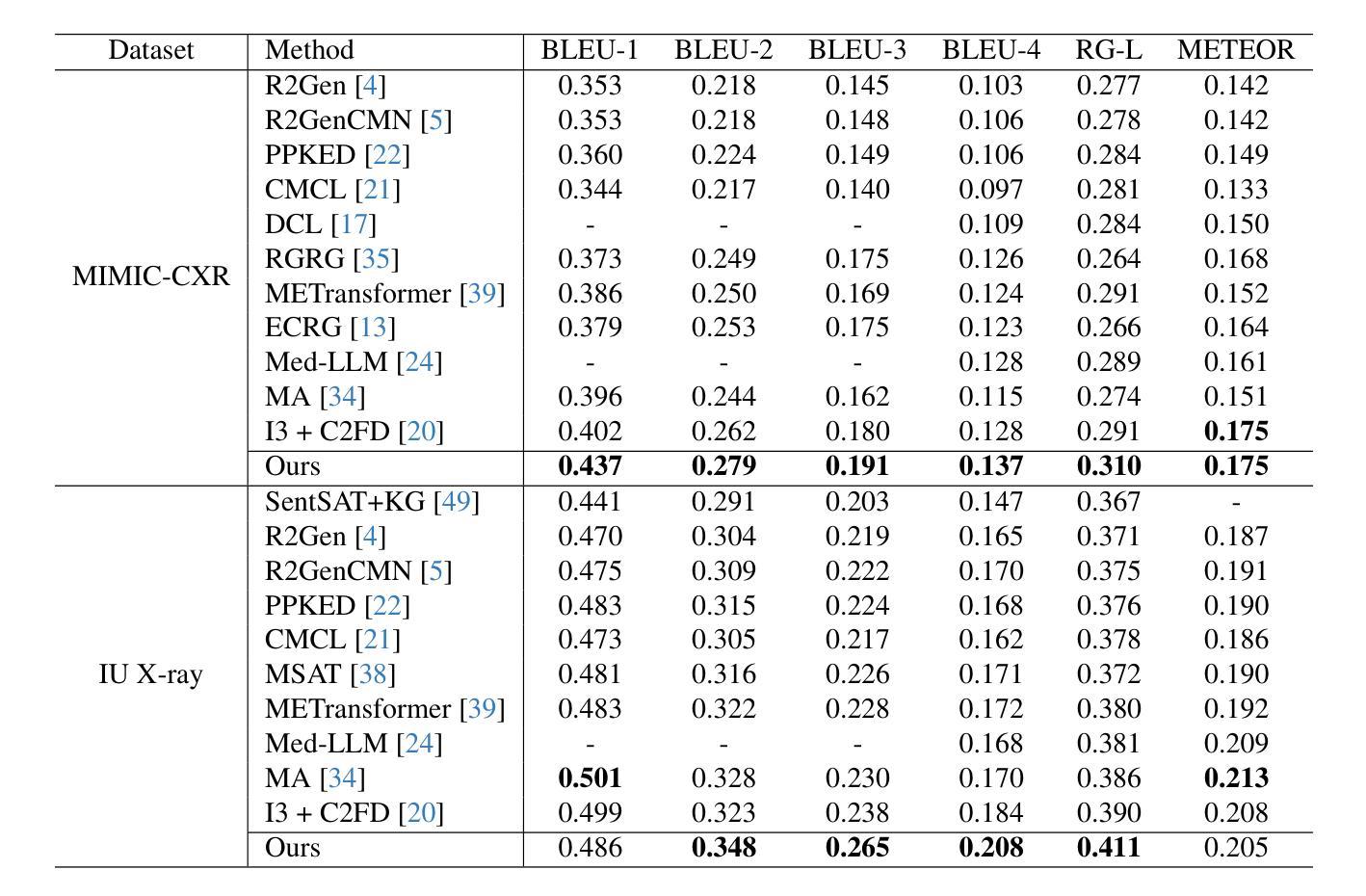
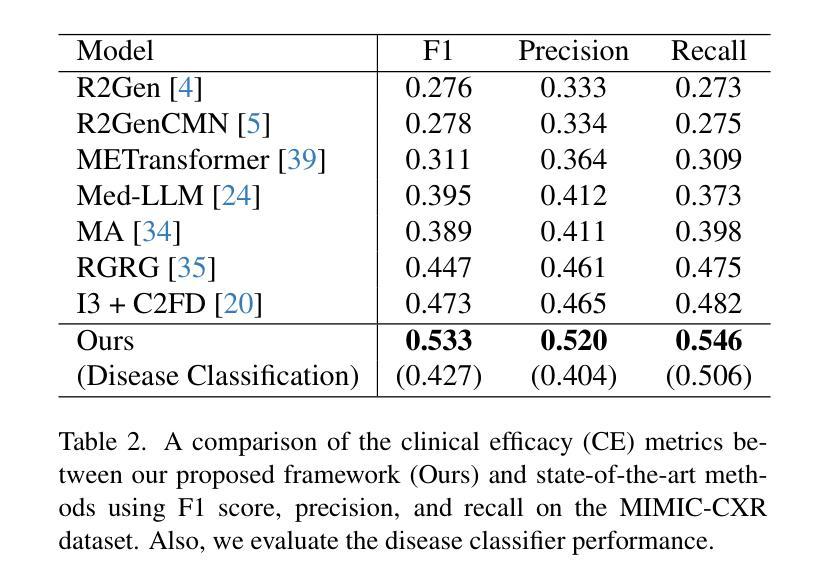
DART: Disease-aware Image-Text Alignment and Self-correcting Re-alignment for Trustworthy Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Sang-Jun Park, Keun-Soo Heo, Dong-Hee Shin, Young-Han Son, Ji-Hye Oh, Tae-Eui Kam
The automatic generation of radiology reports has emerged as a promising solution to reduce a time-consuming task and accurately capture critical disease-relevant findings in X-ray images. Previous approaches for radiology report generation have shown impressive performance. However, there remains significant potential to improve accuracy by ensuring that retrieved reports contain disease-relevant findings similar to those in the X-ray images and by refining generated reports. In this study, we propose a Disease-aware image-text Alignment and self-correcting Re-alignment for Trustworthy radiology report generation (DART) framework. In the first stage, we generate initial reports based on image-to-text retrieval with disease-matching, embedding both images and texts in a shared embedding space through contrastive learning. This approach ensures the retrieval of reports with similar disease-relevant findings that closely align with the input X-ray images. In the second stage, we further enhance the initial reports by introducing a self-correction module that re-aligns them with the X-ray images. Our proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art results on two widely used benchmarks, surpassing previous approaches in both report generation and clinical efficacy metrics, thereby enhancing the trustworthiness of radiology reports.
放射学报告的自动生成已成为减少耗时任务并准确捕捉X光片中与疾病相关的关键发现的一种有前途的解决方案。之前用于生成放射学报告的方法已经表现出了令人印象深刻的效果。然而,通过确保检索到的报告包含与X光图像中相似的疾病相关发现,并通过完善生成的报告,仍存在提高准确性的巨大潜力。在这项研究中,我们提出了一个疾病感知的图像文本对齐和自校正重新对齐的可信放射学报告生成(DART)框架。在第一阶段,我们基于图像到文本的检索生成初步报告,并进行疾病匹配,通过对比学习将图像和文本嵌入到共享嵌入空间中。这种方法确保检索到的报告包含相似的疾病相关发现,与输入的X光图像紧密对齐。在第二阶段,我们通过引入一个自我校正模块来进一步改进初步的报告,该模块使其与X光图像重新对齐。我们提出的框架在两个广泛使用的基准测试上达到了最新结果,在报告生成和临床有效性指标上均超越了以前的方法,从而提高了放射学报告的可信度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于疾病意识的图像文本对齐和自校正重新对齐的可靠放射学报告生成(DART)框架,旨在提高放射学报告的准确性和效率。该框架首先通过图像到文本的检索生成初步报告,确保检索到的报告与X光图像中的疾病相关发现相似并紧密对齐。接着引入自校正模块进一步优化初步报告,使其与X光图像重新对齐,从而提高报告的可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 放射学报告自动生成成为减少耗时任务并准确捕捉X光图像中关键疾病相关发现的有前途的解决方案。
- 现有方法在放射学报告生成方面已表现出令人印象深刻的表现,但仍有改进准确性的潜力。
- DART框架通过疾病意识的图像文本对齐确保检索到的报告与X光图像中的疾病相关发现相似。
- 初步报告基于图像到文本的检索生成,使用对比学习将图像和文本嵌入到共享嵌入空间中。
- 自校正模块进一步优化初步报告,使其与X光图像重新对齐,提高报告的准确性。
- DART框架在两个广泛使用的基准测试上达到最新结果,在报告生成和临床功效指标上超越以前的方法。
- 该框架提高了放射学报告的可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

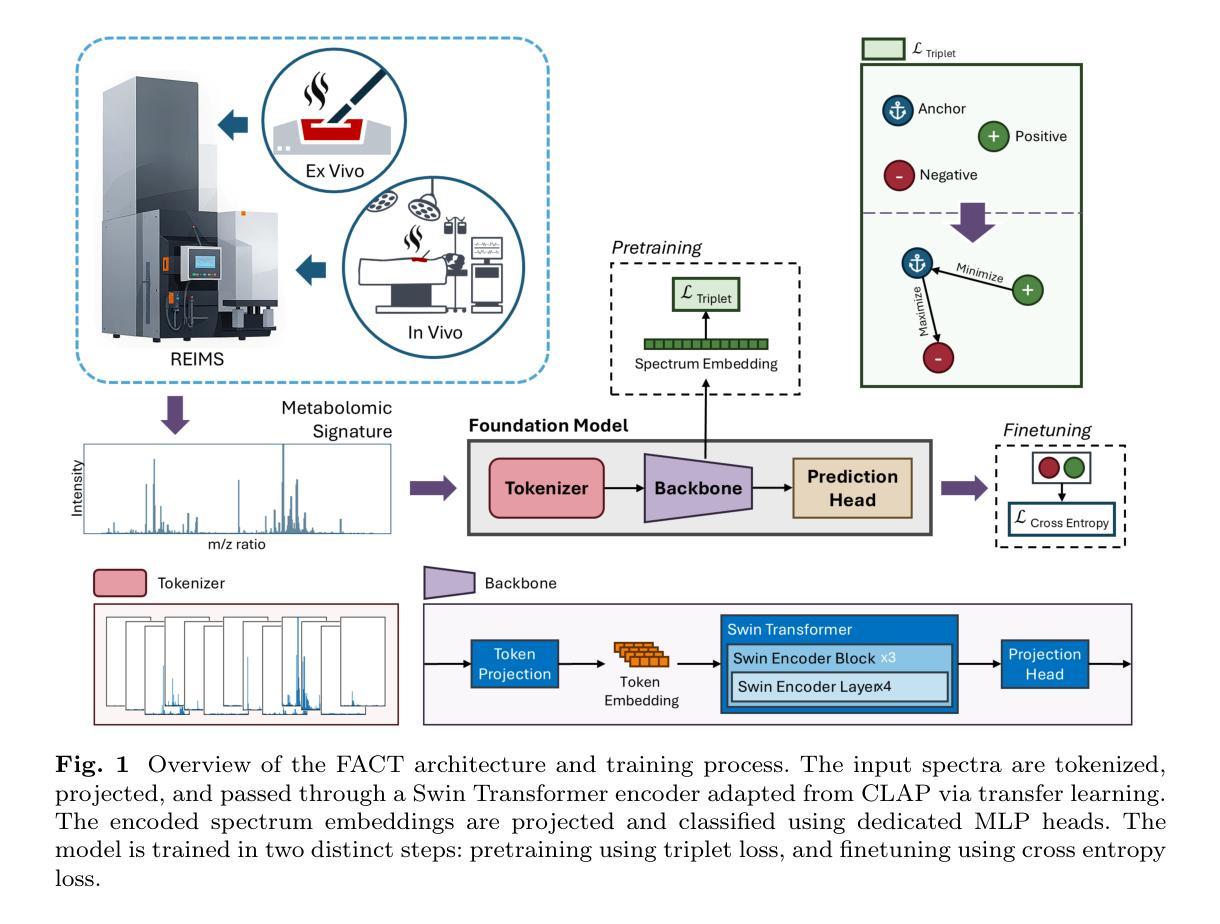
FACT: Foundation Model for Assessing Cancer Tissue Margins with Mass Spectrometry
Authors:Mohammad Farahmand, Amoon Jamzad, Fahimeh Fooladgar, Laura Connolly, Martin Kaufmann, Kevin Yi Mi Ren, John Rudan, Doug McKay, Gabor Fichtinger, Parvin Mousavi
Purpose: Accurately classifying tissue margins during cancer surgeries is crucial for ensuring complete tumor removal. Rapid Evaporative Ionization Mass Spectrometry (REIMS), a tool for real-time intraoperative margin assessment, generates spectra that require machine learning models to support clinical decision-making. However, the scarcity of labeled data in surgical contexts presents a significant challenge. This study is the first to develop a foundation model tailored specifically for REIMS data, addressing this limitation and advancing real-time surgical margin assessment. Methods: We propose FACT, a Foundation model for Assessing Cancer Tissue margins. FACT is an adaptation of a foundation model originally designed for text-audio association, pretrained using our proposed supervised contrastive approach based on triplet loss. An ablation study is performed to compare our proposed model against other models and pretraining methods. Results: Our proposed model significantly improves the classification performance, achieving state-of-the-art performance with an AUROC of $82.4% \pm 0.8$. The results demonstrate the advantage of our proposed pretraining method and selected backbone over the self-supervised and semi-supervised baselines and alternative models. Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that foundation models, adapted and pretrained using our novel approach, can effectively classify REIMS data even with limited labeled examples. This highlights the viability of foundation models for enhancing real-time surgical margin assessment, particularly in data-scarce clinical environments.
目的:在癌症手术中,准确分类组织边界对于确保肿瘤完全切除至关重要。快速蒸发电离质谱法(REIMS)是一种用于实时术中边界评估的工具,能够产生光谱,需要机器学习模型来支持临床决策。然而,手术环境中标记数据的稀缺性构成了重大挑战。本研究首次针对REIMS数据开发基础模型,解决了这一限制,推进了实时手术边界评估的发展。
方法:我们提出了FACT(用于评估癌症组织边界的基础模型)。FACT是对最初为文本-音频关联设计的基础模型的改编,使用我们提出的有监督对比方法基于三元损失进行预训练。我们进行了一项消融研究,将所提出的模型与其他模型和预训练方法进行比较。
结果:我们提出的模型显著提高了分类性能,实现了最先进的性能,曲线下面积(AUROC)为82.4%±0.8。结果表明,我们的预训练方法和所选主干相对于自监督、半监督和替代模型的优势。
结论:我们的研究结果表明,使用我们的新型方法适应和预训练的基础模型,即使在有限的标记示例情况下,也能有效地对REIMS数据进行分类。这突出了基础模型在提高实时手术边界评估方面的可行性,特别是在数据稀缺的临床环境中。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文旨在解决癌症手术中准确分类组织切缘的关键问题,对于确保肿瘤完全切除至关重要。研究中,我们提出使用快速蒸发电离质谱技术(REIMS)进行实时手术切缘评估,并开发了一种针对REIMS数据的基础模型FACT。该模型基于文本-音频关联设计的原始基础模型进行改编,采用我们提出的有监督对比方法进行预训练。研究结果显示,我们的模型在分类性能上显著提高,达到了先进的性能水平,AUROC为$82.4% \pm 0.8$。这表明我们的预训练方法和所选骨干网络的优势,优于自监督、半监督和替代模型的基线水平。我们的研究结果表明,使用我们的新方法适应和预训练的基础模型可以有效地分类REIMS数据,即使在标记样本有限的情况下也是如此。这为在数据稀缺的临床环境中增强实时手术切缘评估提供了可能性。
关键见解
- 研究关注癌症手术中准确分类组织切缘的重要性,以确保肿瘤的完全切除。
- 提出使用REIMS技术进行实时手术切缘评估。
- 开发了一个名为FACT的基础模型,专为REIMS数据设计,解决数据稀缺的挑战。
- 采用有监督对比方法进行预训练,提高了模型的性能。
- 对比研究结果显示,FACT模型在分类性能上达到先进水平。
- 模型的预训练方法和骨干网络的选择显示优势,优于其他预训练方法和模型。
点此查看论文截图

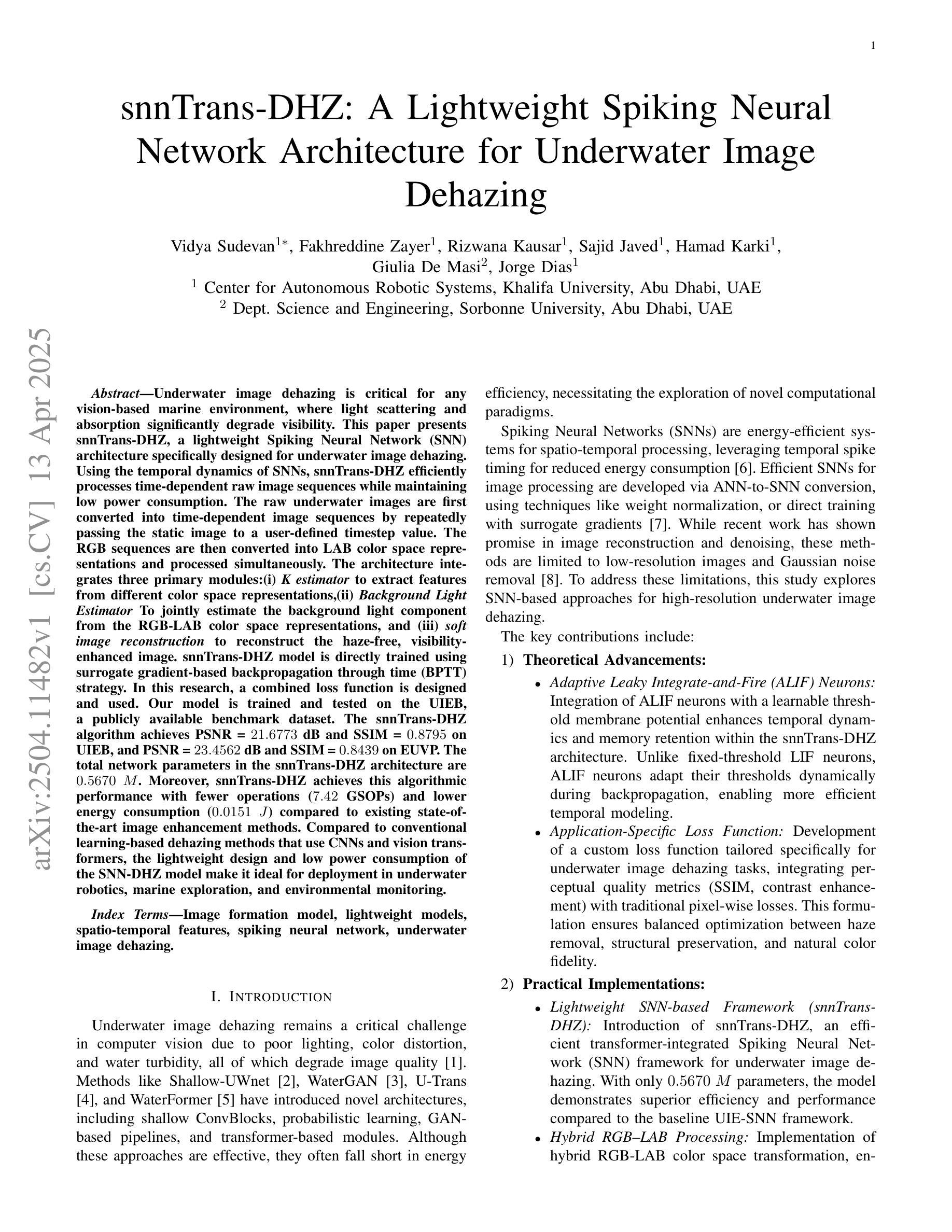
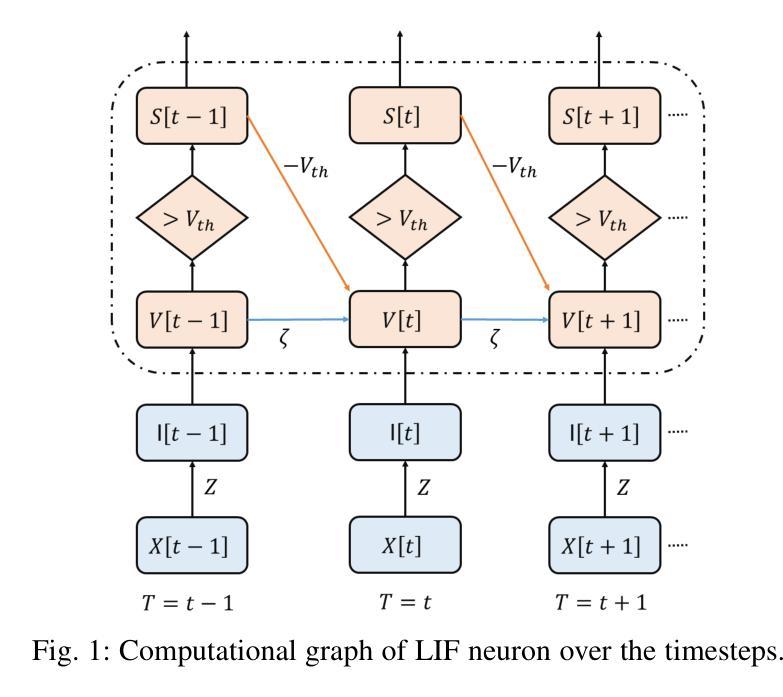
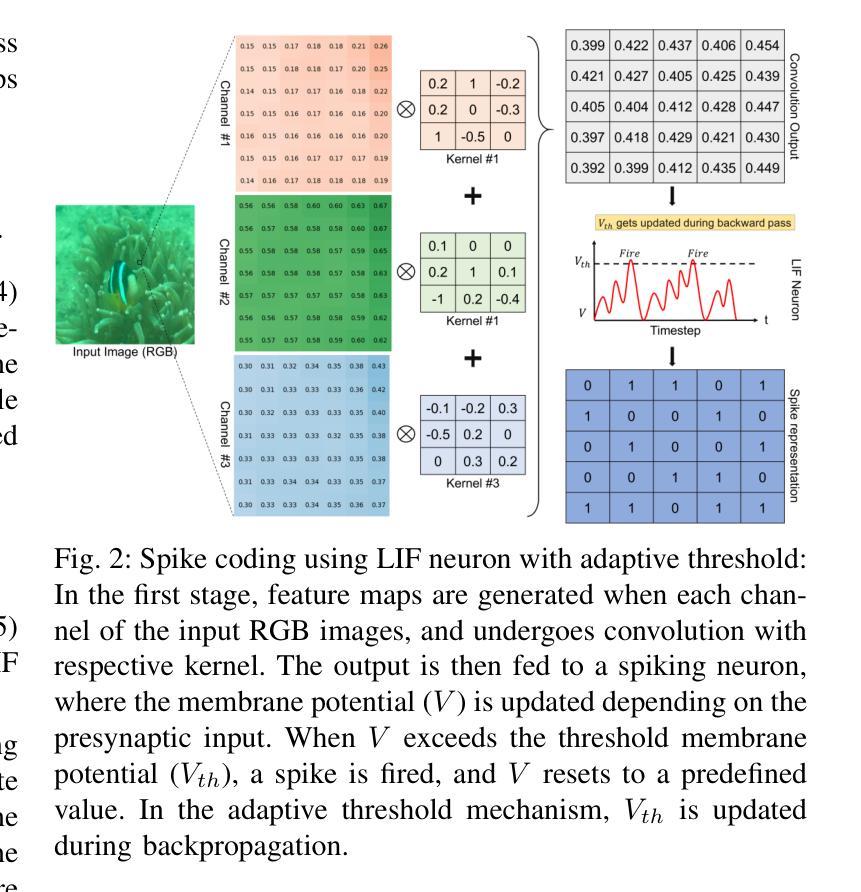
snnTrans-DHZ: A Lightweight Spiking Neural Network Architecture for Underwater Image Dehazing
Authors:Vidya Sudevan, Fakhreddine Zayer, Rizwana Kausar, Sajid Javed, Hamad Karki, Giulia De Masi, Jorge Dias
Underwater image dehazing is critical for vision-based marine operations because light scattering and absorption can severely reduce visibility. This paper introduces snnTrans-DHZ, a lightweight Spiking Neural Network (SNN) specifically designed for underwater dehazing. By leveraging the temporal dynamics of SNNs, snnTrans-DHZ efficiently processes time-dependent raw image sequences while maintaining low power consumption. Static underwater images are first converted into time-dependent sequences by repeatedly inputting the same image over user-defined timesteps. These RGB sequences are then transformed into LAB color space representations and processed concurrently. The architecture features three key modules: (i) a K estimator that extracts features from multiple color space representations; (ii) a Background Light Estimator that jointly infers the background light component from the RGB-LAB images; and (iii) a soft image reconstruction module that produces haze-free, visibility-enhanced outputs. The snnTrans-DHZ model is directly trained using a surrogate gradient-based backpropagation through time (BPTT) strategy alongside a novel combined loss function. Evaluated on the UIEB benchmark, snnTrans-DHZ achieves a PSNR of 21.68 dB and an SSIM of 0.8795, and on the EUVP dataset, it yields a PSNR of 23.46 dB and an SSIM of 0.8439. With only 0.5670 million network parameters, and requiring just 7.42 GSOPs and 0.0151 J of energy, the algorithm significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of efficiency. These features make snnTrans-DHZ highly suitable for deployment in underwater robotics, marine exploration, and environmental monitoring.
水下图像去雾对于基于视觉的海洋操作至关重要,因为光的散射和吸收会严重影响能见度。本文介绍了snnTrans-DHZ,这是一个专门用于水下去雾的轻量级脉冲神经网络(SNN)。通过利用SNN的时空动态特性,snnTrans-DHZ能够高效地处理时间相关的原始图像序列,同时保持低功耗。
首先,将静态水下图像转换为时间相关的序列,通过用户定义的时序反复输入相同的图像。然后,这些RGB序列被转换为LAB颜色空间表示,并并行处理。该架构具有三个关键模块:(i)K估计器,从多个颜色空间表示中提取特征;(ii)背景光估计器,从RGB-LAB图像中联合推断背景光成分;(iii)软图像重建模块,生成无雾、提高可见度的输出。
snnTrans-DHZ模型直接使用基于替代梯度的反向传播和时间(BPTT)策略以及一种新的组合损失函数进行训练。在UIEB基准测试中,snnTrans-DHZ达到21.68分贝的PSNR和0.8795的SSIM;在EUVP数据集上,它达到23.46分贝的PSNR和0.8439的SSIM。该算法只有0.5670百万网络参数,仅需7.42 GSOPs和0.0151焦耳的能量,在效率方面显著优于现有的最先进方法。这些特性使snnTrans-DHZ非常适合用于水下机器人、海洋探索和环境监测。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
水下图像去雾对于基于视觉的海洋操作至关重要,因为光的散射和吸收会严重影响能见度。本文介绍了snnTrans-DHZ,这是一个专为水下图像去雾设计的轻量级脉冲神经网络(SNN)。通过利用SNN的临时动态特性,snnTrans-DHZ能够高效地处理时间相关的原始图像序列,同时保持低功耗。首先,将静态水下图像转换为时间相关的序列,然后通过用户定义的时序反复输入相同的图像。这些RGB序列随后被转换为LAB颜色空间表示并并行处理。该架构具有三个关键模块:(i)特征提取器K,用于从多个颜色空间表示中提取特征;(ii)背景光估计器,用于从RGB-LAB图像中联合推断背景光分量;(iii)软图像重建模块,生成无雾、提高可见度的输出。snnTrans-DHZ模型直接使用替代梯度基于时间的反向传播(BPTT)策略和新颖的组合损失函数进行训练。在UIEB基准测试中,snnTrans-DHZ的PSNR达到21.68 dB,SSIM为0.8795;在EUVP数据集上,其PSNR为23.46 dB,SSIM为0.8439。该算法仅包含0.5670百万个网络参数,需要7.42 GSOPs和0.0151 J的能量,在效率上显著优于现有的最新方法。这些特性使snnTrans-DHZ非常适合用于水下机器人、海洋勘探和环境监测。
要点解析
- 水下图像去雾对于基于视觉的海洋操作至关重要,因为光的散射和吸收严重影响能见度。
- snnTrans-DHZ是一个基于脉冲神经网络(SNN)的水下图像去雾模型。
- snnTrans-DHZ能够处理时间相关的原始图像序列,同时具有低功耗的特性。
- 该模型通过将静态水下图像转换为时间相关的序列来进行处理。
- 模型架构包含三个关键模块:特征提取、背景光估计和软图像重建。
- snnTrans-DHZ在效率上优于其他现有方法,具有较低的网络参数和能量需求。
点此查看论文截图
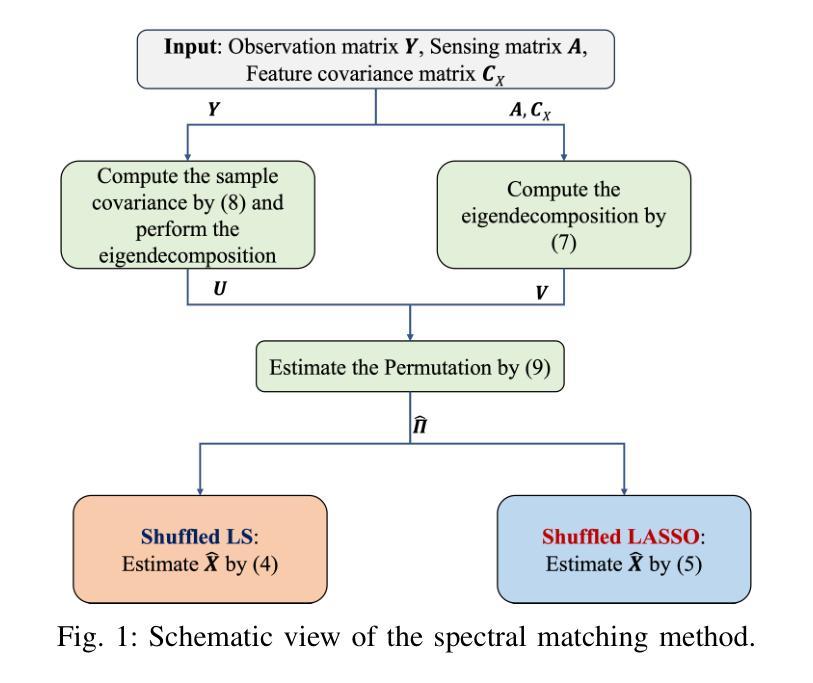
Shuffled Linear Regression via Spectral Matching
Authors:Hang Liu, Anna Scaglione
Shuffled linear regression (SLR) seeks to estimate latent features through a linear transformation, complicated by unknown permutations in the measurement dimensions. This problem extends traditional least-squares (LS) and Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) approaches by jointly estimating the permutation, resulting in shuffled LS and shuffled LASSO formulations. Existing methods, constrained by the combinatorial complexity of permutation recovery, often address small-scale cases with limited measurements. In contrast, we focus on large-scale SLR, particularly suited for environments with abundant measurement samples. We propose a spectral matching method that efficiently resolves permutations by aligning spectral components of the measurement and feature covariances. Rigorous theoretical analyses demonstrate that our method achieves accurate estimates in both shuffled LS and shuffled LASSO settings, given a sufficient number of samples. Furthermore, we extend our approach to address simultaneous pose and correspondence estimation in image registration tasks. Experiments on synthetic datasets and real-world image registration scenarios show that our method outperforms existing algorithms in both estimation accuracy and registration performance.
打乱线性回归(SLR)试图通过线性变换估计潜在特征,但测量维度的未知排列增加了其复杂性。这一问题通过联合估计排列扩展了传统的最小二乘(LS)和最小绝对收缩和选择算子(LASSO)方法,产生了打乱LS和打乱LASSO公式。由于排列恢复的组合复杂性限制,现有方法通常处理测量有限的小规模案例。相比之下,我们专注于大规模SLR,尤其适用于测量样本丰富的环境。我们提出了一种谱匹配方法,通过对齐测量和特征协方差谱成分来解决排列问题。严格的理论分析表明,我们的方法在充足的样本下,在打乱LS和打乱LASSO设置中都能实现准确的估计。此外,我们将我们的方法扩展到解决图像配准任务中的姿态和对应关系估计问题。在合成数据集和真实世界图像配准场景的实验表明,我们的方法在估计准确性和注册性能方面都优于现有算法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
针对测量维度中未知排列的线性回归问题,提出谱匹配方法来解决大规模洗牌线性回归(SLR)。该方法通过对齐测量和特征协方差谱成分来有效解析排列问题。理论分析表明,该方法在足够样本数下能在洗牌最小二乘(LS)和洗牌LASSO设置中准确估计。此外,将其应用于图像注册任务中的姿态和对应关系估计。在合成数据集和真实世界图像注册场景的实验中,该方法在估计准确性和注册性能方面优于现有算法。
Key Takeaways
- SLR旨在通过线性变换估计潜在特征,但面临测量维度中未知排列的问题。
- 现有方法由于排列恢复的组合复杂性,通常只处理小规模案例。
- 提出谱匹配方法,通过对齐测量和特征协方差的谱成分来有效解决大规模SLR问题。
- 谱匹配方法在理论分析中显示出在洗牌LS和洗牌LASSO设置中的准确估计能力。
- 将该方法扩展到图像注册任务中的姿态和对应关系估计。
- 在合成数据集和真实世界图像注册场景的实验中,谱匹配方法表现优于现有算法。
点此查看论文截图

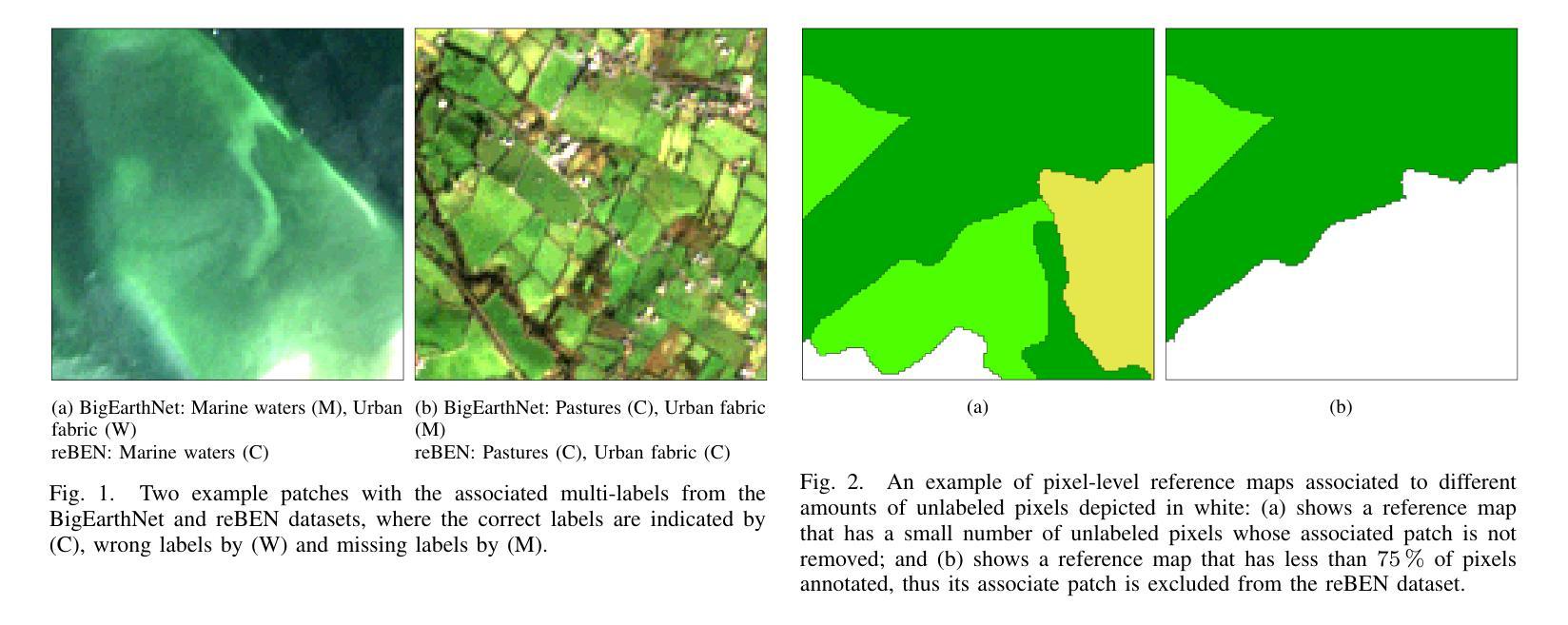
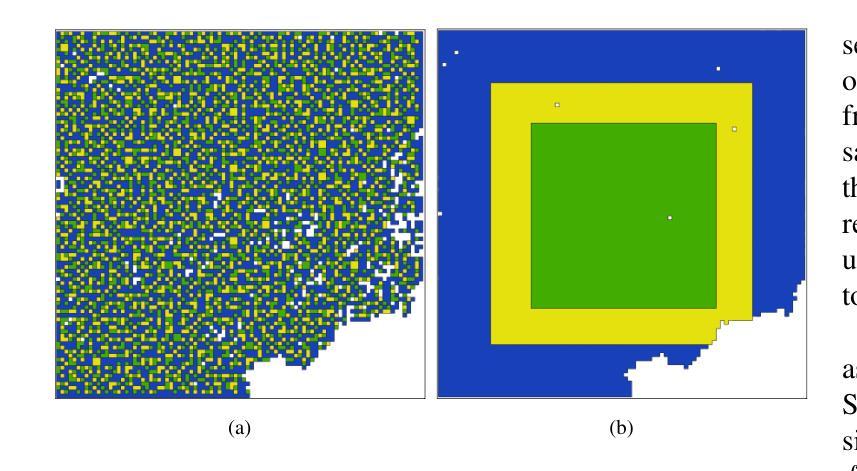
reBEN: Refined BigEarthNet Dataset for Remote Sensing Image Analysis
Authors:Kai Norman Clasen, Leonard Hackel, Tom Burgert, Gencer Sumbul, Begüm Demir, Volker Markl
This paper presents refined BigEarthNet (reBEN) that is a large-scale, multi-modal remote sensing dataset constructed to support deep learning (DL) studies for remote sensing image analysis. The reBEN dataset consists of 549,488 pairs of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 image patches. To construct reBEN, we initially consider the Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 tiles used to construct the BigEarthNet dataset and then divide them into patches of size 1200 m x 1200 m. We apply atmospheric correction to the Sentinel-2 patches using the latest version of the sen2cor tool, resulting in higher-quality patches compared to those present in BigEarthNet. Each patch is then associated with a pixel-level reference map and scene-level multi-labels. This makes reBEN suitable for pixel- and scene-based learning tasks. The labels are derived from the most recent CORINE Land Cover (CLC) map of 2018 by utilizing the 19-class nomenclature as in BigEarthNet. The use of the most recent CLC map results in overcoming the label noise present in BigEarthNet. Furthermore, we introduce a new geographical-based split assignment algorithm that significantly reduces the spatial correlation among the train, validation, and test sets with respect to those present in BigEarthNet. This increases the reliability of the evaluation of DL models. To minimize the DL model training time, we introduce software tools that convert the reBEN dataset into a DL-optimized data format. In our experiments, we show the potential of reBEN for multi-modal multi-label image classification problems by considering several state-of-the-art DL models. The pre-trained model weights, associated code, and complete dataset are available at https://bigearth.net.
本文介绍了精细化的BigEarthNet(reBEN),这是一个为支持遥感图像分析的深度学习(DL)研究而构建的大规模、多模态遥感数据集。reBEN数据集包含549,488对Sentinel-1和Sentinel-2图像补丁。为了构建reBEN,我们首先考虑了用于构建BigEarthNet数据集的Sentinel-1和Sentinel-2瓦片,然后将其划分为大小为1200米x 1200米的补丁。我们对Sentinel-2补丁应用了使用sen2cor工具最新版本的大气校正,与BigEarthNet中现有的补丁相比,这产生了更高质量的补丁。然后,每个补丁都与像素级参考图和场景级多标签相关联。这使得reBEN适合基于像素和场景的学习任务。标签是通过使用与BigEarthNet相同的19类命名法,从最新的2018年CORINE土地覆盖(CLC)地图中得出的。使用最新的CLC地图克服了BigEarthNet中存在的标签噪声。此外,我们引入了一种新的基于地理的分割分配算法,该算法显著减少了训练集、验证集和测试集之间的空间相关性,与BigEarthNet中的情况相比,这增加了深度学习模型评估的可靠性。为了最小化深度学习模型训练时间,我们引入了将reBEN数据集转换为深度学习优化数据格式的软件工具。在我们的实验中,我们通过考虑一些最先进的深度学习模型,展示了reBEN在多模态多标签图像分类问题上的潜力。预训练模型权重、相关代码和完整数据集可在https://bigearth.net上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS) 2025. Our code is available at https://github.com/rsim-tu-berlin/bigearthnet-pipeline
摘要
本论文推出精细化BigEarthNet(reBEN),这是一套大型、多模态遥感数据集,专为支持遥感图像分析的深度学习研究而构建。reBEN数据集包含549488对Sentinel-1和Sentinel-2图像块。reBEN的构建是在BigEarthNet数据集使用的Sentinel-1和Sentinel-2瓦片基础上,将其划分为大小为1200mx1200m的块。我们对Sentinel-2块应用大气校正,使用最新版本的sen2cor工具,得到比BigEarthNet中更高的质量块。每个块都与像素级参考地图和场景级多标签相关联,使reBEN适合基于像素和场景的学习任务。标签是通过利用最新的2018年CORINE土地覆盖图(CLC地图)以及BigEarthNet中的19类命名法得出的,从而克服了BigEarthNet中存在的标签噪声问题。此外,我们引入了一种新的基于地理的分割分配算法,该算法显著降低了训练集、验证集和测试集之间的空间相关性,提高了深度学习模型评估的可靠性。为了缩短深度学习模型的训练时间,我们引入了将reBEN数据集转换为深度学习优化数据格式的软件工具。在实验部分,我们通过考虑一些先进的深度学习模型,展示了reBEN在多模态多标签图像分类问题上的潜力。预训练模型权重、相关代码和完整数据集可在https://bigearth.net获取。
关键见解
- reBEN是一个大型、多模态的遥感数据集,用于支持深度学习在遥感图像分析领域的研究。
- reBEN包含经过大气校正的高质量Sentinel-1和Sentinel-2图像块,适合像素和场景级学习任务。
- 利用最新的CORINE土地覆盖图(CLC地图)来克服BigEarthNet中的标签噪声问题。
- 引入新的地理分割分配算法,降低数据集的空间相关性,提高深度学习模型评估的可靠性。
- 提供软件工具将reBEN数据集转换为深度学习优化数据格式,缩短模型训练时间。
- 通过实验展示reBEN在多模态多标签图像分类问题上的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

Quantum Generative Learning for High-Resolution Medical Image Generation
Authors:Amena Khatun, Kübra Yeter Aydeniz, Yaakov S. Weinstein, Muhammad Usman
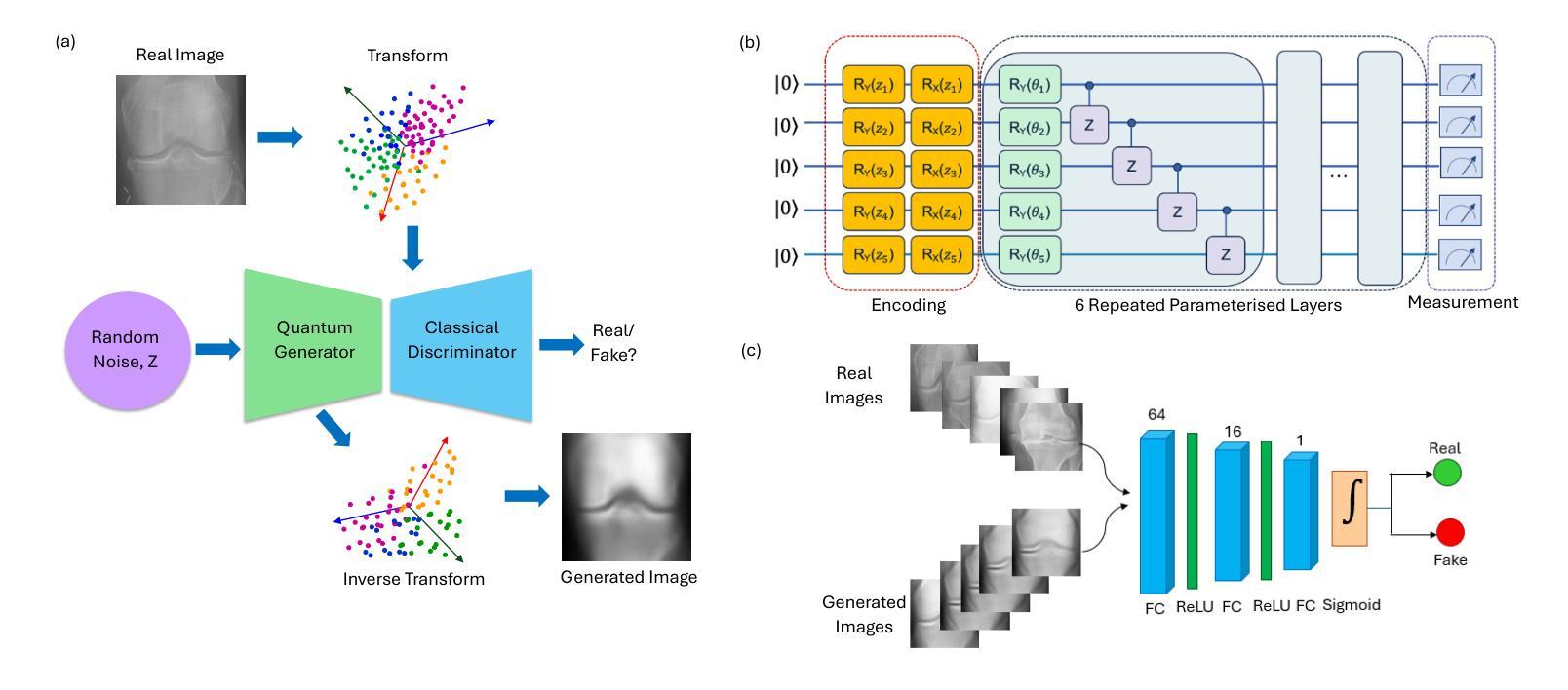
Integration of quantum computing in generative machine learning models has the potential to offer benefits such as training speed-up and superior feature extraction. However, the existing quantum generative adversarial networks (QGANs) fail to generate high-quality images due to their patch-based, pixel-wise learning approaches. These methods capture only local details, ignoring the global structure and semantic information of images. In this work, we address these challenges by proposing a quantum image generative learning (QIGL) approach for high-quality medical image generation. Our proposed quantum generator leverages variational quantum circuit approach addressing scalability issues by extracting principal components from the images instead of dividing them into patches. Additionally, we integrate the Wasserstein distance within the QIGL framework to generate a diverse set of medical samples. Through a systematic set of simulations on X-ray images from knee osteoarthritis and medical MNIST datasets, our model demonstrates superior performance, achieving the lowest Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID) scores compared to its classical counterpart and advanced QGAN models reported in the literature.
将量子计算集成到生成式机器学习模型中,有可能带来训练加速和卓越的特征提取等好处。然而,现有的量子生成对抗网络(QGANs)由于采用基于补丁的逐像素学习方法,无法生成高质量图像。这些方法只能捕捉局部细节,忽略了图像的全局结构和语义信息。在这项工作中,我们通过提出一种用于高质量医学图像生成的量子图像生成学习(QIGL)方法来解决这些挑战。我们提出的量子生成器利用变分量子电路方法,通过从图像中提取主成分而不是将其分成补丁来解决可扩展性问题。此外,我们在QIGL框架中集成了Wasserstein距离,以生成多样化的医学样本集。通过对来自膝关节骨关节炎的X射线图像和医学MNIST数据集的系统模拟,我们的模型表现出卓越的性能,实现了与经典模型和文献中报道的高级QGAN模型相比最低的Fréchet入门距离(FID)得分。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
量子计算集成在生成式机器学习模型中,具有训练加速和卓越特征提取的潜力。然而,现有的量子生成对抗网络(QGANs)由于采用基于补丁的像素级学习方法,无法生成高质量图像。本文提出了一种针对高质量医学图像生成的量子图像生成学习(QIGL)方法,利用变分量子电路解决可扩展性问题,从图像中提取主成分而不是将其分成补丁。此外,我们在QIGL框架中集成了Wasserstein距离,以生成多样化的医学样本。通过一系列针对膝骨关节炎X射线和医学MNIST数据集的模拟,我们的模型表现出卓越性能,实现了与经典模型和文献中报道的高级QGAN模型相比最低的Fréchet入门距离(FID)得分。
Key Takeaways
- 量子计算集成在生成式机器学习模型中可提高训练速度和特征提取质量。
- 现有QGANs因采用基于补丁的像素级学习方法,无法生成高质量图像。
- 提出的QIGL方法利用变分量子电路解决可扩展性问题。
- QIGL方法从图像中提取主成分而非分割成补丁,以提高图像质量。
- QIGL框架集成了Wasserstein距离,以生成多样化的医学样本。
- 模拟实验表明,QIGL模型在生成高质量医学图像方面表现卓越。
点此查看论文截图

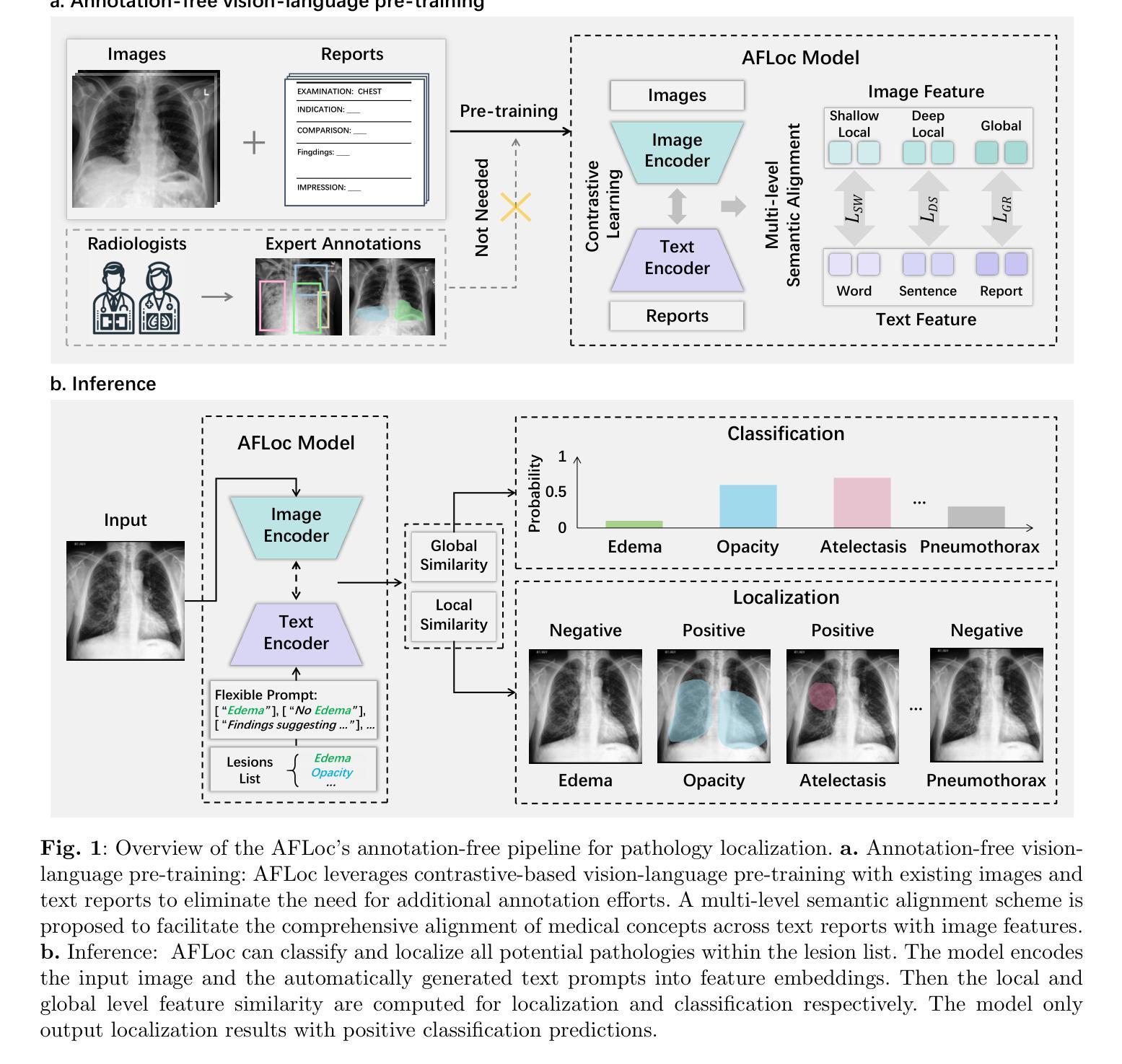
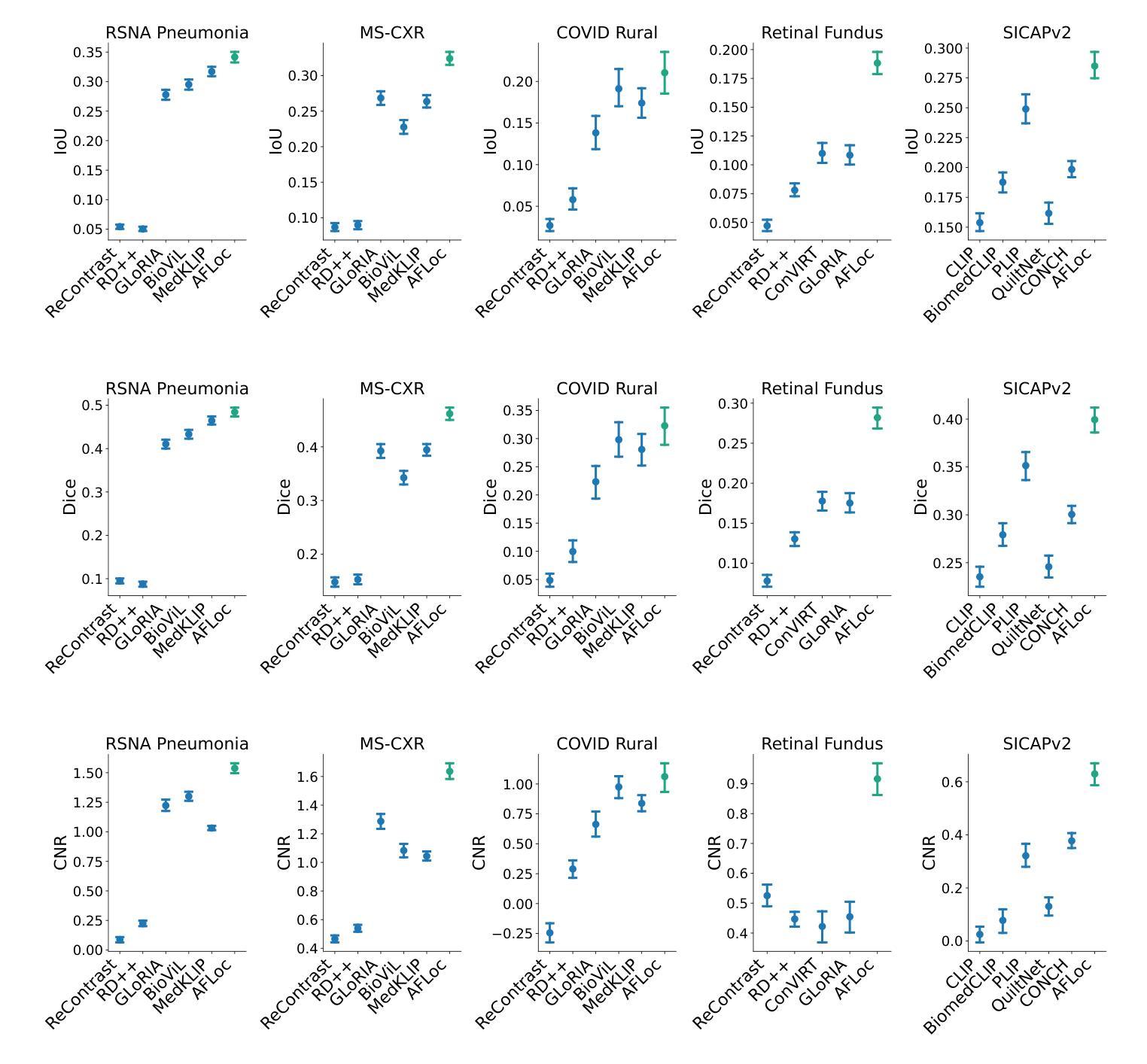
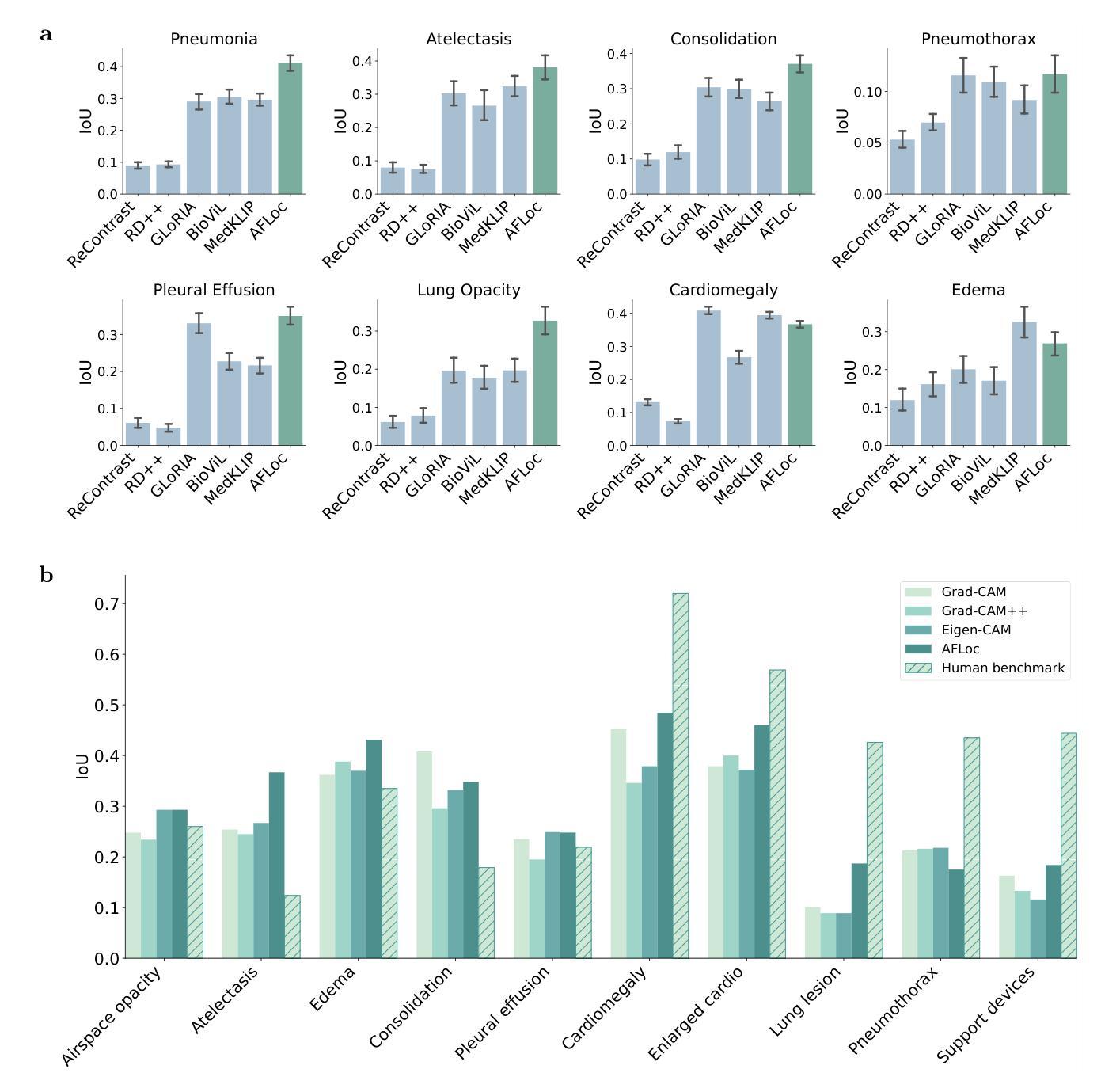
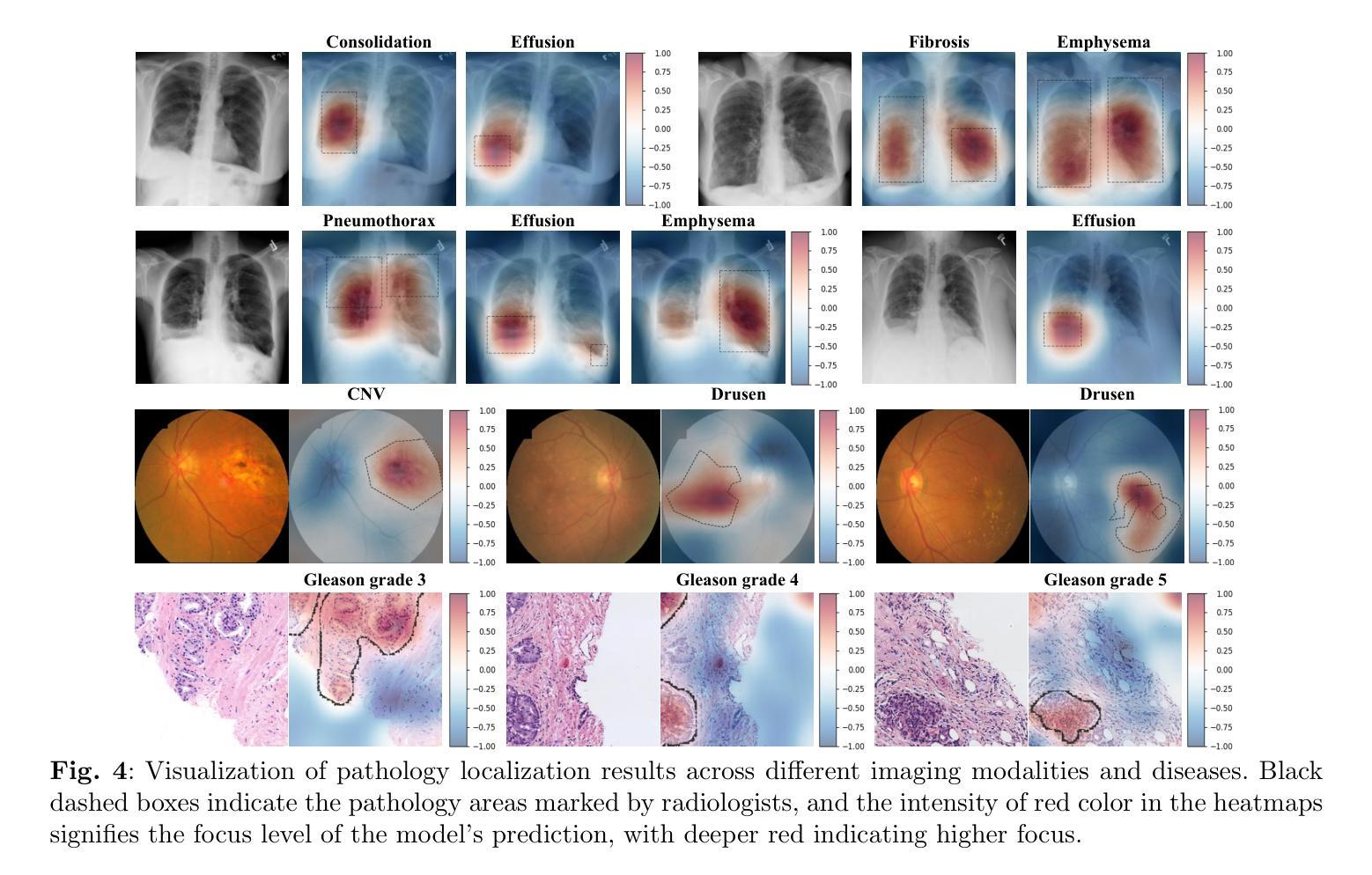
Multi-modal vision-language model for generalizable annotation-free pathology localization and clinical diagnosis
Authors:Hao Yang, Hong-Yu Zhou, Jiarun Liu, Weijian Huang, Zhihuan Li, Yuanxu Gao, Cheng Li, Qiegen Liu, Yong Liang, Qi Yang, Song Wu, Tao Tan, Hairong Zheng, Kang Zhang, Shanshan Wang
Defining pathologies automatically from medical images aids the understanding of the emergence and progression of diseases, and such an ability is crucial in clinical diagnostics. However, existing deep learning models heavily rely on expert annotations and lack generalization capabilities in open clinical environments. In this study, we present a generalizable vision-language model for Annotation-Free pathology Localization (AFLoc). The core strength of AFLoc lies in its extensive multi-level semantic structure-based contrastive learning, which comprehensively aligns multi-granularity medical concepts from reports with abundant image features, to adapt to the diverse expressions of pathologies and unseen pathologies without the reliance on image annotations from experts. We conducted primary experiments on a dataset of 220K pairs of image-report chest X-ray images, and performed extensive validation across six external datasets encompassing 20 types of chest pathologies. The results demonstrate that AFLoc outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both annotation-free localization and classification tasks. Additionally, we assessed the generalizability of AFLoc on other modalities, including histopathology and retinal fundus images. Extensive experiments show that AFLoc exhibits robust generalization capabilities, even surpassing human benchmarks in localizing five different types of pathological images. These results highlight the potential of AFLoc in reducing annotation requirements and its applicability in complex clinical environments.
从医学图像中自动定义病理有助于了解疾病的出现和进展,这种能力在临床诊断中至关重要。然而,现有的深度学习模型严重依赖于专家注释,缺乏开放临床环境中的泛化能力。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种通用的视觉语言模型,用于无注释病理定位(AFLoc)。AFLoc的核心优势在于其基于多层次语义结构的对比学习,该方法全面地对齐报告中的多粒度医学概念与丰富的图像特征,以适应各种病理表达和未见过的病理,无需依赖专家的图像注释。我们在一组包含22万对图像报告胸部X射线图像的数据集上进行了初步实验,并在包含20种胸部病理的六个外部数据集上进行了广泛验证。结果表明,AFLoc在无需注释的定位和分类任务上均优于最先进的方法。此外,我们还评估了AFLoc在其他模态(包括组织病理学和眼底视网膜图像)上的泛化能力。大量实验表明,AFLoc表现出稳健的泛化能力,甚至在定位五种不同类型的病理图像时超越了人类基准测试。这些结果突出了AFLoc在减少注释要求及其在复杂临床环境中的适用性方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种无需标注的自动病理定位模型(AFLoc),该模型基于多层次语义结构对比学习,能够从医学图像中识别出病理特征,无需专家标注。实验结果显示,AFLoc在无需标注的定位和分类任务上均表现出卓越性能,并在多种模态图像中展现出强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- AFLoc模型利用多层次语义结构对比学习,实现对医学图像中病理特征的自动识别和定位。
- 该模型无需专家标注,能够自适应不同的病理表达形式,并对未见过的病理情况进行识别。
- 实验结果显示,AFLoc在胸部位X光图像的数据集上表现出卓越性能。
- AFLoc在六种外部数据集、涵盖20种胸部病理类型的广泛验证中,仍表现出强大的性能。
- AFLoc在其他模态图像(如组织病理学和视网膜基金图像)中也展现出良好的泛化能力。
- AFLoc在定位五种不同类型的病理图像时,甚至超越了人类基准测试的表现。
点此查看论文截图