⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-18 更新
Enhancing Contrastive Learning Inspired by the Philosophy of “The Blind Men and the Elephant”
Authors:Yudong Zhang, Ruobing Xie, Jiansheng Chen, Xingwu Sun, Zhanhui Kang, Yu Wang
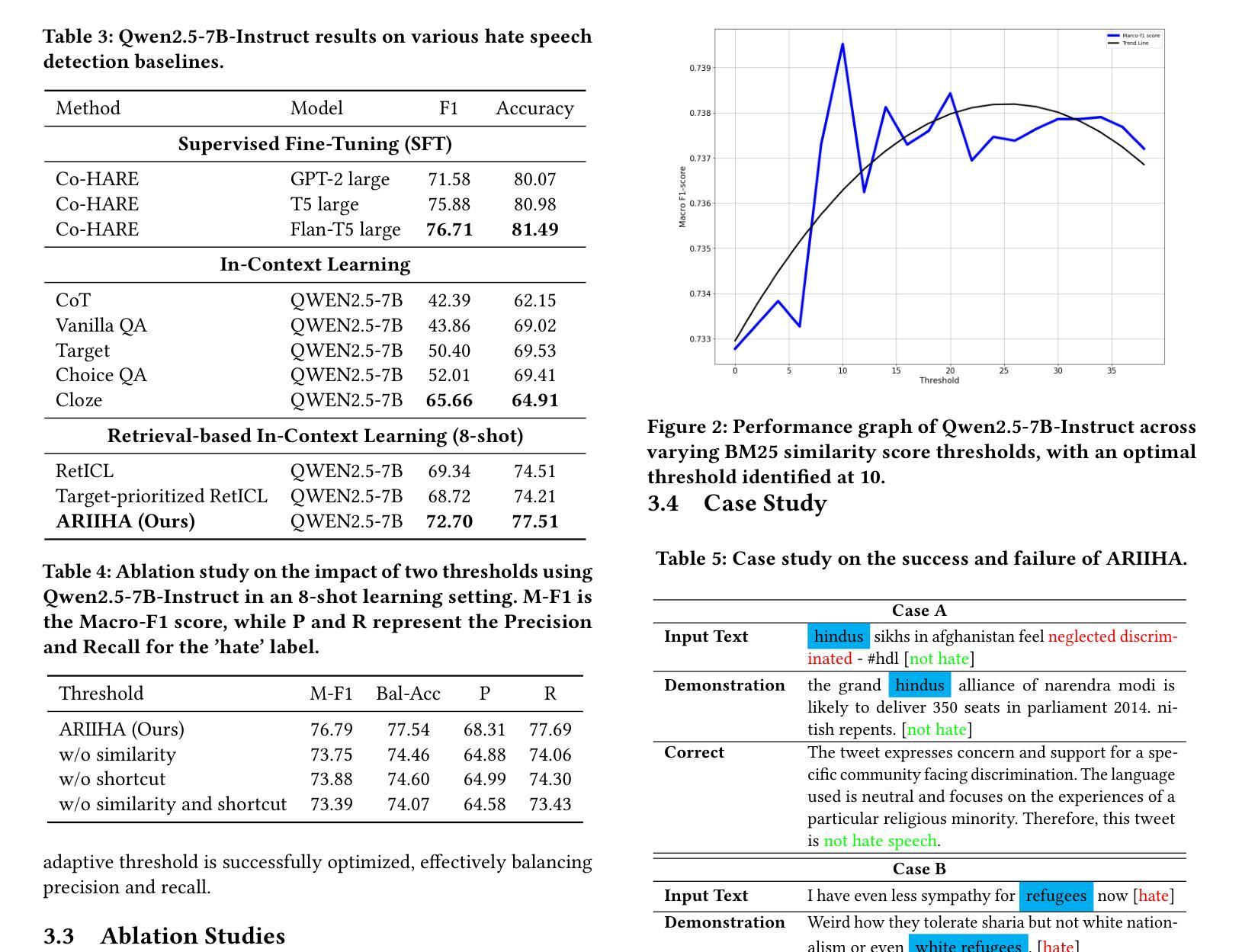
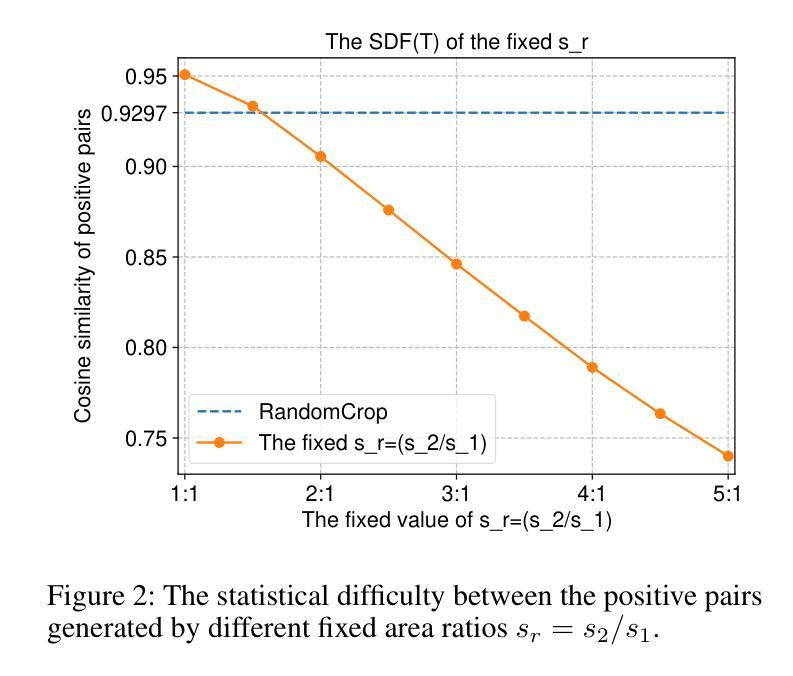
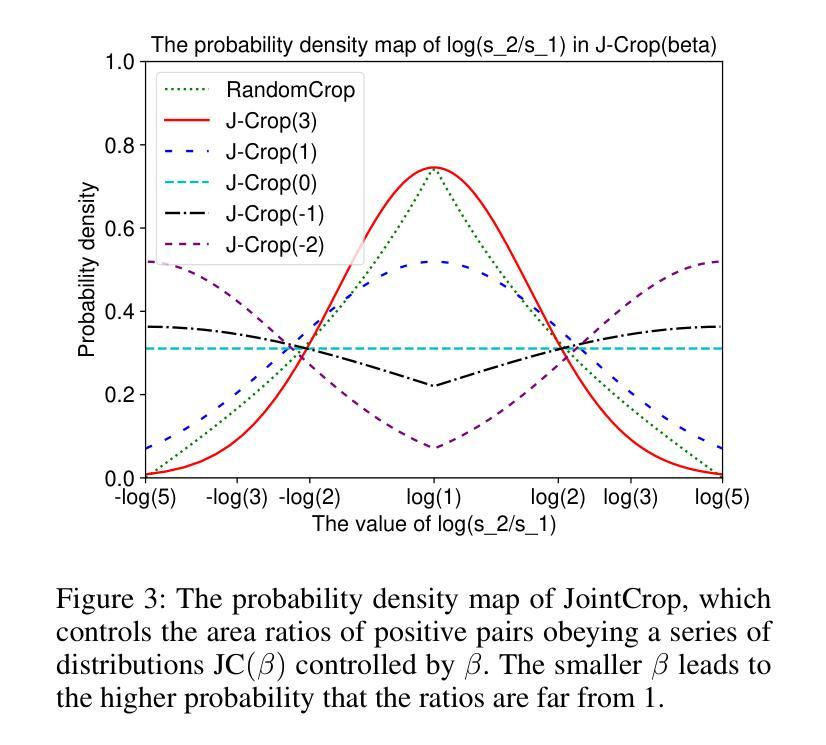
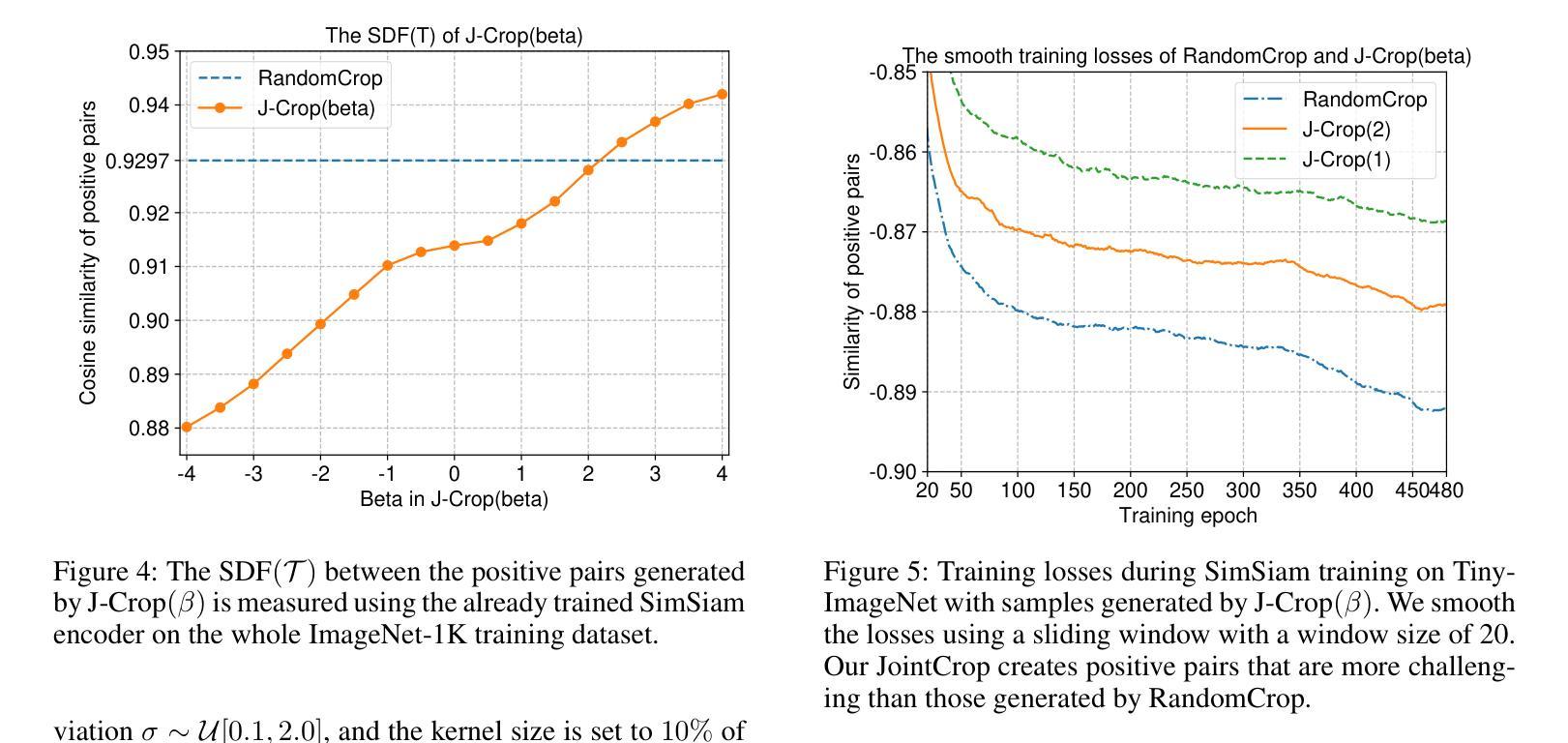
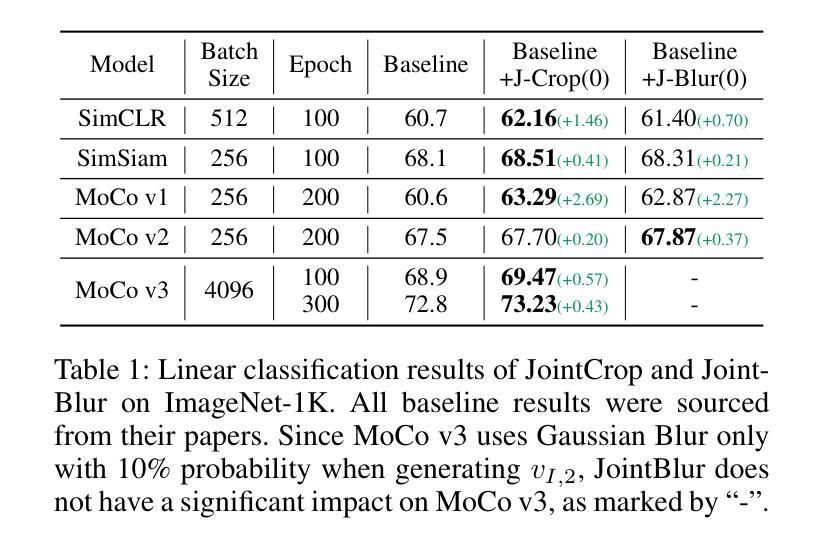
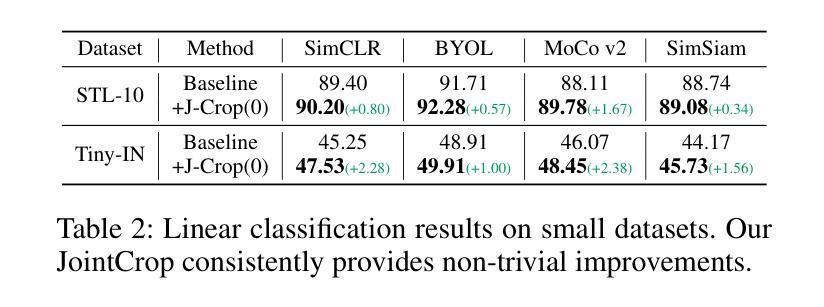
Contrastive learning is a prevalent technique in self-supervised vision representation learning, typically generating positive pairs by applying two data augmentations to the same image. Designing effective data augmentation strategies is crucial for the success of contrastive learning. Inspired by the story of the blind men and the elephant, we introduce JointCrop and JointBlur. These methods generate more challenging positive pairs by leveraging the joint distribution of the two augmentation parameters, thereby enabling contrastive learning to acquire more effective feature representations. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first effort to explicitly incorporate the joint distribution of two data augmentation parameters into contrastive learning. As a plug-and-play framework without additional computational overhead, JointCrop and JointBlur enhance the performance of SimCLR, BYOL, MoCo v1, MoCo v2, MoCo v3, SimSiam, and Dino baselines with notable improvements.
对比学习是自监督视觉表示学习中的一项流行技术,通常通过应用两种数据增强到同一图像来生成正样本对。设计有效的数据增强策略对于对比学习的成功至关重要。受盲人摸象故事的启发,我们引入了JointCrop和JointBlur方法。这些方法通过利用两个增强参数的联合分布,生成更具挑战性的正样本对,从而使对比学习能够获取更有效的特征表示。据我们所知,这是首次明确将两个数据增强参数的联合分布纳入对比学习。JointCrop和JointBlur是一个即插即用的框架,无需额外的计算开销,它们提高了SimCLR、BYOL、MoCo v1、MoCo v2、MoCo v3、SimSiam和Dino基准线的性能,并带来了显著的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary:对比学习是自监督视觉表示学习中的常见技术,通常通过对同一图像应用两种数据增强来生成正样本对。设计有效的数据增强策略对于对比学习的成功至关重要。我们受到盲人摸象故事的启发,推出了JointCrop和JointBlur方法。这些方法通过利用两种增强参数的联合分布来生成更具挑战性的正样本对,使对比学习能够获取更有效的特征表示。据我们所知,这是首次明确地将两个数据增强参数的联合分布纳入对比学习。作为无需额外计算开销的即插即用框架,JointCrop和JointBlur显著提高了SimCLR、BYOL、MoCo v1、MoCo v2、MoCo v3、SimSiam和Dino基准测试的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 对比学习在自监督视觉表示学习中广泛应用,通过生成正样本对进行训练。
- 数据增强策略的设计对于对比学习的效果至关重要。
- 提出了JointCrop和JointBlur方法,通过利用两种增强参数的联合分布生成更具挑战性的正样本对。
- 这是首次将两个数据增强参数的联合分布明确纳入对比学习。
- JointCrop和JointBlur方法提高了多种基准测试的性能。
- JointCrop和JointBlur作为一个即插即用的框架,无需额外的计算开销。
点此查看论文截图

Two Effects, One Trigger: On the Modality Gap, Object Bias, and Information Imbalance in Contrastive Vision-Language Models
Authors:Simon Schrodi, David T. Hoffmann, Max Argus, Volker Fischer, Thomas Brox
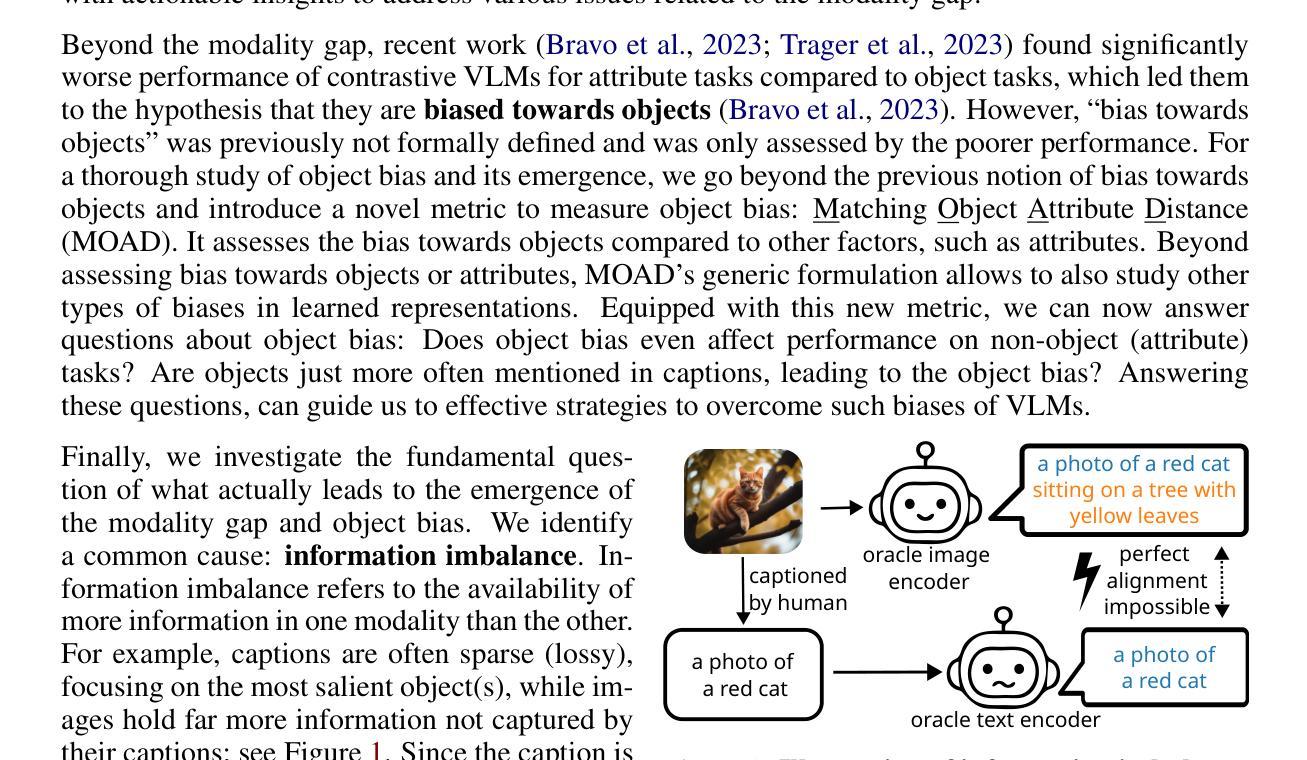
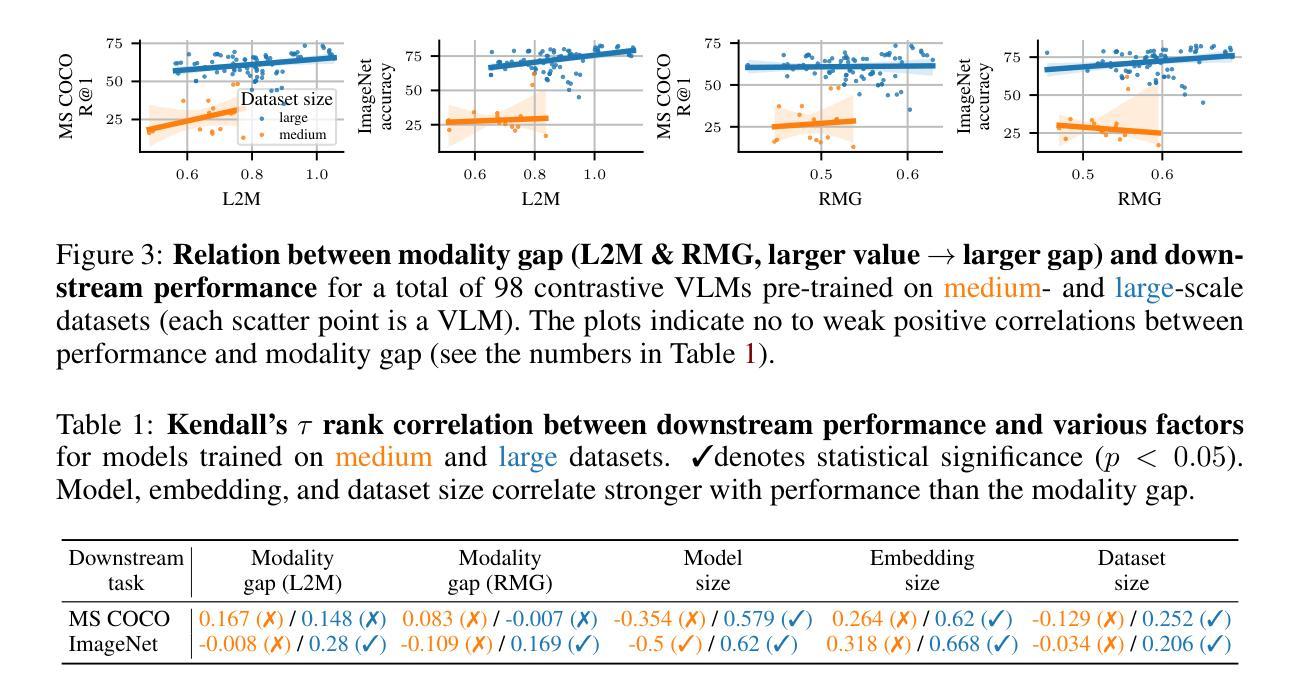
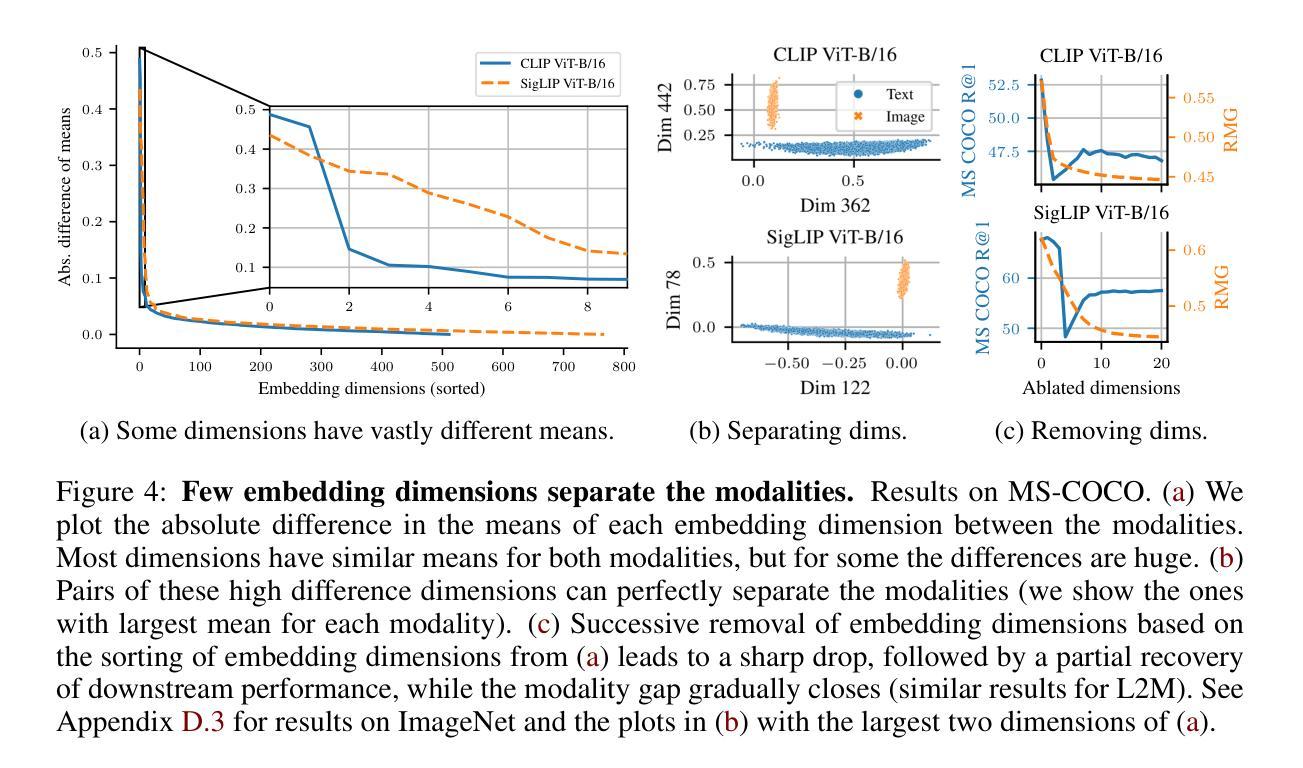
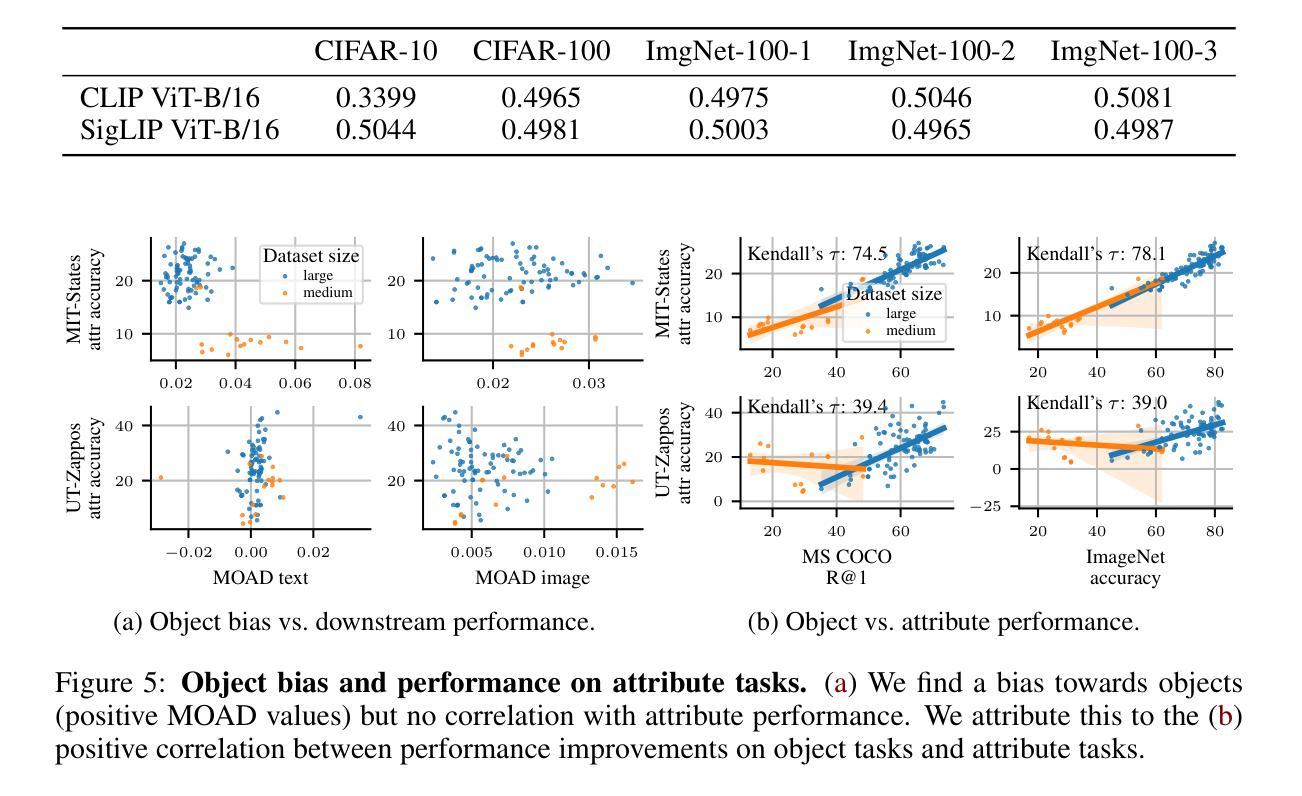
Contrastive vision-language models (VLMs), like CLIP, have gained popularity for their versatile applicability to various downstream tasks. Despite their successes in some tasks, like zero-shot object recognition, they perform surprisingly poor on other tasks, like attribute recognition. Previous work has attributed these challenges to the modality gap, a separation of image and text in the shared representation space, and to a bias towards objects over other factors, such as attributes. In this analysis paper, we investigate both phenomena thoroughly. We evaluated off-the-shelf VLMs and while the gap’s influence on performance is typically overshadowed by other factors, we find indications that closing the gap indeed leads to improvements. Moreover, we find that, contrary to intuition, only few embedding dimensions drive the gap and that the embedding spaces are differently organized. To allow for a clean study of object bias, we introduce a definition and a corresponding measure of it. Equipped with this tool, we find that object bias does not lead to worse performance on other concepts, such as attributes per se. However, why do both phenomena, modality gap and object bias, emerge in the first place? To answer this fundamental question and uncover some of the inner workings of contrastive VLMs, we conducted experiments that allowed us to control the amount of shared information between the modalities. These experiments revealed that the driving factor behind both the modality gap and the object bias, is an information imbalance between images and captions, and unveiled an intriguing connection between the modality gap and entropy of the logits.
对比视觉语言模型(VLMs),如CLIP,因其对各种下游任务的通用适用性而广受欢迎。尽管它们在零样本目标识别等任务中取得了成功,但在属性识别等其他任务上的表现却出人意料地糟糕。之前的工作将这些挑战归因于模态差距,即图像和文本在共享表示空间中的分离,以及对象与其他因素(如属性)之间的偏见。在这篇分析论文中,我们对这两种现象进行了彻底的研究。我们评估了现成的VLMs,虽然性能差距的影响通常被其他因素所掩盖,但我们发现缩小差距确实会导致性能改进的迹象。此外,我们发现,与直觉相反的是,只有少数嵌入维度驱动差距,并且嵌入空间的组织方式不同。为了对对象偏见进行清晰的研究,我们引入了定义和相应的度量标准。使用这个工具,我们发现对象偏见并不会导致对其他概念(如属性本身)的性能更差。然而,为什么会出现模态差距和对象偏见这两种现象呢?为了回答这个问题并揭示对比VLMs的一些内在工作原理,我们进行了一系列实验,以控制模态之间共享信息量的多少。这些实验表明,模态差距和对象偏见背后的驱动因素是图像和字幕之间的信息不平衡,并揭示了模态差距与logits熵之间的有趣联系。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 (Oral)
Summary
本文分析了对比视觉语言模型(VLMs)的挑战,包括模态差距和对象偏见问题。研究发现,模态差距对性能的影响通常被其他因素掩盖,但缩小差距确实有助于提高性能。此外,只有少数嵌入维度驱动差距,且嵌入空间组织方式不同。为了研究对象偏见,本文给出了定义和相应的度量方法。研究发现对象偏见并不导致对属性等概念的性能下降。通过控制模态之间共享信息量的实验,发现模态差距和对象偏见的驱动因素是图像和字幕之间的信息不平衡,并揭示了模态差距和逻辑熵之间的有趣联系。
Key Takeaways
- 对比视觉语言模型(VLMs)如CLIP在多下游任务中表现出广泛应用性,但在某些任务上表现不佳,如属性识别。
- 模态差距是图像和文本在共享表示空间中的分离,对VLM性能产生影响。
- 缩小模态差距有助于提高VLM的性能。
- 只有少数嵌入维度在驱动模态差距中起作用,且嵌入空间组织方式不同。
- 对象偏见并不直接导致对属性等概念的性能下降。
- 模态差距和对象偏见的根本原因是图像和字幕之间的信息不平衡。
- 模态差距与逻辑熵之间存在有趣联系。
点此查看论文截图