⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-18 更新
RADLER: Radar Object Detection Leveraging Semantic 3D City Models and Self-Supervised Radar-Image Learning
Authors:Yuan Luo, Rudolf Hoffmann, Yan Xia, Olaf Wysocki, Benedikt Schwab, Thomas H. Kolbe, Daniel Cremers
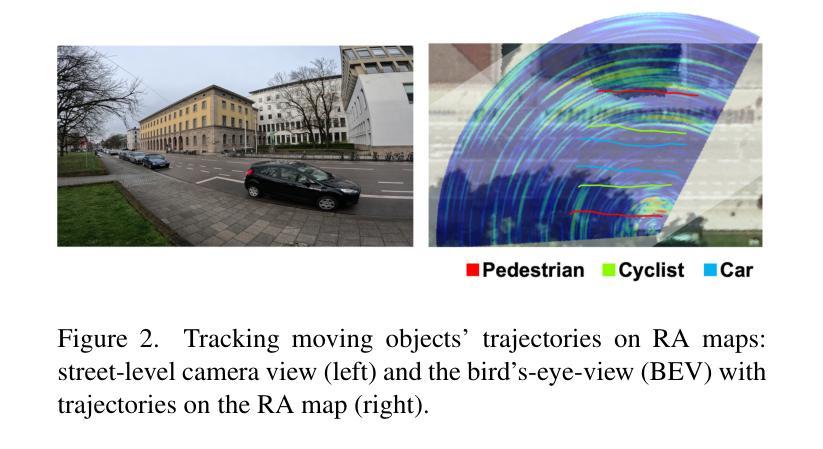
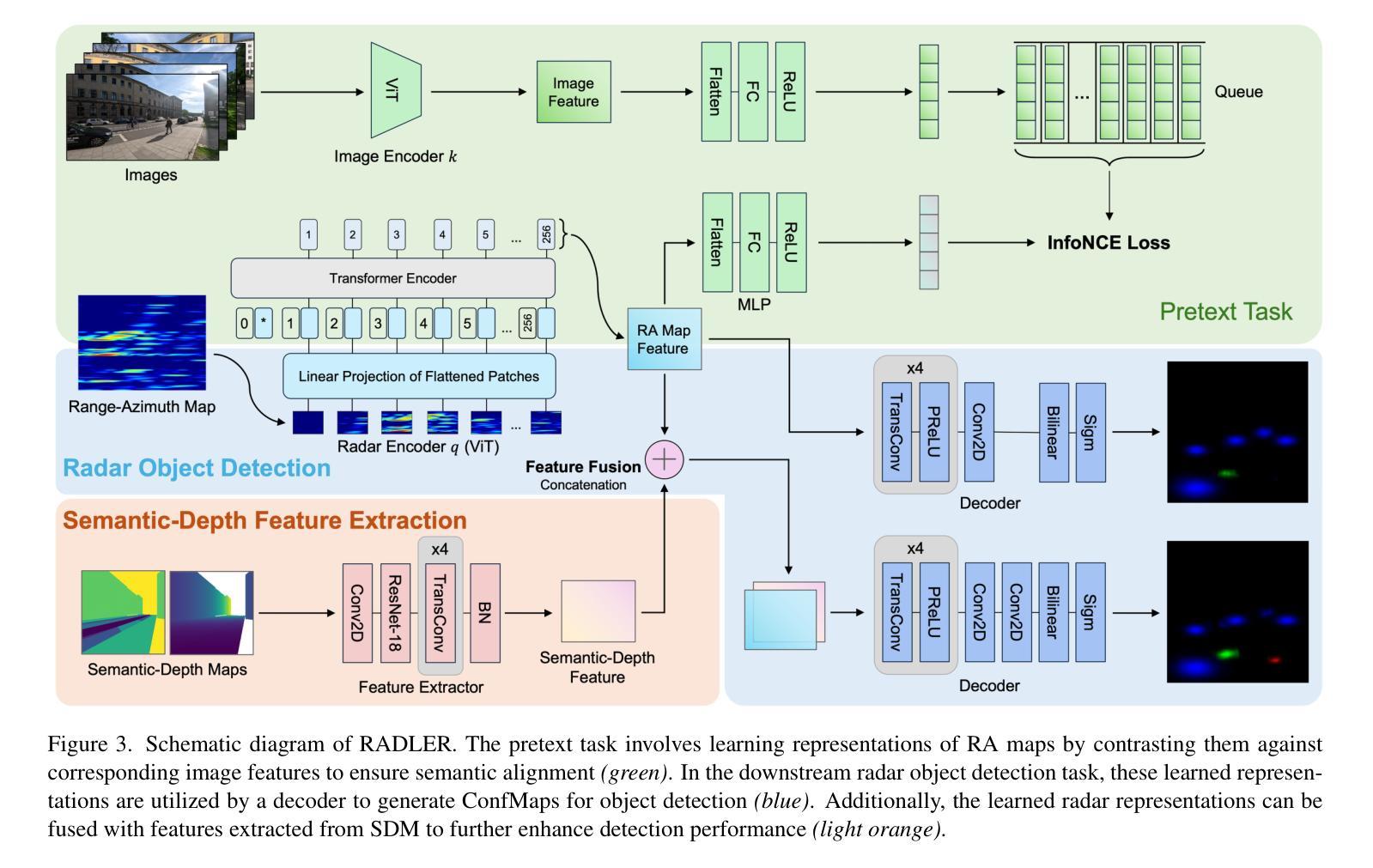
Semantic 3D city models are worldwide easy-accessible, providing accurate, object-oriented, and semantic-rich 3D priors. To date, their potential to mitigate the noise impact on radar object detection remains under-explored. In this paper, we first introduce a unique dataset, RadarCity, comprising 54K synchronized radar-image pairs and semantic 3D city models. Moreover, we propose a novel neural network, RADLER, leveraging the effectiveness of contrastive self-supervised learning (SSL) and semantic 3D city models to enhance radar object detection of pedestrians, cyclists, and cars. Specifically, we first obtain the robust radar features via a SSL network in the radar-image pretext task. We then use a simple yet effective feature fusion strategy to incorporate semantic-depth features from semantic 3D city models. Having prior 3D information as guidance, RADLER obtains more fine-grained details to enhance radar object detection. We extensively evaluate RADLER on the collected RadarCity dataset and demonstrate average improvements of 5.46% in mean avarage precision (mAP) and 3.51% in mean avarage recall (mAR) over previous radar object detection methods. We believe this work will foster further research on semantic-guided and map-supported radar object detection. Our project page is publicly available athttps://gpp-communication.github.io/RADLER .
语义3D城市模型在全球范围内易于访问,提供准确、面向对象和语义丰富的3D先验知识。到目前为止,其减轻雷达目标检测中噪声影响的潜力尚未得到充分探索。在本文中,我们首先介绍了一个独特的数据集RadarCity,它包含54K个同步雷达图像对和语义3D城市模型。此外,我们提出了一种新的神经网络RADLER,它利用对比自我监督学习(SSL)和语义3D城市模型的效力,以提高对行人、自行车和汽车的雷达目标检测。具体来说,我们首先通过雷达图像伪装任务中的SSL网络获得稳健的雷达特征。然后,我们使用简单有效的特征融合策略,融入来自语义3D城市模型的语义深度特征。有了先前的3D信息作为指导,RADLER获得了更精细的细节,提高了雷达目标检测。我们在收集的RadarCity数据集上对RADLER进行了广泛评估,证明其在平均平均精度(mAP)和平均召回率(mAR)上分别比之前的雷达目标检测方法提高了5.46%和3.51%。我们相信这项工作将促进语义引导和地图支持的雷达目标检测的进一步研究。我们的项目页面可公开访问于:https://gpp-communication.github.io/RADLER。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The paper accepted for CVPRW ‘25 (PBVS 2025 - the Perception Beyond the Visible Spectrum)
Summary
语义3D城市模型易于全球访问,能够提供准确、面向对象和语义丰富的3D先验信息。本文介绍了一个独特的数据集RadarCity,并利用语义3D城市模型,提出了一种新型神经网络RADLER,通过对比自我监督学习提高雷达目标检测的准确性。RADLER通过结合雷达图像和语义深度特征,提高了对行人、骑行者和汽车的雷达目标检测的精细度。在RadarCity数据集上的评估表明,与之前的雷达目标检测方法相比,RADLER在平均精度和平均召回率方面有所改进。
Key Takeaways
- 语义3D城市模型提供准确、面向对象和语义丰富的3D先验信息,全球易于访问。
- 介绍了一个独特的数据集RadarCity,包含54K同步雷达图像对和语义3D城市模型。
- 提出了一种新型神经网络RADLER,结合对比自我监督学习和语义3D城市模型,以提高雷达目标检测的准确性。
- RADLER通过结合雷达图像和语义深度特征,提高了对行人、骑行者和汽车的雷达目标检测的精细度。
- 在RadarCity数据集上的评估显示,RADLER在平均精度和平均召回率方面较之前的雷达目标检测方法有平均5.46%和3.51%的改进。
- 该工作将为语义引导和地图支持的雷达目标检测研究带来新的视角和可能性。
点此查看论文截图

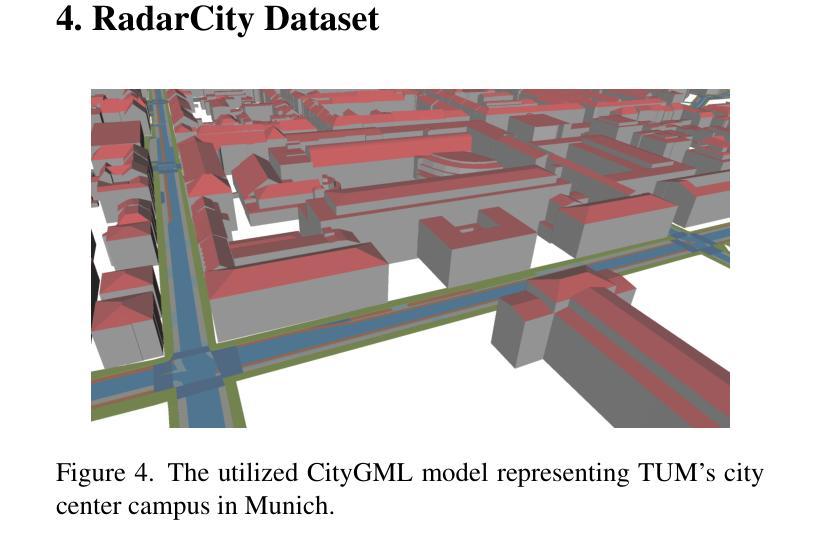
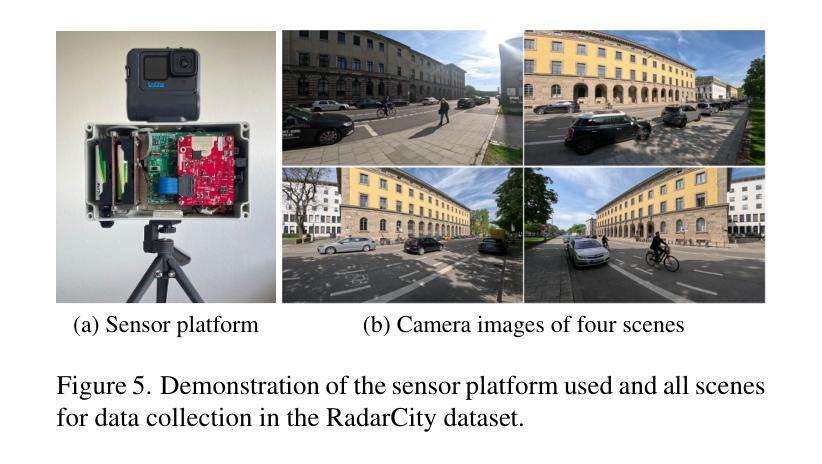
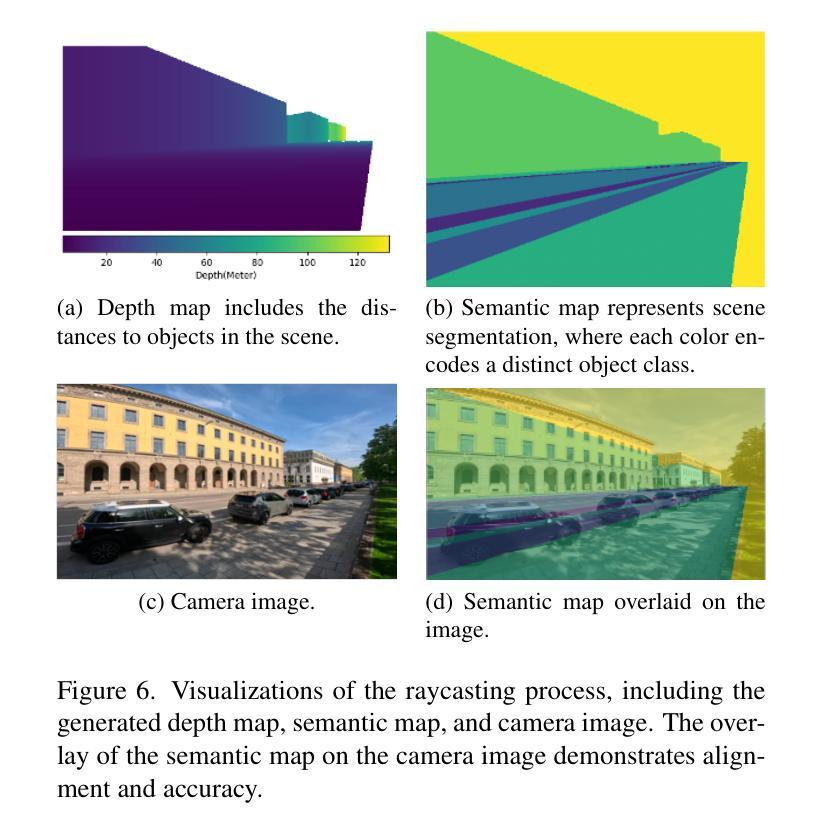

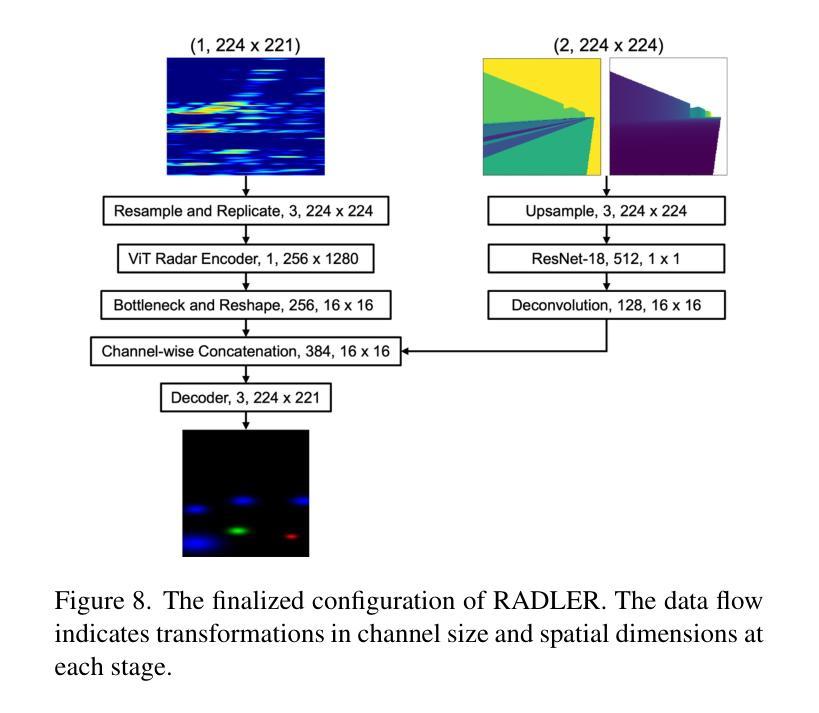
Remote sensing colour image semantic segmentation of trails created by large herbivorous Mammals
Authors:Jose Francisco Diez-Pastor, Francisco Javier Gonzalez-Moya, Pedro Latorre-Carmona, Francisco Javier Perez-Barbería, Ludmila I. Kuncheva, Antonio Canepa-Oneto, Alvar Arnaiz-González, Cesar Garcia-Osorio
Detection of spatial areas where biodiversity is at risk is of paramount importance for the conservation and monitoring of ecosystems. Large terrestrial mammalian herbivores are keystone species as their activity not only has deep effects on soils, plants, and animals, but also shapes landscapes, as large herbivores act as allogenic ecosystem engineers. One key landscape feature that indicates intense herbivore activity and potentially impacts biodiversity is the formation of grazing trails. Grazing trails are formed by the continuous trampling activity of large herbivores that can produce complex networks of tracks of bare soil. Here, we evaluated different algorithms based on machine learning techniques to identify grazing trails. Our goal is to automatically detect potential areas with intense herbivory activity, which might be beneficial for conservation and management plans. We have applied five semantic segmentation methods combined with fourteen encoders aimed at mapping grazing trails on aerial images. Our results indicate that in most cases the chosen methodology successfully mapped the trails, although there were a few instances where the actual trail structure was underestimated. The UNet architecture with the MambaOut encoder was the best architecture for mapping trails. The proposed approach could be applied to develop tools for mapping and monitoring temporal changes in these landscape structures to support habitat conservation and land management programs. This is the first time, to the best of our knowledge, that competitive image segmentation results are obtained for the detection and delineation of trails of large herbivorous mammals.
对生物多样性受到威胁的空间区域进行检测对于生态系统和物种的保护和监测至关重要。大型陆地哺乳动物草食动物是关键的物种,因为它们的活动不仅对土壤、植物和动物产生深远影响,还塑造景观地貌,作为异源生态系统工程师的角色。指示强烈草食动物活动和可能影响生物多样性的一个关键景观特征是放牧轨迹的形成。放牧轨迹是由大型草食动物持续的践踏活动形成的,会产生复杂的裸露土壤轨迹网络。在这里,我们评估了基于机器学习技术的不同算法来识别放牧轨迹。我们的目标是自动检测潜在的草食活动强烈区域,这可能对保护和计划管理有益。我们应用了五种语义分割方法,结合十四种编码器,旨在将空中图像上的放牧轨迹进行映射。我们的结果表明,在大多数情况下,所选方法成功地绘制了轨迹图,尽管在某些情况下实际轨迹结构被低估了。使用MambaOut编码器的UNet架构是绘制轨迹的最佳架构。所提出的方法可应用于开发工具和监测这些景观结构随时间的变化,以支持栖息地的保护和土地管理项目。据我们所知,这是首次在大型草食动物的足迹检测和划定方面取得竞争的图像分割结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 6 figures. Submitted to Computers and Geosciences
Summary
采用机器学习算法检测大型草食动物放牧路径对于生态系统保护和监测至关重要。研究对比了五种语义分割方法和十四种编码器在航空图像上识别放牧路径的效果。结果显示,所选方法大多成功绘制出路径,但少数情况下实际路径结构被低估。UNet架构与MambaOut编码器是绘制路径的最佳组合。该方法可应用于开发工具,以监测这些景观结构的时空变化,支持栖息地保护和土地管理计划。这是首次成功运用图像分割技术检测并划定大型草食动物的放牧路径。
Key Takeaways
- 大型草食动物放牧路径的检测对生态系统保护和监测至关重要。
- 研究评估了多种语义分割方法和编码器在航空图像上识别放牧路径的效果。
- UNet架构与MambaOut编码器组合在绘制放牧路径方面表现最佳。
- 所选方法在多数情况下成功绘制出路径,但存在低估实际路径结构的情况。
- 该方法可应用于监测放牧路径的时空变化,并支持栖息地保护和土地管理计划。
- 这是首次成功运用图像分割技术检测并划定大型草食动物的放牧路径。
点此查看论文截图

Single-shot Star-convex Polygon-based Instance Segmentation for Spatially-correlated Biomedical Objects
Authors:Trina De, Adrian Urbanski, Artur Yakimovich
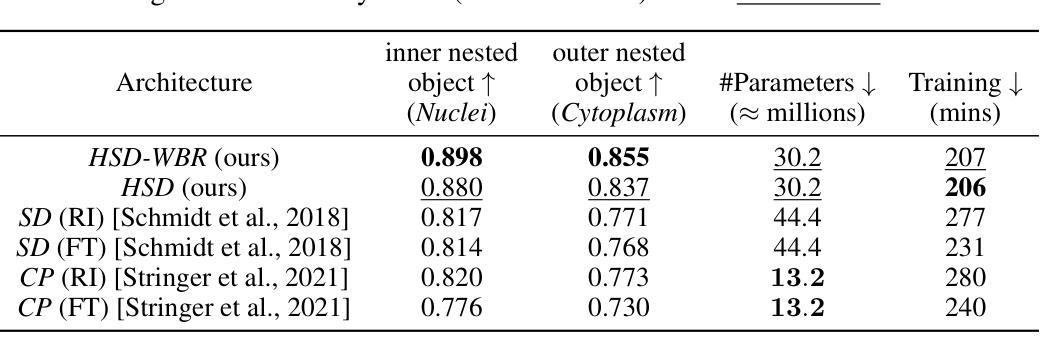
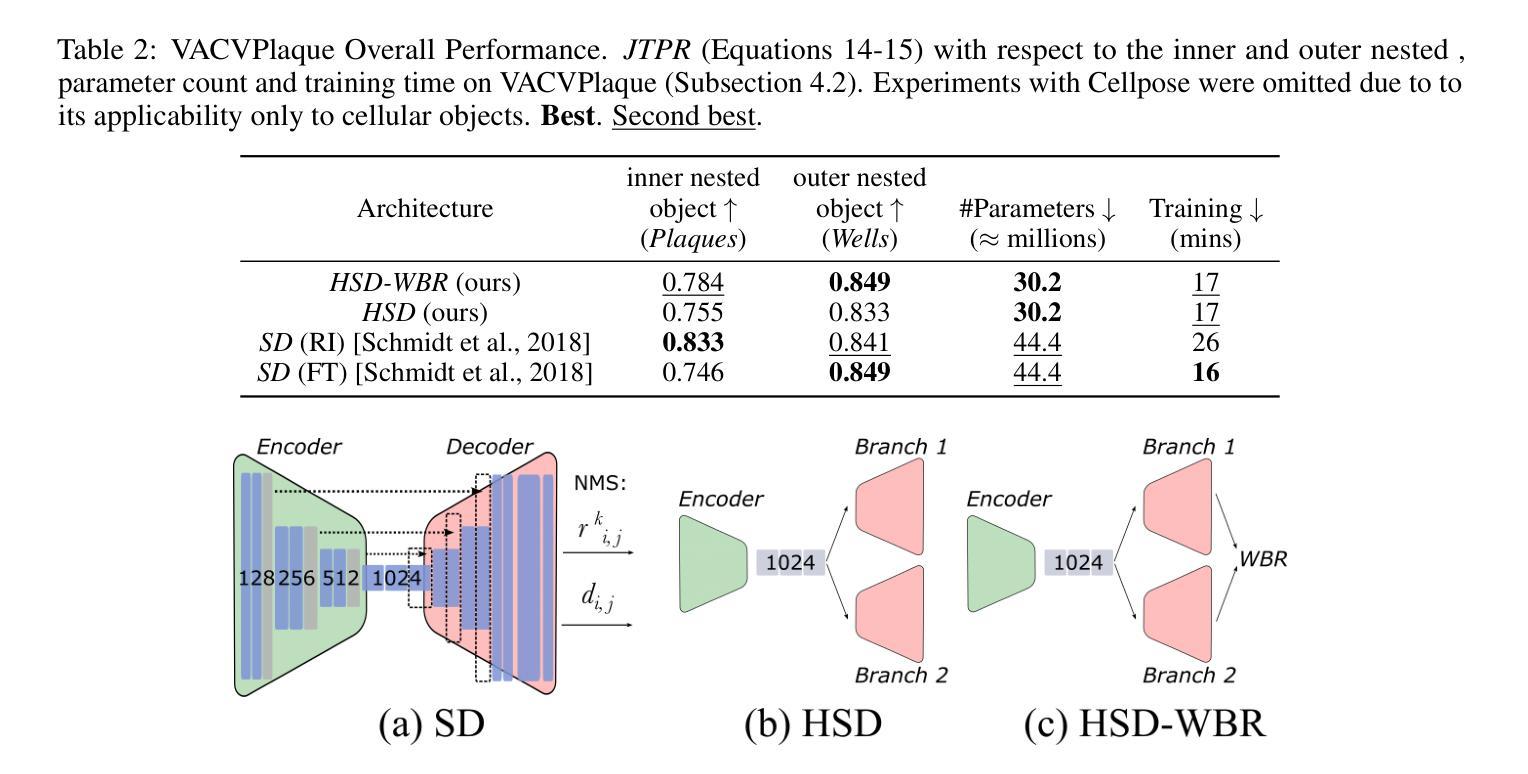
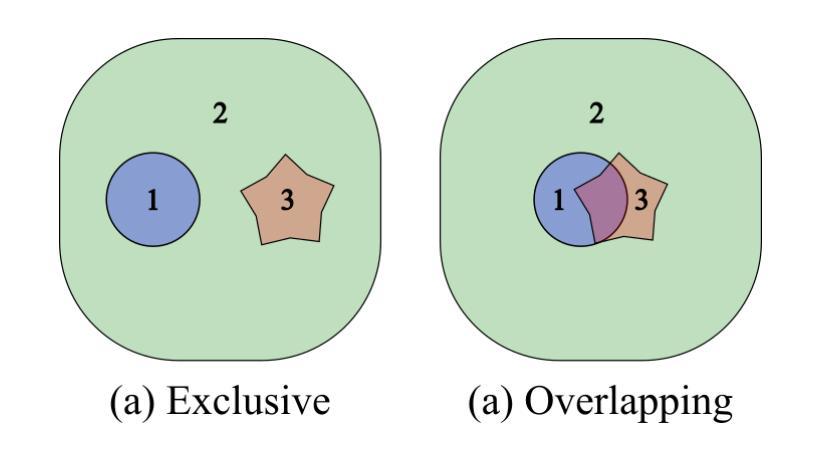
Biomedical images often contain objects known to be spatially correlated or nested due to their inherent properties, leading to semantic relations. Examples include cell nuclei being nested within eukaryotic cells and colonies growing exclusively within their culture dishes. While these semantic relations bear key importance, detection tasks are often formulated independently, requiring multi-shot analysis pipelines. Importantly, spatial correlation could constitute a fundamental prior facilitating learning of more meaningful representations for tasks like instance segmentation. This knowledge has, thus far, not been utilised by the biomedical computer vision community. We argue that the instance segmentation of two or more categories of objects can be achieved in parallel. We achieve this via two architectures HydraStarDist (HSD) and the novel (HSD-WBR) based on the widely-used StarDist (SD), to take advantage of the star-convexity of our target objects. HSD and HSD-WBR are constructed to be capable of incorporating their interactions as constraints into account. HSD implicitly incorporates spatial correlation priors based on object interaction through a joint encoder. HSD-WBR further enforces the prior in a regularisation layer with the penalty we proposed named Within Boundary Regularisation Penalty (WBR). Both architectures achieve nested instance segmentation in a single shot. We demonstrate their competitiveness based on $IoU_R$ and AP and superiority in a new, task-relevant criteria, Joint TP rate (JTPR) compared to their baseline SD and Cellpose. Our approach can be further modified to capture partial-inclusion/-exclusion in multi-object interactions in fluorescent or brightfield microscopy or digital imaging. Finally, our strategy suggests gains by making this learning single-shot and computationally efficient.
生物医学图像中的对象通常由于其固有属性而具有空间相关性或嵌套关系,从而导致语义关系。例如,细胞核位于真核细胞内,菌落仅在培养皿中生长。尽管这些语义关系非常重要,但检测任务通常被独立制定,需要多阶段分析流程。重要的是,空间相关性可能构成一种基本先验,有助于学习更具意义的表示形式,用于实例分割等任务。然而,迄今为止,生物医学计算机视觉界尚未利用这一知识。我们主张可以并行实现两个或多个类别的实例分割。我们通过两种架构实现了这一点:HydraStarDist(HSD)和基于广泛使用StarDist(SD)的新型HSD-WBR,以利用目标对象的星形凸性。HSD和HSD-WBR被构建为能够考虑其交互作为约束。HSD通过联合编码器隐式地结合基于对象交互的空间相关性先验。HSD-WBR通过我们提出的名为“边界内正则化惩罚”(WBR)的惩罚措施,在正则化层中进一步实施先验。两种架构都可以在单次拍摄中实现嵌套实例分割。我们根据IoUR和AP证明了自己的竞争力,并在新的与任务相关的标准——联合TP率(JTPR)上优于基线SD和Cellpose。我们的方法可以进一步修改,以捕获荧光或明场显微镜或数字成像中多对象交互的部分包含/排除关系。最后,我们的策略表明,通过使这种学习成为单镜头和计算上高效的方式,可以获得收益。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures
Summary
生物医学图像中由于固有属性存在空间关联或嵌套的对象,导致语义关系重要。检测任务常独立制定,需多阶段分析流程。空间关联可构成基本先验,有助于学习更有意义的表示,如实例分割任务。迄今,此知识未被生物医学计算机视觉领域利用。我们主张并行实现两类以上对象的实例分割。通过HydraStarDist(HSD)和新型HSD-WBR架构实现这一目标,两者基于广泛使用的StarDist(SD),利用目标星凸性。HSD能隐式结合空间关联先验和对象交互约束。HSD-WBR进一步在正则化层加强先验,提出名为“边界内正则化惩罚”(WBR)的惩罚措施。两者均实现单次嵌套实例分割。我们基于IoUR和AP标准证明其竞争力,并在新任务相关标准JTPR上优于基线SD和Cellpose。我们的方法可进一步修改,以捕捉多对象交互中的部分包含/排除关系,适用于荧光或明场显微镜或数字成像。最终,我们的策略表明通过使学习变得单次和计算高效来获得收益。
Key Takeaways
- 生物医学图像中的对象由于空间关联或嵌套具有语义关系重要性。
- 目前检测任务常独立制定,需要复杂的多阶段分析流程。
- 空间关联可以作为一个基本先验来促进实例分割任务的学习。
- HydraStarDist (HSD) 和 HSD-WBR-WBR架构利用StarDist (SD),并考虑对象的星凸性以实现实例分割。
- HSD隐式结合空间关联先验和对象交互约束,而HSD-WBR通过正则化层加强这一先验。
- HSD和HSD-WBR实现单次嵌套实例分割,相较于基线方法具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

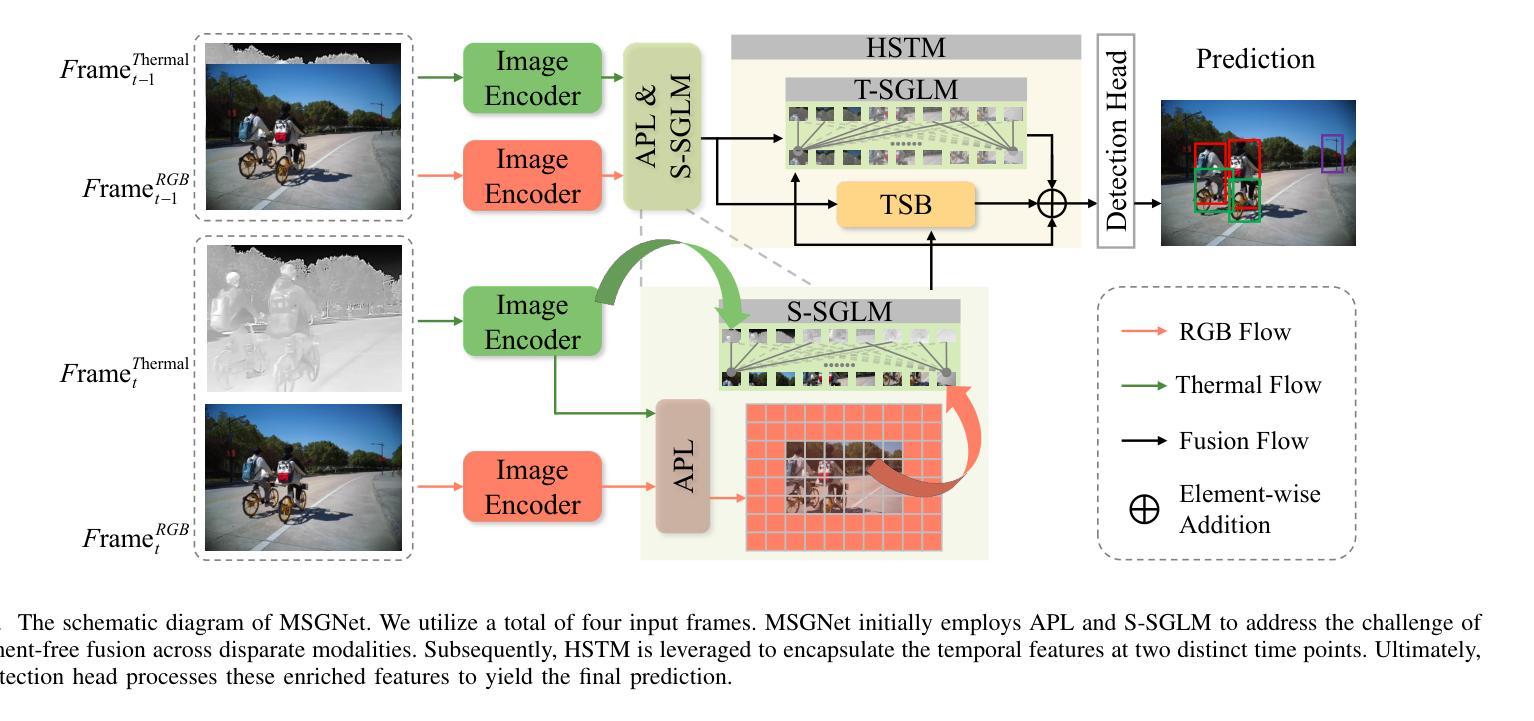
Multimodal Spatio-temporal Graph Learning for Alignment-free RGBT Video Object Detection
Authors:Qishun Wang, Zhengzheng Tu, Chenglong Li, Bo Jiang
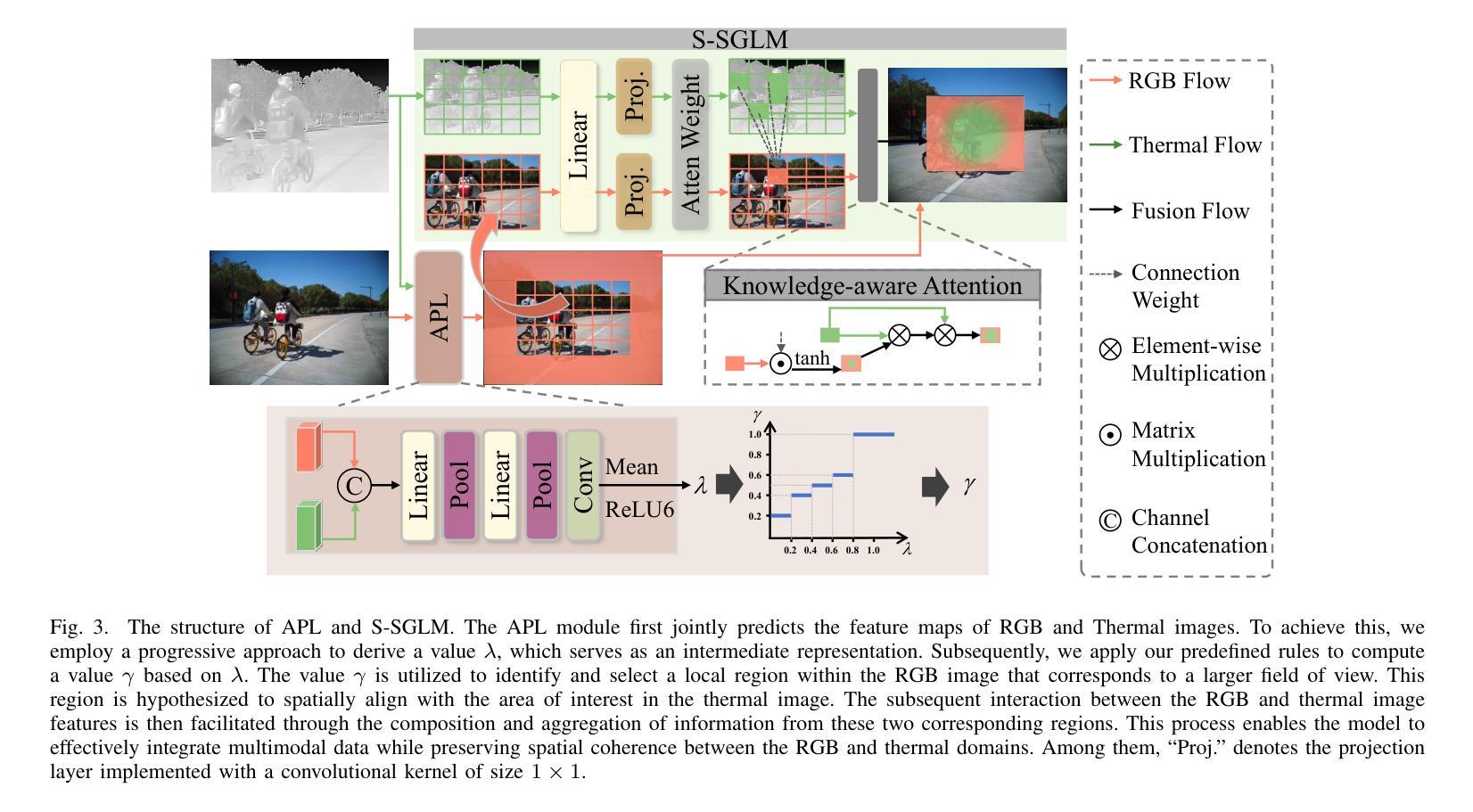
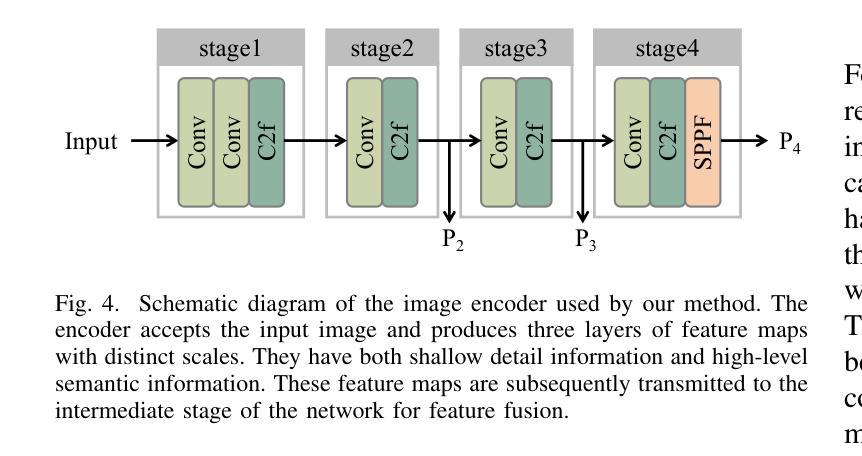
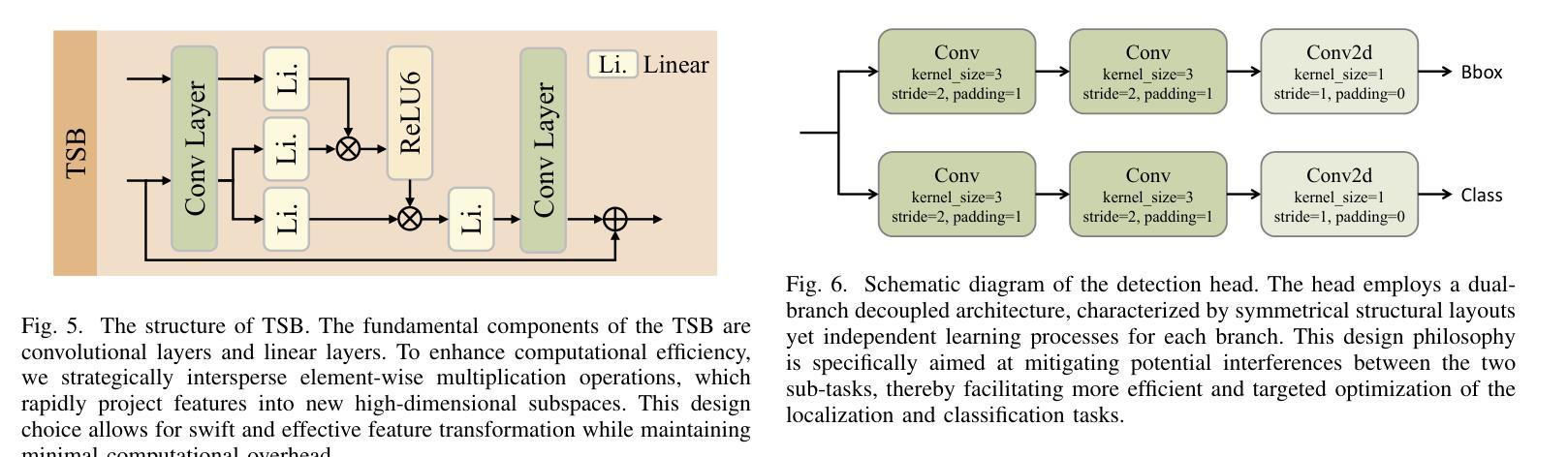
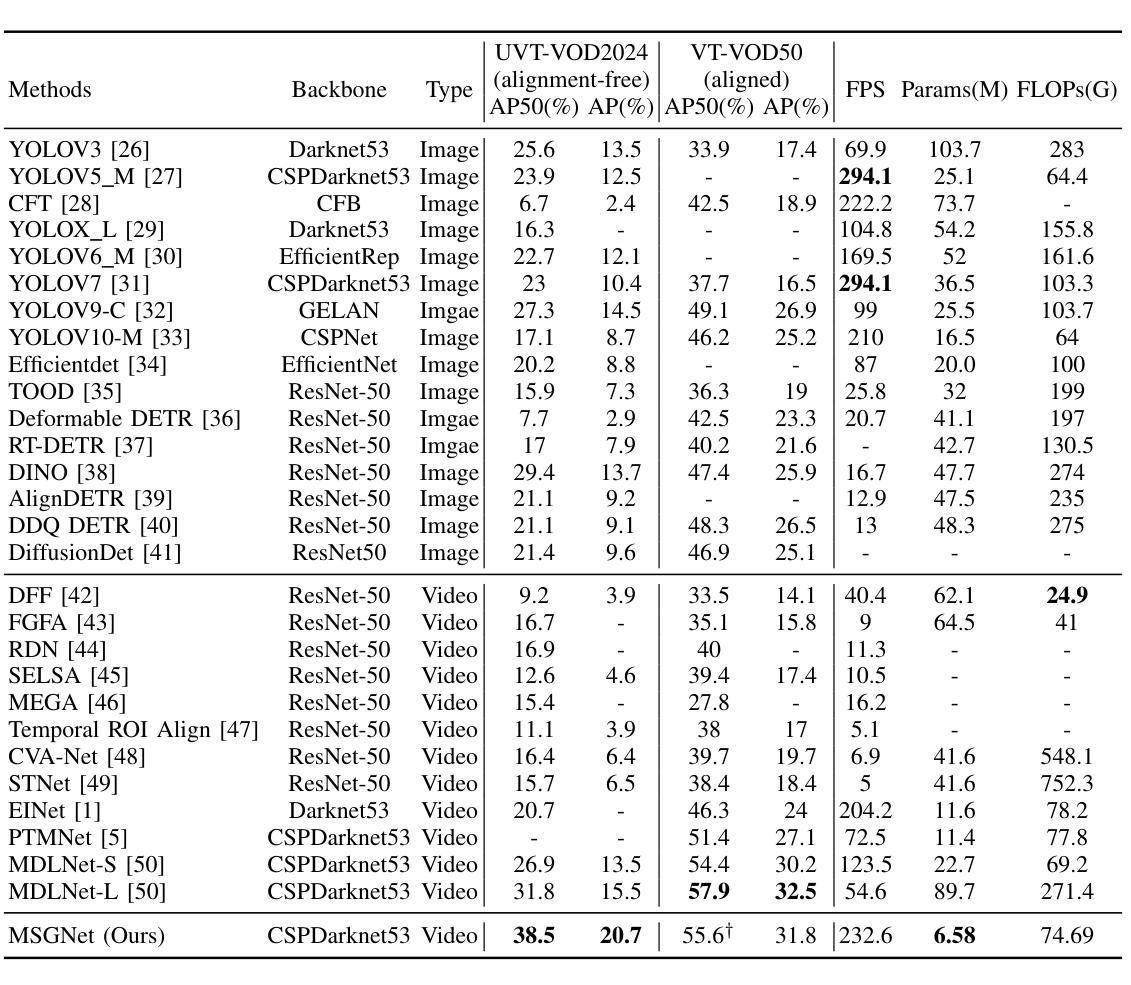
RGB-Thermal Video Object Detection (RGBT VOD) can address the limitation of traditional RGB-based VOD in challenging lighting conditions, making it more practical and effective in many applications. However, similar to most RGBT fusion tasks, it still mainly relies on manually aligned multimodal image pairs. In this paper, we propose a novel Multimodal Spatio-temporal Graph learning Network (MSGNet) for alignment-free RGBT VOD problem by leveraging the robust graph representation learning model. Specifically, we first design an Adaptive Partitioning Layer (APL) to estimate the corresponding regions of the Thermal image within the RGB image (high-resolution), achieving a preliminary inexact alignment. Then, we introduce the Spatial Sparse Graph Learning Module (S-SGLM) which employs a sparse information passing mechanism on the estimated inexact alignment to achieve reliable information interaction between different modalities. Moreover, to fully exploit the temporal cues for RGBT VOD problem, we introduce Hybrid Structured Temporal Modeling (HSTM), which involves a Temporal Sparse Graph Learning Module (T-SGLM) and Temporal Star Block (TSB). T-SGLM aims to filter out some redundant information between adjacent frames by employing the sparse aggregation mechanism on the temporal graph. Meanwhile, TSB is dedicated to achieving the complementary learning of local spatial relationships. Extensive comparative experiments conducted on both the aligned dataset VT-VOD50 and the unaligned dataset UVT-VOD2024 demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed method. Our project will be made available on our website for free public access.
RGB-热成像视频目标检测(RGBT VOD)能够解决传统基于RGB的VOD在复杂光照条件下的局限性,使其在多种应用中更加实用和有效。然而,与大多数RGBT融合任务相似,它仍然主要依赖于手动对齐的多模态图像对。在本文中,我们提出了一种无需对齐的RGBT VOD问题的多模态时空图学习网络(MSGNet),利用稳健的图表示学习模型。具体来说,我们首先设计了一个自适应分区层(APL)来估计热成像图在RGB图像(高分辨率)中的相应区域,实现初步的不精确对齐。然后,我们引入了空间稀疏图学习模块(S-SGLM),该模块在估计的不精确对齐上采用稀疏信息传递机制,实现不同模态之间的可靠信息交互。此外,为了充分探索RGBT VOD问题的时间线索,我们引入了混合结构时间建模(HSTM),其中包括时间稀疏图学习模块(T-SGLM)和时间星块(TSB)。T-SGLM旨在通过时间图上的稀疏聚合机制过滤掉相邻帧之间的某些冗余信息。同时,TSB致力于实现局部空间关系的互补学习。在已对齐的数据集VT-VOD50和未对齐的数据集UVT-VOD2024上进行的广泛对比实验表明了我们提出方法的有效性和优越性。我们的项目将发布在我们的网站上供公众免费访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种无需对齐的多模态时空图学习网络(MSGNet),用于RGB-Thermal视频目标检测(RGBT VOD)。通过自适应分区层(APL)初步实现不对齐的热图区域估计,引入空间稀疏图学习模块(S-SGLM)实现不同模态之间的可靠信息交互。同时,通过混合结构时空建模(HSTM)挖掘时序线索,实现RGBT VOD问题的优化。在VT-VOD50对齐数据集和UVT-VOD2024不对齐数据集上的对比实验证明了该方法的有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- RGBT VOD能克服传统RGB基VOD在恶劣光照条件下的局限,提高实际应用效果。
- 提出一种无需对齐的多模态时空图学习网络(MSGNet)用于RGBT VOD。
- 通过自适应分区层(APL)初步实现热图区域的估计。
- 引入空间稀疏图学习模块(S-SGLM)实现不同模态间的信息交互。
- 混合结构时空建模(HSTM)挖掘时序线索,优化RGBT VOD问题。
- 在VT-VOD50和UVT-VOD2024数据集上的实验证明了方法的有效性和优越性。
点此查看论文截图