⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-18 更新
Mind2Matter: Creating 3D Models from EEG Signals
Authors:Xia Deng, Shen Chen, Jiale Zhou, Lei Li
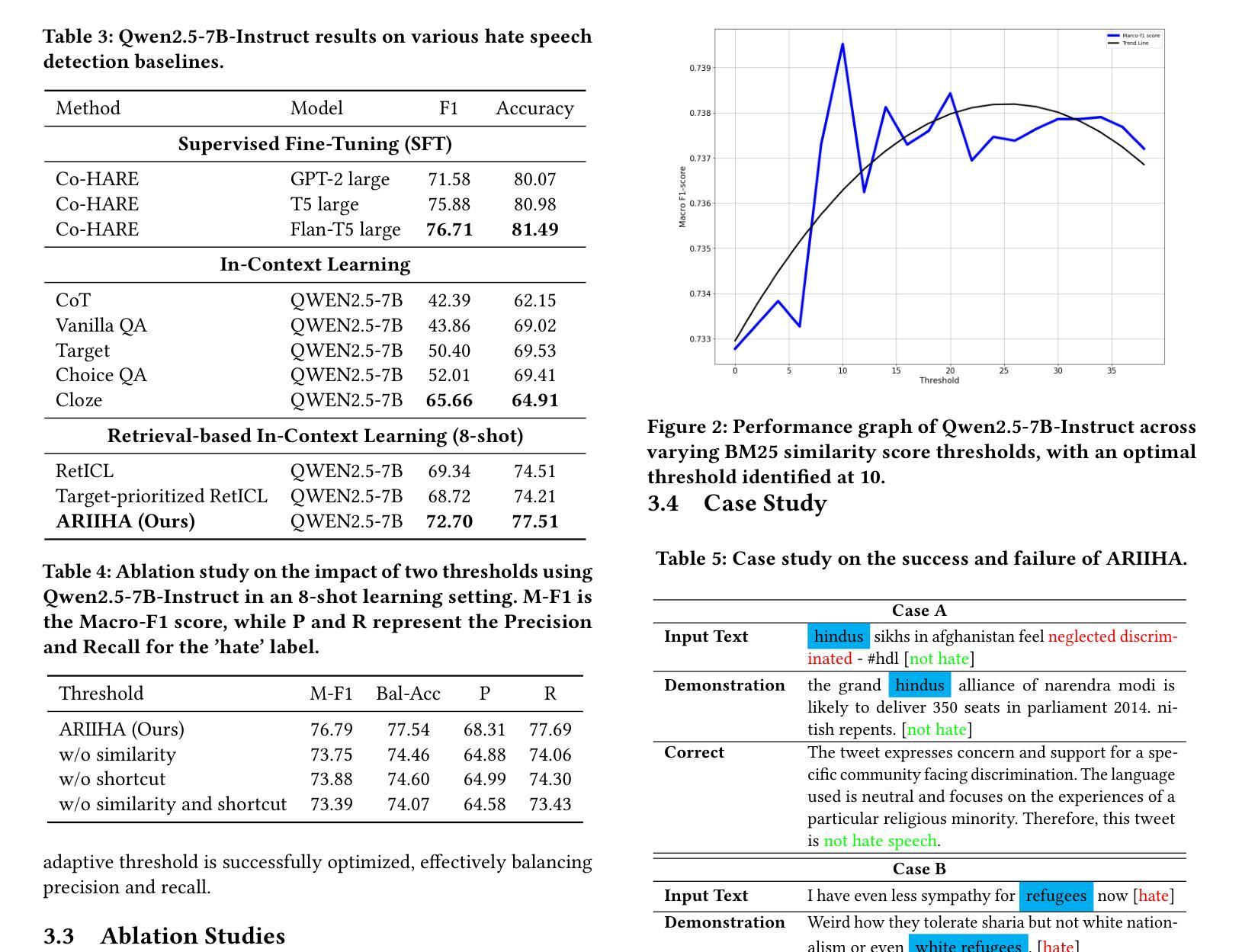
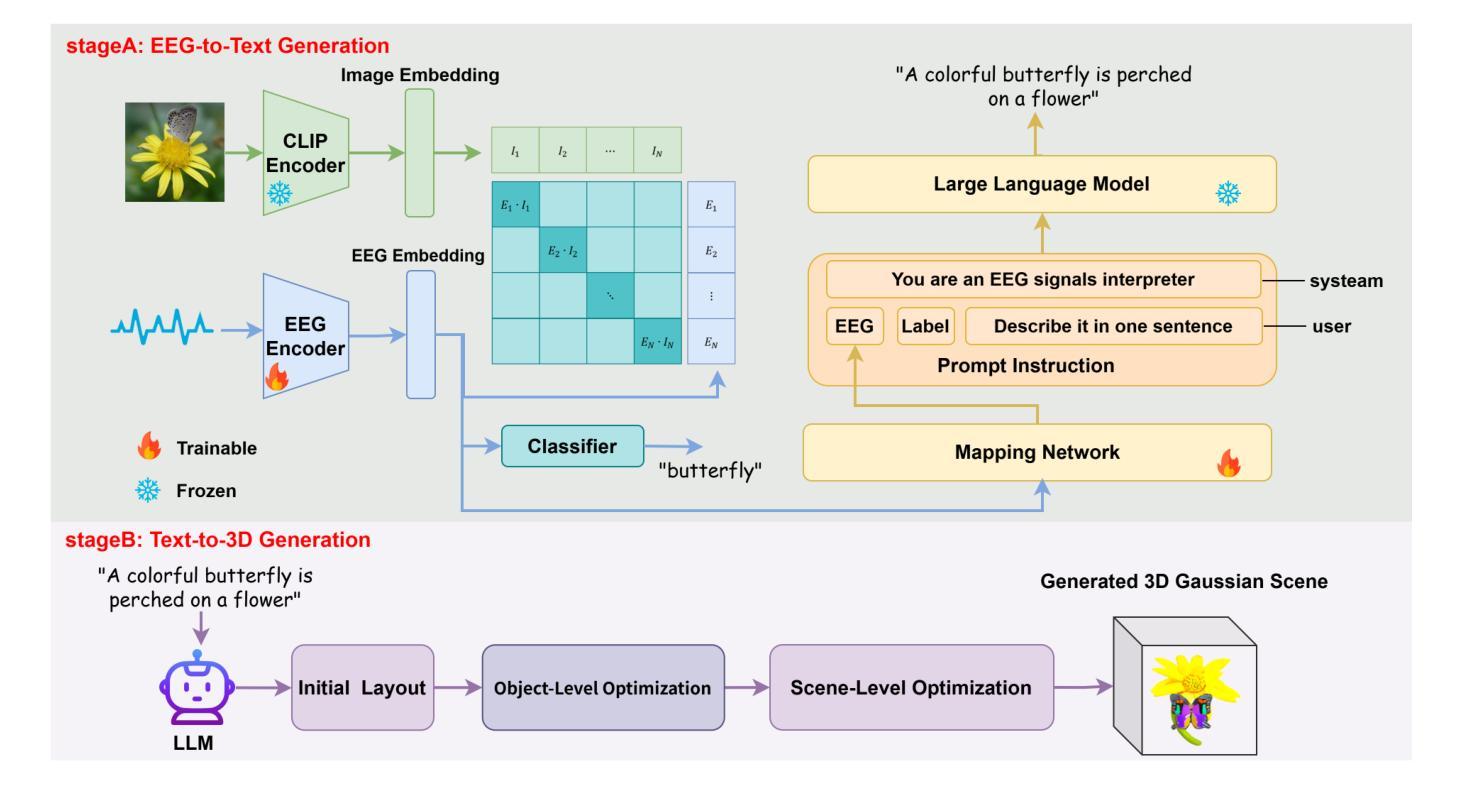
The reconstruction of 3D objects from brain signals has gained significant attention in brain-computer interface (BCI) research. Current research predominantly utilizes functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) for 3D reconstruction tasks due to its excellent spatial resolution. Nevertheless, the clinical utility of fMRI is limited by its prohibitive costs and inability to support real-time operations. In comparison, electroencephalography (EEG) presents distinct advantages as an affordable, non-invasive, and mobile solution for real-time brain-computer interaction systems. While recent advances in deep learning have enabled remarkable progress in image generation from neural data, decoding EEG signals into structured 3D representations remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that translates EEG recordings into 3D object reconstructions by leveraging neural decoding techniques and generative models. Our approach involves training an EEG encoder to extract spatiotemporal visual features, fine-tuning a large language model to interpret these features into descriptive multimodal outputs, and leveraging generative 3D Gaussians with layout-guided control to synthesize the final 3D structures. Experiments demonstrate that our model captures salient geometric and semantic features, paving the way for applications in brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), virtual reality, and neuroprosthetics.Our code is available in https://github.com/sddwwww/Mind2Matter.
从脑信号重建3D物体在脑机接口(BCI)研究中获得了广泛关注。目前的研究主要利用功能磁共振成像(fMRI)进行3D重建任务,因其具有出色的空间分辨率。然而,fMRI的临床应用受到其高昂成本和无法支持实时操作的限制。相比之下,脑电图(EEG)作为实时脑机交互系统的经济实惠、无创和可移动解决方案,具有明显优势。虽然深度学习领域的最新进展在基于神经数据的图像生成方面取得了显著进展,但将EEG信号解码为结构化3D表示仍未被充分探索。在本文中,我们提出了一种利用神经解码技术和生成模型将EEG记录转换为3D对象重建的新框架。我们的方法包括训练EEG编码器以提取时空视觉特征,微调大型语言模型以将这些特征解释为描述性多模式输出,并利用带有布局指导控制的生成性3D高斯来合成最终的3D结构。实验表明,我们的模型捕捉了显著的几何和语义特征,为脑机接口(BCI)、虚拟现实和神经假肢的应用铺平了道路。我们的代码可在https://github.com/sddwwww/Mind2Matter找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了利用脑电波(EEG)进行三维物体重建的新方法,此方法借助神经解码技术和生成模型将EEG记录转化为三维物体重建。通过训练EEG编码器提取时空视觉特征,微调大型语言模型以解释这些特征并生成多模式输出,并利用布局引导的生成性三维高斯模型合成最终的三维结构。此方法有望应用于脑机接口、虚拟现实和神经仿生技术等领域。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究关注利用脑电波(EEG)信号重建三维物体的新技术。
- 使用功能磁共振成像(fMRI)的局限性推动了对EEG的研究,因其为非侵入性和低成本提供了实时脑计算机交互系统的潜力。
- 提出了一种新的框架,结合了神经解码技术和生成模型来转化EEG记录为三维物体重建。
- 训练EEG编码器提取时空视觉特征是该框架的关键步骤之一。
- 大型语言模型被微调以解释EEG特征并产生多模式输出。
- 利用生成性三维高斯模型和布局指导控制来合成最终的三维结构。
点此查看论文截图

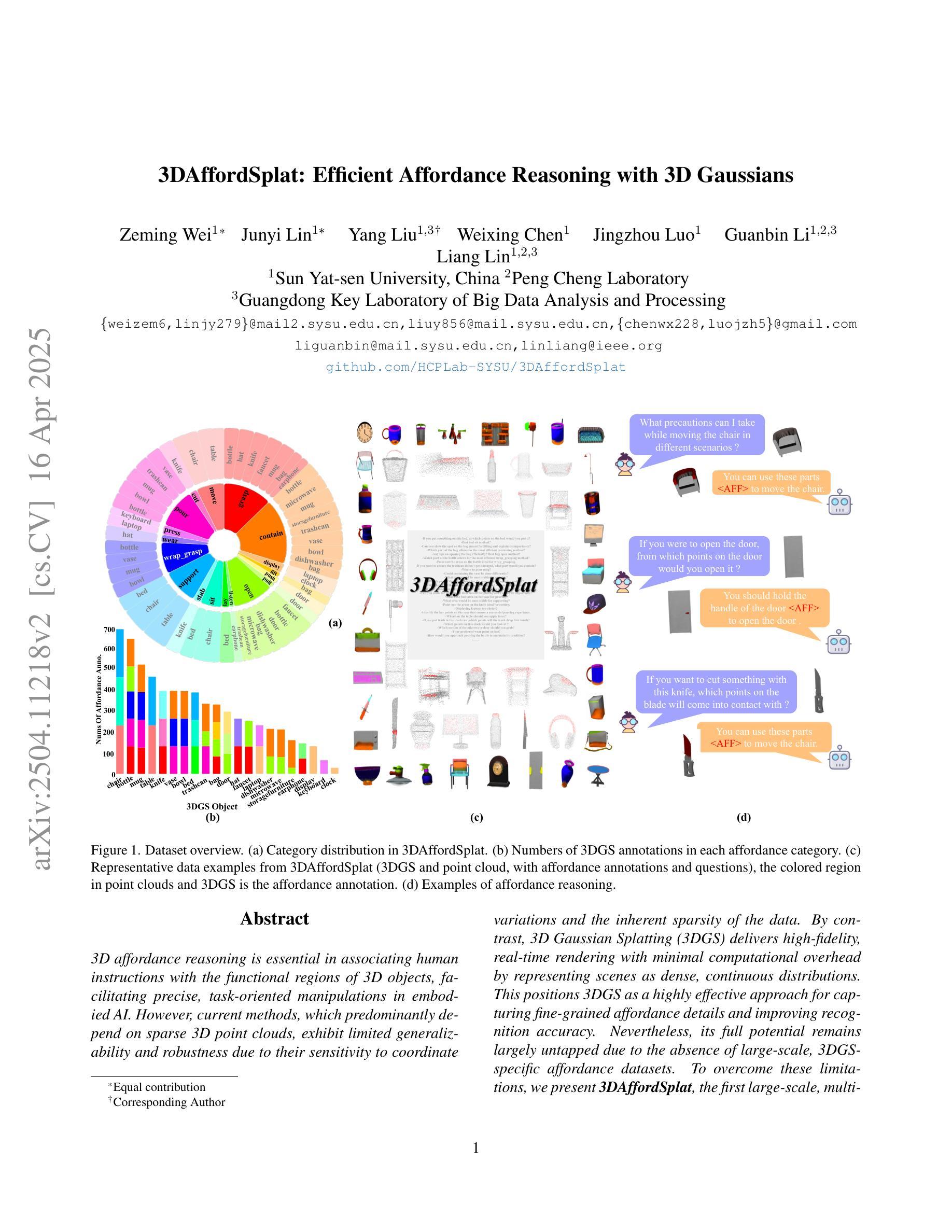
3DAffordSplat: Efficient Affordance Reasoning with 3D Gaussians
Authors:Zeming Wei, Junyi Lin, Yang Liu, Weixing Chen, Jingzhou Luo, Guanbin Li, Liang Lin
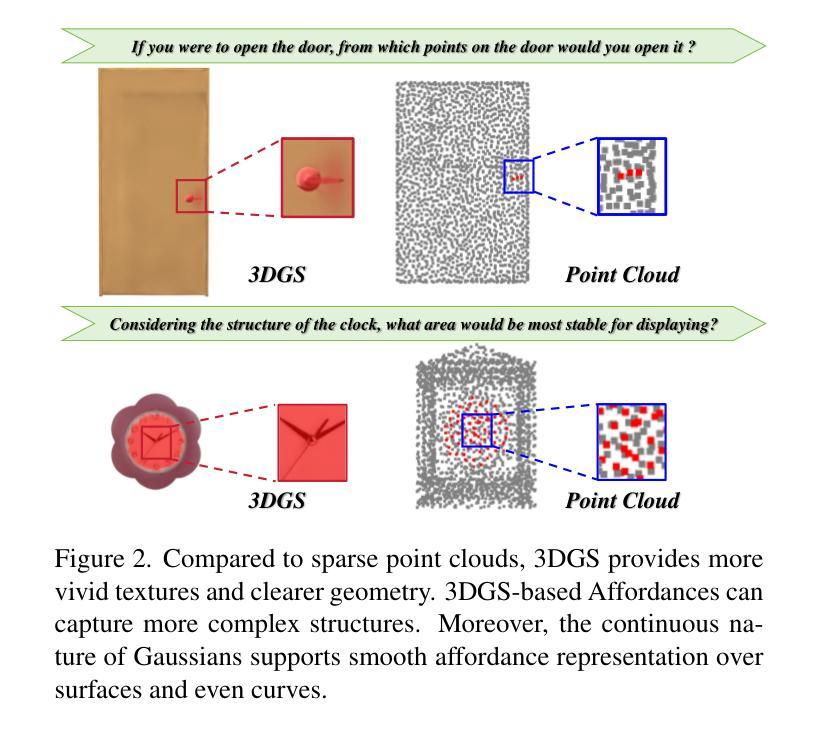
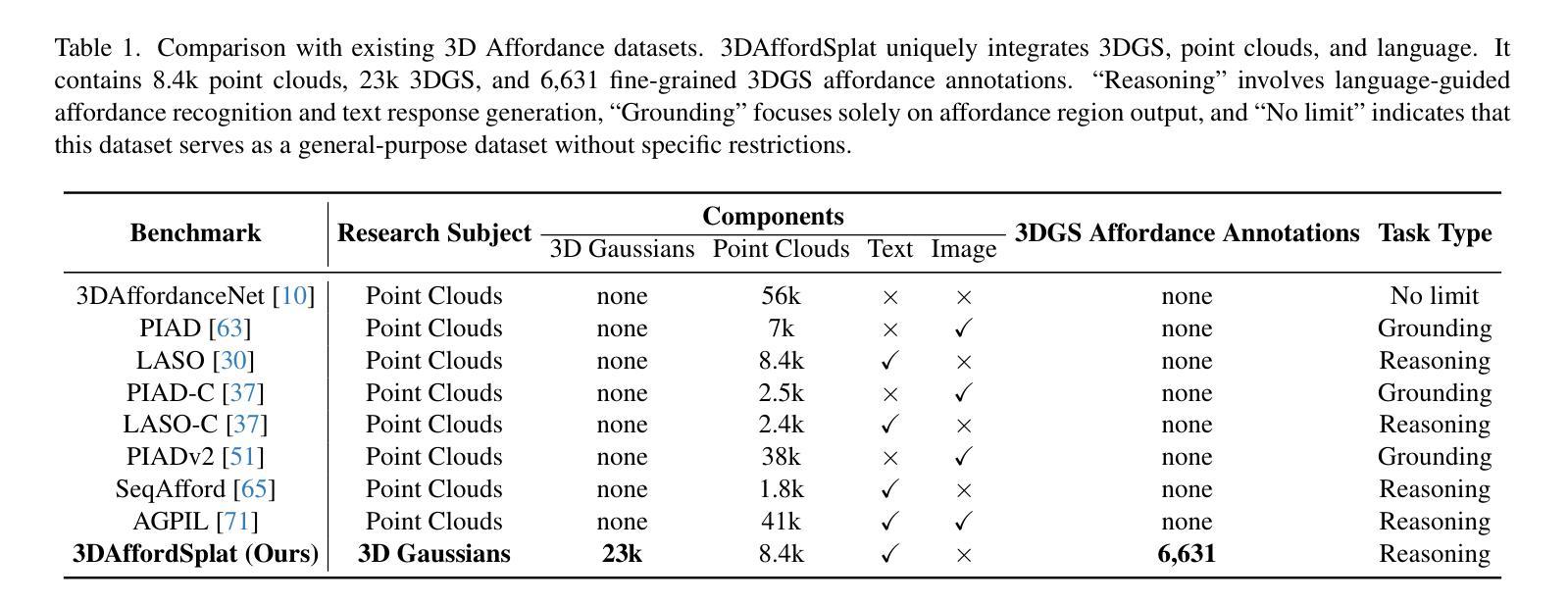
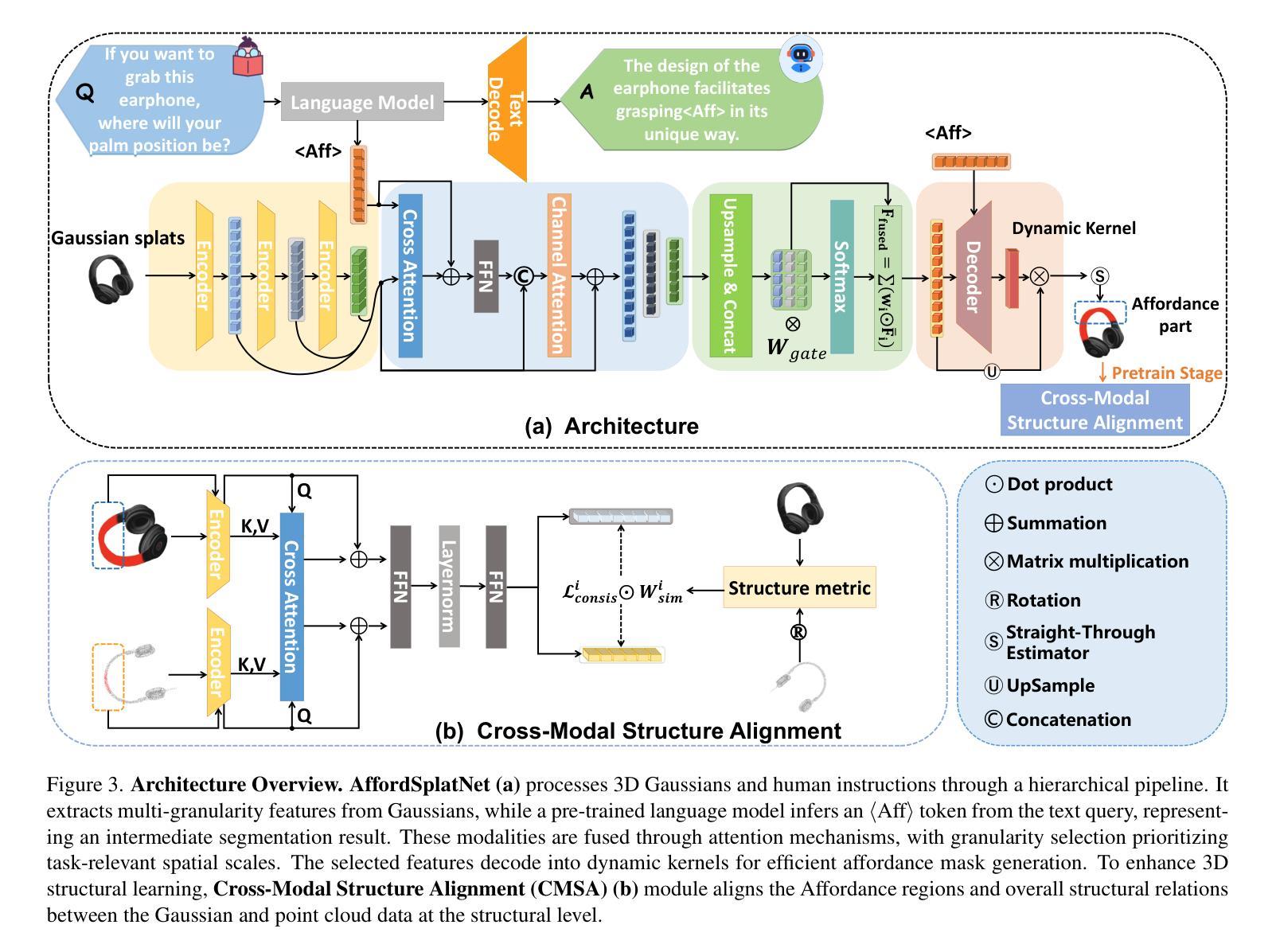
3D affordance reasoning is essential in associating human instructions with the functional regions of 3D objects, facilitating precise, task-oriented manipulations in embodied AI. However, current methods, which predominantly depend on sparse 3D point clouds, exhibit limited generalizability and robustness due to their sensitivity to coordinate variations and the inherent sparsity of the data. By contrast, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) delivers high-fidelity, real-time rendering with minimal computational overhead by representing scenes as dense, continuous distributions. This positions 3DGS as a highly effective approach for capturing fine-grained affordance details and improving recognition accuracy. Nevertheless, its full potential remains largely untapped due to the absence of large-scale, 3DGS-specific affordance datasets. To overcome these limitations, we present 3DAffordSplat, the first large-scale, multi-modal dataset tailored for 3DGS-based affordance reasoning. This dataset includes 23,677 Gaussian instances, 8,354 point cloud instances, and 6,631 manually annotated affordance labels, encompassing 21 object categories and 18 affordance types. Building upon this dataset, we introduce AffordSplatNet, a novel model specifically designed for affordance reasoning using 3DGS representations. AffordSplatNet features an innovative cross-modal structure alignment module that exploits structural consistency priors to align 3D point cloud and 3DGS representations, resulting in enhanced affordance recognition accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the 3DAffordSplat dataset significantly advances affordance learning within the 3DGS domain, while AffordSplatNet consistently outperforms existing methods across both seen and unseen settings, highlighting its robust generalization capabilities.
3D关联推理对于将人类指令与3D对象的功能区域相关联至关重要,有助于实现实体人工智能的精确、任务导向型操作。然而,当前的方法主要依赖于稀疏的3D点云,由于其对坐标变化的敏感性和数据固有的稀疏性,其通用性和稳健性受到限制。相比之下,3D高斯贴图(3DGS)通过表示为密集、连续分布的场景,以高保真、实时渲染的方式呈现出最小的计算开销。这使得3DGS成为捕获精细粒度关联细节并提高识别准确性的高效方法。然而,由于缺乏大规模、针对3DGS的关联数据集,其全部潜力尚未得到充分发掘。为了克服这些限制,我们推出了3DAffordSplat,这是专为基于3DGS的关联推理量身定制的第一个大规模、多模式数据集。该数据集包含23677个高斯实例、8354个点云实例和6631个手动标注的关联标签,涵盖21个对象类别和18种关联类型。在此基础上,我们引入了AffordSplatNet,这是一个专为使用3DGS表示进行关联推理而设计的新型模型。AffordSplatNet具有创新性的跨模态结构对齐模块,该模块利用结构一致性先验来对齐3D点云和3DGS表示,从而提高关联识别准确性。大量实验表明,3DAffordSplat数据集显著推进了3DGS领域的关联学习,而AffordSplatNet在可见和不可见环境中均表现出优于现有方法的性能,凸显了其稳健的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first large-scale 3D Gaussians Affordance Reasoning Benchmark
摘要
在虚拟人工智能中实现人体指令与三维物体功能区域的精确任务导向型操控,关键在于利用三维物件的操纵感知推理。然而,当前主要依赖稀疏三维点云的方法因坐标变化敏感性和数据固有稀疏性而具有局限性和稳健性不足的问题。相比之下,三维高斯贴图技术(3DGS)以其高保真实时渲染能力显著提高了对精细操纵感知细节的捕捉和识别准确性。然而,由于缺乏大规模的三维高斯贴图特定操纵感知数据集,其潜力尚未得到充分发掘。为了克服这些局限性,我们推出了首个针对三维高斯贴图技术的大规模多模式数据集——三维感知贴图数据集(3DAffordSplat)。该数据集包含23,677个高斯实例、8,354个点云实例和6,631个手动标注的操纵感知标签,涵盖21个物体类别和18种操纵感知类型。在此基础上,我们引入了专为利用三维高斯贴图技术进行操纵感知推理而设计的全新模型——感知贴图网络(AffordSplatNet)。该网络具备跨模态结构对齐模块,借助结构一致性先验实现三维点云和三维高斯贴图表示的精准对齐,提升了操纵感知识别的准确性。经过广泛实验验证,感知贴图数据集在推动三维高斯贴图领域的感知学习方面表现显著,而感知贴图网络在已知和未知场景中均表现优于现有方法,展现了强大的泛化能力。
关键见解
- 3DGS技术在捕捉三维物体的精细操纵感知细节方面表现出显著优势。
- 当前基于点云的方法在应对坐标变化和稀疏数据时存在局限性。
- 缺乏针对三维高斯贴图技术的专用大规模数据集限制了3DGS的发展。
- 新推出的数据集(如3DAffordSplat)有望克服这些限制并推动该领域的发展。
- AffordSplatNet模型利用跨模态对齐技术提高了操纵感知识别的准确性。
- AffordSplatNet在各种场景中表现优于现有方法,显示出强大的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图
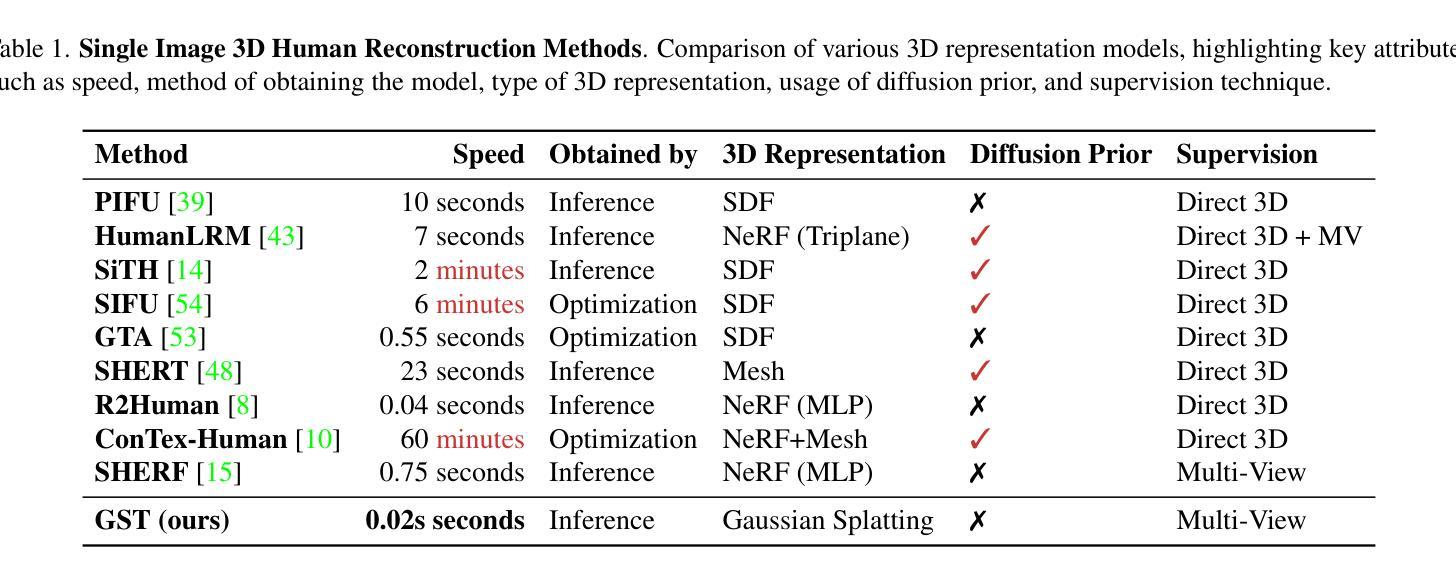
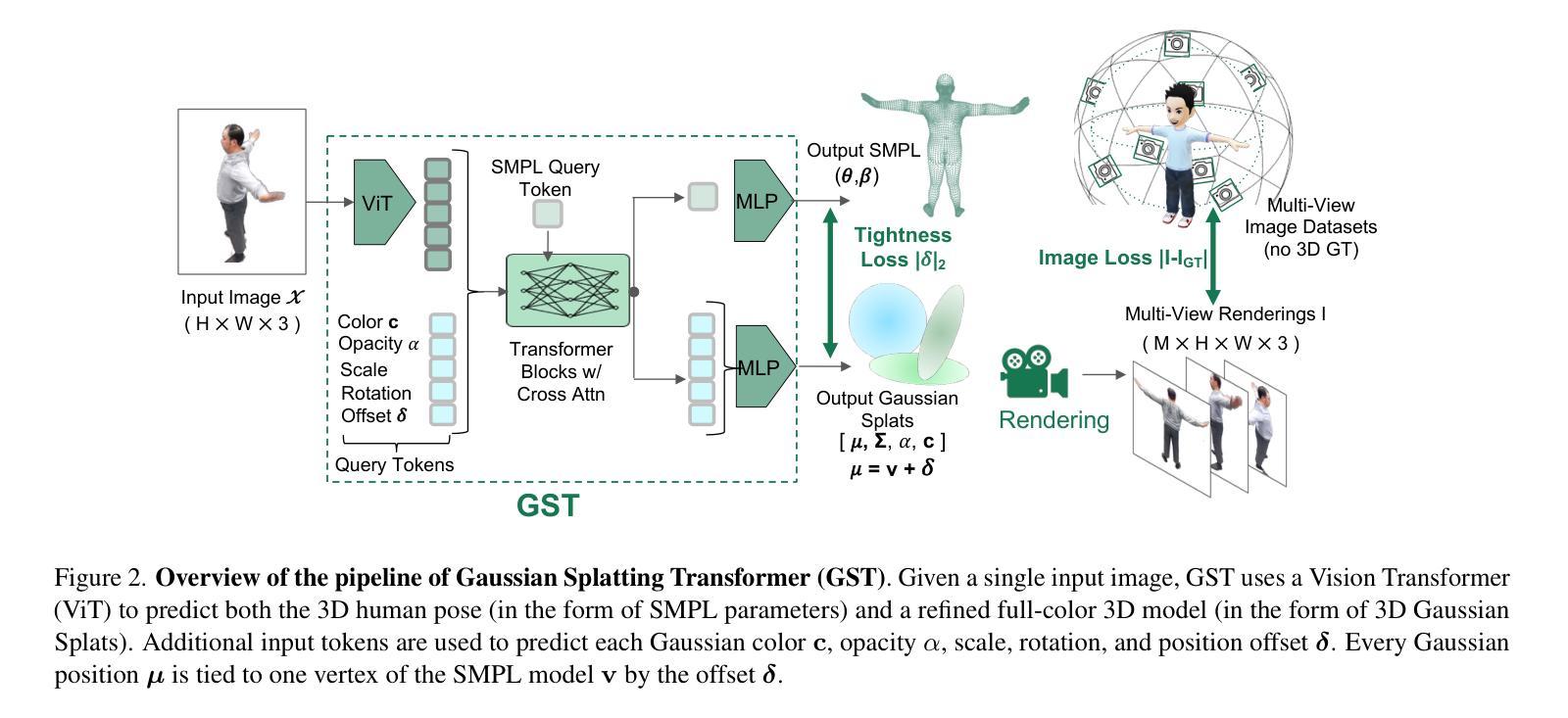
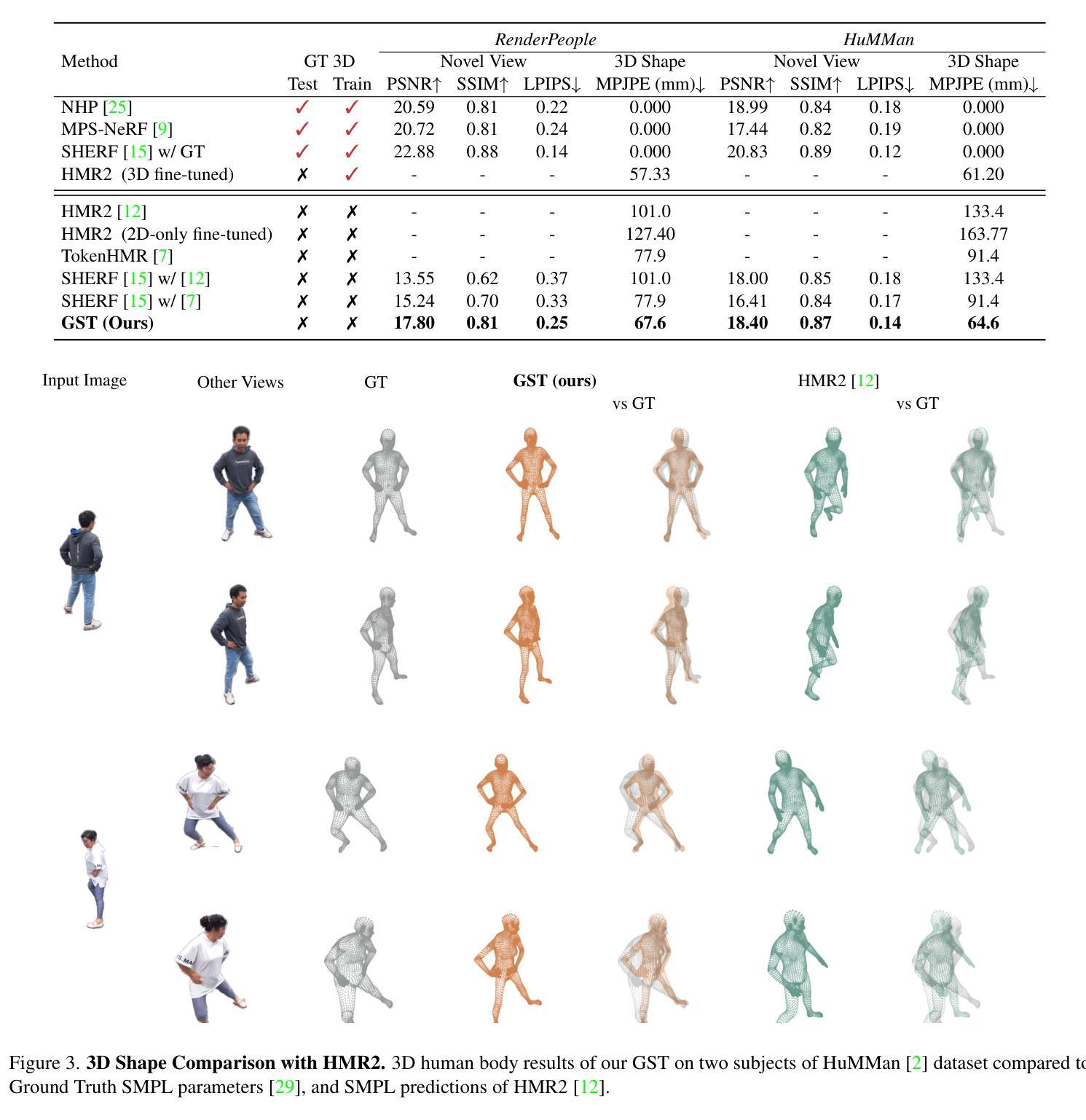
GST: Precise 3D Human Body from a Single Image with Gaussian Splatting Transformers
Authors:Lorenza Prospero, Abdullah Hamdi, Joao F. Henriques, Christian Rupprecht
Reconstructing posed 3D human models from monocular images has important applications in the sports industry, including performance tracking, injury prevention and virtual training. In this work, we combine 3D human pose and shape estimation with 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), a representation of the scene composed of a mixture of Gaussians. This allows training or fine-tuning a human model predictor on multi-view images alone, without 3D ground truth. Predicting such mixtures for a human from a single input image is challenging due to self-occlusions and dependence on articulations, while also needing to retain enough flexibility to accommodate a variety of clothes and poses. Our key observation is that the vertices of standardized human meshes (such as SMPL) can provide an adequate spatial density and approximate initial position for the Gaussians. We can then train a transformer model to jointly predict comparatively small adjustments to these positions, as well as the other 3DGS attributes and the SMPL parameters. We show empirically that this combination (using only multi-view supervision) can achieve near real-time inference of 3D human models from a single image without expensive diffusion models or 3D points supervision, thus making it ideal for the sport industry at any level. More importantly, rendering is an effective auxiliary objective to refine 3D pose estimation by accounting for clothes and other geometric variations. The code is available at https://github.com/prosperolo/GST.
从单目图像重建设定好的3D人体模型在体育产业中具有重要应用,包括性能跟踪、伤害预防和虚拟训练等方面。在这项工作中,我们将3D人体姿态和形状估计与3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)相结合,这是一种由高斯混合组成的场景表示。这允许仅在多视角图像上训练或微调人体模型预测器,无需3D真实数据。从单个输入图像预测人体的这种混合是充满挑战的,因为存在自我遮挡和依赖于关节活动,同时还需要保持足够的灵活性以适应各种衣物和姿态。我们的关键观察是,标准化网格(如SMPL)的顶点可以提供足够的空间密度和近似初始位置来估算高斯分布。然后,我们可以训练一个转换模型来联合预测这些位置的微小调整以及其他3DGS属性和SMPL参数。我们通过实验证明,这种组合(仅使用多视角监督)可以实现从单个图像中进行近乎实时的3D人体模型推断,无需昂贵的扩散模型或3D点监督,因此使其成为各级体育产业的理想选择。更重要的是,渲染是细化3D姿态估计的有效辅助目标,它可以通过考虑衣物和其他几何变化来实现。代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/prosperolo/GST 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Camera ready for CVSports workshop at CVPR 2025
Summary
本文利用三维高斯贴片(3DGS)结合三维人体姿态与形状估计技术,实现了从单张图像重建三维人体模型的方法。该方法适用于体育行业,如性能追踪、运动损伤预防及虚拟训练等。通过标准化网格顶点提供空间密度和初始位置,训练变换器模型预测微小调整以及其它3DGS属性和网格模型参数。此方法仅需多视角监督即可实现近实时的三维人体模型预测,无需昂贵的扩散模型或三维点监督,特别适用于体育产业。渲染可作为优化三维姿态估计的有效辅助目标,以考虑衣物和其它几何变化。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术结合三维人体姿态与形状估计,用于从单张图像重建三维人体模型。
- 该方法在体育行业有广泛应用,如性能追踪、运动损伤预防及虚拟训练。
- 通过标准化网格顶点提供空间密度和初始位置,为预测提供基础。
- 训练变换器模型预测微小调整和其它属性参数,以适应各种衣物和姿态。
- 该方法仅需多视角监督,无需昂贵的扩散模型或三维点监督,实现近实时预测。
- 渲染作为辅助目标,有助于优化三维姿态估计,考虑衣物和几何变化。
点此查看论文截图