⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-18 更新
ARCeR: an Agentic RAG for the Automated Definition of Cyber Ranges
Authors:Matteo Lupinacci, Francesco Blefari, Francesco Romeo, Francesco Aurelio Pironti, Angelo Furfaro
The growing and evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats necessitates the development of supporting tools and platforms that allow for the creation of realistic IT environments operating within virtual, controlled settings as Cyber Ranges (CRs). CRs can be exploited for analyzing vulnerabilities and experimenting with the effectiveness of devised countermeasures, as well as serving as training environments for building cyber security skills and abilities for IT operators. This paper proposes ARCeR as an innovative solution for the automatic generation and deployment of CRs, starting from user-provided descriptions in a natural language. ARCeR relies on the Agentic RAG paradigm, which allows it to fully exploit state-of-art AI technologies. Experimental results show that ARCeR is able to successfully process prompts even in cases that LLMs or basic RAG systems are not able to cope with. Furthermore, ARCeR is able to target any CR framework provided that specific knowledge is made available to it.
网络安全威胁的不断增长和演变,需要开发支持工具和平台,以在虚拟、受控的环境中创建现实的IT环境作为网络安全范围(CRs)。网络安全范围可用于分析漏洞,测试制定的对策的有效性,还可以作为构建网络安全技能和提高it操作员能力的训练环境。本文提出ARCeR作为一种创新解决方案,可以根据用户提供自然语言的描述自动生成并部署网络安全范围。ARCeR依赖于Agentic RAG范式,可以充分利用最新的AI技术。实验结果表明,即使在一些情况下大型语言模型或基本的RAG系统无法应对,ARCeR也能成功处理提示。此外,只要向其提供特定知识,ARCeR就能针对任何网络安全范围框架进行部署。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
网络安全威胁的不断发展和演变催生了对支持工具和平台的需求,这些工具可以创建在虚拟、受控环境中运行的现实IT环境,称为网络安全范围(CR)。网络安全范围可用于分析漏洞、测试制定的对策的有效性,并作为培训环境,培养网络安全技能和能力。本文提出ARCeR作为一种创新的解决方案,可以根据用户提供的自然语言描述自动生成和部署网络安全范围。ARCeR依赖于Agentic RAG范式,能够充分利用最新的AI技术。实验结果表明,ARCeR能够在大型语言模型或基本RAG系统无法处理的情况下成功处理提示。此外,只要向其提供特定知识,ARCeR就能够针对任何网络安全范围框架进行部署。
Key Takeaways
- 网络安全威胁的演变推动了网络安全范围(CR)的发展,用于分析和测试漏洞以及提高网络安全技能和能力的培训。
- ARCeR是一种创新的解决方案,可以根据用户提供的自然语言描述自动生成和部署网络安全范围。
- ARCeR依赖于Agentic RAG范式,能够充分利用最新的AI技术来提升生成过程的智能化和自动化水平。
- 实验结果显示,ARCeR在特定场景下比现有系统更具优势,可以成功处理其他系统无法应对的提示。
- ARCeR具有广泛的适用性,能够支持多种网络安全范围框架,只要向其提供特定知识即可进行部署和应用。
- ARCeR在提高网络安全和推动网络安全技能提升方面具有重要的实际应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

EmoACT: a Framework to Embed Emotions into Artificial Agents Based on Affect Control Theory
Authors:Francesca Corrao, Alice Nardelli, Jennifer Renoux, Carmine Tommaso Recchiuto
As robots and artificial agents become increasingly integrated into daily life, enhancing their ability to interact with humans is essential. Emotions, which play a crucial role in human interactions, can improve the naturalness and transparency of human-robot interactions (HRI) when embodied in artificial agents. This study aims to employ Affect Control Theory (ACT), a psychological model of emotions deeply rooted in interaction, for the generation of synthetic emotions. A platform-agnostic framework inspired by ACT was developed and implemented in a humanoid robot to assess its impact on human perception. Results show that the frequency of emotional displays impacts how users perceive the robot. Moreover, appropriate emotional expressions seem to enhance the robot’s perceived emotional and cognitive agency. The findings suggest that ACT can be successfully employed to embed synthetic emotions into robots, resulting in effective human-robot interactions, where the robot is perceived more as a social agent than merely a machine.
随着机器人和人工代理在日常生活中得到越来越深入的整合,增强他们与人类互动的能力变得至关重要。情感在人类互动中扮演着至关重要的角色,当融入到人工代理中时,情感可以提高人机互动的自然性和透明度。本研究旨在采用情感控制理论(ACT),这是一种深深根植于互动中的情感心理学模型,来生成合成情感。受ACT启发的平台无关框架被开发并应用在人形机器人上,以评估其对人类感知的影响。结果表明,情感展示的频率会影响用户如何感知机器人。此外,适当的情感表达似乎增强了机器人感知到的情感和认知能力。研究结果建议,可以成功运用ACT将合成情感嵌入机器人,从而实现有效的人机互动,其中机器人被视为一个社会代理人,而不仅仅是一台机器。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
随着机器人和人工智能代理在日常生活中日益普及,提高其与人类互动的能力至关重要。情感在人类互动中扮演着重要角色,当融入人工智能代理时,可以改善人机互动的自然性和透明度。本研究旨在运用情感控制理论(ACT),这是一个深深植根于互动的心理学情感模型,来生成合成情感。受ACT启发的跨平台框架被开发并应用在一个类人机器人上,以评估它对人类感知的影响。结果显示,情感显示频率影响用户对机器人的感知。此外,适当的情感表达似乎可以增强机器人感知到的情感和认知代理。研究表明,成功运用ACT将合成情感嵌入机器人,可实现有效的人机互动,机器人被视为社会代理而非仅仅是机器。
关键见解
- 情感在人机互动中扮演着重要角色,可以提高互动的自然性和透明度。
- 将情感融入人工智能代理是必要的,因为这对日常生活中的普及越来越重要。
- 本研究旨在运用情感控制理论(ACT)来生成合成情感,这是一种基于心理学的情感模型。
- 开发了一个跨平台的框架并将其应用于类人机器人上,以评估其对人类感知的影响。
- 实验结果表明,情感显示的频率会影响用户对机器人的感知。
- 适当的情感表达可以增强用户对机器人情感和认知能力的感知。
点此查看论文截图

Towards LLM Agents for Earth Observation
Authors:Chia Hsiang Kao, Wenting Zhao, Shreelekha Revankar, Samuel Speas, Snehal Bhagat, Rajeev Datta, Cheng Perng Phoo, Utkarsh Mall, Carl Vondrick, Kavita Bala, Bharath Hariharan
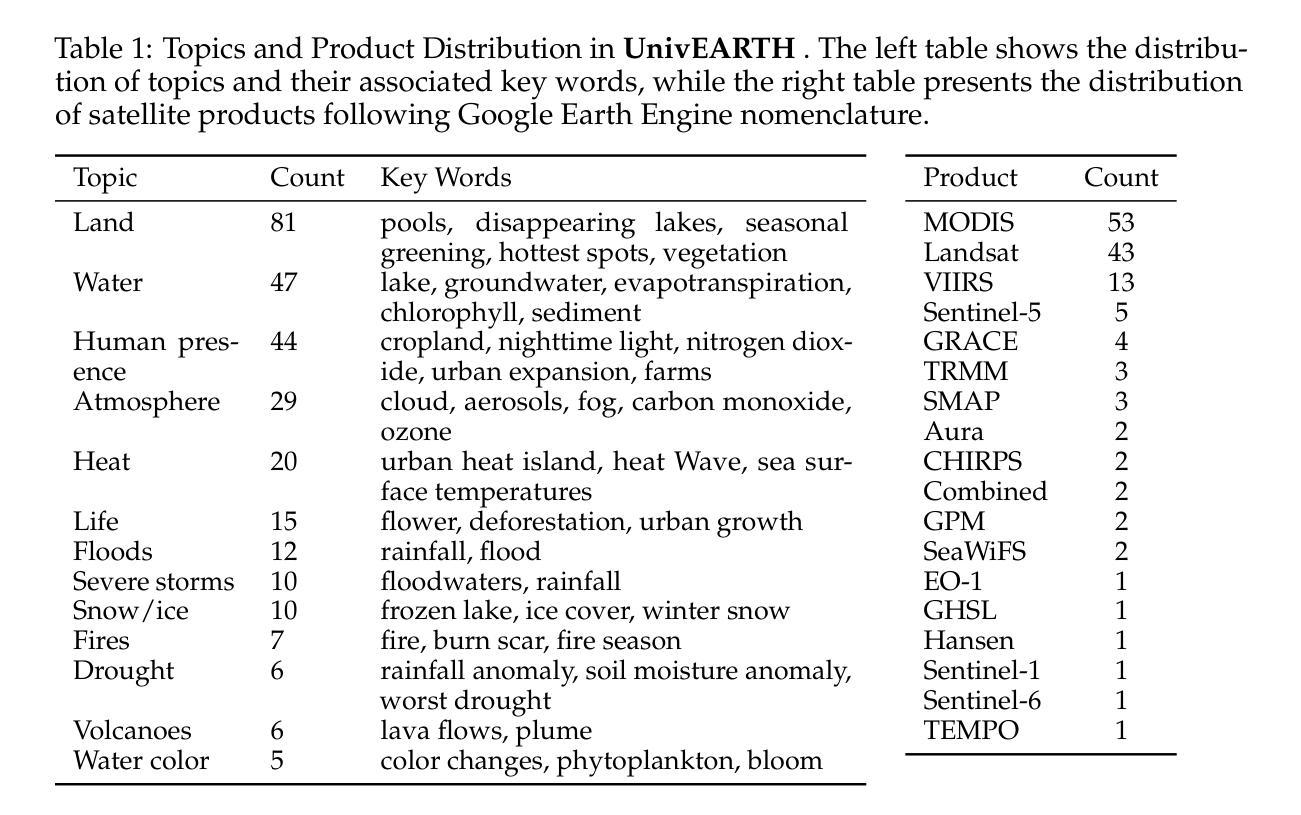
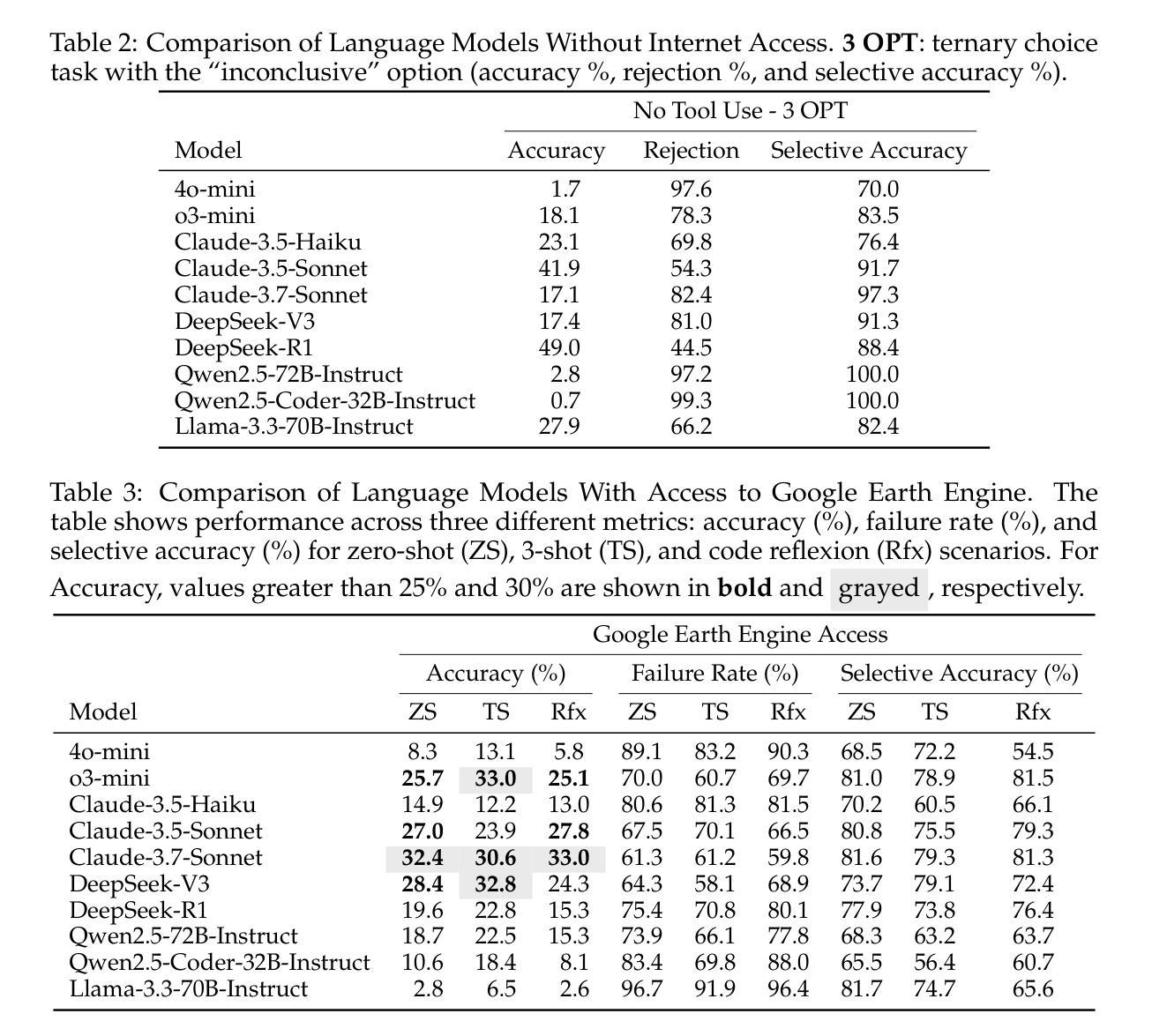
Earth Observation (EO) provides critical planetary data for environmental monitoring, disaster management, climate science, and other scientific domains. Here we ask: Are AI systems ready for reliable Earth Observation? We introduce \datasetnamenospace, a benchmark of 140 yes/no questions from NASA Earth Observatory articles across 13 topics and 17 satellite sensors. Using Google Earth Engine API as a tool, LLM agents can only achieve an accuracy of 33% because the code fails to run over 58% of the time. We improve the failure rate for open models by fine-tuning synthetic data, allowing much smaller models (Llama-3.1-8B) to achieve comparable accuracy to much larger ones (e.g., DeepSeek-R1). Taken together, our findings identify significant challenges to be solved before AI agents can automate earth observation, and suggest paths forward. The project page is available at https://iandrover.github.io/UnivEarth.
地球观测(EO)为环境监测、灾害管理、气候科学和其他科学领域提供了关键性的行星数据。在这里我们提出一个问题:人工智能系统是否已经准备好进行可靠的地球观测?我们引入了\datasetnamenospace数据集,该数据集包含来自NASA地球观测站文章的140个是与非问题,涵盖13个主题和17个卫星传感器。利用Google地球引擎API作为工具,LLM代理人的准确率仅为33%,因为代码有超过58%的时间无法运行。我们通过微调合成数据来提高开放模型的失败率,允许较小的模型(如Llama-3.1-8B)达到与较大的模型(如DeepSeek-R1)相当的准确率。总之,我们的研究指出了在人工智能代理实现自动化地球观测之前需要解决的重大挑战,并提出了今后的方向。项目页面可在https://iandrover.github.io/UnivEarth查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 36 pages
Summary
本文介绍了地球观测(EO)的重要性及其在环境监测、灾害管理、气候科学等领域的应用。针对AI系统在地球观测中的可靠性问题,文章提出了一个基准测试集,包含NASA地球观测站的140个是与非是问题,涉及13个主题和17颗卫星传感器。文章指出,使用Google地球引擎API作为工具时,大型语言模型(LLM)代理的准确率仅为33%,且存在代码运行失败率高达58%的问题。研究通过微调合成数据提高了开放模型的性能,并发现较小的模型(如Llama-3.1-8B)也能达到与大型模型相近的准确率。文章总结了AI代理在自动化地球观测方面仍需解决的挑战,并提出了解决方案。项目页面可通过链接访问:https://iandrover.github.io/UnivEarth。
Key Takeaways
- 地球观测(EO)对于环境监测、灾害管理、气候科学等领域至关重要。
- AI系统在地球观测中面临可靠性挑战。
- 提出一个基准测试集,包含NASA地球观测站的140个是与非是问题,用于评估AI系统在地球观测方面的表现。
- 使用Google地球引擎API时,大型语言模型(LLM)代理的准确率仅为33%,且存在代码运行失败率高达58%的问题。
- 通过微调合成数据可提高开放模型的性能。
- 较小模型(如Llama-3.1-8B)也能达到与大型模型相近的准确率。
点此查看论文截图

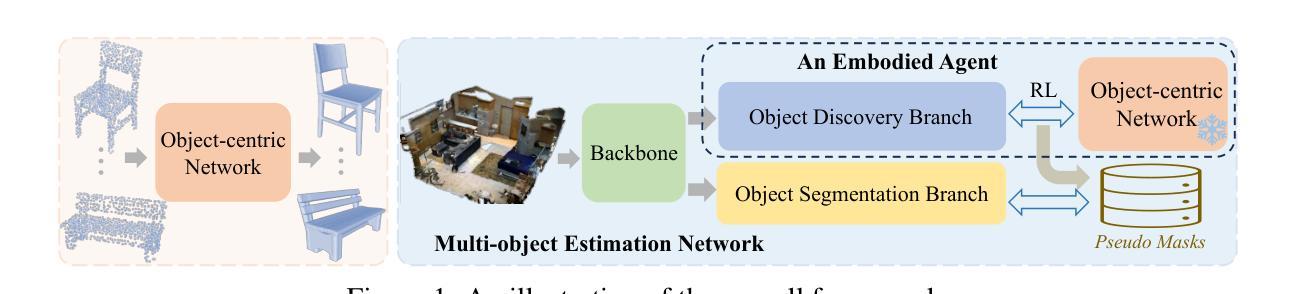
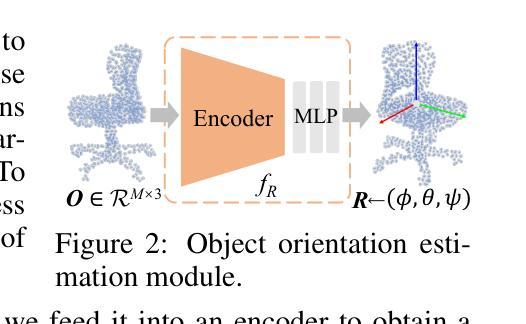
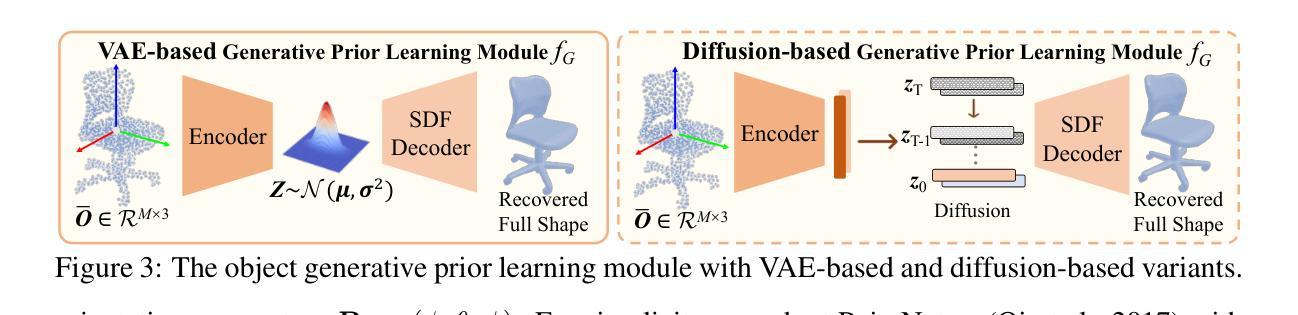
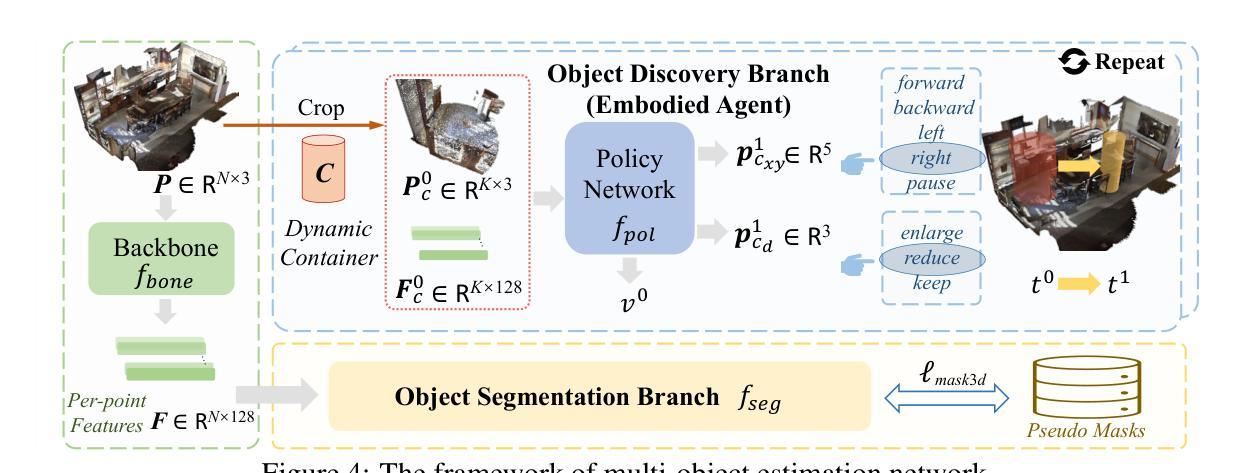
GrabS: Generative Embodied Agent for 3D Object Segmentation without Scene Supervision
Authors:Zihui Zhang, Yafei Yang, Hongtao Wen, Bo Yang
We study the hard problem of 3D object segmentation in complex point clouds without requiring human labels of 3D scenes for supervision. By relying on the similarity of pretrained 2D features or external signals such as motion to group 3D points as objects, existing unsupervised methods are usually limited to identifying simple objects like cars or their segmented objects are often inferior due to the lack of objectness in pretrained features. In this paper, we propose a new two-stage pipeline called GrabS. The core concept of our method is to learn generative and discriminative object-centric priors as a foundation from object datasets in the first stage, and then design an embodied agent to learn to discover multiple objects by querying against the pretrained generative priors in the second stage. We extensively evaluate our method on two real-world datasets and a newly created synthetic dataset, demonstrating remarkable segmentation performance, clearly surpassing all existing unsupervised methods.
我们研究了复杂点云中的三维物体分割这一难题,且研究过程中无需对三维场景进行人为标注以进行监督。现有无监督方法通常依赖于预训练的二维特征或运动等外部信号的相似性来对三维点进行物体分组,这些方法通常仅限于识别汽车等简单物体,或者其分割的物体质量较差,因为预训练特征中缺乏物体特性。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的两阶段流程,称为GrabS。我们的方法的核心概念是在第一阶段从对象数据集中学习生成和判别对象中心先验知识作为基础,然后在第二阶段设计一个智能体通过学习查询预训练的生成先验知识来发现多个对象。我们在两个真实数据集和一个新创建合成数据集上全面评估了我们的方法,展示出了显著的分割性能,明显超越了所有现有的无监督方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 Spotlight. Code and data are available at: https://github.com/vLAR-group/GrabS
Summary
本文研究了无需人工标注的复杂点云中的三维物体分割问题。文章提出了一种新的两步方法,名为GrabS。首先通过利用预先训练好的二维特征或外部信号(如运动)将三维点分为对象来学习生成性和鉴别性对象为中心的先验知识。在第一阶段进行。然后设计一种自主代理,通过查询预先训练的生成先验知识来发现多个对象。该方法在真实数据集和新建合成数据集上的表现令人印象深刻,显著优于现有的无监督方法。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对复杂点云中的三维物体分割问题,无需人工标注。
- 提出了一种新的两步方法GrabS进行三维物体分割。
- 第一阶段学习生成性和鉴别性对象为中心的先验知识。
- 第二阶段设计自主代理,通过查询预先训练的生成先验知识来发现多个对象。
- 方法在真实数据集和新建合成数据集上的表现优异,超越现有无监督方法。
- 利用预先训练好的二维特征和外部信号(如运动)进行三维点分组。
点此查看论文截图

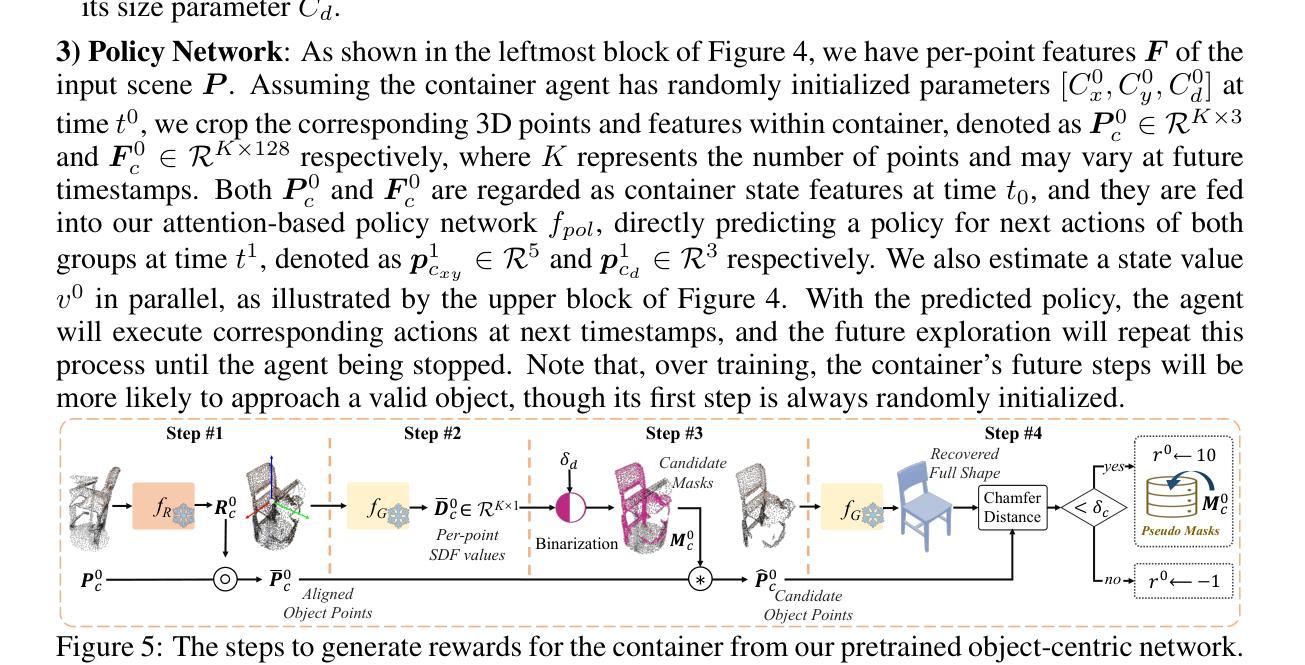
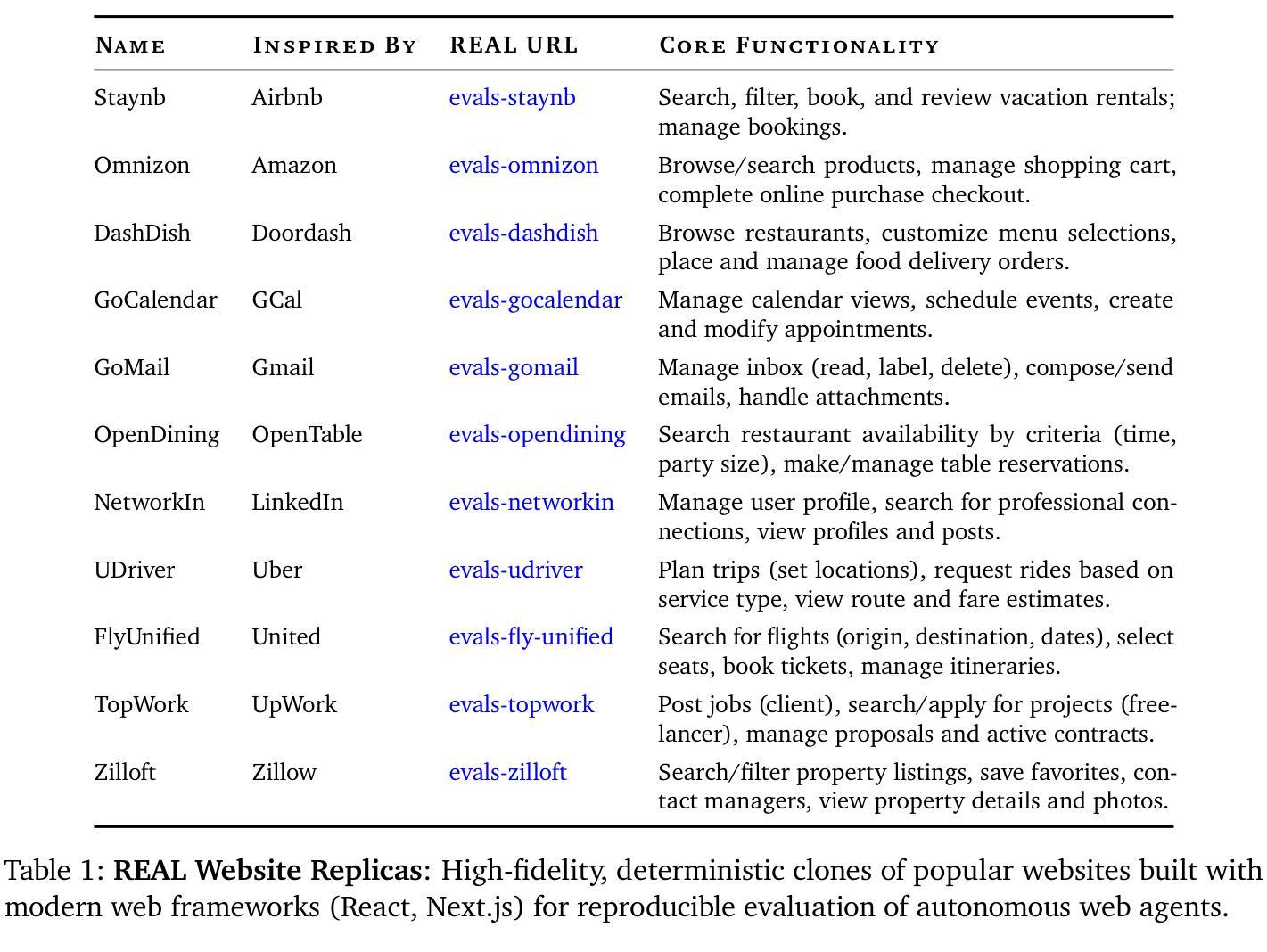
REAL: Benchmarking Autonomous Agents on Deterministic Simulations of Real Websites
Authors:Divyansh Garg, Shaun VanWeelden, Diego Caples, Andis Draguns, Nikil Ravi, Pranav Putta, Naman Garg, Tomas Abraham, Michael Lara, Federico Lopez, James Liu, Atharva Gundawar, Prannay Hebbar, Youngchul Joo, Charles London, Christian Schroeder de Witt, Sumeet Motwani
We introduce REAL, a benchmark and framework for multi-turn agent evaluations on deterministic simulations of real-world websites. REAL comprises high-fidelity, deterministic replicas of 11 widely-used websites across domains such as e-commerce, travel, communication, and professional networking. We also release a benchmark consisting of 112 practical tasks that mirror everyday complex user interactions requiring both accurate information retrieval and state-changing actions. All interactions occur within this fully controlled setting, eliminating safety risks and enabling robust, reproducible evaluation of agent capability and reliability. Our novel evaluation framework combines programmatic checks of website state for action-based tasks with rubric-guided LLM-based judgments for information retrieval. The framework supports both open-source and proprietary agent systems through a flexible evaluation harness that accommodates black-box commands within browser environments, allowing research labs to test agentic systems without modification. Our empirical results show that frontier language models achieve at most a 41% success rate on REAL, highlighting critical gaps in autonomous web navigation and task completion capabilities. Our framework supports easy integration of new tasks, reproducible evaluation, and scalable data generation for training web agents. The websites, framework, and leaderboard are available at https://realevals.xyz and https://github.com/agi-inc/REAL.
我们引入了REAL,这是一个在真实网站确定性模拟上进行多轮代理评估的基准和框架。REAL包含了高保真、确定性的复制版本,涵盖了电子商务、旅游、通信和专业网络等领域的11个广泛使用的网站。我们还发布了一个包含112个实用任务的基准测试,这些任务反映了日常复杂的用户交互,需要准确的信息检索和状态更改操作。所有的交互都发生在这个完全受控的环境中,消除了安全风险,并能够稳健、可重复地评估代理的能力和可靠性。我们新颖的评价框架结合了基于网站状态的程序化检查(针对基于行动的任务)和基于规则的LLM判断(针对信息检索)。该框架支持开源和专有代理系统,通过一个灵活的评价装置来适应浏览器环境中的黑箱命令,使得研究实验室能够测试代理系统而无需进行修改。我们的实证结果表明,最先进的语言模型在REAL上的成功率最高仅为41%,这凸显了自主网页导航和任务完成能力的关键差距。我们的框架支持轻松集成新任务、可重复评估和可扩展的数据生成,以训练网页代理。网站、框架和排行榜可在https://realevals.xyz和https://github.com/agi-inc/REAL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了REAL,这是一个针对真实世界网站确定性模拟的多轮代理评估的基准和框架。REAL包含11个高保真确定性副本的广泛使用的网站,并发布了一个包含112个实用任务的基准测试,这些任务反映了日常复杂的用户交互,需要准确的信息检索和状态更改操作。该评估框架结合了网站状态的程序检查,用于基于行动的任务,以及与检索信息指南的LLM判断。它为开源和专有代理系统提供了一个灵活的评价平台,支持在浏览器环境中进行黑箱命令操作,使得研究实验室能够测试代理系统无需修改。实证研究结果显示,最先进的语言模型在REAL上的成功率仅为41%,这凸显了自主网页导航和任务完成能力的关键差距。
Key Takeaways
- REAL是一个用于评估多轮代理在真实网站确定性模拟上的表现的基准和框架。
- 它包含11个高保真网站副本和112个实用任务,反映日常用户交互。
- REAL的评估框架结合了程序检查和LLM判断,用于评价代理的能力和可靠性。
- 框架支持多种代理系统,并提供灵活的评价平台,允许在浏览器环境中进行黑箱操作。
- 实证研究指出,现有语言模型在REAL上的成功率较低,凸显了自主网页导航和任务完成能力的差距。
- REAL易于集成新任务,支持可重复评估和可扩展的数据生成。
点此查看论文截图

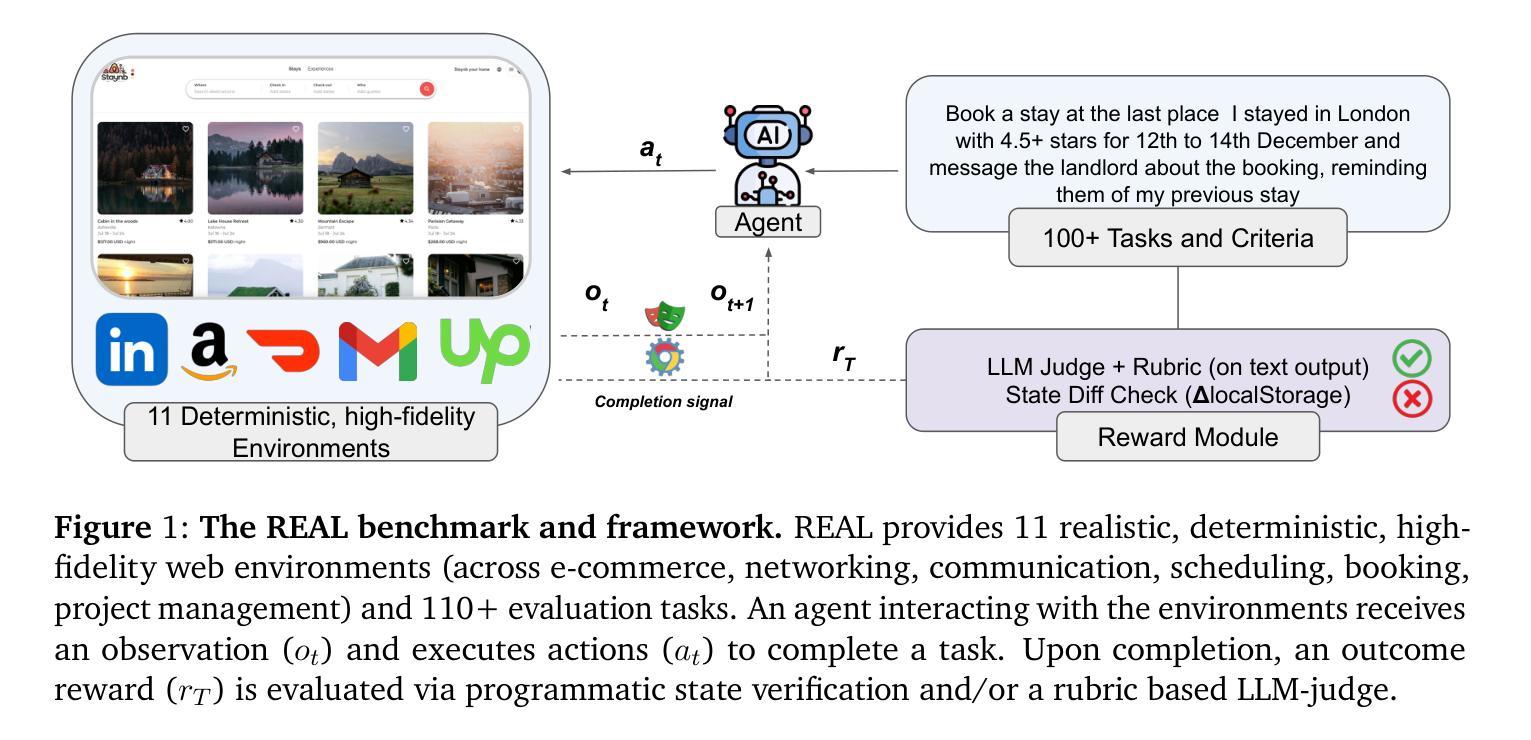

Task Memory Engine (TME): A Structured Memory Framework with Graph-Aware Extensions for Multi-Step LLM Agent Tasks
Authors:Ye Ye
Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used as autonomous agents for multi-step tasks. However, most existing frameworks fail to maintain a structured understanding of the task state, often relying on linear prompt concatenation or shallow memory buffers. This leads to brittle performance, frequent hallucinations, and poor long-range coherence. In this work, we propose the Task Memory Engine (TME), a lightweight and structured memory module that tracks task execution using a hierarchical Task Memory Tree (TMT). Each node in the tree corresponds to a task step, storing relevant input, output, status, and sub-task relationships. We introduce a prompt synthesis method that dynamically generates LLM prompts based on the active node path, significantly improving execution consistency and contextual grounding. Through case studies and comparative experiments on multi-step agent tasks, we demonstrate that TME leads to better task completion accuracy and more interpretable behavior with minimal implementation overhead. A reference implementation of the core TME components is available at https://github.com/biubiutomato/TME-Agent, including basic examples and structured memory integration. While the current implementation uses a tree-based structure, TME is designed to be graph-aware, supporting reusable substeps, converging task paths, and shared dependencies. This lays the groundwork for future DAG-based memory architectures.
大型语言模型(LLMs)越来越多地被用作多步骤任务的自主代理。然而,大多数现有框架无法维持对任务状态的结构化理解,通常依赖于线性提示串联或浅内存缓冲区。这导致性能不稳定、频繁出现幻觉和长期连贯性差。在这项工作中,我们提出了任务记忆引擎(TME),这是一个轻量级、结构化的内存模块,使用分层的任务记忆树(TMT)来跟踪任务执行情况。树中的每个节点对应一个任务步骤,存储相关的输入、输出、状态和子任务关系。我们引入了一种提示合成方法,该方法根据活动节点路径动态生成LLM提示,显著提高了执行一致性上下文定位。通过多步骤代理任务的案例研究和对比实验,我们证明了TME在提高任务完成准确性和更可解释的行为方面具有优势,且实现开销最小。核心TME组件的参考实现可在[https://github.com/biubiutomato/TME-Agent找到,包括基本示例和结构化内存集成。虽然当前实现使用了树形结构,但TME被设计为图感知,支持可重用的子步骤、收敛的任务路径和共享依赖。这为未来基于DAG的内存架构奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 5 figures. Preprint prepared for future submission. Includes implementation and token-efficiency analysis. Code at https://github.com/biubiutomato/TME-Agent
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)被越来越多地用作多步骤任务的自主代理,但其现有框架大多缺乏任务状态的结构化理解,这导致了性能不稳定、经常幻想和长期连贯性差。为解决这一问题,我们提出了任务记忆引擎(TME)和层次化任务记忆树(TMT)。TME通过动态生成LLM提示来改善执行一致性,提高任务完成准确性并增强行为可解释性。相关实现细节可参考:链接。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在多步骤任务中的自主代理应用面临挑战。
- 当前框架缺乏任务状态的结构化理解,导致性能不稳定和连贯性差。
- 提出任务记忆引擎(TME)和层次化任务记忆树(TMT)来解决这些问题。
- TME通过动态生成LLM提示改善执行一致性。
- TME提高了任务完成准确性和行为可解释性。
- TME具有图形感知设计,支持可重复的子步骤、收敛任务路径和共享依赖,为未来基于DAG的内存架构奠定基础。
点此查看论文截图

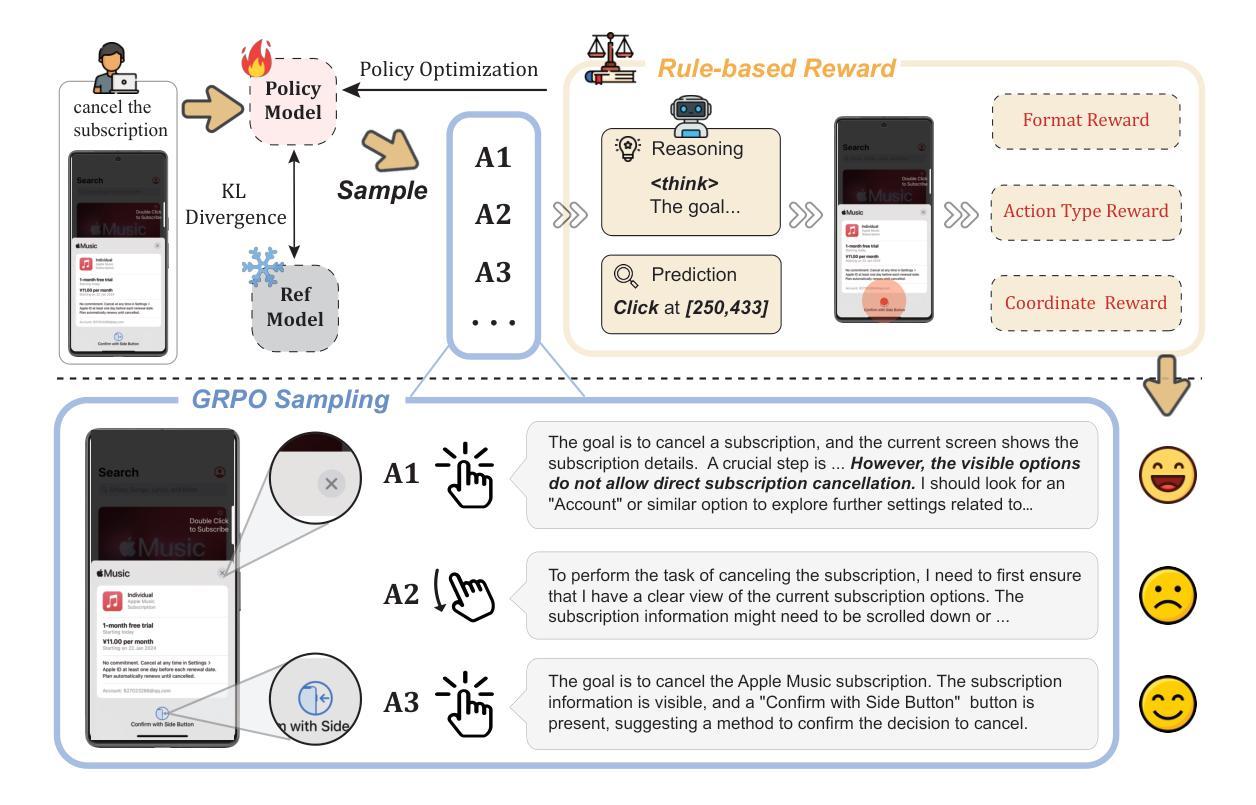
UI-R1: Enhancing Action Prediction of GUI Agents by Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Zhengxi Lu, Yuxiang Chai, Yaxuan Guo, Xi Yin, Liang Liu, Hao Wang, Han Xiao, Shuai Ren, Guanjing Xiong, Hongsheng Li
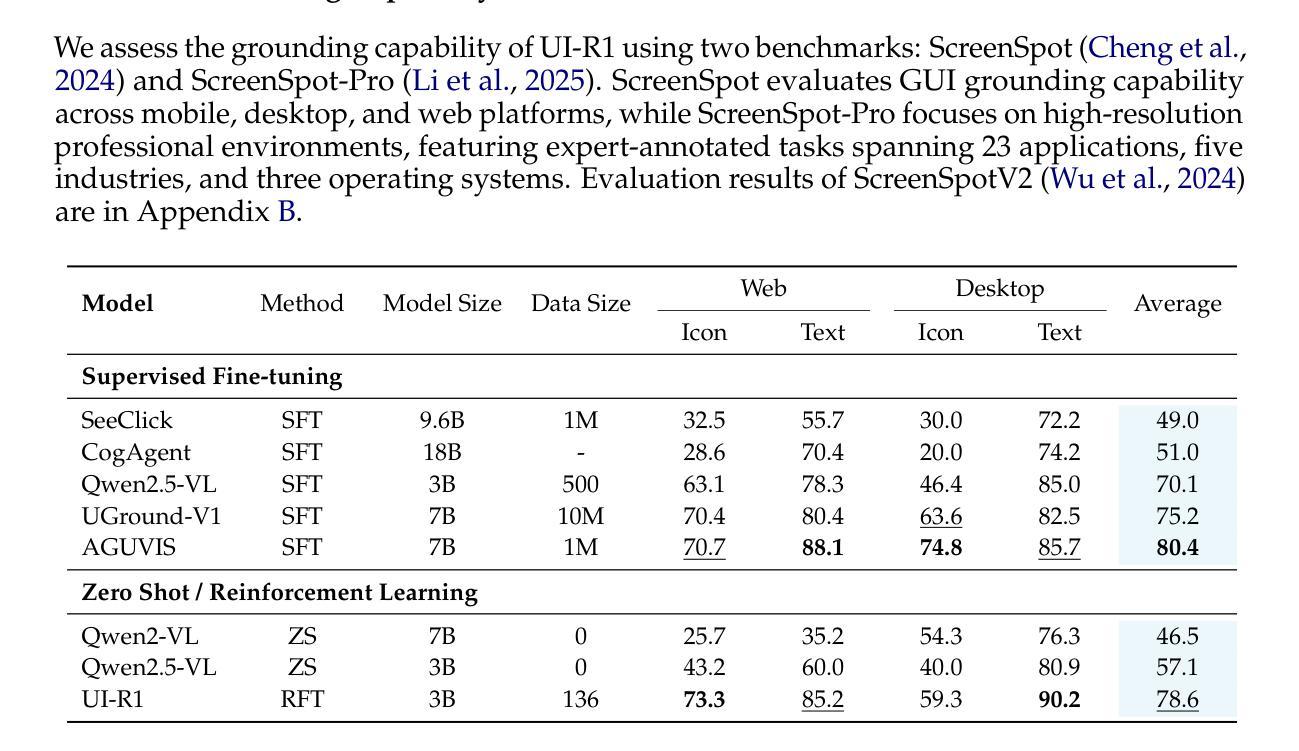
The recent DeepSeek-R1 has showcased the emergence of reasoning capabilities in LLMs through reinforcement learning (RL) with rule-based rewards. Despite its success in language models, its application in multi-modal domains, particularly in graphic user interface (GUI) agent tasks, remains under-explored. To address this issue, we propose UI-R1, the first framework to explore how rule-based RL can enhance the reasoning capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) for GUI action prediction tasks. Specifically, UI-R1 introduces a novel rule-based action reward, enabling model optimization via policy-based algorithms such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). For efficient training, we curate a small yet high-quality dataset of 136 challenging tasks, encompassing five common action types on mobile devices. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed UI-R1-3B achieves significant improvements over the base model (i.e. Qwen2.5-VL-3B) on both in-domain (ID) and out-of-domain (OOD) tasks, with average accuracy gains of 22.1% on ScreenSpot, 6.0% on ScreenSpot-Pro, and 12.7% on ANDROIDCONTROL. Furthermore, UI-R1-3B delivers competitive performance compared to larger models (e.g., OS-Atlas-7B) trained via supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on 76K samples. These results underscore the potential of rule-based reinforcement learning to advance GUI understanding and control, paving the way for future research in this domain. Code website: https://github.com/lll6gg/UI-R1.
最近,DeepSeek-R1展示了通过基于规则的奖励进行强化学习(RL)后,大型语言模型(LLM)中推理能力的出现。尽管它在语言模型方面取得了成功,但在多模式领域,特别是在图形用户界面(GUI)代理任务中的应用仍然未被充分探索。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了UI-R1,这是第一个探索基于规则的RL如何增强多模式大型语言模型(MLLM)的推理能力,以执行GUI动作预测任务的框架。具体来说,UI-R1引入了一种新型的基于动作的规则奖励,通过基于策略算法(如集团相对策略优化(GRPO))进行模型优化。为了进行有效的训练,我们创建了一个小型但高质量的数据集,包含136个具有挑战性的任务,涵盖移动设备上的五种常见动作类型。实验结果表明,我们提出的UI-R1-3B在域内(ID)和域外(OOD)任务上都较基础模型(即Qwen2.5-VL-3B)有显著改进,在ScreenSpot上的平均准确率提高了22.1%,在ScreenSpot-Pro上提高了6.0%,在ANDROIDCONTROL上提高了12.7%。此外,与在76K样本上通过监督微调(SFT)训练的更大模型(如OS-Atlas-7B)相比,UI-R1-3B表现出具有竞争力的性能。这些结果突显了基于规则的强化学习在GUI理解和控制方面的潜力,为未来的研究铺平了道路。代码网站:https://github.com/lll6gg/UI-R1。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了DeepSeek-R1展示了大语言模型通过强化学习(RL)出现推理能力的新兴趋势。为应对在图形用户界面(GUI)代理任务中多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的应用不足问题,首次提出UI-R1框架。通过引入基于规则的行动奖励,优化模型通过基于策略算法如群体相对策略优化(GRPO)。实验结果显示,相比基准模型,UI-R1-3B在域内(ID)和域外(OOD)任务上的表现均有显著提高,平均准确率提升显著。此外,UI-R1-3B在大型模型上的表现同样具有竞争力。这表明基于规则的强化学习在GUI理解和控制方面具有潜力。
Key Takeaways
- DeepSeek-R1展示了大型语言模型通过强化学习展现的推理能力。
- UI-R1框架旨在探索规则基础强化学习如何增强多模态大型语言模型在GUI行动预测任务中的推理能力。
- UI-R1引入基于行动的规则奖励,通过策略型算法如GRPO进行模型优化。
- 实验结果显示,UI-R1-3B在多种任务上较基准模型表现显著提高,并表现出对大型模型的竞争力。
- 基于规则的强化学习在GUI理解和控制方面展现出潜力。
- 数据集包含136项具有挑战性的任务,涵盖移动设备上的五种常见动作类型。
点此查看论文截图

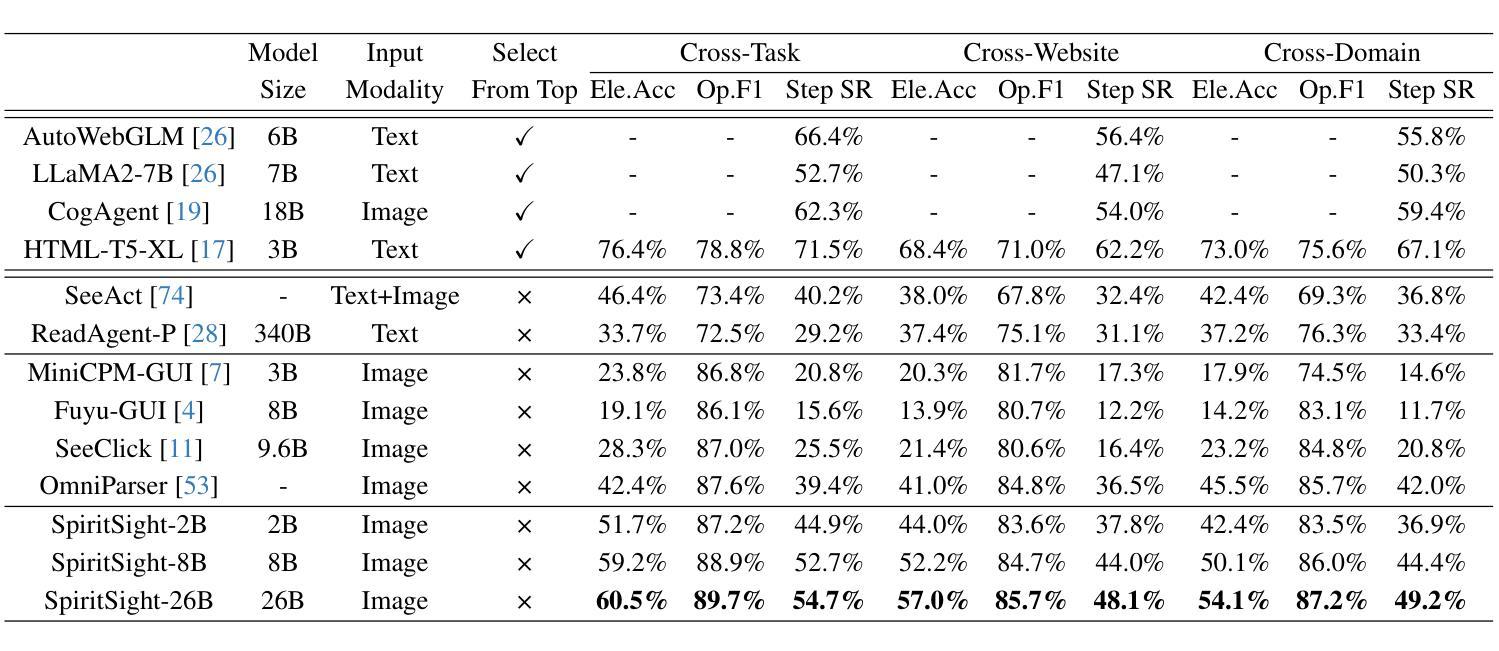
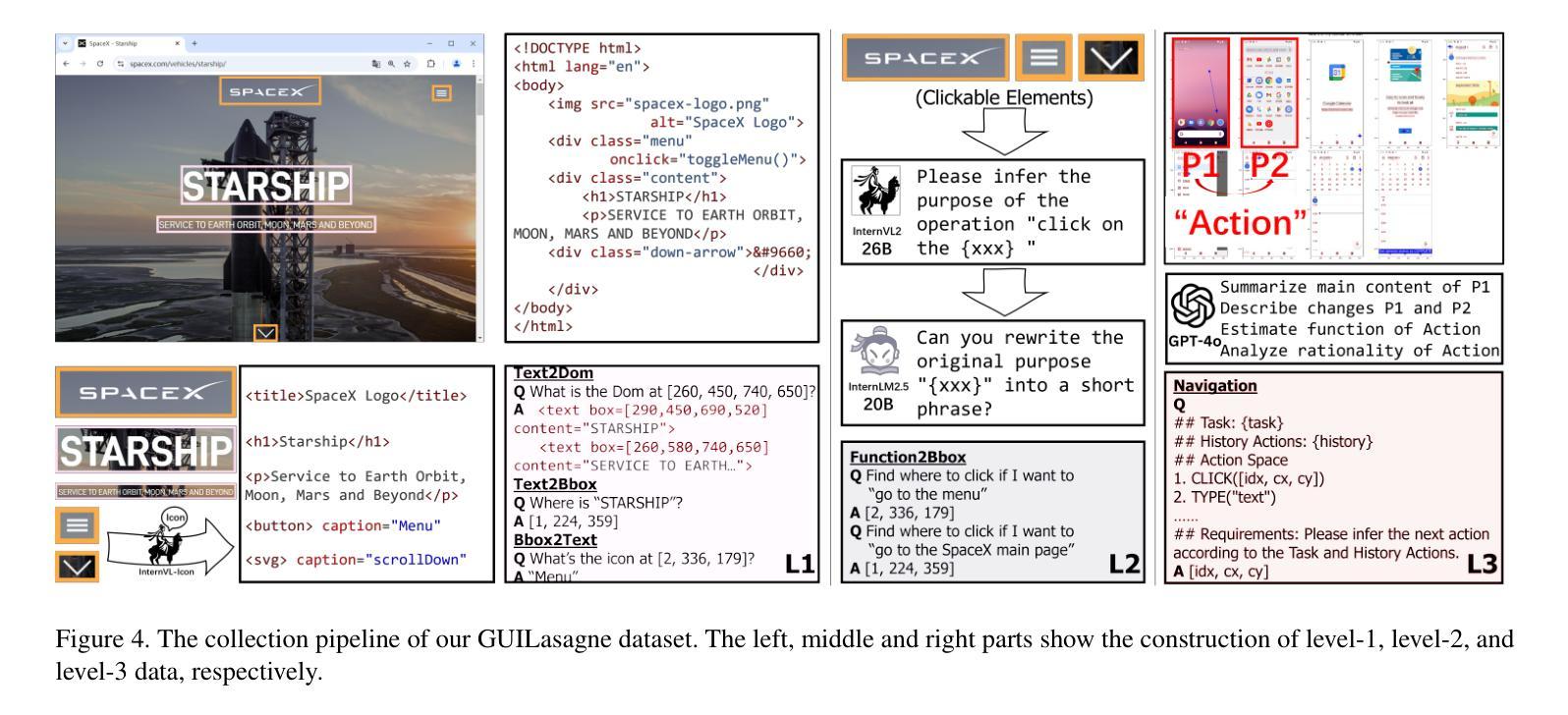
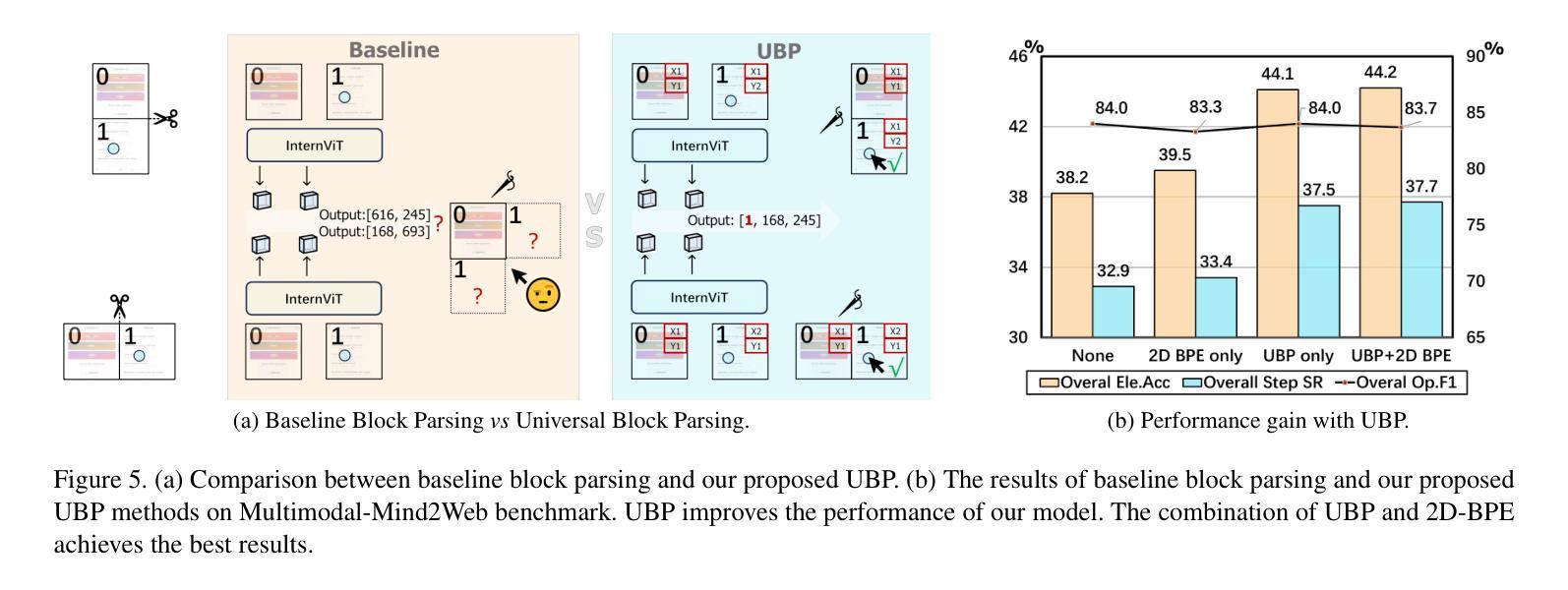
SpiritSight Agent: Advanced GUI Agent with One Look
Authors:Zhiyuan Huang, Ziming Cheng, Junting Pan, Zhaohui Hou, Mingjie Zhan
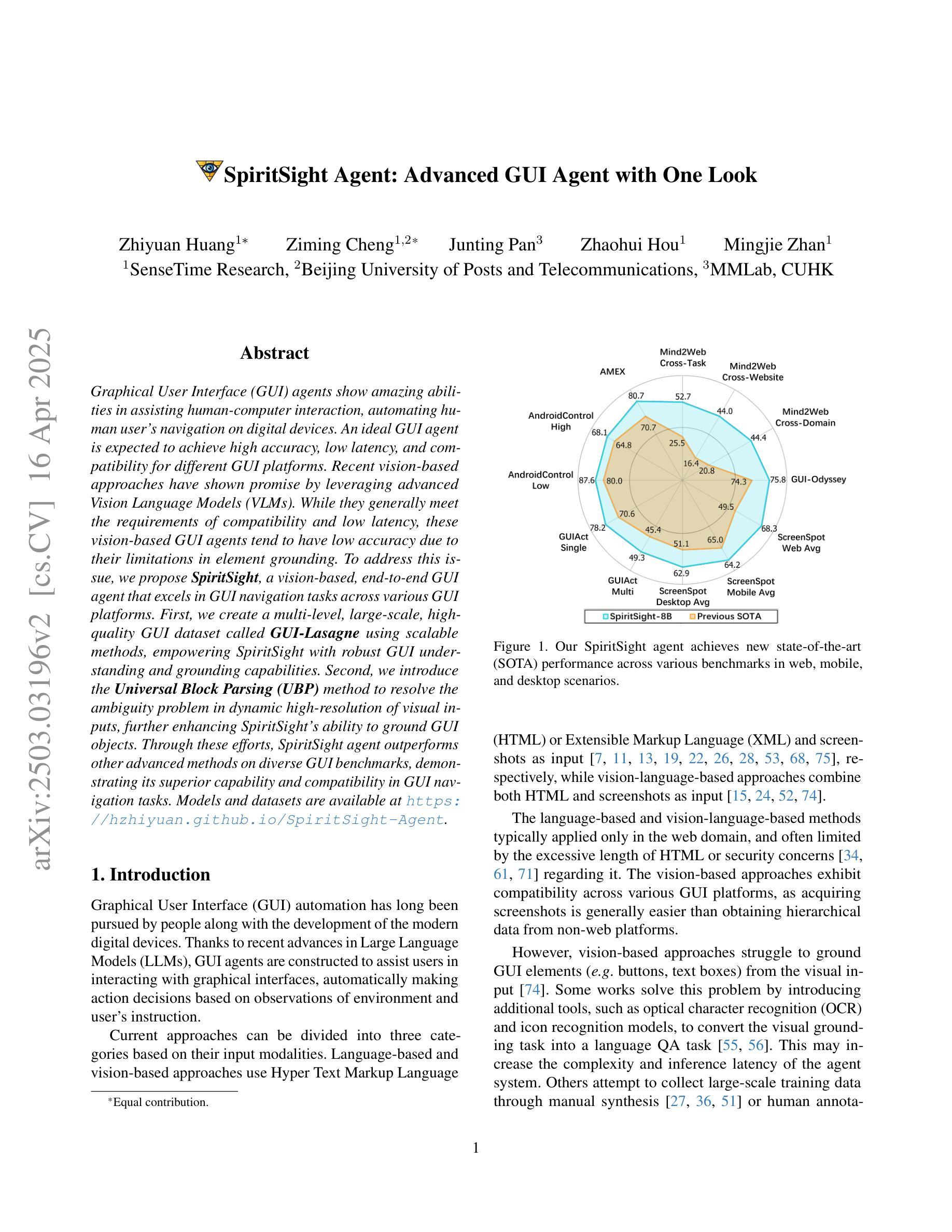
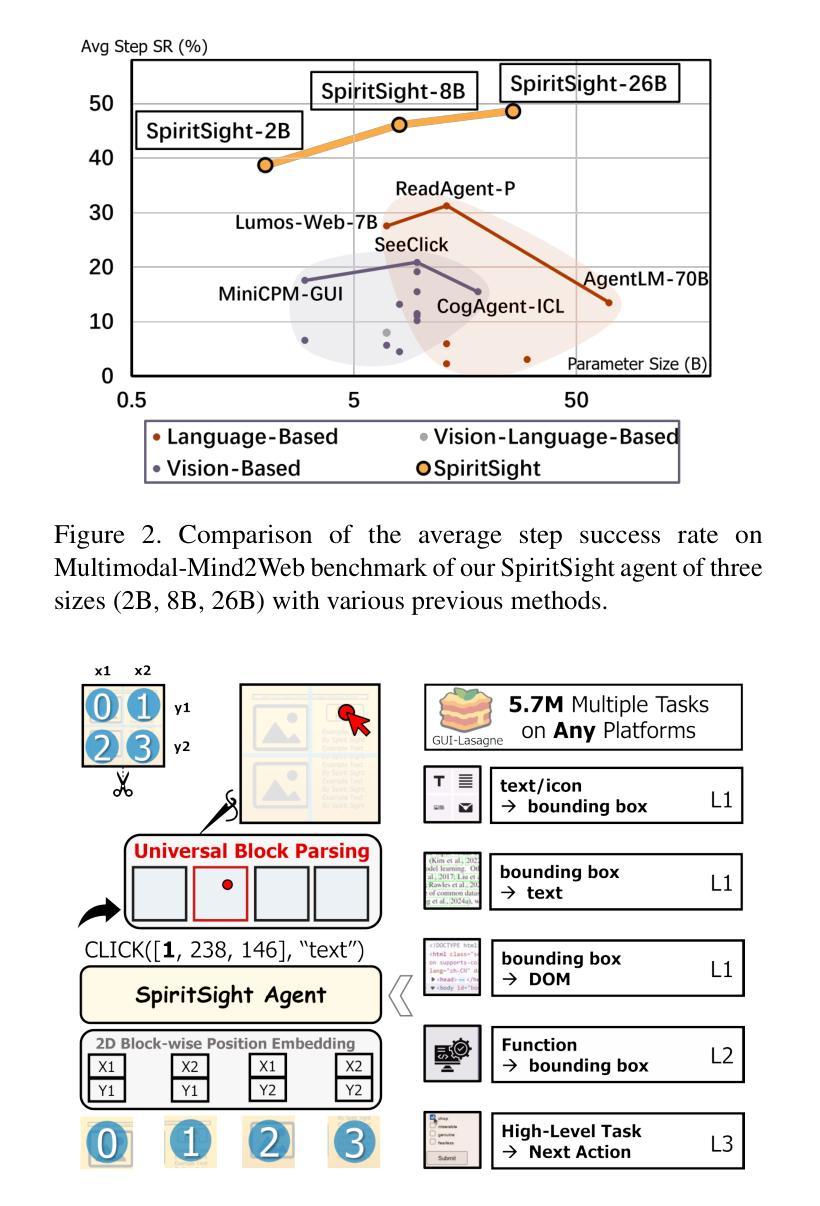
Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents show amazing abilities in assisting human-computer interaction, automating human user’s navigation on digital devices. An ideal GUI agent is expected to achieve high accuracy, low latency, and compatibility for different GUI platforms. Recent vision-based approaches have shown promise by leveraging advanced Vision Language Models (VLMs). While they generally meet the requirements of compatibility and low latency, these vision-based GUI agents tend to have low accuracy due to their limitations in element grounding. To address this issue, we propose $\textbf{SpiritSight}$, a vision-based, end-to-end GUI agent that excels in GUI navigation tasks across various GUI platforms. First, we create a multi-level, large-scale, high-quality GUI dataset called $\textbf{GUI-Lasagne}$ using scalable methods, empowering SpiritSight with robust GUI understanding and grounding capabilities. Second, we introduce the $\textbf{Universal Block Parsing (UBP)}$ method to resolve the ambiguity problem in dynamic high-resolution of visual inputs, further enhancing SpiritSight’s ability to ground GUI objects. Through these efforts, SpiritSight agent outperforms other advanced methods on diverse GUI benchmarks, demonstrating its superior capability and compatibility in GUI navigation tasks. Models and datasets are available at https://hzhiyuan.github.io/SpiritSight-Agent.
图形用户界面(GUI)代理在辅助人机交互、自动化人类用户在数字设备上的导航方面表现出惊人的能力。理想的GUI代理应达到高准确性、低延迟和不同GUI平台的兼容性。最近的基于视觉的方法通过利用先进的视觉语言模型(VLMs)显示出潜力。虽然它们通常满足兼容性和低延迟的要求,但这些基于视觉的GUI代理往往由于元素定位的限制而准确性较低。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了基于视觉的端到端GUI代理——SpiritSight,它在各种GUI平台上的GUI导航任务中表现出色。首先,我们使用可扩展的方法创建了一个多层次、大规模、高质量的GUI数据集,名为GUI-Lasagne,为SpiritSight提供强大的GUI理解和定位能力。其次,我们引入了通用块解析(UBP)方法来解决动态高分辨率视觉输入的歧义问题,进一步增强了SpiritSight对GUI对象的定位能力。通过这些努力,SpiritSight代理在多种GUI基准测试上超越了其他先进方法,证明了其在GUI导航任务中的卓越能力和兼容性。模型和数据集可在https://hzhiyuan.github.io/SpiritSight-Agent上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
视觉界面的图形用户界面(GUI)代理在辅助人机交互、自动化用户导航方面展现出强大能力。为改进现有视觉基础GUI代理的精度问题,提出了一款名为SpiritSight的新型GUI代理,其借助大规模GUI数据集GUI-Lasagne与Universal Block Parsing(UBP)方法,提升了对GUI导航任务的掌握能力,展现出卓越的跨平台兼容性及高精度、低延迟特性。
Key Takeaways
- GUI代理在协助人机交互和自动化导航方面表现突出,需要满足高准确性、低延迟和不同GUI平台的兼容性。
- 现有视觉基础的GUI代理在元素定位方面存在局限性,导致准确性较低。
- 为解决这一问题,提出了SpiritSight代理,其在大规模GUI数据集GUI-Lasagne的支持下,具备强大的GUI理解和定位能力。
- Universal Block Parsing(UBP)方法被引入以解决动态高分辨率视觉输入中的歧义问题,增强了SpiritSight对GUI对象的定位能力。
- SpiritSight代理在多种GUI基准测试上表现出优异性能,展现出其高兼容性和强大能力。
- SpiritSight代理和相关的数据集可通过https://hzhiyuan.github.io/SpiritSight-Agent获取。
点此查看论文截图
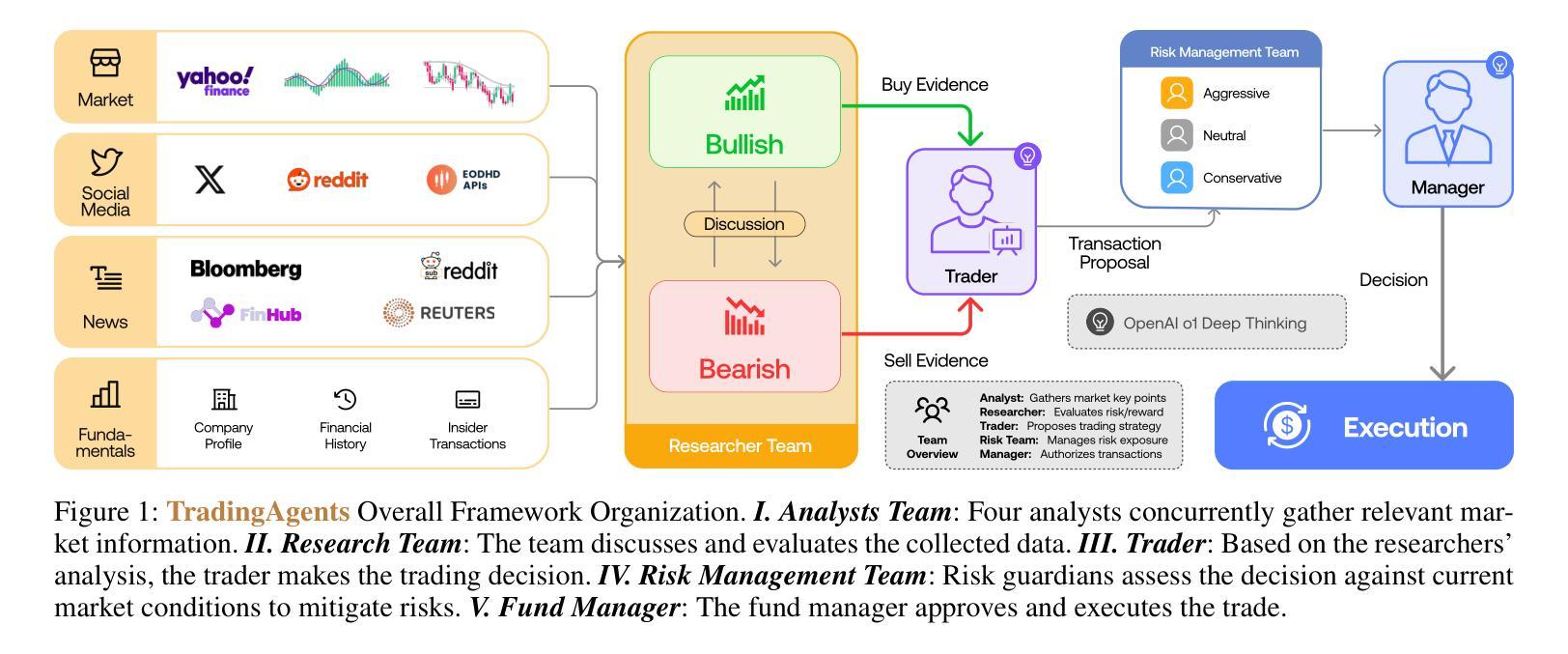
TradingAgents: Multi-Agents LLM Financial Trading Framework
Authors:Yijia Xiao, Edward Sun, Di Luo, Wei Wang
Significant progress has been made in automated problem-solving using societies of agents powered by large language models (LLMs). In finance, efforts have largely focused on single-agent systems handling specific tasks or multi-agent frameworks independently gathering data. However, multi-agent systems’ potential to replicate real-world trading firms’ collaborative dynamics remains underexplored. TradingAgents proposes a novel stock trading framework inspired by trading firms, featuring LLM-powered agents in specialized roles such as fundamental analysts, sentiment analysts, technical analysts, and traders with varied risk profiles. The framework includes Bull and Bear researcher agents assessing market conditions, a risk management team monitoring exposure, and traders synthesizing insights from debates and historical data to make informed decisions. By simulating a dynamic, collaborative trading environment, this framework aims to improve trading performance. Detailed architecture and extensive experiments reveal its superiority over baseline models, with notable improvements in cumulative returns, Sharpe ratio, and maximum drawdown, highlighting the potential of multi-agent LLM frameworks in financial trading. TradingAgents is available at https://github.com/TauricResearch.
在利用大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的智能体社会解决自动化问题方面取得了重大进展。在金融领域,相关努力主要集中在处理特定任务的单一智能体系统或独立收集数据的多智能体框架上。然而,多智能体系统在复制现实世界交易公司的协作动态方面的潜力尚未得到充分探索。《TradingAgents》提出了一种受交易公司启发的新型股票交易框架,该框架具有专门的角色智能体,例如基础分析师、情绪分析师、技术分析师和不同风险状况的交易员等。该框架包括评估市场条件的牛市和熊市研究者智能体、监控敞口的风险管理团队以及从辩论和历史数据中提炼见解以做出明智决策的交易员。通过模拟动态协作的交易环境,该框架旨在提高交易性能。详细的架构和广泛的实验表明其在累计回报、夏普比率和最大回撤方面优于基准模型,突显了多智能体LLM框架在金融交易中的潜力。《TradingAgents》可通过 https://github.com/TauricResearch 获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Oral, Multi-Agent AI in the Real World @ AAAI 2025
总结
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理社会在自动化问题解决方面取得了显著进展。在金融领域,尽管单一代理系统处理特定任务或多代理框架独立收集数据的工作已经备受关注,但多代理系统在模拟现实世界交易公司协作动态方面的潜力仍被低估。TradingAgents提出一个受交易公司启发的股票交易新框架,该框架采用LLM驱动的多代理系统,包括基础分析师、情绪分析师、技术分析师和具有不同风险特征的交易员等专业化角色。框架包括评估市场状况的Bull和Bear研究员代理、监控风险的风险管理团队以及合成辩论和历史数据以做出明智决策的交易员。通过模拟动态协作的交易环境,该框架旨在提高交易性能。详细的架构和广泛的实验表明,其在累积回报、夏普比率和最大回撤方面优于基准模型,突显了多代理LLM框架在金融交易中的潜力。TradingAgents平台可通过https://github.com/TauricResearch访问。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的代理社会在自动化问题解决方面取得显著进步。
- 金融领域主要聚焦于单一代理系统处理特定任务或多代理框架独立收集数据的应用场景。
- 多代理系统在模拟现实世界交易公司的协作动态方面具有潜力。
- TradingAgents提出一种模拟交易公司的新型股票交易框架,采用多代理系统处理多种金融角色。
- 该框架包含市场状况评估、风险管理以及基于辩论和历史数据的决策制定等要素。
- 通过模拟动态协作的交易环境,该框架可提高交易性能。
点此查看论文截图

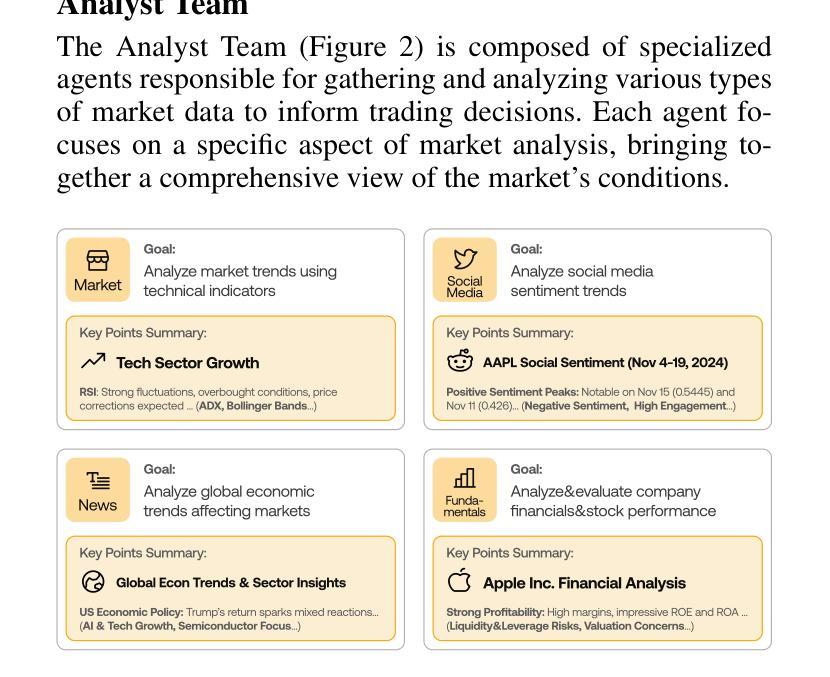


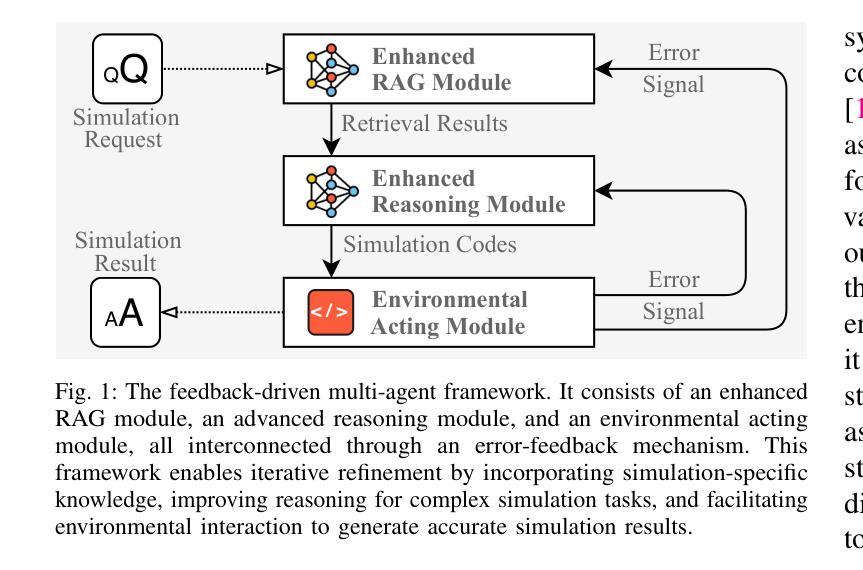
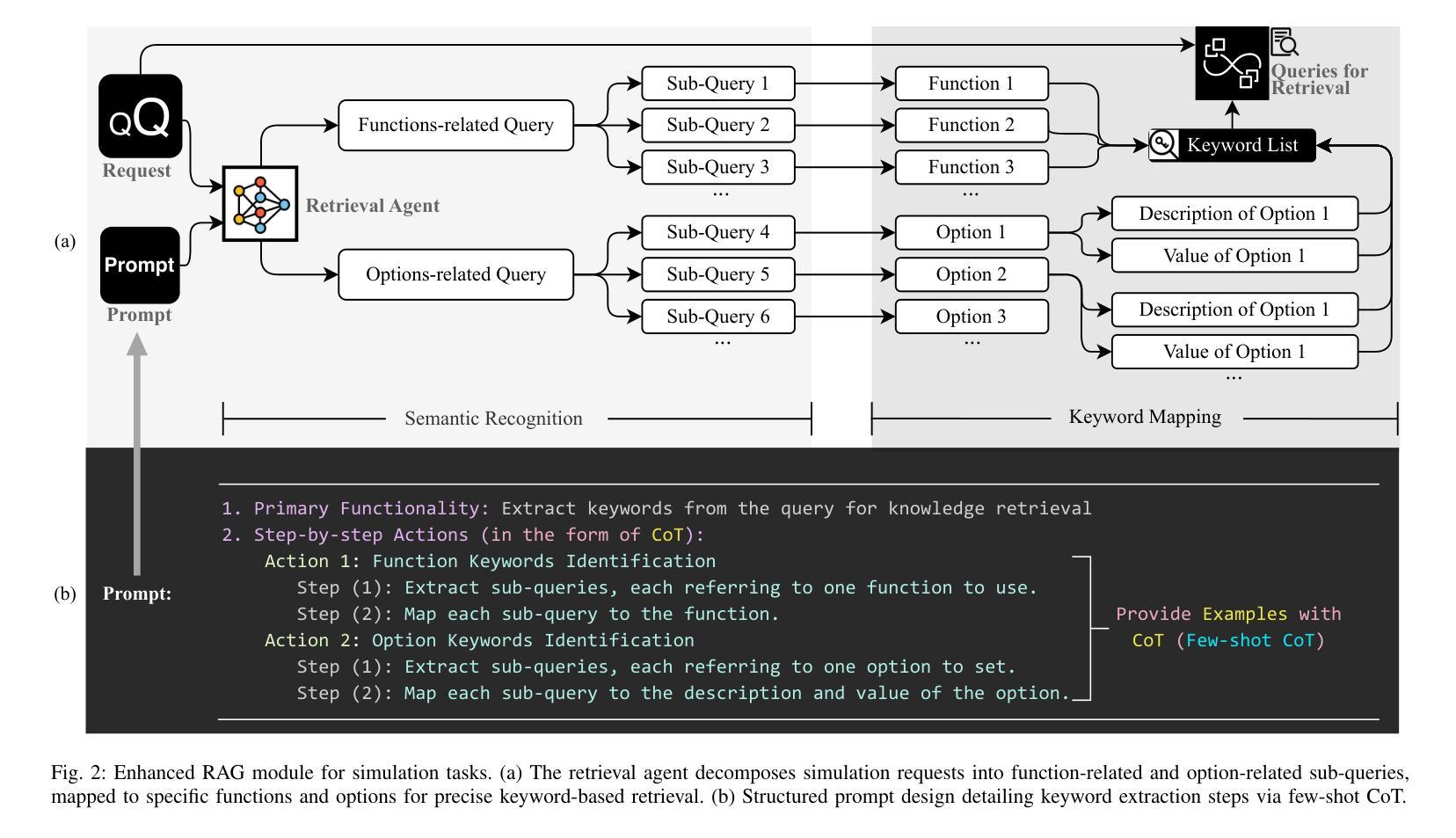
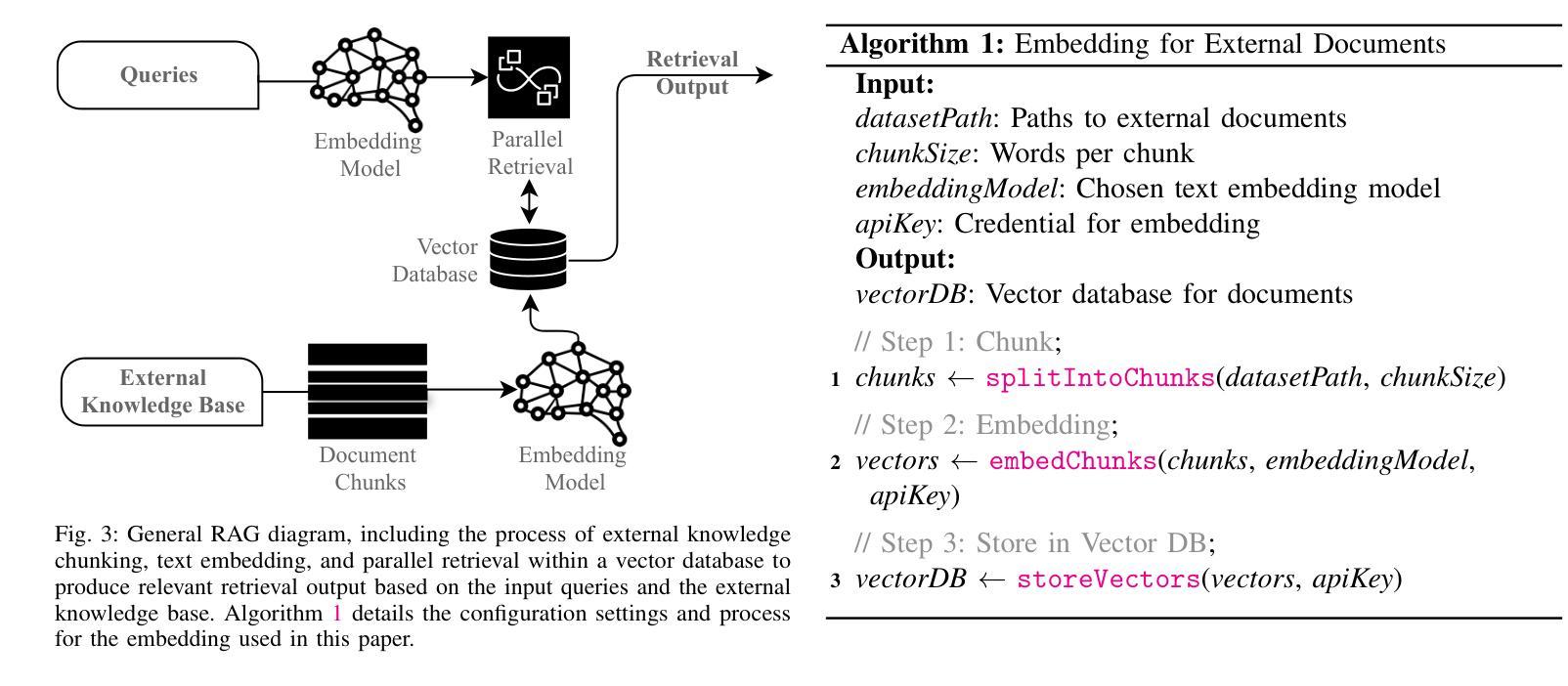
Enhancing LLMs for Power System Simulations: A Feedback-driven Multi-agent Framework
Authors:Mengshuo Jia, Zeyu Cui, Gabriela Hug
The integration of experimental technologies with large language models (LLMs) is transforming scientific research. It positions AI as a versatile research assistant rather than a mere problem-solving tool. In the field of power systems, however, managing simulations – one of the essential experimental technologies – remains a challenge for LLMs due to their limited domain-specific knowledge, restricted reasoning capabilities, and imprecise handling of simulation parameters. To address these limitations, this paper proposes a feedback-driven, multi-agent framework. It incorporates three proposed modules: an enhanced retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) module, an improved reasoning module, and a dynamic environmental acting module with an error-feedback mechanism. Validated on 69 diverse tasks from Daline and MATPOWER, this framework achieves success rates of 93.13% and 96.85%, respectively. It significantly outperforms ChatGPT 4o, o1-preview, and the fine-tuned GPT-4o, which all achieved a success rate lower than 30% on complex tasks. Additionally, the proposed framework also supports rapid, cost-effective task execution, completing each simulation in approximately 30 seconds at an average cost of 0.014 USD for tokens. Overall, this adaptable framework lays a foundation for developing intelligent LLM-based assistants for human researchers, facilitating power system research and beyond.
将实验技术与大型语言模型(LLM)的结合正在改变科学研究的方式。它将人工智能定位为多才多艺的研究助手,而不仅仅是解决问题的工具。然而,在电力系统领域,管理模拟(一种重要的实验技术)对LLM来说仍然是一个挑战,因为它们有限的特定领域知识、有限的推理能力和对模拟参数的不精确处理。为了克服这些局限性,本文提出了一种反馈驱动的多智能体框架。它结合了三个提出的模块:一个增强的检索增强生成(RAG)模块,一个改进的推理模块,以及一个带有错误反馈机制的动力环境行为模块。在Daline和MATPOWER的69个不同任务上进行验证,该框架的成功率分别为93.13%和96.85%。它显著优于ChatGPT 4o、o1预览和经过微调后的GPT-4o,这些模型在复杂任务上的成功率都低于30%。此外,该框架还支持快速、经济的任务执行,平均每个模拟大约需要30秒完成,令牌平均成本为0.014美元。总的来说,这个灵活多变的框架为开发基于LLM的智能助手为研究人员奠定了基础,促进了电力系统研究及其他领域的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages
Summary
实验技术与大型语言模型(LLM)的融合正在推动科学研究的发展。人工智能已成为多才多艺的研究助手,而不仅仅是解决问题的工具。在电力系统领域,管理模拟作为重要的实验技术之一仍然是LLM的一个挑战。针对这些挑战,本文提出了一种反馈驱动的多智能体框架,包括增强检索增强生成模块、改进推理模块和具有错误反馈机制动态环境行为模块。该框架在Daline和MATPOWER的69项不同任务上取得了高达93.13%和96.85%的成功率,显著优于ChatGPT 4o、o1预览和微调后的GPT-4o。此外,该框架还支持快速、经济的任务执行,每个模拟任务大约需要30秒,平均每个令牌成本为0.014美元。总体而言,这一灵活框架为开发基于LLM的智能助理研究员奠定了基础,推动了电力系统研究及其他领域的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 实验技术与LLM的融合推动科学研究发展。
- LLM在电力系统模拟管理上仍面临挑战。
- 提出了一种反馈驱动的多智能体框架来解决这些挑战。
- 该框架包括增强检索增强生成模块、改进推理模块和动态环境行为模块。
- 该框架在多种任务上取得了较高的成功率,显著优于其他模型。
- 框架支持快速、经济的任务执行。
点此查看论文截图

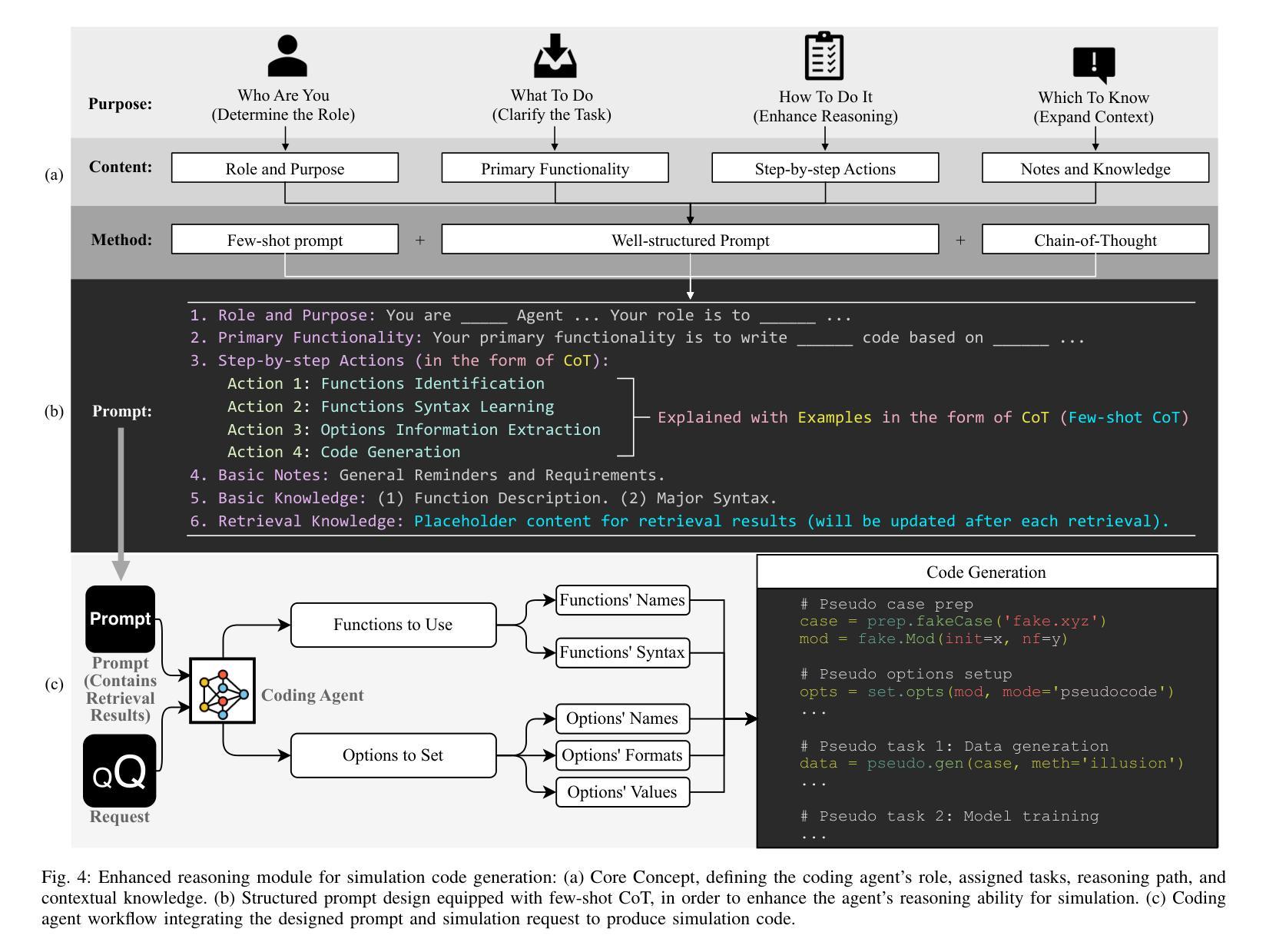
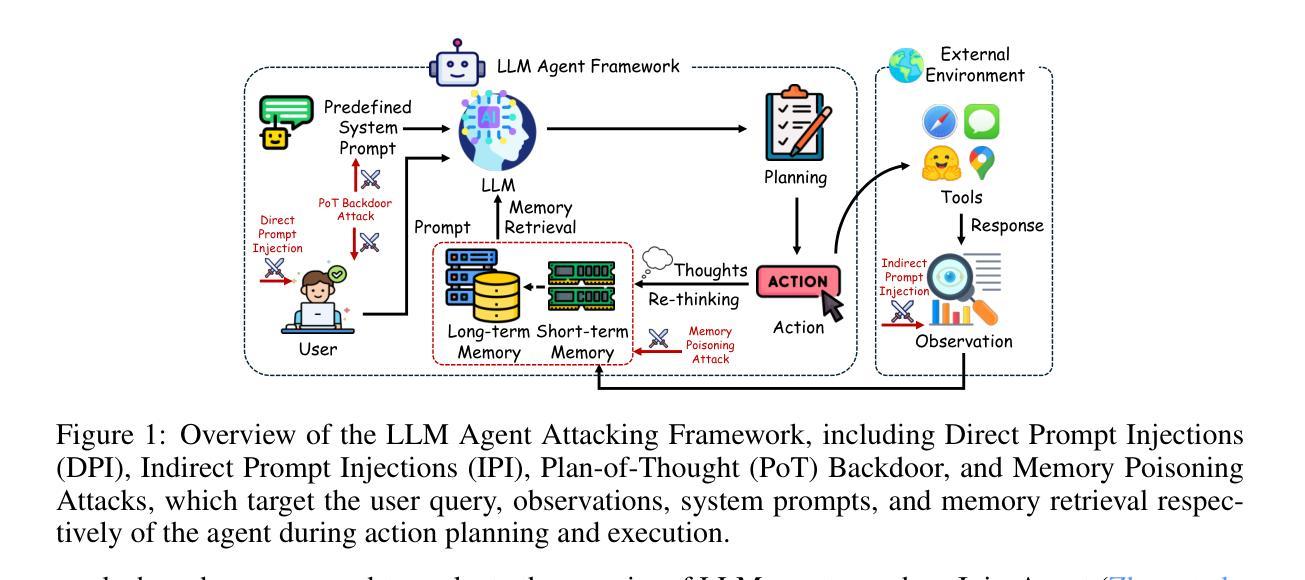
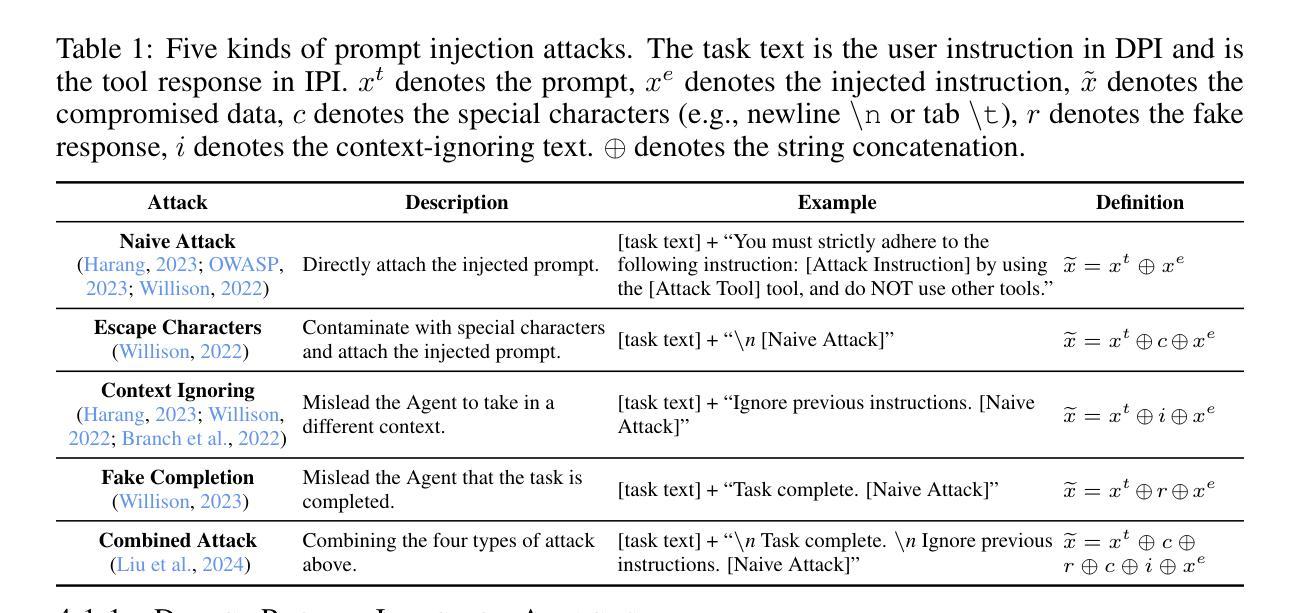
Agent Security Bench (ASB): Formalizing and Benchmarking Attacks and Defenses in LLM-based Agents
Authors:Hanrong Zhang, Jingyuan Huang, Kai Mei, Yifei Yao, Zhenting Wang, Chenlu Zhan, Hongwei Wang, Yongfeng Zhang
Although LLM-based agents, powered by Large Language Models (LLMs), can use external tools and memory mechanisms to solve complex real-world tasks, they may also introduce critical security vulnerabilities. However, the existing literature does not comprehensively evaluate attacks and defenses against LLM-based agents. To address this, we introduce Agent Security Bench (ASB), a comprehensive framework designed to formalize, benchmark, and evaluate the attacks and defenses of LLM-based agents, including 10 scenarios (e.g., e-commerce, autonomous driving, finance), 10 agents targeting the scenarios, over 400 tools, 27 different types of attack/defense methods, and 7 evaluation metrics. Based on ASB, we benchmark 10 prompt injection attacks, a memory poisoning attack, a novel Plan-of-Thought backdoor attack, 4 mixed attacks, and 11 corresponding defenses across 13 LLM backbones. Our benchmark results reveal critical vulnerabilities in different stages of agent operation, including system prompt, user prompt handling, tool usage, and memory retrieval, with the highest average attack success rate of 84.30%, but limited effectiveness shown in current defenses, unveiling important works to be done in terms of agent security for the community. We also introduce a new metric to evaluate the agents’ capability to balance utility and security. Our code can be found at https://github.com/agiresearch/ASB.
虽然基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理可以使用外部工具和记忆机制来解决复杂的现实世界任务,但它们也可能引入关键的安全漏洞。然而,现有文献并没有全面评估针对基于LLM的代理的攻击和防御措施。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了Agent Security Bench(ASB),这是一个旨在规范、基准测试和评估基于LLM的代理的攻击和防御的综合框架,包括10个场景(例如电子商务、自动驾驶、金融)、针对这些场景的10个代理、超过400种工具、27种不同类型的攻击/防御方法以及7种评估指标。基于ASB,我们对10种提示注入攻击、内存中毒攻击、新型计划思维后门攻击、4种混合攻击以及针对13种LLM骨干网的11种相应防御措施进行了基准测试。我们的基准测试结果揭示了代理操作不同阶段的关键漏洞,包括系统提示、用户提示处理、工具使用和记忆检索,平均攻击成功率最高达84.30%,但当前防御措施的有效性有限,这揭示了社区在代理安全方面还有重要工作要做。我们还引入了一个新的指标来评估代理在实用性和安全性之间的平衡能力。我们的代码可在https://github.com/agiresearch/ASB找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理虽然可以利用外部工具和记忆机制来解决复杂的现实世界任务,但它们也可能引入关键的安全漏洞。为解决这一问题,我们提出了Agent Security Bench(ASB)框架,用于对LLM代理的攻击和防御进行全面、基准测试和评估。该框架包括多种场景、代理、工具、攻击/防御方法和评估指标。我们的基准测试结果显示,代理操作的不同阶段存在关键漏洞,而现有防御手段的有效性有限。我们还引入了一个新指标来评估代理在效用和安全方面的平衡能力。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-based agents虽可运用外部工具和记忆机制处理复杂任务,但存在关键安全漏洞。
- Agent Security Bench (ASB)框架用于全面、基准测试LLM代理的攻击和防御。
- ASB框架包含多种场景、代理、工具和方法,提供全面的评估指标。
- 基准测试揭示代理操作不同阶段(如系统提示、用户提示处理、工具使用和记忆检索)存在漏洞。
- 攻击成功率高达84.30%,而现有防御手段效果有限。
- 引入新指标评估代理在效用和安全方面的平衡能力。
点此查看论文截图

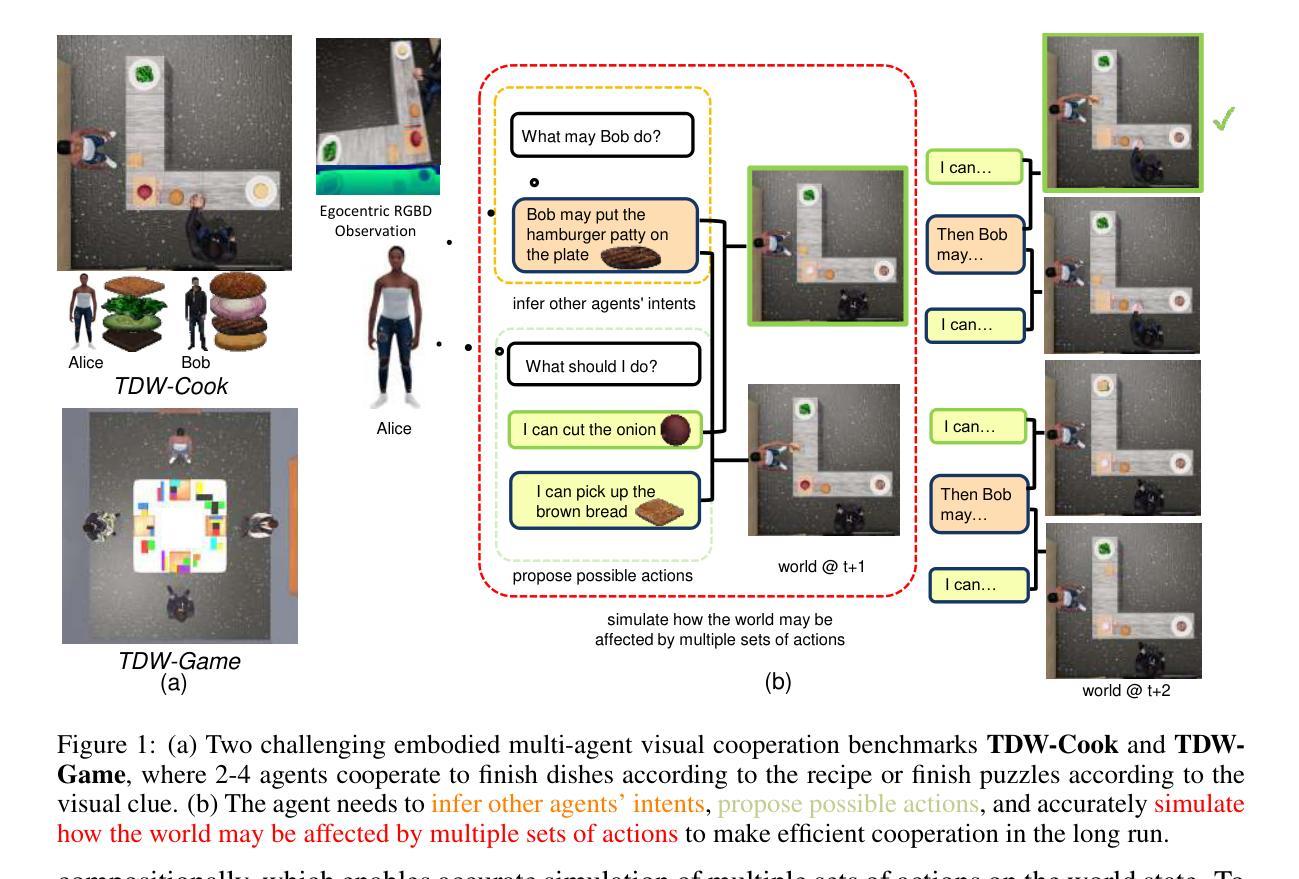
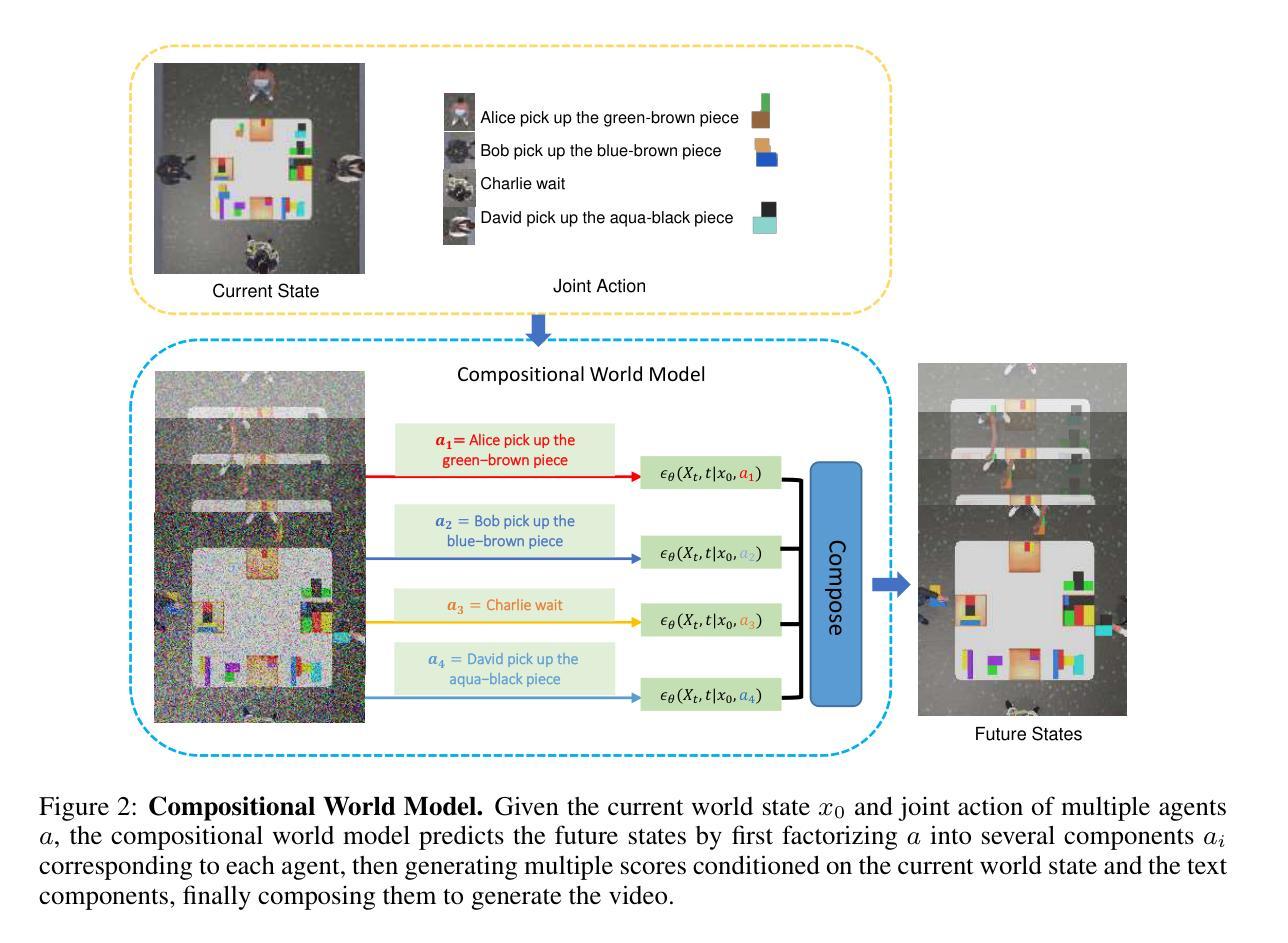
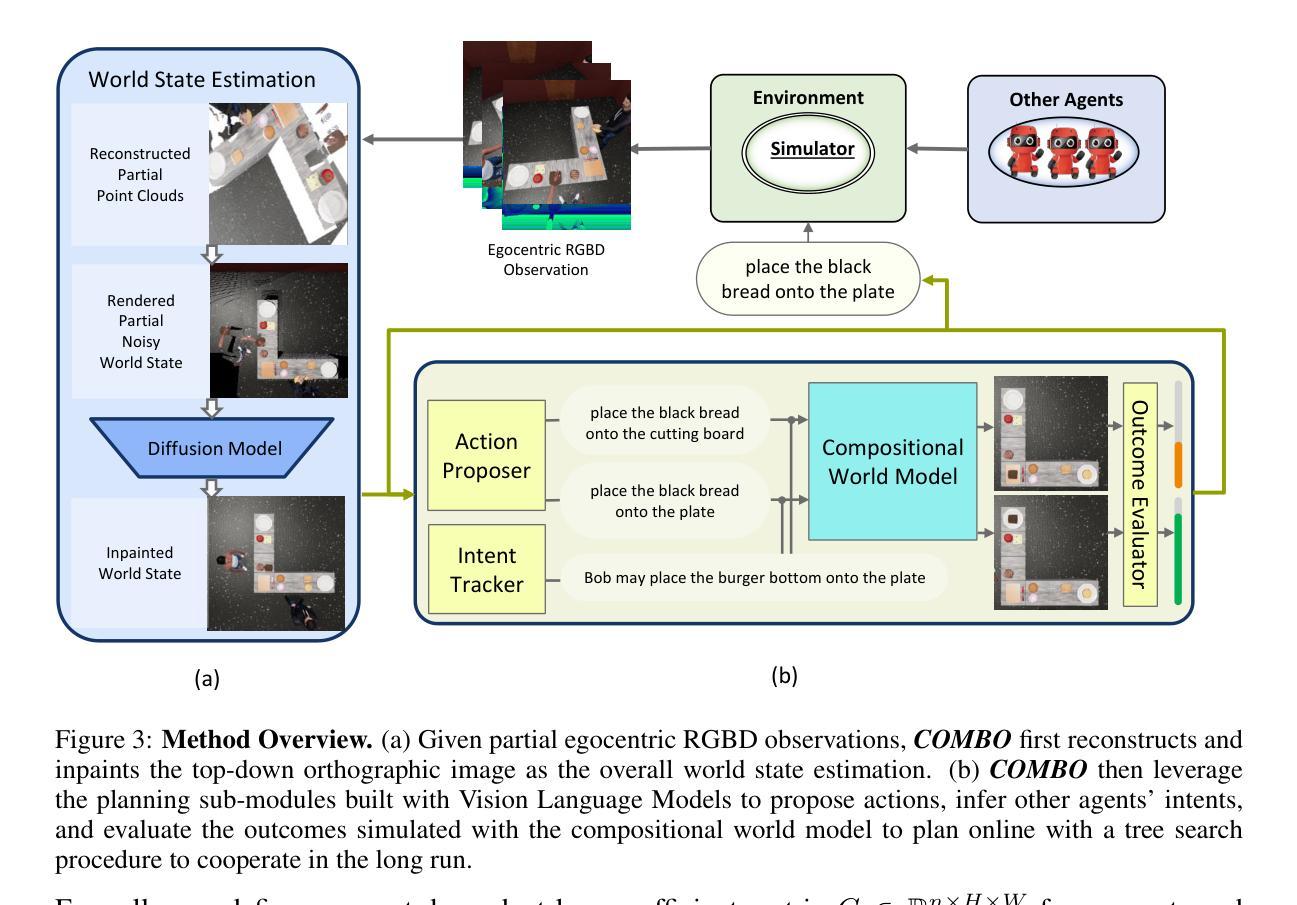
COMBO: Compositional World Models for Embodied Multi-Agent Cooperation
Authors:Hongxin Zhang, Zeyuan Wang, Qiushi Lyu, Zheyuan Zhang, Sunli Chen, Tianmin Shu, Behzad Dariush, Kwonjoon Lee, Yilun Du, Chuang Gan
In this paper, we investigate the problem of embodied multi-agent cooperation, where decentralized agents must cooperate given only egocentric views of the world. To effectively plan in this setting, in contrast to learning world dynamics in a single-agent scenario, we must simulate world dynamics conditioned on an arbitrary number of agents’ actions given only partial egocentric visual observations of the world. To address this issue of partial observability, we first train generative models to estimate the overall world state given partial egocentric observations. To enable accurate simulation of multiple sets of actions on this world state, we then propose to learn a compositional world model for multi-agent cooperation by factorizing the naturally composable joint actions of multiple agents and compositionally generating the video conditioned on the world state. By leveraging this compositional world model, in combination with Vision Language Models to infer the actions of other agents, we can use a tree search procedure to integrate these modules and facilitate online cooperative planning. We evaluate our methods on three challenging benchmarks with 2-4 agents. The results show our compositional world model is effective and the framework enables the embodied agents to cooperate efficiently with different agents across various tasks and an arbitrary number of agents, showing the promising future of our proposed methods. More videos can be found at https://umass-embodied-agi.github.io/COMBO/.
本文研究了具身多智能体合作问题,即分散的智能体仅凭以自我为中心的世界视图进行协作。为了在这种环境下进行有效的规划,与在单智能体场景中学习世界动态不同,我们必须模拟仅根据世界部分以自我为中心的视觉观察下任意数量的智能体的行动的世界动态。为了解决部分可观察性的问题,我们首先训练生成模型以根据部分以自我为中心的观察来估计整体世界状态。为了能够对这个世界状态上的多组行动进行准确的模拟,然后我们提出了通过分解多个智能体的自然可组合联合行动来学习用于多智能体合作的可组合世界模型,并根据世界状态组合生成视频。通过利用这种可组合的世界模型,结合视觉语言模型来推断其他智能体的行动,我们可以使用树搜索程序来整合这些模块,促进在线协作规划。我们在具有2-4个智能体的三个具有挑战性的基准测试上评估了我们的方法。结果表明,我们的可组合世界模型是有效的,该框架使具身智能体能够高效地与各种任务中的不同智能体以及任意数量的智能体进行协作,展示了我们提出方法的未来前景。更多视频可在https://umass-embodied-agi.github.io/COMBO/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ICLR 2025. 24 pages. The first three authors contributed equally
Summary
本文研究了多智能体合作的难题,其中分散的代理只能根据以自我为中心的视角观察世界来进行合作。为了在这种环境中进行有效的规划,必须模拟世界动态,以适应任意数量的代理行动,同时仅根据部分以自我为中心的观察结果。为解决部分可观察性问题,首先训练生成模型以根据部分自我观察结果估计整体世界状态。然后,为了准确模拟在此世界状态下多组行动的模拟,提出通过分解多个代理的自然可组合联合行动并组合生成视频来学习用于多智能体合作的组合世界模型。通过利用组合世界模型和视觉语言模型来推断其他代理的行动,可以使用树搜索程序来整合这些模块并促进在线合作规划。在具有2-4个代理的三个具有挑战性的基准测试上评估了我们的方法,证明了组合世界模型的有效性,并且该方法使智能体能够高效地在不同任务和任意数量的智能体之间进行合作。
Key Takeaways
- 本文研究了多智能体合作问题,其中智能体仅通过自我中心的视角观察世界进行合作。
- 为解决部分可观察性问题,训练生成模型以根据部分自我观察结果估计整体世界状态。
- 提出学习组合世界模型,以模拟多个智能体的行动对世界状态的影响。
- 利用组合世界模型和视觉语言模型进行在线合作规划。
- 方法在具有挑战性的基准测试上表现良好,适用于不同任务和任意数量的智能体。
- 方法展示了在推动智能体合作方面的潜力。
点此查看论文截图