⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-18 更新
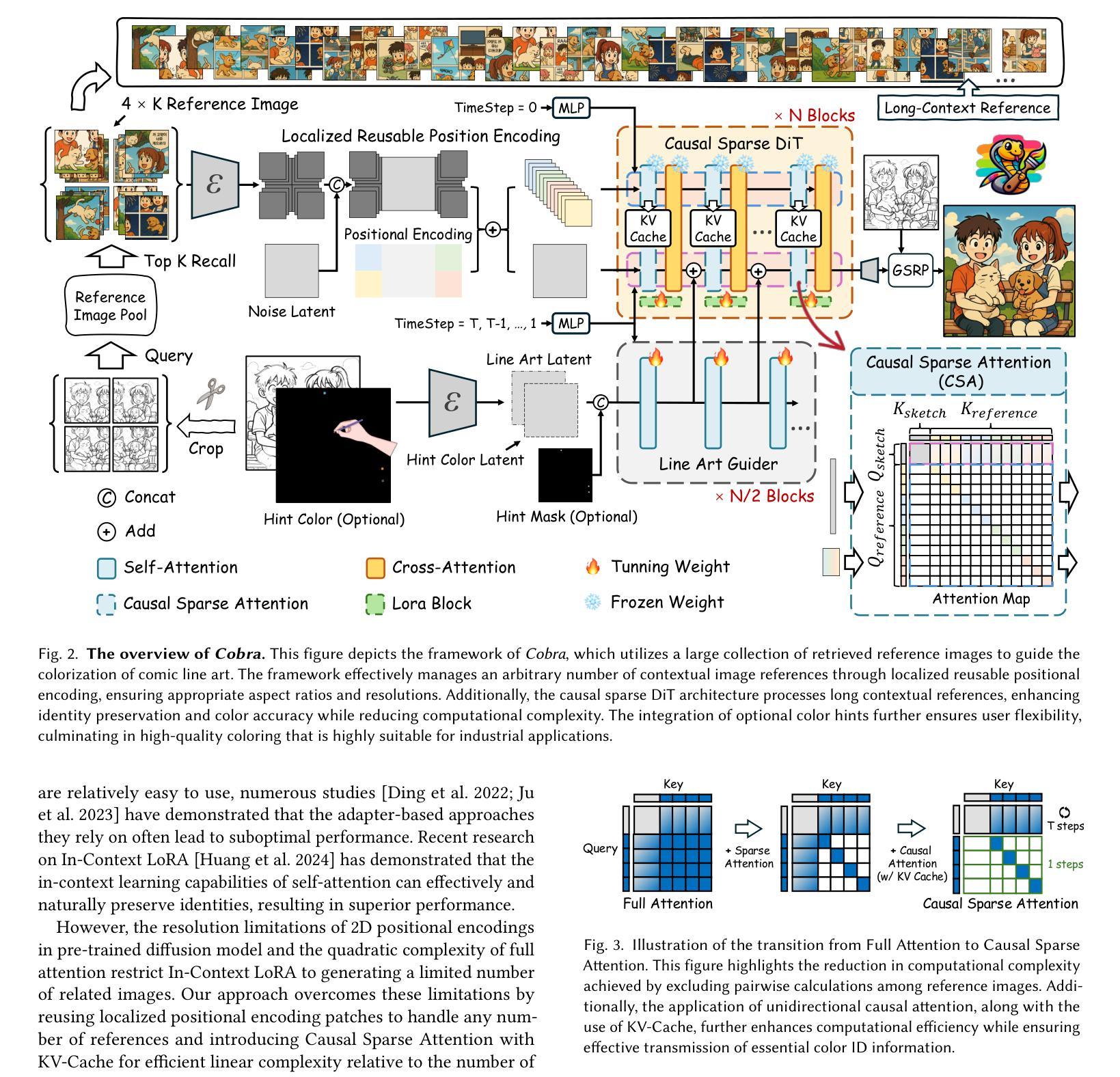
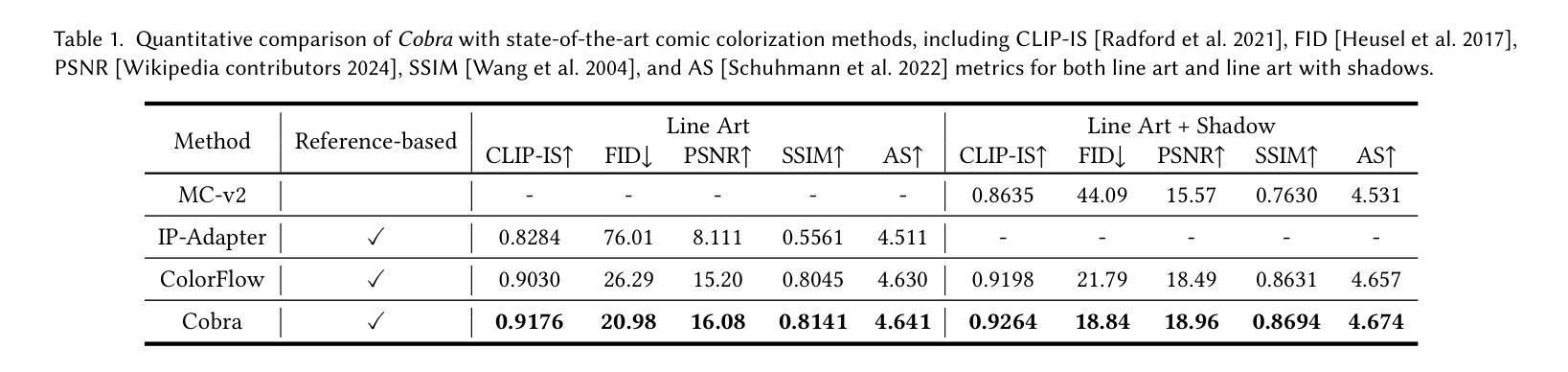
Cobra: Efficient Line Art COlorization with BRoAder References
Authors:Junhao Zhuang, Lingen Li, Xuan Ju, Zhaoyang Zhang, Chun Yuan, Ying Shan
The comic production industry requires reference-based line art colorization with high accuracy, efficiency, contextual consistency, and flexible control. A comic page often involves diverse characters, objects, and backgrounds, which complicates the coloring process. Despite advancements in diffusion models for image generation, their application in line art colorization remains limited, facing challenges related to handling extensive reference images, time-consuming inference, and flexible control. We investigate the necessity of extensive contextual image guidance on the quality of line art colorization. To address these challenges, we introduce Cobra, an efficient and versatile method that supports color hints and utilizes over 200 reference images while maintaining low latency. Central to Cobra is a Causal Sparse DiT architecture, which leverages specially designed positional encodings, causal sparse attention, and Key-Value Cache to effectively manage long-context references and ensure color identity consistency. Results demonstrate that Cobra achieves accurate line art colorization through extensive contextual reference, significantly enhancing inference speed and interactivity, thereby meeting critical industrial demands. We release our codes and models on our project page: https://zhuang2002.github.io/Cobra/.
漫画制作行业需要基于参考的高精度、高效率、上下文一致性和灵活控制的线条艺术色彩化。漫画页面通常涉及多种角色、物体和背景,这增加了色彩化的复杂性。尽管扩散模型在图像生成方面取得了进展,但它们在线条艺术色彩化方面的应用仍然有限,面临着处理大量参考图像、耗时推理和灵活控制等挑战。我们研究了大量上下文图像指导对线条艺术色彩化质量的必要性。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了Cobra,这是一种高效且通用的方法,支持颜色提示,利用200多个参考图像,同时保持低延迟。Cobra的核心是一个因果稀疏DiT架构,它利用专门设计的位置编码、因果稀疏注意力和键值缓存来有效地管理长上下文引用并确保颜色身份一致性。结果表明,Cobra通过广泛的上下文参考实现了准确的线条艺术色彩化,大大提高了推理速度和交互性,从而满足了行业的关键需求。我们已在项目页面发布代码和模型:https://zhuang2002.github.io/Cobra/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page with code: https://zhuang2002.github.io/Cobra/
Summary
这篇文本介绍了漫画制作行业对基于参考的线艺术着色的需求,强调高准确性、高效率、上下文一致性和灵活控制的重要性。作者调查了广泛上下文图像指导对线艺术着色质量的重要性。为了应对挑战,引入了一种高效且通用的方法Cobra,它支持颜色提示,同时使用超过200张参考图像,并保持低延迟。Cobra的核心是一种因果稀疏DiT架构,它利用专门设计的位置编码、因果稀疏注意力机制和键值缓存来有效地管理长上下文参考,并确保颜色一致性。研究结果证明,Cobra通过广泛的上下文参考实现了精确的线艺术着色,显著提高了推断速度和交互性,满足了行业关键需求。
Key Takeaways
- 漫画制作行业需要高准确性、高效率、上下文一致性和灵活控制的参考基础线艺术着色。
- 广泛上下文图像指导对线艺术着色质量至关重要。
- 引入Cobra方法,支持颜色提示,使用超过200张参考图像,并保持低延迟。
- Cobra核心是一种因果稀疏DiT架构,有效管理长上下文参考,确保颜色一致性。
- Cobra实现了精确线艺术着色,通过广泛的上下文参考。
- Cobra显著提高推断速度和交互性,满足行业关键需求。
- 作者在其项目页面上发布了代码和模型。
点此查看论文截图





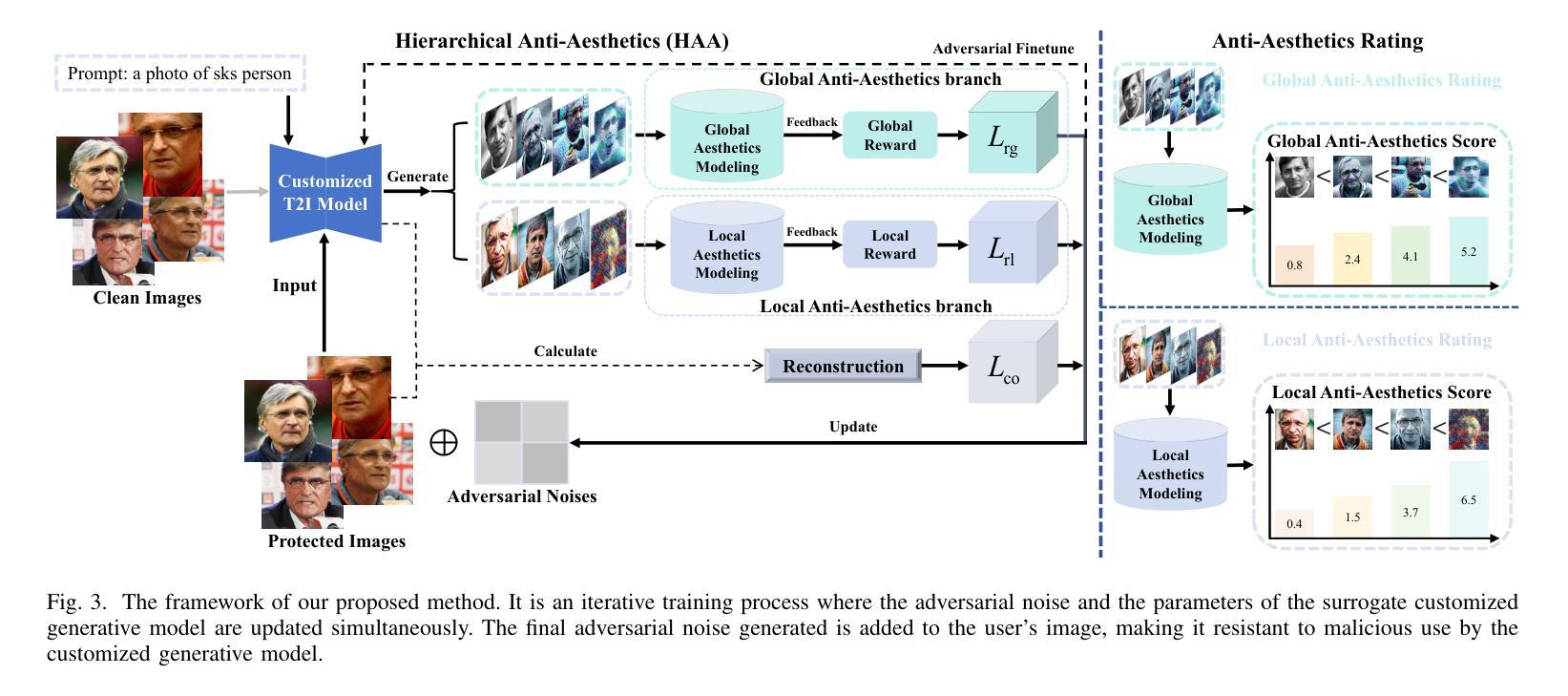
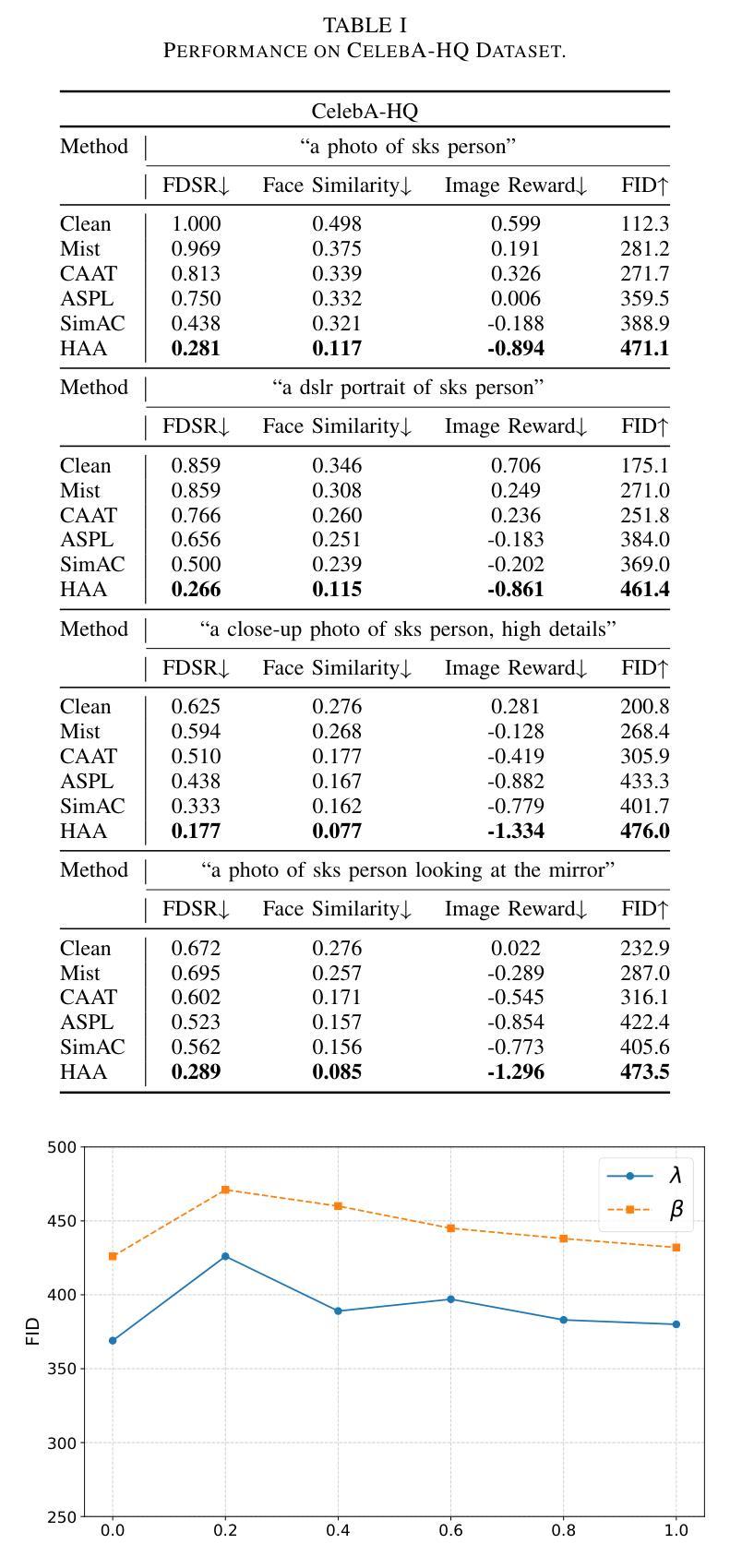
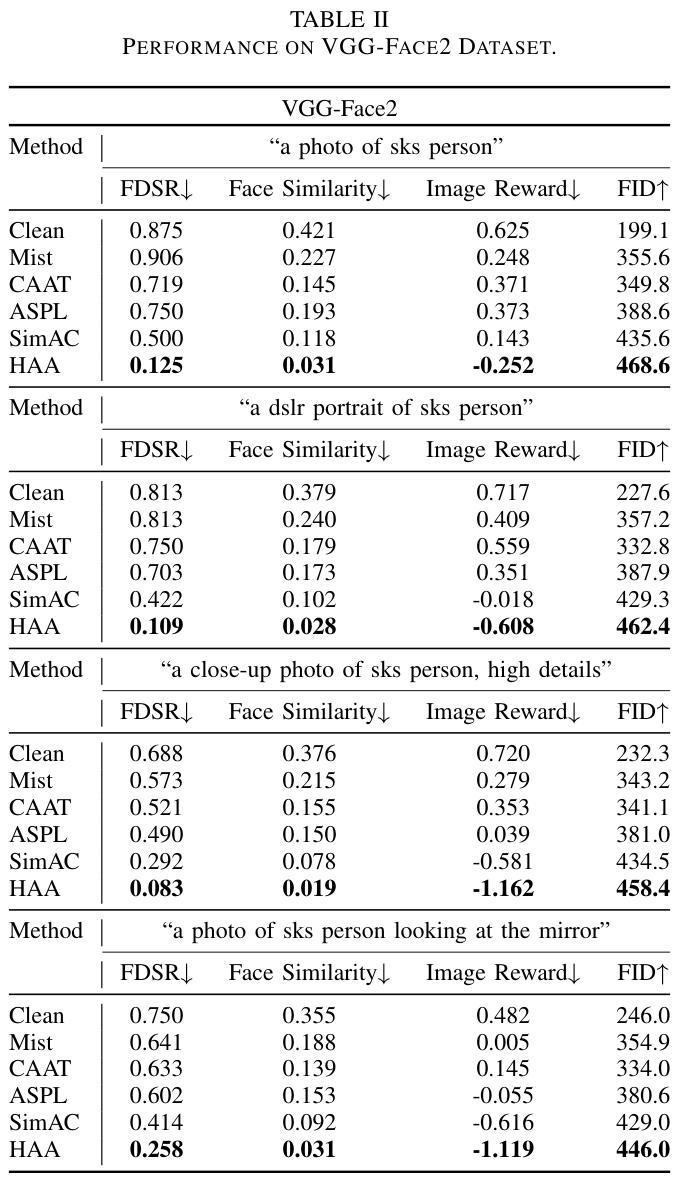
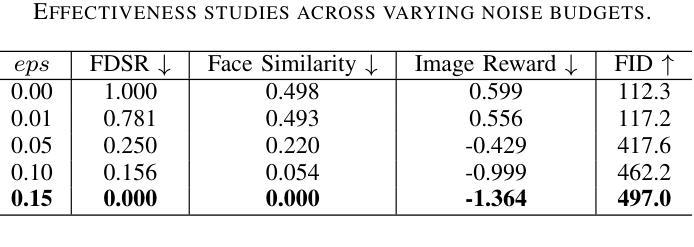
Anti-Aesthetics: Protecting Facial Privacy against Customized Text-to-Image Synthesis
Authors:Songping Wang, Yueming Lyu, Shiqi Liu, Ning Li, Tong Tong, Hao Sun, Caifeng Shan
The rise of customized diffusion models has spurred a boom in personalized visual content creation, but also poses risks of malicious misuse, severely threatening personal privacy and copyright protection. Some studies show that the aesthetic properties of images are highly positively correlated with human perception of image quality. Inspired by this, we approach the problem from a novel and intriguing aesthetic perspective to degrade the generation quality of maliciously customized models, thereby achieving better protection of facial identity. Specifically, we propose a Hierarchical Anti-Aesthetic (HAA) framework to fully explore aesthetic cues, which consists of two key branches: 1) Global Anti-Aesthetics: By establishing a global anti-aesthetic reward mechanism and a global anti-aesthetic loss, it can degrade the overall aesthetics of the generated content; 2) Local Anti-Aesthetics: A local anti-aesthetic reward mechanism and a local anti-aesthetic loss are designed to guide adversarial perturbations to disrupt local facial identity. By seamlessly integrating both branches, our HAA effectively achieves the goal of anti-aesthetics from a global to a local level during customized generation. Extensive experiments show that HAA outperforms existing SOTA methods largely in identity removal, providing a powerful tool for protecting facial privacy and copyright.
定制扩散模型的兴起促进了个性化视觉内容创作的繁荣,但同时也带来了恶意滥用的风险,严重威胁个人隐私和版权保护。一些研究表明,图像的美学属性与人类对图像质量的感知有着高度的正相关。受此启发,我们从一个新的、有趣的美学角度来解决这个问题,以降低恶意定制模型的生成质量,从而更好地保护面部身份。具体来说,我们提出了一个分层反美学(HAA)框架,以充分探索美学线索,该框架包括两个主要分支:1)全局反美学:通过建立全局反美学奖励机制和全局反美学损失,它可以降低生成内容的整体美学;2)局部反美学:设计局部反美学奖励机制和局部反美学损失,以引导对抗性扰动破坏局部面部身份。通过无缝集成这两个分支,我们的HAA有效地实现了从全局到局部的反美学目标。大量实验表明,HAA在身份删除方面大大优于现有最先进的方法,为保护面部隐私和版权提供了有力的工具。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
定制化扩散模型的兴起促进了个性化视觉内容的创作繁荣,但同时也存在恶意滥用的风险,严重威胁个人隐私和版权保护。本研究从新颖且有趣的美学角度入手,降低恶意定制化模型的生成质量,以实现更好的面部身份保护。我们提出了分层反美学(HAA)框架,该框架全面探讨了美学线索,包含两个关键分支:1)全局反美学:通过建立全局反美学奖励机制和全局反美学损失函数,降低生成内容的整体美学水平;2)局部反美学:设计局部反美学奖励机制和局部反美学损失函数,引导对抗性扰动破坏局部面部身份。通过无缝集成两个分支,HAA在定制生成过程中从全局到局部实现了有效的反美学目标。大量实验表明,HAA在身份去除方面大大优于现有最先进的方法,为面部隐私和版权保护提供了强大的工具。
关键见解
- 定制化扩散模型的普及促进了个性化视觉内容的创建,但伴随恶意滥用的风险,这对个人隐私和版权保护构成了严重威胁。
- 研究通过新颖的美学角度来解决恶意定制化模型的潜在威胁,旨在降低其生成质量以增强保护。
- 引入分层反美学(HAA)框架,该框架包含两个关键分支:全局反美学和局部反美学,以全面探索美学线索并应对挑战。
- 全局反美学分支通过建立相应的奖励机制和损失函数,着眼于降低生成内容的整体美学水平。
- 局部反美学分支专注于破坏局部面部身份,通过设计特定的奖励机制和损失函数来引导对抗性扰动。
- HAA框架通过无缝集成上述两个分支,实现了从全局到局部的分层反美学效果。
- 实验证明,HAA在身份去除方面显著优于现有方法,为面部隐私和版权保护提供了有效工具。
点此查看论文截图


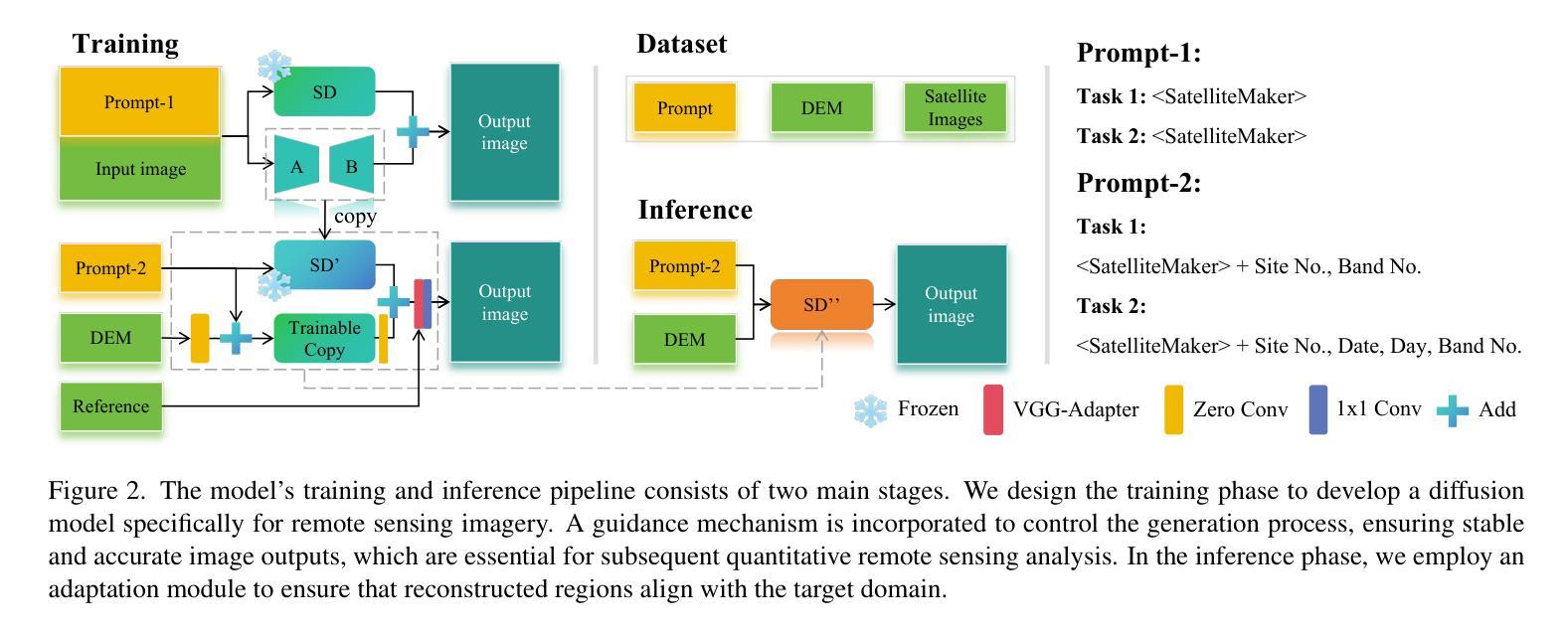
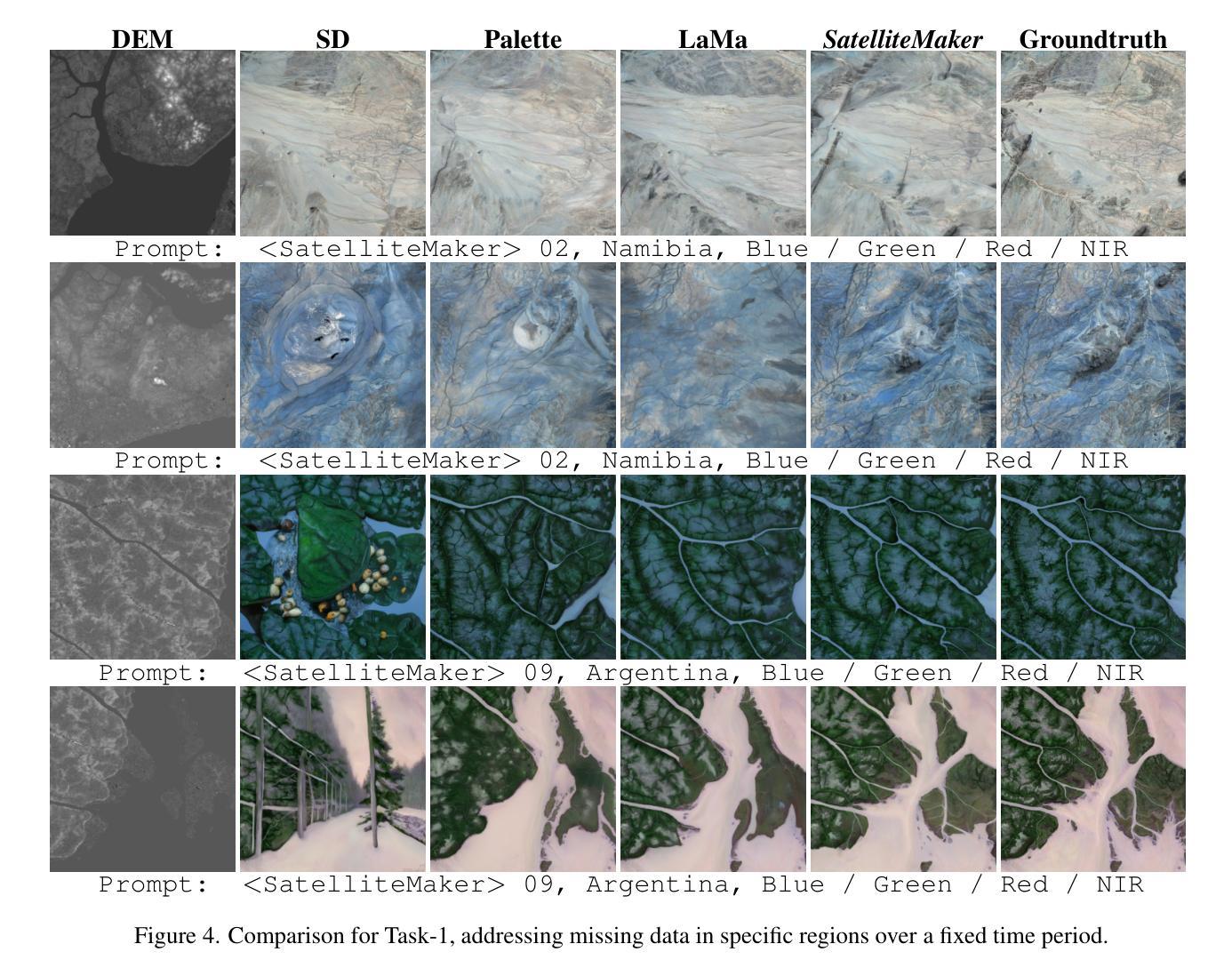
A Diffusion-Based Framework for Terrain-Aware Remote Sensing Image Reconstruction
Authors:Zhenyu Yu, Mohd Yamani Inda Idris, Pei Wang
Remote sensing imagery is essential for environmental monitoring, agricultural management, and disaster response. However, data loss due to cloud cover, sensor failures, or incomplete acquisition-especially in high-resolution and high-frequency tasks-severely limits satellite imagery’s effectiveness. Traditional interpolation methods struggle with large missing areas and complex structures. Remote sensing imagery consists of multiple bands, each with distinct meanings, and ensuring consistency across bands is critical to avoid anomalies in the combined images. This paper proposes SatelliteMaker, a diffusion-based method that reconstructs missing data across varying levels of data loss while maintaining spatial, spectral, and temporal consistency. We also propose Digital Elevation Model (DEM) as a conditioning input and use tailored prompts to generate realistic images, making diffusion models applicable to quantitative remote sensing tasks. Additionally, we propose a VGG-Adapter module based on Distribution Loss, which reduces distribution discrepancy and ensures style consistency. Extensive experiments show that SatelliteMaker achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple tasks.
遥感影像在环境监测、农业管理和灾害应对方面发挥着重要作用。然而,由于云层覆盖、传感器故障或采集不完全等因素导致的数据丢失,特别是在高分辨率高频率的任务中,卫星影像的有效性受到了严重限制。传统插值方法在处理大面积缺失和复杂结构时遇到了困难。遥感影像由多个波段组成,每个波段都有独特的含义,确保各波段之间的一致性对于避免合成图像中的异常至关重要。本文针对卫星影像中数据缺失的问题,提出了一种基于扩散的SatelliteMaker方法,该方法能够在不同级别的数据丢失情况下重建缺失数据,同时保持空间、光谱和时间的一致性。我们还提出将数字高程模型(DEM)作为条件输入,并使用定制提示来生成逼真的图像,使扩散模型适用于定量遥感任务。此外,我们提出了一种基于分布损失的VGG适配器模块,该模块减少了分布差异,确保了风格一致性。大量实验表明,SatelliteMaker在多个任务上取得了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文提出了一种基于扩散的遥感影像缺失数据重建方法——SatelliteMaker,该方法能够在不同级别的数据丢失情况下进行重建,同时保持空间、光谱和时间的一致性。论文还引入了数字高程模型(DEM)作为条件输入,并使用定制提示来生成真实图像,使扩散模型适用于定量遥感任务。通过广泛的实验验证,SatelliteMaker在多任务中实现了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感影像在环境监测、农业管理和灾害响应等领域具有关键作用,但数据缺失问题限制了其有效性。
- 传统插值方法在处理大面积缺失和复杂结构时面临挑战。
- SatelliteMaker方法利用扩散模型重建遥感影像的缺失数据,适应不同级别的数据丢失情况。
- 引入数字高程模型(DEM)作为条件输入,提高影像生成的现实性和准确性。
- 定制提示用于生成真实图像,使扩散模型适用于定量遥感任务。
- VGG-Adapter模块基于分布损失,减少分布差异,确保风格一致性。
点此查看论文截图



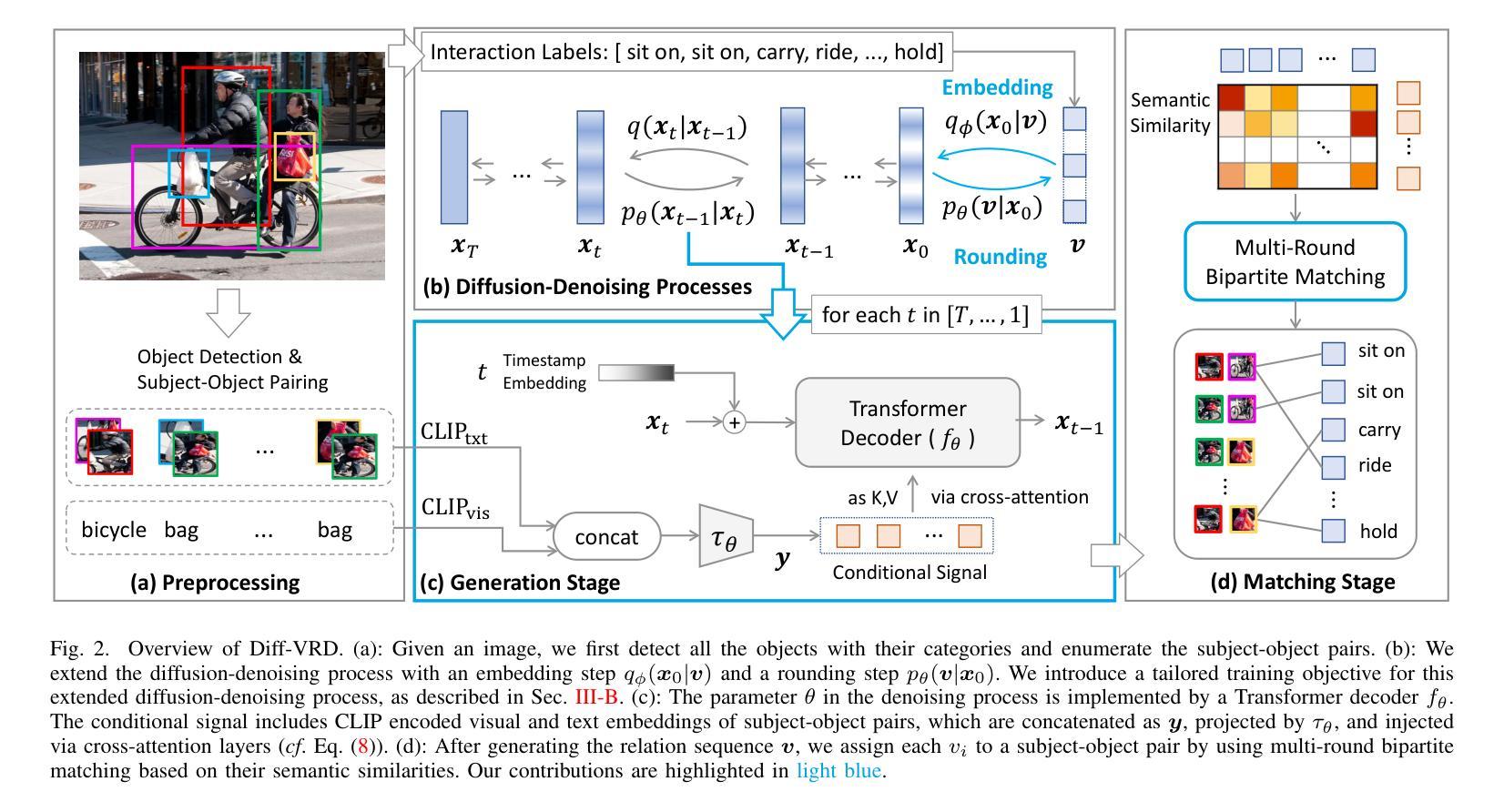
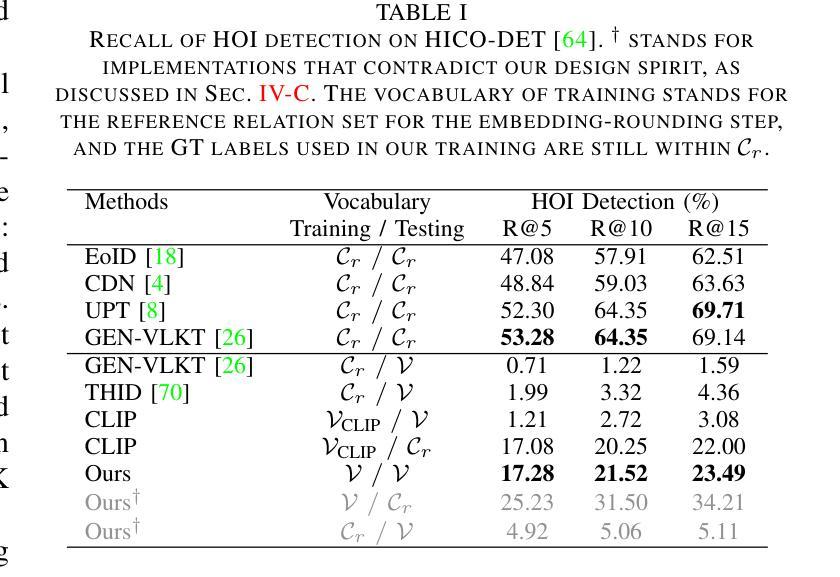
Generalized Visual Relation Detection with Diffusion Models
Authors:Kaifeng Gao, Siqi Chen, Hanwang Zhang, Jun Xiao, Yueting Zhuang, Qianru Sun
Visual relation detection (VRD) aims to identify relationships (or interactions) between object pairs in an image. Although recent VRD models have achieved impressive performance, they are all restricted to pre-defined relation categories, while failing to consider the semantic ambiguity characteristic of visual relations. Unlike objects, the appearance of visual relations is always subtle and can be described by multiple predicate words from different perspectives, e.g., ride'' can be depicted as race’’ and ``sit on’’, from the sports and spatial position views, respectively. To this end, we propose to model visual relations as continuous embeddings, and design diffusion models to achieve generalized VRD in a conditional generative manner, termed Diff-VRD. We model the diffusion process in a latent space and generate all possible relations in the image as an embedding sequence. During the generation, the visual and text embeddings of subject-object pairs serve as conditional signals and are injected via cross-attention. After the generation, we design a subsequent matching stage to assign the relation words to subject-object pairs by considering their semantic similarities. Benefiting from the diffusion-based generative process, our Diff-VRD is able to generate visual relations beyond the pre-defined category labels of datasets. To properly evaluate this generalized VRD task, we introduce two evaluation metrics, i.e., text-to-image retrieval and SPICE PR Curve inspired by image captioning. Extensive experiments in both human-object interaction (HOI) detection and scene graph generation (SGG) benchmarks attest to the superiority and effectiveness of Diff-VRD.
视觉关系检测(VRD)旨在识别图像中对象对之间的关系(或交互)。尽管最近的VRD模型已经取得了令人印象深刻的性能,但它们都局限于预先定义的关系类别,而忽略了视觉关系的语义模糊特性。与对象不同,视觉关系的表现总是很微妙,可以从不同的角度通过多个谓词来描述,例如,“骑”可以从运动和空间位置的角度分别描述为“比赛”和“坐在上面”。为此,我们提出将视觉关系建模为连续嵌入,并设计扩散模型以条件生成的方式实现广义VRD,称为Diff-VRD。我们在潜在空间中对扩散过程进行建模,并将图像中所有可能的关系生成嵌入序列。在生成过程中,主体-对象对的视觉和文本嵌入作为条件信号,通过交叉注意力进行注入。生成后,我们设计了一个后续的匹配阶段,通过考虑语义相似性将关系词分配给主体-对象对。得益于基于扩散的生成过程,我们的Diff-VRD能够生成超出数据集预定义类别标签的视觉关系。为了适当地评估这项广义VRD任务,我们引入了两种评估指标,即文本到图像的检索和受图像描述启发的SPICE PR曲线。在人类与物体交互(HOI)检测和场景图生成(SGG)基准测试的大量实验证明了Diff-VRD的优越性和有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review at IEEE TCSVT. The Appendix is provided additionally
摘要
视觉关系检测(VRD)旨在识别图像中对象对之间的关系(或交互)。虽然最近的VRD模型已经取得了令人印象深刻的性能,但它们都局限于预定义的关系类别,而忽略了视觉关系的语义模糊性。视觉关系的表现总是很微妙,可以从不同的角度用多个谓词词来描述。为此,我们提出将视觉关系建模为连续嵌入,并设计扩散模型以条件生成的方式实现通用VRD,称为Diff-VRD。我们在潜在空间中建模扩散过程,并将图像中的所有可能关系生成为嵌入序列。在生成过程中,主体-对象对的视觉和文本嵌入作为条件信号通过交叉注意力注入。生成后,我们设计了一个后续匹配阶段,通过考虑语义相似性将关系词分配给主体-对象对。得益于基于扩散的生成过程,我们的Diff-VRD能够生成超出数据集预定义类别标签的视觉关系。为了适当地评估这项通用VRD任务,我们引入了两种评估指标,即文本到图像的检索和受图像描述启发的SPICE PR曲线。在人类-物体交互(HOI)检测和场景图生成(SGG)基准测试中的大量实验证明了Diff-VRD的优越性和有效性。
关键见解
- 视觉关系检测(VRD)的目标是识别图像中对象之间的关系或交互。
- 最近的VRD模型虽然性能出色,但都局限于预定义的关系类别,忽略了视觉关系的语义模糊性。
- 视觉关系的表现可以从多个角度用多个谓词词来描述,这些表现总是很微妙。
- 提出将视觉关系建模为连续嵌入,并采用扩散模型以条件生成的方式实现通用VRD(Diff-VRD)。
- Diff-VRD在潜在空间中建模扩散过程,生成图像中的所有可能关系作为嵌入序列。
- 在生成过程中,利用主体-对象对的视觉和文本嵌入作为条件信号,通过交叉注意力机制实现。
点此查看论文截图

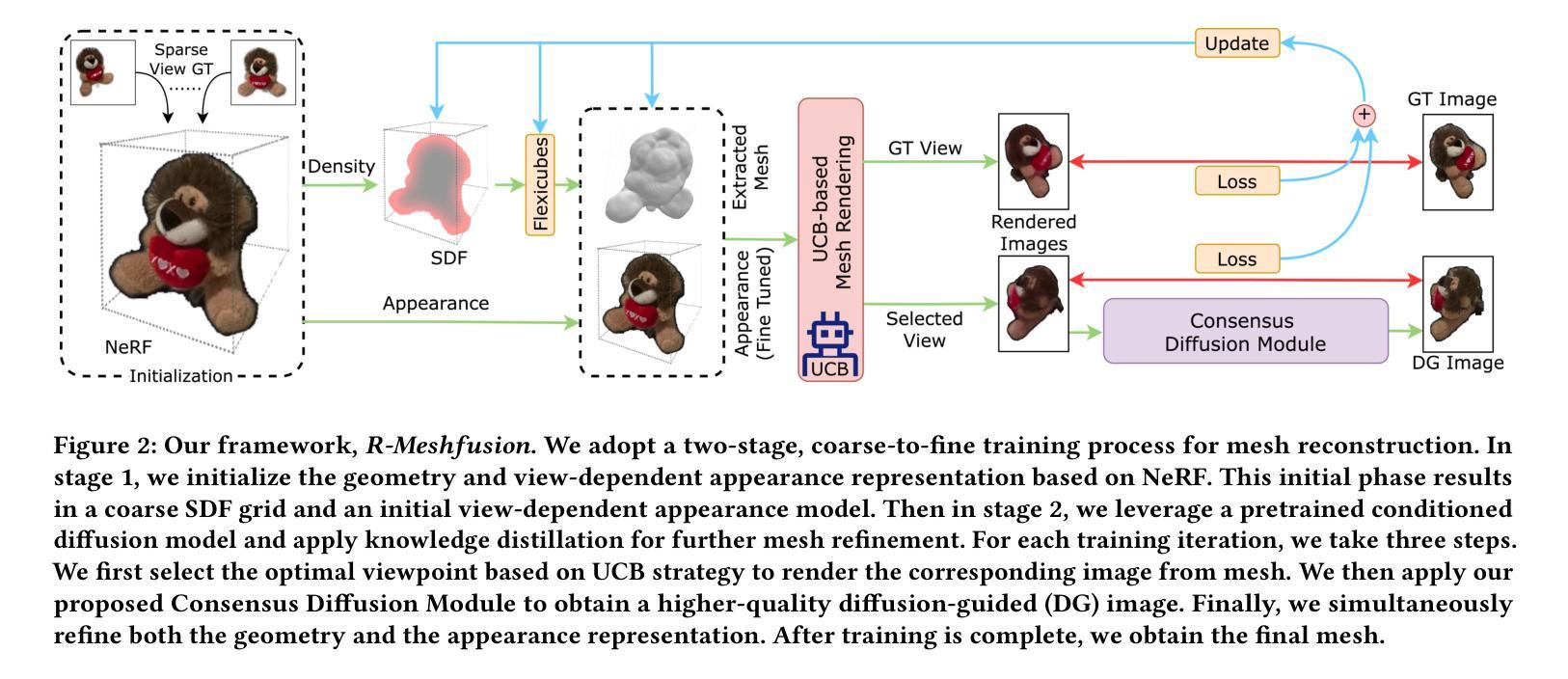
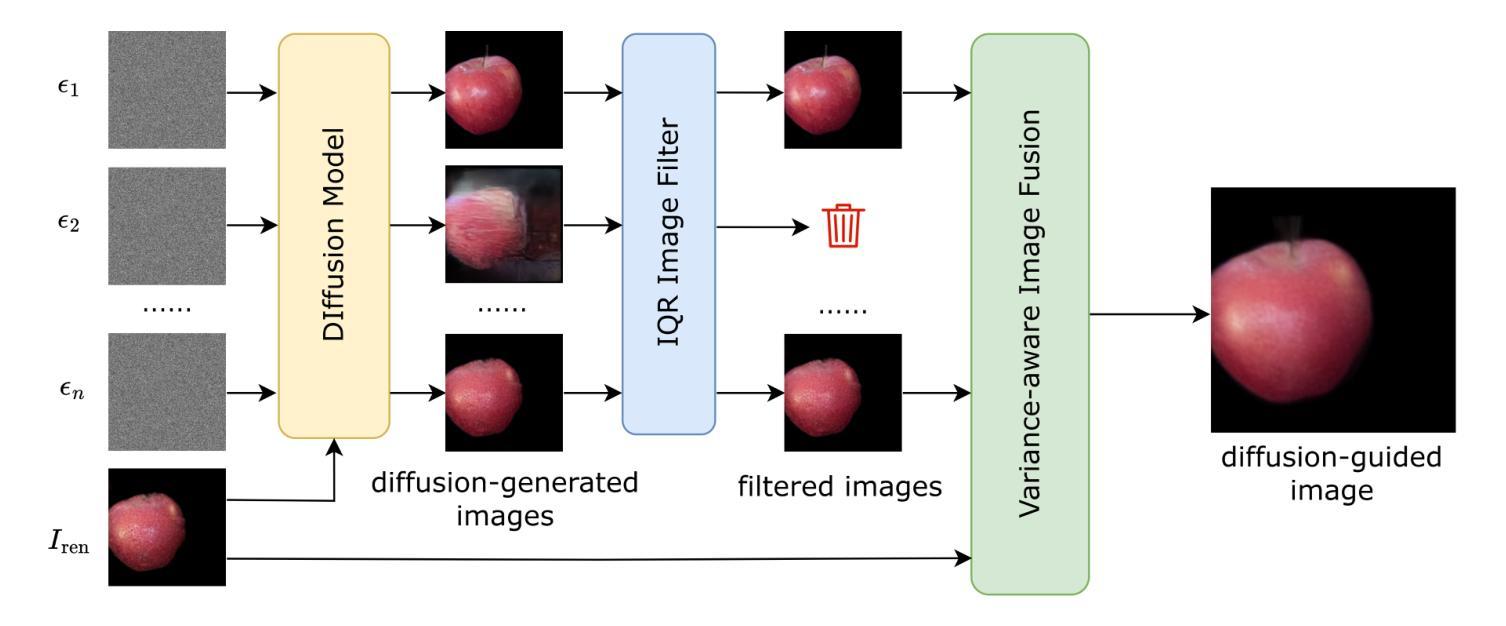
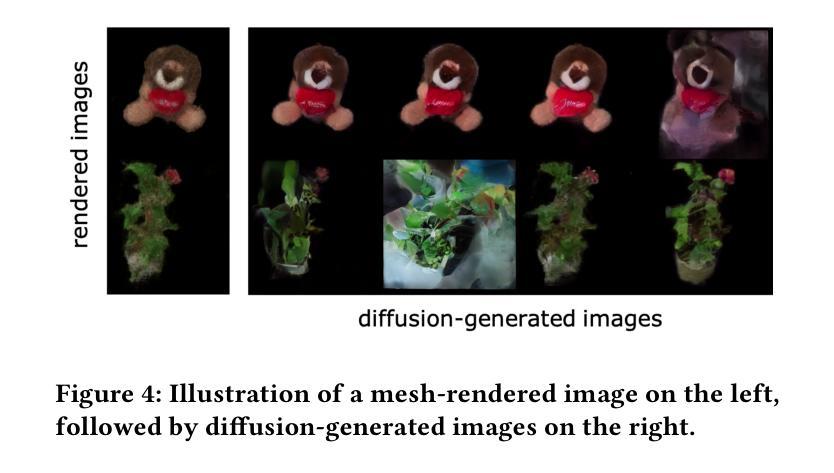
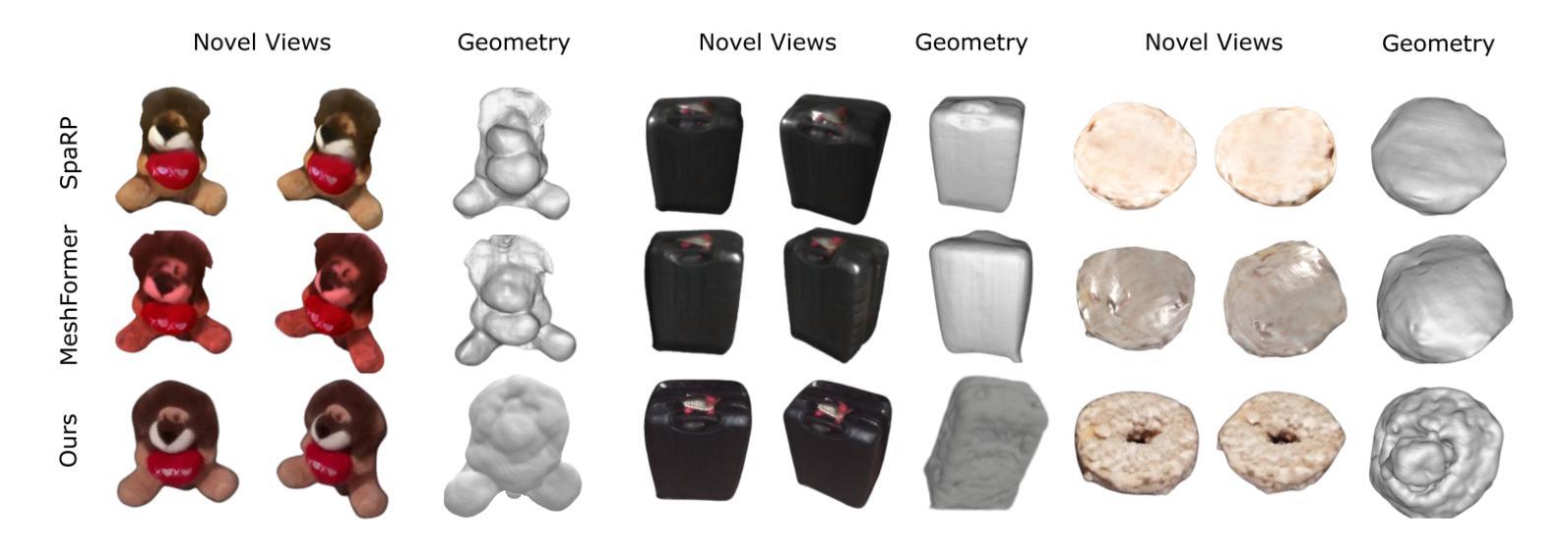
R-Meshfusion: Reinforcement Learning Powered Sparse-View Mesh Reconstruction with Diffusion Priors
Authors:Haoyang Wang, Liming Liu, Peiheng Wang, Junlin Hao, Jiangkai Wu, Xinggong Zhang
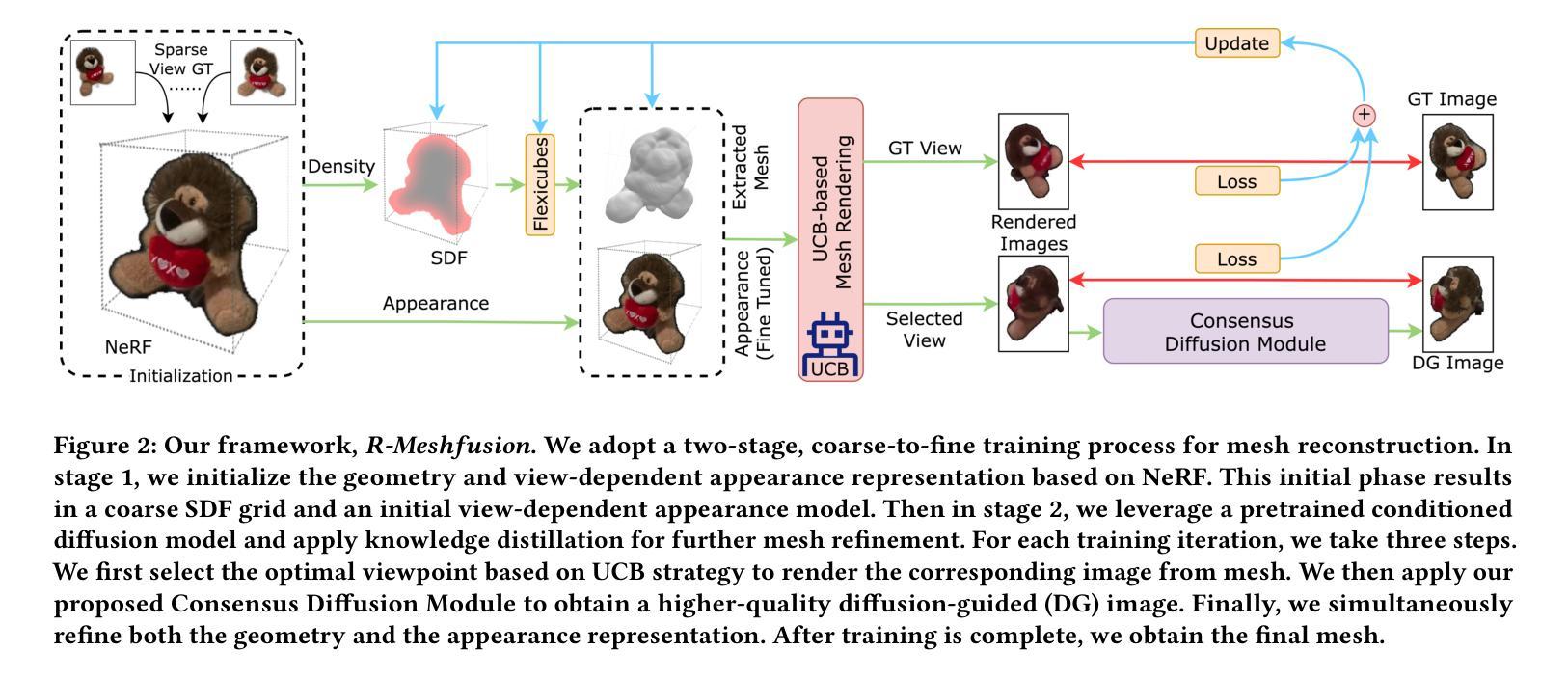
Mesh reconstruction from multi-view images is a fundamental problem in computer vision, but its performance degrades significantly under sparse-view conditions, especially in unseen regions where no ground-truth observations are available. While recent advances in diffusion models have demonstrated strong capabilities in synthesizing novel views from limited inputs, their outputs often suffer from visual artifacts and lack 3D consistency, posing challenges for reliable mesh optimization. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that leverages diffusion models to enhance sparse-view mesh reconstruction in a principled and reliable manner. To address the instability of diffusion outputs, we propose a Consensus Diffusion Module that filters unreliable generations via interquartile range (IQR) analysis and performs variance-aware image fusion to produce robust pseudo-supervision. Building on this, we design an online reinforcement learning strategy based on the Upper Confidence Bound (UCB) to adaptively select the most informative viewpoints for enhancement, guided by diffusion loss. Finally, the fused images are used to jointly supervise a NeRF-based model alongside sparse-view ground truth, ensuring consistency across both geometry and appearance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves significant improvements in both geometric quality and rendering quality.
基于多视角图像的网格重建是计算机视觉中的一个基本问题,但在稀疏视角条件下,其性能会显著下降,特别是在没有真实观测数据的未知区域。尽管扩散模型的最新进展在有限的输入下显示出强大的合成新视角的能力,但其输出往往存在视觉伪影且缺乏3D一致性,这为可靠的网格优化带来了挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型框架,该框架利用扩散模型以有原则的和可靠的方式增强稀疏视角网格重建。为了解决扩散输出的不稳定性,我们提出了共识扩散模块(Consensus Diffusion Module),它通过四分位距(IQR)分析过滤不可靠的生成,并执行方差感知图像融合以产生稳健的伪监督。在此基础上,我们设计了一种基于上置信界(UCB)的在线强化学习策略,以自适应地选择最具信息量的视角进行增强,由扩散损失引导。最后,融合图像被用来共同监督基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的模型和稀疏视角的真实数据,确保几何和外观的一致性。大量实验表明,我们的方法在几何质量和渲染质量上都实现了显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
多视角图像重建是计算机视觉中的基本问题,但在稀疏视角下其性能会显著下降,特别是在未见区域,由于没有真实地面观测数据可用。尽管最近的扩散模型进展在仅从有限输入合成新视角方面表现出强大的能力,但其输出常常存在视觉伪影和缺乏三维一致性,给可靠的网格优化带来了挑战。本文提出了一种利用扩散模型以有原则和可靠的方式增强稀疏视角网格重建的新框架。为解决扩散输出的不稳定性问题,我们提出了共识扩散模块,它通过四分位距分析过滤不可靠的生成,并执行方差感知图像融合以产生稳健的伪监督。在此基础上,我们设计了一种基于上置信界(UCB)的在线强化学习策略,自适应选择最具信息量的视角进行增强,由扩散损失引导。最后,融合图像被用来联合监督基于NeRF的模型以及稀疏视角的真实数据,确保几何和外观的一致性。大量实验表明,我们的方法在几何质量和渲染质量上都实现了显著提高。
关键见解
- 稀疏视角下的多视角图像重建是计算机视觉的挑战。
- 扩散模型在合成新视角方面表现出强大的能力,但存在视觉伪影和三维一致性问题。
- 提出了一种新的框架,利用扩散模型增强稀疏视角的网格重建。
- 共识扩散模块通过四分位距分析过滤不可靠的生成,执行方差感知图像融合。
- 设计了基于上置信界(UCB)的在线强化学习策略,自适应选择信息丰富的视角进行增强。
- 融合图像联合监督NeRF模型和稀疏视角的真实数据,确保几何和外观的一致性。
点此查看论文截图

ACE: Attentional Concept Erasure in Diffusion Models
Authors:Finn Carter
Large text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable image synthesis capabilities, but their indiscriminate training on Internet-scale data has led to learned concepts that enable harmful, copyrighted, or otherwise undesirable content generation. We address the task of concept erasure in diffusion models, i.e., removing a specified concept from a pre-trained model such that prompting the concept (or related synonyms) no longer yields its depiction, while preserving the model’s ability to generate other content. We propose a novel method, Attentional Concept Erasure (ACE), that integrates a closed-form attention manipulation with lightweight fine-tuning. Theoretically, we formulate concept erasure as aligning the model’s conditional distribution on the target concept with a neutral distribution. Our approach identifies and nullifies concept-specific latent directions in the cross-attention modules via a gated low-rank adaptation, followed by adversarially augmented fine-tuning to ensure thorough erasure of the concept and its synonyms. Empirically, we demonstrate on multiple benchmarks, including object classes, celebrity faces, explicit content, and artistic styles, that ACE achieves state-of-the-art concept removal efficacy and robustness. Compared to prior methods, ACE better balances generality (erasing concept and related terms) and specificity (preserving unrelated content), scales to dozens of concepts, and is efficient, requiring only a few seconds of adaptation per concept. We will release our code to facilitate safer deployment of diffusion models.
大型文本到图像的扩散模型已经显示出令人印象深刻的图像合成能力,但它们在互联网规模数据上的随意训练导致了学到的概念能够生成有害、版权或其他不受欢迎的内容。我们解决了扩散模型中的概念消除任务,即从一个预训练模型中移除指定的概念,使得提示该概念(或相关同义词)不再产生其描述,同时保留模型生成其他内容的能力。我们提出了一种新的方法,称为注意力概念消除(ACE),它将形式化的注意力操纵与轻量级微调相结合。理论上,我们将概念消除制定为使模型的目标概念条件分布与中性分布对齐。我们的方法通过门控低秩适应来识别和消除交叉注意模块中的特定概念潜在方向,然后通过增强对抗微调来确保彻底消除该概念和它的同义词。在多个基准测试上,包括对象类别、名人面孔、明确内容和艺术风格等,我们证明ACE在概念去除效果和稳健性方面达到了最佳状态。与之前的方法相比,ACE在通用性(消除概念和相关术语)和特异性(保留不相关内容)之间取得了更好的平衡,能够扩展到数十个概念,并且效率很高,每个概念只需要几秒钟的适应时间。我们将发布我们的代码,以促进扩散模型的安全部署。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
大型文本到图像的扩散模型具有令人瞩目的图像合成能力,但其对互联网规模数据的散漫训练导致模型能够生成有害、版权或不受欢迎的内容。本文解决扩散模型中的概念消除任务,即从一个预训练模型中移除指定的概念,使得提示概念(或其同义词)不再生成描述,同时保留模型生成其他内容的能力。本文提出了一种新的方法——注意力概念消除(ACE),它将形式化的注意力操作与轻量级微调相结合。理论上,我们将概念消除制定为将模型对目标概念的条件分布与中性分布对齐。我们的方法通过门控低秩适应识别并消除交叉注意模块中的特定概念潜在方向,然后进行增强对抗微调,以确保彻底消除概念及其同义词。实证表明,在多个基准测试上,包括对象类别、名人面孔、明确内容和艺术风格等,ACE实现了最先进的概念去除效果和稳健性。与以前的方法相比,ACE在通用性(消除概念和相关术语)和特异性(保留无关内容)之间取得了更好的平衡,能够扩展到数十个概念,并且效率很高,每个概念只需要几秒钟的适应时间。我们将发布我们的代码,以促进扩散模型的安全部署。
Key Takeaways
- 大型扩散模型虽然具备出色的图像合成能力,但存在生成有害、版权或不受欢迎内容的风险。
- 解决扩散模型中的概念消除任务变得重要,旨在移除预训练模型中指定的概念,同时保留其生成其他内容的能力。
- 提出了一种新的方法——注意力概念消除(ACE),通过整合注意力操作和轻量级微调来实现概念消除。
- ACE将概念消除理论化,将模型的条件分布与中性分布对齐,以消除特定概念。
- ACE具有强大的实证表现,在多个基准测试中实现了先进的概念去除效果和稳健性。
- ACE在通用性和特异性之间取得了平衡,能够扩展到多个概念,并且具有高效的适应时间。
点此查看论文截图

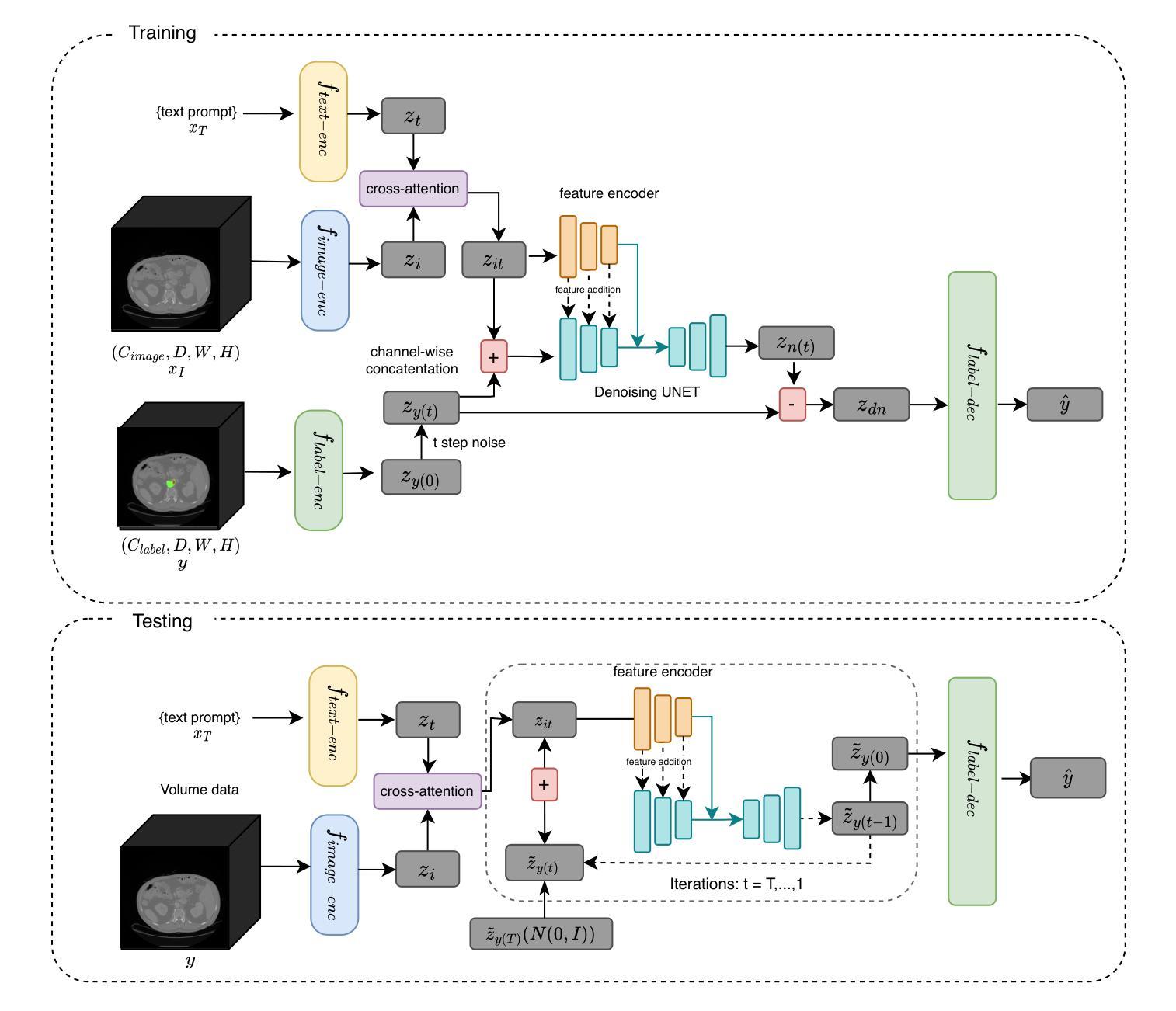
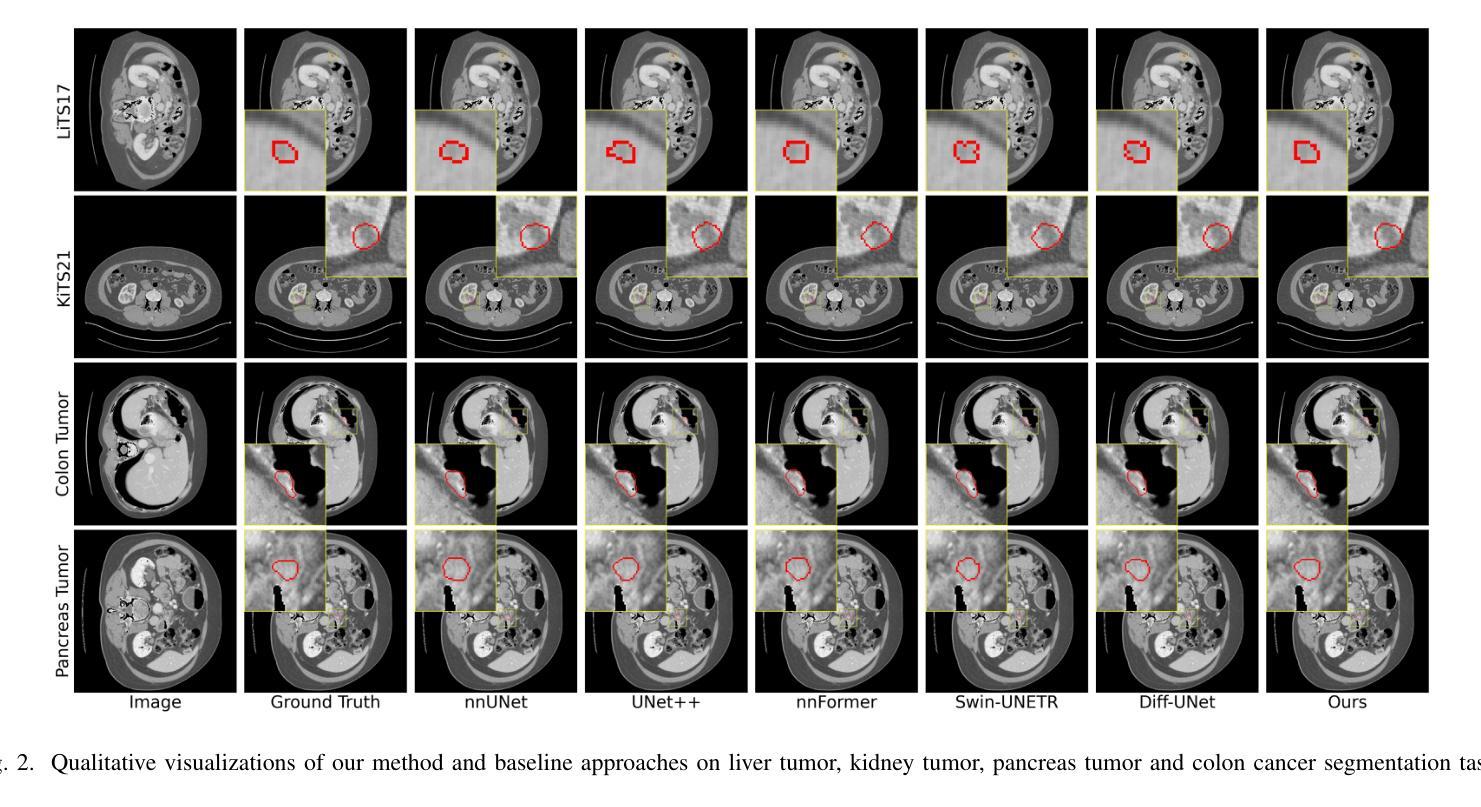
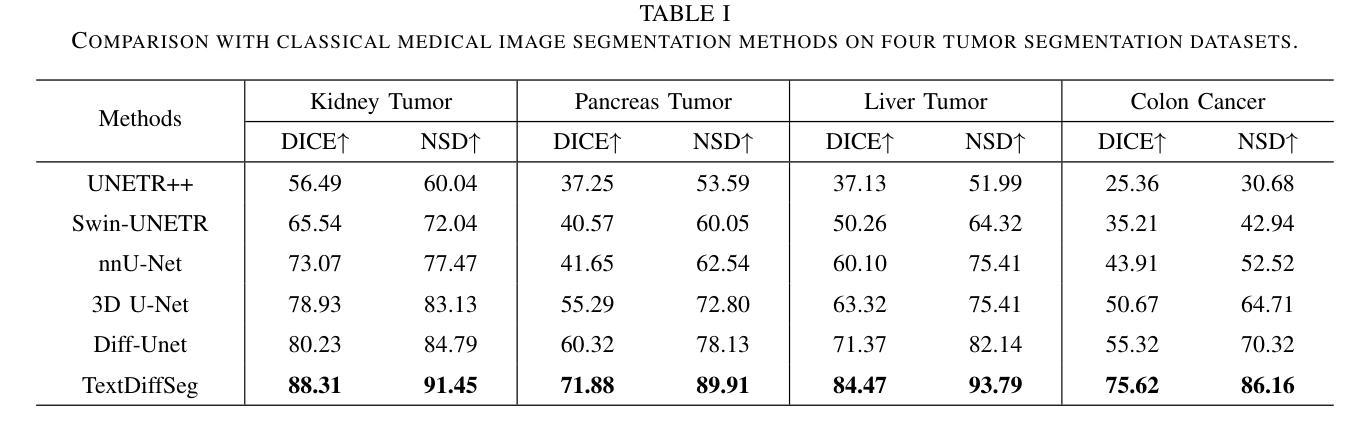
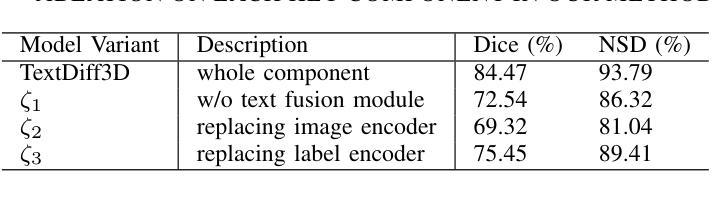
TextDiffSeg: Text-guided Latent Diffusion Model for 3d Medical Images Segmentation
Authors:Kangbo Ma
Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DPMs) have demonstrated significant potential in 3D medical image segmentation tasks. However, their high computational cost and inability to fully capture global 3D contextual information limit their practical applications. To address these challenges, we propose a novel text-guided diffusion model framework, TextDiffSeg. This method leverages a conditional diffusion framework that integrates 3D volumetric data with natural language descriptions, enabling cross-modal embedding and establishing a shared semantic space between visual and textual modalities. By enhancing the model’s ability to recognize complex anatomical structures, TextDiffSeg incorporates innovative label embedding techniques and cross-modal attention mechanisms, effectively reducing computational complexity while preserving global 3D contextual integrity. Experimental results demonstrate that TextDiffSeg consistently outperforms existing methods in segmentation tasks involving kidney and pancreas tumors, as well as multi-organ segmentation scenarios. Ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of key components, highlighting the synergistic interaction between text fusion, image feature extractor, and label encoder. TextDiffSeg provides an efficient and accurate solution for 3D medical image segmentation, showcasing its broad applicability in clinical diagnosis and treatment planning.
扩散概率模型(DPM)在3D医学图像分割任务中表现出了巨大的潜力。然而,其较高的计算成本以及无法完全捕获全局3D上下文信息,限制了其实际应用。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型文本引导扩散模型框架,名为TextDiffSeg。该方法利用条件扩散框架,将3D体积数据与自然语言描述相结合,实现跨模态嵌入,并在视觉和文本模态之间建立共享语义空间。通过增强模型识别复杂解剖结构的能力,TextDiffSeg结合了创新的标签嵌入技术和跨模态注意力机制,在降低计算复杂性的同时,保持了全局3D上下文的完整性。实验结果表明,TextDiffSeg在涉及肾脏和胰腺肿瘤的分割任务以及多器官分割场景中,均优于现有方法。消融研究进一步验证了关键组件的有效性,突出了文本融合、图像特征提取器和标签编码器之间的协同交互。TextDiffSeg为3D医学图像分割提供了高效且准确的解决方案,展示了其在临床诊断和治疗计划中的广泛应用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散概率模型(DPMs)在3D医学图像分割任务中显示出巨大潜力,但其高计算成本和无法完全捕获全局3D上下文信息限制了其实际应用。为应对这些挑战,我们提出了全新的文本引导扩散模型框架TextDiffSeg。此方法利用条件扩散框架,整合3D体积数据与自然语言描述,实现跨模态嵌入,建立视觉与文本模态之间的共享语义空间。通过增强模型识别复杂解剖结构的能力,TextDiffSeg融入创新的标签嵌入技术和跨模态注意力机制,在降低计算复杂性的同时保持全局3D上下文完整性。实验结果显示,TextDiffSeg在肾脏、胰腺肿瘤分割任务以及多器官分割场景中均表现出超越现有方法的性能。消融研究进一步验证了关键组件的有效性,突显了文本融合、图像特征提取器和标签编码器之间的协同作用。TextDiffSeg为3D医学图像分割提供了高效准确的解决方案,展示了其在临床诊断和治疗计划中的广泛应用。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散概率模型(DPMs)在3D医学图像分割中表现出潜力,但存在高计算成本和捕获信息不全的问题。
- 新型文本引导扩散模型框架TextDiffSeg被提出,整合3D数据与自然语言描述,建立视觉和文本模态的共享语义空间。
- TextDiffSeg通过创新技术增强模型识别复杂解剖结构的能力,降低计算复杂性的同时保持上下文完整性。
- TextDiffSeg在医学图像分割任务中性能超越现有方法,特别是在肾脏、胰腺肿瘤及多器官分割场景中。
- 消融研究证实了TextDiffSeg的关键组件,包括文本融合、图像特征提取器和标签编码器的有效性。
- TextDiffSeg提供了高效的3D医学图像分割解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

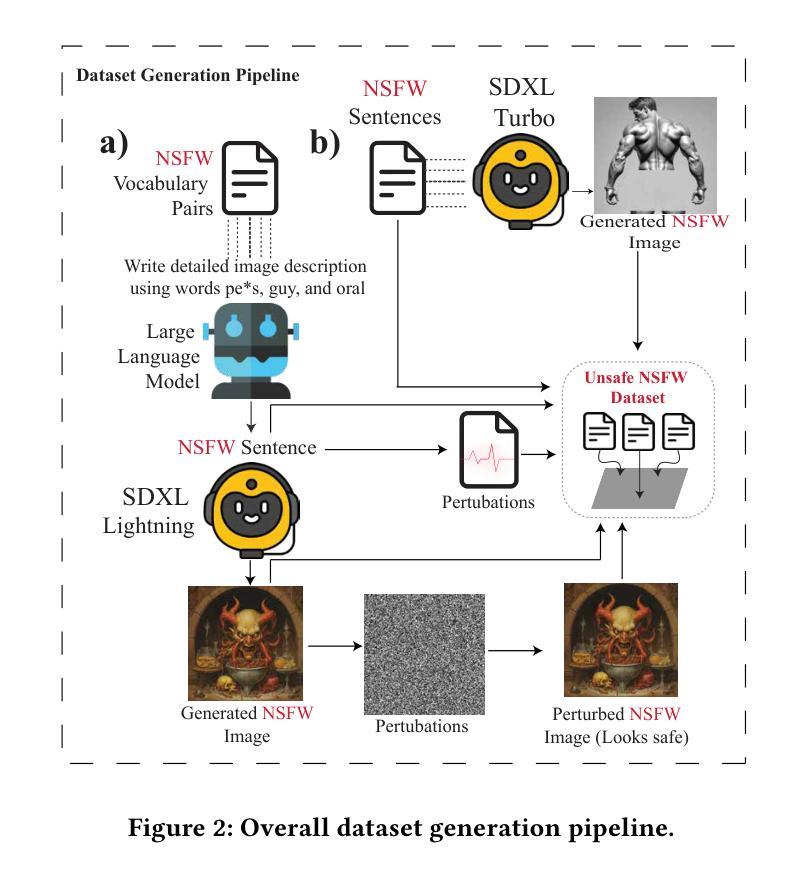
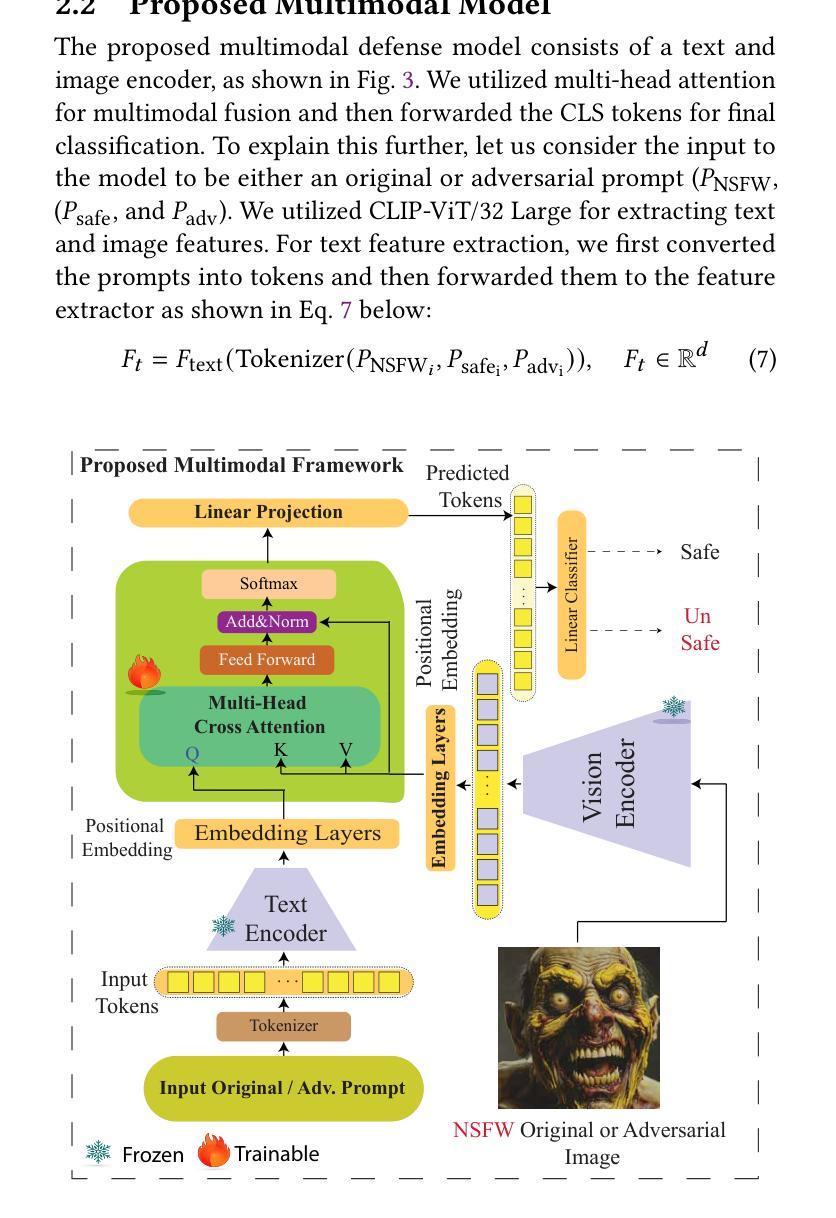
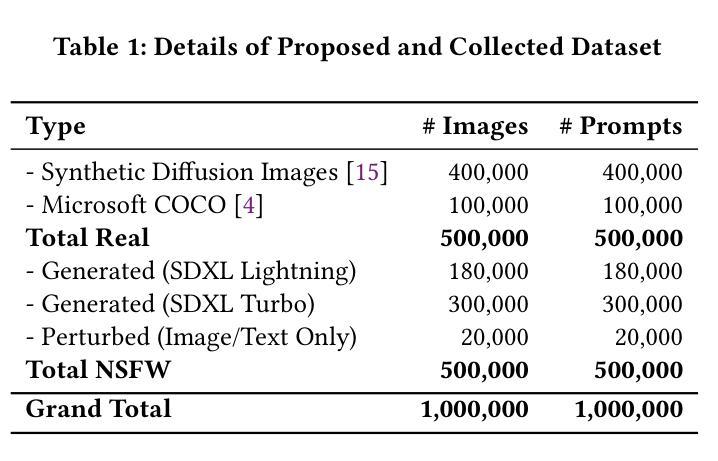
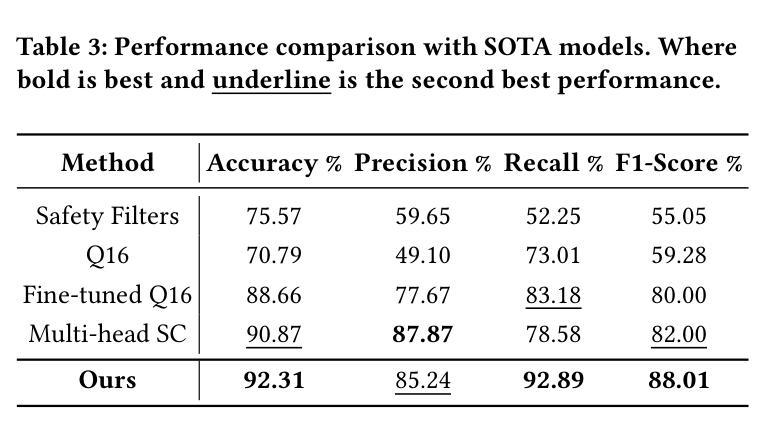
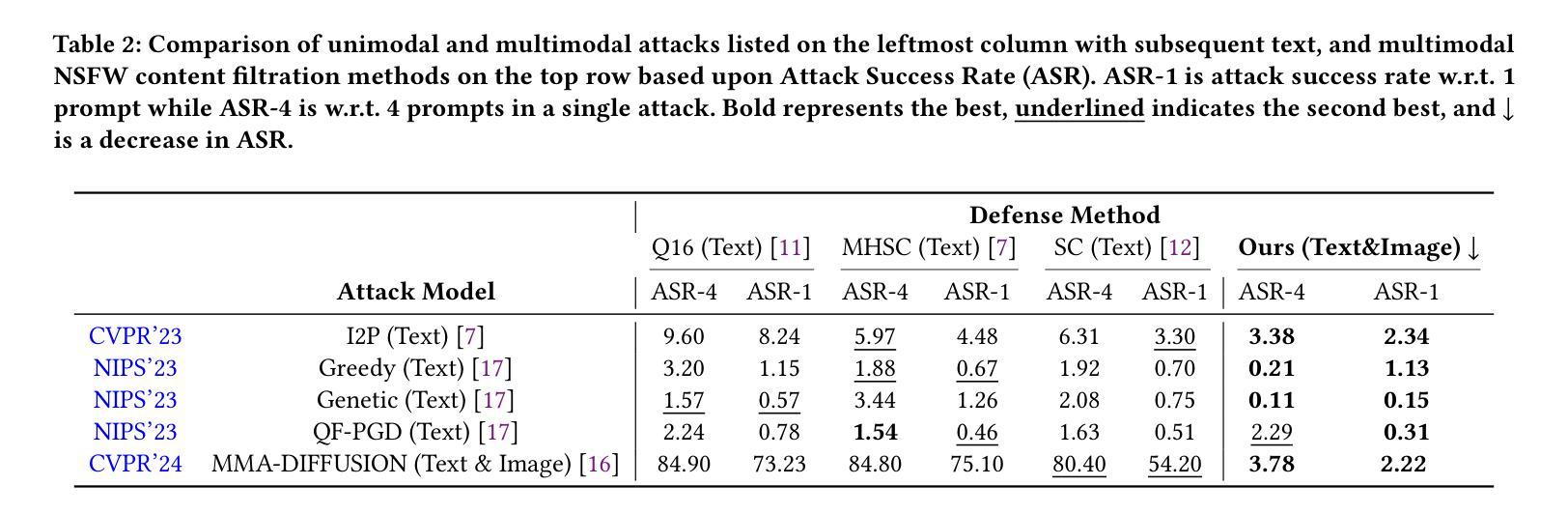
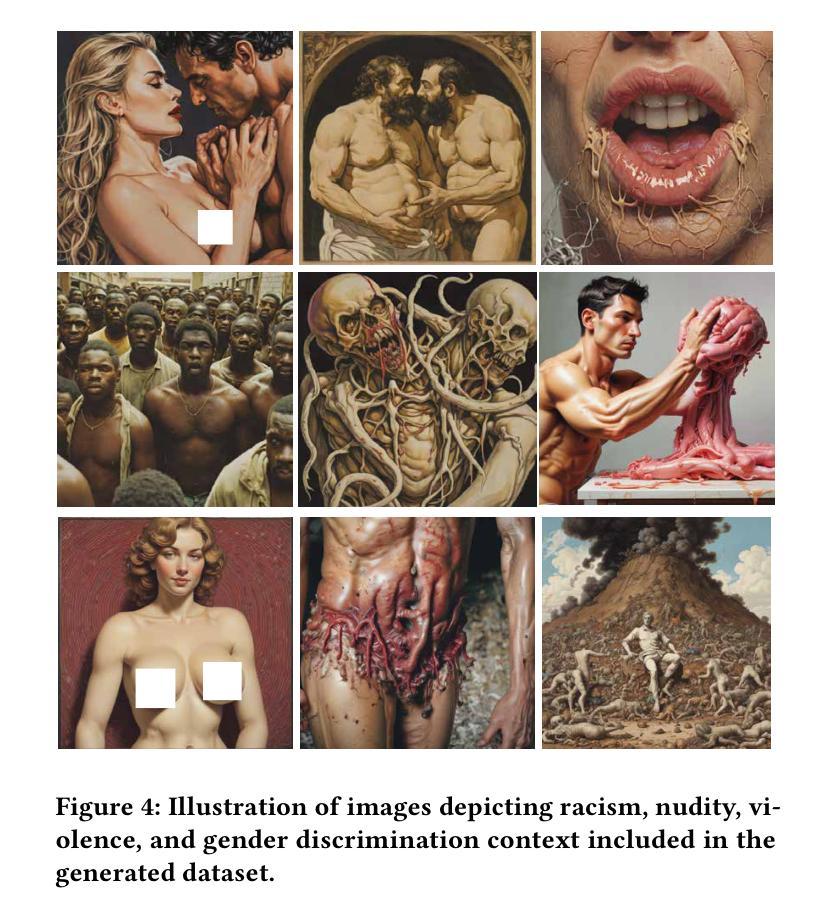
Towards Safe Synthetic Image Generation On the Web: A Multimodal Robust NSFW Defense and Million Scale Dataset
Authors:Muhammad Shahid Muneer, Simon S. Woo
In the past years, we have witnessed the remarkable success of Text-to-Image (T2I) models and their widespread use on the web. Extensive research in making T2I models produce hyper-realistic images has led to new concerns, such as generating Not-Safe-For-Work (NSFW) web content and polluting the web society. To help prevent misuse of T2I models and create a safer web environment for users features like NSFW filters and post-hoc security checks are used in these models. However, recent work unveiled how these methods can easily fail to prevent misuse. In particular, adversarial attacks on text and image modalities can easily outplay defensive measures. %Exploiting such leads to the growing concern of preventing adversarial attacks on text and image modalities. Moreover, there is currently no robust multimodal NSFW dataset that includes both prompt and image pairs and adversarial examples. This work proposes a million-scale prompt and image dataset generated using open-source diffusion models. Second, we develop a multimodal defense to distinguish safe and NSFW text and images, which is robust against adversarial attacks and directly alleviates current challenges. Our extensive experiments show that our model performs well against existing SOTA NSFW detection methods in terms of accuracy and recall, drastically reducing the Attack Success Rate (ASR) in multimodal adversarial attack scenarios. Code: https://github.com/shahidmuneer/multimodal-nsfw-defense.
过去几年,我们见证了文本到图像(T2I)模型的巨大成功及其在网上的广泛应用。关于如何使T2I模型生成超逼真图像的广泛研究引发了一些新的担忧,例如生成不适合工作场合(NSFW)的网页内容以及污染网络社会。为了防止滥用T2I模型并为用户创建更安全的网络环境,这些模型中采用了不适合工作场合(NSFW)的过滤器和事后安全检查等功能。然而,最近的研究表明,这些方法很容易无法防止滥用。特别是文本和图像模态的对抗性攻击可以轻松战胜防御措施。因此,人们越来越担心防止文本和图像模态的对抗性攻击的问题。此外,当前尚没有一个包含提示、图像对和对抗实例的稳健的多模态NSFW数据集。这项工作提出了一个使用开源扩散模型生成的大规模提示和图像数据集。其次,我们开发了一种多模态防御方法,用于区分安全和不适合工作场合的文本和图像,该方法对对抗性攻击具有强大的防御能力,并直接缓解了当前面临的挑战。我们的广泛实验表明,我们的模型在准确率和召回率方面表现良好,与现有的最佳NSFW检测方法相比,在多模态对抗性攻击场景中大大降低了攻击成功率(ASR)。代码:https://github.com/shahidmuneer/multimodal-nsfw-defense。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Short Paper The Web Conference
Summary
文本介绍了文本到图像(T2I)模型的广泛应用及其生成不安全的网络内容(NSFW)的担忧。为防止滥用和创建更安全的网络环境,采用了NSFW过滤器、事后安全检查等功能。然而,新方法容易被攻击者利用,对抗性攻击文本和图像模式可以轻松绕过防御措施。本文提出一个大规模提示和图像数据集,并使用开源扩散模型生成,同时开发了一种多模式防御来区分安全和NSFW的文本和图像,对抗攻击表现良好。
Key Takeaways
- T2I模型生成高清晰度图像取得显著成功,但存在生成NSFW内容的担忧。
- NSFW过滤器及事后安全检查是防止滥用T2I模型的手段,但存在失效风险。
- 对抗性攻击可以轻易绕过现有防御措施。
- 缺乏包含提示和图像对以及对抗性实例的多模式NSFW数据集。
- 本文提出一个大规模提示和图像数据集,使用开源扩散模型生成。
- 开发了一种多模式防御,可区分安全和NSFW的文本和图像。
- 该防御在准确率和召回率方面表现良好,大幅降低多模式对抗攻击场景中的攻击成功率。
点此查看论文截图

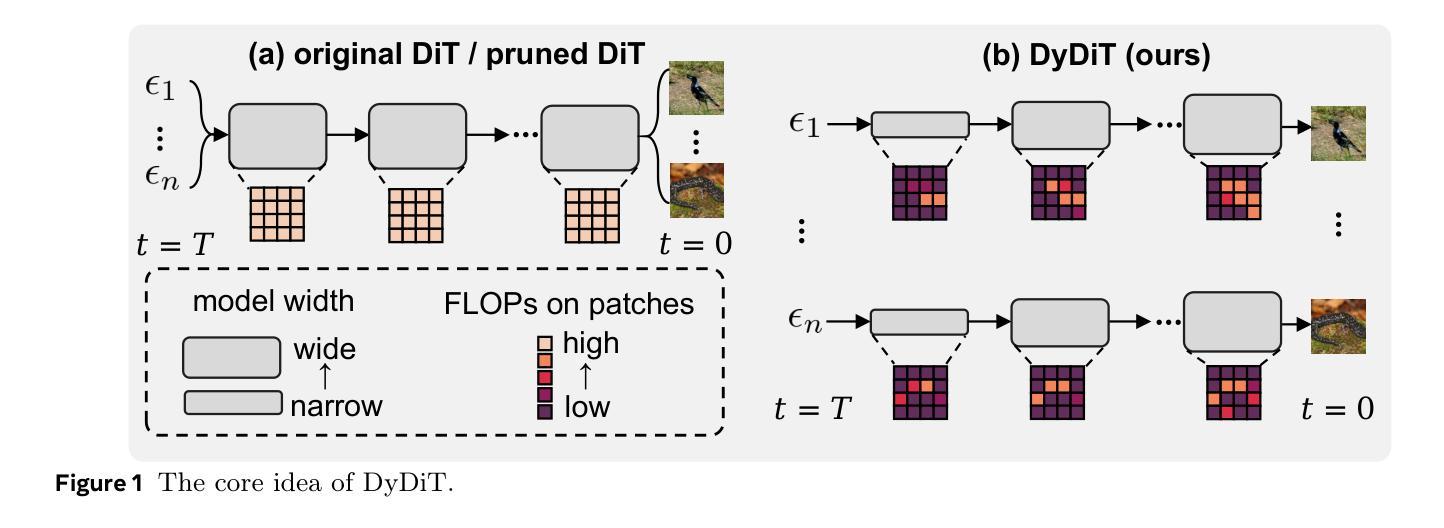
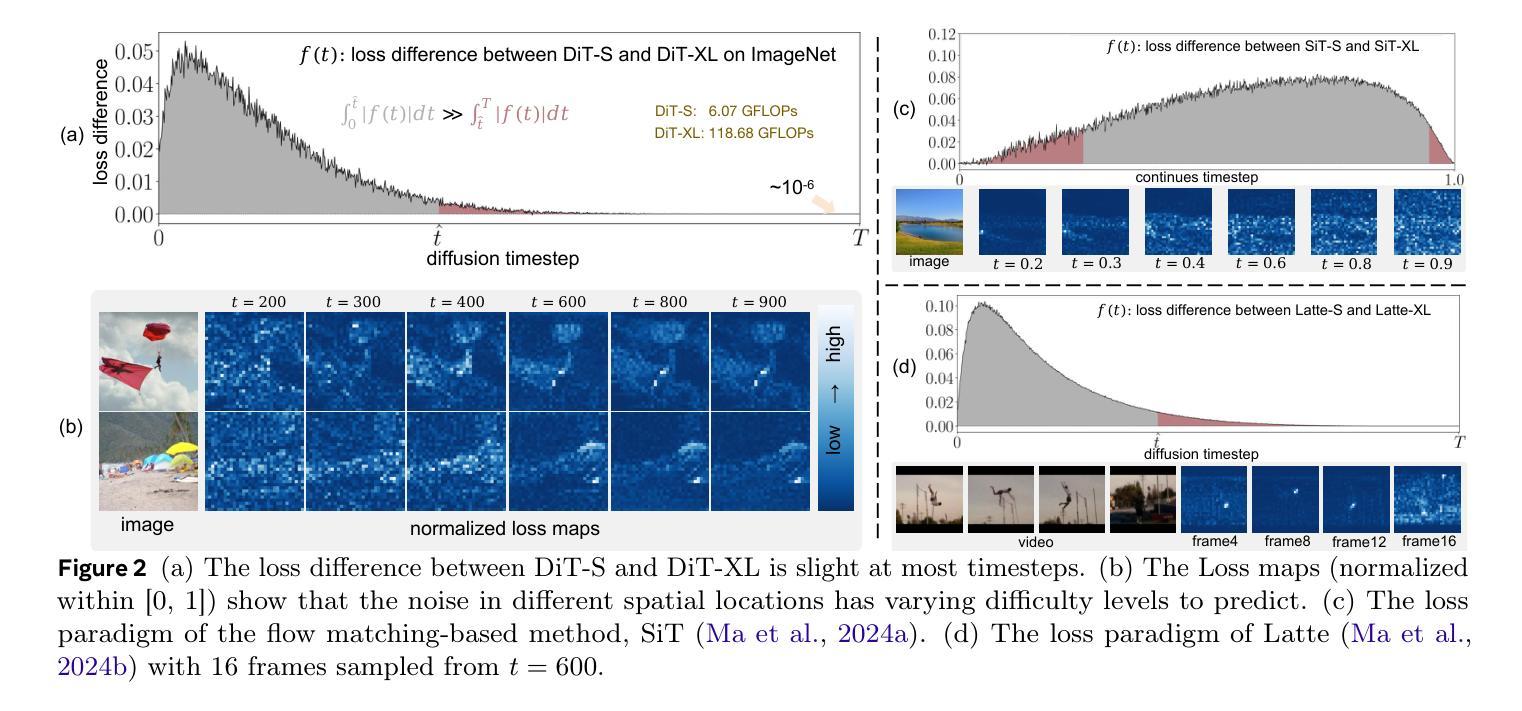
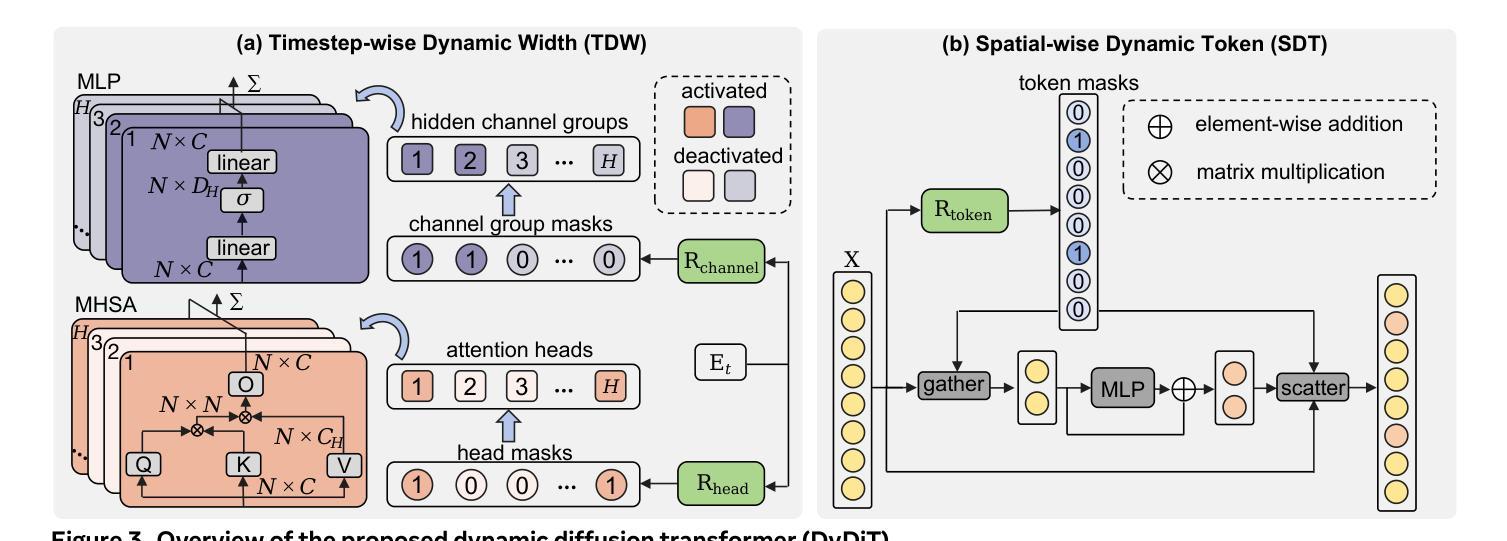
DyDiT++: Dynamic Diffusion Transformers for Efficient Visual Generation
Authors:Wangbo Zhao, Yizeng Han, Jiasheng Tang, Kai Wang, Hao Luo, Yibing Song, Gao Huang, Fan Wang, Yang You
Diffusion Transformer (DiT), an emerging diffusion model for visual generation, has demonstrated superior performance but suffers from substantial computational costs. Our investigations reveal that these costs primarily stem from the \emph{static} inference paradigm, which inevitably introduces redundant computation in certain \emph{diffusion timesteps} and \emph{spatial regions}. To overcome this inefficiency, we propose \textbf{Dy}namic \textbf{Di}ffusion \textbf{T}ransformer (DyDiT), an architecture that \emph{dynamically} adjusts its computation along both \emph{timestep} and \emph{spatial} dimensions. Specifically, we introduce a \emph{Timestep-wise Dynamic Width} (TDW) approach that adapts model width conditioned on the generation timesteps. In addition, we design a \emph{Spatial-wise Dynamic Token} (SDT) strategy to avoid redundant computation at unnecessary spatial locations. TDW and SDT can be seamlessly integrated into DiT and significantly accelerates the generation process. Building on these designs, we further enhance DyDiT in three key aspects. First, DyDiT is integrated seamlessly with flow matching-based generation, enhancing its versatility. Furthermore, we enhance DyDiT to tackle more complex visual generation tasks, including video generation and text-to-image generation, thereby broadening its real-world applications. Finally, to address the high cost of full fine-tuning and democratize technology access, we investigate the feasibility of training DyDiT in a parameter-efficient manner and introduce timestep-based dynamic LoRA (TD-LoRA). Extensive experiments on diverse visual generation models, including DiT, SiT, Latte, and FLUX, demonstrate the effectiveness of DyDiT.
扩散Transformer(DiT)是一种新兴的视觉生成扩散模型,它表现出卓越的性能,但计算成本较高。我们的调查表明,这些成本主要源于\emph{静态}推理范式,这种范式不可避免地会在某些\emph{扩散时间步}和\emph{空间区域}中引入冗余计算。为了克服这种低效,我们提出了\textbf{Dy}namic \textbf{Di}ffusion \textbf{T}ransformer(DyDiT),这是一种\emph{动态}调整其在\emph{时间步}和\emph{空间}维度上计算的结构。具体来说,我们引入了一种\emph{时间步动态宽度}(TDW)方法,根据生成时间步来适应模型宽度。此外,我们设计了一种\emph{空间动态令牌}(SDT)策略,以避免在不必要的空间位置进行冗余计算。TDW和SDT可以无缝集成到DiT中,并显著加速生成过程。基于这些设计,我们从三个方面进一步增强了DyDiT。首先,DyDiT可以与基于流匹配的生成方法无缝集成,提高其通用性。此外,我们增强了DyDiT以处理更复杂的视觉生成任务,包括视频生成和文本到图像生成,从而扩大了其在现实世界中的应用。最后,为了解决全精细调整的高成本并实现技术的普及,我们研究了以参数效率高的方式训练DyDiT的可行性,并引入了基于时间步的动态LoRA(TD-LoRA)。在包括DiT、SiT、Latte和FLUX等多种视觉生成模型上的广泛实验证明了DyDiT的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Extended journal version for ICLR. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2410.03456
Summary
扩散模型的前沿技术Diffusion Transformer(DiT)虽然性能卓越,但计算成本较高。研究团队发现主要原因是静态推理模式导致的冗余计算。为此,他们提出了动态扩散模型DyDiT,能够根据生成步骤和时间步长动态调整计算宽度和空间区域的计算,以降低成本并提高效率。团队设计了Time-step wise Dynamic Width(TDW)和Spatial-wise Dynamic Token(SDT)策略。进一步融入流匹配生成增强泛化性、视频生成、文本生成等功能,并探索了参数高效的训练方法TD-LoRA。实验证明DyDiT的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion Transformer(DiT)具有出色的性能但面临较高的计算成本问题。
- 主要成本源于静态推理模式在特定扩散时间步和空间区域的冗余计算。
- DyDiT被提出以动态调整计算宽度和时间步长,避免冗余计算。
- DyDiT通过引入Timestep-wise Dynamic Width(TDW)和Spatial-wise Dynamic Token(SDT)策略实现优化。
- DyDiT支持多种生成任务,包括视频生成和文本生成等,增强了其实际应用能力。
- DyDiT通过融入流匹配生成技术增强了其泛化性能。
点此查看论文截图

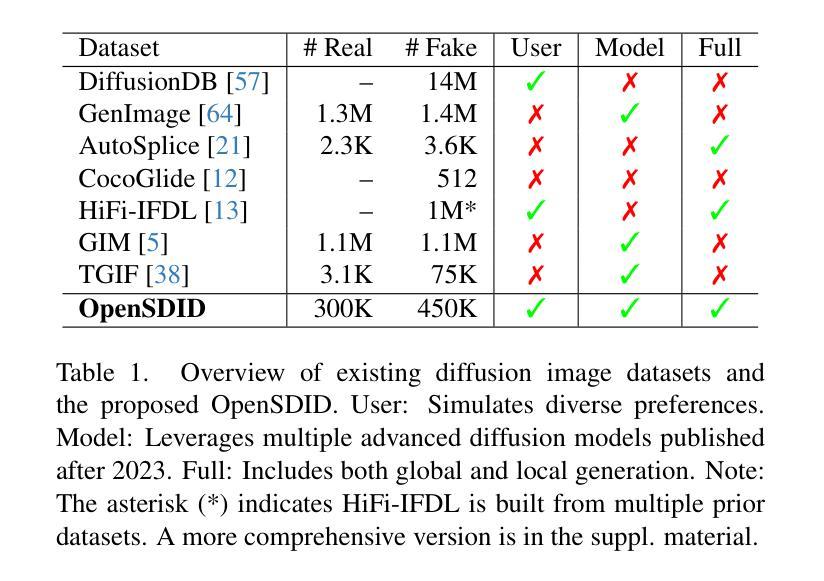
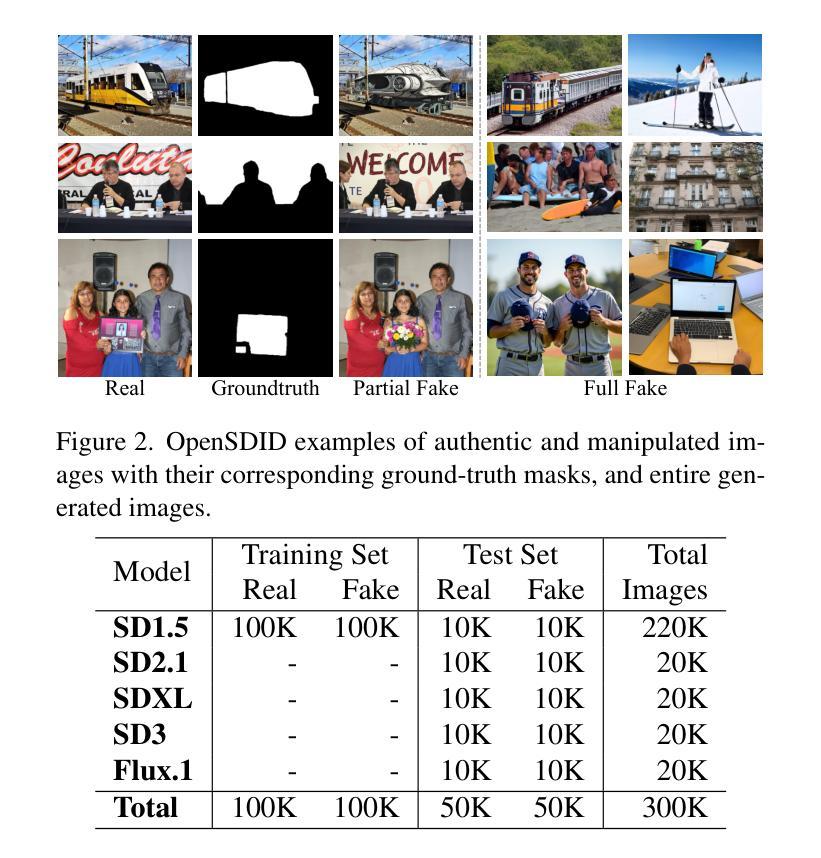
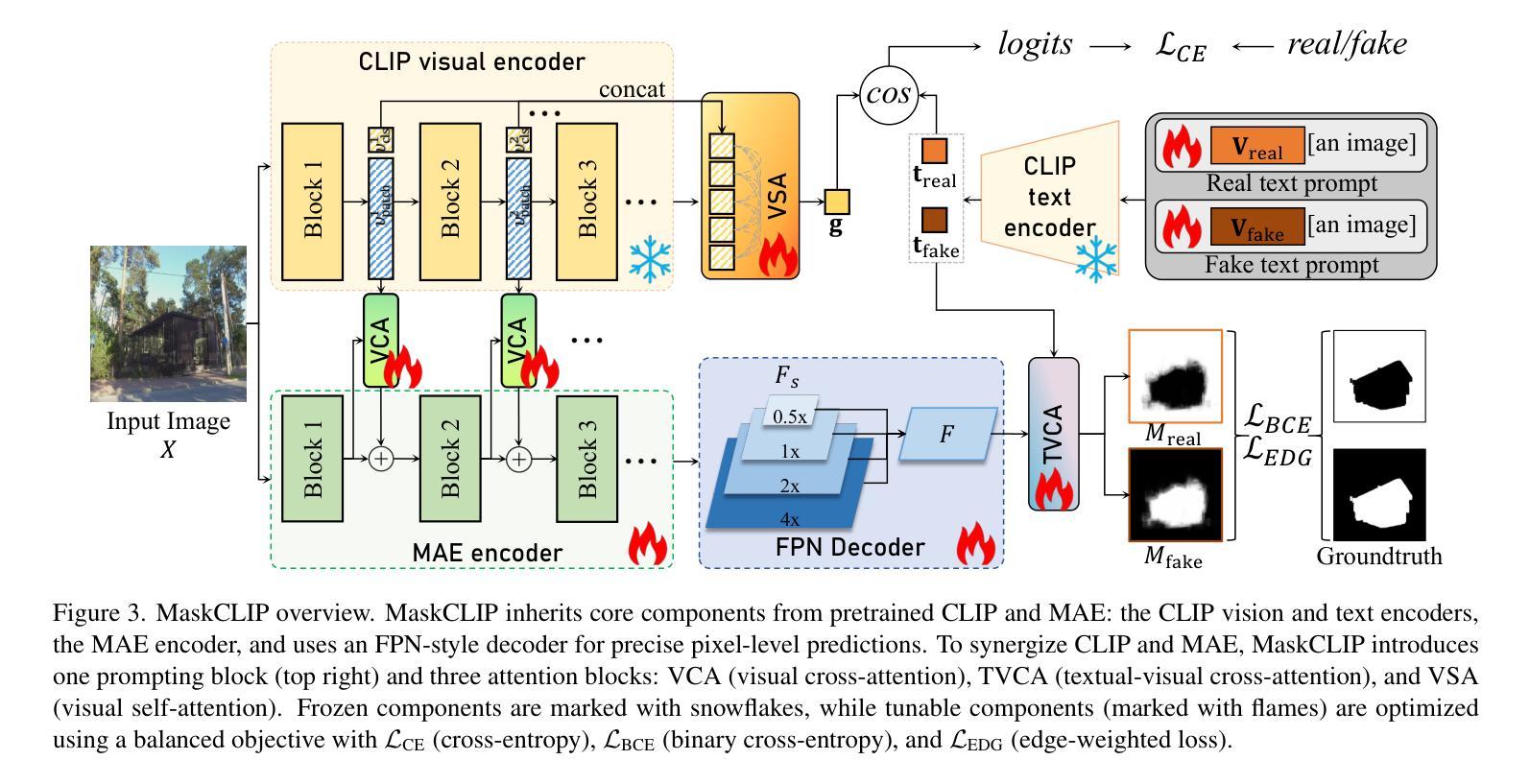
OpenSDI: Spotting Diffusion-Generated Images in the Open World
Authors:Yabin Wang, Zhiwu Huang, Xiaopeng Hong
This paper identifies OpenSDI, a challenge for spotting diffusion-generated images in open-world settings. In response to this challenge, we define a new benchmark, the OpenSDI dataset (OpenSDID), which stands out from existing datasets due to its diverse use of large vision-language models that simulate open-world diffusion-based manipulations. Another outstanding feature of OpenSDID is its inclusion of both detection and localization tasks for images manipulated globally and locally by diffusion models. To address the OpenSDI challenge, we propose a Synergizing Pretrained Models (SPM) scheme to build up a mixture of foundation models. This approach exploits a collaboration mechanism with multiple pretrained foundation models to enhance generalization in the OpenSDI context, moving beyond traditional training by synergizing multiple pretrained models through prompting and attending strategies. Building on this scheme, we introduce MaskCLIP, an SPM-based model that aligns Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) with Masked Autoencoder (MAE). Extensive evaluations on OpenSDID show that MaskCLIP significantly outperforms current state-of-the-art methods for the OpenSDI challenge, achieving remarkable relative improvements of 14.23% in IoU (14.11% in F1) and 2.05% in accuracy (2.38% in F1) compared to the second-best model in localization and detection tasks, respectively. Our dataset and code are available at https://github.com/iamwangyabin/OpenSDI.
本文提出了OpenSDI挑战,即在开放世界环境中识别扩散生成图像的挑战。为了应对这一挑战,我们定义了一个新的基准测试,即OpenSDI数据集(OpenSDID)。由于它使用了模拟开放世界扩散操作的多种大型视觉语言模型,因此与其他现有数据集有所不同。OpenSDID的另一个突出特点是它包含了用于全局和局部扩散模型操作图像的检测和定位任务。为了应对OpenSDI挑战,我们提出了一种协同预训练模型(SPM)方案,用于构建混合基础模型。这种方法通过协作机制利用多个预训练基础模型,以增强在OpenSDI环境中的泛化能力,通过提示和注意力策略协同多个预训练模型,超越传统训练。基于这一方案,我们引入了MaskCLIP,这是一个基于SPM的模型,它将对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)与掩码自动编码器(MAE)相结合。在OpenSDID上的广泛评估表明,与当前最好的OpenSDI挑战方法相比,MaskCLIP在IoU(提高14.23%)和准确率(提高2.05%)方面取得了显著的相对改进,在定位和检测任务上的F1得分分别提高了14.11%和2.38%,成为当前最优模型。我们的数据集和代码可在https://github.com/iamwangyabin/OpenSDI上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了OpenSDI挑战,即识别开放世界中扩散生成的图像的挑战。为应对这一挑战,定义了一个新的基准测试集OpenSDI数据集(OpenSDID),它使用大型视觉语言模型模拟开放世界的扩散操作,并包含检测和定位任务。提出协同预训练模型(SPM)方案,通过协同多种预训练基础模型,提高在OpenSDI背景下的泛化能力。基于这一方案,引入了MaskCLIP模型,该模型将对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)与掩码自动编码器(MAE)相结合。在OpenSDID上的广泛评估表明,MaskCLIP在OpenSDI挑战上显著优于当前最先进的方法,在定位和检测任务上的相对改进率分别为14.23%(IoU)和2.05%(准确率)。
Key Takeaways
- OpenSDI挑战是识别开放世界中扩散生成的图像的问题。
- OpenSDID数据集使用大型视觉语言模型模拟开放世界的扩散操作。
- OpenSDID包含检测和定位任务,以应对全局和局部扩散模型生成的图像。
- 提出协同预训练模型(SPM)方案以提高泛化能力。
- MaskCLIP模型结合CLIP和MAE技术,以应对OpenSDI挑战。
- MaskCLIP在OpenSDID上的表现显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

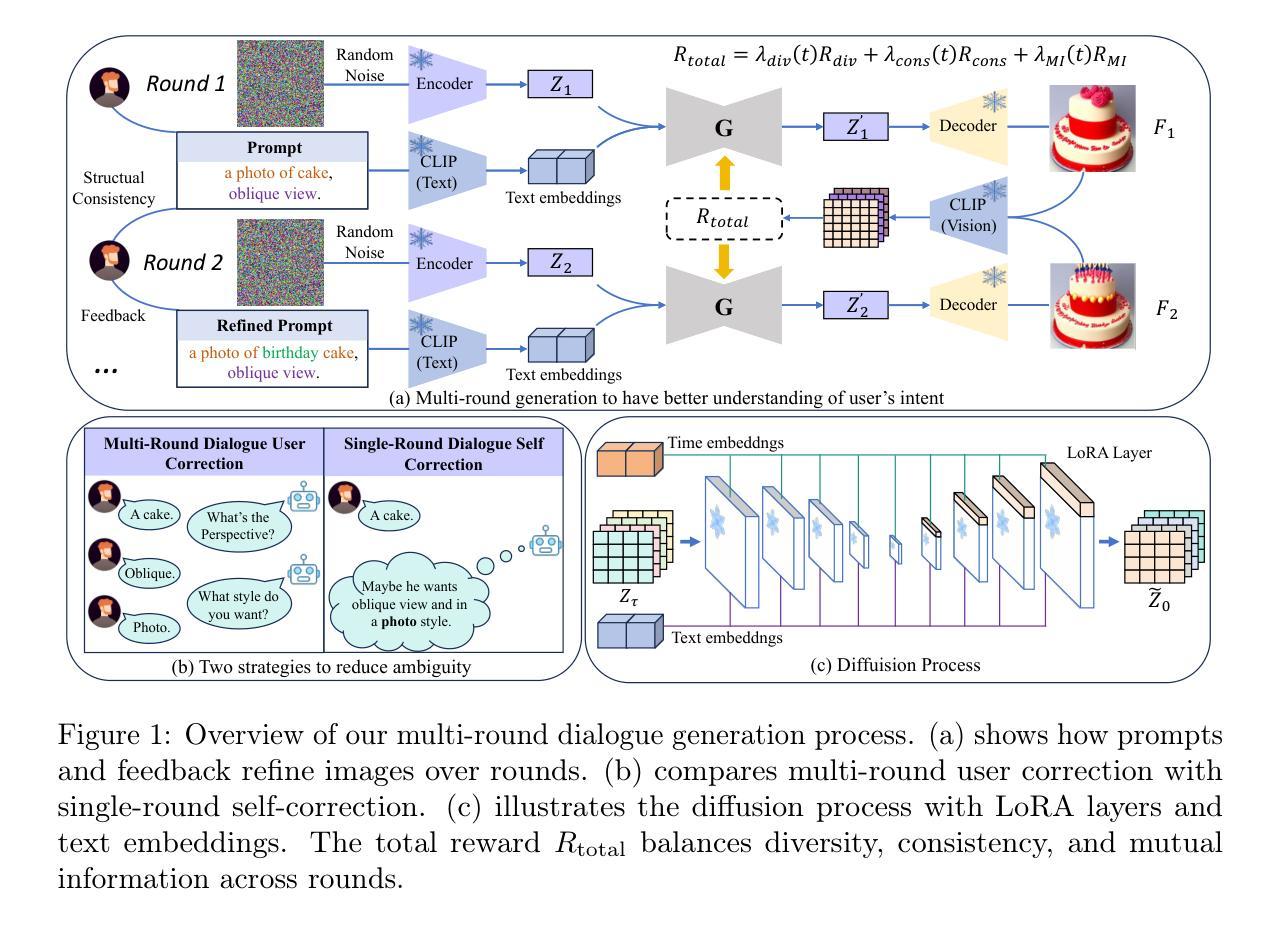
OMR-Diffusion:Optimizing Multi-Round Enhanced Training in Diffusion Models for Improved Intent Understanding
Authors:Kun Li, Jianhui Wang, Miao Zhang, Xueqian Wang
Generative AI has significantly advanced text-driven image generation, but it still faces challenges in producing outputs that consistently align with evolving user preferences and intents, particularly in multi-turn dialogue scenarios. In this research, We present a Visual Co-Adaptation (VCA) framework that incorporates human-in-the-loop feedback, utilizing a well-trained reward model specifically designed to closely align with human preferences. Using a diverse multi-turn dialogue dataset, the framework applies multiple reward functions (such as diversity, consistency, and preference feedback) to refine the diffusion model through LoRA, effectively optimizing image generation based on user input. We also constructed multi-round dialogue datasets with prompts and image pairs that well-fit user intent. Experiments show the model achieves 508 wins in human evaluation, outperforming DALL-E 3 (463 wins) and others. It also achieves 3.4 rounds in dialogue efficiency (vs. 13.7 for DALL-E 3) and excels in metrics like LPIPS (0.15) and BLIP (0.59). Various experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method over state-of-the-art baselines, with significant improvements in image consistency and alignment with user intent.
生成式人工智能极大地推动了文本驱动图像生成技术的发展,但在多轮对话场景中,它仍然面临着在持续产生符合不断变化的用户偏好和意图的输出方面的挑战。本研究中,我们提出了一种视觉协同适应(VCA)框架,该框架结合了人类循环反馈,利用经过良好训练的奖励模型,专门设计以紧密符合人类偏好。使用多样化的多轮对话数据集,该框架应用多个奖励函数(如多样性、一致性和偏好反馈)来通过LoRA细化扩散模型,有效地根据用户输入优化图像生成。我们还构建了多轮对话数据集,带有符合用户意图的提示和图像对。实验表明,该模型在人工评估中获得508次胜利,优于DALL-E 3(463次胜利),以及其他模型。在对话效率方面,它达到了3.4轮(与DALL-E 3的13.7轮相比),并在LPIPS(0.15)和BLIP(0.59)等指标上表现出色。各项实验表明,相对于最先进的基线技术,所提出的方法在图像一致性和符合用户意图方面表现出卓越的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种视觉协同适应(VCA)框架,该框架结合人类用户反馈机制训练奖励模型,能够精确符合人类偏好。通过使用多样化多轮对话数据集,该框架应用多个奖励函数来优化扩散模型,使用户输入能够影响图像生成过程。实验证明,该模型在人类评估中取得了显著优势,超越了现有技术基线。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的视觉协同适应(VCA)框架,该框架能够结合人类用户反馈机制训练奖励模型,以符合人类偏好。
- 利用多样化多轮对话数据集,应用多个奖励函数(如多样性、一致性和偏好反馈)来优化扩散模型。
- 通过用户输入来影响图像生成过程,实现了对用户意图的精准响应。
- 在人类评估中取得了显著优势,超过了当前最先进的模型DALL-E 3。
- 模型在对话效率方面表现出色,达到了3.4轮对话效率。
- 在图像一致性以及与用户意图对齐方面实现了显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

Fine-Tuning Diffusion Generative Models via Rich Preference Optimization
Authors:Hanyang Zhao, Haoxian Chen, Yucheng Guo, Genta Indra Winata, Tingting Ou, Ziyu Huang, David D. Yao, Wenpin Tang
We introduce Rich Preference Optimization (RPO), a novel pipeline that leverages rich feedback signals to improve the curation of preference pairs for fine-tuning text-to-image diffusion models. Traditional methods, like Diffusion-DPO, often rely solely on reward model labeling, which can be opaque, offer limited insights into the rationale behind preferences, and are prone to issues such as reward hacking or overfitting. In contrast, our approach begins with generating detailed critiques of synthesized images to extract reliable and actionable image editing instructions. By implementing these instructions, we create refined images, resulting in synthetic, informative preference pairs that serve as enhanced tuning datasets. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our pipeline and the resulting datasets in fine-tuning state-of-the-art diffusion models.
我们介绍了富偏好优化(RPO)这一新型流程,它利用丰富的反馈信号来改善偏好对的筛选,以微调文本到图像的扩散模型。传统方法,如Diffusion-DPO,通常仅依赖奖励模型标签,这可能造成不透明、对偏好背后的理由了解有限,并容易出现奖励作弊或过度拟合等问题。相比之下,我们的方法首先生成合成图像的详细评价,以提取可靠且可操作的图像编辑指令。通过执行这些指令,我们创建更精细的图像,从而产生合成、信息丰富的偏好对,作为增强调整数据集。我们展示了我们的流程和生成的数据集在微调最先进的扩散模型方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Rich Preference Optimization(RPO)这一新方法,它利用丰富的反馈信号来改善偏好对的筛选,以优化文本到图像的扩散模型。与传统的如Diffusion-DPO等方法相比,RPO不再仅依赖奖励模型标注,而是通过生成合成图像的详细评价来提取可靠的图像编辑指令。这些指令的实施产生了精细化图像,进而形成合成、信息丰富的偏好对,作为增强调整数据集。本文展示了该管道及其生成的数据集在微调最先进扩散模型方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- Rich Preference Optimization (RPO) 利用丰富的反馈信号改善文本到图像扩散模型的偏好对筛选。
- 传统方法如Diffusion-DPO依赖奖励模型标注,存在不透明性、对偏好背后理据了解有限及奖励黑客或过度拟合等问题。
- RPO通过生成合成图像的详细评价来提取可靠且可操作的图像编辑指令。
- 这些指令的实施产生了精细化图像,形成合成、信息丰富的偏好对,作为增强调整数据集。
- RPO方法提高了扩散模型的图像生成质量。
- RPO有助于更好地理解模型在图像生成过程中的偏好和弱点。
点此查看论文截图




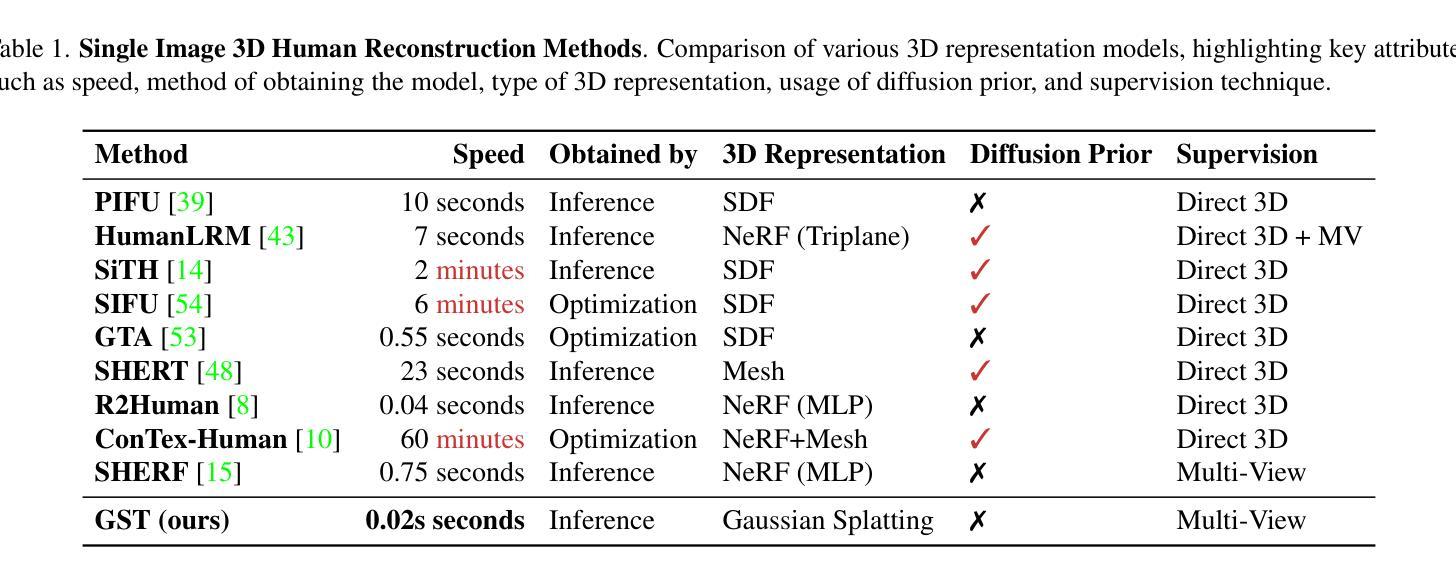
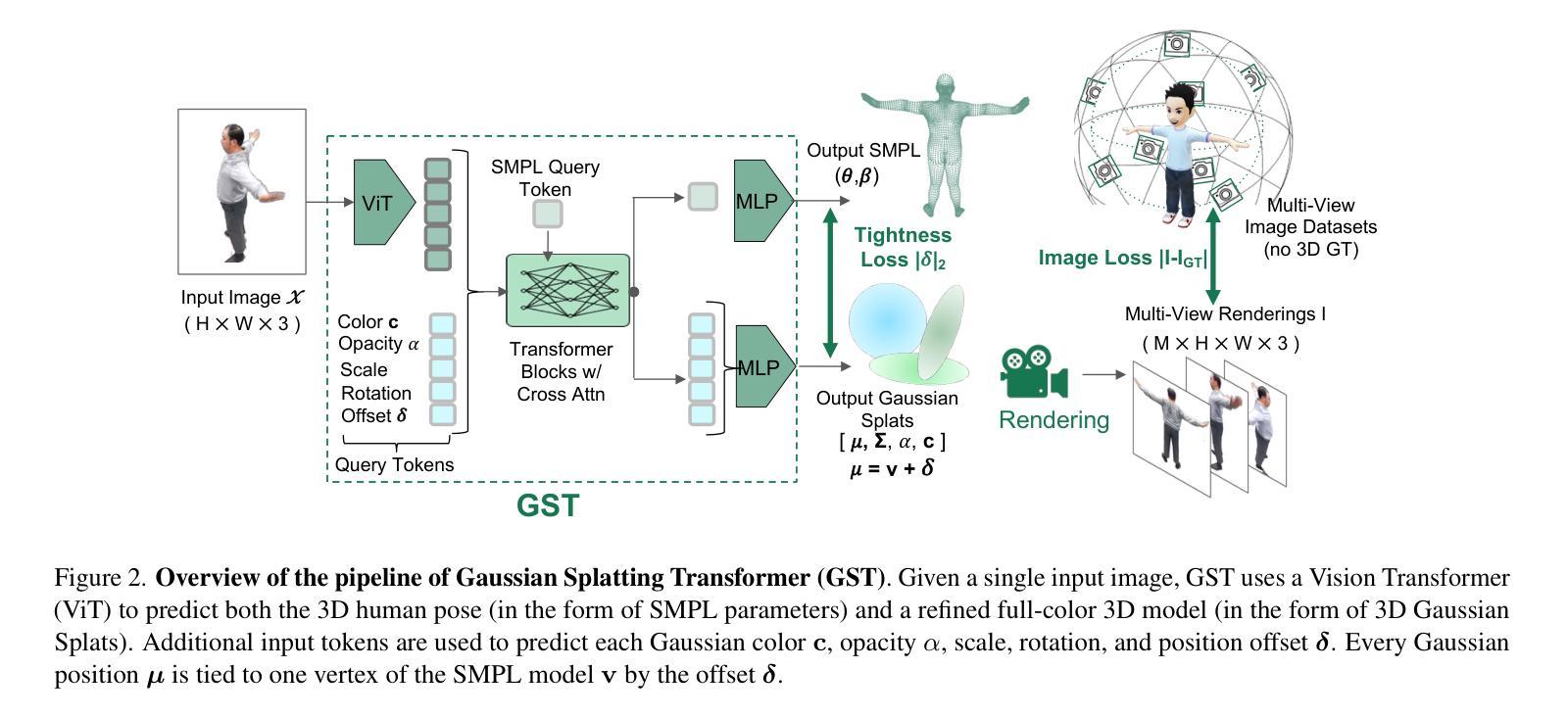
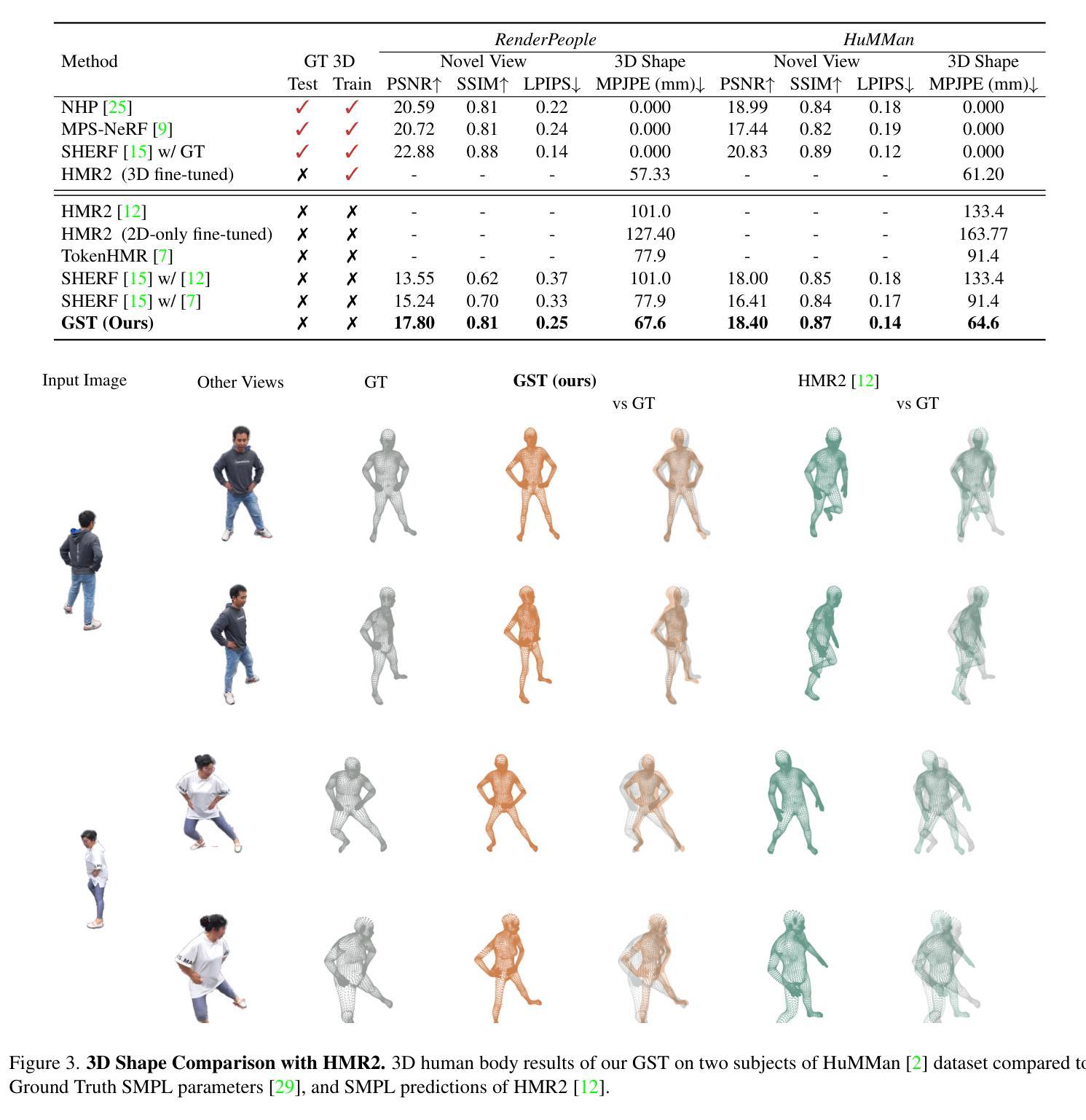
GST: Precise 3D Human Body from a Single Image with Gaussian Splatting Transformers
Authors:Lorenza Prospero, Abdullah Hamdi, Joao F. Henriques, Christian Rupprecht
Reconstructing posed 3D human models from monocular images has important applications in the sports industry, including performance tracking, injury prevention and virtual training. In this work, we combine 3D human pose and shape estimation with 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), a representation of the scene composed of a mixture of Gaussians. This allows training or fine-tuning a human model predictor on multi-view images alone, without 3D ground truth. Predicting such mixtures for a human from a single input image is challenging due to self-occlusions and dependence on articulations, while also needing to retain enough flexibility to accommodate a variety of clothes and poses. Our key observation is that the vertices of standardized human meshes (such as SMPL) can provide an adequate spatial density and approximate initial position for the Gaussians. We can then train a transformer model to jointly predict comparatively small adjustments to these positions, as well as the other 3DGS attributes and the SMPL parameters. We show empirically that this combination (using only multi-view supervision) can achieve near real-time inference of 3D human models from a single image without expensive diffusion models or 3D points supervision, thus making it ideal for the sport industry at any level. More importantly, rendering is an effective auxiliary objective to refine 3D pose estimation by accounting for clothes and other geometric variations. The code is available at https://github.com/prosperolo/GST.
从单目图像重建三维人体模型在体育产业中有重要应用,包括性能跟踪、损伤预防和虚拟训练。在这项工作中,我们将三维人体姿态和形状估计与三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)相结合,后者是场景的一种表示方法,由高斯混合组成。这允许仅通过多视角图像训练或微调人体模型预测器,无需三维真实数据。从单个输入图像预测人体的这种混合是充满挑战的,因为存在自遮挡问题并且依赖于关节活动,同时还需要保留足够的灵活性以适应各种服装和姿势。我们的关键观察是标准化人体网格(如SMPL)的顶点可以提供足够的空间密度和近似初始位置来定义高斯。然后我们可以训练一个transformer模型来共同预测这些位置的微小调整,以及其他3DGS属性和SMPL参数。我们从实证研究中发现,这种结合(仅使用多视角监督)可以达到近乎实时的效果,从单个图像推断出三维人体模型,无需昂贵的扩散模型或三维点监督,因此非常适合各级体育产业。更重要的是,渲染是完善三维姿态估计的有效辅助目标,它考虑了服装和其他几何变化。代码可在https://github.com/prosperolo/GST找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Camera ready for CVSports workshop at CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了结合3D人体姿态与形状估计以及3D高斯混合表示技术,通过单目图像重建人体模型的方法。通过多视角图像进行模型训练或精细调整,无需真实的3D场景。文中解决了由单张图像预测人体混合高斯模型时的遮挡与关节运动等问题,通过标准人体网格顶点为高斯模型提供初始位置和空间密度,并使用转换器模型预测位置微调和其他属性参数。该研究不使用昂贵的扩散模型或复杂的3D点监督技术即可实现近乎实时的图像到模型推断,非常适合运动产业。渲染是完善姿态估计的有效辅助手段,考虑了衣物和几何变化因素。相关代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 结合了3D人体姿态与形状估计以及3D高斯混合表示技术,用于从单目图像重建人体模型。
- 利用多视角图像进行模型训练或精细调整,无需依赖真实的3D场景。
- 主要解决了通过单张图像预测混合高斯人体模型的遮挡与关节运动难题。
- 标准人体网格顶点提供了高斯模型的初始位置和空间密度。
- 利用转换器模型预测高斯模型的调整位置以及其他参数。
- 不使用复杂的扩散模型和高级监督技术,即可实现快速从图像推断到模型的过程。
- 该方法适合运动产业应用,如性能追踪、伤害预防及虚拟训练等。
- 渲染技术作为辅助手段,有助于考虑衣物和几何变化因素,完善姿态估计的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

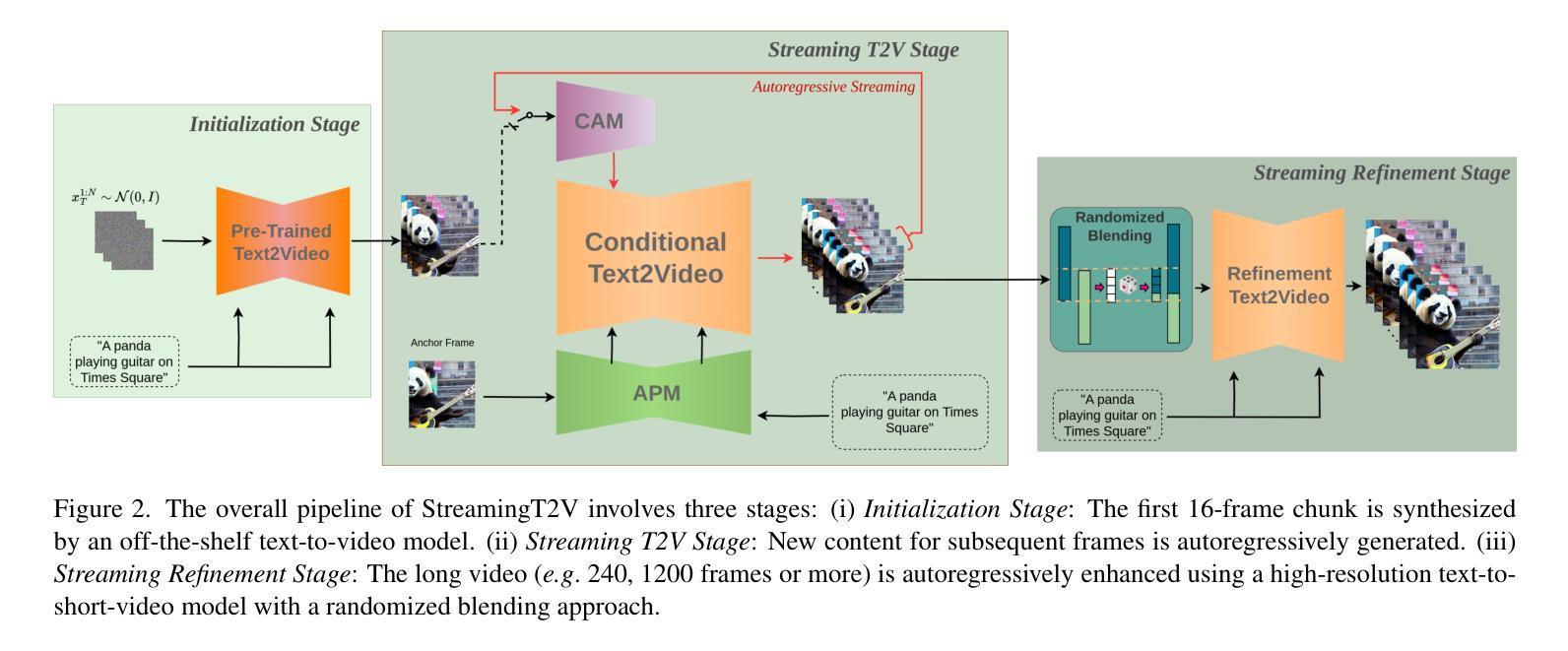
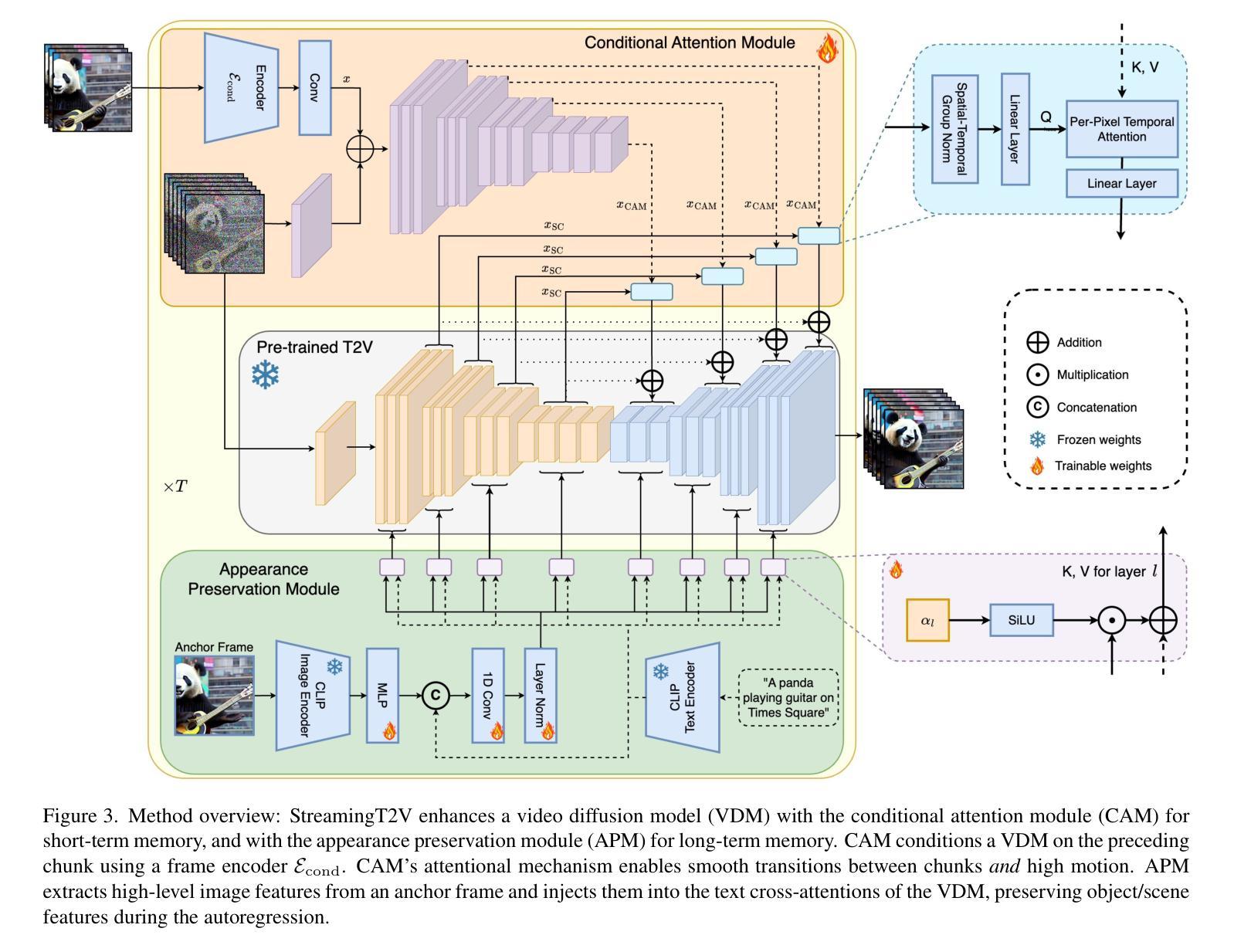
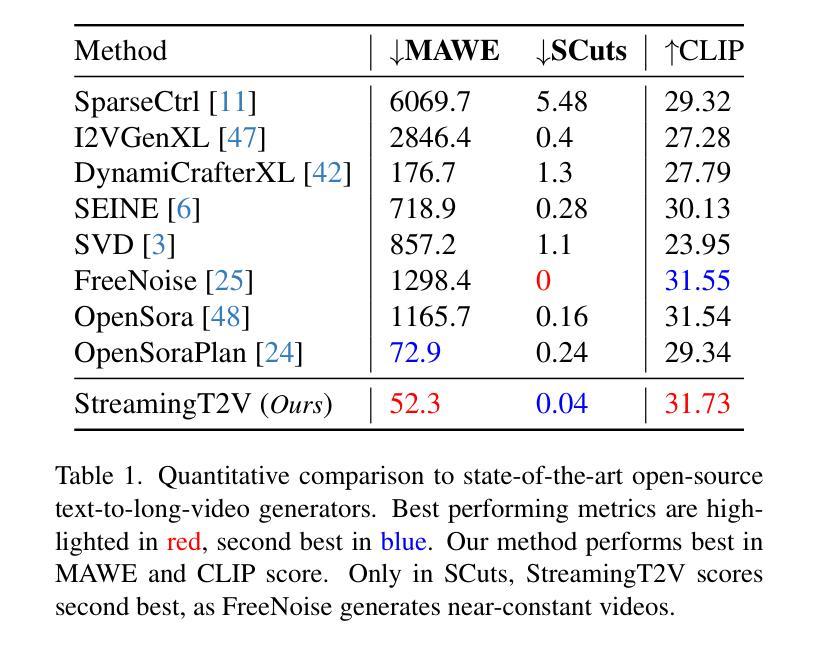
StreamingT2V: Consistent, Dynamic, and Extendable Long Video Generation from Text
Authors:Roberto Henschel, Levon Khachatryan, Hayk Poghosyan, Daniil Hayrapetyan, Vahram Tadevosyan, Zhangyang Wang, Shant Navasardyan, Humphrey Shi
Text-to-video diffusion models enable the generation of high-quality videos that follow text instructions, making it easy to create diverse and individual content. However, existing approaches mostly focus on high-quality short video generation (typically 16 or 24 frames), ending up with hard-cuts when naively extended to the case of long video synthesis. To overcome these limitations, we introduce StreamingT2V, an autoregressive approach for long video generation of 80, 240, 600, 1200 or more frames with smooth transitions. The key components are:(i) a short-term memory block called conditional attention module (CAM), which conditions the current generation on the features extracted from the previous chunk via an attentional mechanism, leading to consistent chunk transitions, (ii) a long-term memory block called appearance preservation module, which extracts high-level scene and object features from the first video chunk to prevent the model from forgetting the initial scene, and (iii) a randomized blending approach that enables to apply a video enhancer autoregressively for infinitely long videos without inconsistencies between chunks. Experiments show that StreamingT2V generates high motion amount. In contrast, all competing image-to-video methods are prone to video stagnation when applied naively in an autoregressive manner. Thus, we propose with StreamingT2V a high-quality seamless text-to-long video generator that outperforms competitors with consistency and motion. Our code will be available at: https://github.com/Picsart-AI-Research/StreamingT2V
文本到视频扩散模型能够根据文本指令生成高质量的视频,使得创建多样化和个性化内容变得轻松。然而,现有方法主要集中在高质量短视频生成(通常为16或24帧),在扩展到长视频合成时会出现生硬剪辑的情况。为了克服这些限制,我们推出了StreamingT2V,这是一种用于生成80、240、600、1200或更多帧的长视频的自动回归方法,具有平滑过渡。关键组件包括:(i)一个名为条件注意模块(CAM)的短期记忆块,它通过注意机制根据从上一个块提取的特征来条件当前生成,从而实现一致的块过渡;(ii)一个名为外观保留模块的长期记忆块,它从第一个视频块中提取高级场景和对象特征,以防止模型忘记初始场景;(iii)一种随机混合方法,使视频增强器能够自动应用于无限长的视频,而不会在不同块之间出现不一致。实验表明,StreamingT2V能产生大量的运动。相比之下,所有竞争性的图像到视频的方法在采用自动回归方式时都容易出现视频停滞的情况。因此,我们提出StreamingT2V,这是一个高质量的无缝文本到长视频生成器,在一致性和运动方面超越竞争对手。我们的代码将在https://github.com/Picsart-AI-Research/StreamingT2V上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/Picsart-AI-Research/StreamingT2V
Summary
本文介绍了文本到视频扩散模型在生成高质量视频方面的应用,尤其是针对长视频生成的挑战。为解决现有方法的局限性,提出了一种新的方法StreamingT2V,通过引入短期记忆块(条件注意力模块)和长期记忆块(外观保留模块)以及随机混合技术,实现了高质量的长视频生成。该方法克服了现有方法的不足,表现出出色的连贯性和运动性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到视频扩散模型能生成遵循文本指令的高质量视频内容。
- 现有方法主要关注短视频生成,但在长视频合成时存在硬切割问题。
- StreamingT2V是一种用于长视频生成的方法,具有80帧及以上的流畅过渡功能。
- 条件注意力模块是实现一致过渡的关键组件之一。它根据注意力机制将当前生成与先前片段的特征联系起来。
- 外观保留模块作为长期记忆块,从第一个视频片段中提取高级场景和对象特征,防止模型忘记初始场景。
- 随机混合技术使得视频增强器可以应用于无限长的视频,而无需在片段之间出现不一致。
点此查看论文截图

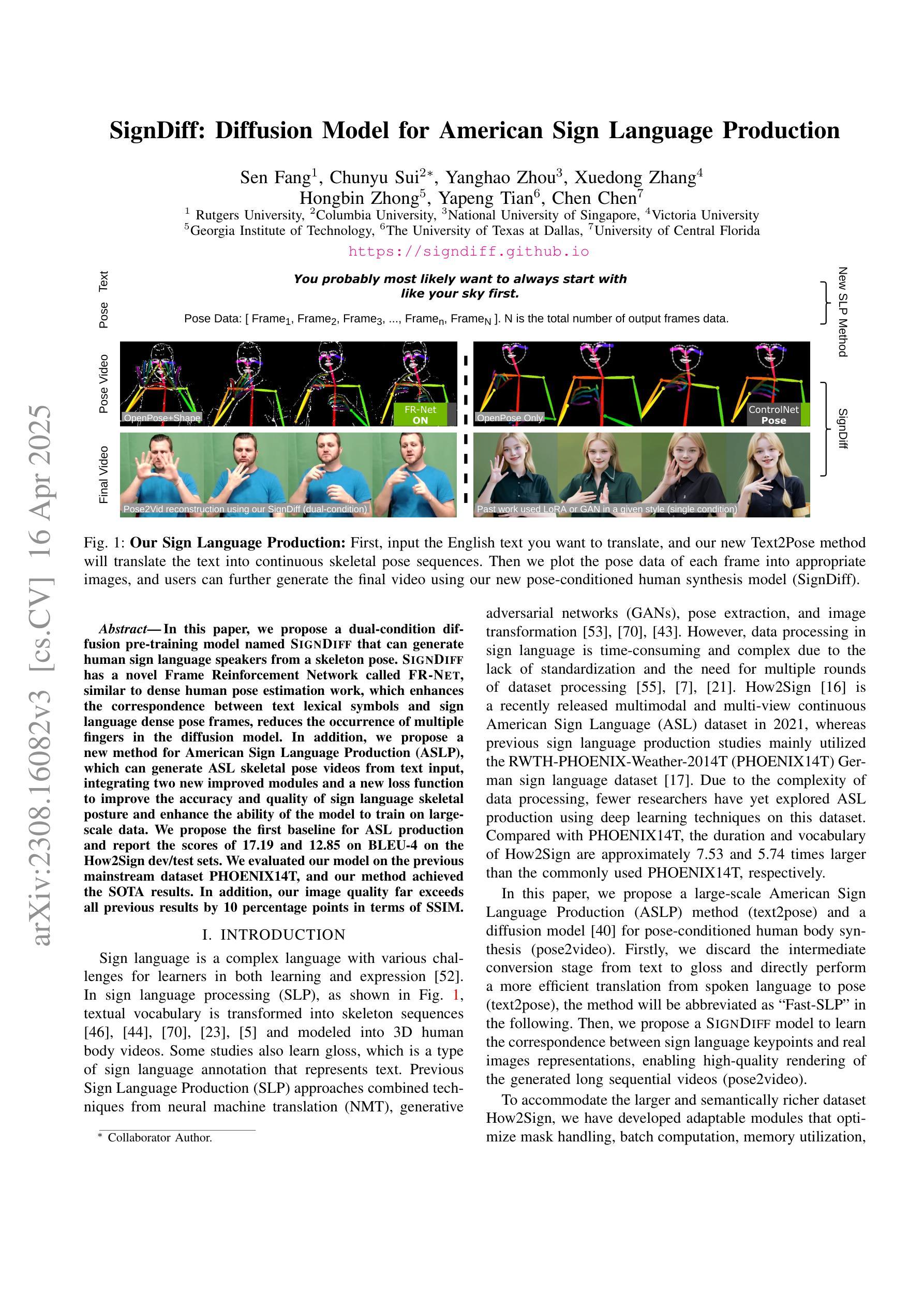
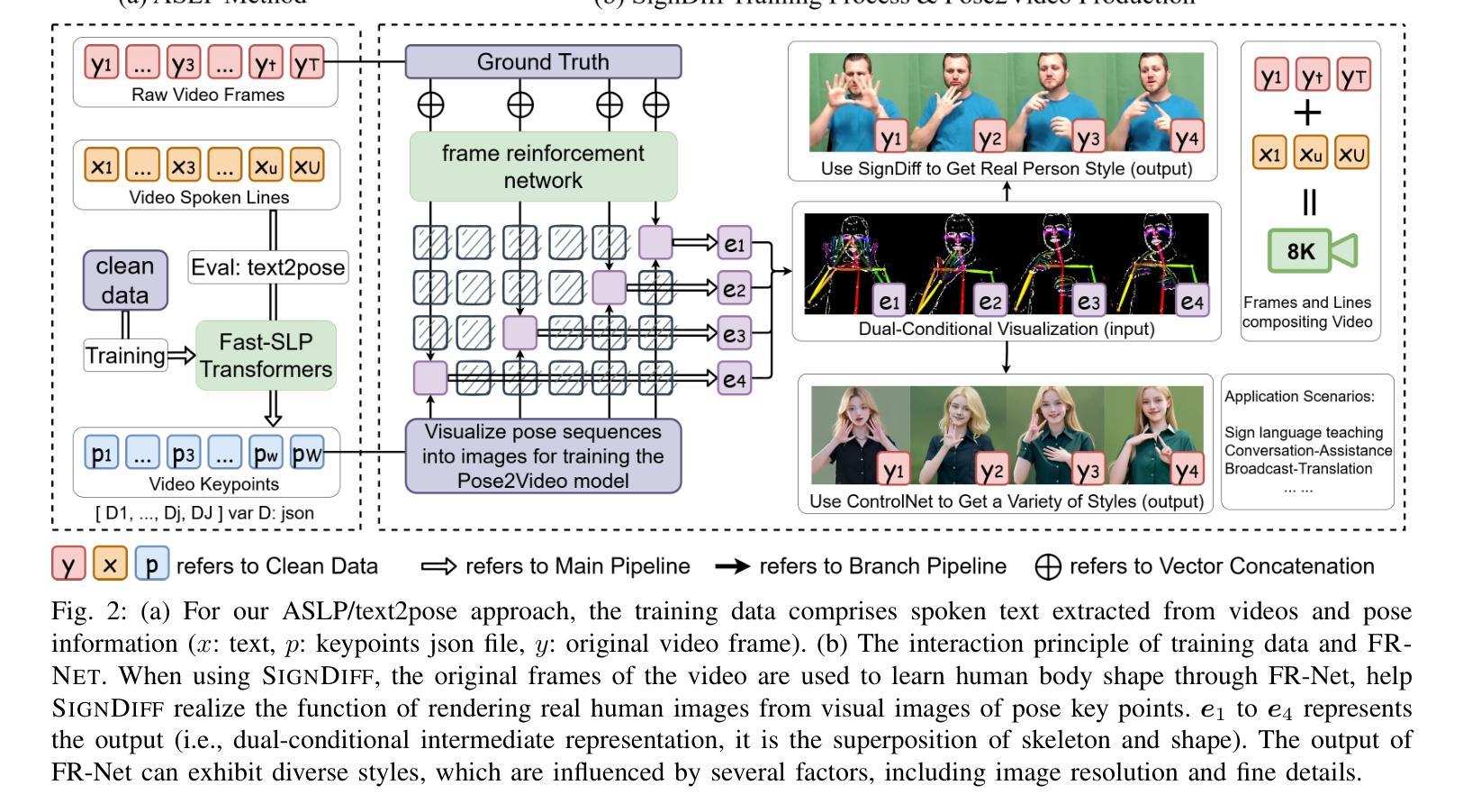
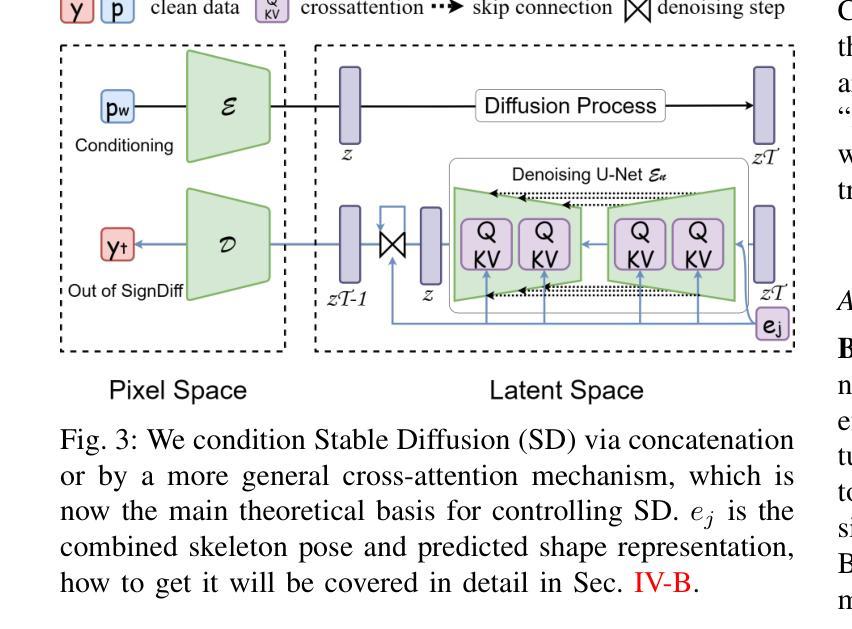
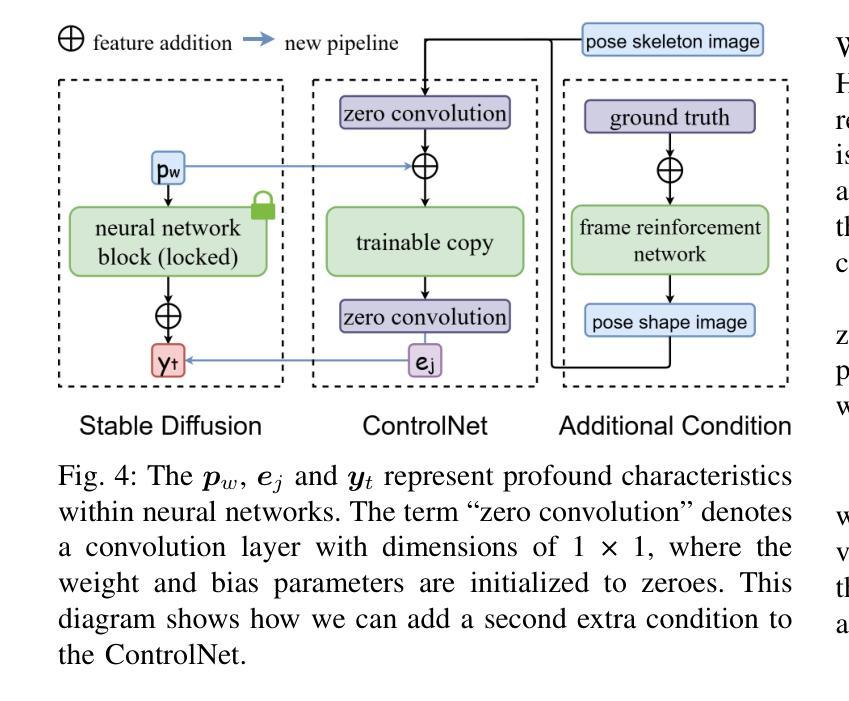
SignDiff: Diffusion Model for American Sign Language Production
Authors:Sen Fang, Chunyu Sui, Yanghao Zhou, Xuedong Zhang, Hongbin Zhong, Yapeng Tian, Chen Chen
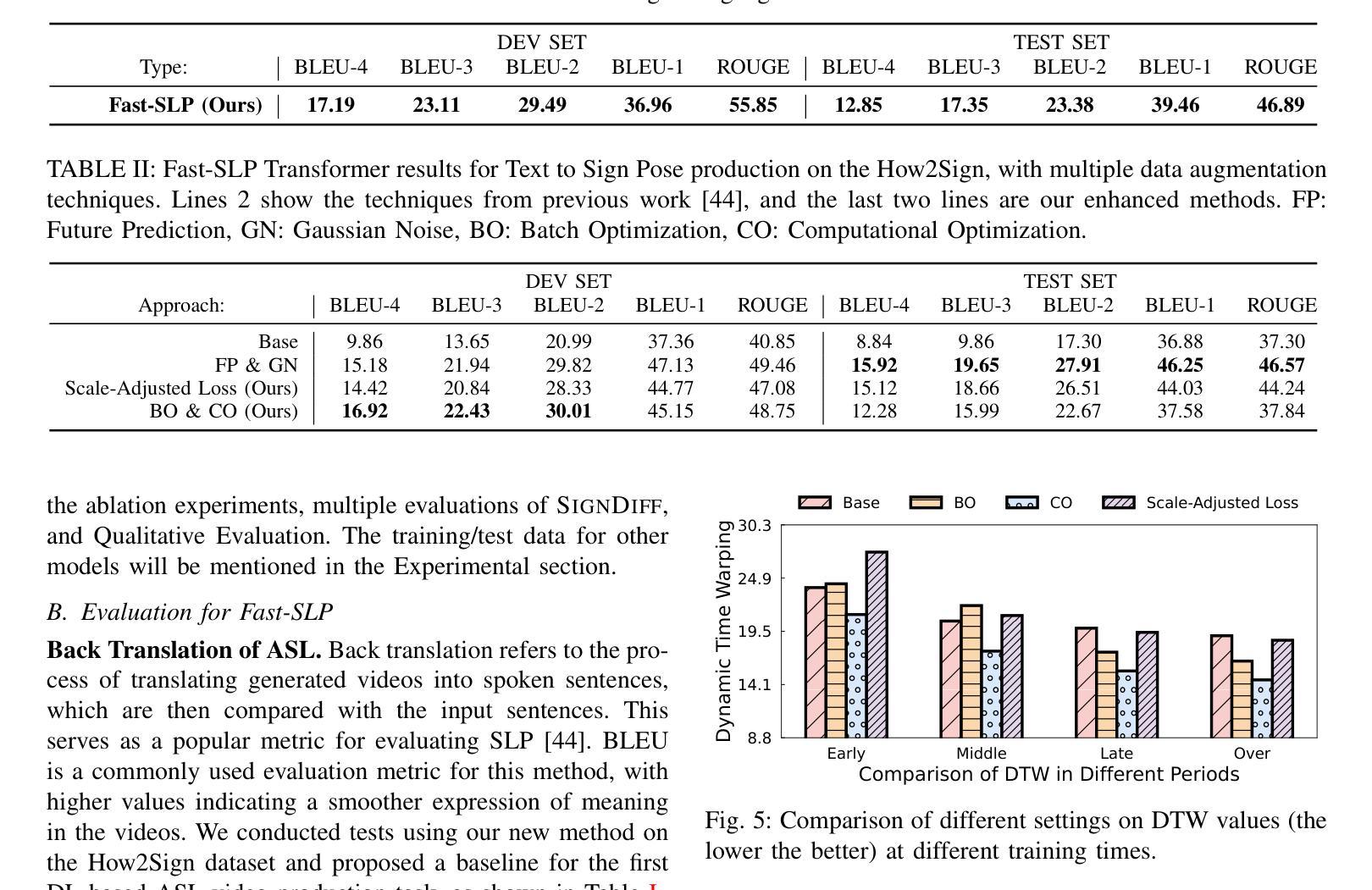
In this paper, we propose a dual-condition diffusion pre-training model named SignDiff that can generate human sign language speakers from a skeleton pose. SignDiff has a novel Frame Reinforcement Network called FR-Net, similar to dense human pose estimation work, which enhances the correspondence between text lexical symbols and sign language dense pose frames, reduces the occurrence of multiple fingers in the diffusion model. In addition, we propose a new method for American Sign Language Production (ASLP), which can generate ASL skeletal pose videos from text input, integrating two new improved modules and a new loss function to improve the accuracy and quality of sign language skeletal posture and enhance the ability of the model to train on large-scale data. We propose the first baseline for ASL production and report the scores of 17.19 and 12.85 on BLEU-4 on the How2Sign dev/test sets. We evaluated our model on the previous mainstream dataset PHOENIX14T, and the experiments achieved the SOTA results. In addition, our image quality far exceeds all previous results by 10 percentage points in terms of SSIM.
本文提出了一种名为SignDiff的双条件扩散预训练模型,该模型可以从骨架姿态生成人类手语。SignDiff具有一个名为FR-Net的新型框架强化网络,类似于密集人体姿态估计工作,它增强了文本词汇符号与手语密集姿态框架之间的对应关系,减少了扩散模型中多个手指的出现。此外,我们提出了一种新的美国手语生产(ASLP)方法,可以从文本输入生成ASL骨架姿态视频,集成两个新改进模块和新的损失函数,以提高手语骨架姿态的准确性和质量,并增强模型在大规模数据上的训练能力。我们为ASL生产提出了第一个基准线,并在How2Sign的dev/test集上报告了BLEU-4得分为17.19和12.85。我们在之前的主流数据集PHOENIX14T上评估了我们的模型,实验达到了SOTA结果。此外,我们的图像质量在SSIM方面超过了以前所有结果,提高了10个百分点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page at https://signdiff.github.io
Summary
文本提出了一种名为SignDiff的双条件扩散预训练模型,该模型可以从骨架姿态生成人类手势语言。SignDiff拥有一个新颖的帧强化网络FR-Net,类似于密集的人类姿态估计工作,它可以增强文本词汇符号与手势语言密集姿态帧之间的对应关系,减少扩散模型中多个手指的出现。此外,文本还提出了美国手势语言生产(ASLP)的新方法,可以从文本输入生成ASL骨架姿态视频,集成两个新改进模块和新的损失函数,以提高手势语言骨架姿态的准确性和质量,并增强模型在大规模数据上的训练能力。实验结果表明,该模型在How2Sign开发/测试集上的BLEU-4分数为17.19和12.85,并在PHOENIX14T主流数据集上取得了最佳结果。此外,我们的图像质量在SSIM方面超过了之前所有结果10个百分点。
Key Takeaways
- SignDiff是一个双条件扩散预训练模型,可从骨架姿态生成人类手势语言。
- SignDiff具有FR-Net网络,增强了文本与手势语言姿态之间的对应关系。
- 提出了美国手势语言生产(ASLP)的新方法,结合了两个改进模块和新的损失函数。
- 模型在How2Sign开发/测试集上的BLEU-4分数达到新的水平。
- 模型在PHOENIX14T数据集上取得了最佳结果。
- 与先前的结果相比,模型在图像质量上有了显著提高,特别是在SSIM方面。
点此查看论文截图