⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-18 更新
Logits DeConfusion with CLIP for Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Shuo Li, Fang Liu, Zehua Hao, Xinyi Wang, Lingling Li, Xu Liu, Puhua Chen, Wenping Ma
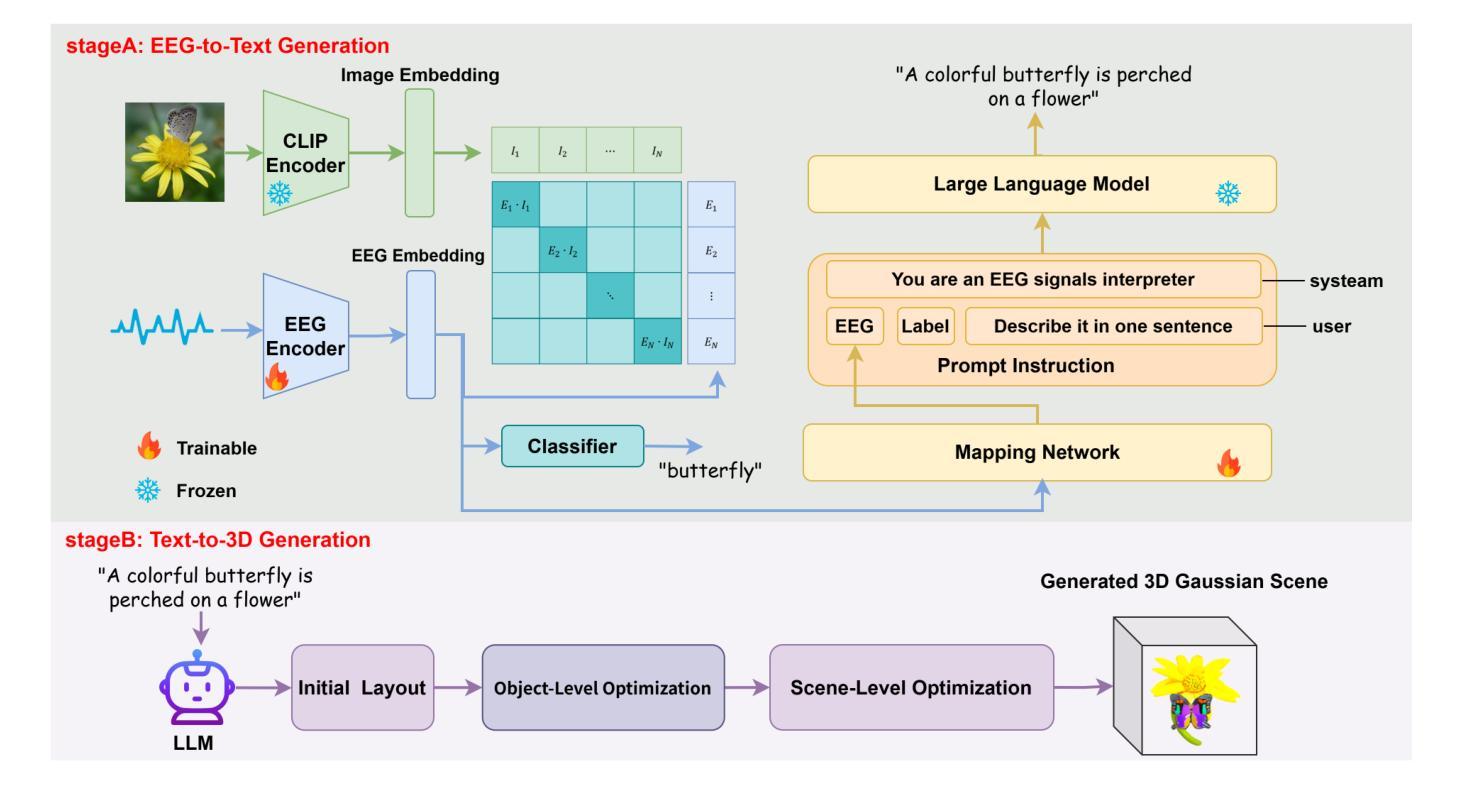
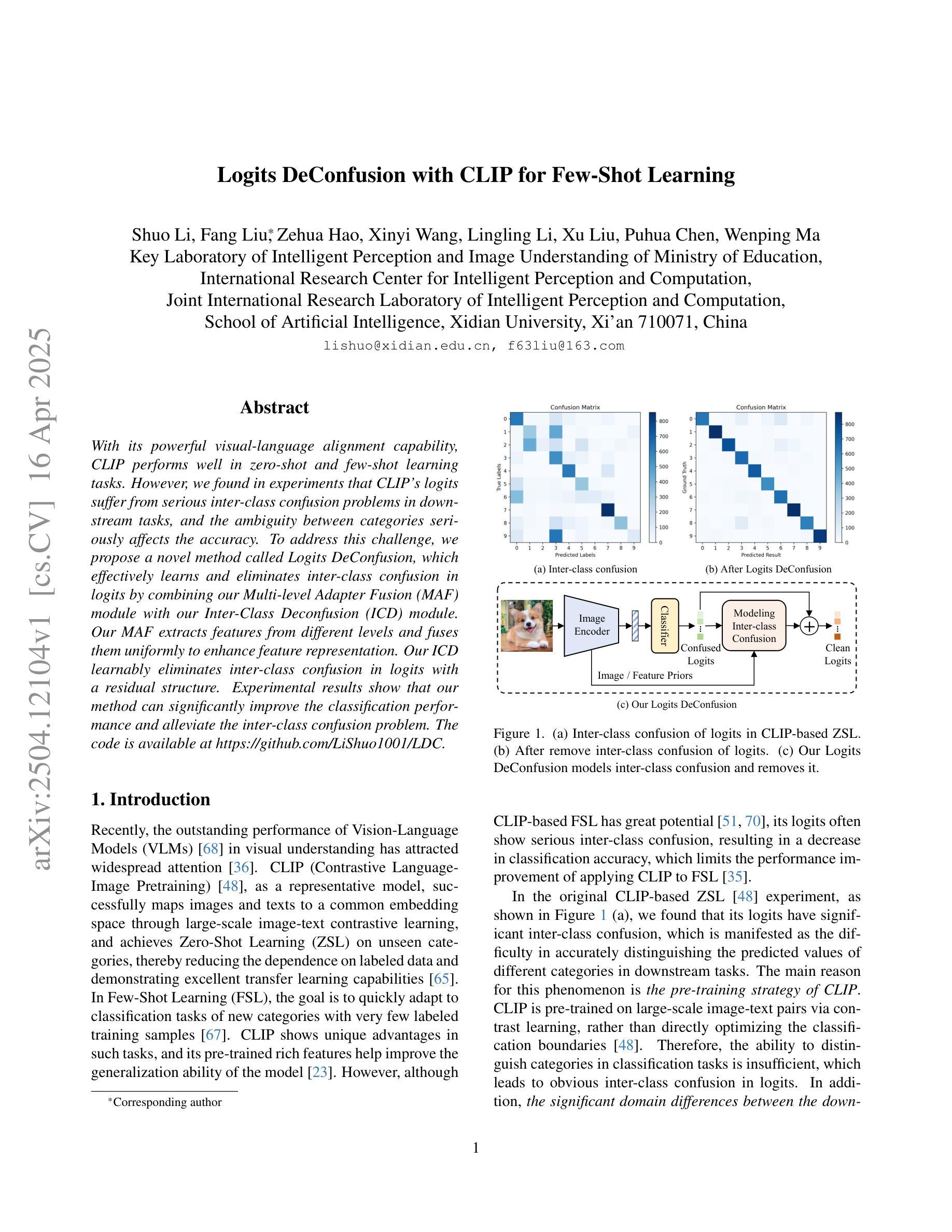
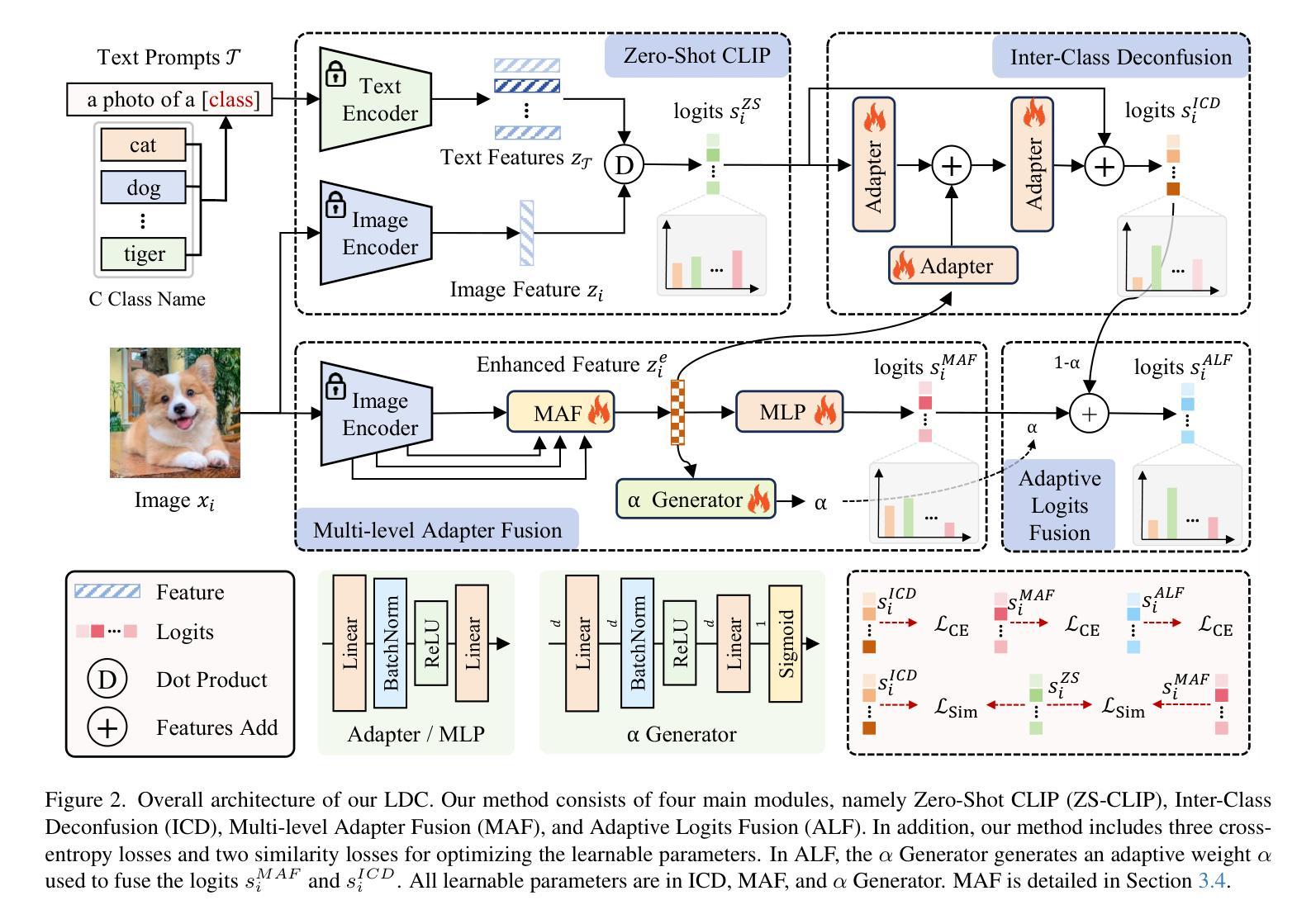
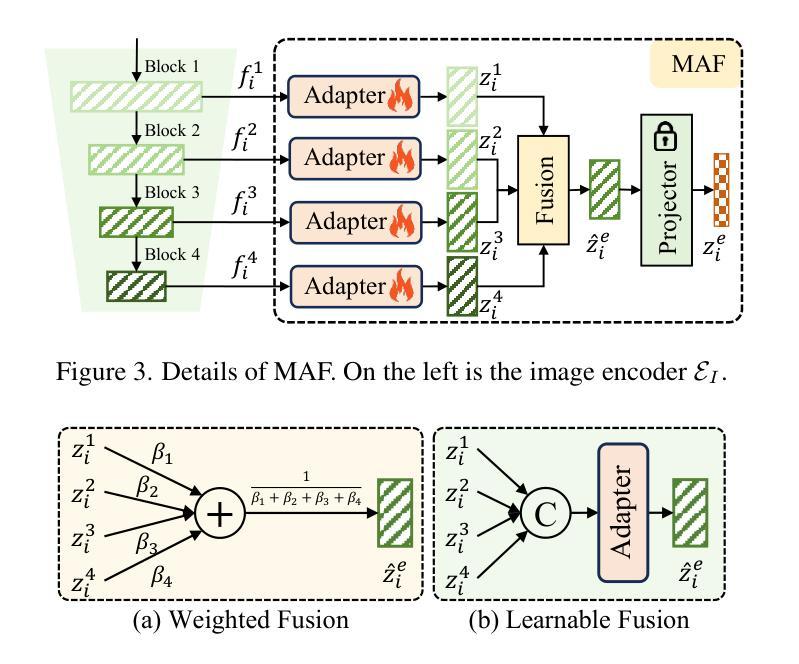
With its powerful visual-language alignment capability, CLIP performs well in zero-shot and few-shot learning tasks. However, we found in experiments that CLIP’s logits suffer from serious inter-class confusion problems in downstream tasks, and the ambiguity between categories seriously affects the accuracy. To address this challenge, we propose a novel method called Logits DeConfusion, which effectively learns and eliminates inter-class confusion in logits by combining our Multi-level Adapter Fusion (MAF) module with our Inter-Class Deconfusion (ICD) module. Our MAF extracts features from different levels and fuses them uniformly to enhance feature representation. Our ICD learnably eliminates inter-class confusion in logits with a residual structure. Experimental results show that our method can significantly improve the classification performance and alleviate the inter-class confusion problem. The code is available at https://github.com/LiShuo1001/LDC.
CLIP凭借其强大的视觉语言对齐能力,在零样本和少样本学习任务中表现良好。然而,我们在实验中发现CLIP的logits在下游任务中存在严重的跨类混淆问题,类别之间的模糊性严重影响了准确性。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种名为Logits DeConfusion的新方法,该方法通过结合我们的多层次适配器融合(MAF)模块和跨类去混淆(ICD)模块,有效地学习和消除logits中的跨类混淆。我们的MAF从不同层级提取特征,并对其进行统一融合,以增强特征表示。我们的ICD使用残差结构可学习地消除logits中的跨类混淆。实验结果表明,我们的方法可以显著提高分类性能,并缓解跨类混淆问题。代码可在https://github.com/LiShuo1001/LDC找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
CLIP模型具备强大的视觉语言对齐能力,在零样本和少样本学习任务中表现优异。但在下游任务中,CLIP的logits面临严重的类间混淆问题,影响准确性。为此,我们提出Logits DeConfusion方法,通过结合多级别适配器融合(MAF)和类间去混淆(ICD)模块,有效学习和消除类间混淆。MAF从不同级别提取特征并统一融合,增强特征表示。ICD使用残差结构可学习地消除logits中的类间混淆。实验结果显示,该方法能显著提高分类性能,缓解类间混淆问题。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP模型在零样本和少样本学习任务中表现出强大的视觉语言对齐能力。
- CLIP的logits在下游任务中存在严重的类间混淆问题。
- Logits DeConfusion方法通过结合MAF和ICD模块,有效学习和消除类间混淆。
- MAF模块能够提取不同级别的特征并进行统一融合,增强特征表示。
- ICD模块使用残差结构,能够学习地消除logits中的类间混淆。
- Logits DeConfusion方法能显著提高分类性能,并缓解类间混淆问题。
点此查看论文截图
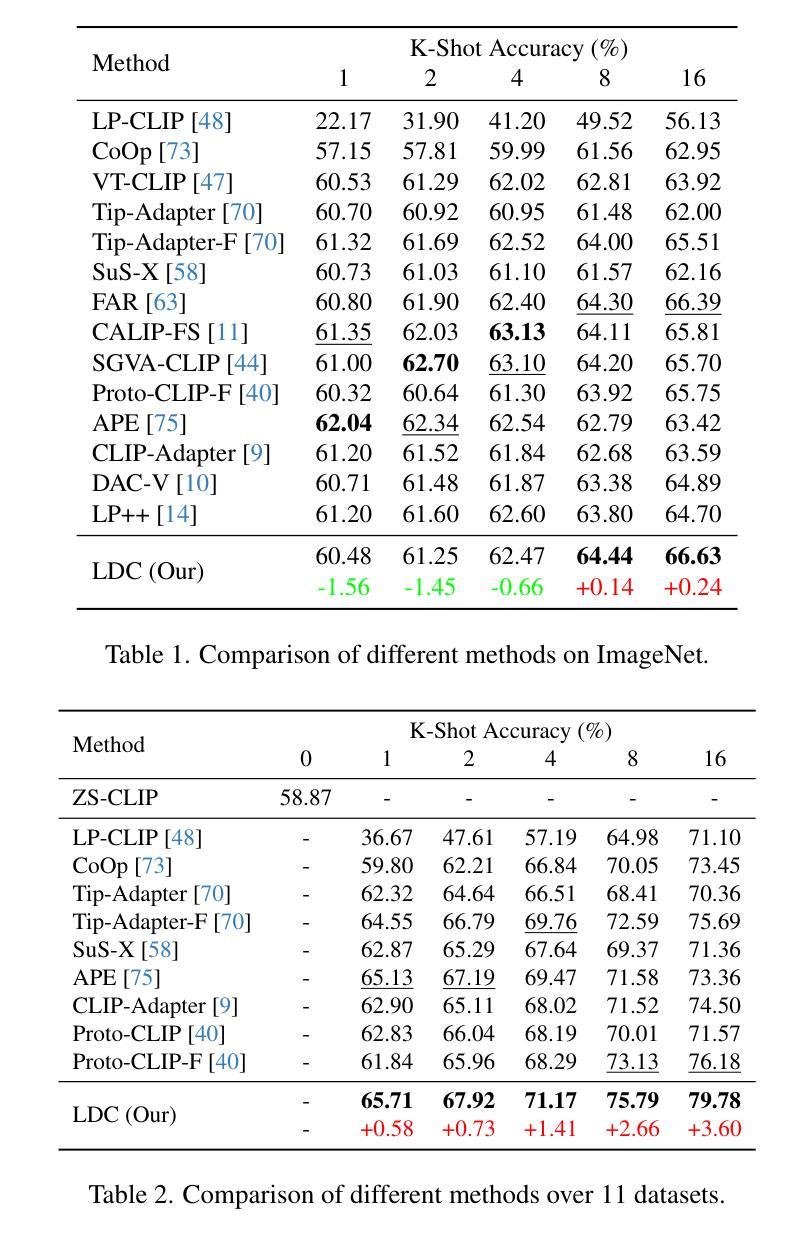
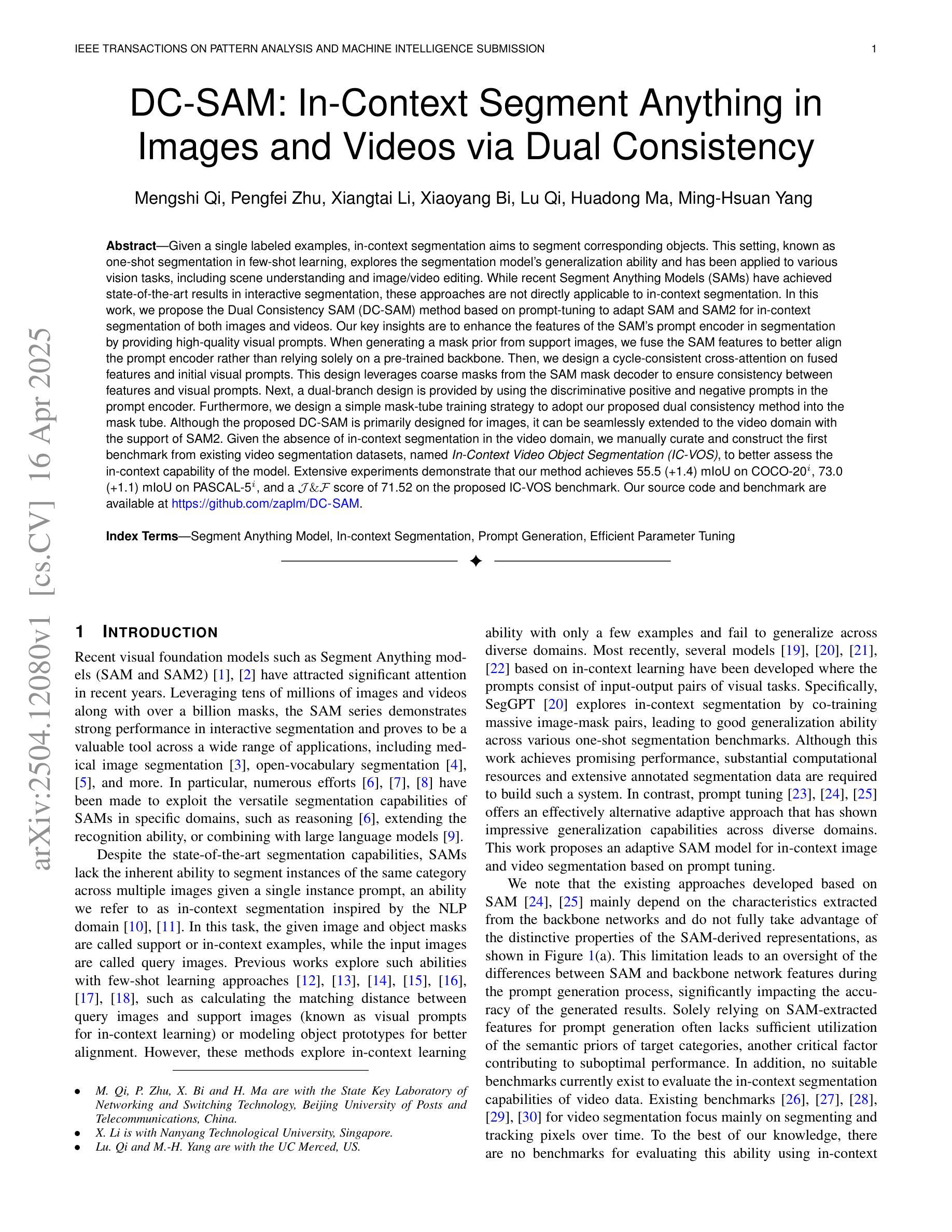
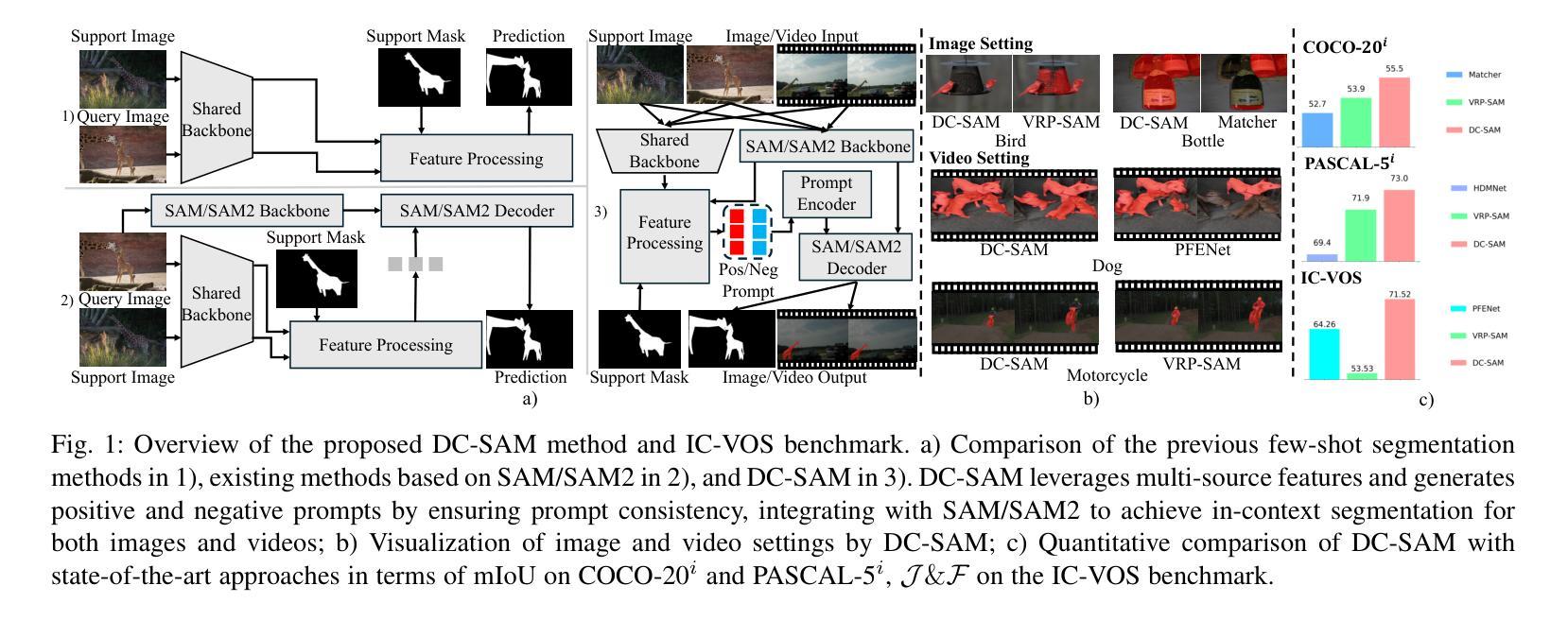
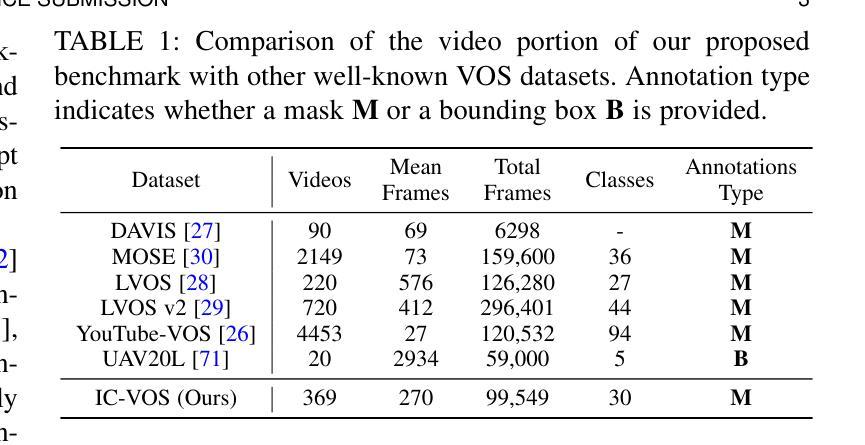
DC-SAM: In-Context Segment Anything in Images and Videos via Dual Consistency
Authors:Mengshi Qi, Pengfei Zhu, Xiangtai Li, Xiaoyang Bi, Lu Qi, Huadong Ma, Ming-Hsuan Yang
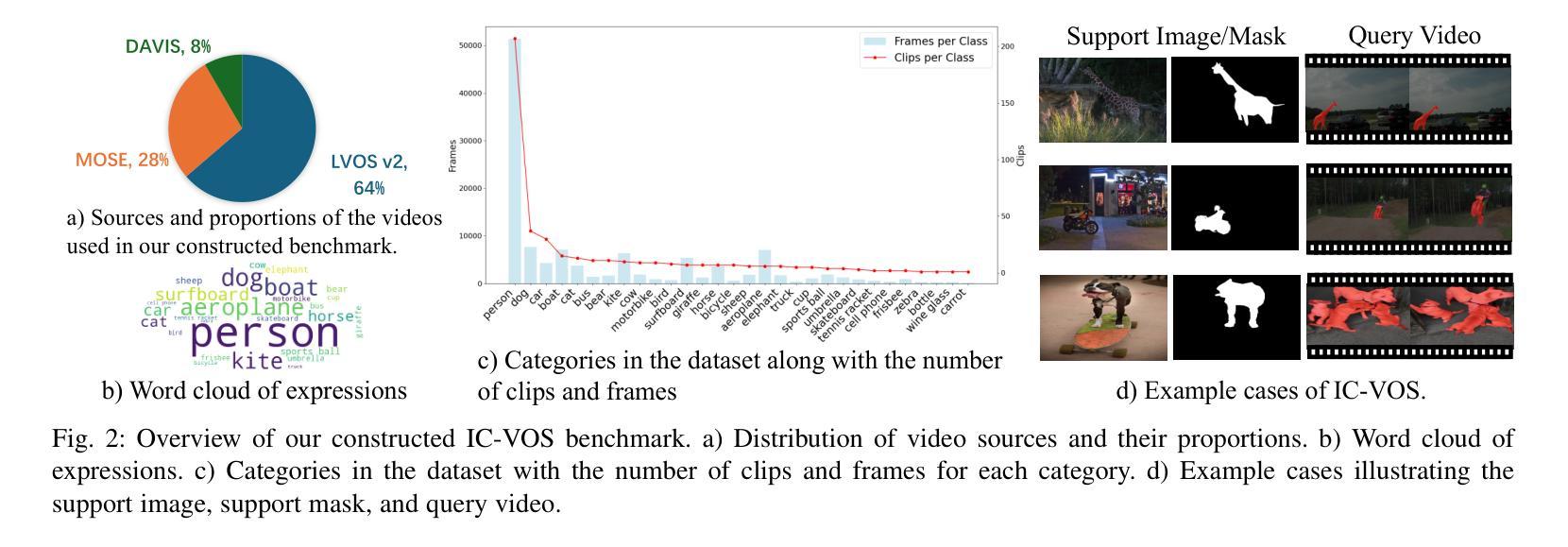
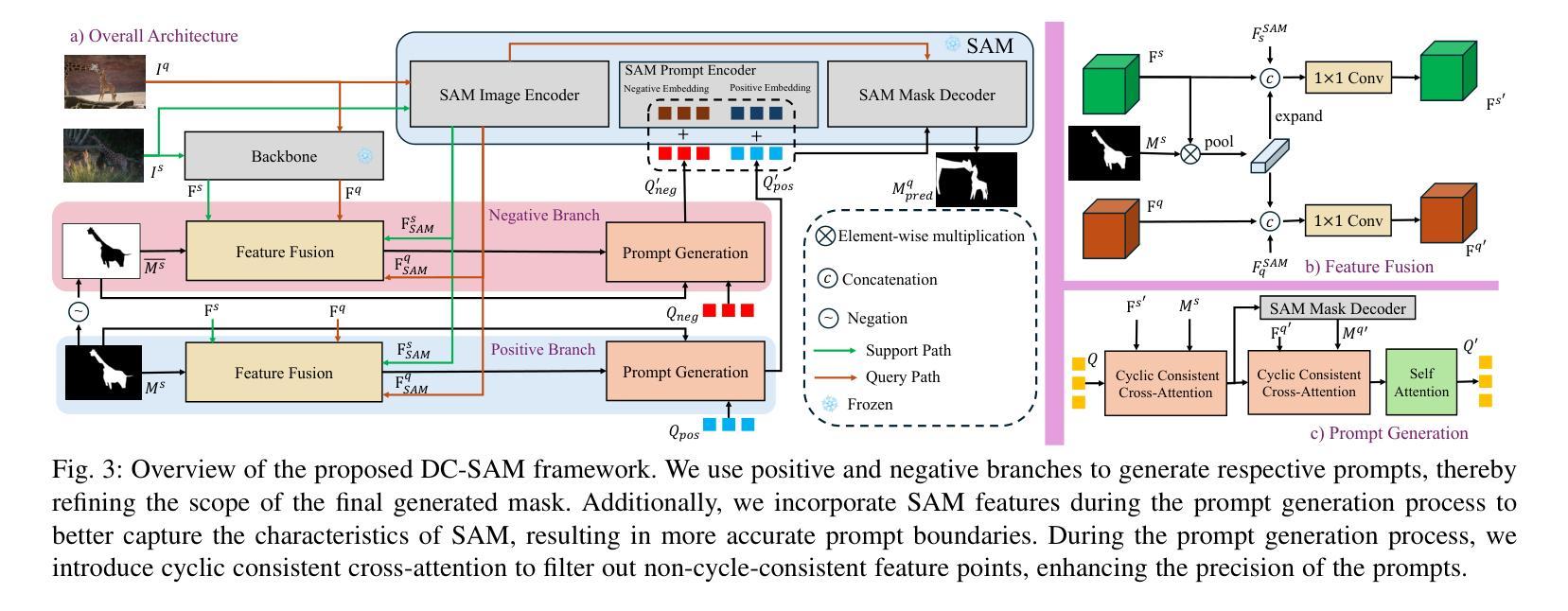
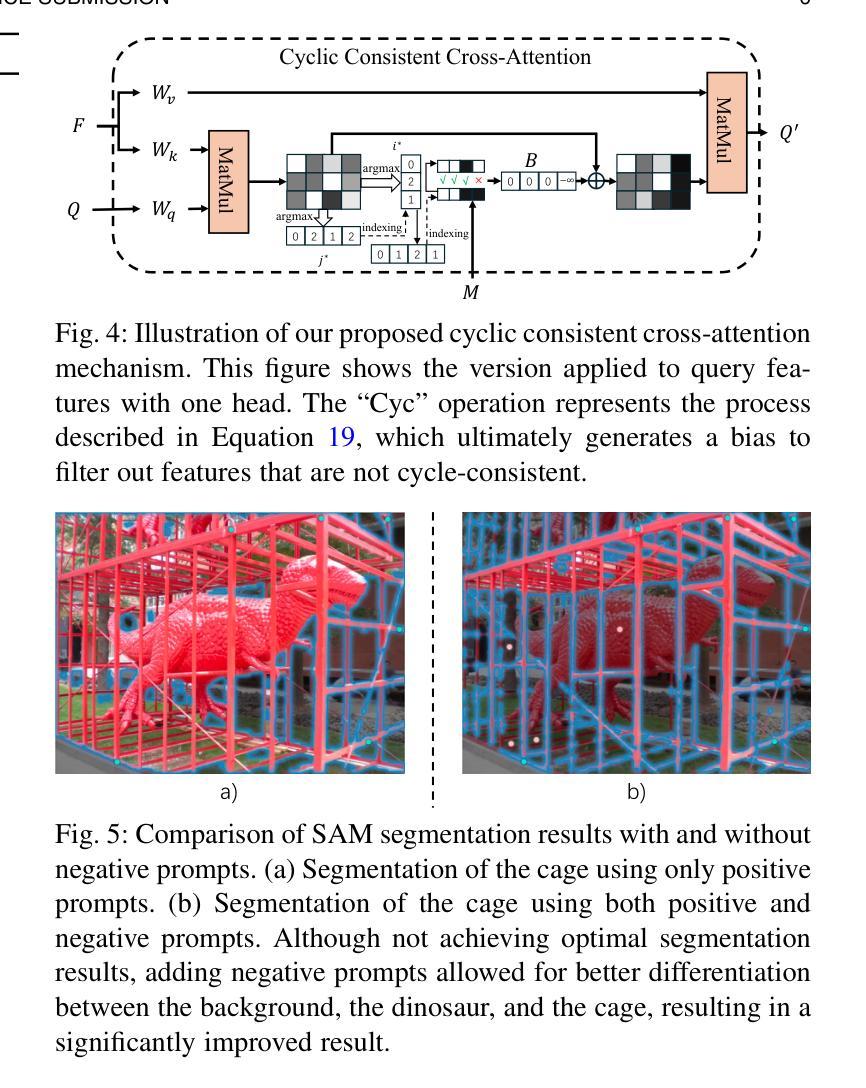
Given a single labeled example, in-context segmentation aims to segment corresponding objects. This setting, known as one-shot segmentation in few-shot learning, explores the segmentation model’s generalization ability and has been applied to various vision tasks, including scene understanding and image/video editing. While recent Segment Anything Models have achieved state-of-the-art results in interactive segmentation, these approaches are not directly applicable to in-context segmentation. In this work, we propose the Dual Consistency SAM (DC-SAM) method based on prompt-tuning to adapt SAM and SAM2 for in-context segmentation of both images and videos. Our key insights are to enhance the features of the SAM’s prompt encoder in segmentation by providing high-quality visual prompts. When generating a mask prior, we fuse the SAM features to better align the prompt encoder. Then, we design a cycle-consistent cross-attention on fused features and initial visual prompts. Next, a dual-branch design is provided by using the discriminative positive and negative prompts in the prompt encoder. Furthermore, we design a simple mask-tube training strategy to adopt our proposed dual consistency method into the mask tube. Although the proposed DC-SAM is primarily designed for images, it can be seamlessly extended to the video domain with the support of SAM2. Given the absence of in-context segmentation in the video domain, we manually curate and construct the first benchmark from existing video segmentation datasets, named In-Context Video Object Segmentation (IC-VOS), to better assess the in-context capability of the model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves 55.5 (+1.4) mIoU on COCO-20i, 73.0 (+1.1) mIoU on PASCAL-5i, and a J&F score of 71.52 on the proposed IC-VOS benchmark. Our source code and benchmark are available at https://github.com/zaplm/DC-SAM.
给定一个带标签的样本,上下文内分割旨在分割对应的目标对象。这种设置被称为小样本学习中的一次分割,旨在探索分割模型的泛化能力,并已应用于各种视觉任务,包括场景理解和图像/视频编辑。虽然最近的任何事物分割模型在交互式分割方面达到了最新结果,但这些方法并不直接适用于上下文分割。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于提示调整的双一致性SAM(DC-SAM)方法,以适应图像和视频的上下文分割。我们的关键见解是通过提供高质量视觉提示来增强SAM提示编码器的分割特征。在生成遮罩先验时,我们融合SAM特征以更好地对齐提示编码器。然后,我们在融合的特征和初始视觉提示上设计了一个循环一致的交叉注意力。接下来,通过使用提示编码器中的鉴别性正负提示来实现双分支设计。此外,我们设计了一个简单的遮罩管训练策略,将所提出的双一致性方法应用于遮罩管中。虽然提出的DC-SAM主要为图像设计,但在SAM2的支持下,它可以无缝扩展到视频领域。鉴于视频领域缺乏上下文分割,我们从现有的视频分割数据集中手动筛选和构建了一个名为IC-VOS(上下文视频目标分割)的第一个基准测试集,以更好地评估模型的上下文能力。大量实验表明,我们的方法在COCO-20i上实现了55.5(+1.4)的mIoU,在PASCAL-5i上实现了73.0(+1.1)的mIoU,在提出的IC-VOS基准测试集上达到了71.52的J&F得分。我们的源代码和基准测试集可在https://github.com/zaplm/DC-SAM获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文关注于单次示例下的目标分割任务,即给定单个标记样本进行上下文分割。提出一种基于提示调整(prompt-tuning)的Dual Consistency SAM(DC-SAM)方法,用于图像和视频上下文分割。通过增强SAM提示编码器的特征和提高掩模先验的质量,设计循环一致的跨注意力机制和双重分支设计,实现在图像和视频的上下文分割任务中的优秀表现。并创建了第一个针对视频域上下文分割的IC-VOS基准测试集。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种名为DC-SAM的方法,基于提示调整(prompt-tuning)技术,用于适应上下文分割任务。
- DC-SAM方法通过增强SAM提示编码器的特征质量来提高分割性能。
- DC-SAM采用掩模先验生成,并通过融合SAM特征进行改进。
- 引入循环一致的跨注意力机制来加强模型的特征对齐。
- 设计了双重分支设计,使用判别性的正负提示在提示编码器中进行优化。
- 提出了一种简单的掩模管训练策略,将双一致性方法纳入掩模管中。
点此查看论文截图
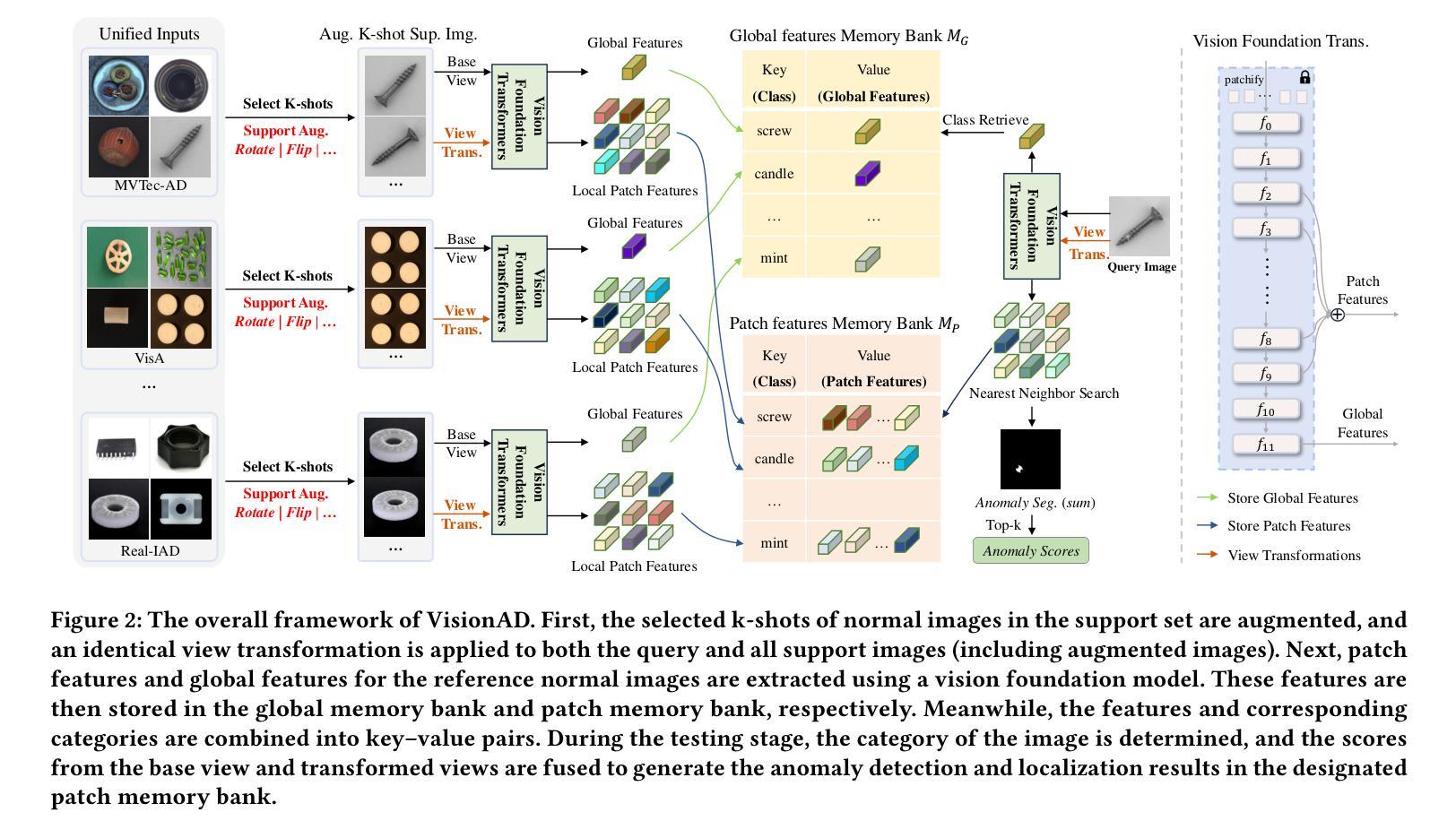
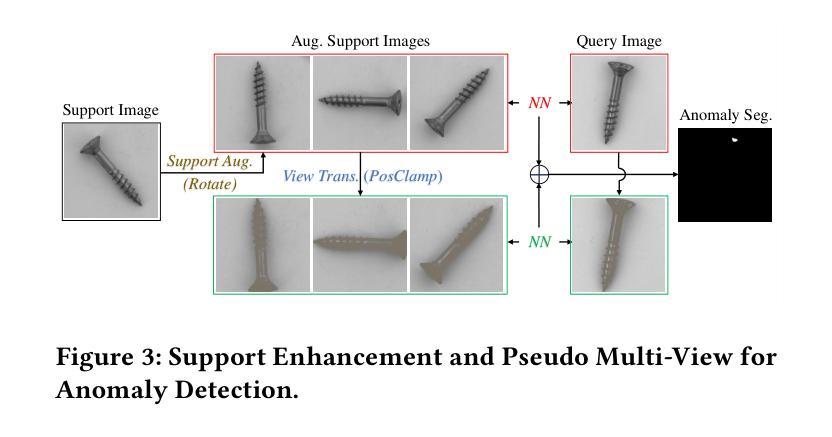
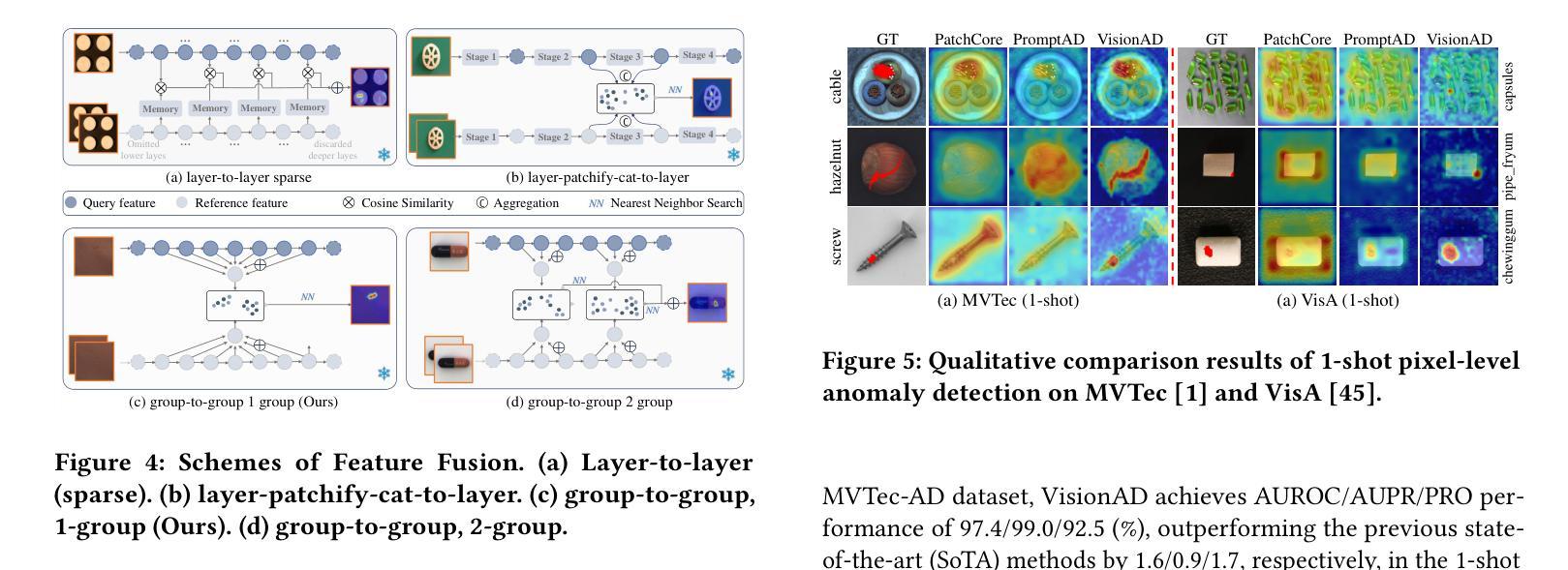
Search is All You Need for Few-shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Qishan Wang, Jia Guo, Shuyong Gao, Haofen Wang, Li Xiong, Junjie Hu, Hanqi Guo, Wenqiang Zhang
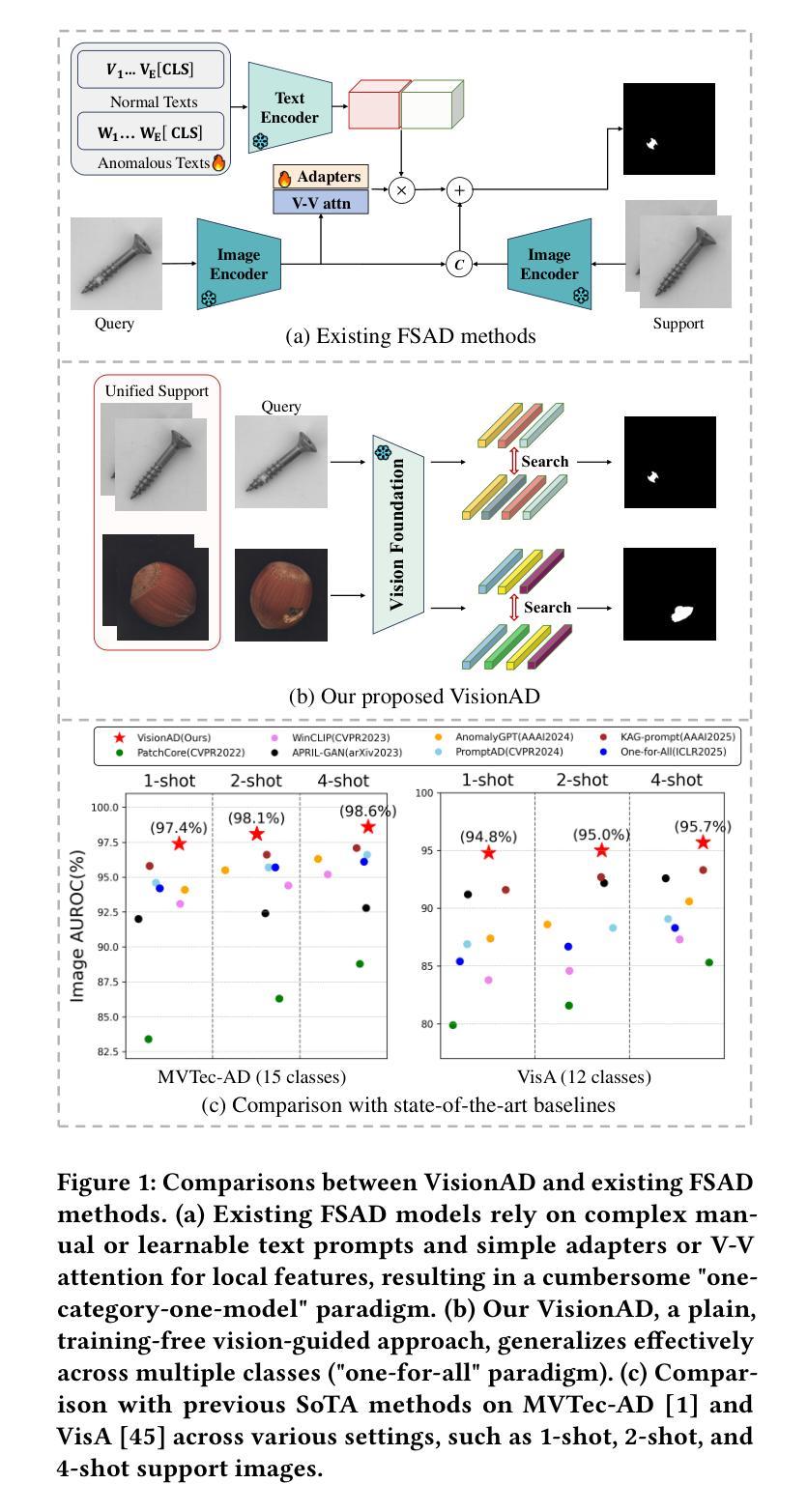
Few-shot anomaly detection (FSAD) has emerged as a crucial yet challenging task in industrial inspection, where normal distribution modeling must be accomplished with only a few normal images. While existing approaches typically employ multi-modal foundation models combining language and vision modalities for prompt-guided anomaly detection, these methods often demand sophisticated prompt engineering and extensive manual tuning. In this paper, we demonstrate that a straightforward nearest-neighbor search framework can surpass state-of-the-art performance in both single-class and multi-class FSAD scenarios. Our proposed method, VisionAD, consists of four simple yet essential components: (1) scalable vision foundation models that extract universal and discriminative features; (2) dual augmentation strategies - support augmentation to enhance feature matching adaptability and query augmentation to address the oversights of single-view prediction; (3) multi-layer feature integration that captures both low-frequency global context and high-frequency local details with minimal computational overhead; and (4) a class-aware visual memory bank enabling efficient one-for-all multi-class detection. Extensive evaluations across MVTec-AD, VisA, and Real-IAD benchmarks demonstrate VisionAD’s exceptional performance. Using only 1 normal images as support, our method achieves remarkable image-level AUROC scores of 97.4%, 94.8%, and 70.8% respectively, outperforming current state-of-the-art approaches by significant margins (+1.6%, +3.2%, and +1.4%). The training-free nature and superior few-shot capabilities of VisionAD make it particularly appealing for real-world applications where samples are scarce or expensive to obtain. Code is available at https://github.com/Qiqigeww/VisionAD.
少量样本异常检测(FSAD)在工业检测中是一项至关重要且充满挑战的任务,只需要少量的正常图像即可完成正常分布建模。尽管现有方法通常采用多模态基础模型,结合语言和视觉模式进行提示引导异常检测,但这些方法往往需要进行复杂的提示工程和大量的手动调整。在本文中,我们展示了简单的最近邻搜索框架可以在单类和多类FSAD场景中超越最新技术性能。我们提出的方法VisionAD由四个简单但至关重要的组件构成:(1)可扩展的视觉基础模型,用于提取通用和判别特征;(2)双增强策略——支持增强以提高特征匹配的适应性,查询增强以解决单视图预测的遗漏;(3)多层特征融合,以最小的计算开销捕获低频全局上下文和高频局部细节;(4)类感知视觉内存库,实现高效的一对多类检测。在MVTec-AD、VisA和Real-IAD等多个基准测试上的广泛评估表明,VisionAD具有卓越的性能。仅使用1张正常图像作为支持,我们的方法在图像级AUROC得分上分别实现了97.4%、94.8%和70.8%的显著成绩,显著优于当前最新方法(分别提高1.6%、3.2%和1.4%)。VisionAD的无训练性质和优越的少量样本能力使其特别适用于样本稀缺或昂贵的实际应用场景。代码可访问:https://github.com/Qiqigeww/VisionAD。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
少数样本异常检测(FSAD)在工业检测中是一项重要且具有挑战性的任务,只需少量正常图像即可完成正常分布建模。现有方法通常采用多模态基础模型结合语言和视觉模态进行提示引导异常检测,但需求复杂的提示工程和繁琐的手动调整。本研究展示了一个简单的最近邻搜索框架,在单类和多类FSAD场景中均超越现有技术性能。方法包括四个关键部分:可扩展的视觉基础模型、双重增强策略、多层特征融合和类感知视觉记忆库。在MVTec-AD、VisA和Real-IAD基准测试上的评估证明了其卓越性能。仅使用一张正常图像作为支持,我们的方法在图像级AUROC得分上实现了惊人的成绩,显著优于当前先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- 少数样本异常检测(FSAD)在工业检测中具有重要意义,仅需少量正常图像进行正常分布建模。
- 现有方法通常结合语言和视觉模态进行异常检测,但需求复杂的提示工程和手动调整。
- 本研究提出一个简洁的VisionAD方法,包含四个关键组件:可扩展的视觉基础模型、双重增强策略、多层特征融合和类感知视觉记忆库。
- VisionAD在MVTec-AD、VisA和Real-IAD等多个基准测试上表现出卓越性能。
- 使用仅一张正常图像作为支持,VisionAD在图像级AUROC得分上实现显著成绩。
- VisionAD具有无需训练的优势,特别适用于样本稀缺或获取成本高昂的实际应用场景。
点此查看论文截图

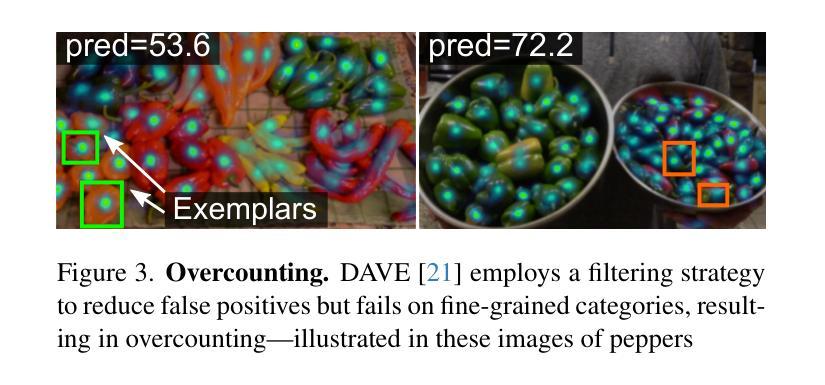
Learning What NOT to Count
Authors:Adriano D’Alessandro, Ali Mahdavi-Amiri, Ghassan Hamarneh
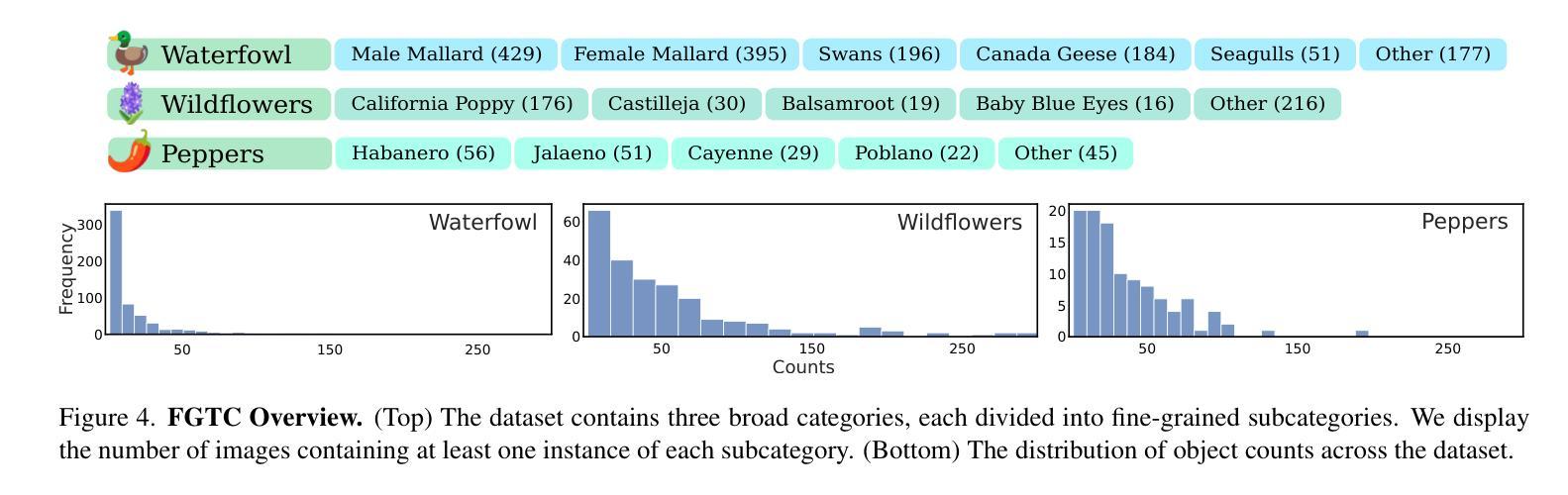
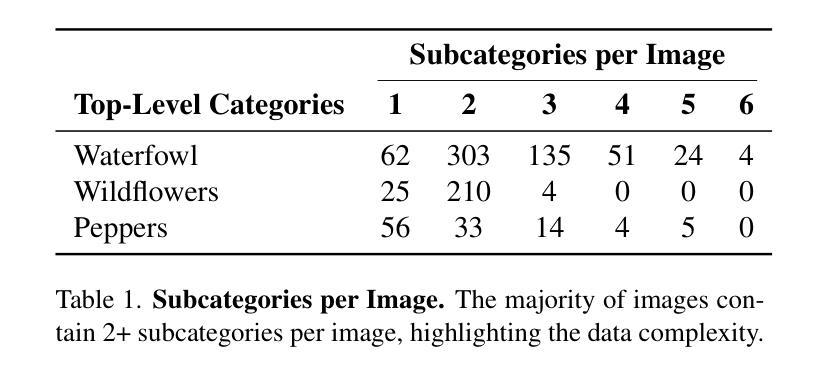
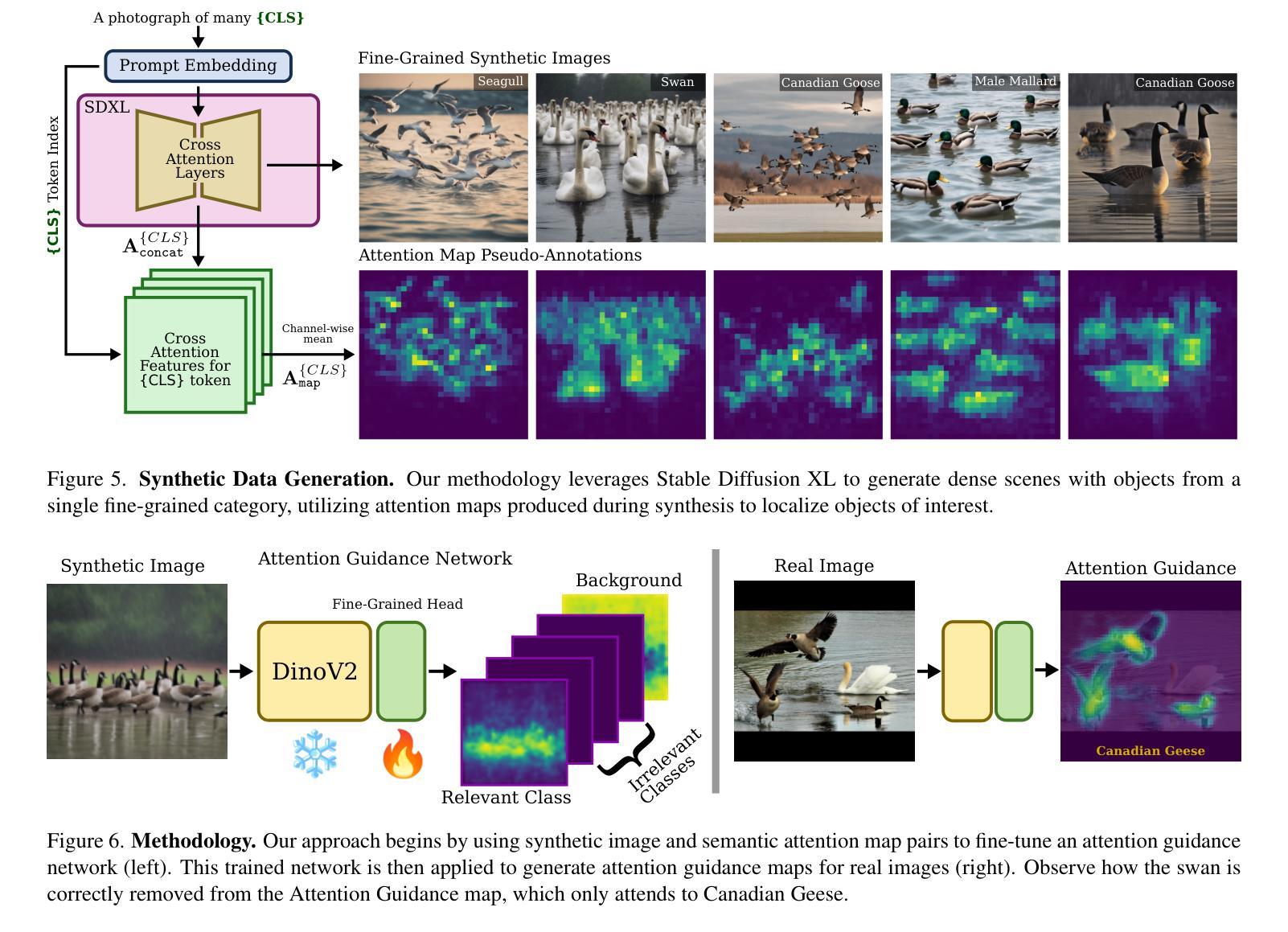
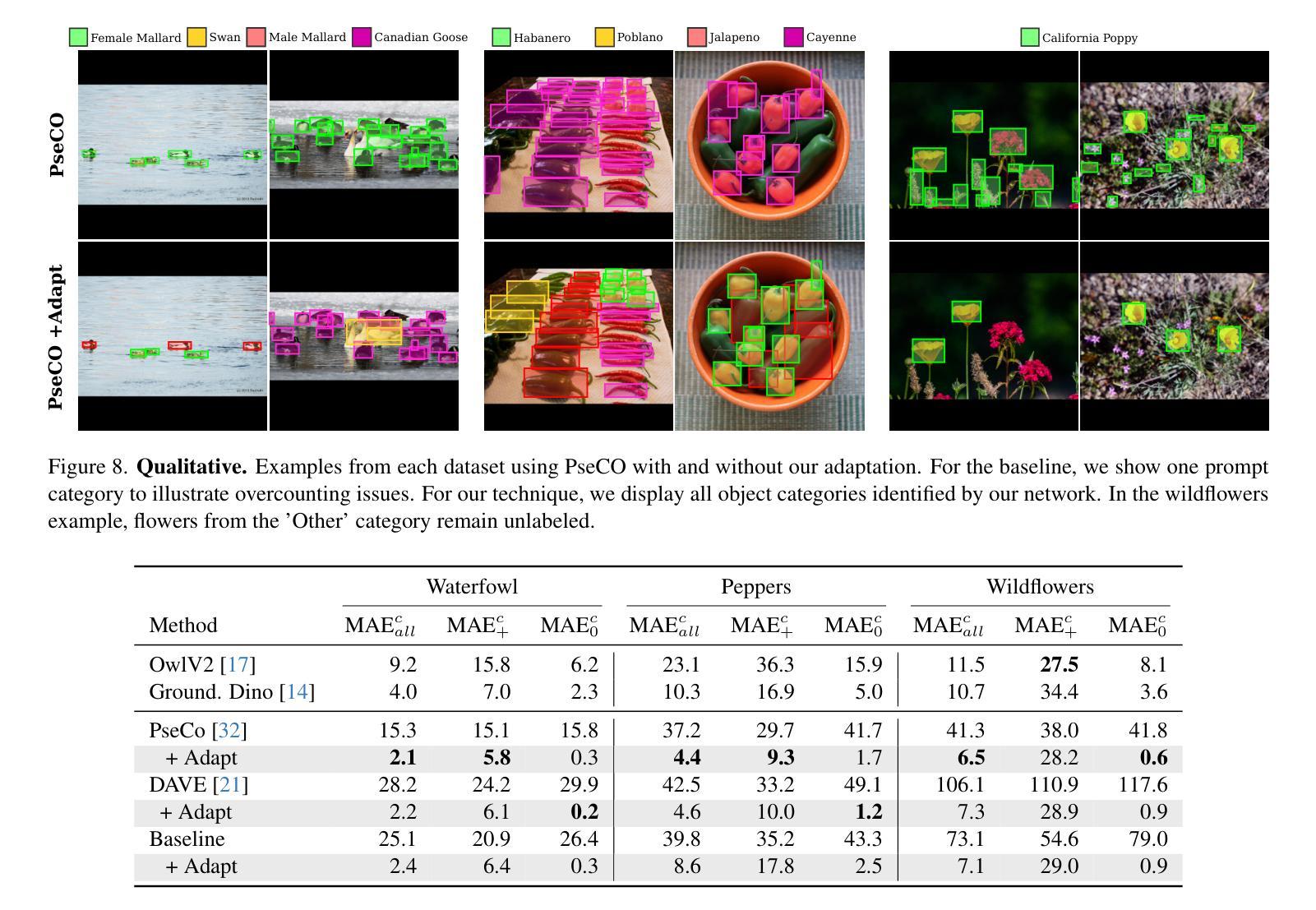
Few/zero-shot object counting methods reduce the need for extensive annotations but often struggle to distinguish between fine-grained categories, especially when multiple similar objects appear in the same scene. To address this limitation, we propose an annotation-free approach that enables the seamless integration of new fine-grained categories into existing few/zero-shot counting models. By leveraging latent generative models, we synthesize high-quality, category-specific crowded scenes, providing a rich training source for adapting to new categories without manual labeling. Our approach introduces an attention prediction network that identifies fine-grained category boundaries trained using only synthetic pseudo-annotated data. At inference, these fine-grained attention estimates refine the output of existing few/zero-shot counting networks. To benchmark our method, we further introduce the FGTC dataset, a taxonomy-specific fine-grained object counting dataset for natural images. Our method substantially enhances pre-trained state-of-the-art models on fine-grained taxon counting tasks, while using only synthetic data. Code and data to be released upon acceptance.
少量/零样本目标计数方法减少了大量标注的需求,但在区分精细类别时常常遇到困难,特别是在同一场景中出现多个相似物体时。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种无需标注的方法,可以无缝地将新的精细类别集成到现有的少量/零样本计数模型中。通过利用潜在生成模型,我们合成高质量、特定类别的拥挤场景,为适应新类别提供了丰富的训练源,无需手动标注。我们的方法引入了一个注意力预测网络,该网络使用仅合成伪注释数据来训练精细类别边界。在推断时,这些精细的注意力估计值会优化现有的少量/零样本计数网络的输出。为了评估我们的方法,我们还引入了FGTC数据集,这是一个针对自然图像的特定分类精细目标计数数据集。我们的方法在精细类别计数任务上大幅提高了预训练的最先进模型的表现,且仅使用合成数据。论文通过后将公开代码和数据。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
本文提出了一种无需标注的精细粒度目标计数方法,通过利用潜在生成模型合成高质量、特定类别的拥挤场景,为现有少数或零样本计数模型适应新类别提供了丰富的训练来源。引入注意力预测网络来识别仅使用合成伪标注数据训练的精细粒度类别边界。在推理过程中,这些精细粒度注意力估计对现有的少数或零样本计数网络输出进行了改进。新方法极大地提升了预训练先进模型在精细粒度分类计数任务上的性能,且仅使用合成数据。
关键见解
- 少数或零样本目标计数方法可以减少对大量标注的需求,但在区分精细粒度类别时经常遇到困难。
- 提出了一种无需标注的精细粒度计数方法,利用潜在生成模型合成特定类别的拥挤场景。
- 通过引入注意力预测网络,能够使用仅合成的伪标注数据进行训练,识别精细粒度类别边界。
- 提出了新的数据集FGTC,专为自然图像的精细粒度目标计数而设计。
- 方法在预训练的先进模型上显著提高了在精细粒度计数任务上的性能。
- 该方法仅使用合成数据,降低了对真实标注数据的依赖。
- 代码和数据将在接受后发布。
点此查看论文截图



Can GPT tell us why these images are synthesized? Empowering Multimodal Large Language Models for Forensics
Authors:Yiran He, Yun Cao, Bowen Yang, Zeyu Zhang
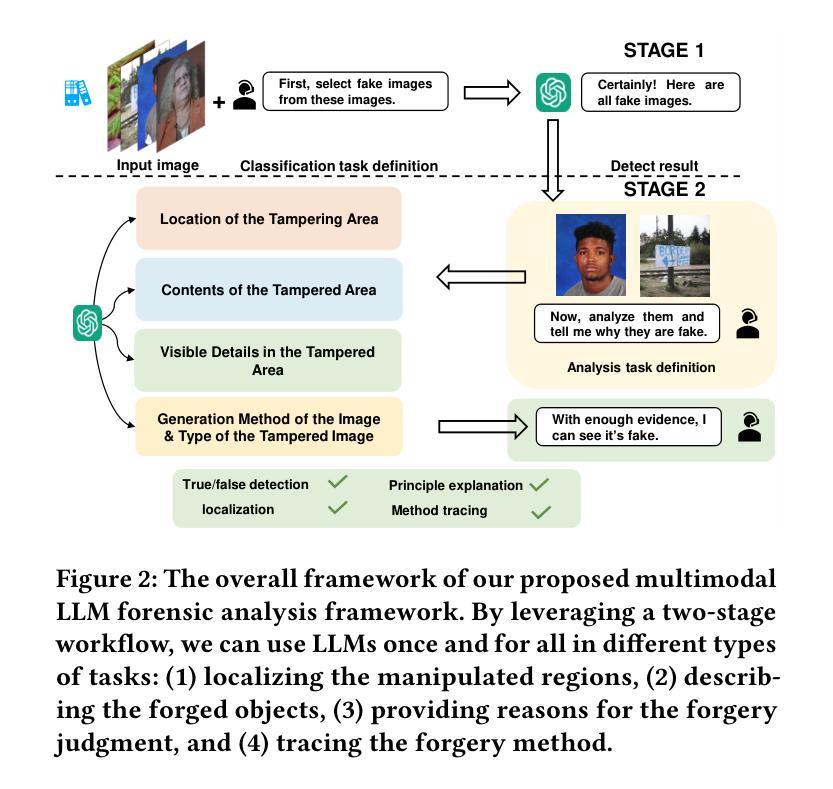
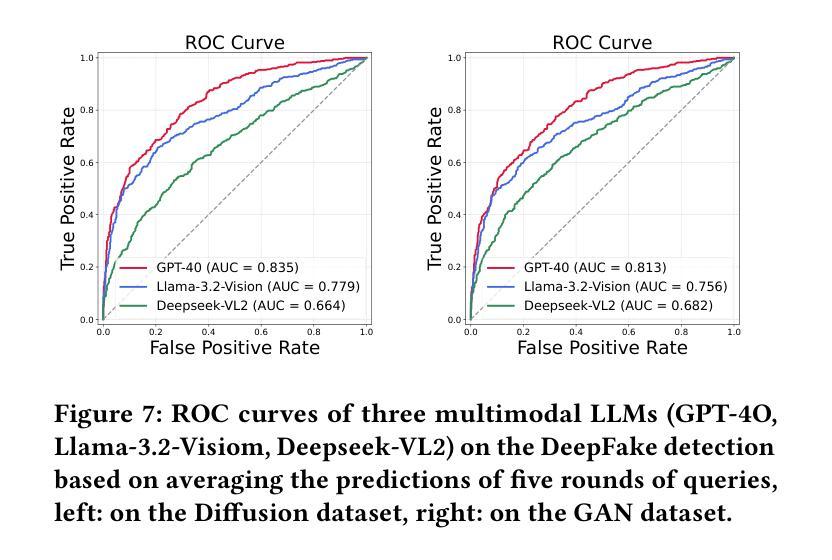
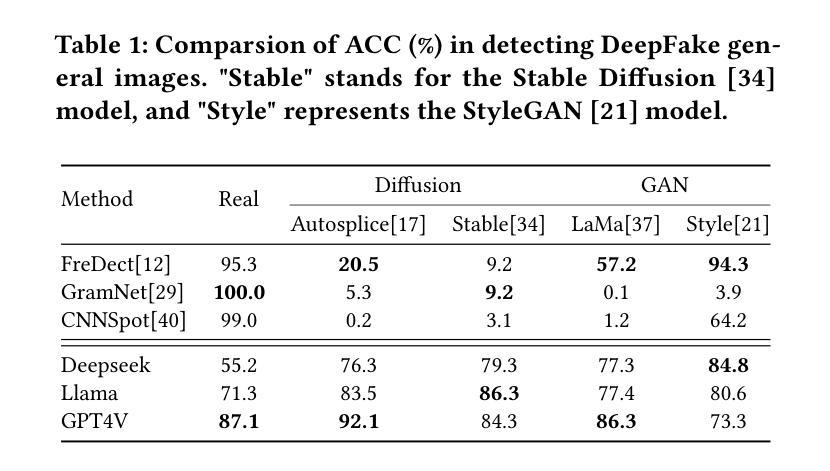
The rapid development of generative AI facilitates content creation and makes image manipulation easier and more difficult to detect. While multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) have encoded rich world knowledge, they are not inherently tailored for combating AI-generated Content (AIGC) and struggle to comprehend local forgery details. In this work, we investigate the application of multimodal LLMs in forgery detection. We propose a framework capable of evaluating image authenticity, localizing tampered regions, providing evidence, and tracing generation methods based on semantic tampering clues. Our method demonstrates that the potential of LLMs in forgery analysis can be effectively unlocked through meticulous prompt engineering and the application of few-shot learning techniques. We conduct qualitative and quantitative experiments and show that GPT4V can achieve an accuracy of 92.1% in Autosplice and 86.3% in LaMa, which is competitive with state-of-the-art AIGC detection methods. We further discuss the limitations of multimodal LLMs in such tasks and propose potential improvements.
随着生成式AI的快速发展,内容创建变得更加容易,图像操作也变得更加简单且难以检测。虽然多模态大型语言模型(LLM)已经编码了丰富的世界知识,但它们并非天生就适合对抗AI生成的内容(AIGC),在理解局部伪造细节方面存在困难。在这项工作中,我们研究了多模态LLM在伪造检测中的应用。我们提出了一个能够评估图像真实性、定位篡改区域、提供证据并根据语义篡改线索追踪生成方法的框架。我们的方法表明,通过细致的提示工程和少量学习技术的应用,LLM在伪造分析中的潜力可以得到有效解锁。我们进行了定性和定量实验,结果表明GPT4V在Autosplice中可以达到92.1%的准确率,在LaMa中可以达到86.3%,与最先进的AIGC检测方法具有竞争力。我们还进一步讨论了多模态LLM在此类任务中的局限性,并提出了潜在的改进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 11 figures, 13IHMMSec2025
Summary
生成性AI的快速发展促进了内容创作,使得图像操作更加容易且难以检测。本研究探讨了多模态大型语言模型(LLM)在伪造检测中的应用,提出了一种能够评估图像真实性、定位篡改区域、提供证据并追溯基于语义篡改线索的生成方法的框架。该研究通过精细的提示工程和少样本学习技术的应用,展示了LLM在伪造分析中的潜力。实验表明,GPT4V在Autosplice和LaMa任务中的准确率分别达到了92.1%和86.3%,具有与最新AIGC检测方法竞争的实力。
Key Takeaways
- 生成性AI促进了内容创作,使得图像操作更易于进行且难以检测。
- 多模态大型语言模型(LLM)在伪造检测中具有潜在应用价值。
- 提出的框架能够评估图像真实性、定位篡改区域,并提供证据和追溯生成方法。
- 通过精细的提示工程和少样本学习技术的应用,LLM在伪造分析中的潜力得以解锁。
- GPT4V在Autosplice和LaMa任务中的准确率较高,具有竞争力。
- 研究讨论了多模态LLM在此类任务中的局限性。
点此查看论文截图


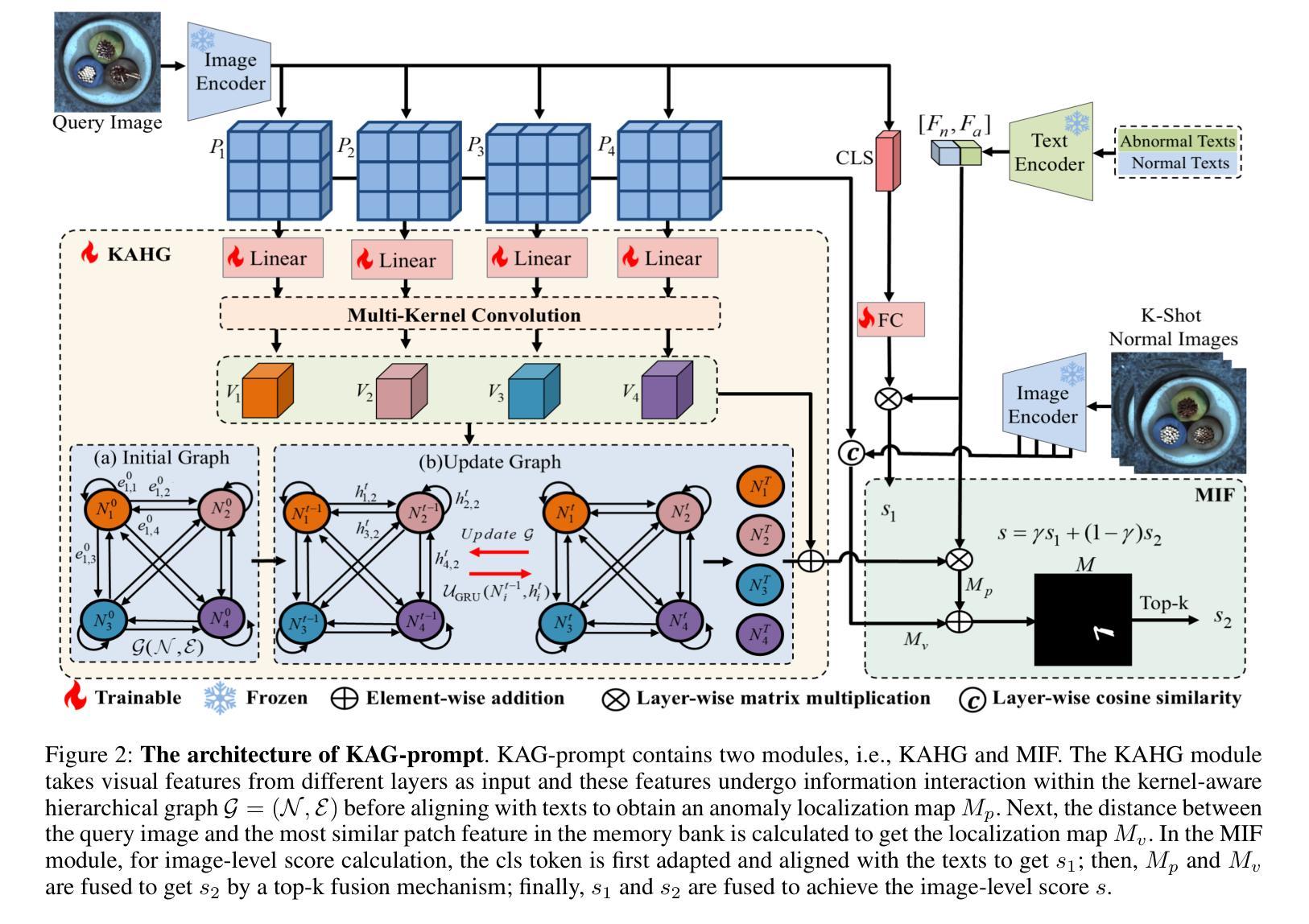
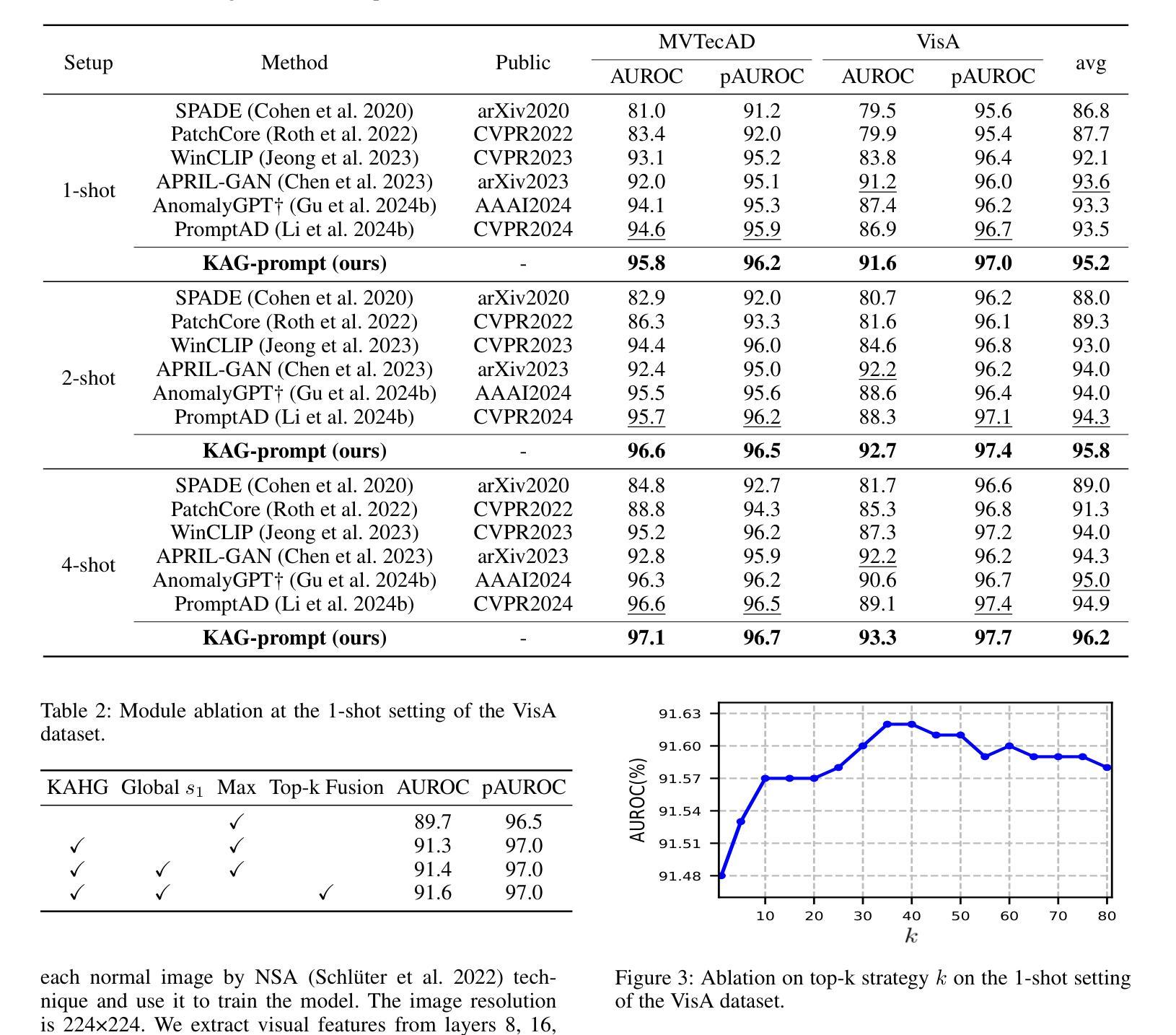
Kernel-Aware Graph Prompt Learning for Few-Shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Fenfang Tao, Guo-Sen Xie, Fang Zhao, Xiangbo Shu
Few-shot anomaly detection (FSAD) aims to detect unseen anomaly regions with the guidance of very few normal support images from the same class. Existing FSAD methods usually find anomalies by directly designing complex text prompts to align them with visual features under the prevailing large vision-language model paradigm. However, these methods, almost always, neglect intrinsic contextual information in visual features, e.g., the interaction relationships between different vision layers, which is an important clue for detecting anomalies comprehensively. To this end, we propose a kernel-aware graph prompt learning framework, termed as KAG-prompt, by reasoning the cross-layer relations among visual features for FSAD. Specifically, a kernel-aware hierarchical graph is built by taking the different layer features focusing on anomalous regions of different sizes as nodes, meanwhile, the relationships between arbitrary pairs of nodes stand for the edges of the graph. By message passing over this graph, KAG-prompt can capture cross-layer contextual information, thus leading to more accurate anomaly prediction. Moreover, to integrate the information of multiple important anomaly signals in the prediction map, we propose a novel image-level scoring method based on multi-level information fusion. Extensive experiments on MVTecAD and VisA datasets show that KAG-prompt achieves state-of-the-art FSAD results for image-level/pixel-level anomaly detection. Code is available at https://github.com/CVL-hub/KAG-prompt.git.
小样异常检测(FSAD)旨在使用同一类别中的少量正常支持图像来检测未见的异常区域。现有的FSAD方法通常通过直接设计复杂的文本提示来与流行的大型视觉语言模型范式下的视觉特征对齐来发现异常。然而,这些方法几乎总是忽略了视觉特征中的内在上下文信息,例如不同视觉层之间的交互关系,这是全面检测异常的重要线索。为此,我们提出了一个核心感知图提示学习框架,称为KAG-prompt,通过推理视觉特征之间的跨层关系来进行FSAD。具体来说,以关注不同大小异常区域的不同层特征作为节点,构建了一个核心感知分层图,同时,任意节点对之间的关系代表图的边。通过在此图上进行消息传递,KAG-prompt可以捕获跨层上下文信息,从而导致更准确的异常预测。此外,为了整合预测图中多个重要异常信号的信息,我们提出了一种基于多层次信息融合的新型图像级评分方法。在MVTecAD和VisA数据集上的大量实验表明,KAG-prompt在图像级/像素级的异常检测中达到了最先进的FSAD结果。代码可在https://github.com/CVL-hub/KAG-prompt.git找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AAAI 2025
Summary
少数样本异常检测旨在利用少数同类正常样本作为参考进行异常区域检测。现有方法大多通过设计复杂的文本提示来与视觉特征对齐,但在大型视觉语言模型范式下忽略了视觉特征中的内在上下文信息,如不同视觉层之间的关系。为此,我们提出了一个核心感知图提示学习框架KAG-prompt,通过推理不同层之间的关系来进行少数样本异常检测。KAG-prompt通过构建核心感知层次图来捕捉跨层上下文信息,实现了更准确的异常预测。此外,我们还提出了一种基于多层次信息融合的新型图像级评分方法,用于整合预测图中的多个重要异常信号。在MVTecAD和VisA数据集上的实验表明,KAG-prompt在图像级和像素级的异常检测方面取得了最先进的少数样本异常检测结果。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 少数样本异常检测的目标是借助少数同类正常样本检测异常区域。
- 现有方法主要通过复杂的文本提示与视觉特征进行对齐,但忽略了视觉特征的内在上下文信息。
- KAG-prompt框架通过构建核心感知层次图来捕捉跨层上下文信息,提高异常检测的准确性。
- KAG-prompt利用多层次信息融合进行图像级评分,整合预测图中的多个重要异常信号。
点此查看论文截图

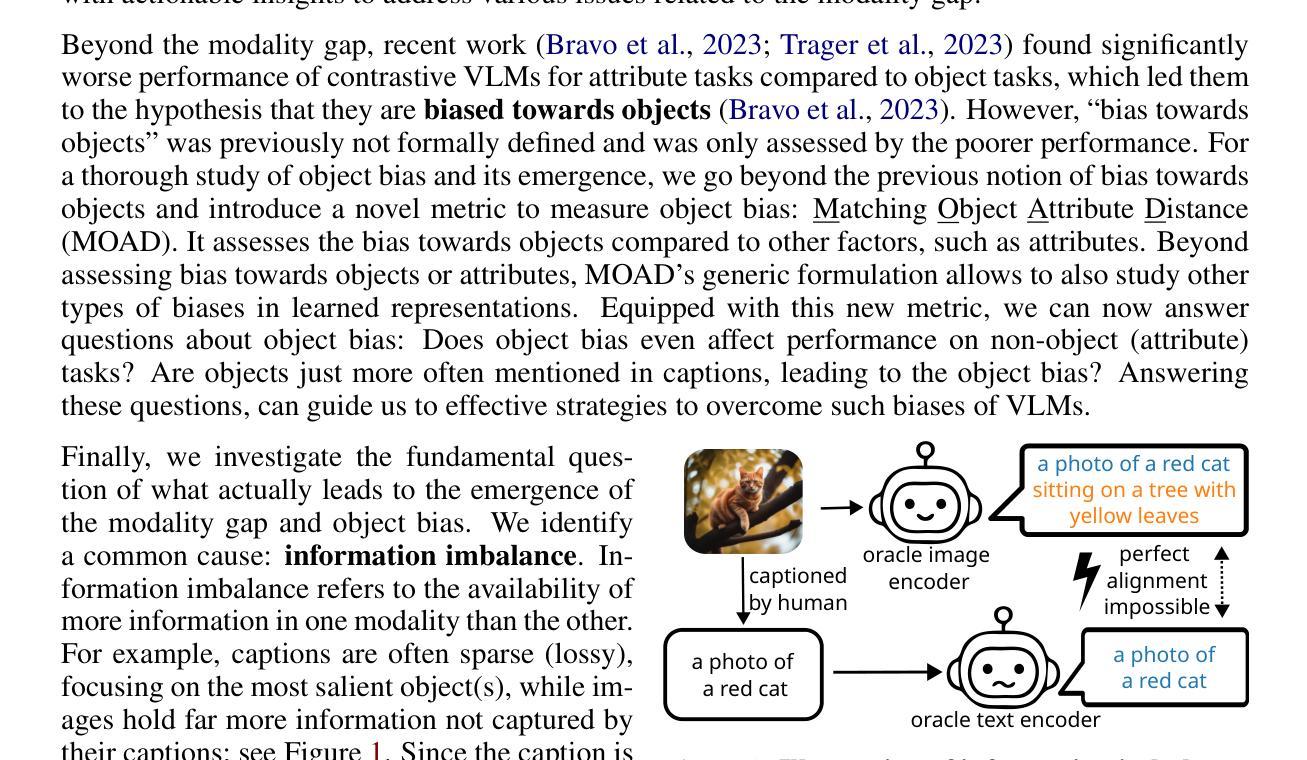
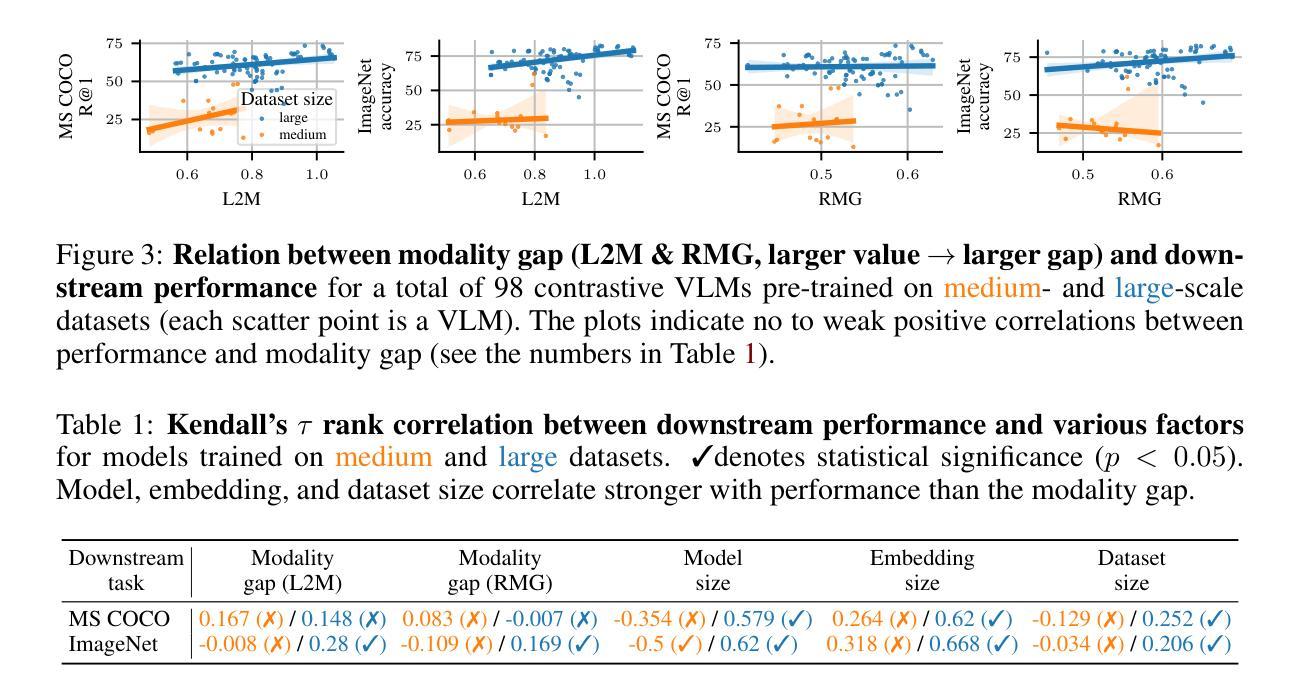
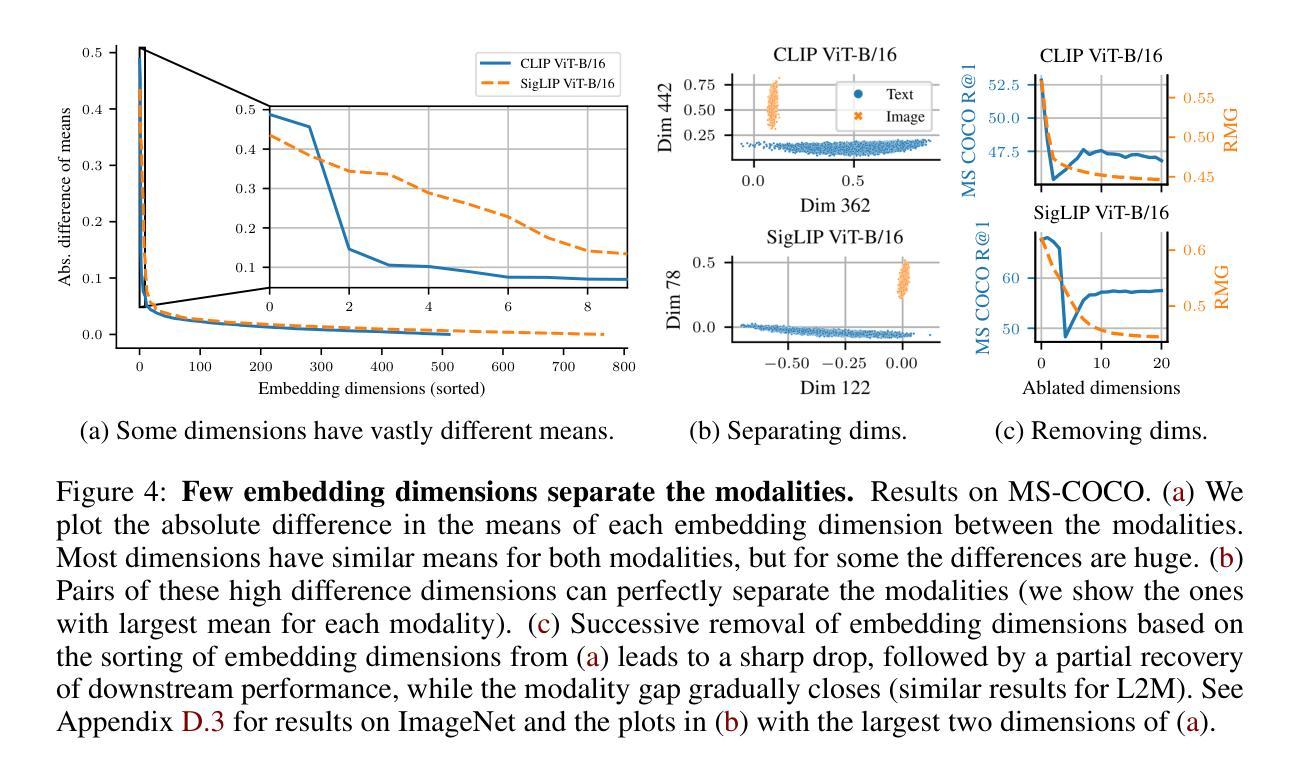
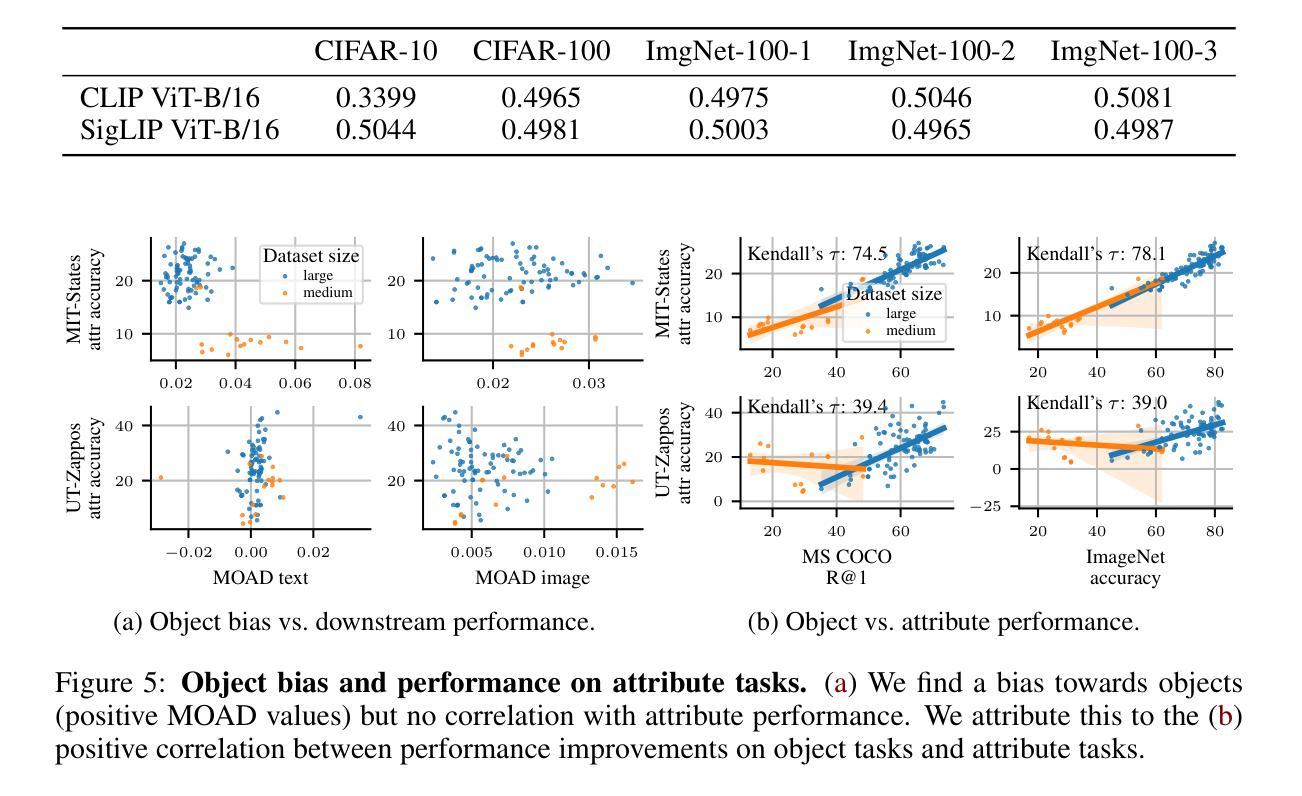
Two Effects, One Trigger: On the Modality Gap, Object Bias, and Information Imbalance in Contrastive Vision-Language Models
Authors:Simon Schrodi, David T. Hoffmann, Max Argus, Volker Fischer, Thomas Brox
Contrastive vision-language models (VLMs), like CLIP, have gained popularity for their versatile applicability to various downstream tasks. Despite their successes in some tasks, like zero-shot object recognition, they perform surprisingly poor on other tasks, like attribute recognition. Previous work has attributed these challenges to the modality gap, a separation of image and text in the shared representation space, and to a bias towards objects over other factors, such as attributes. In this analysis paper, we investigate both phenomena thoroughly. We evaluated off-the-shelf VLMs and while the gap’s influence on performance is typically overshadowed by other factors, we find indications that closing the gap indeed leads to improvements. Moreover, we find that, contrary to intuition, only few embedding dimensions drive the gap and that the embedding spaces are differently organized. To allow for a clean study of object bias, we introduce a definition and a corresponding measure of it. Equipped with this tool, we find that object bias does not lead to worse performance on other concepts, such as attributes per se. However, why do both phenomena, modality gap and object bias, emerge in the first place? To answer this fundamental question and uncover some of the inner workings of contrastive VLMs, we conducted experiments that allowed us to control the amount of shared information between the modalities. These experiments revealed that the driving factor behind both the modality gap and the object bias, is an information imbalance between images and captions, and unveiled an intriguing connection between the modality gap and entropy of the logits.
对比视觉语言模型(VLMs),如CLIP,因其对各种下游任务的通用适用性而广受欢迎。尽管它们在零样本目标识别等任务中取得了成功,但在属性识别等其他任务上的表现却令人惊讶地不佳。以前的工作将这些挑战归因于模态差距,即图像和文本在共享表示空间中的分离,以及相对于其他因素(如属性)对目标的偏向。在这篇分析论文中,我们对这两种现象进行了彻底的研究。我们评估了现成的VLMs,虽然模态差距对性能的影响通常被其他因素所掩盖,但我们发现缩小差距确实会导致性能提高的迹象。此外,我们发现与直觉相反的是,只有少数嵌入维度在驱动差距,且这些嵌入空间的组织方式是不同的。为了能够对目标偏见进行清晰的研究,我们引入了定义和相应的度量标准。利用这一工具,我们发现目标偏见并不会导致对属性等概念的表现下降。然而,为什么模态差距和目标偏见这两种现象首先会出现呢?为了回答这个问题并揭示对比VLMs的一些内在工作原理,我们进行了一些实验,以控制图像和字幕之间共享信息量的多少。这些实验表明,模态差距和目标偏见背后的驱动因素是图像和字幕之间的信息不平衡,并揭示了模态差距与逻辑熵之间的有趣联系。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 (Oral)
Summary
该分析论文探讨了对比视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在下游任务应用中的性能差异问题。对于模态间隙和挑战,研究发现该间隙通常在其它因素掩盖下被忽略,但缩小间隙能提高性能。研究发现,驱动间隙的关键因素在于少量嵌入维度,且嵌入空间组织不同。为解决对象偏见问题,论文引入了定义和相应度量标准。研究还发现对象偏见并不会导致其他概念(如属性)性能恶化。最终实验显示,图像和字幕间信息量失衡是驱动模态间隙和对象偏见的主要因素,并揭示了模态间隙与对数熵之间的有趣联系。
Key Takeaways
- 对比视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多种下游任务中表现出广泛的应用性,但在某些任务上表现不佳。
- 模态间隙是图像和文本在共享表示空间中的分离,对性能影响被其它因素掩盖,但缩小间隙有助于提高性能。
- 只有少数嵌入维度驱动模态间隙,且嵌入空间组织方式不同。
- 论文引入了对象偏见的定义和相应度量标准。
- 对象偏见并不会导致对属性等其它概念的性能恶化。
- 信息量失衡是驱动模态间隙和对象偏见的主要因素。
点此查看论文截图