⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-18 更新
Flow Intelligence: Robust Feature Matching via Temporal Signature Correlation
Authors:Jie Wang, Chen Ye Gan, Caoqi Wei, Jiangtao Wen, Yuxing Han
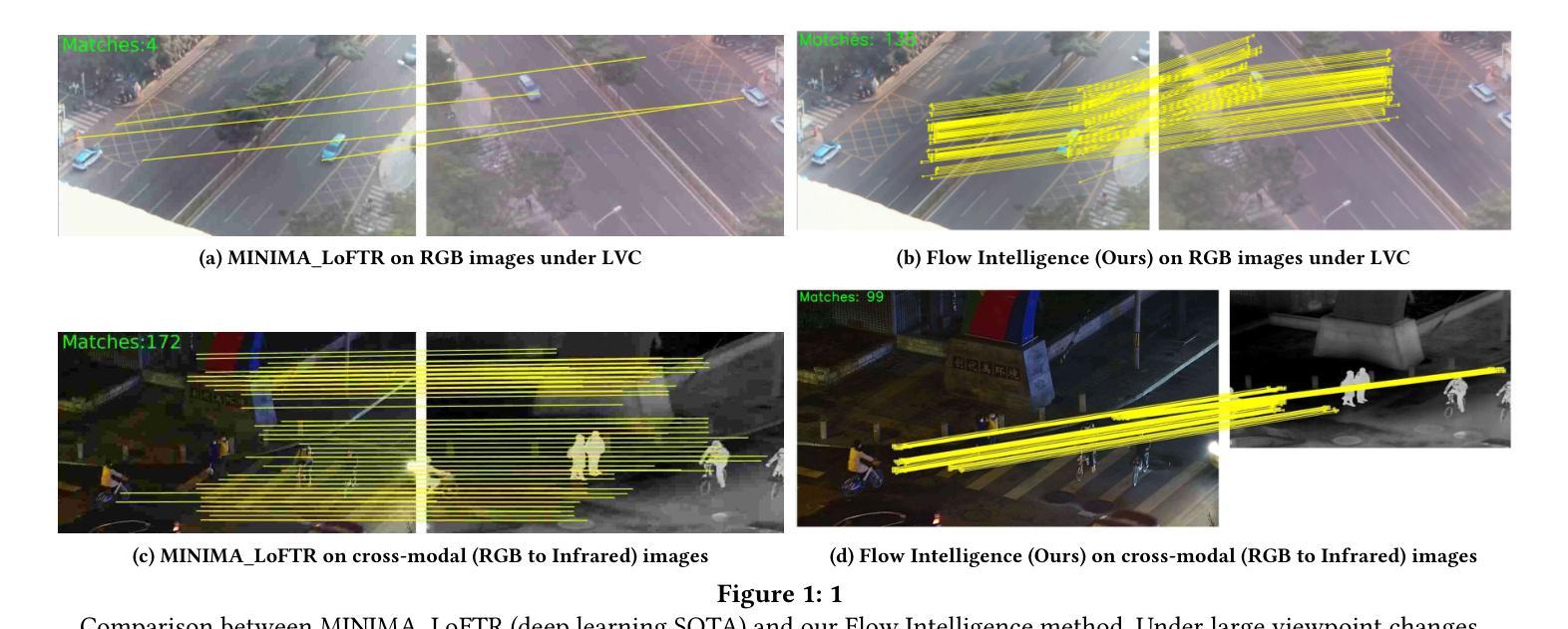
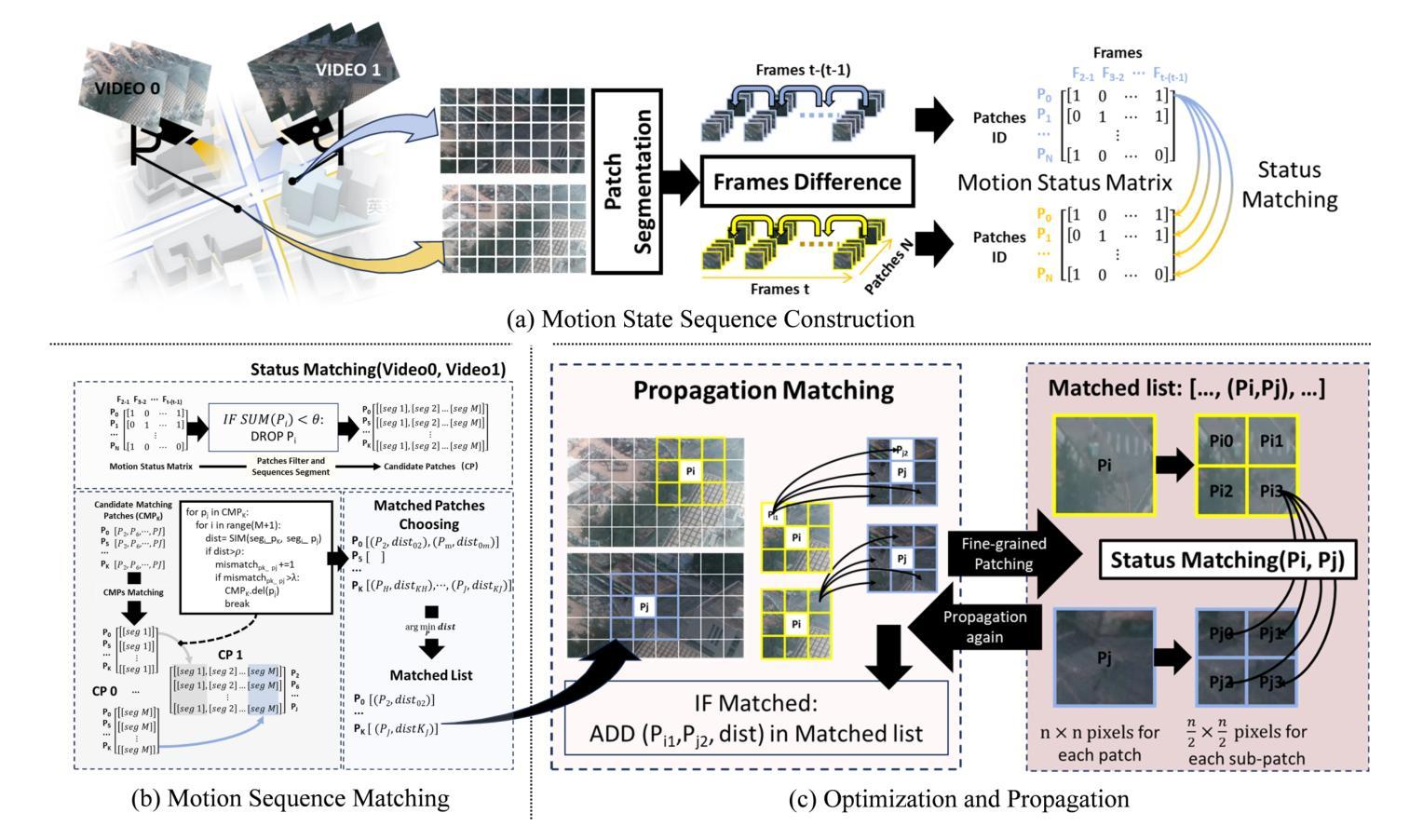
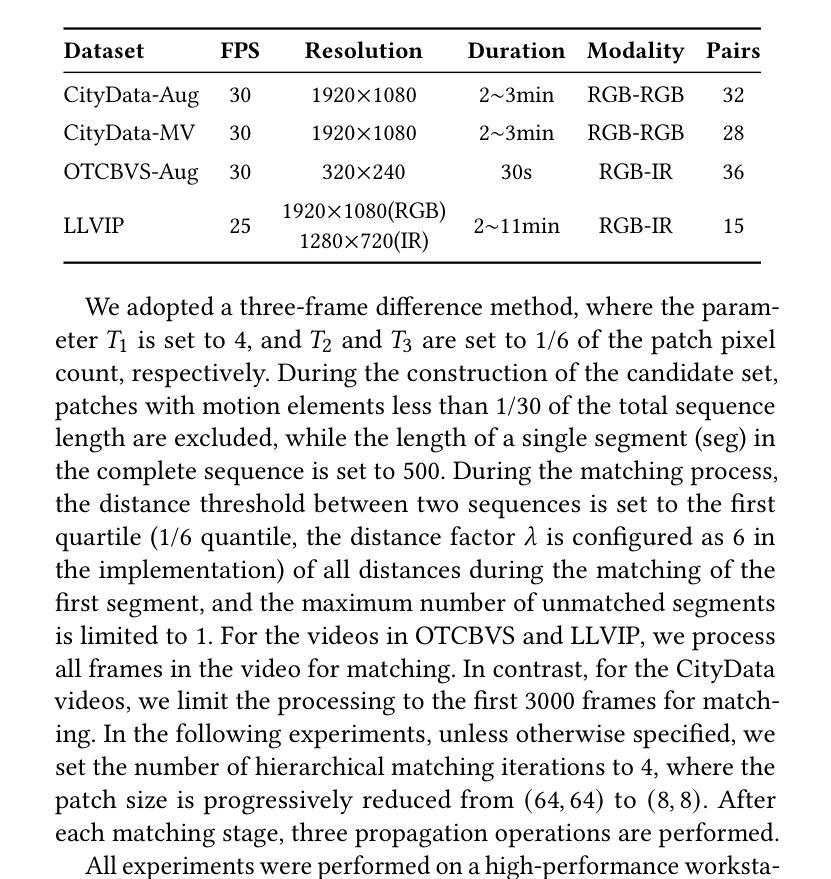
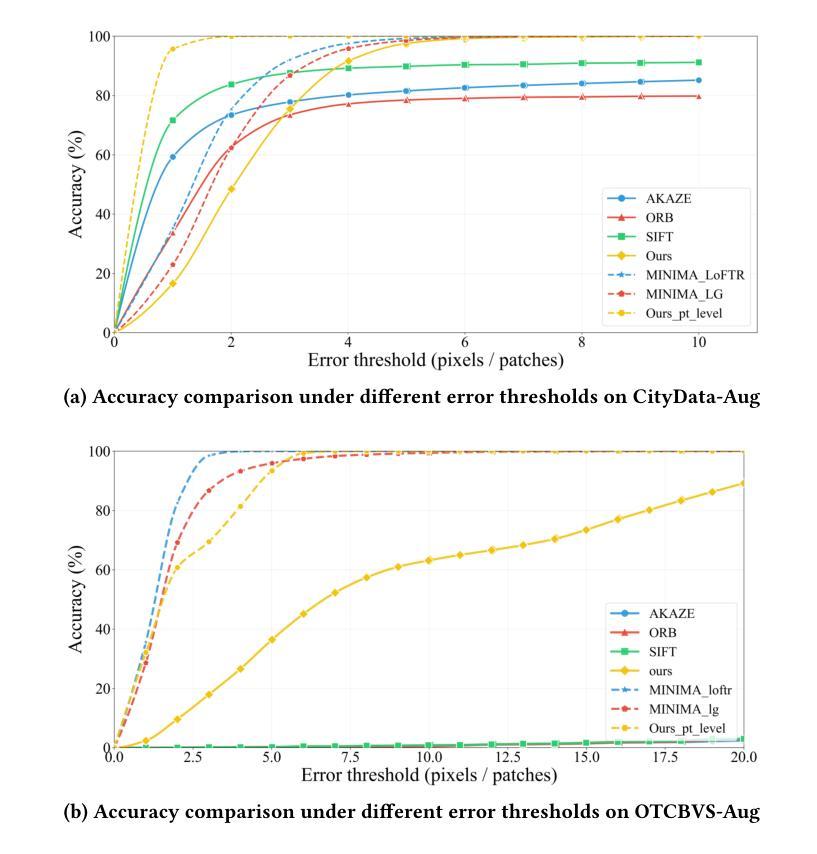
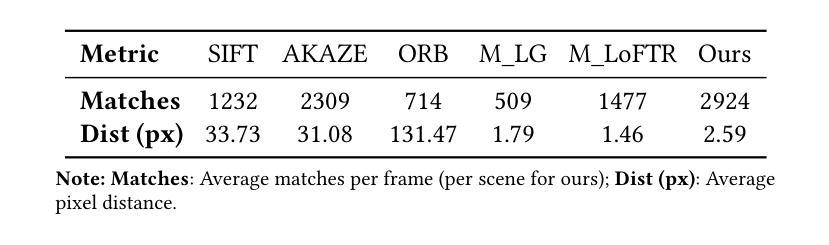
Feature matching across video streams remains a cornerstone challenge in computer vision. Increasingly, robust multimodal matching has garnered interest in robotics, surveillance, remote sensing, and medical imaging. While traditional rely on detecting and matching spatial features, they break down when faced with noisy, misaligned, or cross-modal data. Recent deep learning methods have improved robustness through learned representations, but remain constrained by their dependence on extensive training data and computational demands. We present Flow Intelligence, a paradigm-shifting approach that moves beyond spatial features by focusing on temporal motion patterns exclusively. Instead of detecting traditional keypoints, our method extracts motion signatures from pixel blocks across consecutive frames and extract temporal motion signatures between videos. These motion-based descriptors achieve natural invariance to translation, rotation, and scale variations while remaining robust across different imaging modalities. This novel approach also requires no pretraining data, eliminates the need for spatial feature detection, enables cross-modal matching using only temporal motion, and it outperforms existing methods in challenging scenarios where traditional approaches fail. By leveraging motion rather than appearance, Flow Intelligence enables robust, real-time video feature matching in diverse environments.
视频流中的特征匹配仍然是计算机视觉领域的一个核心挑战。随着其在机器人技术、监控、遥感和医学影像等领域的普及,稳健的多模态匹配越来越受到人们的关注。虽然传统的方法依赖于检测和匹配空间特征,但当面对噪声、错位或跨模态数据时,它们的效果会变得很差。最近采用深度学习方法通过学到的表现改善了稳健性,但仍然受到依赖大量训练数据和计算需求的制约。本文提出Flow Intelligence(流程智能),这是一种超越空间特征的范式转变方法,专注于纯粹的动态模式。我们的方法不是检测传统关键点,而是从连续帧中的像素块中提取运动特征,并在视频之间提取动态运动特征。这些基于运动的描述符实现了对平移、旋转和尺度变化的自然不变性,同时在不同成像模态下保持稳健性。这一新方法不需要预先训练数据,消除了对空间特征检测的需求,仅凭动态运动即可实现跨模态匹配,并且在传统方法失败的具有挑战性的场景中表现优于现有方法。通过利用运动而非外观,Flow Intelligence可在各种环境中实现稳健的实时视频特征匹配。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Flow Intelligence的新方法,它通过专注于纯粹的临时运动模式来超越空间特征的限制,实现视频流之间的特性匹配。这种方法不需要预先训练数据,直接从连续的像素块中提取运动签名,并利用运动描述器在不同成像模态之间进行鲁棒匹配。在挑战性的场景中,即使传统方法失败,Flow Intelligence也表现出卓越的鲁棒性和实时性能。通过利用运动而不是外观信息,Flow Intelligence可在不同的环境中实现强大的视频特征匹配。
Key Takeaways
- Flow Intelligence是一种基于临时运动模式的视频流特征匹配方法。
- 它专注于运动签名,超越了对空间特征的依赖。
- 该方法无需预先训练数据,可直接从连续的像素块中提取运动特征。
- Flow Intelligence具有对不同成像模态的鲁棒性匹配能力。
- 通过提取运动描述器,该方法能够在不同的场景中实现出色的匹配性能。
- 相比传统方法,Flow Intelligence在挑战性场景下表现出更高的鲁棒性和实时性能。
点此查看论文截图


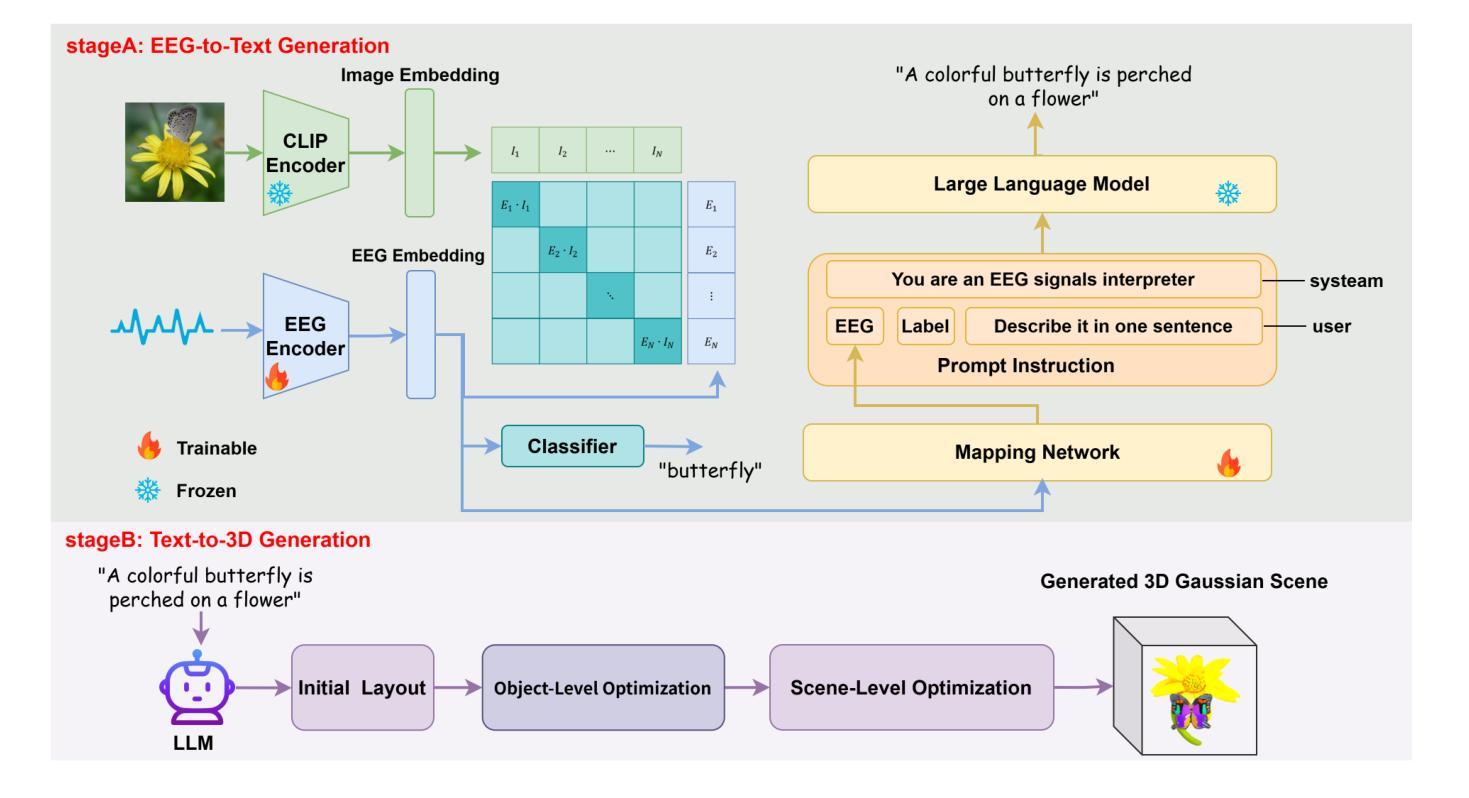
Mind2Matter: Creating 3D Models from EEG Signals
Authors:Xia Deng, Shen Chen, Jiale Zhou, Lei Li
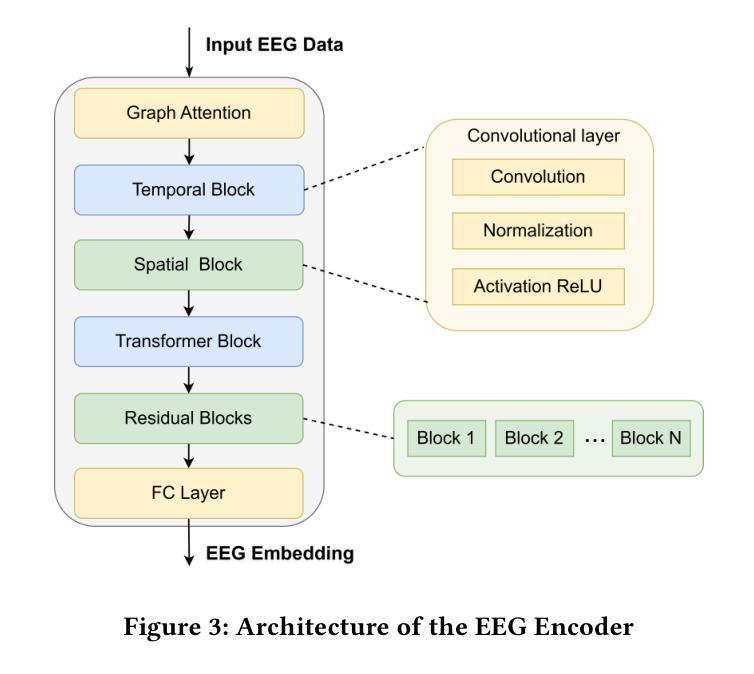
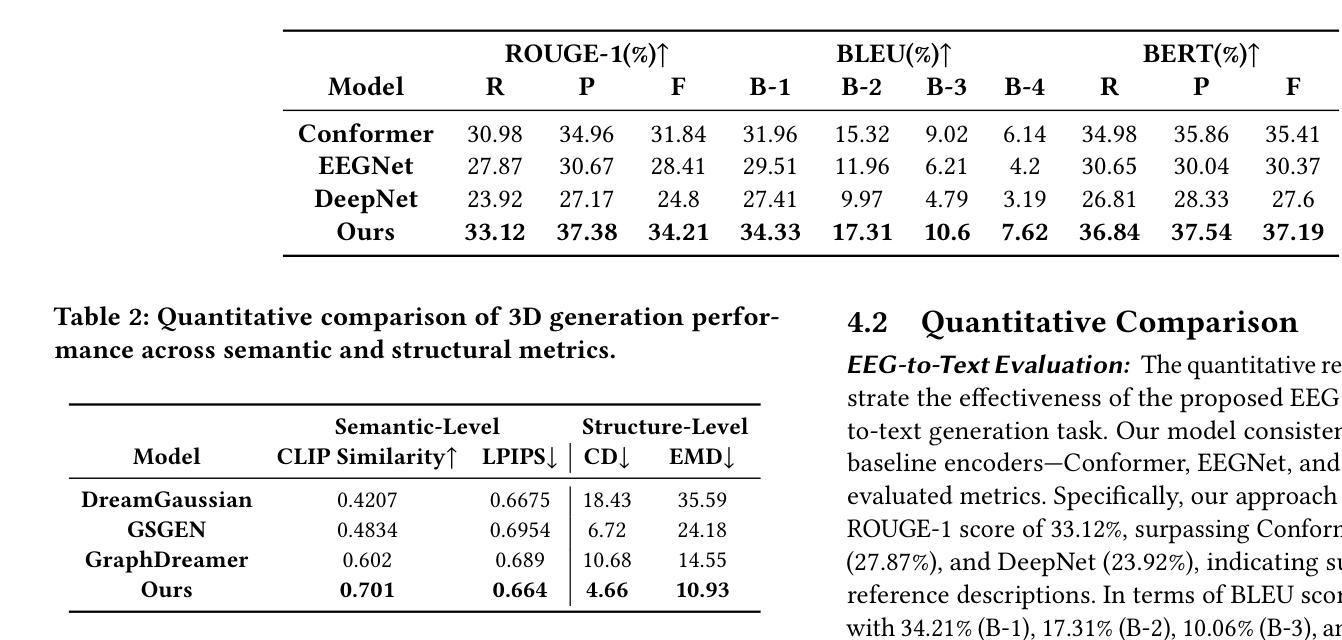
The reconstruction of 3D objects from brain signals has gained significant attention in brain-computer interface (BCI) research. Current research predominantly utilizes functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) for 3D reconstruction tasks due to its excellent spatial resolution. Nevertheless, the clinical utility of fMRI is limited by its prohibitive costs and inability to support real-time operations. In comparison, electroencephalography (EEG) presents distinct advantages as an affordable, non-invasive, and mobile solution for real-time brain-computer interaction systems. While recent advances in deep learning have enabled remarkable progress in image generation from neural data, decoding EEG signals into structured 3D representations remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that translates EEG recordings into 3D object reconstructions by leveraging neural decoding techniques and generative models. Our approach involves training an EEG encoder to extract spatiotemporal visual features, fine-tuning a large language model to interpret these features into descriptive multimodal outputs, and leveraging generative 3D Gaussians with layout-guided control to synthesize the final 3D structures. Experiments demonstrate that our model captures salient geometric and semantic features, paving the way for applications in brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), virtual reality, and neuroprosthetics.Our code is available in https://github.com/sddwwww/Mind2Matter.
从脑信号重建3D物体在脑机接口(BCI)研究中获得了广泛关注。目前的研究主要利用功能磁共振成像(fMRI)进行3D重建任务,因其卓越的空间分辨率。然而,fMRI的临床实用性受到其高昂成本和无法支持实时操作等的限制。相比之下,脑电图(EEG)作为实时脑机交互系统的经济、无创、可移动解决方案,具有明显优势。虽然深度学习领域的最新进展在根据神经数据生成图像方面取得了显著进展,但将EEG信号解码为结构化3D表示仍然很少探索。在本文中,我们提出了一种利用神经解码技术和生成模型将EEG记录转化为3D对象重建的新框架。我们的方法包括训练EEG编码器以提取时空视觉特征,微调大型语言模型以将这些特征解释为描述性多模式输出,并利用布局指导控制的生成性3D高斯来合成最终的3D结构。实验表明,我们的模型能够捕获重要的几何和语义特征,为脑机接口(BCI)、虚拟现实和神经仿生学等领域的应用铺平了道路。我们的代码可在https://github.com/sddwwww/Mind2Matter上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于神经解码技术和生成模型,将脑电图(EEG)信号转换为三维物体重建的新框架。该研究训练EEG编码器提取时空视觉特征,微调大型语言模型以解释这些特征并生成多模式输出,最后利用布局引导的生成性三维高斯分布合成最终的三维结构。此模型在捕捉几何和语义特征方面具有显著优势,有望在脑机接口(BCI)、虚拟现实和神经矫正术等领域应用。
Key Takeaways
- 重建三维物体从脑信号在脑机接口(BCI)研究中受到关注。
- 目前研究主要使用功能磁共振成像(fMRI)进行三维重建任务,但其成本高昂且不支持实时操作。
- 与之相比,脑电图(EEG)作为实时脑机交互系统的经济、无创和移动解决方案具有明显优势。
- 本文提出了一种基于神经解码技术和生成模型的新框架,能将EEG信号转换为三维物体重建。
- 该框架包括训练EEG编码器提取时空视觉特征,微调大型语言模型生成多模式输出,并利用布局引导的生成性三维高斯分布合成三维结构。
- 实验证明该模型能捕捉显著几何和语义特征。
- 此模型的应用前景广泛,如脑机接口、虚拟现实和神经矫正术等领域。
点此查看论文截图