⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-18 更新
R-Meshfusion: Reinforcement Learning Powered Sparse-View Mesh Reconstruction with Diffusion Priors
Authors:Haoyang Wang, Liming Liu, Peiheng Wang, Junlin Hao, Jiangkai Wu, Xinggong Zhang
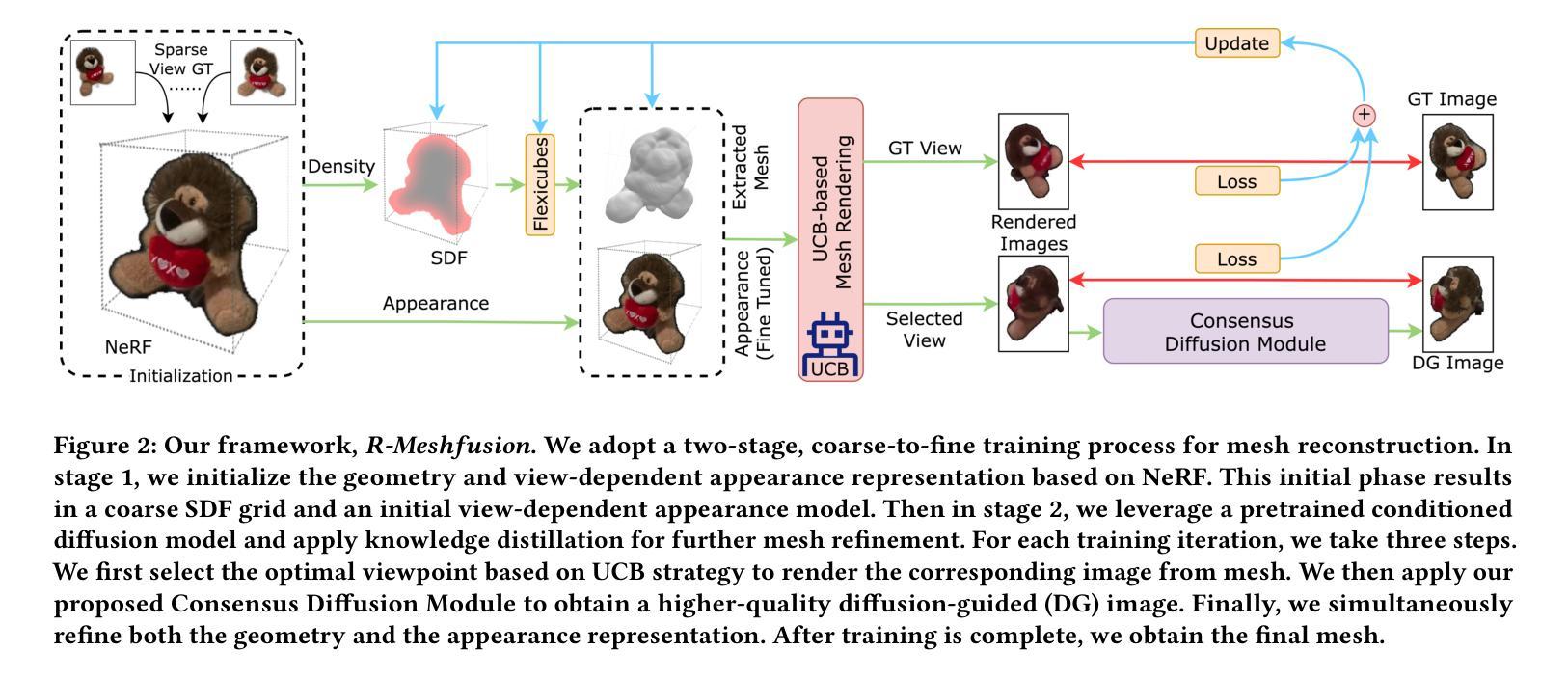
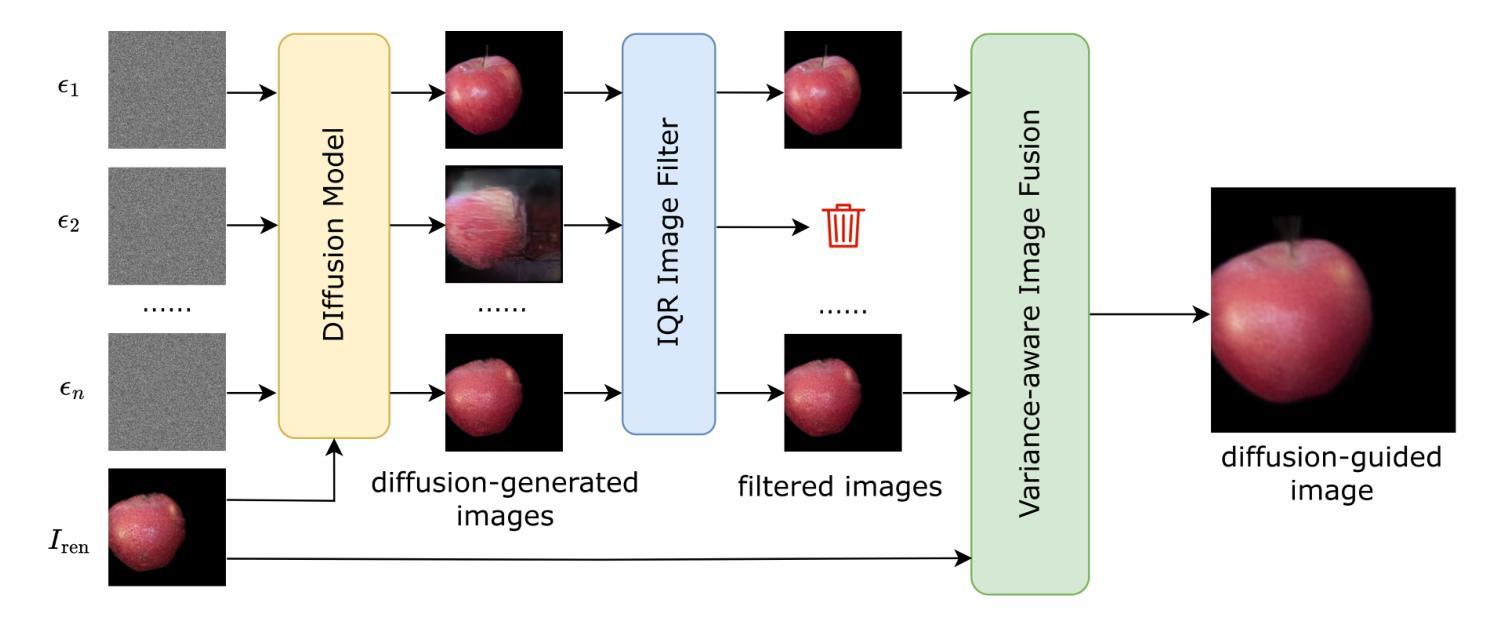
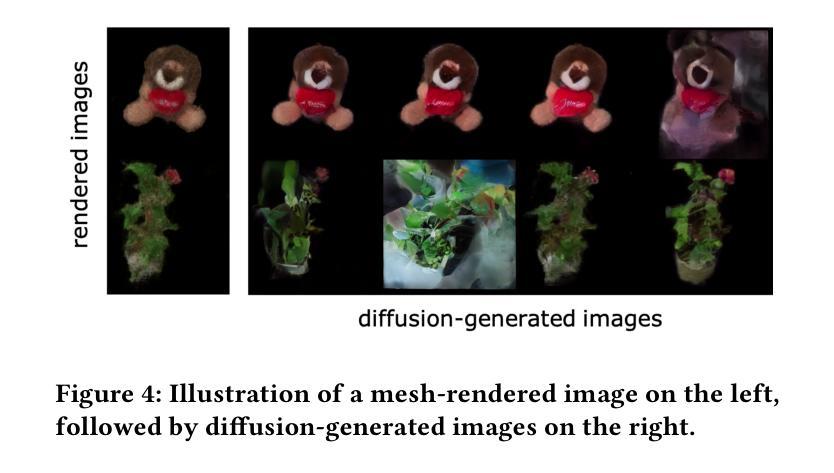
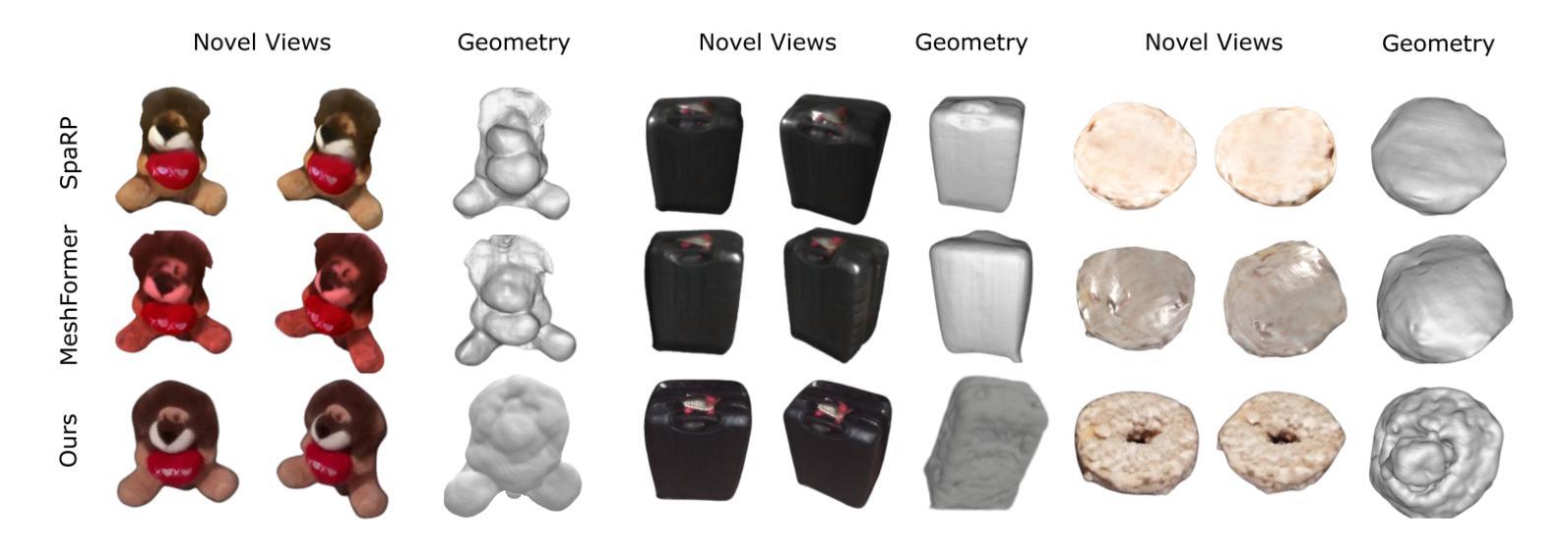
Mesh reconstruction from multi-view images is a fundamental problem in computer vision, but its performance degrades significantly under sparse-view conditions, especially in unseen regions where no ground-truth observations are available. While recent advances in diffusion models have demonstrated strong capabilities in synthesizing novel views from limited inputs, their outputs often suffer from visual artifacts and lack 3D consistency, posing challenges for reliable mesh optimization. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that leverages diffusion models to enhance sparse-view mesh reconstruction in a principled and reliable manner. To address the instability of diffusion outputs, we propose a Consensus Diffusion Module that filters unreliable generations via interquartile range (IQR) analysis and performs variance-aware image fusion to produce robust pseudo-supervision. Building on this, we design an online reinforcement learning strategy based on the Upper Confidence Bound (UCB) to adaptively select the most informative viewpoints for enhancement, guided by diffusion loss. Finally, the fused images are used to jointly supervise a NeRF-based model alongside sparse-view ground truth, ensuring consistency across both geometry and appearance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves significant improvements in both geometric quality and rendering quality.
从多视角图像进行网格重建是计算机视觉领域的一个基本问题,但在稀疏视角条件下,其性能会显著下降,特别是在没有地面真实观测的未见区域。虽然最近的扩散模型进展在有限的输入下合成新视角方面表现出强大的能力,但它们的输出常常存在视觉伪影且缺乏3D一致性,给可靠的网格优化带来了挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一个利用扩散模型以有原则的和可靠的方式增强稀疏视角网格重建的新框架。为了解决扩散输出的不稳定性,我们提出了共识扩散模块,它通过四分位距(IQR)分析过滤不可靠的生成,并执行方差感知图像融合,以产生稳健的伪监督。在此基础上,我们设计了一种基于上界置信(UCB)的在线强化学习策略,以自适应选择最具信息量的视角进行增强,由扩散损失引导。最后,融合图像被用来共同监督基于NeRF的模型和稀疏视角的地面真实情况,确保几何和外观的一致性。大量实验表明,我们的方法在几何质量和渲染质量方面都取得了显著的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多视角图像重建是计算机视觉领域的一个基本问题,但在稀疏视角条件下性能会显著下降。本文提出了一种利用扩散模型增强稀疏视角网格重建的新框架,通过共识扩散模块和方差感知图像融合技术解决扩散输出不稳定的问题。在此基础上,设计了一种基于置信上界(UCB)的在线强化学习策略,自适应选择最有信息量的视角进行增强。融合图像与稀疏视角真实值一起监督NeRF模型,确保几何和外观的一致性。实验证明,该方法在几何和渲染质量上取得了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型用于增强稀疏视角网格重建。
- 共识扩散模块通过IQR分析过滤不可靠生成,执行方差感知图像融合产生稳健的伪监督。
- 提出基于UCB的在线强化学习策略,自适应选择信息丰富的视角进行增强。
- 融合图像与稀疏视角真实值共同监督NeRF模型,确保几何与外观一致性。
- 方法显著提高几何和渲染质量。
- 框架具有稳定性和可靠性,适用于不同场景的多视角图像重建。
点此查看论文截图

Probabilistic causal graphs as categorical data synthesizers: Do they do better than Gaussian Copulas and Conditional Tabular GANs?
Authors:Olha Shaposhnyk, Noor Abid, Mouri Zakir, Svetlana Yanushkevich
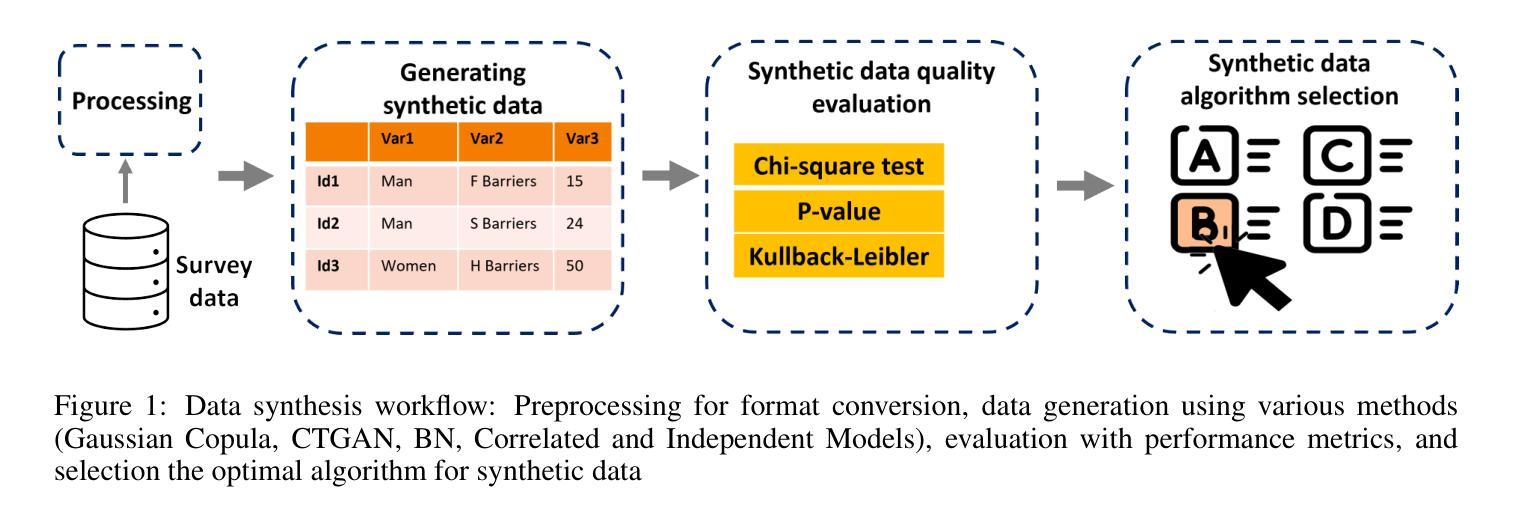
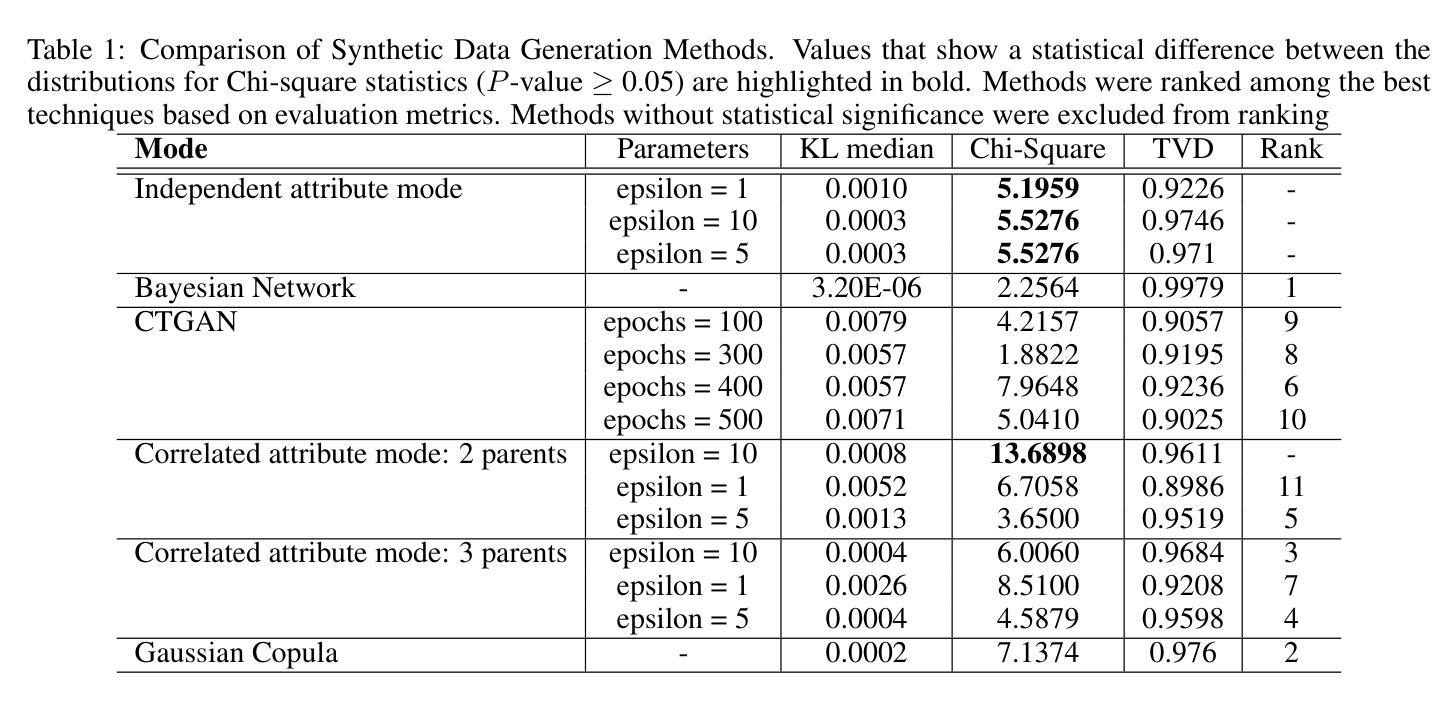
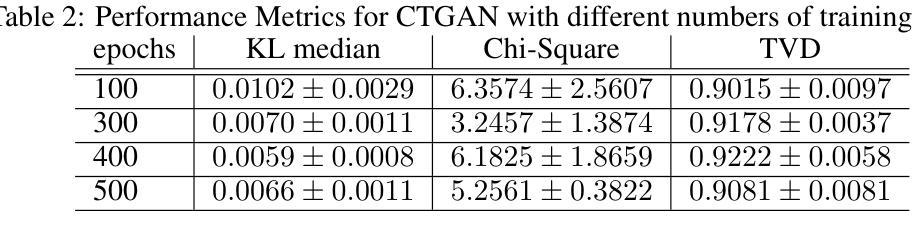
This study investigates the generation of high-quality synthetic categorical data, such as survey data, using causal graph models. Generating synthetic data aims not only to create a variety of data for training the models but also to preserve privacy while capturing relationships between the data. The research employs Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) followed by Bayesian Networks (BN). We used the categorical data that are based on the survey of accessibility to services for people with disabilities. We created both SEM and BN models to represent causal relationships and to capture joint distributions between variables. In our case studies, such variables include, in particular, demographics, types of disability, types of accessibility barriers and frequencies of encountering those barriers. The study compared the SEM-based BN method with alternative approaches, including the probabilistic Gaussian copula technique and generative models like the Conditional Tabular Generative Adversarial Network (CTGAN). The proposed method outperformed others in statistical metrics, including the Chi-square test, Kullback-Leibler divergence, and Total Variation Distance (TVD). In particular, the BN model demonstrated superior performance, achieving the highest TVD, indicating alignment with the original data. The Gaussian Copula ranked second, while CTGAN exhibited moderate performance. These analyses confirmed the ability of the SEM-based BN to produce synthetic data that maintain statistical and relational validity while maintaining confidentiality. This approach is particularly beneficial for research on sensitive data, such as accessibility and disability studies.
本研究旨在利用因果图模型生成高质量的合成分类数据,如调查数据。生成合成数据的目标不仅是创建用于训练模型的各种数据,而且还要在捕获数据之间的关系的同时保护隐私。该研究采用结构方程模型(SEM)和随后的贝叶斯网络(BN)。我们使用的分类数据是基于对残疾人服务可及性的调查。我们创建了SEM和BN模型来代表因果关系并捕捉变量之间的联合分布。在我们的案例研究中,这些变量主要包括人口统计、残疾类型、可及性障碍的类型以及遇到这些障碍的频率。该研究将基于SEM的BN方法与概率高斯Copula技术和条件表格生成对抗网络(CTGAN)等生成模型等其他方法进行了比较。在统计指标方面,所提出的方法(包括卡方检验、Kullback-Leibler散度和总变异距离(TVD))的表现优于其他方法。特别是,BN模型表现出卓越的性能,达到了最高的TVD值,表明其与原始数据的一致性。高斯Copula排名第二,而CTGAN表现中等。这些分析证实了基于SEM的BN生成合成数据的能力,这些合成数据能够保持统计和关系有效性,同时保持机密性。这种方法对于敏感数据的研究(如无障碍和残疾研究)尤其有益。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究利用因果图模型生成高质量合成分类数据,如调查数据。研究旨在创建用于训练模型的各种数据,同时保留隐私并捕捉数据之间的关系。该研究采用结构方程模型(SEM)和贝叶斯网络(BN),并使用基于残障人士服务可及性的调查分类数据。研究比较了基于SEM的BN方法与概率高斯copula技术和其他生成模型,如条件表格生成对抗网络(CTGAN)。基于SEM的BN方法在统计指标上表现优于其他方法,包括卡方检验、Kullback-Leibler散度和总变异距离(TVD)。特别是BN模型表现出卓越的性能,实现了最高的TVD值,表明其与原始数据的吻合度最高。这一方法对于处理敏感数据的研究具有特殊优势,如无障碍和残障研究。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究使用因果图模型生成合成分类数据,旨在创建多种训练数据并保护隐私同时保留数据间的关系。
- 研究采用结构方程模型(SEM)和贝叶斯网络(BN)来处理数据并建立因果关系的模型。
- 该研究使用基于残障人士服务可及性的调查数据。
- 对比了基于SEM的BN方法与其他方法,如高斯copula和CTGAN,在统计指标上表现优越。
- BN模型在总变异距离(TVD)上表现最佳,显示其与原始数据的高度一致性。
- 基于SEM的BN方法能够产生在统计和关系上有效的合成数据,同时保持机密性。
点此查看论文截图