⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-18 更新
Advancing Arabic Speech Recognition Through Large-Scale Weakly Supervised Learning
Authors:Mahmoud Salhab, Marwan Elghitany, Shameed Sait, Syed Sibghat Ullah, Mohammad Abusheikh, Hasan Abusheikh
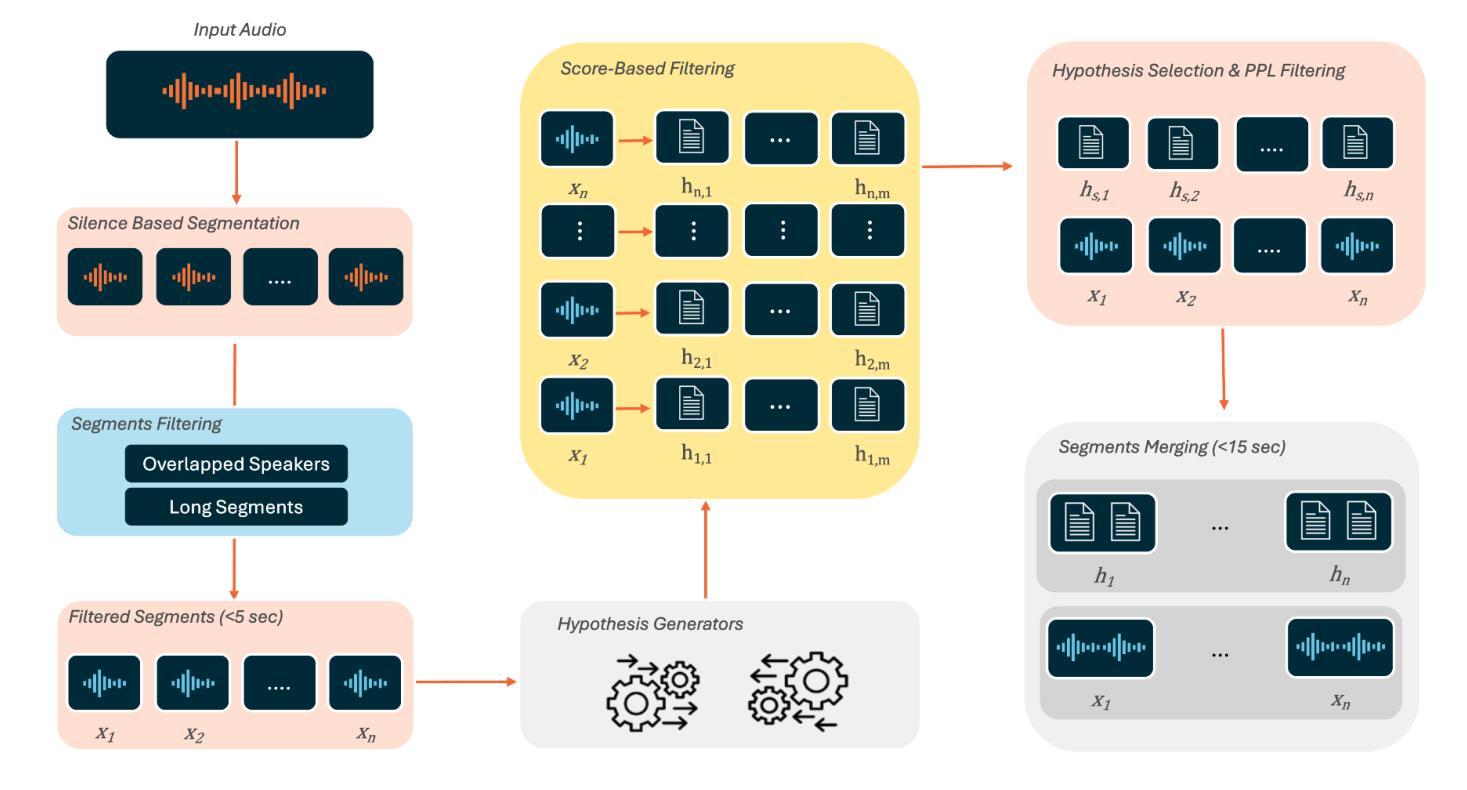
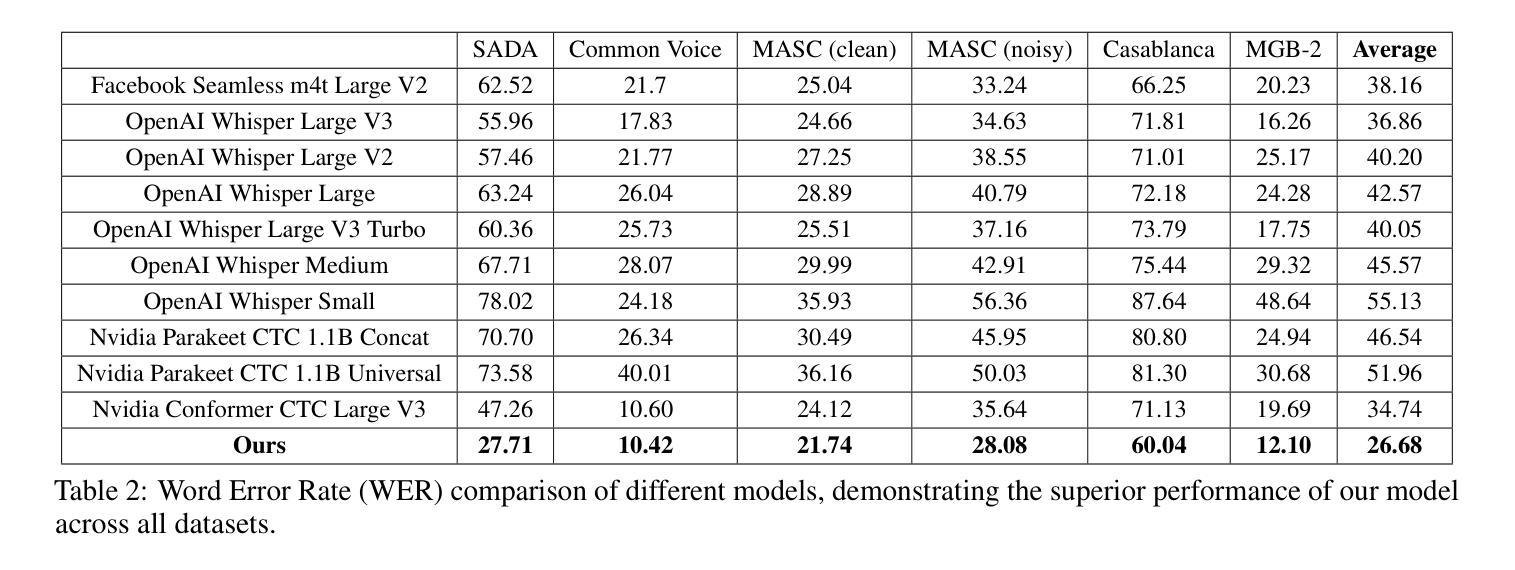
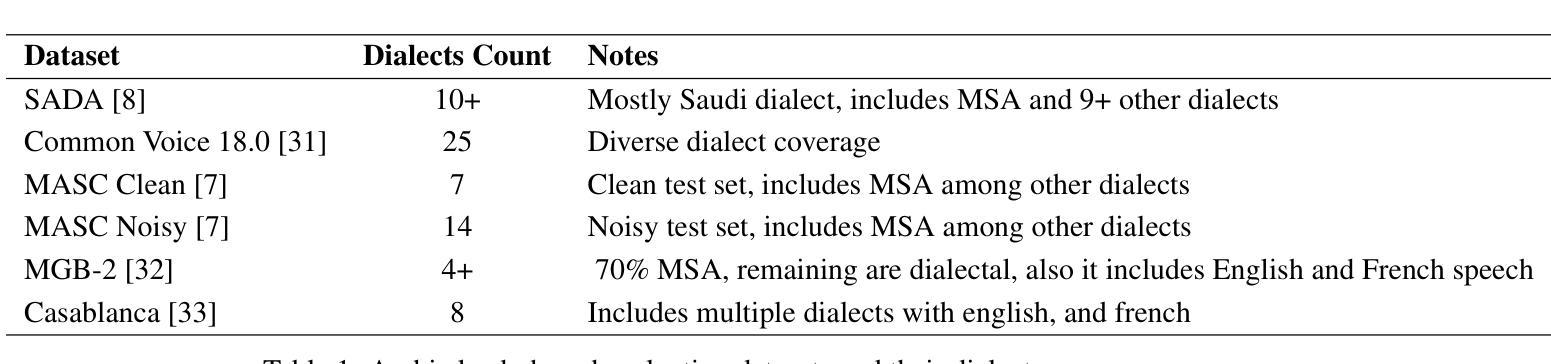
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) is crucial for human-machine interaction in diverse applications like conversational agents, industrial robotics, call center automation, and automated subtitling. However, developing high-performance ASR models remains challenging, particularly for low-resource languages like Arabic, due to the scarcity of large, labeled speech datasets, which are costly and labor-intensive to produce. In this work, we employ weakly supervised learning to train an Arabic ASR model using the Conformer architecture. Our model is trained from scratch on 15,000 hours of weakly annotated speech data covering both Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) and Dialectal Arabic (DA), eliminating the need for costly manual transcriptions. Despite the absence of human-verified labels, our approach attains state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance, exceeding all previous efforts in the field of Arabic ASR on the standard benchmarks. By demonstrating the effectiveness of weak supervision as a scalable, cost-efficient alternative to traditional supervised approaches, paving the way for improved ASR systems in low resource settings.
自动语音识别(ASR)在对话代理、工业机器人、呼叫中心自动化和自动字幕等多样化应用中的人机交互中起着至关重要的作用。然而,开发高性能的ASR模型仍然是一个挑战,特别是对于阿拉伯语等低资源语言来说,由于大规模、标记的语音数据集稀缺,而这些数据集的生成成本高昂且劳动密集。在这项工作中,我们采用弱监督学习,使用Conformer架构训练阿拉伯ASR模型。我们的模型从零开始在涵盖现代标准阿拉伯语(MSA)和方言阿拉伯语(DA)的15000小时弱注释语音数据上进行训练,无需昂贵的人工转录。尽管没有人工验证的标签,我们的方法仍达到了最先进的性能,在标准基准测试中超过了阿拉伯ASR领域的所有先前努力。通过展示弱监督作为传统监督方法的可扩展、成本效益高的替代方案的有效性,为低资源环境中的ASR系统改进铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
阿拉伯语自动语音识别(ASR)在低资源语言环境中面临挑战,因缺乏大规模、标注的语音数据集。本研究采用基于Conformer架构的弱监督学习方法训练阿拉伯语ASR模型,在仅使用弱标注语音数据的情况下达到最先进的性能水平,为低资源环境下的ASR系统改进提供了可行的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 自动语音识别(ASR)在多种应用中都至关重要,如对话代理、工业机器人、呼叫中心自动化和自动字幕等。
- 对于低资源语言如阿拉伯语,开发高性能的ASR模型具有挑战性,因为大规模标注的语音数据集稀缺且制作成本高昂。
- 研究采用弱监督学习方法训练阿拉伯语ASR模型,使用Conformer架构。
- 模型在仅使用弱标注语音数据的情况下训练,无需昂贵的人工转录。
- 模型达到当前最佳性能水平,在标准基准测试中超越此前所有努力。
- 弱监督方法作为可扩展、成本效益高的传统监督方法的替代方案被证明有效。
点此查看论文截图


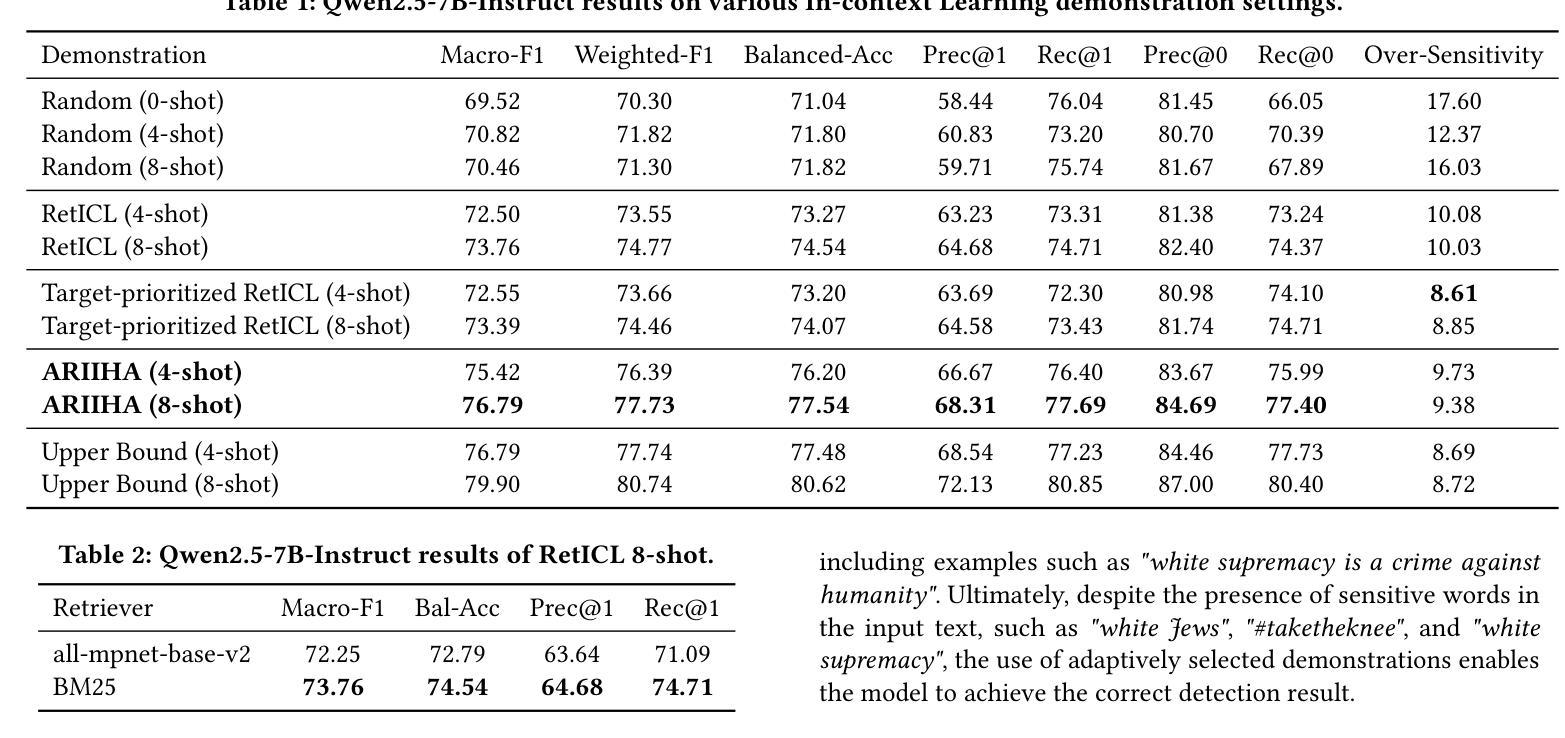
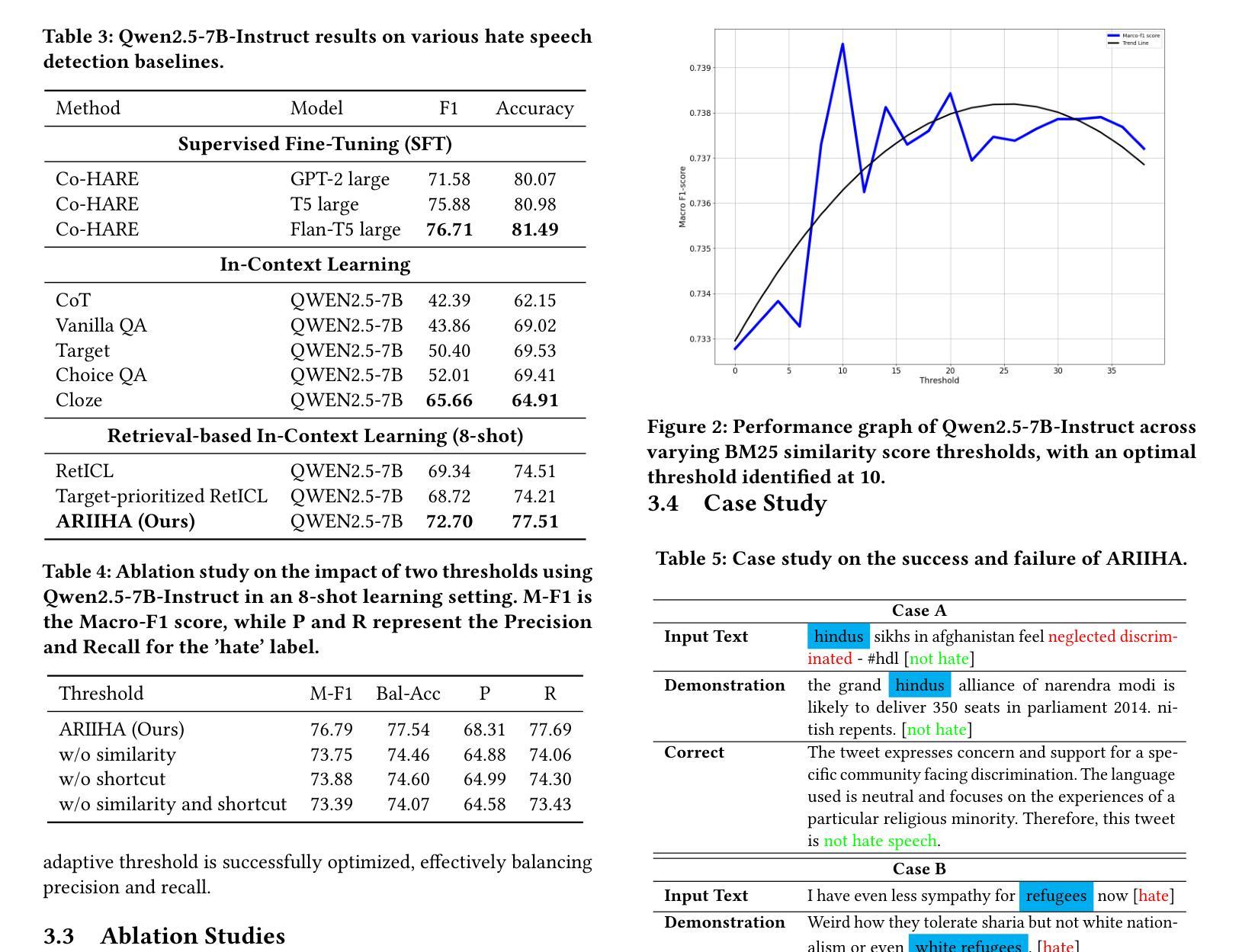
Selective Demonstration Retrieval for Improved Implicit Hate Speech Detection
Authors:Yumin Kim, Hwanhee Lee
Hate speech detection is a crucial area of research in natural language processing, essential for ensuring online community safety. However, detecting implicit hate speech, where harmful intent is conveyed in subtle or indirect ways, remains a major challenge. Unlike explicit hate speech, implicit expressions often depend on context, cultural subtleties, and hidden biases, making them more challenging to identify consistently. Additionally, the interpretation of such speech is influenced by external knowledge and demographic biases, resulting in varied detection results across different language models. Furthermore, Large Language Models often show heightened sensitivity to toxic language and references to vulnerable groups, which can lead to misclassifications. This over-sensitivity results in false positives (incorrectly identifying harmless statements as hateful) and false negatives (failing to detect genuinely harmful content). Addressing these issues requires methods that not only improve detection precision but also reduce model biases and enhance robustness. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method, which utilizes in-context learning without requiring model fine-tuning. By adaptively retrieving demonstrations that focus on similar groups or those with the highest similarity scores, our approach enhances contextual comprehension. Experimental results show that our method outperforms current state-of-the-art techniques. Implementation details and code are available at TBD.
仇恨言论检测是自然语言处理研究的关键领域,对于确保网络社区安全至关重要。然而,检测隐性的仇恨言论仍然是一个重大挑战,其中有害意图以微妙或间接的方式传达。与显性的仇恨言论不同,隐性表达往往依赖于上下文、文化细微差别和隐含偏见,因此难以始终保持一致的识别。此外,此类言论的解读受到外部知识和人口统计偏见的影响,导致不同语言模型之间的检测结果存在差异。另外,大型语言模型往往对有毒语言和弱势群体的提及表现出高度敏感性,这可能导致误判。这种过度敏感性会导致误报(错误地将无害声明识别为仇恨言论)和漏报(未能检测到真正有害的内容)。要解决这些问题,需要的方法不仅要提高检测精度,而且要减少模型偏见并提高稳健性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种新方法,它利用上下文学习,无需对模型进行微调。通过自适应检索关注相似群体或具有最高相似度得分的演示样本,我们的方法增强了上下文理解。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于当前最先进的技术。具体实现和代码可见于(待定)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了仇恨言论检测领域的研究挑战,特别是针对隐含仇恨言论的检测。文中指出,由于上下文、文化细微差别和隐含偏见等因素的影响,隐含仇恨言论的检测是一大挑战。大型语言模型对此类言论的解读存在偏差,易出现误判。为解决这些问题,提出了一种利用上下文学习的新方法,通过检索相似群体或高相似度分数的示例来提高语境理解能力,实验结果表明该方法优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 仇恨言论检测是自然语言处理中的一个重要研究领域,对于确保在线社区安全至关重要。
- 隐含仇恨言论的检测是一大挑战,因为其表达方式间接、微妙,依赖于上下文和文化因素。
- 大型语言模型在解读仇恨言论时存在偏差,导致误判。
- 现有的仇恨言论检测方法存在误报和漏报的问题。
- 一种新的仇恨言论检测方法被提出,该方法利用上下文学习,通过检索相似示例来提高语境理解能力。
- 该新方法在实验中表现出优于现有技术的性能。
点此查看论文截图