⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-18 更新
Comparative Evaluation of Radiomics and Deep Learning Models for Disease Detection in Chest Radiography
Authors:Zhijin He, Alan B. McMillan
The application of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging has revolutionized diagnostic practices, enabling advanced analysis and interpretation of radiological data. This study presents a comprehensive evaluation of radiomics-based and deep learning-based approaches for disease detection in chest radiography, focusing on COVID-19, lung opacity, and viral pneumonia. While deep learning models, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs), learn directly from image data, radiomics-based models extract and analyze quantitative features, potentially providing advantages in data-limited scenarios. This study systematically compares the diagnostic accuracy and robustness of various AI models, including Decision Trees, Gradient Boosting, Random Forests, Support Vector Machines (SVM), and Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLP) for radiomics, against state-of-the-art computer vision deep learning architectures. Performance metrics across varying sample sizes reveal insights into each model’s efficacy, highlighting the contexts in which specific AI approaches may offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities. The results aim to inform the integration of AI-driven diagnostic tools in clinical practice, particularly in automated and high-throughput environments where timely, reliable diagnosis is critical. This comparative study addresses an essential gap, establishing guidance for the selection of AI models based on clinical and operational needs.
人工智能(AI)在医学影像领域的应用已经彻底改变了诊断实践,使放射学数据的先进分析和解释成为可能。本研究全面评估了基于放射组学和基于深度学习的方法在胸部放射摄影中检测疾病的性能,重点关注COVID-19、肺部不透明和病毒性肺炎。深度学习模型,特别是卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉变压器(ViT),直接从图像数据中学习,而基于放射组学的模型则提取并分析定量特征,在数据有限的场景中可能具有潜在优势。本研究系统地比较了各种AI模型的诊断准确性和稳健性,包括用于放射组学的决策树、梯度提升、随机森林、支持向量机(SVM)和多层感知器(MLP)与最先进的计算机视觉深度学习架构之间的比较。不同样本量下的性能指标揭示了每种模型的有效性,突出了特定AI方法可能在哪些情况下提供增强的诊断能力。研究结果旨在为AI驱动的诊断工具在临床实践中的整合提供信息,特别是在及时可靠的诊断至关重要的自动化和高通量环境中。这项比较研究解决了重要的问题,根据临床和运营需求为选择AI模型提供了指导。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能在医学影像领域的应用已经彻底改变了诊断实践,促进了对放射数据的深入分析和解读。本研究全面评估了基于放射组学和深度学习的方法在胸部放射摄影中疾病检测的表现,重点研究COVID-19、肺部不透明度和病毒性肺炎。深度学习模型,尤其是卷积神经网络和视觉转换器,直接从图像数据中学习;而基于放射组学的模型则提取和分析定量特征,可能在数据有限的场景中提供优势。本研究系统地比较了各种人工智能模型的诊断准确性和稳健性,包括决策树、梯度提升、随机森林、支持向量机和多层感知器(用于放射组学),以及最先进的计算机视觉深度学习架构。不同样本量下的性能指标揭示了每种模型的有效性,并突出了特定人工智能方法在哪些情况下可能提供增强的诊断能力。研究结果旨在为在临床实践中整合人工智能驱动的诊断工具提供信息,特别是在需要及时可靠诊断的自动化和高通量环境中。这项比较研究填补了一个重要空白,根据临床和运营需求提供了选择人工智能模型的指导。
Key Takeaways
- AI在医学影像领域的应用已经改变了诊断实践,促进了放射数据的深入分析。
- 本研究比较了基于放射组学和深度学习的方法在疾病检测中的表现,特别是针对COVID-19、肺部不透明度和病毒性肺炎。
- 深度学习模型,特别是卷积神经网络和视觉转换器,直接从图像数据中学习特征。
- 基于放射组学的模型在提取和分析定量特征方面可能具有优势,尤其在数据有限的场景中。
- 研究通过比较不同人工智能模型的诊断准确性和稳健性,包括多种传统机器学习方法与先进的深度学习架构。
- 不同样本量下的性能指标显示了各种模型的有效性,并指出特定AI方法在特定情境下的优势。
点此查看论文截图

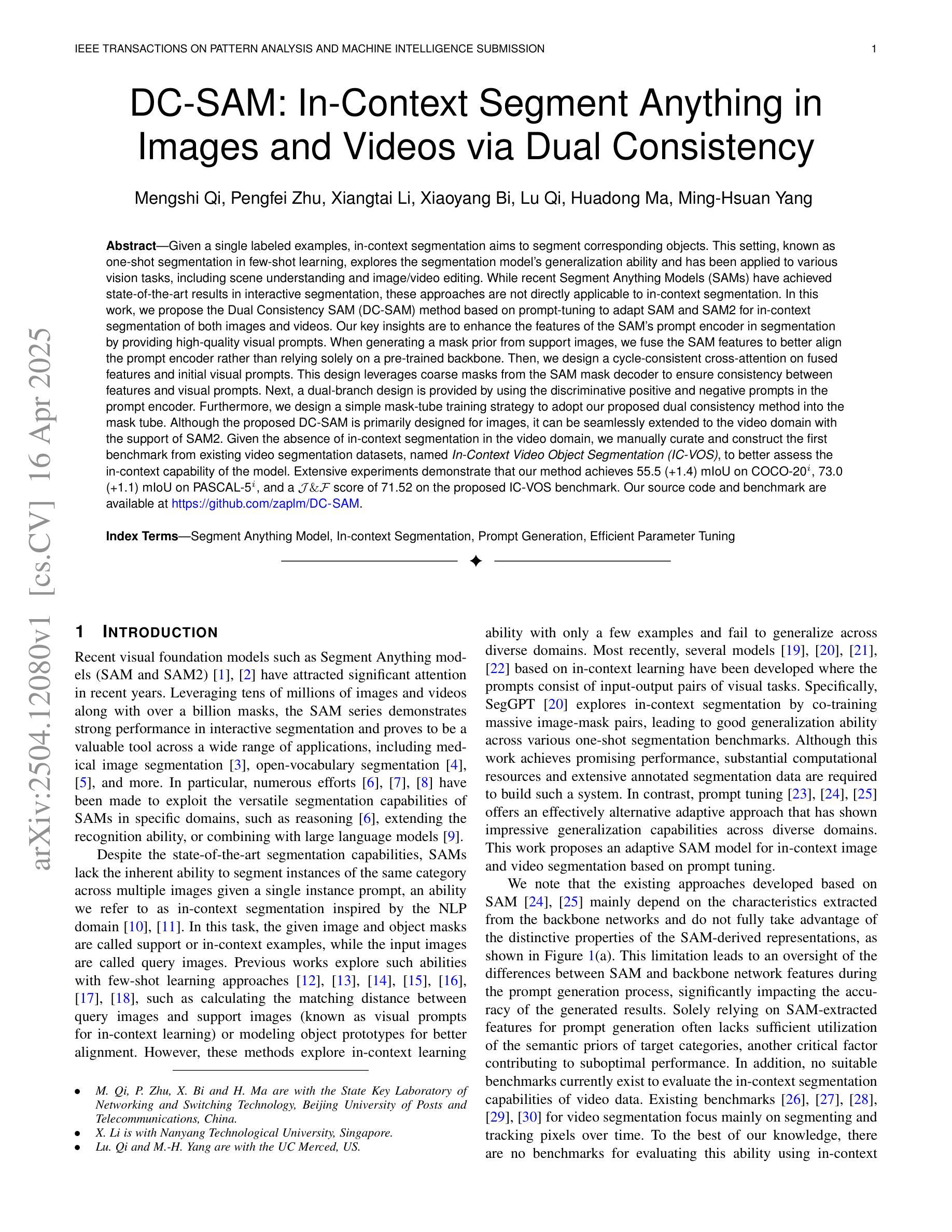
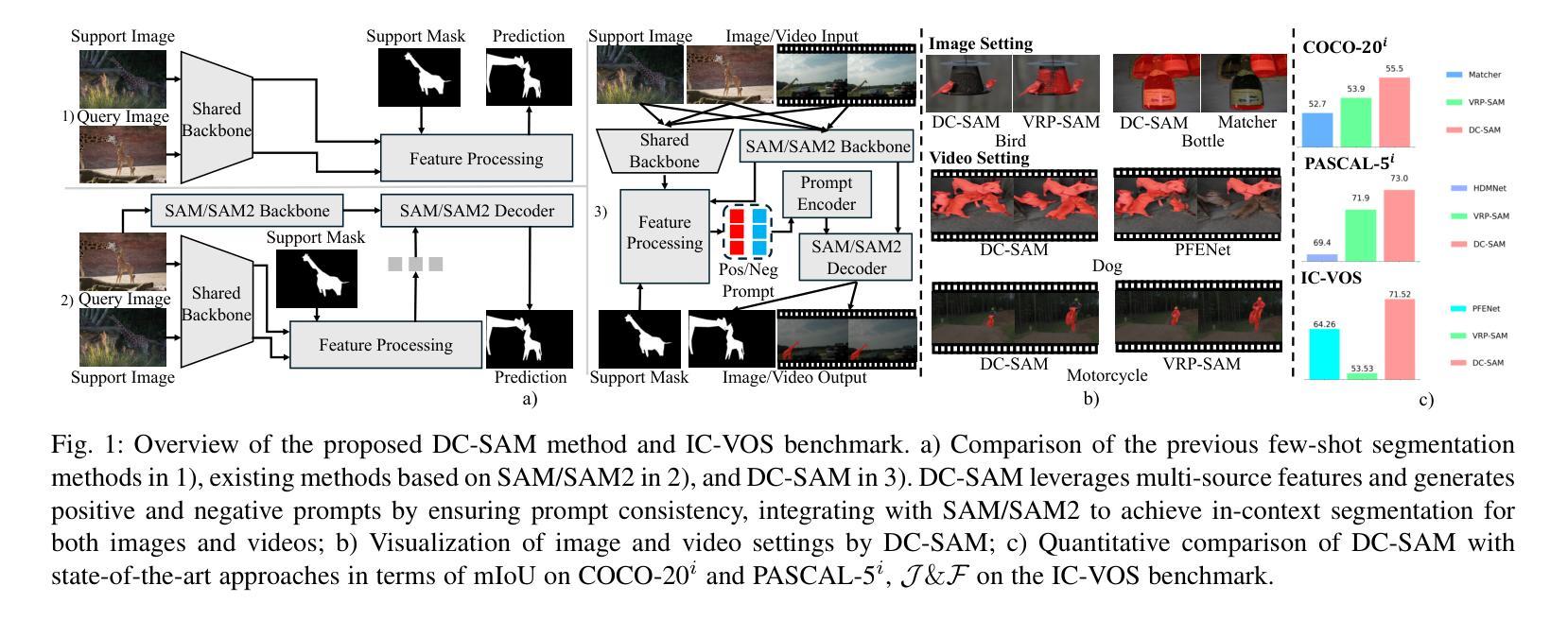
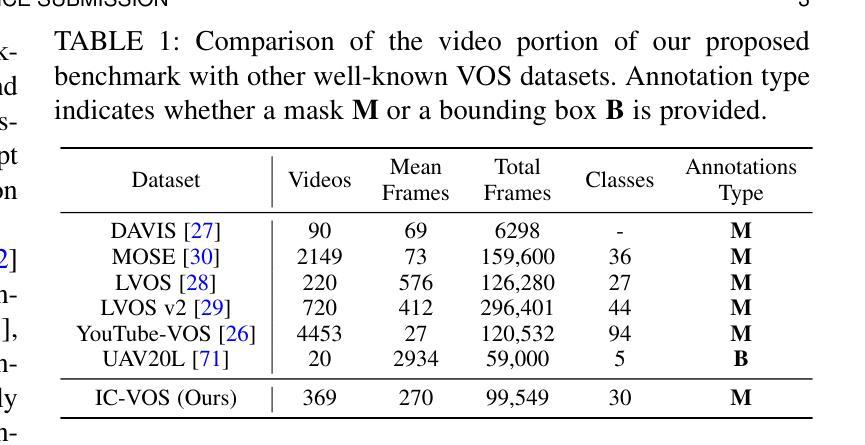
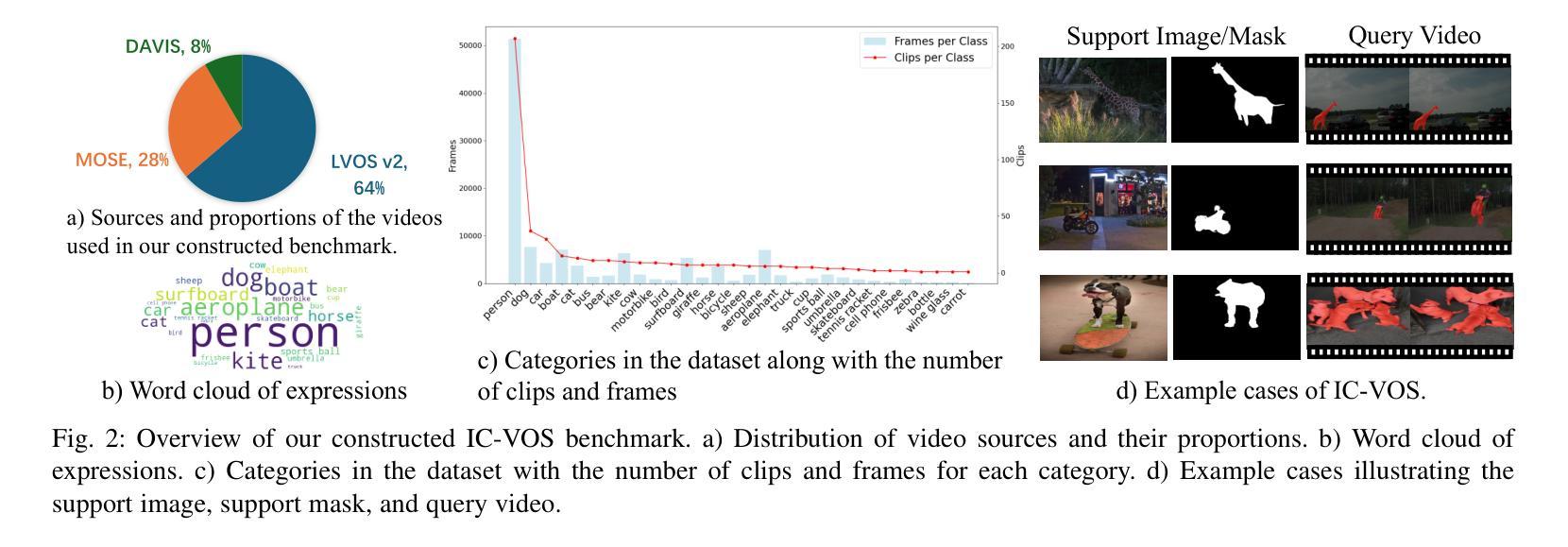
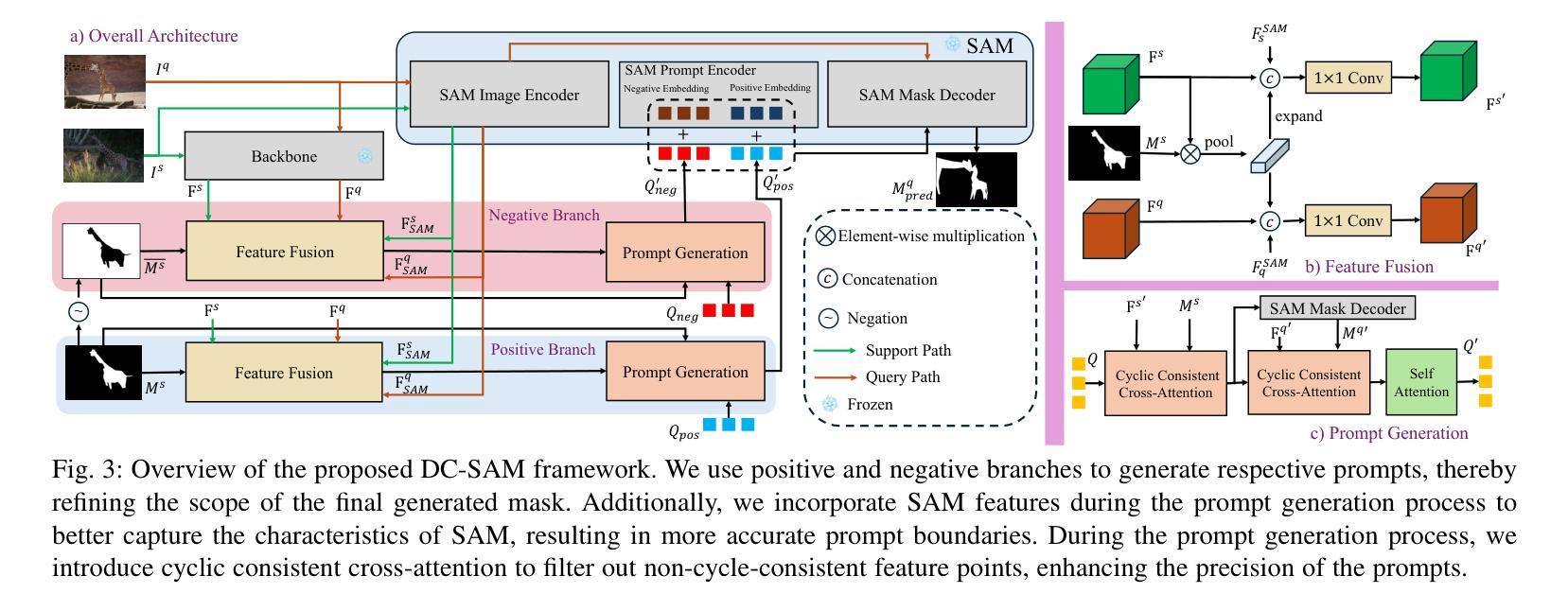
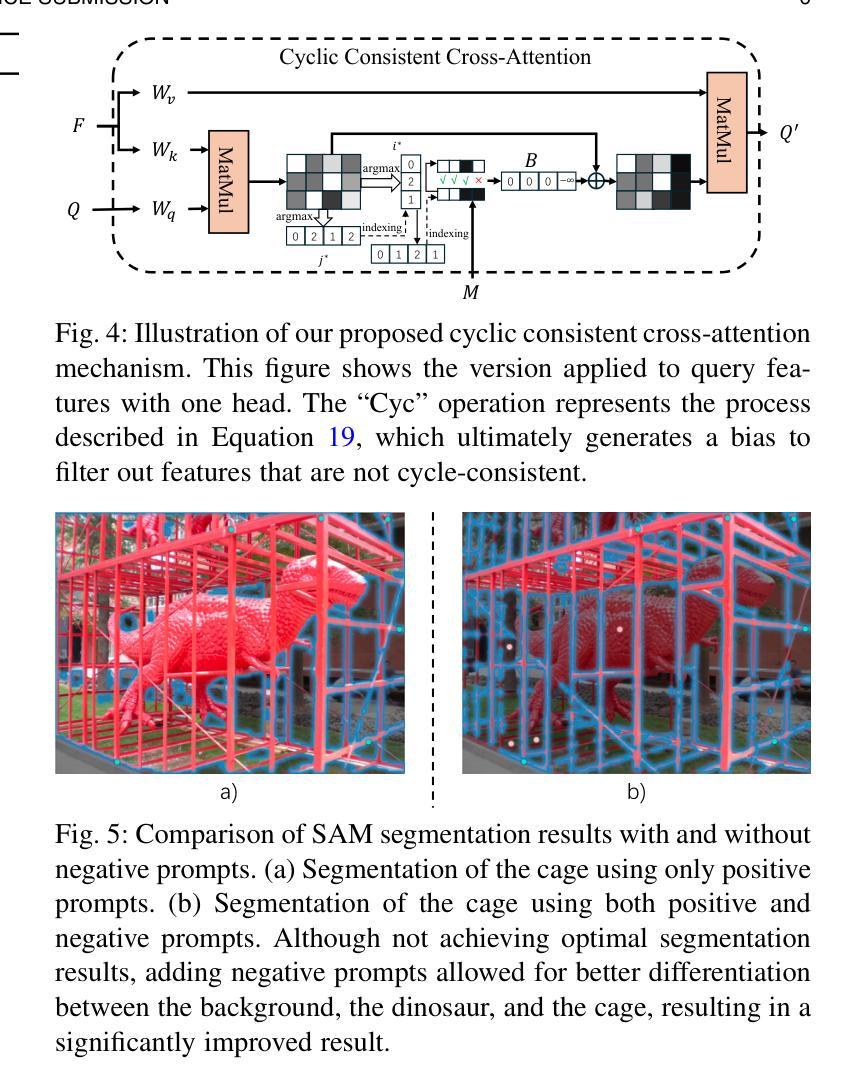
DC-SAM: In-Context Segment Anything in Images and Videos via Dual Consistency
Authors:Mengshi Qi, Pengfei Zhu, Xiangtai Li, Xiaoyang Bi, Lu Qi, Huadong Ma, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Given a single labeled example, in-context segmentation aims to segment corresponding objects. This setting, known as one-shot segmentation in few-shot learning, explores the segmentation model’s generalization ability and has been applied to various vision tasks, including scene understanding and image/video editing. While recent Segment Anything Models have achieved state-of-the-art results in interactive segmentation, these approaches are not directly applicable to in-context segmentation. In this work, we propose the Dual Consistency SAM (DC-SAM) method based on prompt-tuning to adapt SAM and SAM2 for in-context segmentation of both images and videos. Our key insights are to enhance the features of the SAM’s prompt encoder in segmentation by providing high-quality visual prompts. When generating a mask prior, we fuse the SAM features to better align the prompt encoder. Then, we design a cycle-consistent cross-attention on fused features and initial visual prompts. Next, a dual-branch design is provided by using the discriminative positive and negative prompts in the prompt encoder. Furthermore, we design a simple mask-tube training strategy to adopt our proposed dual consistency method into the mask tube. Although the proposed DC-SAM is primarily designed for images, it can be seamlessly extended to the video domain with the support of SAM2. Given the absence of in-context segmentation in the video domain, we manually curate and construct the first benchmark from existing video segmentation datasets, named In-Context Video Object Segmentation (IC-VOS), to better assess the in-context capability of the model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves 55.5 (+1.4) mIoU on COCO-20i, 73.0 (+1.1) mIoU on PASCAL-5i, and a J&F score of 71.52 on the proposed IC-VOS benchmark. Our source code and benchmark are available at https://github.com/zaplm/DC-SAM.
给定单个有标签的样本,上下文分割旨在分割对应的对象。这种设置被称为小样本学习中的一次分割,它探索了分割模型的泛化能力,并已应用于各种视觉任务,包括场景理解、图像/视频编辑等。虽然最近的任何分割模型在交互式分割方面取得了最新结果,但这些方法并不能直接应用于上下文分割。在这项工作中,我们提出了基于提示调整的Dual Consistency SAM(DC-SAM)方法,以适应图像和视频的上下文分割。我们的关键见解是通过提供高质量的视觉提示来增强SAM提示编码器在分割中的功能。在生成掩膜先验时,我们融合了SAM特征以更好地对齐提示编码器。然后,我们在融合的特征和初始视觉提示上设计了一个循环一致的交叉注意力。接下来,通过使用提示编码器中的判别性正向和负向提示,提供了一个双分支设计。此外,我们设计了一个简单的掩膜管训练策略,将我们所提出的双重一致性方法应用于掩膜管。虽然提出的DC-SAM主要是为图像设计的,但它可以无缝地扩展到视频领域,得到SAM2的支持。由于在视频领域缺乏上下文分割,我们从现有的视频分割数据集中手动筛选和构建了第一个基准测试,名为In-Context Video Object Segmentation(IC-VOS),以更好地评估模型的上下文能力。大量实验表明,我们的方法在COCO-20i上实现了55.5(+1.4)的mIoU,在PASCAL-5i上实现了73.0(+1.1)的mIoU,在提出的IC-VOS基准测试上达到了71.52的J&F分数。我们的源代码和基准测试可在https://github.com/zaplm/DC-SAM找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于提示调整(prompt-tuning)的Dual Consistency SAM(DC-SAM)方法,用于实现基于单个示例的一键式上下文感知分割。本文首次建立了适用于视频的上下文分割评估基准IC-VOS,并展示了DC-SAM在图像和视频分割任务上的优越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文章提出了基于提示调整的Dual Consistency SAM(DC-SAM)方法,用于实现基于单个示例的上下文感知分割。
- DC-SAM方法通过增强SAM的提示编码器特征,并结合使用高质量视觉提示,生成遮罩先验。
- 文章设计了一种循环一致的跨注意力机制,用于融合特征和初始视觉提示。
- 通过采用判别性的正负提示,设计了一种双分支设计,用于提示编码器。
- 为适应所提出的双一致性方法,文章设计了一种简单的遮罩管训练策略。
- DC-SAM方法不仅适用于图像分割,还可无缝扩展到视频领域。
点此查看论文截图
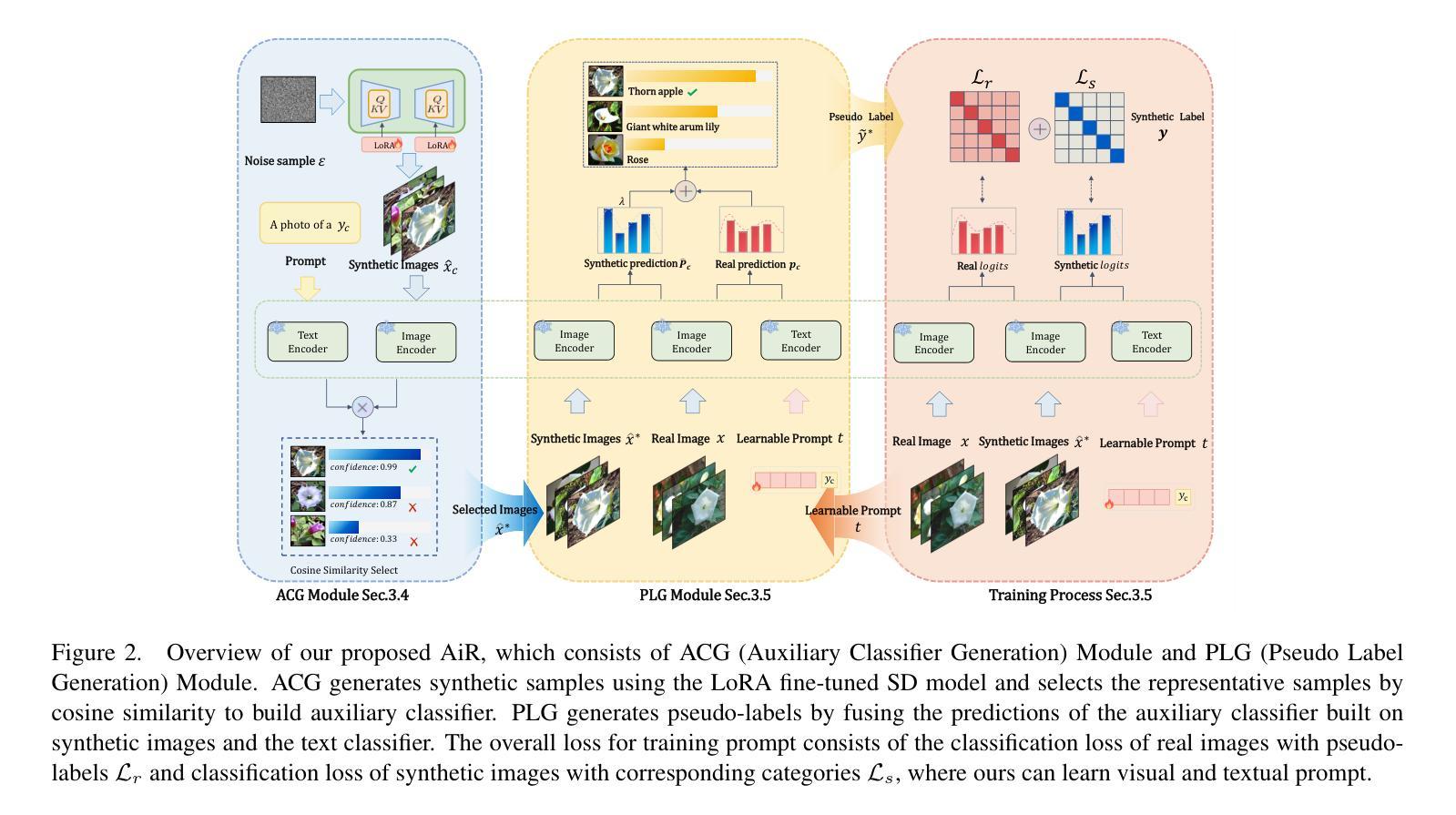
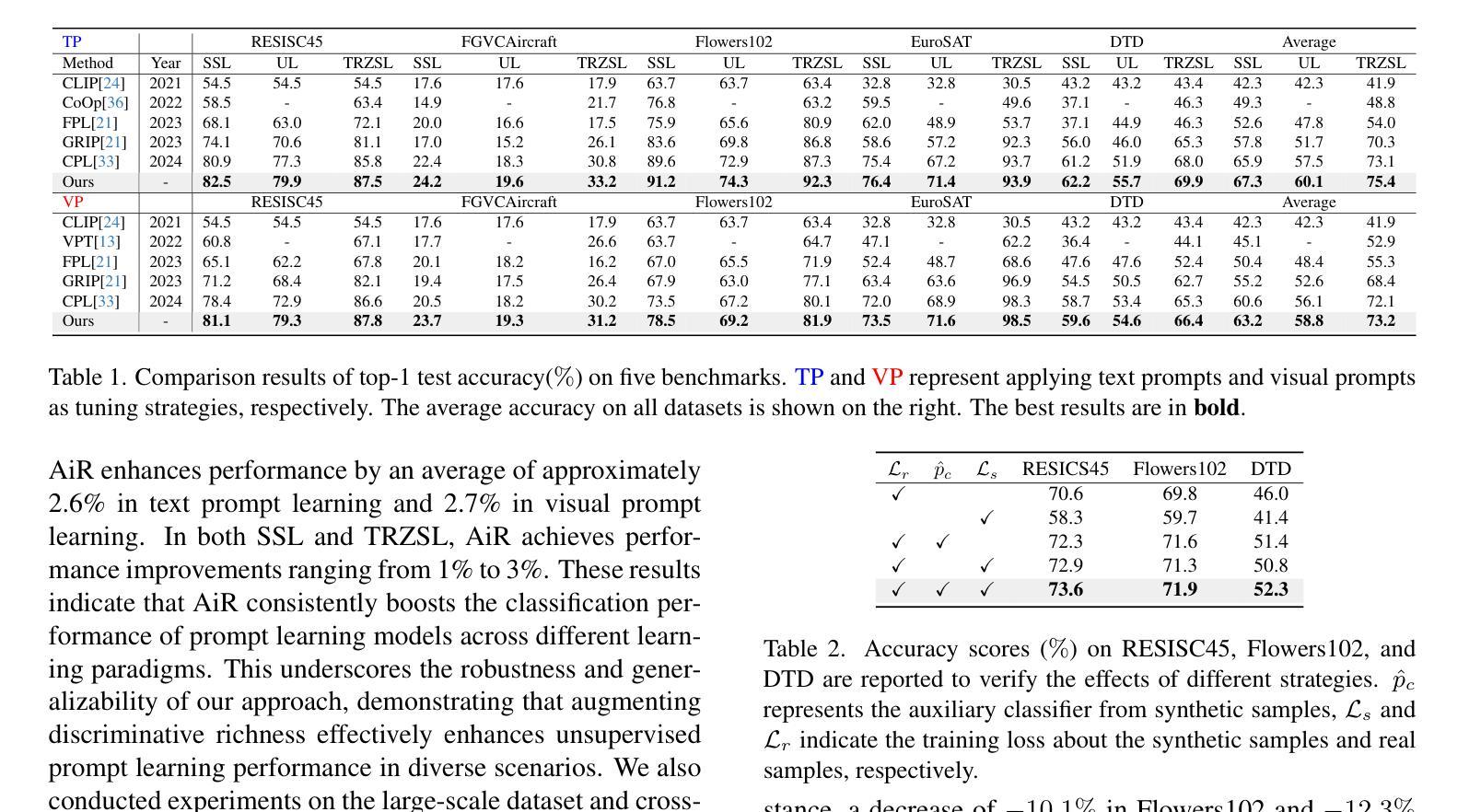
Beyond Words: Augmenting Discriminative Richness via Diffusions in Unsupervised Prompt Learning
Authors:Hairui Ren, Fan Tang, He Zhao, Zixuan Wang, Dandan Guo, Yi Chang
Fine-tuning vision-language models (VLMs) with large amounts of unlabeled data has recently garnered significant interest. However, a key challenge remains the lack of high-quality pseudo-labeled data. Current pseudo-labeling strategies often struggle with mismatches between semantic and visual information, leading to sub-optimal performance of unsupervised prompt learning (UPL) methods. In this paper, we introduce a simple yet effective approach called \textbf{A}ugmenting D\textbf{i}scriminative \textbf{R}ichness via Diffusions (AiR), toward learning a richer discriminating way to represent the class comprehensively and thus facilitate classification. Specifically, our approach includes a pseudo-label generation module that leverages high-fidelity synthetic samples to create an auxiliary classifier, which captures richer visual variation, bridging text-image-pair classification to a more robust image-image-pair classification. Additionally, we exploit the diversity of diffusion-based synthetic samples to enhance prompt learning, providing greater information for semantic-visual alignment. Extensive experiments on five public benchmarks, including RESISC45 and Flowers102, and across three learning paradigms-UL, SSL, and TRZSL-demonstrate that AiR achieves substantial and consistent performance improvements over state-of-the-art unsupervised prompt learning methods.
对大量无标签数据进行视觉语言模型(VLMs)的微调最近引起了极大的兴趣。然而,缺乏高质量的伪标签数据仍然是关键挑战。当前的伪标签策略通常面临语义和视觉信息之间的不匹配问题,导致无监督提示学习(UPL)方法性能不佳。在本文中,我们介绍了一种简单有效的方法,称为通过扩散增强辨别丰富性(AiR),旨在学习一种更丰富的辨别方式,以全面代表类别,从而促进分类。具体来说,我们的方法包括一个伪标签生成模块,该模块利用高保真合成样本创建一个辅助分类器,以捕捉更丰富的视觉变化,将文本图像对分类转变为更稳健的图像图像对分类。此外,我们利用基于扩散的合成样本的多样性来增强提示学习,为语义视觉对齐提供更多信息。在五个公共基准测试(包括RESISC45和Flowers102)以及三种学习模式(UL、SSL和TRZSL)上的大量实验表明,与最先进的无监督提示学习方法相比,AiR实现了显著且一致的性能改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种简单有效的方法——AiR(通过扩散增强判别丰富性),用于解决大规模视觉语言模型的无监督提示学习面临的挑战。通过使用高保真合成样本生成伪标签,AiR能捕捉更丰富多样的视觉特征,从而将文本图像配对分类提升为更稳健的图像图像配对分类。同时,利用基于扩散的合成样本多样性增强提示学习,促进语义与视觉的对齐。在五个公共基准测试上的实验结果表明,AiR在多种学习模式下均实现了显著且持续的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种名为AiR的新方法,旨在解决大规模视觉语言模型无监督提示学习中的挑战。
- 利用高保真合成样本生成伪标签,创建了辅助分类器以捕捉更丰富多样的视觉特征。
- 通过将文本图像配对分类转化为图像图像配对分类,提高了模型的稳健性。
- 利用基于扩散的合成样本多样性增强提示学习,促进语义与视觉的对齐。
- 在五个公共基准测试上的实验结果表明AiR性能优越。
点此查看论文截图

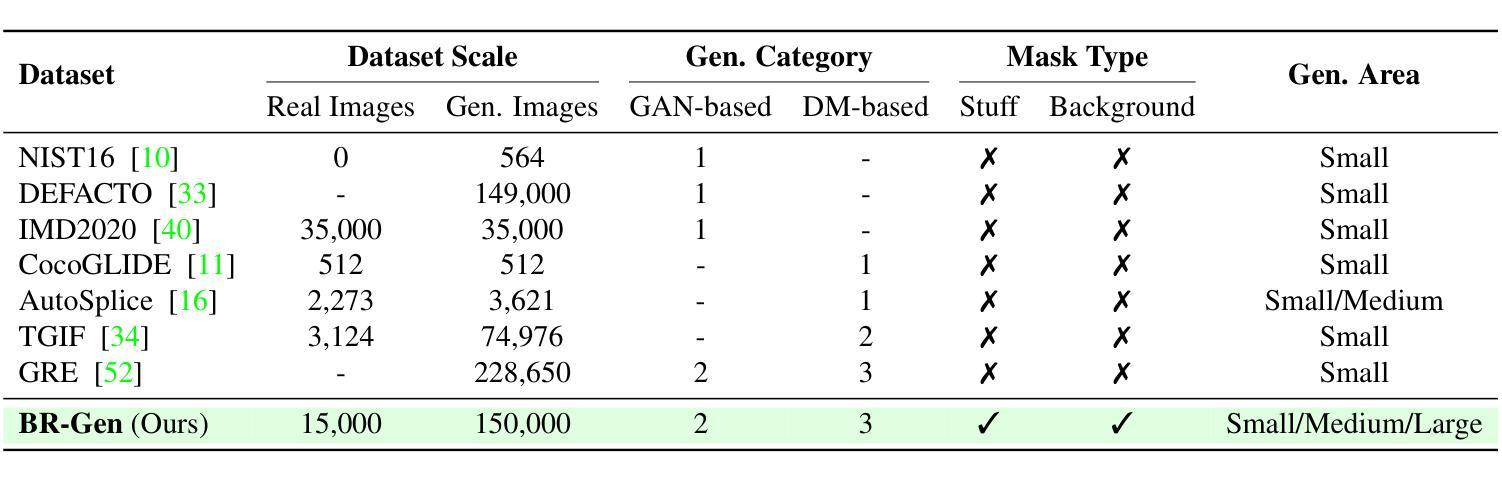
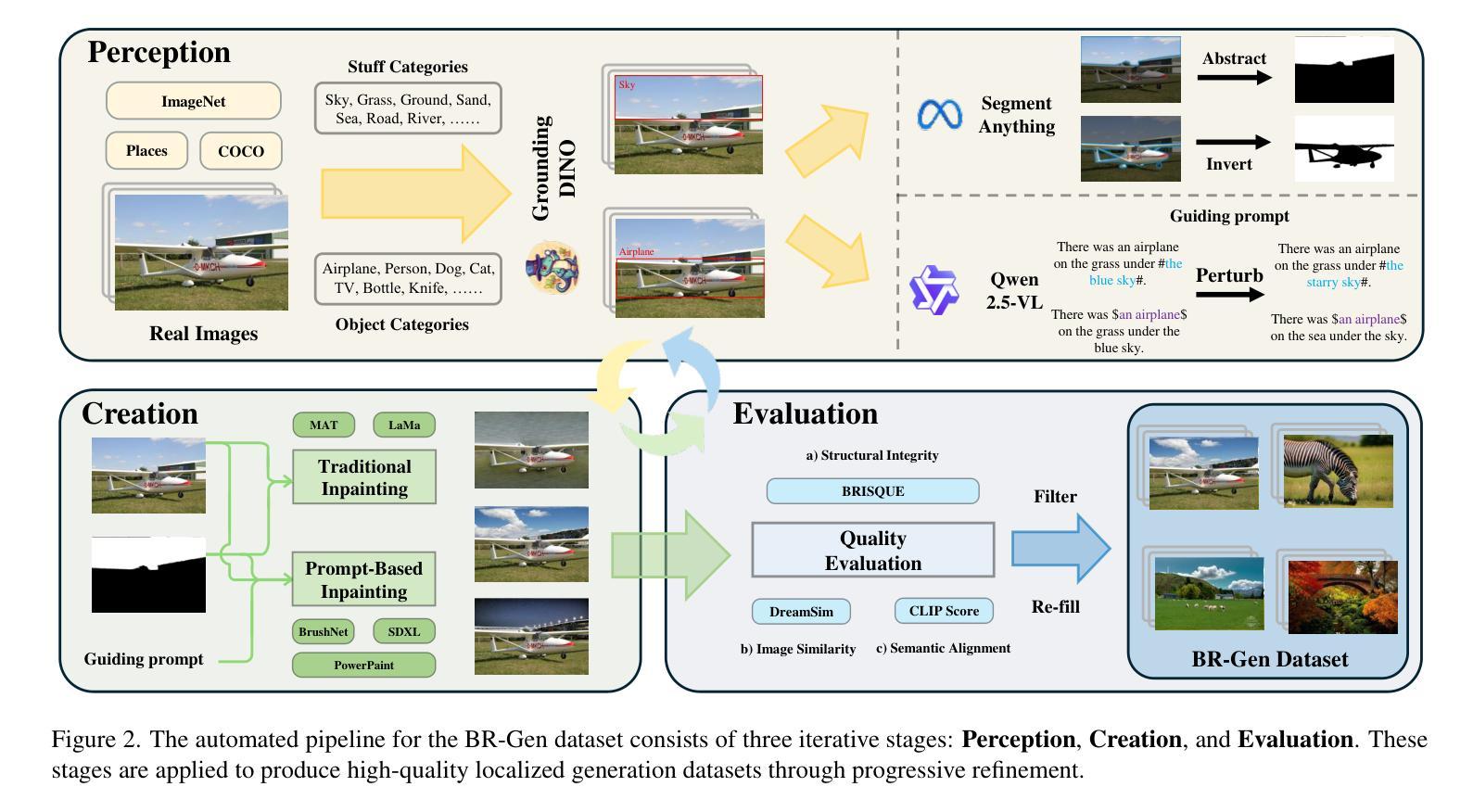
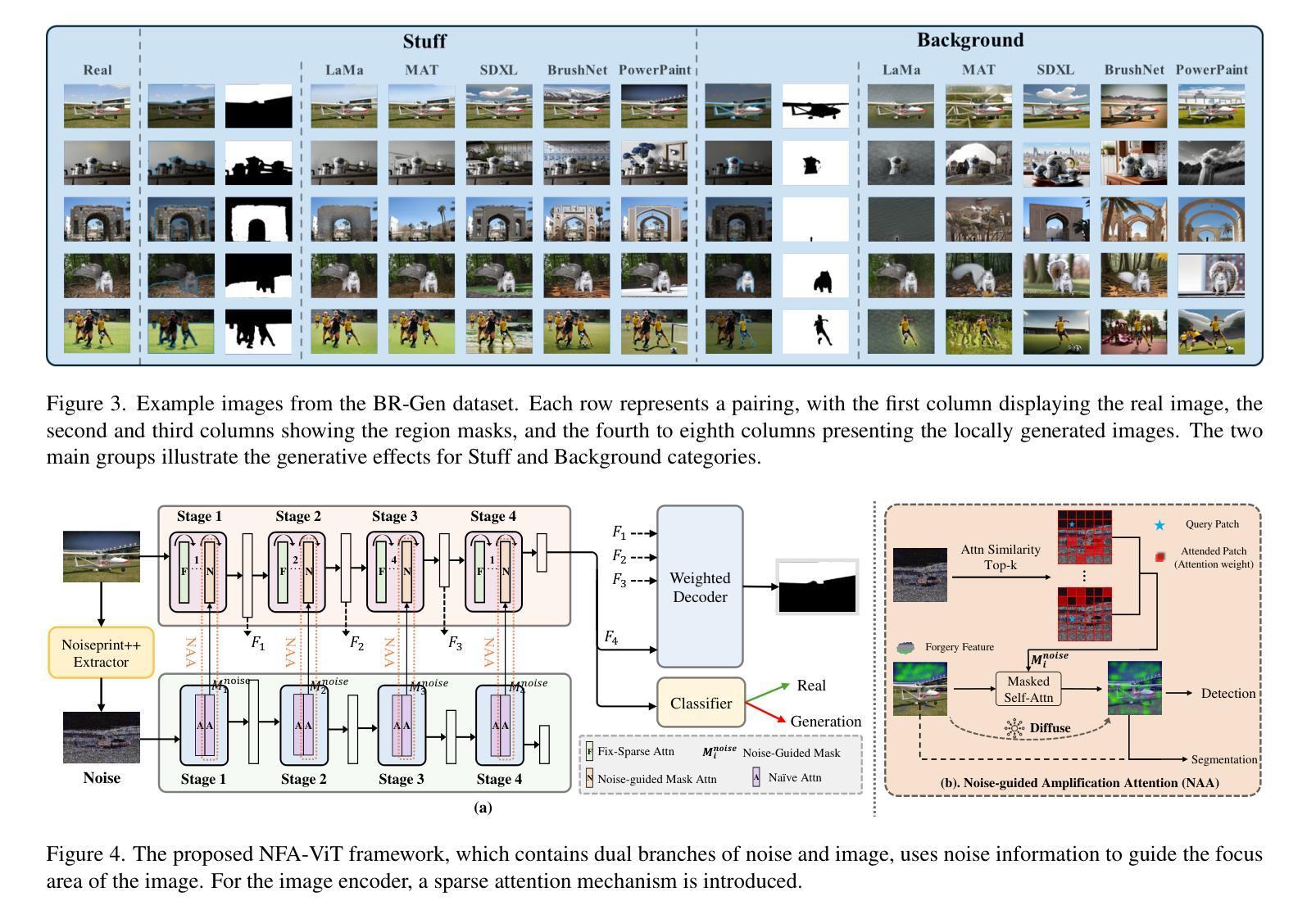
Zooming In on Fakes: A Novel Dataset for Localized AI-Generated Image Detection with Forgery Amplification Approach
Authors:Lvpan Cai, Haowei Wang, Jiayi Ji, YanShu ZhouMen, Yiwei Ma, Xiaoshuai Sun, Liujuan Cao, Rongrong Ji
The rise of AI-generated image editing tools has made localized forgeries increasingly realistic, posing challenges for visual content integrity. Although recent efforts have explored localized AIGC detection, existing datasets predominantly focus on object-level forgeries while overlooking broader scene edits in regions such as sky or ground. To address these limitations, we introduce \textbf{BR-Gen}, a large-scale dataset of 150,000 locally forged images with diverse scene-aware annotations, which are based on semantic calibration to ensure high-quality samples. BR-Gen is constructed through a fully automated Perception-Creation-Evaluation pipeline to ensure semantic coherence and visual realism. In addition, we further propose \textbf{NFA-ViT}, a Noise-guided Forgery Amplification Vision Transformer that enhances the detection of localized forgeries by amplifying forgery-related features across the entire image. NFA-ViT mines heterogeneous regions in images, \emph{i.e.}, potential edited areas, by noise fingerprints. Subsequently, attention mechanism is introduced to compel the interaction between normal and abnormal features, thereby propagating the generalization traces throughout the entire image, allowing subtle forgeries to influence a broader context and improving overall detection robustness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BR-Gen constructs entirely new scenarios that are not covered by existing methods. Take a step further, NFA-ViT outperforms existing methods on BR-Gen and generalizes well across current benchmarks. All data and codes are available at https://github.com/clpbc/BR-Gen.
随着人工智能生成的图像编辑工具的普及,局部伪造图像的真实性越来越高,这给视觉内容完整性带来了挑战。尽管最近的研究已经探索了局部AIGC检测,但现有数据集主要集中在对象级别的伪造上,而忽略了天空或地面等区域的更广泛的场景编辑。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了BR-Gen,这是一个包含15万张局部伪造图像的大规模数据集,具有基于语义校准的多样化场景感知注释,以确保高质量样本。BR-Gen通过全自动的感知-创建-评估流程构建,以确保语义连贯和视觉真实性。此外,我们进一步提出了NFA-ViT,这是一种噪声引导的伪造放大视觉转换器,通过放大整个图像中的伪造相关特征,增强局部伪造的检测。NFA-ViT通过噪声指纹挖掘图像中的异构图地区,即潜在编辑区域。随后,引入注意力机制,迫使正常和异常特征之间的交互,从而在整幅图像中传播泛化痕迹,使细微的伪造能够影响更广泛的上下文,提高检测的整体稳健性。大量实验表明,BR-Gen构建的场景完全超出了现有方法覆盖的范围。更进一步的是,NFA-ViT在BR-Gen上的表现优于现有方法,并在当前基准测试中具有良好的泛化能力。所有数据和代码都可在https://github.com/clpbc/BR-Gen上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了AI生成图像编辑工具的兴起带来的局部篡改挑战。针对现有数据集主要关注对象级篡改,而忽视天空或地面等更广泛场景编辑的问题,提出了BR-Gen数据集。该数据集包含15万张局部伪造图像,具有基于语义校准的丰富场景感知注释。此外,还提出了NFA-ViT模型,通过噪声引导的伪造放大视觉转换器,增强对局部篡改的检测。该模型通过噪声指纹挖掘图像中的异质区域,引入注意力机制,迫使正常和异常特征之间的交互,提高检测稳健性。实验表明,BR-Gen数据集开创了全新场景,而NFA-ViT在BR-Gen上的表现优于现有方法,并在当前基准测试中具有良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成的图像编辑工具使得局部伪造图像越来越逼真,对视觉内容完整性构成挑战。
- 现有数据集主要关注对象级伪造,而忽视更广泛的场景编辑,如天空或地面。
- 引入BR-Gen数据集,包含15万张局部伪造图像,具有丰富场景感知注释,基于语义校准确保高质量样本。
- 提出NFA-ViT模型,通过噪声引导的伪造放大视觉转换器增强局部伪造检测。
- NFA-ViT模型通过噪声指纹挖掘图像中的异质区域,并引入注意力机制来提高检测稳健性。
- 实验表明BR-Gen数据集具有创新性,NFA-ViT在BR-Gen上的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

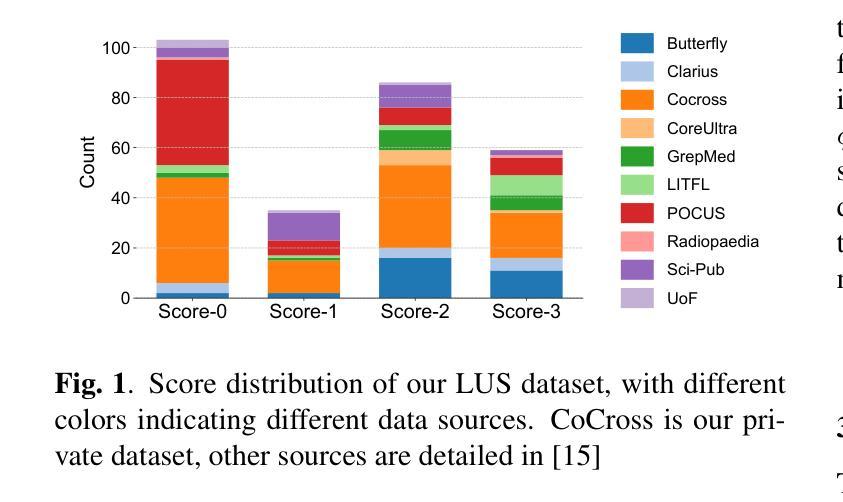
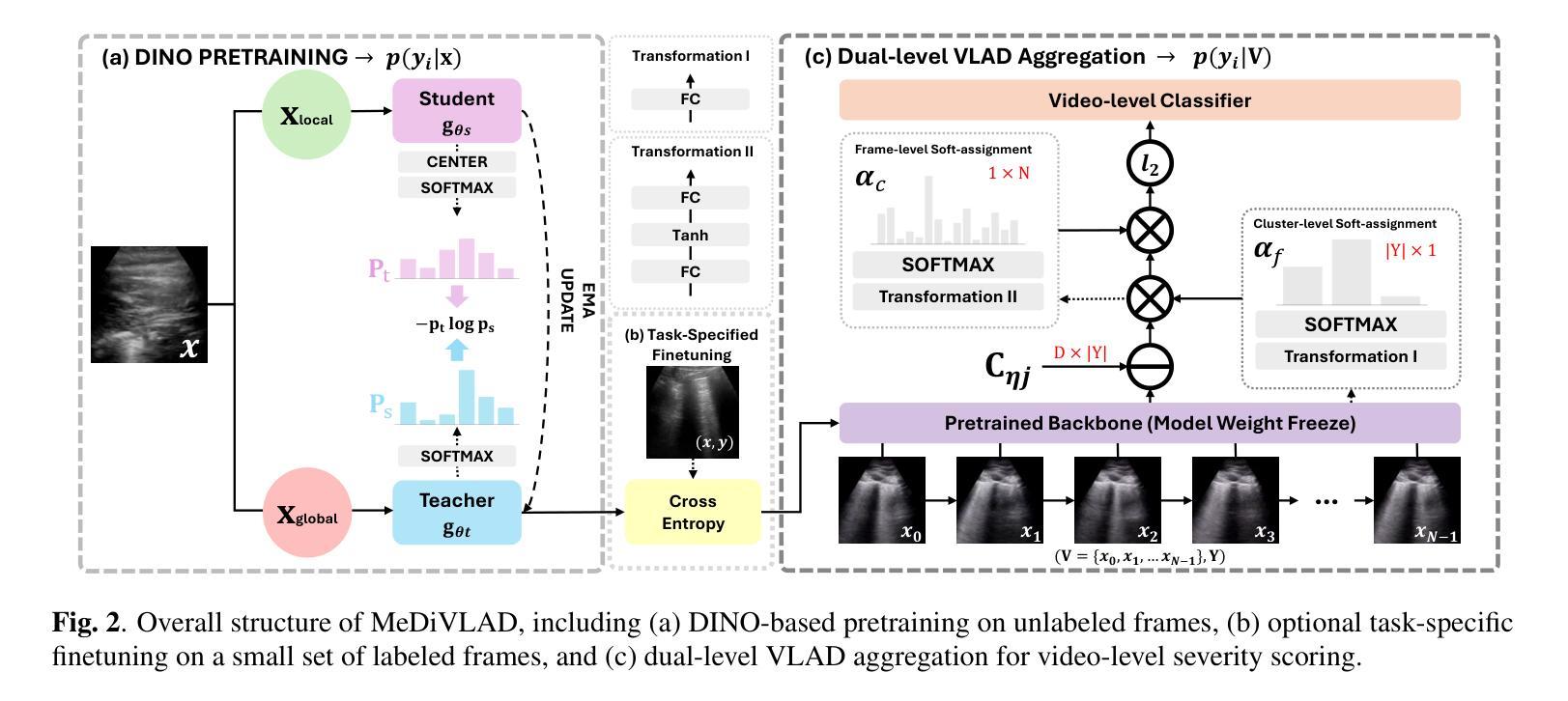
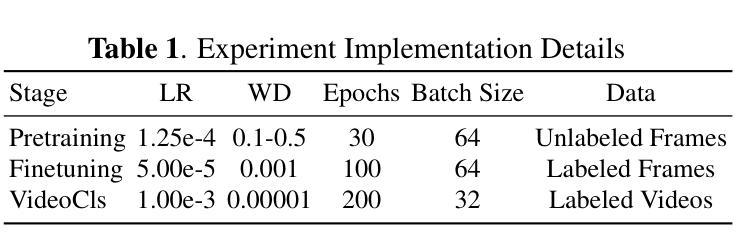
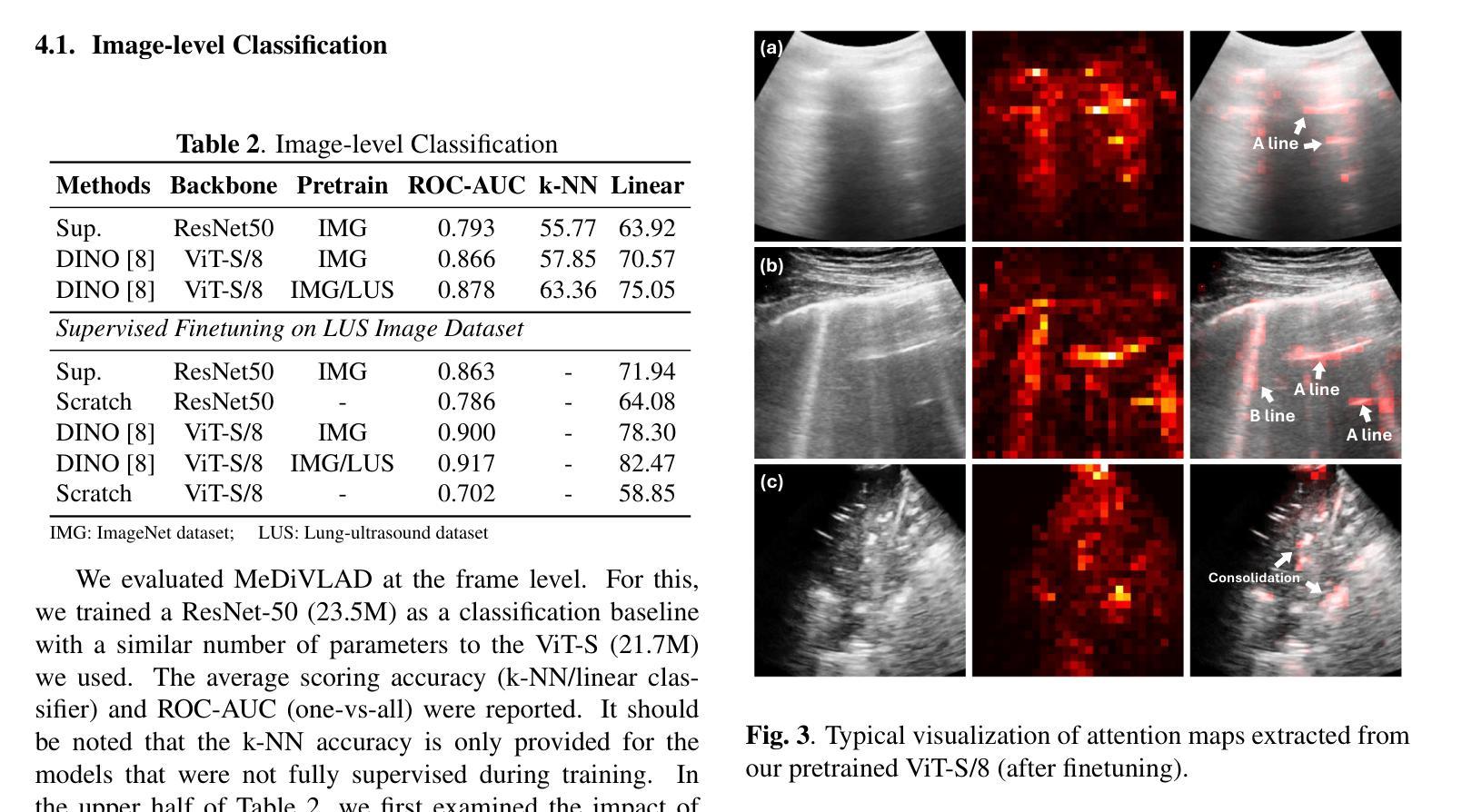
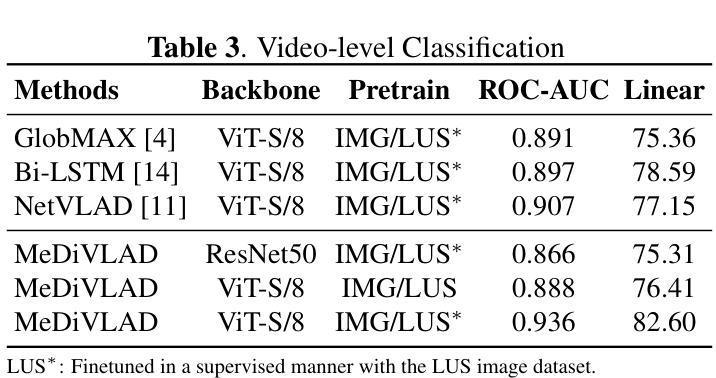
Efficient Lung Ultrasound Severity Scoring Using Dedicated Feature Extractor
Authors:Jiaqi Guo, Yunan Wu, Evangelos Kaimakamis, Georgios Petmezas, Vasileios E. Papageorgiou, Nicos Maglaveras, Aggelos K. Katsaggelos
With the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, ultrasound imaging has emerged as a promising technique for COVID-19 detection, due to its non-invasive nature, affordability, and portability. In response, researchers have focused on developing AI-based scoring systems to provide real-time diagnostic support. However, the limited size and lack of proper annotation in publicly available ultrasound datasets pose significant challenges for training a robust AI model. This paper proposes MeDiVLAD, a novel pipeline to address the above issue for multi-level lung-ultrasound (LUS) severity scoring. In particular, we leverage self-knowledge distillation to pretrain a vision transformer (ViT) without label and aggregate frame-level features via dual-level VLAD aggregation. We show that with minimal finetuning, MeDiVLAD outperforms conventional fully-supervised methods in both frame- and video-level scoring, while offering classification reasoning with exceptional quality. This superior performance enables key applications such as the automatic identification of critical lung pathology areas and provides a robust solution for broader medical video classification tasks.
随着COVID-19大流行的到来,由于其无创、负担得起和便携的特点,超声成像已崭露头角为一种有前景的COVID-19检测技术。为此,研究人员致力于开发基于人工智能的评分系统,以提供实时诊断支持。然而,公开可用的超声数据集的规模有限且缺乏适当的注释,给训练稳健的人工智能模型带来了巨大挑战。本文提出了MeDiVLAD,这是一个新颖的管道流程,旨在解决上述针对多级肺超声(LUS)严重性评分的问题。特别是,我们利用自我知识蒸馏对视觉转换器(ViT)进行预训练,而无需标签并聚集帧级特征的双级VLAD聚合。我们表明,通过最小的微调,MeDiVLAD在帧级和视频级评分方面都优于传统的全监督方法,同时提供出色的分类推理质量。这种卓越的性能能够应用于自动识别关键肺部病理区域的关键应用,并为更广泛的医学视频分类任务提供了稳健的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE ISBI 2025 (Selected for oral presentation) 2025/4/15 (v2): Corrected a notation error in Figure 2
Summary
随着COVID-19的爆发,超声成像因其无创性、可负担性和便携性而成为检测COVID-19的有前途的技术。研究人员致力于开发基于人工智能的评分系统以提供实时诊断支持。然而,公开可用的超声数据集的大小有限且缺乏适当的注释,给训练稳健的AI模型带来挑战。本文提出MeDiVLAD,一个针对多级肺部超声(LUS)严重性评分问题的新型管道。我们利用自我知识蒸馏对视觉转换器(ViT)进行预训练,并通过双级VLAD聚合技术聚合帧级特征。结果表明,MeDiVLAD在帧级和视频级评分上均优于传统的全监督方法,同时提供出色的分类推理质量。其卓越性能使得自动识别关键肺部病理区域成为可能,并为更广泛的医疗视频分类任务提供了稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 超声成像因其在COVID-19检测中的无创性、可负担性和便携性而受到关注。
- 公开可用的超声数据集存在大小有限和缺乏适当注释的问题。
- MeDiVLAD是一个针对多级肺部超声严重性评分的新型管道。
- 利用自我知识蒸馏对视觉转换器(ViT)进行预训练。
- 通过双级VLAD聚合技术聚合帧级特征。
- MeDiVLAD在帧级和视频级评分上表现出卓越性能,优于传统全监督方法。
点此查看论文截图

Kernel-Aware Graph Prompt Learning for Few-Shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Fenfang Tao, Guo-Sen Xie, Fang Zhao, Xiangbo Shu
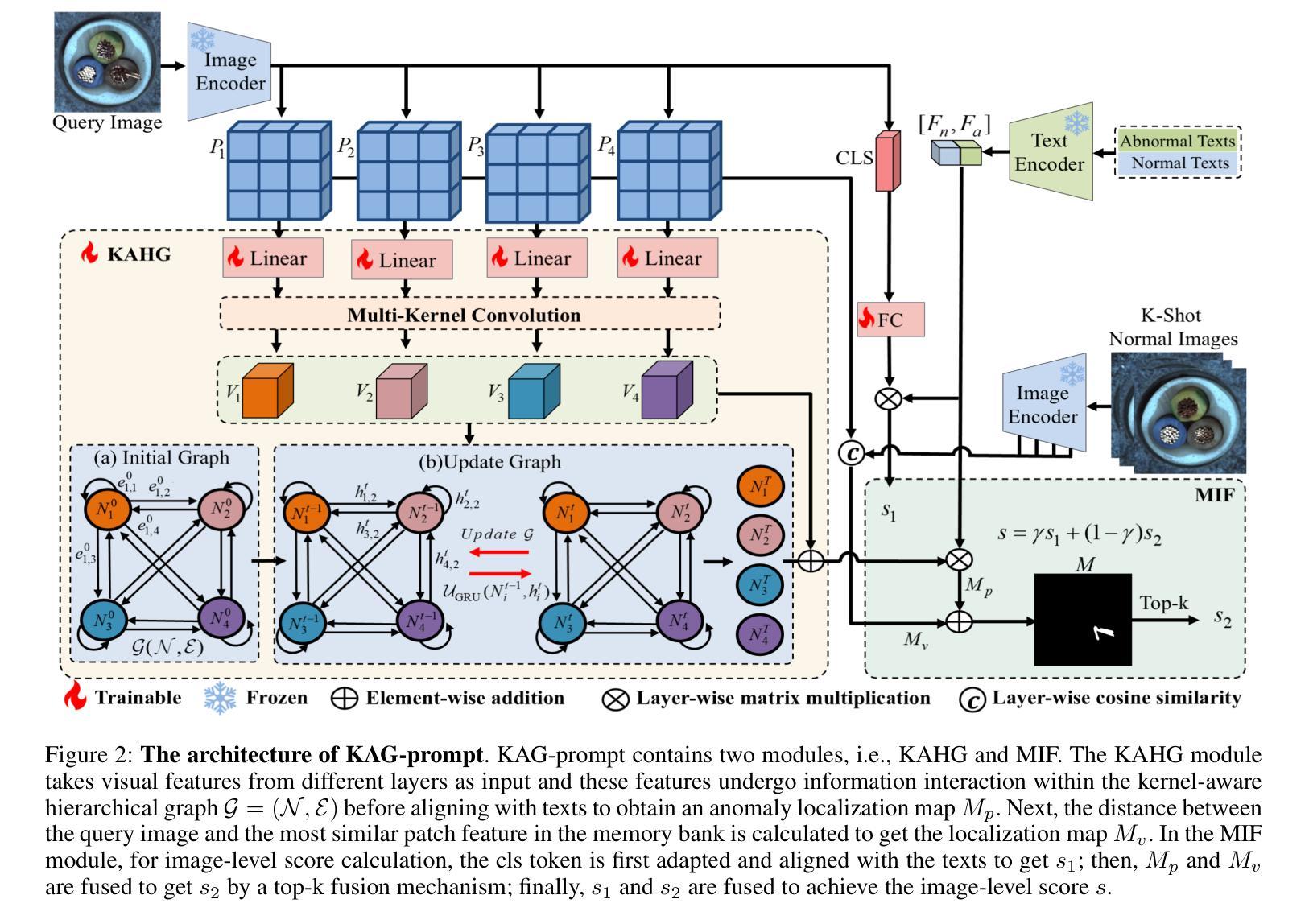
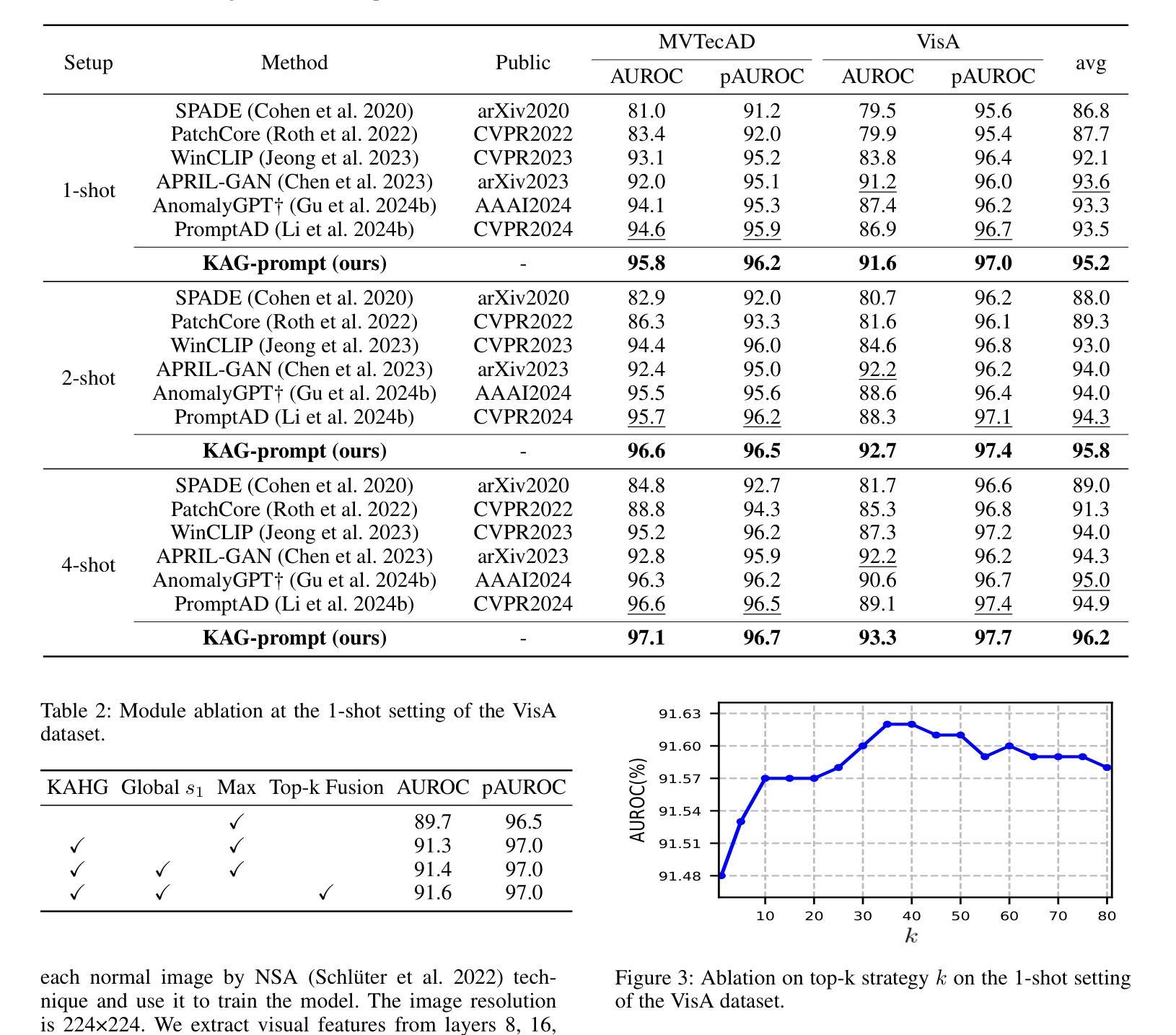
Few-shot anomaly detection (FSAD) aims to detect unseen anomaly regions with the guidance of very few normal support images from the same class. Existing FSAD methods usually find anomalies by directly designing complex text prompts to align them with visual features under the prevailing large vision-language model paradigm. However, these methods, almost always, neglect intrinsic contextual information in visual features, e.g., the interaction relationships between different vision layers, which is an important clue for detecting anomalies comprehensively. To this end, we propose a kernel-aware graph prompt learning framework, termed as KAG-prompt, by reasoning the cross-layer relations among visual features for FSAD. Specifically, a kernel-aware hierarchical graph is built by taking the different layer features focusing on anomalous regions of different sizes as nodes, meanwhile, the relationships between arbitrary pairs of nodes stand for the edges of the graph. By message passing over this graph, KAG-prompt can capture cross-layer contextual information, thus leading to more accurate anomaly prediction. Moreover, to integrate the information of multiple important anomaly signals in the prediction map, we propose a novel image-level scoring method based on multi-level information fusion. Extensive experiments on MVTecAD and VisA datasets show that KAG-prompt achieves state-of-the-art FSAD results for image-level/pixel-level anomaly detection. Code is available at https://github.com/CVL-hub/KAG-prompt.git.
少数镜头异常检测(FSAD)旨在通过同一类别中非常少的正常支持图像来检测未见过的异常区域。现有的FSAD方法通常通过设计复杂的文本提示来与流行的大型视觉语言模型范式下的视觉特征对齐来发现异常值。然而,这些方法几乎总是忽略了视觉特征中的内在上下文信息,例如不同视觉层之间的交互关系,这是全面检测异常值的重要线索。为此,我们提出了一个核心感知图提示学习框架,称为KAG-prompt,通过推理FSAD中视觉特征的跨层关系。具体来说,以不同层特征(以不同大小的异常区域作为节点)为基础构建了一个核心感知分层图,同时,任意节点对之间的关系代表图的边。通过在此图上进行消息传递,KAG-prompt可以捕获跨层上下文信息,从而进行更准确的异常预测。此外,为了整合预测图中多个重要异常信号的信息,我们提出了一种基于多层次信息融合的新颖图像级评分方法。在MVTecAD和VisA数据集上的大量实验表明,KAG-prompt在图像级/像素级的异常检测中达到了最新的FSAD结果。代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/CVL-hub/KAG-prompt.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AAAI 2025
Summary
少量样本异常检测(FSAD)旨在利用同一类别中的少量正常支持图像来检测未见过的异常区域。现有FSAD方法主要通过设计复杂的文本提示来与视觉特征对齐,忽略视觉特征的内在上下文信息,如不同视觉层之间的关系。为此,我们提出了一个核心感知图提示学习框架,称为KAG-prompt,通过推理视觉特征的跨层关系来进行FSAD。该框架建立了一个核心感知层次图,以不同层级的特征(重点关注不同大小的异常区域)作为节点,任意两个节点之间的关系作为图的边。通过图上的信息传递,KAG-prompt可以捕捉跨层上下文信息,从而实现更准确的异常预测。此外,我们提出了一种基于多层级信息融合的新颖图像级评分方法,以整合预测图中的多个重要异常信号信息。在MVTecAD和VisA数据集上的实验表明,KAG-prompt在图像级和像素级的异常检测中实现了最先进的FSAD结果。
Key Takeaways
- 现有FSAD方法主要通过复杂文本提示与视觉特征对齐来检测异常,忽略了视觉特征的内在上下文信息。
- 提出了一种新的学习框架KAG-prompt,通过构建核心感知层次图来捕捉视觉特征的跨层关系。
- 异常区域的不同尺寸被作为不同层级的特征节点,而任意两个节点间的关系构成了图的边。
- 通过在图上传递消息,KAG-prompt能更准确地预测异常。
- 引入了一种基于多层级信息融合的新颖图像级评分方法,以整合预测图中的多个重要异常信号。
- 在MVTecAD和VisA数据集上的实验表明,KAG-prompt实现了先进的FSAD结果。
点此查看论文截图