⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-19 更新
EchoWorld: Learning Motion-Aware World Models for Echocardiography Probe Guidance
Authors:Yang Yue, Yulin Wang, Haojun Jiang, Pan Liu, Shiji Song, Gao Huang
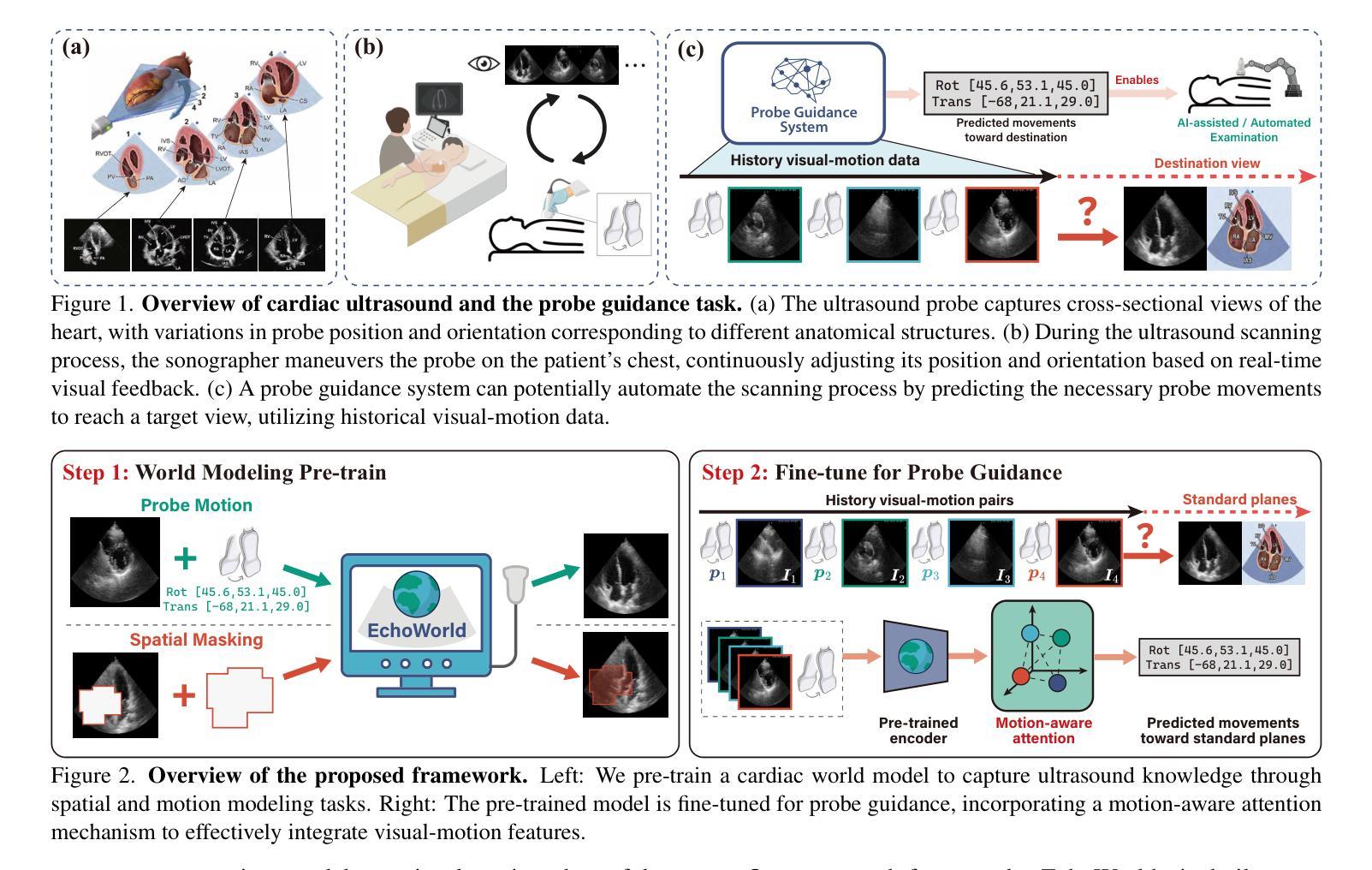
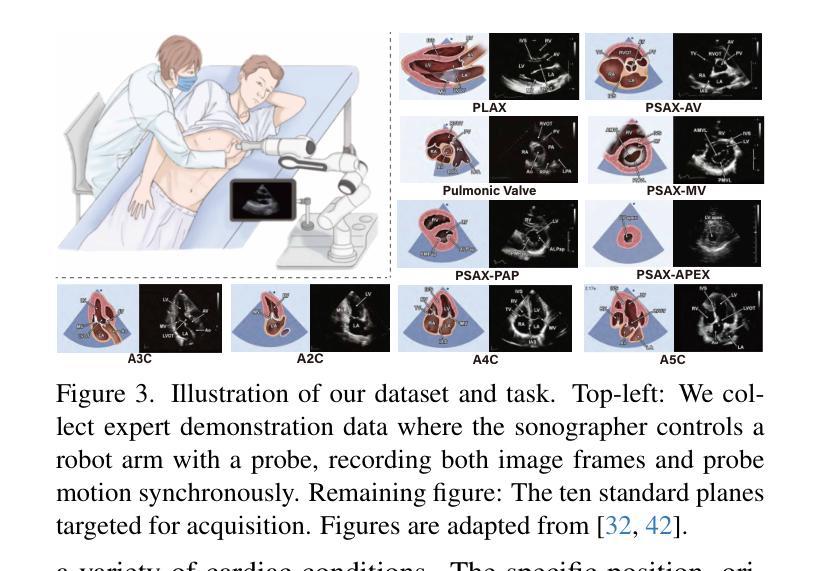
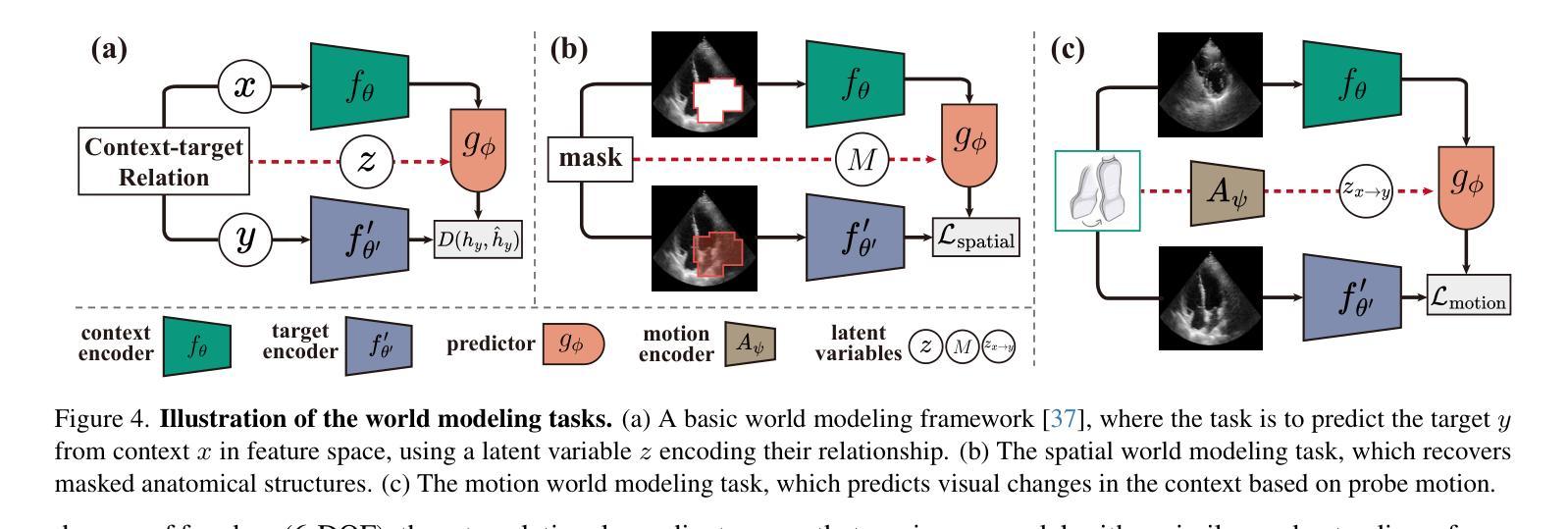
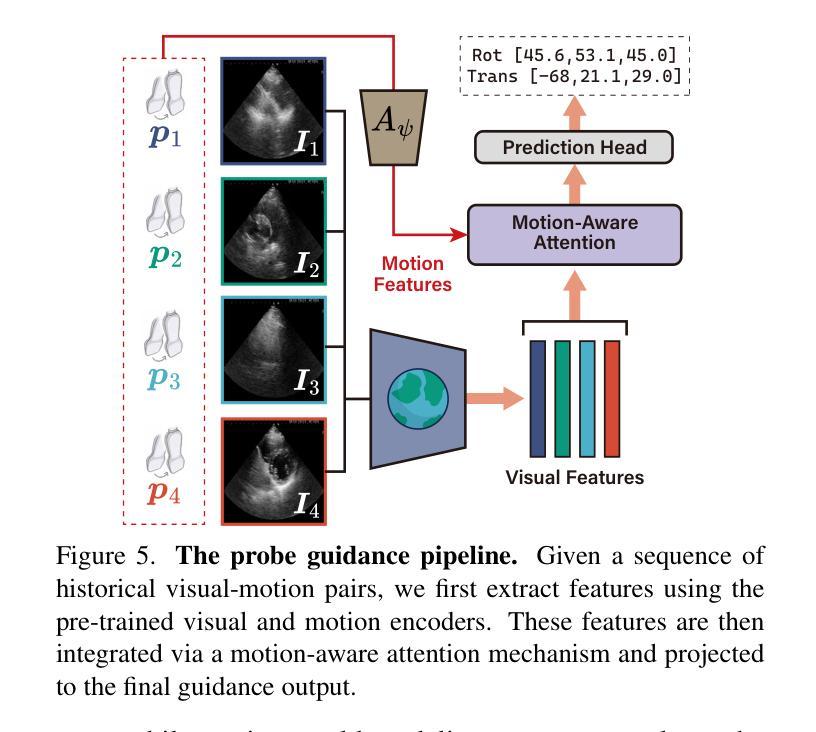
Echocardiography is crucial for cardiovascular disease detection but relies heavily on experienced sonographers. Echocardiography probe guidance systems, which provide real-time movement instructions for acquiring standard plane images, offer a promising solution for AI-assisted or fully autonomous scanning. However, developing effective machine learning models for this task remains challenging, as they must grasp heart anatomy and the intricate interplay between probe motion and visual signals. To address this, we present EchoWorld, a motion-aware world modeling framework for probe guidance that encodes anatomical knowledge and motion-induced visual dynamics, while effectively leveraging past visual-motion sequences to enhance guidance precision. EchoWorld employs a pre-training strategy inspired by world modeling principles, where the model predicts masked anatomical regions and simulates the visual outcomes of probe adjustments. Built upon this pre-trained model, we introduce a motion-aware attention mechanism in the fine-tuning stage that effectively integrates historical visual-motion data, enabling precise and adaptive probe guidance. Trained on more than one million ultrasound images from over 200 routine scans, EchoWorld effectively captures key echocardiographic knowledge, as validated by qualitative analysis. Moreover, our method significantly reduces guidance errors compared to existing visual backbones and guidance frameworks, excelling in both single-frame and sequential evaluation protocols. Code is available at https://github.com/LeapLabTHU/EchoWorld.
超声心动图是检测心血管疾病的关键手段,但很大程度上依赖于经验丰富的超声心动图技师。超声心动图探头引导系统能够提供实时移动指令,获取标准平面图像,为人工智能辅助或全自动扫描提供了前景广阔的解决方案。然而,开发此项任务的有效机器学习模型仍然充满挑战,因为它们必须掌握心脏结构以及探头运动与视觉信号之间的复杂相互作用。针对这一问题,我们提出了EchoWorld,这是一个用于探头引导的运动感知世界建模框架,它编码了解结构知识以及运动引起的视觉动态,同时有效地利用过去的视觉运动序列来提高引导精度。EchoWorld采用了一种受世界建模原理启发的预训练策略,其中模型会预测被遮挡的结构区域并模拟探头调整后的视觉结果。在此基础上,我们在微调阶段引入了一种运动感知注意力机制,有效地集成了历史视觉运动数据,实现了精确和自适应的探头引导。EchoWorld在超过200次常规扫描的超过100万张超声图像上进行训练,有效地捕获了关键超声心动图知识,并通过定性分析得到了验证。此外,我们的方法与现有的视觉主干和引导框架相比,在指导误差方面有了显著的降低,在单帧和顺序评估协议方面都表现出色。相关代码可访问https://github.com/LeapLabTHU/EchoWorld获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
超声心动图在心血管疾病检测中至关重要,但依赖于经验丰富的超声医师。超声心动图探头引导系统提供实时运动指令以获取标准平面图像,为人工智能辅助或全自动扫描提供了有前景的解决方案。然而,开发此任务的有效机器学习模型具有挑战性,需理解心脏解剖结构和探头运动与视觉信号的复杂交互。为此,我们提出EchoWorld,一个用于探头引导的运动感知世界建模框架,编码解剖知识和运动引起的视觉动态,有效利用过去的视觉运动序列以提高引导精度。EchoWorld采用受世界建模原理启发的预训练策略,其中模型预测被遮挡的解剖区域并模拟探头调整的视觉结果。在基于预训练模型的基础上,我们在微调阶段引入运动感知注意力机制,有效整合历史视觉运动数据,实现精确自适应的探头引导。在超过二十万例常规扫描的超声图像上训练,EchoWorld有效捕捉关键超声心动图知识,定性分析得到验证。与现有视觉主干和指导框架相比,我们的方法显著减少了指导误差,在单帧和序列评估协议中均表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 超声心动图在心血管疾病检测中非常重要,但依赖于专业超声医师的操作。
- 超声心动图探头引导系统提供实时运动指令,有助于人工智能辅助或全自动扫描。
- 机器学习模型在开发超声心动图探头引导系统时面临挑战,需理解心脏解剖和探头运动与视觉信号的复杂交互。
- EchoWorld是一个运动感知世界建模框架,用于探头引导,编码解剖知识和视觉动态,提高引导精度。
- EchoWorld采用预训练策略并引入运动感知注意力机制,有效整合历史视觉运动数据。
- EchoWorld在大量超声图像数据上训练,表现优异,显著减少探头引导误差。
- EchoWorld代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

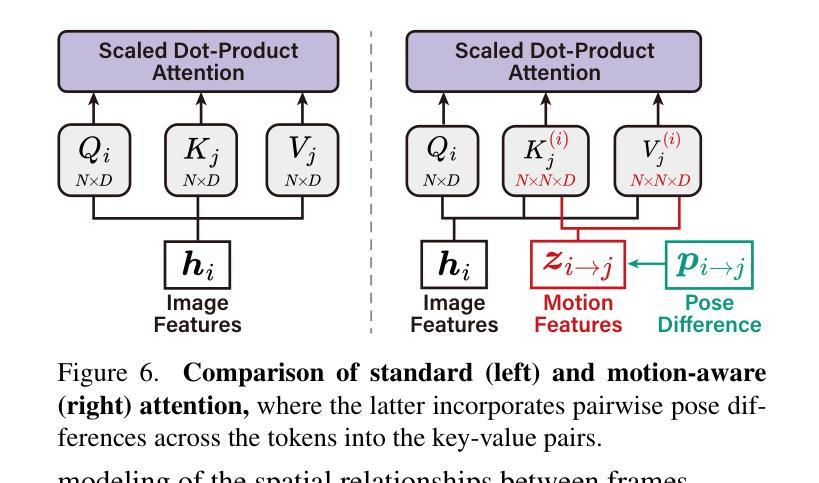
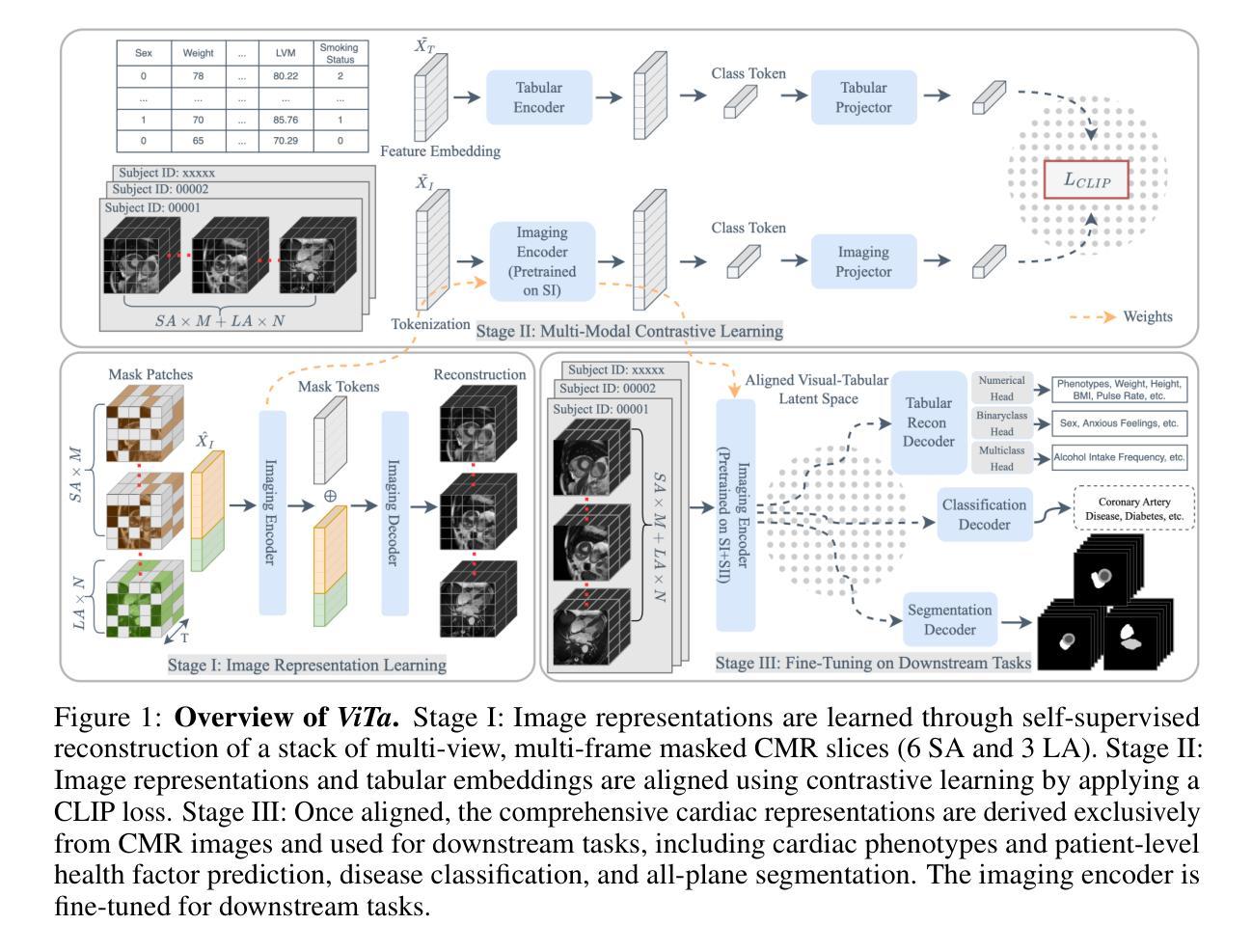
Towards Cardiac MRI Foundation Models: Comprehensive Visual-Tabular Representations for Whole-Heart Assessment and Beyond
Authors:Yundi Zhang, Paul Hager, Che Liu, Suprosanna Shit, Chen Chen, Daniel Rueckert, Jiazhen Pan
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging is the gold standard for non-invasive cardiac assessment, offering rich spatio-temporal views of the cardiac anatomy and physiology. Patient-level health factors, such as demographics, metabolic, and lifestyle, are known to substantially influence cardiovascular health and disease risk, yet remain uncaptured by CMR alone. To holistically understand cardiac health and to enable the best possible interpretation of an individual’s disease risk, CMR and patient-level factors must be jointly exploited within an integrated framework. Recent multi-modal approaches have begun to bridge this gap, yet they often rely on limited spatio-temporal data and focus on isolated clinical tasks, thereby hindering the development of a comprehensive representation for cardiac health evaluation. To overcome these limitations, we introduce ViTa, a step toward foundation models that delivers a comprehensive representation of the heart and a precise interpretation of individual disease risk. Leveraging data from 42,000 UK Biobank participants, ViTa integrates 3D+T cine stacks from short-axis and long-axis views, enabling a complete capture of the cardiac cycle. These imaging data are then fused with detailed tabular patient-level factors, enabling context-aware insights. This multi-modal paradigm supports a wide spectrum of downstream tasks, including cardiac phenotype and physiological feature prediction, segmentation, and classification of cardiac and metabolic diseases within a single unified framework. By learning a shared latent representation that bridges rich imaging features and patient context, ViTa moves beyond traditional, task-specific models toward a universal, patient-specific understanding of cardiac health, highlighting its potential to advance clinical utility and scalability in cardiac analysis.
心脏磁共振成像在非侵入式心脏评估中是金标准,它提供了丰富的关于心脏解剖结构和生理功能的时空视图。已知患者层面的健康因素,如人口统计学特征、新陈代谢和生活方式,会对心血管健康和疾病风险产生重大影响,但这些因素仅靠心脏磁共振成像无法捕捉。为了全面了解心脏健康并为个人的疾病风险提供最准确的解释,必须在综合框架中联合利用心脏磁共振成像和患者层面的因素。最近的多种模态方法已经开始弥补这一差距,但它们通常依赖于有限的时空数据并专注于孤立的临床任务,从而阻碍了心脏健康评估的全面表示的发展。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了ViTa,它朝着基础模型迈出了一步,提供了对心脏的全面表示和对个人疾病风险的精确解释。ViTa利用来自42,000名英国生物银行参与者的数据,整合了短轴和长轴视图的3D+T电影堆栈,能够完全捕捉心脏周期。然后,这些成像数据与详细的表格患者层面因素相融合,提供情境感知的见解。这种多模态范式支持广泛的下游任务,包括心脏表型预测和生理特征预测、分割以及在一个统一的框架内对心脏和代谢疾病的分类。通过学习丰富的成像特征和患者上下文的共享潜在表示,ViTa超越了传统的、针对特定任务的模型,朝着通用、针对特定患者的理解心脏健康的方向发展,这突显了其在心脏分析的临床实用性和可扩展性方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
心脏磁共振成像(CMR)是评估心脏健康的金标准,提供了丰富的时空视图。然而,患者级别的健康因素(如人口统计学、代谢和生活方式)对心血管健康及疾病风险有重要影响,而CMR无法捕获这些因素。为全面了解心脏健康及进行个体化的疾病风险评估,需要将CMR与患者级别因素在综合框架内联合利用。ViTa模型是一个朝着基础模型迈进的步骤,提供了心脏的综合表征和精确的疾病风险评估。它融合了来自UK Biobank的4.2万名参与者的数据,整合了来自短轴和长轴视图的3D+T电影堆栈,捕捉了整个心脏周期。成像数据与详细的表格患者级别因素相结合,提供了情境感知的见解。这一多模式范式支持广泛的下游任务,包括心脏表型预测、生理特征预测、分割以及单一统一框架内的代谢性疾病分类。ViTa通过学习一个共享的潜在表征,该表征连接了丰富的成像特征和患者上下文,从而超越了传统的任务特定模型,朝着患者特异性的心脏健康通用理解发展。
Key Takeaways
- 心脏磁共振成像(CMR)是评估心脏健康的金标准,但无法捕获患者级别的健康因素如人口统计学、代谢和生活方式等。
- 为全面了解心脏健康和进行最佳疾病风险评估,需要将CMR与患者级别因素在综合框架内联合利用。
- ViTa模型是一个综合的心脏健康表征模型,能够精确评估个体疾病风险。
- ViTa模型融合了丰富的成像数据和患者级别因素,支持多种下游任务,包括心脏表型预测、生理特征预测、分割以及疾病分类。
- ViTa模型通过共享潜在表征连接丰富的成像特征和患者上下文,从而超越了传统的任务特定模型。
- ViTa模型具有潜力提高心脏分析的临床实用性和可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图

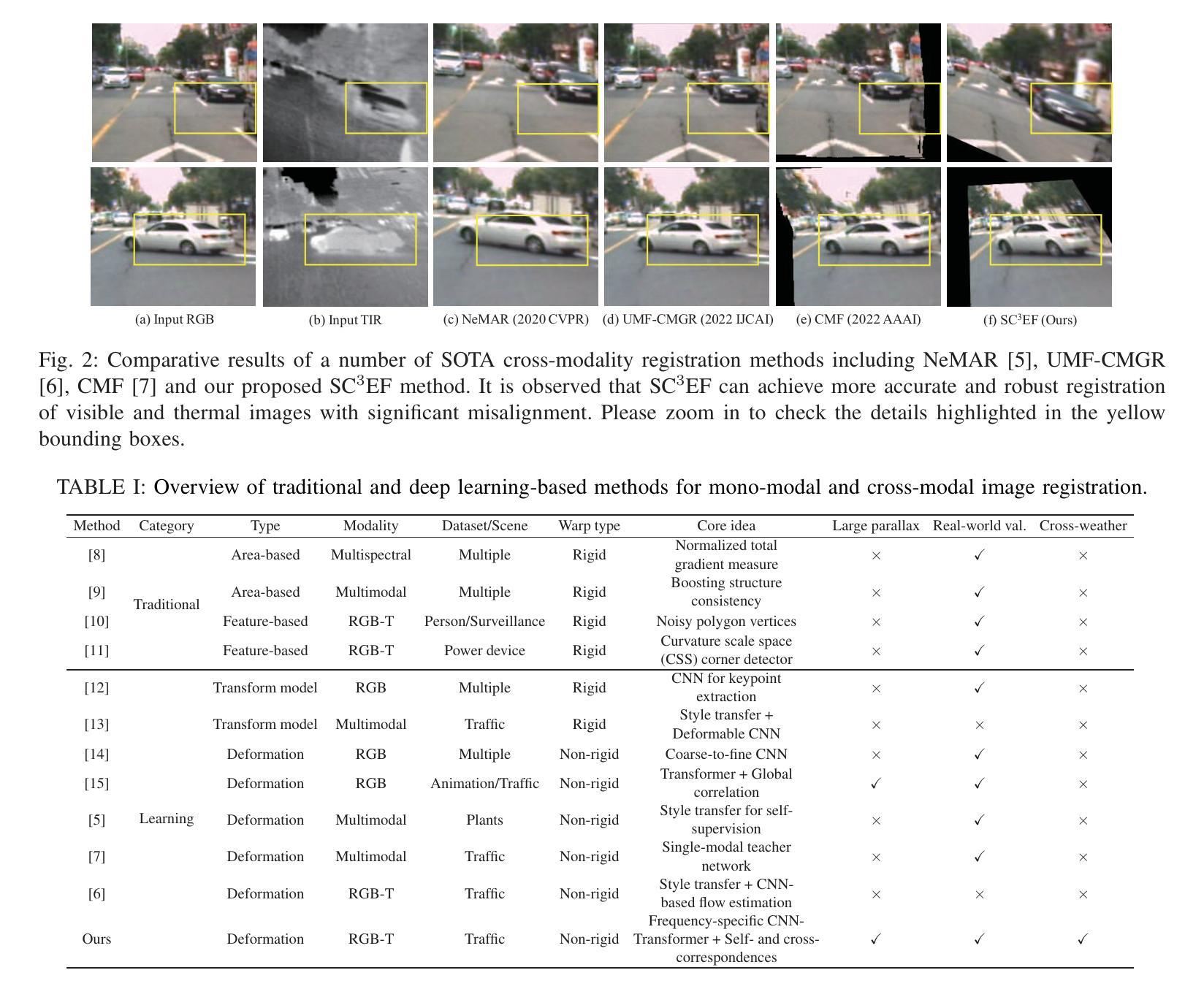
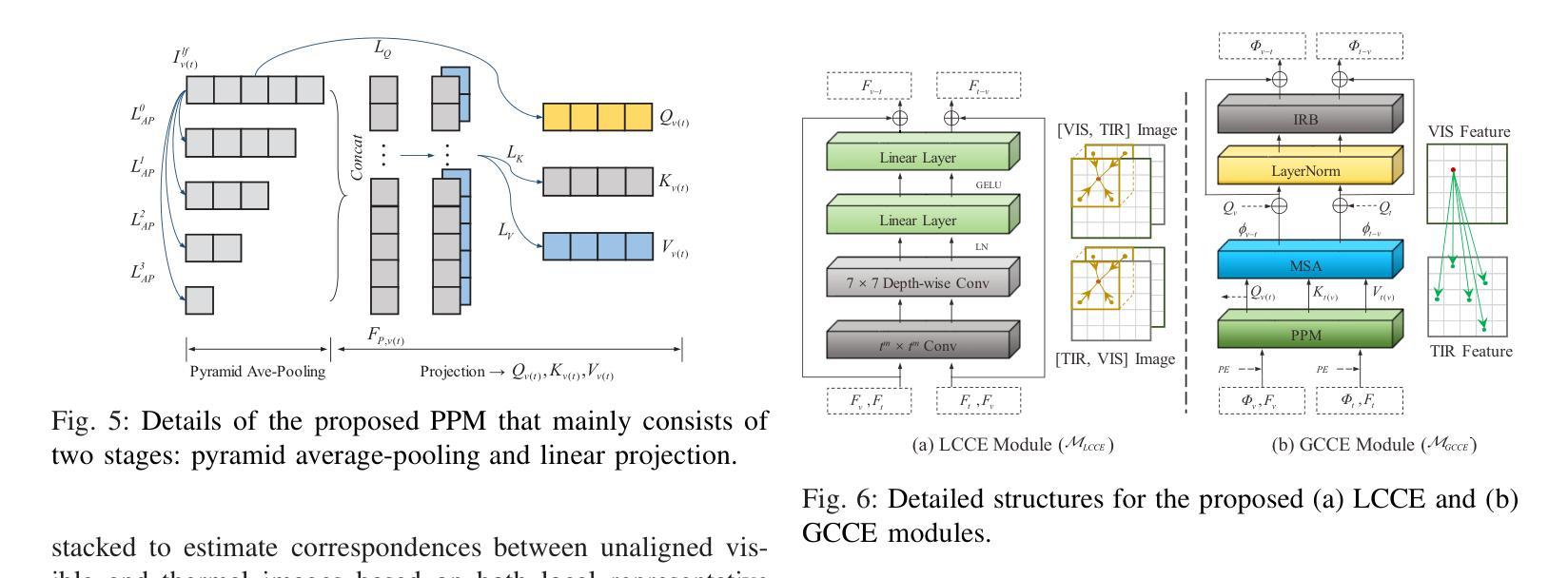
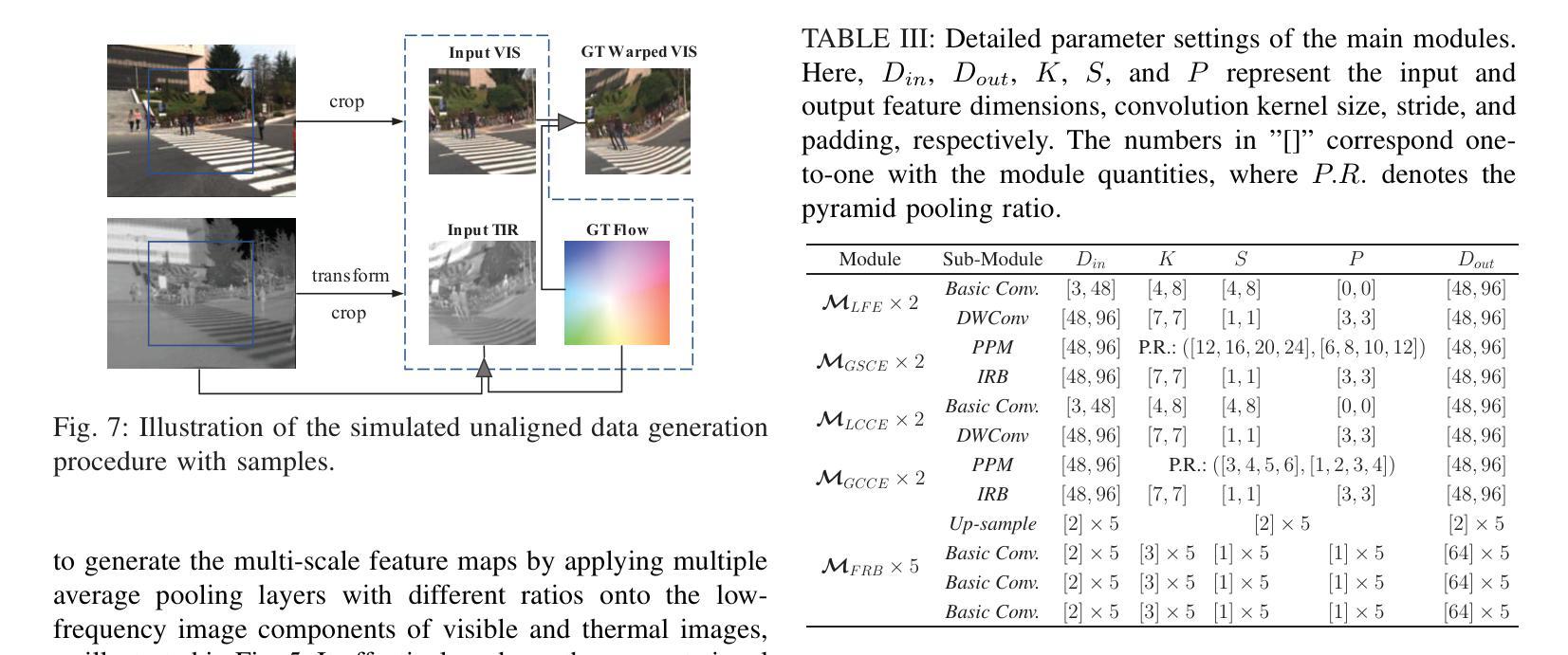
SC3EF: A Joint Self-Correlation and Cross-Correspondence Estimation Framework for Visible and Thermal Image Registration
Authors:Xi Tong, Xing Luo, Jiangxin Yang, Yanpeng Cao
Multispectral imaging plays a critical role in a range of intelligent transportation applications, including advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), traffic monitoring, and night vision. However, accurate visible and thermal (RGB-T) image registration poses a significant challenge due to the considerable modality differences. In this paper, we present a novel joint Self-Correlation and Cross-Correspondence Estimation Framework (SC3EF), leveraging both local representative features and global contextual cues to effectively generate RGB-T correspondences. For this purpose, we design a convolution-transformer-based pipeline to extract local representative features and encode global correlations of intra-modality for inter-modality correspondence estimation between unaligned visible and thermal images. After merging the local and global correspondence estimation results, we further employ a hierarchical optical flow estimation decoder to progressively refine the estimated dense correspondence maps. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method, outperforming the current state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on representative RGB-T datasets. Furthermore, it also shows competitive generalization capabilities across challenging scenarios, including large parallax, severe occlusions, adverse weather, and other cross-modal datasets (e.g., RGB-N and RGB-D).
多光谱成像在智能交通应用的各个领域都扮演着关键角色,包括高级驾驶辅助系统(ADAS)、交通监控和夜视。然而,由于模态差异较大,准确的可见光和热(RGB-T)图像配准是一个巨大的挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的联合自相关和交叉对应估计框架(SC3EF),利用局部代表性特征和全局上下文线索来有效地生成RGB-T对应关系。为此,我们设计了一个基于卷积转换器的管道,以提取局部代表性特征并编码模态内全局相关性,用于未对齐的可见光和热图像之间的模态间对应关系估计。在合并局部和全局对应估计结果后,我们进一步采用分层光流估计解码器来逐步优化估计的密集对应地图。大量实验表明,我们提出的方法非常有效,在代表性RGB-T数据集上的性能超过了当前最先进的(SOTA)方法。此外,它在具有挑战性的场景中还显示出具有竞争力的泛化能力,包括大视差、严重遮挡、恶劣天气和其他跨模态数据集(如RGB-N和RGB-D)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了多光谱成像在智能交通应用中的关键作用,包括高级驾驶辅助系统、交通监测和夜视。针对可见光和热成像(RGB-T)图像配准的挑战,提出了一种新的联合自相关和交叉对应估计框架(SC3EF)。该框架利用局部代表性特征和全局上下文线索,通过卷积-变压器基础的管道设计,有效生成RGB-T对应关系。通过合并局部和全局对应估计结果,进一步采用分层光流估计解码器,逐步优化估计的密集对应地图。实验表明,该方法在代表性RGB-T数据集上优于现有先进技术,并在具有挑战性的场景中显示出良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 多光谱成像在智能交通应用中扮演重要角色,如高级驾驶辅助系统、交通监测和夜视。
- RGB-T图像配准是一个重大挑战,因为不同模态之间的差异很大。
- 提出了SC3EF框架,该框架利用局部代表性特征和全局上下文线索来生成有效的RGB-T对应关系。
- 通过卷积-变压器基础的管道设计进行特征提取和编码。
- 合并局部和全局对应估计结果后,采用分层光流估计解码器逐步优化估计的密集对应地图。
- 实验表明,该方法在代表性RGB-T数据集上表现优异,优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图


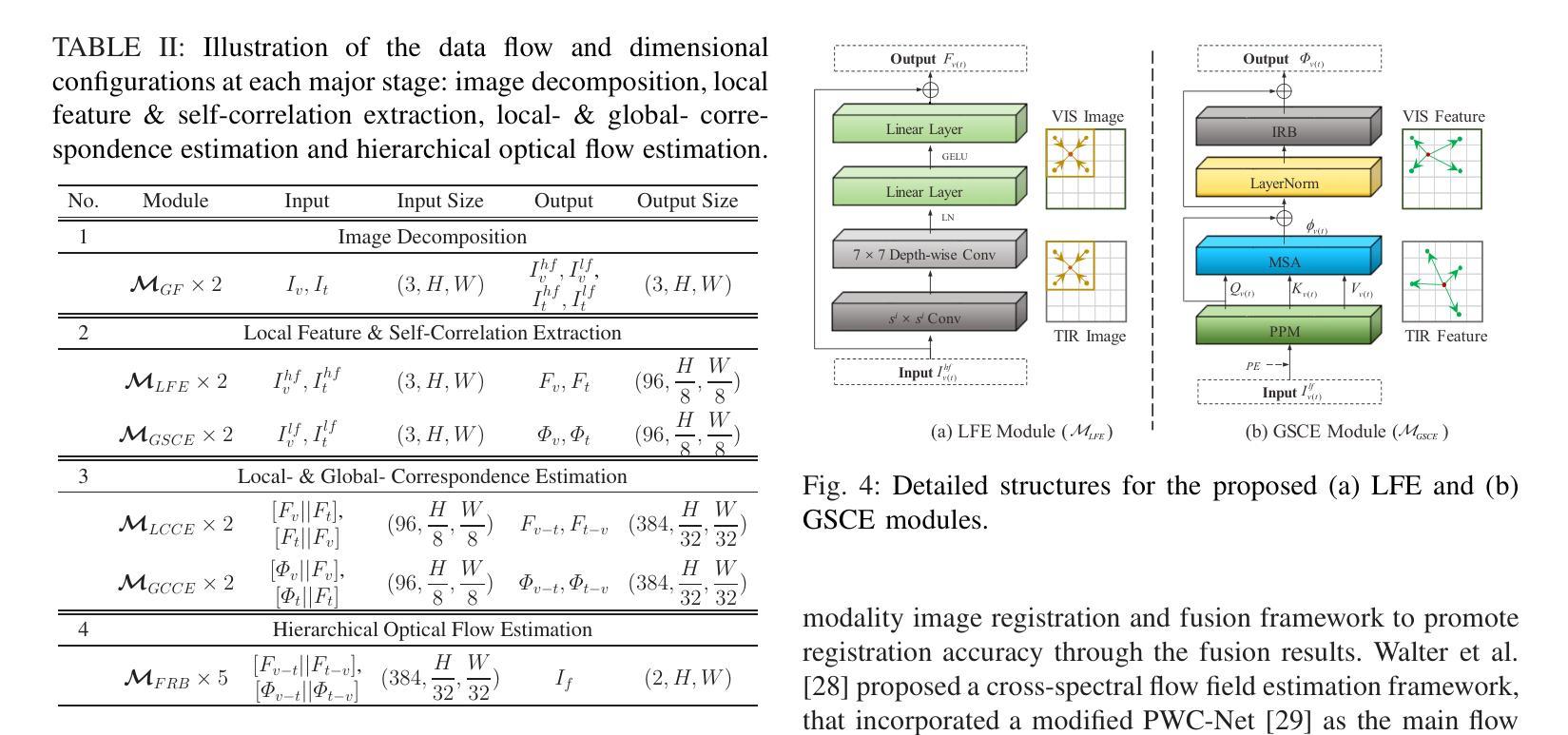
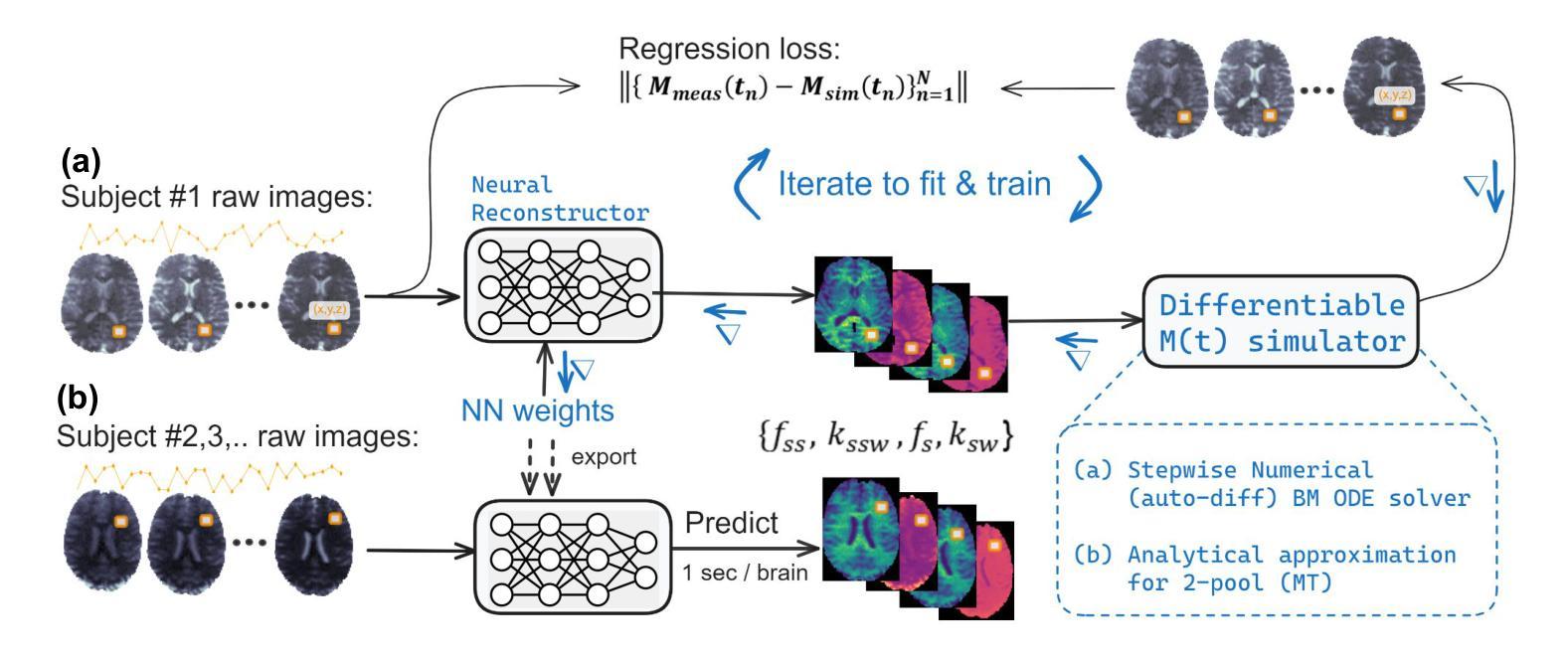
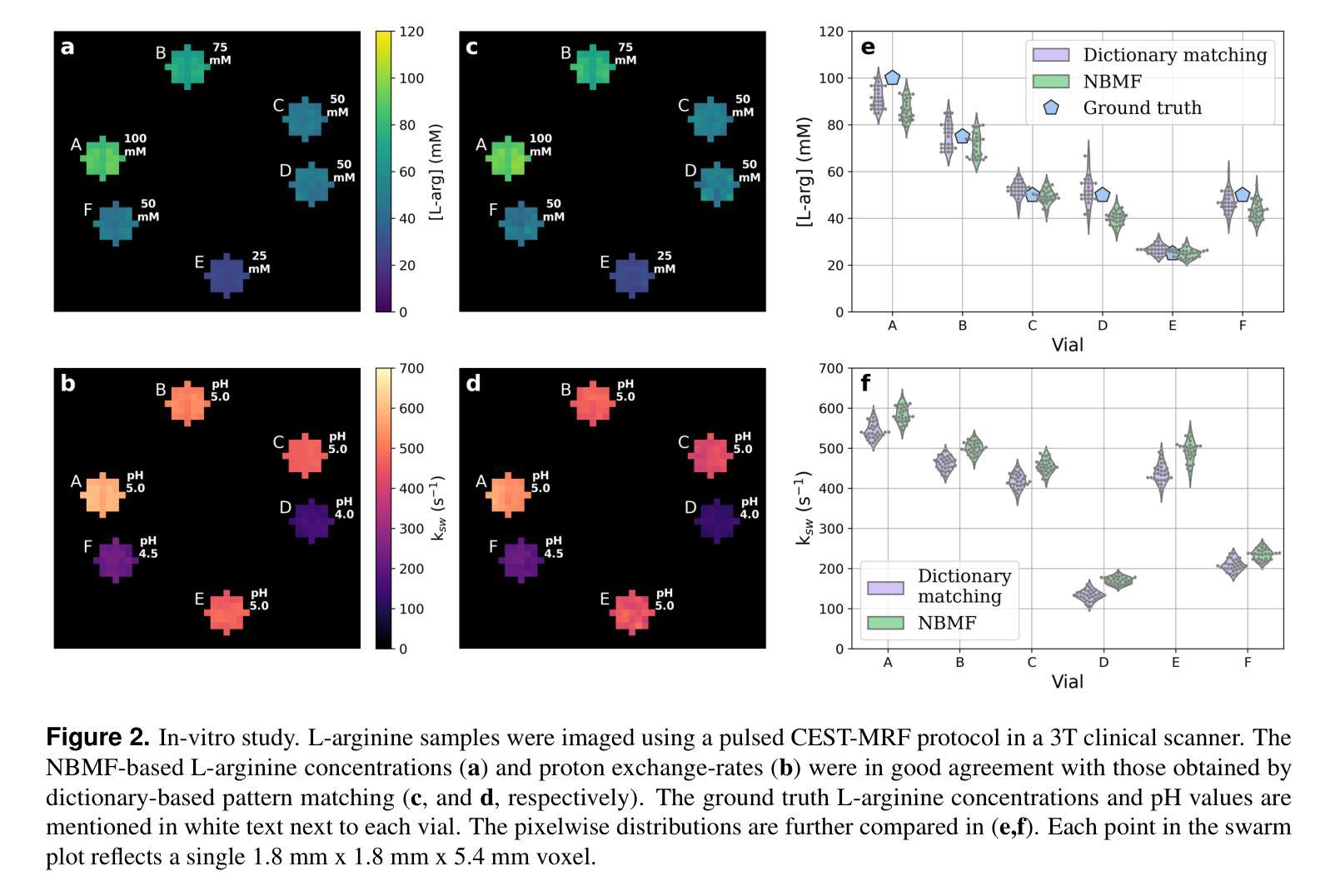
Multi-Parameter Molecular MRI Quantification using Physics-Informed Self-Supervised Learning
Authors:Alex Finkelstein, Nikita Vladimirov, Moritz Zaiss, Or Perlman
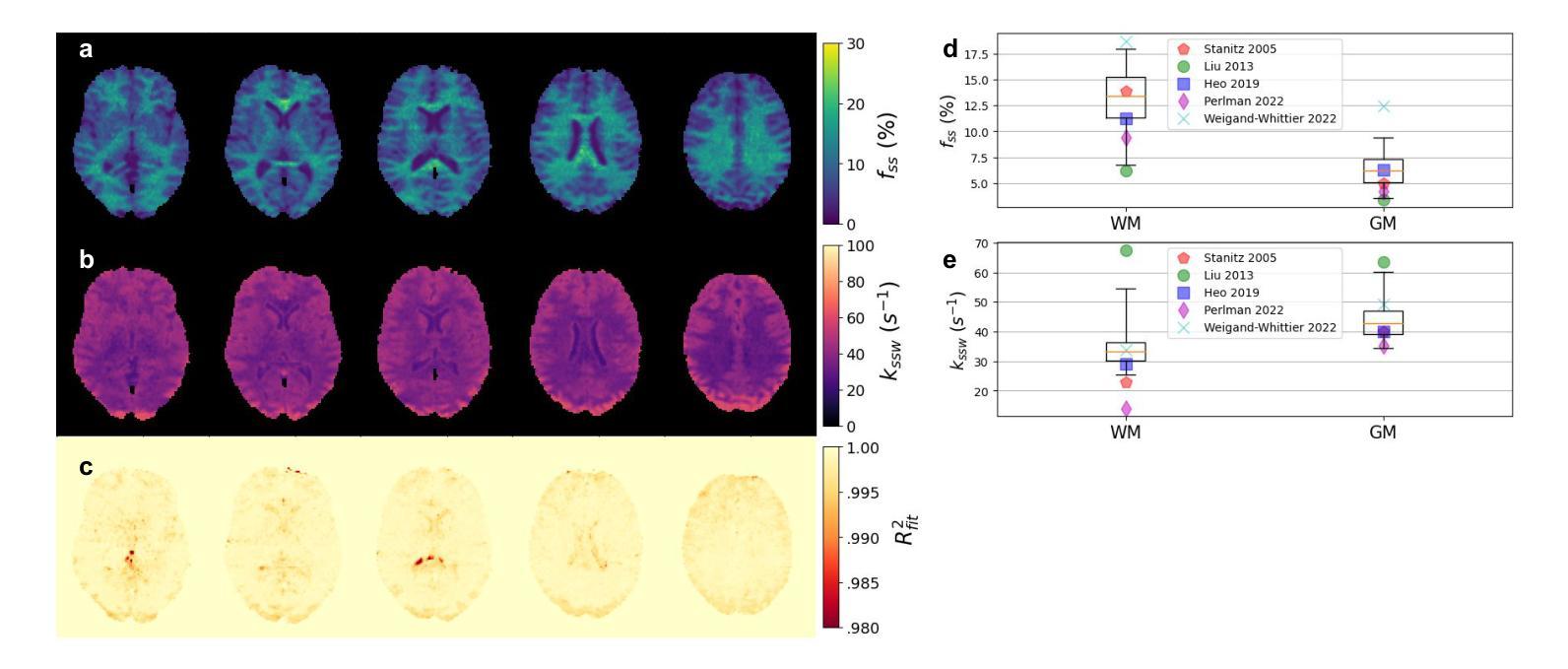
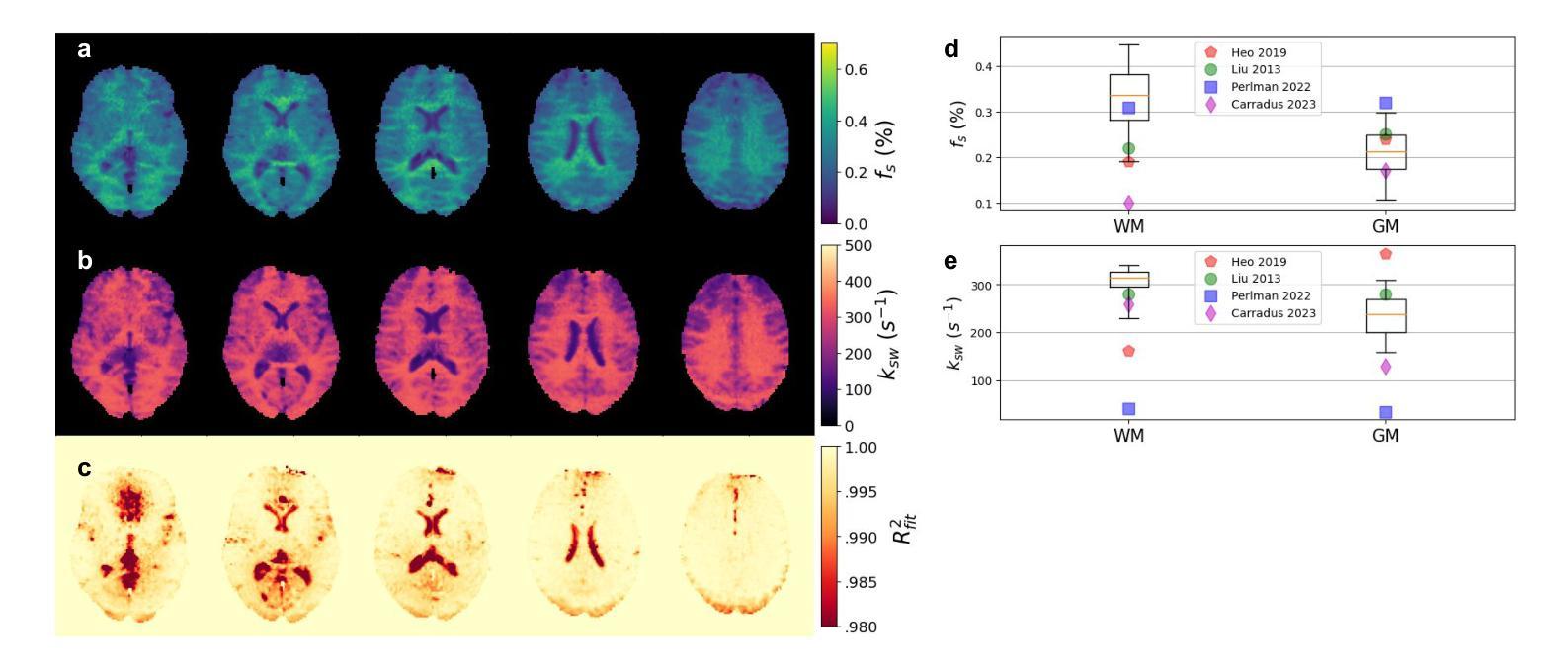
Biophysical model fitting plays a key role in obtaining quantitative parameters from physiological signals and images. However, the model complexity for molecular magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) often translates into excessive computation time, which makes clinical use impractical. Here, we present a generic computational approach for solving the parameter extraction inverse problem posed by ordinary differential equation (ODE) modeling coupled with experimental measurement of the system dynamics. This is achieved by formulating a numerical ODE solver to function as a step-wise analytical one, thereby making it compatible with automatic differentiation-based optimization. This enables efficient gradient-based model fitting, and provides a new approach to parameter quantification based on self-supervised learning from a single data observation. The neural-network-based train-by-fit pipeline was used to quantify semisolid magnetization transfer (MT) and chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) amide proton exchange parameters in the human brain, in an in-vivo molecular MRI study (n = 4). The entire pipeline of the first whole brain quantification was completed in 18.3 $\pm$ 8.3 minutes. Reusing the single-subject-trained network for inference in new subjects took 1.0 $\pm$ 0.2 s, to provide results in agreement with literature values and scan-specific fit results.
生物物理模型拟合在从生理信号和图像中获得定量参数方面起着关键作用。然而,分子磁共振成像(MRI)的模型复杂性通常会导致计算时间过长,使得其在临床上的实际应用变得不切实际。在这里,我们提出了一种解决由常微分方程(ODE)建模所引发参数提取反问题的通用计算方法,该方法结合了系统动力学的实验测量。我们通过制定数值ODE求解器来使其作为逐步分析的工具,从而使其与基于自动微分的优化相兼容。这实现了有效的基于梯度的模型拟合,并提供了一种基于单一数据观察的自我监督学习的新参数量化方法。基于神经网络训练-拟合管道被用于量化半固态磁化转移(MT)和化学交换饱和转移(CEST)酰胺质子交换参数在人脑内,在一次活体分子MRI研究(n=4)。首个全脑量化整个管道在18.3±8.3分钟内完成。对于新受试者进行推理时重复使用单个受试者训练的网络需要花费1.0±0.2秒,其研究结果与文献值和特定扫描结果一致。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This project was funded by the European Union (ERC, BabyMagnet, project no. 101115639), the Ministry of Innovation, Science and Technology, Israel, and a grant from the Tel Aviv University Center for AI and Data Science (TAD, The Blavatnik AI and Data Science Fund). None of above can be held responsible for views and opinions expressed, which are those of the authors alone
Summary
本研究提出一种解决生理信号和图像中参数提取逆问题的通用计算方法。通过构建数值常微分方程(ODE)求解器,实现逐步分析,与基于自动微分优化相结合,提高了模型拟合效率,并基于单数据观测的自监督学习实现参数量化。在人体脑部活体分子MRI研究中(n=4),利用神经网络训练拟合管道量化半固体磁化转移(MT)和化学交换饱和转移(CEST)酰胺质子交换参数,首次完成全脑量化流程耗时约18分钟。对新受试者的推断使用单一受试者训练的网络即可完成耗时不超过一秒的预测结果。结果符合文献值和扫描特定拟合结果。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一种解决生理信号和图像参数提取的通用计算方法,适用于复杂模型中的参数提取问题。
- 通过构建数值ODE求解器,实现逐步分析,提高了模型拟合效率。
- 结合自动微分优化技术,使得基于自监督学习的参数量化成为可能。
- 在人体脑部活体分子MRI研究中应用该方法,成功量化半固体磁化转移和化学交换饱和转移参数。
- 完成首次全脑量化流程耗时约18分钟,新受试者推断耗时不超过一秒。
- 结果符合文献值和扫描特定拟合结果,证明了该方法的准确性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

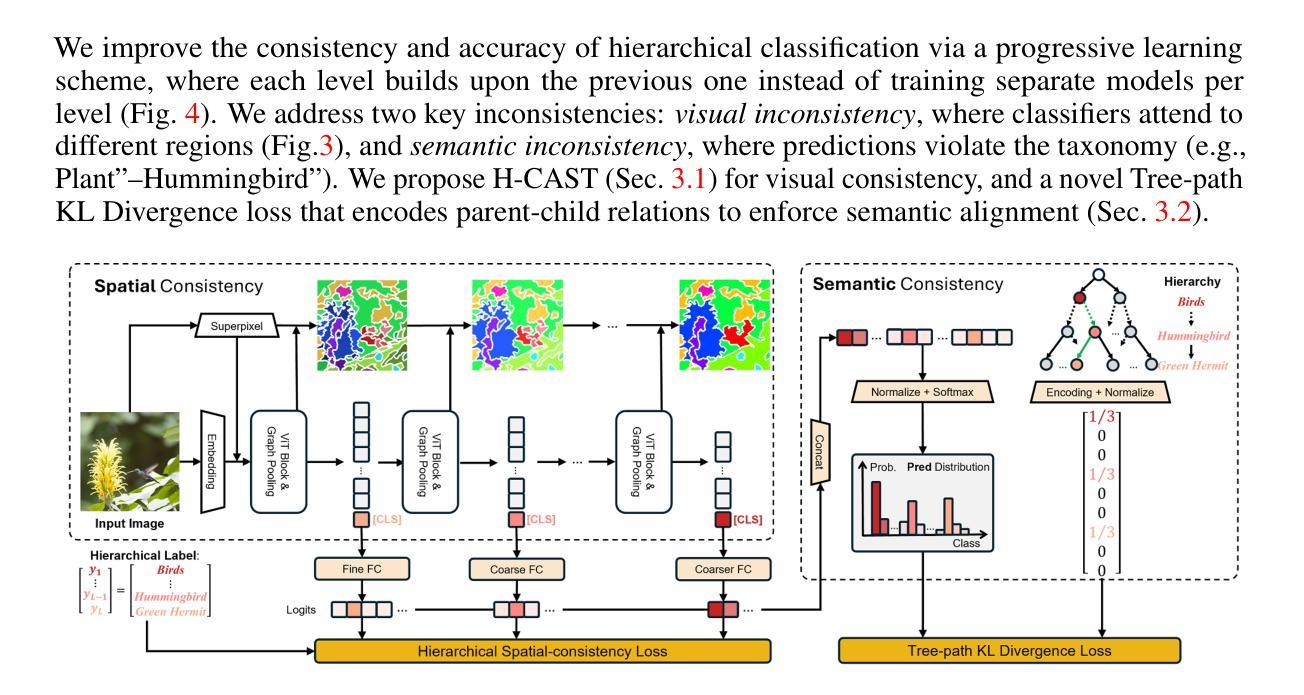
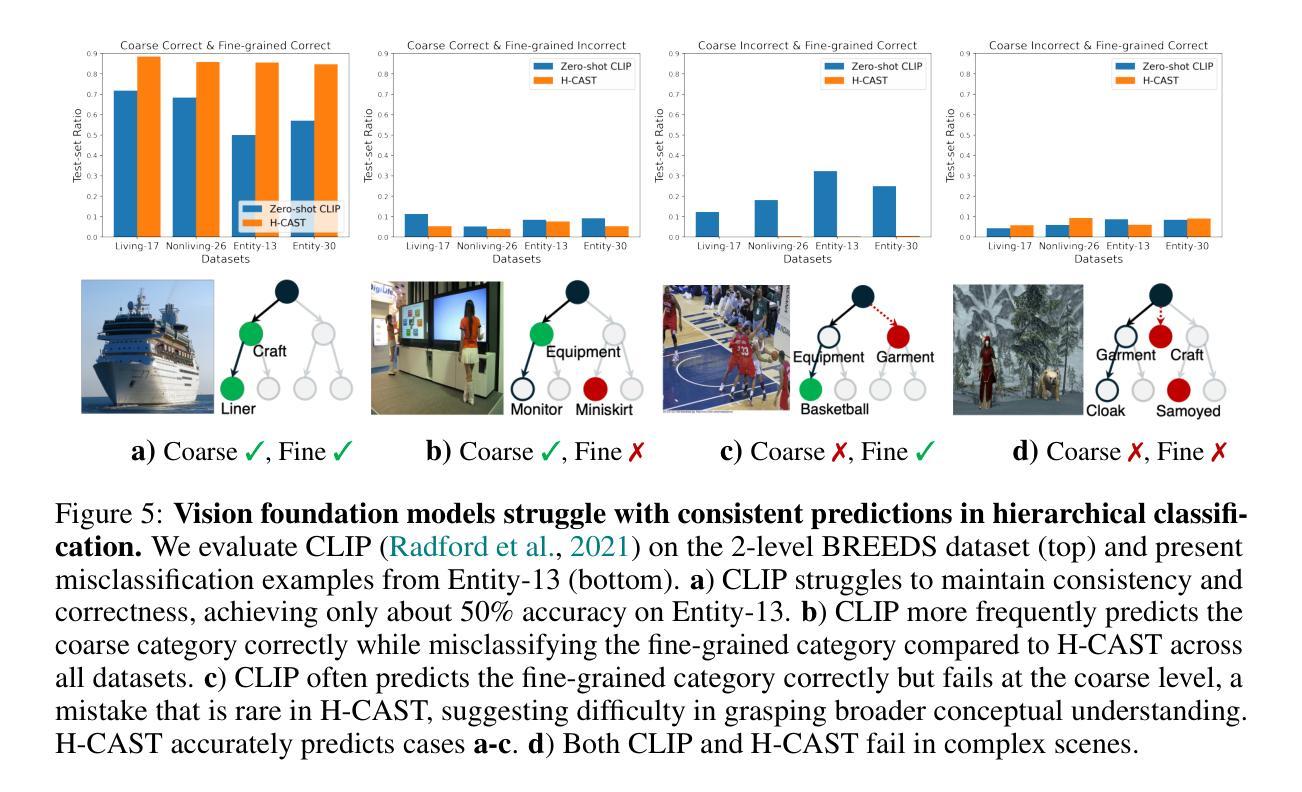
Visually Consistent Hierarchical Image Classification
Authors:Seulki Park, Youren Zhang, Stella X. Yu, Sara Beery, Jonathan Huang
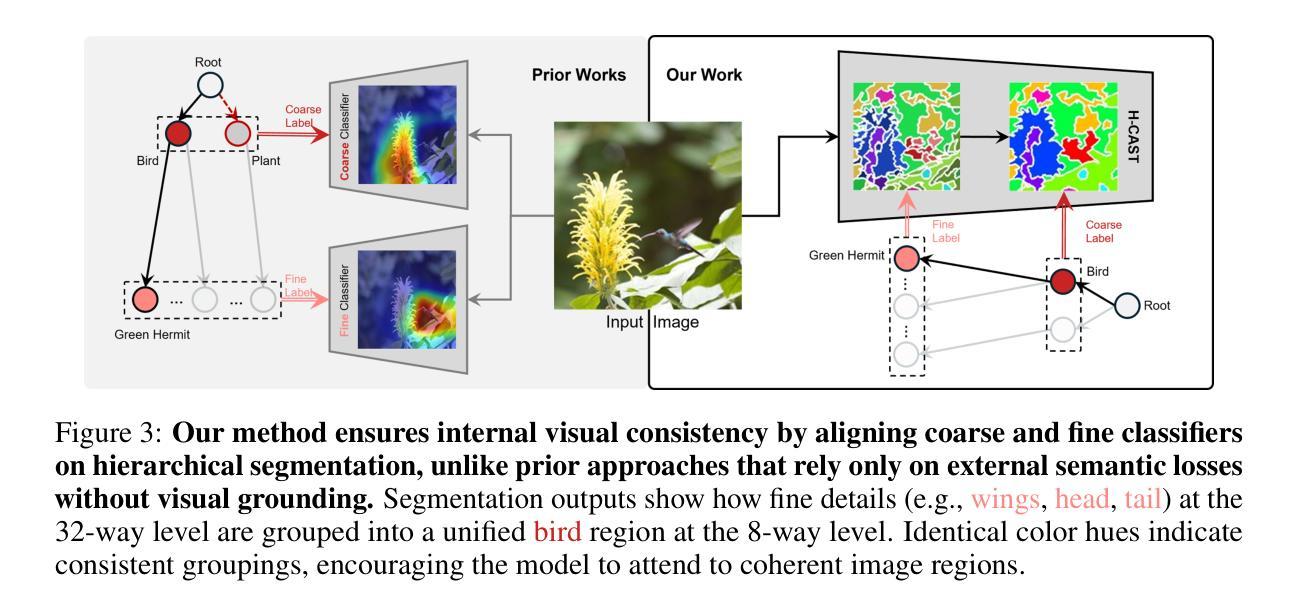
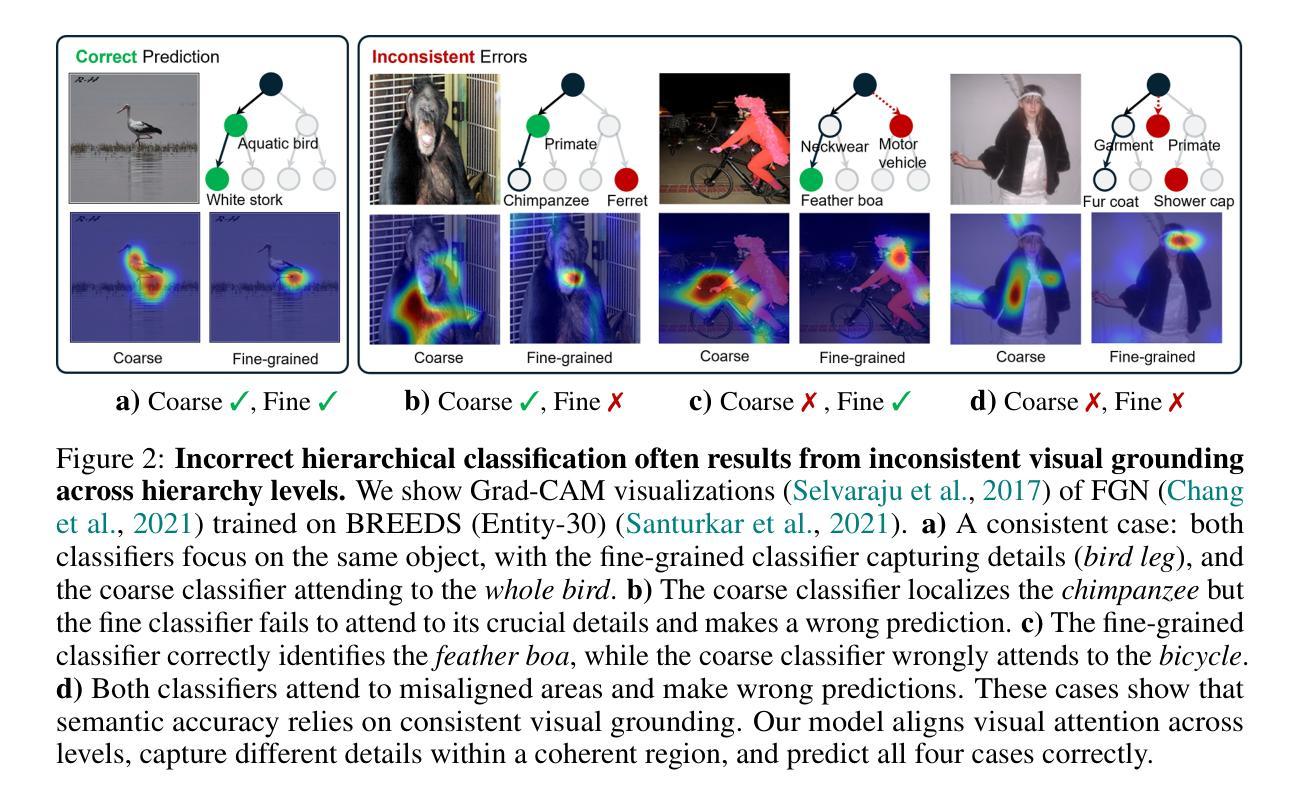
Hierarchical classification predicts labels across multiple levels of a taxonomy, e.g., from coarse-level ‘Bird’ to mid-level ‘Hummingbird’ to fine-level ‘Green hermit’, allowing flexible recognition under varying visual conditions. It is commonly framed as multiple single-level tasks, but each level may rely on different visual cues: Distinguishing ‘Bird’ from ‘Plant’ relies on global features like feathers or leaves, while separating ‘Anna’s hummingbird’ from ‘Green hermit’ requires local details such as head coloration. Prior methods improve accuracy using external semantic supervision, but such statistical learning criteria fail to ensure consistent visual grounding at test time, resulting in incorrect hierarchical classification. We propose, for the first time, to enforce internal visual consistency by aligning fine-to-coarse predictions through intra-image segmentation. Our method outperforms zero-shot CLIP and state-of-the-art baselines on hierarchical classification benchmarks, achieving both higher accuracy and more consistent predictions. It also improves internal image segmentation without requiring pixel-level annotations.
层次分类预测了分类体系中的多级标签,例如从粗略级别的“鸟”到中级别的“蜂鸟”再到精细级别的“绿翅绿鹊”,这在不同的视觉条件下实现了灵活的识别。它通常被视为多个单一级别的任务,但每个级别可能依赖于不同的视觉线索:区分“鸟”和“植物”依赖于羽毛或叶子等全局特征,而将“安娜蜂鸟”与“绿翅绿鹊”区分开则需要局部细节,例如头色。之前的方法通过外部语义监督提高了准确性,但这样的统计学习标准不能保证测试时的视觉一致性,从而导致错误的层次分类。我们首次提出通过图像内分割对精细到粗略的预测进行对齐来强制执行内部视觉一致性。我们的方法在层次分类基准测试上的表现优于零样本CLIP和最新基线,实现了更高的准确性和更一致的预测。同时,它还提高了无需像素级注释的内部图像分割效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了层次分类技术在图像识别中的应用,该技术可以预测多个级别的标签,如从粗级别的“鸟”到中级别的“蜂鸟”再到细级别的“绿翅蜂鸟”。文章指出,虽然层次分类常被看作多个单一级别的任务,但每个级别可能依赖于不同的视觉线索。作者提出一种新方法,通过图像内部分割来强制实施内部视觉一致性,实现对精细到粗糙预测的对齐,该方法在层次分类基准测试上的表现优于零样本CLIP和现有先进技术,提高了准确性和预测的一致性,并能在无需像素级别注释的情况下改善图像分割。
Key Takeaways
- 层次分类可以预测多个级别的标签,适应不同视觉条件下的灵活识别。
- 每一层次的分类可能依赖于不同的视觉线索。
- 现有方法通过外部语义监督提高准确性,但在测试时无法保证视觉一致性。
- 首次提出通过图像内部分割来强制实施内部视觉一致性。
- 该方法提高了层次分类的准确性和预测的一致性。
- 该方法在不需像素级别注释的情况下改善了图像分割。
点此查看论文截图

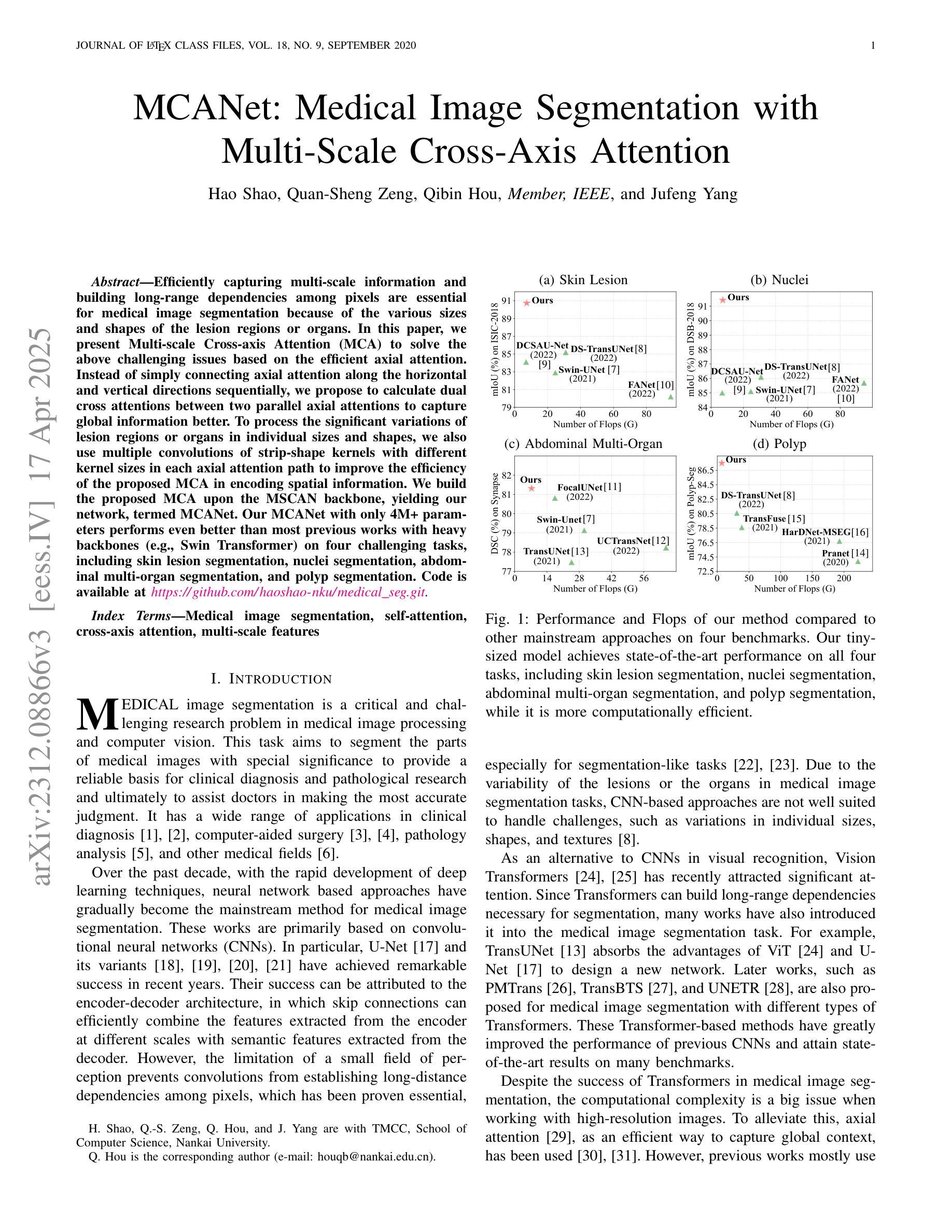
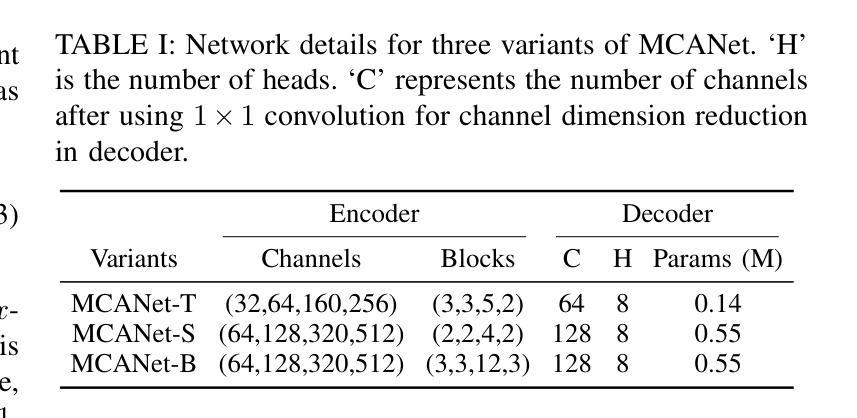
MCANet: Medical Image Segmentation with Multi-Scale Cross-Axis Attention
Authors:Hao Shao, Quansheng Zeng, Qibin Hou, Jufeng Yang
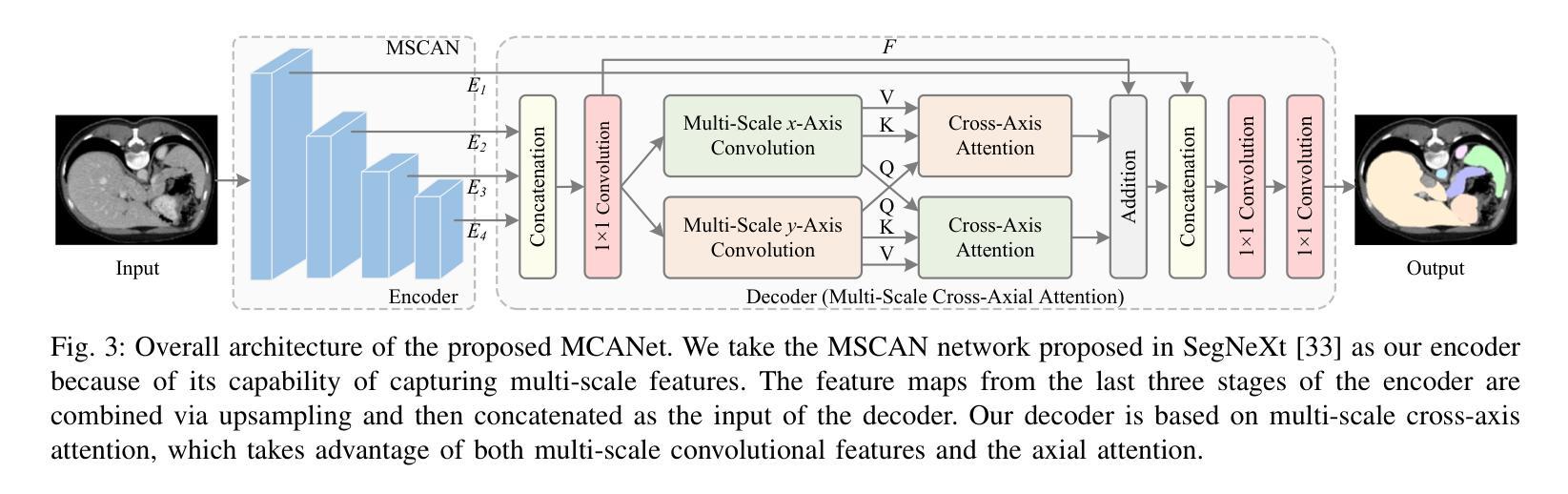
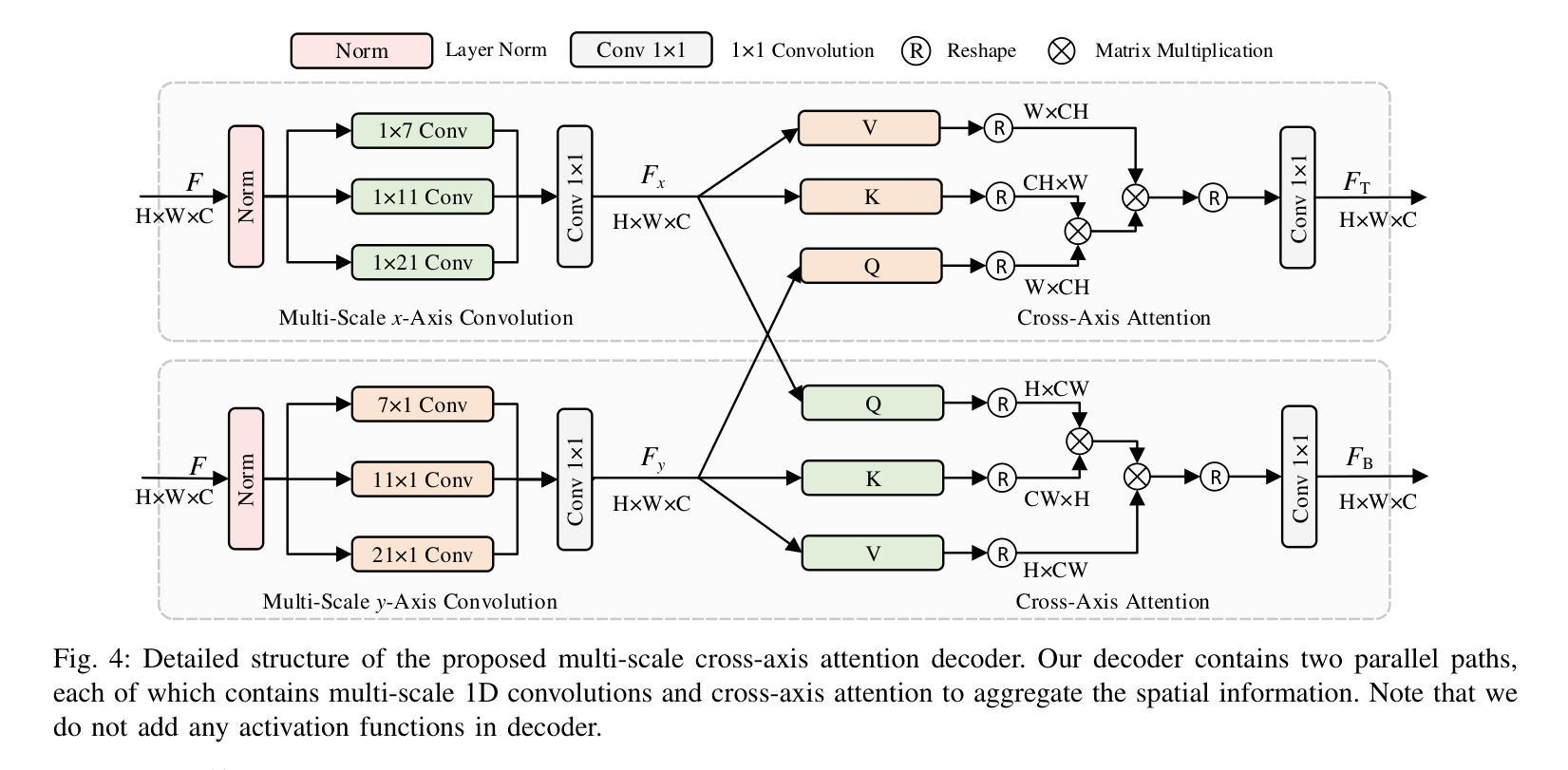
Efficiently capturing multi-scale information and building long-range dependencies among pixels are essential for medical image segmentation because of the various sizes and shapes of the lesion regions or organs. In this paper, we present Multi-scale Cross-axis Attention (MCA) to solve the above challenging issues based on the efficient axial attention. Instead of simply connecting axial attention along the horizontal and vertical directions sequentially, we propose to calculate dual cross attentions between two parallel axial attentions to capture global information better. To process the significant variations of lesion regions or organs in individual sizes and shapes, we also use multiple convolutions of strip-shape kernels with different kernel sizes in each axial attention path to improve the efficiency of the proposed MCA in encoding spatial information. We build the proposed MCA upon the MSCAN backbone, yielding our network, termed MCANet. Our MCANet with only 4M+ parameters performs even better than most previous works with heavy backbones (e.g., Swin Transformer) on four challenging tasks, including skin lesion segmentation, nuclei segmentation, abdominal multi-organ segmentation, and polyp segmentation. Code is available at https://github.com/haoshao-nku/medical_seg.
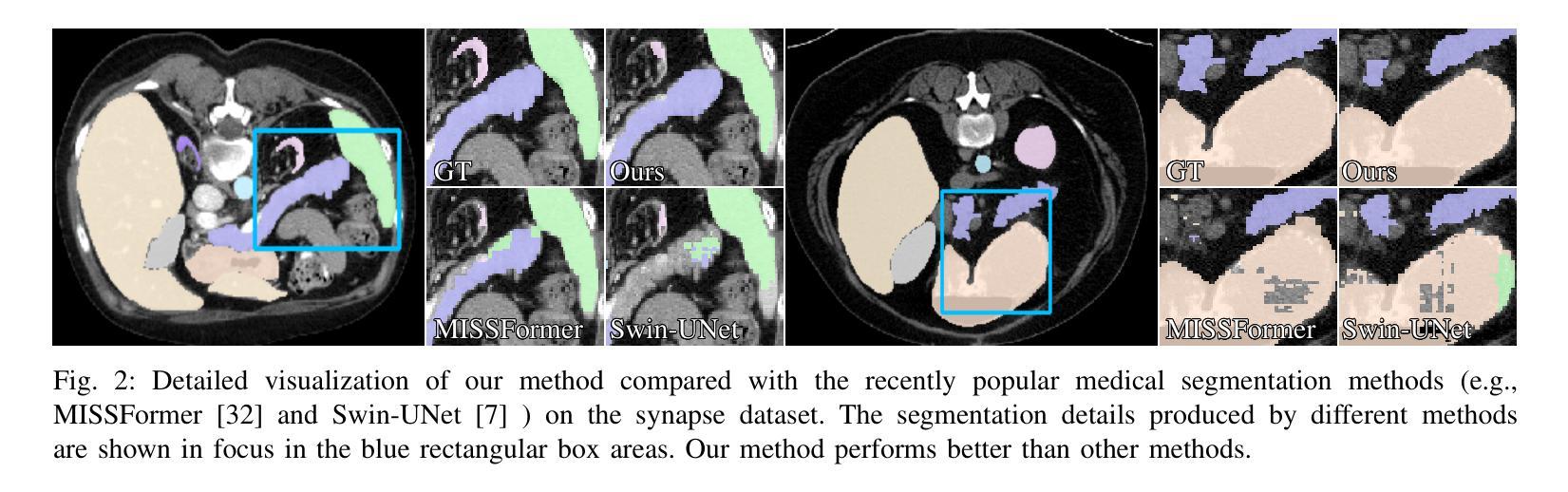
在医学图像分割中,由于病变区域或器官的大小和形状各异,有效地捕获多尺度信息以及建立像素之间的长距离依赖关系至关重要。针对以上挑战性问题,本文提出了基于高效轴向注意力的多尺度跨轴注意力(MCA)来解决。我们并不只是简单地按顺序在水平和垂直方向上连接轴向注意力,而是提议计算两个并行轴向注意力之间的双重交叉注意力,以更好地捕获全局信息。为了处理病变区域或器官在大小和形状上的显著差异,我们还将在每个轴向注意力路径中使用不同内核大小的条形卷积核进行多次卷积,以提高所提出MCA编码空间信息的效率。我们将所提出MCA建立在MSCAN主干网络上,形成了我们的网络,称为MCANet。我们的MCANet仅有4M+的参数,在四项具有挑战性的任务上表现甚至超过了以前大多数使用重型骨干网络的工作(例如Swin Transformer),这四项任务包括皮肤病变分割、细胞核分割、腹部多器官分割和息肉分割。相关代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/haoshao-nku/medical_seg。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accept to Machine Intelligence Research.DOI: 10.1007/s11633-025-1552-6
Summary
该文提出了多尺度交叉轴注意力(MCA)机制,用于解决医疗图像分割中的多尺度信息捕捉和长程像素依赖性问题。基于轴向注意力,通过计算两个平行轴向注意力之间的双重交叉注意力来更好地捕捉全局信息。为提高MCANet的效率,采用不同大小的条形卷积核进行多次卷积处理,以应对病灶区域或器官大小和形状的显著变化。MCANet在四个具有挑战性的任务上表现优异,包括皮肤病变分割、细胞核分割、腹部多器官分割和息肉分割。
Key Takeaways
- 多尺度信息捕捉和长程像素依赖性是医疗图像分割中的关键挑战。
- 提出的多尺度交叉轴注意力(MCA)机制旨在解决这些挑战。
- MCA通过计算两个平行轴向注意力之间的双重交叉注意力来捕捉全局信息。
- 为提高效率,采用多种尺寸的条形卷积核处理不同大小和形状的病灶区域或器官。
- MCANet在四个挑战性的医疗图像分割任务上表现优秀。
- MCANet参数仅4M+,但性能优于大多数带有重型骨干网(如Swin Transformer)的先前工作。
点此查看论文截图