⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-19 更新
Stronger, Steadier & Superior: Geometric Consistency in Depth VFM Forges Domain Generalized Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Siyu Chen, Ting Han, Changshe Zhang, Xin Luo, Meiliu Wu, Guorong Cai, Jinhe Su
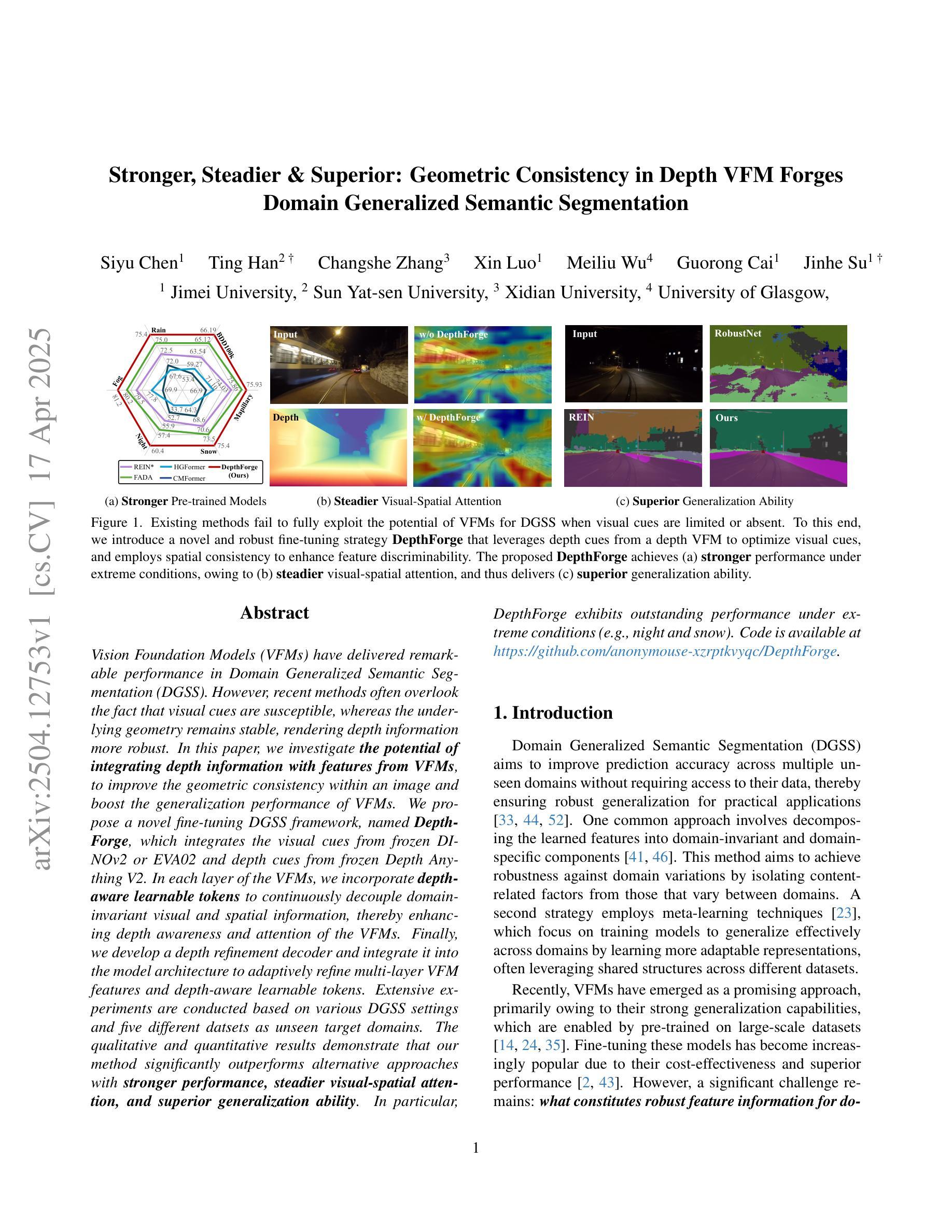
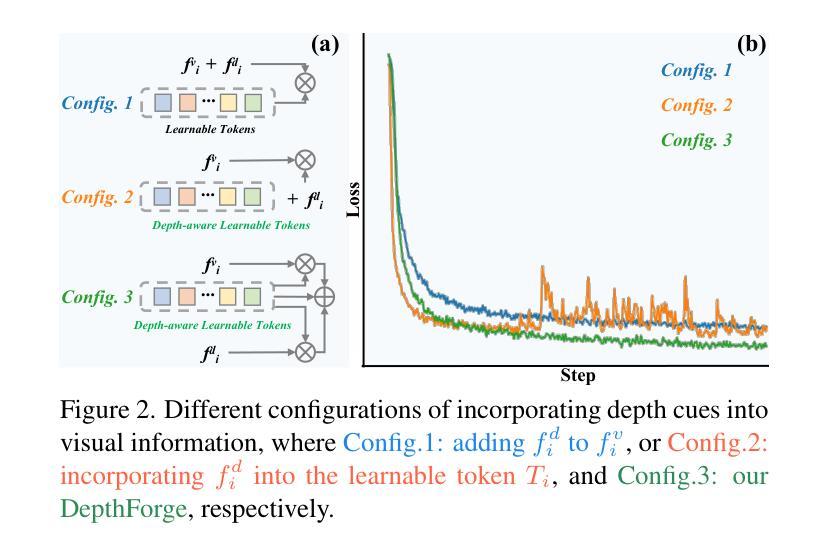
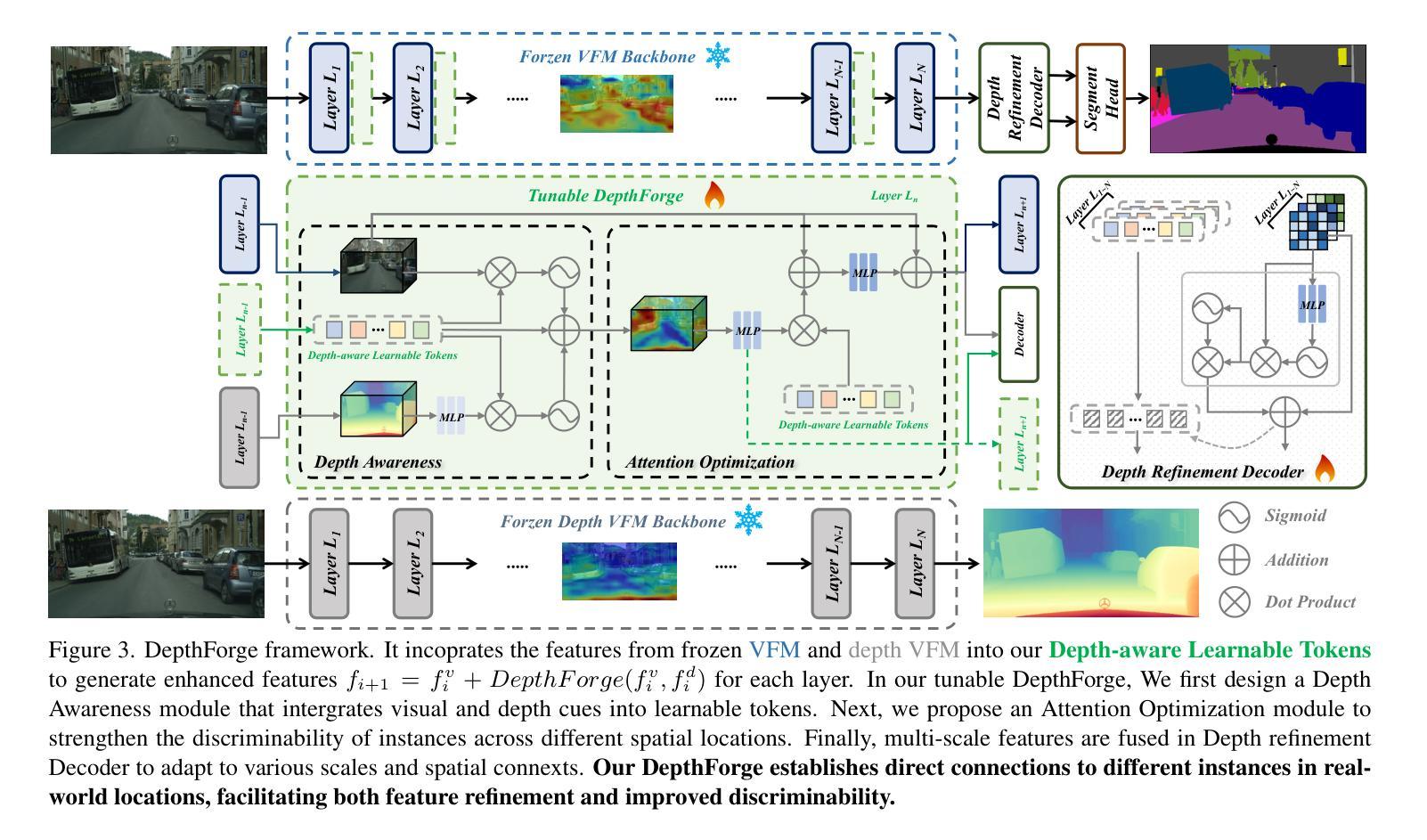
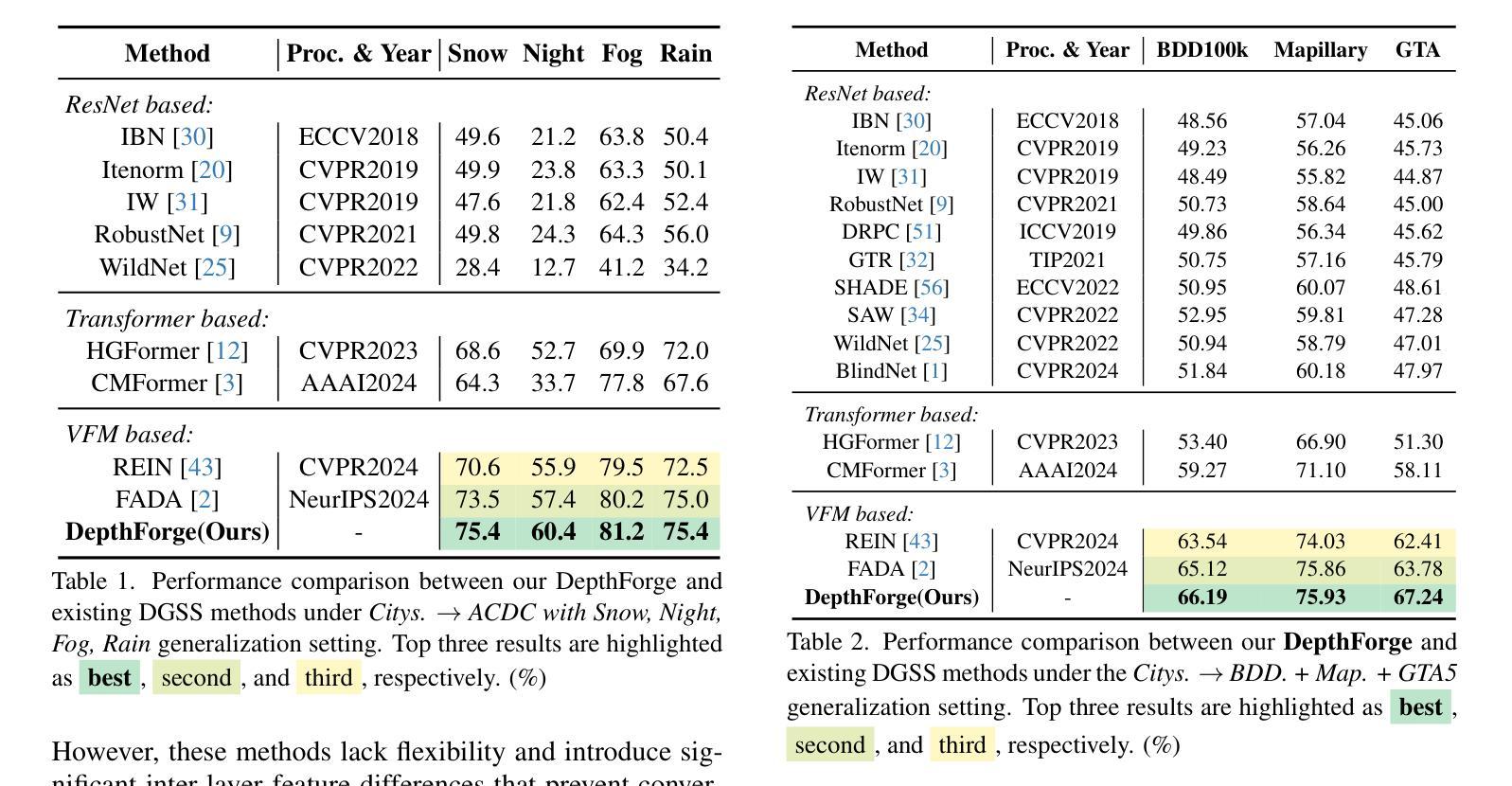
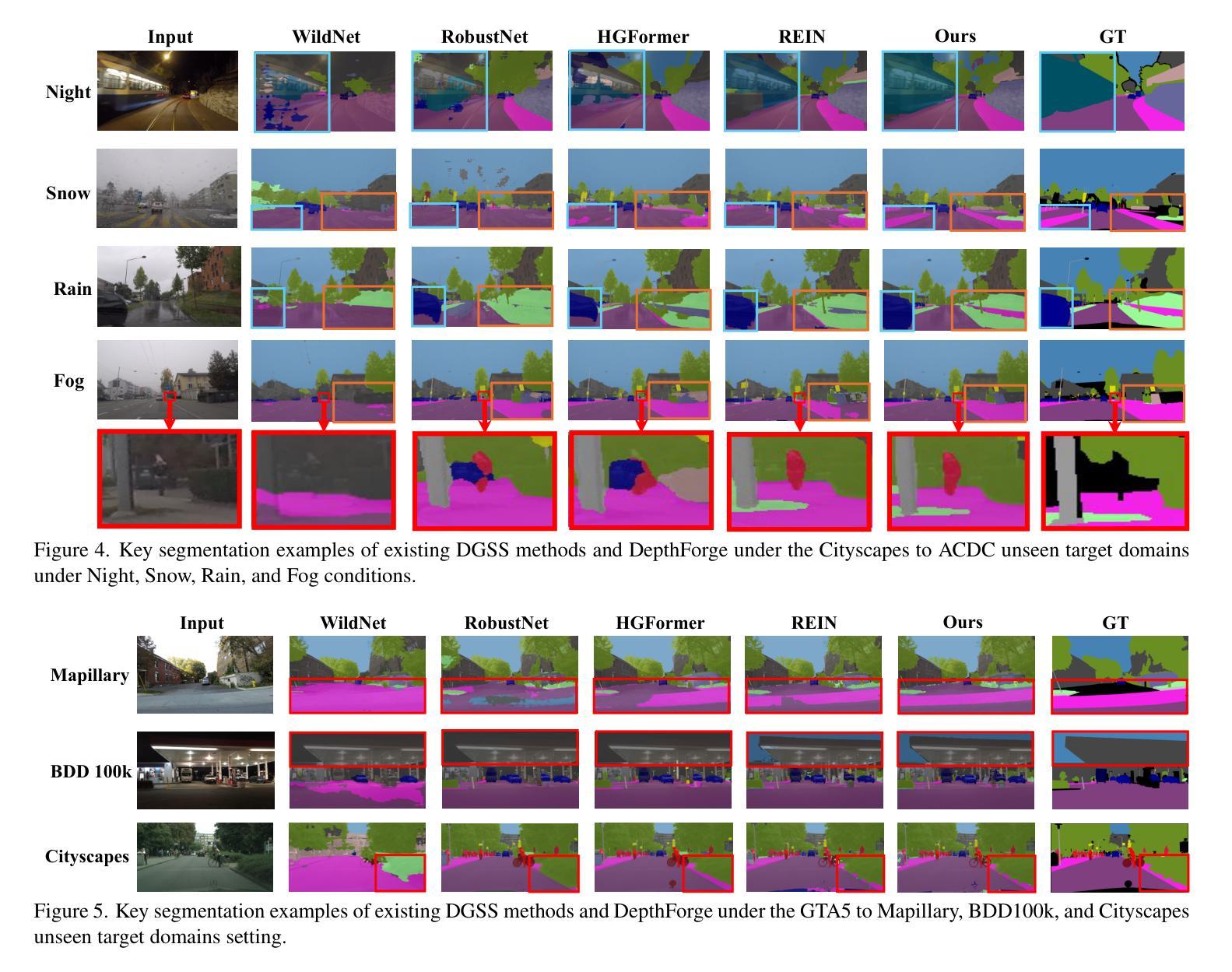
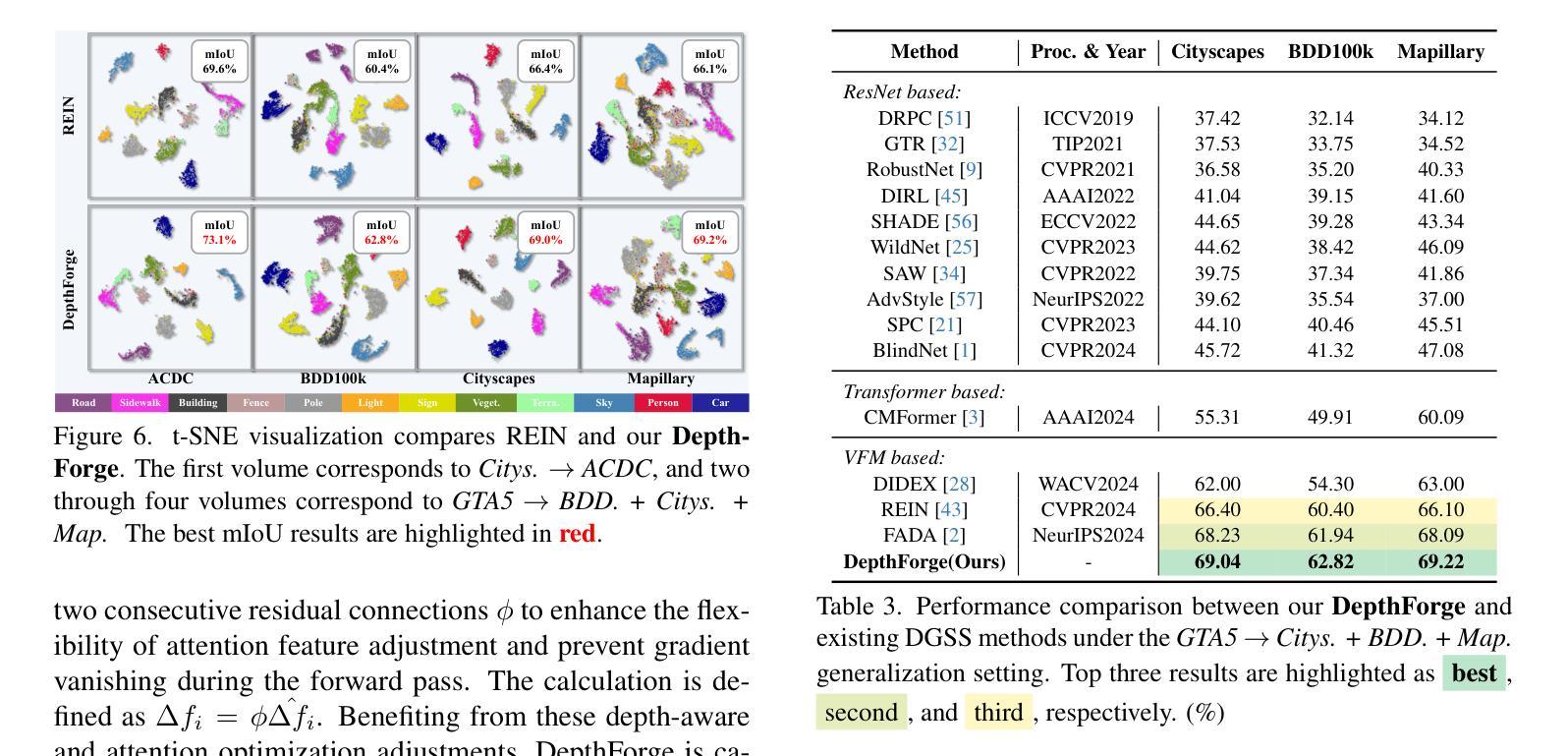
Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) have delivered remarkable performance in Domain Generalized Semantic Segmentation (DGSS). However, recent methods often overlook the fact that visual cues are susceptible, whereas the underlying geometry remains stable, rendering depth information more robust. In this paper, we investigate the potential of integrating depth information with features from VFMs, to improve the geometric consistency within an image and boost the generalization performance of VFMs. We propose a novel fine-tuning DGSS framework, named DepthForge, which integrates the visual cues from frozen DINOv2 or EVA02 and depth cues from frozen Depth Anything V2. In each layer of the VFMs, we incorporate depth-aware learnable tokens to continuously decouple domain-invariant visual and spatial information, thereby enhancing depth awareness and attention of the VFMs. Finally, we develop a depth refinement decoder and integrate it into the model architecture to adaptively refine multi-layer VFM features and depth-aware learnable tokens. Extensive experiments are conducted based on various DGSS settings and five different datsets as unseen target domains. The qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms alternative approaches with stronger performance, steadier visual-spatial attention, and superior generalization ability. In particular, DepthForge exhibits outstanding performance under extreme conditions (e.g., night and snow). Code is available at https://github.com/anonymouse-xzrptkvyqc/DepthForge.
视觉基础模型(VFMs)在域通用语义分割(DGSS)方面取得了显著的性能。然而,最近的方法常常忽略一个事实,即视觉线索是易变的,而基础几何则保持相对稳定,这使得深度信息更加稳健。在本文中,我们探讨了将深度信息与VFMs的特征相结合,以提高图像内的几何一致性并提升VFMs的泛化性能。我们提出了一种新颖的微调DGSS框架,名为DepthForge,它将来自冻结的DINOv2或EVA02的视觉线索和来自冻结的Depth Anything V2的深度线索相结合。在VFMs的每一层中,我们引入了深度感知的可学习令牌,以连续地解耦域不变视觉和空间信息,从而提高VFMs的深度感知和注意力。最后,我们开发了一个深度细化解码器,并将其集成到模型架构中,以自适应地细化多层VFM特征和深度感知的可学习令牌。基于各种DGSS设置和五个不同数据集作为未见过的目标域,进行了广泛的实验。定性和定量结果表明,我们的方法显著优于其他方法,具有更强的性能、更稳定的视觉-空间注意力和更好的泛化能力。特别是,DepthForge在极端条件下(例如夜晚和雪地)表现出卓越的性能。代码可在https://github.com/anonymouse-xzrptkvyqc/DepthForge上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探索了将深度信息融入视觉基础模型(VFMs)以提升图像几何一致性和泛化性能的可能性。提出了一种名为DepthForge的新型微调域泛化语义分割(DGSS)框架,该框架结合了视觉线索和深度线索。在VFM的每个层次上,引入深度感知学习令牌以连续地分离出领域不变视觉和空间信息,并开发了一个深度细化解码器来优化多层VFM特征和深度感知学习令牌。实验证明,该方法在多种DGSS设置和五个不同数据集上实现了显著优于其他方法的结果。特别是在极端条件下(例如夜晚和雪地)表现尤为出色。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- VFMs在域泛化语义分割(DGSS)中表现出卓越性能,但忽略了视觉线索易受干扰而底层几何更稳定的事实。
- 本研究提出了DepthForge框架,结合了视觉线索和深度线索,旨在提高几何一致性和泛化性能。
- DepthForge在每个VFM层次上引入深度感知学习令牌,以分离领域不变的视觉和空间信息。
点此查看论文截图
Efficient Fourier Filtering Network with Contrastive Learning for UAV-based Unaligned Bi-modal Salient Object Detection
Authors:Pengfei Lyu, Pak-Hei Yeung, Xiaosheng Yu, Xiufei Cheng, Chengdong Wu, Jagath C. Rajapakse
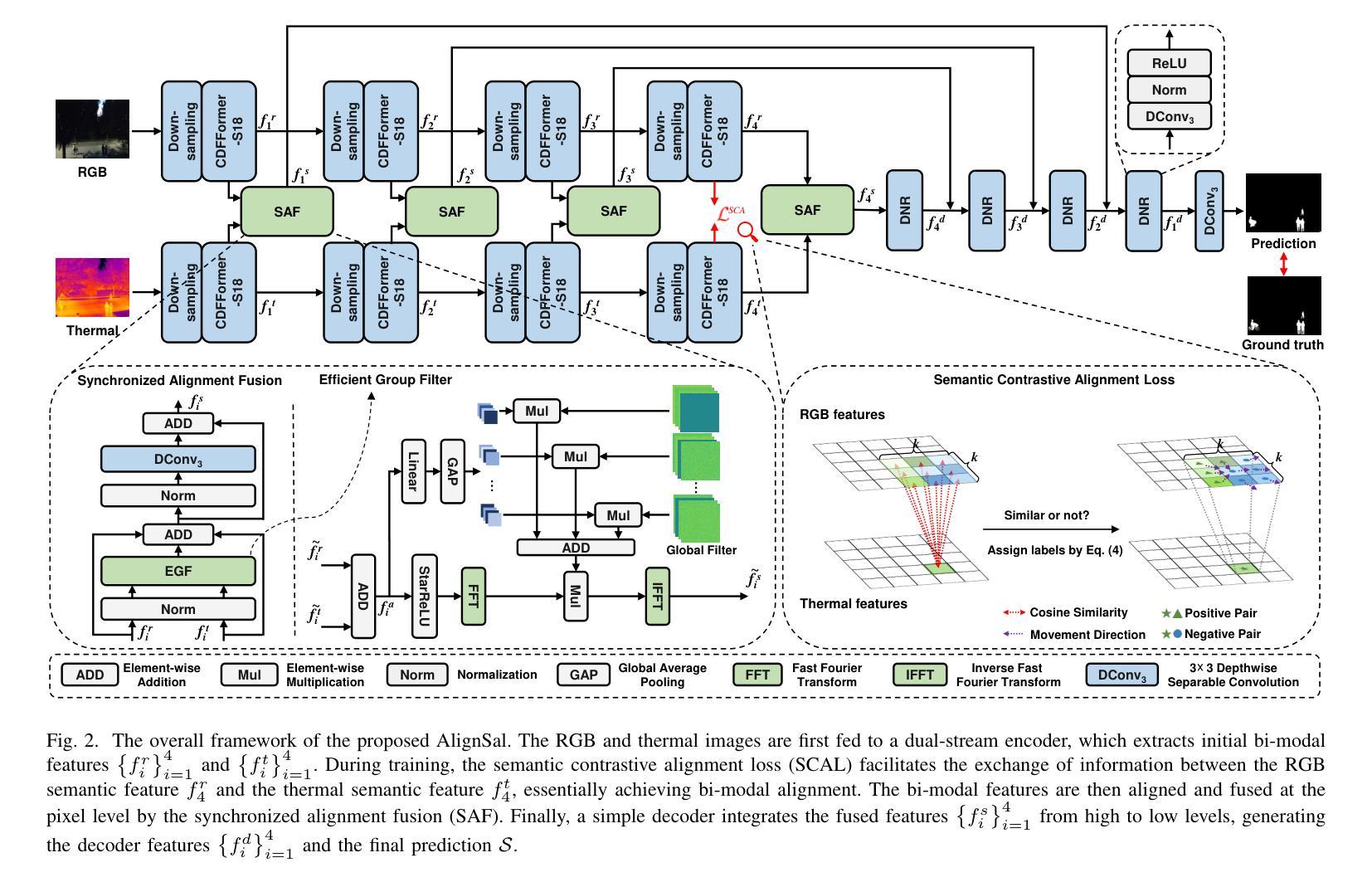
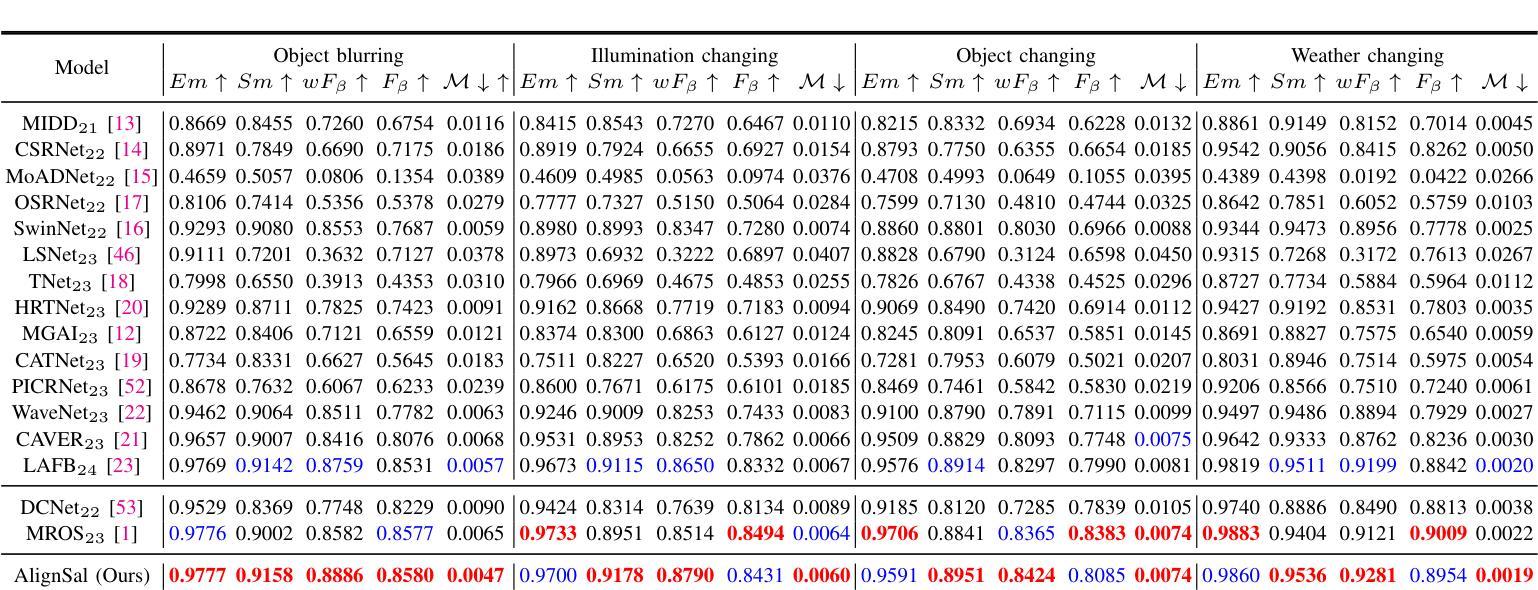
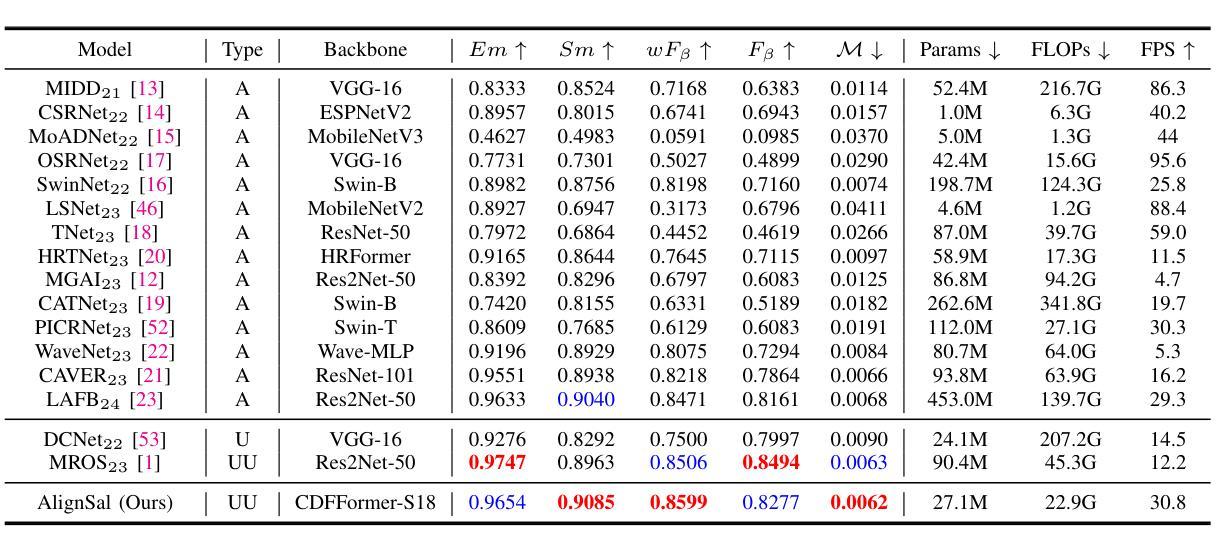
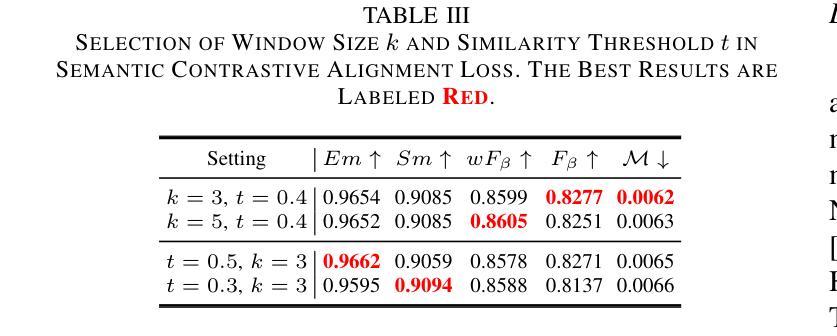
Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based bi-modal salient object detection (BSOD) aims to segment salient objects in a scene utilizing complementary cues in unaligned RGB and thermal image pairs. However, the high computational expense of existing UAV-based BSOD models limits their applicability to real-world UAV devices. To address this problem, we propose an efficient Fourier filter network with contrastive learning that achieves both real-time and accurate performance. Specifically, we first design a semantic contrastive alignment loss to align the two modalities at the semantic level, which facilitates mutual refinement in a parameter-free way. Second, inspired by the fast Fourier transform that obtains global relevance in linear complexity, we propose synchronized alignment fusion, which aligns and fuses bi-modal features in the channel and spatial dimensions by a hierarchical filtering mechanism. Our proposed model, AlignSal, reduces the number of parameters by 70.0%, decreases the floating point operations by 49.4%, and increases the inference speed by 152.5% compared to the cutting-edge BSOD model (i.e., MROS). Extensive experiments on the UAV RGB-T 2400 and seven bi-modal dense prediction datasets demonstrate that AlignSal achieves both real-time inference speed and better performance and generalizability compared to nineteen state-of-the-art models across most evaluation metrics. In addition, our ablation studies further verify AlignSal’s potential in boosting the performance of existing aligned BSOD models on UAV-based unaligned data. The code is available at: https://github.com/JoshuaLPF/AlignSal.
基于无人机的双模态显著目标检测(BSOD)旨在利用未对齐的RGB和热成像对中的互补线索来分割场景中的显著目标。然而,现有基于无人机的BSOD模型计算成本高,限制了它们在真实世界无人机设备中的应用。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种具有对比学习的有效傅里叶滤波器网络,实现了实时和准确的性能。具体来说,我们首先设计了一种语义对比对齐损失,在语义层面上对齐两种模态,以无参数的方式促进相互细化。其次,受到快速傅里叶变换以线性复杂度获得全局相关性的启发,我们提出了同步对齐融合,通过分层过滤机制在通道和空间维度上对齐和融合双模态特征。我们提出的AlignSal模型将参数数量减少了70.0%,将浮点运算减少了49.4%,与最先进的BSOD模型(即MROS)相比,推理速度提高了152.5%。在UAV RGB-T 2400和七个双模态密集预测数据集上的大量实验表明,与十九种最先进的模型相比,AlignSal在大多数评估指标上实现了实时推理速度和更好的性能和泛化能力。此外,我们的消融研究进一步验证了AlignSal在提升现有对齐BSOD模型在基于无人机的未对齐数据上的潜力。代码可在https://github.com/JoshuaLPF/AlignSal获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TGRS 2025
Summary
该文本介绍了一种基于无人机的双模态显著目标检测(BSOD)新方法。针对现有模型的计算成本高的问题,提出了一个高效的傅里叶滤波器网络,并结合对比学习实现实时准确性能。通过设计语义对比对齐损失,实现两种模态在语义层面的对齐,并通过快速傅里叶变换启发下的同步对齐融合,实现对双模态特征的层次过滤机制融合。与前沿BSOD模型相比,新模型AlignSal减少了参数和计算量,提高了推理速度,并在多个数据集上表现出更好的性能和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- UAV-based bi-modal salient object detection (BSOD)利用非对齐的RGB和红外图像对中的互补线索来分割场景中的显著目标。
- 现有UAV-based BSOD模型面临高计算费用的问题,限制了其在真实世界无人机设备中的应用。
- 提出了一种高效的傅里叶滤波器网络,结合对比学习实现实时准确性能。
- 设计了语义对比对齐损失,实现两种模态在语义层面的对齐,促进无参数互校。
- 同步对齐融合方法通过层次过滤机制融合双模态特征。
- AlignSal模型相比前沿BSOD模型减少了参数和计算量,提高了推理速度。
- AlignSal模型在多个数据集上表现出更好的性能和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图
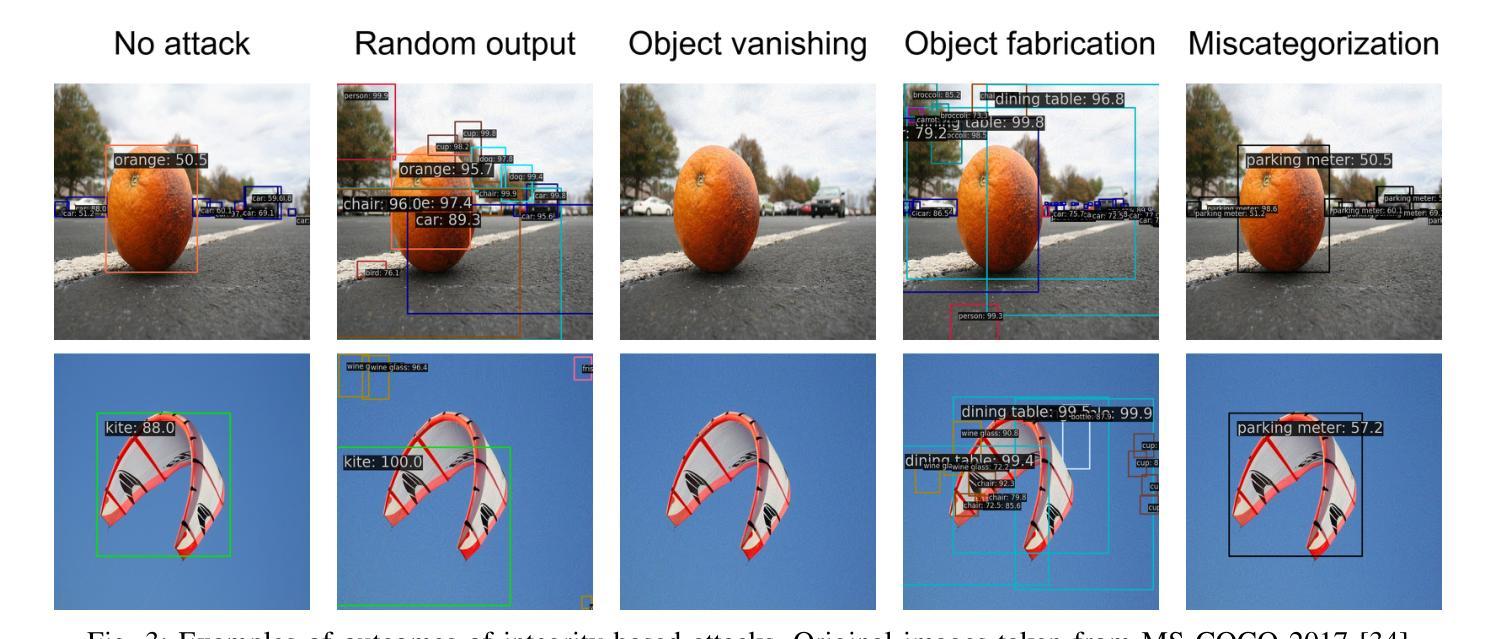
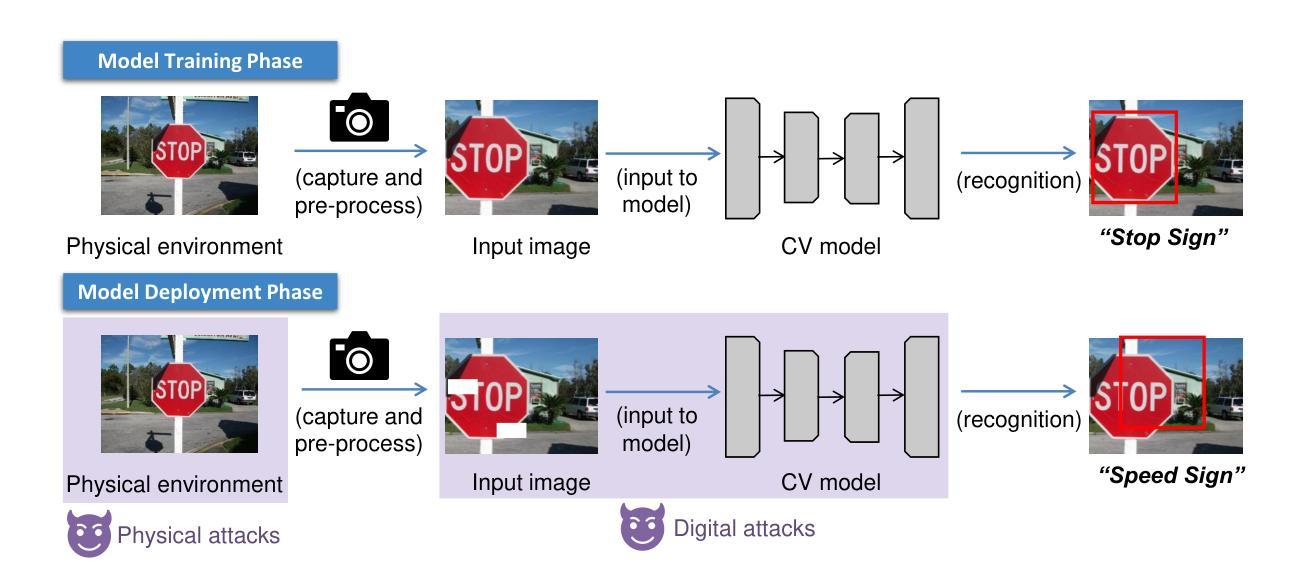
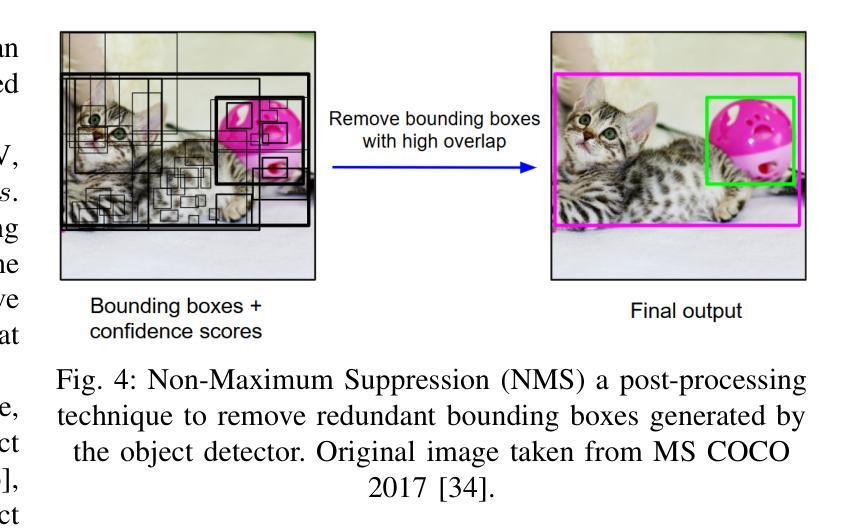
A Survey and Evaluation of Adversarial Attacks for Object Detection
Authors:Khoi Nguyen Tiet Nguyen, Wenyu Zhang, Kangkang Lu, Yuhuan Wu, Xingjian Zheng, Hui Li Tan, Liangli Zhen
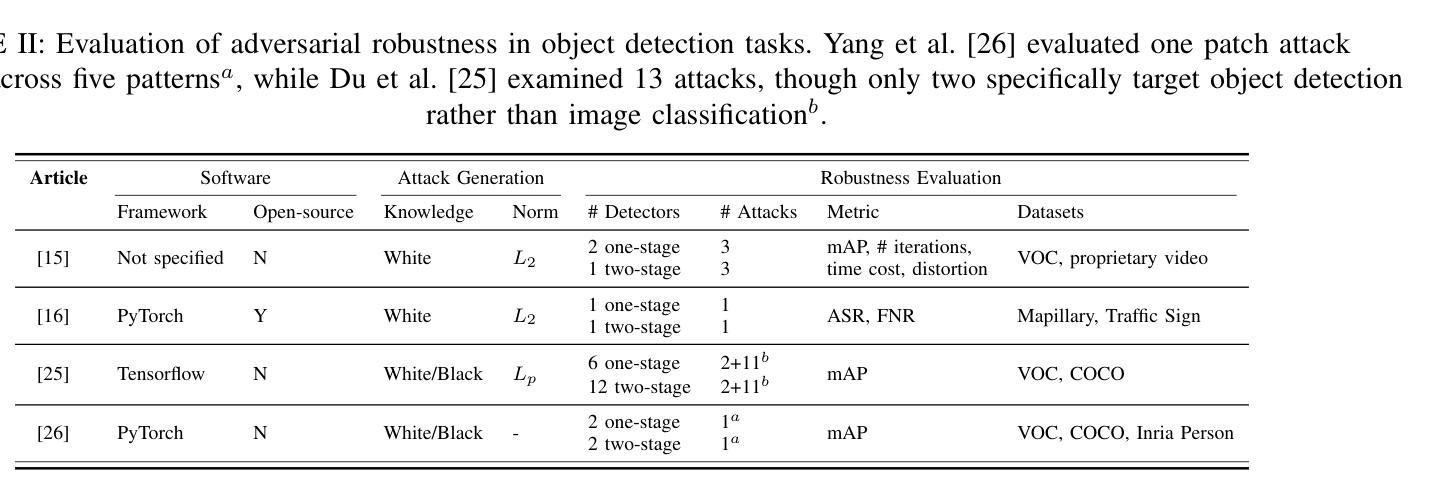
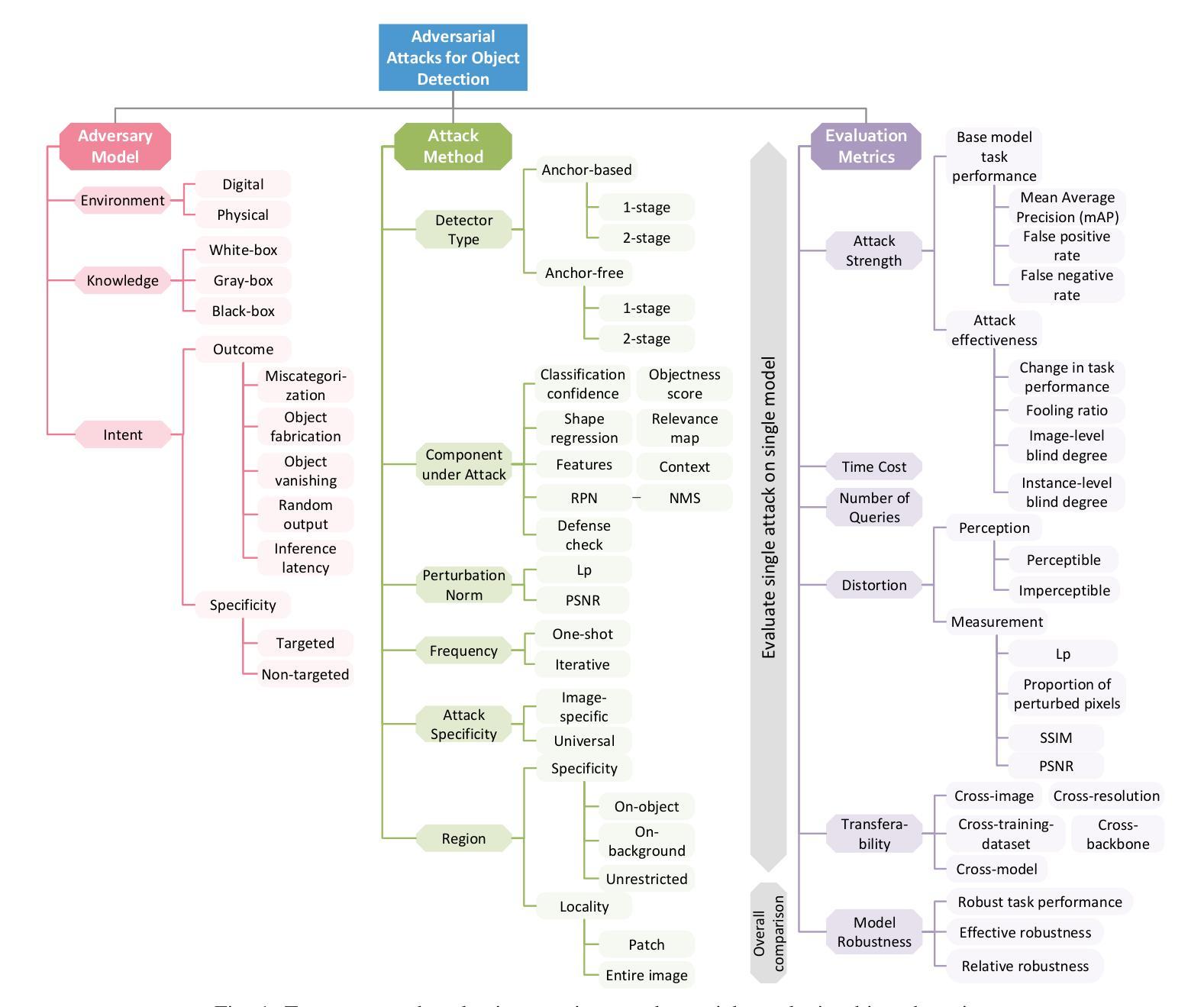
Deep learning models achieve remarkable accuracy in computer vision tasks, yet remain vulnerable to adversarial examples–carefully crafted perturbations to input images that can deceive these models into making confident but incorrect predictions. This vulnerability pose significant risks in high-stakes applications such as autonomous vehicles, security surveillance, and safety-critical inspection systems. While the existing literature extensively covers adversarial attacks in image classification, comprehensive analyses of such attacks on object detection systems remain limited. This paper presents a novel taxonomic framework for categorizing adversarial attacks specific to object detection architectures, synthesizes existing robustness metrics, and provides a comprehensive empirical evaluation of state-of-the-art attack methodologies on popular object detection models, including both traditional detectors and modern detectors with vision-language pretraining. Through rigorous analysis of open-source attack implementations and their effectiveness across diverse detection architectures, we derive key insights into attack characteristics. Furthermore, we delineate critical research gaps and emerging challenges to guide future investigations in securing object detection systems against adversarial threats. Our findings establish a foundation for developing more robust detection models while highlighting the urgent need for standardized evaluation protocols in this rapidly evolving domain.
深度学习模型在计算机视觉任务中取得了令人瞩目的准确性,但仍然容易受到对抗样本的威胁。对抗样本是对输入图像进行精心制作的扰动,可以欺骗这些模型做出自信但错误的预测。这种脆弱性在高风险应用(如自动驾驶、安全监控和关键安全检测系统)中构成了重大风险。尽管现有文献广泛涵盖了图像分类中的对抗性攻击,但对目标检测系统中此类攻击的综合分析仍然有限。本文提出了一个针对目标检测架构的对抗性攻击的新型分类框架,综合了现有的稳健性指标,并对流行目标检测模型上的最新攻击方法进行了全面的实证评估,包括传统检测器和具有视觉语言预训练的现代检测器。通过对开源攻击实现的严格分析以及它们在多种检测架构中的有效性,我们获得了关于攻击特性的关键见解。此外,我们明确了关键的研究空白和新兴挑战,以指导未来对保护目标检测系统免受对抗性威胁的研究。我们的研究为开发更稳健的检测模型奠定了基础,同时强调了在这一快速发展领域中迫切需要标准化评估协议。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in the IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems (TNNLS)
Summary
深度学习模型在计算机视觉任务中取得了惊人的准确性,但在面对对抗样本时仍表现出脆弱性。对抗样本是对输入图像进行精心设计的扰动,可以欺骗模型做出错误但自信的预测。在自动驾驶、安全监控和安全关键检测系统等高风险应用中,这种脆弱性带来了重大风险。本文对专门针对对象检测架构的对抗性攻击进行了新型分类学框架的呈现,对现有的鲁棒性度量进行了综合,并对流行的对象检测模型上的最新攻击方法进行了全面的实证研究,包括对传统的检测器和具有视觉语言预训练的现代检测器。通过对开源攻击实现的严格分析以及它们在各种检测架构中的有效性评估,我们得出了关于攻击特性的关键见解。此外,本文还指出了关键的研究空白和新兴挑战,为未来的研究中保障对象检测系统对抗威胁的安全性提供了指导。本研究为开发更稳健的检测模型奠定了基础,并强调了在这一快速演变的领域中标准化评估协议方面的迫切需求。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型在计算机视觉任务中表现卓越,但面临对抗样本的威胁,这在高风险应用中带来显著风险。
- 对抗样本是精心设计的输入图像扰动,能够欺骗模型做出错误预测。
- 目前对于对象检测系统的对抗性攻击的综合分析仍有限。
- 本文提出了一个新的分类学框架来分类针对对象检测系统的对抗性攻击。
- 论文综合了现有的鲁棒性度量,并对最新的攻击方法在流行的对象检测模型上进行了实证研究。
- 通过分析开源攻击实现及其在多种检测架构中的有效性,研究得出了关于攻击特性的关键见解。
点此查看论文截图

Unified Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Zhe Zhang, Gaochang Wu, Jing Zhang, Xiatian Zhu, Dacheng Tao, Tianyou Chai
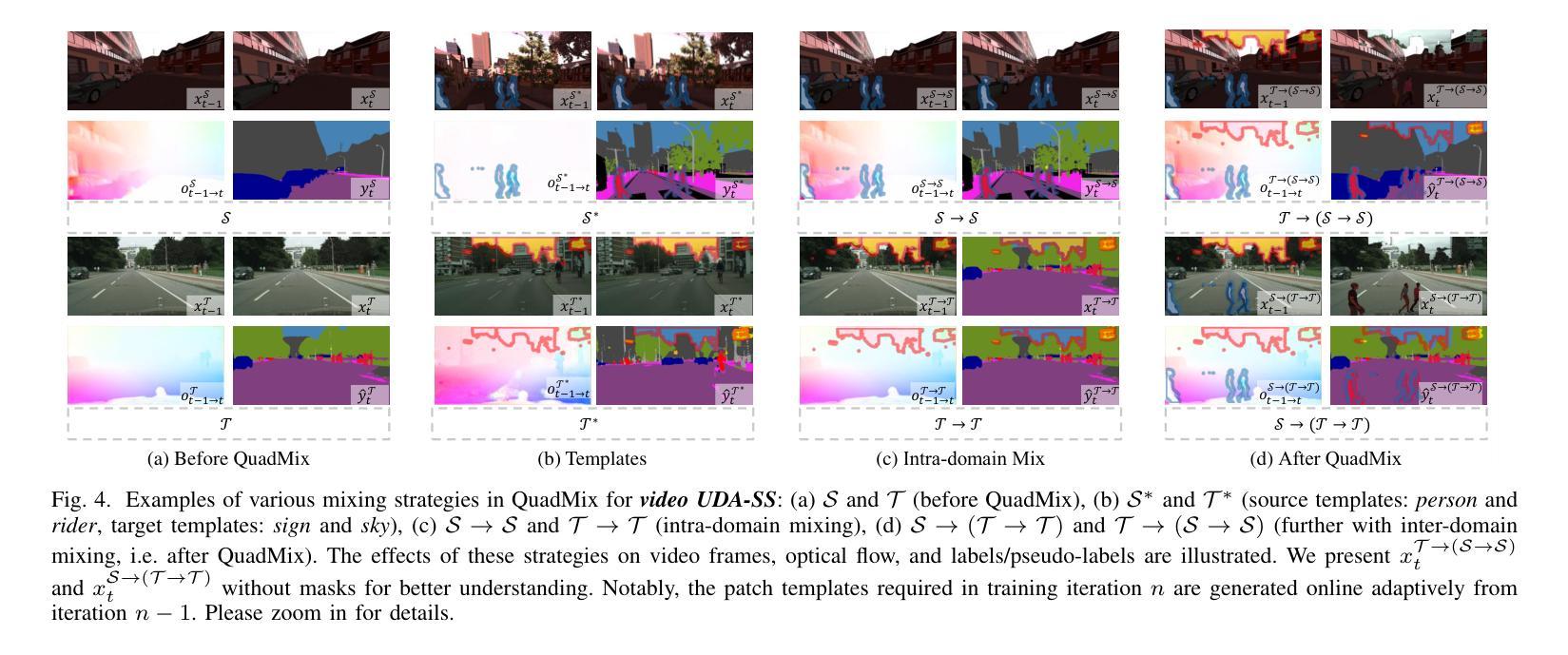
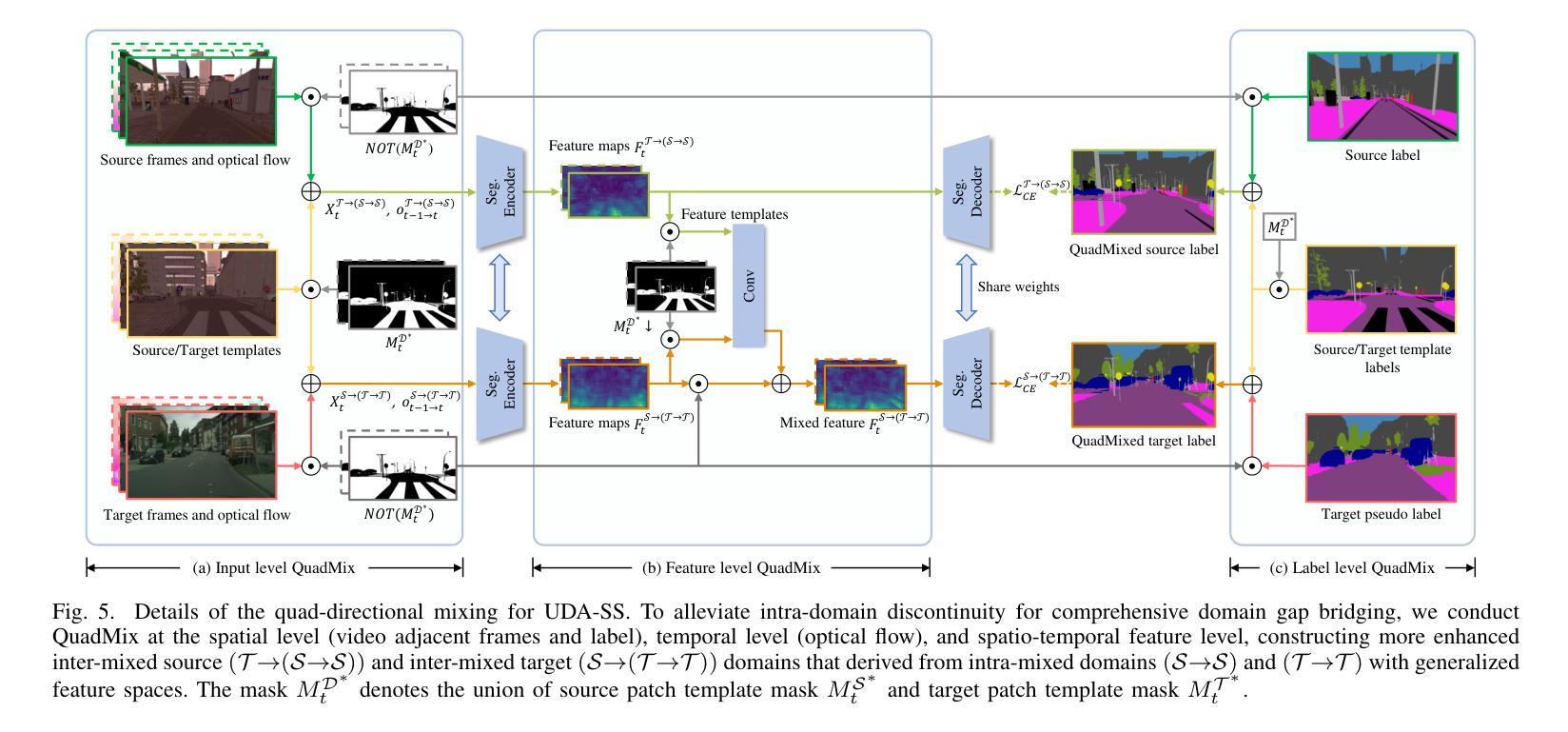
Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation (UDA-SS) aims to transfer the supervision from a labeled source domain to an unlabeled target domain. The majority of existing UDA-SS works typically consider images whilst recent attempts have extended further to tackle videos by modeling the temporal dimension. Although the two lines of research share the major challenges – overcoming the underlying domain distribution shift, their studies are largely independent, resulting in fragmented insights, a lack of holistic understanding, and missed opportunities for cross-pollination of ideas. This fragmentation prevents the unification of methods, leading to redundant efforts and suboptimal knowledge transfer across image and video domains. Under this observation, we advocate unifying the study of UDA-SS across video and image scenarios, enabling a more comprehensive understanding, synergistic advancements, and efficient knowledge sharing. To that end, we explore the unified UDA-SS from a general data augmentation perspective, serving as a unifying conceptual framework, enabling improved generalization, and potential for cross-pollination of ideas, ultimately contributing to the overall progress and practical impact of this field of research. Specifically, we propose a Quad-directional Mixup (QuadMix) method, characterized by tackling distinct point attributes and feature inconsistencies through four-directional paths for intra- and inter-domain mixing in a feature space. To deal with temporal shifts with videos, we incorporate optical flow-guided feature aggregation across spatial and temporal dimensions for fine-grained domain alignment. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art works by large margins on four challenging UDA-SS benchmarks. Our source code and models will be released at https://github.com/ZHE-SAPI/UDASS.
无监督域自适应语义分割(UDA-SS)的目标是将有标签源域的监督信息转移到无标签目标域。大多数现有的UDA-SS工作主要关注图像,而最近的尝试通过进一步建模时间维度来处理视频。尽管这两类研究面临的主要挑战是克服潜在的域分布转移问题,但他们的研究在很大程度上是独立的,导致碎片化的见解、缺乏整体理解和错过了相互传播思想的机会。这种碎片化阻碍了方法的统一,导致了冗余的努力和跨图像和视频域的次优知识转移。基于此观察,我们主张统一跨视频和图像场景的UDA-SS研究,以便更全面的理解、协同发展和有效的知识共享。为此,我们从一般的数据增强角度探索了统一的UDA-SS,作为统一的概念框架,以实现更好的泛化和思想相互传播的可能性,最终为这一研究领域取得总体进展和实际应用做出贡献。具体来说,我们提出了一种四方向混合(QuadMix)方法,其特点是解决不同点的属性和特征不一致的问题,通过四个方向的路径在特征空间内进行和跨域混合。为了处理视频的临时变化,我们结合了光学流动引导的特征聚合在空间和时间维度上进行精细的域对齐。大量实验表明,我们的方法在四个具有挑战性的UDA-SS基准测试上大大优于最新作品。我们的源代码和模型将在https://github.com/ZHE-SAPI/UDASS发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages,11 figures, 11 tables. Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2025
摘要
无监督域自适应语义分割(UDA-SS)旨在将从有标签的源域的监督转移到无标签的目标域。大多数现有的UDA-SS工作主要考虑图像,而最近的尝试通过建模时间维度进一步扩展到视频处理。虽然这两类研究都面临主要的挑战——克服潜在的域分布转移,但他们的研究在很大程度上是独立的,导致碎片化的见解、缺乏整体理解和错失交叉授粉的机会。这种碎片化阻碍了方法的统一,导致了冗余的努力和次优的知识在图像和视频域之间的转移。基于这些观察,我们主张统一UDA-SS在视频和图像场景的研究,以实现更全面的理解、协同发展和有效的知识共享。为此,我们从一般的数据增强角度探索了统一的UDA-SS,作为统一的概念框架,以实现改进泛化和潜在的思想交叉授粉,最终促进这一研究领域整体的进步和实际应用的影响。具体来说,我们提出了一种Quad-directional Mixup(QuadMix)方法,其特点是解决不同点的属性和特征不一致性,通过四个方向的路径在特征空间进行域内和域间混合。为了处理视频的临时移位,我们结合了光学流动引导的特征在空间和时间的维度上的聚合,进行精细的域对齐。大量实验表明,我们的方法在四个具有挑战性的UDA-SS基准测试上大大优于最新作品。我们的源代码和模型将在https://github.com/ZHE-SAPI/UDASS发布。
要点提炼
- UDA-SS旨在将从源域的监督转移到目标域,尤其关注图像和视频的处理。
- 当前研究存在碎片化问题,图像和视频领域的UDA-SS研究相对独立,缺乏整体理解和交叉融合。
- 提出统一UDA-SS研究的重要性,以实现更全面的理解、协同发展和知识共享。
- 从数据增强角度探索统一的UDA-SS作为概念框架,改善泛化能力并促进思想交流。
- 介绍了QuadMix方法,通过四个方向的路径解决特征不一致性问题,实现域内和域间的混合。
- 为处理视频的临时移位,结合光学流动引导的特征聚合技术。
点此查看论文截图