⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-19 更新
Online Video Understanding: OVBench and VideoChat-Online
Authors:Zhenpeng Huang, Xinhao Li, Jiaqi Li, Jing Wang, Xiangyu Zeng, Cheng Liang, Tao Wu, Xi Chen, Liang Li, Limin Wang
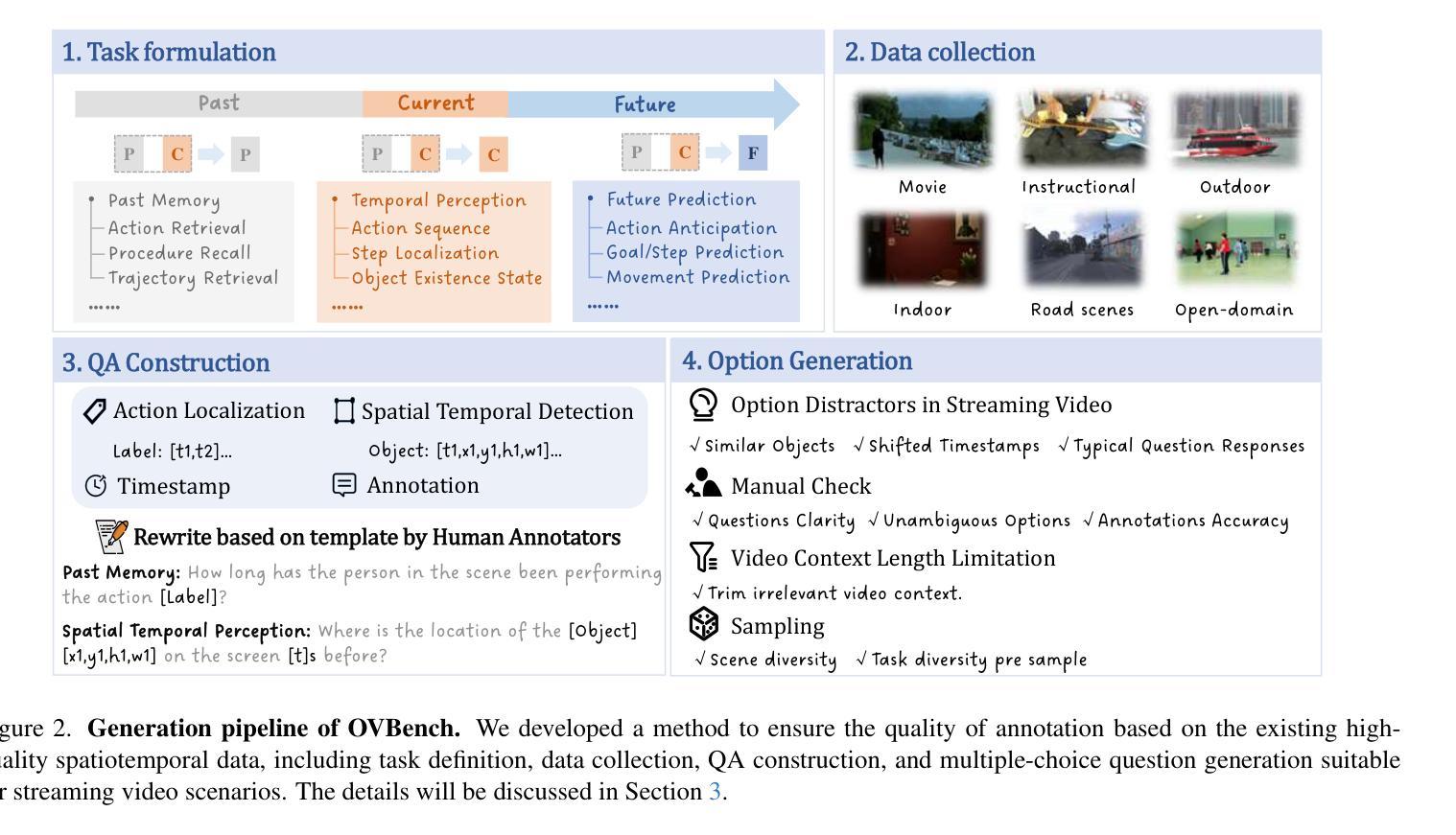
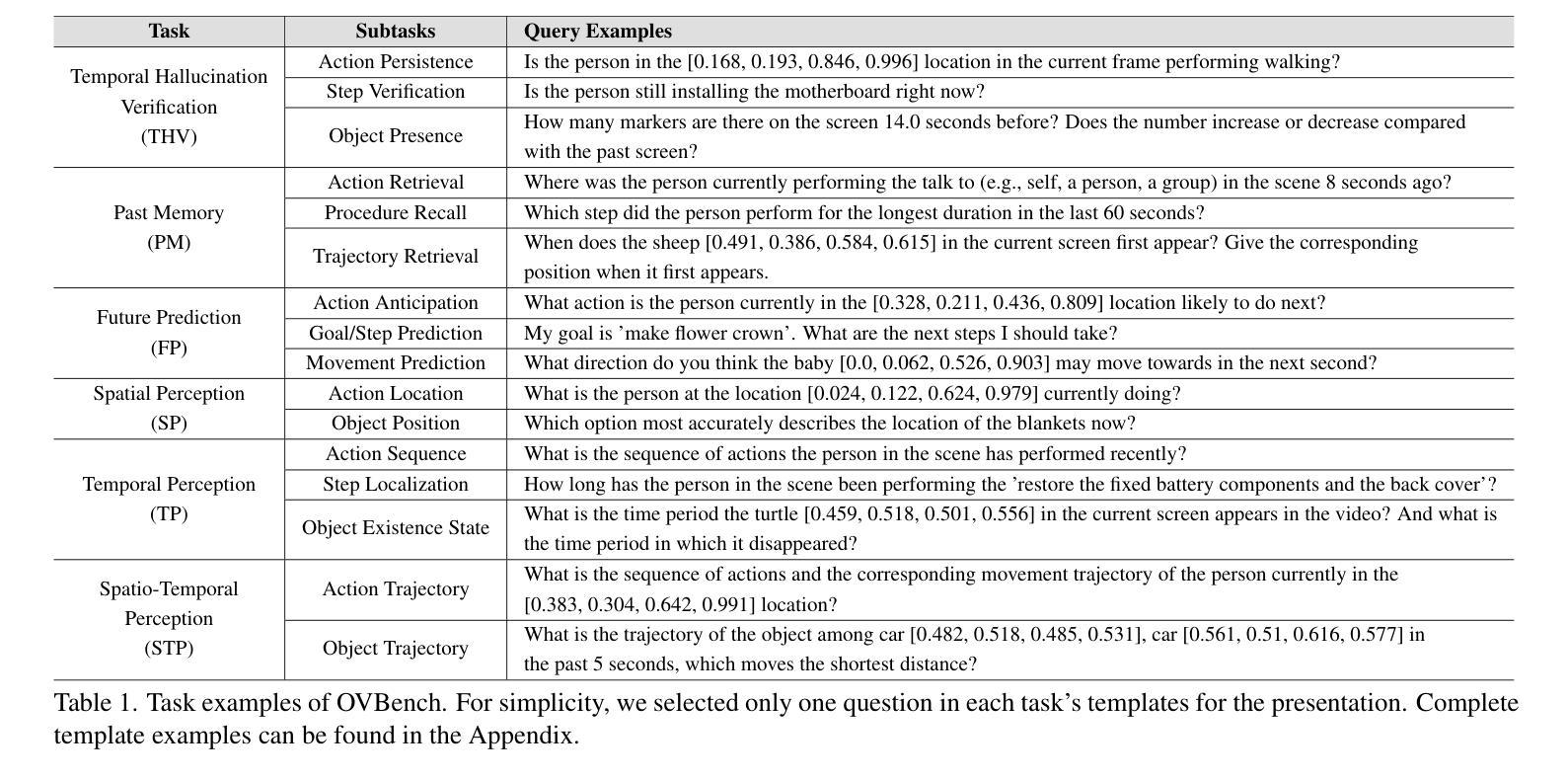
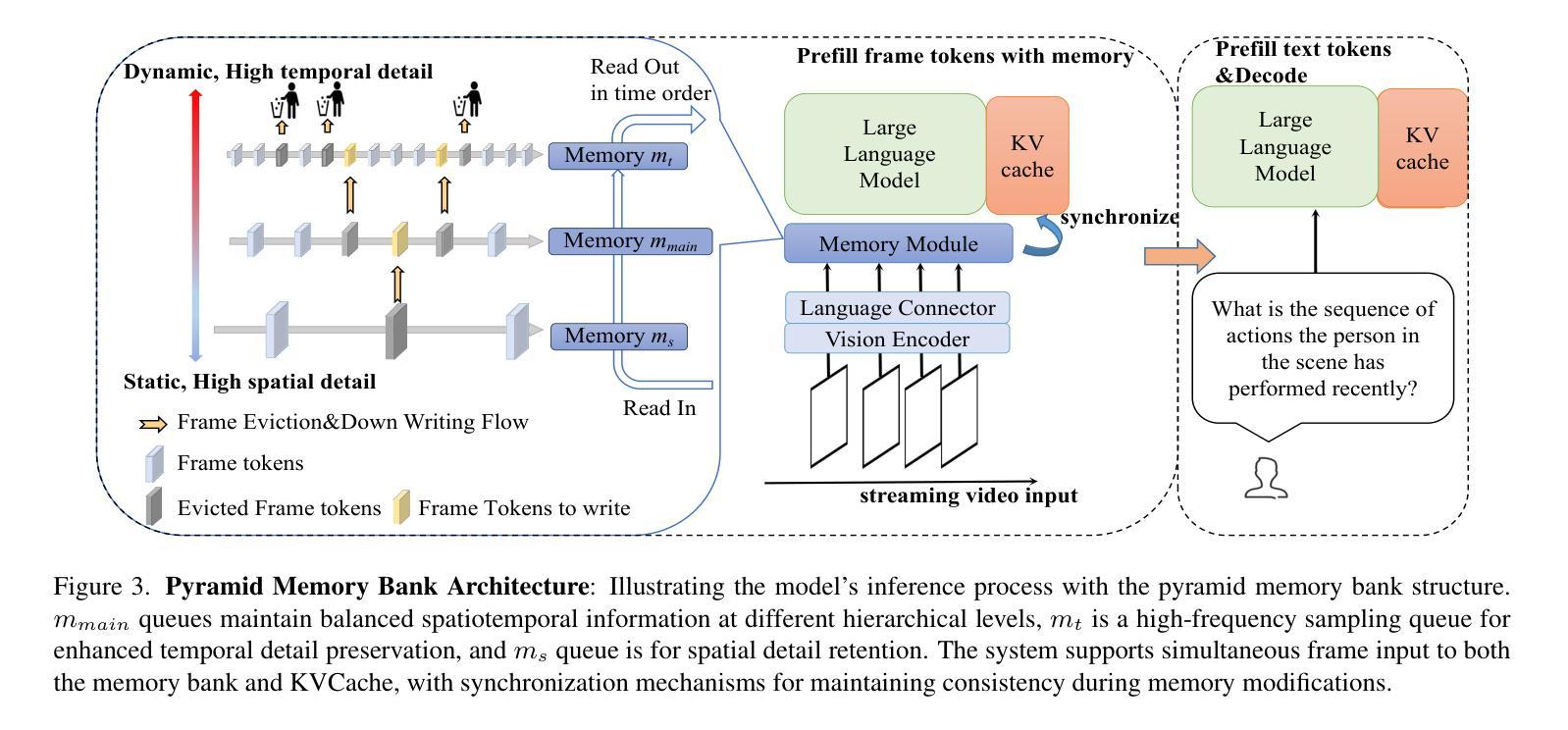
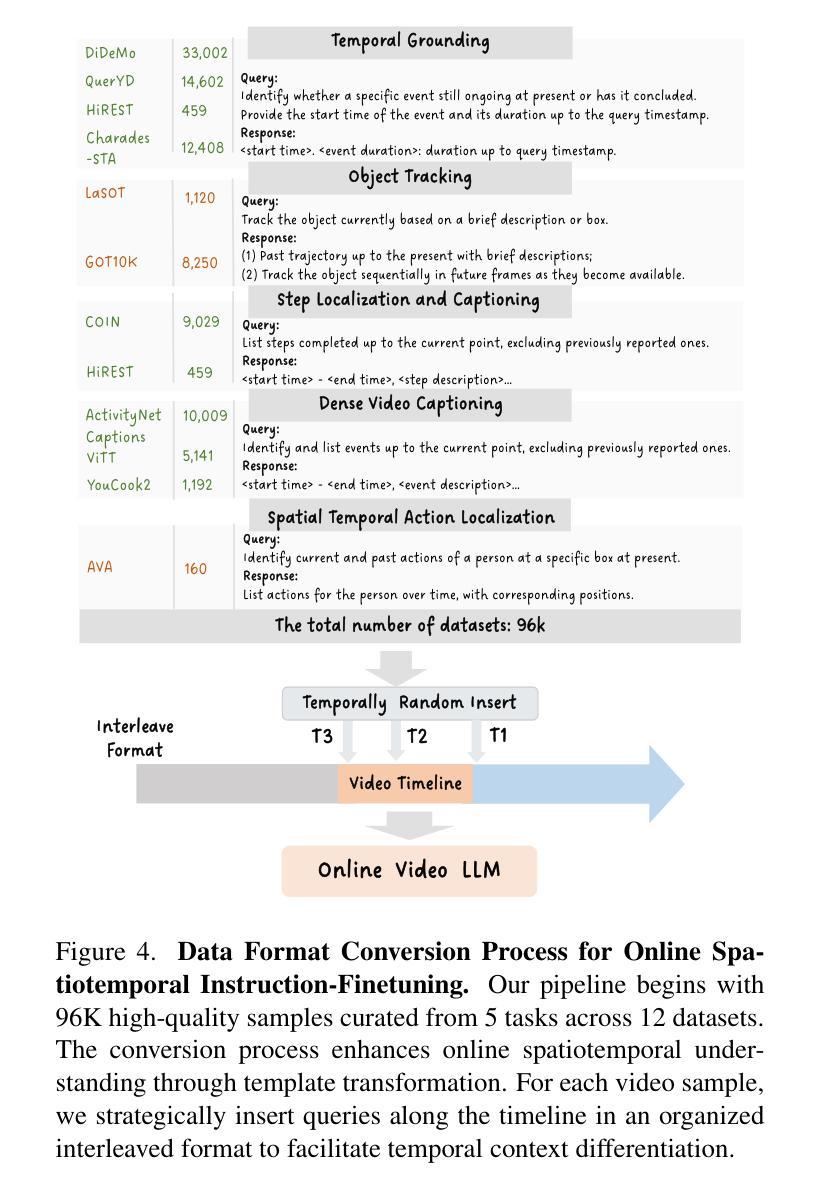
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have significantly progressed in offline video understanding. However, applying these models to real-world scenarios, such as autonomous driving and human-computer interaction, presents unique challenges due to the need for real-time processing of continuous online video streams. To this end, this paper presents systematic efforts from three perspectives: evaluation benchmark, model architecture, and training strategy. First, we introduce OVBench, a comprehensive question-answering benchmark designed to evaluate models’ ability to perceive, memorize, and reason within online video contexts. It features 6 core task types across three temporal contexts-past, current, and future-forming 16 subtasks from diverse datasets. Second, we propose a new Pyramid Memory Bank (PMB) that effectively retains key spatiotemporal information in video streams. Third, we proposed an offline-to-online learning paradigm, designing an interleaved dialogue format for online video data and constructing an instruction-tuning dataset tailored for online video training. This framework led to the development of VideoChat-Online, a robust and efficient model for online video understanding. Despite the lower computational cost and higher efficiency, VideoChat-Online outperforms existing state-of-the-art offline and online models across popular offline video benchmarks and OVBench, demonstrating the effectiveness of our model architecture and training strategy. % Our approach surpasses existing state-of-the-art offline models Qwen2-VL 7B and online models Flash-VStream, by 4.19% and 23.7% on OVBench, respectively.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在离线视频理解方面取得了显著进展。然而,将这些模型应用于现实世界场景,如自动驾驶和人机交互,由于需要实时处理连续的在线视频流,面临着独特的挑战。为此,本文从评估基准、模型架构和训练策略三个方面进行了系统研究。首先,我们介绍了OVBench,这是一个旨在评估模型在在线视频上下文中的感知、记忆和推理能力的综合问答基准。它涵盖了过去、当前和未来的三个时间上下文,包含来自不同数据集构成的16个子任务。其次,我们提出了一种新的金字塔内存银行(PMB),能够有效保留视频流中的关键时空信息。第三,我们提出了从离线到在线的学习范式,为在线视频数据设计了一种交替对话格式,并构建了一个用于在线视频训练的指令调整数据集。这导致了VideoChat-Online的开发,这是一个用于在线视频理解的稳健而高效的模型。尽管计算成本较低,效率更高,VideoChat-Online在流行的离线视频基准测试和OVBench上的表现仍优于现有的最先进的离线模型和在线模型,证明了我们的模型架构和训练策略的有效性。我们的方法在OVBench上超越了现有的最先进的离线模型Qwen2-VL 7B和在线模型Flash-VStream,分别提高了4.19%和23.7%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 Camera Ready Version. Project Page: https://videochat-online.github.io
Summary:
本文介绍了针对在线视频理解的多模态大型语言模型的研究。文章从评估基准、模型架构和训练策略三个方面进行了系统阐述。文章提出了OVBench评估基准,用于评估模型在在线视频环境中的感知、记忆和推理能力;同时引入了金字塔记忆库(PMB),有效保留视频流中的关键时空信息;此外,文章还提出了离线到在线的学习范式,为在线视频数据设计了一种交替对话格式,并构建了针对在线视频训练的指令调整数据集。这些成果最终促成了VideoChat-Online模型的开发,该模型在在线视频理解方面表现出稳健高效的特点,且在流行的离线视频基准测试和OVBench上超越了现有最先进的离线模型和在线模型。
Key Takeaways:
- 介绍了MLLMs在在线视频理解方面的应用挑战。
- 提出了OVBench评估基准,涵盖在线视频的感知、记忆和推理能力。
- 引入了金字塔记忆库(PMB)以保留视频流中的关键时空信息。
- 提出了离线到在线的学习范式,为在线视频数据设计交替对话格式。
- 构建了针对在线视频训练的指令调整数据集。
- 开发了VideoChat-Online模型,用于在线视频理解,表现出稳健高效的特点。
点此查看论文截图