⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-19 更新
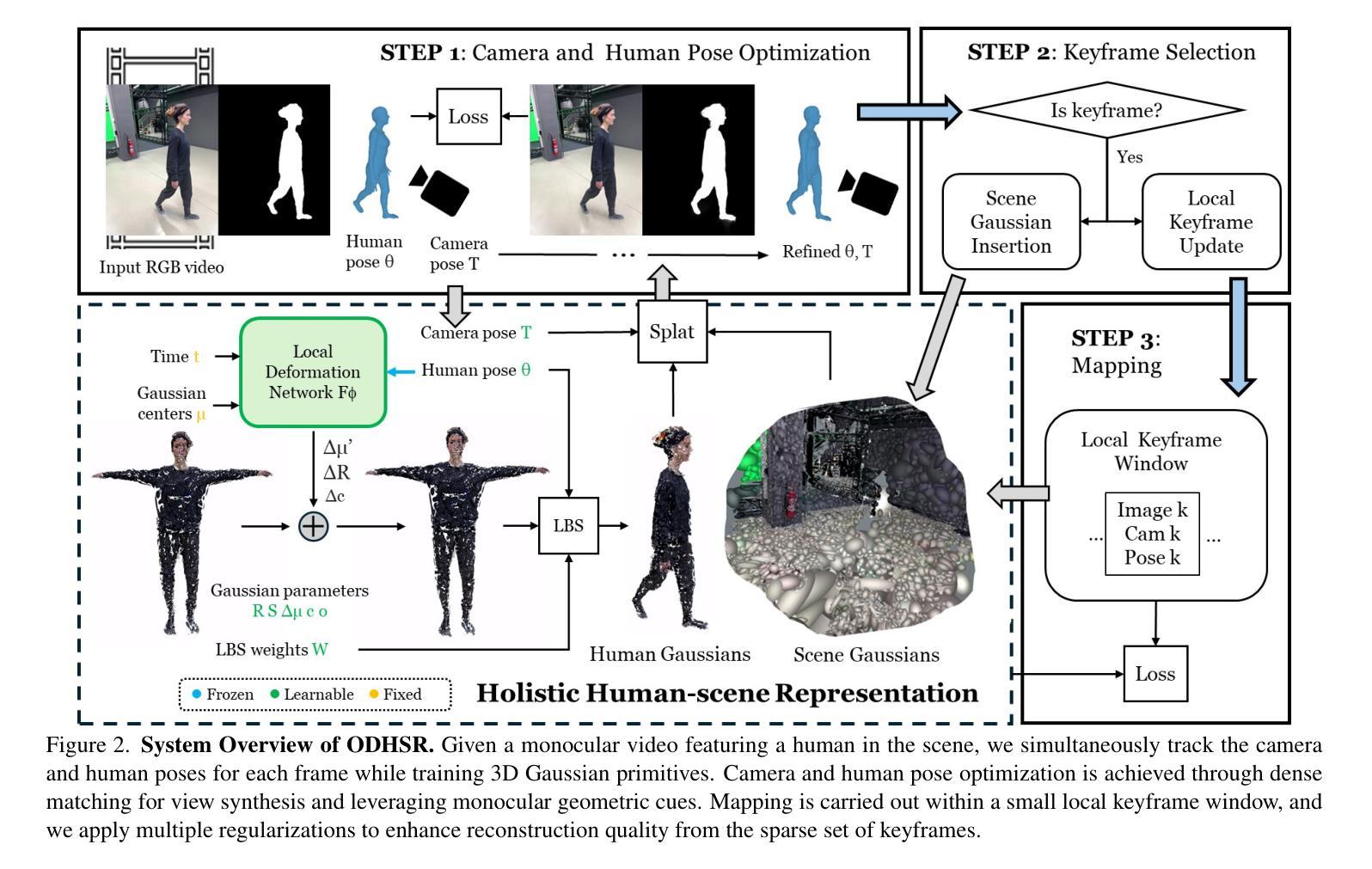
ODHSR: Online Dense 3D Reconstruction of Humans and Scenes from Monocular Videos
Authors:Zetong Zhang, Manuel kaufmann, Lixin Xue, Jie Song, Martin R. Oswald
Creating a photorealistic scene and human reconstruction from a single monocular in-the-wild video figures prominently in the perception of a human-centric 3D world. Recent neural rendering advances have enabled holistic human-scene reconstruction but require pre-calibrated camera and human poses, and days of training time. In this work, we introduce a novel unified framework that simultaneously performs camera tracking, human pose estimation and human-scene reconstruction in an online fashion. 3D Gaussian Splatting is utilized to learn Gaussian primitives for humans and scenes efficiently, and reconstruction-based camera tracking and human pose estimation modules are designed to enable holistic understanding and effective disentanglement of pose and appearance. Specifically, we design a human deformation module to reconstruct the details and enhance generalizability to out-of-distribution poses faithfully. Aiming to learn the spatial correlation between human and scene accurately, we introduce occlusion-aware human silhouette rendering and monocular geometric priors, which further improve reconstruction quality. Experiments on the EMDB and NeuMan datasets demonstrate superior or on-par performance with existing methods in camera tracking, human pose estimation, novel view synthesis and runtime. Our project page is at https://eth-ait.github.io/ODHSR.
创建真实场景和从单一单目野生视频中进行人体重建,这在以人类为中心的3D世界的感知中占据重要地位。最近的神经渲染技术进展已经实现了整体的人类场景重建,但需要预先校准的相机和人体姿势,以及数天的训练时间。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新颖的统一框架,以在线方式同时执行摄像机跟踪、人体姿态估计和人机场景重建。利用3D高斯拼贴技术有效地学习人体和场景的高斯基元,并设计基于重建的相机跟踪和人体姿态估计模块,以实现整体理解和有效的姿态与外观分离。具体来说,我们设计了一个人体变形模块来重建细节,并忠实地提高对外分布姿势的通用性。为了准确学习人体与场景之间的空间相关性,我们引入了遮挡感知的人体轮廓渲染和单目几何先验,这进一步提高了重建质量。在EMDB和NeuMan数据集上的实验表明,在摄像机跟踪、人体姿态估计、新视角合成和运行时等方面,我们的性能优于或等同于现有方法。我们的项目页面是https://eth-ait.github.io/ODHSR。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型统一框架,可同时进行摄像机跟踪、人体姿态估计和人体-场景重建。采用3D高斯拼贴技术高效学习人类和场景的高斯原始数据,并设计基于重建的摄像头跟踪和人体姿态估计模块,以实现整体理解和姿态与外观的有效分离。通过设计人体变形模块,可重建细节并提高对分布外的姿势的泛化能力。引入遮挡感知的人体轮廓渲染和单目几何先验,以准确学习人体与场景之间的空间关联,进一步提高重建质量。
Key Takeaways
- 新型统一框架实现了摄像机跟踪、人体姿态估计和人体-场景重建的在线同时进行。
- 采用3D高斯拼贴技术,高效学习人类和场景的高斯原始数据。
- 基于重建的摄像头跟踪和人体姿态估计模块设计,实现整体理解和姿态与外观的有效分离。
- 通过设计人体变形模块,能够重建细节并提高对非标准姿势的泛化能力。
- 引入遮挡感知的人体轮廓渲染,准确学习人体与场景之间的空间关联。
- 通过单目几何先验进一步提高重建质量。
点此查看论文截图

Digital Twin Generation from Visual Data: A Survey
Authors:Andrew Melnik, Benjamin Alt, Giang Nguyen, Artur Wilkowski, Maciej Stefańczyk, Qirui Wu, Sinan Harms, Helge Rhodin, Manolis Savva, Michael Beetz
This survey explores recent developments in generating digital twins from videos. Such digital twins can be used for robotics application, media content creation, or design and construction works. We analyze various approaches, including 3D Gaussian Splatting, generative in-painting, semantic segmentation, and foundation models highlighting their advantages and limitations. Additionally, we discuss challenges such as occlusions, lighting variations, and scalability, as well as potential future research directions. This survey aims to provide a comprehensive overview of state-of-the-art methodologies and their implications for real-world applications. Awesome list: https://github.com/ndrwmlnk/awesome-digital-twins
本次调查探讨了从视频中生成数字双胞胎的最新发展。这种数字双胞胎可用于机器人应用、媒体内容创建或设计和建造工作。我们分析了各种方法,包括3D高斯喷绘、生成性补全、语义分割和基础模型,突出了它们的优点和局限性。此外,我们还讨论了遮挡、光照变化和可扩展性等挑战,以及潜在的未来研究方向。本次调查旨在提供最新方法的全面概述及其对现实世界应用的影响。精彩列表:https://github.com/ndrwmlnk/awesome-digital-twins
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文调查了从视频中生成数字双胞胎的最新发展,涵盖了多种方法,包括3D高斯拼贴、生成式填充、语义分割和基准模型,并讨论了其优缺点。文章还介绍了遮挡、光照变化和可扩展性等挑战,以及未来研究方向。旨在为现实世界应用提供对最新方法论的全面概述。
Key Takeaways
- 文中探讨了从视频中生成数字双胞胎的最新技术进展。
- 介绍了多种方法,包括3D高斯拼贴、生成式填充、语义分割和基准模型。
- 分析了各种方法的优点和局限性。
- 指出遮挡、光照变化和可扩展性是主要挑战。
- 文章提供了对数字双胞胎技术的全面概述。
- 介绍了数字双胞胎技术在机器人应用、媒体内容创建和设计施工等领域的应用潜力。
- 列出了相关资源链接(如:https://github.com/ndrwmlnk/awesome-digital-twins)。
点此查看论文截图


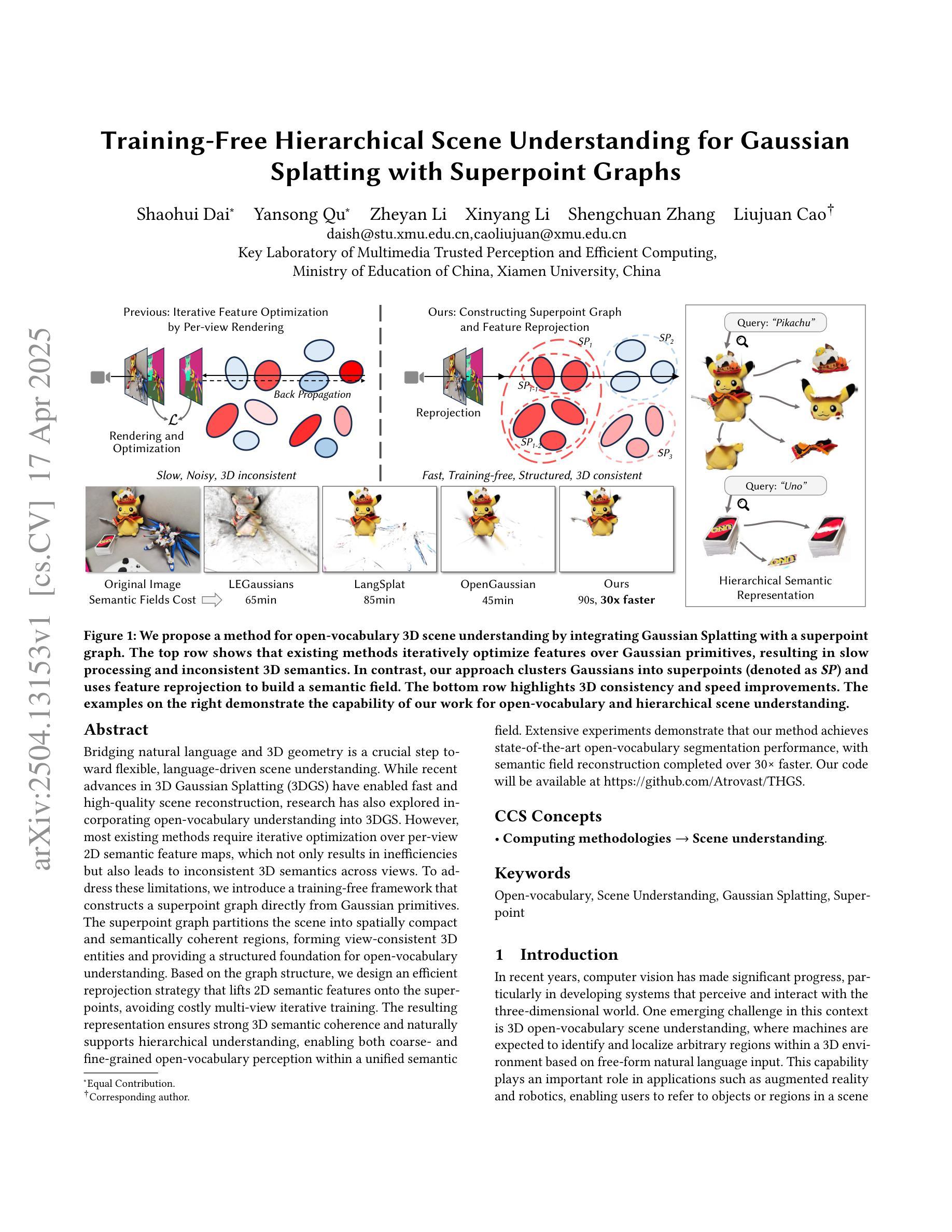
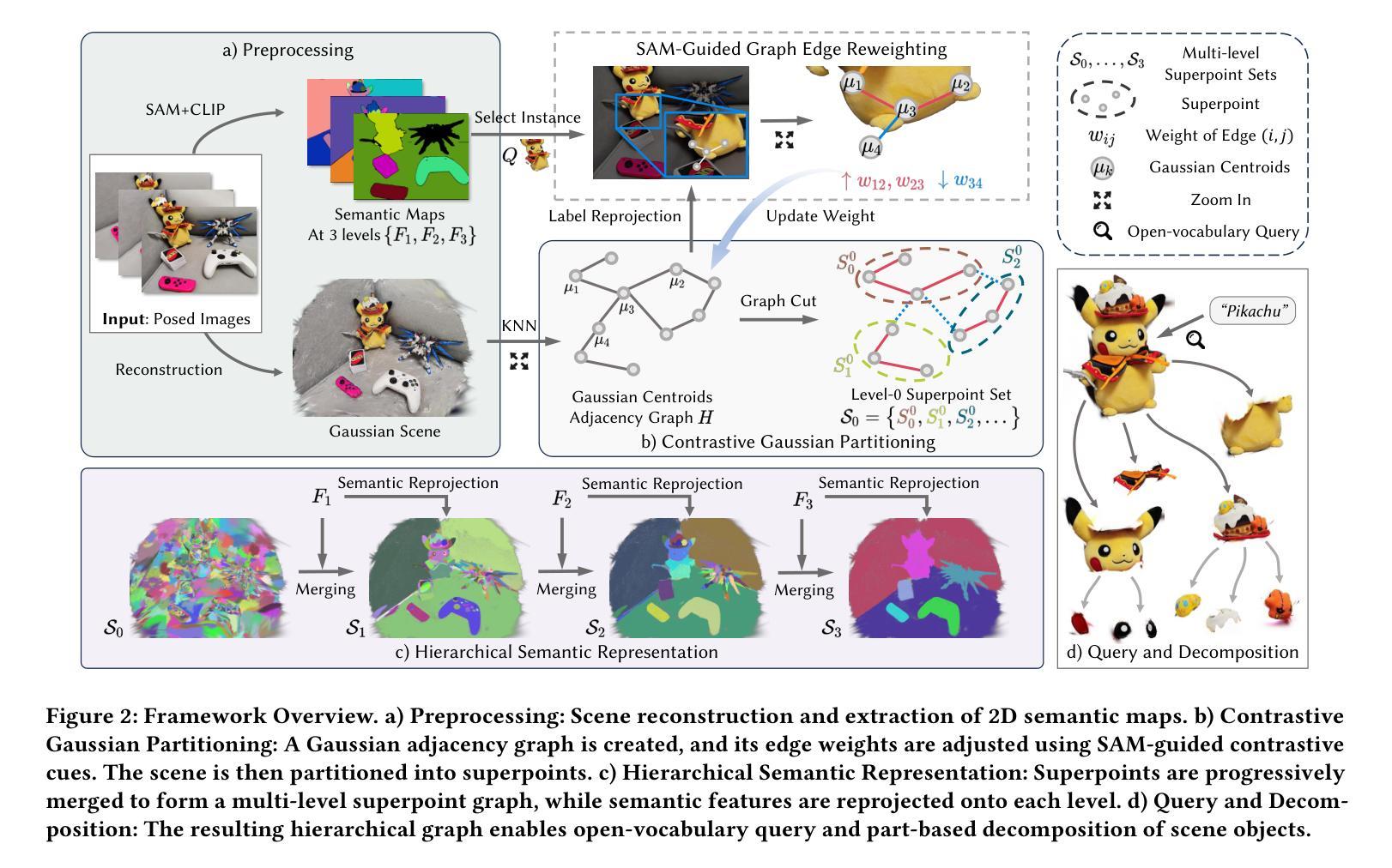
Training-Free Hierarchical Scene Understanding for Gaussian Splatting with Superpoint Graphs
Authors:Shaohui Dai, Yansong Qu, Zheyan Li, Xinyang Li, Shengchuan Zhang, Liujuan Cao
Bridging natural language and 3D geometry is a crucial step toward flexible, language-driven scene understanding. While recent advances in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have enabled fast and high-quality scene reconstruction, research has also explored incorporating open-vocabulary understanding into 3DGS. However, most existing methods require iterative optimization over per-view 2D semantic feature maps, which not only results in inefficiencies but also leads to inconsistent 3D semantics across views. To address these limitations, we introduce a training-free framework that constructs a superpoint graph directly from Gaussian primitives. The superpoint graph partitions the scene into spatially compact and semantically coherent regions, forming view-consistent 3D entities and providing a structured foundation for open-vocabulary understanding. Based on the graph structure, we design an efficient reprojection strategy that lifts 2D semantic features onto the superpoints, avoiding costly multi-view iterative training. The resulting representation ensures strong 3D semantic coherence and naturally supports hierarchical understanding, enabling both coarse- and fine-grained open-vocabulary perception within a unified semantic field. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art open-vocabulary segmentation performance, with semantic field reconstruction completed over $30\times$ faster. Our code will be available at https://github.com/Atrovast/THGS.
建立自然语言与三维几何之间的桥梁是实现灵活、语言驱动的场景理解的关键步骤。虽然最近三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)的进展为实现快速高质量的场景重建提供了可能,但研究也在探索将开放式词汇表理解融入3DGS中。然而,现有的大多数方法都需要在针对每个视图的二维语义特征图上进行优化迭代,这不仅导致效率低下,而且会导致不同视图之间的三维语义不一致。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了一个无需训练即可构建超点图的框架,该框架直接从高斯原始数据构建。超点图将场景划分为空间紧凑且语义连贯的区域,形成视角一致的三维实体,并为开放式词汇表理解提供了结构化基础。基于图结构,我们设计了一种高效的再投影策略,将二维语义特征提升到超点上,避免了昂贵的多视图迭代训练。所得表示确保了强大的三维语义连贯性,并自然地支持分层理解,能够在统一的语义场中实现粗粒度和细粒度的开放式词汇感知。大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的开放式词汇分割性能,语义场重建的速度提高了超过30倍。我们的代码将在https://github.com/Atrovast/THGS上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了桥接自然语言与三维几何在灵活、语言驱动的场景理解中的重要性。针对现有三维高斯摊铺(3DGS)技术在场景重建中的不足,研究引入了一种无训练框架,直接构建超级点图,实现对场景的空间紧凑和语义连贯性区域的划分,形成视角一致的3D实体,为开放词汇理解提供结构化基础。设计了一种高效的再投影策略,避免了昂贵的多视角迭代训练,确保了强大的三维语义连贯性,并支持分层理解,实现了统一语义场内的粗粒度和细粒度开放词汇感知。实验结果证明了该方法在开放词汇分割方面的卓越性能,语义场重建速度提高了30倍以上。
Key Takeaways
- 桥接自然语言与三维几何对于实现灵活、语言驱动的场景理解至关重要。
- 现有3DGS技术在场景重建中存在效率与语义连贯性问题。
- 引入了一种无训练框架,通过构建超级点图,实现场景的空间紧凑和语义连贯性划分。
- 设计了高效的再投影策略,避免了多视角迭代训练,提高了三维语义连贯性。
- 支持分层理解,实现了统一语义场内的粗粒度和细粒度开放词汇感知。
- 方法在开放词汇分割方面表现卓越,语义场重建速度大幅提升。
点此查看论文截图

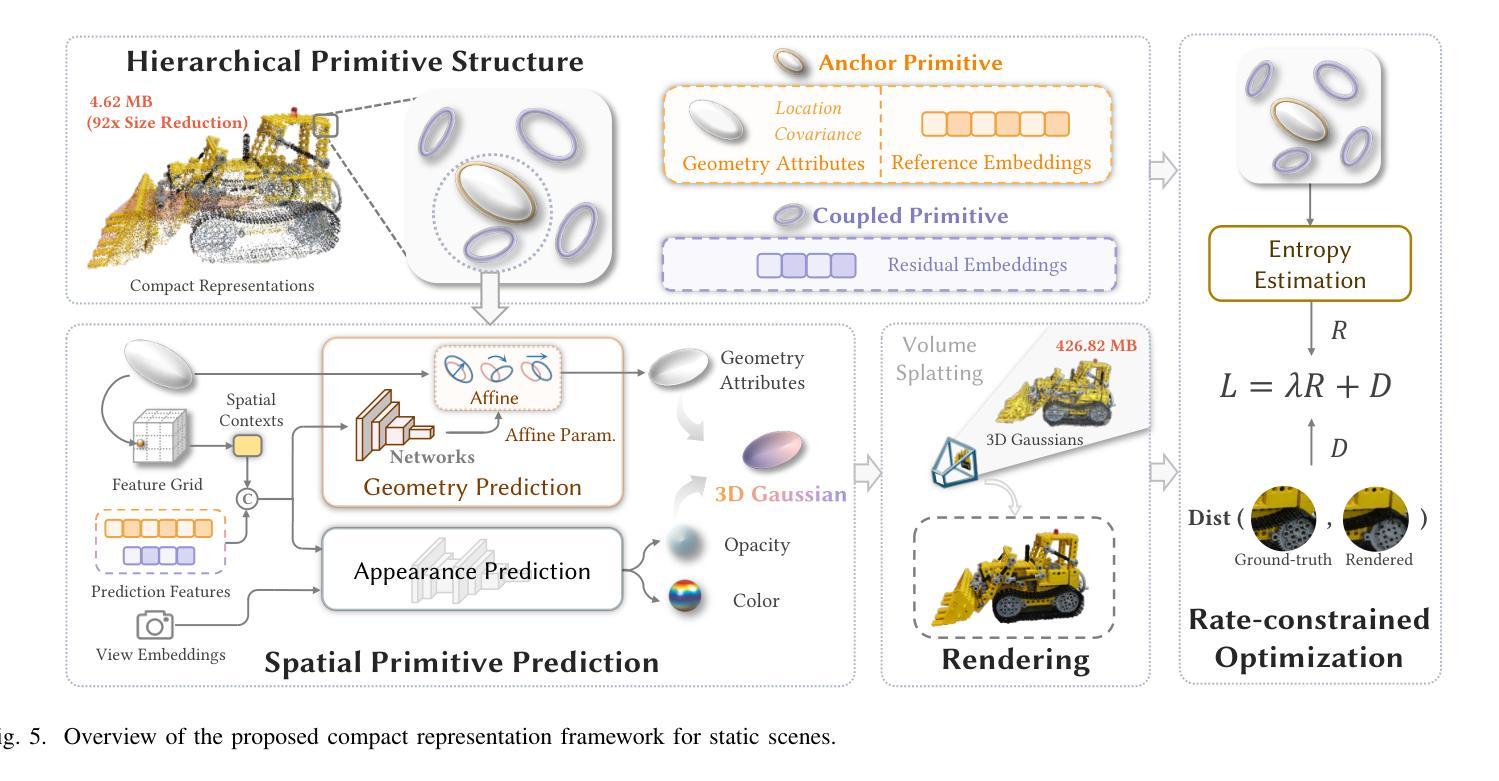
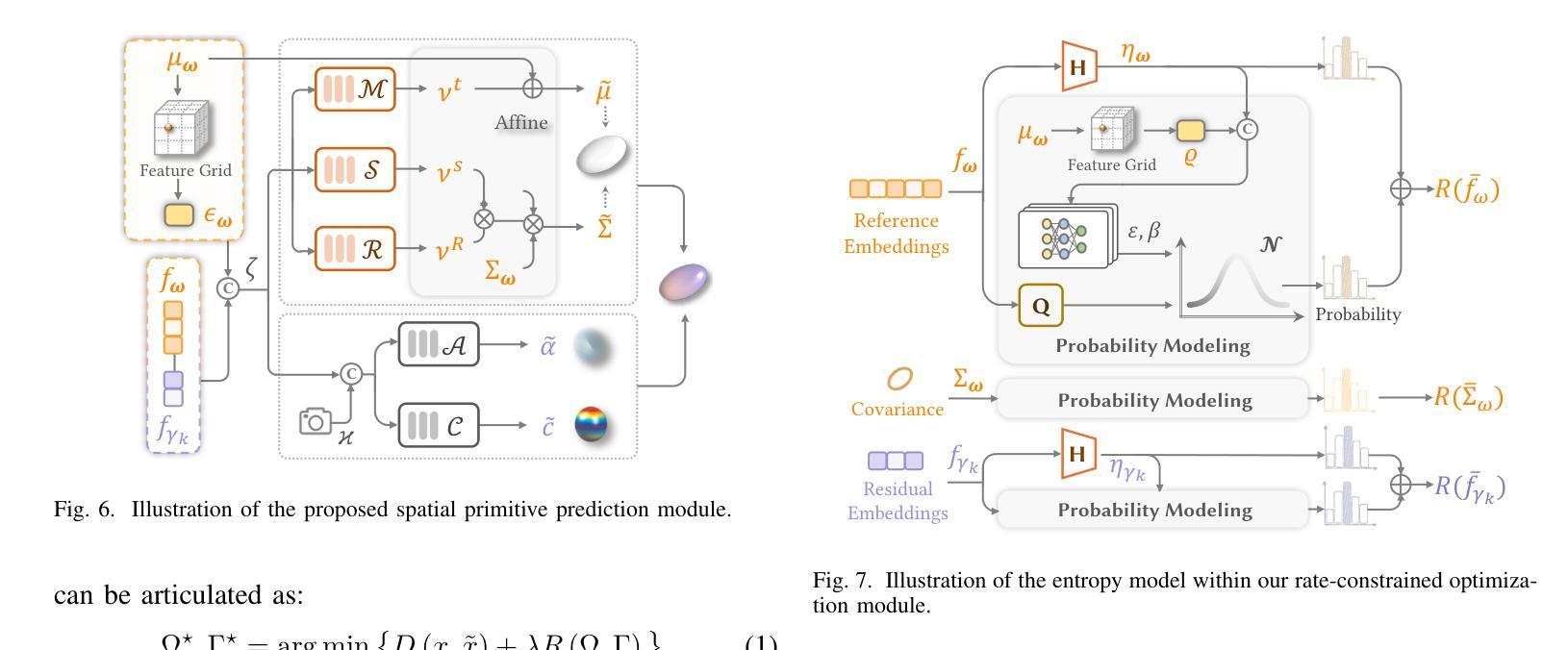
CompGS++: Compressed Gaussian Splatting for Static and Dynamic Scene Representation
Authors:Xiangrui Liu, Xinju Wu, Shiqi Wang, Zhu Li, Sam Kwong
Gaussian splatting demonstrates proficiency for 3D scene modeling but suffers from substantial data volume due to inherent primitive redundancy. To enable future photorealistic 3D immersive visual communication applications, significant compression is essential for transmission over the existing Internet infrastructure. Hence, we propose Compressed Gaussian Splatting (CompGS++), a novel framework that leverages compact Gaussian primitives to achieve accurate 3D modeling with substantial size reduction for both static and dynamic scenes. Our design is based on the principle of eliminating redundancy both between and within primitives. Specifically, we develop a comprehensive prediction paradigm to address inter-primitive redundancy through spatial and temporal primitive prediction modules. The spatial primitive prediction module establishes predictive relationships for scene primitives and enables most primitives to be encoded as compact residuals, substantially reducing the spatial redundancy. We further devise a temporal primitive prediction module to handle dynamic scenes, which exploits primitive correlations across timestamps to effectively reduce temporal redundancy. Moreover, we devise a rate-constrained optimization module that jointly minimizes reconstruction error and rate consumption. This module effectively eliminates parameter redundancy within primitives and enhances the overall compactness of scene representations. Comprehensive evaluations across multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that CompGS++ significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving superior compression performance while preserving accurate scene modeling. Our implementation will be made publicly available on GitHub to facilitate further research.
高斯喷溅技术展示了其在3D场景建模方面的专业能力,但由于其固有的原始数据冗余,导致数据量巨大。为了实现未来逼真的3D沉浸式视觉通信应用,对现有互联网基础设施进行传输时,显著的数据压缩是必要的。因此,我们提出了压缩高斯喷溅技术(CompGS++),这是一种新型框架,它利用紧凑的高斯原始数据实现准确的3D建模,并显著减少静态和动态场景的体积。我们的设计基于消除原始数据之间和内部的冗余原则。具体来说,我们开发了一种全面的预测范式,通过空间和时间原始预测模块解决原始数据之间的冗余问题。空间原始预测模块建立了场景原始数据的预测关系,使大多数原始数据能够编码为紧凑的残差,从而大大减少空间冗余。我们进一步设计了一个时间原始预测模块来处理动态场景,该模块利用时间戳之间的原始数据相关性,有效地减少时间冗余。此外,我们还设计了一个受速率限制的优化模块,该模块联合最小化重建误差和速率消耗。该模块有效地消除了原始数据中的参数冗余,提高了场景表示的整体紧凑性。在多个基准数据集上的综合评估表明,CompGS++显著优于现有方法,在保持准确场景建模的同时实现了出色的压缩性能。我们的实现将在GitHub上公开提供,以便进行进一步的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to a journal
Summary
基于高斯点云法展示出的出色三维场景建模能力,针对其大量数据引发的原始冗余问题,本文提出了压缩高斯点云法(CompGS++)。此方法通过紧凑的高斯基本元素实现了准确的三维建模,并显著减少了静态和动态场景的体积。它通过消除基本元素间的冗余和内部冗余来实现压缩。此外,还设计了预测范式来处理动态场景,并通过优化模块最小化重建误差和速率消耗。此方法在多个基准数据集上的评估结果显示出优异的压缩性能且能保证精准的场景建模。该算法已实现并将在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
一、Gaussian splatting方法用于三维场景建模具有优势,但由于存在大量的原始数据,面临数据量大、冗余度高的问题。为解决此问题,提出新的压缩框架——压缩高斯点云法(CompGS++)。
二、CompGS++采用紧凑的高斯基本元素实现准确的三维建模,并显著减少静态和动态场景的体积。它通过消除基本元素间的冗余和内部冗余来减少数据量,从而提升效率。具体手段包括开发综合预测范式来降低基础元素的冗余现象以及开发优化模块来最小化重建误差和速率消耗等。这些措施共同提升了场景表示的紧凑性。
点此查看论文截图



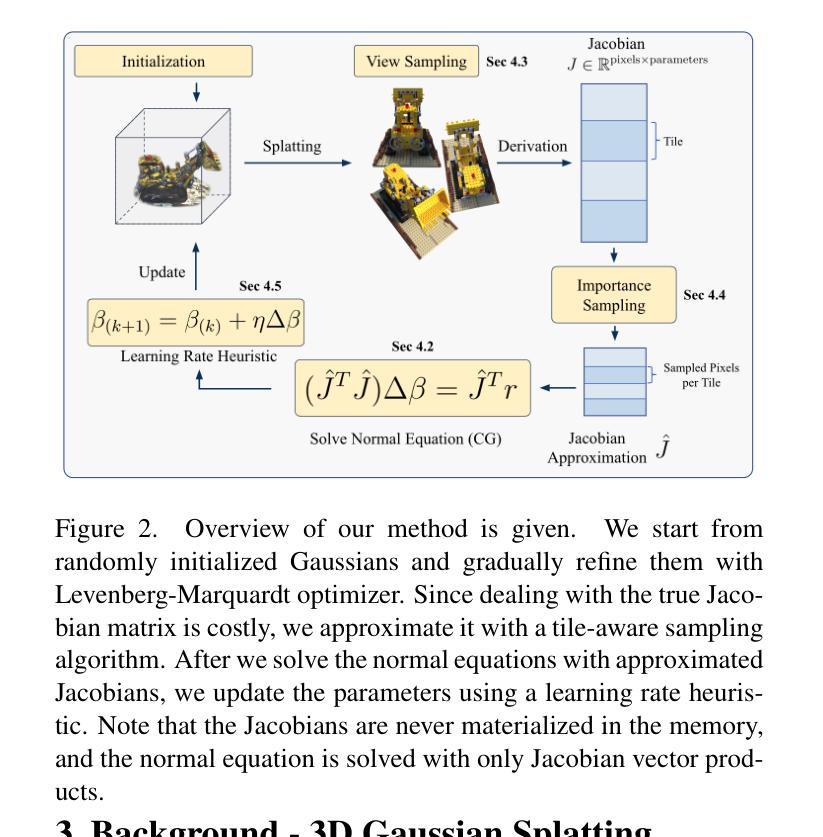
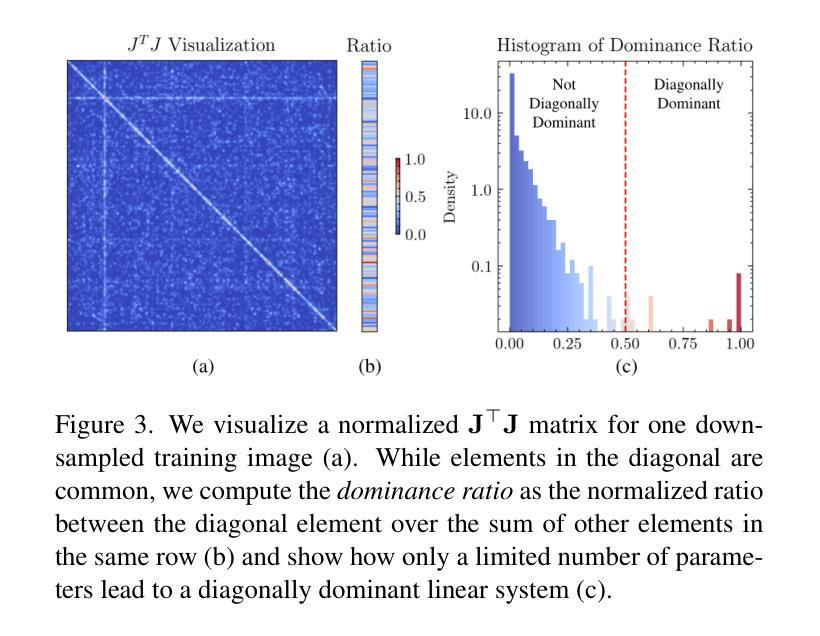
Second-order Optimization of Gaussian Splats with Importance Sampling
Authors:Hamza Pehlivan, Andrea Boscolo Camiletto, Lin Geng Foo, Marc Habermann, Christian Theobalt
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) is widely used for novel view synthesis due to its high rendering quality and fast inference time. However, 3DGS predominantly relies on first-order optimizers such as Adam, which leads to long training times. To address this limitation, we propose a novel second-order optimization strategy based on Levenberg-Marquardt (LM) and Conjugate Gradient (CG), which we specifically tailor towards Gaussian Splatting. Our key insight is that the Jacobian in 3DGS exhibits significant sparsity since each Gaussian affects only a limited number of pixels. We exploit this sparsity by proposing a matrix-free and GPU-parallelized LM optimization. To further improve its efficiency, we propose sampling strategies for both the camera views and loss function and, consequently, the normal equation, significantly reducing the computational complexity. In addition, we increase the convergence rate of the second-order approximation by introducing an effective heuristic to determine the learning rate that avoids the expensive computation cost of line search methods. As a result, our method achieves a $3\times$ speedup over standard LM and outperforms Adam by $~6\times$ when the Gaussian count is low while remaining competitive for moderate counts. Project Page: https://vcai.mpi-inf.mpg.de/projects/LM-IS
3D高斯采样(3DGS)因其高质量的渲染和快速的推理时间而被广泛应用于新型视图合成。然而,3DGS主要依赖于一阶优化器,如Adam,导致训练时间较长。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一种基于Levenberg-Marquardt(LM)和共轭梯度(CG)的新型二阶优化策略,并针对高斯采样进行了专门定制。我们的关键见解是,由于每个高斯只影响有限的像素数,因此3DGS中的雅可比矩阵表现出显著的稀疏性。我们利用这种稀疏性,提出了无矩阵和GPU并行化的LM优化。为了进一步提高效率,我们为相机视角和损失函数提出了采样策略,并据此简化了正规方程,大大降低了计算复杂度。此外,我们通过引入有效的启发式方法来确定学习率,提高了二阶近似的收敛速度,避免了线性搜索方法的昂贵计算成本。因此,我们的方法在标准LM上实现了3倍的速度提升,并在高斯计数较低时超过了Adam的约6倍性能,同时在中等计数下保持竞争力。项目页面:https://vcai.mpi-inf.mpg.de/projects/LM-IS
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)提出的一种新型二阶优化策略。该策略基于Levenberg-Marquardt(LM)和共轭梯度(CG)算法,并针对Gaussian Splatting进行优化。利用Jacobian矩阵的稀疏性,提出一种无矩阵和GPU并行化的LM优化方法。通过采样策略和启发式学习率确定方法,提高了计算效率和收敛速度。该方法在Gaussian计数低时实现了标准LM的3倍速,并在与Adam的比较中表现出优势。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS广泛用于新型视图合成,但主要依赖如Adam的一阶优化器,导致训练时间长。
- 提出一种基于Levenberg-Marquardt(LM)和共��X梯度(CG)的二阶优化策略,针对Gaussian Splatting进行优化。
- 利用Jacobian矩阵的稀疏性,实现了一种无矩阵和GPU并行化的LM优化,提高计算效率。
- 通过采样策略对相机视角、损失函数和正常方程进行采样,进一步降低计算复杂性。
- 引入启发式学习率确定方法,提高二阶近似的收敛速度,避免线性搜索方法的昂贵计算成本。
点此查看论文截图
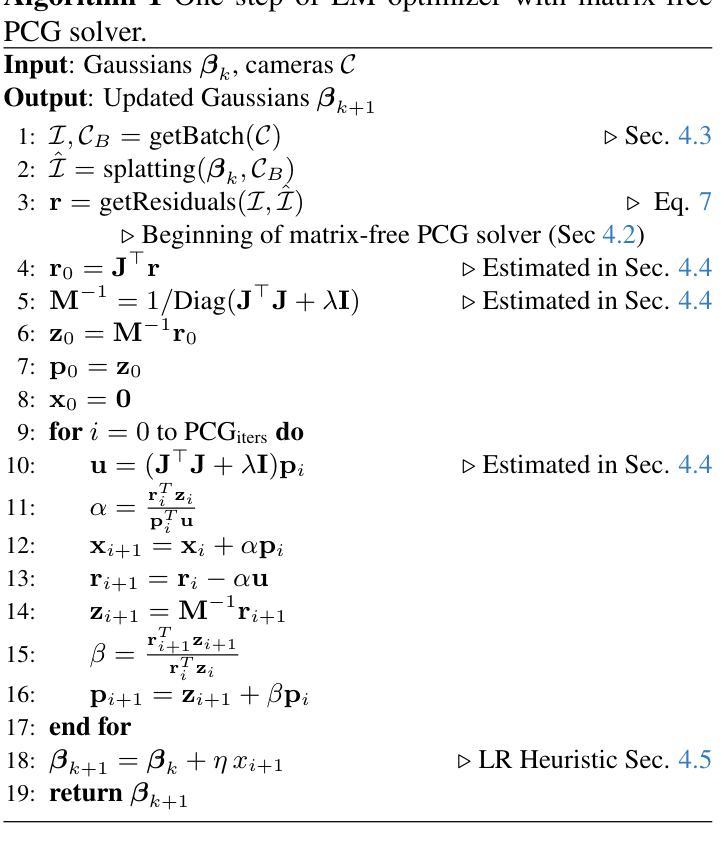
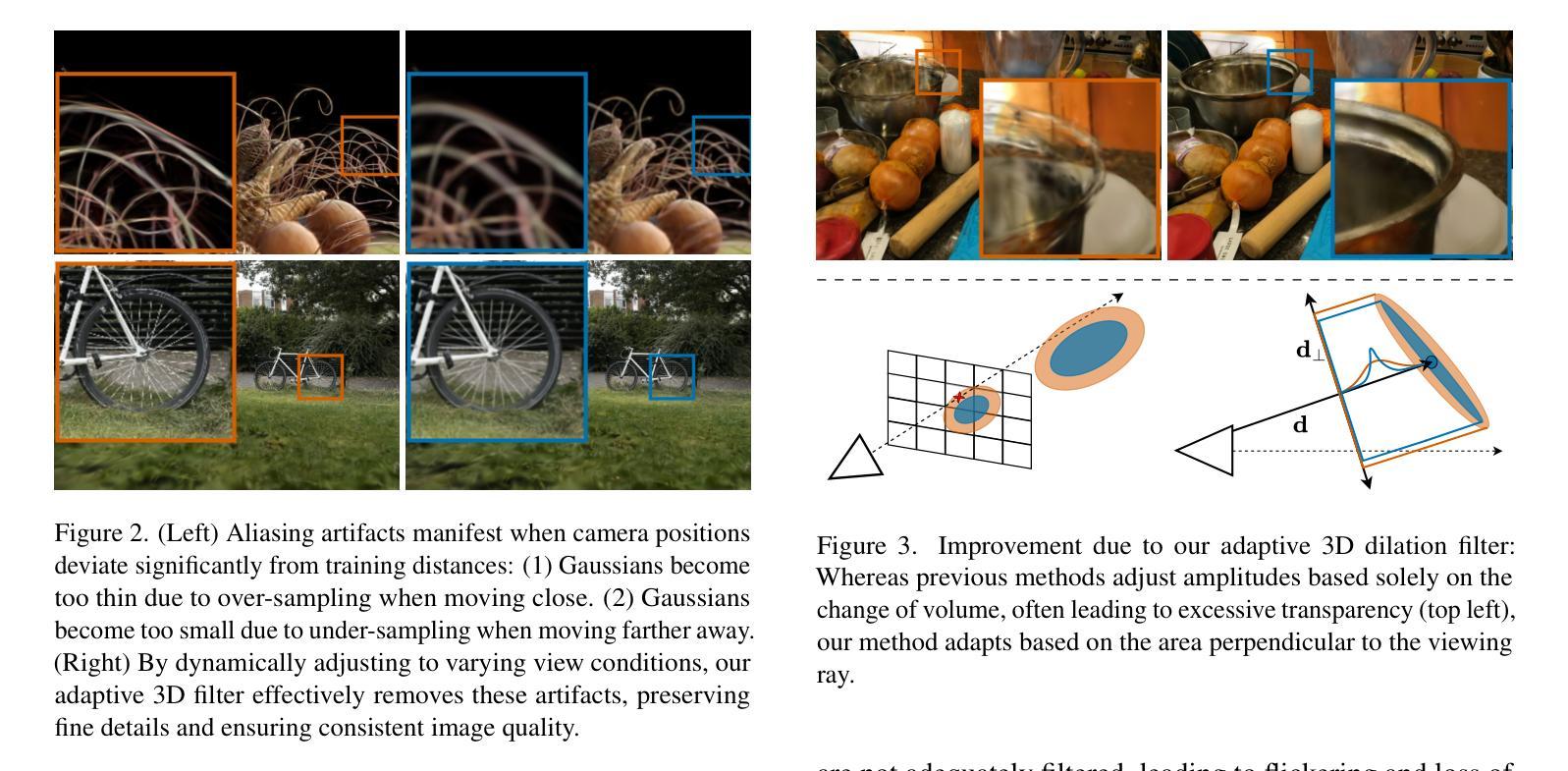
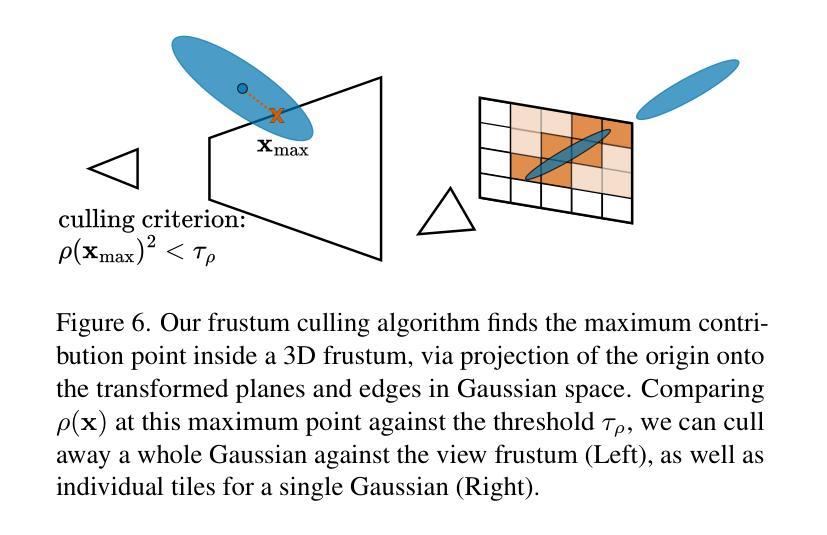
AAA-Gaussians: Anti-Aliased and Artifact-Free 3D Gaussian Rendering
Authors:Michael Steiner, Thomas Köhler, Lukas Radl, Felix Windisch, Dieter Schmalstieg, Markus Steinberger
Although 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has revolutionized 3D reconstruction, it still faces challenges such as aliasing, projection artifacts, and view inconsistencies, primarily due to the simplification of treating splats as 2D entities. We argue that incorporating full 3D evaluation of Gaussians throughout the 3DGS pipeline can effectively address these issues while preserving rasterization efficiency. Specifically, we introduce an adaptive 3D smoothing filter to mitigate aliasing and present a stable view-space bounding method that eliminates popping artifacts when Gaussians extend beyond the view frustum. Furthermore, we promote tile-based culling to 3D with screen-space planes, accelerating rendering and reducing sorting costs for hierarchical rasterization. Our method achieves state-of-the-art quality on in-distribution evaluation sets and significantly outperforms other approaches for out-of-distribution views. Our qualitative evaluations further demonstrate the effective removal of aliasing, distortions, and popping artifacts, ensuring real-time, artifact-free rendering.
尽管3D高斯贴图技术(3DGS)已经实现了对三维重建的革新,但它仍然面临着诸如混叠、投影伪影和视图不一致等挑战,这主要是因为将贴图视为二维实体时的简化处理所导致的。我们主张在3DGS管道中融入高斯的全三维评估,这样可以有效地解决这些问题,同时保持光线投射的效率。具体来说,我们引入了一种自适应的3D平滑滤波器来缓解混叠现象,并提出了一种稳定的视图空间边界方法,当高斯值超出视锥体时,这种方法可以消除突然出现的伪影。此外,我们将基于瓦片的剔除提升到了三维空间中的屏幕平面,加速了渲染过程,并降低了层次光线投射的排序成本。我们的方法在内部评估集上达到了业界领先水平,并在外部视图上显著优于其他方法。我们的定性评估进一步证明了混叠、失真和突然出现的伪影的有效去除,确保了实时且无伪影的渲染。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了3D高斯展铺(3DGS)在3D重建中的挑战,如混叠、投影伪影和视图不一致性问题。文章主张在3DGS管道中融入高斯的全3D评估,以解决这些问题并保持光栅化效率。引入自适应的3D平滑滤波器来减轻混叠现象,并提出稳定的视图空间边界方法,以消除高斯超出视锥体时的弹出伪影。此外,文章提倡将基于瓦片的剔除扩展到三维屏幕空间平面,以加速渲染并降低层次光栅化的排序成本。该方法在内部评估集上达到了最先进的品质,并在外部视角上显著优于其他方法。质量评估进一步证明了消除混叠、失真和弹出伪影的有效性,确保了实时且无伪影的渲染。
Key Takeaways
- 指出当前使用3DGS进行3D重建面临的挑战包括混叠、投影伪影和视图不一致性。这些问题的根源在于将展点简化为二维实体。
- 提出通过融入高斯的全三维评估来解决上述问题并保持光栅化效率的方法。具体包括自适应的3D平滑滤波器来减轻混叠现象和稳定的视图空间边界方法来消除弹出伪影。
- 采用基于瓦片的剔除技术扩展到三维屏幕空间平面,以提高渲染速度并降低层次光栅化的排序成本。
- 在内部评估集上取得了最先进的性能表现,并在处理外部视角时显著优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

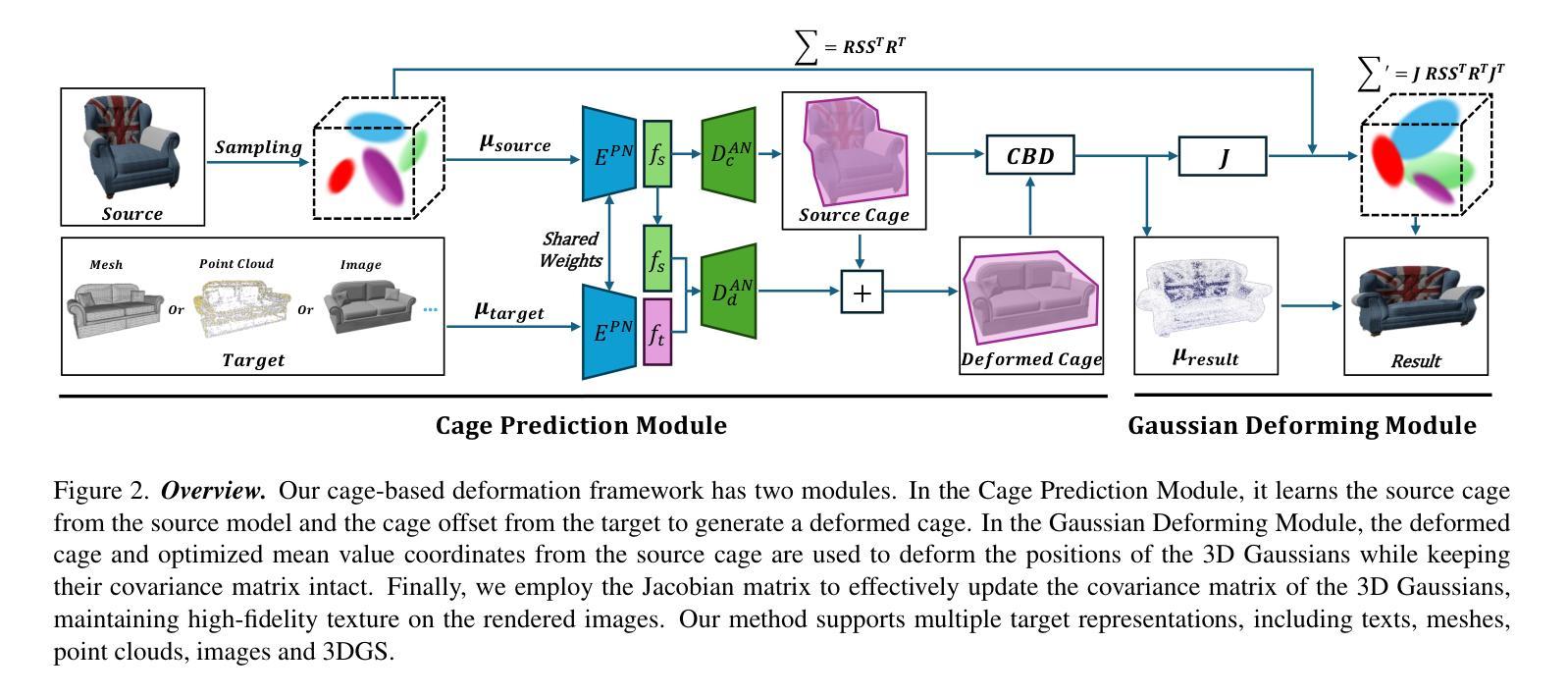
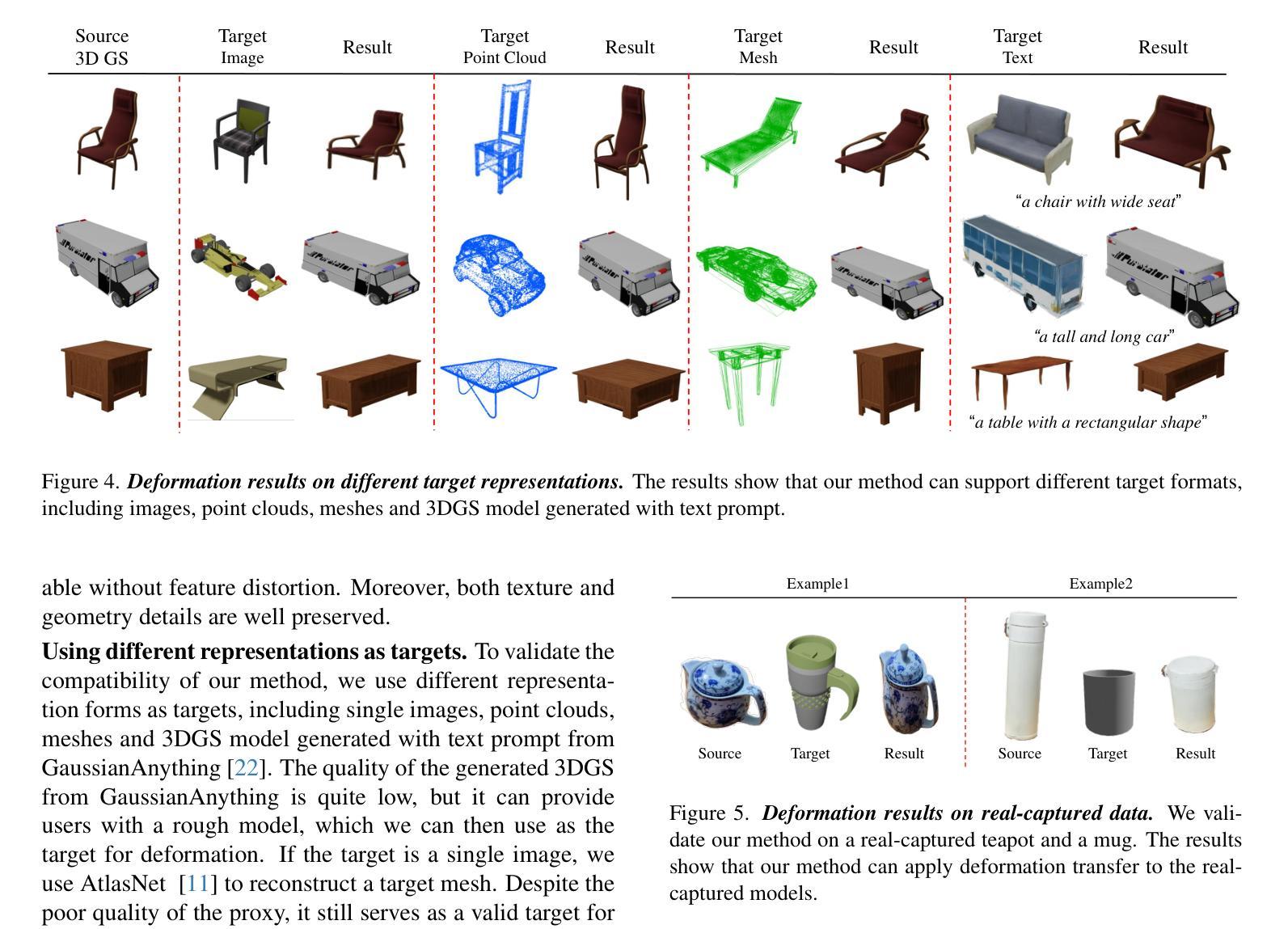
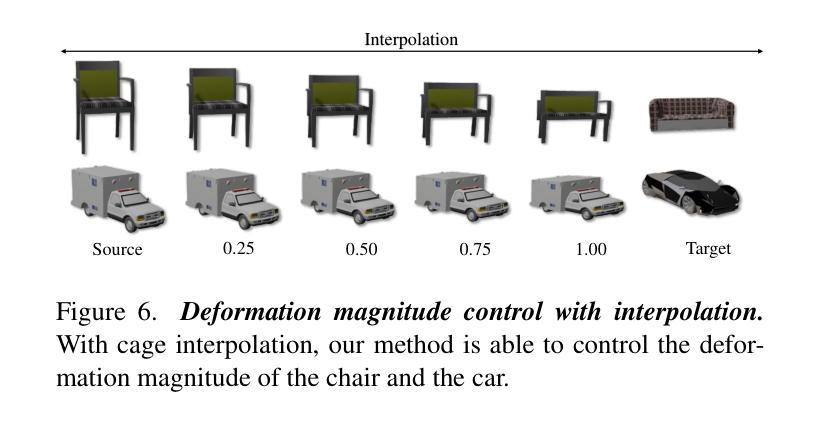
CAGE-GS: High-fidelity Cage Based 3D Gaussian Splatting Deformation
Authors:Yifei Tong, Runze Tian, Xiao Han, Dingyao Liu, Fenggen Yu, Yan Zhang
As 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) gains popularity as a 3D representation of real scenes, enabling user-friendly deformation to create novel scenes while preserving fine details from the original 3DGS has attracted significant research attention. We introduce CAGE-GS, a cage-based 3DGS deformation method that seamlessly aligns a source 3DGS scene with a user-defined target shape. Our approach learns a deformation cage from the target, which guides the geometric transformation of the source scene. While the cages effectively control structural alignment, preserving the textural appearance of 3DGS remains challenging due to the complexity of covariance parameters. To address this, we employ a Jacobian matrix-based strategy to update the covariance parameters of each Gaussian, ensuring texture fidelity post-deformation. Our method is highly flexible, accommodating various target shape representations, including texts, images, point clouds, meshes and 3DGS models. Extensive experiments and ablation studies on both public datasets and newly proposed scenes demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing techniques in both efficiency and deformation quality.
随着3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)作为真实场景的3D表示形式越来越受欢迎,能够在保留原始3DGS精细细节的同时,实现用户友好的变形以创建新场景,这引起了研究人员的广泛关注。我们介绍了CAGE-GS,这是一种基于笼子的3DGS变形方法,它无缝地对齐源3DGS场景与用户定义的目标形状。我们的方法从目标中学习变形笼子,引导源场景的几何变换。虽然笼子有效地控制了结构对齐,但由于协方差参数的复杂性,保持3DGS的纹理外观仍然是一个挑战。为解决这一问题,我们采用基于雅可比矩阵的策略来更新每个高斯分布的协方差参数,以确保变形后的纹理保真度。我们的方法高度灵活,能够适应各种目标形状表示,包括文本、图像、点云、网格和3DGS模型。在公共数据集和新提出的场景上的大量实验和消融研究表明,我们的方法在效率和变形质量上显著优于现有技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着三维场景的不断重建和应用领域的不断拓展,3D高斯喷射法(3DGS)成为了研究和应用的热点。在此背景下,文章介绍了一种基于网格结构的网格形变法CAGE-GS,该方法能够无缝地将源场景与目标形状进行对齐。通过从目标物体学习到变形网格的方法,来控制源场景几何转换后的形变过程。在保证纹理还原效果上仍有很大挑战,故引入了基于雅可比矩阵的策略来更新每个高斯分布的协方差参数,确保形变后的纹理保真度。此方法灵活多变,能够适应多种目标形状表示形式,包括文本、图像、点云和三维场景模型等。通过实验证明,该方法在效率和形变质量上均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- CAGE-GS是基于网格结构的形变方法,将源场景无缝地与目标形状对齐。
- 该方法学习到目标物体的变形网格来控制源场景的几何变换过程。
- 使用雅可比矩阵更新协方差参数,确保纹理在形变后保持保真度。
- 方法灵活多变,适应多种目标形状表现形式如文本、图像、点云等。
- 实验证明该方法在效率和形变质量上优于现有技术。
- 该方法对于复杂的三维场景重建具有重要意义和实用价值。
点此查看论文截图


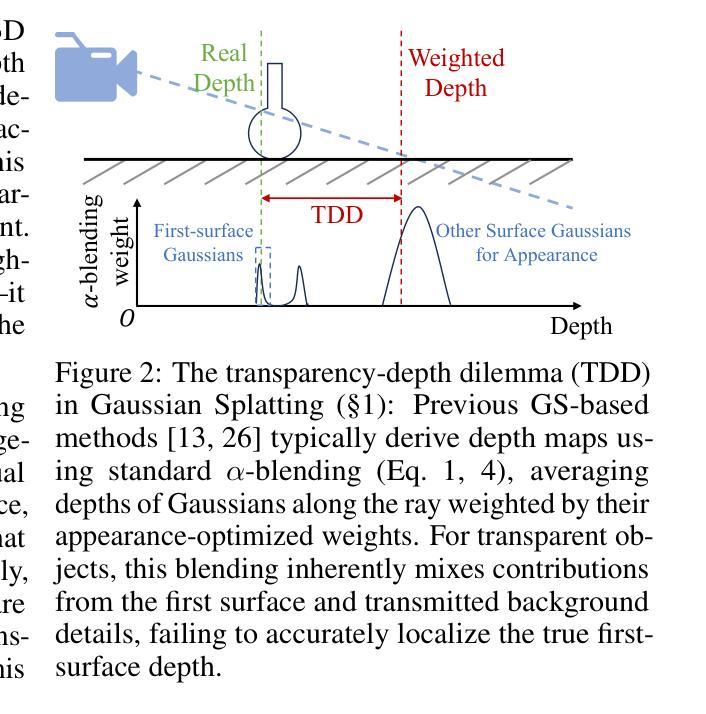
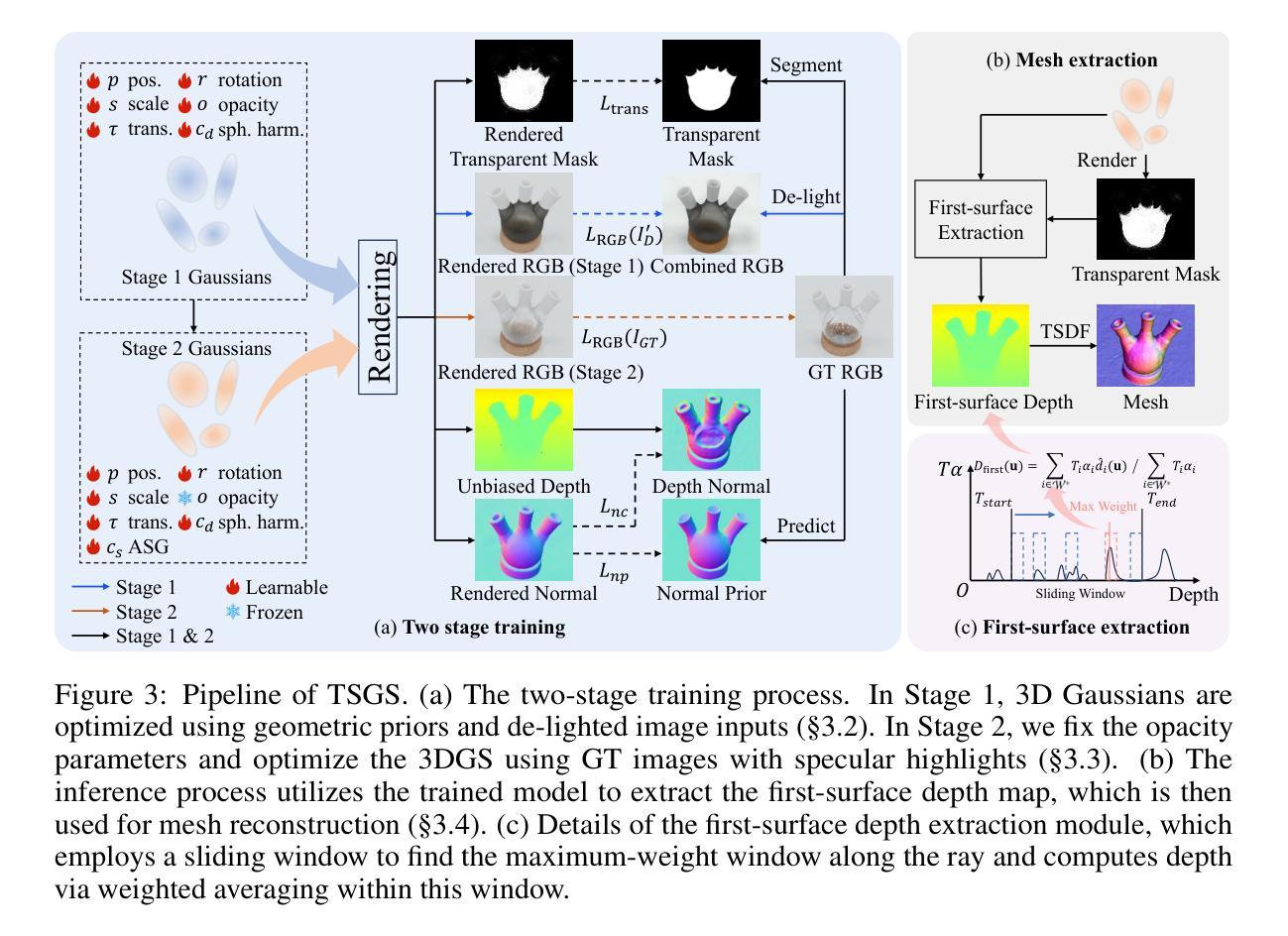
TSGS: Improving Gaussian Splatting for Transparent Surface Reconstruction via Normal and De-lighting Priors
Authors:Mingwei Li, Pu Pang, Hehe Fan, Hua Huang, Yi Yang
Reconstructing transparent surfaces is essential for tasks such as robotic manipulation in labs, yet it poses a significant challenge for 3D reconstruction techniques like 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). These methods often encounter a transparency-depth dilemma, where the pursuit of photorealistic rendering through standard $\alpha$-blending undermines geometric precision, resulting in considerable depth estimation errors for transparent materials. To address this issue, we introduce Transparent Surface Gaussian Splatting (TSGS), a new framework that separates geometry learning from appearance refinement. In the geometry learning stage, TSGS focuses on geometry by using specular-suppressed inputs to accurately represent surfaces. In the second stage, TSGS improves visual fidelity through anisotropic specular modeling, crucially maintaining the established opacity to ensure geometric accuracy. To enhance depth inference, TSGS employs a first-surface depth extraction method. This technique uses a sliding window over $\alpha$-blending weights to pinpoint the most likely surface location and calculates a robust weighted average depth. To evaluate the transparent surface reconstruction task under realistic conditions, we collect a TransLab dataset that includes complex transparent laboratory glassware. Extensive experiments on TransLab show that TSGS achieves accurate geometric reconstruction and realistic rendering of transparent objects simultaneously within the efficient 3DGS framework. Specifically, TSGS significantly surpasses current leading methods, achieving a 37.3% reduction in chamfer distance and an 8.0% improvement in F1 score compared to the top baseline. The code and dataset will be released at https://longxiang-ai.github.io/TSGS/.
重建透明表面对于实验室中的机器人操作等任务至关重要,然而,它为3D重建技术(例如3D高斯拼贴(3DGS))带来了重大挑战。这些方法经常面临透明度与深度之间的两难困境,即通过标准alpha混合追求逼真的渲染会破坏几何精度,导致对透明材料的深度估计出现重大误差。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了透明表面高斯拼贴(TSGS)的新框架,该框架将几何学习与外观细化分开。在几何学习阶段,TSGS通过使用抑制镜面反射的输入来准确表示表面,从而专注于几何。在第二阶段,TSGS通过各向异性镜面建模提高视觉保真度,关键的是保持已建立的不透明度以确保几何精度。为了提高深度推断,TSGS采用了一种首表面深度提取方法。该技术使用alpha混合权重上的滑动窗口来确定最可能的表面位置,并计算稳健的加权平均深度。为了在实际条件下评估透明表面重建任务,我们收集了一个TransLab数据集,其中包括复杂的透明实验室玻璃器皿。在TransLab上的广泛实验表明,TSGS在3DGS框架内实现了透明物体的准确几何重建和逼真渲染。特别是,TSGS显著超越了当前领先的方法,与顶级基线相比,chamfer距离减少了37.3%,F1分数提高了8.0%。代码和数据集将在https://longxiang-ai.github.io/TSGS/发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://longxiang-ai.github.io/TSGS/
Summary
本文介绍了针对透明表面重建任务的新框架——透明表面高斯溅射(TSGS)。该框架解决了现有三维重建技术(如3D高斯溅射)在处理透明物体时面临的挑战,实现了准确的几何重建和逼真的渲染。TSGS通过分离几何学习和外观优化,采用特种技术处理透明物体的几何特性和视觉表现,提高了深度推断的准确度。实验证明,TSGS在复杂透明实验室器皿的重建任务上表现出色,代码和数据集已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 透明表面重建是实验室机器人操作等任务的关键挑战。
- 现有3D重建技术在处理透明物体时面临透明度与深度之间的权衡问题。
- TSGS框架通过分离几何学习与外观优化解决这一问题。
- TSGS在几何学习阶段使用抗镜面反射输入来准确表示表面。
- TSGS通过各向异性镜面建模提高视觉保真度,同时保持不透明度以确保几何精度。
- TSGS采用一种名为“首表面深度提取法”的技术增强深度推断。
点此查看论文截图


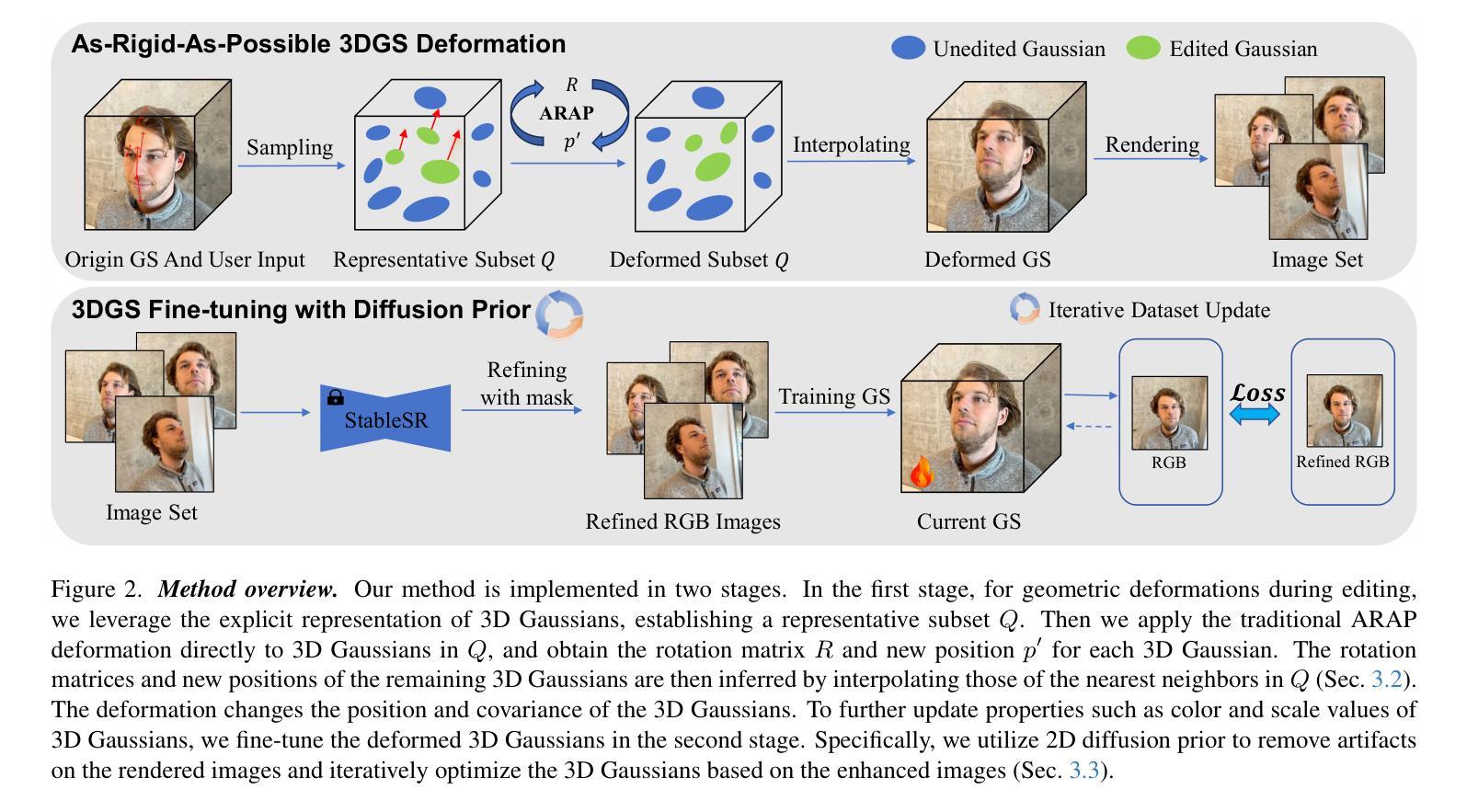
ARAP-GS: Drag-driven As-Rigid-As-Possible 3D Gaussian Splatting Editing with Diffusion Prior
Authors:Xiao Han, Runze Tian, Yifei Tong, Fenggen Yu, Dingyao Liu, Yan Zhang
Drag-driven editing has become popular among designers for its ability to modify complex geometric structures through simple and intuitive manipulation, allowing users to adjust and reshape content with minimal technical skill. This drag operation has been incorporated into numerous methods to facilitate the editing of 2D images and 3D meshes in design. However, few studies have explored drag-driven editing for the widely-used 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) representation, as deforming 3DGS while preserving shape coherence and visual continuity remains challenging. In this paper, we introduce ARAP-GS, a drag-driven 3DGS editing framework based on As-Rigid-As-Possible (ARAP) deformation. Unlike previous 3DGS editing methods, we are the first to apply ARAP deformation directly to 3D Gaussians, enabling flexible, drag-driven geometric transformations. To preserve scene appearance after deformation, we incorporate an advanced diffusion prior for image super-resolution within our iterative optimization process. This approach enhances visual quality while maintaining multi-view consistency in the edited results. Experiments show that ARAP-GS outperforms current methods across diverse 3D scenes, demonstrating its effectiveness and superiority for drag-driven 3DGS editing. Additionally, our method is highly efficient, requiring only 10 to 20 minutes to edit a scene on a single RTX 3090 GPU.
拖拽式编辑凭借其通过简单直观的操控来修改复杂几何结构的能力,在设计师中广受欢迎。它使用户能够以最少的技术技能来调整内容并改变其形状。这种拖拽操作已被纳入多种方法,以简化设计中的2D图像和3D网格的编辑过程。然而,对于广泛使用的3D高斯点云表示(3DGS)的拖拽式编辑研究却很少,因为在保持形状连贯性和视觉连续性的同时变形3DGS仍然具有挑战性。在本文中,我们介绍了ARAP-GS,这是一个基于尽可能刚性(As-Rigid-As-Possible,ARAP)变形的拖拽式3DGS编辑框架。与以前的3DGS编辑方法不同,我们是第一个将ARAP变形直接应用于3D高斯点的研究,从而实现灵活、拖拽式的几何变换。为了保持变形后的场景外观,我们在迭代优化过程中融入图像超分辨率的高级扩散先验。这种方法在提高视觉质量的同时,保持了编辑结果的多视角一致性。实验表明,ARAP-GS在多种3D场景中的表现优于当前方法,证明了其在拖拽式3DGS编辑中的有效性和优越性。此外,我们的方法非常高效,在单个RTX 3090 GPU上编辑场景仅需10到20分钟。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于ARAP变形的拖放式编辑框架ARAP-GS在三维高斯映射(3DGS)中的应用。该方法通过直接应用于三维高斯函数的ARAP变形技术实现灵活的三维几何变换,同时通过优化过程融合超分辨率扩散先验,提升了视觉质量并保持了多视角一致性。实验表明,ARAP-GS在多种场景下优于现有方法,适用于高效的拖放式三维编辑。
Key Takeaways
- ARAP-GS是一个基于拖放式编辑的框架,应用于三维高斯映射(3DGS)。
- ARAP变形技术被直接应用于三维高斯函数,实现灵活的三维几何变换。
- ARAP-GS通过优化过程融合超分辨率扩散先验,提升了视觉质量。
- 该方法能够在保持多视角一致性的同时,实现场景变形后的外观保护。
- 实验结果显示,ARAP-GS在多种场景下表现优异,优于现有方法。
- ARAP-GS适用于高效的拖放式三维编辑,编辑一个场景仅需10到20分钟。
点此查看论文截图