⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-19 更新
Exploring Expert Failures Improves LLM Agent Tuning
Authors:Li-Cheng Lan, Andrew Bai, Minhao Cheng, Ruochen Wang, Cho-Jui Hsieh, Tianyi Zhou
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown tremendous potential as agents, excelling at tasks that require multiple rounds of reasoning and interactions. Rejection Sampling Fine-Tuning (RFT) has emerged as an effective method for finetuning LLMs as agents: it first imitates expert-generated successful trajectories and further improves agentic skills through iterative fine-tuning on successful, self-generated trajectories. However, since the expert (e.g., GPT-4) succeeds primarily on simpler subtasks and RFT inherently favors simpler scenarios, many complex subtasks remain unsolved and persistently out-of-distribution (OOD). Upon investigating these challenging subtasks, we discovered that previously failed expert trajectories can often provide valuable guidance, e.g., plans and key actions, that can significantly improve agent exploration efficiency and acquisition of critical skills. Motivated by these observations, we propose Exploring Expert Failures (EEF), which identifies beneficial actions from failed expert trajectories and integrates them into the training dataset. Potentially harmful actions are meticulously excluded to prevent contamination of the model learning process. By leveraging the beneficial actions in expert failures, EEF successfully solves some previously unsolvable subtasks and improves agent tuning performance. Remarkably, our approach achieved a 62% win rate in WebShop, outperforming RFT (53. 6%) and GPT-4 (35. 6%), and to the best of our knowledge, setting a new state-of-the-art as the first method to surpass a score of 0.81 in WebShop and exceed 81 in SciWorld.
大型语言模型(LLM)作为代理表现出了巨大的潜力,擅长需要多轮推理和交互的任务。拒绝采样微调(RFT)作为一种有效的微调LLM作为代理的方法已经出现:它首先模仿专家生成的成功轨迹,并通过在成功的自我生成轨迹上进行迭代微调来进一步提高代理技能。然而,由于专家(例如GPT-4)主要在较简单的子任务上取得成功,而RFT本质上更倾向于简单的场景,因此许多复杂的子任务仍然无法解决,并且持续处于超出分布(OOD)的状态。在调查这些具有挑战性的子任务时,我们发现之前失败的专家轨迹通常可以提供有价值的指导,例如计划和关键行动,这可以显著提高代理的探索效率和关键技能的获取。受这些观察的启发,我们提出了“探索专家失败”(EEF)方法,该方法可以识别失败专家轨迹中的有益行动并将其整合到训练数据集中。可能会产生有害影响的行动被精心排除,以防止对模型学习过程造成污染。通过利用专家失败中的有益行动,EEF成功解决了一些之前无法解决的子任务,并提高了代理调整性能。值得注意的是,我们的方法在网络商店任务中的胜率达到了62%,超越了RFT(53.6%)和GPT-4(3.5%),据我们所知,这是第一个在WebShop上得分超过0.81分并在SciWorld上得分超过81分的方法,创下了新的技术顶尖水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型作为智能体展现出多任务推理和交互的优势。拒绝采样微调法通过模仿专家成功轨迹和自我生成成功轨迹的迭代微调来提升智能体技能。然而,专家主要在简单任务上成功,拒绝采样微调法更偏向于简单场景,导致复杂任务解决不足和分布外问题。为此,我们提出探索专家失败法,从失败的专家轨迹中提取有益动作并整合到训练数据集中,同时排除有害动作以防污染模型学习过程。此方法成功解决了一些之前的难题,提升了智能体性能。在WebShop任务中,探索专家失败法取得了62%的胜率,优于拒绝采样微调法的53.6%和GPT-4的35.6%,并创下了新的最高纪录。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型作为智能体具有多任务推理和交互的优势。
- 拒绝采样微调法是一种有效的LLM智能体微调方法,通过模仿和自我生成轨迹进行迭代改进。
- 专家主要在简单任务上成功,拒绝采样微调法倾向于简单场景,导致复杂任务解决不足和分布外问题。
- 探索专家失败法从失败的专家轨迹中提取有益动作,提高智能体在复杂任务上的性能。
- 探索专家失败法通过整合有益动作到训练数据集并排除有害动作,防止模型学习过程受到污染。
- 探索专家失败法在WebShop任务中取得了显著成果,超越了拒绝采样微调法和GPT-4的表现。
点此查看论文截图

QLLM: Do We Really Need a Mixing Network for Credit Assignment in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning?
Authors:Zhouyang Jiang, Bin Zhang, Airong Wei, Zhiwei Xu
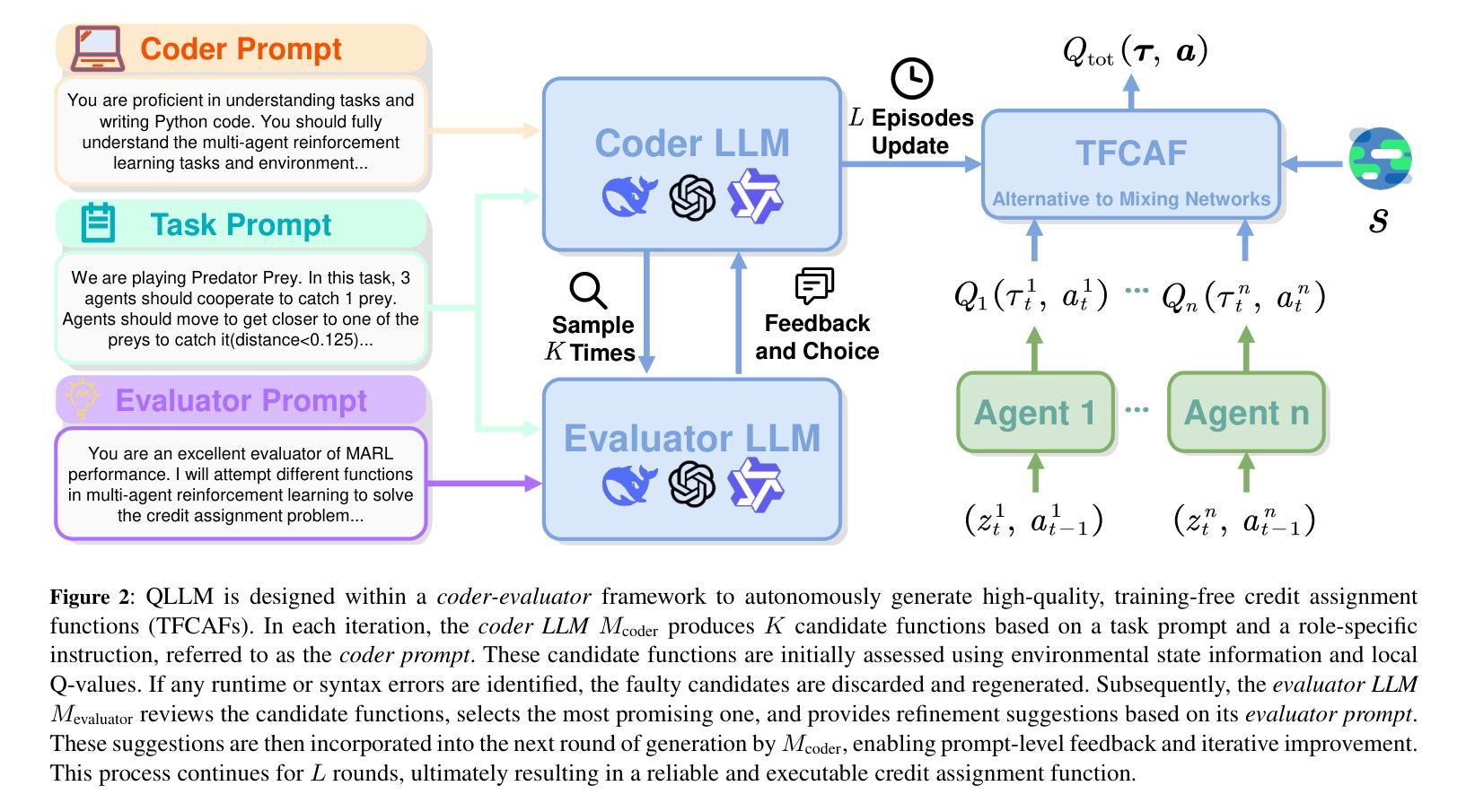
Credit assignment has remained a fundamental challenge in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). Previous studies have primarily addressed this issue through value decomposition methods under the centralized training with decentralized execution paradigm, where neural networks are utilized to approximate the nonlinear relationship between individual Q-values and the global Q-value. Although these approaches have achieved considerable success in various benchmark tasks, they still suffer from several limitations, including imprecise attribution of contributions, limited interpretability, and poor scalability in high-dimensional state spaces. To address these challenges, we propose a novel algorithm, \textbf{QLLM}, which facilitates the automatic construction of credit assignment functions using large language models (LLMs). Specifically, the concept of \textbf{TFCAF} is introduced, wherein the credit allocation process is represented as a direct and expressive nonlinear functional formulation. A custom-designed \textit{coder-evaluator} framework is further employed to guide the generation, verification, and refinement of executable code by LLMs, significantly mitigating issues such as hallucination and shallow reasoning during inference. Extensive experiments conducted on several standard MARL benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed method consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art baselines. Moreover, QLLM exhibits strong generalization capability and maintains compatibility with a wide range of MARL algorithms that utilize mixing networks, positioning it as a promising and versatile solution for complex multi-agent scenarios.
在多智能体强化学习(MARL)中,信用分配一直是一个基本挑战。之前的研究主要通过集中训练与分散执行范式下的价值分解方法来解决这个问题,利用神经网络来近似个体Q值的全局Q值之间的非线性关系。尽管这些方法在各种基准任务上取得了相当大的成功,但它们仍然存在一些局限性,包括贡献归因不准确、解释性有限以及在高维状态空间中可扩展性差。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型算法QLLM,它利用大型语言模型(LLM)自动构建信用分配函数。具体来说,引入了TFCAF的概念,其中信用分配过程被表示为直接而富有表现力的非线性函数公式。进一步采用定制设计的编码评估器框架,以指导LLM生成、验证和精炼可执行代码,从而在推理过程中显著缓解幻觉和浅推理等问题。在多个标准MARL基准测试上进行的广泛实验表明,该方法始终优于现有的最新基线。此外,QLLM表现出强大的泛化能力,并与使用混合网络的一系列MARL算法保持兼容性,使其成为复杂多智能体场景中有前途和多功能解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 7 figures
Summary:
多智能体强化学习中的信用分配问题一直是基本挑战。虽然基于价值分解方法已经取得了一些成功,但它们仍然面临贡献分配不准确、解释性差以及高维状态空间中可扩展性差的问题。为此,本文提出了一种利用大型语言模型自动构建信用分配函数的新算法QLLM。在TFCAF概念下,该算法通过将信用分配过程表述为直观的非线性函数公式来简化任务。实验结果证明了其在多个标准MARL基准测试上的表现优于现有技术。QLLM具有良好的泛化能力和与多种使用混合网络的MARL算法的兼容性,为复杂的多智能体场景提供了有前途和通用的解决方案。
Key Takeaways:
- 多智能体强化学习中的信用分配问题仍然是关键挑战。
- 价值分解方法虽然取得了一定成功,但仍存在贡献分配不准确、解释性差等问题。
- QLLM算法利用大型语言模型自动构建信用分配函数,通过TFCAF概念简化任务。
- QLLM算法在多个标准MARL基准测试中表现优异。
- QLLM具有良好的泛化能力和广泛的兼容性,适用于复杂的多智能体场景。
点此查看论文截图

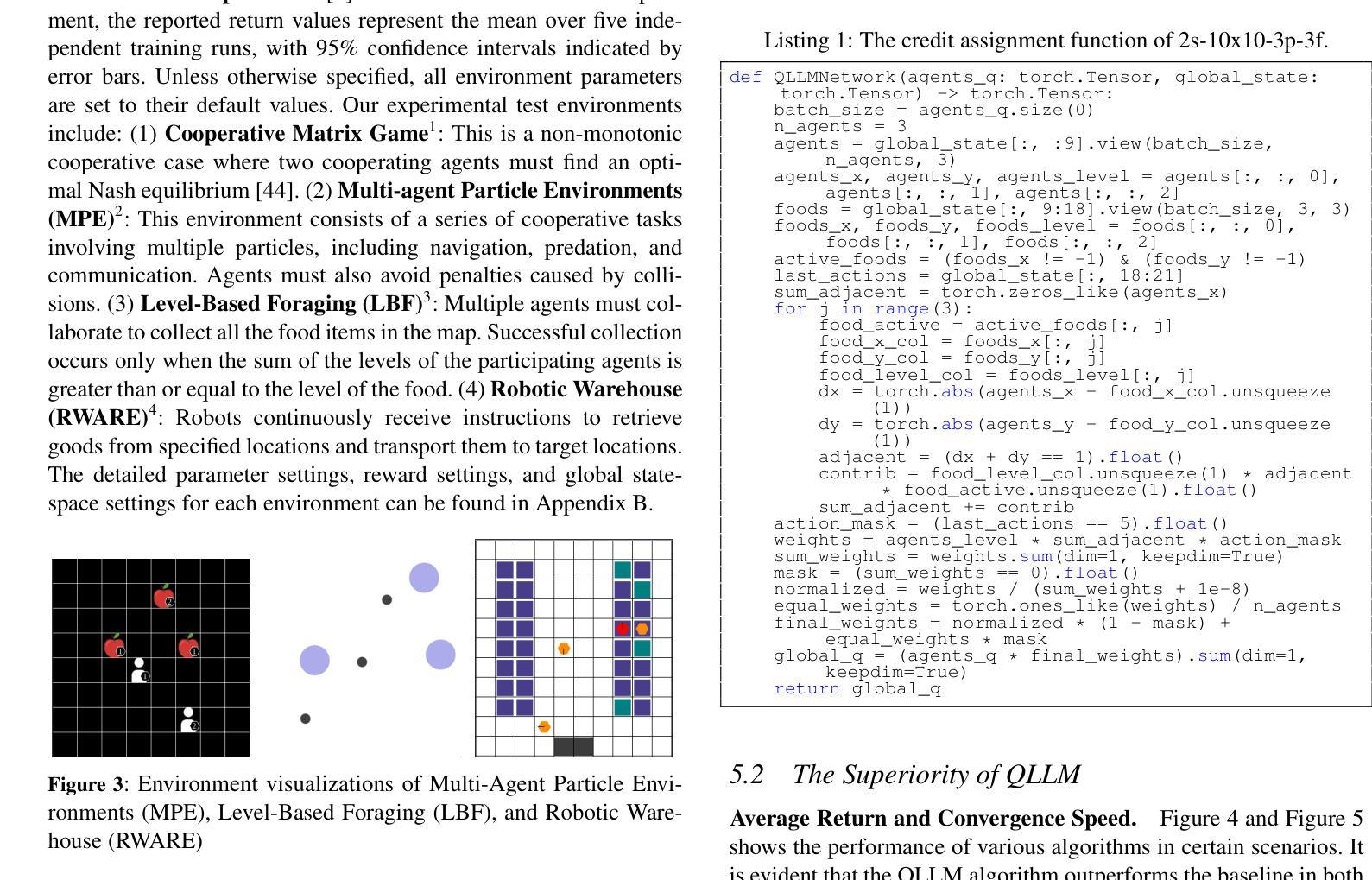
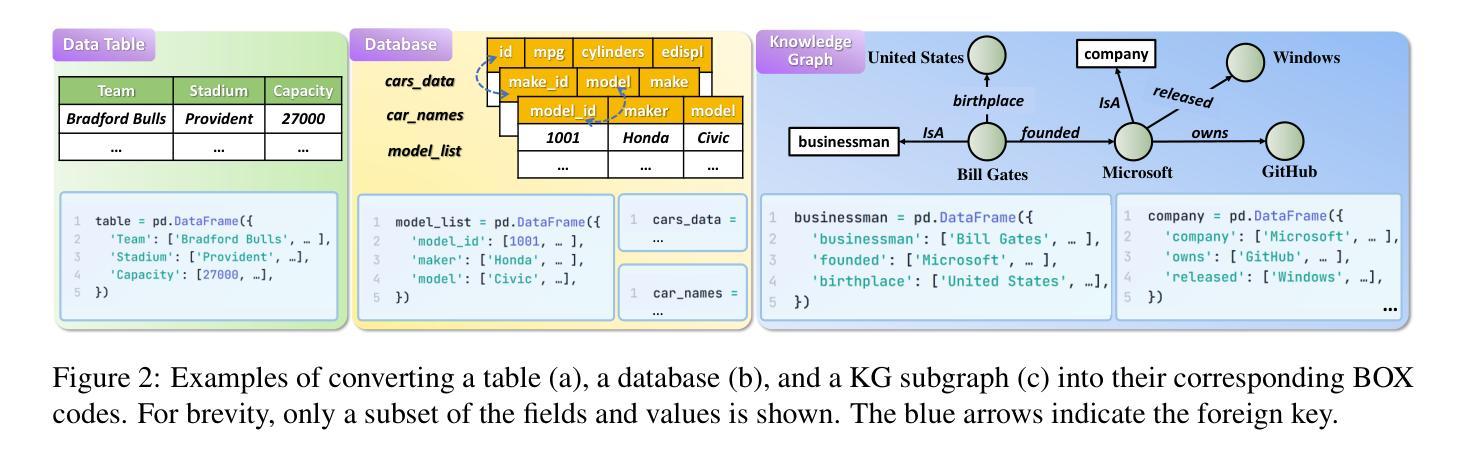
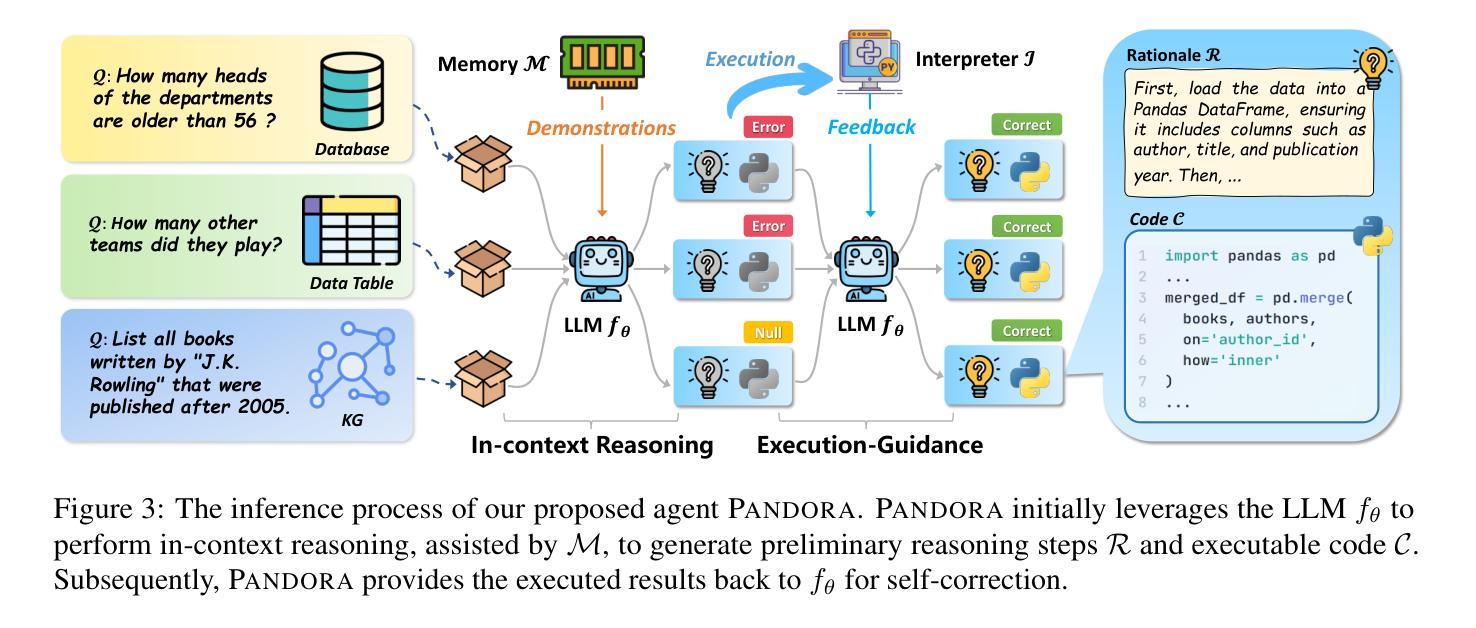
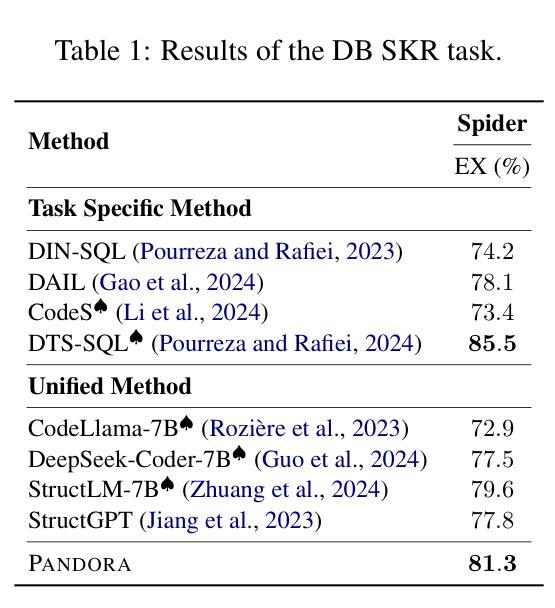
Pandora: A Code-Driven Large Language Model Agent for Unified Reasoning Across Diverse Structured Knowledge
Authors:Yongrui Chen, Junhao He, Linbo Fu, Shenyu Zhang, Rihui Jin, Xinbang Dai, Jiaqi Li, Dehai Min, Nan Hu, Yuxin Zhang, Guilin Qi, Yi Huang, Tongtong Wu
Unified Structured Knowledge Reasoning (USKR) aims to answer natural language questions (NLQs) by using structured sources such as tables, databases, and knowledge graphs in a unified way. Existing USKR methods either rely on employing task-specific strategies or custom-defined representations, which struggle to leverage the knowledge transfer between different SKR tasks or align with the prior of LLMs, thereby limiting their performance. This paper proposes a novel USKR framework named \textsc{Pandora}, which takes advantage of \textsc{Python}’s \textsc{Pandas} API to construct a unified knowledge representation for alignment with LLM pre-training. It employs an LLM to generate textual reasoning steps and executable Python code for each question. Demonstrations are drawn from a memory of training examples that cover various SKR tasks, facilitating knowledge transfer. Extensive experiments on four benchmarks involving three SKR tasks demonstrate that \textsc{Pandora} outperforms existing unified frameworks and competes effectively with task-specific methods.
统一结构化知识推理(USKR)旨在通过结构化来源(如表格、数据库和知识图谱)以统一的方式回答自然语言问题(NLQs)。现有的USKR方法要么依赖于采用特定任务策略,要么依赖于自定义表示,这很难利用不同SKR任务之间的知识转移或与大型语言模型(LLMs)的先验知识对齐,从而限制了它们的性能。本文提出了一种新型的USKR框架,名为Pandora,它利用Python的Pandas API构建统一的知识表示,与LLM预训练进行对齐。它利用LLM生成每个问题的文本推理步骤和可执行的Python代码。演示内容来自涵盖各种SKR任务的训练样本库,促进知识迁移。在涉及三个SKR任务的四个基准测试上的大量实验表明,Pandora优于现有的统一框架,并与特定任务的方法进行有效竞争。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文章介绍了Unified Structured Knowledge Reasoning(USKR)通过统一的知识源回答问题的方法。现有的USKR方法依赖特定的策略和自定义表示,难以在不同SKR任务间转移知识或与大型语言模型(LLMs)对齐,限制了性能。本文提出的\textsc{Pandora}框架利用Python的Pandas API构建统一知识表示,与LLM预训练对齐。它利用LLM生成文本推理步骤和可执行Python代码来回答问题。实验表明,\textsc{Pandora}在多种SKR任务上的表现优于现有统一框架,并与特定任务的方法竞争。
Key Takeaways
- Unified Structured Knowledge Reasoning (USKR) 旨在利用结构化源(如表格、数据库和知识图谱)以统一的方式回答自然语言问题(NLQs)。
- 现有USKR方法依赖特定策略和自定义表示,难以在不同SKR任务间转移知识或与大型语言模型(LLMs)对齐。
- \textsc{Pandora}框架利用Python的Pandas API构建统一知识表示,旨在解决上述问题。
- \textsc{Pandora}使用LLM生成文本推理步骤和可执行Python代码来回答问题。
- \textsc{Pandora}通过记忆训练样例来促进各种SKR任务间的知识转移。
- 在四个基准测试上的广泛实验表明,\textsc{Pandora}在多种SKR任务上的性能优于现有统一框架。
点此查看论文截图

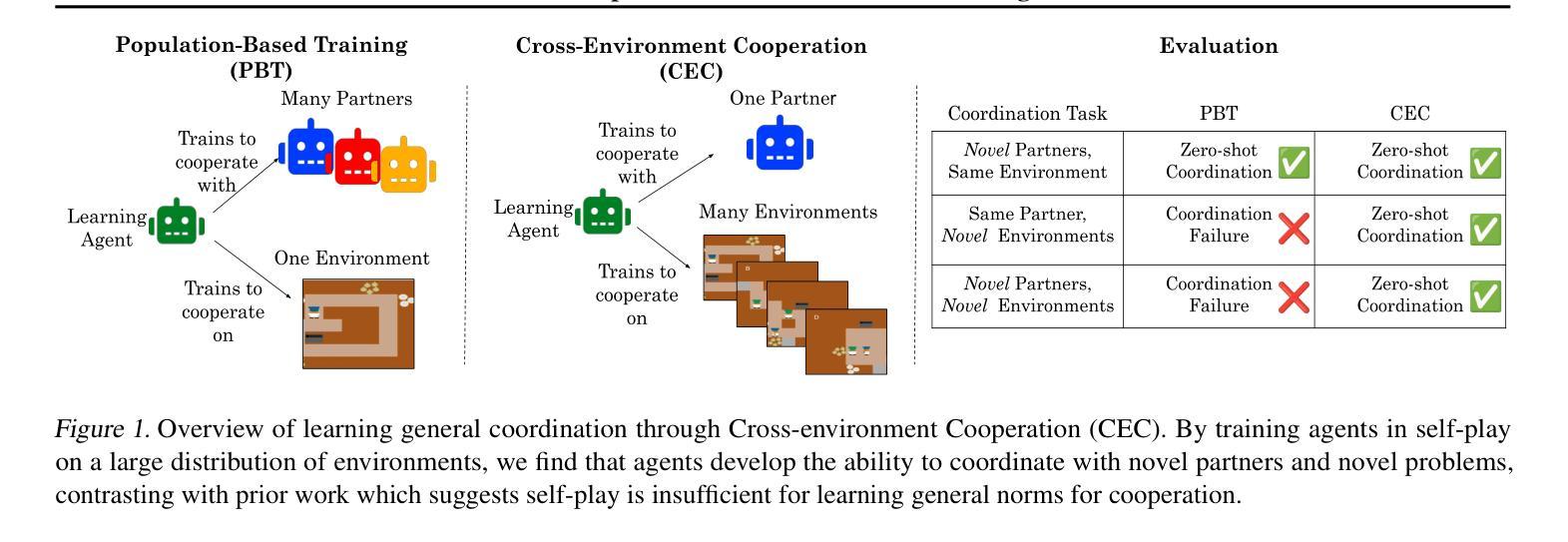
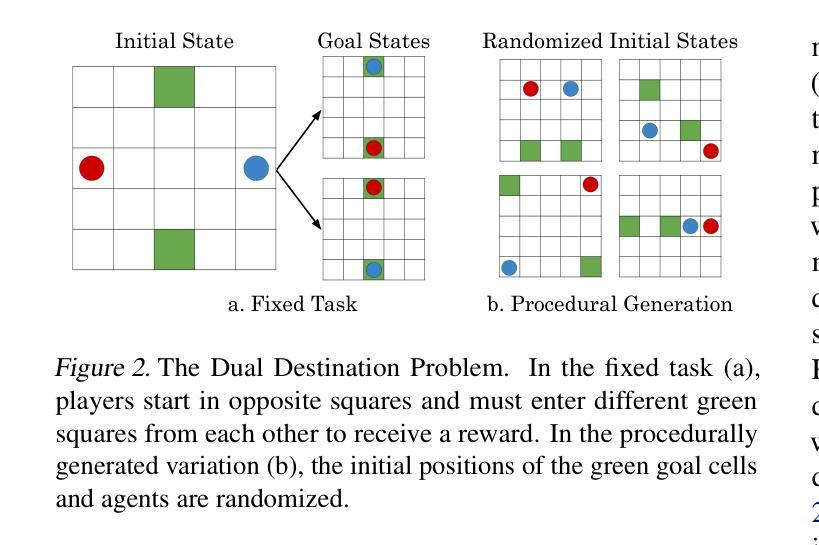
Cross-environment Cooperation Enables Zero-shot Multi-agent Coordination
Authors:Kunal Jha, Wilka Carvalho, Yancheng Liang, Simon S. Du, Max Kleiman-Weiner, Natasha Jaques
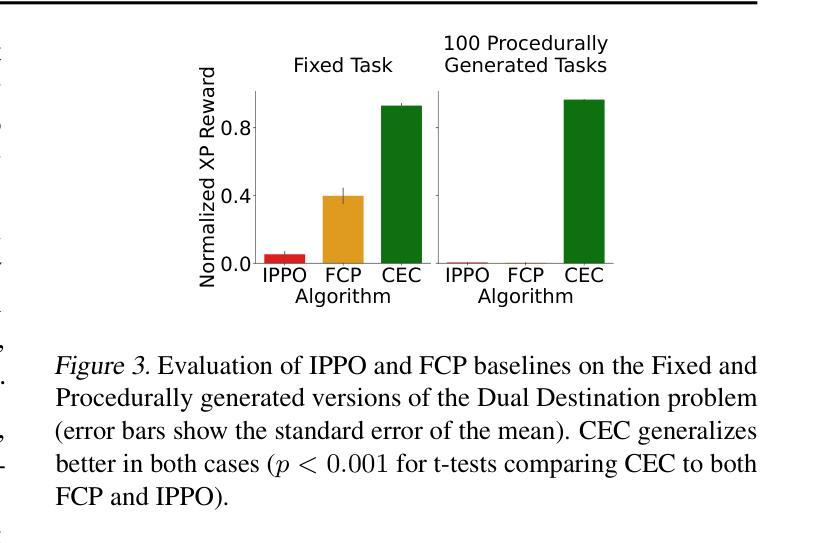
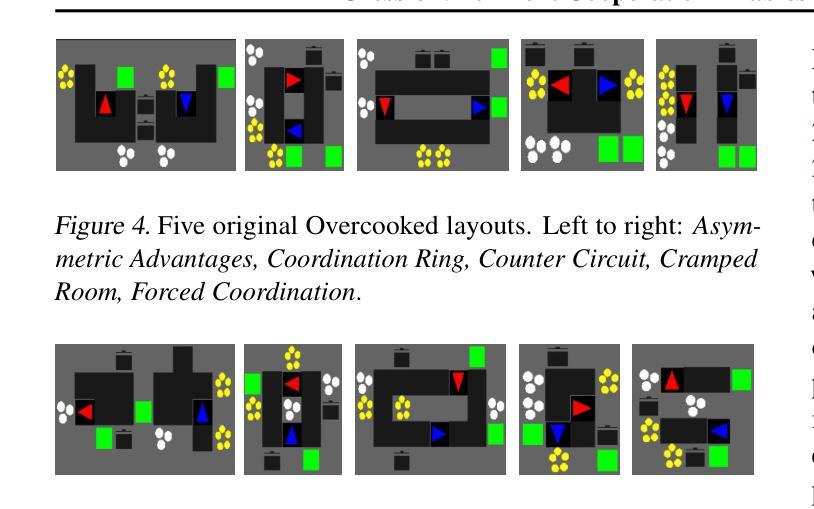
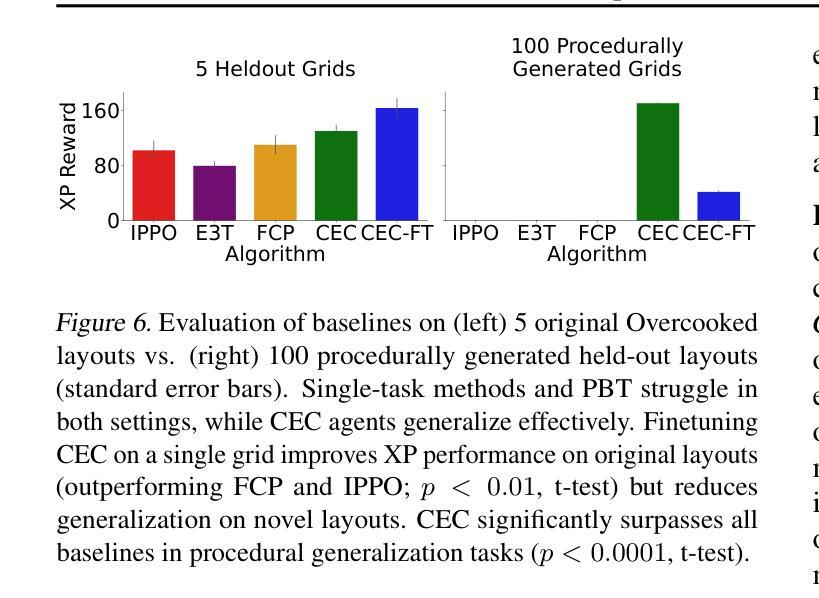
Zero-shot coordination (ZSC), the ability to adapt to a new partner in a cooperative task, is a critical component of human-compatible AI. While prior work has focused on training agents to cooperate on a single task, these specialized models do not generalize to new tasks, even if they are highly similar. Here, we study how reinforcement learning on a distribution of environments with a single partner enables learning general cooperative skills that support ZSC with many new partners on many new problems. We introduce two Jax-based, procedural generators that create billions of solvable coordination challenges. We develop a new paradigm called Cross-Environment Cooperation (CEC), and show that it outperforms competitive baselines quantitatively and qualitatively when collaborating with real people. Our findings suggest that learning to collaborate across many unique scenarios encourages agents to develop general norms, which prove effective for collaboration with different partners. Together, our results suggest a new route toward designing generalist cooperative agents capable of interacting with humans without requiring human data.
零拍摄协调(ZSC)是适应合作任务中新伙伴的能力,是人类兼容人工智能的关键组成部分。虽然以前的工作主要集中在训练代理人在单一任务上进行合作,但这些专用模型并不适用于新任务,即使它们高度相似。在这里,我们研究了在单一伙伴的多种环境分布上进行强化学习如何使代理学习通用的合作技能,这些技能支持零射击协调与许多新伙伴在许多新问题上的合作。我们介绍了两个基于Jax的、可生成数十亿可解决协调挑战的程序生成器。我们开发了一种称为跨环境合作(CEC)的新范式,并展示了它在与真实的人合作时在数量和质上的优越性超过了竞争对手的基础线。我们的研究发现,跨多个独特场景的合作学习鼓励代理人制定通用的规范,这些规范在与不同伙伴的合作中证明是有效的。总之,我们的结果指出了设计能够与人类交互而无需人类数据的通用合作代理人的新途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CogSci 2025, In-review for ICML 2025
Summary
本文研究了零射击协调(ZSC)在人工智能与人类合作中的重要性。传统的专注于单一任务合作的模型无法泛化到新任务。本文研究通过在不同的环境及单一伙伴上进行强化学习,学习通用的合作技能,从而支持与新伙伴在不同任务上的零射击协调。引入了基于Jax的程序生成器,创建数十亿可解决的协调挑战。提出新的合作范式——跨环境合作(CEC),在与人合作时,无论在数量上还是质量上都超越了竞争基线。研究结果表明,在多场景合作中学习有助于代理人建立通用的规范,这些规范在与不同伙伴的协作中证明了其有效性。这为设计能够与人类互动而无需人类数据的全能合作代理人开辟了一条新途径。
Key Takeaways
- 零射击协调(ZSC)是人工智能与人类合作中的一个关键能力,指的是适应新合作伙伴进行协同任务的能力。
- 传统的单一任务合作模型无法泛化到新任务,限制了人工智能的适应性。
- 强化学习在多种环境及不同伙伴中的应用有助于学习通用的合作技能,支持在不同任务上的零射击协调。
- 引入基于Jax的程序生成器,可以创建大量可解决的协调挑战。
- 提出新的合作范式——跨环境合作(CEC),在与人合作时表现优于其他方法。
- 学习跨场景合作有助于代理人建立通用规范,这些规范在与其他不同伙伴的协作中表现出有效性。
点此查看论文截图

WebLists: Extracting Structured Information From Complex Interactive Websites Using Executable LLM Agents
Authors:Arth Bohra, Manvel Saroyan, Danil Melkozerov, Vahe Karufanyan, Gabriel Maher, Pascal Weinberger, Artem Harutyunyan, Giovanni Campagna
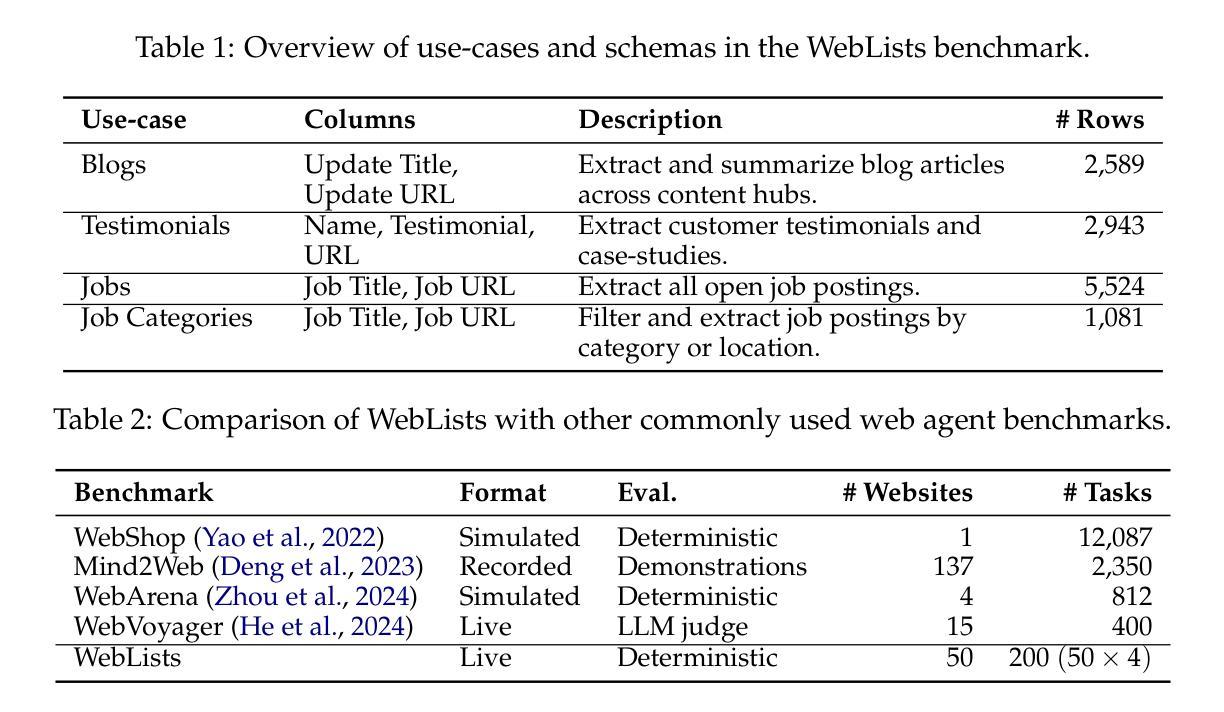
Most recent web agent research has focused on navigation and transaction tasks, with little emphasis on extracting structured data at scale. We present WebLists, a benchmark of 200 data-extraction tasks across four common business and enterprise use-cases. Each task requires an agent to navigate to a webpage, configure it appropriately, and extract complete datasets with well-defined schemas. We show that both LLMs with search capabilities and SOTA web agents struggle with these tasks, with a recall of 3% and 31%, respectively, despite higher performance on question-answering tasks. To address this challenge, we propose BardeenAgent, a novel framework that enables web agents to convert their execution into repeatable programs, and replay them at scale across pages with similar structure. BardeenAgent is also the first LLM agent to take advantage of the regular structure of HTML. In particular BardeenAgent constructs a generalizable CSS selector to capture all relevant items on the page, then fits the operations to extract the data. On the WebLists benchmark, BardeenAgent achieves 66% recall overall, more than doubling the performance of SOTA web agents, and reducing cost per output row by 3x.
最近的Web代理研究主要集中在导航和交易任务上,对大规模提取结构化数据的研究相对被忽略。我们推出WebLists,这是一组包含200个数据提取任务的基准测试,涵盖了四种常见的商业和企业用例。每个任务都需要一个代理导航到网页,进行适当的配置,并提取具有明确定义模式的数据集。我们发现,即使在问答任务上表现优异,但具备搜索能力的LLM和当前的Web代理在这些任务上的表现仍然很挣扎,召回率分别为3%和31%。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了BardeenAgent,这是一个新型框架,能够让Web代理将其执行转换为可重复的程序,并在具有相似结构的页面上大规模进行重播。BardeenAgent也是首个利用HTML常规结构的LLM代理。特别是,BardeenAgent构建了一个可概括的CSS选择器来捕获页面上的所有相关项目,然后将操作与数据提取相适应。在WebLists基准测试中,BardeenAgent的总体召回率达到了66%,不仅使当前Web代理的性能提高了两倍以上,而且使每输出行的成本降低了三倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
WebLists基准测试包含200个数据提取任务,涉及四种常见的商业和企业用例。当前网络代理在数据提取任务上表现不佳,提出BardeenAgent框架,能转化网络代理执行成为可重复的程序,并在WebLists基准测试中实现66%的召回率,性能优于现有网络代理。
Key Takeaways
- WebLists基准测试展示了网络代理在数据提取任务上的挑战。
- 当前的研究主要关注导航和交易任务,对数据提取任务的重视不足。
- LLMs和现有的网络代理在数据提取任务上的表现不尽如人意,召回率较低。
- BardeenAgent框架能将网络代理的执行转化为可重复的程序,提高了性能。
- BardeenAgent通过构建可概括的CSS选择器来捕获页面上的所有相关项,然后拟合操作以提取数据。
- BardeenAgent在WebLists基准测试中的召回率超过66%,优于现有的网络代理。
点此查看论文截图


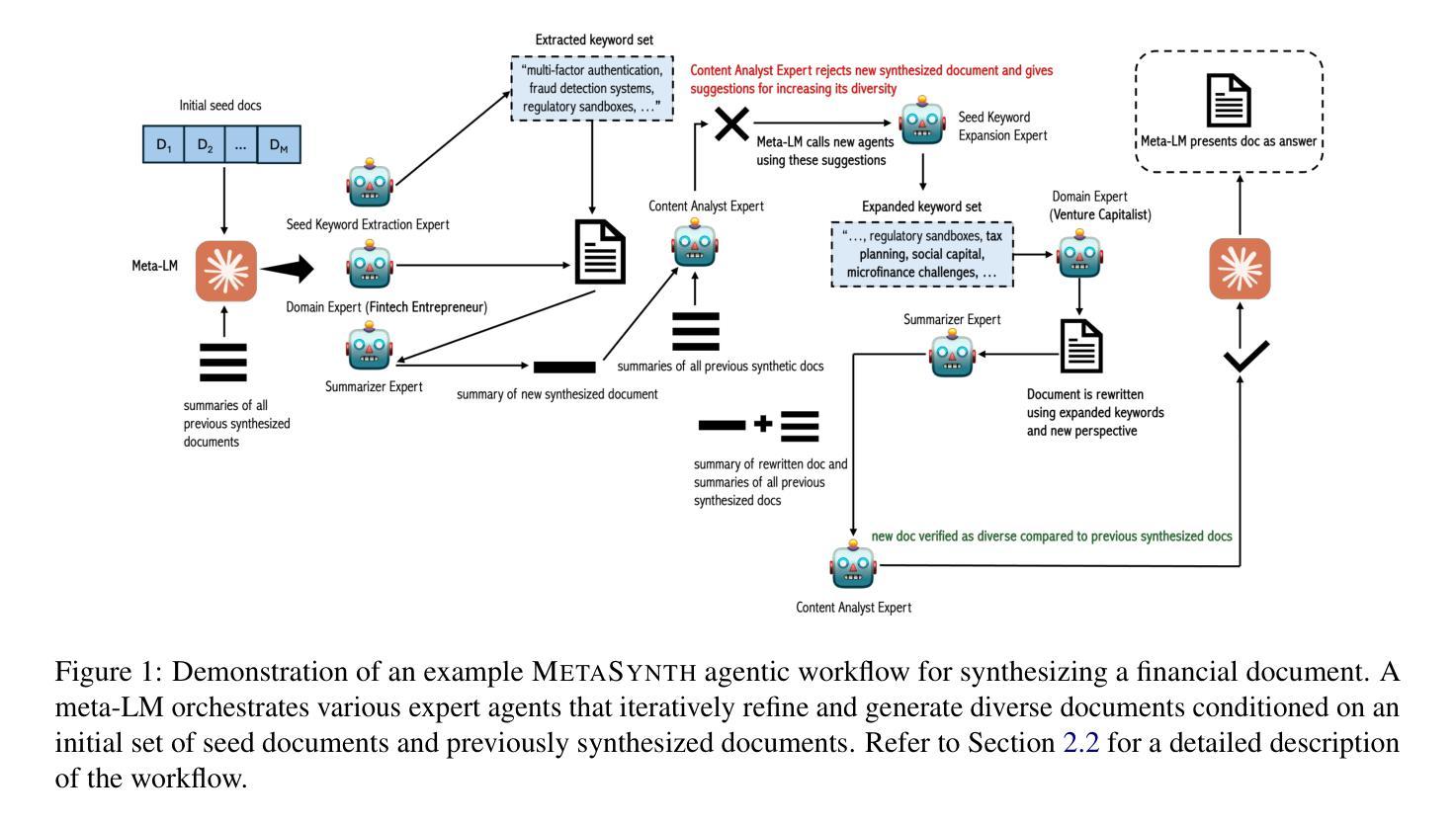
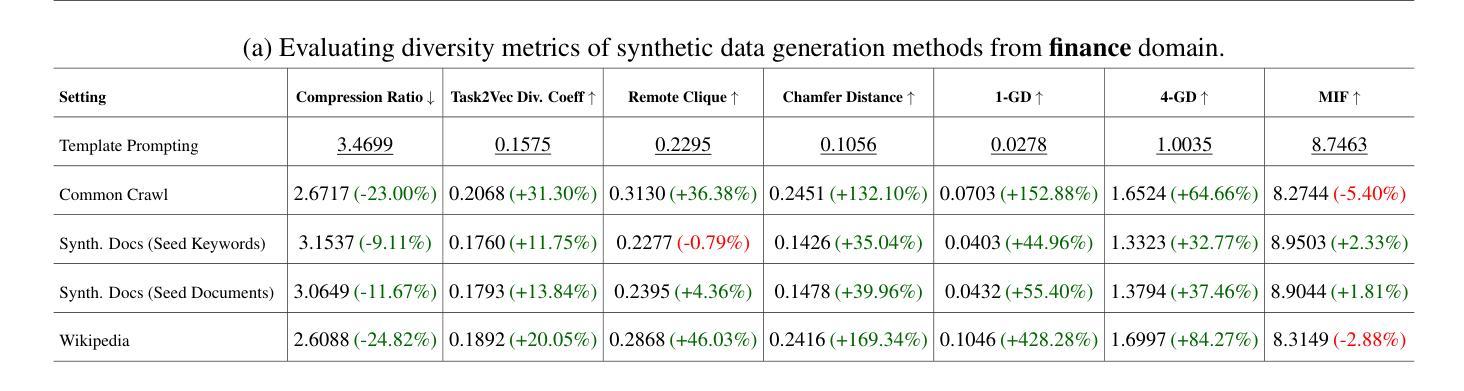
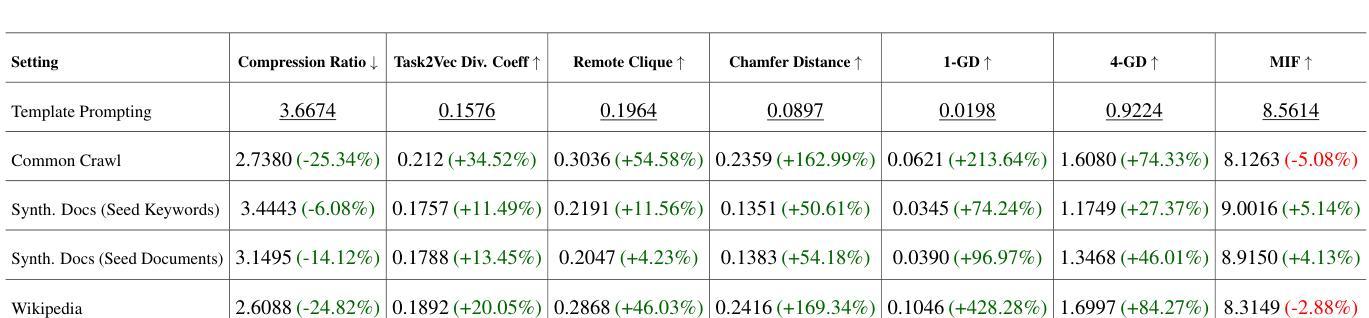
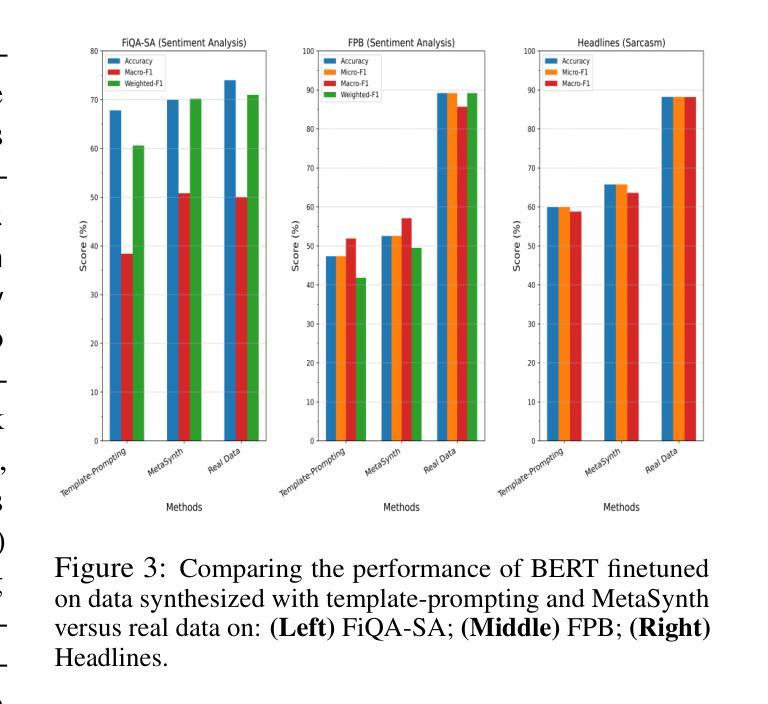
MetaSynth: Meta-Prompting-Driven Agentic Scaffolds for Diverse Synthetic Data Generation
Authors:Haris Riaz, Sourav Bhabesh, Vinayak Arannil, Miguel Ballesteros, Graham Horwood
Recent smaller language models such Phi-3.5 and Phi-4 rely on synthetic data generated using larger Language models. Questions remain about leveraging synthetic data for other use cases, such as adapting LLMs to specific domains. A key limitation of synthetic data is low diversity, which negatively impacts its downstream applicability for improving other models. To address this, we propose MetaSynth, a method for generating synthetic data that enhances diversity through meta-prompting, where a language model orchestrates multiple “expert” LLM agents to collaboratively generate data. Using only 25 million tokens of synthetic data generated with MetaSynth, we successfully adapt a well-trained LLM (Mistral-7B-v0.3) to two specialized domains-Finance and Biomedicine-without compromising the capabilities of the resulting model in general tasks. In addition, we evaluate the diversity of our synthetic data using seven automated metrics, and find that it approaches the diversity of LLM pre-training corpora. Continually pre-training Mistral-7B-v0.3 with MetaSynth notably outperforms the base LLM, showing improvements of up to 4.08% in Finance and 13.75% in Biomedicine. The same model shows degraded performance when trained on data generated using a template prompt, even when the template includes prior generations and varying In-Context exemplars of real data. Our findings suggest that a few million tokens of diverse synthetic data without mixing any real data, is sufficient for effective domain adaptation when using MetaSynth.
最近的小型语言模型,如Phi-3.5和Phi-4,都依赖于使用大型语言模型生成合成数据。如何利用合成数据用于其他用例,例如将大型语言模型 (LLM) 适配到特定领域,仍然存在疑问。合成数据的关键局限性是多样性不足,这对其在提高其他模型的适用性方面产生了负面影响。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了MetaSynth方法,这是一种通过元提示生成合成数据的方法,语言模型通过协调多个“专家”大型语言模型 (LLM) 代理来协作生成数据,从而提高数据的多样性。仅使用MetaSynth生成的2500万令牌合成数据,我们成功地将一个训练良好的大型语言模型(Mistral-7B-v0.3)适应到金融和生物医学两个专业领域,同时不损害模型在一般任务中的能力。此外,我们使用七个自动化指标评估了合成数据的多样性,发现它接近大型语言模型预训练语料库的多样性。使用MetaSynth持续预训练的Mistral-7B-v0.3显著优于基础大型语言模型,在金融领域和生物医学领域分别提高了最多4.08%和最多13.75%。该模型在模板提示生成的数据上进行训练时表现下降,即使模板包含先前的生成和不断变化的实际数据的上下文示例也是如此。我们的研究结果表明,使用MetaSynth时,几百万个令牌的多样合成数据就足以进行有效的领域适应,无需混合任何真实数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 33 pages, 17 figures. Preprint
Summary
本文介绍了利用MetaSynth方法生成合成数据,以提高语言模型的多样性并适应特定领域。通过仅使用25百万个标记的合成数据,成功将训练良好的LLM适应金融和生物医学两个专业领域,且不影响其在一般任务中的能力。评估显示,MetaSynth生成的合成数据多样性接近LLM预训练语料库。持续使用MetaSynth预训练LLM,在金融和生物医学领域分别提升了最多达4.08%和最高至最高达提高了高出了他们最先水平的技术高难度门槛儿的达到到了13.75%。相比之下,使用模板提示生成的数据会降低模型性能。研究表明,无需混合任何真实数据,只需几百万个标记的多样合成数据即可实现有效的领域适应。通过持续使用MetaSynth方法对其产品进行拓展探索尝试将会是计算机在进步自我的旅途中的重要突破和有趣的选择未来开展科学研究活动进行的过程的一步重要。简单来说就是用少量的合成数据适应更多的特定领域研究的一个方式进步方案而已。
Key Takeaways
点此查看论文截图

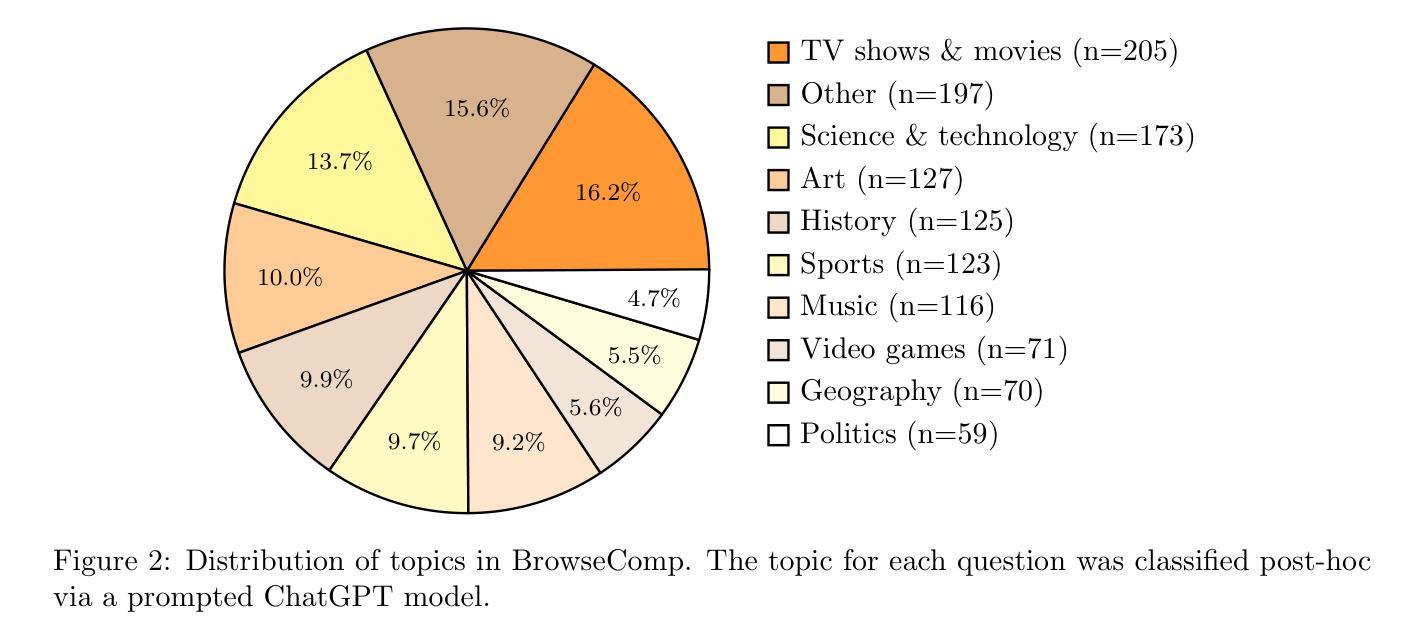
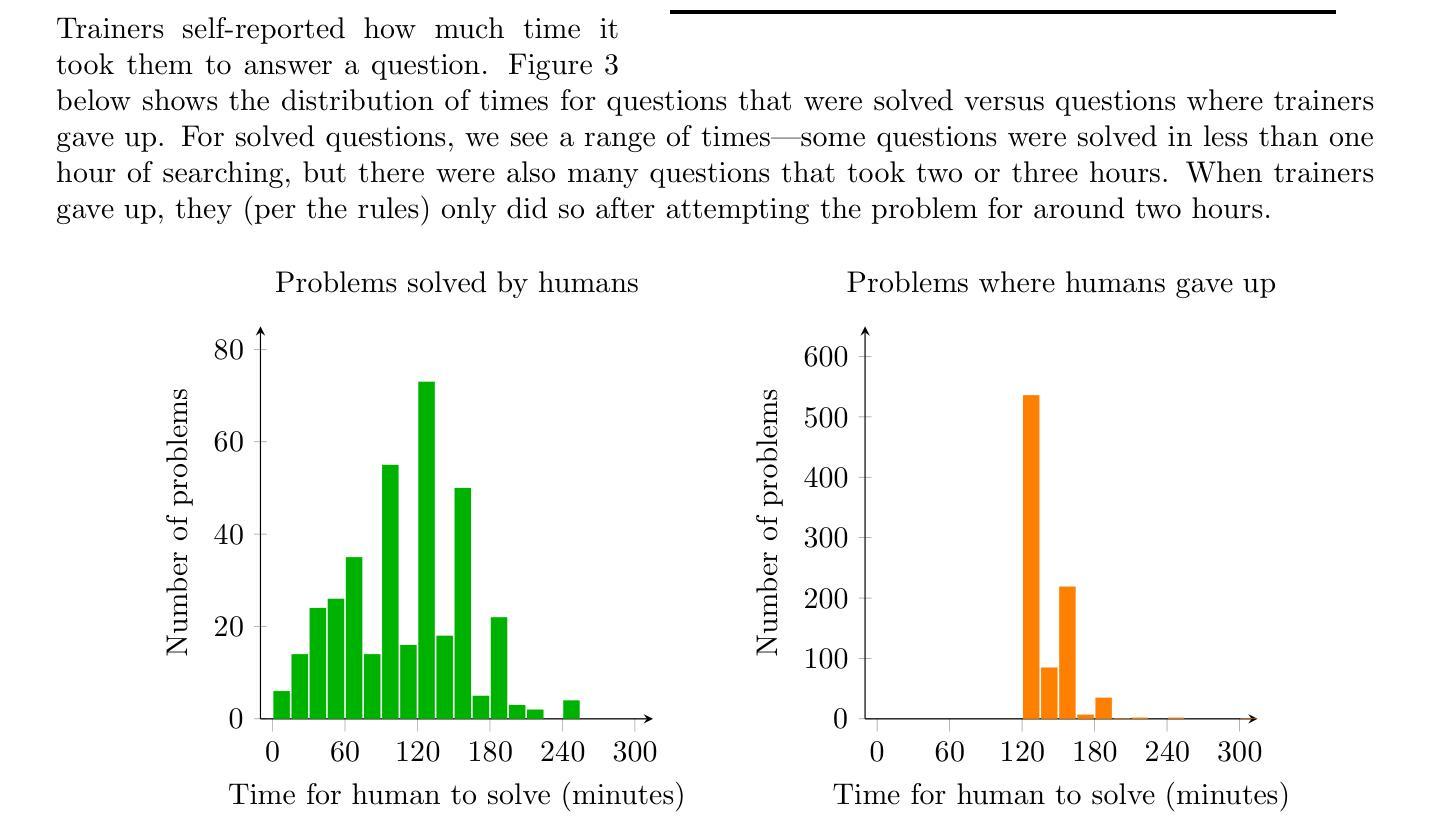
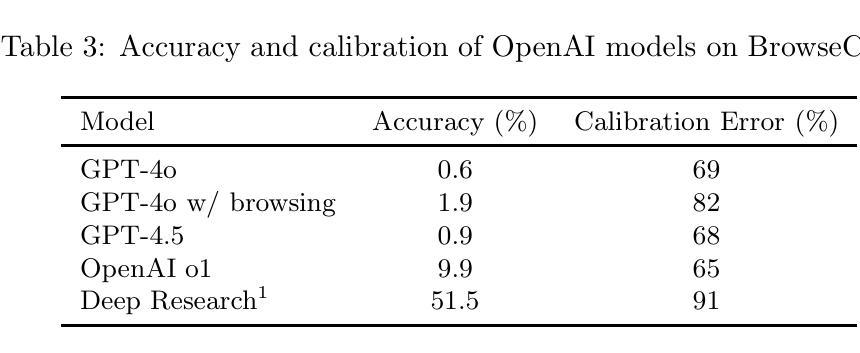
BrowseComp: A Simple Yet Challenging Benchmark for Browsing Agents
Authors:Jason Wei, Zhiqing Sun, Spencer Papay, Scott McKinney, Jeffrey Han, Isa Fulford, Hyung Won Chung, Alex Tachard Passos, William Fedus, Amelia Glaese
We present BrowseComp, a simple yet challenging benchmark for measuring the ability for agents to browse the web. BrowseComp comprises 1,266 questions that require persistently navigating the internet in search of hard-to-find, entangled information. Despite the difficulty of the questions, BrowseComp is simple and easy-to-use, as predicted answers are short and easily verifiable against reference answers. BrowseComp for browsing agents can be seen as analogous to how programming competitions are an incomplete but useful benchmark for coding agents. While BrowseComp sidesteps challenges of a true user query distribution, like generating long answers or resolving ambiguity, it measures the important core capability of exercising persistence and creativity in finding information. BrowseComp can be found at https://github.com/openai/simple-evals.
我们推出了BrowseComp,这是一个简单但具有挑战性的基准测试,用于衡量代理的网页浏览能力。BrowseComp包含1266个问题,需要持续浏览互联网寻找难以找到、纠缠不清的信息。尽管这些问题难度很大,但BrowseComp简单且易于使用,因为预测答案简短,易于与参考答案进行核对。对于浏览代理而言,BrowseComp类似于编程竞赛对于编码代理的不完全但有用的基准测试。虽然BrowseComp避开了真正的用户查询分布的挑战,如生成长答案或解决歧义,但它衡量了寻找信息的重要核心能力,即持久性和创造力的发挥。您可以在https://github.com/openai/simple-evals上找到BrowseComp。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:我们推出了BrowseComp,这是一个简单而具有挑战性的基准测试,用于衡量代理人在网络上浏览的能力。BrowseComp包含1266个问题,需要不断上网寻找难以找到、错综复杂的信息。尽管问题具有挑战性,但BrowseComp简单易用,预测的答案是简短且易于与参考答案进行验证的。对于浏览代理而言,BrowseComp类似于编程竞赛是不完全但有用的基准测试。尽管BrowseComp避开了真实用户查询分布的挑战,如生成长答案或解决歧义性,但它仍能有效衡量核心功能的重要性,即在进行信息检索时展现出持之以恒的创造力和恒心精神。如需了解详情请访问https://github.com/openai/simple-evals。
Key Takeaways:
- BrowseComp是一个基准测试,用于评估代理的网页浏览能力。
- 它包含多个复杂问题需要持续进行在线信息搜索才能解决。
- 尽管问题难以解决,但BrowseComp提供易于使用的简短预测答案便于验证答案准确性。
- BrowseComp的类比编程竞赛旨在作为简单而不完全的系统评估工具来衡量代理的性能。
- 该测试通过让代理坚持搜索找到难以找到的复杂信息来评估其持续性和创造力。
点此查看论文截图

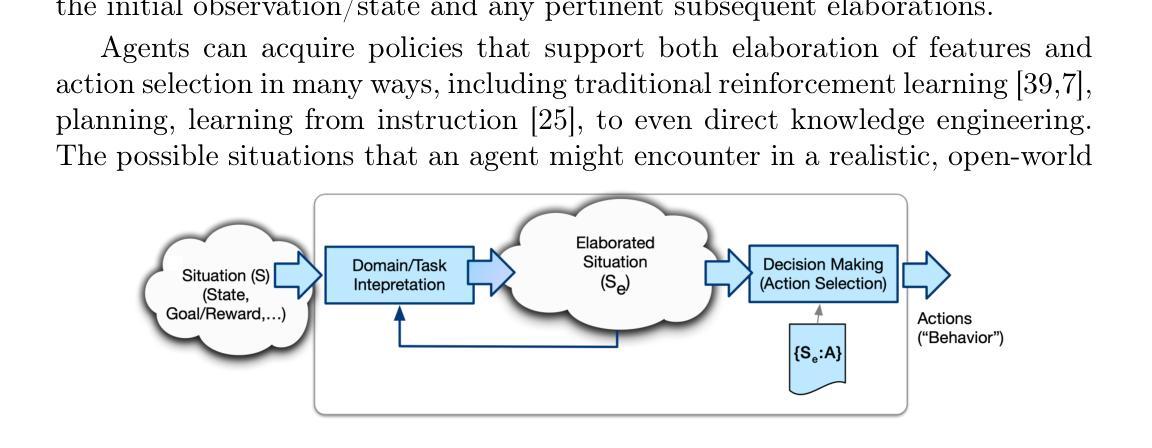
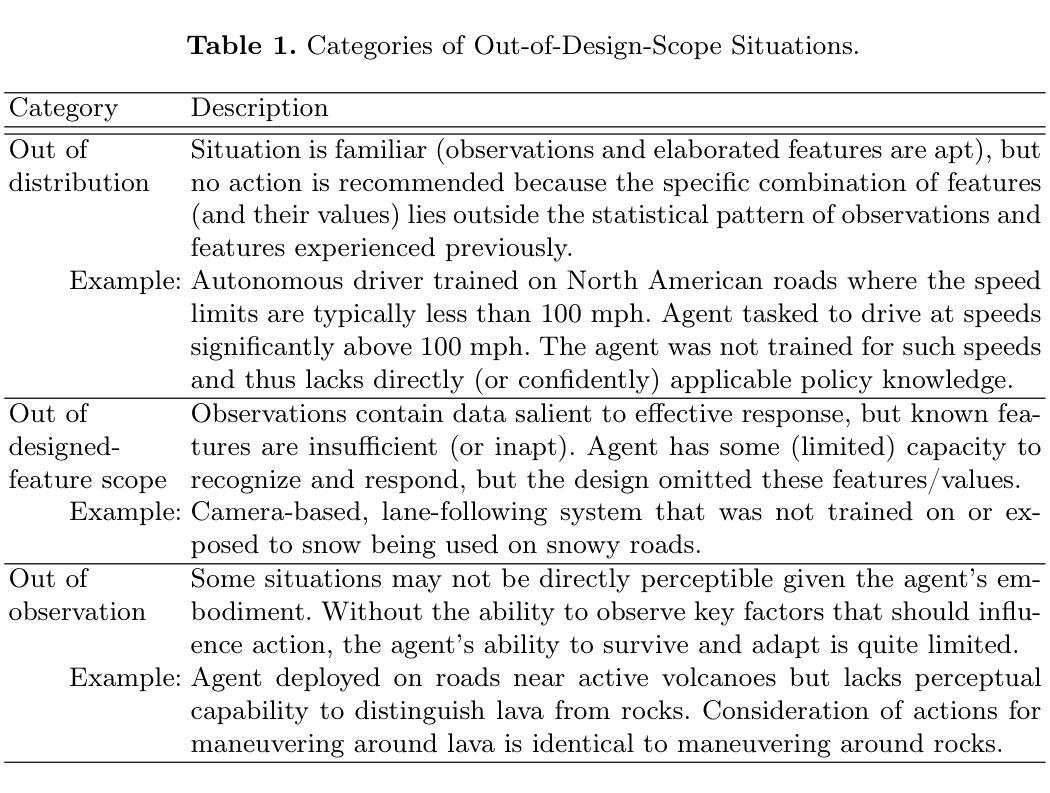
Heuristic Recognition and Rapid Response to Unfamiliar Events Outside of Agent Design Scope
Authors:Robert E. Wray, Steven J. Jones, John E. Laird
Regardless of past learning, an agent in an open world will face unfamiliar situations and events outside of prior experience, existing models, or policies. Further, the agent will sometimes lack relevant knowledge and/or sufficient time to assess the situation, generate and evaluate options, and pursue a robustly considered course of action. How can an agent respond reasonably to situations that are outside of its original design scope? How can it recognize such situations sufficiently quickly and reliably to determine reasonable, adaptive courses of action? We identify key characteristics needed for solutions, evaluate the state-of-the-art by these requirements, and outline a proposed, novel approach that combines domain-general meta-knowledge (in the form of appraisals inspired by human cognition) and metareasoning. It has the potential to provide fast, adaptive responses to unfamiliar situations, more fully meeting the performance characteristics required for open-world, general agents.
无论过去的经验如何,开放世界中的智能体会面临超出其先前经验、现有模型或策略范围之外的未知情境和事件。此外,智能体有时会缺乏相关知识或充足的时间来评估情况、生成并评估选项,并追求经过深思熟虑的行动方案。智能体如何对超出其原始设计范围的情境做出合理响应?如何快速可靠地识别这样的情境,以确定合理的适应性行动方案?我们确定了解决方案所需的关键特征,按照这些要求对最新技术进行评估,并概述了一种新颖的方法,该方法结合了领域通用的元知识(以人类认知启发的评价形式)和元推理。它有潜力对不熟悉的情况提供快速、灵活的响应,更充分地满足开放世界通用智能体的性能特性要求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 3 figures. Submitted to AGI25 conference
Summary:
在开放世界中,智能体会遇到超出其先验知识、模型或政策范围的未知情境和事件。智能体缺乏相关知识及时间时,需快速识别未知情境并决定合理应对措施是一大挑战。为应对这一挑战,我们提出了融合领域一般元知识和元推理的方法。这种方法汲取了人类认知的灵感,有助于智能体快速适应未知情境,满足开放世界智能体的性能要求。
Key Takeaways:
- 智能体会遇到超出其先验知识范围的未知情境和事件。
- 智能体在缺乏相关知识及时间时,需要快速识别未知情境并作出决策。
- 为应对这一挑战,需要融合领域一般元知识和元推理的方法。
- 元知识可以汲取人类认知的灵感,帮助智能体更好地适应未知情境。
- 该方法有助于智能体快速响应未知情境,满足开放世界智能体的性能要求。
- 通过评价和元推理,该方法可以自适应地处理各种复杂情况。
点此查看论文截图

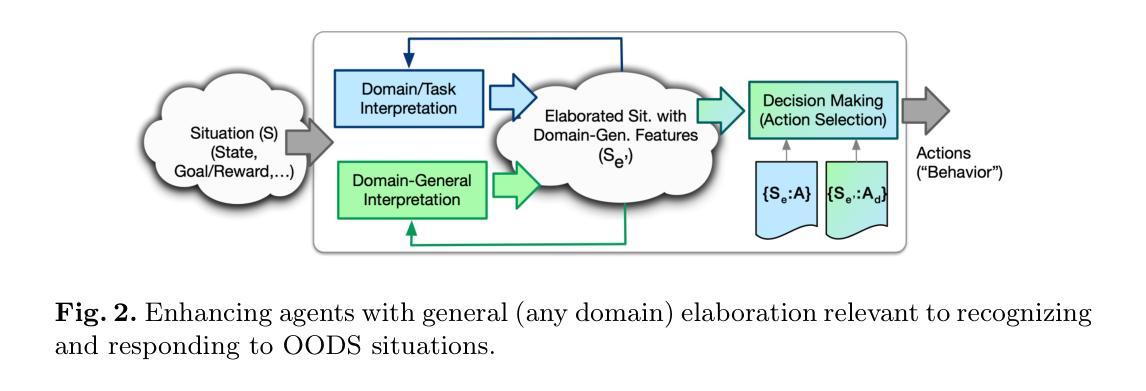
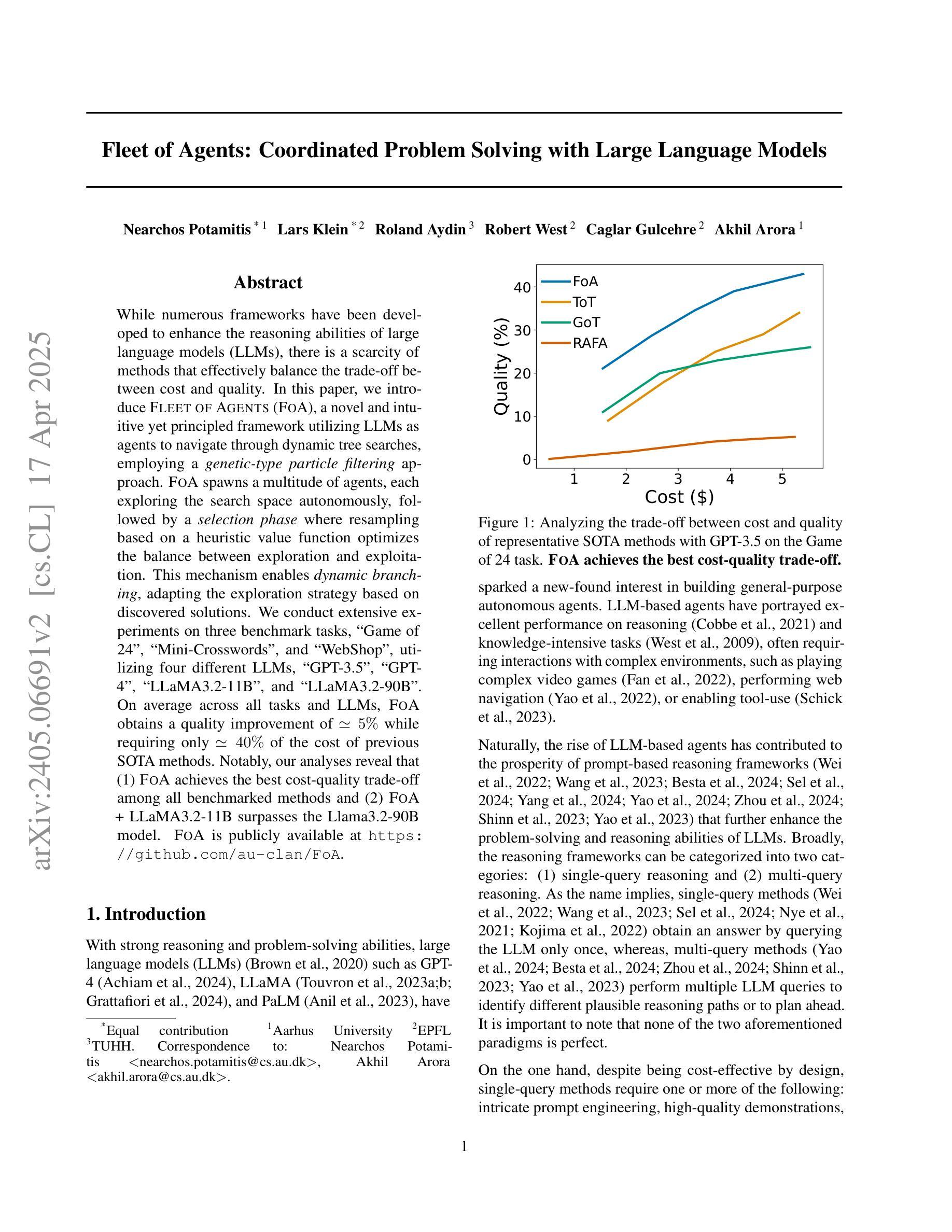
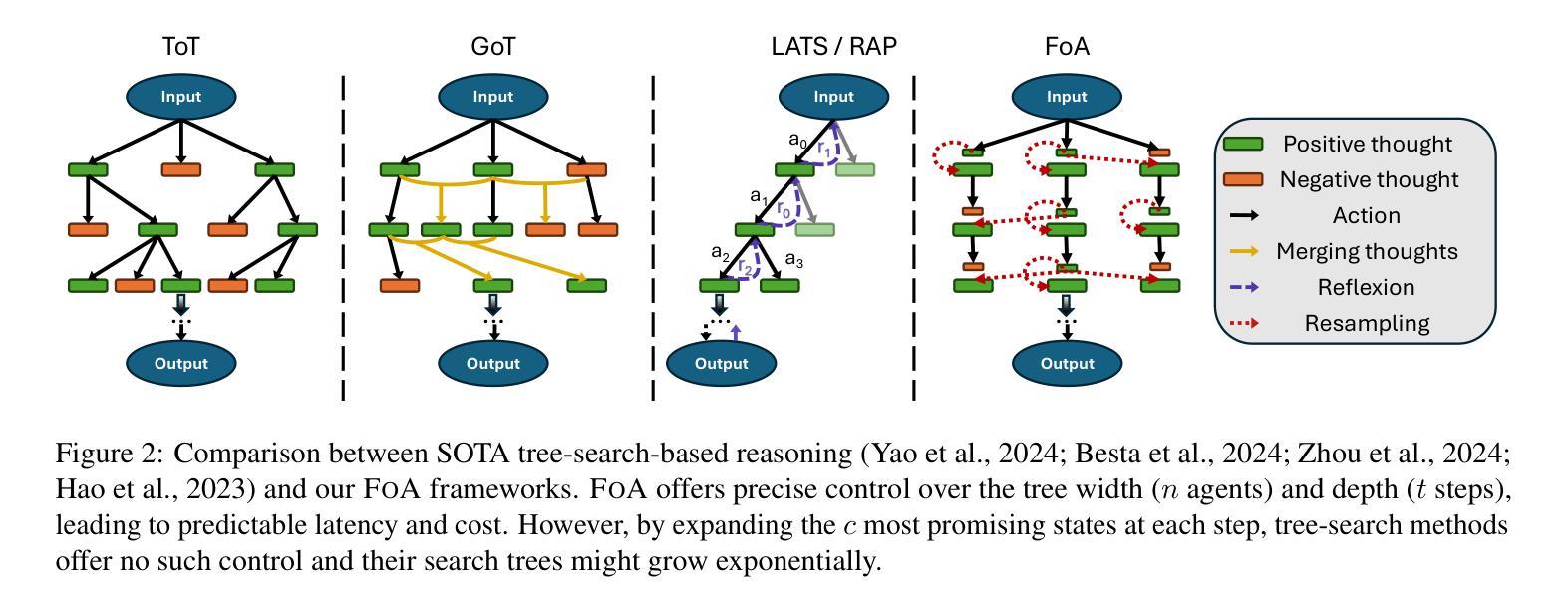
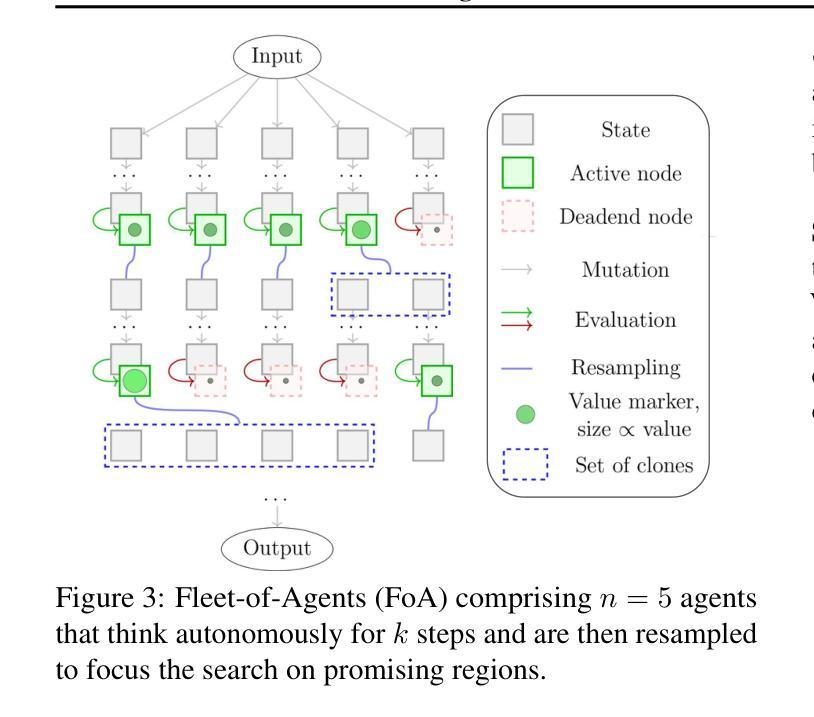
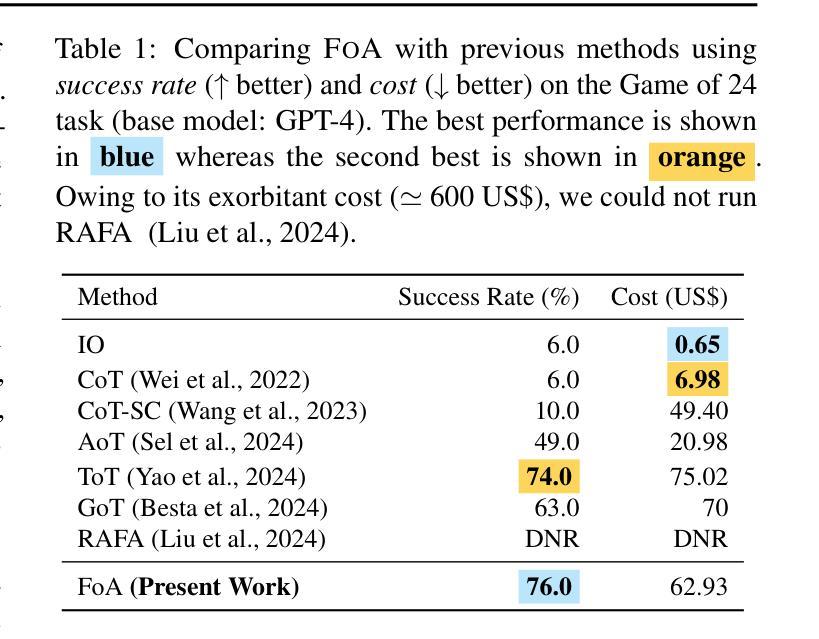
Fleet of Agents: Coordinated Problem Solving with Large Language Models
Authors:Nearchos Potamitis, Lars Klein, Roland Aydin, Robert West, Caglar Gulcehre, Akhil Arora
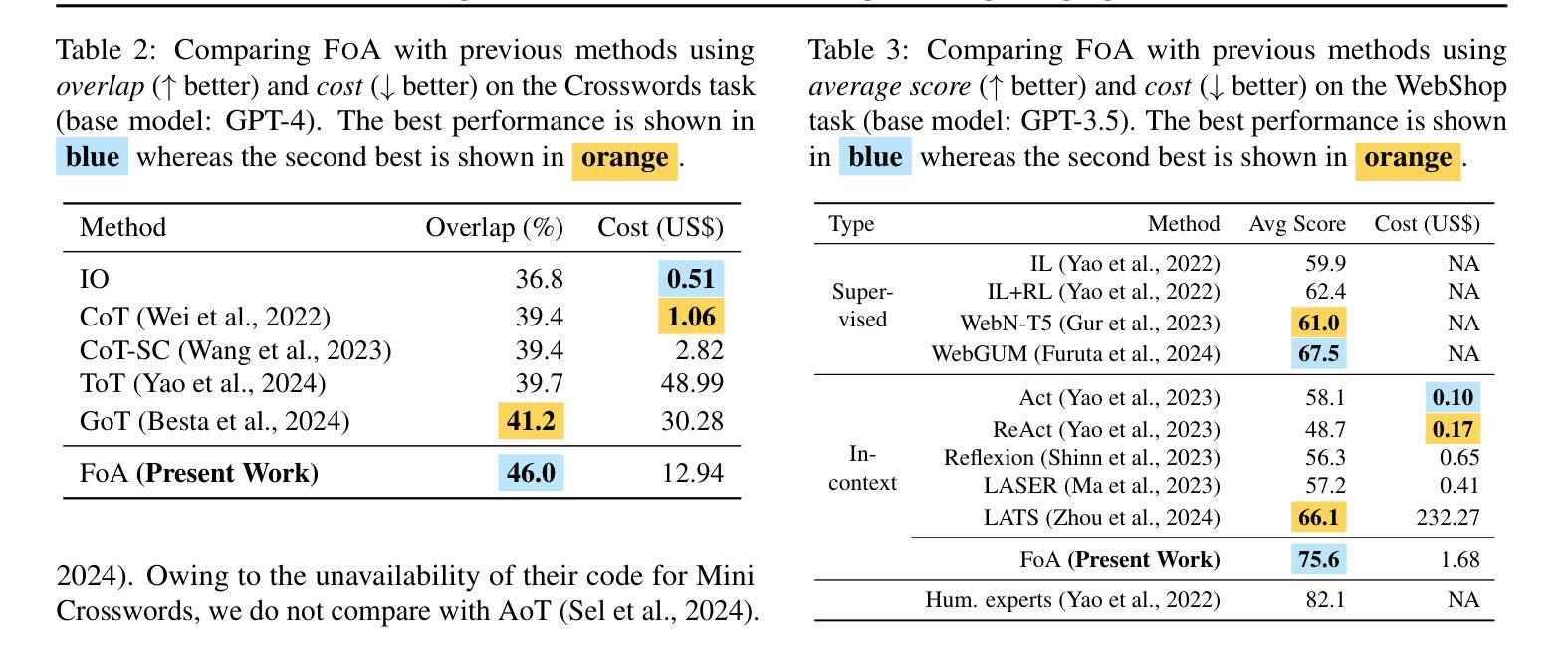
While numerous frameworks have been developed to enhance the reasoning abilities of large language models (LLMs), there is a scarcity of methods that effectively balance the trade-off between cost and quality. In this paper, we introduce Fleet of Agents (FoA), a novel and intuitive yet principled framework utilizing LLMs as agents to navigate through dynamic tree searches, employing a genetic-type particle filtering approach. FoA spawns a multitude of agents, each exploring the search space autonomously, followed by a selection phase where resampling based on a heuristic value function optimizes the balance between exploration and exploitation. This mechanism enables dynamic branching, adapting the exploration strategy based on discovered solutions. We conduct extensive experiments on three benchmark tasks, Game of 24'', Mini-Crosswords’’, and WebShop'', utilizing four different LLMs, GPT-3.5’’, GPT-4'', LLaMA3.2-11B’’, and ``LLaMA3.2-90B’’. On average across all tasks and LLMs, FoA obtains a quality improvement of ~5% while requiring only ~40% of the cost of previous SOTA methods. Notably, our analyses reveal that (1) FoA achieves the best cost-quality trade-off among all benchmarked methods and (2) FoA + LLaMA3.2-11B surpasses the Llama3.2-90B model. FoA is publicly available at https://github.com/au-clan/FoA.
虽然已经开发了许多框架来提高大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力,但能够有效平衡成本与质量之间权衡的方法仍然稀缺。在本文中,我们介绍了基于LLM作为代理在动态树搜索中进行导航的舰队代理(FoA)这一新颖而直观的原则性框架。它采用遗传型粒子滤波方法。FoA产生多个代理,每个代理自主探索搜索空间,随后进入选择阶段,基于启发式值函数进行重采样,优化探索与利用之间的平衡。这种机制能够实现动态分支,根据发现的解决方案调整探索策略。我们在三个基准任务:“游戏24”、“迷你填字游戏”和“网上购物”,以及四种不同的LLM:“GPT-3.5”、“GPT-4”、“LLaMA3.2-11B”和“LLaMA3.2-90B”上进行了广泛实验。在所有任务和LLM上的平均结果表明,FoA在提高质量约5%的同时,仅需先前最先进方法成本的40%。值得注意的是,我们的分析表明(1)FoA在所有基准方法中实现了最佳的成本效益权衡;(2)FoA与LLaMA3.2-11B的组合超越了LLama3.2-90B模型。FoA可在https://github.com/au-clan/FoA上公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 68 figures, 8 tables
摘要
本文提出了一种新型框架Fleet of Agents(FoA),该框架利用大型语言模型(LLM)作为智能体进行动态树搜索导航。通过遗传型粒子滤波方法,FoA能够孵化多个自主探索搜索空间的智能体,并在启发式价值函数优化的选择阶段实现探索与开发的平衡。这种机制使FoA能根据已发现的解决方案动态调整探索策略。在Game of 24、Mini-Crosswords和WebShop三个基准任务上进行的实验表明,与之前的最佳方法相比,FoA在提高大约5%质量的同时仅需要约40%的成本。此外,分析显示FoA在所有基准方法中实现了最佳的成本效益权衡,并且与LLaMA3.2-11B模型的结合超过了LLaMA3.2-90B模型的表现。FoA已在公开平台上发布。
关键见解
- Fleet of Agents(FoA)框架利用大型语言模型(LLM)作为智能体进行动态树搜索导航,为平衡成本与质量提供了新方法。
- FoA采用遗传型粒子滤波方法,通过孵化多个智能体自主探索搜索空间,并优化探索与开发之间的平衡。
- 动态分支机制允许FoA根据已发现的解决方案调整探索策略。
- 在多个基准任务上的实验表明,FoA在提高任务质量的同时降低了成本。
- FoA实现了最佳的成本效益权衡,与其他方法相比具有优势。
- 结合LLaMA3.2-11B模型的FoA表现超过了LLaMA3.2-90B模型。
- FoA框架已公开发布,便于研究者和开发者使用。
点此查看论文截图