⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-19 更新
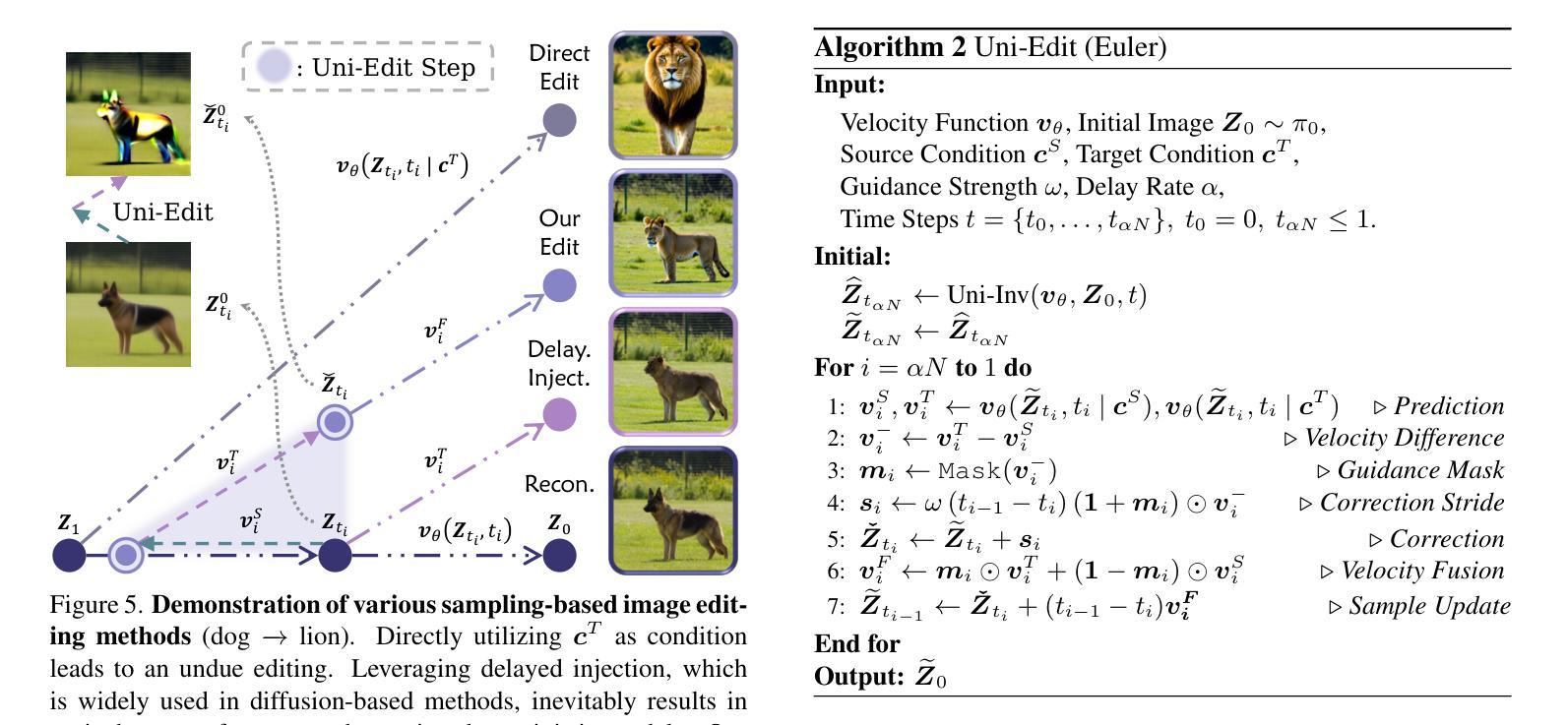
UniEdit-Flow: Unleashing Inversion and Editing in the Era of Flow Models
Authors:Guanlong Jiao, Biqing Huang, Kuan-Chieh Wang, Renjie Liao
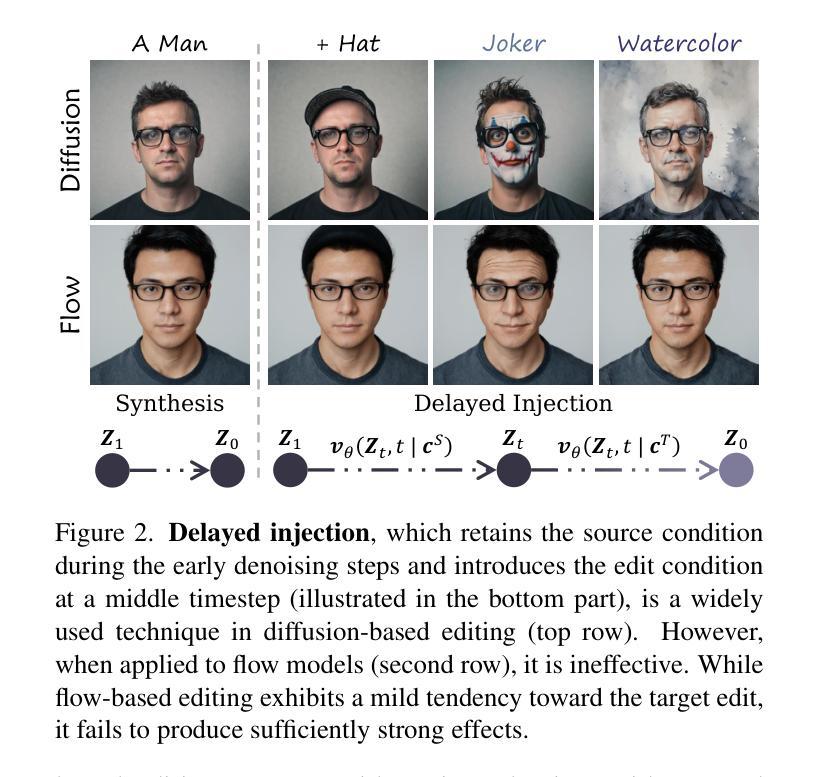
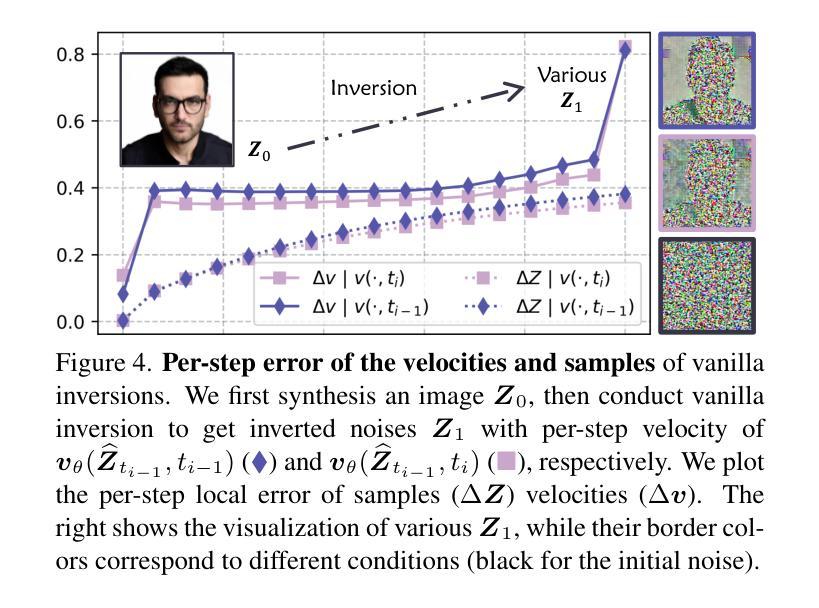
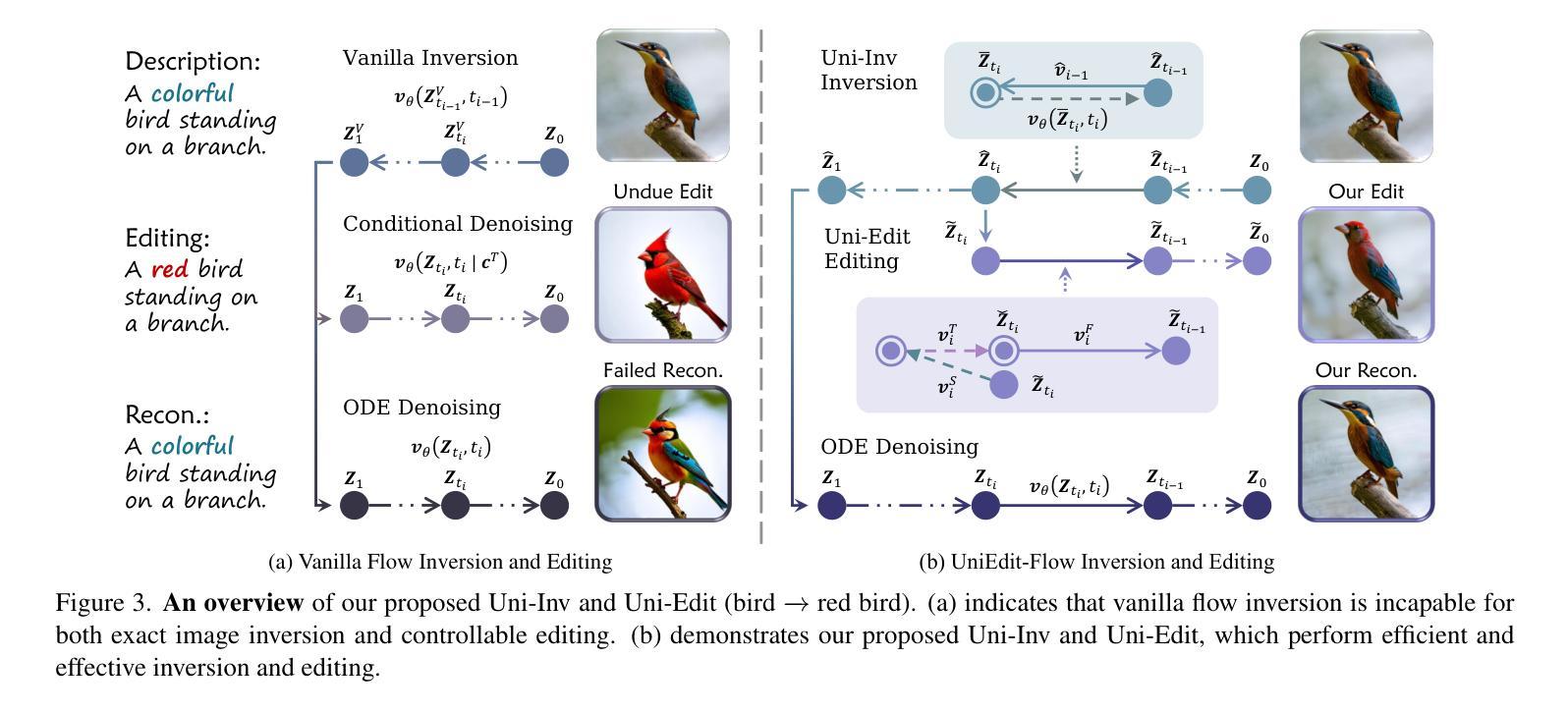
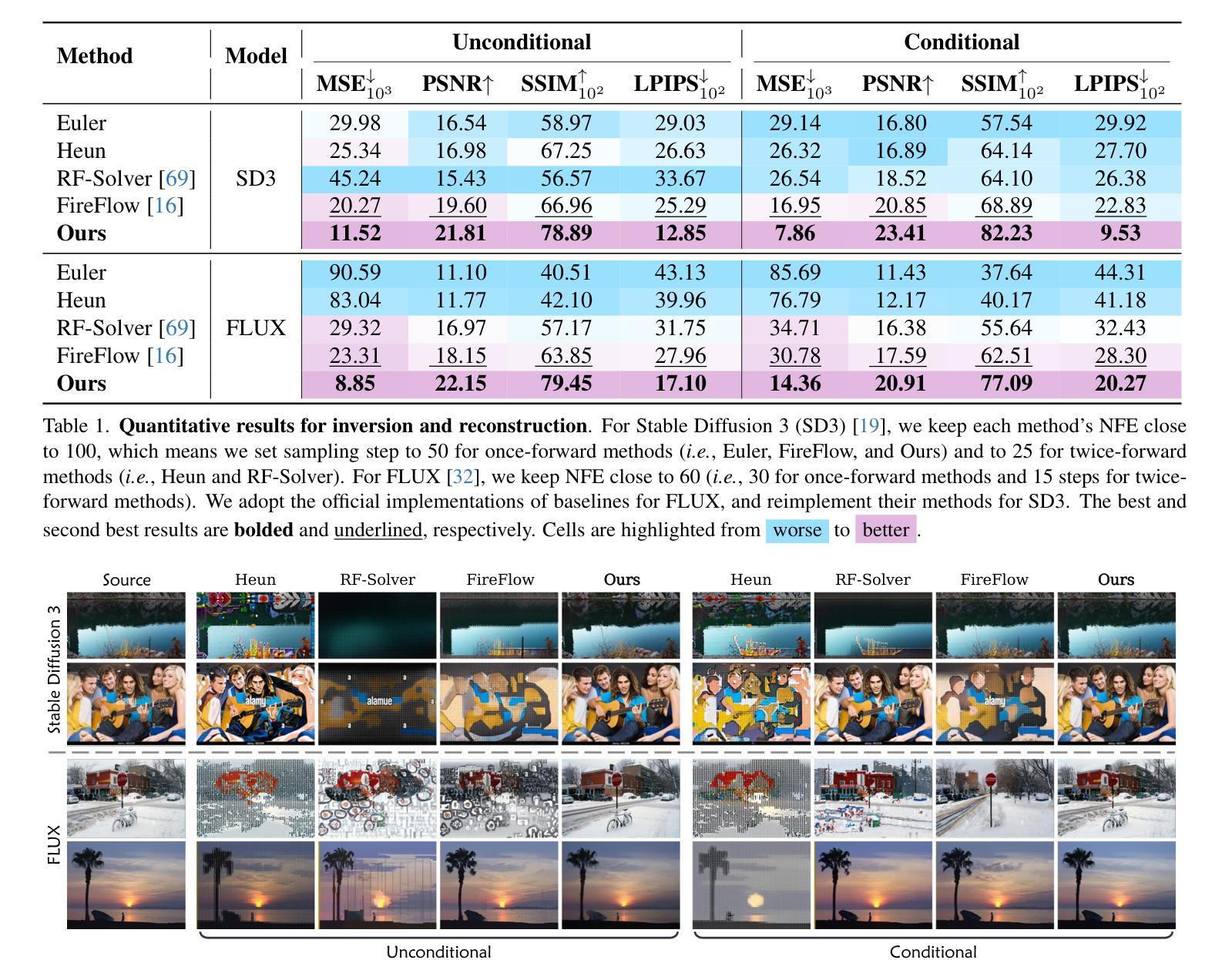
Flow matching models have emerged as a strong alternative to diffusion models, but existing inversion and editing methods designed for diffusion are often ineffective or inapplicable to them. The straight-line, non-crossing trajectories of flow models pose challenges for diffusion-based approaches but also open avenues for novel solutions. In this paper, we introduce a predictor-corrector-based framework for inversion and editing in flow models. First, we propose Uni-Inv, an effective inversion method designed for accurate reconstruction. Building on this, we extend the concept of delayed injection to flow models and introduce Uni-Edit, a region-aware, robust image editing approach. Our methodology is tuning-free, model-agnostic, efficient, and effective, enabling diverse edits while ensuring strong preservation of edit-irrelevant regions. Extensive experiments across various generative models demonstrate the superiority and generalizability of Uni-Inv and Uni-Edit, even under low-cost settings. Project page: https://uniedit-flow.github.io/
流匹配模型作为扩散模型的强大替代品已经崭露头角,但是为扩散模型设计的现有反转和编辑方法往往对其无效或不可应用。流模型的直线、非交叉轨迹为基于扩散的方法带来了挑战,但也为新颖解决方案打开了通道。在本文中,我们介绍了基于预测校正器框架的流模型反转和编辑方法。首先,我们提出Uni-Inv,一种针对准确重建的有效反转方法。在此基础上,我们将延迟注入的概念扩展到流模型,并引入Uni-Edit,一种区域感知、稳健的图像编辑方法。我们的方法是免调试的、模型无关的、高效的、有效的,能够在确保编辑无关区域得到强烈保留的同时,实现多样化的编辑。在各种生成模型上的广泛实验证明了Uni-Inv和Uni-Edit的优越性和通用性,即使在低成本设置下也是如此。项目页面:https://uniedit-flow.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://uniedit-flow.github.io/
Summary
文本介绍了一种针对流匹配模型的预测校正框架,用于进行反演和编辑操作。提出了Uni-Inv反演方法和Uni-Edit图像编辑方法,具有准确性、区域感知性、鲁棒性等特点,无需调整参数,适用于多种生成模型,并在实验上证明了其优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 流匹配模型作为扩散模型的替代方案,对现有扩散模型的反演和编辑方法提出了挑战。
- 流匹配模型的直线、非交叉轨迹特性对现有扩散模型的方法构成挑战,但也为新的解决方案提供了机会。
- 引入了一种基于预测校正框架的方法,用于流匹配模型中的反演和编辑操作。
- 提出了Uni-Inv反演方法,旨在实现准确的重建。
- 扩展了延迟注入的概念,并引入了Uni-Edit图像编辑方法,具有区域感知性和鲁棒性。
- 该方法无需调整参数,适用于多种生成模型。
点此查看论文截图

TTRD3: Texture Transfer Residual Denoising Dual Diffusion Model for Remote Sensing Image Super-Resolution
Authors:Yide Liu, Haijiang Sun, Xiaowen Zhang, Qiaoyuan Liu, Zhouchang Chen, Chongzhuo Xiao
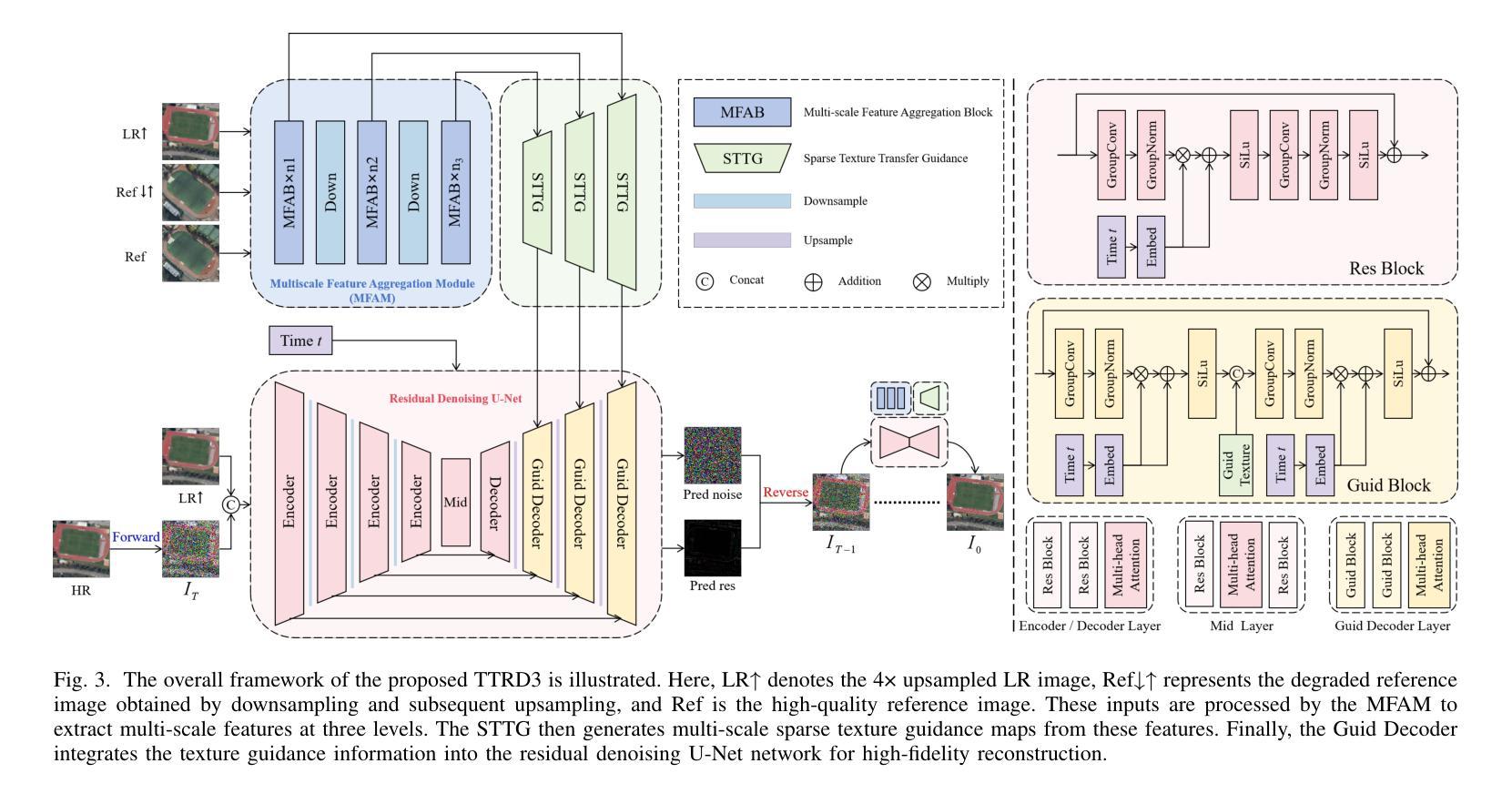
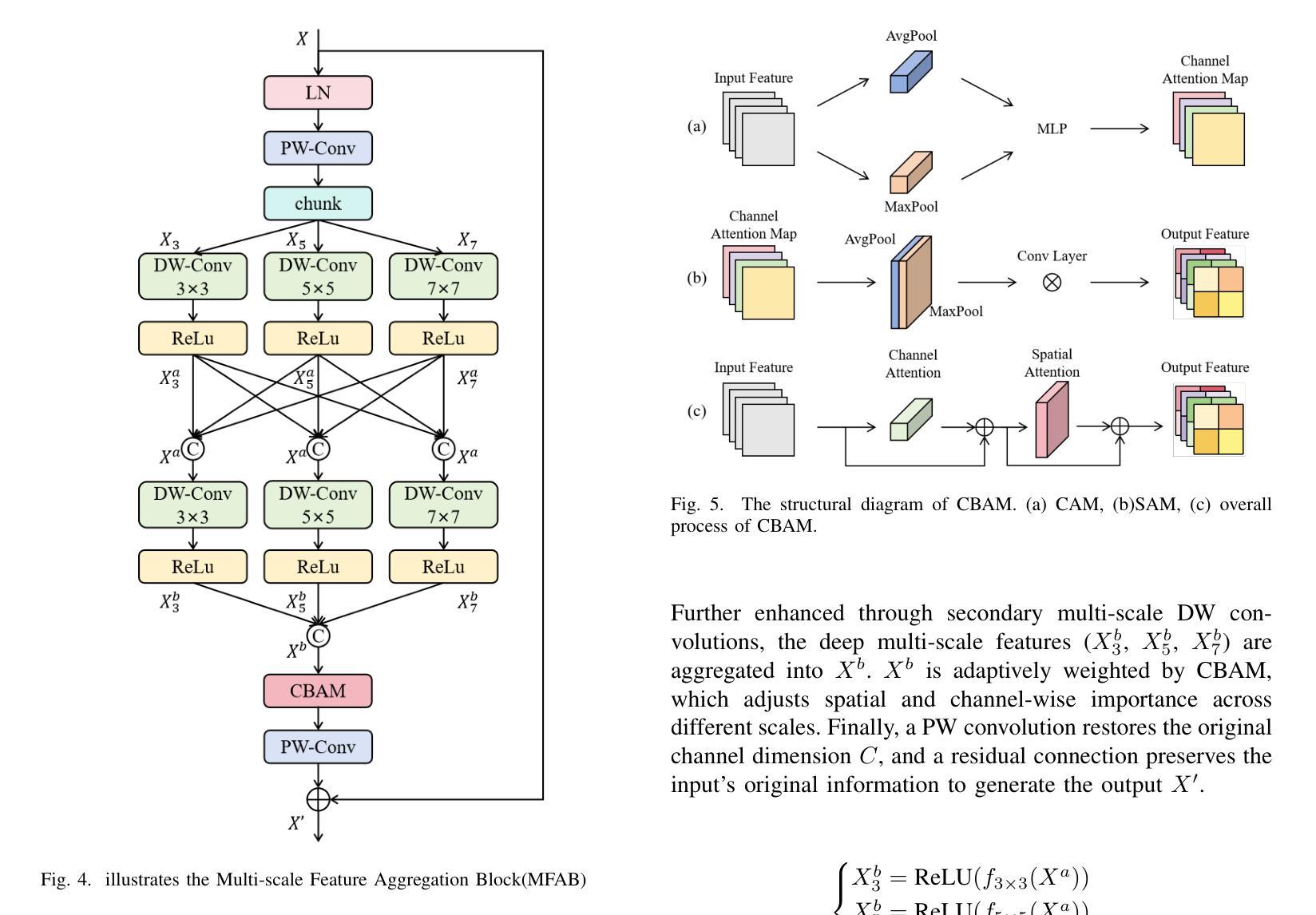
Remote Sensing Image Super-Resolution (RSISR) reconstructs high-resolution (HR) remote sensing images from low-resolution inputs to support fine-grained ground object interpretation. Existing methods face three key challenges: (1) Difficulty in extracting multi-scale features from spatially heterogeneous RS scenes, (2) Limited prior information causing semantic inconsistency in reconstructions, and (3) Trade-off imbalance between geometric accuracy and visual quality. To address these issues, we propose the Texture Transfer Residual Denoising Dual Diffusion Model (TTRD3) with three innovations: First, a Multi-scale Feature Aggregation Block (MFAB) employing parallel heterogeneous convolutional kernels for multi-scale feature extraction. Second, a Sparse Texture Transfer Guidance (STTG) module that transfers HR texture priors from reference images of similar scenes. Third, a Residual Denoising Dual Diffusion Model (RDDM) framework combining residual diffusion for deterministic reconstruction and noise diffusion for diverse generation. Experiments on multi-source RS datasets demonstrate TTRD3’s superiority over state-of-the-art methods, achieving 1.43% LPIPS improvement and 3.67% FID enhancement compared to best-performing baselines. Code/model: https://github.com/LED-666/TTRD3.
遥感图像超分辨率(RSISR)技术从低分辨率的输入中重建高分辨率(HR)的遥感图像,以支持精细地面对象的解读。现有方法面临三个主要挑战:(1)从空间异质的遥感场景中提取多尺度特征的困难;(2)有限的先验信息导致重建中的语义不一致;(3)几何精度与视觉质量之间的权衡失衡。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了具有三项创新的纹理转移残差去噪双重扩散模型(TTRD3):首先,采用并行异构卷积核的多尺度特征聚合块(MFAB),用于多尺度特征提取。其次,提出了稀疏纹理转移指导(STTG)模块,该模块从类似场景的参考图像中转移高分辨率纹理先验。第三,结合残差扩散进行确定性重建和噪声扩散进行多样化生成的残差去噪双重扩散模型(RDDM)框架。在多源遥感数据集上的实验表明,TTRD3优于最新方法,与最佳基线相比,实现了1.43%的LPIPS改进和3.67%的FID提升。代码/模型:https://github.com/LED-666/TTRD3。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
远程遥感图像超分辨率重建技术旨在从低分辨率图像重建出高分辨率图像,以支持精细地面目标解读。针对现有方法面临的多尺度特征提取难、语义不一致和几何精度与视觉质量平衡难题,提出纹理传输残差去噪双重扩散模型(TTRD3)。该模型包括多尺度特征聚合块、稀疏纹理传输引导模块和残差去噪双重扩散框架。实验表明,TTRD3在多源遥感数据集上优于现有方法,实现了性能的提升。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像超分辨率重建(RSISR)旨在从低分辨率图像重建高分辨率图像,以促进精细地面目标解读。
- 现有方法面临三大挑战:多尺度特征提取难、语义不一致以及几何精度与视觉质量的平衡问题。
- TTRD3模型通过多尺度特征聚合块提取多尺度特征,采用稀疏纹理传输引导模块转移高分辨率纹理先验信息。
- TTRD3模型结合残差扩散进行确定性重建和噪声扩散进行多样生成的RDDM框架。
- 实验证明,TTRD3在多源遥感数据集上的性能优于现有方法,实现了LPIPS改进1.43%,FID提升3.67%。
- TTRD3模型的代码和模型已公开,可访问https://github.com/LED-666/TTRD3获取。
点此查看论文截图


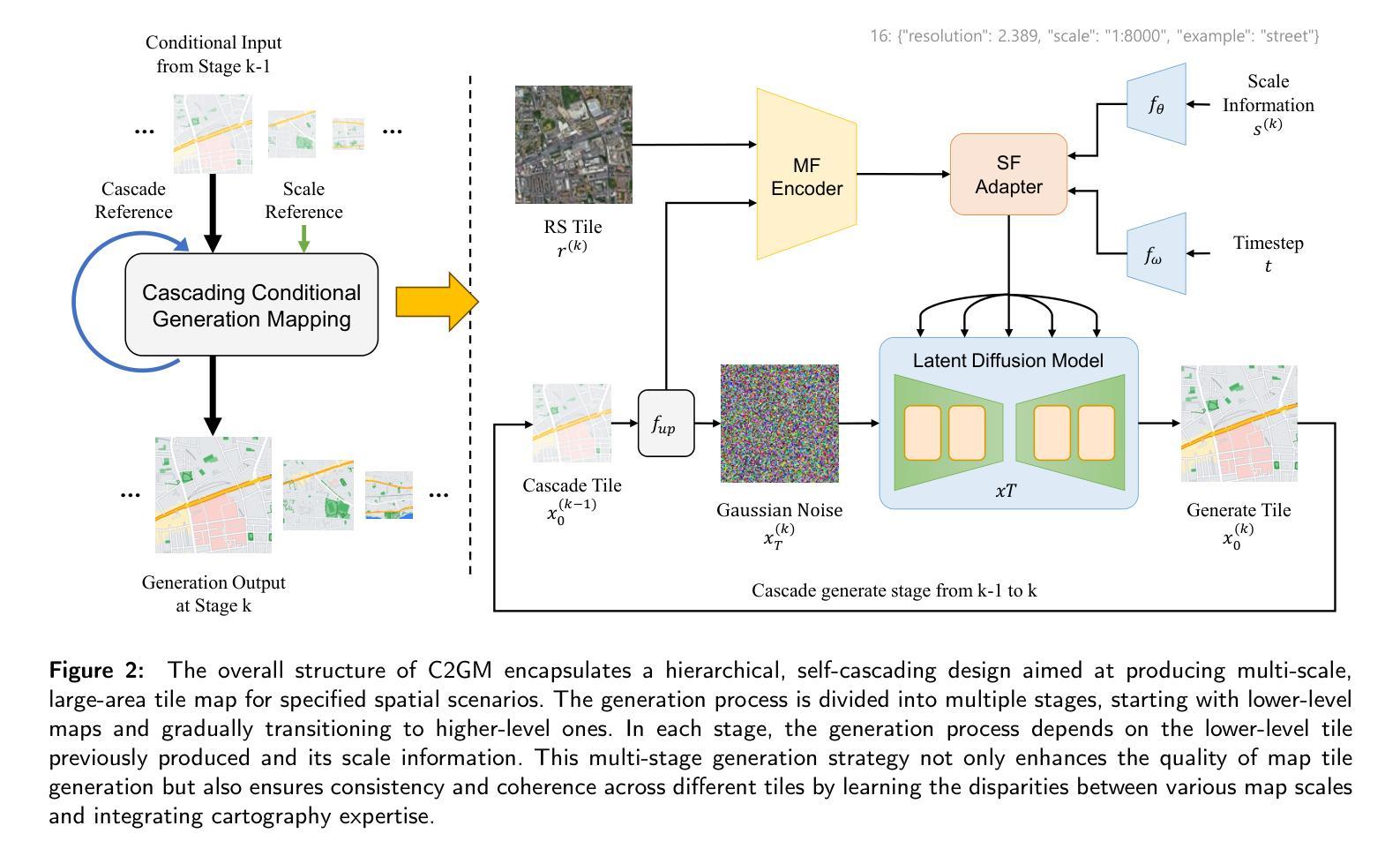
C2GM: Cascading conditional generative cartography framework for multi-scale tile map generation with geographic feature constraints
Authors:Chenxing Sun, Yongyang Xu, Xuwei Xu, Xixi Fan, Jing Bai, Xiechun Lu, Zhanlong Chen
Multi-scale maps are essential representations of surveying and cartographic results, serving as fundamental components of geographic services. Current image generation networks can quickly produce map tiles from remote-sensing images. However, generative models designed for natural images often focus on texture features, neglecting the unique characteristics of remote-sensing features and the scale attributes of tile maps. This limitation in generative models impairs the accurate representation of geographic information, and the quality of tile map generation still needs improvement. Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable success in various image generation tasks, highlighting their potential to address this challenge. This paper presents C2GM, a novel framework for generating multi-scale tile maps through conditional guided diffusion and multi-scale cascade generation. Specifically, we implement a conditional feature fusion encoder to extract object priors from remote sensing images and cascade reference double branch input, ensuring an accurate representation of complex features. Low-level generated tiles act as constraints for high-level map generation, enhancing visual continuity. Moreover, we incorporate map scale modality information using CLIP to simulate the relationship between map scale and cartographic generalization in tile maps. Extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that C2GM consistently achieves the state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on all metrics, facilitating the rapid and effective generation of multi-scale large-format maps for emergency response and remote mapping applications.
多尺度地图是测绘和地图制作结果的重要表现形式,也是地理服务的基本组成部分。当前的图像生成网络能够快速地从遥感图像中生成地图瓦片。然而,针对自然图像设计的生成模型通常更注重纹理特征,而忽略了遥感特征的独特性以及瓦地图的尺度属性。生成模型的这一局限性影响了地理信息的准确表示,瓦片地图生成的质量仍有待提高。扩散模型在各种图像生成任务中表现出了显著的成功,突显了其解决这一挑战的潜力。本文提出了一种新的生成多尺度瓦片地图的框架C2GM,该框架通过条件引导扩散和多尺度级联生成实现。具体来说,我们实现了条件特征融合编码器,从遥感图像中提取对象先验,并采用级联参考双分支输入,以确保复杂特征的准确表示。低级生成的瓦片作为高级地图生成的约束,增强了视觉连续性。此外,我们利用CLIP结合地图尺度模态信息,模拟瓦片地图中地图尺度和制图概括之间的关系。大量的实验评估表明,C2GM在所有指标上均达到最新技术水平,可实现快速有效地生成多尺度大幅面地图,用于应急响应和远程映射应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多尺度地图是测绘和地图成果的重要表现形式,也是地理服务的基本组成部分。当前图像生成网络能够从遥感图像快速生成地图瓦片,但为自然图像设计的生成模型往往关注纹理特征,忽略了遥感特征的独特性以及地图瓦片的尺度属性。这限制了生成模型对地理信息准确表达的能力,地图瓦片生成的质量仍有待提高。本文提出一种基于扩散模型的新型框架C2GM,通过条件引导扩散和多尺度级联生成技术生成多尺度地图瓦片。实验证明,C2GM在各项指标上均达到最佳效果,能够快速有效地用于生成多尺度大幅面地图,为应急响应和遥感应用提供支持。
Key Takeaways
- 多尺度地图在地理服务中起重要作用,用于表达测绘和地图成果。
- 当前图像生成网络能够从遥感图像生成地图瓦片,但存在对地理信息表达不准确的局限性。
- 生成模型在关注纹理特征的同时忽略了遥感特征的独特性和地图瓦片的尺度属性。
- 扩散模型在图像生成任务中表现出显著成功,具有解决此挑战的潜力。
- C2GM框架通过条件引导扩散和多尺度级联生成技术解决多尺度地图瓦片生成问题。
- C2GM使用条件特征融合编码器和级联参考双分支输入,确保复杂特征的准确表达。
点此查看论文截图

Good Seed Makes a Good Crop: Discovering Secret Seeds in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Katherine Xu, Lingzhi Zhang, Jianbo Shi
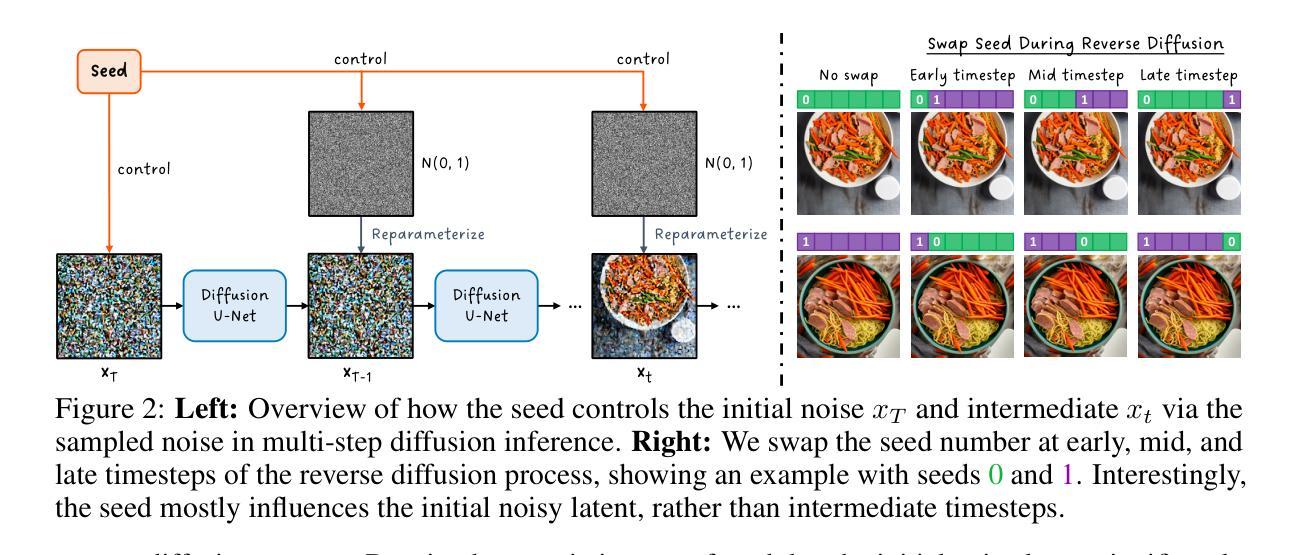
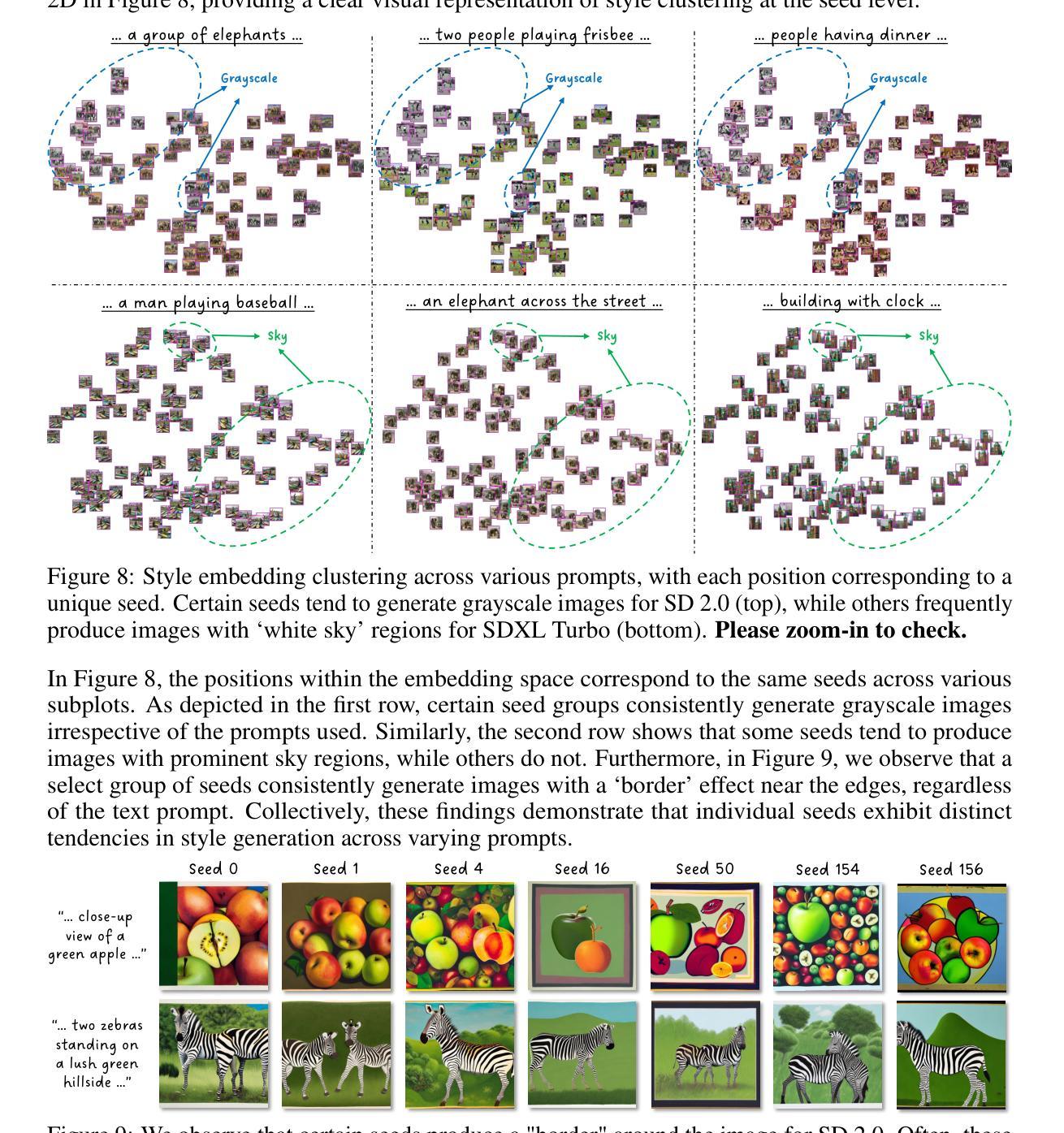
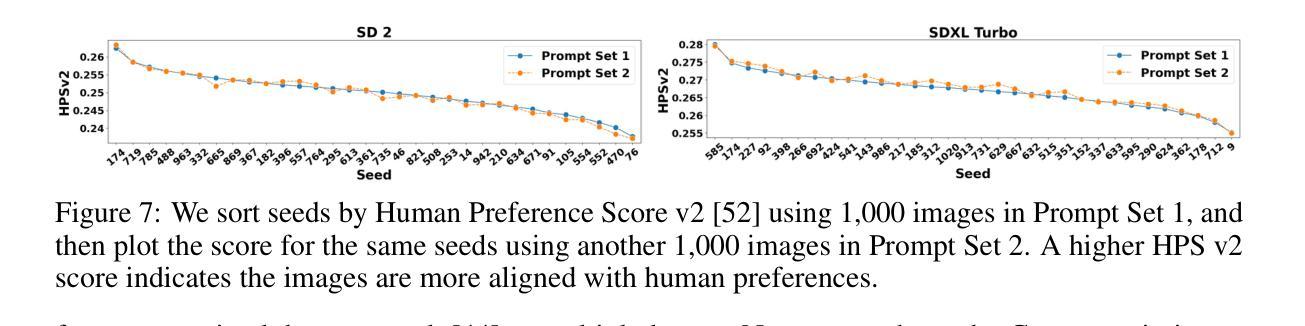
Recent advances in text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have facilitated creative and photorealistic image synthesis. By varying the random seeds, we can generate many images for a fixed text prompt. Technically, the seed controls the initial noise and, in multi-step diffusion inference, the noise used for reparameterization at intermediate timesteps in the reverse diffusion process. However, the specific impact of the random seed on the generated images remains relatively unexplored. In this work, we conduct a large-scale scientific study into the impact of random seeds during diffusion inference. Remarkably, we reveal that the best ‘golden’ seed achieved an impressive FID of 21.60, compared to the worst ‘inferior’ seed’s FID of 31.97. Additionally, a classifier can predict the seed number used to generate an image with over 99.9% accuracy in just a few epochs, establishing that seeds are highly distinguishable based on generated images. Encouraged by these findings, we examined the influence of seeds on interpretable visual dimensions. We find that certain seeds consistently produce grayscale images, prominent sky regions, or image borders. Seeds also affect image composition, including object location, size, and depth. Moreover, by leveraging these ‘golden’ seeds, we demonstrate improved image generation such as high-fidelity inference and diversified sampling. Our investigation extends to inpainting tasks, where we uncover some seeds that tend to insert unwanted text artifacts. Overall, our extensive analyses highlight the importance of selecting good seeds and offer practical utility for image generation.
最近文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的进展促进了创造性且逼真的图像合成。通过改变随机种子,我们可以为固定的文本提示生成许多图像。从技术上讲,种子控制初始噪声,并且在多步扩散推断中,用于反向扩散过程中中间时间点的重新参数化的噪声。然而,关于随机种子对生成图像的具体影响尚未得到充分探索。在这项工作中,我们对扩散推断过程中的随机种子影响进行了大规模的科学研究。值得注意的是,我们发现最佳“黄金”种子取得了令人印象深刻的FID(Frechet Inception Distance)得分21.60,而最差的“低级”种子的FID为31.97。此外,分类器能够以超过99.9%的准确率预测用于生成图像的种子编号,这表明基于生成的图像,种子之间具有高度可区分性。基于这些发现,我们考察了种子对可解释的视觉维度的影响。我们发现某些种子会始终产生灰度图像、突出的天空区域或图像边界。种子还会影响图像构图,包括物体位置、大小和深度。此外,通过利用这些“黄金”种子,我们展示了改进的图像生成,如高保真推断和多样化采样。我们的调查还扩展到图像修复任务,我们发现某些种子倾向于插入不需要的文本伪影。总体而言,我们广泛的分析强调了选择良好种子的重要性,并为图像生成提供了实际效用。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的最新进展促进了创造性与逼真的图像合成。通过改变随机种子,我们可以为固定的文本提示生成多个图像。技术上,种子控制初始噪声,并在多步扩散推断中,用于反向扩散过程中间时步的重新参数化的噪声。然而,关于随机种子对生成图像的具体影响尚未得到充分探索。在这项工作中,我们对扩散推断过程中随机种子的影响进行了大规模的科学研究。值得注意的是,我们发现了最佳的“黄金”种子,其FID达到了令人印象深刻的21.60,而最差“劣质”种子的FID为31.97。此外,分类器可以在仅仅几个epoch内以超过99.9%的准确率预测用于生成图像的种子编号,这证明了基于生成的图像,种子之间的区分度极高。受这些发现的鼓舞,我们研究了种子对可解释的视觉维度的影响。我们发现某些种子会一致地产生灰度图像、突出的天空区域或图像边界。种子还会影响图像构图,包括对象的位置、大小和深度。此外,通过利用这些“黄金”种子,我们展示了改进的图像生成,如高保真推断和多样化的采样。我们的调查还扩展到了修复任务,在那里我们发现某些种子倾向于插入不需要的文本伪影。总的来说,我们深入的分析强调了选择良好种子的重要性,并为图像生成提供了实际效用。
要点
- 文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的最新进展推动了创造性与逼真的图像合成的发展。
- 随机种子在生成图像中具有显著影响,最佳“黄金”种子能生成高质量的图像。
- 通过分类器预测生成图像的种子编号,证明了种子之间的区分度极高。
- 种子影响图像的多方面特征,如灰度、天空区域、图像边界、对象位置、大小和深度。
- 利用“黄金”种子可改进图像生成,包括高保真推断和多样化采样。
- 在修复任务中,某些种子可能产生不需要的文本伪影。
点此查看论文截图



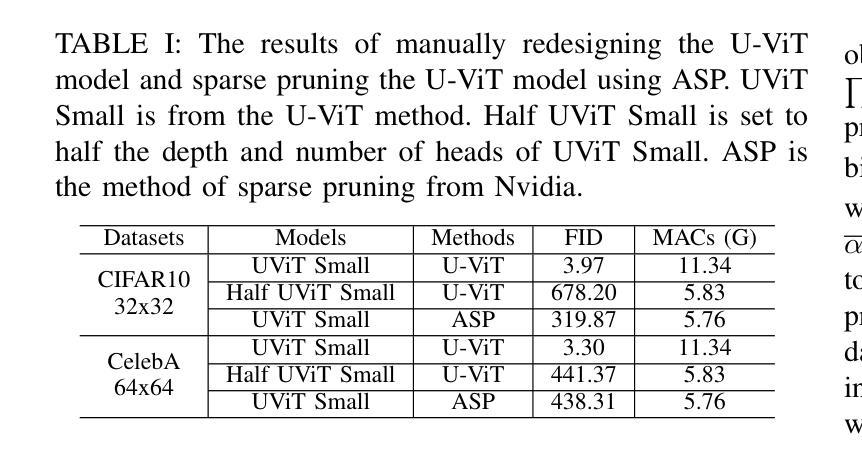
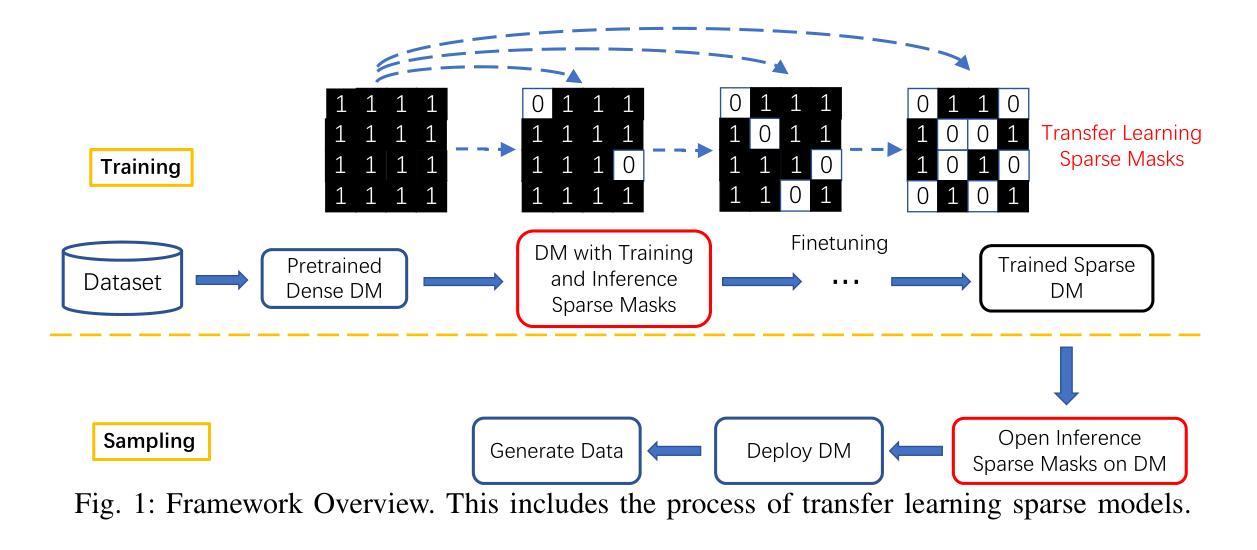
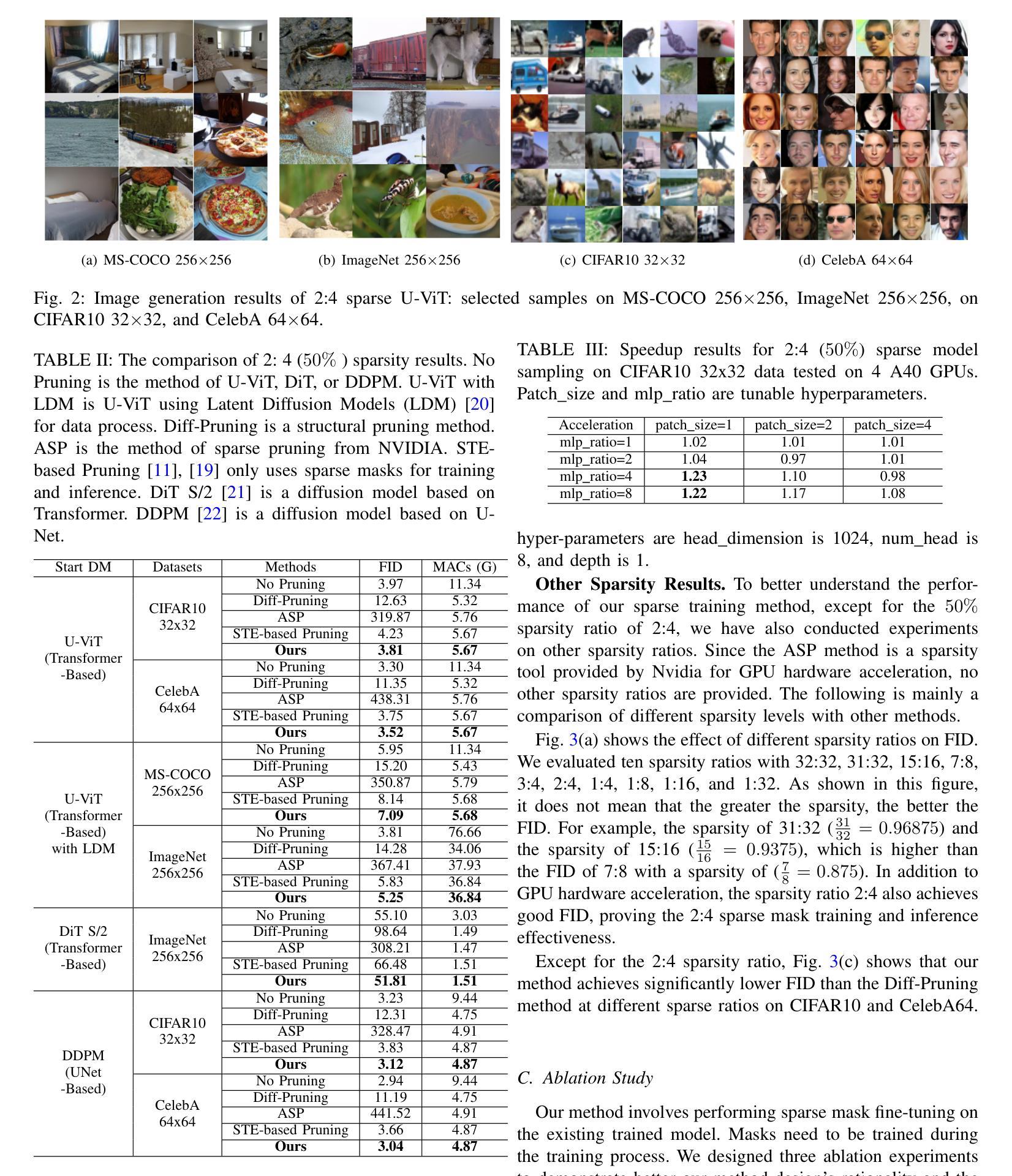
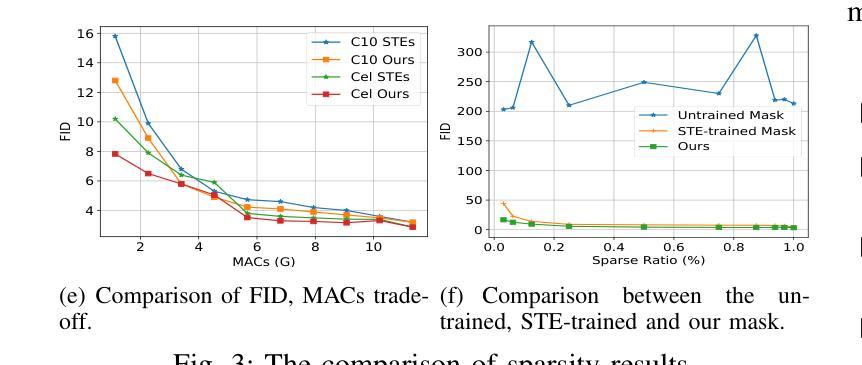
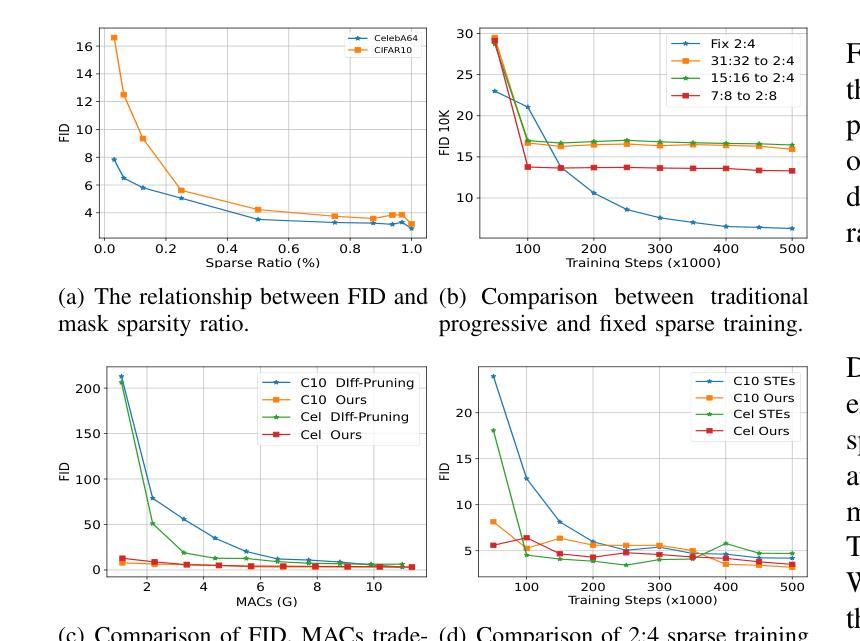
SparseDM: Toward Sparse Efficient Diffusion Models
Authors:Kafeng Wang, Jianfei Chen, He Li, Zhenpeng Mi, Jun Zhu
Diffusion models represent a powerful family of generative models widely used for image and video generation. However, the time-consuming deployment, long inference time, and requirements on large memory hinder their applications on resource constrained devices. In this paper, we propose a method based on the improved Straight-Through Estimator to improve the deployment efficiency of diffusion models. Specifically, we add sparse masks to the Convolution and Linear layers in a pre-trained diffusion model, then transfer learn the sparse model during the fine-tuning stage and turn on the sparse masks during inference. Experimental results on a Transformer and UNet-based diffusion models demonstrate that our method reduces MACs by 50% while maintaining FID. Sparse models are accelerated by approximately 1.2x on the GPU. Under other MACs conditions, the FID is also lower than 1 compared to other methods.
扩散模型是一种强大的生成模型家族,广泛应用于图像和视频生成。然而,其耗时的部署、长的推理时间以及对大内存的要求,阻碍了其在资源受限设备上的应用。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于改进后的直通估计器的方法,以提高扩散模型的部署效率。具体来说,我们在预训练的扩散模型的卷积和线性层中添加稀疏掩码,然后在微调阶段对稀疏模型进行迁移学习,并在推理阶段启用稀疏掩码。在基于Transformer和UNet的扩散模型上的实验结果表明,我们的方法将乘加运算(MACs)减少了50%,同时保持了FID。稀疏模型在GPU上的速度提高了大约1.2倍。在其他MACs条件下,与其他方法相比,FID也低于1。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by ICME 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于改进直通估计器的方法,用于提高扩散模型的部署效率。通过在预训练的扩散模型中的卷积和线性层添加稀疏掩码,然后进行微调阶段的迁移学习,并在推理阶段启用稀疏掩码,实验结果表明,该方法在保持FID不变的情况下,将MACs降低了50%,并实现了GPU上的近似1.2倍加速。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型广泛应用于图像和视频生成,但其在资源受限设备上的部署存在时间消耗长、推理时间长和大内存要求等问题。
- 本文提出一种基于改进直通估计器的方法来提高扩散模型的部署效率。
- 通过添加稀疏掩码到预训练的扩散模型中的卷积和线性层,然后进行迁移学习,实验结果表明能够降低计算复杂度(MACs)并加速推理。
- 方法在保持图像质量(FID)不变的情况下,将计算量降低了50%。
- 在GPU上实现了近似1.2倍的加速效果。
- 在不同的计算条件下,该方法的FID低于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

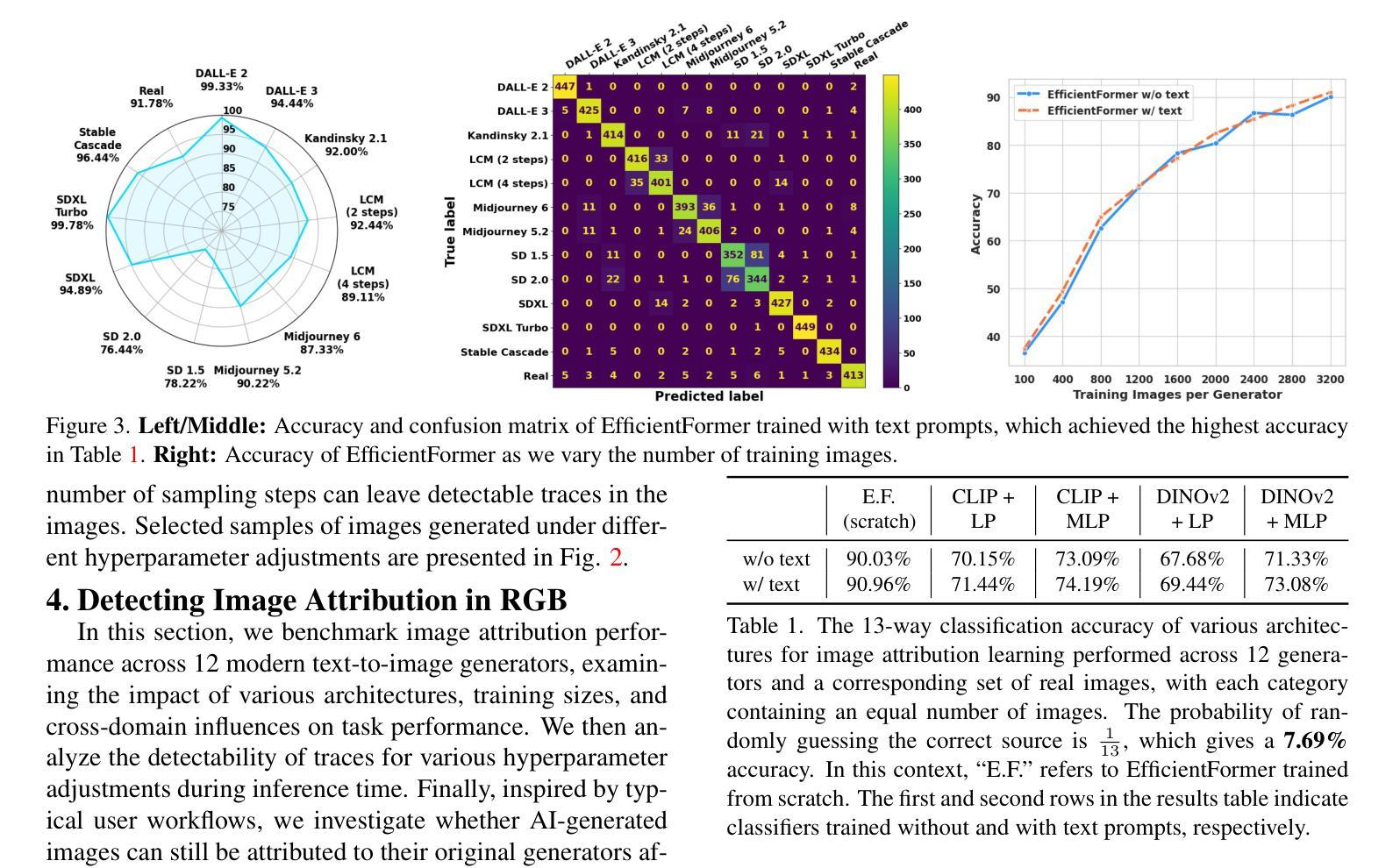
Detecting Origin Attribution for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Katherine Xu, Lingzhi Zhang, Jianbo Shi
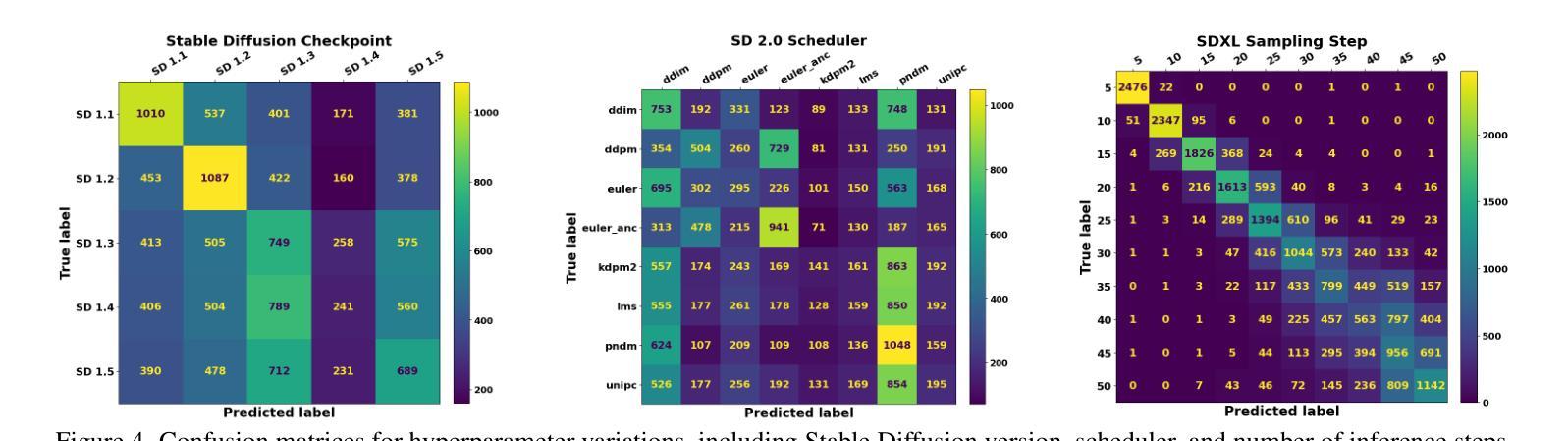
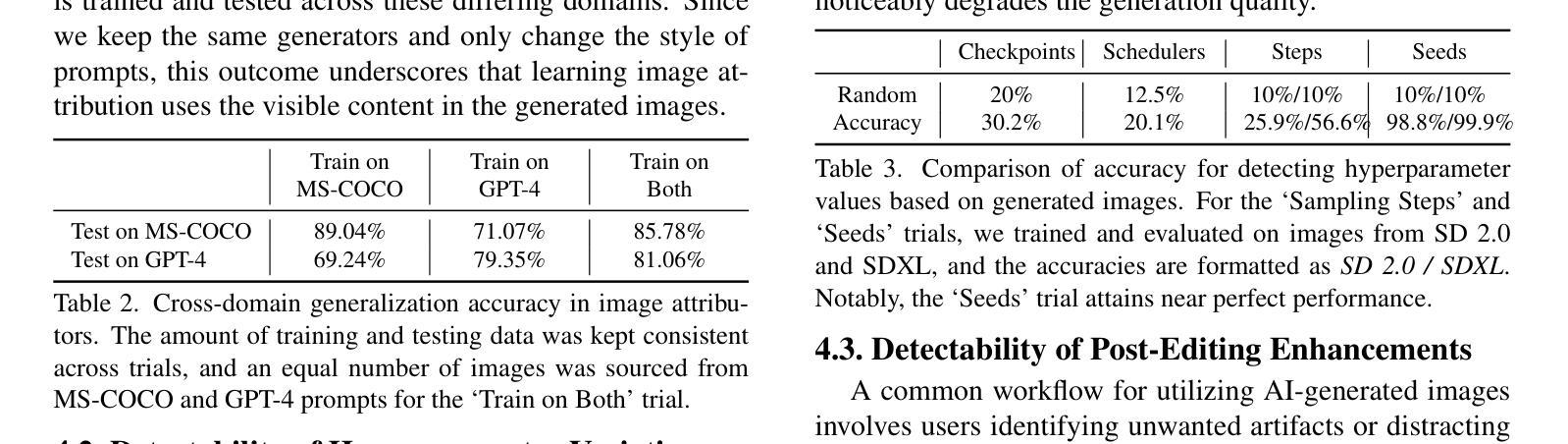
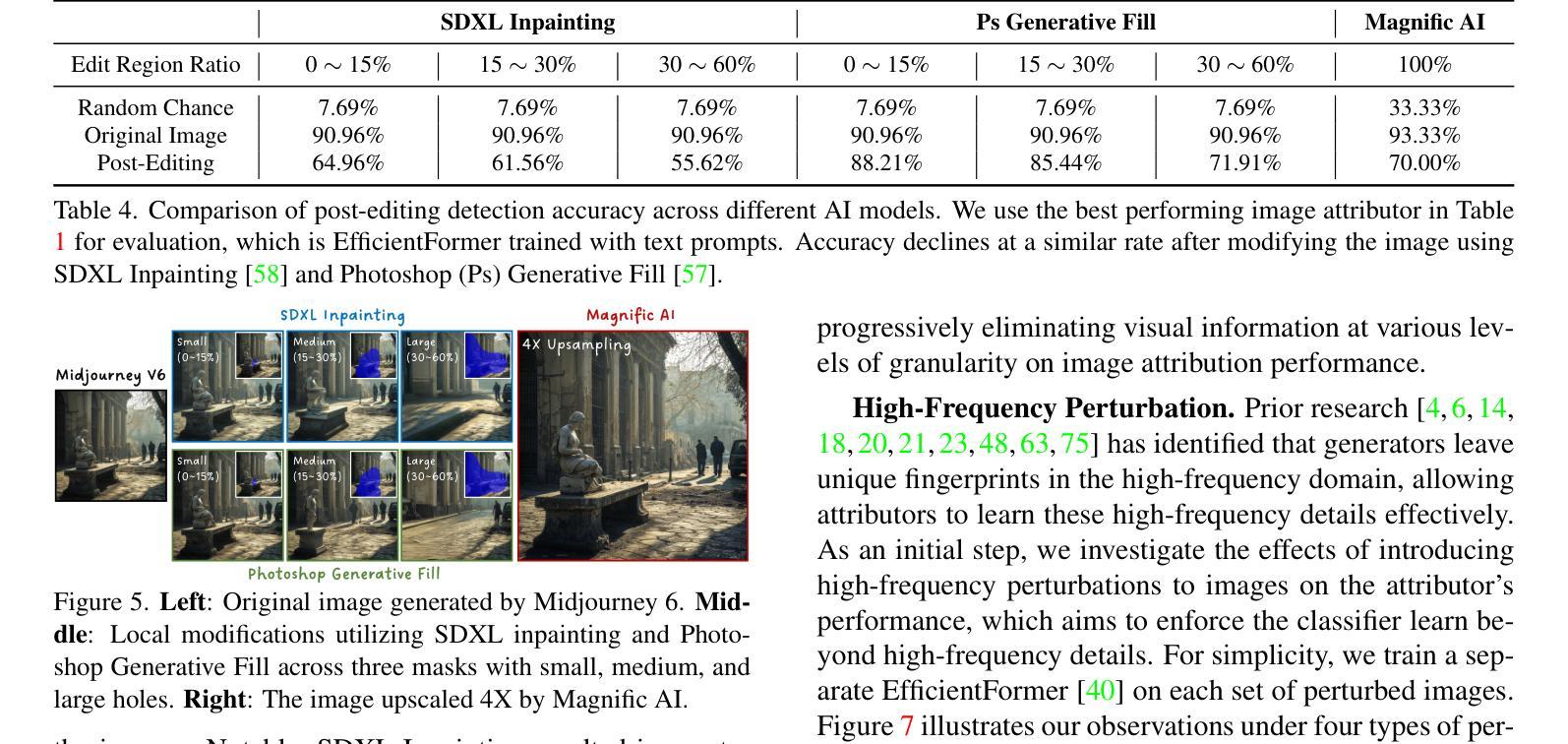
Modern text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models can generate images with remarkable realism and creativity. These advancements have sparked research in fake image detection and attribution, yet prior studies have not fully explored the practical and scientific dimensions of this task. In addition to attributing images to 12 state-of-the-art T2I generators, we provide extensive analyses on what inference stage hyperparameters and image modifications are discernible. Our experiments reveal that initialization seeds are highly detectable, along with other subtle variations in the image generation process to some extent. We further investigate what visual traces are leveraged in image attribution by perturbing high-frequency details and employing mid-level representations of image style and structure. Notably, altering high-frequency information causes only slight reductions in accuracy, and training an attributor on style representations outperforms training on RGB images. Our analyses underscore that fake images are detectable and attributable at various levels of visual granularity.
现代文本到图像(T2I)的扩散模型能够生成具有显著真实感和创造力的图像。这些进展引发了关于虚假图像检测和归属的研究,但先前的研究并未完全探索此任务的实际和科学层面。除了将图像归于12种最先进的T2I生成器之外,我们还对推理阶段超参数和图像修改的可识别性进行了广泛的分析。我们的实验表明,初始化种子是高度可检测的,图像生成过程中的其他细微变化也在一定程度上可检测。我们通过扰动高频细节并采用图像风格和结构的中级表示,进一步调查图像归属中利用了什么视觉痕迹。值得注意的是,改变高频信息只会略微降低准确性,而且在风格表示上训练归属者优于在RGB图像上训练。我们的分析强调,虚假图像在各种视觉粒度级别上都是可检测和可归属的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code available at https://github.com/k8xu/ImageAttribution
Summary
本文探讨了现代文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型生成的图像的检测与归因问题。研究发现,除了能将图像归因于先进的T2I生成器之外,通过调整推断阶段的超参数和图像修改,可以检测出生成图像的初始化种子等细微变化。同时,通过对图像风格和结构的中级表示进行扰动,发现视觉痕迹在图像归因中的利用方式。实验表明,改变高频信息对准确率影响较小,而以风格表征训练归因器的方法优于以RGB图像训练的方法。研究强调,在视觉粒度不同层面,假图像是可检测和可归因的。
Key Takeaways
- 现代文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型可以生成非常逼真和具有创意的图像。
- T2I生成的图像的检测与归因问题引起了研究关注。
- 通过调整推断阶段的超参数和图像修改,可以检测出生成图像的初始化种子等细微变化。
- 初始化种子在图像生成过程中的检测是一个关键。
- 通过对图像风格和结构的中级表示进行扰动,揭示了视觉痕迹在图像归因中的重要性。
- 改变高频信息对假图像检测与归因的准确性影响较小。
点此查看论文截图