⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-19 更新
Can Masked Autoencoders Also Listen to Birds?
Authors:Lukas Rauch, Ilyass Moummad, René Heinrich, Alexis Joly, Bernhard Sick, Christoph Scholz
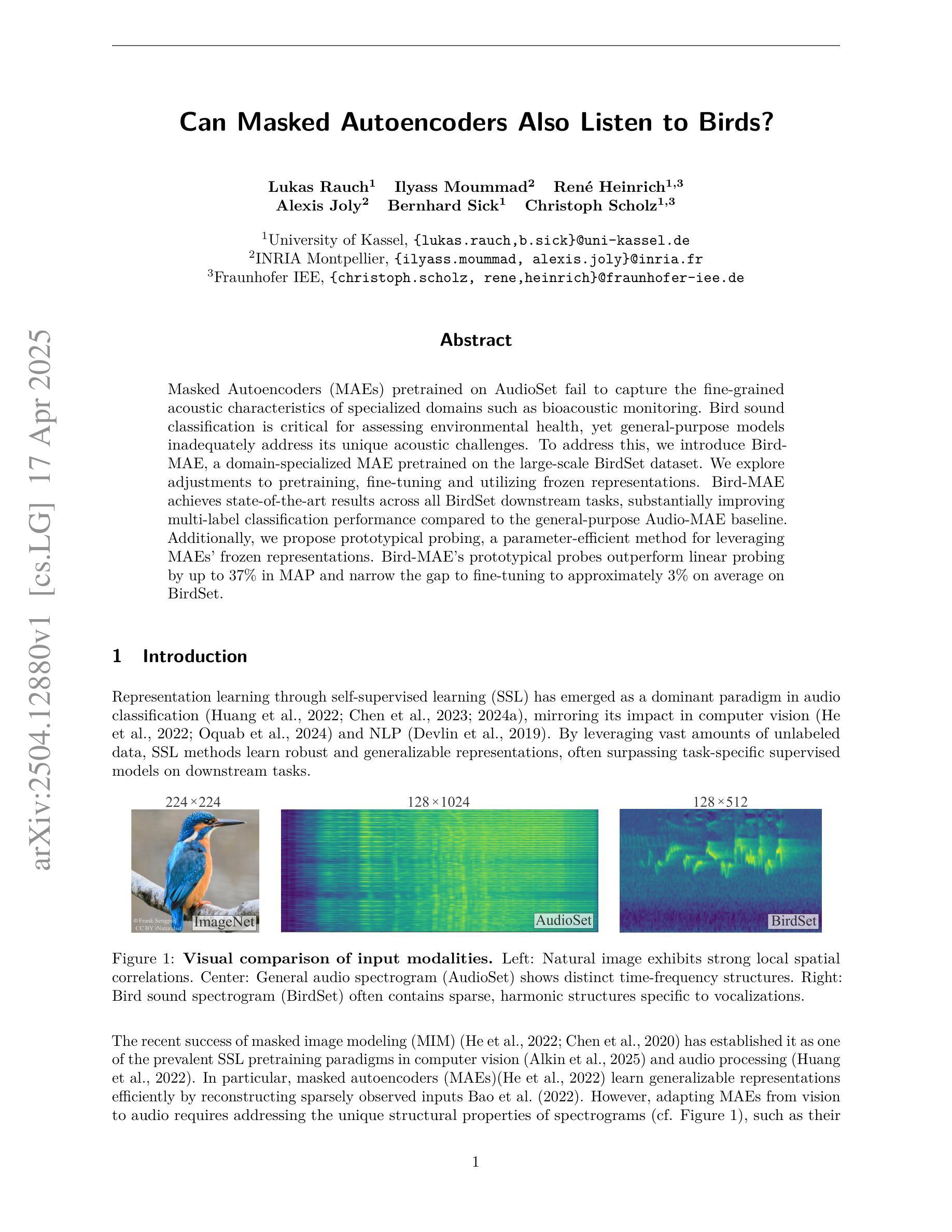
Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) pretrained on AudioSet fail to capture the fine-grained acoustic characteristics of specialized domains such as bioacoustic monitoring. Bird sound classification is critical for assessing environmental health, yet general-purpose models inadequately address its unique acoustic challenges. To address this, we introduce Bird-MAE, a domain-specialized MAE pretrained on the large-scale BirdSet dataset. We explore adjustments to pretraining, fine-tuning and utilizing frozen representations. Bird-MAE achieves state-of-the-art results across all BirdSet downstream tasks, substantially improving multi-label classification performance compared to the general-purpose Audio-MAE baseline. Additionally, we propose prototypical probing, a parameter-efficient method for leveraging MAEs’ frozen representations. Bird-MAE’s prototypical probes outperform linear probing by up to 37% in MAP and narrow the gap to fine-tuning to approximately 3% on average on BirdSet.
基于AudioSet预训练的Masked Autoencoders(MAEs)无法捕获生物声学监测等特定领域的精细声学特征。鸟类声音分类对于评估环境健康至关重要,但通用模型不足以应对其独特的声学挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了Bird-MAE,这是一个在大型BirdSet数据集上预训练的领域专用MAE。我们探讨了预训练、微调和使用冻结表示的调整方法。Bird-MAE在所有BirdSet下游任务中都实现了最佳结果,与通用Audio-MAE基线相比,多标签分类性能得到了实质性提升。此外,我们提出了原型探测(prototypical probing),这是一种利用MAEs冻结表示的参数高效方法。Bird-MAE的原型探针在MAP上的表现比线性探针高出高达37%,并将与微调在BirdSet上的差距缩小到平均约3%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练于AudioSet的Masked Autoencoders(MAEs)在特定领域如生物声监测中无法捕捉精细的声学特征。为解决通用模型在鸟声分类中的不足,我们引入了针对大型鸟集数据集BirdSet的域专业化MAE——Bird-MAE。通过调整预训练、微调和使用冻结表示的方法,Bird-MAE在所有BirdSet下游任务中实现了最先进的成果,与通用Audio-MAE基线相比,多标签分类性能得到了显著提高。此外,我们还提出了原型探针法,这是一种利用MAE冻结表示的参数量高效方法。Bird-MAE的原型探针在MAP上的表现优于线性探针高达37%,并将与微调在BirdSet上的差距缩小到平均约3%。
Key Takeaways
- MAEs预训练于AudioSet无法捕捉特定领域的精细声学特征,如生物声监测。
- 鸟声分类对评估环境健康至关重要,但通用模型无法满足其独特声学挑战。
- 引入针对BirdSet数据集的域专业化MAE——Bird-MAE。
- Bird-MAE在所有BirdSet下游任务中实现最先进成果,多标签分类性能显著提高。
- 提出原型探针法,利用MAE冻结表示,参数量效率更高。
- Bird-MAE的原型探针在MAP上的表现优于线性探针。
点此查看论文截图
“It Listens Better Than My Therapist”: Exploring Social Media Discourse on LLMs as Mental Health Tool
Authors:Anna-Carolina Haensch
The emergence of generative AI chatbots such as ChatGPT has prompted growing public and academic interest in their role as informal mental health support tools. While early rule-based systems have been around for several years, large language models (LLMs) offer new capabilities in conversational fluency, empathy simulation, and availability. This study explores how users engage with LLMs as mental health tools by analyzing over 10,000 TikTok comments from videos referencing LLMs as mental health tools. Using a self-developed tiered coding schema and supervised classification models, we identify user experiences, attitudes, and recurring themes. Results show that nearly 20% of comments reflect personal use, with these users expressing overwhelmingly positive attitudes. Commonly cited benefits include accessibility, emotional support, and perceived therapeutic value. However, concerns around privacy, generic responses, and the lack of professional oversight remain prominent. It is important to note that the user feedback does not indicate which therapeutic framework, if any, the LLM-generated output aligns with. While the findings underscore the growing relevance of AI in everyday practices, they also highlight the urgent need for clinical and ethical scrutiny in the use of AI for mental health support.
随着ChatGPT等生成式AI聊天机器人的出现,公众和学术界对其在心理健康支持工具方面的作用越来越感兴趣。虽然早期的基于规则的系统已经存在几年了,但大型语言模型(LLM)在会话流畅度、共情模拟和可用性方面提供了新的能力。本研究通过分析超过10,000条来自TikTok上提及LLM作为心理健康工具的视频评论,探讨了用户如何利用LLM作为心理健康工具。我们使用自行开发的分层编码架构和监督分类模型来识别用户经验、态度和反复出现的主题。结果显示,近20%的评论反映了个人使用,这些用户表达的态度几乎是积极的。常见的益处包括可及性、情感支持和感知到的治疗价值。然而,关于隐私、通用响应和缺乏专业监督的担忧仍然突出。值得注意的是,用户反馈并不能表明LLM生成的输出是否与任何治疗框架相符。虽然这些发现强调了AI在日常实践中的日益重要性,但它们也突出了在心理健康支持中使用AI进行临床和道德审查的迫切需求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This study does not endorse or encourage the use of AI tools as substitutes for professional mental health support. The findings are presented for research purposes only, and any interpretation should take into account the limitations and potential risks of relying on AI in mental health contexts
Summary
随着ChatGPT等生成式人工智能聊天机器人的出现,公众和学术界对其在心理健康支持工具方面的作用越来越感兴趣。相比早期的基于规则的系统,大型语言模型(LLMs)在会话流畅度、情感模拟和可用性方面提供了新的能力。本研究通过分析超过10,000条关于LLMs作为心理健康工具的视频TikTok评论,探索用户如何与之互动。结果表明,近20%的评论反映了个人使用经验,这些用户表达了压倒性的积极态度。常见的益处包括可访问性、情感支持和感知到的治疗价值。然而,隐私、通用响应和缺乏专业监督的担忧仍然突出。用户反馈并不表明LLM生成的输出与哪种治疗框架相符。虽然这些发现强调了人工智能在日常实践中的日益重要性,但它们也突显了对人工智能用于心理健康支持的临床和道德审查的迫切需求。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式人工智能聊天机器人(如ChatGPT)在心理健康支持工具方面的作用引起了公众和学术界的广泛关注。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)提供了会话流畅度、情感模拟和可用性方面的新能力。
- 用户对LLMs作为心理健康工具持积极态度,常见的益处包括可访问性、情感支持和感知到的治疗价值。
- 存在关于隐私、通用响应和缺乏专业监督的担忧。
- 用户反馈并未明确显示LLM生成的输出与特定治疗框架的关联。
- 人工智能在日常心理健康实践中的应用日益重要。
点此查看论文截图

OnRL-RAG: Real-Time Personalized Mental Health Dialogue System
Authors:Ahsan Bilal, Beiyu Lin
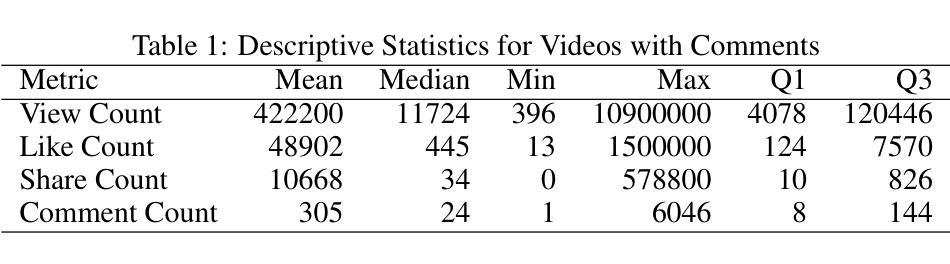
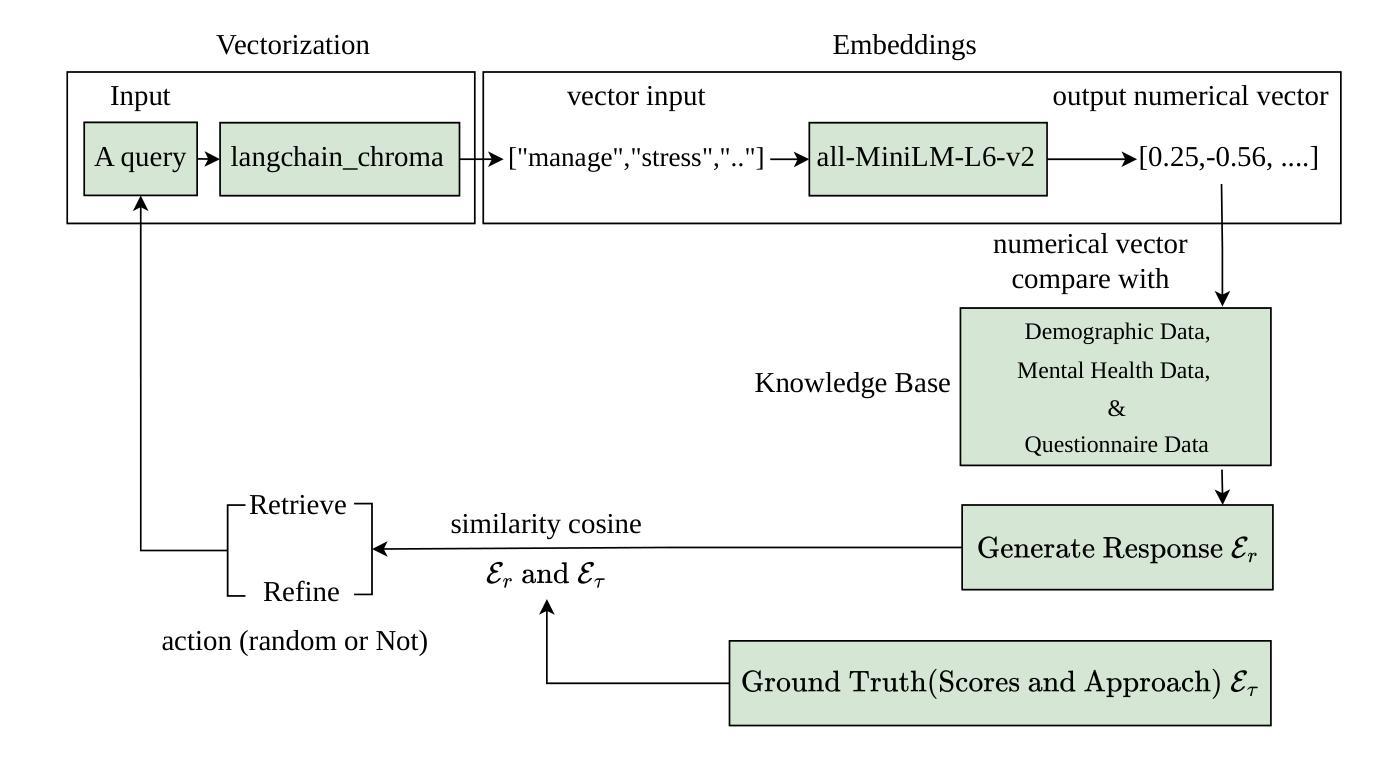
Large language models (LLMs) have been widely used for various tasks and applications. However, LLMs and fine-tuning are limited to the pre-trained data. For example, ChatGPT’s world knowledge until 2021 can be outdated or inaccurate. To enhance the capabilities of LLMs, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), is proposed to augment LLMs with additional, new, latest details and information to LLMs. While RAG offers the correct information, it may not best present it, especially to different population groups with personalizations. Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) adapts to user needs by aligning model responses with human preference through feedback loops. In real-life applications, such as mental health problems, a dynamic and feedback-based model would continuously adapt to new information and offer personalized assistance due to complex factors fluctuating in a daily environment. Thus, we propose an Online Reinforcement Learning-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (OnRL-RAG) system to detect and personalize the responding systems to mental health problems, such as stress, anxiety, and depression. We use an open-source dataset collected from 2028 College Students with 28 survey questions for each student to demonstrate the performance of our proposed system with the existing systems. Our system achieves superior performance compared to standard RAG and simple LLM via GPT-4o, GPT-4o-mini, Gemini-1.5, and GPT-3.5. This work would open up the possibilities of real-life applications of LLMs for personalized services in the everyday environment. The results will also help researchers in the fields of sociology, psychology, and neuroscience to align their theories more closely with the actual human daily environment.
大型语言模型(LLMs)已广泛应用于各种任务和应用。然而,LLMs和微调都受限于预训练数据。例如,ChatGPT截至2021年的世界知识可能已过时或不准确。为了增强LLMs的功能,提出了检索增强生成(RAG)来向LLMs添加额外、最新、详细的资讯。虽然RAG提供了正确的信息,但它可能无法最佳地呈现它,尤其是对于具有个性化的不同人群。强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)通过反馈循环使模型响应与人类偏好对齐,从而适应用户需求。在现实生活应用,如心理健康问题中,一个动态且基于反馈的模型由于日常环境中的复杂因素波动而持续适应新信息并提供个性化援助。因此,我们提出了基于在线强化学习的检索增强生成(OnRL-RAG)系统来检测和个性化应对诸如压力、焦虑和抑郁等精神健康问题。我们使用从28名大学生收集的开源数据集进行演示,每名学生接受28个调查问题以展示我们系统相较于现有系统的性能。我们的系统相较于标准RAG、GPT-4o、GPT-4o-mini、Gemini-1.5和GPT-3.5所表现出的性能更加优越。这项工作将为LLMs在日常生活环境中的个性化服务实际应用开辟可能性。结果也将有助于社会、心理和神经科学领域的研究人员将其理论更加紧密地与实际的日常人类环境相结合。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)广泛应用于各种任务和应用,但其知识和能力受限于预训练数据。为增强LLMs的能力,提出了检索增强生成(RAG)方法,并结合强化学习人类反馈(RLHF)以适应不同用户需求。针对心理健康问题,本文提出在线强化学习基础的检索增强生成系统(OnRL-RAG),利用开源数据集演示其性能优越性。此研究有助于LLMs在个性化服务中的实际应用,并有助于社会学、心理学和神经科学领域的研究者更好地了解人类日常环境。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs受限于预训练数据,知识和能力可能过时或不准确。
- RAG方法用于增强LLMs的能力和提供最新信息。
- RLHF适应不同用户需求,通过对模型响应与人类偏好进行对齐来实现。
- OnRL-RAG系统针对心理健康问题提出,如压力、焦虑和抑郁,并展示其性能优越性。
- 使用开源数据集演示OnRL-RAG系统的性能,涉及2028名大学生的调查数据。
- OnRL-RAG系统在性能上超越了标准RAG和其他LLMs,如GPT-4o、GPT-4o-mini、Gemini-1.5和GPT-3.5。
点此查看论文截图

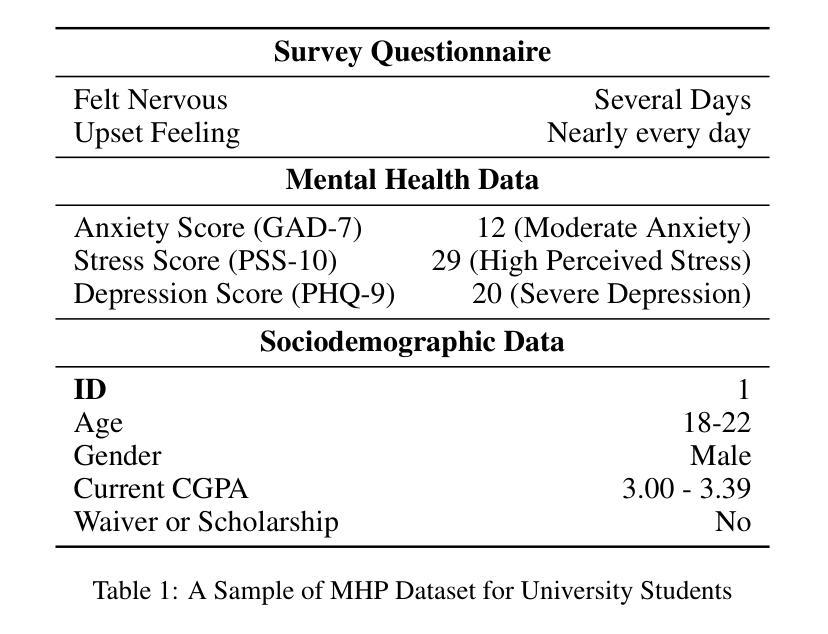
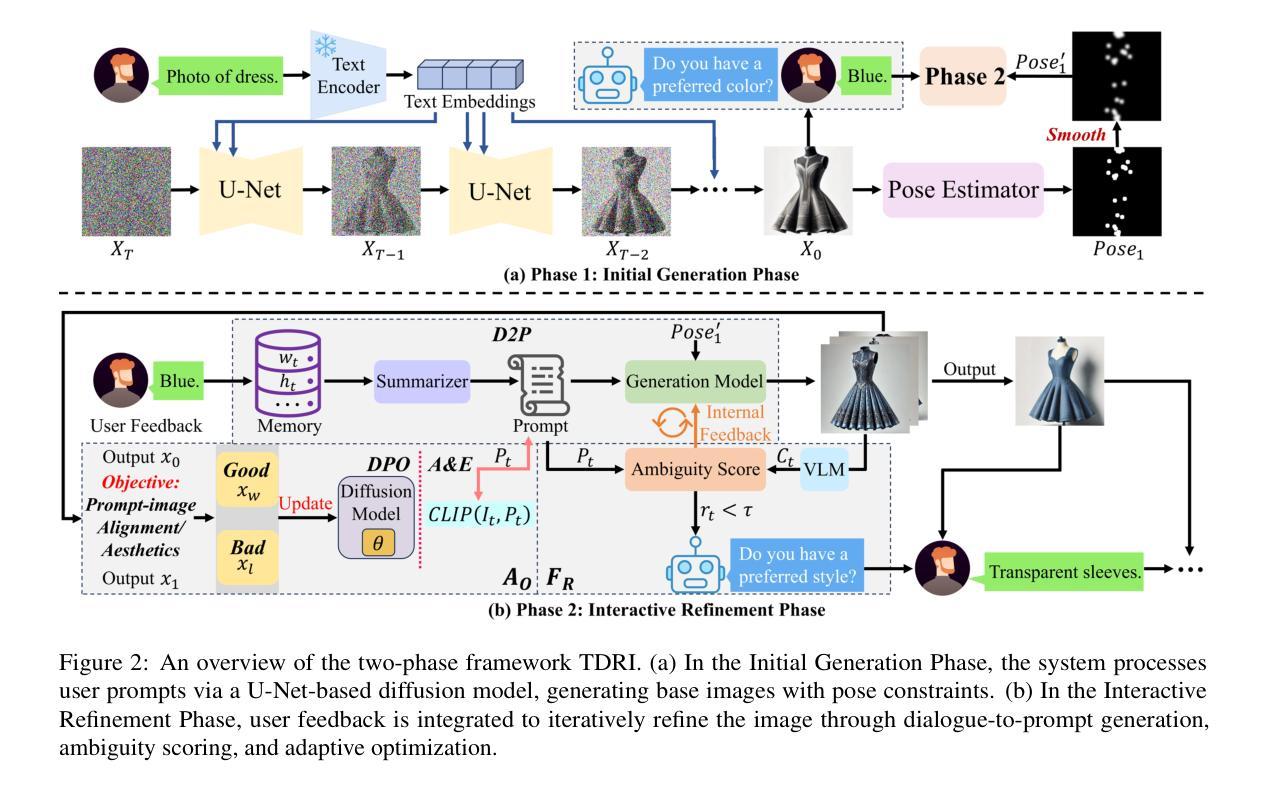
TDRI: Two-Phase Dialogue Refinement and Co-Adaptation for Interactive Image Generation
Authors:Yuheng Feng, Jianhui Wang, Kun Li, Sida Li, Tianyu Shi, Haoyue Han, Miao Zhang, Xueqian Wang
Although text-to-image generation technologies have made significant advancements, they still face challenges when dealing with ambiguous prompts and aligning outputs with user intent.Our proposed framework, TDRI (Two-Phase Dialogue Refinement and Co-Adaptation), addresses these issues by enhancing image generation through iterative user interaction. It consists of two phases: the Initial Generation Phase, which creates base images based on user prompts, and the Interactive Refinement Phase, which integrates user feedback through three key modules. The Dialogue-to-Prompt (D2P) module ensures that user feedback is effectively transformed into actionable prompts, which improves the alignment between user intent and model input. By evaluating generated outputs against user expectations, the Feedback-Reflection (FR) module identifies discrepancies and facilitates improvements. In an effort to ensure consistently high-quality results, the Adaptive Optimization (AO) module fine-tunes the generation process by balancing user preferences and maintaining prompt fidelity. Experimental results show that TDRI outperforms existing methods by achieving 33.6% human preference, compared to 6.2% for GPT-4 augmentation, and the highest CLIP and BLIP alignment scores (0.338 and 0.336, respectively). In iterative feedback tasks, user satisfaction increased to 88% after 8 rounds, with diminishing returns beyond 6 rounds. Furthermore, TDRI has been found to reduce the number of iterations and improve personalization in the creation of fashion products. TDRI exhibits a strong potential for a wide range of applications in the creative and industrial domains, as it streamlines the creative process and improves alignment with user preferences
尽管文本到图像生成技术已经取得了重大进展,但在处理模糊提示以及将输出与用户意图对齐时仍然面临挑战。我们提出的框架TDRI(Two-Phase Dialogue Refinement and Co-Adaptation,两阶段对话精炼与协同适应)通过迭代用户交互增强图像生成来解决这些问题。它分为两个阶段:初始生成阶段,根据用户提示创建基础图像;以及交互细化阶段,通过三个关键模块集成用户反馈。对话到提示(D2P)模块确保用户反馈有效地转化为可操作提示,这提高了用户意图与模型输入的匹配度。通过评估生成输出与用户期望之间的对比,反馈反射(FR)模块识别差异并促进改进。为了确保持续的高质量结果,自适应优化(AO)模块通过平衡用户偏好并保持提示的真实性来微调生成过程。实验结果表明,TDRI在现有方法的基础上实现了超越,达到了33.6%的人类偏好率(GPT-4增强的方法为6.2%),并在CLIP和BLIP对齐方面取得了最高分数(分别为0.338和0.336)。在迭代反馈任务中,经过8轮后用户满意度增加到88%,超过6轮后的回报逐渐递减。此外,发现TDRI在创建时尚产品时减少了迭代次数并提高了个性化程度。TDRI在创意和工业领域具有广泛的应用潜力,因为它简化了创意过程并提高了与用户偏好的匹配度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本提出一个名为TDRI的框架,旨在通过迭代用户交互提高图像生成的质量。它分为两个阶段,通过整合用户反馈和调节模型输入,提高了图像与用户意图的对齐度。实验结果显示,TDRI在多个指标上优于现有方法,提高了用户满意度,并适用于创意和工业领域的广泛应用。
Key Takeaways
- TDRI框架通过迭代用户交互增强图像生成技术,解决了模糊提示和对齐用户意图的问题。
- TDRI包含两个阶段:初始生成阶段和交互式细化阶段,后者通过三个关键模块整合用户反馈。
- D2P模块确保用户反馈转化为可操作的提示,提高用户意图与模型输入的对齐度。
- FR模块通过评估生成输出与用户期望之间的差距,发现差异并促进改进。
- AO模块通过平衡用户偏好和保持提示保真度来微调生成过程,确保高质量结果。
- 实验结果表明,TDRI在多个指标上优于GPT-4增强方法和其他现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

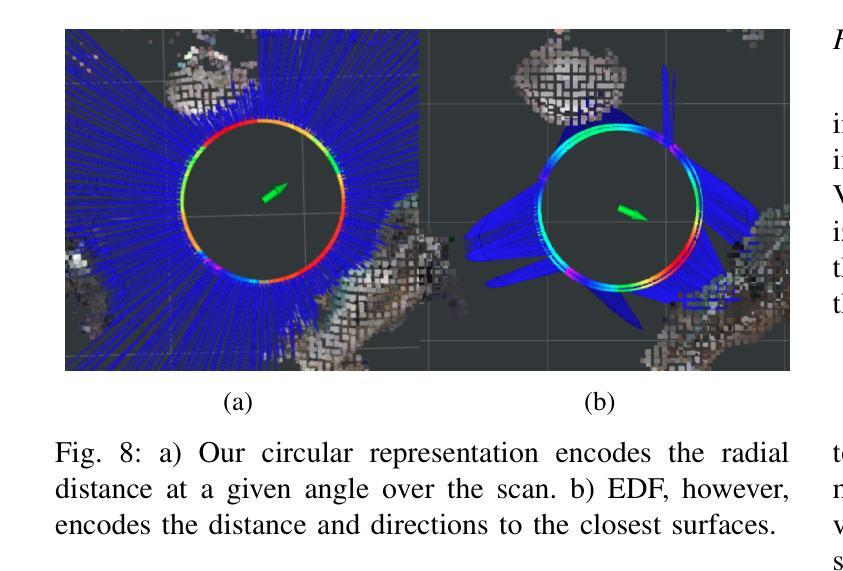
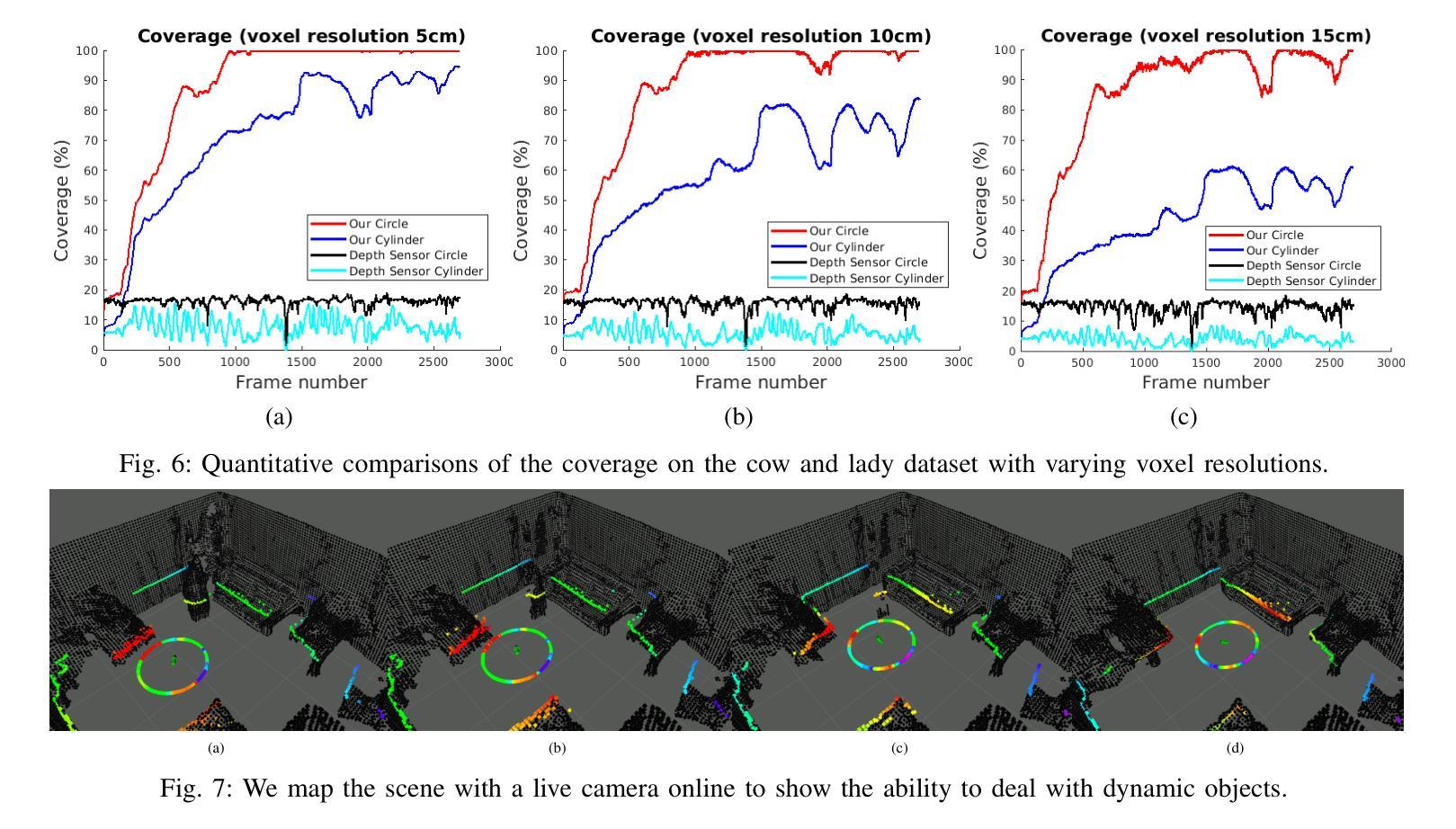
Listen to Your Map: An Online Representation for Spatial Sonification
Authors:Lan Wu, Craig Jin, Monisha Mushtary Uttsha, Teresa Vidal-Calleja
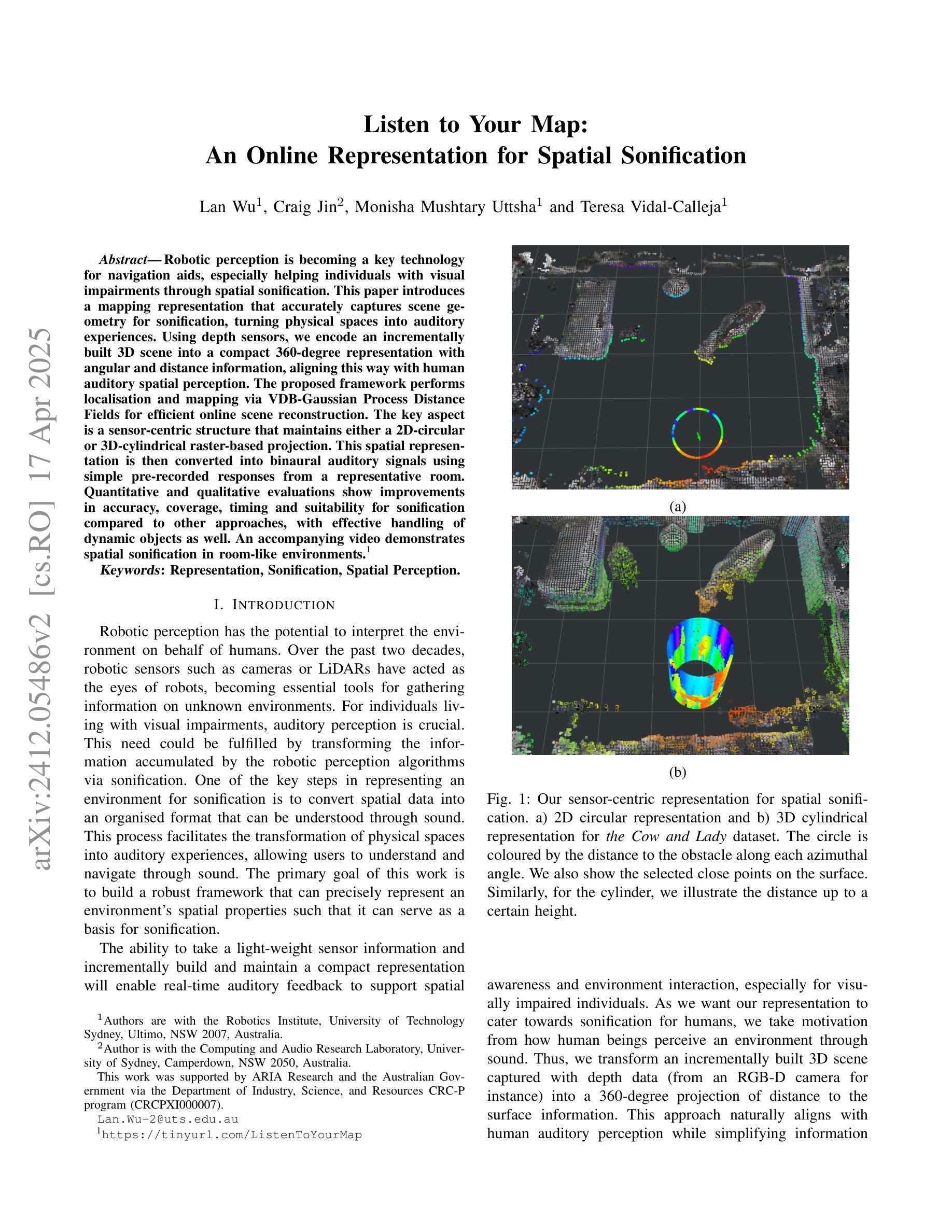
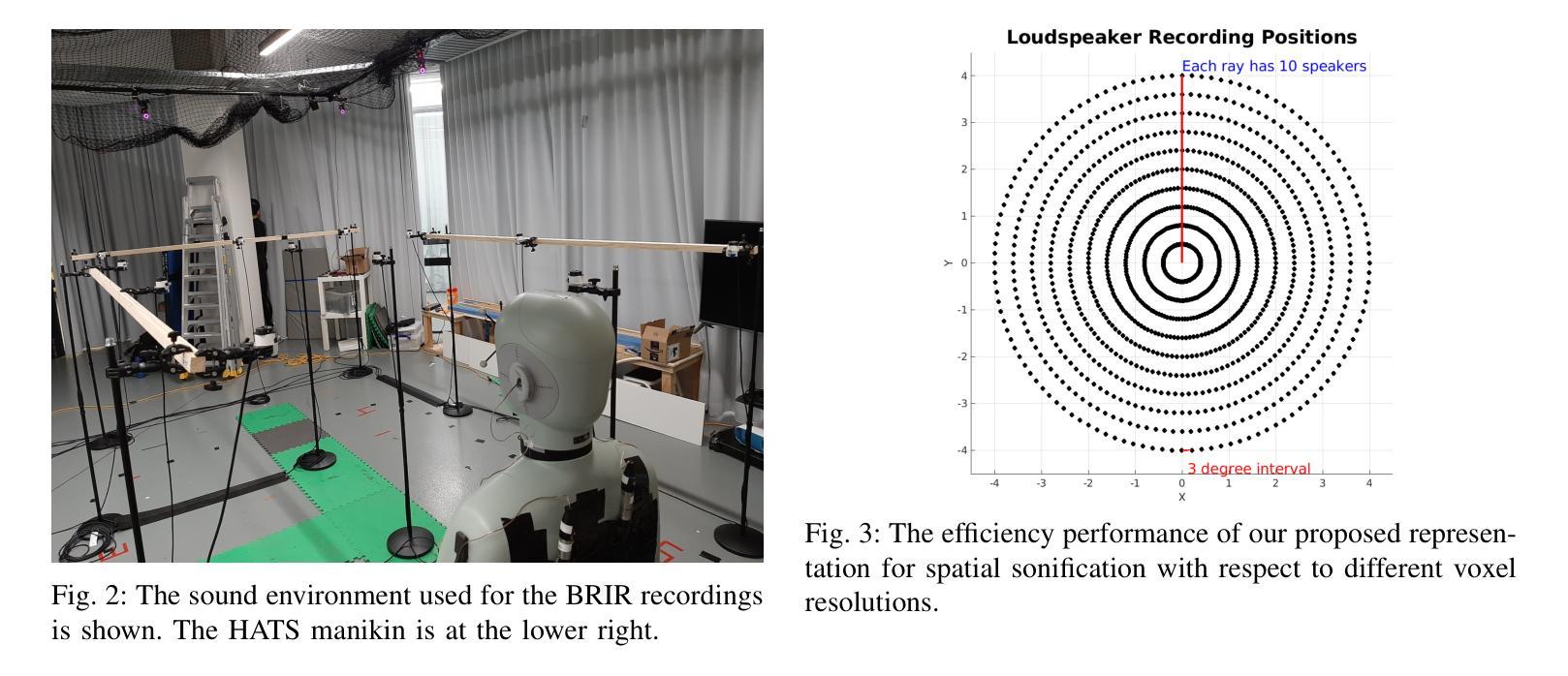
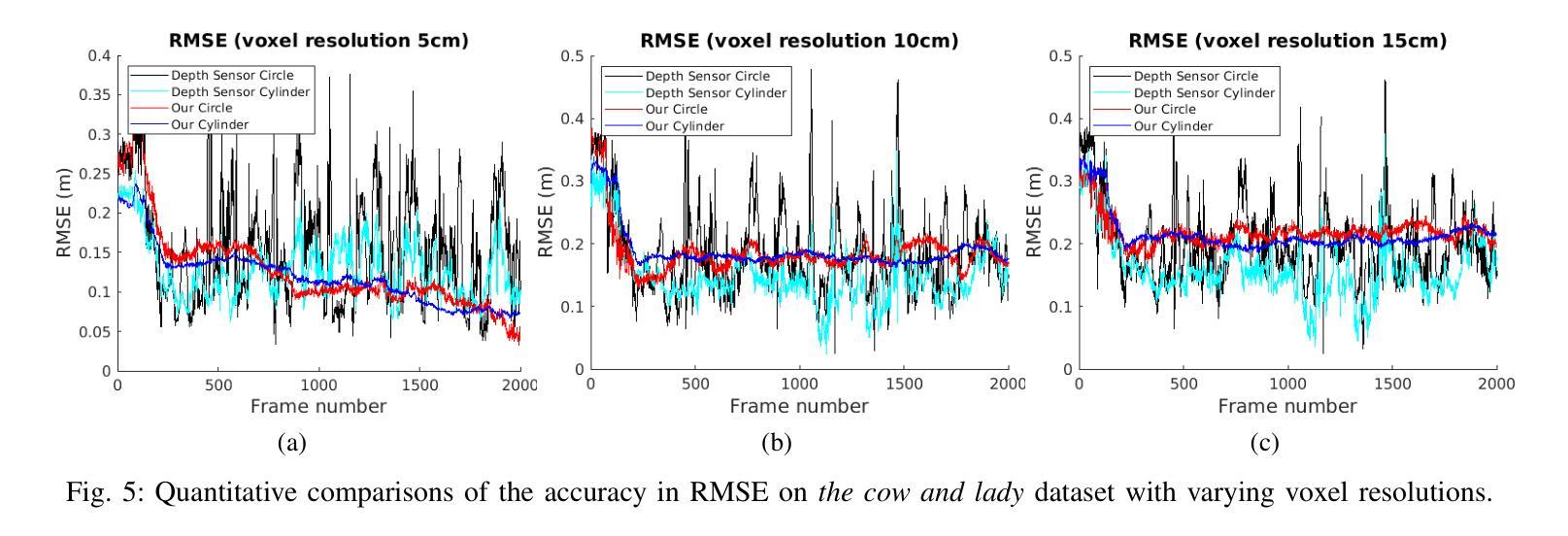
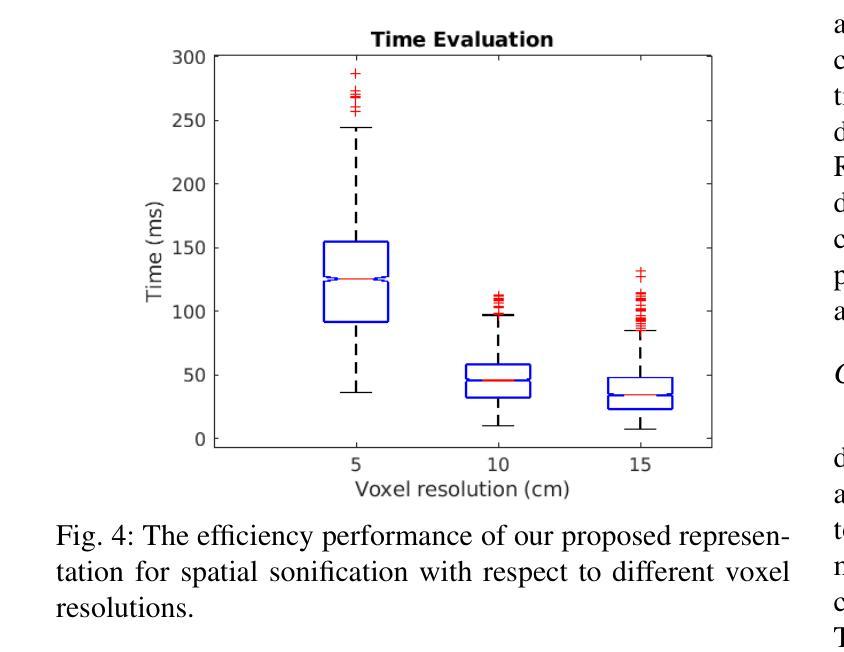
Robotic perception is becoming a key technology for navigation aids, especially helping individuals with visual impairments through spatial sonification. This paper introduces a mapping representation that accurately captures scene geometry for sonification, turning physical spaces into auditory experiences. Using depth sensors, we encode an incrementally built 3D scene into a compact 360-degree representation with angular and distance information, aligning this way with human auditory spatial perception. The proposed framework performs localisation and mapping via VDB-Gaussian Process Distance Fields for efficient online scene reconstruction. The key aspect is a sensor-centric structure that maintains either a 2D-circular or 3D-cylindrical raster-based projection. This spatial representation is then converted into binaural auditory signals using simple pre-recorded responses from a representative room. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations show improvements in accuracy, coverage, timing and suitability for sonification compared to other approaches, with effective handling of dynamic objects as well. An accompanying video demonstrates spatial sonification in room-like environments. https://tinyurl.com/ListenToYourMap
机器人感知已成为导航辅助的关键技术,尤其通过空间声音化帮助视觉障碍人士。本文介绍了一种映射表示法,它能准确地捕捉场景几何形状以供声音化,将物理空间转化为听觉体验。我们使用深度传感器将逐渐构建的3D场景编码为紧凑的360度表示,其中包含角度和距离信息,这种方式与人耳的听觉空间感知相吻合。所提出的框架通过VDB-高斯过程距离场执行定位和映射,以实现高效的在线场景重建。关键方面是以传感器为中心的结构,保持2D圆形或3D圆柱形基于光栅的投影。然后,这种空间表示形式通过使用来自典型房间的简单预录响应转换为双耳听觉信号。定量和定性评估表明,与其他方法相比,在准确性、覆盖范围、时间和声音化的适用性方面都有所改进,并且能有效处理动态对象。随附的视频展示了在类似房间环境中的空间声音化效果。相关链接:https://tinyurl.com/ListenToYourMap
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
机器人感知技术已成为导航辅助的关键技术,特别是对于视觉障碍者的空间声呐应用。本文介绍了一种映射表示法,它能准确地捕捉场景几何结构,用于声呐处理,从而将物理空间转化为听觉体验。该研究使用深度传感器对三维场景进行增量式构建,形成紧凑的360度表示,包含角度和距离信息,与人类的听觉空间感知相匹配。该研究的关键在于采用传感器中心结构,保持二维圆形或三维圆柱形的栅格投影。这种空间表示随后被转换成双耳听觉信号,并利用一个代表性房间的预先录制的响应进行简单处理。定量和定性评估表明,与现有方法相比,该方法在准确性、覆盖范围、时间以及声呐处理的适用性方面都有所改进,并能有效处理动态物体。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人感知技术已成为导航辅助的重要工具,尤其在视觉障碍者的空间声呐应用方面展现出巨大潜力。
- 一种新的映射表示法准确捕捉场景几何结构以支持声呐处理。
- 该技术通过将物理空间转化为听觉体验来提升导航能力。
- 利用深度传感器对三维场景进行增量构建,形成一种包含角度和距离信息的紧凑360度表示。
- 研究采用了传感器中心结构以维护二维或三维的空间表示。
- 这种空间表示被转换成双耳听觉信号以产生更准确的听觉体验。
点此查看论文截图